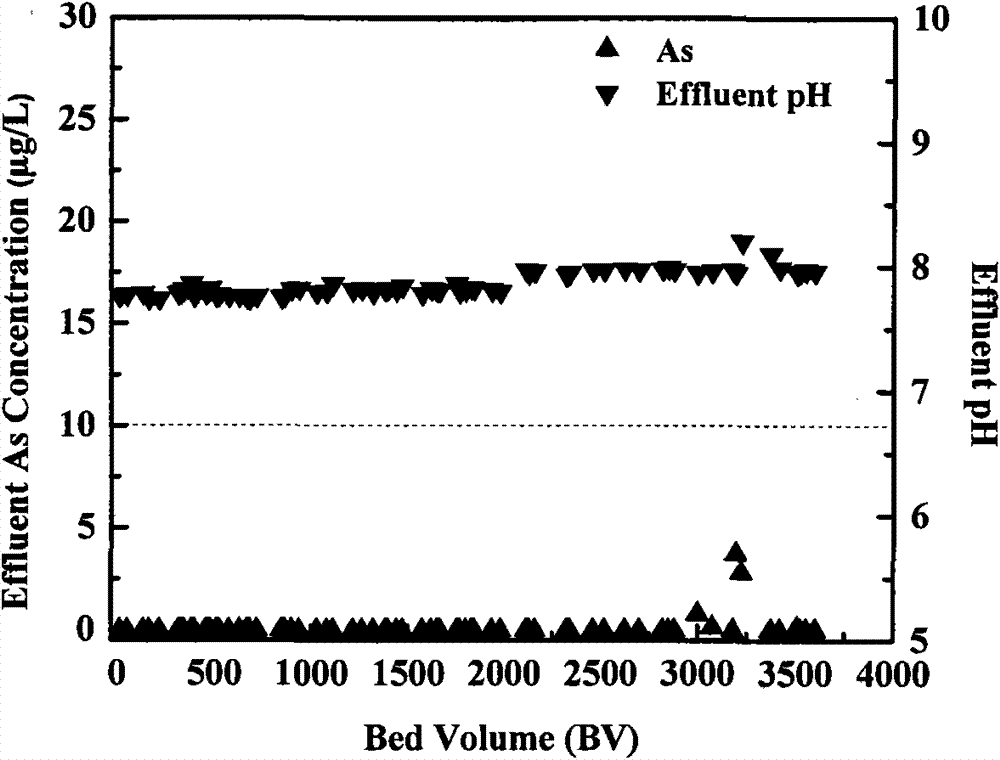
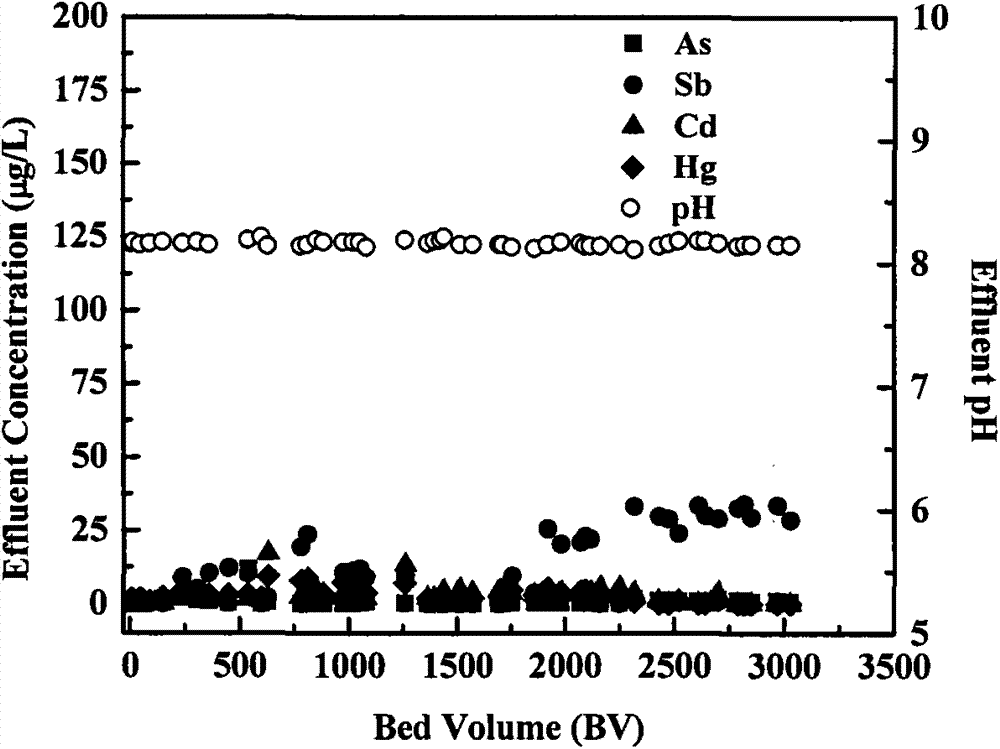
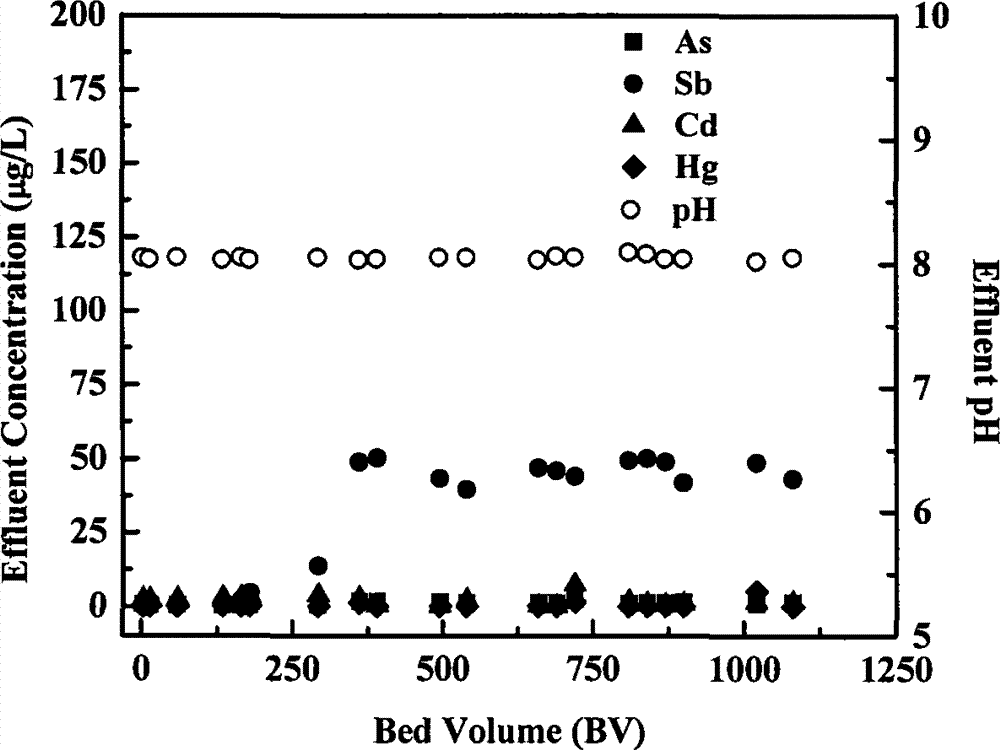
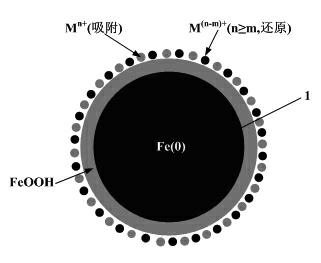
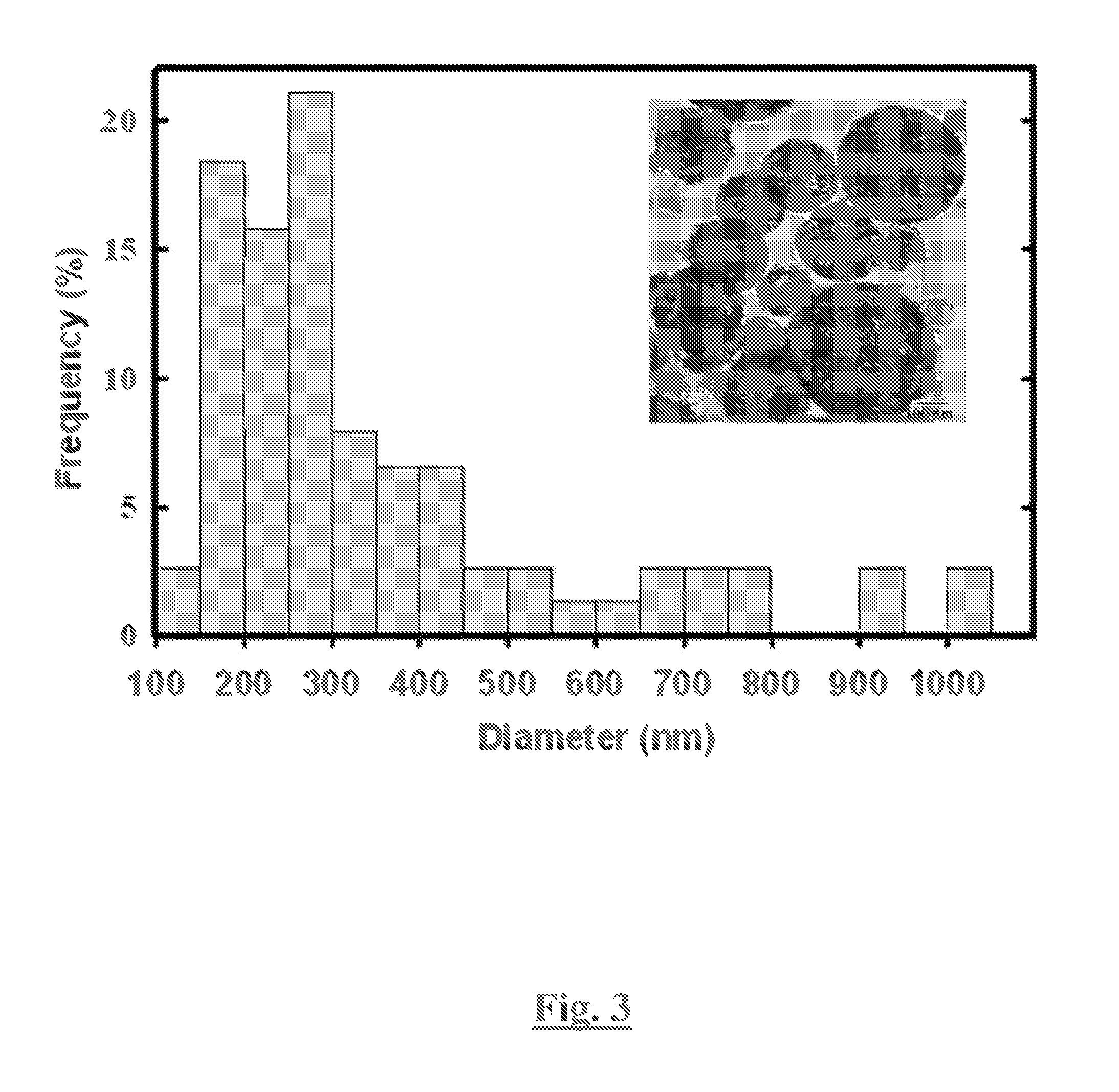
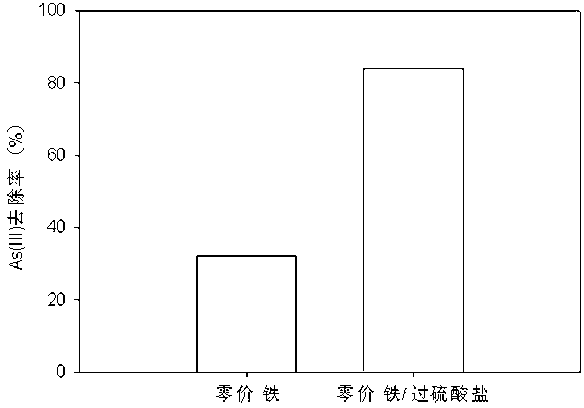
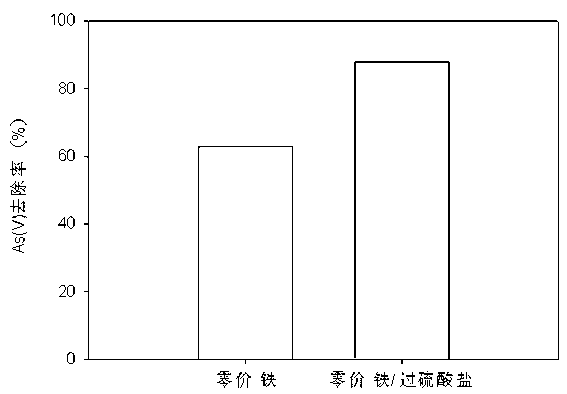
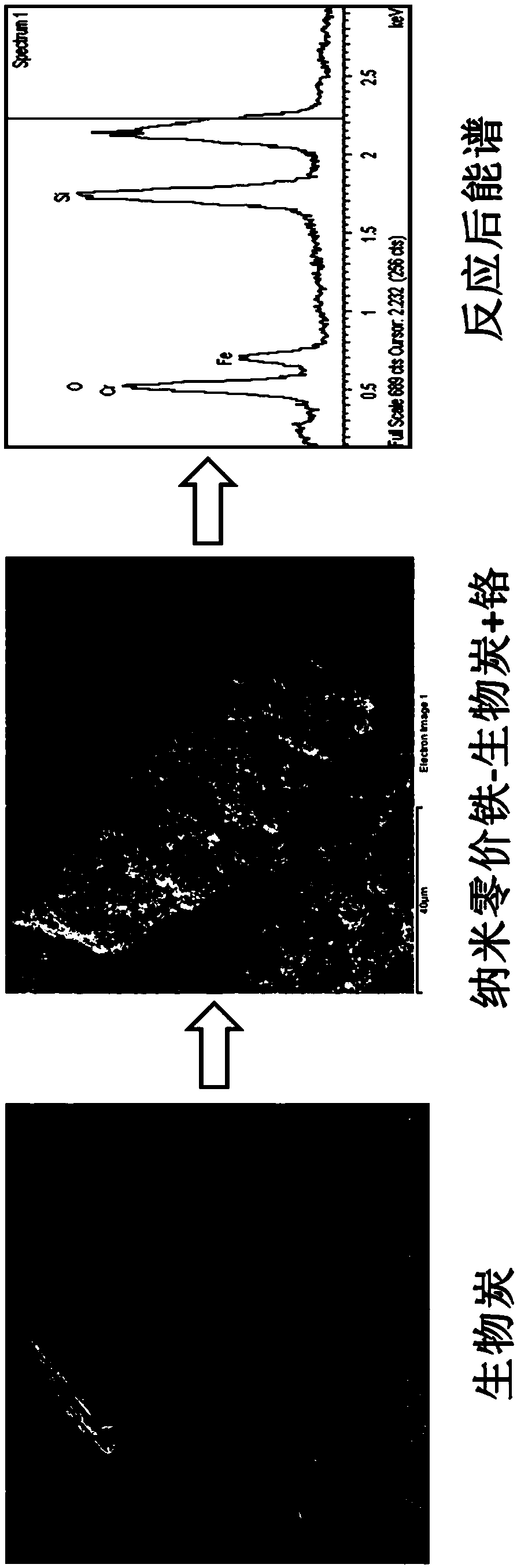
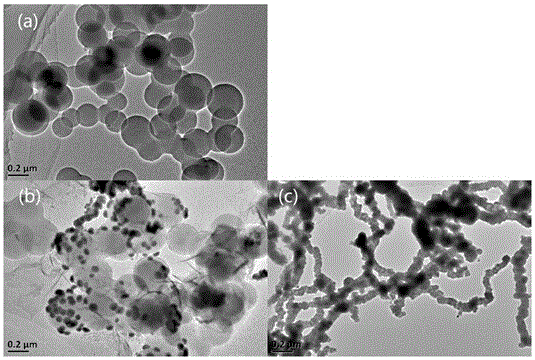
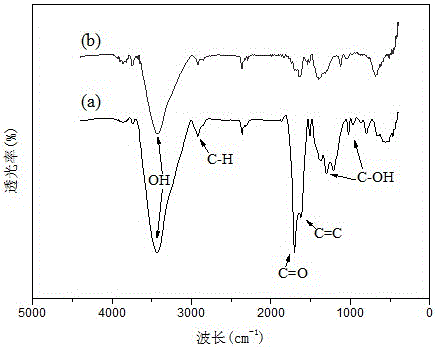
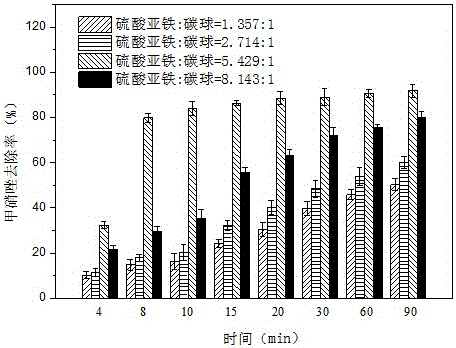
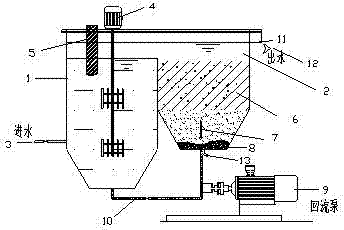
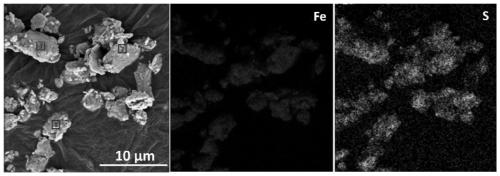
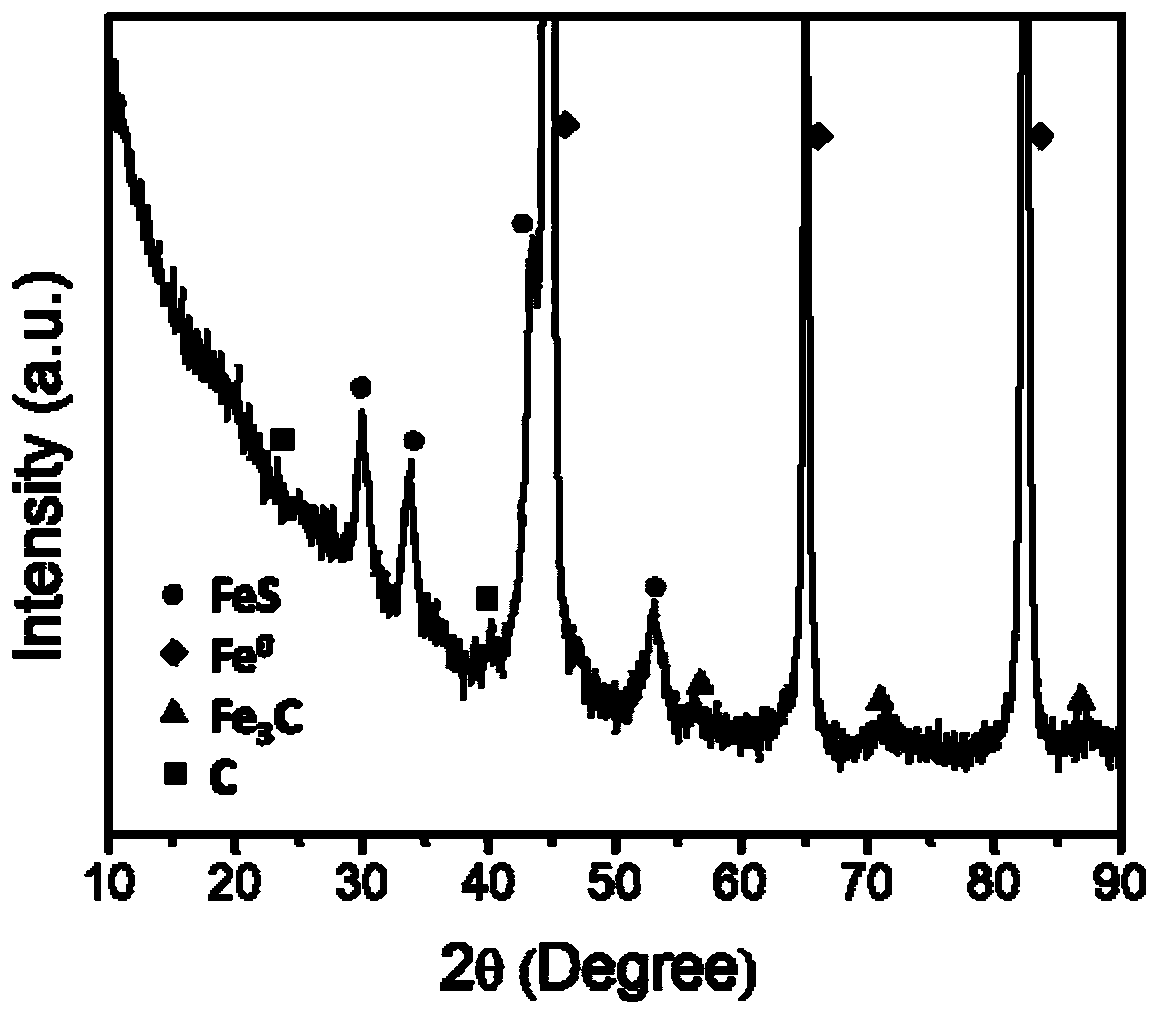
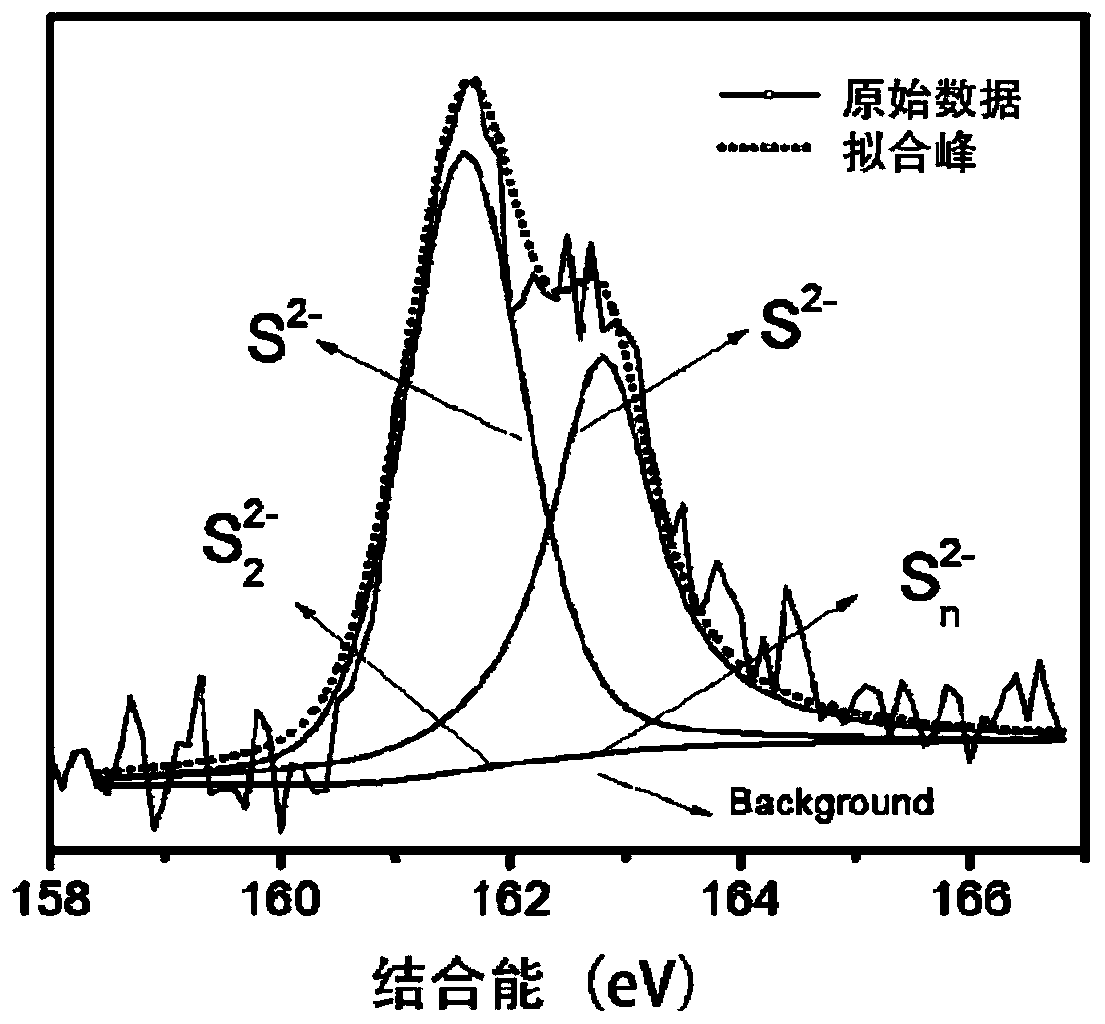
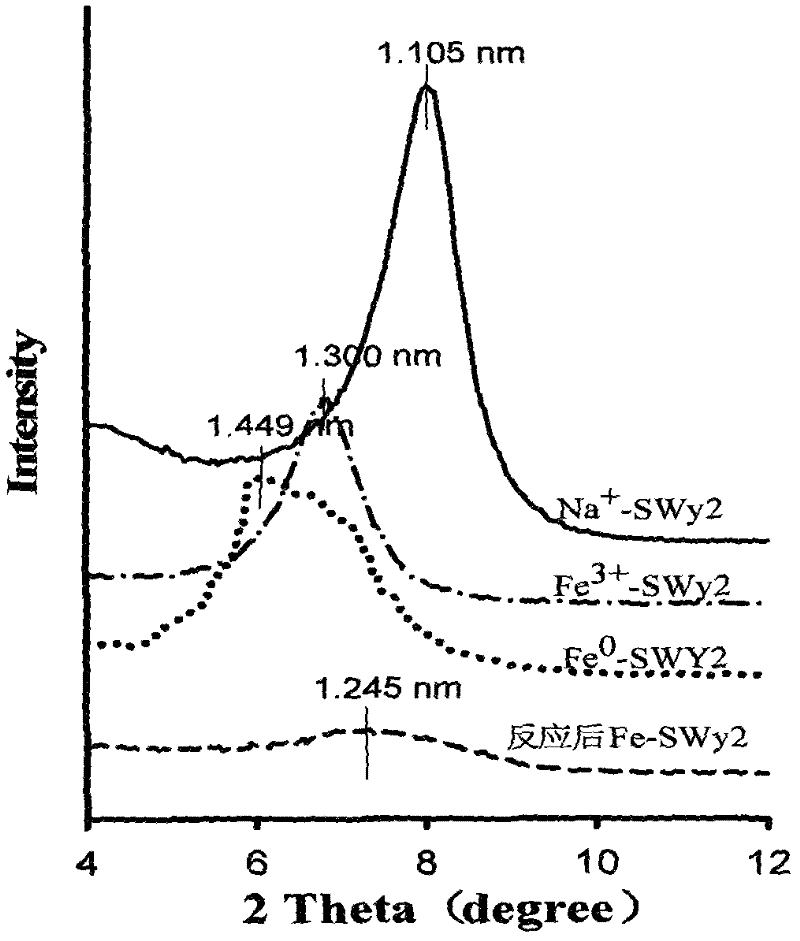
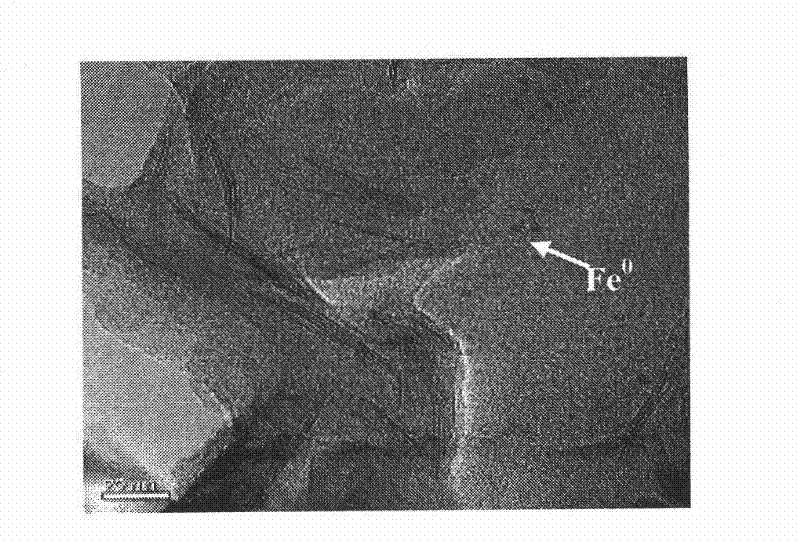
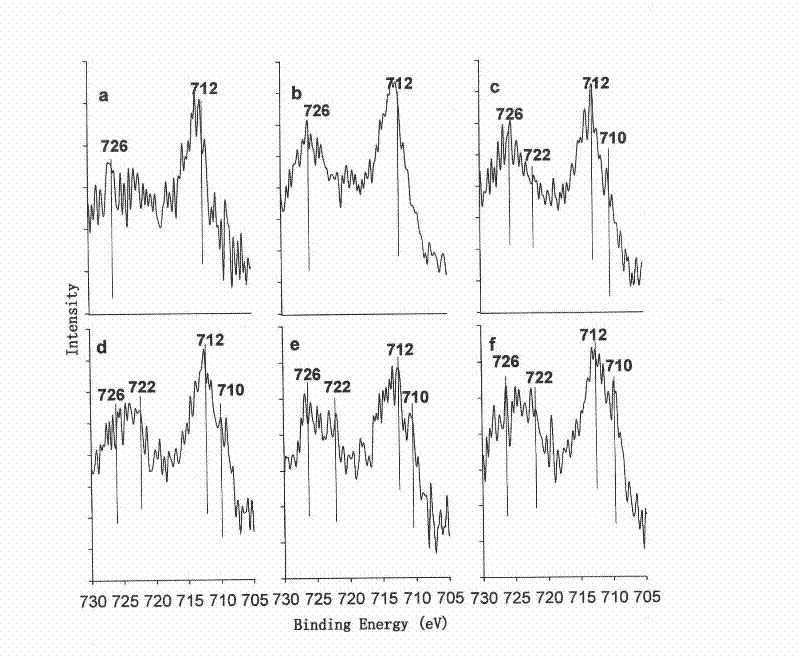
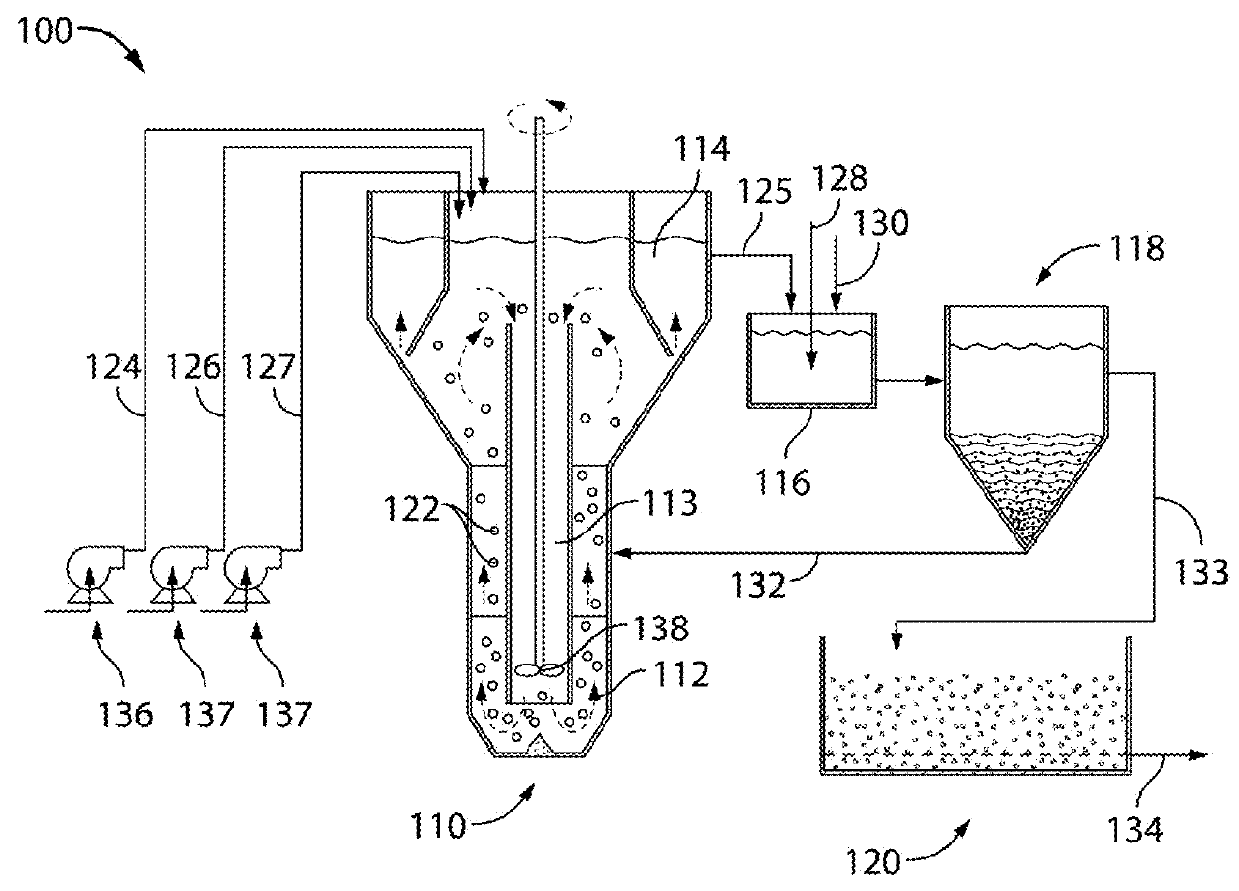
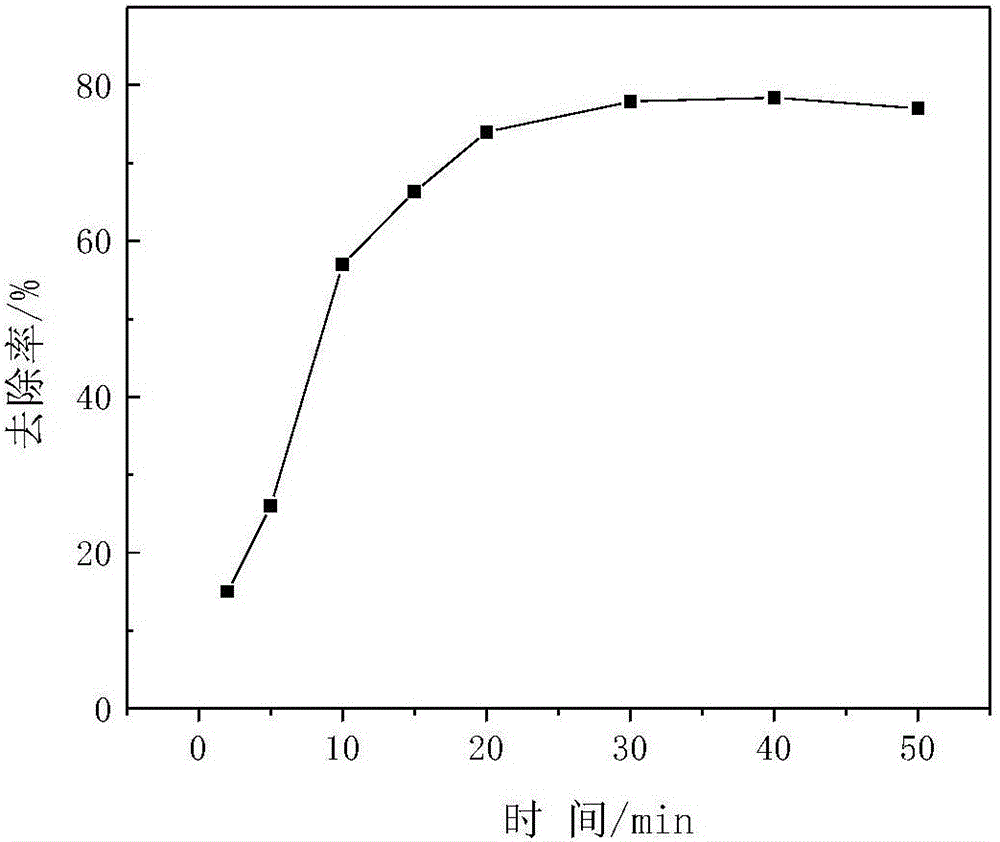
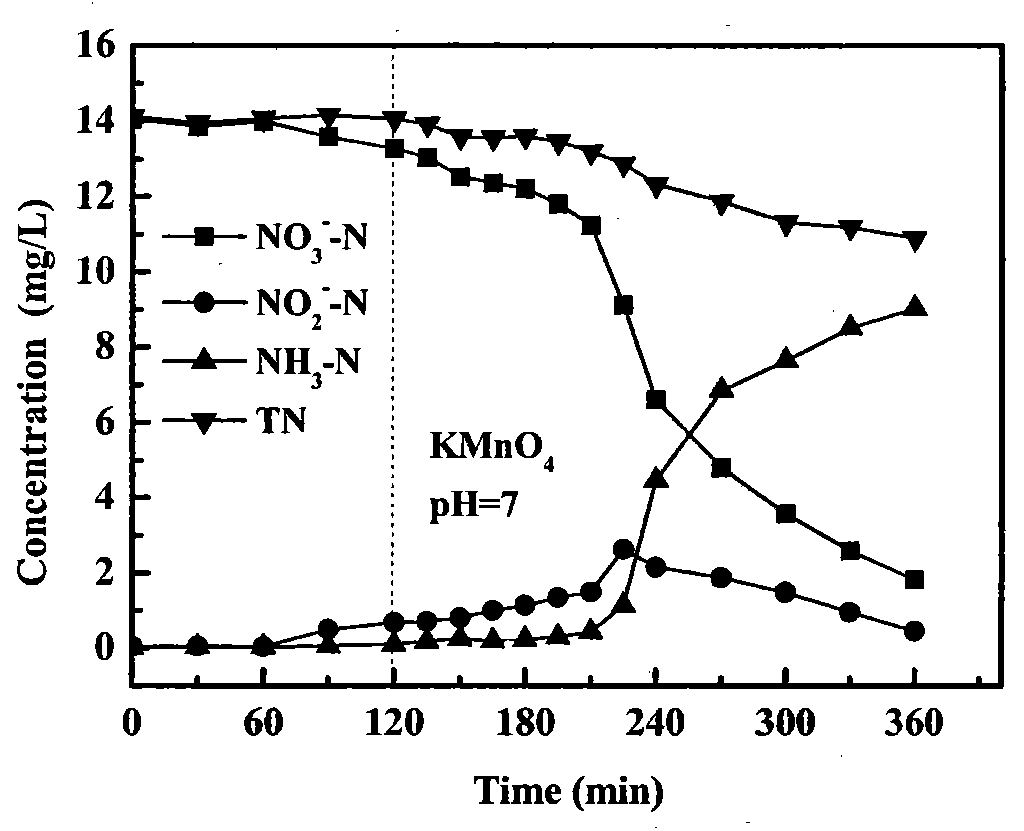
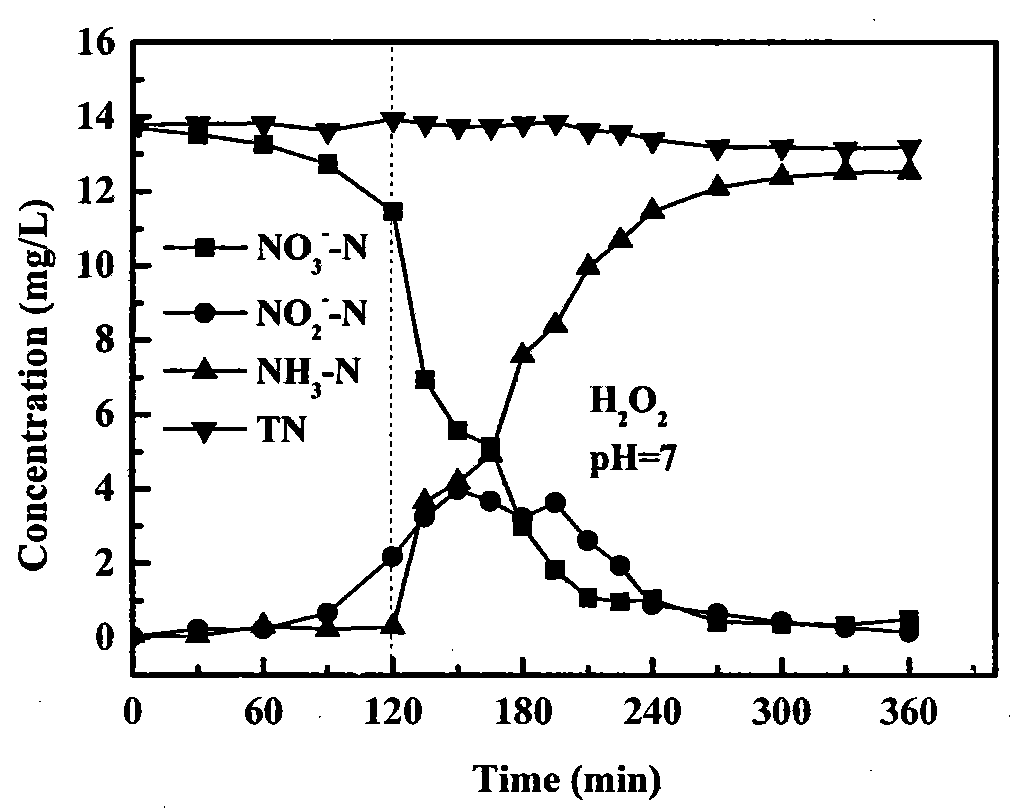
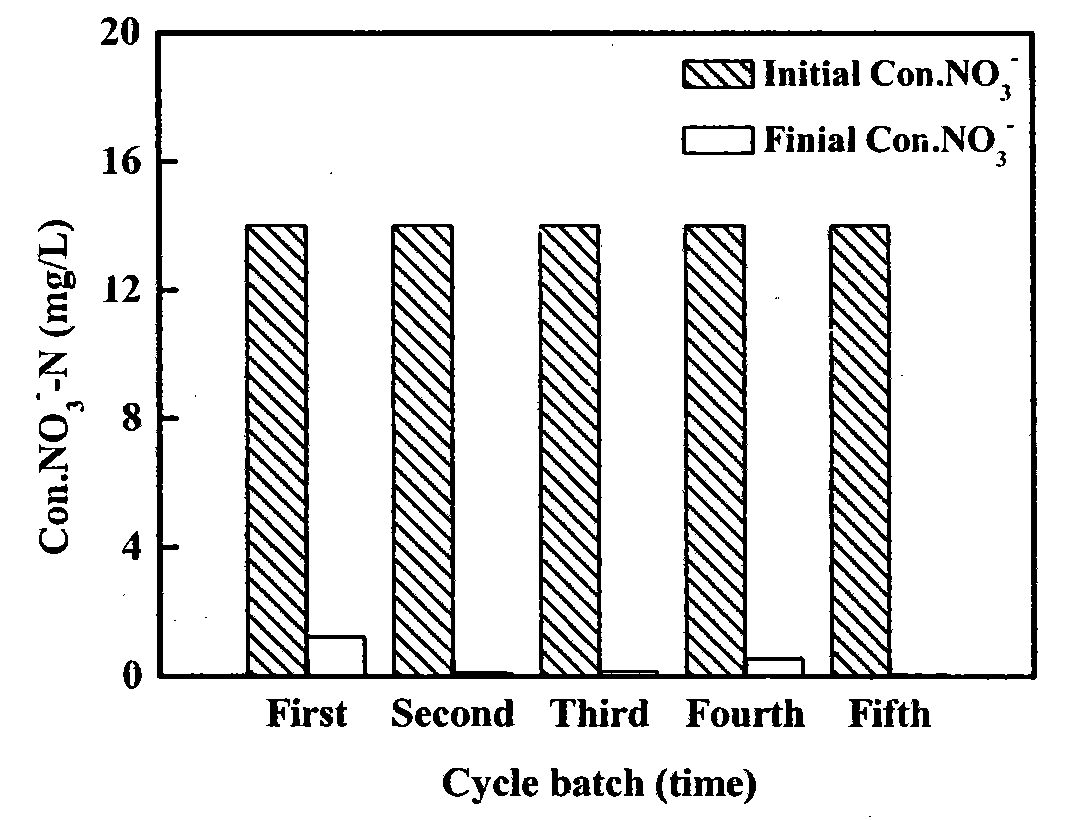
Patents
Literature
431 results about "Zerovalent iron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
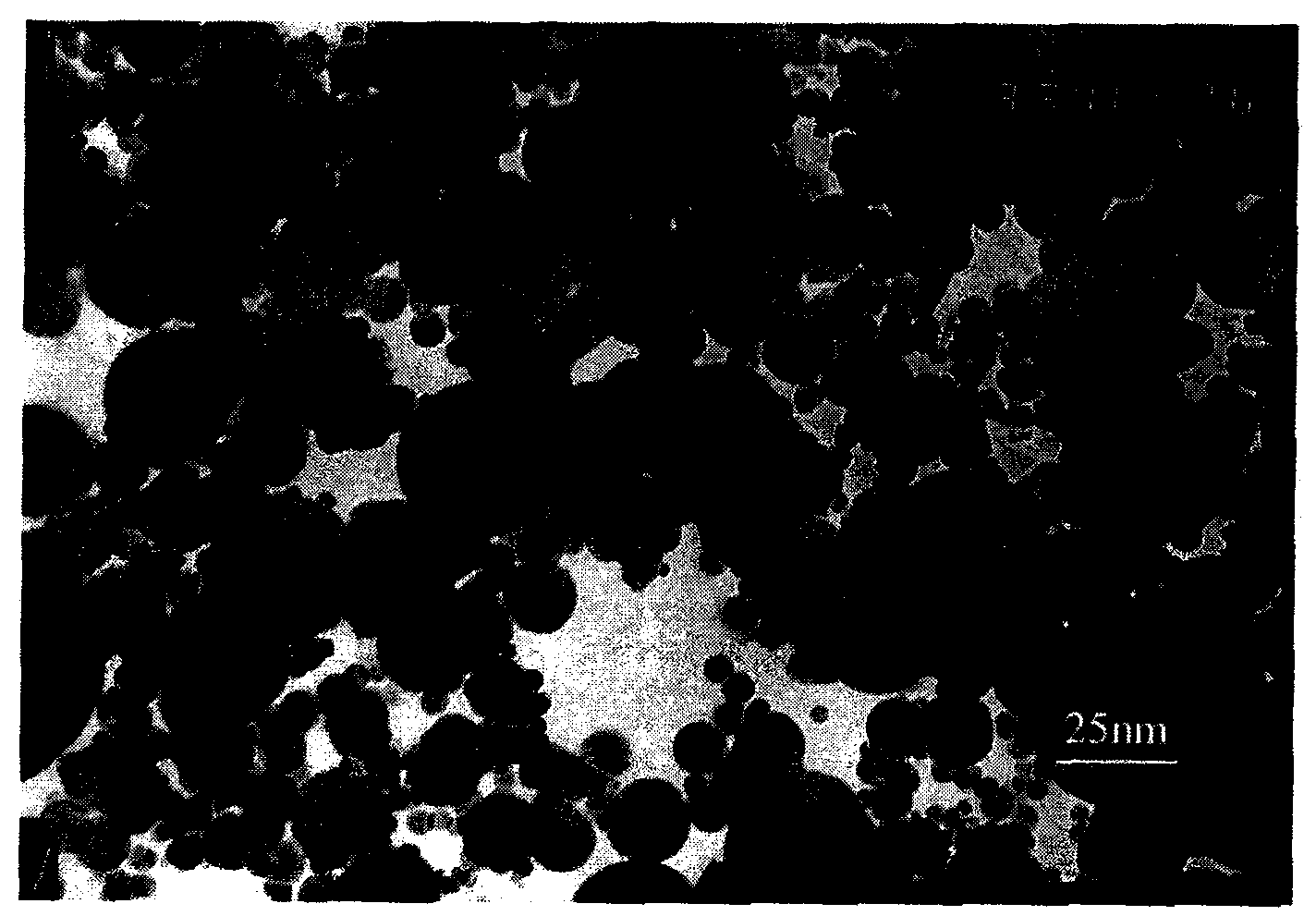
Zerovalent iron and other zerovalent metals (ZVI and ZVM, respectively) have a variety of applications ranging from filters to electrodes to trenches. One of the emerging uses for ZVI is iron wall remediation. This technology uses ZVIs to form a permeable reactive barrier (PRB) which filters out contaminants in groundwater, leaving only decontaminated groundwater and dissolved iron on the other side of the PRB.
Method for quickly and efficiently removing heavy metals in water body
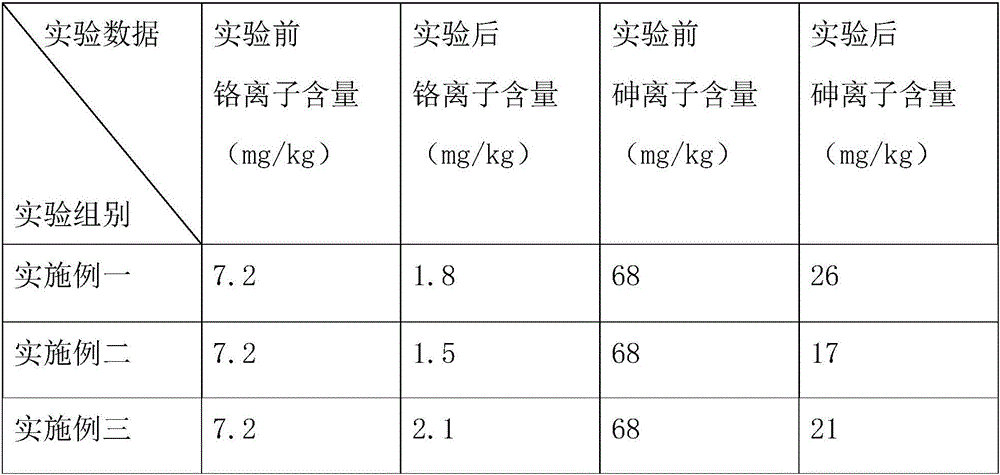
ActiveCN104276646AImprove cleanlinessGood chromaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPotassium permanganatePrecipitation
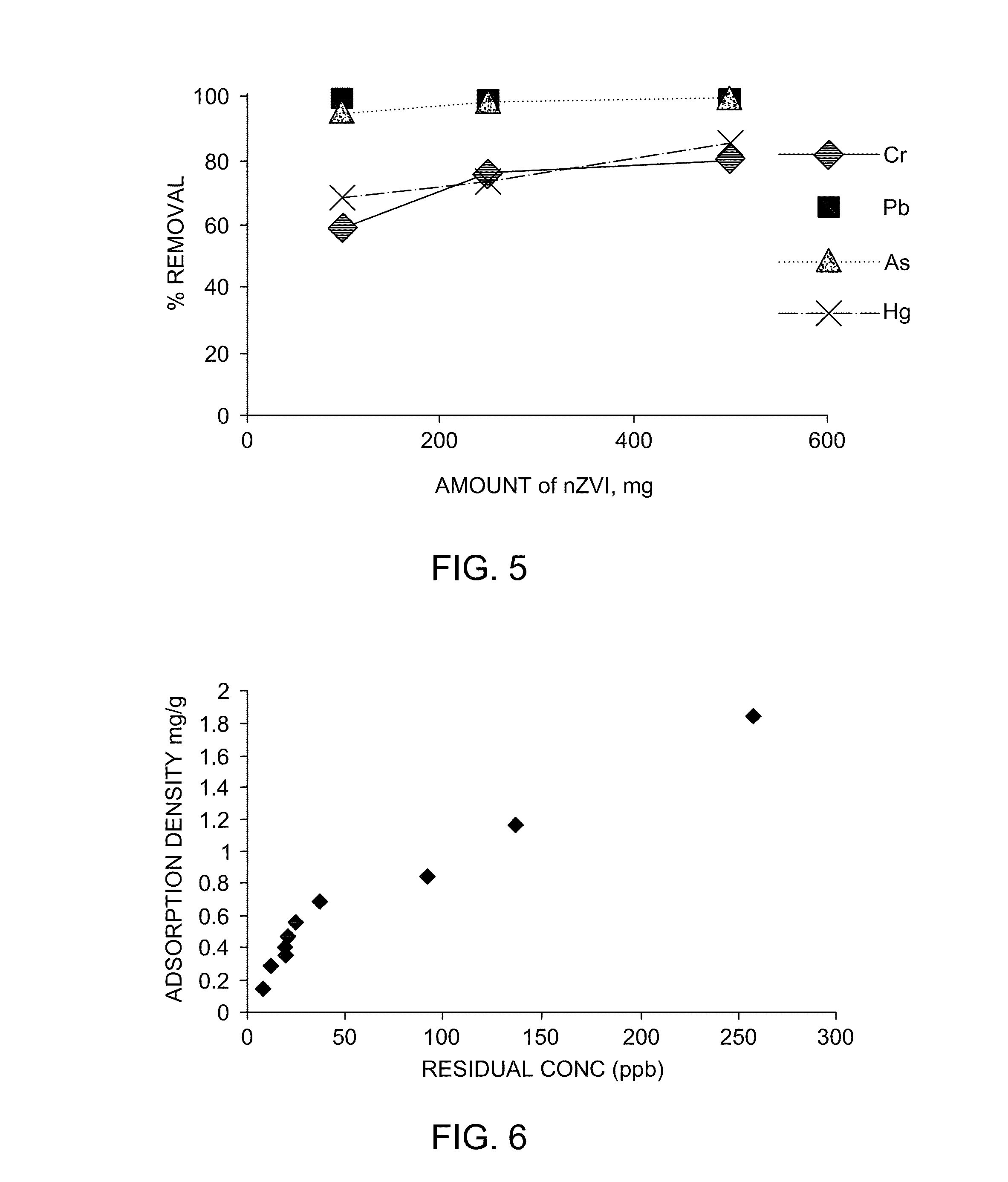
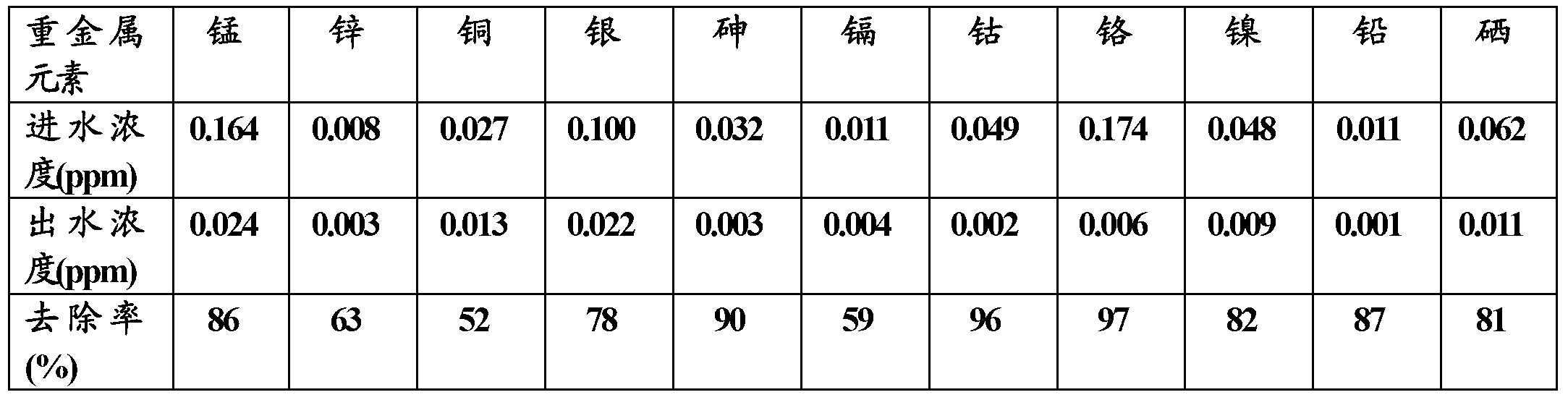
The invention relates to a method for removing heavy metals in a water body, which is characterized in that common oxidizers for water treatment, such as hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, potassium permanganate and the like, are utilized for oxidization to activate the zero-valent iron surface and continuously generate fresh iron (III) / (II) (hydro)oxide and other active components, thereby quickly and efficiently removing heavy metals in the water body, including As, Hg, Cd, Pb, Cr, Se, Sb, Cu, Zn and the like, in a mode of adsorption, precipitation, redox or the like.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for repairing heavy metal-polluted soil or sludge with nano-zero-valent iron (nZVI)
InactiveCN102380505ASimple structurePractical structureSludge treatmentContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceSludge
The invention relates to a method for repairing heavy metal-polluted soil or sludge with nano-zero-valent iron (nZVI). The method comprises the following steps of: fully mixing treated soil, sludge and the nZVI by using a nanotechnology, wherein a part of heavy metals in the soil or sludge is reduced by the nZVI, and the other part is adsorbed onto the surface of the nZVI, so that the heavy metals in the soil or sludge are removed; and separating the nZVI containing heavy metals by adopting a magnet, so that the change of the physicochemical property of the soil or sludge during or after the removing process is reduced. The method is easy to operate, has a remarkable effect, can be used for removing copper, nickel, zinc, cobalt, chromium, cadmium, lead and the like existing in the soil orsludge in one step, and has the characteristics of low cost, high repairing rate and the like when applied to the type of heavy-metal-polluted soil. In the invention, certain adjustment can be performed on parameters, such as nZVI concentration, treating time, liquid-solid rate and the like, according to different kinds and contents of heavy metals contained in different polluted soil or sludge. Purified soil or sludge gets back to farmlands, so that secondary pollution is not caused.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Novel multifunctional materials for in-situ environmental remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130058724A1Low costEasy to removeMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesSorbentMicrosphere
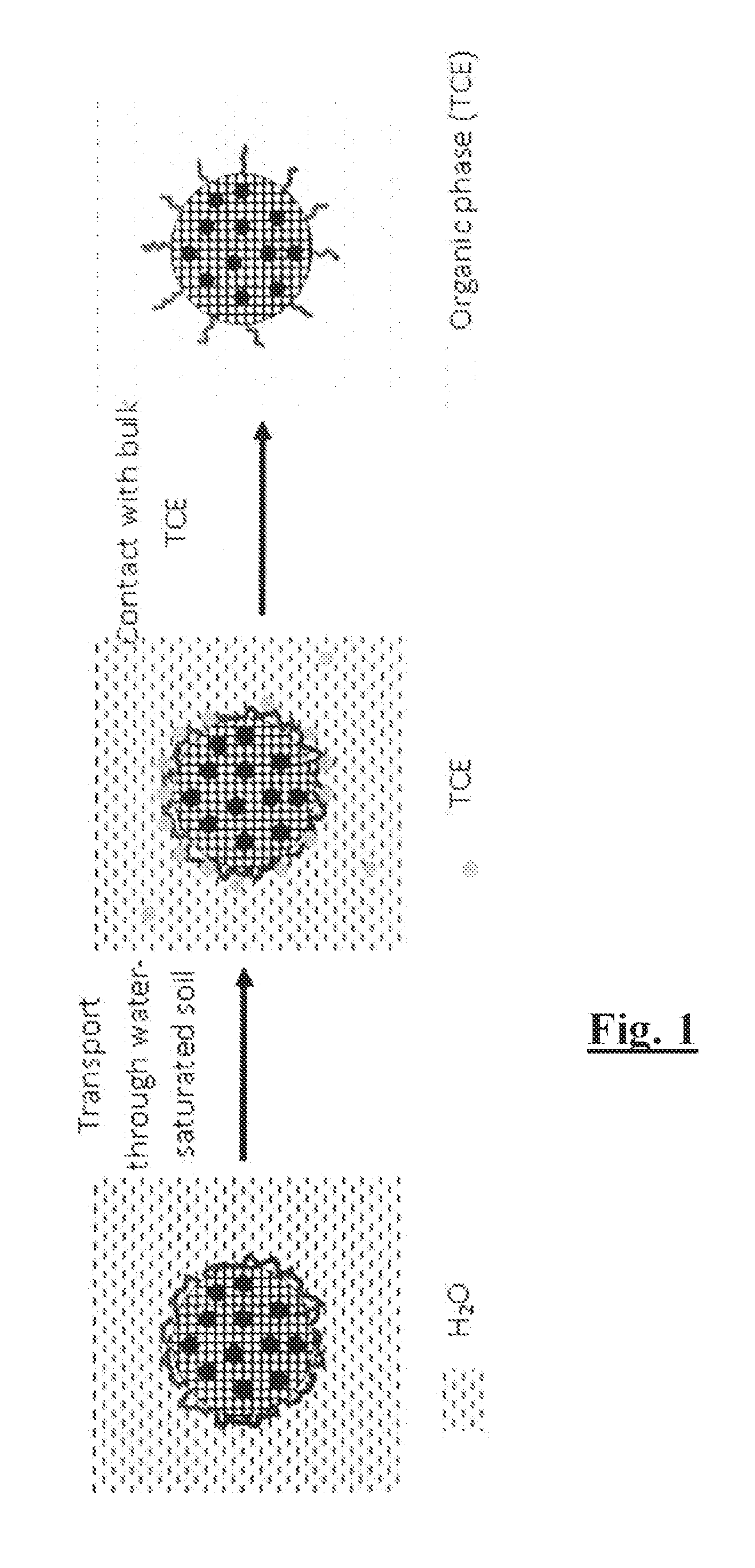
Effective in-situ injection technology for the remediation of dense nonaqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) such as trichloroethylene (TCE) benefits from the use of decontamination agents that effectively migrate through the soil media, and react efficiently with both dissolved TCE and bulk TCE. A novel decontamination system contains highly uniform carbon microspheres preferably in the optimal size range for transport through the soil. The microspheres are preferably enveloped in a polyelectrolyte (such as carboxymethyl cellulose, CMC) to which preferably a bimetallic nanoparticle system of zerovalent iron and Pd is attached. The carbon serves as a strong adsorbent to TCE, while the bimetallic nanoparticles system provides the reactivity. The polyelectrolyte serves to stabilize the carbon microspheres in aqueous solution. The overall system resembles a colloidal micelle with a hydrophilic shell (the polyelectrolyte coating) and a hard hydrophobic core (carbon). In contact with bulk TCE, there is a sharp partitioning of the system to the TCE side of the interface due to the hydrophobicity of the core. These multifunctional systems appear to satisfy criteria related to remediation and are relatively inexpensive and made with potentially environmentally benign materials. An aerosol process is preferably used to produce zerovalent iron particles supported on carbon. A method of lubricating includes creating carbon microspheres produced from a monosaccharide or polysaccharide, the carbon microspheres having a diameter of 50 nm to 6 microns, coating the microspheres with a surface coating and using the carbon microspheres as a lubricant.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Water treatment method for removing arsenic by strengthening zero-valent iron
ActiveCN103342410AEasy to operateEasy to useWater/sewage treatment by oxidationWater treatment systemPersulfate
The invention relates to a technology for removing and controlling arsenic which has very high toxicity in water, and discloses a water treatment method for removing arsenic by strengthening zero-valent iron, which can be used for groundwater repair, drinking water treatment, industrial arsenic-containing wastewater treatment, sewage deep treatment and integrated small-scale water treatment systems. The water treatment method specifically comprises the following steps of: adding persulfate and zero-valent iron into water containing arsenic, wherein the persulfate is added in a molar ratio of the persulfate to arsenic of (5:1)-(100:1), and the molar ratio of the zero-valent iron to the persulfate in the water is (1:1)-(10:1); and when the mixed solution is fully mixed, filtering or depositing to finish the removal of arsenic. The water treatment method is very simple to operate, easy to popularize and apply and safe to use, and can be used for ensuring the water quality safety.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nanometer zero-valent iron-biochar composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108911005AStrong reductionStable in natureWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionHigh activityBiochar
The invention provides a nanometer zero-valent iron-biochar composite material, and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, a carrier is a series of biochar with different cracking temperatures; the biochar is cheap and easily-available, has large specific surface area and contains a plurality of mineral components; nanometer zero-valent iron particles carried bythe carrier have strong activity; thus, the nanometer zero-valent iron particles have high activity; and the nanometer zero-valent iron-biochar composite material prepared from the carrier has high activity, and has the advantages of stable properties and low price at the same time. Screening of the series of different cracking temperatures shows that the composite material formed by the biochar generated by cracking of straw at medium and high temperatures and the nanometer zero-valent iron has strong removal effect on heavy metals. Meanwhile, the nanometer zero-valent iron-biochar compositematerial provided by the invention has excellent adsorption performance of the biochar and strong reduction capacity of the nanometer iron, and can provide theoretical basis and technical support forprevention, control and remediation of heavy metal pollution to groundwater.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of modified micron zero-valent iron and application method of modified micron zero-valent iron in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN106180735AAvoid secondary pollutionGood dispersionContaminated soil reclamationSoil treatmentSlag
The invention discloses a preparation method of modified micron zero-valent iron and an application method of the modified micron zero-valent iron in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The preparation method of the modified micron zero-valent iron comprises the steps of cleaning of iron raw materials, preparation of micro iron, ultrafine grinding and modifying treatment. A modifying agent composed of water, xanthan gum, sulfide, a stabilizing agent, zeolite and blast furnace slag is adopted in the step of modifying treatment. The preparation method of the modified micron zero-valent iron has the beneficial effects that the production process of the modified micron zero-valent iron is simple, and the effect similar or superior to micron zero-valent iron is achieved while the cost is reduced; and in addition, the reaction activity is controlled, the oxidation rate is decreased, excellent stability is obtained, and the acting time of the micron zero-valent iron is longer. By the adoption of the application method of the modified micron zero-valent iron, the remediation cost of heavy metal contaminated underground water is further reduced. According to the preparation method of the modified micron zero-valent iron and the application method of the modified micron zero-valent iron in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil, organic fertilizer is added in the soil treatment process so that the fertility of soil can be improved, the structure of soil can be improved through humic acid produced by the organic fertilizer, heavy metal elements, such as lead, chromium and arsenic, in underground water can be removed, and the concentration of pollutants such as nitrate and perchlorate can be reduced.
Owner:CHINESE ACADEMY FOR ENVIRONMENTAL PLANNING
Method for removing heavy metal cadmium and lead pollutants in water by sodium alginate/gelatin coated nano zero-valent iron
ActiveCN104722279AStable storageEasy to recycleOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionIonPollutant
The invention relates to a method for removing heavy metal cadmium and lead pollutants in water by sodium alginate / gelatin coated nano zero-valent iron. By using sodium alginate / gelatin as a main raw material and CaCl2 as a crosslinking agent, the nano zero-valent iron is synergically immobilized. Researches show that the nano zero-valent iron has very high stability and researches on the effect of removing heavy metal ions Cd<2+> and Pb<2+> show that the zero-valent iron has a relatively good removal effect which can reach over 95%. The immobilized nano zero-valent iron prepared by the invention has the advantages of being green and environmental-friendly, has relatively high reaction activity and stability, and has a relatively good removal effect on heavy metal ions both Cd<2+> and Pb<2+>.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR
Preparation method and application of carbon sphere loaded nanoscale zero valent iron composite material
ActiveCN106044921AWide variety of sourcesLow priceWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsDispersityPotassium borohydride
The invention provides a preparation method of a carbon sphere loaded nanoscale zero valent iron composite material. The method comprises: (1) preparing carbon spheres containing hydrophilic functional groups (-OH, -COOH) by a hydrothermal method; (2) chelating iron ions and the functional groups by soaking; (3) finally, dropping potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride solution into carbon sphere mixed solution with the iron ions, and forming the carbon sphere loaded nanoscale zero valent iron composite material by a strong reducing effect. The material prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention not only simultaneously has an adsorption effect of the carbon spheres and the strong reducing effect of nanoscale zero valent iron, but also can form a micro primary cell between the iron and carbon; not only are the problems of clustering and the like of nanoscale zero valent iron particles solved, but also electron transfer is reinforced and a degrading effect on polluted waste water is promoted; the method provided by the invention is low in cost and simple to operate, and the nano particles have high dispersity and stability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for restoring polychlorinated biphenyl polluted site soil
InactiveCN105290101AAchieve economyRealize practicalContaminated soil reclamationActivated carbonChemistry
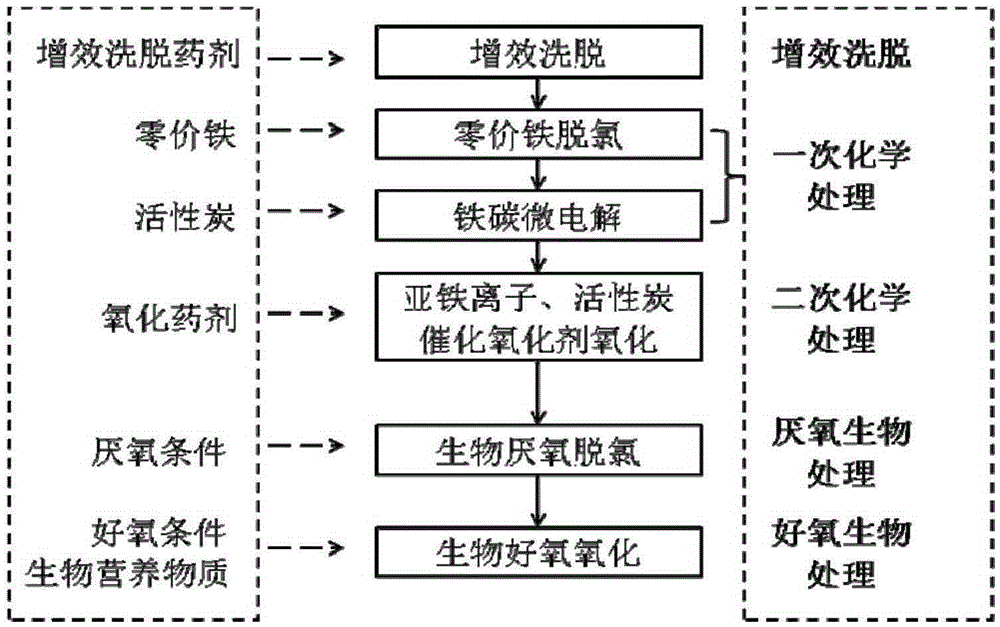
The invention belongs to the field of the environmental engineering polluted site soil restoration, and particularly relates to a method for restoring polychlorinated biphenyl polluted site soil. The method comprises the following steps: synergistic elution, primary chemical treatment, secondary chemical treatment, anaerobic organism treatment and aerobic organism treatment. For the soil restoration problem of the real polychlorinated biphenyl polluted site, a restoration process combining the chemical treatment of chemical elution, acid regulation, zero-valent iron dechloridation, iron carbon micro-electrolysis, catalytic oxidation, biological anaerobic dechloridation and biological aerobic oxidation and biological treatment. Various effects such as chemical dechloridation (dechloridation effect of zero-valent iron), chemical oxidation (iron carbon micro-electrolytic effect of the zero-valent iron and active carbon and catalytic oxidation effect of oxidized medicine), biological anaerobic dechloridation effect and biological aerobic oxidation effect are reasonably integrated in one technology, so that the optimization of technology, economy, practicability and feasibility is realized.
Owner:天津环科立嘉环境修复科技有限公司
Mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle (SiO2@ FeOOH@ Fe) and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102701297AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationMicrosphereIron nanoparticle
The invention discloses a mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof. The mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle has a structure as follows: the center is mesoporous SiO2, the middle layer is FeOOH, the surface of the outermost layer is coated with FeO, and ultimately a SiO2@ FeOOH@Fe structure, namely a spherical particle, is formed. The preparation method is easy to operate and mild in reaction conditions, can be carried out at room temperature and normal pressure, and is short in time consumption and low in energy consumption; the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles have the particle size of 400-500nm and are spherical particles; the specific surface areas of the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles are detected to be 383.477m2 / g by a BET-N2 specific surface area analysis method; and the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles are good in lattice morphology, good in fluidity and good in dispersion and can be used for decomposing organic pollutants in the environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Biochar-loaded zero-valent iron composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109939680ASave raw materialsRaw materials are easy to getOther chemical processesWater contaminantsBiomassAtmosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic matter catalytic degradation materials, and provides a biochar-loaded zero-valent iron composite material and a preparation method thereof. Thepreparation method comprises the following steps that 1, a biomass material is mixed with an aqueous solution of an iron source, and ultrasonic dispersion is carried out to obtain a raw material mixture, wherein the iron source is at least one of iron salt and ferrous salt; 2, a hydrothermal reaction is carried out on the raw material mixture to obtain an iron-carbon precursor; 3, the iron-carbonprecursor is calcined in an inert gas atmosphere to obtain the biochar-loaded zero-valent iron composite material. According to the method, a reducing agent is not needed, the raw materials are cheapand easy to obtain, the amount of generated wastewater is small, the operation is simple, and the method is an environment-friendly process.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for restoring hexavalent-chromium-polluted underground water by virtue of stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles
InactiveCN103949469AEasy to moveLarge specific surface areaContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment by reductionIn situ remediationIron nanoparticle
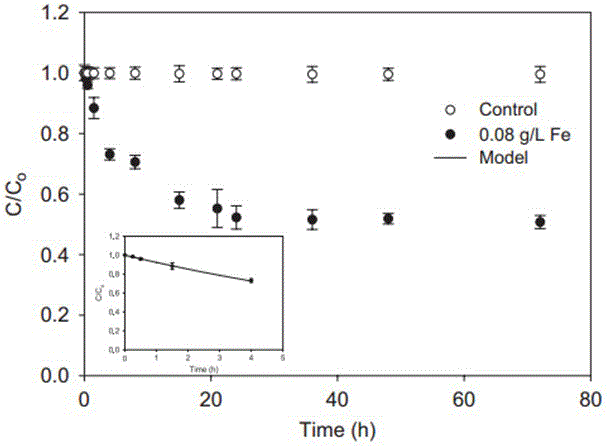
The invention relates to a method for restoring hexavalent-chromium-polluted underground water by virtue of stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles. According to the method, for preventing the agglomeration of the nanoparticles and prolonging the reaction activities of the nanoparticles, water-soluble polysaccharide (CMC) is utilized as a stabilizer and a dispersing agent to synthesize stable iron-based nanoparticles, so that high dispersity and long reaction activities can be realized, the nanoparticles are effectively transferred to a target pollution source of a heavy metal pollution field by virtue of an injection method, and toxic heavy metal Cr (VI) contained in the nanoparticles is reduced, adsorbed and fixed, so that the transfer capabilities of the nanoparticles in soil and underground water are reduced, and finally an in-situ restoring purpose of the pollution field is realized; the method can be applied to the industries such as electroplating, printing and dyeing, electronic device machining, heavy metal machining and the like, and zero-valent iron and nanometer iron oxide have excellent application prospects in restoring processes of environmental pollutants due to special superiorities and wide decontamination and water purification capacities.
Owner:山西敏达科技有限公司
Adsorbent composition by a green process and a process for toxic metal ion removal
InactiveUS20140116949A1Reduce heavy metalsLess complexWaste water treatment from quariesMaterial nanotechnologyIron saltsNanoparticle
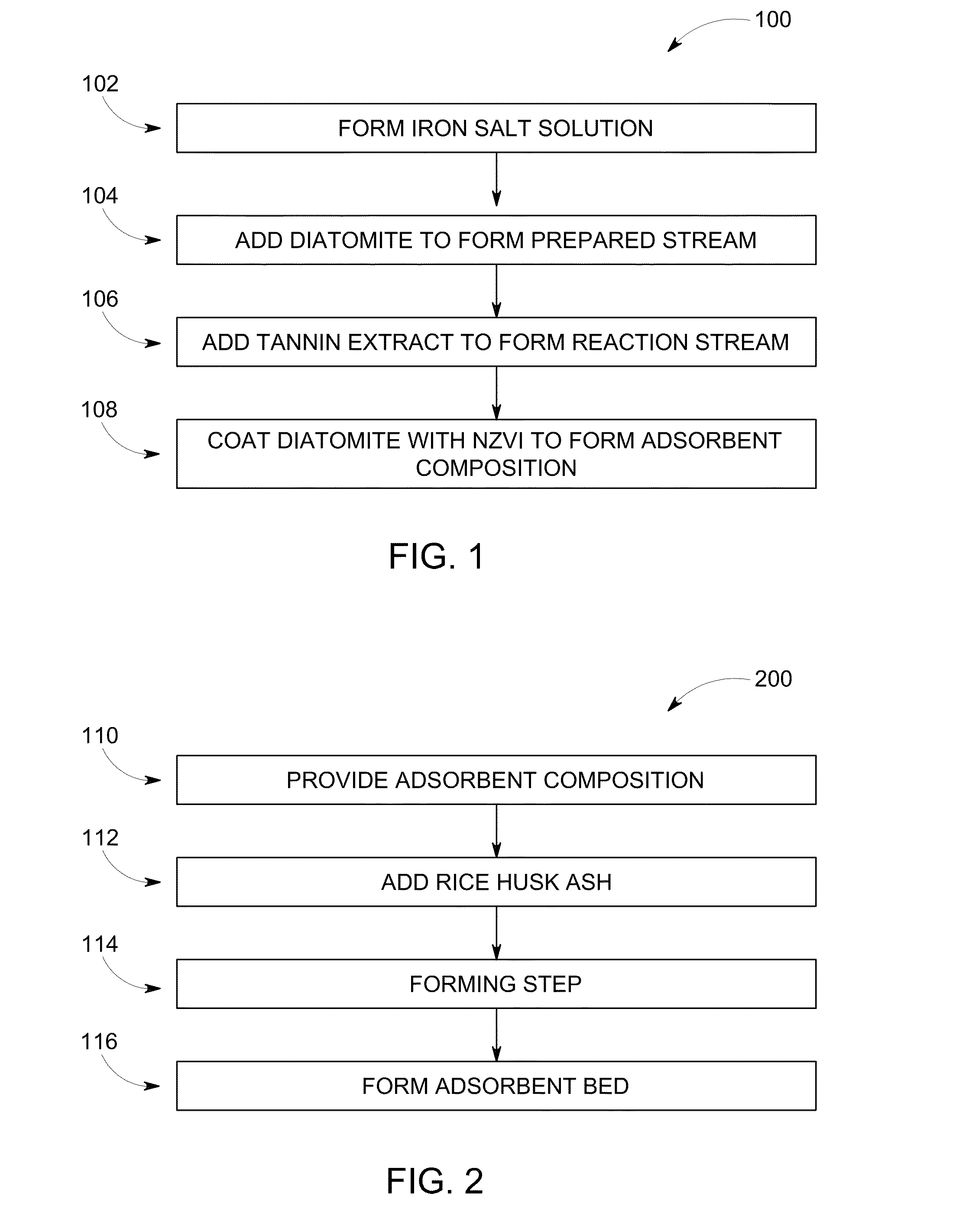
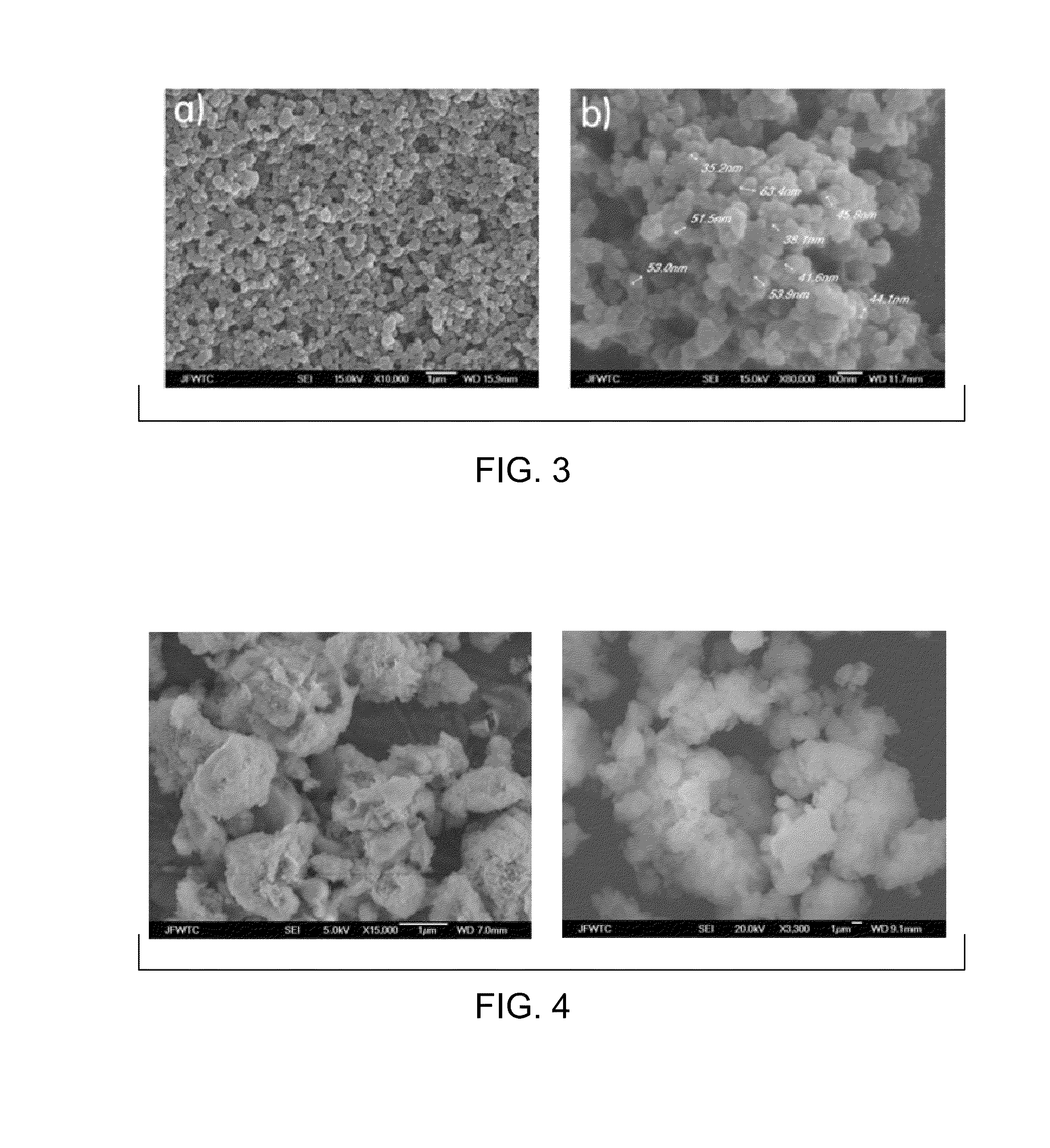
An adsorbent composition of a carrier coated with nanoparticles of zerovalent iron (“NZVI”) is disclosed. The NZVI are synthesized in situ using a tannin extract. Methods of making the adsorbent composition comprise providing a liquid stream; dispersing iron salts in the liquid stream to form an iron salt solution; adding a carrier to the iron salt solution to form a prepared stream; adding a tannin extract to the prepared stream to form a reaction stream; and forming the adsorbent composition in the reaction stream. Methods of reducing toxic metal ions in an aqueous stream are also disclosed. The methods comprise providing said aqueous stream; providing an adsorbent composition having a carrier coated with in situ nanoparticles of zerovalent iron (“NZVI”) therein; and contacting the aqueous stream with the adsorbent composition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Water treatment method of zero-valent iron-copper bi-metal activated persulfate
InactiveCN105253983ASolve the problem of low production volumeRemove completelyWater contaminantsContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentSulfate radicalsPolychlorinated biphenyl
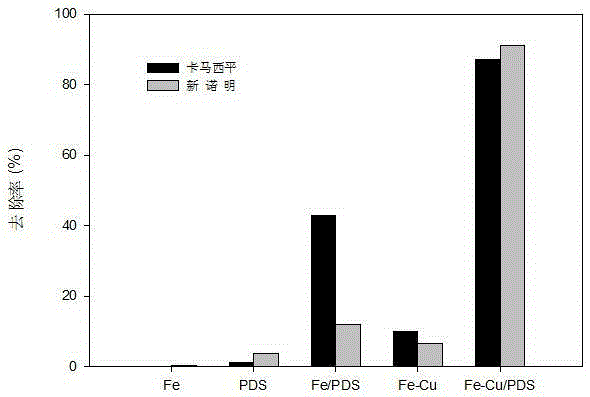
The invention discloses a water treatment method of zero-valent iron-copper bi-metal activated persulfate. The water treatment method specifically comprises the steps that bi-metals including zero-valent iron and copper are added into water containing micro-pollutants, then persulfate is added, full mixing is performed, the bi-metals including the zero-valent iron and the copper are utilized to activate the persulfate so as to remove the micro-pollutants in the water. The water treatment method utilizes the bi-metals including the zero-valent iron and the copper to efficiently activate the persulfate so as to produce free sulfate radicals having strong oxidizing property, can achieve the purpose of quickly and thoroughly removing micro-pollutants, including multiple types of poisonous and harmful micro-pollutants in water, such as polychlorinated biphenyl, brominated flame retardants, drugs and personal care products (PPCPs) and algal toxin, and has the advantages of high activation efficiency, high oxidation and degradation efficiency of pollutants, wide pH using range, convenient operation and the like. The water treatment method can be applied to underground water remediation, treatment of industrial water (including electroplating wastewater, hospital wastewater, printing and dyeing wastewater and the like), drinking water treatment, wastewater treatment and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Silica micropowder loaded type nano zerovalent iron particle and preparation method thereof
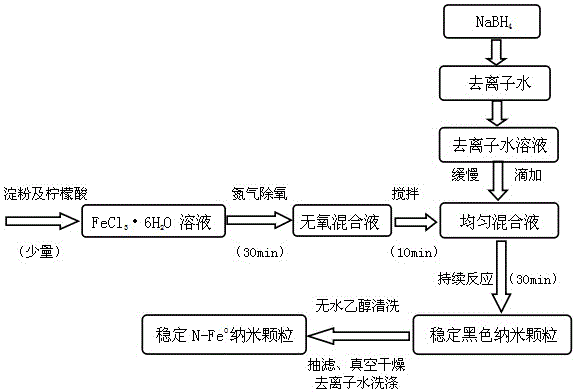
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano material preparation and relates to a silica micropowder loaded type nano zerovalent iron particle and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing modified silica micropowder; (2) removing oxygen; (3) preparing a nano iron solution; and (4) preparing nano zerovalent iron particles. In the invention, a liquid-phase reduction method is adopted to prepare the silica micropowder loaded type nano zerovalent iron particles, and a strong reducing agent KBH4 or NaBH4 is used for reducing Fe<3+> to obtain Fe<0>; loading is carried out through the silica micropowder to ensure that the agglomeration resistance of the nano zerovalent iron particle is greatly improved; the prepared nano zerovalent iron particles are uniformly distributed and have small mean grain size and large specific surface area; and the pollutant removal capacity of the nano zerovalent iron particles is far higher than that unloaded nano iron, and the nano zerovalent iron particles have stronger mobility in simulated soil, and can be widely applied to the field of environmental modification.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method and application of nano zero-valence iron and copper double-metal particles
ActiveCN105195758APrevent oxidationEasy to getContaminated soil reclamationNanotechnologyWater bathsIron salts
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of nano zero-valence iron and copper double-metal particles. In one embodiment, the preparation method comprises the following steps: adding an iron salt and a copper salt into a three-opening flask at a mol ratio of (3-10) to 1; taking 50mL-100mL of an ethanol solution to be added into the three-opening flask; stirring in a water bath at 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C for 10 minutes to 30 minutes; adding a hydroborate solution into the three-opening flask; after stirring for 10 minutes to 40 minutes, filtering to obtain sediment; washing the sediment with absolute ethyl alcohol and acetone respectively and then filtering; and putting the sediment into a vacuum drying box to be dried for 1 hour to 24 hours at 25 DEG C to 80 DEG C to obtain the nano zero-valence iron and copper double-metal particles. According to the embodiment provided by the invention, a preparation process is simple and the utilization is safe; and by adjusting the pH of chromium polluted soil, the application amount of the nano zero-valence iron and copper double-metal particles and a reaction temperature, hexavalent chromium in the chromium polluted soil can be rapidly reduced, so that the embodiment has a great application value in the field of repairing the chromium polluted soil.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Fe/C composite porous structure material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105776506AHigh particle strengthHas a bonding effectTreatment using aerobic processesContaminated soil reclamationPorosityMagnetic susceptibility
The invention discloses a Fe / C composite porous structure material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Fe / C composite porous structure material is characterized by being prepared from low-grade sedimentary iron ore and biomass as raw materials in manners of crushing, mixing, extrusion molding and pyrolysis and reduction reaction in the presence of hydrogen atmosphere at 650-900 DEG C, wherein the main phase composition comprises biomass carbon and zero-valent iron. The Fe / C composite porous structure material disclosed by the invention is high in opening porosity, magnetic susceptibility, adsorbability and biological chemical activity, can be used for treating eutrophicated river water, living sewage and landscape water bodies, or can be used for mediation of underground water pollution and polluted soil.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
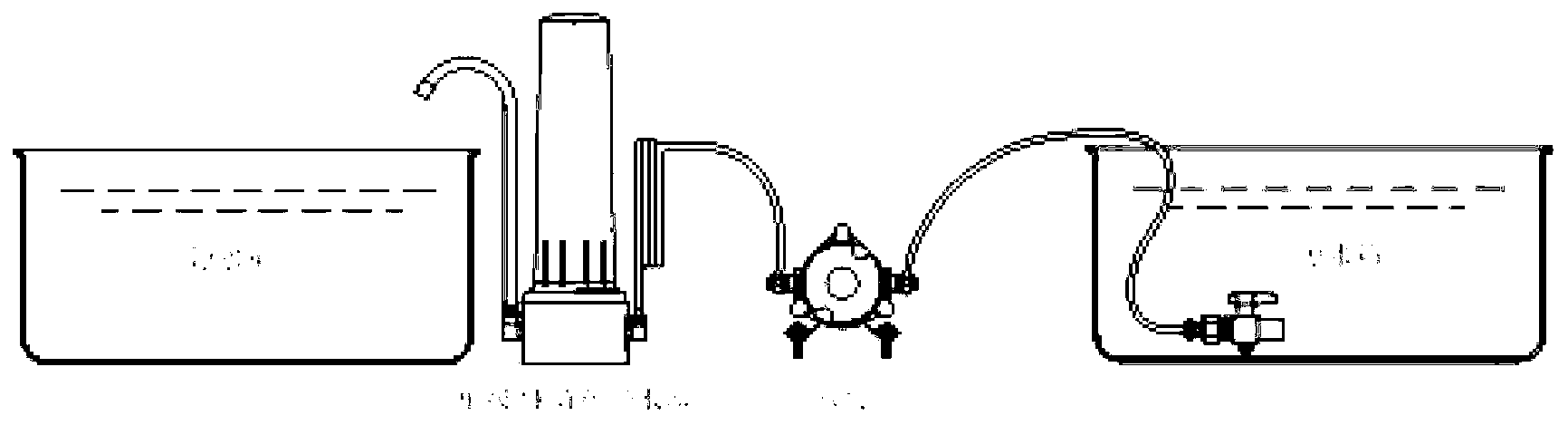
Method and device for purifying cadmium in waste water through nano zero-valent iron
ActiveCN102897889ASimple processEasy to operateWater/sewage treatment by sorptionWater/sewage treatment by reductionZerovalent ironEnvironmental chemistry
The invention relates to a method and a device for purifying cadmium in waste water through nano zero-valent iron, and the cadmium-contained waste water refers to the waste water with severe pollution and needing to be purified in the production and application field of smelting and different cadmium compounds. By adopting the nano technology, a great amount of cadmium elements in the waste water is purified and removed by utilizing nano zero-valent iron through a continuous flow secondary reaction device. Water is discharged in a weir flow way after the waste waster flows by a secondary treatment device consisting of a reaction chamber and a separation chamber, the waste water is adequately contacted and reacted with the nano zero-valent iron particles through the electric blending inside the reaction chamber, the nano zero-valent iron particles are promoted to precipitate by utilizing an oblique plate inside the separation chamber so as to be separated from the waste water, and the precipitated nano zero-valent iron backflows to the reaction chamber to be circulated. A layer of filter membrane is paved on a water outlet of a weir flow water outlet groove so as to filter the nano zero-valent iron particles which are not completely precipitated in the water. The process flow for removing cadmium pollutant in the waste water is simple, the cost is low, convenience in operation is achieved, the treatment effect is good, and no secondary pollution is caused.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method and application of carbon-sulfur doped zero-valent iron composite material
InactiveCN110482671ARich sourcesLow costWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationIron powderIron sulfide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbon-sulfur doped zero-valent iron composite material, which comprises the following the step: proportionally mixing and ball-milling a sulfur reagent, iron powder and carbon powder to obtain the carbon-sulfur doped zero-valent iron composite material; the sulfur reagent is elemental sulfur powder, iron sulfide powder or pyrite powder; the mass percentage ratio of the sulfur reagent to the iron powder to the carbon powder is (0.5-20): (70-99): (0.5-10). The sulfur reagent, the iron powder and the carbon powder are mixed and then subjected toball milling to obtain the carbon-sulfur doped zero-valent iron composite material, and the carbon-sulfur doped zero-valent iron composite material can be used for in-situ removal and degradation of heavy metal pollutants, pesticide pollutants, azo dye pollutants, halogenated organic matter pollutants and / or nitro organic matter pollutants in underground water and soil and has high removal and degradation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Wastewater treatment filtering material, and preparation method and use thereof
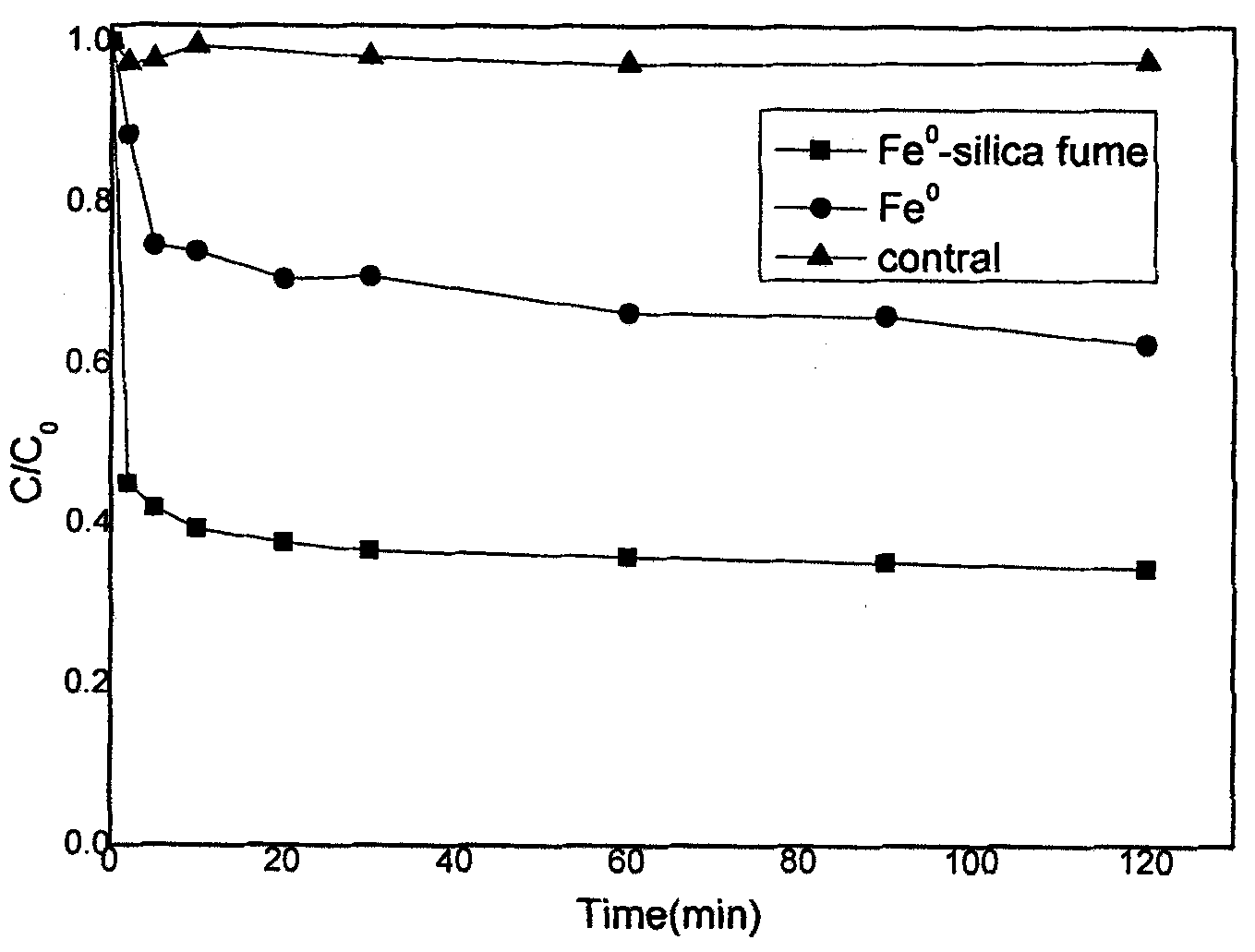
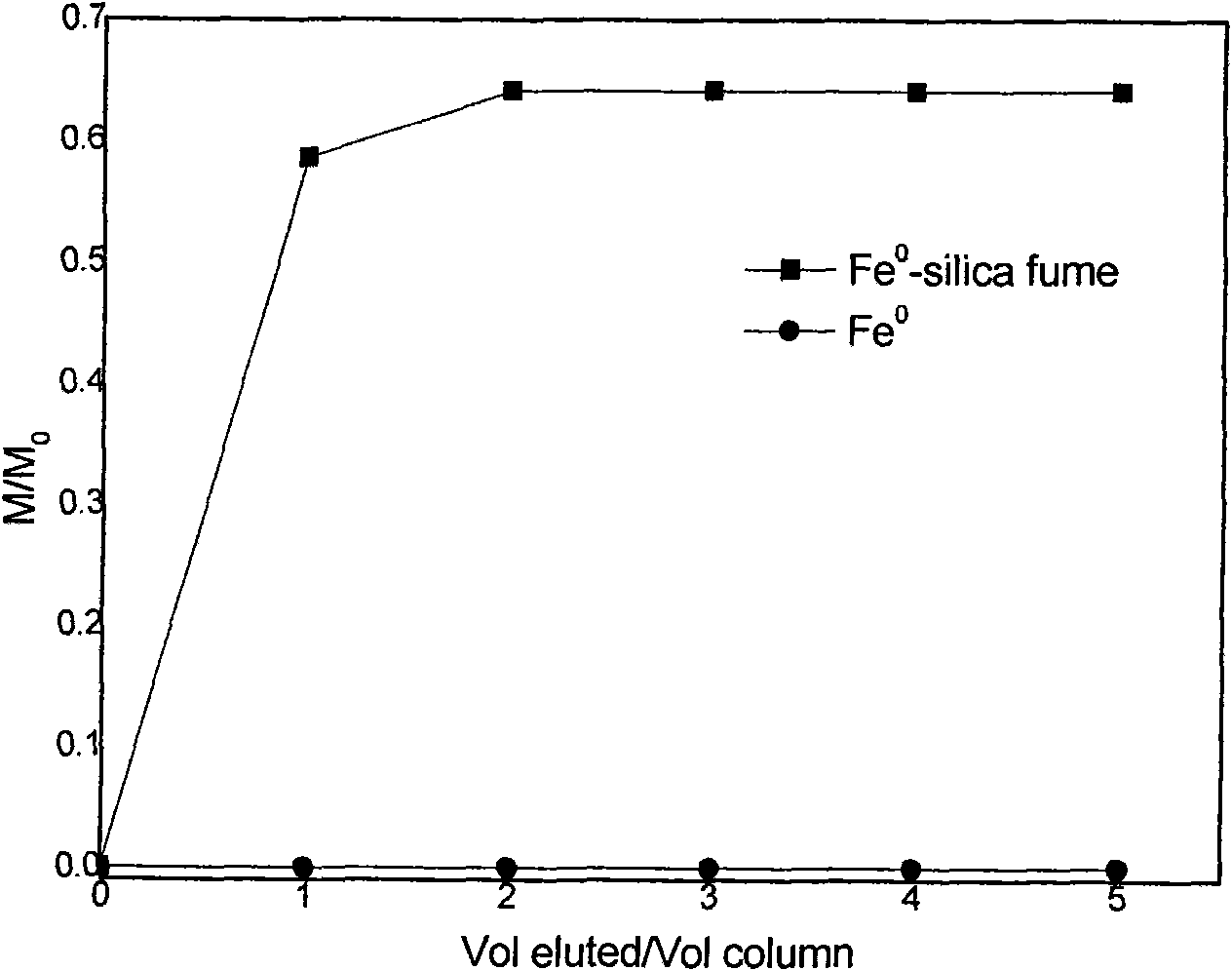
ActiveCN103316544AHigh adsorption and fixation functionStable weak alkalineOther chemical processesFiltration separationWater qualityZerovalent iron
The invention relates to a wastewater treatment filtering material, and a preparation method and a use thereof. The filtering material is formed by a porous ceramic matrix having an amount of porosity of 35-85% and nanometer zerovalent iron particles in-situ generated in the porous ceramic matrix, the micropore size of the porous ceramic matrix is 2-10mum, a fuzzy amorphous silicon-iron-carbon structure is formed in the micropore and can form an adsorbing film after absorbing water, and the material of the porous ceramic matrix is composed of 55-65 parts by weight of diatomite, 12-15 parts by weight of calcium-based bentonite, 7-12 parts by weight of carbon powder, 2-3 parts by weight of starch, and 4-6 parts by weight of kaolin. The filtering material obtained in the invention forms a nose-like porous fluffy filtering structure in the microstructure and generates the adsorbing film, so the absorbing efficiency is greatly improved, and the filtering material can be adapted to the chemical environment change of water. The shedding or heavy metal precipitation of the used filtering material does not appear, and the use safety of the filtering material is good.
Owner:SUZHOU MICRO CERAMICS HEAVY METAL FILTER TECH
Simple method for loading ultrafine nano zero-valent iron on porous material
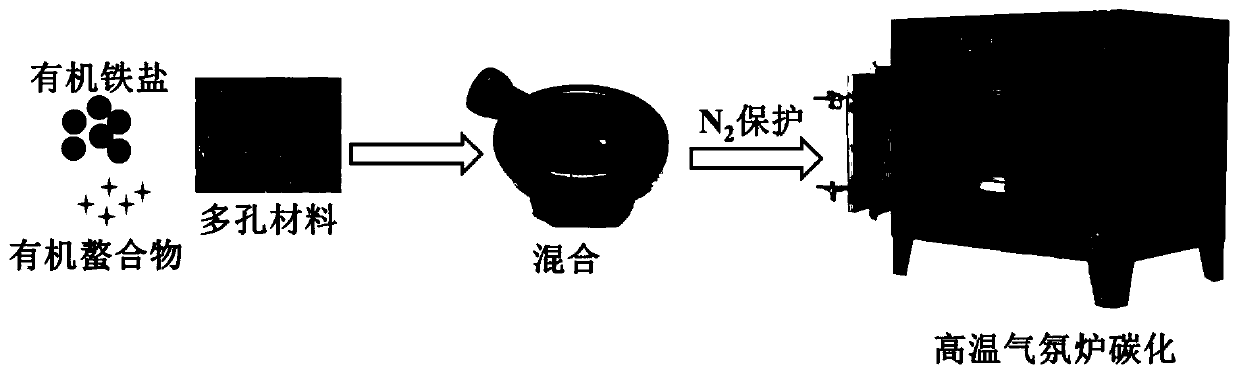
ActiveCN111097414AEasy accessPrevent oxidationOther chemical processesWater contaminantsIron saltsPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-toxicity pollutant treatment, and relates to a simple and convenient method for loading superfine nano zero-valent iron on a porous material and application of the porous material as an adsorbent and a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for degrading and removing pollutants. The organic iron salt, the organic ligand and the porous material only needto be simply mixed and then are subjected to high-temperature carbonization under the protection of inert gas, so that the superfine zero-valent iron can be uniformly loaded on the inner and outer surfaces and pore passages of the porous material. According to the method, a complex, time-consuming and harsh liquid-phase impregnation process in a conventional liquid-phase reduction method is omitted, no solvent or dispersing agent is needed, and the utilization rate of raw materials is high. The obtained zero-valent iron is large in loading capacity, good in crystallinity and small in particlesize. The porous material loaded with the superfine nanoscale zero-valent iron can be used as an adsorbent and a catalyst, and high-toxicity inorganic and organic pollutants in a water body are removed by utilizing adsorption, an Fe-C micro-electrolysis technology and a Fenton oxidation technology.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of zero-valent iron sulfide and application thereof
ActiveCN109607635ALess energy consumptionSimple and efficient operationWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentHeavy metalsAqueous solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of zero-valent iron sulfide and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that under the ambient temperature condition, zero-valent iron and simple-substance powdered sulfur are mixed to be subjected to a reaction in a water solution to obtain zero-valent iron sulfide. According to the method, zero-valent iron and simple-substancepowdered sulfur are mixed to be subjected to the reaction in the water solution, little energy is consumed, operation is easy and convenient, the preparation time is relatively short, the preparationcost is low, and the obtained zero-valent iron sulfide has the high removal efficiency for heavy metal and organic contaminants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing montmorillonite in situ intercalation type nanoscale zero-valent iron
InactiveCN102344194AAvoid reunionImprove liquidityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionWater/sewage treatment by reductionMontmorilloniteMaterials science
The present invention relates to a method for preparing montmorillonite in situ intercalation type nanoscale zero-valent iron. According to the method, a template is adopted, wherein the template is prepared through adopting montmorillonite clay as nanoscale zero-valent iron; the in situ intercalation method is adopted to prepare the montmorillonite-loaded nanoscale (sub-nanometer) zero-valent iro; the montmorillonite in situ intercalation type nanoscale zero-valent iron is prepared through the following preparation steps: pretreatment of montmorillonite, preparation of Fe<3+> saturated montmorillonite, acidification of Fe<3+> saturated montmorillonite and preparation of montmorillonite-loaded zero-valent iron. The nanoscale zero-valent iron in the prepared montmorillonite-loaded type zero-valent iron composite material through the method provided by the present invention is positioned between the montmorillonite layers, and exists in nanometer or sub-nanometer atom cluster scale; compared to other nanoscale zero-valent irons, the nanoscale zero-valent iron provided by the present invention has higher reaction activity and higher reducing effectiveness. According to the present invention, with the template prepared through adopting the montmorillonite as the zero-valent iron, the agglomeration of the zero-valent iron particles can be prevented, the fluidity of the zero-valent iron is enhanced, the zero-valent iron can be protected to a great degree, such that the oxidation of the zero-valent iron due to water molecules can be avoided; with the method, the problems of easy agglomeration, easy oxidation due to the water and poor fluidity during the synthesis and the application process of the nanoscale zero-valent iron are solved; an effective material and technology is provided for environmental pollution treating.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Zero valent iron systems and methods for treatment of contaminated wastewater
ActiveUS20160052808A1Easy maintenanceOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPollutantEnvironmental chemistry
Hybrid zero-valent iron systems and methods for treating a fluid containing a contaminant that removes or reduces the concentration of contaminants, such as toxic metals, metalloids, oxyanions, and dissolved silica.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of novel iron-based biochar
InactiveCN105753608AOvercoming the lack of repair functionImprove repair efficiencyEnergy inputFertilizer mixturesElectrode potentialTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to the field of preparation and application of novel iron-based biochar, in particular to a preparation method for a novel iron-based biochar repair material which is used for treating polluted soil. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: performing anaerobic dry distillation on a biomass raw material which is carried with an iron oxide in a dry distillation furnace; performing reducing, cracking and polymerizing reactions on the biomass to generate energy conversion; separating reductive gases, namely CO and H2; under a proper temperature, gradually reducing part iron oxide which is loaded on the surface of the biomass into zero-valent iron. Electrode potential difference exists between iron and carbon, so that a micro primary cell can be formed in soil solution; moreover, the iron oxide which remains on the surface of the biochar has a very good removal capacity to arsenic, so that the treatment effect on the pollutants in soil is enhanced very well; according to the preparation method and the application of the novel iron-based biochar, environmental effects of the biochar, the zero-valent iron and the iron oxide are combined, so that the problem of repair function loss of the biochar is solved; the repair efficiency is improved; the application potential of the novel iron-based biochar in the aspect of soil body pollution control is expanded.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A method of removing nitrates from water by utilization of a zero-valent iron/oxidizing agent/zeolite synergetic system
ActiveCN104341055AHigh removal rateLow costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentReduction ActivityIron powder
A method of removing nitrates from water by utilization of a zero-valent iron / oxidizing agent / zeolite synergetic system is provided. The zero-valent iron is common iron powder. The oxidizing agent is a common oxidizing agent used in water treatment. The zeolite is natural zeolite or artificial zeolite. The method is characterized in that: the oxidizing agent in the system oxidizes and strips a passivation layer formed on the surface of the zero-valent iron to allow electrons in the zero-valent iron to be transferred continuously to the outside, so that the zero-valent iron maintains high reduction activity to reduce the nitrates into ammonia nitrogen. Then efficient selective absorption of the zeolite to the ammonia nitrogen is utilized to remove the ammonia nitrogen in the water body. The method is environmental friendly, simple, feasible, low in cost, and capable of being efficiently used for treatment of waste water containing nitrates of industrial enterprises and nitrate restoration and removal for underground water.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Advanced redox water treatment technology based on nitrogen-doped iron-carbon material with core-shell structure and for magnetic field recovery
ActiveCN108940335ASimple methodReduce heat consumptionPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsMaterials science and technologyCarbon composites
The invention relates to the fields of new material science and technology and environmental protection technology and particularly discloses a preparation method of a nitrogen-doped iron-carbon material with a core-shell structure and suitable for magnetic field recovery and an application method thereof in an advanced redox water treatment technology. The nitrogen-doped iron-containing metal organic framework is a high-performance iron-carbon composite material obtained through precursor one-step carbonization. The iron element in the material is mainly fixed in the form of zero-valent ironin the porous carbon material so that a core-shell structure is formed. The nitrogen-doped carbon material shell can protect the zero-valent iron and prolong the service life of the iron-carbon composite material. The iron-carbon composite material has the catalytic oxidation ability of an activated peroxide oxidant, can be applied to the advanced oxidation system, has good interface reducing ability of zero-valent iron and realizes efficient removal of multiple pollutants in the water.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and applications of vulcanized modified zero-valent iron composite material
ActiveCN110627187AIncrease profitHigh selectivityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationMaterials preparationPyrite
The invention discloses a vulcanized modified zero-valent iron composite material preparation method, which comprises: (1) mixing pyrite and zero-valent iron according to a certain mass ratio, and putting the mixture into a ball milling tank; (2) adding ball-milling beads with a diameter of 3-12 mm, uniformly mixing the ball-milling beads, the pyrite and the zero-valent iron, and directly performing dry ball-milling without auxiliary agents and atmosphere; (3) setting the rotating speed of ball milling at 200-800 rpm, performing ball milling for 5-10 min each time, pausing for the same time, changing the ball milling steering, and sequentially circulating 3-6 times; and (4) after the ball milling is finished, screening with a 100-200 mesh sieve mesh, placing the collected vulcanized modified zero-valent iron composite material in a dryer so as to be stored. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process and low in cost, has reinforced removal effect on heavy metals and chlorinated organic pollutants in wastewater, and has large-scale production and engineering application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method and application of modified zeolite permeable reactive wall filling carrying zero-valent iron powder
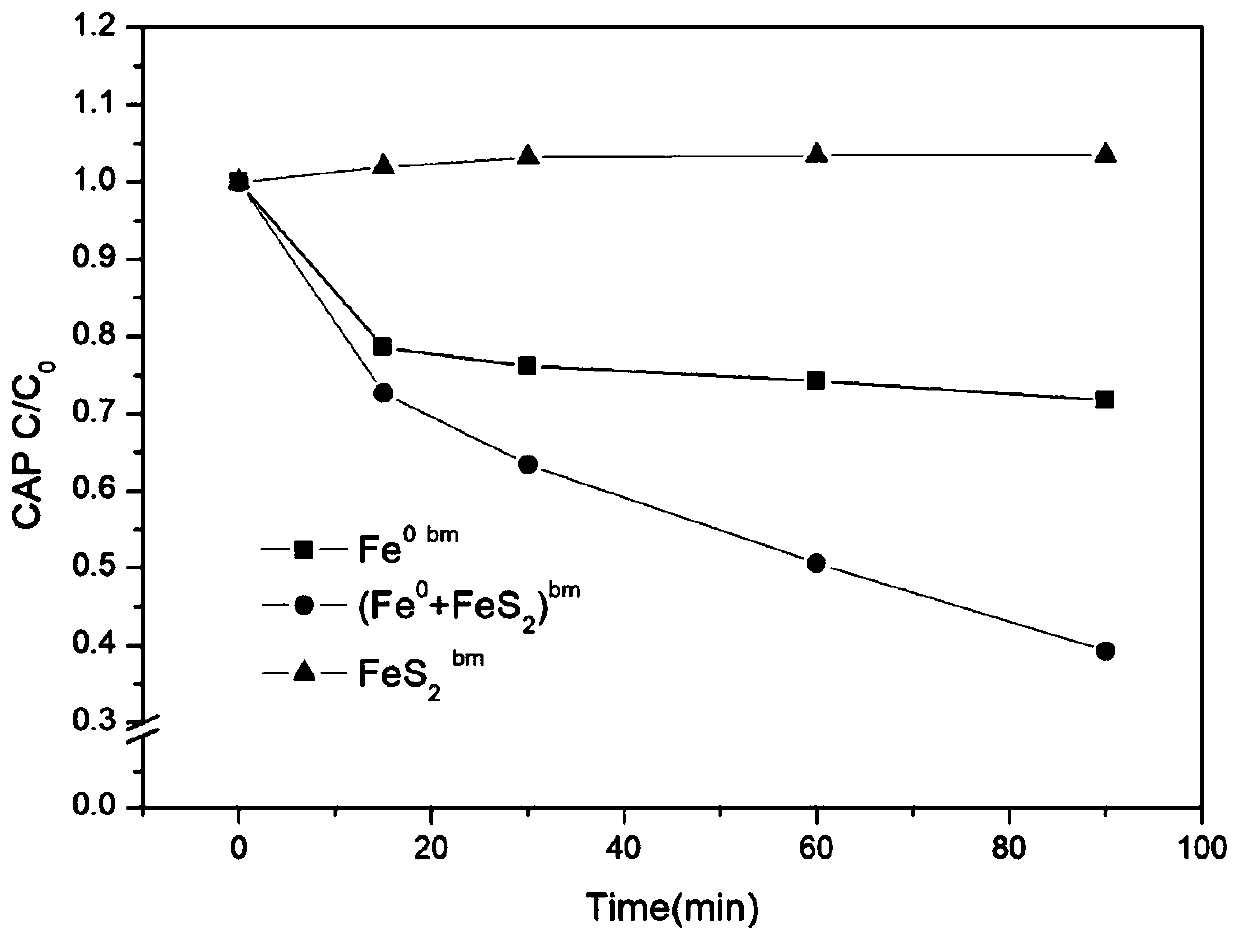
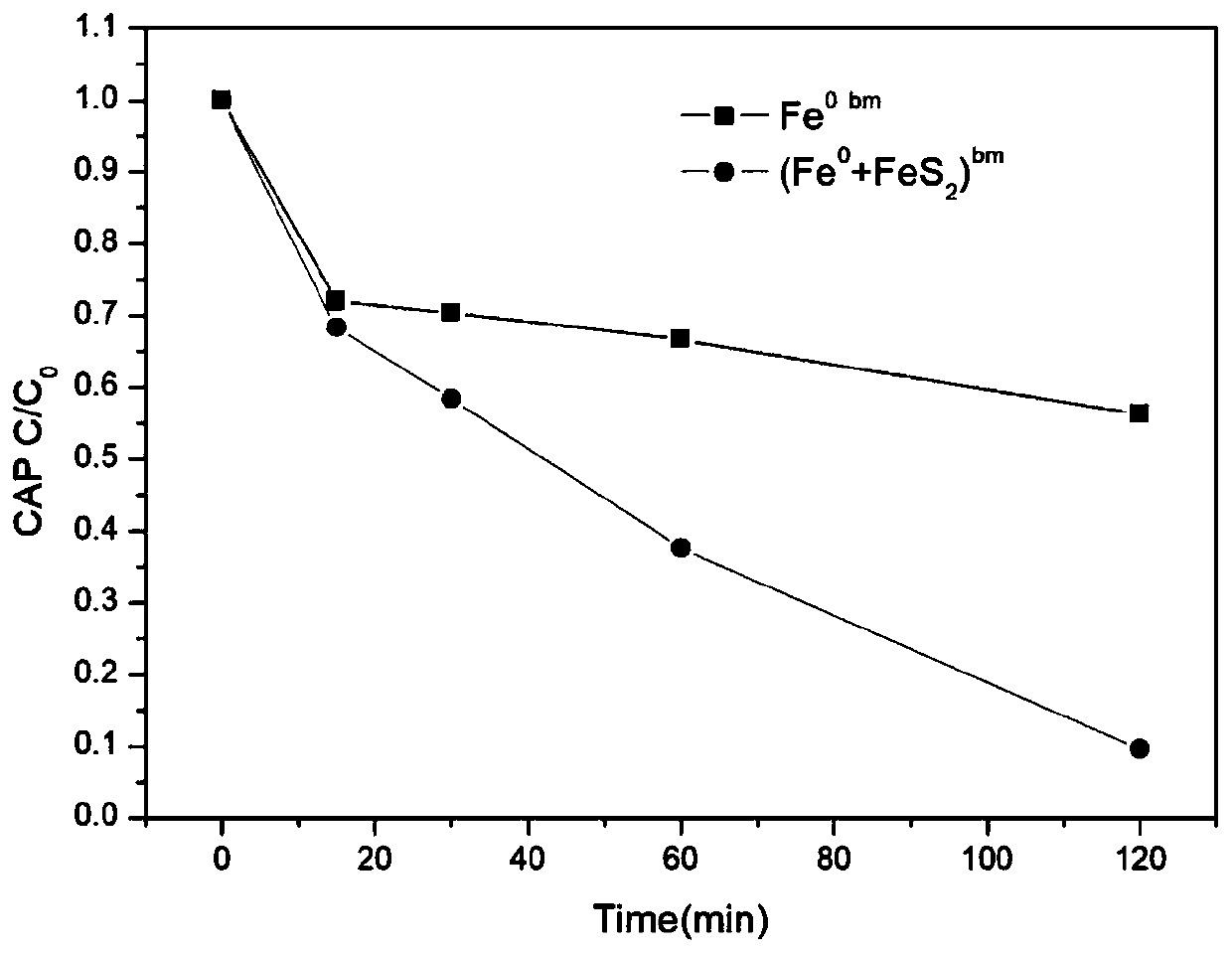
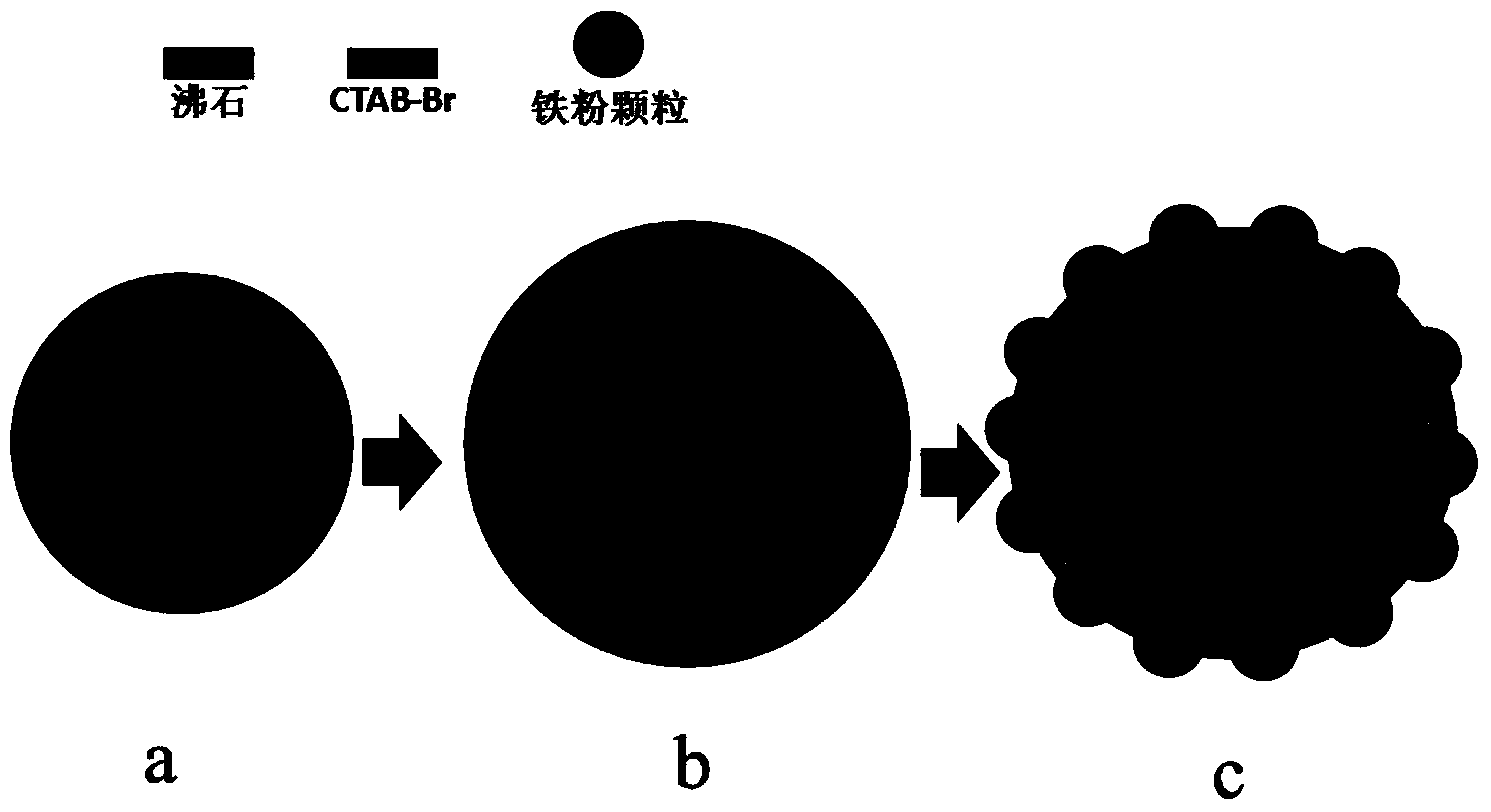
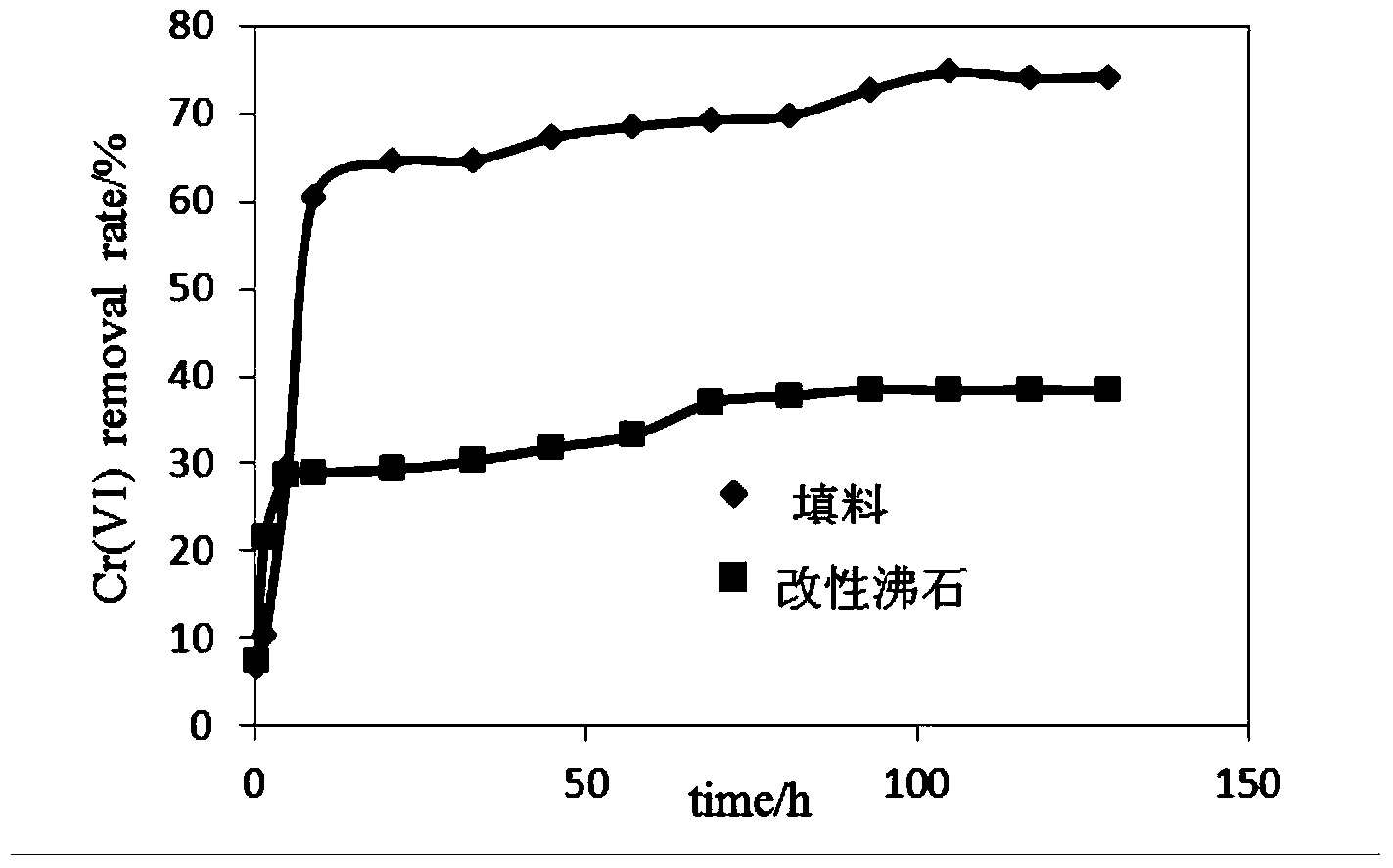
InactiveCN103769033ASolve the loss of iron powderSolve churnWater contaminantsChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesHexavalent chromiumWater environment
The invention discloses a preparation method and the application of modified zeolite permeable reactive wall filling carrying zero-valent iron powder, and belongs to the field of underground water environment modification. The method comprises the following steps: soaking clinoptilolite in 16-20g / L of cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) Br solution, and modifying the clinoptilolite for over 12h in a constant-temperature shaking table at normal temperature; washing the modified clinoptilolite for 5-6 times with distilled water, and drying the clinoptilolite for later use; adding iron powder into 10-30g / L of sodium alginate solution; performing full and uniform stirring to form a mixture of the iron powder and the sodium alginate solution; performing full stirring to uniformly disperse the mixture of the iron powder and the sodium alginate solution on the surface of the modified zeolite; pouring the mixture into 20-40g / L of CaCl2 solution, and soaking and maintaining the mixture for 24h with the CaCl2 solution; stirring and washing the mixture with hydrochloric acid, and then washing the mixture to be neutral with the distilled water. According to the preparation method, the problem of loss of the iron powder is effectively solved, and the removal rate of hexavalent chromium with modified zeolite filling carrying the iron powder is two times of the removal rate of the hexavalent chromium with the modified zeolite.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
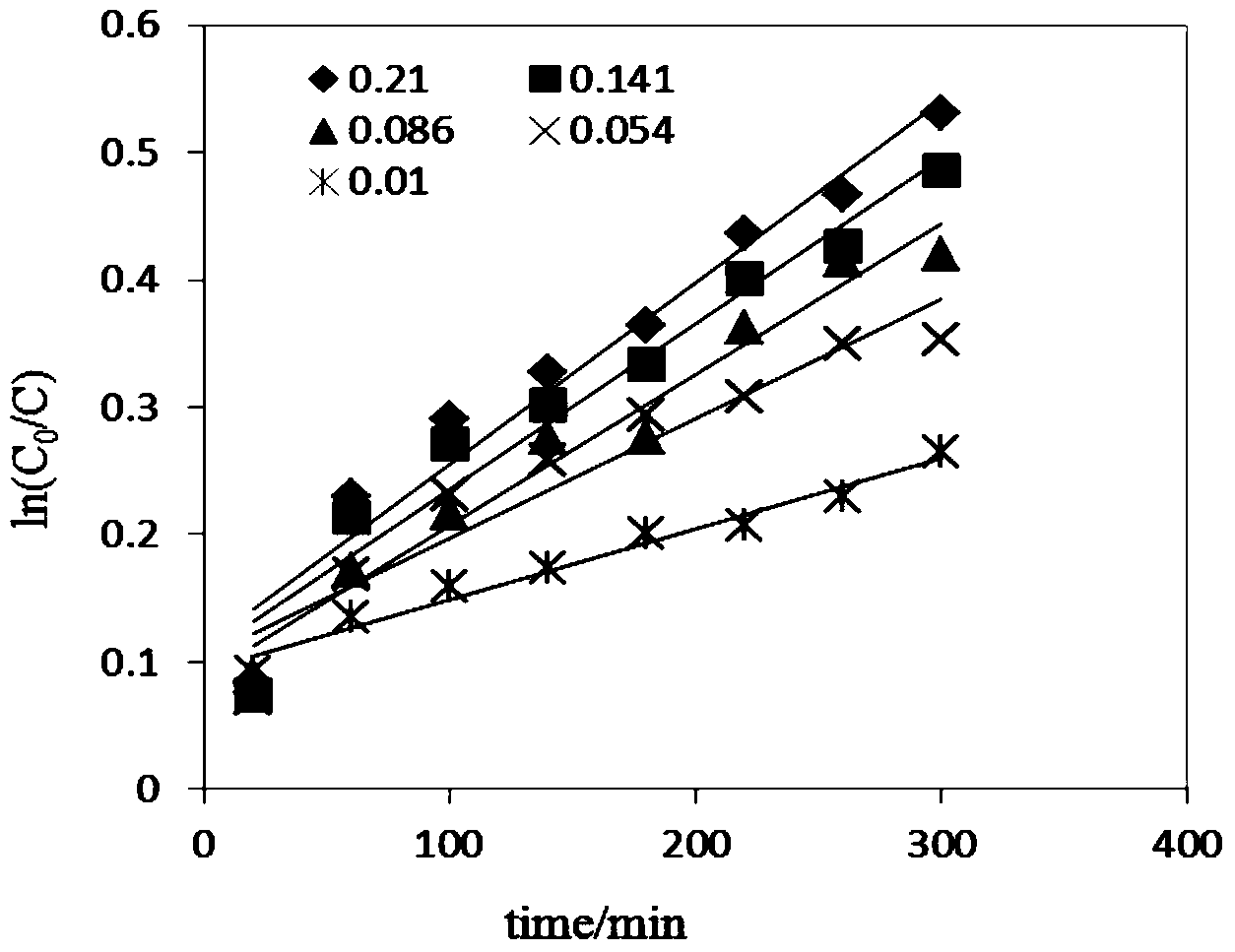
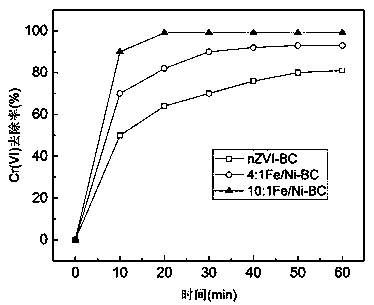
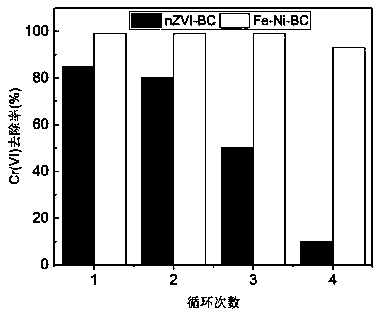
Method for removing hexavalent chromium in water by using biochar-loaded nanometer iron-nickel composite material
InactiveCN110745935AHigh activityImprove stabilityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by reductionMetallic materialsZerovalent iron
The invention discloses a method for removing hexavalent chromium in water by using a biochar-loaded nanometer iron-nickel composite material, and relates to a remediation method for heavy metal pollution in a water body. According to the invention, the biochar-loaded nanometer zero-valent iron-nickel bimetallic composite material is prepared in one step by using a simplified biochar-supported bimetallic material preparation process without the use of a high-cost strong reducing agent, and is applied to removal of Cr (VI) in water, so that the problems of easy surface passivation, low reactionactivity and low utilization rate in the treatment of heavy metals in a water body with nanometer zero-valent iron; and the method has advantages of low cost, simple operation and no secondary pollution, and the Cr (VI) removal activity and the stability of the biochar-loaded iron-nickel bimetallic material are higher than the Cr (VI) removal activity and the stability of the biochar-loaded nanometer zero-valent iron material.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com