Preparation method of hydrogel porous microspheres and porous scaffold material
A technology of hydrogel microspheres and porous microspheres is applied in the field of tissue engineering materials, which can solve the problems of uncontrollable and stable formation of spheres, and achieve the effect of maintaining cell viability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] According to different hydrogel materials, this application also provides a method for preparing porous hydrogel microspheres, which includes the following steps:
[0043] A) Mixing the hydrogel material and the buffer to obtain a hydrogel solution; mixing the oily material and the surfactant to obtain the oily solution;
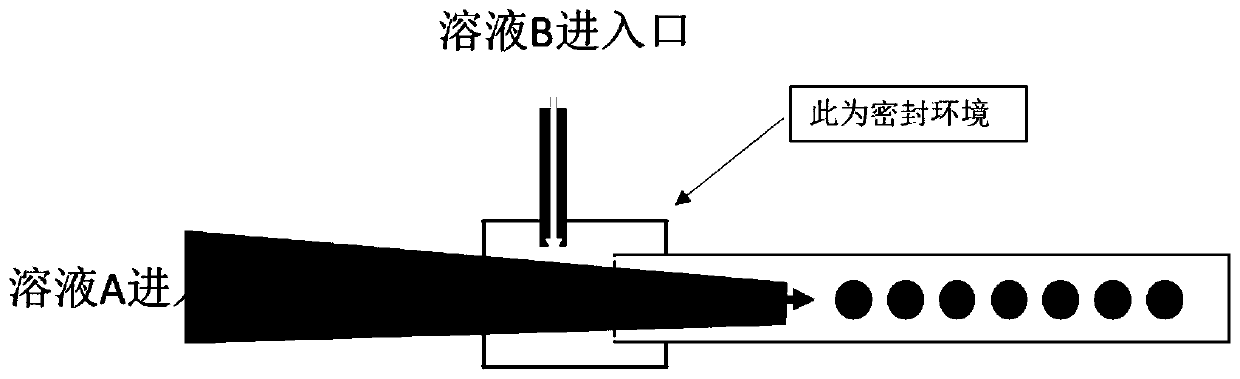
[0044] B) The first container is partially nested into the second container, the inner diameter of the inlet end of the first container is greater than the inner diameter of the outlet end, and the inner diameter of the outlet end of the first container is smaller than the inner diameter of the second container; The hydrogel solution is injected into the first container, the oily solution is injected into the intersection of the first container and the second container, and the oily solution and the hydrogel solution are under the action of flow shearing force. Form water-in-oil droplets;
[0045] C) Cross-linking the water-in-oil droplets to obtain hydroge...
Embodiment 1
[0055] 1) Solution A: Add 2ml of phosphate buffer solution to 100mg of methacrylic group-modified gelatin, and add 20mg of photoinitiator at the same time, place it in a 60°C water bath for 45 minutes, shake it up intermittently, and fully dissolve it. The solution becomes colorless, clear and transparent for use;
[0056] 2) Solution B: Take 50ml of perfluorinated oil and add 1% by mass to the surfactant span80, shake to dissolve, and remove bubbles by ultrasound;
[0057] 3) Capillary glass tube C: Take a capillary glass tube with an inner diameter of 100 μm, draw a wire at the distal end, and cut a capillary with an outlet inner diameter of 50 μm under a microscope;
[0058] 4) Capillary glass tube D: Capillary glass tube with an inner diameter of 100μm;
[0059] 5) Sleeve the outlet end of tube C into tube D, place it on a glass slide, and fix it with gum; use a 21G syringe needle nest to close the junction of tube C and tube D, and at the same time nest a 21G syringe needle at th...
Embodiment 2
[0073] 1) Solution A: Add 2ml of deionized water to 80mg of methacrylic group-modified gelatin, then add 20mg of sodium alginate, and add 20mg of photoinitiator at the same time, place it in a 60℃ water bath for 45 minutes with intermittent shaking Evenly, fully dissolve, wait for the solution to become colorless, clear and transparent;
[0074] 2) Solution B: Take 50ml of perfluorinated oil and add 1% by mass to the surfactant span80, shake to dissolve, and remove bubbles by ultrasound;
[0075] 3) Capillary glass tube C: Take a capillary glass tube with an inner diameter of 100 μm, draw a wire at the distal end, and cut a capillary with an outlet inner diameter of 50 μm under a microscope;
[0076] 4) Capillary glass tube D: Capillary glass tube with an inner diameter of 100μm;
[0077] 5) Put the outlet end of tube C into tube D, place it on a glass slide, fix it with gum, and close the junction of tube C and tube D with a 21G syringe needle nesting, and at the same time nest a 21G...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com