A method of removing nitrates from water by utilization of a zero-valent iron/oxidizing agent/zeolite synergetic system
A technology of zero-valent iron and oxidant, which is applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of high preparation cost of nano-scale zero-valent iron, abnormal use of water body, and reduced reaction rate, etc., and achieve good application prospects, high nitrate removal rate, low energy consumption effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
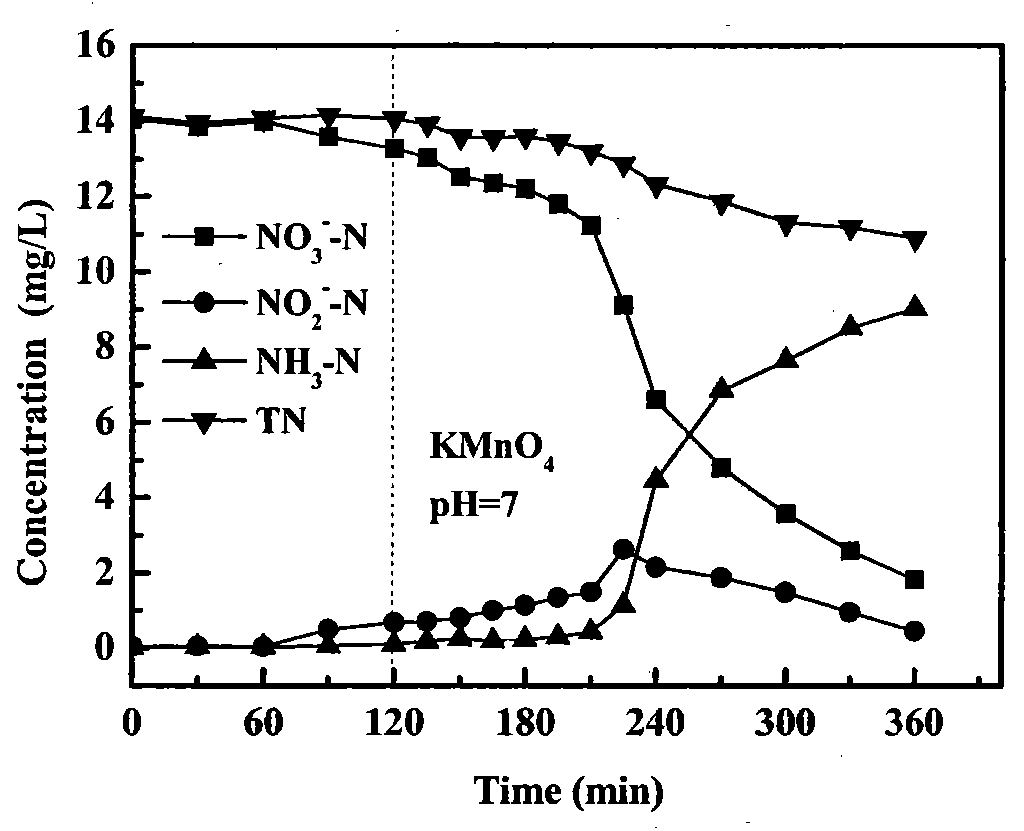
[0019] Nitrate (NO 3 - ) was removed in a 250ml three-neck flask. NO in the experiment 3 - The initial concentration of -N is 1mmol / L, the solution volume is 200ml, and the mass of iron powder is 1.00g. Use 0.1mol / L HCl and NaOH solutions to adjust the pH of the solution to keep it stable at 7.0. Add KMnO when the reaction reaches 120 minutes 4 , the dosage is such that the initial concentration in the solution is 1mmol / L, the reaction is continued for 240 minutes, and samples are taken and analyzed at regular intervals. After 240 minutes, transfer the remaining reaction solution (150mL) to a new 250ml three-neck flask, add 1.00g zeolite (20-80 mesh in particle size), stir (200rpm) at room temperature for 1 hour, and periodically take samples for analysis . Reductive removal of nitrate and its products vary with time as figure 1 shown. The adsorption and removal amount of ammonia nitrogen is shown in Table 1.
[0020] Experiments show that if no oxidant KMnO is added ...
Embodiment 2
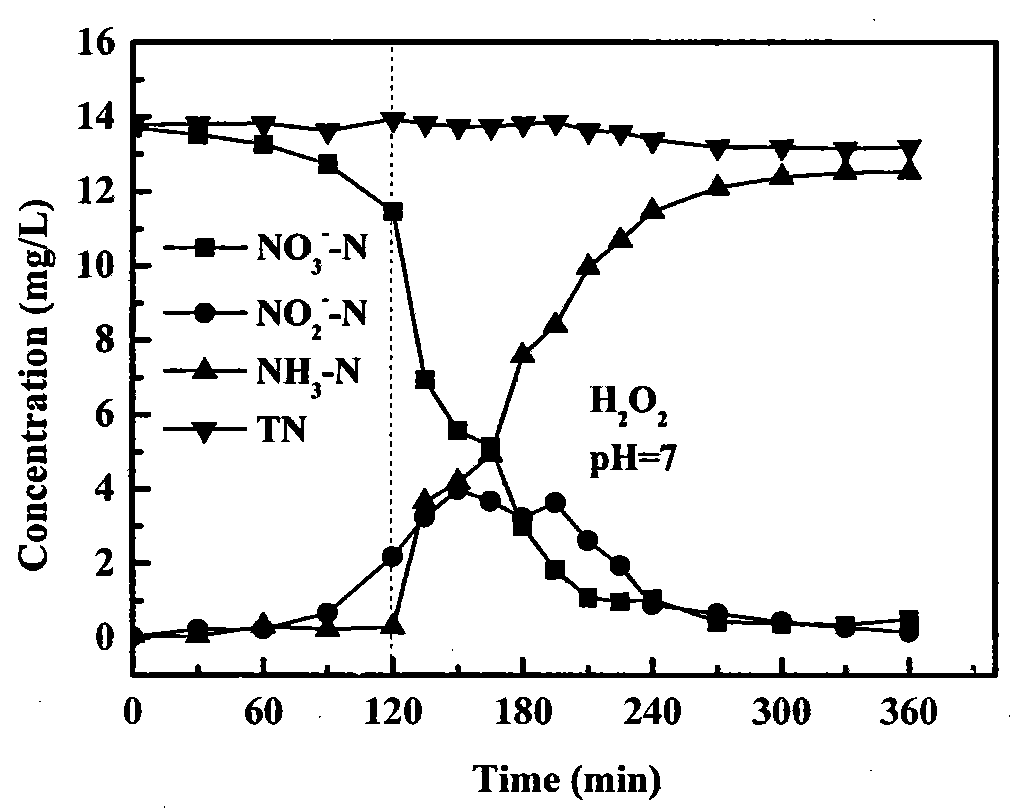
[0024] Nitrate (NO 3 - ) was removed in a 250ml three-neck flask. NO in the experiment 3 - The initial concentration of -N is 1mmol / L, the solution volume is 200ml, and the mass of iron powder is 1.00g. Use 0.1mol / L HCl and NaOH solutions to adjust the pH of the solution to keep it stable at 7.0. Add H when the reaction reaches 120 minutes 2 o 2 , the dosage is such that the initial concentration in the solution is 1mmol / L, the reaction is continued for 240 minutes, and samples are taken and analyzed at regular intervals. After 240 minutes, the reaction residue (150mL) was transferred to a new 250ml three-neck flask, 1.00g of zeolite (20-80 mesh in particle size) was added, and stirred (200rpm) at room temperature for 1 hour, during which time sampling and analysis were performed. Reductive removal of nitrate and its products vary with time as figure 2 shown. The adsorption and removal amount of ammonia nitrogen is shown in Table 2.
[0025] Experiments show that if ...
Embodiment 3
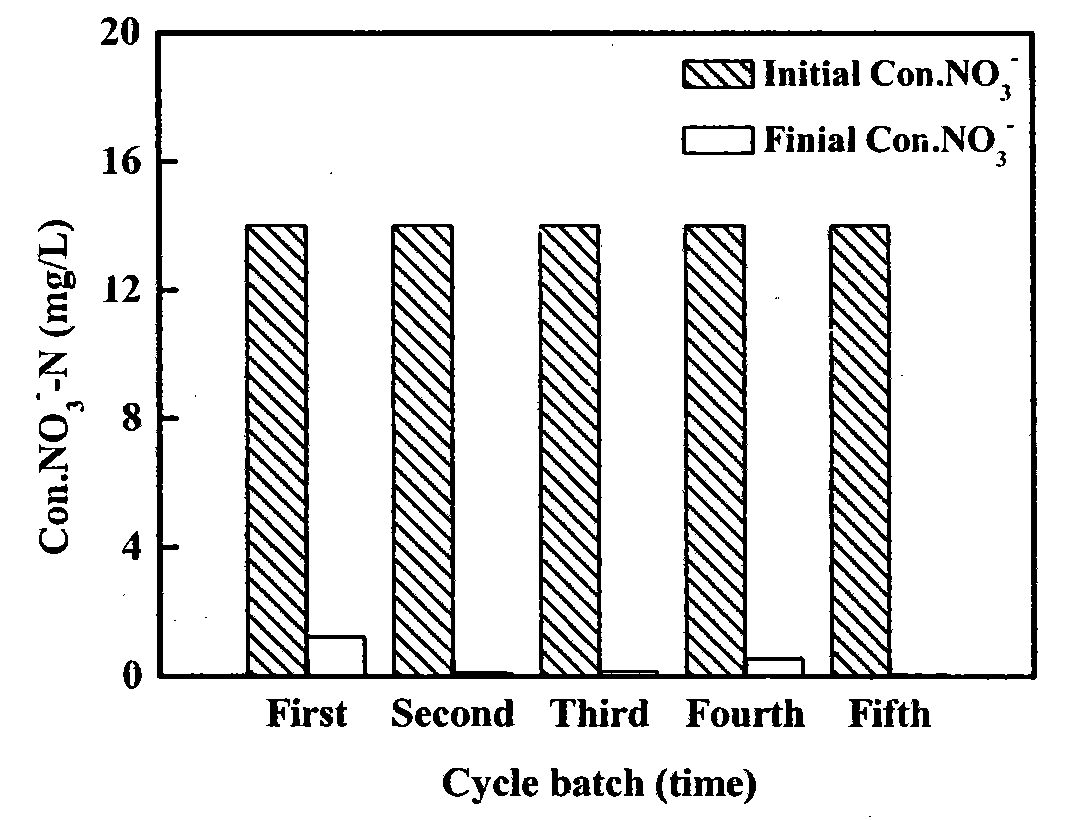
[0029] Nitrate removal was carried out in a 250ml three-neck flask. NO in the experiment 3 - The initial concentration of -N is 1mmol / L (14mg / L), the volume of the solution is 200ml, the mass of iron powder added is 2.00g, and H 2 o 2 , the dosage is such that the initial concentration in the solution is 1 mmol / L, and the pH of the solution is adjusted with 0.1 mol / L HCl and NaOH solutions to keep it stably at 7.0. Stir (200rpm) at room temperature and react for 3 hours, during which periodical sampling and analysis are carried out. After the reaction, the waste liquid is discarded, but the residual iron powder is kept, and 200ml of nitrate solution (1mmol / L) is added again, and H 2 o 2 , the dosage still makes its initial concentration 1mmol / L. Repeat this 4 times. The results of reduction and removal of nitrate are as follows image 3 shown. The experimental results show that in the continuous treatment of five batches of nitrate solution, the removal rate of each ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com