Patents
Literature
191 results about "Porous hydrogel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogels having enhanced elasticity and mechanical strength properties
InactiveUS6960617B2Great compression modulusEnhanced water absorbencePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsPolyelectrolytePolymer science
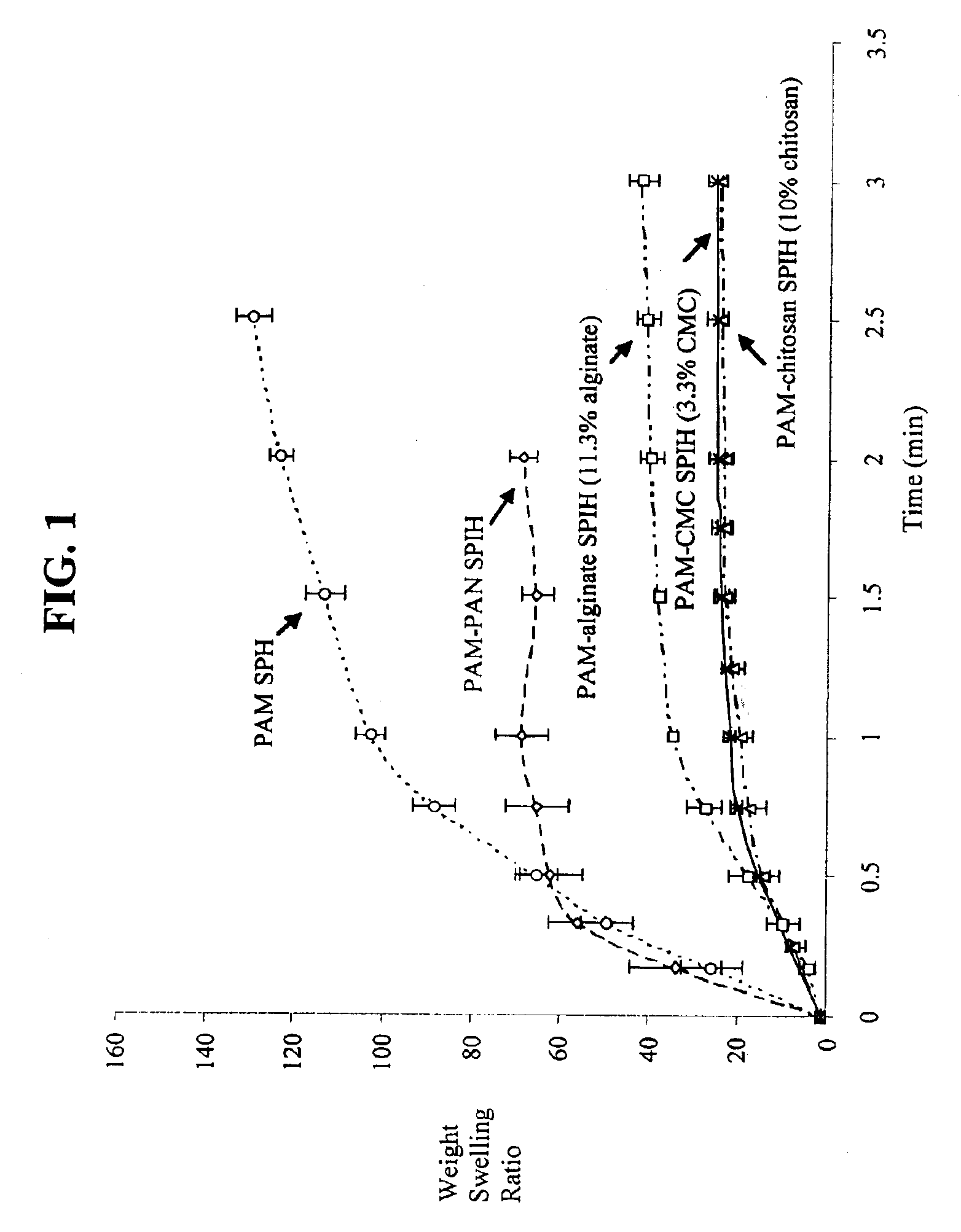
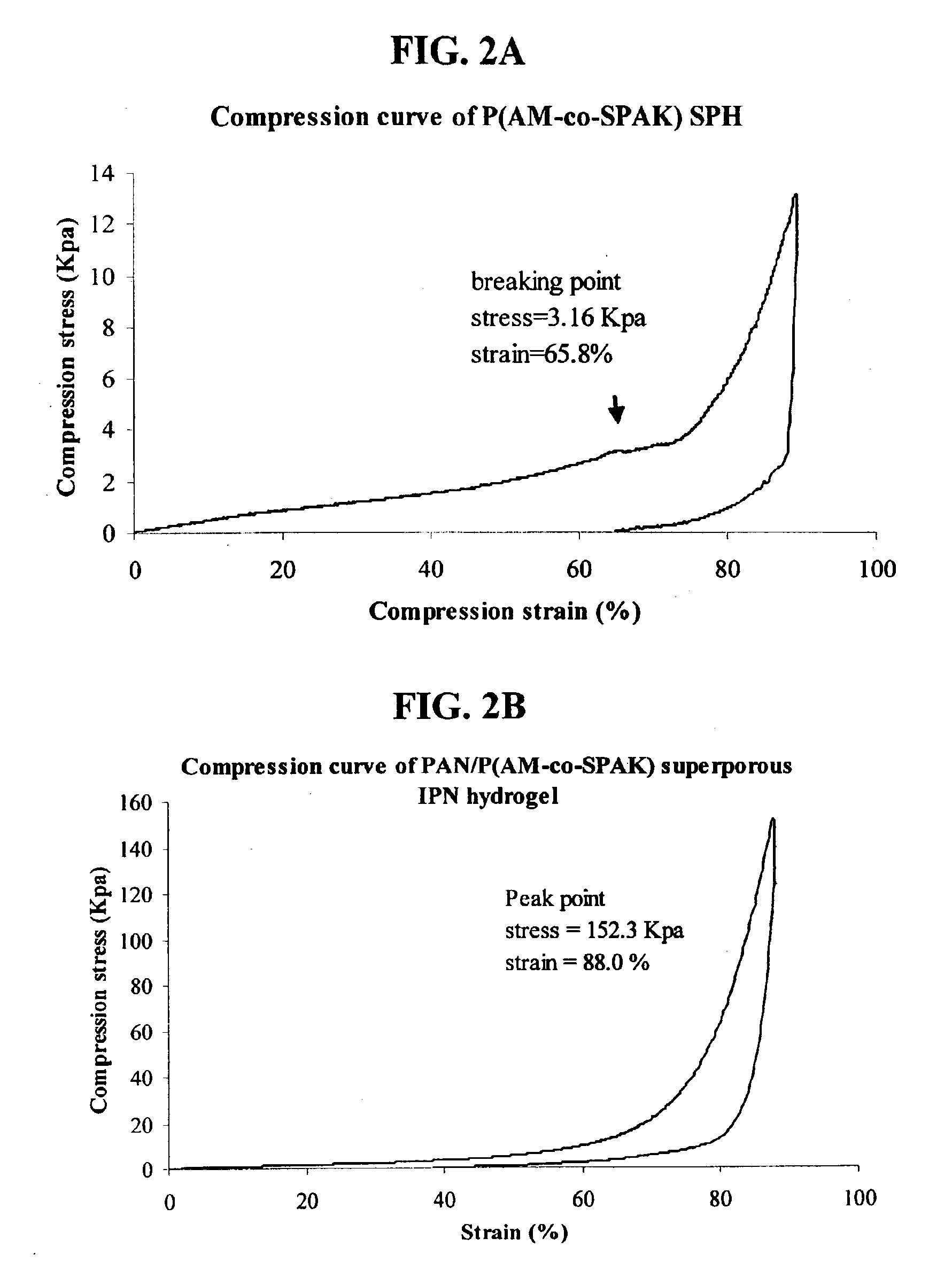
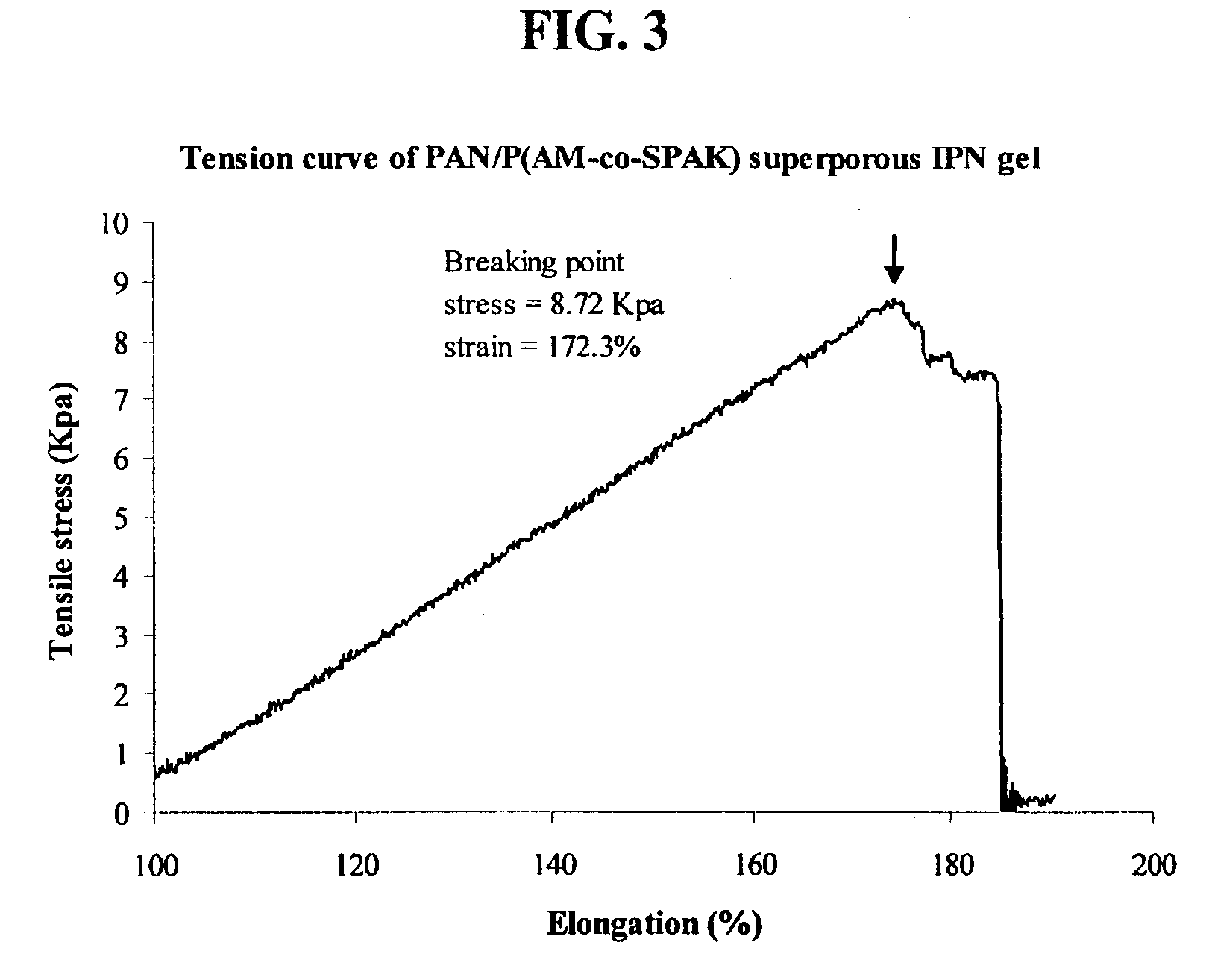
Hydrogels having improved elasticity and mechanical strength properties are obtained by subjecting a hydrogel formulation containing a strengthening agent to chemical or physical crosslinking conditions subsequent to initial gel formation. Superporous hydrogels having improved elasticity and mechanical strength properties are similarly obtained whenever the hydrogel formulation is provided with a foaming agent. Interpenetrating networks of polymer chains comprised of primary polymer(s) and strengthening polymer(s) are thereby formed. The primary polymer affords capillary-based water sorption properties while the strengthening polymer imparts significantly enhanced mechanical strength and elasticity to the hydrogel or superporous hydrogel. Suitable strengthening agents can be natural or synthetic polymers, polyelectrolytes, or neutral, hydrophilic polymers.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
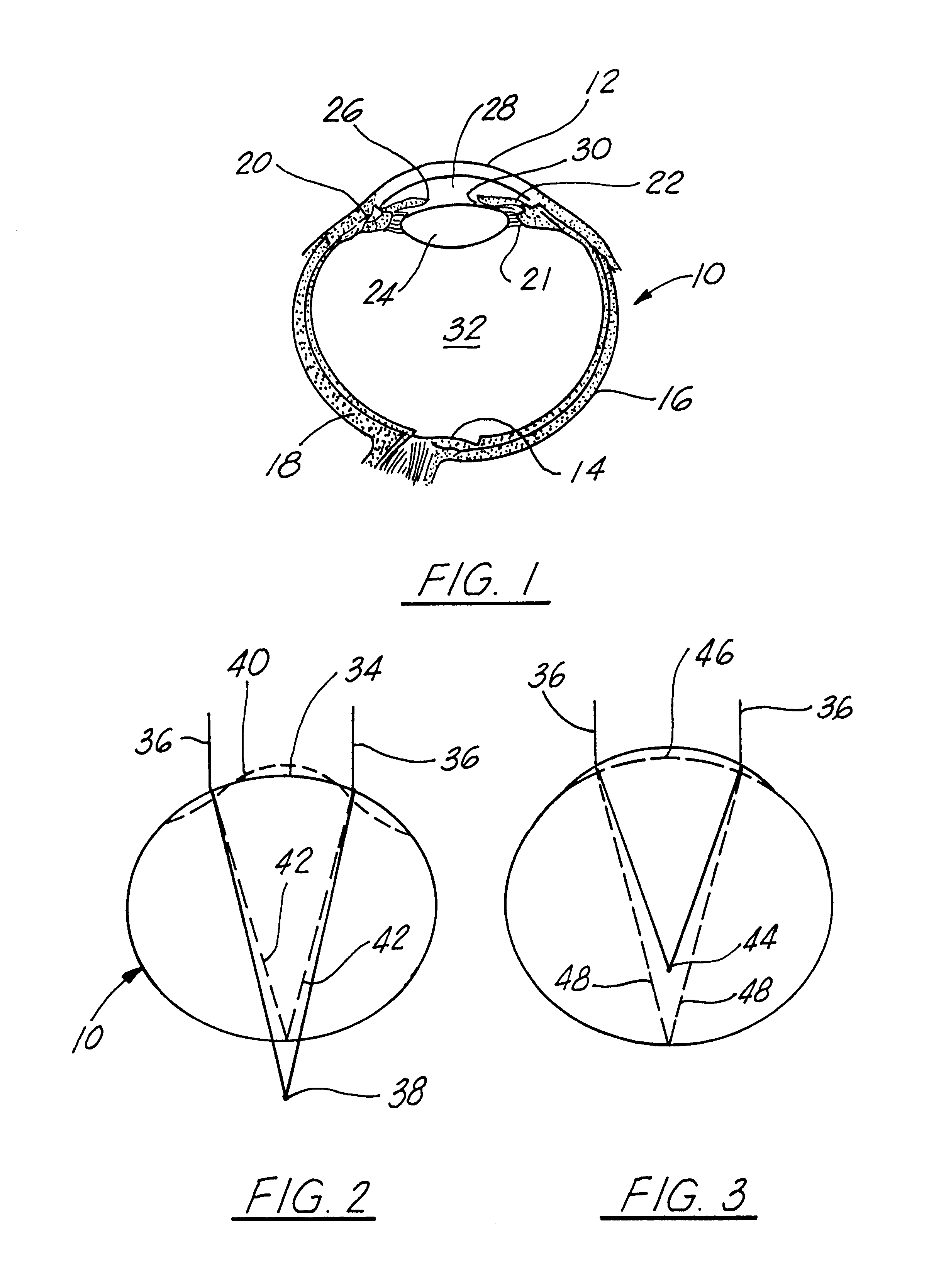
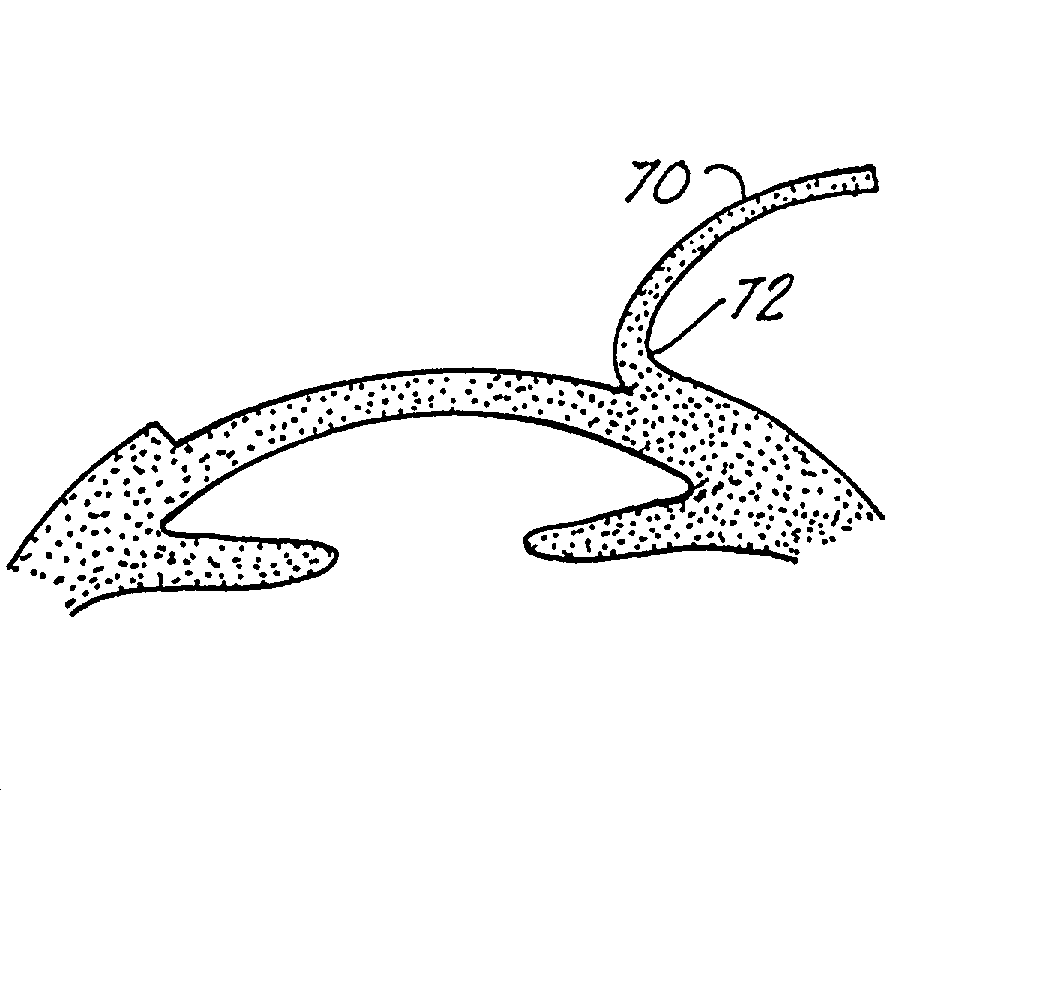
Corneal implant and method of manufacture
Prosthetic implants designed to be implanted in the cornea for modifying the cornea curvature and altering the corneal refractive power for correcting myopia, and myopia with astigmatism, such implants formed of a micro-porous hydrogel material.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
Tissue-engineering scaffolds containing self-assembled-peptide hydrogels
ActiveUS20080145934A1Good tissue responseSuitable mechanical propertyAnimal cellsCell culture supports/coatingPore diameterMechanical property
The present invention is directed to tissue-engineering scaffolds containing both a microporous scaffold made from a biocompatible material suitable for use in tissue-engineering scaffolds and a nanofiberous, nanoporous hydrogel formed from a self-assembling peptide, where at least a portion of the hydrogel is disposed within the pores of the microporous scaffold, thus providing tissue-engineering scaffolds having average pore diameters in the nanometer range and that provide both mechanical properties suitable for implantation into a body of a mammal and excellent tissue response once implanted in the body.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
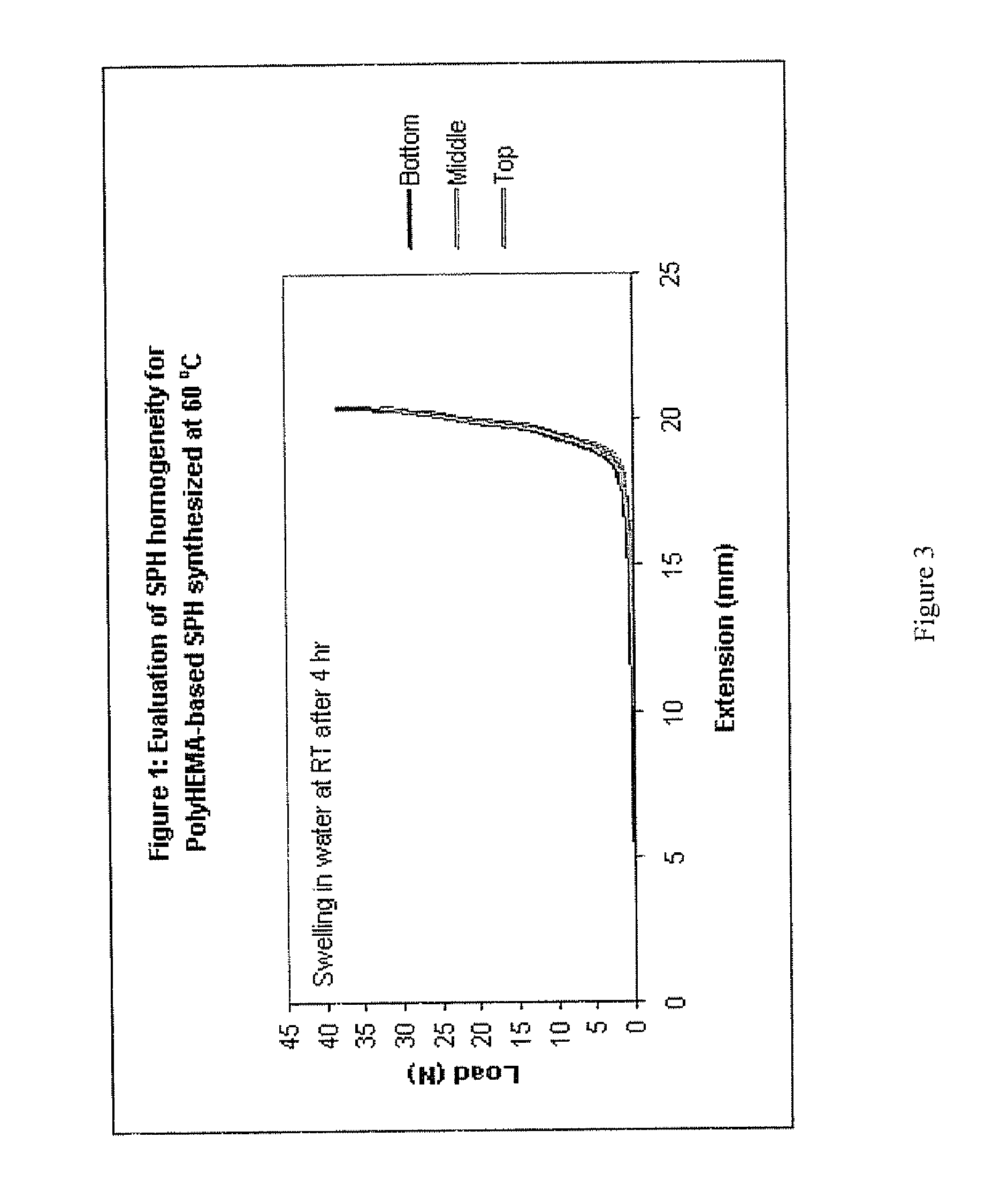
Superporous hydrogels for heavy-duty applications
InactiveUS7988992B2Improved strength and mechanical propertyPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsPolymer scienceGastric fluid
The present invention features modified superporous hydrogels (SPHs) and methods for their formation. The SPHs of the present invention are prepared by careful selection of the hydrophobic / hydrophilic reactive ingredients and by harmonizing the foaming and polymerization reactions, which results in the formation of SPHs having a homogeneous structure and favorable physical and mechanical properties, including swelling, strength, ruggedness, and resiliency. The SPHs of the present invention are particularly useful when employed in very harsh swelling environments, such as the low pH environment of the gastric fluid of the stomach, for extended periods of time.
Owner:KOS LIFE SCI
Absorbent multilayer hydrogel wound dressings
ActiveUS20060200063A1Acceptable water uptake speedGood flexibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
The invention provides wound dressings comprising an absorbent (porous) hydrogel composition comprising a foam portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having an internal cellular structure, and a continuous portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having relatively continuous internal structure. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition includes apertures providing fluid flow communication through the continuous portion between an external surface of the continuous portion and the foam portion whereby the foam portion can take up external water or other fluid into the cellular structure through the apertures of the continuous portion. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition may be tacky to the skin, allowing its use as a bioadhesive.
Owner:KCI USA
Corneal implant and method of manufacture
Prosthetic implants designed to be implanted in the cornea for modifying the cornea curvature and altering the corneal refractive power for correcting myopia, and myopia with astigmatism, such implants formed of a micro-porous hydrogel material.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
Alleviation of non-specific binding in microarray assays
InactiveUS7258990B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysosomeSolid particle
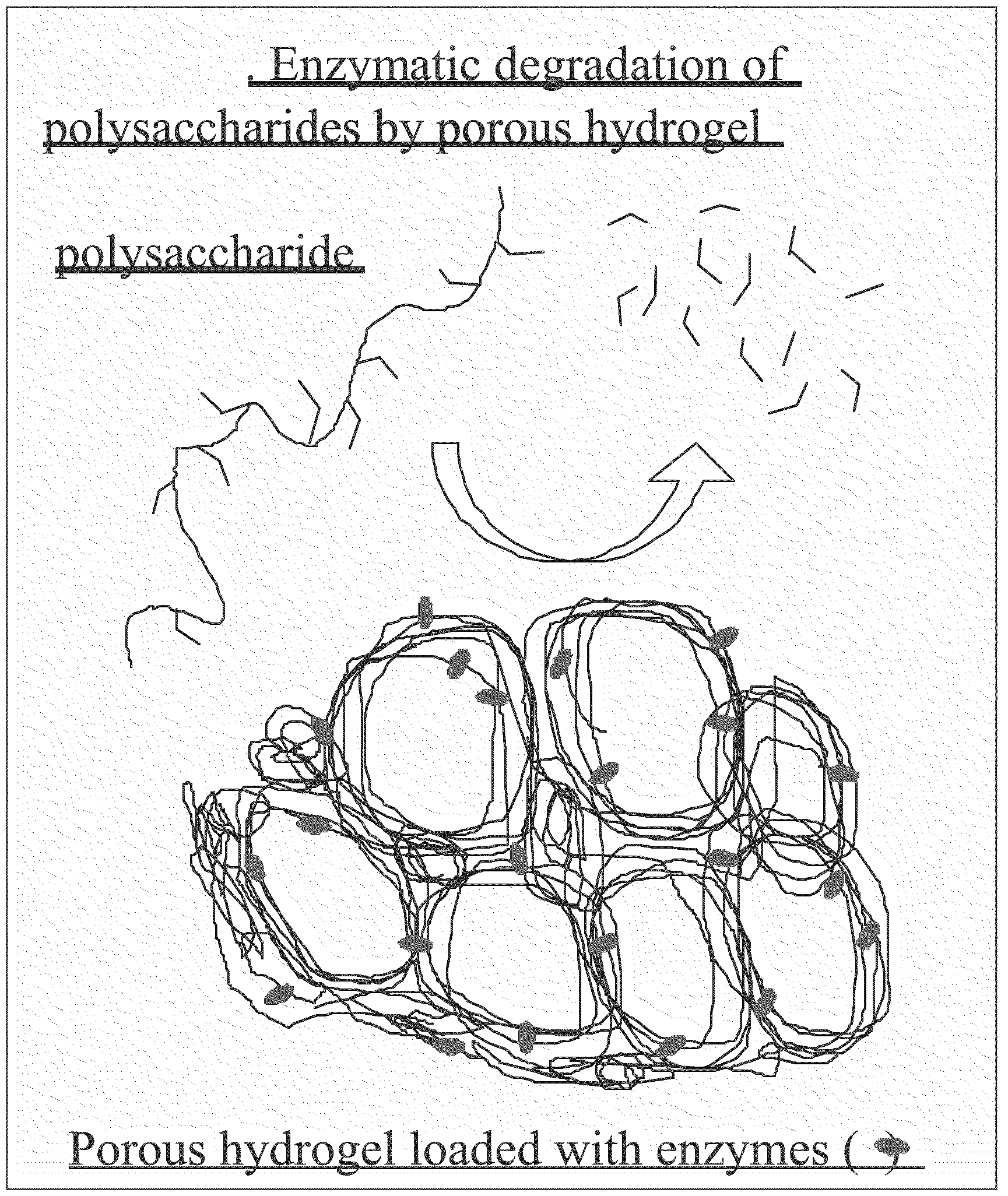
A post-incubation treatment is employed to effectively remove targets, such as proteins / protein complexes, or other label-bearing moieties that may non-specifically bind to a microarray substrate during a binding assay. Following incubation, a one-step wash is carried out with a liquid containing digester, e.g., a digestive enzyme (protease) or lysosome, which is effective to remove non-specifically bound targets or at least labeled portions of such targets from the substrate. Proteases are bound to or coated onto large molecules or onto solid particles of such a size such that they are prohibited from entering the porous surfaces of 3-D hydrogel microspots and are unable to reach and digest labeled target-probe complexes that are disposed within such porous hydrogel microspots. Digested segments of such protein which contain labels (or of essentially the entire protein) are carried away in the wash liquid and thus are not present to create background noise during imaging.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Interpenetrating network polymer type super porous aquogel, its prepn. method and application
InactiveCN1757662AOral administration is convenientHigh mechanical strengthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesCross-linkFoaming agent
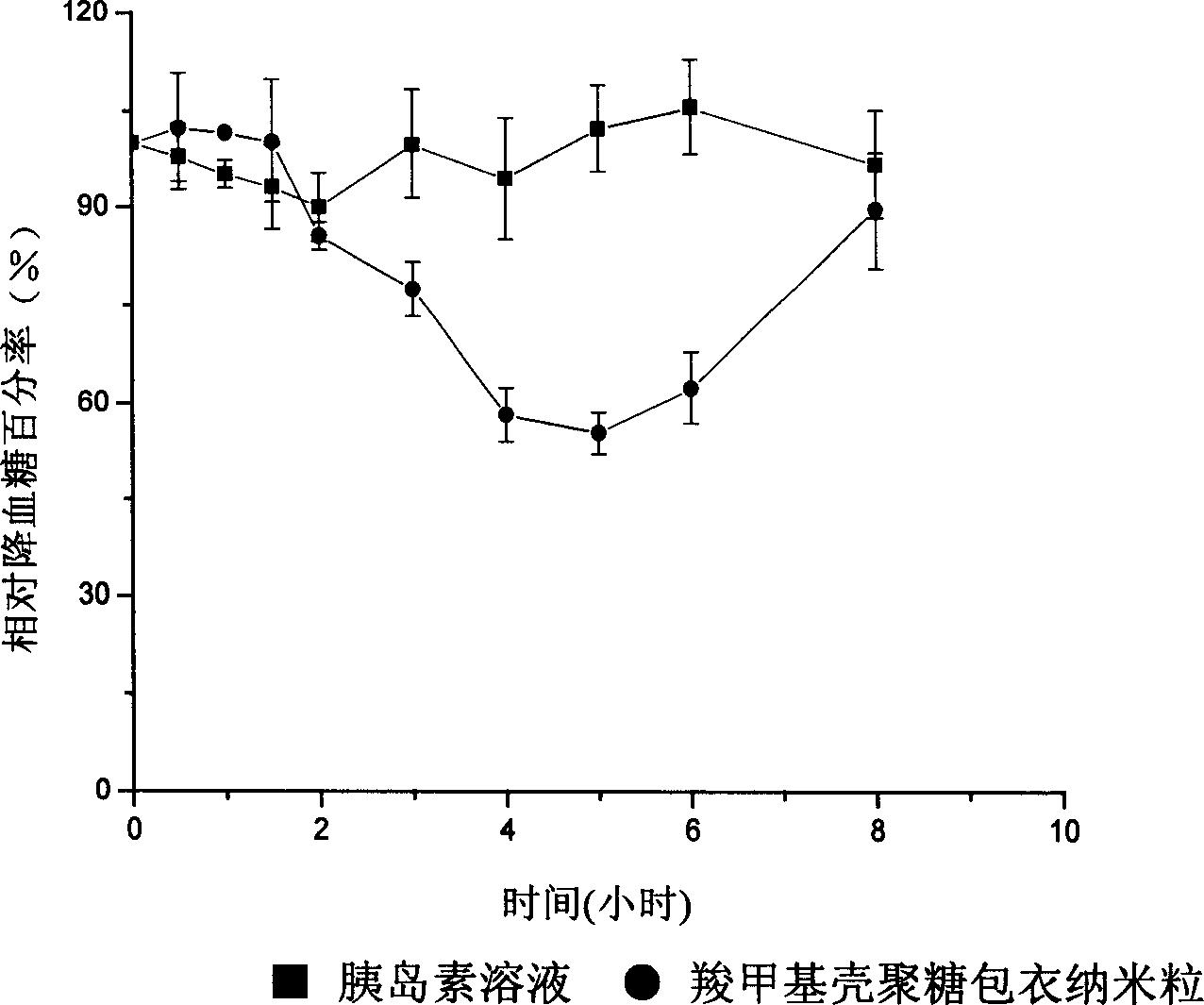
A super-porous aqueo-gel of an interpenetrating network polymer used for the orally applying system of protein polypeptide to suppress proteinase and break the close linking between epithelial cells contains two polymers: a cross-linked polymer and a cross-linked polyose polymer. Its preparing process includes such steps as mixing at least one unsaturated enylmonomer, at least one polyenyl cross-linking agent, a linear polyose polymer and a foaming agent to generate the super-porous aqueo-gel of semi-interpenetrating network polymer, and cross-linking with linear polyose.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multi-component non-biodegradable implant, a method of making and a method of implantation
ActiveUS20140324169A1Maximizes integrationEasy to integrateBone implantSurgerySacroiliac jointMusculoskeletal tissue
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Formation of strong superporous hydrogels
InactiveUS7056957B2With mechanical propertiesStrong water absorptionPowder deliverySurgerySuperporous hydrogelsUltimate tensile strength
The present invention features a method for the formation of superporous hydrogels using an ion-equilibration technique. Anionic polysaccharides are included in the hydrogel reaction mixture and cations are introduced either during or after hydrogel formation. Properties of the resulting hydrogel can be subsequently adjusted by treating the cation-complexed gel with a different cation or cation mixture under equilibrating conditions. It has been found that by properly adjusting the cations and the sequence in which they are used in the equilibration process, superporous hydrogels can be formed that are highly absorbent while maintaining favorable structural properties, including strength, ruggedness, and resiliency. It has also been found that applying appropriate dehydration conditions to them after their formation can further stabilize the superporous hydrogels formed by the method of the invention.
Owner:KOS LIFE SCI
Ultra porous hydrogel complex substance, preparing method and use in pharmaceutics thereof
InactiveCN1488331AHigh mechanical strengthGood bioadhesionPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCross-linkFoaming agent
The invention discloses an ultra-multiaperture hydrogel compound, making method and application in pharmacy. It contains cross-linked polymer and Carbomer. At least one unsaturated alkene monomer and polyene cross-linking agent polymerize to develop it. The making steps: mix at least one unsaturated alkene monomer, one polyene cross-linking agent, Carbomer and one foaming agent; the mixture develops it on the condition of polymerizing and foaming. It can be used in stomach floating preparation and protein polypeptide oral medicine supplying system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Corneal implant and method of manufacture
Prosthetic implants designed to be implanted in the cornea for modifying the cornea curvature and altering the corneal refractive power for correcting myopia, and myopia with astigmatism, such implants formed of a micro-porous hydrogel material.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
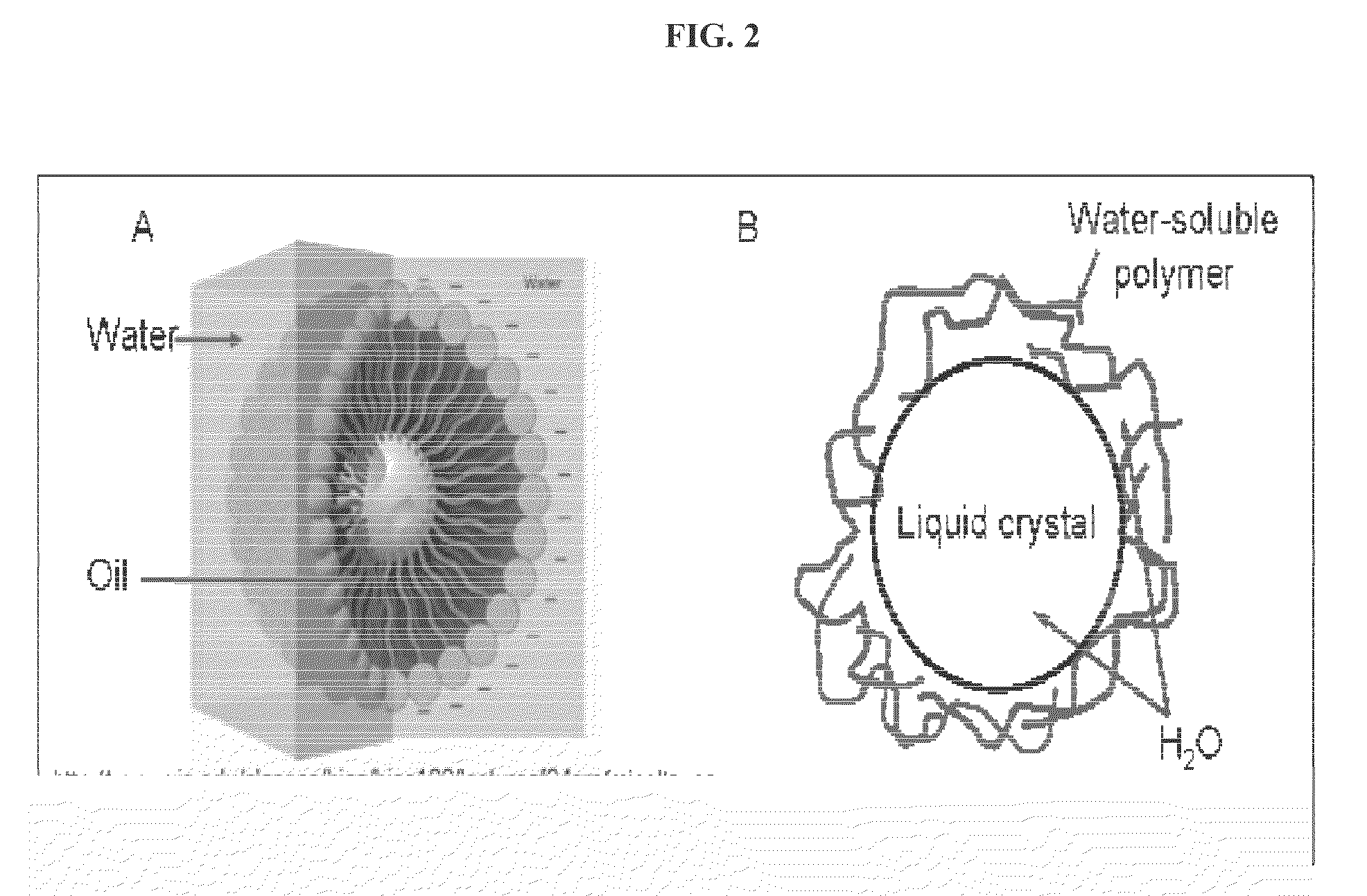
Non-amphiphile-based water-in-water emulsion and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090269323A1Satisfies needMeet actual needsLiquid crystal compositionsBiocideDisodium cromoglycateMesogen
The present invention relates to a non-amphiphile-based water-in-water emulsion composition. The non-amphiphile-based water-in-water emulsion composition includes a water-soluble polymer, a non-amphiphilic lyotropic mesogen encapsulated by the water-soluble polymer; and water. In one embodiment, the non-amphiphilic lyotropic mesogen includes, without limitation, a lyotropic chromonic liquid crystal, and more specifically disodium cromoglycate (DSCG). In another embodiment, the water-soluble polymer can include, without limitation, a polyacrylamide, a polyol, a polyvinylpyrrolidone, a polysaccharide, or a water-soluble fluoride-bearing polymer. The present invention also relates to a porous hydrogel made with the use of the non-amphiphile-based water-in-water emulsion. The present invention further relates to using the emulsion and hydrogel for various applications.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of ultra-porous hydrogel containing natural plant polysaccharide
InactiveCN102492093APromote swellingIncrease in sizePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkFoaming agent
The invention provides ultra-porous hydrogel containing natural plant polysaccharide, which is prepared by the steps of dissolving reaction components in water to form a solution after weighing the reaction components according to a certain proportion, adding the natural plant polysaccharide into the solution, and shaking and mixing evenly the natural plant polysaccharide and the solution, wherein the reaction components include, by weight, monomer 0.50-3.00%, distilled water 0.60-4.50%, initiating agent 0.02-0.15%, cross-linking agent 0.03-0.20%, foam stabilizer 0.02-0.18%, foaming agent 0.07-1.00% and the natural plant polysaccharide 0.06-2.00%. The natural plant polysaccharide is introduced into the ultra-porous hydrogel to prepare the ultra-porous hydrogel containing the natural plantpolysaccharide, so that the ultra-porous hydrogel is capable of swelling rapidly in the water, increased in volume and excellent in mechanical strength. Furthermore, the ultra-porous hydrogel containing the natural plant polysaccharide can take advantages of the natural plant polysaccharide completely, and new application fields can be opened up.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
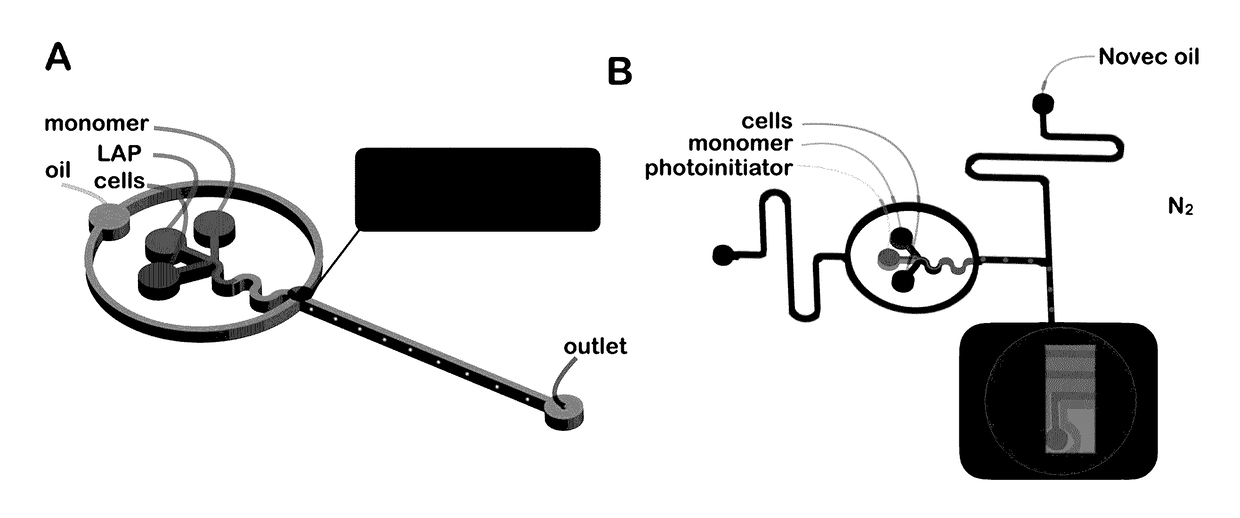
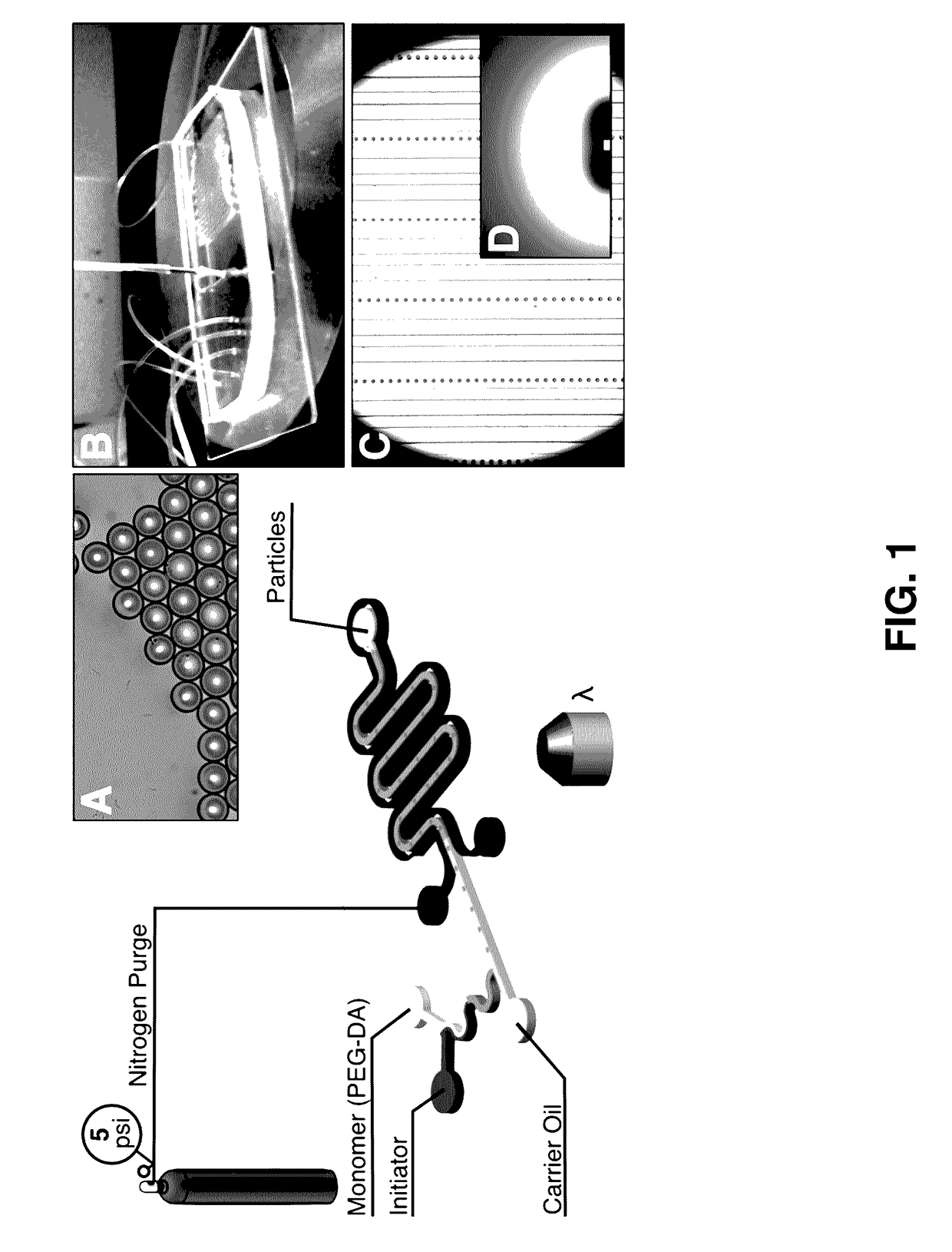
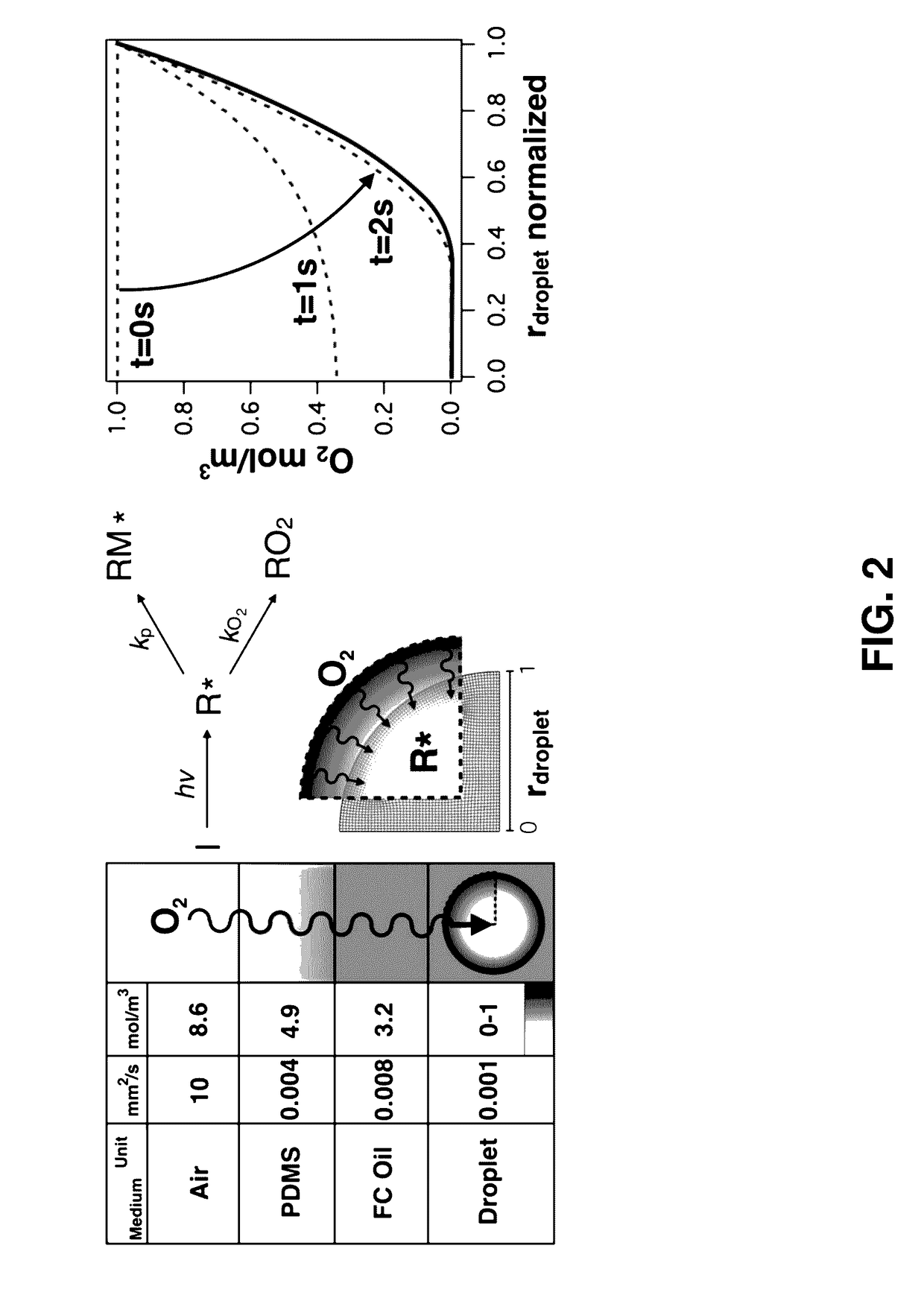
Methods of Generating Microparticles and Porous Hydrogels Using Microfluidics
PendingUS20170145169A1Ability to control the amount of oxygen presentInhibition of polymerizationFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMicrofluidicsAqueous droplet
Provided herein are methods utilizing microfluidics for the oxygen-controlled generation of microparticles and hydrogels having controlled microparticle sizes and size distributions and products from provided methods. The included methods provide the generation of microparticles by polymerizing an aqueous solution dispersed in a non-aqueous continuous phase in an oxygen-controlled environment. The process allows for control of size of the size of the aqueous droplets and, thus, control of the size of the generated microparticles which may be used in biological applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
The preparation method of the radiant crosslink porous reticular cells amnionic hydro gel dressing and its preparation method
InactiveCN1943796AOvercome the shortcomings of low mechanical strength and poor complianceConvenient for clinical operationAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze-dryingPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an irradiative crosslink network cellular porous hydrogel dressing of amniotic membrane, the specific methods are: put the hydrogel solutions comprising of PVA, chitosan and acrylic acid-acrylamide copolymer on the porous stainless steel plate used to put the netty cellular amniotic membrane, add a small amount of agar, agitate uniformly, evacuate, and the hydrogel prototype was obtained; then press the hydrogel to film; then expose the membrane to 60Coy- ray irradiation in room temperature to crosslink, then dehydrate, freeze-dried, radiative sterilized, packed under aseptic conditions. The invention possesses good protection treatments, such as alleviate pain, resist to phlogosis and bacterium, and promote healing. It also has good hygroscopic properties, water retention, permeability and flexibility, further more we can have a selection of drugs according to sensitive bacteria of wound, pain, the need of arristing or activzte bleeding to and to help achieve sustained-release drug treatment purposes.
Owner:关志广
Ultra-multiple-pore hydrogel for microbial fermentation and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to an ultra-multiple-pore hydrogel for microbial fermentation and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes: (1) preparing gel pre-polymerizing liquid; (2) rehydration activation of dried yeast; (3) preparation of ultra-multiple-pore gel; and (4) purification of the ultra-multiple-pore gel. The theory is that after rehydration activation of the dried yeast, fermentation reaction is conducted in the gel to generate carbon dioxide, so that the effect of the foaming agents is played to generate the ultra-multiple-pore gel. The ultra-multiple-pore hydrogel is combined with the fermentation technology of microorganisms, can achieve non-toxic and harmless production and production efficiency of the porous gel preparation process, has generality and universality and can be applied to the field of dye absorption, heavy metal ion enrichment and recovering, drug carriers and biomedicine support materials.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Starch-based porous hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a starch-based porous hydrogel prepared from a starch liquid, an initiating agent, a monomer and a cross-linking agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the initiating agent, the monomer and cross-linking agent into the starch liquid; after each component is added, mixing uniformly, and heating for full reaction, thereby obtaining a starch-based hydrogel; and washing and swelling the obtained starch-based hydrogel, immerging the washed and swelled starch-based hydrogel into an organic solvent-water mixed solution with specific components so as to perform gradient solvent exchange, and drying, thereby obtaining the starch-based porous hydrogel. The starch-based porous hydrogel has the characteristics of simple and convenient preparation method, good open pore property, controllable porous structure and stable three-dimensional structure.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Structural color contact lens based on coffee ring effect and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102323679AColorfulHigh light transmittanceOptical articlesOptical partsCoffee ring effectTransmittance
The invention discloses a structural color contact lens based on coffee ring effect and a preparation method thereof; the contact lens comprises a contact lens substrate, and is characterized in that the contact lens substrate contains ordered porous hydrogel which is used to form structural colors, is arranged annularly or circularly and is close-packed. With respect to other structural color contact lenses, the process of the preparation method is simple, and the prepared structural color contact lens has good biocompatibility, high light transmittance, and very good practicality.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of living cell based complex three-dimensional microchannel porous support
A preparation method of a living cell based complex three-dimensional microchannel porous support. The method comprises steps of: first, preparing two parts of hydrogel collosol with different hydrogel monomer concentrations; then preparing two mixed liquors containing the hydrogel collosol and cell culture solution; putting the two mixed liquors into two sets of different injectors of a cell printer; then printing the mixed liquors on a petri dish surface until formation of a required three-dimensional cell-laden hydrogel support; cultivating the cell-laden hydrogel support in an incubator; then soaking the cell-laden hydrogel support in lauryl sodium sulfate to complete split and kill the cells; flushing with Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline and deionized water successively; finally obtaining the three-dimensional porous hydrogel support with complex microchannels. According to the invention, living cells are employed as a porogenic agent; size and density of the holes are controlled through controlling of the cell concentration and culture conditions; distribution of the holes is controlled through controlling of a printing platform; and a complex and controllable microchannel structure is formed in the hydrogel support.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Pineapple waste hemicellulose based pH sensitive type porous hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105131185AConducive to high-value utilizationRich sourcesOther chemical processesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkFreeze-drying
The invention belongs to the technical field of high polymer materials and discloses pineapple waste hemicellulose based pH sensitive type porous hydrogel as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises steps as follows: pineapple waste is preprocessed firstly, hemicellulose in the preprocessed pineapple waste is extracted with a classification extraction method through alkali liquor, washed and subjected to freeze drying, and hemicellulose is obtained; the hemicellulose is dissolved in deionized water, a pore-forming agent is added, the mixture is heated and stirred to be uniformly mixed and completely dissolved, and a solution I is obtained; monomers and an initiator are added to the solution I, the solution I is stirred continuously, then a cross-linking agent is added, and the solution I is stirred until a system is completely dissolved and the solution is in a clear and transparent state, the solution is left to stand, soaked, washed and subjected to freeze drying, and the pineapple waste hemicellulose based pH sensitive type porous hydrogel is obtained. The preparation method is simple, and raw materials have abundant sources; the prepared porous hydrogel has controllable aperture, excellent texture characteristics, mechanical characteristics and pH sensitivity and can be applied to the fields of medicine and adsorption.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
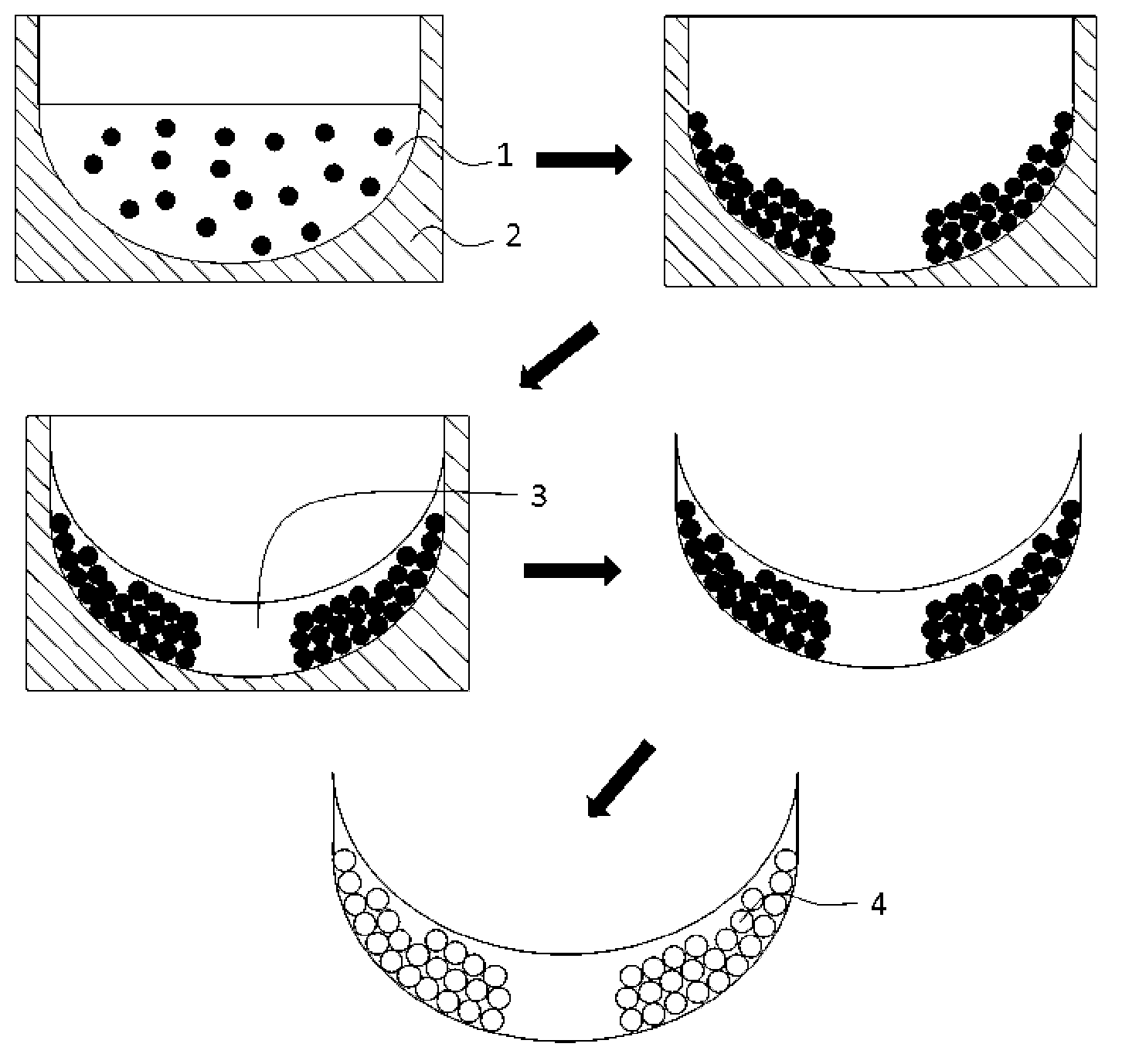
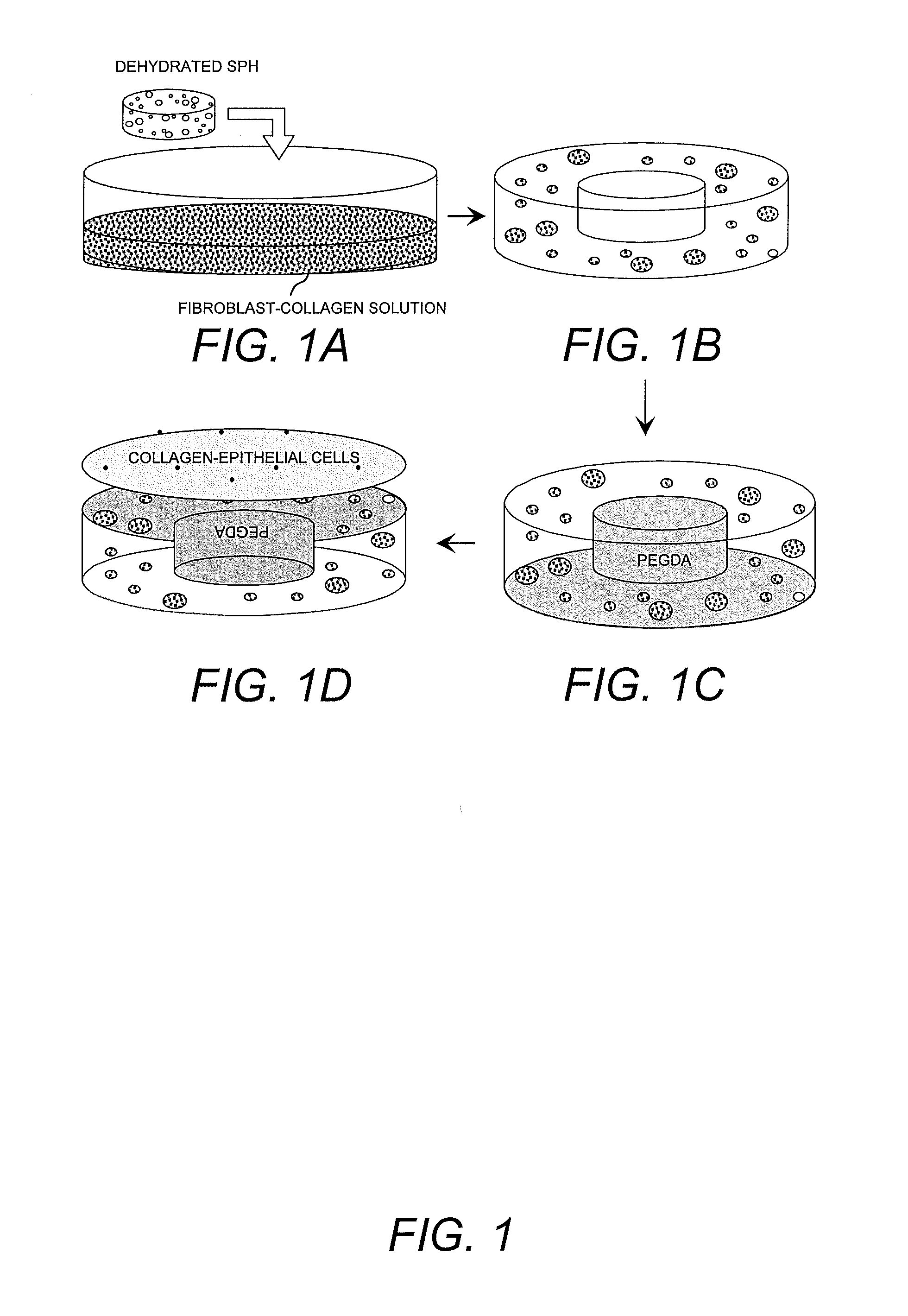
Hybrid superporous hydrogel scaffold for cornea regeneration
The present invention features a hybrid superporous hydrogel scaffold for cornea regeneration and a method for producing the same. The hybrid hydrogel is composed of a superporous hydrogen matrix with collagen and cells embedded within the pores of the matrix.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
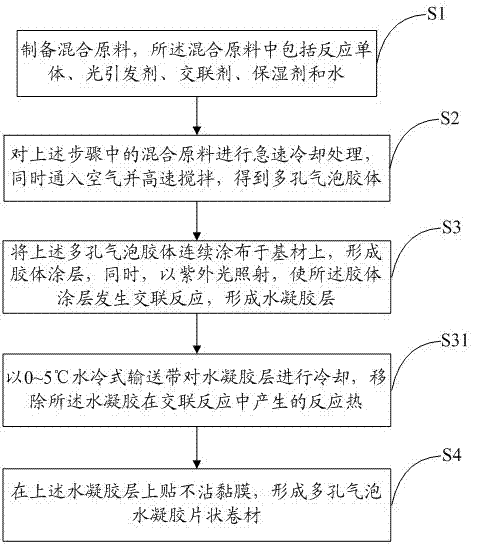
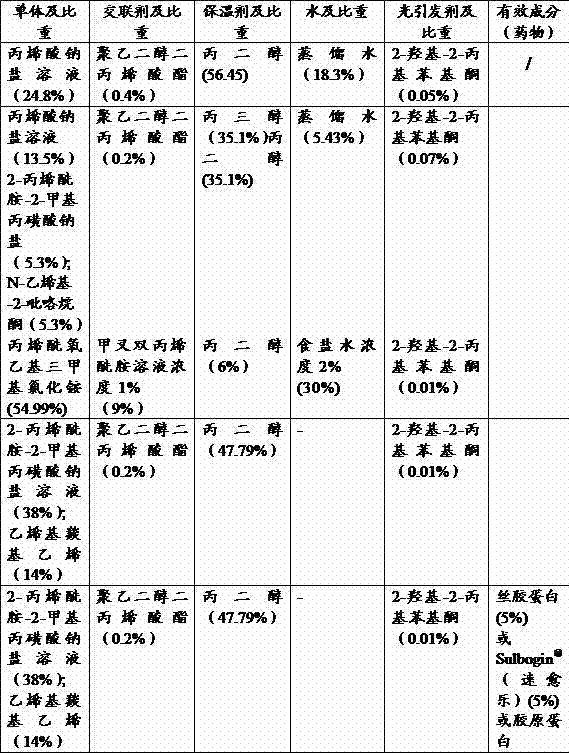
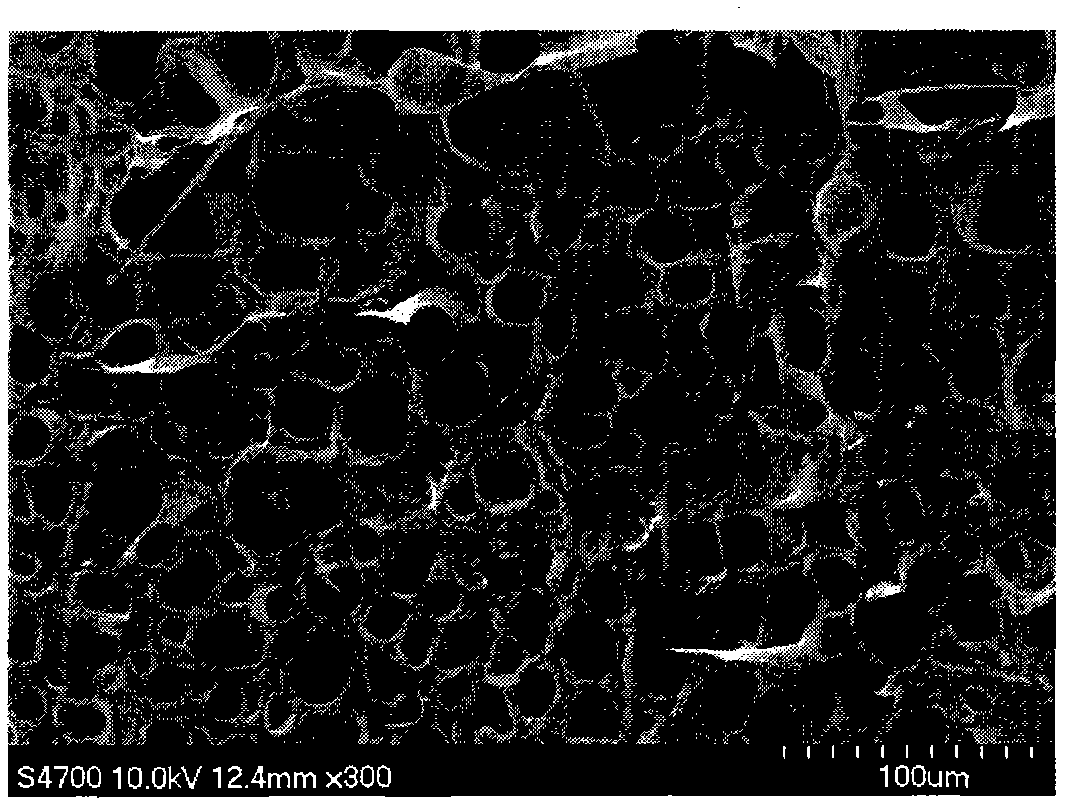
Preparation processes of porous hydrogel and nonporous hydrogel
InactiveCN103044703AReduce manufacturing costEasy to manufactureAbsorbent padsBandagesColloidUltraviolet irradiation
The invention relates to a porous hydrogel preparation process which comprises the following steps: preparing mixed raw materials, quickly cooling the mixed raw materials, simultaneously introducing air, and stirring at a high speed to obtain porous bubble colloid; then, continuously coating the porous bubble colloid onto a substrate, and simultaneously performing ultraviolet irradiation to form a hydrogel layer; and finally, bonding a non-adhesive film on the hydrogel layer to form a porous bubble hydrogel sheet-like coiled material. The invention also provides a nonporous hydrogel preparation process. According to the invention, porous bubble hydrogel and nonporous hydrogel dressings can be manufactured in a continuous production mode, and the manufacturing process of the hydrogel dressings can be simplified, thereby greatly improving the preparation efficiency of the hydrogel dressings and achieving the purpose of lowering the hydrogel production cost.
Owner:古元安
New method for preparing porous hydrogel by adopting low temperature photopolymerization
The invention mainly relates to a new method for preparing porous hydrogel by adopting the low temperature photopolymerization. In the method, the temperature of the low temperature environment is 0-150 DEG C; the hydrogel uses one or two of epoxy acrylate, urethane acrylate, polyester acrylate, polyether acrylate and acrylic resin as a main body; and one or water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, acetonitrile, dioxane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, tetrahydrofuran, propanol, butanol, dichloromethane, toluene, diethyl ether, propyl ether, heptane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane and petroleum ether is used as solvent; the weight proportion of acrylic resin is 10%-500%; and the initiator adopts common photoinitiator BP, 651, 907, ITX, 1173, 184, 2959, 369, TPO, 819, CQ or 784 and is 0.1wt%-5wt% of acrylic resin.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
High-temperature proton exchange membrane in porous hydrogel base as well as preparation method and application of membrane
InactiveCN103094596AImprove conductivityImprove adsorption capacitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsHydrophilic monomerElectrical conductor
The invention provides a high-temperature proton exchange membrane in a porous hydrogel base as well as a preparation method and an application of the membrane. The preparation method of the high-temperature proton exchange membrane comprises the following steps of: automatically-polymerizing a hydrophilic monomer or enabling the hydrophilic monomer and a hydrophilic macromolecule to form a (semi) interpenetrating network structure hydrogel film; swelling the (semi) interpenetrating network structure hydrogel film by adsorbing deionized water; and adsorbing a proton conductor aqueous solution through vacuum-freezing and drying to obtain the high-temperature proton exchange membrane in the porous hydrogel base, wherein the proton conductivity of the prepared proton exchange membrane in the porous hydrogel base can reach 0.1S.cm<-1> to 0.15S.cm<-1>. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is better than the conventional preparation method for the proton exchange membrane doped with a proton conductor, and capable of adsorbing the proton conductor to the three-dimensional network structure of the hydrogel film and firmly sealing the proton conductor by utilizing the porous structure, the swelling property, the unique adsorption and the retainability of the hydrogel film. The high-temperature proton exchange membrane in the porous hydrogel base is large in proton conductor adsorbing capacity, high in proton conductivity, wide in operation temperature range, simple and easy in preparation method, low in cost and large in improvement space.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
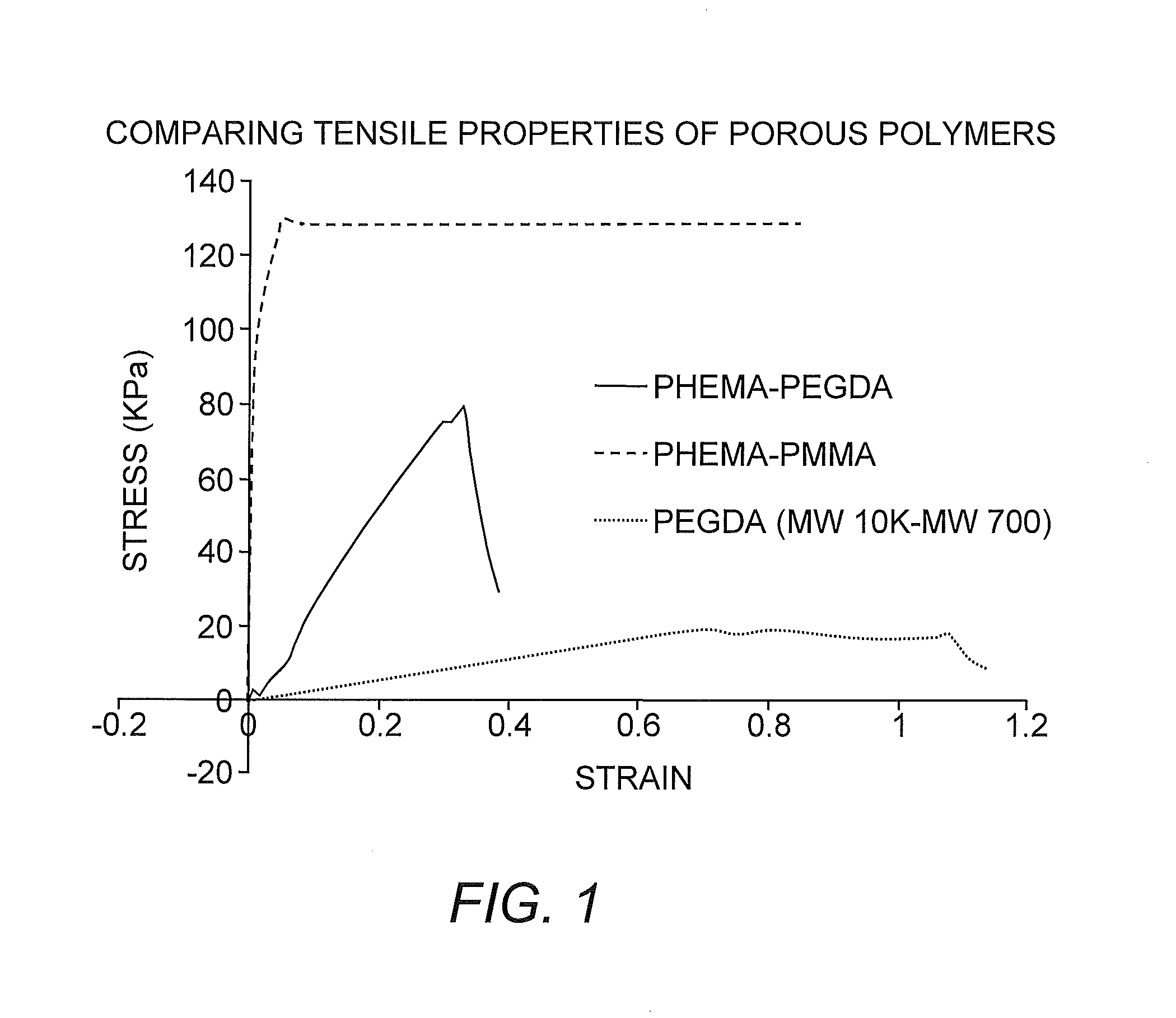
Suturable Hybrid Superporous Hydrogel Keratoprosthesis for Cornea
The present invention features a hybrid superporous hydrogel scaffold for cornea regeneration and a method for producing the same. The hybrid hydrogel is composed of a superporous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) copolymer mixed with collagen. The hybrid scaffold can be used as a suturable hybrid corneal implant or keratoprosthesis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Shaped article made of porous hydrogel, manufacturing process therefor and use thereof
ActiveUS20140353248A1High strengthImprove survivabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolymer sciencePolyvinyl alcohol
There is provided a shaped article made of porous hydrogel that contains a polyvinyl alcohol acetalized with a dialdehyde, wherein the shaped article after freeze-drying has a pore size of 0.1 to 50 μm. Preferably, the shaped article made of porous hydrogel further contains a water-soluble polysaccharide. Also preferably, an acetalization degree of the polyvinyl alcohol is 1 to 50 mol %. Also preferably, the shaped article made of porous hydrogel is in the form of particles with a sphere-equivalent diameter of 1 to 20 mm. Such a shaped article made of porous hydrogel exhibits high strength and good survivability of microorganisms.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Multi-component non-biodegradable implant, a method of making and a method of implantation
ActiveUS9545310B2Maximizes integrationHigh and low viscosityBone implantSurgeryBiodegradable implantsBiomedical engineering
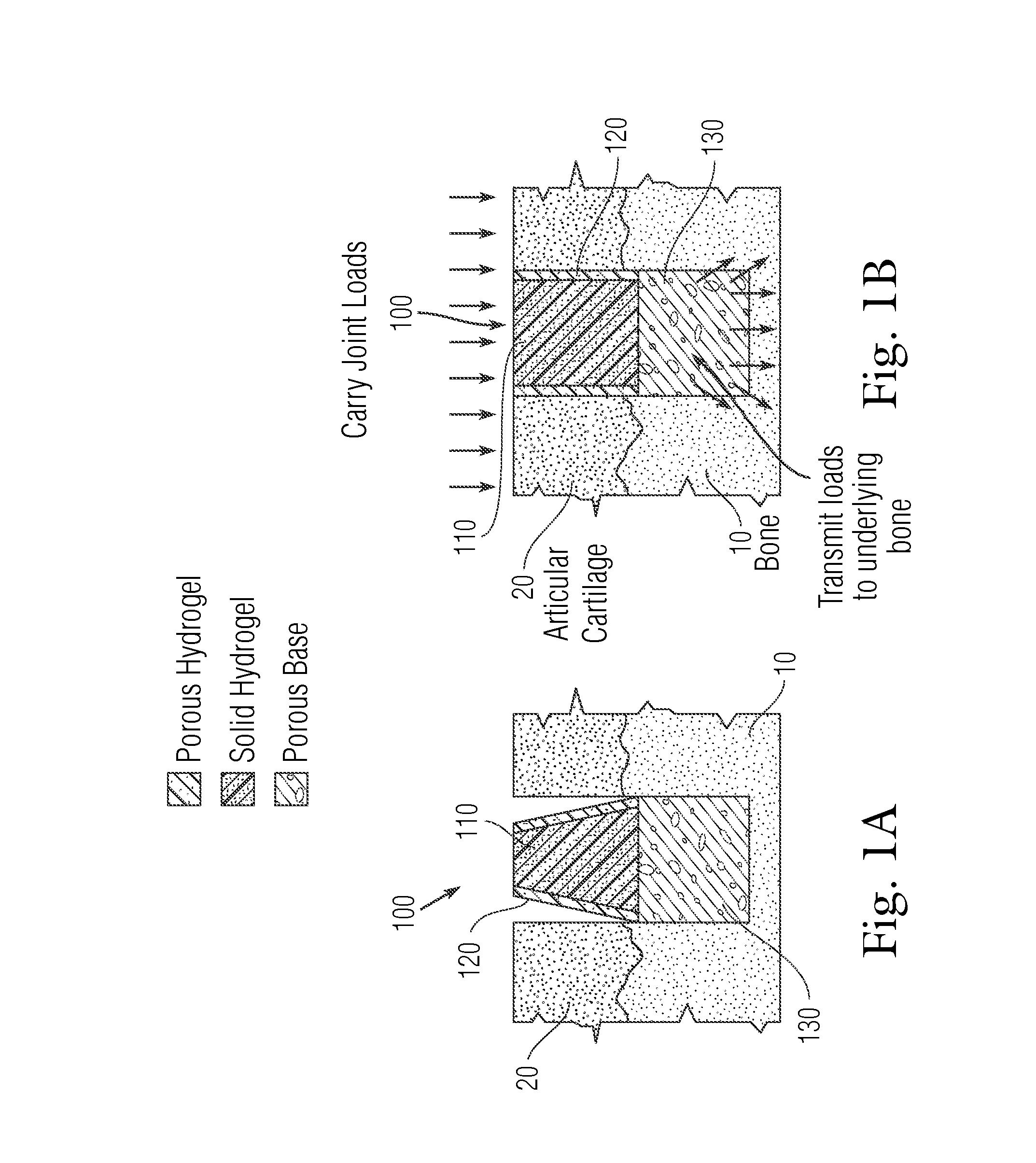
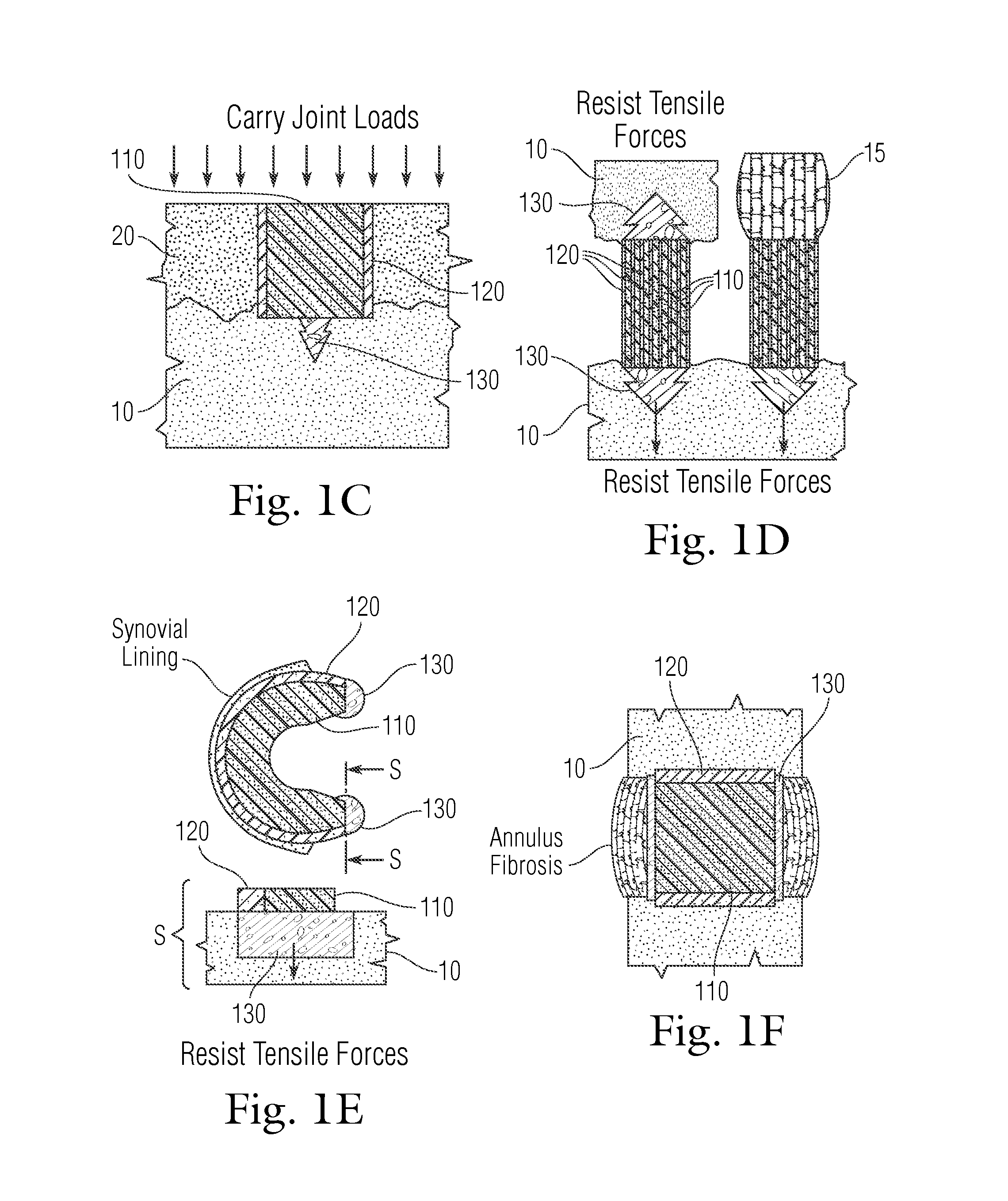
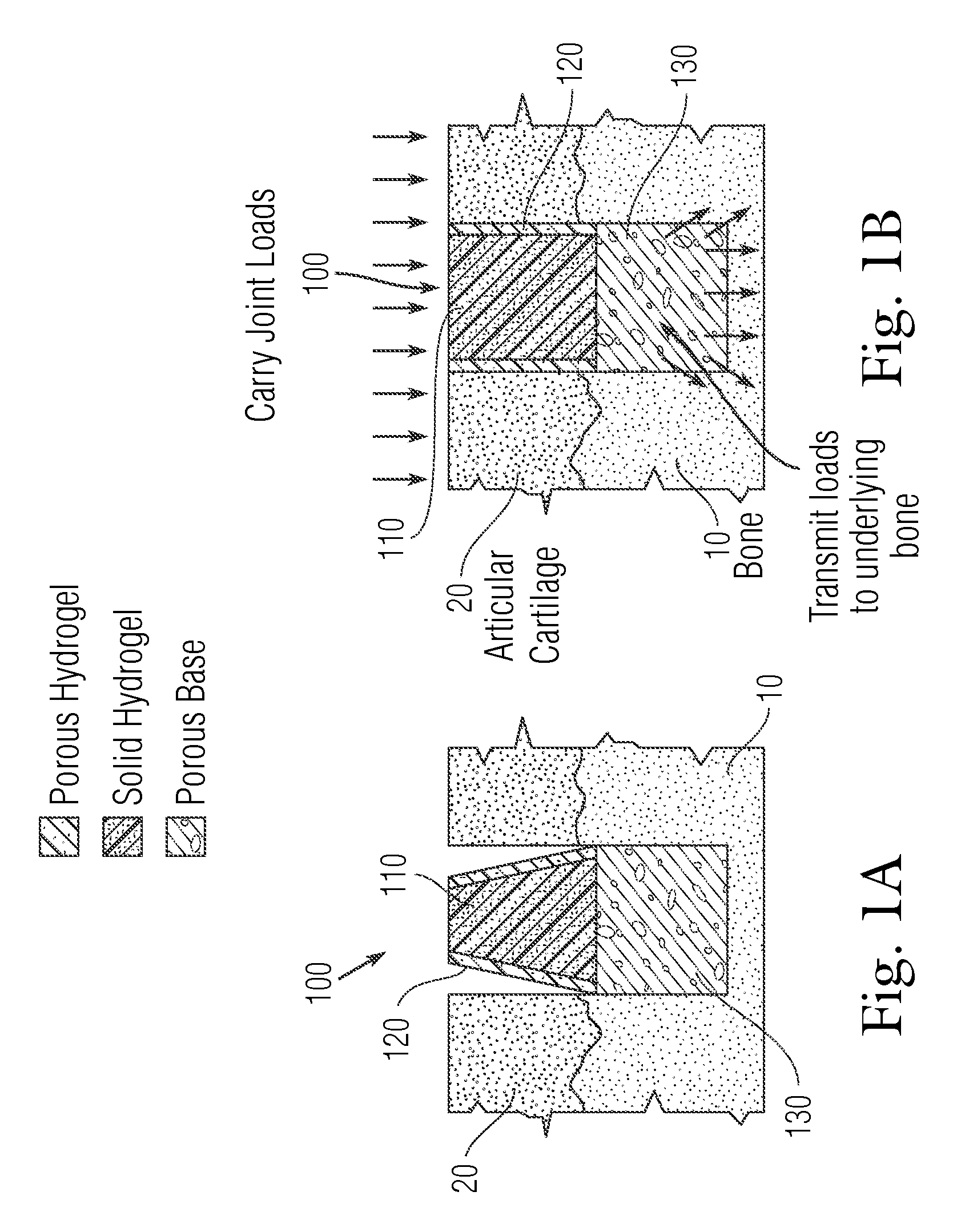
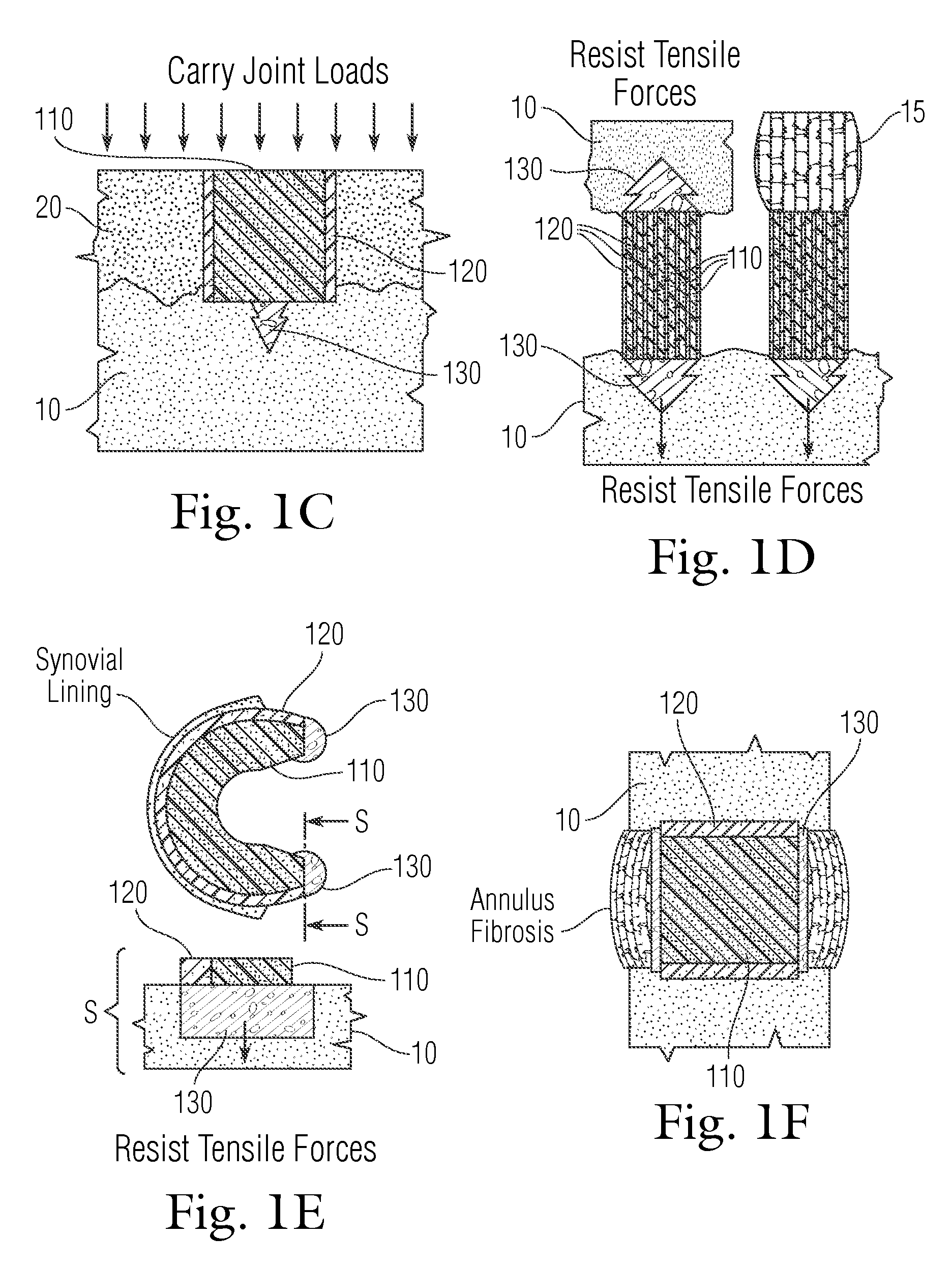
An implant having at least three components, namely, a solid hydrogel, a porous hydrogel adjacent to or surrounding the solid hydrogel (together considered “the hydrogel”), and a porous rigid base. The solid hydrogel and porous rigid base carry joint load, and the porous hydrogel layer and the porous rigid base allow for cellular migration into and around the implant. The invention is also a novel method of manufacturing the implant, a novel method of implanting the implant, and a method of treating, repairing or replacing biological tissue, more preferably musculoskeletal tissue, with the implant.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Substitute material for repairing articular cartilage and preparation method
The invention relates to a substitute material for rehabilitating articular cartilage and a preparation method thereof. A substitute material body is a porous hydrogel structural body with an interpenetrating network structure polymerized by PVA and PVP type components; the mass ratio of polyvinyl alcohol to pyrrolidone type components is 1: (0.01 to 1); and the elastic modulus is 0.5 to 10 MPa. The substitute material is prepared by adopting an in-situ solution polymerization method and the preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the monomers of the PVP type components in PVA solution and mixing completely and uniformly; adding a free radical initiator and polymerizing to obtain a blending system of the PVP type components; then adding a cross-linking agent to continuously carry out cross-linking polymerization reaction to obtain a hydrogel product; and finally preparing the substitute material through repeatedly freezing / unfreezing till the hardness reach the expected index. The substitute material is of a porous structure with an interpenetrating network which can contain a large amount of water and is a permeable material; liquid can be permeated and extruded as a lubricant under the load action; and furthermore, the substitute material has good mechanical strength approximate to the mechanical property of the articular cartilage, is similar to natural cartilage tissues, and has good biological compatibility.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing porous hydrogel through freezing-illumination
ActiveUS20170210864A1Convenient and efficient controlRegulate the spatial distribution of the pore structure within a gelSulfurWavelength
The present invention discloses a freezing-illumination method for preparing porous gels, comprising the steps of: (a) synthesizing the gels containing dynamic exchangeable bonds; (b) illuminating the gels under frozen state by certain wavelength light source; (c) elevating the temperature and melt the ice crystals within the gels to get the porous structure. The dynamic exchangeable bonds existing in the gels include double / multi-sulfur bond, hydrazine bond, boronic ester bond. Catalyst is also included in the gel composition to activate the bond exchange reactions under illumination. This new method for preparing porous gels is easy to operate and suitable for most kinds of gels. Meanwhile, it can spatially control the pore structure within the gels by local illumination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com