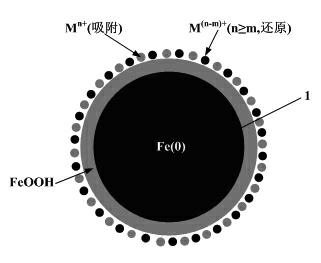
Method for repairing heavy metal-polluted soil or sludge with nano-zero-valent iron (nZVI)
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and polluted soil, which is applied in the restoration of polluted soil, sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of simple system structure, low energy consumption and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The soil is collected at a depth of 10-100cm in a certain place. The content of heavy metals (zinc, lead, cobalt, nickel, copper) in the soil is between 3-100mg / Kg, and the pH value is between 6.8-7.5. In this study, several soil samples with the same heavy metal content were designed. For several samples with the same conditions, the amount of nZVI was increased sequentially, and the change of the removal rate of heavy metals in the soil was investigated with the increase of the amount of nZVI. In order to make the experimental effect more obvious, the heavy metal soil spiked method was adopted. The heavy metal spiked concentration was 500-1500mg / Kg, where the soil amount was 10-100g, the water volume was 100-1000 mL, and the nZVI amount was 2-50 g. According to the technological process of this study, the water and the spiked soil were mixed for 15-24 hours through the mixing reaction device, and the contents of heavy metals in the mixed liquid water and soil were resp...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The soil is collected at a depth of 10-100cm in a certain place. The local content of heavy metals (zinc, lead, cobalt, nickel, copper) in the soil is between 3-100mg / Kg, and the pH value is between 6.8-7.5. This study is designed as a soil sample with a specific heavy metal content (500-1500mg / Kg). The same amount of nZVI (2-20g) was added to the sample in batches, and nZVI was not added once. After the reaction is sufficient, the heavy metals will be adsorbed. The separation of nZVI was used to determine the removal rate of heavy metals in soil. In order to make the experimental effect more obvious, the method of adding heavy metals to the soil is adopted, and the concentration of heavy metals is 500-1500mg / Kg. Here, the amount of soil is 10-100g, and the volume of water is 100-1000 mL. According to the technological process of this study, the water and the spiked soil were mixed for 15-25 hours through the mixing reaction device, and the contents of heavy metals in t...
Embodiment 3
[0036] In contrast to the removal of heavy metals from soil or sludge by nanoscale zero-valent iron, the removal of heavy metals (zinc, lead, cobalt, nickel, copper) in pure water was studied. The volume of the aqueous solution is 100-1000mL, the concentration of heavy metals in the aqueous solution is 10-150mg / L, and the dosage of nZVI is 0.1-25g / L. Prepare aqueous solutions containing different concentrations of heavy metals, add different amounts of nZVI, mix thoroughly for 1-10 hours, and then introduce the reaction separation zone. In the reaction separation zone, water, nZVI and the electromagnet are in full contact, and the nZVI adsorbed with heavy metals is absorbed by the electromagnet. After separation, the separated water is directly subjected to ICP test after routine digestion, and the removal rate of heavy metals in water is calculated according to the concentration change of heavy metals in water before and after adding nZVI. The removal rate of 5 kinds of metal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com