Patents
Literature
183results about How to "Shorten the leaching time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for extracting high-valence manganese from manganese carbonate ore
This invention has provided one kind of method to leach high price manganese from manganese carbonateore, which belongs to the hydrometallurgy domain. It takes the glucose or the plant biomass and sulfuric acid as reducing agent of high pricemanganese in manganese carbonate ore, adopting microwave radiation glucose to promote high price manganese to revert, the concrete step includes: Takes 1 copy 100-200 sieve manganese carbonateore, add 10 -20 copy water to modulate the pulp; Again add 60% density sulfuric acid to pulp, the load ratio of mineral powder and sulfuric acid is 1: 6 -9; Simultaneously, add glucose or plant biomass, the load ratio of mineral powder and glucose or plant biomass is 10 -15: 1, stir evenly; radiate under 500 -1000W microwave, stir and respond for 4-10min, leach temperature is controlled at 50degree C-60 degree C, then get lixivium by filtering. This invention has the merits of lower reaction temperature, reducing acid consume and reduce leaching time of the manganese ore, high thermal using and respond rapidly.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites
InactiveCN101560485APromote leachingReduce inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFerroplasma thermophilum
The invention discloses a moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites, comprising five mineral leaching microorganisms: acidithiobacillus caldus S2, leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, sulfobacillus acidophilus ZW-1, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans YN22 and ferroplasma thermophilum L1; the pH value and the temperature which are most suitable for the growth of the enriched substance are respectively 1.4-2.0 and 45-48 DEG C. Compared with the existing microorganisms used for brass bio-heap leaching, the enriched substance not only improves the leaching reaction kinetics and shortens the leaching period, but also reduces the passivation inhibition phenomenon and increases the bioleaching speed and the leaching rate of the copper pyrites; furthermore, the enriched substance can endure high concentration metallic ion at the late stage of bioleaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for recovering copper and cadmium from copper and cadmium slag and device for recovering cadmium from zinc sulfate solution rich in cadmium
ActiveCN103556180APromote leachingImprove leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention discloses a method for recovering copper and cadmium from copper and cadmium slag and a device for recovering cadmium from a zinc sulfate solution rich in cadmium. The method comprises the following steps of firstly mixing copper and cadmium slag with a gas carrier substance uniformly; then using a sulfuric acid solution to carry out acid leaching on the copper and cadmium slag under certain conditions to leach all copper, cadmium and zinc in the copper and cadmium slag into the solution; then adopting zinc powder as a reducing agent to preferably reduce copper ions in the acid leachate into elemental copper to be precipitated under certain conditions, and adopting the device for recovering cadmium from a zinc sulfate solution rich in cadmium to selectively extract cadmium from the obtained zinc sulfate solution rich in cadmium, thus obtaining a high-grade sponge cadmium and zinc sulfate solution, wherein sponge cadmium can be directly subjected to casting-electrorefining or rectifying to obtain high-purity cadmium, and the zinc sulfate solution can be directly returned to an electrolytic zinc system to produce electrolytic zinc.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for leaching manganese sulfate from low grade pyrolusite
InactiveCN102358917ATo achieve the purpose of leachingPromote redox processElectrolysis componentsPyrolusiteSlurry
The invention provides a method for leaching manganese sulfate from low grade pyrolusite. The method comprises the steps of crushing low grade pyrolusite and pyrite, placing crushed pyrolusite and pyrite in a leaching tank and mixing crushed pyrolusite and pyrite with sulfuric acid to prepare ore slurry. According to the invention, the mass percentage of manganese in pyrolusite is 9% to 21%, the mass ratio of pyrolusite to pyrite is 5-3:1, the molar concentration of sulfuric acid is 1 to 1.2 mol / L, and the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to pyrolusite and pyrite is 6-8:1; electrocatalytic reinforcement is carried out on the ore slurry so as to accelerate a reduction reaction. The method for leaching manganese sulfate from poor pyrolusite provided in the invention has the advantages of low cost, easy operation, short time, a high leaching rate of manganese, etc.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
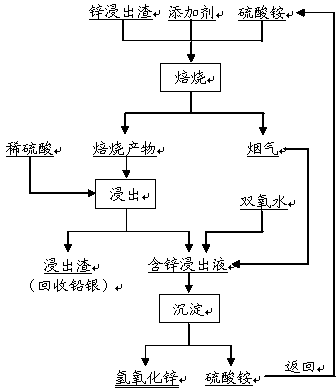
Method for separating zinc and iron from zinc leaching residues
InactiveCN104178642AAchieve regenerationIncrease incidenceProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideSulfate zinc
The invention discloses a method for separating zinc and iron from zinc leaching residues. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing the zinc leaching residues with ammonium sulfate and an additive, then performing roasting to ensure that zinc ferrite and the like in the zinc leaching residues are changed into soluble zinc sulfate and insoluble ferric oxide; secondly, directly leaching out a roasted product by using a dilute sulfuric acid solution; and finally, introducing fume which is produced during roasting and mainly contains ammonia gas into a zinc leaching solution to perform deposition so as to produce zinc hydroxide and an ammonium sulfate solution, and concentrating and crystallizing the ammonium sulfate solution to prepare ammonium sulfate which is returned to the ammonium sulfate roasting process. The ammonium sulfate roasting process in the method can ensure that a zinc ferrite phase in the zinc leaching residues is changed into soluble zinc sulfate, the leaching rate of zinc is more than 97%, and the leaching rate of iron is lower than 2%, so that the separation of zinc and iron is effectively realized; the ammonia gas produced in the ammonium sulfate roasting process is directly used for depositing zinc from the leaching solution, and the regeneration of ammonium sulfate can be realized while a zinc hydroxide product is generated; the comprehensive recovery rate of zinc is more than 96%; the method can realize closed-loop circulation and is relatively environment-friendly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Industrial microwave ultrasonic reactor
InactiveUS20150144480A1Limited rangeReduce uniformityMechanical vibrations separationChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsMicrowaveEngineering
An industrial microwave ultrasonic reactor has an inner wall liner. A microwave generation device is formed by microwave units distributed on an outer sidewall, or by a microwave pipe disposed outside the reactor and microwave units distributed on the microwave pipe. One end of the microwave pipe communicates with the bottom of the reactor via a connection pipe I, and the other end communicates with the top via a return pipe. A shield is disposed outside the microwave generation device to separate the microwave units from the outside, and a heat removal device is disposed outside the shield. An ultrasonic wave generation device is formed by 10 to 30 sets of ultrasonic pulse units disposed at intervals along the outer sidewall. Each set has 10 to 50 members distributed along the circumferential direction of the reactor. A stirring shaft is fixed below a stirring motor and extends into the reactor.
Owner:SONGXIAN EXPLOITER MOLYBDENUM
Method for recovering rare earth in neodymium-iron-boron waste by high-temperature and high-pressure leaching
The invention relates to a method for recovering rare earth in neodymium-iron-boron waste by high-temperature and high-pressure leaching. The neodymium-iron-boron waste is subjected to oxidation roasting, hydrochloric acid high-temperature and high-pressure leaching, and oxidation and impurity removal purification on Fe2+ in a leachate so as to obtain a rare-earth chloride leachate; and the rare-earth chloride leachate can be used as a subsequent process and a product raw material, rare earth is obtained through extraction and separation, rare earth carbonate is prepared through precipitation,or rare earth oxide is prepared through precipitation-roasting. According to the method, a closed high-pressure reaction kettle is adopted as leaching equipment, so that the dynamic condition of theleaching process is excellent, the requirement for the particle size of the leached raw materials is low, a large amount of dust generated by the fine grinding process of the raw materials is avoided,the leaching rate of rare earth in the leaching process is high, the utilization rate of hydrochloric acid is high, no acid gas is discharged, energy is saved, and the environment is protected; and in addition, the method has the advantages of being short in process flow, simple in process conditions and low in recovery cost, and the method has considerable economic, social and environmental protection benefits for large-scale recovery of the neodymium-iron-boron waste.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for acid leaching extraction of vanadium from vanadium-containing raw material
InactiveCN101509070AAvoid problems with going into solutionShorten the leaching timeWastewaterIon exchange
The invention relates to a method for extracting vanadium(V) from vanadium-containing materials, in particular to a method for acid-leaching vanadium from the vanadium-containing materials. The method comprises the following steps: a. adding water to the vanadium-containing materials and evenly stirring; gradually adding sulfuric acid with the mass fraction being 20% to 60% to adjust the pH value of the acid-leaching reaction system to 2.5 to 3.3; and filtering to obtain residue and acid-leaching solution upon completion of acid-leaching; and b. leaching vanadium from the acid-leaching solution obtained in Step a with SO4 type anion exchange resin by ion-exchange. The method can effectively prevent ions, such as Fe, Mg, Al, Mn, P, Cr and the like, in the vanadium-containing materials from entering the acid-leaching solution during acid-leaching process and greatly reduce the pressure on the subsequent purification of the acid-leaching solution; and the ion-exchange raffinate can be recycled in the acid-leaching step, thereby increasing the overall recovery rate of vanadium and avoiding problems in environmental pollution caused by discharging a large quantity of vanadium-leaching waste water.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +3
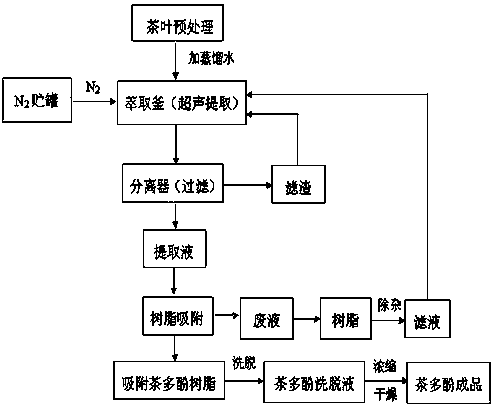
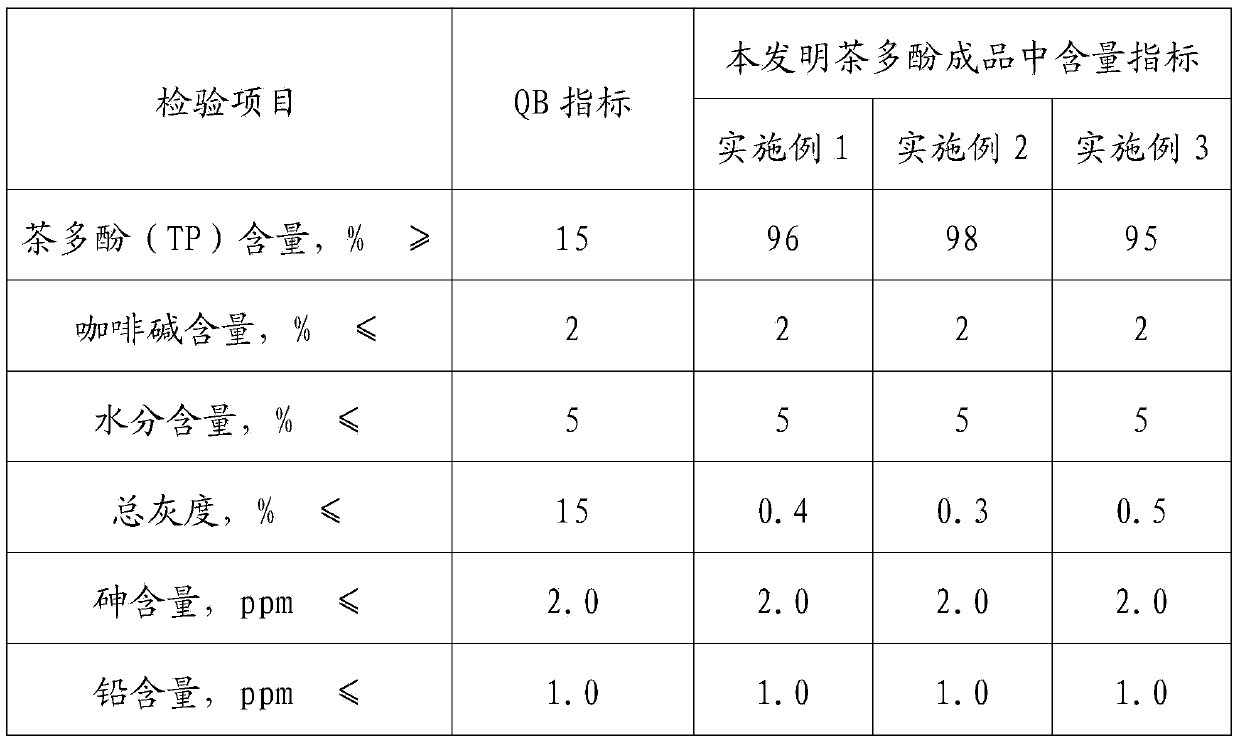
Preparation process for extracting green tea polyphenols from tea
InactiveCN103992359AIncrease the speed of diffusionHigh extraction rateOrganic chemistryGreen Tea PolyphenolsPhenolic content in tea
Belonging to the field of green tea polyphenol extraction processes, the invention discloses a preparation process for extracting green tea polyphenols from tea. The preparation process includes the following six steps: pretreatment of tea, nitrogen protection, ultrasonic extraction, separation and filtration, resin adsorption, concentration and drying. The process provided by the invention solves the problems of serious destruction of effective components, low product yield and purity, high production cost and pollution in existing green tea polyphenol extraction. The preparation method disclosed in the invention not only has the advantages of high recovery rate, time saving, high extraction rate and the like, but also avoids the use of toxic solvents, and is conducive to reducing energy consumption and lowering the production cost, thus having good industrial promotion value.
Owner:梁树钦
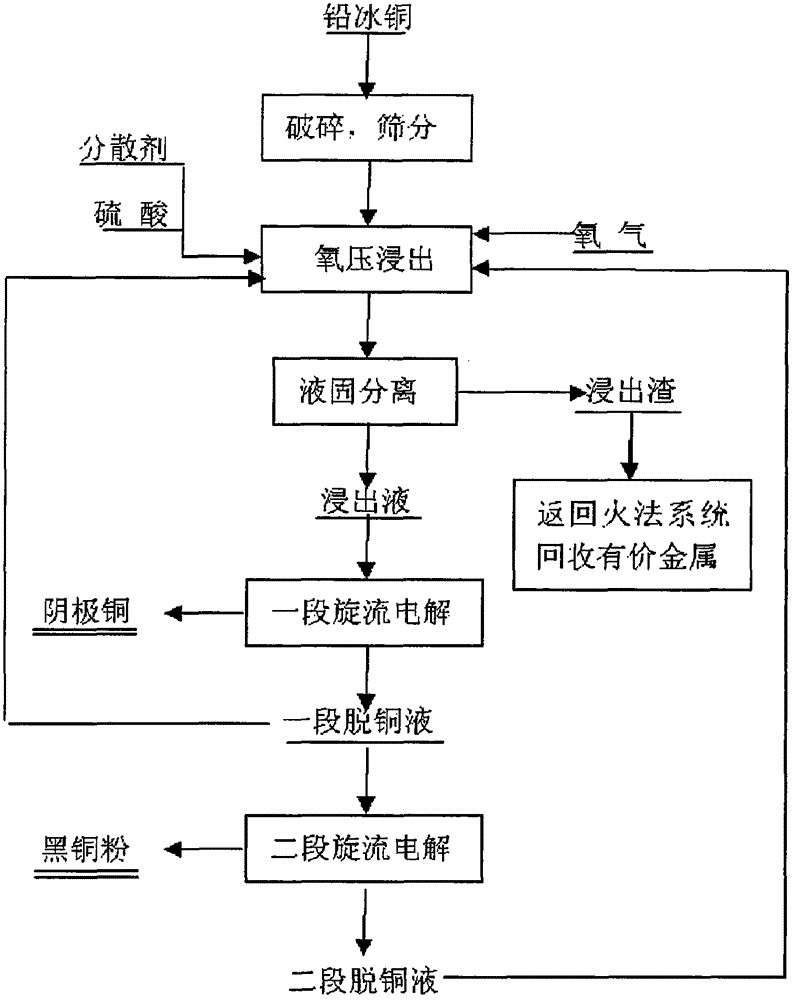
Process of efficiently recovering copper from lead matte according to oxygen pressure acid leaching and vortex electrolysis techniques
InactiveCN104831064AAdaptableImprove leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of nonferrous metal hydrometallurgy and discloses a process of efficiently recovering copper from lead matte according to oxygen pressure acid leaching and vortex electrolysis techniques. The method includes: taking lead matte as a raw material, crushing and grinding the lead matte, screening through a 100-mesh sieve, adding into a high-pressure autoclave along with sulfuric acid and a dispersing agent, feeding oxygen for leaching, carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain solution containing copper sulfate, subjecting the solution containing copper sulfate to vortex electrolytic decopperation to obtain cathode copper, and returning after-electrodeposition liquid to the leaching procedure to replace sulfuric acid serving as the leaching agent. High efficiency in copper recycling can be realized, electrodeposition of copper can be selectively carried out according to the vortex electrolysis techniques, and high current level and current efficiency, low reagent consumption, reduction of production cost and improvement of enterprise benefits are realized. In addition, due to closed cycle of solution, harmful gas emission is avoided, and current concepts of circular economy and environment protection are met.
Owner:XIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for strongly leaching laterite-nickel ore at normal pressure by using sulphuric acid
InactiveCN103146919AImprove leaching rateHighly corrosiveProcess efficiency improvementThermal insulationEmission standard
The invention relates to a method for strongly leaching laterite-nickel ore at normal pressure by using sulphuric acid, which comprises the following steps of: adding laterite-nickel ore into leacheate, mixing and ball-milling to be less than or equal to 100 mesh, adding concentrated sulphuric acid according to the liquid-solid ratio of (4-9):1, increasing the temperature to 150-160 DEG C, maintaining reaction for 20-60 minutes, decreasing the temperature to 80-100 DEG C, filter pressing, and pressing filtrate in a thermal insulation storage tank; adding leacheate, the volume of which is the same to that of a filter cake, to carry out pressure washing and filter pressing, obtaining filtrate and the filter cake again, also pressing the filtrate in the thermal insulation storage tank, discharging the filter cake, mixing and washing by using hot water so that crystal substances are thoroughly dissolved, and filtering to obtain the filtrate and the filter cake; and purifying the filtrate and removing impurities from the filtrate, continuously carrying out pressure washing by using clean water through the filter cake in a counter-current manner, and continuously detecting the pH value of pressure washing liquid until leached residues achieve emission standard. According to the invention, the leaching efficiency of nickel-cobalt can be increased by above 99wt%; most of all metallic elements which can be dissolved by sulphuric acid can be leached; silica gel does not exist in the leaching process; and the filtering performance of the leached residues is good.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
Method for vanadium leaching by sulfate-adding wet-pile oxidation conversion of stone coal under atmospheric temperature and atmosphere pressure
InactiveCN101082085AReduce energy consumptionShorten the leaching timeProcess efficiency improvementSulfateAtmospheric temperature
The normal temperature and normal pressure process of leaching vanadium from stone coal includes the following steps: 1. grinding stone coal to below 60 mesh; 2. adding 70-98 wt% concentration sulfuric acid solution in the material / acid weight ratio of 100 to 26-35 via stirring; 3. piling the mixture in the height greater than 0.5 m at normal temperature and normal pressure for 4-15 days; 4. exothermic reaction inside the pile to complete the oxidation of vanadium inside stone coal with oxygen in the air at temperature over 85 deg.c; and 5. adding water in 1-3 times the solid at normal temperature and normal pressure, and stirring for 3-8 hr to leach out vanadium in 65-97.7 %. The process of leaching out vanadium from stone coal is wide applicable for original stone coal ore and oxidized stone coal ore.
Owner:刘健 +1
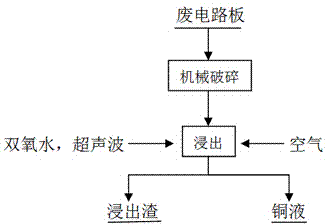
Method for recovering copper from waste circuit board
InactiveCN104745824ALow impurity contentReduce recycling costsProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method for recovering copper from a waste circuit board and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly crushing the waste circuit board into powder, fully mixing the powder, an ammonia water solution, an ammonium chloride solution and water to obtain ore pulp, introducing air into the ore pulp, and carrying out ultrasonic wave intensified leaching under a stirring condition; and periodically adding hydrogen peroxide in the intensified leaching process so as to leach copper from the waste circuit board, wherein the leaching rate of copper from the waste circuit board leached in 1 hour reaches over 98%. The method disclosed by the invention realizes resource utilization of effective components of the waste circuit board and moreover, the method has the advantages of being environment-friendly, mild in reaction and short in technological process, the production cost can be lowered and the metal copper recovery rate is high, and the method is suitable for recovering valuable metals in the waste circuit board.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intensified uranium ore heap leaching method
ActiveCN101560613AShorten the leaching timeDowngradeProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionUranium ore
The invention provides an intensified uranium ore heap leaching method, which comprises the following steps: (1) uranium ores are crushed firstly and then transported to a heap leaching field for heaping; (2) a leaching agent is sprayed on stock heap for leaching; (3) leachate obtained from step (2) is absorbed or extracted. Saturated resin containing metallic uranium or saturated organic phase goes through a post treatment process, and absorption tailing solution or raffinate water phase is added with acid and then returned for being used as a leaching agent for the next heap; when the leaching agent is sprayed in step (2), the leaching agent spraying is called off if the leaching ratio of the metallic uranium reaches 70 percent to 80 percent. After prospective tailings are dried and heaped for a plurality of days, a curing agent with a weight of 0.08 to 0.12 time of that of the prospective tailings is used for curing and the prospective tailings are cured for a plurality of days and then leached in a sprayed manner. The leachate obtained from sprayed leaching can return and be used as the leaching agent for the next heap. After the neutralization, the tailings are discharged into a tailing tank. The uranium ores are heap leached by the method so that the grade of the tailings can be reduced and leaching time can be shortened.
Owner:中核赣州金瑞铀业有限公司
Method for preparing puddling iron concentrate by high-alumina iron ore
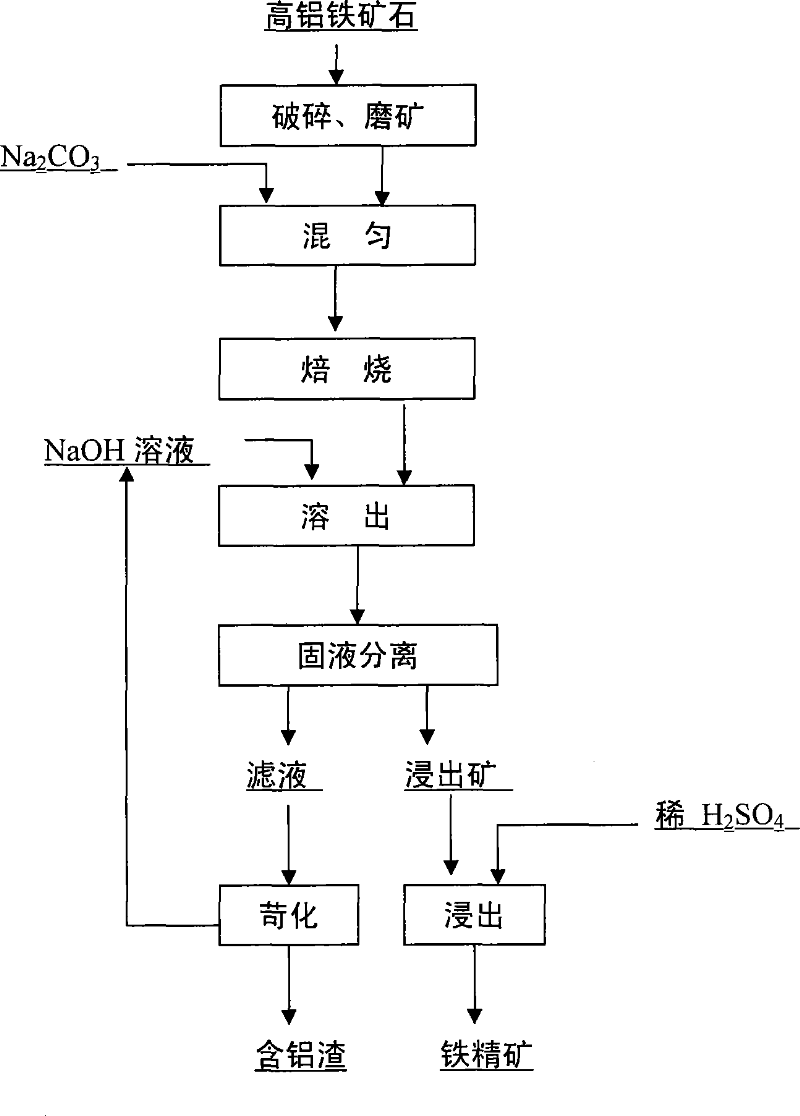
ActiveCN101037722ATo achieve the effect of dealuminationReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementGranularityLower grade
The invention disclosed a method for manufacturing the iron ore concentrate for ironmaking by the high aluminium iron ore, wherein after iron ore is broken to the granularity of less than 1.0mm which is in 40%-60%, it is mixed with Na2CO3 based on the proportion of 10-40 weight percent, and is braked for 10-30 minutes at the temperature of 900-1050 DEG C, then placed in the reactor to be extracted by 100-150 g / l solution at the temperature of 80-150 DEG C based on the liquid-solid quality rate of 3 / 1 -6 / 1 for 5-30 minutes, the filtrate can be extracted by the dilute sulphuric acid of 1.0-15 mass concentration percent at the temperature of 80-120 DEG C after solid-liquid separation for 10-30 minutes, and the solid is the iron ore concentrate after solid-liquid separation. The content of Al2O3 and Na2O in ore concentrate satisfies the requirement of blast furnace ironmaking materials using the invention. The invention can sufficiently and reasonably use existing rich high aluminium low-grade iron ore with good dealuminzation and low cost for reusing the extractive alkali liquor. The invention is suitable for the dealuminzation of each aluminiferous iron ore, in particular, high aluminium iron ore for reducing the close symbiosis and interdigitating of aluminium-containing minerals and iron-containing minerals, the manufactured iron ore concentrate can be used as the blast furnace ironmaking materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Wet-process comprehensive recovery and utilization method for zinc replacement residues
InactiveCN106834693AImprove leaching rateEnhanced leaching processProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteCopper
The invention discloses a wet-process comprehensive recovery and utilization method for zinc replacement residues. The wet-process comprehensive recovery and utilization method can efficiently recover zinc, germanium, gallium, copper, iron and silicon dioxide in the zinc replacement residues, and the leaching rates of all the metals are all higher than 94%. The wet-process comprehensive recovery and utilization method is conductive to improving the metal comprehensive recovery rate, meanwhile, the energy consumption in the whole technological process is reduced, generated waste liquid is returned for leaching to achieve the purpose of cyclic utilization, the problem of environmental pollution is solved, and the wet-process comprehensive recovery and utilization method is environment-friendly.
Owner:GUIZHOU HONGDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Bagged Chinese medicine pieces prepared for decoction and its preparation method
InactiveCN1443553AThe dissolution rate of active ingredients is improvedShorten the leaching timePharmaceutical delivery mechanismUnknown materialsMedicinal herbsFilter paper
The present invention provides a Chinese herbal medicine pieces bag and its preparation method. Its preparation method includes the following steps: preparing every Chinese herbal medicine by adopting traditional preparation process; drying moistening, pulverizing to obtain medicinal coarse pieces, coarse granules or coarse powder whose grain size is 0.5-10mm; then intermittent drying the pulverized medicinal materials at 37-110 deg.C to make water content of medicinal material be less than or equal to 8%; and using filter paper and steril-packaging so as to obtain the invented finished product.
Owner:李小海
Process for making constrained filament niobium-based superconductor composite
InactiveUS6543123B1Reduce distanceShorten the leaching timeHot-dipping/immersion processesReservationsPorous layerNiobium
A niobium-based superconductor is manufactured by establishing multiple niobium components in a billet of a ductile metal, working the composite billet through a series of reduction steps to form the niobium components into elongated elements, each niobium element having a thickness on the order of 1 to 25 microns, surrounding the billet prior to the last reduction step with a porous confining layer of an acid resistant metal, immersing the confined billet in an acid to remove the ductile metal from between the niobium elements while the niobium elements remain confined by said porous layer, exposing the confined mass of niobium elements to a material capable of reacting with Nb to form a superconductor.
Owner:COMPOSITE MATERIALS TECH
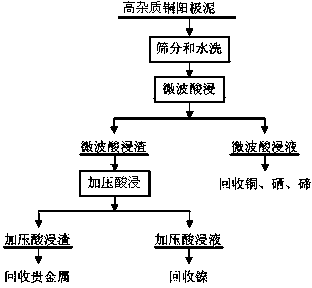
Method for pre-treating high-impurity copper anode slime rich in noble metals
ActiveCN103509953ASimple purification processHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSeleniumCopper
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy of non-ferrous metals, and particularly relates to a method for pre-treating high-impurity copper anode slime rich in noble metals. The method comprises the following special steps: adding sulfuric acid in the dried copper anode slime to mix size, placing in a microwave reactor, carrying out the microwave acid leaching for 5-30 min, performing the solid-liquid separation to obtain microwave acid leaching slag and a microwave acid leaching solution, adding dilute sulphuric acid in the microwave acid leaching slag to mix size, placing the microwave acid leaching sizing agent in a high-pressure reaction kettle under the pressure of 0.8-1.2 MPa after oxygen introducing, carrying out pressure acid leaching for 4-6 h to obtain pressure acid leaching slag and a pressure acid leaching solution, recovering gold and silver from the pressure acid leaching slag, and recovering nickel from the pressure acid leaching solution. The method adopting the technical scheme improves the recovery rate of copper, selenium, tellurium and nickel in the impurity copper anode slime, shortens the processing time of the copper anode slime, increases the processing capacity of the copper anode slime, enables the trend of the noble metals to be reasonable and concentrated, and is favorable for comprehensive recovery.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
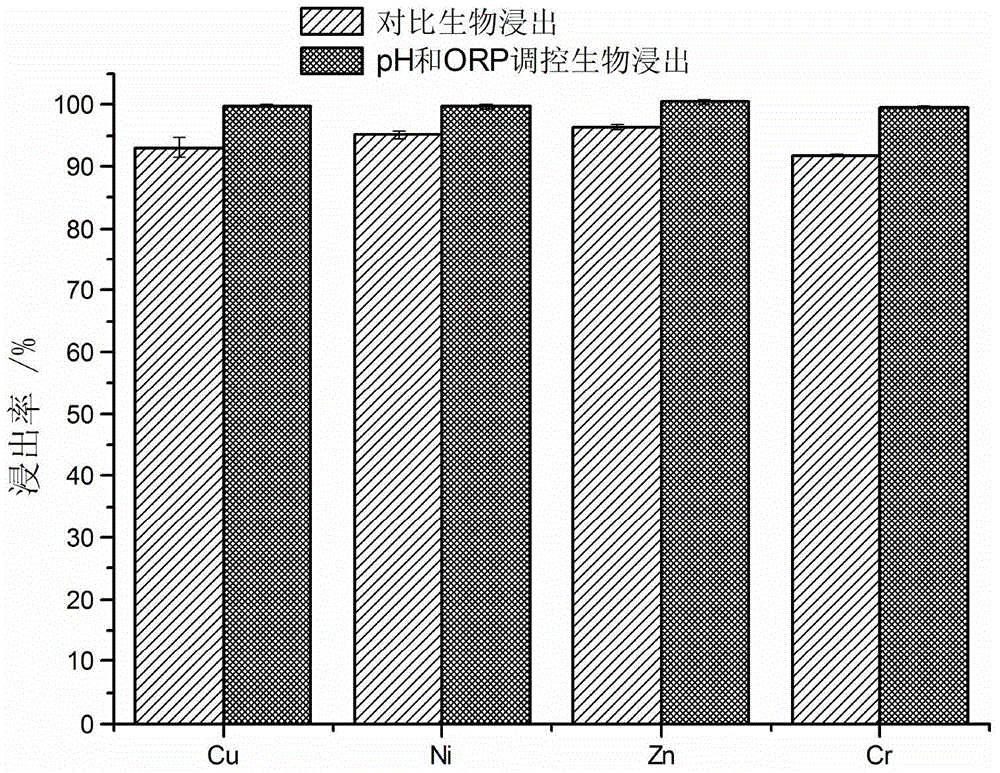
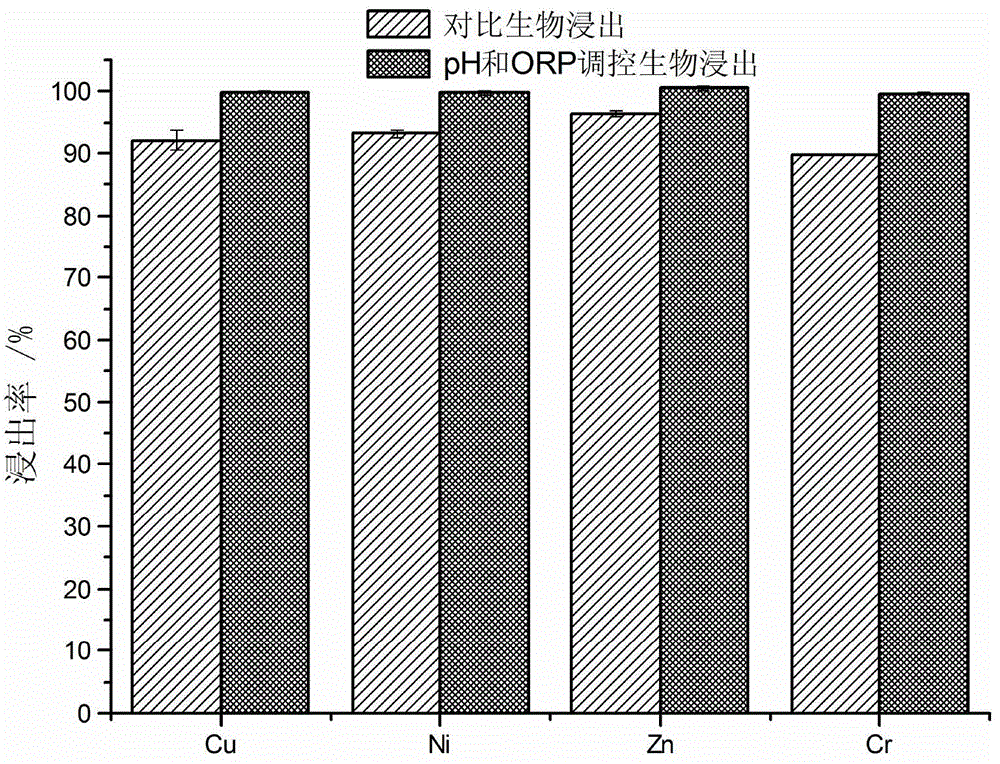
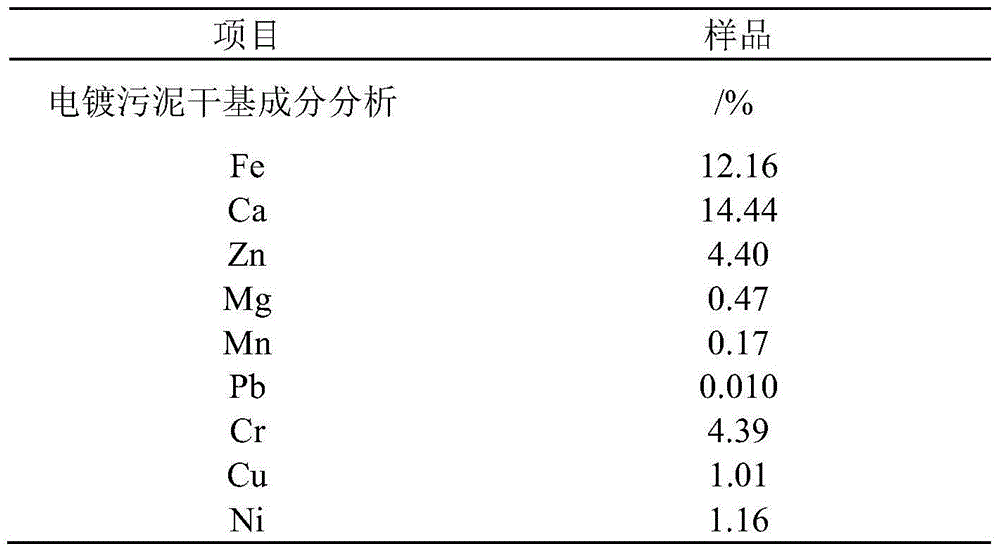
Method for biologically leaching heavy metal from heavy metal-contained waste based on pH and potential co-regulation
ActiveCN104862474AAvoid interactionEfficient DissolutionProcess efficiency improvementCo-regulationSludge
The invention discloses a method for biologically leaching heavy metal from a heavy metal-contained waste based on pH and potential co-regulation. The method comprises the following steps: in a process of leaching out the heavy metal-contained waste by an acidophilic iron oxide microbial agent, the pH value of the leaching system is controlled within 1.0-4.0 in the whole process; meanwhile, an oxidizing agent is combined with a reducing agent to regulate the redox potential of the leaching system, so that the redox potential of the leaching system is controlled within 420-650 mV; the pH value of the leaching system is gradually increased phase by phase in the leaching process; the redox potential of the leaching system is gradually increased phase by phase; the total leaching time is within 8 hours; and finally, the efficient leaching of the heavy metal from the heavy metal-contained waste by the acidophilic iron oxide microbial agent is realized. The method can accelerate biologic leaching of metal from sludge to shorten the leaching time and to reduce the acid consumption, and can greatly improve the biologic leaching efficiency.
Owner:厦门资生环保科技有限公司
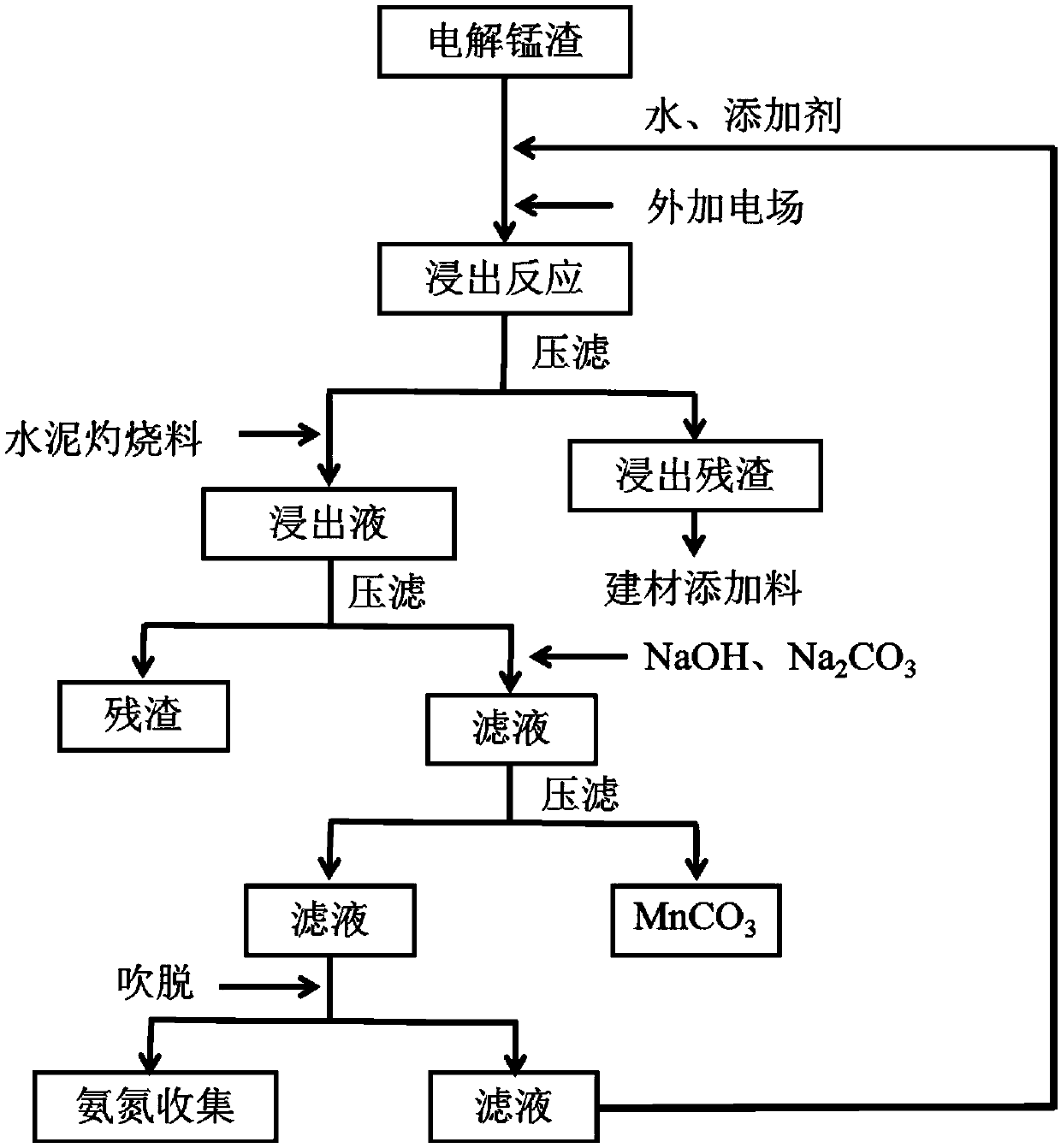
Electrolytic manganese residue harmless treatment and resource utilization method
ActiveCN109554546AReduce heavy metalsReduce ammonia nitrogen contentProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention discloses an electrolytic manganese residue harmless treatment and resource utilization method. The electrolytic manganese residue harmless treatment and resource utilization method comprises the steps that firstly, a calcium oxide additive and a calcium carbonate additive are added into leaching liquid, and impurities such as iron, magnesium and calcium in the leaching liquid are effectively removed; secondly, the pH value of the leaching liquid is regulated through sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate is added to react, and thus a manganese carbonate product is obtained; and finally, by adding calcium oxide, high-concentration ammonia nitrogen in filtrate is removed in an air stripping mode, escaping gas is absorbed through clear water, and the filtrate is reused. According to the electrolytic manganese residue harmless treatment and resource utilization method, the contents of heavy metal and the ammonia nitrogen in electrolytic manganese residues are effectively decreased, the manganese and ammonia nitrogen leaching time is shortened, and the leaching rates of manganese and the ammonia nitrogen in the electrolytic manganese residues are increased; and manganese in the leaching liquid is mainly recycled as manganese carbonate, a product can be directly used as electrolytic manganese residue raw materials, and in addition, the leaching liquid after a stripping reaction can be recycled.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Leaching method of positive electrode active material of waste lithium ion battery
ActiveCN106834703AImprove gas/solid reaction efficiencyShorten the leaching timeWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementReaction rateElectrical battery
The invention discloses a leaching method of a positive electrode active material of a waste lithium ion battery, which comprises the steps of performing short-circuit discharging, disassembling, binder stripping, crushing and screening on the waste lithium ion battery to obtain electrode material powder; roasting the electrode material powder under a sulfur dioxide carrier gas atmosphere to obtain a roasted product, wherein the sulfur dioxide carrier gas flow is 30 to 50L / h, and the roasting temperature is 300 to 450 DEG C; dispersing the roasted product into water, stirring and filtering to obtain an aqueous solution of the positive electrode active material. The leaching method has the characteristics that the reaction rate and efficiency are greatly improved, the environmental friendliness and pollution-free are realized, the process is simple, and the commerce practical application cost is greatly reduced at the same time; the leaching method is capable of realizing large-scale production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
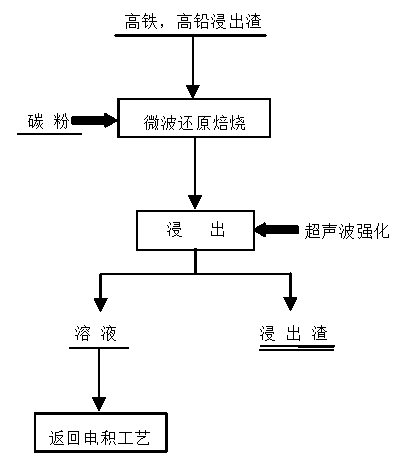
Method for recovering zinc from high iron and high lead leaching residue through microwave-ultrasonic wave combination
ActiveCN103352116APenetratingWith selective heatingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionMicrowave
The invention provides a method for recovering zinc from high iron and high lead leaching residue through microwave-ultrasonic wave combination, and belongs to the technical field of microwave and ultrasonic wave applications. The method comprises: taking high iron and high lead leaching residue, adding carbon powder, uniformly mixing, carrying out microwave heating to a temperature of 550-950 DEG C, carrying out constant temperature maintaining for 1-3 h, stopping heating, introducing a N2 protection atmosphere, cooling to a temperature of less than 100 DEG C to obtain after-reduction leaching residue, adding the after-reduction leaching residue to an acid liquid, carrying out ultrasonic wave radiation on the mixed solution at a temperature of 45-85 DEG C to carry out enhancement leaching, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a leaching solution, carrying out subsequent purification on the leaching solution, and recovering metal zinc through electrowinning. Compared to the conventional hot acid leaching, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics that: a leaching time is significantly shortened, a leaching acidity and a leaching temperature are reduced, and 90-98% of zinc can be recovered. With the present invention, the difficult problem of low recovery rate of the high lead and high iron system is overcome, the process is simple, the treatment effect is good, zinc and other valuable metals can be efficiently recovered, and problems of environmental pollution and resource waste caused by stockpiling of a lot of abandoned residue are solved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing molybdenum disulfide from molybdenite
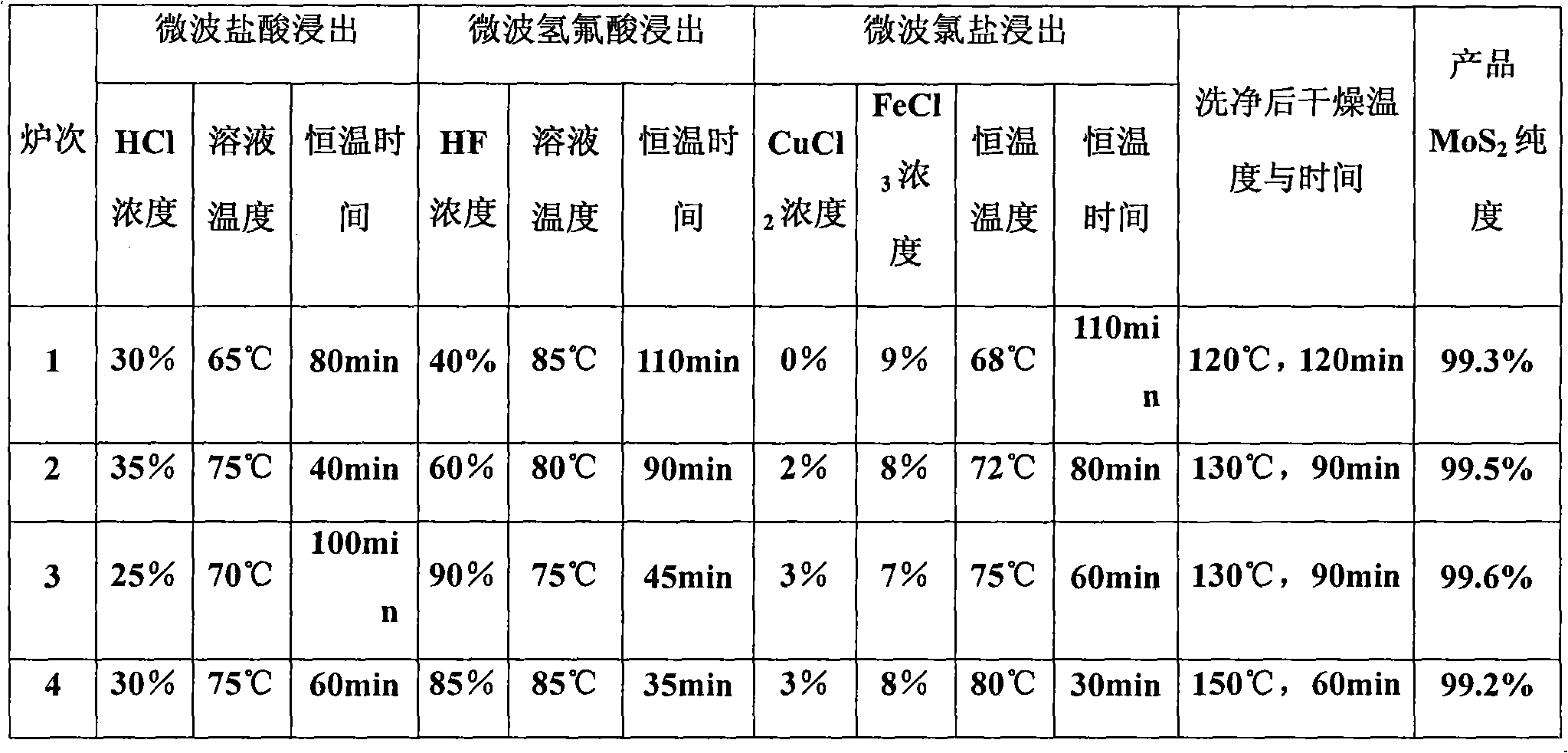
InactiveCN101898795AImprove leaching efficiencyHigh purityMolybdenum sulfidesHydrofluoric acidChloride
The invention provides a method for preparing molybdenum disulfide from molybdenite. The polybdenum disulfide is prepared by microwave assisted multi-stage leaching, and the molybdenum disulfide with the purity of over 99.2 percent, excellent quality and stable performance can be obtained. By adopting the polybdenite by using microwave assisted leaching, the method for preparing the molybdenum disulfide from the molybdenite comprises the following four steps of: 1, hydrochloric acid leaching by using microwaves; 2, hydrofluoric acid leaching by using microwaves; 3, chloride leaching by using microwaves; and 4, cleaning the powder with deionized water, drying the powder to obtain the polybdenum disulfide powder with the purity of over 99.2 percent. The method has the advantages of simple method and convenient operation, improvement on the working efficiency, and simultaneously improvement on the product quality and market competitive power.
Owner:洛阳开拓者投资管理有限公司
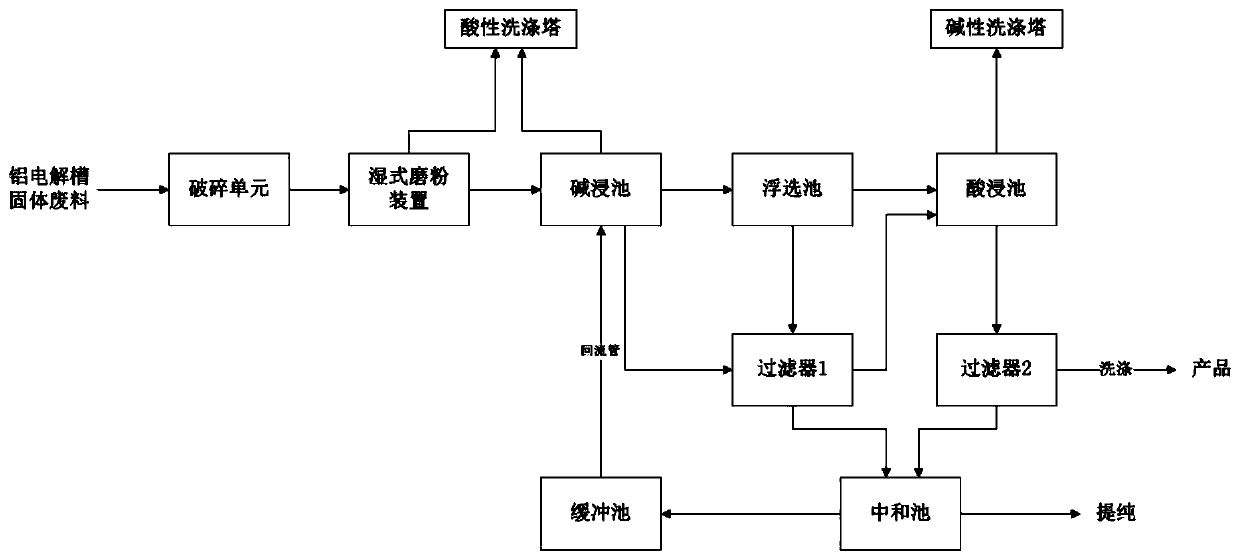
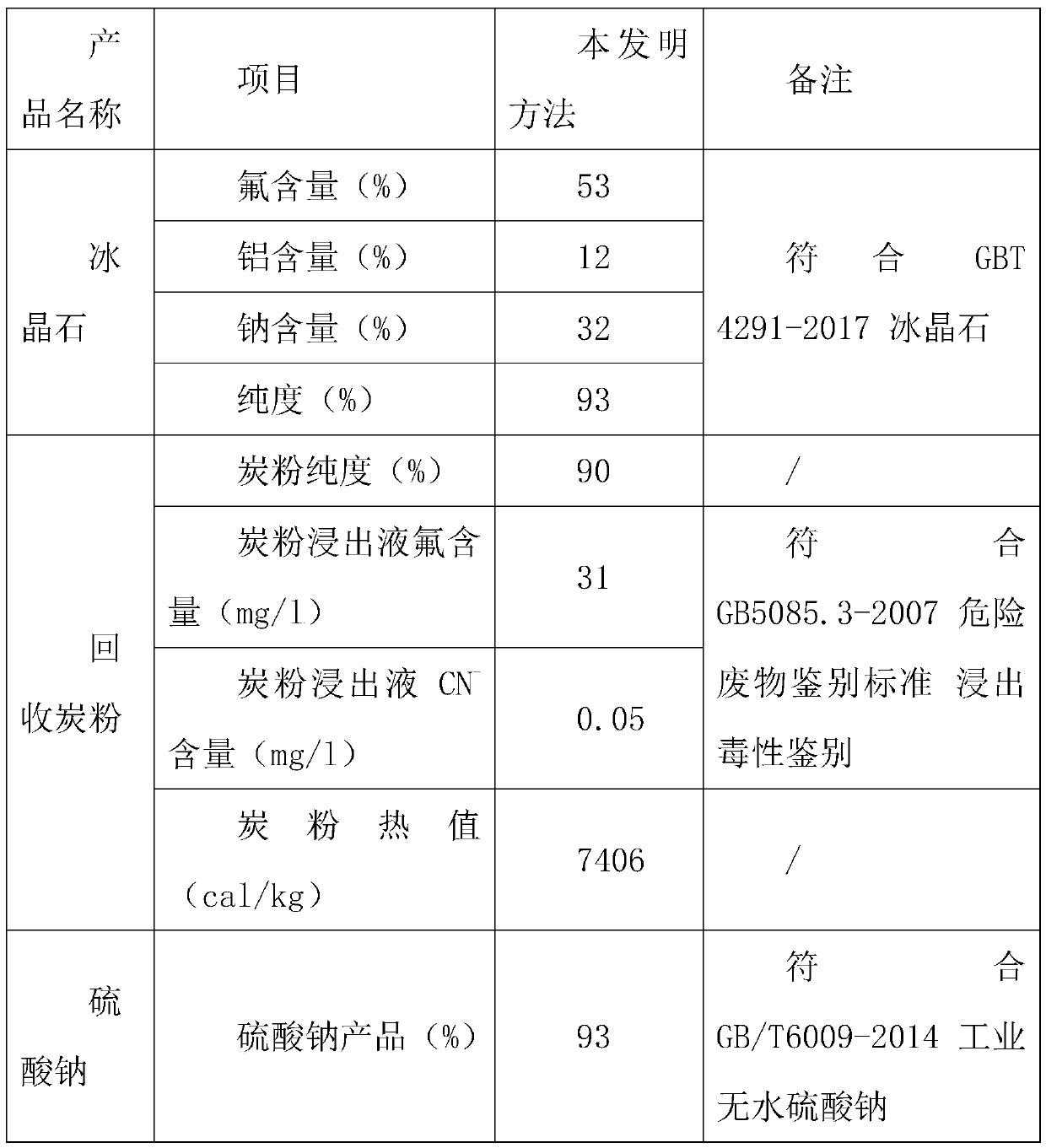
Solid waste recycling treatment system and method for aluminum electrolysis cell
InactiveCN109719118AImprove processing efficiencyAchieving processing powerSolid waste disposalAluminium electrolysisSodium sulfate
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrolytic aluminum solid waste resource treatment, and particularly discloses a solid waste recycling treatment system and method for an aluminum electrolysis cell. The system comprises a crushing unit, a wet grinding device, an alkaline leaching tank, a flotation tank, a filter 1, an acid leaching tank, a filter 2, a neutralizing tank, a buffer tank and an exhaust gas treatment system. The invention further provides a method for treating the solid waste of the aluminum electrolysis cell by utilizing the treatment system, which comprises the following steps of crushing, wet grinding, alkaline leaching, floatation, acid leaching, neutralization, purification. According to the system and method, the aluminum electrolysis cell waste tank liner, the waste cathode carbon block and the anode carbon slag can be efficiently treated and finally obtain a carbon powder with high purity, a cryolite, a regenerated silica sand and a sodium sulfate products, the cyanide and the waste gas are subjected to harmless treatment in the treatment process, no waste water is discharged, and the harmless resource reutilization of the solid waste of the aluminum electrolysis cell is really realized.
Owner:ASIA PACIFIC ENVIRONMENTAL CORP
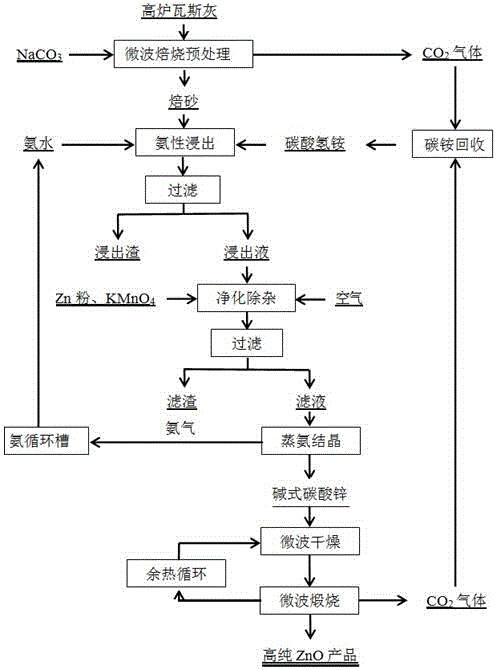
Method for preparing ZnO from blast furnace gas ash through microwave roasting pretreatment and ammonia leaching
ActiveCN105543490AImprove leaching rateShorten the leaching timeProcess efficiency improvementSlagDistillation
The invention relates to a method for preparing ZnO from blast furnace gas ash through microwave roasting pretreatment and ammonia leaching, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the steps that 1, microwave roasting pretreatment is conducted, specifically, Na2CO3 with the blast furnace gas ash mass being 5-20% is added into the blast furnace gas ash to be uniformly mixed, a mixed material is obtained, microwave roasting is conducted on the mixed material for 0.5-2 h at the temperature of 200 DEG C-600 DEG C, and a roasted product is obtained; 2, mixing and leaching are conducted on the roasted product through ammonia water with the total ammonia concentration being 3-6 mol / L and a NH4HCO3 solution for 0.5-1.0 h at the temperature of 25 DEG C-45 DEG C, then solid-liquid separating is conducted, washing treatment is conducted on solid slag through a 5% ammonia water solution for many times, and leaching liquid and leaching residues are obtained; and 3, the ZnO is prepared after purifying and impurity removing, ammonia distillation and crystallization and microwave calcining are conducted. According to the method for preparing the ZnO from the blast furnace gas ash through microwave roasting pretreatment and ammonia leaching, ferrous metallurgy smoke dust containing zinc can be cleanly and efficiently utilized, the recovery utilization rate of secondary resources is increased, and meanwhile a high-quality ZnO product is prepared with low energy consumption.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
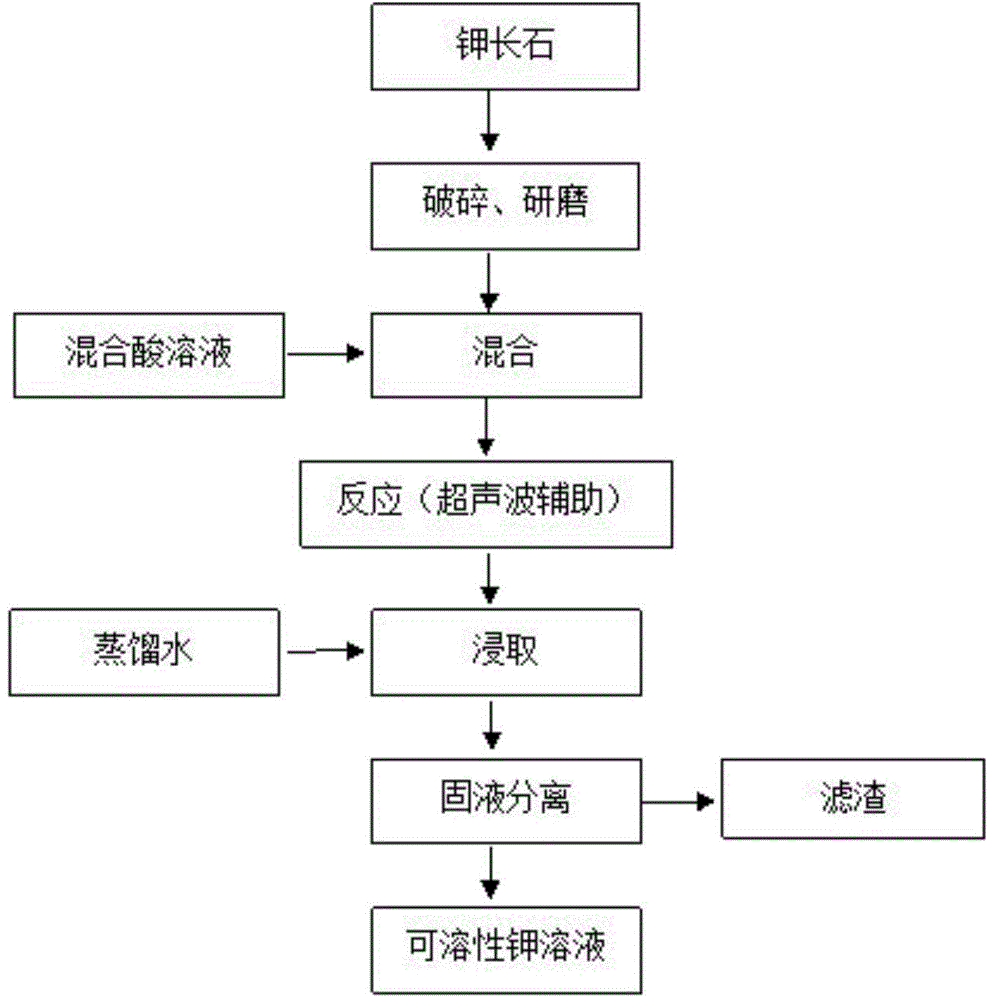
Ultrasonic-assisted method for leaching potassium at low temperature under normal pressure
ActiveCN104878197AExtraction is economical, environmentally friendly and efficientEfficient extractionProcess efficiency improvementAcid dissolutionReaction temperature
The invention relates to an ultrasonic-assisted method for leaching potassium at low temperature under normal pressure, which comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding: crushing and grinding potash feldspar ore until the fineness is about 150 meshes: acid-ore mixing: adding 5-15mL of phosphoric acid-organic acid mixed solution to every gram of potash feldspar, and uniformly mixing, wherein the mixing ratio of the phosphoric acid to the organic acid is (1-4):1; leaching reaction: carrying out leaching reaction on the acid-ore mixture under normal pressure at 30-100 DEG C for 10-48 hours under the assistance of ultrasonic; extraction: adding distilled water into the leaching reaction product to the original volume of the acid-ore mixture, and extracting; and carrying out solid-liquid separation to remove the filter residue, thereby obtaining the soluble potassium solution. The method is beneficial to the development of the pore fracture and the formation of the new reaction interface, promotes the action of acid dissolution, has the characteristics of short leaching time, low facility requests and the like, does not need high-temperature calcination, can perform reaction at low temperature under normal pressure, and greatly saves the production cost; and the mixed acid solution can be easily purchased in the market, and is friendly to the reaction environment.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
Method for leaching lead by wet method through copper anode slime silver-extracted sediment
ActiveCN104878210AHigh activityImprove leaching effectProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionMicrowave
The invention belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy, and specifically relates to a method leaching lead by the wet method through copper anode slime silver-extracted sediment. The method is that 100 to 350g / L by concentration of sodium hydroxide solution is added to the silver-extracted sediment to perform size mixing; the weight concentration of the size is controlled to be 10 to 40%; after size mixing, the size is fed into a microwave reaction furnace to perform leaching reaction for 5 to 25 minutes under the normal pressure; then the size is discharged and subjected to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain the lead-containing leaching liquid. With the adoption of the method, lead in the silver-extracted sediment can be efficiently and quickly leached, overcomes the shortages of small leaching rate, long process and heavy environmental pollution in the traditional process can be overcome, and has the advantages of being simple in process, small in cost, quick to leach, environmentally friendly, small in treatment time, and high in comprehensive recovering benefit; the leaching rate of lead is 93 to 98%.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
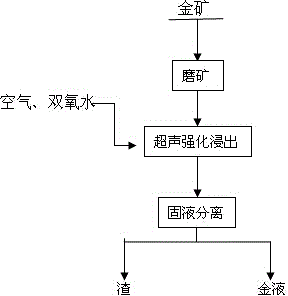
Method for collaboratively leaching gold in refractory gold ores by virtue of ultrasonic enhancement, chlorination and oxidization
InactiveCN104630466AImprove leaching rateShorten the leaching timeProcess efficiency improvementOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The invention discloses a method for collaboratively leaching gold in refractory gold ores by virtue of ultrasonic enhancement, chlorination and oxidization, and belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, crushing gold ores into ore powder, thoroughly mixing the ore powder with sodium hydroxide, sodium hypochlorite and water to obtain ore pulp, introducing air into the ore pulp, and performing ultrasonic enhanced leaching under a stirring condition; periodically adding hydrogen peroxide in the enhanced leaching process. According to the method, at the same time of ultrasonic enhancement, a redox reaction is performed by virtue of the synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide; the synergistic effect of the hydrogen peroxide and the sodium hydroxide is far better than the independent oxidization effect of each of the hydrogen peroxide and the sodium hydroxide. The ultrasonic enhancement is capable of improving the gold leaching effect while shortening the reaction time, and therefore, the reagent cost can be saved and the gold ore leaching efficiency also can be improved; as long as the method is adopted for leaching, the leaching rate can be above 98%; in addition, the sodium hypochlorite is adopted as a leaching agent for the method and no pressure is caused on the environment; besides, the method is capable of realizing one-step enhanced leaching of the gold ores and shortening the leaching steps.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for regenerating waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material
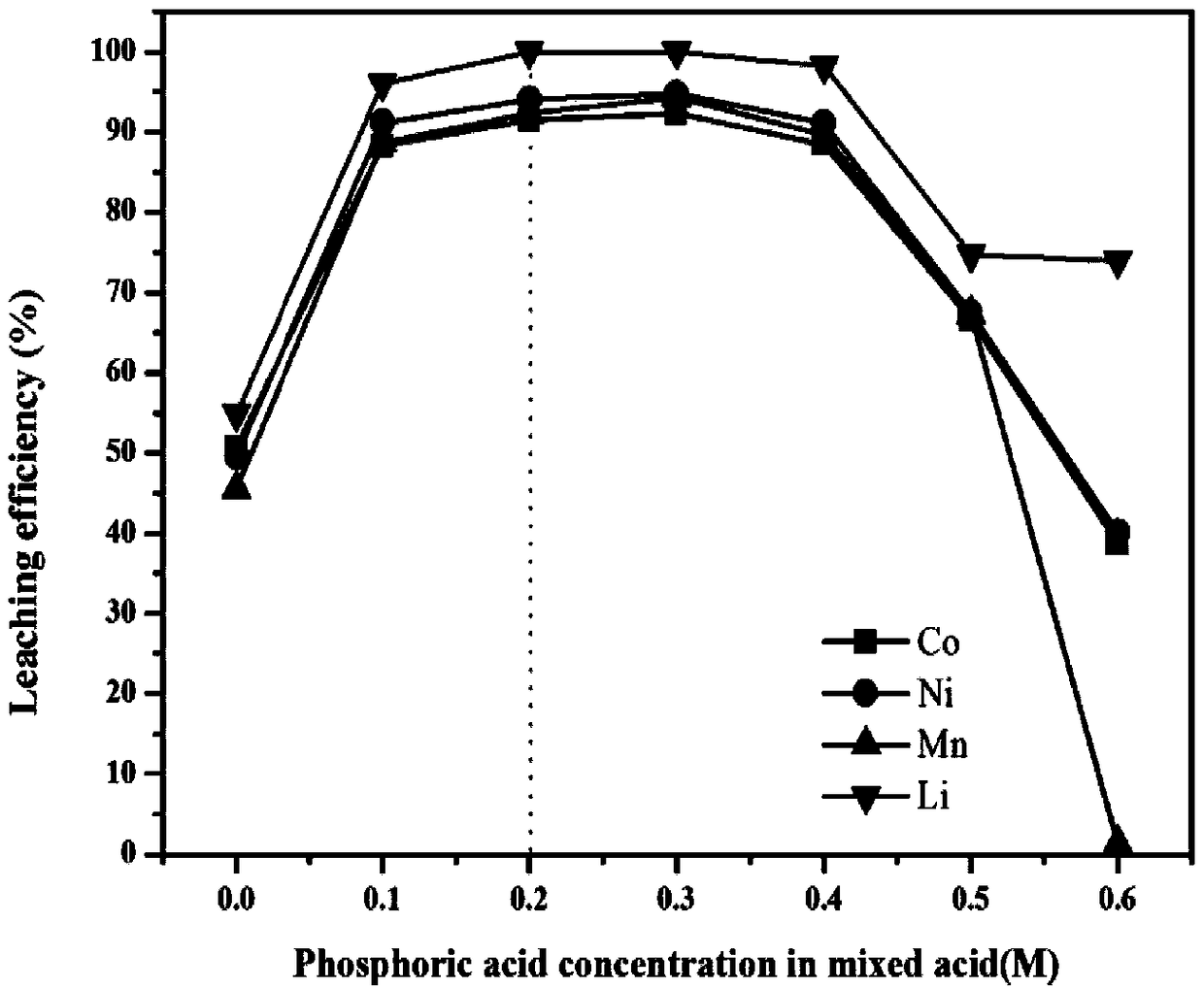
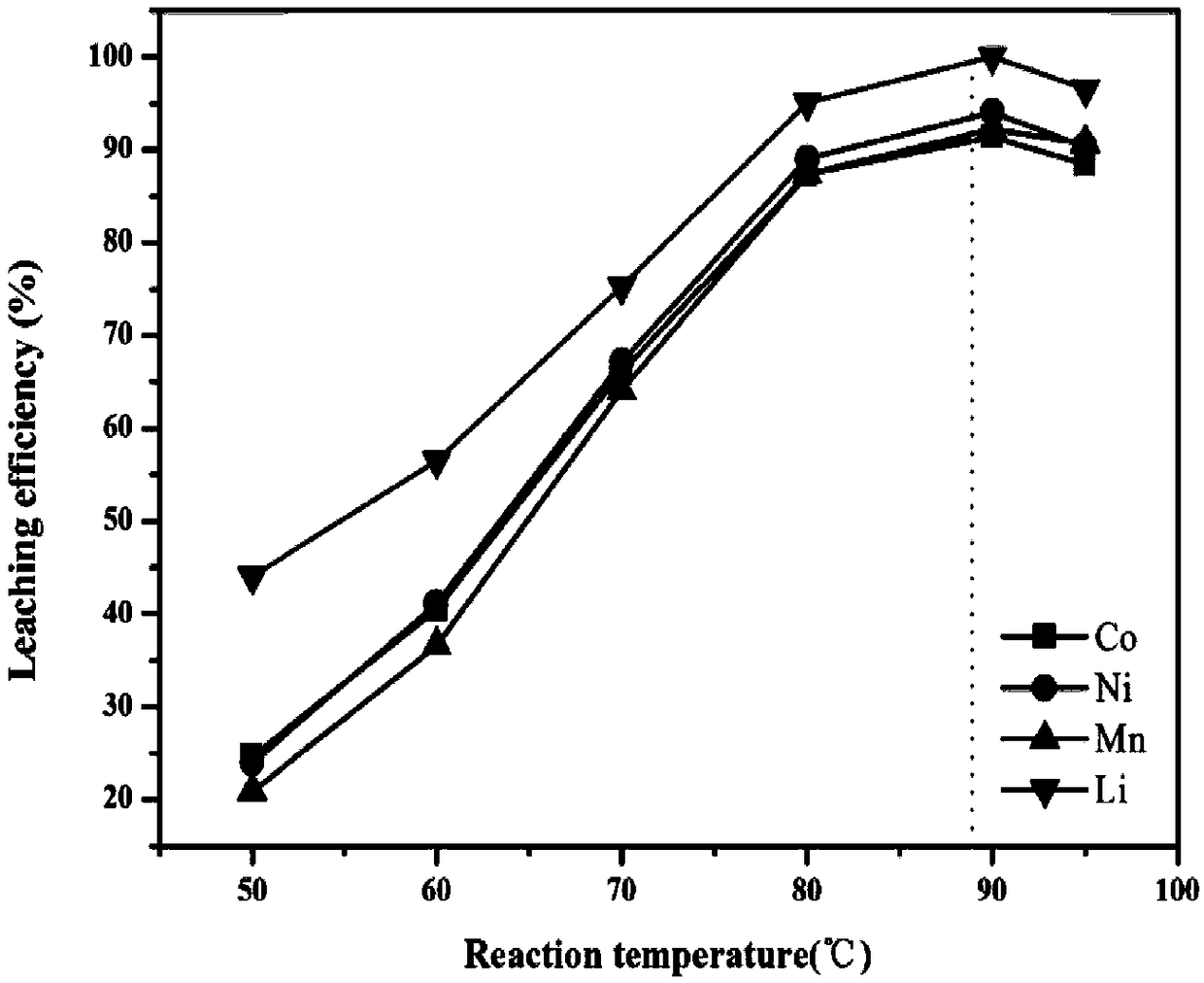
ActiveCN109065996AReduce acid consumptionShorten the leaching timeCell electrodesTransportation and packagingOxideOxalate
The invention discloses a method for regenerating waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material of. The method comprises lixiviating the waste lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternarycathode material by using phosphoric acid- citric acid mixed acid solution to obtain a lixivium; adjusting the metal ion ratio of the lixivium by a nickel salt, a cobalt salt and a manganese salt, andthen adding the lixivium into an oxalic acid solution for coprecipitation reaction; pre-calcining the obtained precipitate to obtain nickel cobalt manganese oxide, and grinding and mixing the nickelcobalt manganese oxide with a lithium source, calcining a resultant object to obtain a regenerated lithium nickel cobalt manganate ternary cathode material; The method adopts mixed acid lixiviating process, the acid consumption is small, the lixiviating time is short, the cost is low, the environmental impact is small, and the reducing agent is not needed, and the process is simple; The mixed acidlixivium is directly used for synthesizing ternary cathode materials, thereby avoiding the complicated process of separating and purifying various metals in the lixivium in the prior art, and realizing the closed-loop recycling utilization of metals.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com