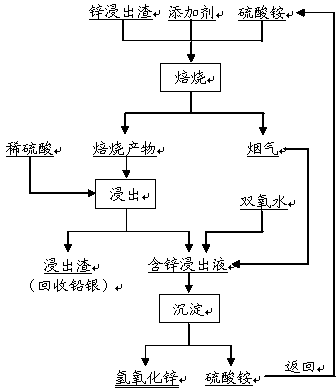
Method for separating zinc and iron from zinc leaching residues
A zinc leaching slag and leaching technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of good comprehensive utilization effect of raw materials, high equipment material requirements, large investment costs, etc., and achieve the effects of low production labor intensity, shortening leaching time, and improving production rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The main components of zinc leaching slag are calculated in mass percentage (%): Zn 18.57%, Fe 21.74%, SiO 2 12.96%. Industrial grade ammonium sulfate, of which nitrogen content ≥ 20.5%, moisture ≤ 1.0%; industrial grade sulfuric acid, of which H 2 SO 4 ≥98%; industrial grade hydrogen peroxide, of which H 2 o 2 ≥35%; industrial grade anhydrous calcium sulfate, of which CaSO 4 ≥98%.
[0024] Weigh 100g of zinc leaching slag, mix it evenly with 90g of ammonium sulfate and 3g of calcium sulfate, put it into the furnace, and roast it at 600°C for 2 hours. 3 48%, N 2 15%, SO 2 30%.
[0025] Cool 108.2g of the roasted product obtained after roasting, put it in 400mL of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.00005mol / L for slurrying, react at a temperature of 25°C for 1 hour, filter, wash and dry to obtain 53.8g of leaching residue, the main Composition: Zn 0.39%, Fe 40.29%, SiO 2 24.09%; the obtained zinc-containing leachate was 392mL, and its main co...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The main components of zinc leaching slag are calculated in mass percentage (%): Zn 21.40%, Fe 23.56%, SiO 2 10.38%. Industrial grade ammonium sulfate, of which nitrogen content ≥ 20.5%, moisture ≤ 1.0%; industrial grade sulfuric acid, of which H 2 SO 4 ≥98%; industrial grade hydrogen peroxide, of which H 2 o 2 ≥35%; technical grade anhydrous magnesium sulfate, of which MgSO 4 ≥98%.
[0029] Weigh 100g of zinc leaching slag, mix it with 42g of ammonium sulfate and 2g of magnesium sulfate, put it into the furnace, and roast it at 500°C for 3 hours. 3 60%, N 2 10%, SO 2 twenty two%.
[0030] Cool 102.4 g of the roasted product obtained after roasting, put it in 400 mL of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.30 mol / L for slurrying, react at a temperature of 25 ° C for 1 hour, filter, wash, and dry to obtain 53.0 g of leaching residue. Composition: Zn 1.06%, Fe 44.35%, SiO 2 19.58%; the obtained zinc-containing leachate was 396mL, and its main com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com