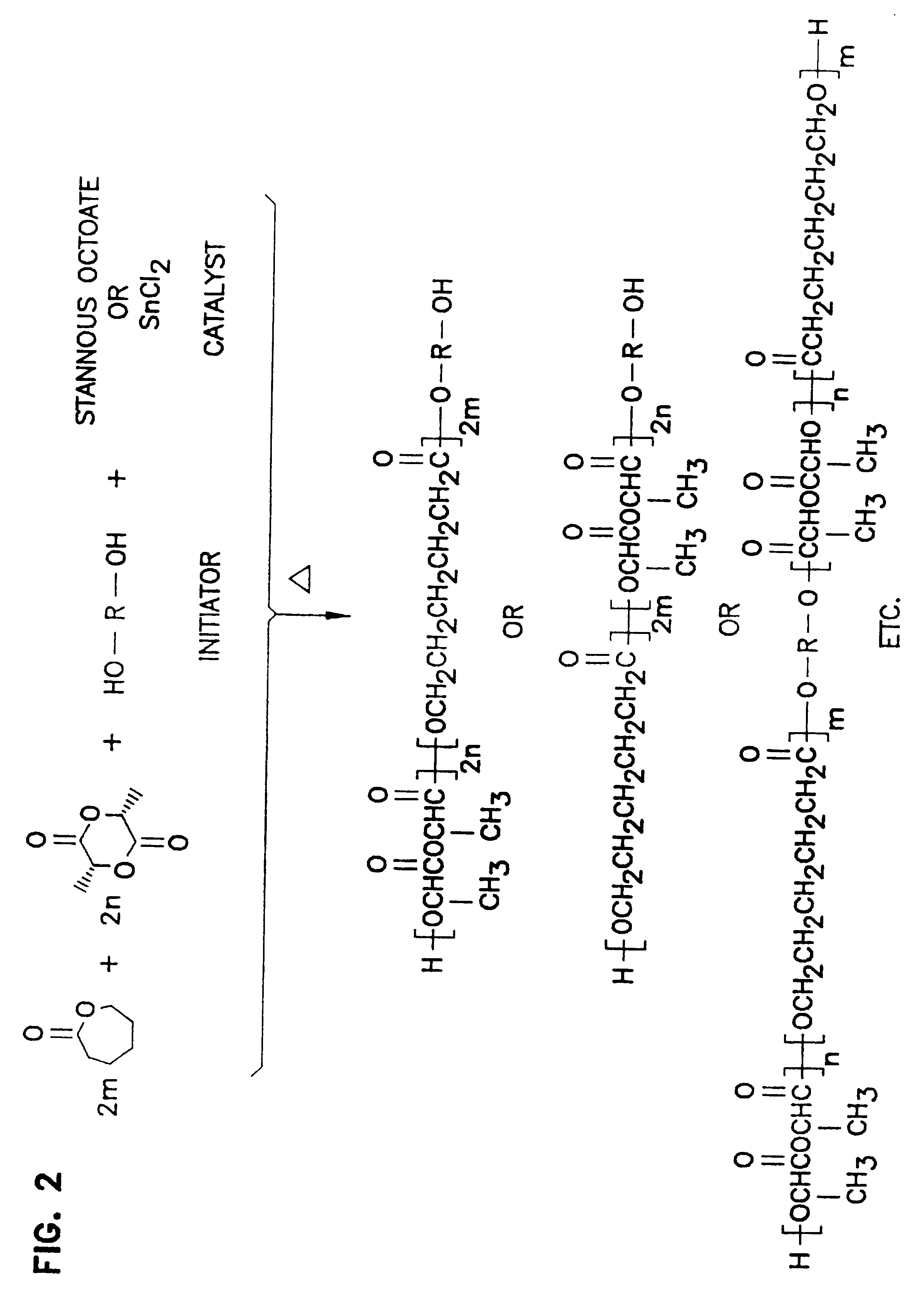
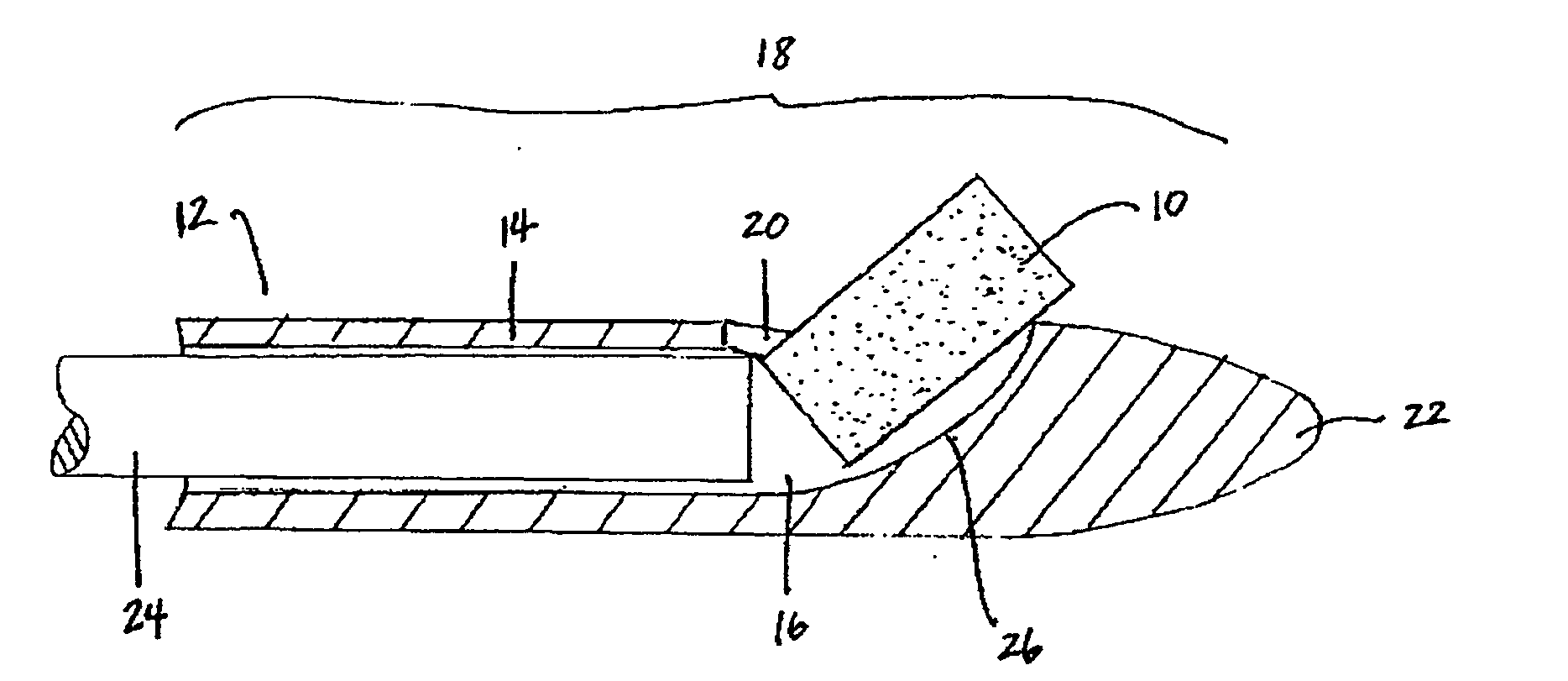
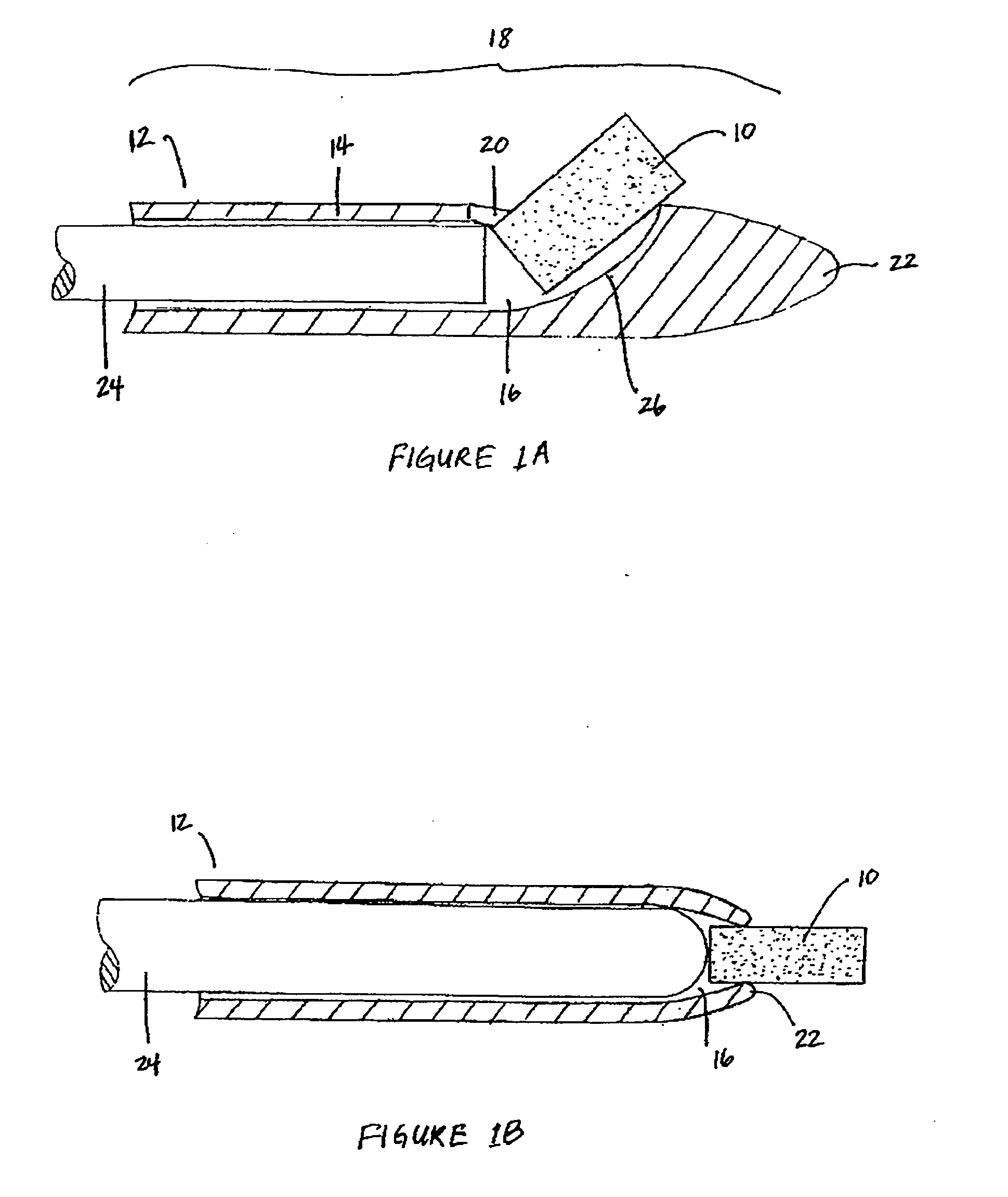
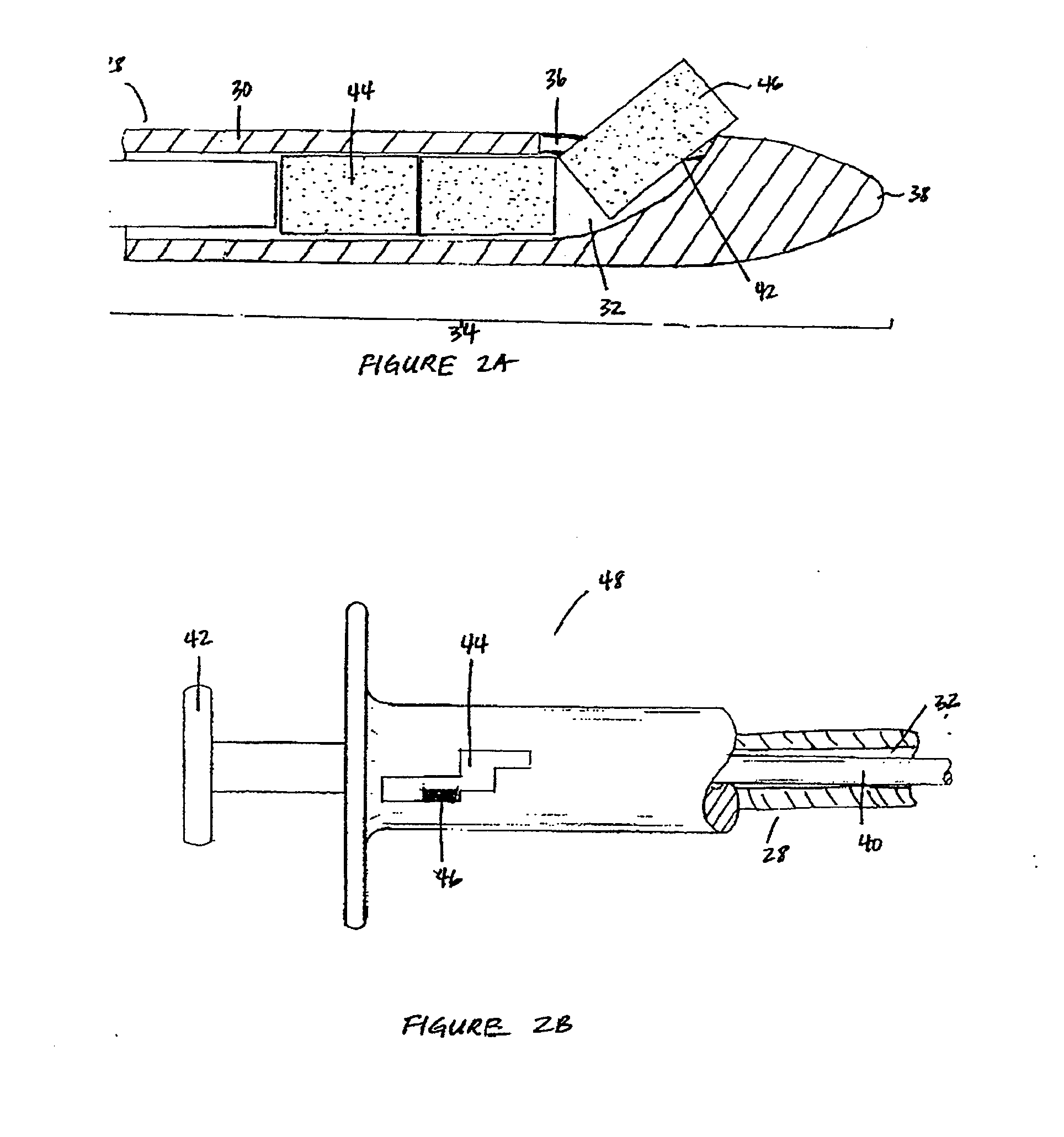
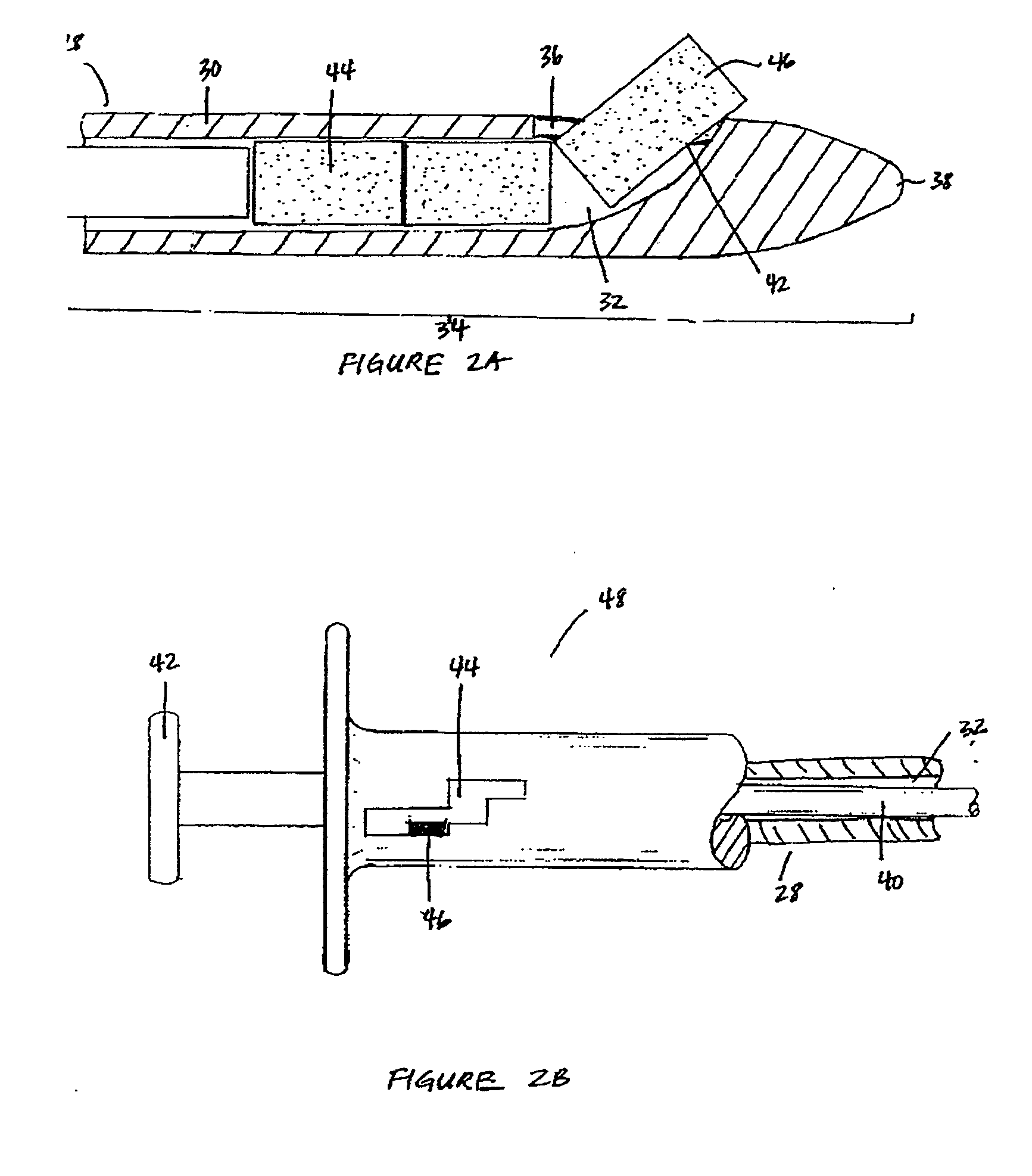
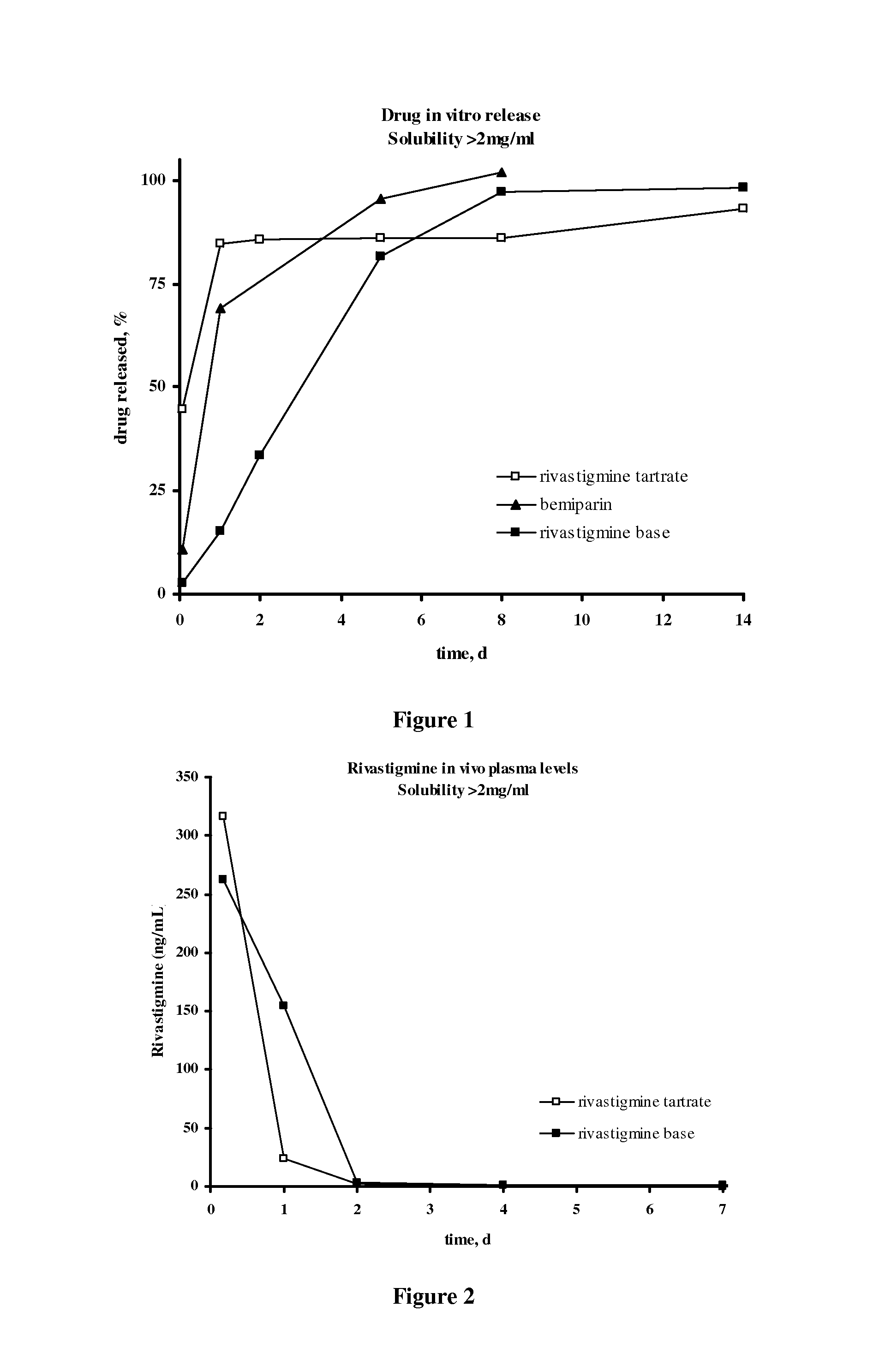
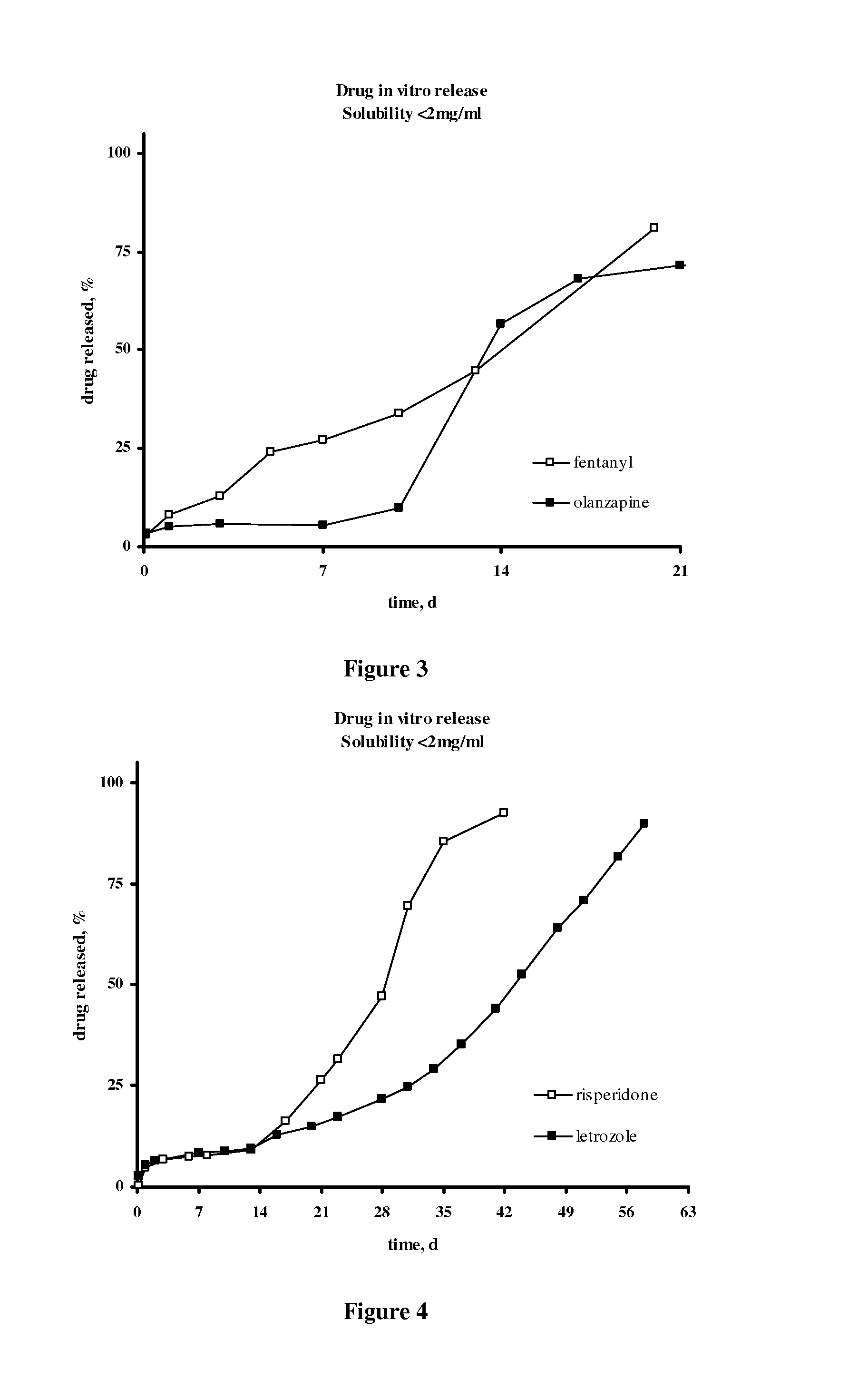
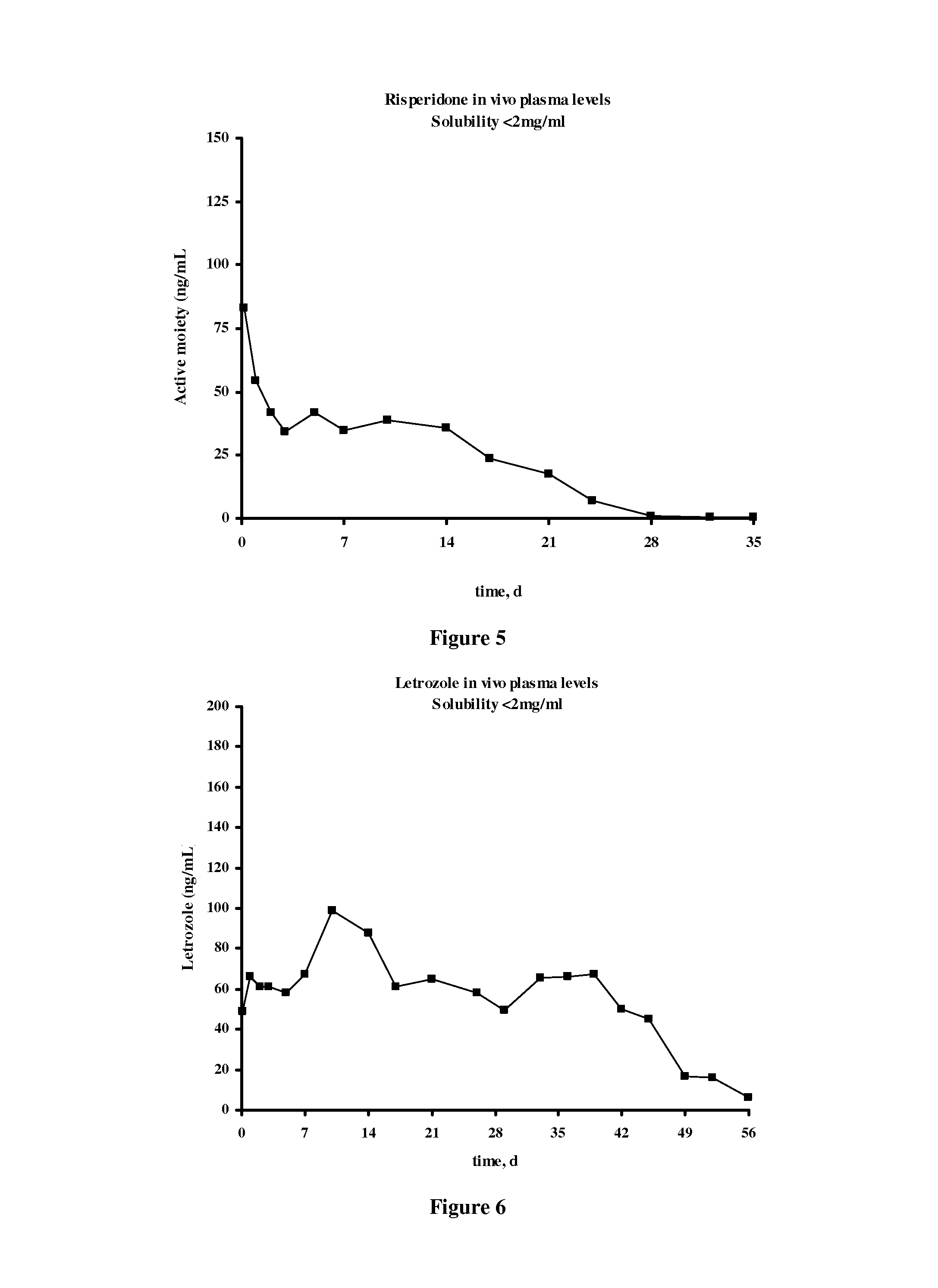
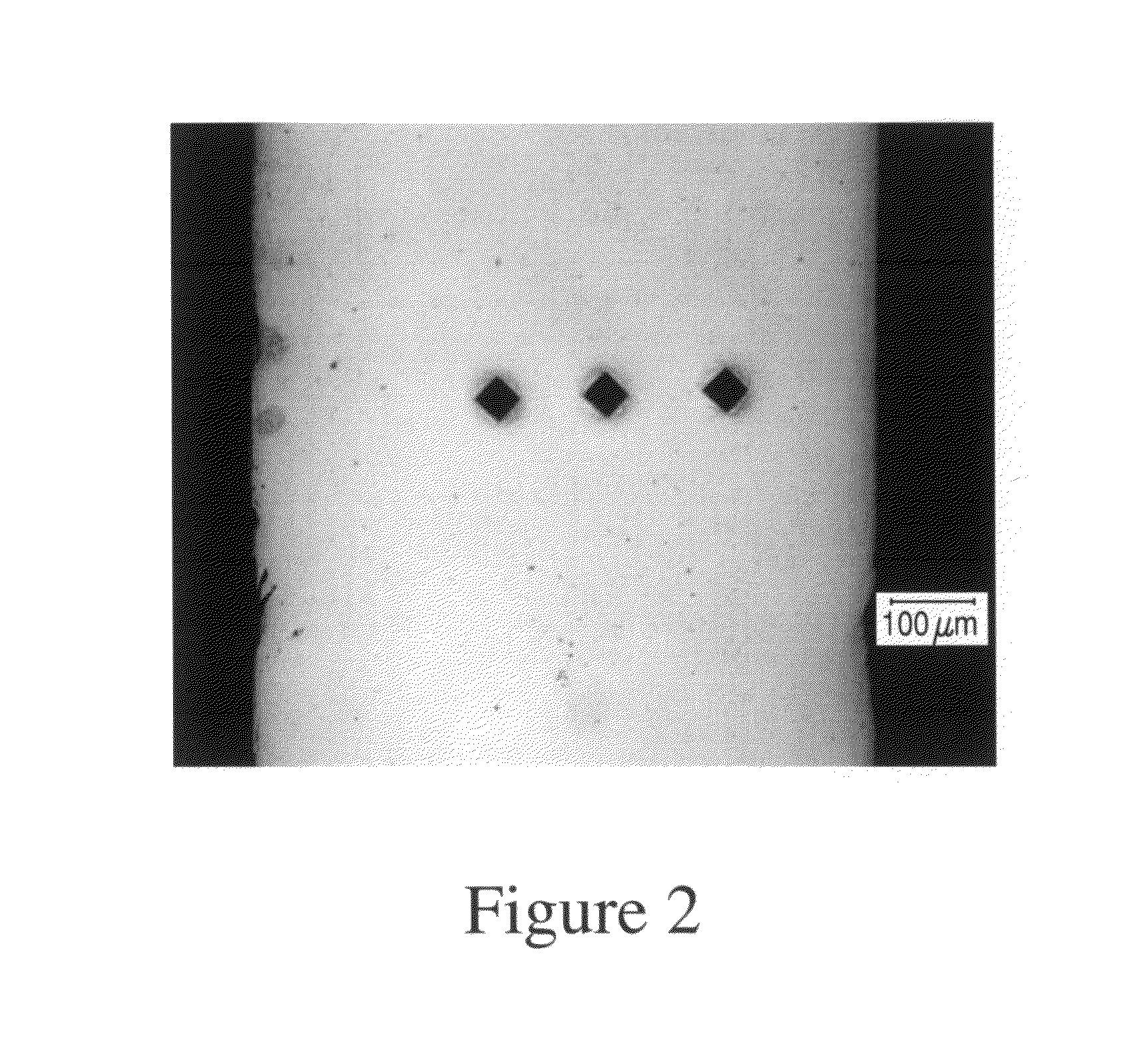
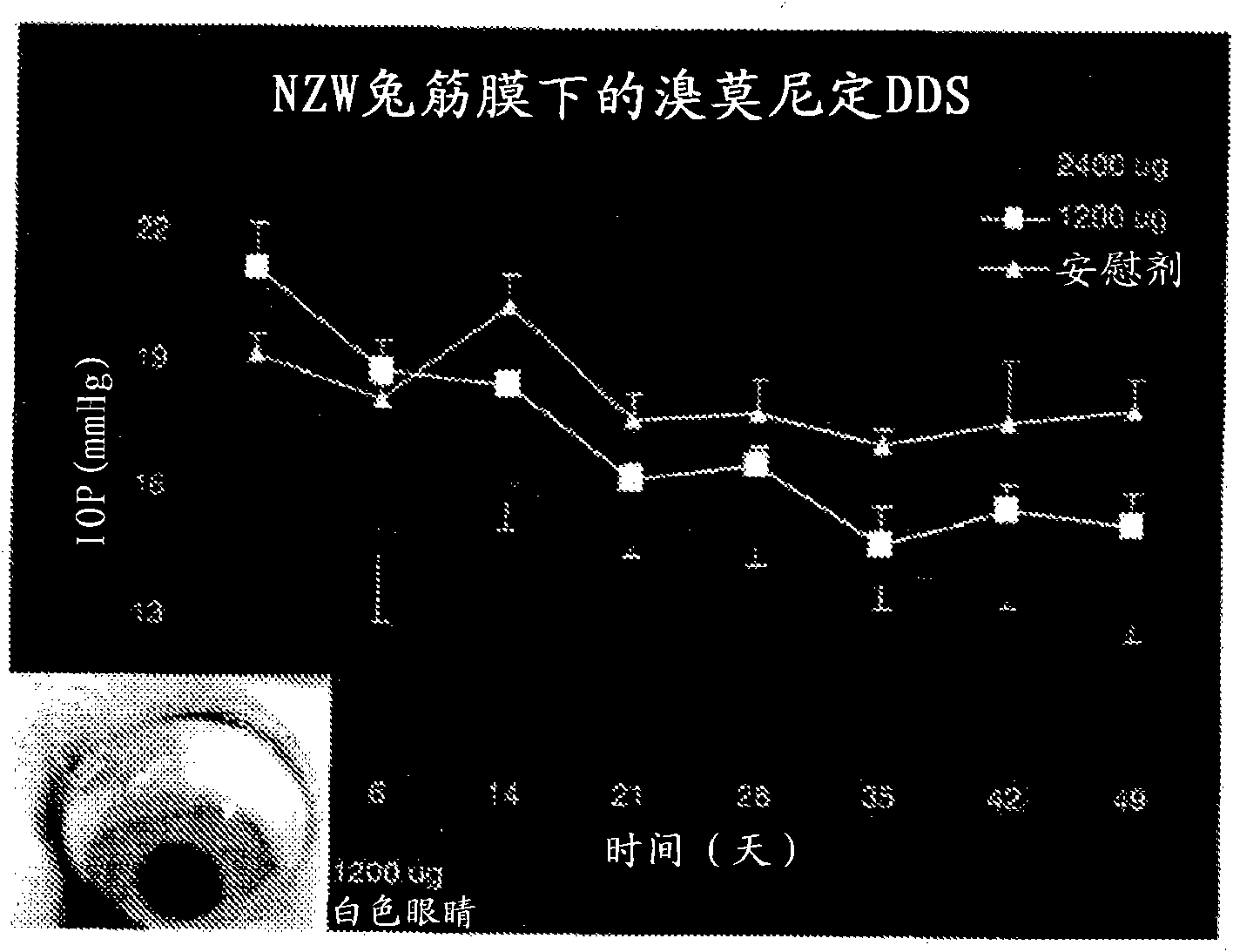
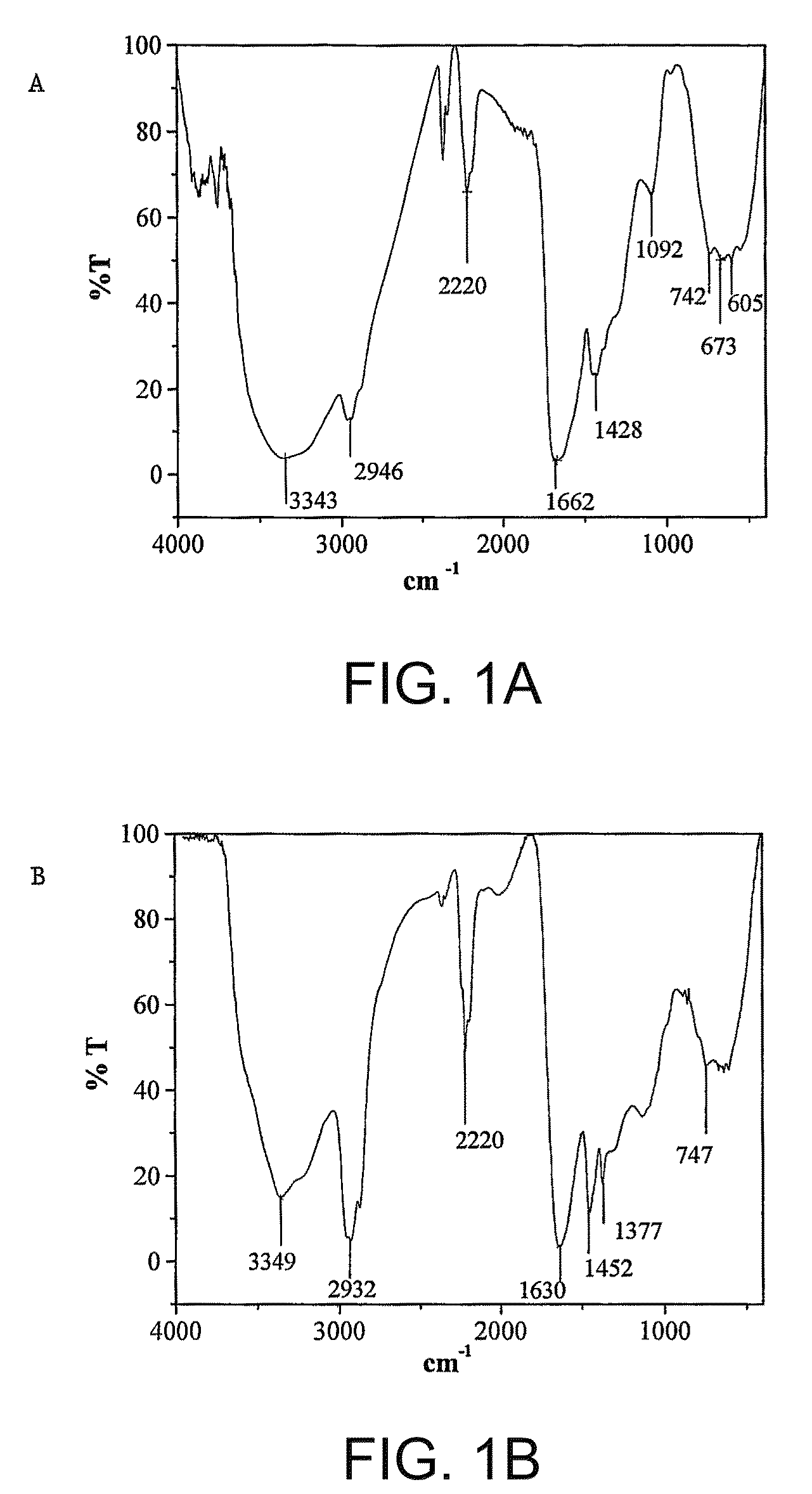
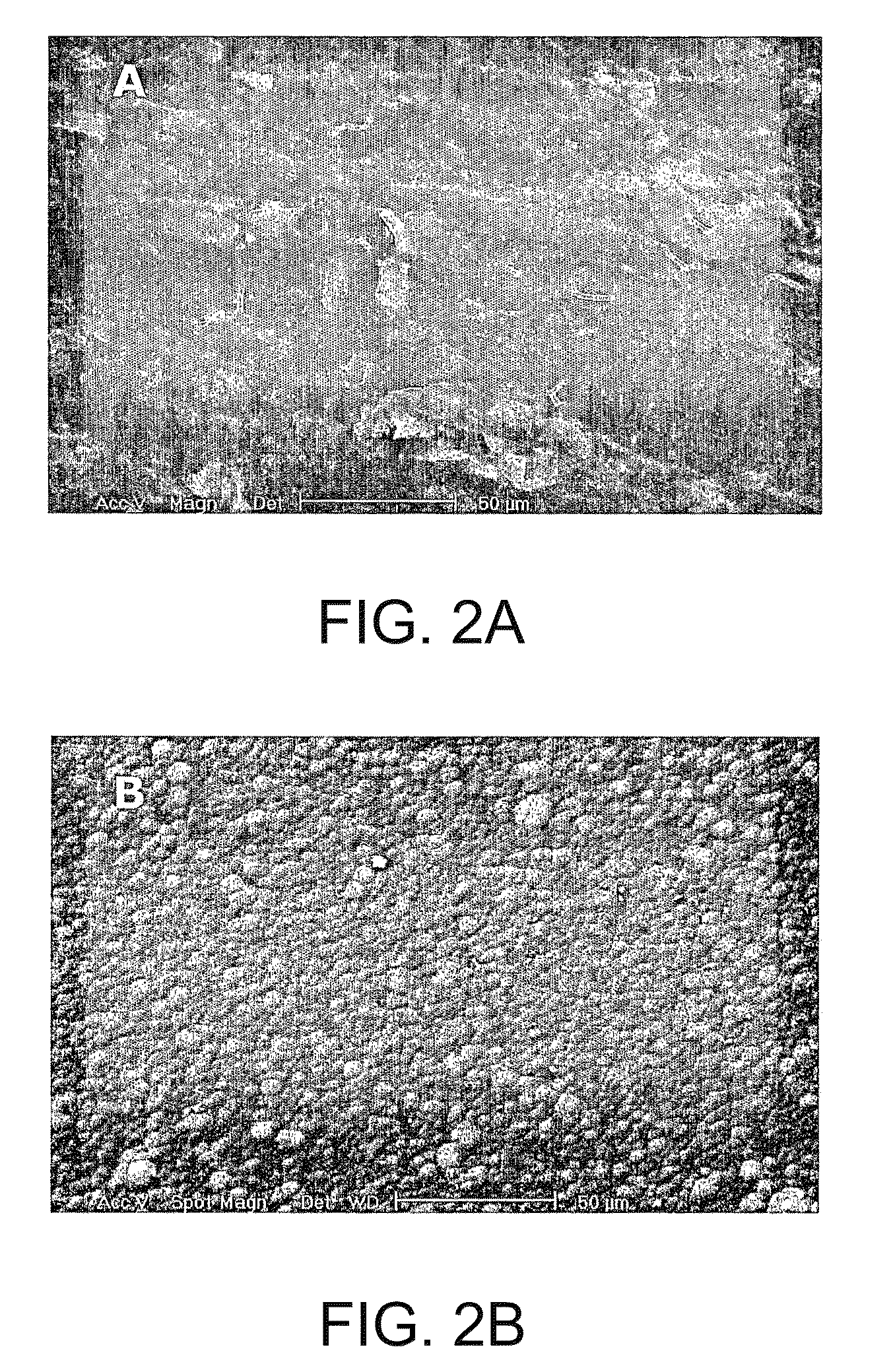
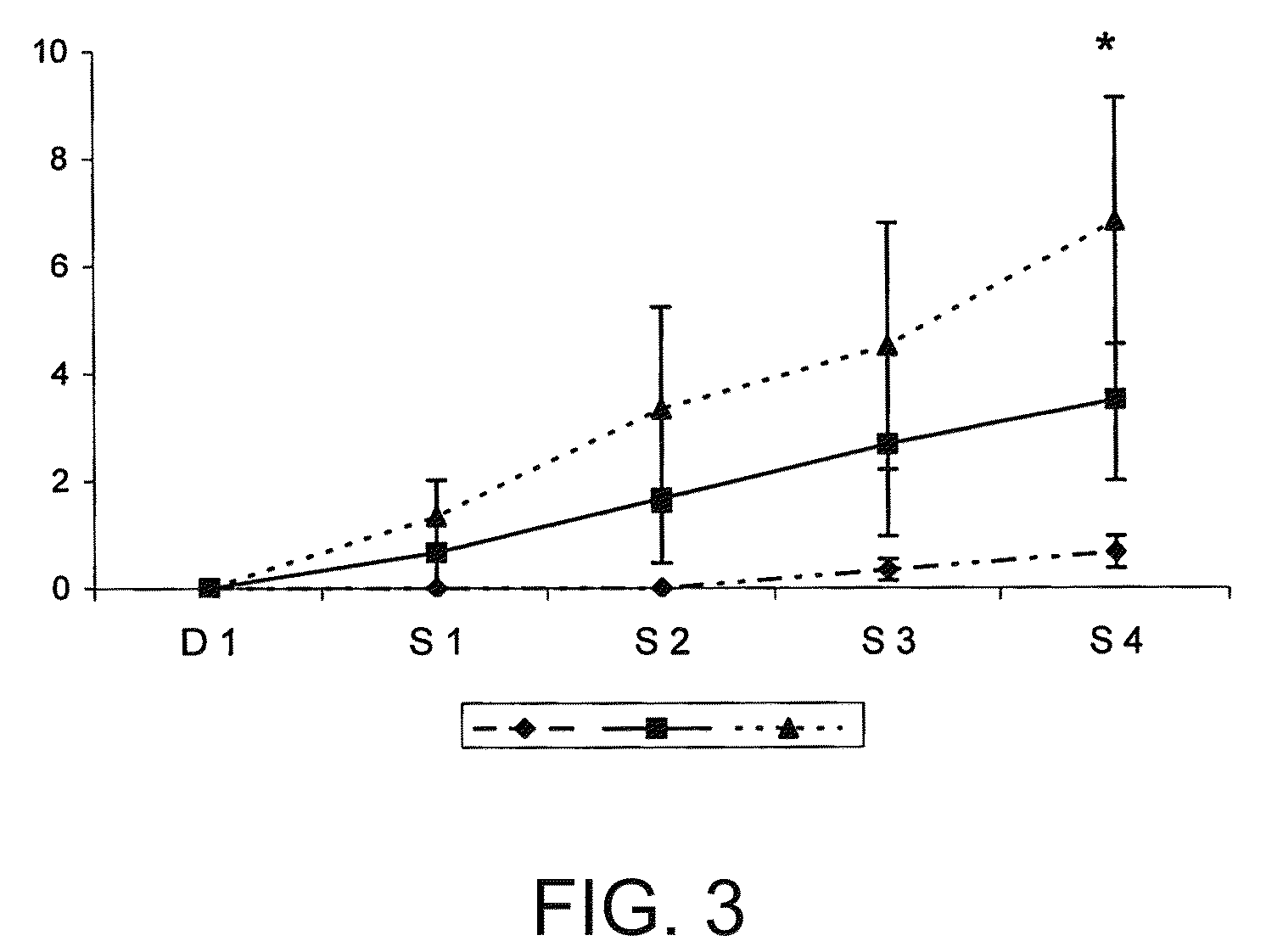
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Biodegradable implants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
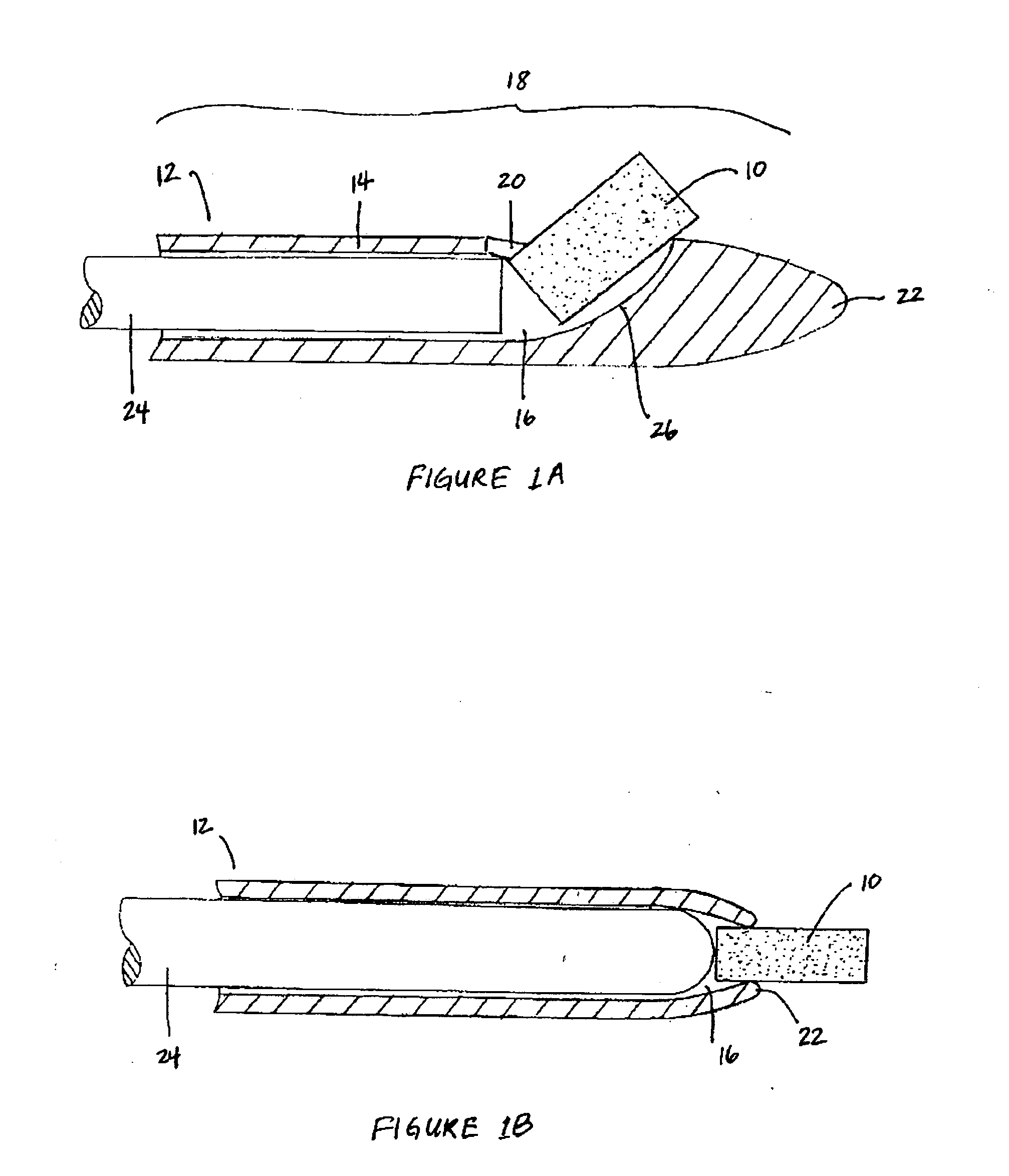
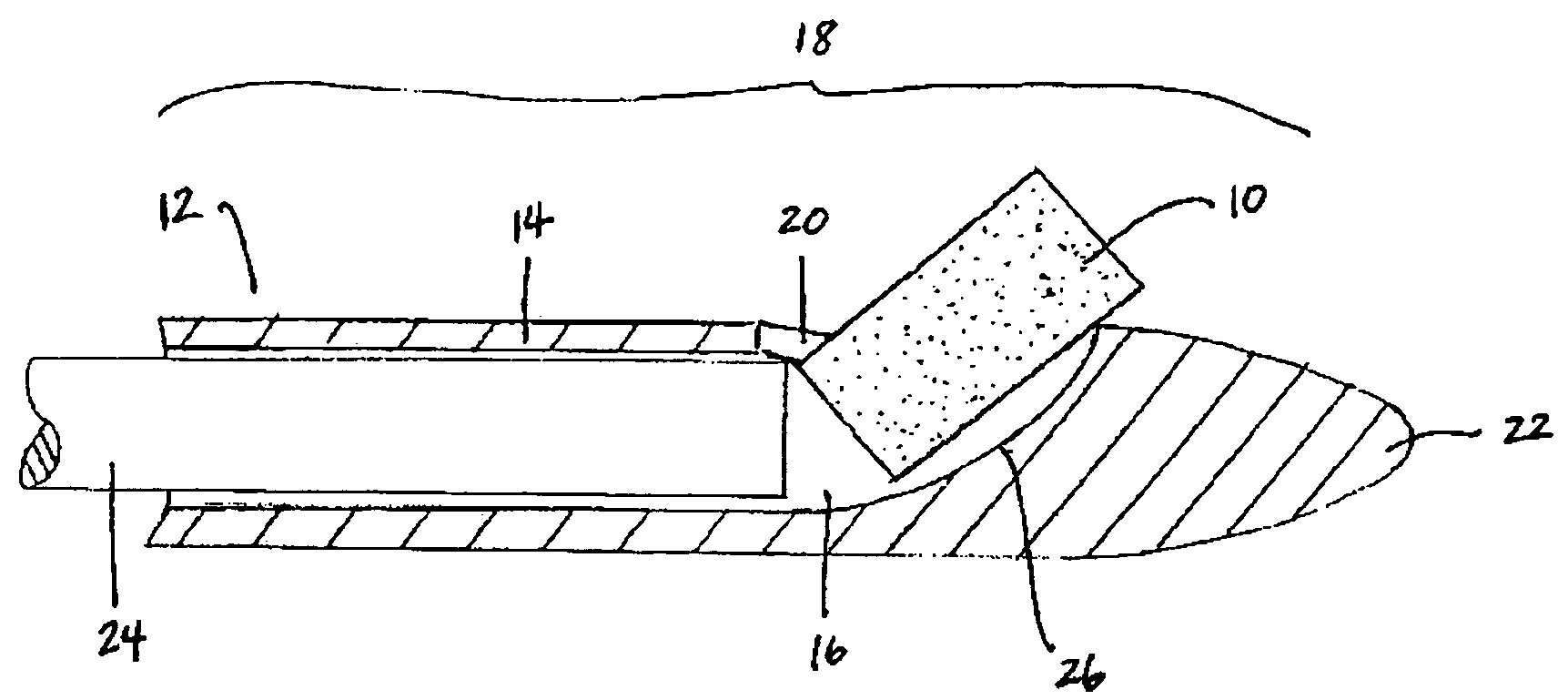
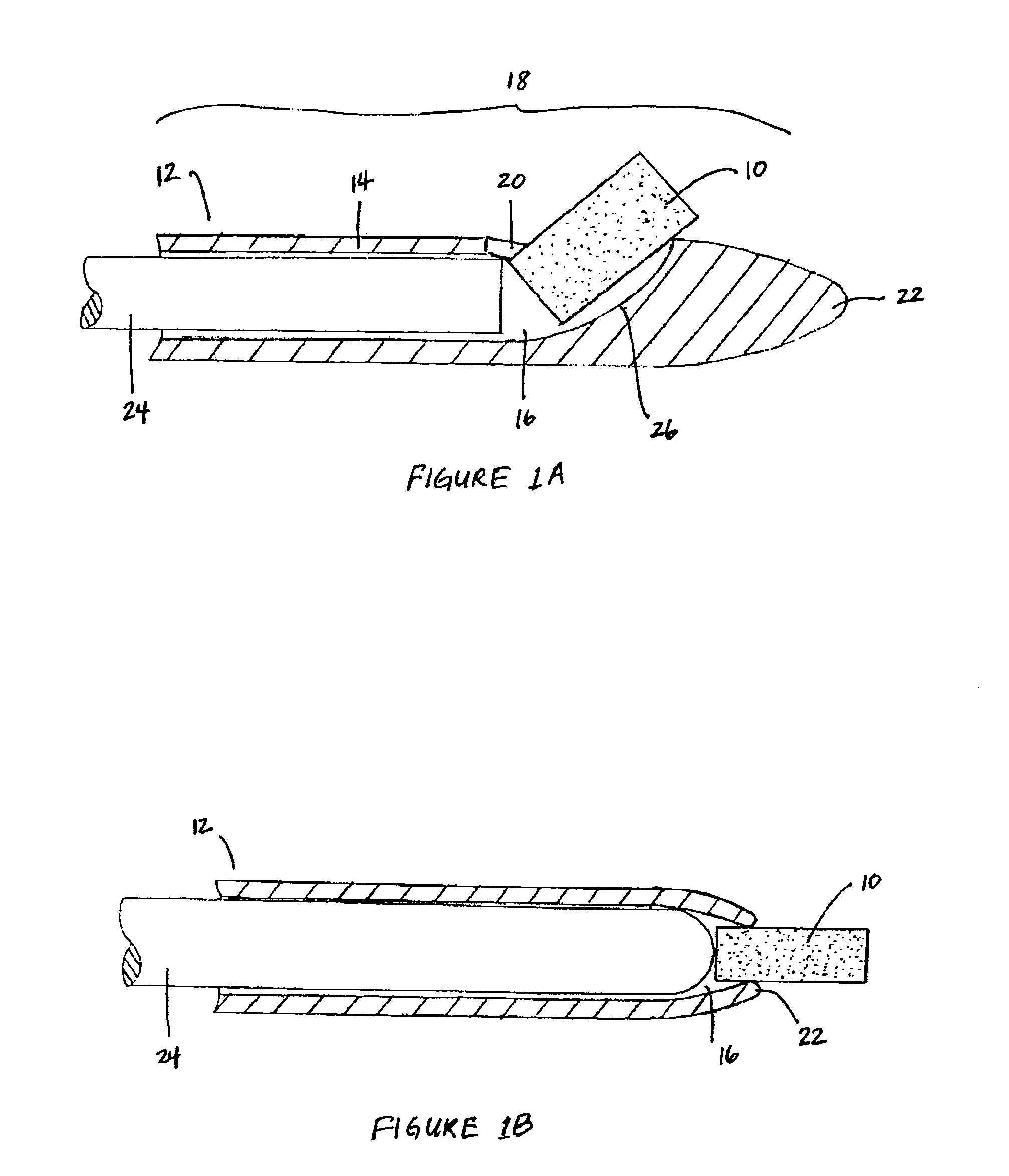
In contrast, biodegradable implants are infiltrated by FBGCs that phagocytose and completely degrade the biomaterial. Since resorption of the biodegradable implant is the ultimate goal, and the regression of FBGCs is seen with the resorption of the biomaterial, the FBGCs are not indicative of insufficient biocompatibility and implant failure.
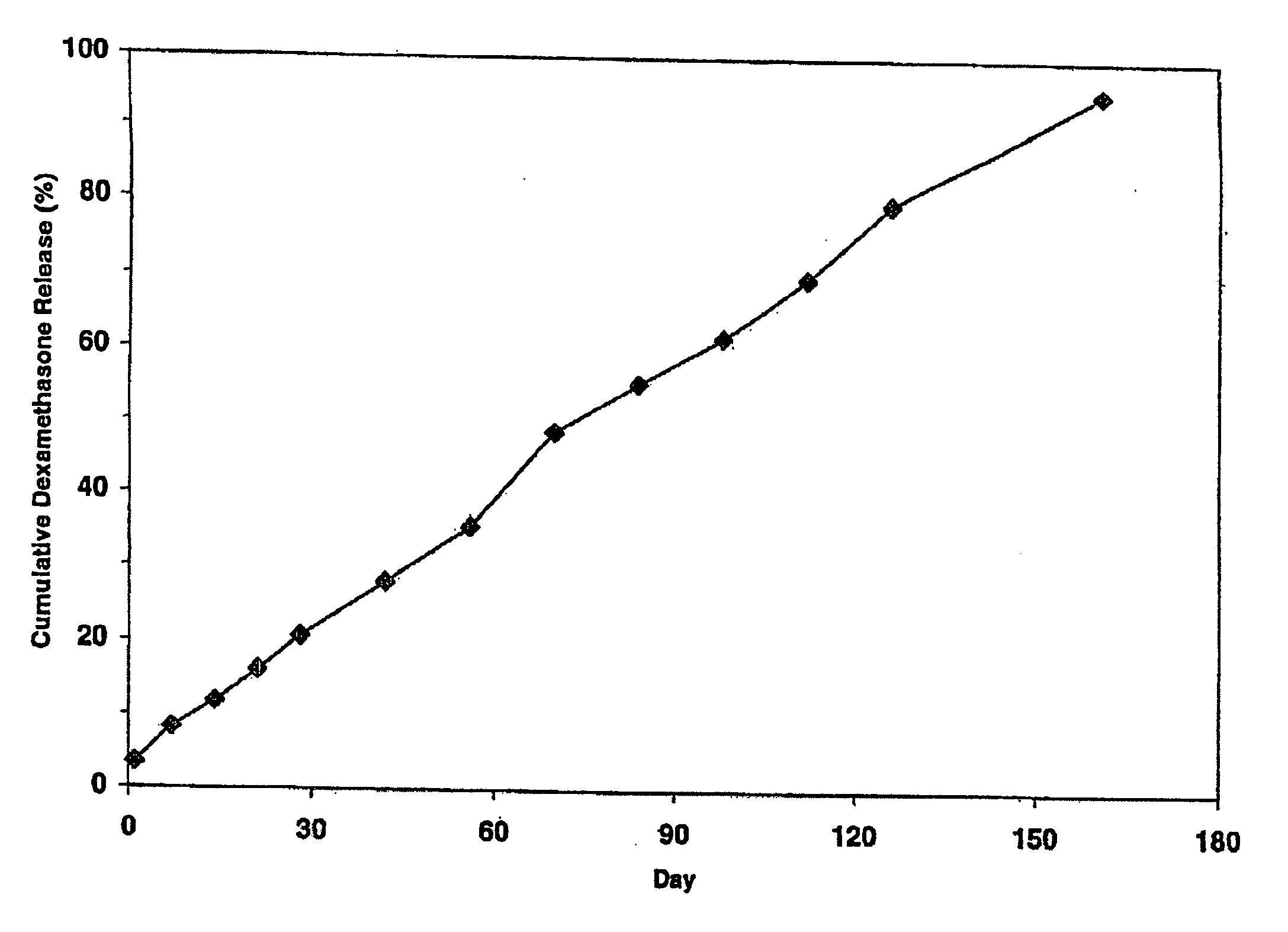
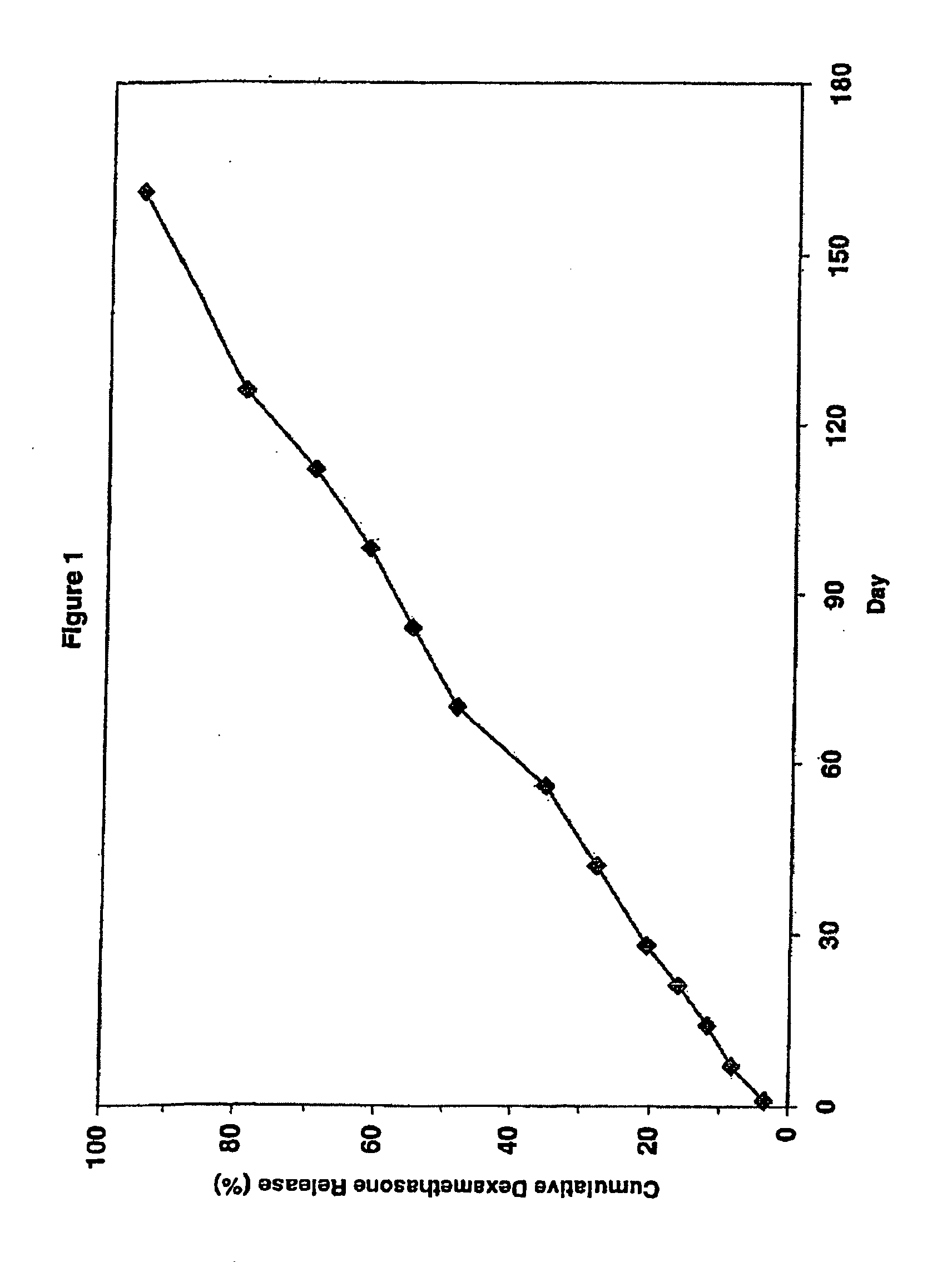
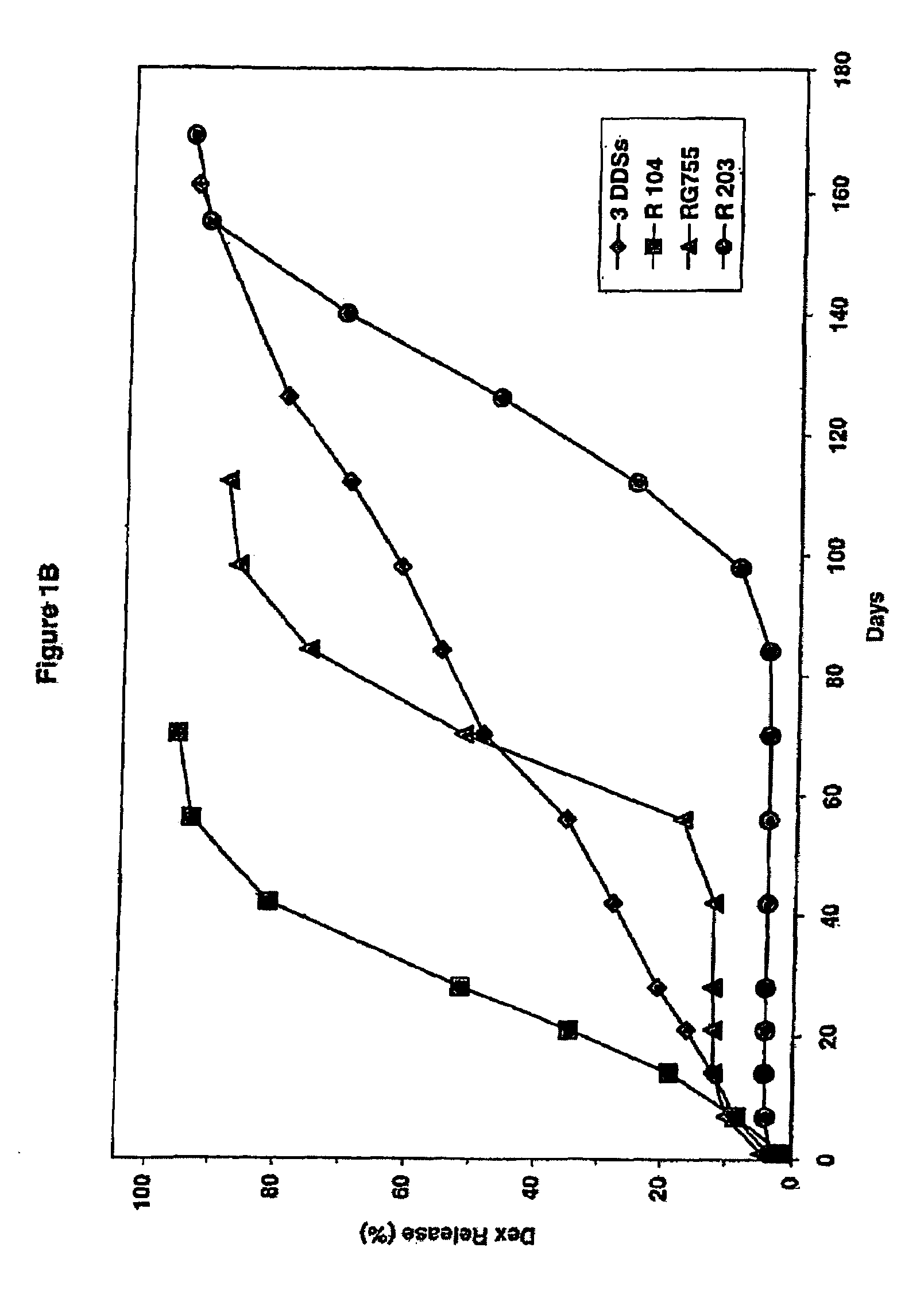
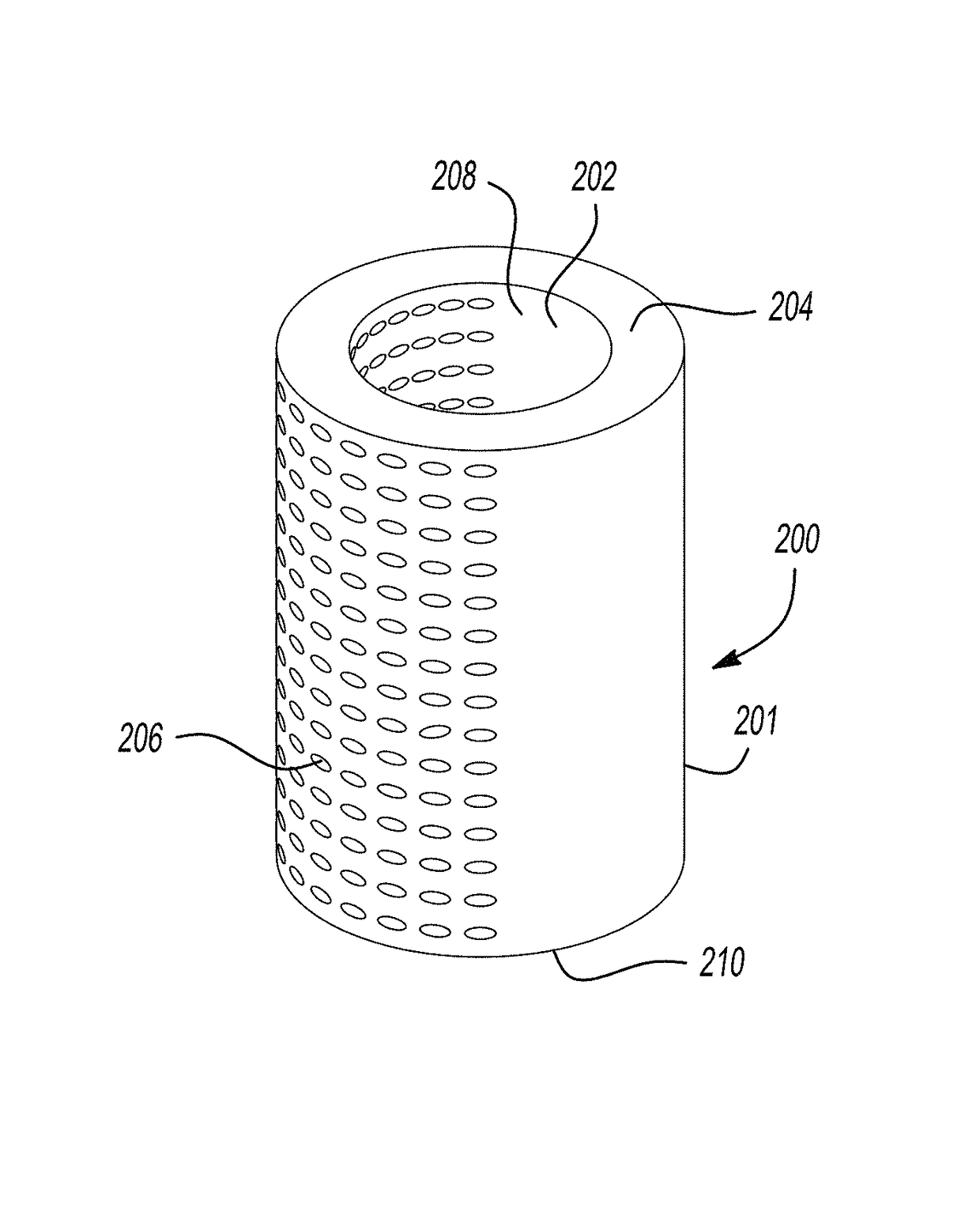
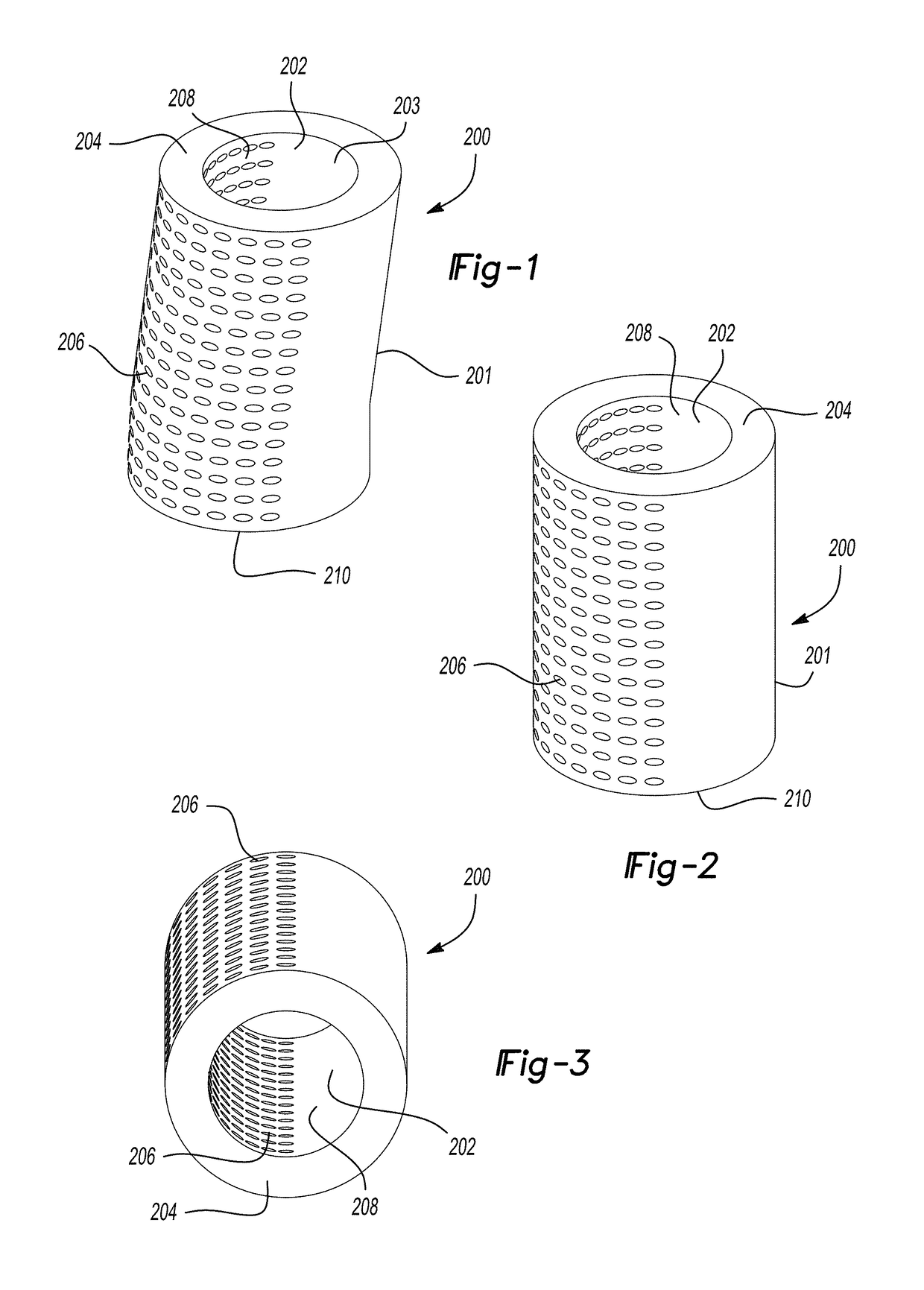
Extended release biodegradable ocular implants
Biodegradable implants sized and suitable for implantation in an ocular region or site and methods for treating ocular conditions. The implants provide an extended release of an active agent at a therapeutically effective amount for a period of time between 50 days and one year, or longer.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Sinus delivery of sustained release therapeutics
ActiveUS20050043706A1Easy accessReduce inflammationMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSinusitisMicroparticle
The invention provides biodegradable implants for treating sinusitis. The biodegradable implants have a size, shape, density, viscosity, and / or mucoadhesiveness that prevents them from being substantially cleared by the mucociliary lining of the sinuses during the intended treatment period. The biodegradable implants include a sustained release therapeutic, e.g., an antibiotic, a steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, or both. The biodegradable implants may take various forms, such as rods, pellets, beads, strips, or microparticles, and may be delivered into a sinus in various pharmaceutically acceptable carriers.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
Sinus delivery of sustained release therapeutics
The invention provides biodegradable implants for treating sinusitis. The biodegradable implants have a size, shape, density, viscosity, and / or mucoadhesiveness that prevents them from being substantially cleared by the mucociliary lining of the sinuses during the intended treatment period. The biodegradable implants include a sustained release therapeutic, e.g., an antibiotic, a steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, or both. The biodegradable implants may take various forms, such as rods, pellets, beads, strips, or microparticles, and may be delivered into a sinus in various pharmaceutically acceptable carriers.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
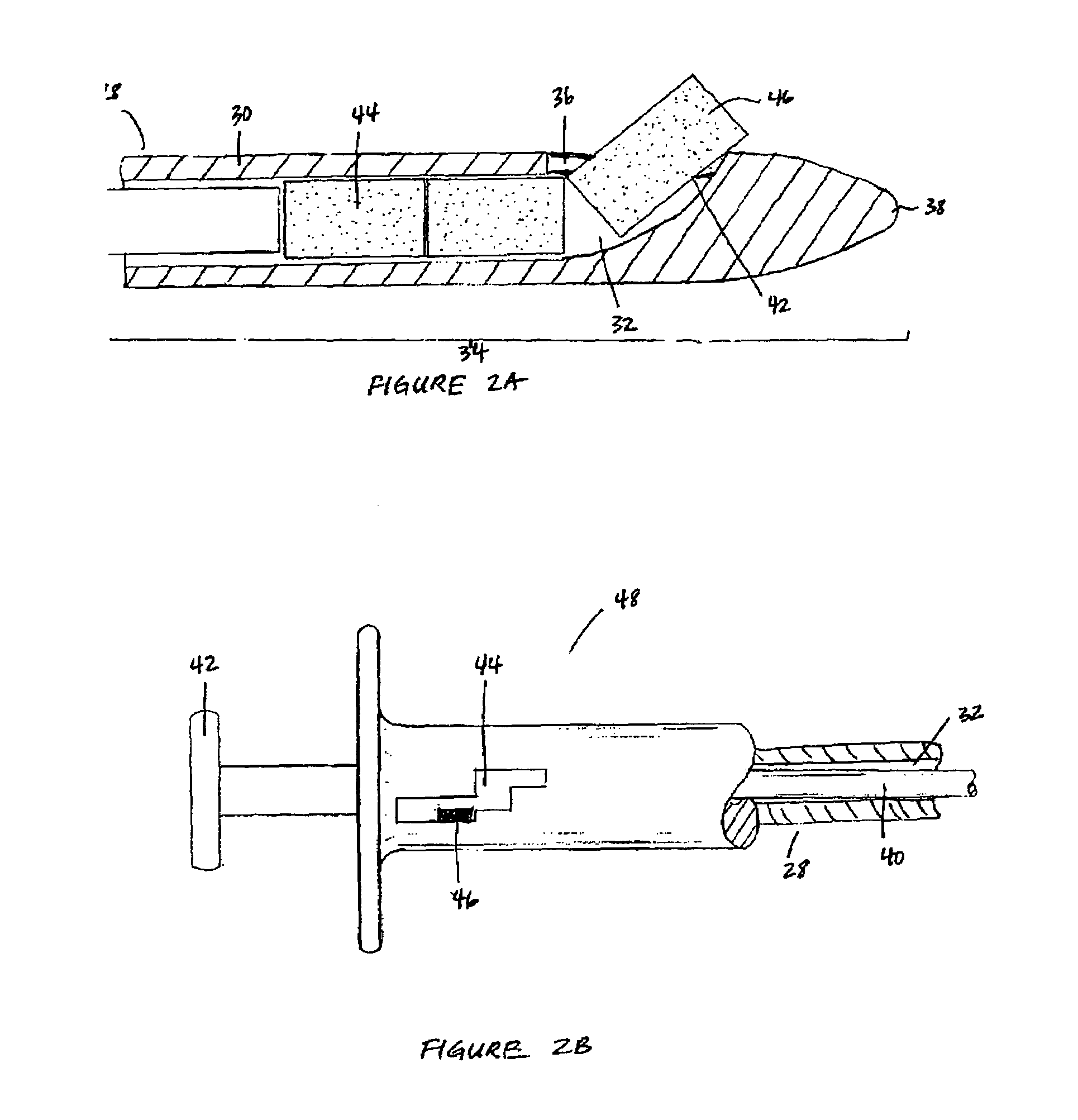
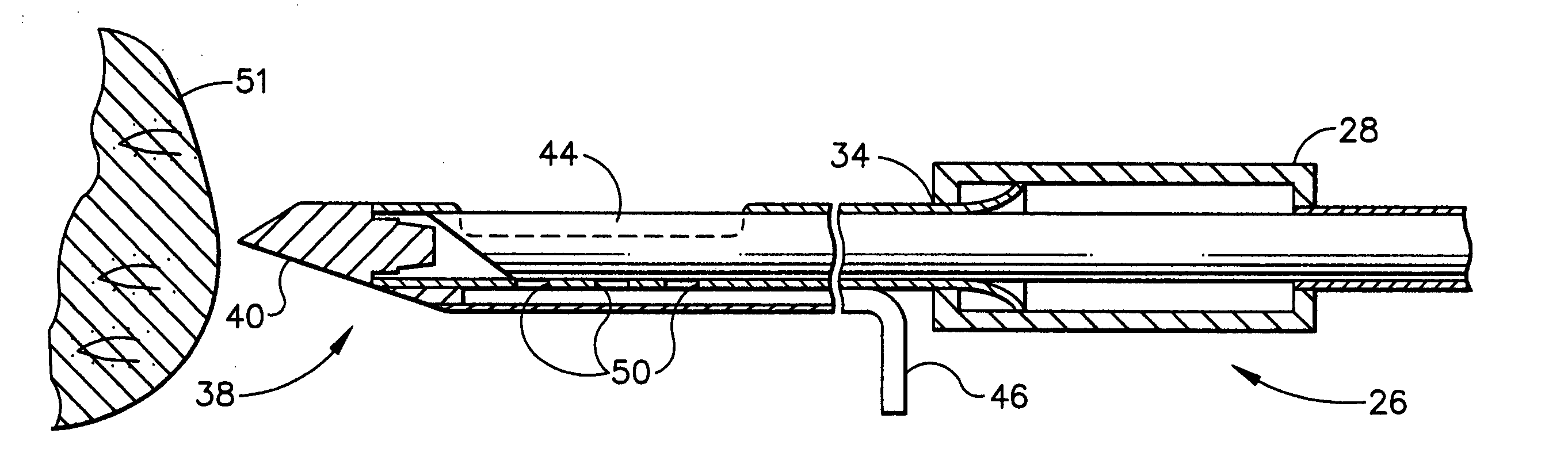
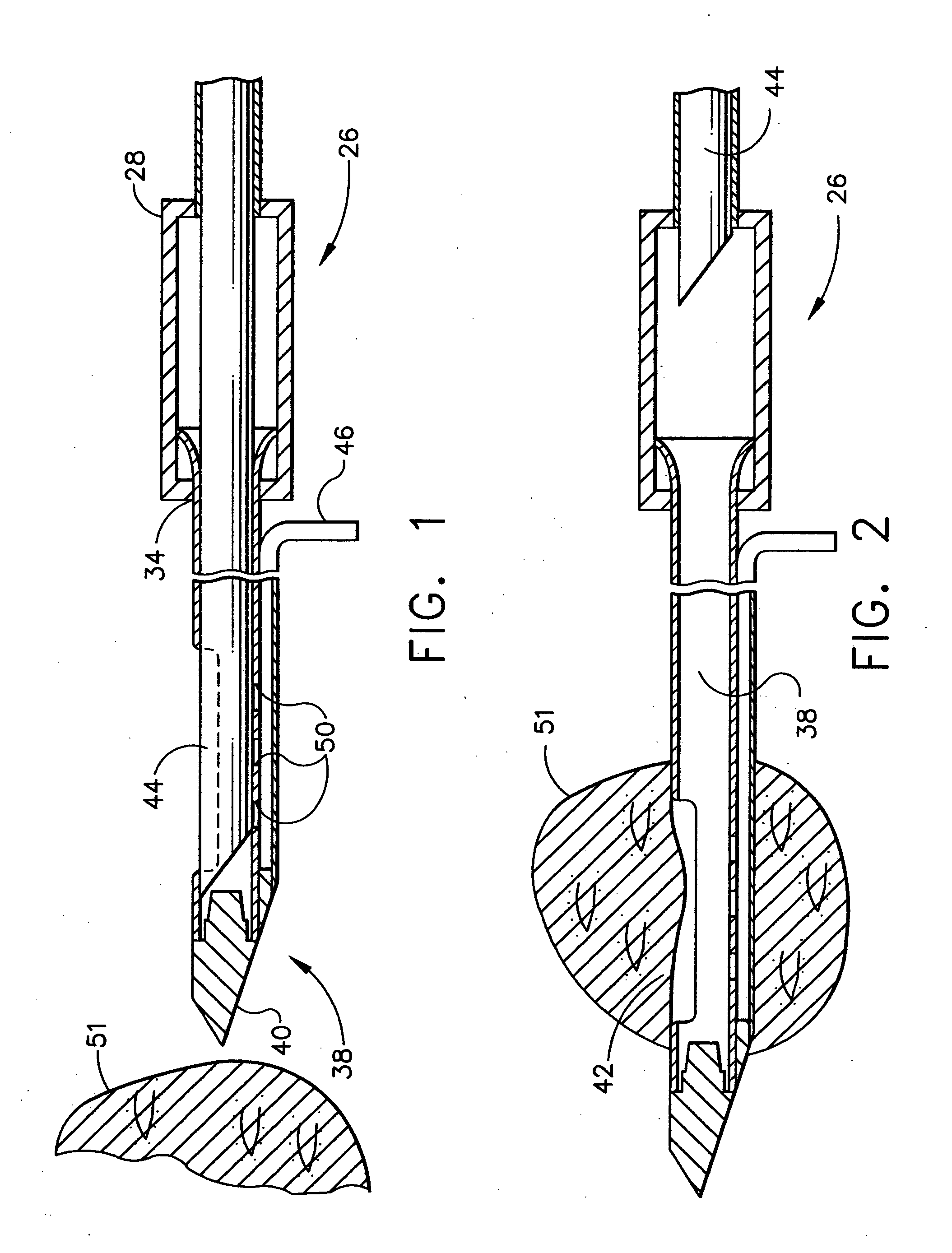
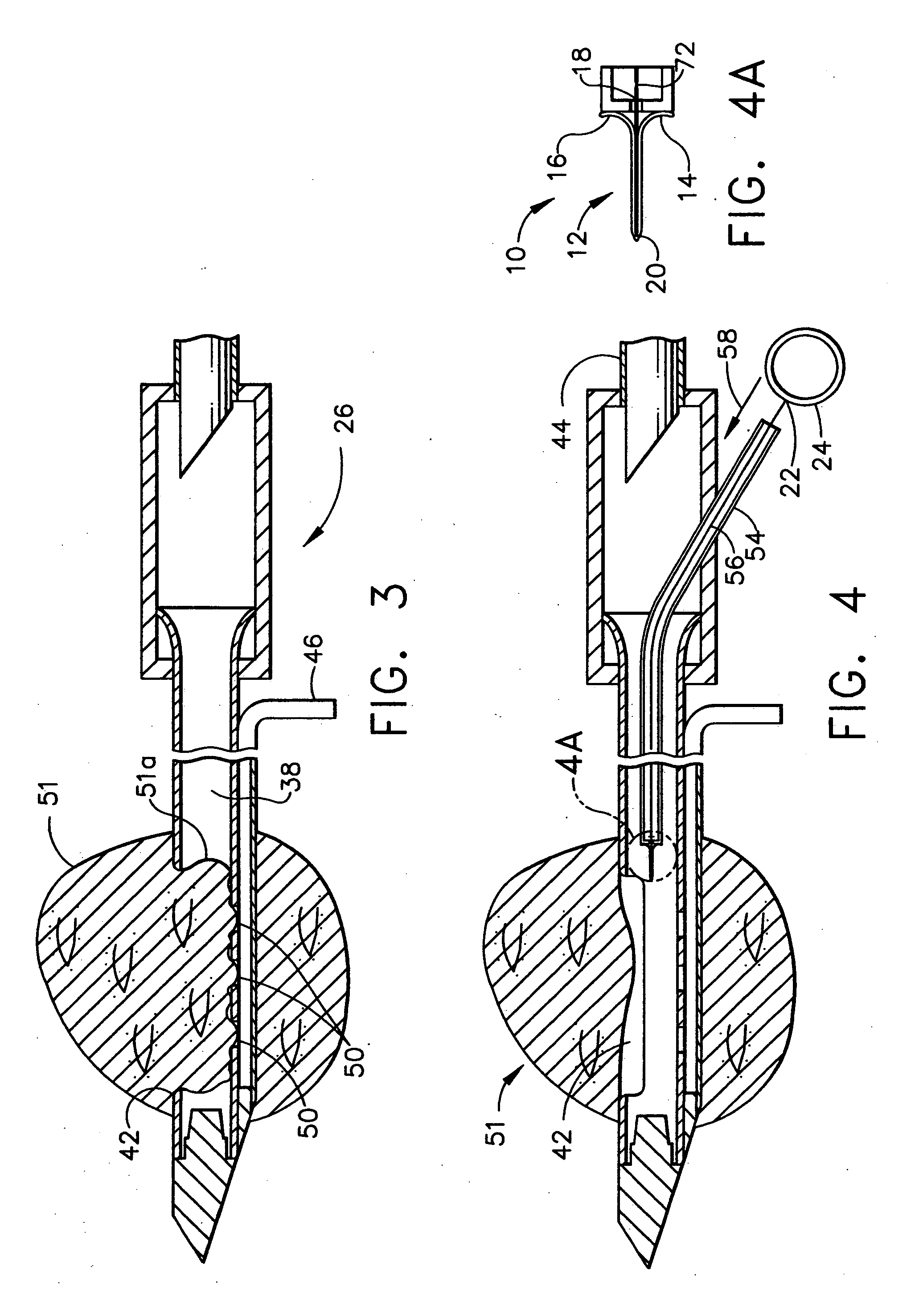
Methods for marking a biopsy site
InactiveUS20050049489A1Improve visualizationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsImplanted deviceTissue sample
Implantable devices and methods of use are disclosed for marking the location of a biopsy or surgery for the purpose of identification. The methods include providing a biodegradable radiodense implant and taking a tissue sample from a biopsy site within a breast of a patient. The biodegradable implant is then positioned at the biopsy site. The tissue sample is tested and the biopsy site is then relocated. In one embodiment, the entire implant is radiodense. In another embodiment, the entire implant is biodegradable. Methods of using a biodegradable implant having a radiodense material and a biodegradable implant that is visible using an imaging system are also included.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
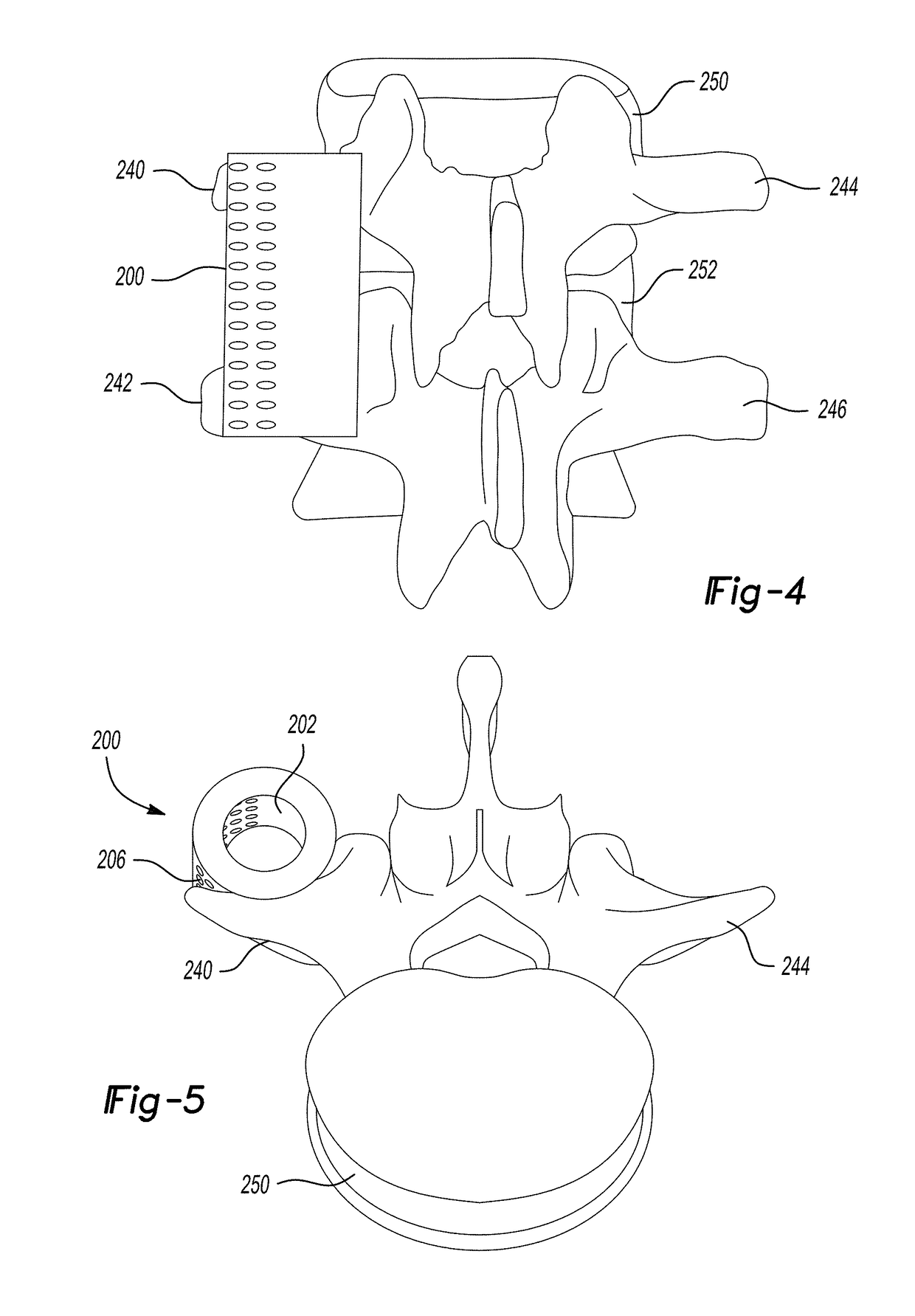
Vertebral implant for bone fixation or interbody use
InactiveUS20060142765A9Minimized reactivityOvercome limitationsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCouplingIliac screw
The present invention provides a biodegradable implant which can be used as fixation and / or interbody implants. The implant is formed of a biodegradable material and may be used as a cervical stabilizing system. The stabilizing system comprises a body constructed of a biodegradable, polymeric material, which when implanted within the body will maintain a predetermined structural integrity for at least a predetermined period of time while minimizing reactivity with adjacent tissues. In an embodiment of the invention, the stabilization system comprises a fixation member which includes apertures to allow selective coupling to bone segments by means of biodegradable screws. In another embodiment, the stabilization system includes a bone column implant which maintains space between at least two bone segments of a bone column. The body member is dimensioned to substantially maintain the distance, geometry and continuity between the at least two bone segments. The invention is also directed to a combination device comprising a fixation device along with an interbody implant and methods for using the stabilization system.
Owner:ALTUS PARTNERS
Biodegradable in-situ forming implants and methods of producing the same
A biodegradable polymer is provided for use in providing syringeable, in-situ forming, solid biodegradable implants for animals. The polymer is placed into the animal in liquid form and cures to form the implant in-situ. A thermoplastic system to form said implant comprises the steps of dissolving a non-reactive polymer in biocompatible solvent to form a liquid, placing the liquid within the animal, and allowing the solvent to dissipate to produce the implant. An alternative, thermosetting system comprises mixing together effective amounts of a liquid acrylic ester terminated, biodegradable prepolymer and a curing agent, placing the liquid mixture within an animal and allowing the prepolymer to cure to form the implant. Both systems provide a syringeable, solid biodegradable delivery system by the addition of an effective level of biologically active agent to the liquid before injection into the body.
Owner:ATRIX LAB
Sinus delivery of sustained release therapeutics
The invention provides biodegradable implants for treating sinusitis. The biodegradable implants have a size, shape, density, viscosity, and / or mucoadhesiveness that prevents them from being substantially cleared by the mucociliary lining of the sinuses during the intended treatment period. The biodegradable implants include a sustained release therapeutic, e.g., an antibiotic, a steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, or both. The biodegradable implants may take various forms, such as rods, pellets, beads, strips, or microparticles, and may be delivered into a sinus in various pharmaceutically acceptable carriers.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
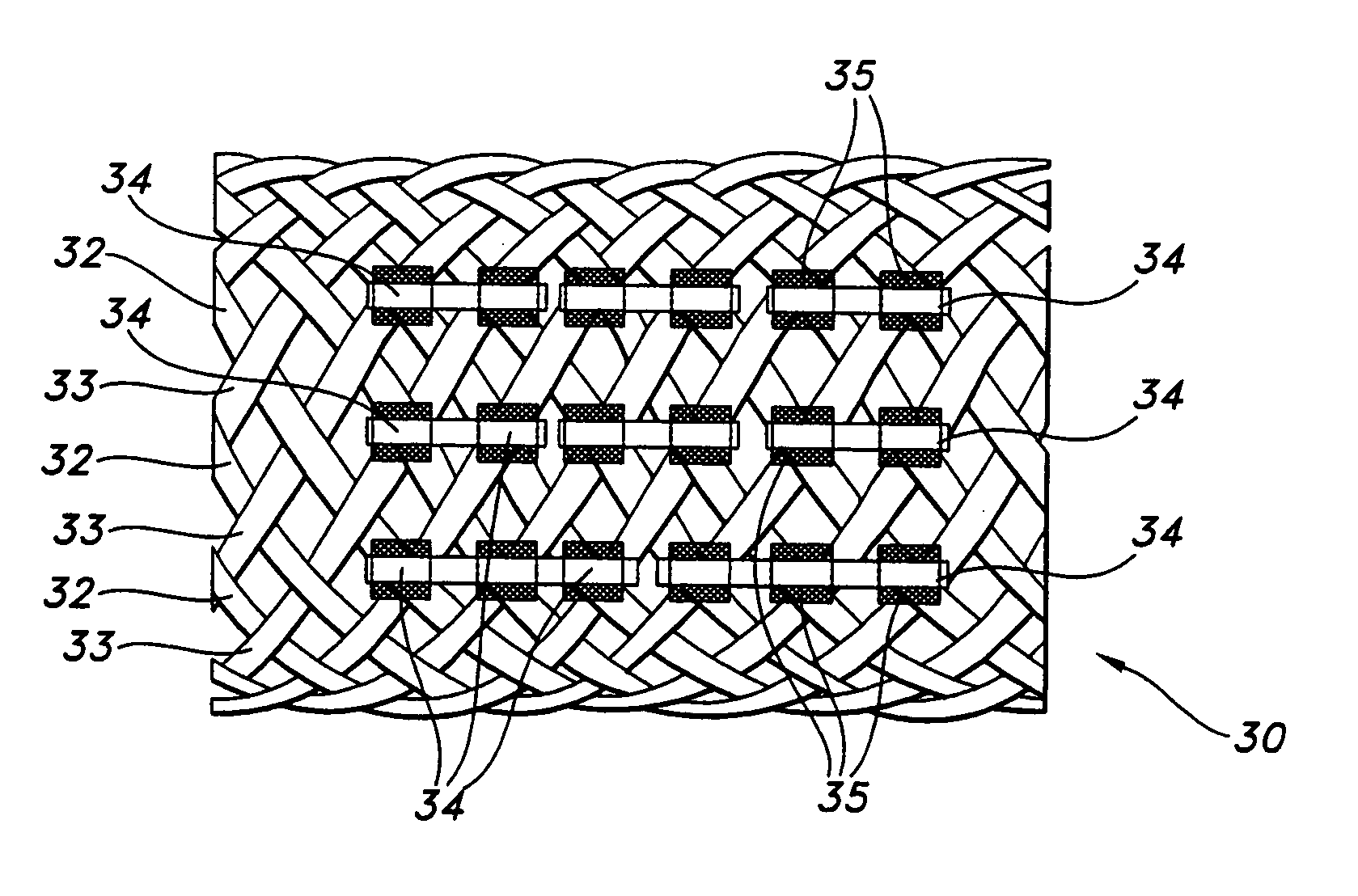
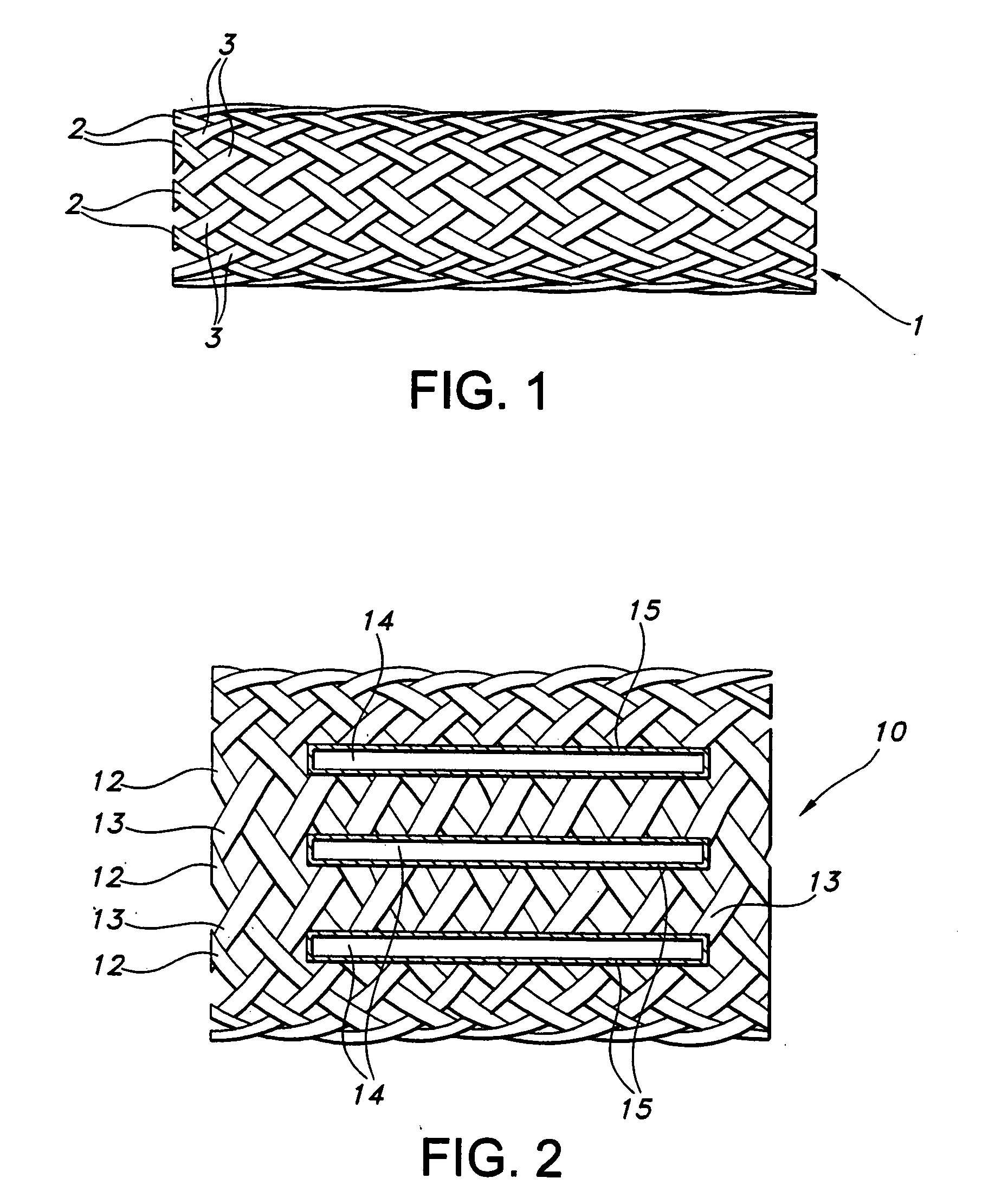
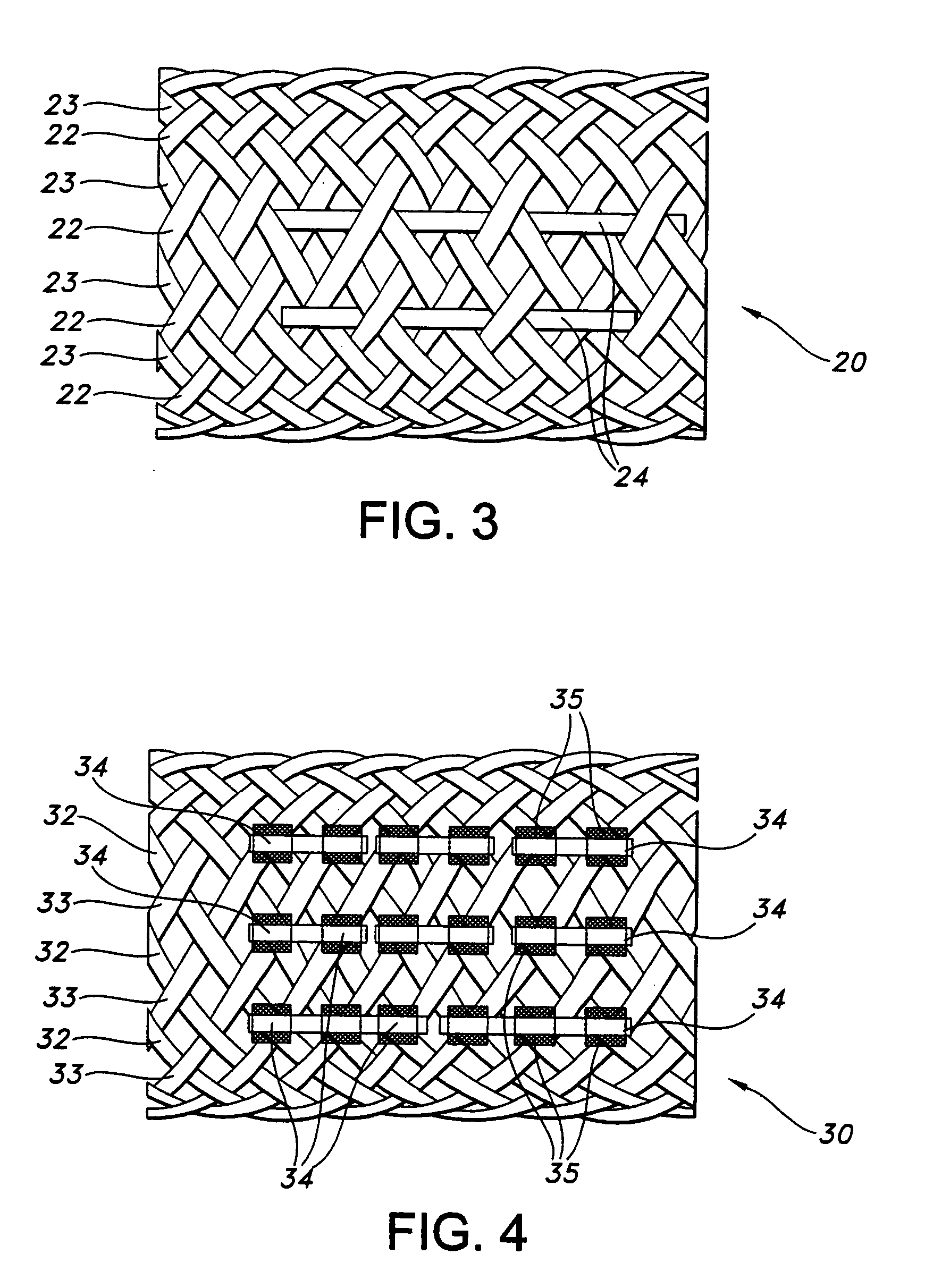
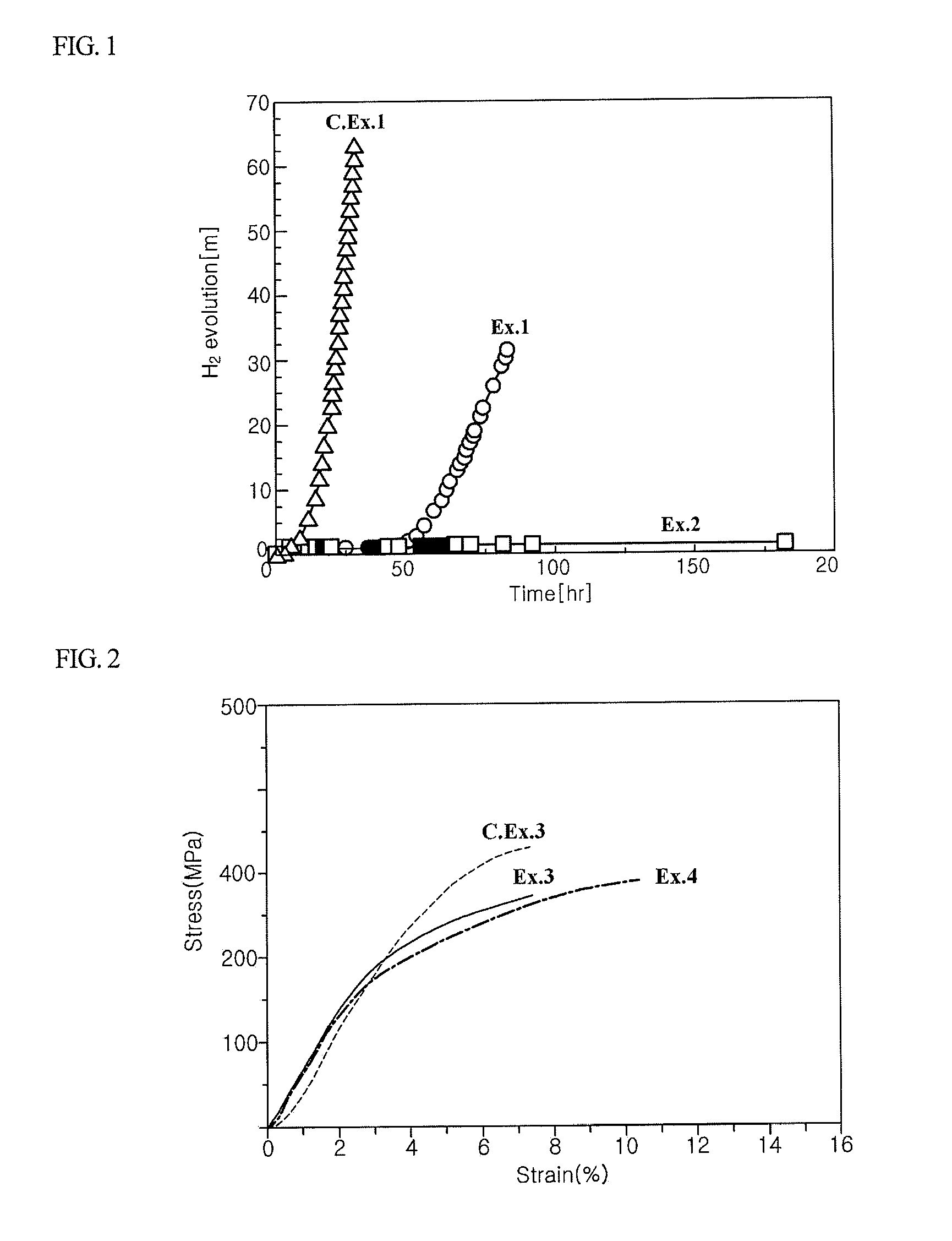
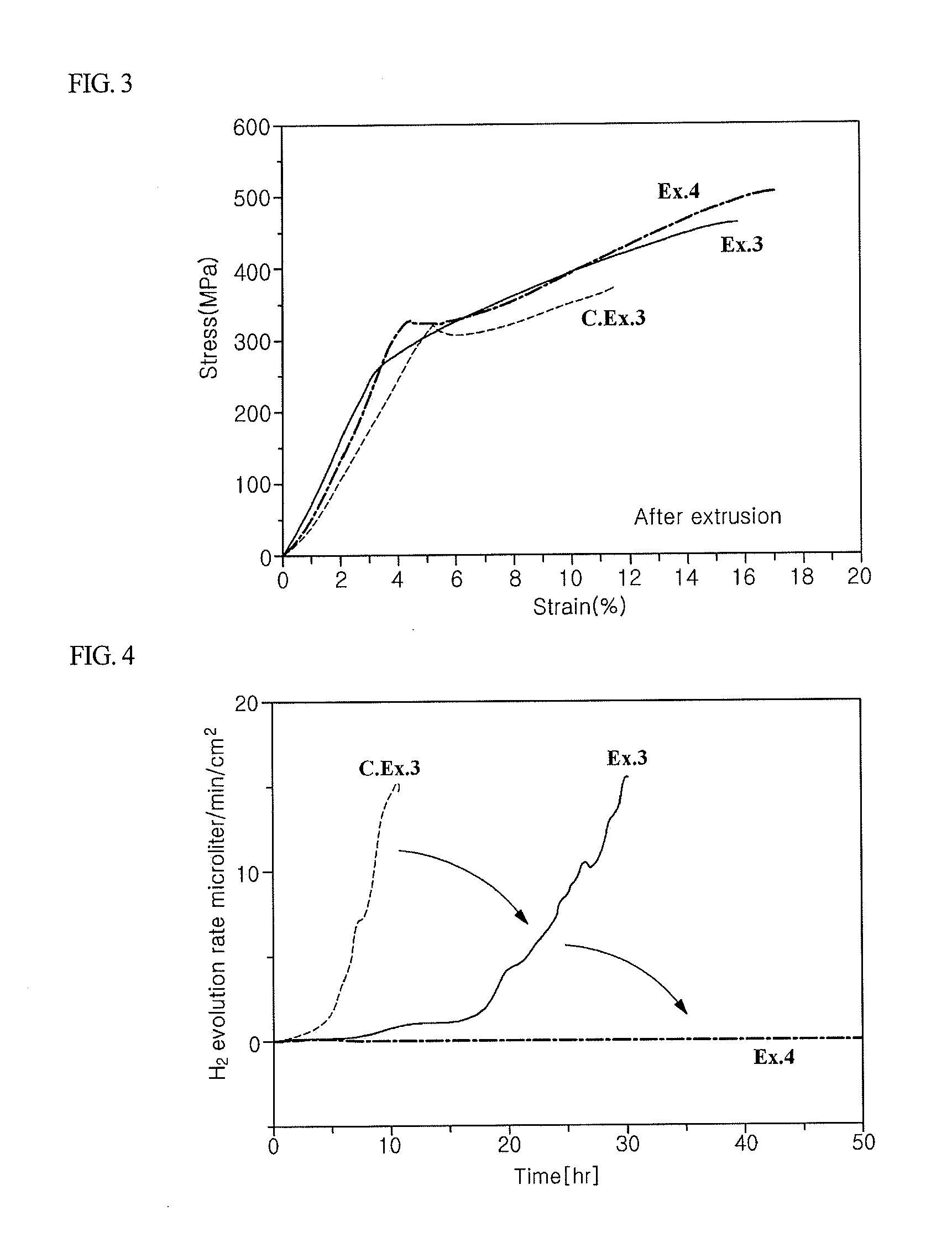
Biodegradable implants having accelerated biodegradation properties in vivo
InactiveUS20070203564A1Reduced mechanical propertiesReduce probabilityStentsElectric discharge tubesBiodegradable implantsBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed to a biodegradable implant including a biodegradable polymer previously exposed to conditions of biodegradation such as chemical, thermal or radiation degradation. The present invention further includes the possibility of attaching axial runners to the implant. The present invention is further directed to a method of forming a biodegradable implant, such as a stent, by irradiation of the individual filaments or fibers, or irradiation of the formed implant.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
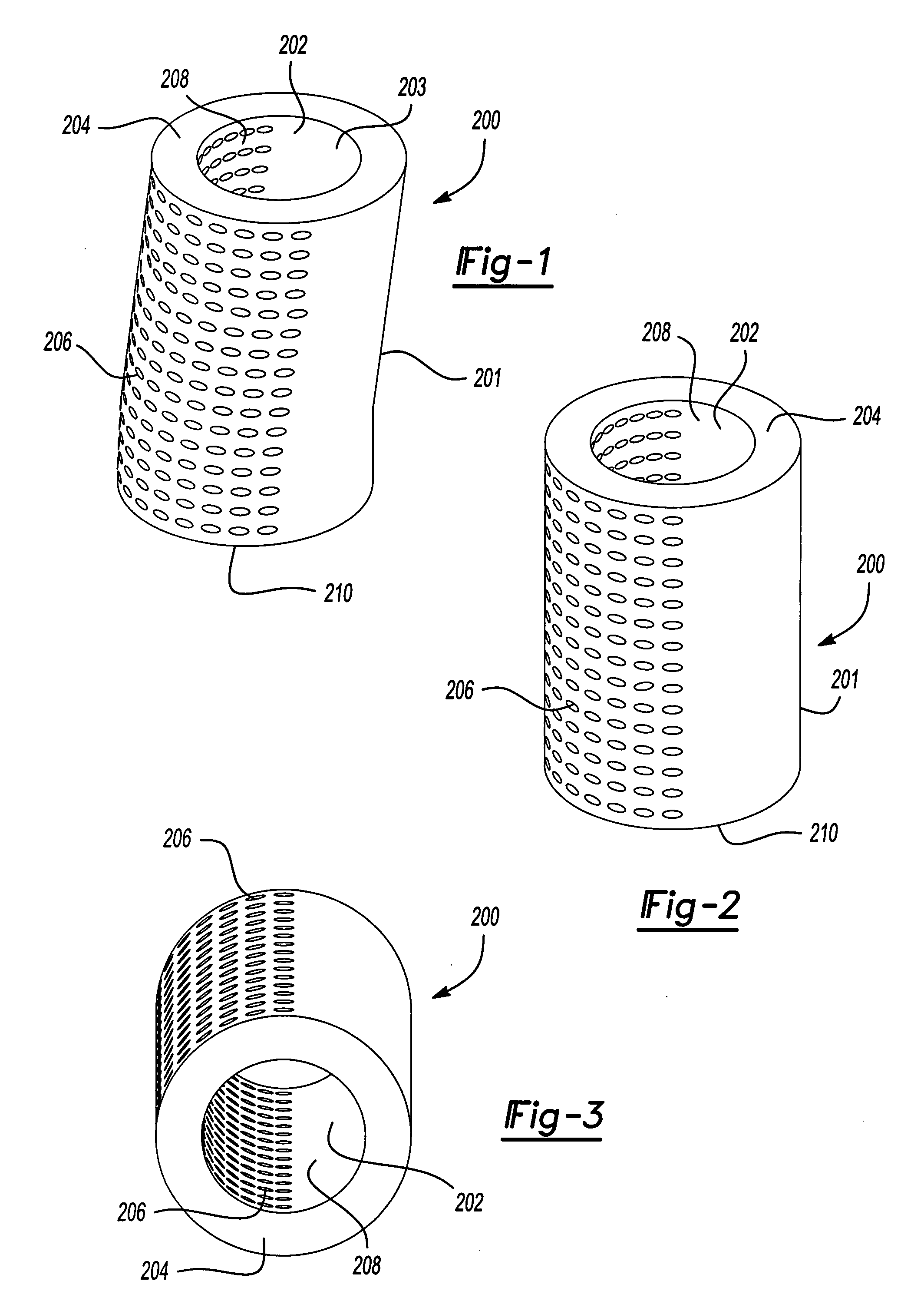
Fiber-reinforced, porous, biodegradable implant device
InactiveUS20050240281A1Promote regenerationProvide strengthBone implantLaminationArticular cartilagePolymer
A fiber-reinforced, polymeric implant material useful for tissue engineering, and method of making same are provided. The fibers are preferably aligned predominantly parallel to each other, but may also be aligned in a single plane. The implant material comprises a polymeric matrix, preferably a biodegradable matrix, having fibers substantially uniformly distributed therein. Inorganic particles may also be included in the implant material. In preferred embodiments, porous tissue scaffolds are provided which facilitate regeneration of load-bearing tissues such as articular cartilage and bone. Non-porous fiber-reinforced implant materials are also provided herein useful as permanent implants for load-bearing sites.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
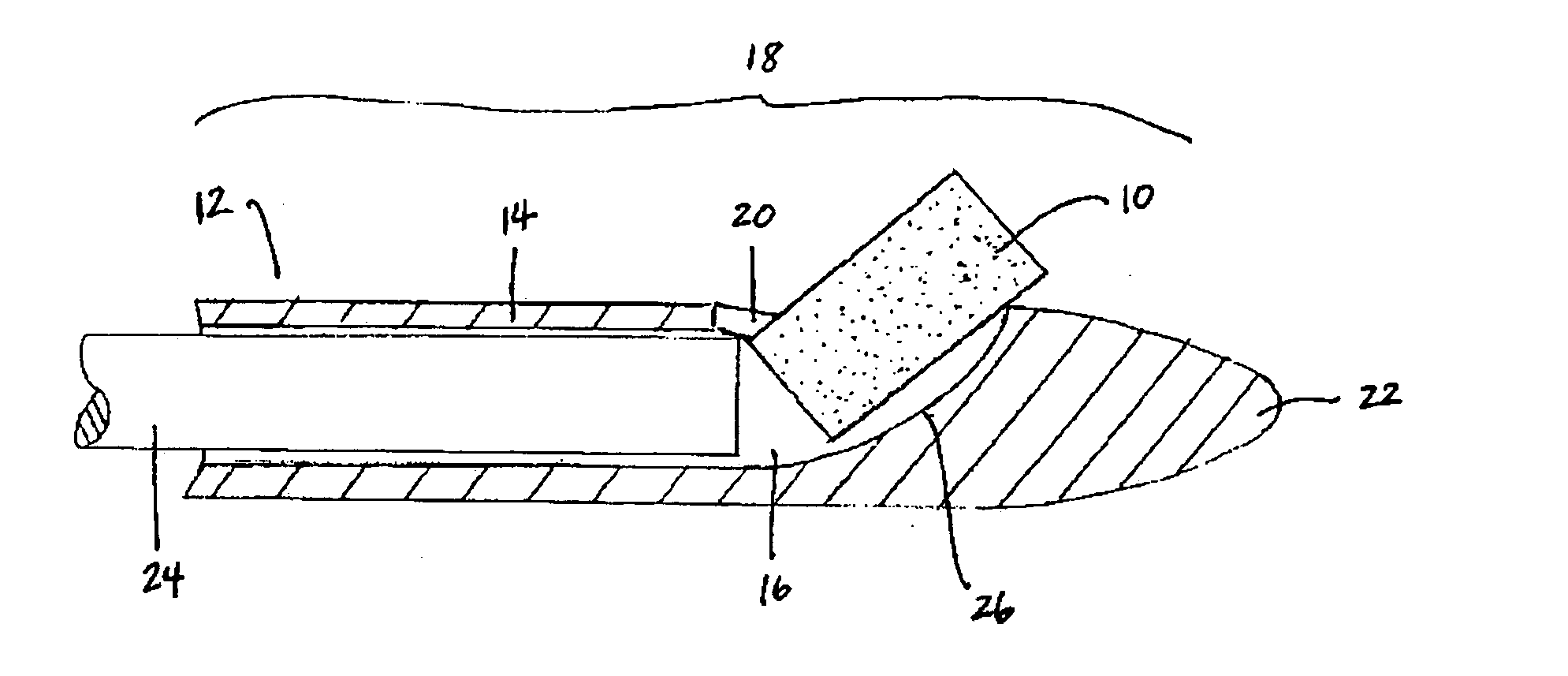
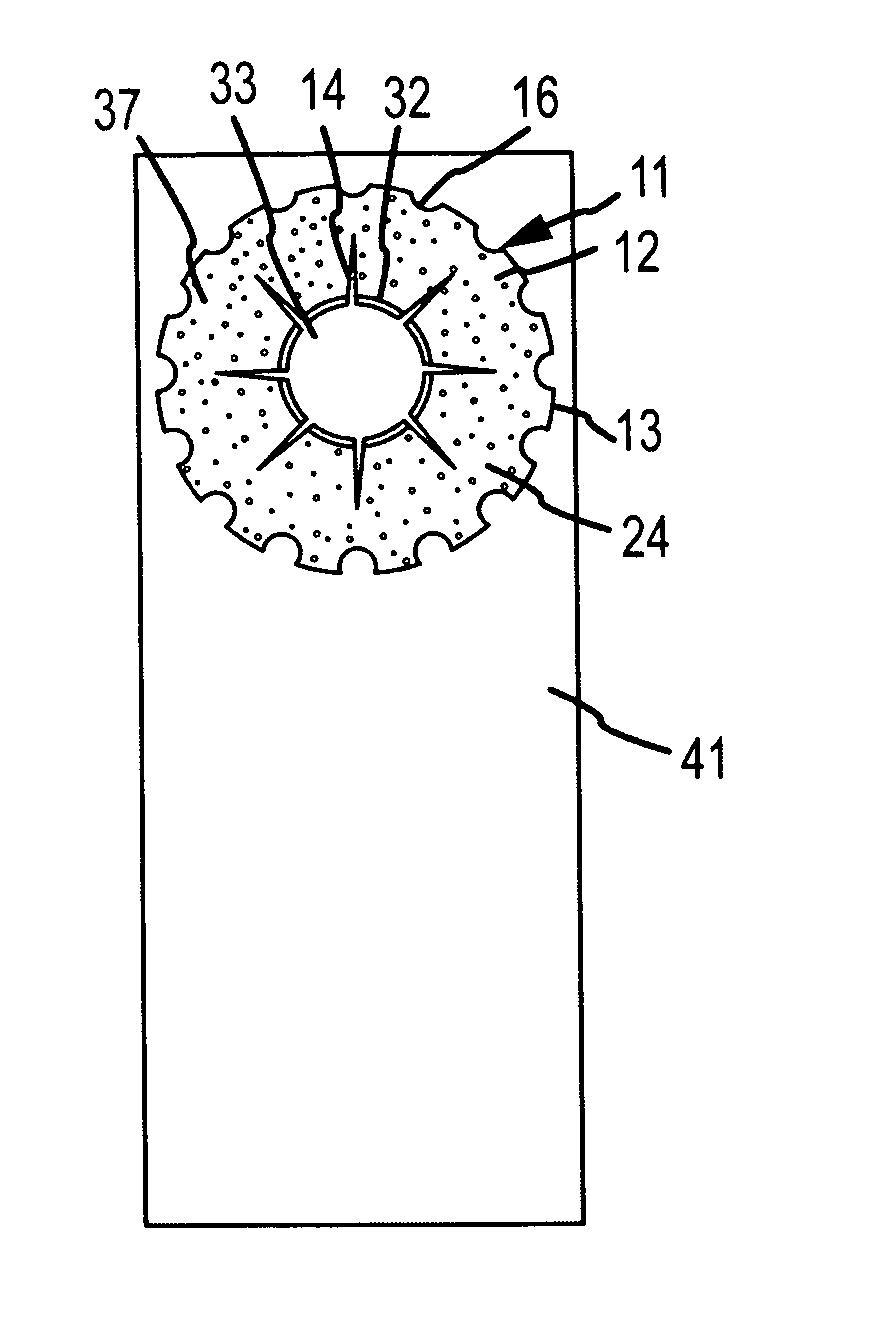
Biocompatible biodegradable intraocular implant system
InactiveUS20110230963A1Prevent proliferationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEye treatmentIntraocular lensActive agent
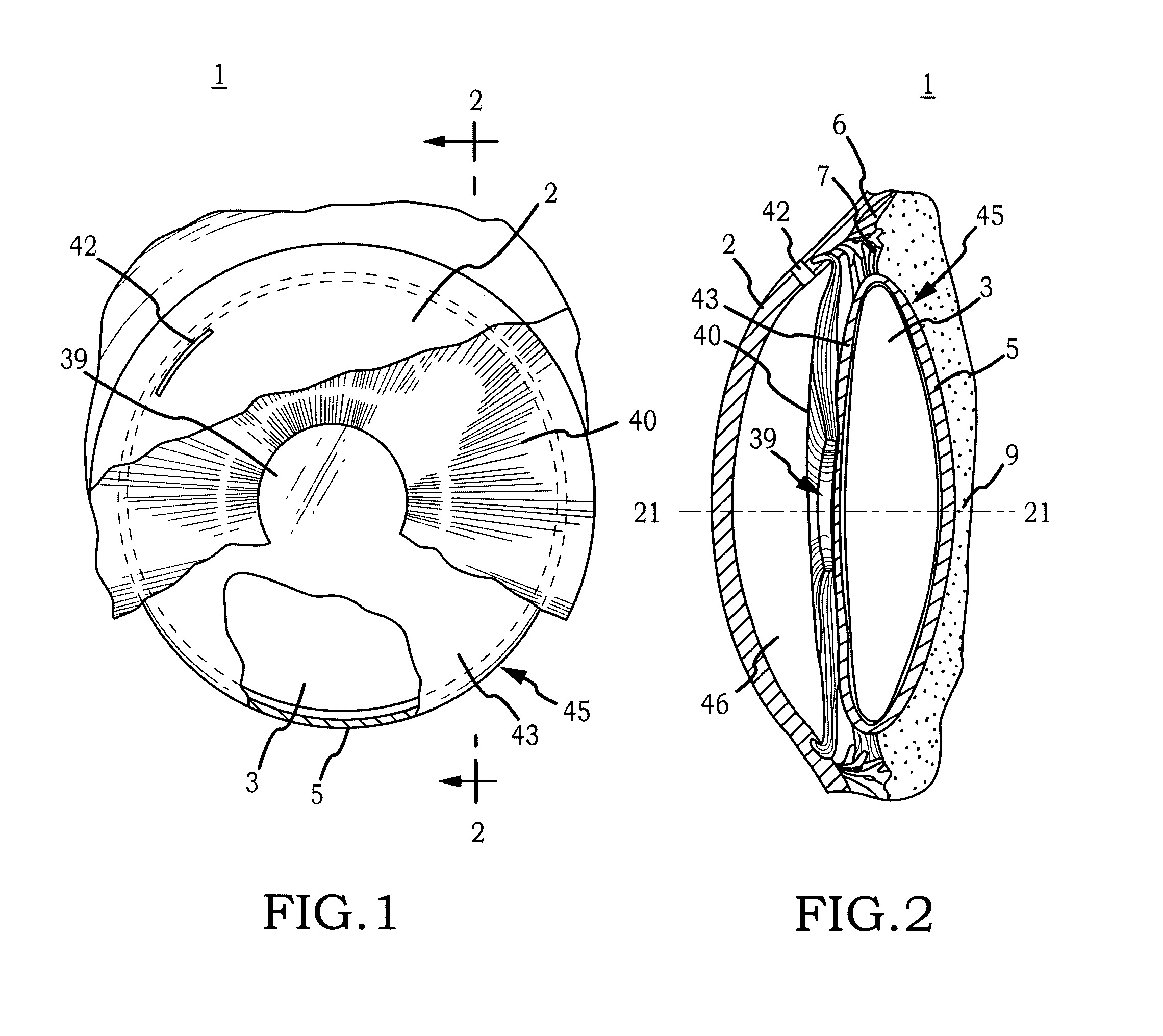
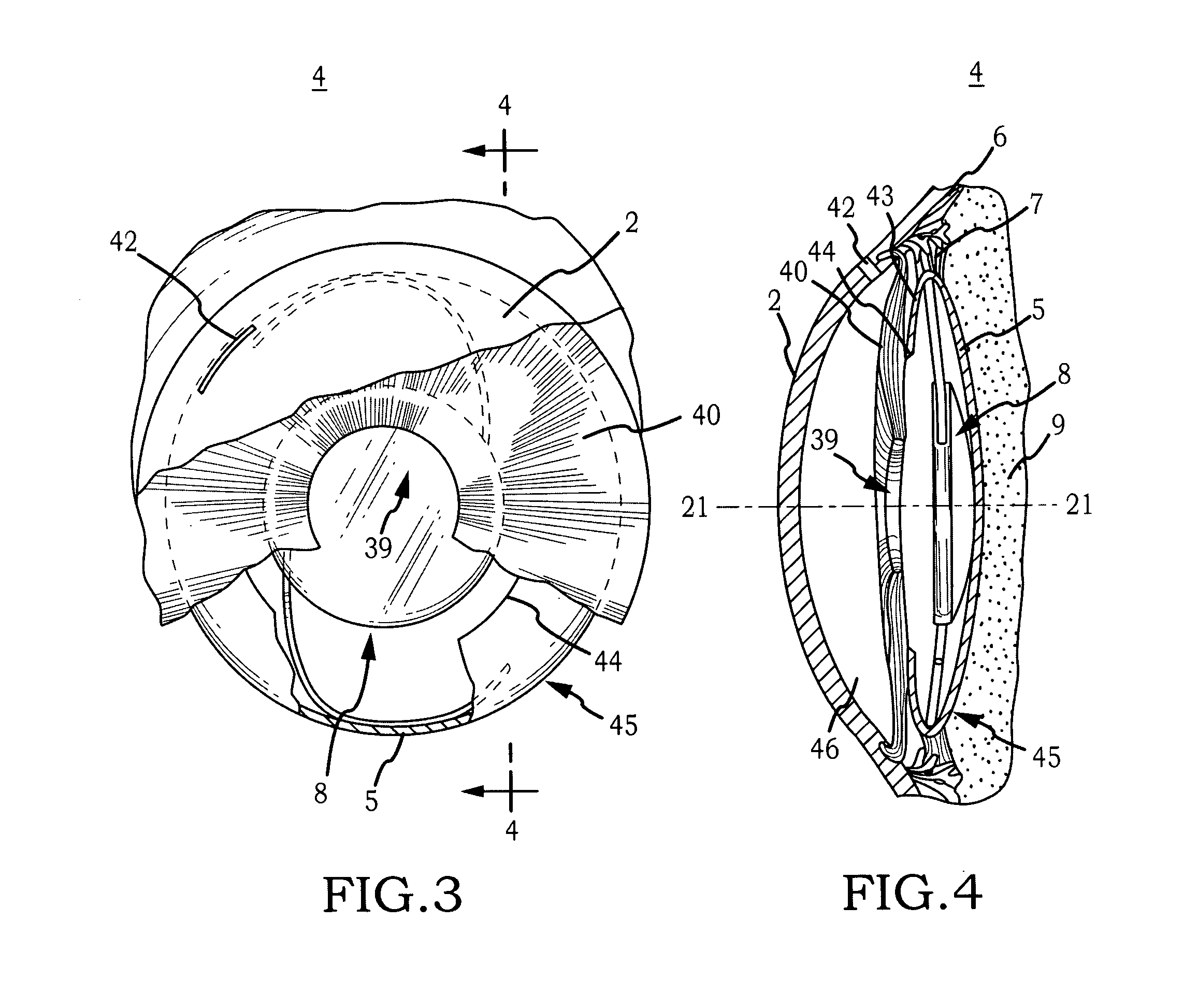
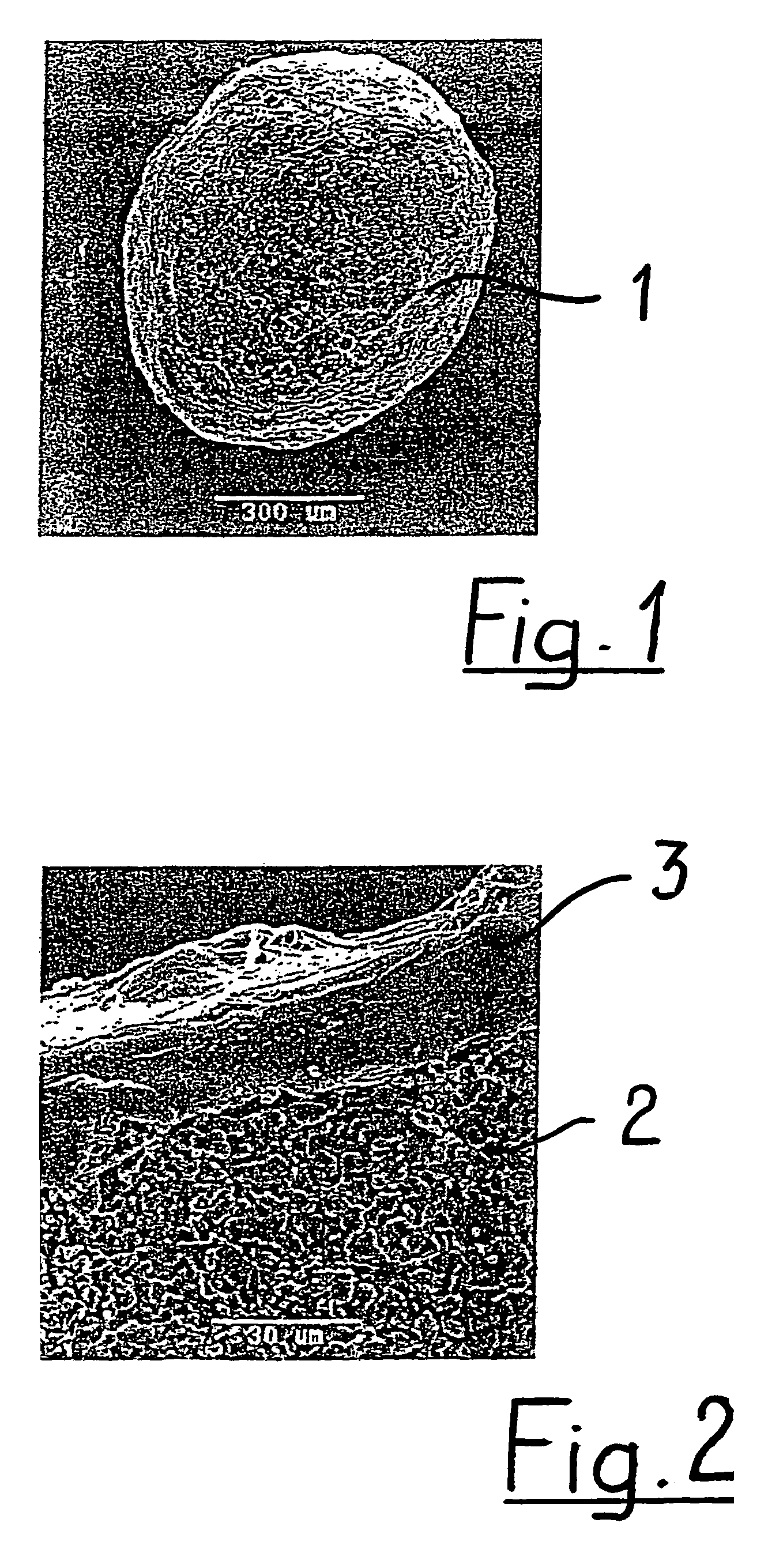
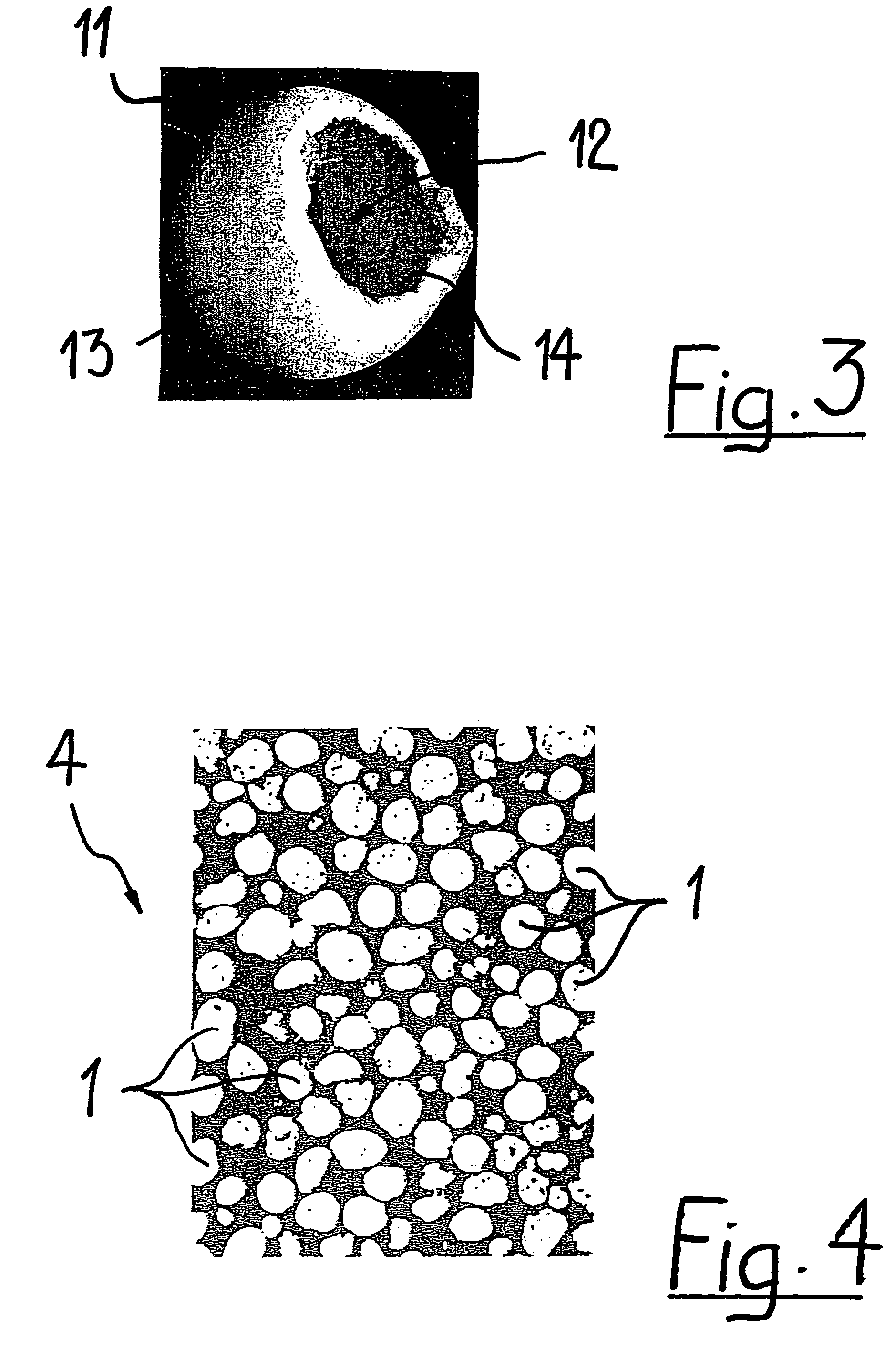
Generally, an intraocular implant and methods for treating an ocular condition. As to certain embodiments, an intraocular biocompatible biodegradable implant (11) which can provide a biocompatible biodegradable material in the form of a flexible membrane (12) containing an active agent (24) which implanted between an intraocular lens (8) and the surface of the posterior capsule (5) of the eye (1)(4) inhibits migration of residual lens epithelial cells after cataract surgery by providing structural or pharmaceutical barriers to reduce posterior capsule (5) opacification of the eye (1)(4).
Owner:INSIGHT INNOVATIONS
Sinus delivery of sustained release therapeutics
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
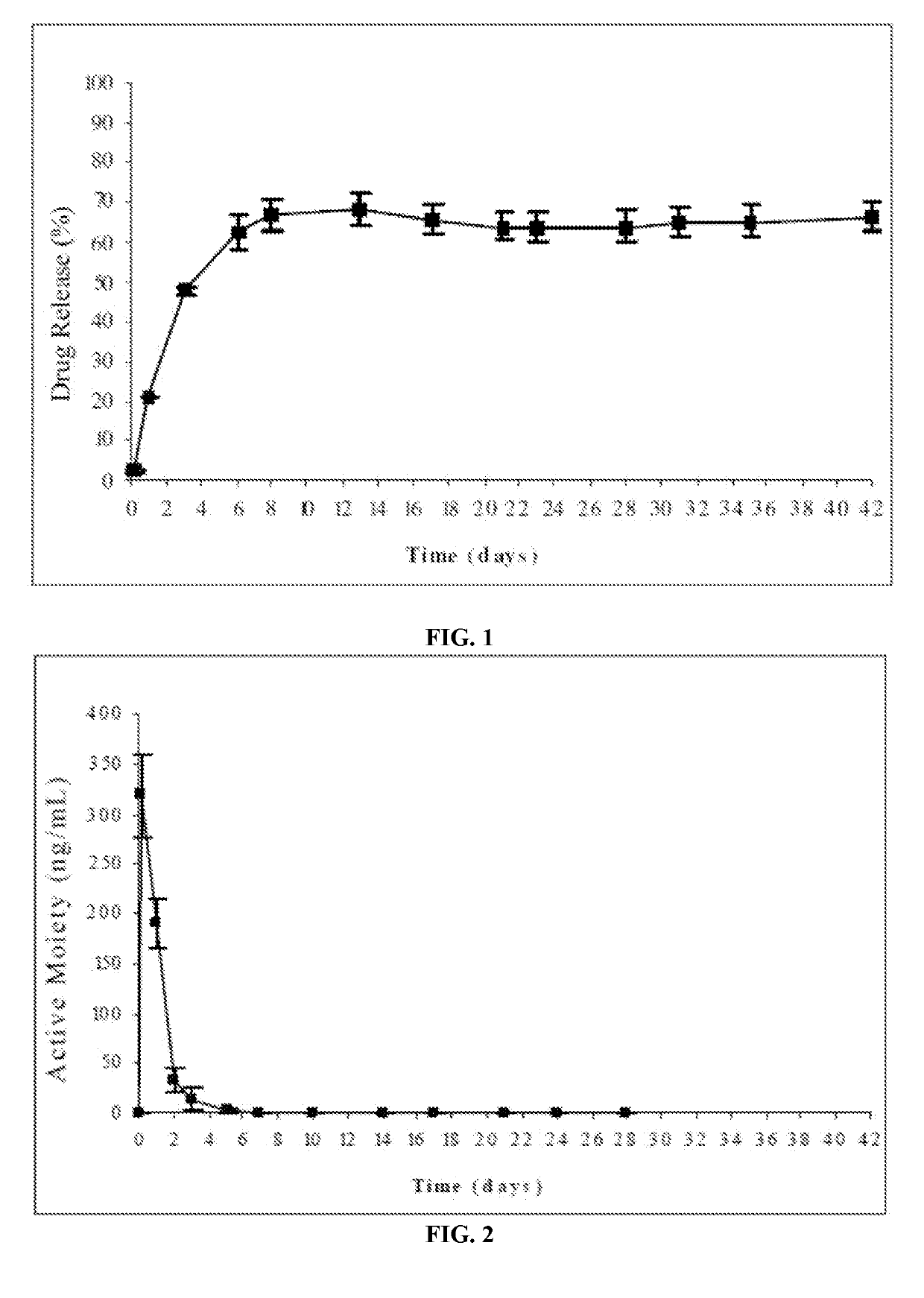
Methods for the Preparation of Injectable Depot Compositions
ActiveUS20130177603A1Simple methodConstant and effective plasma levelBiocideNervous disorderMedicineGlycolic acid
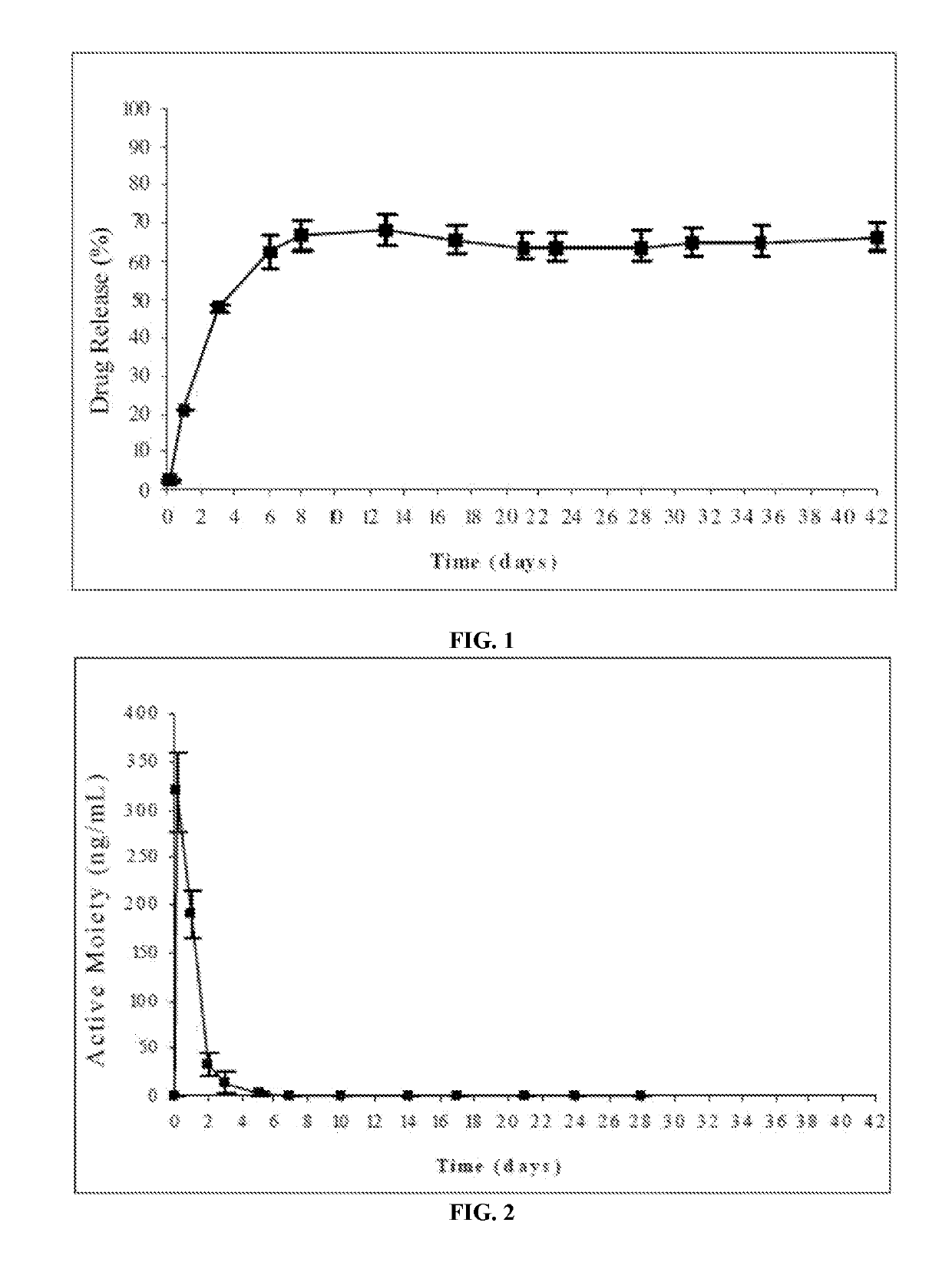
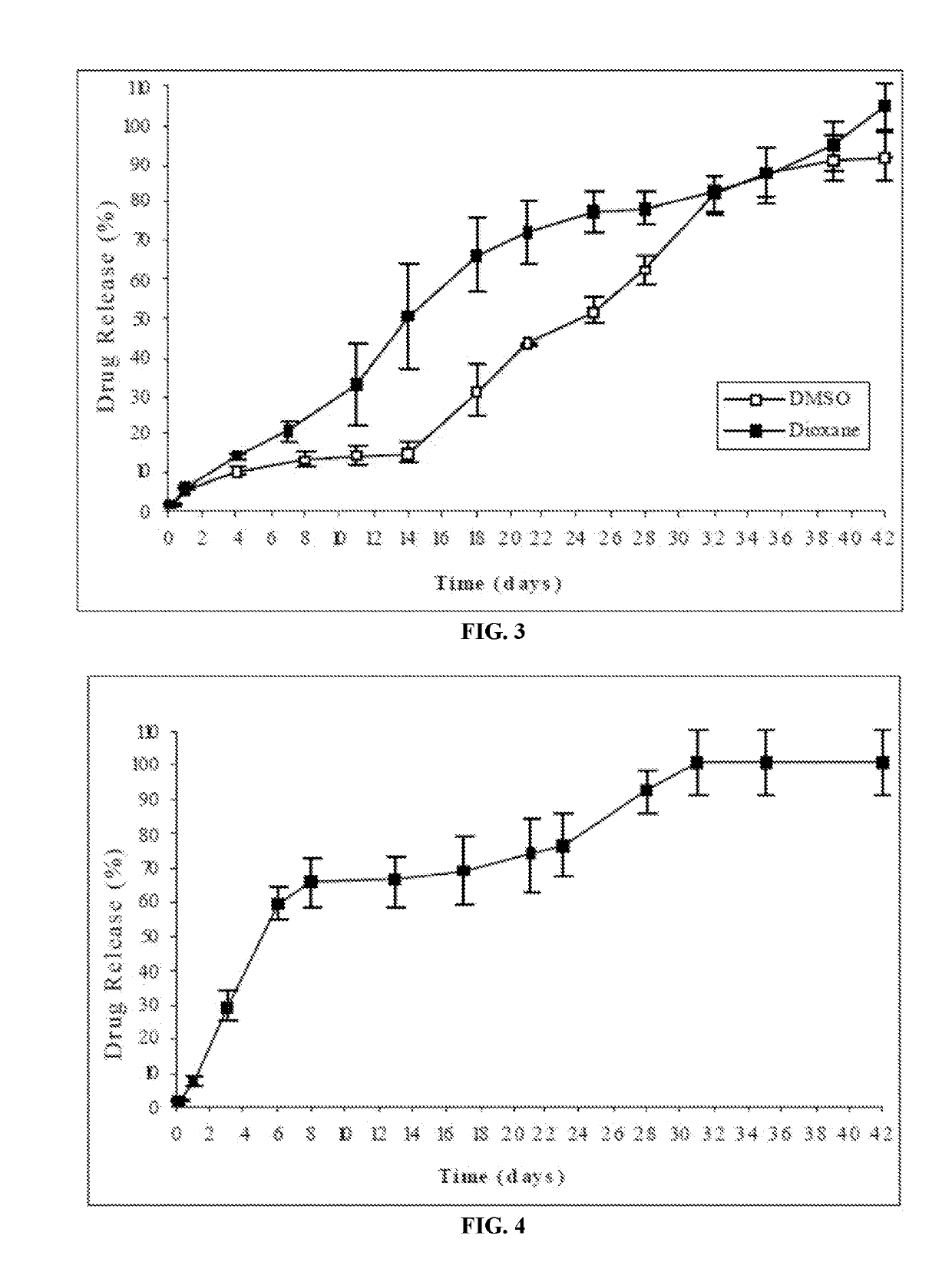
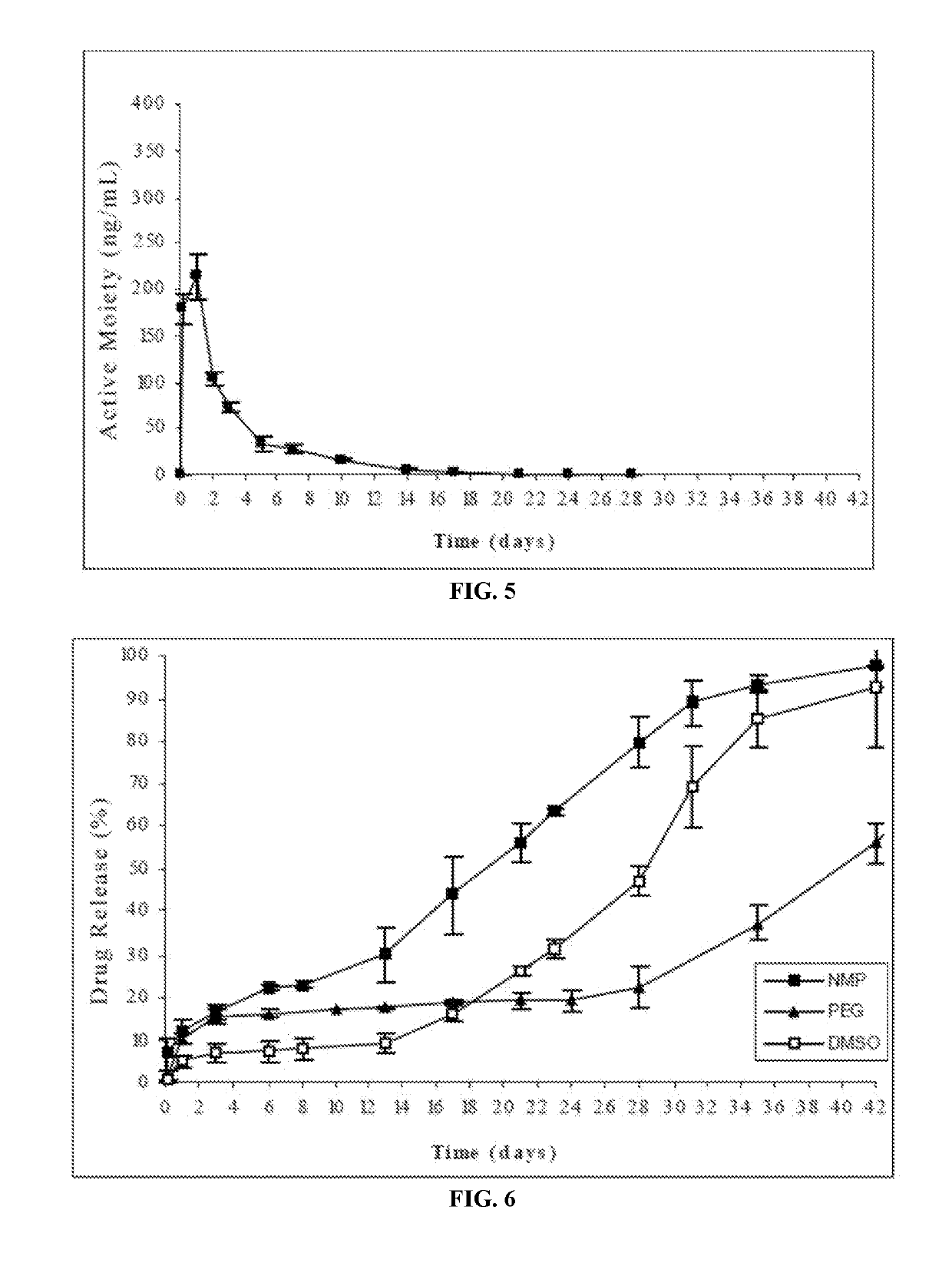
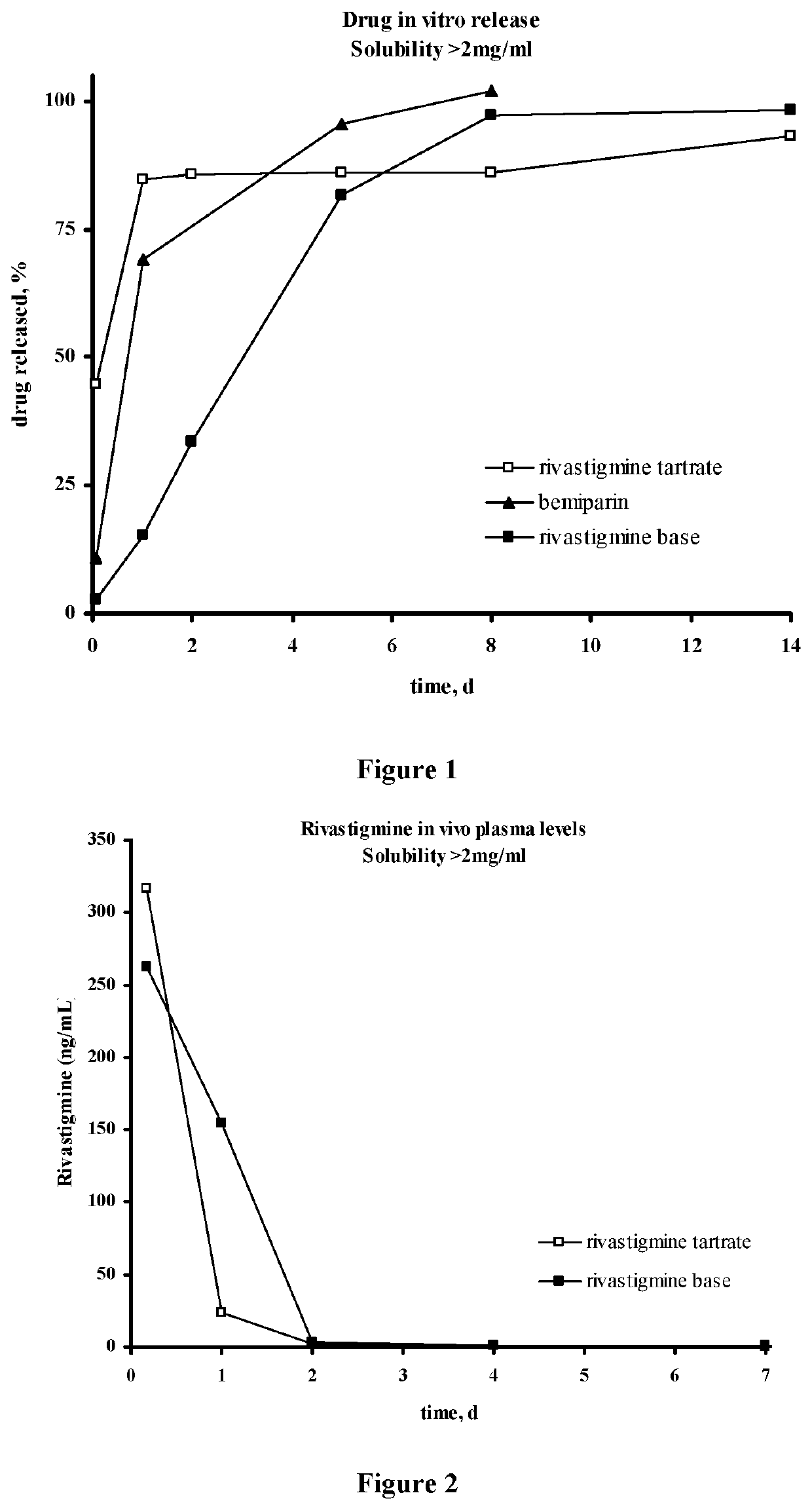
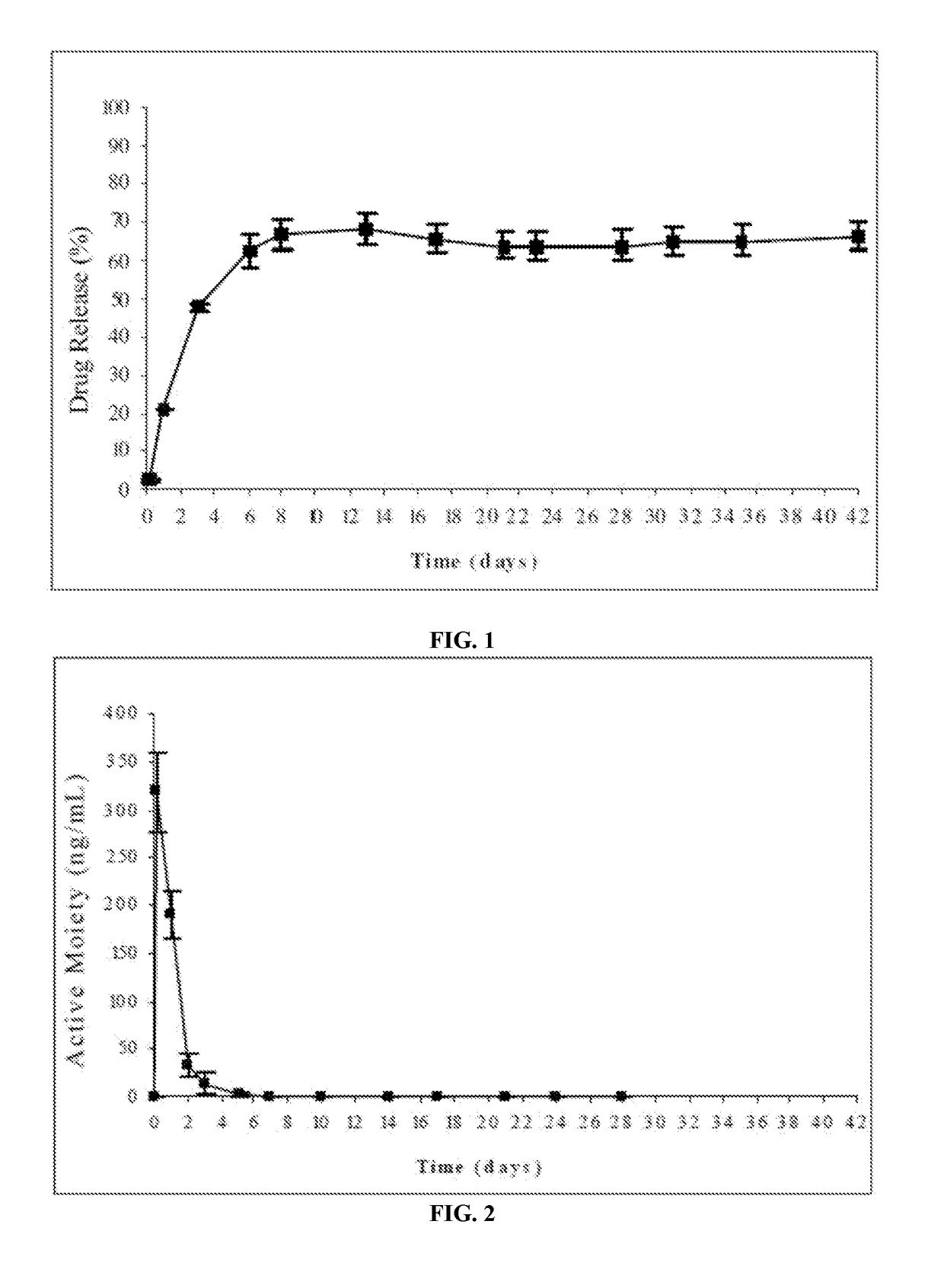
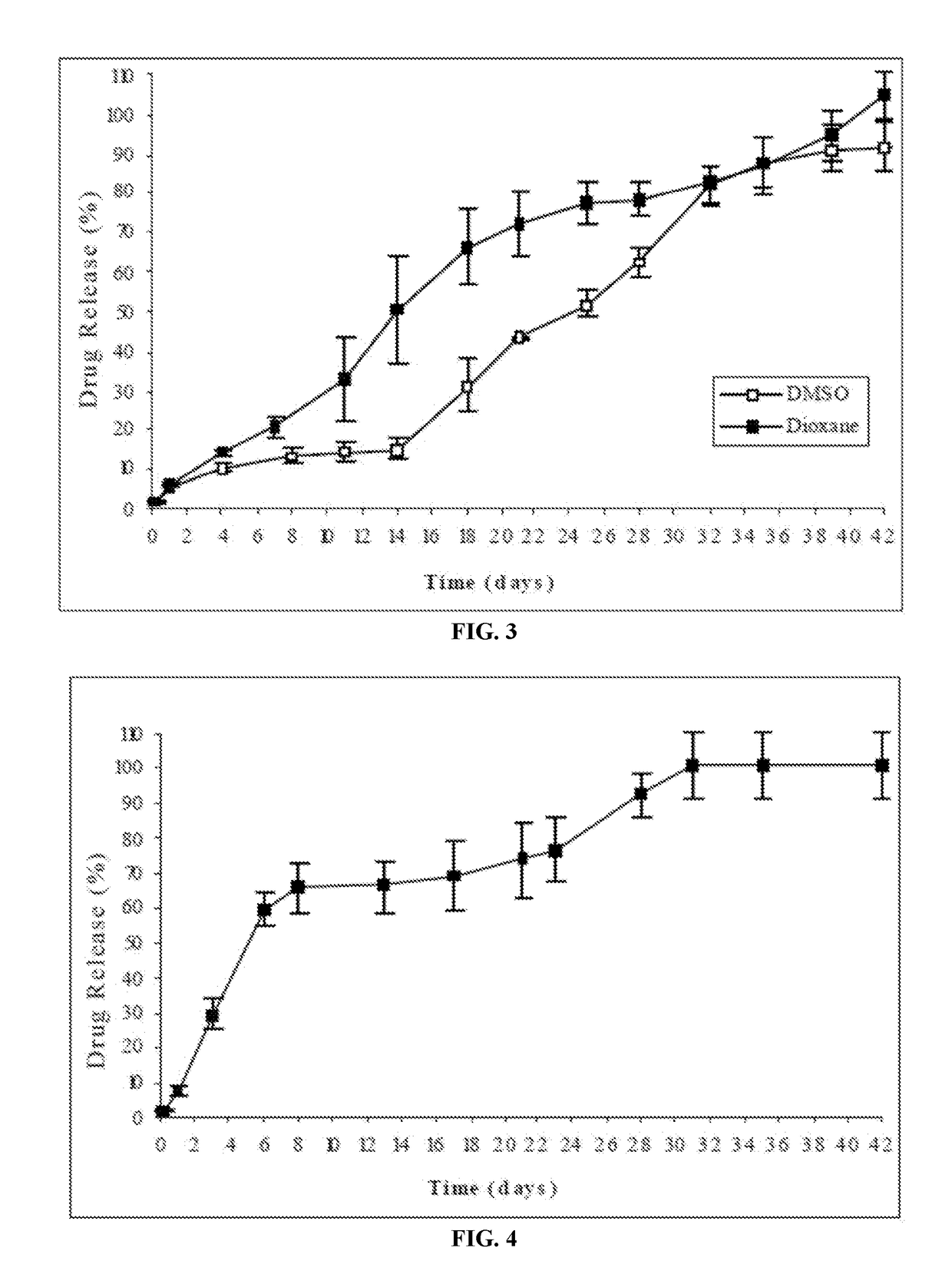
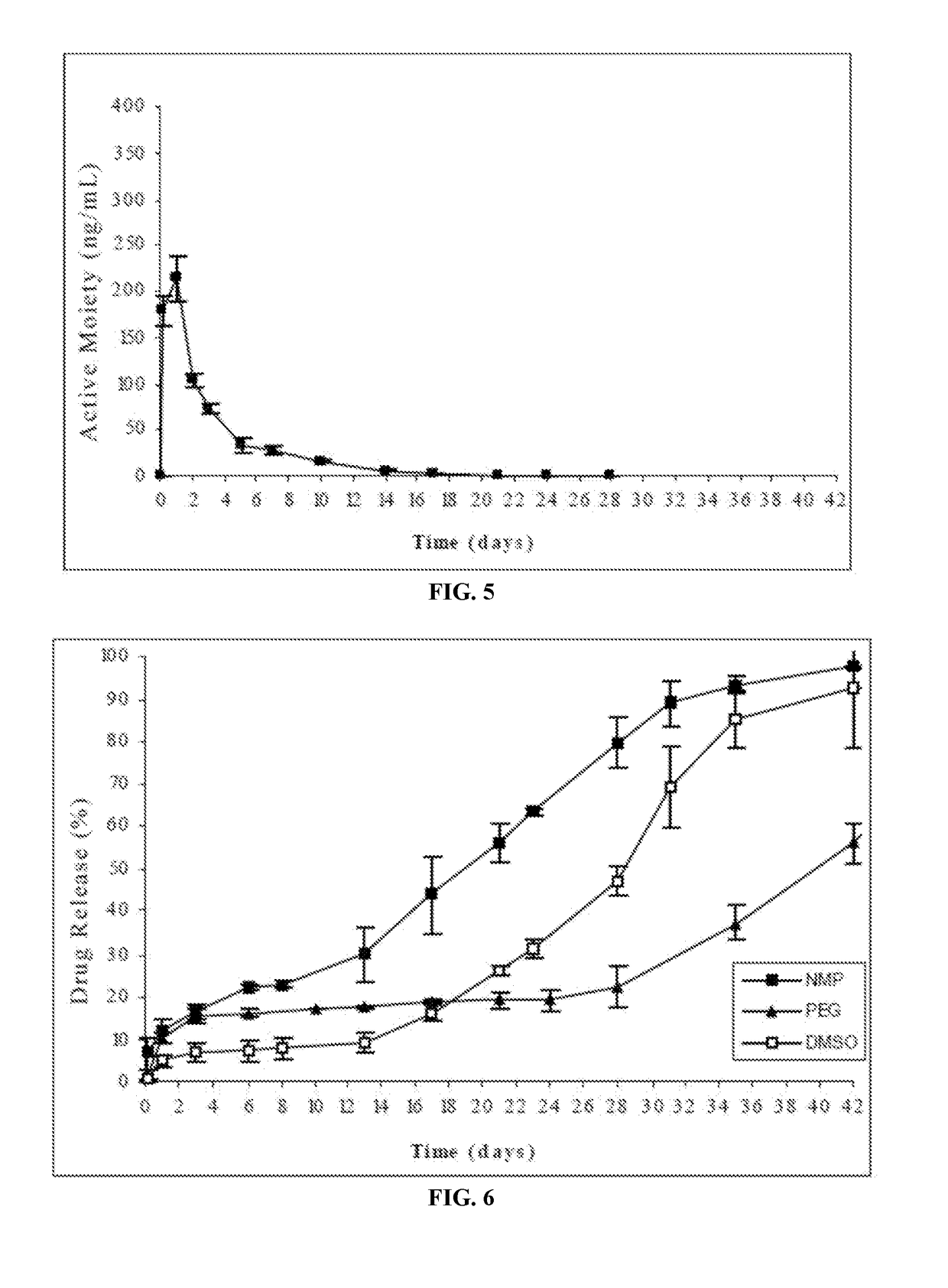
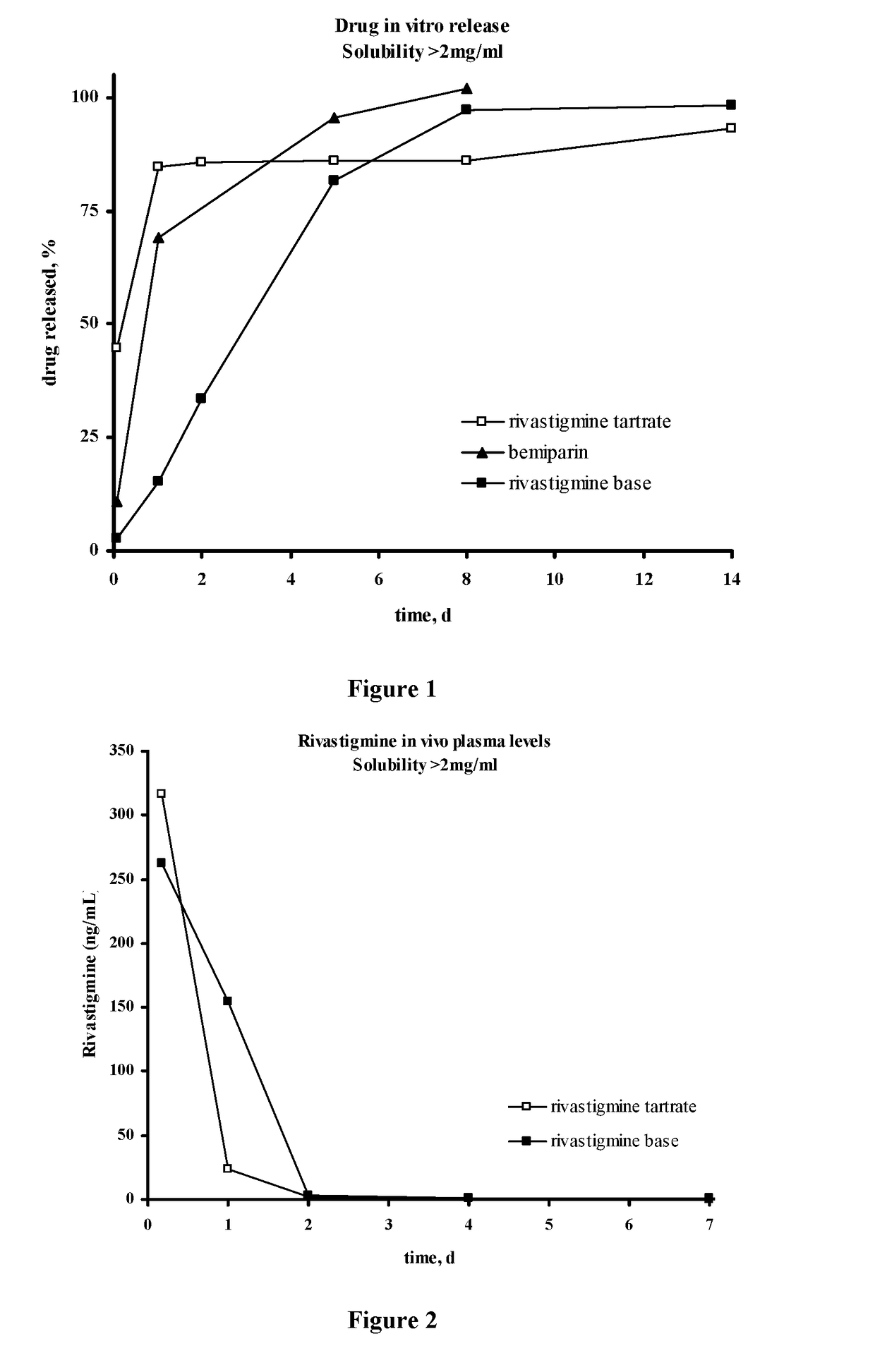
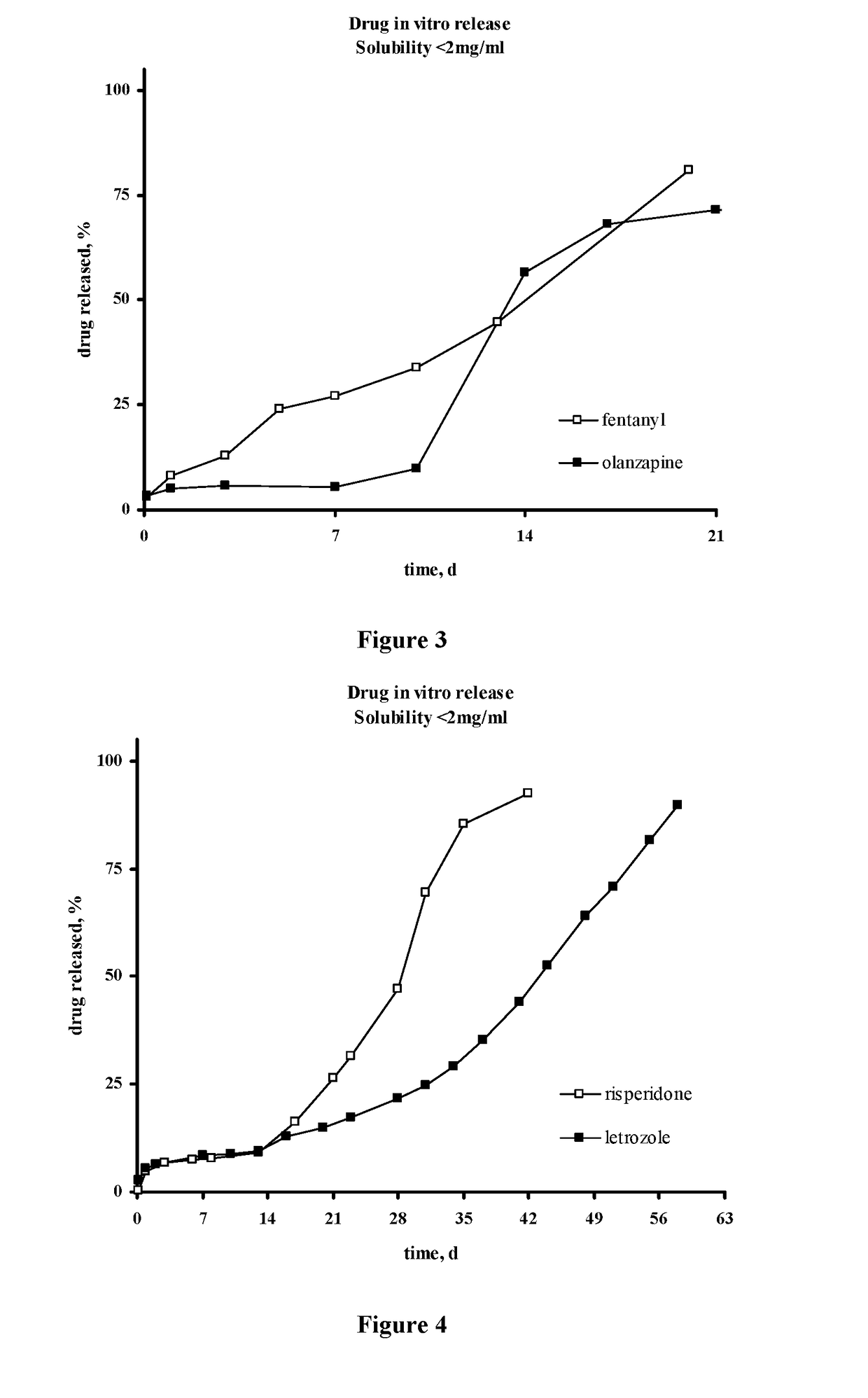
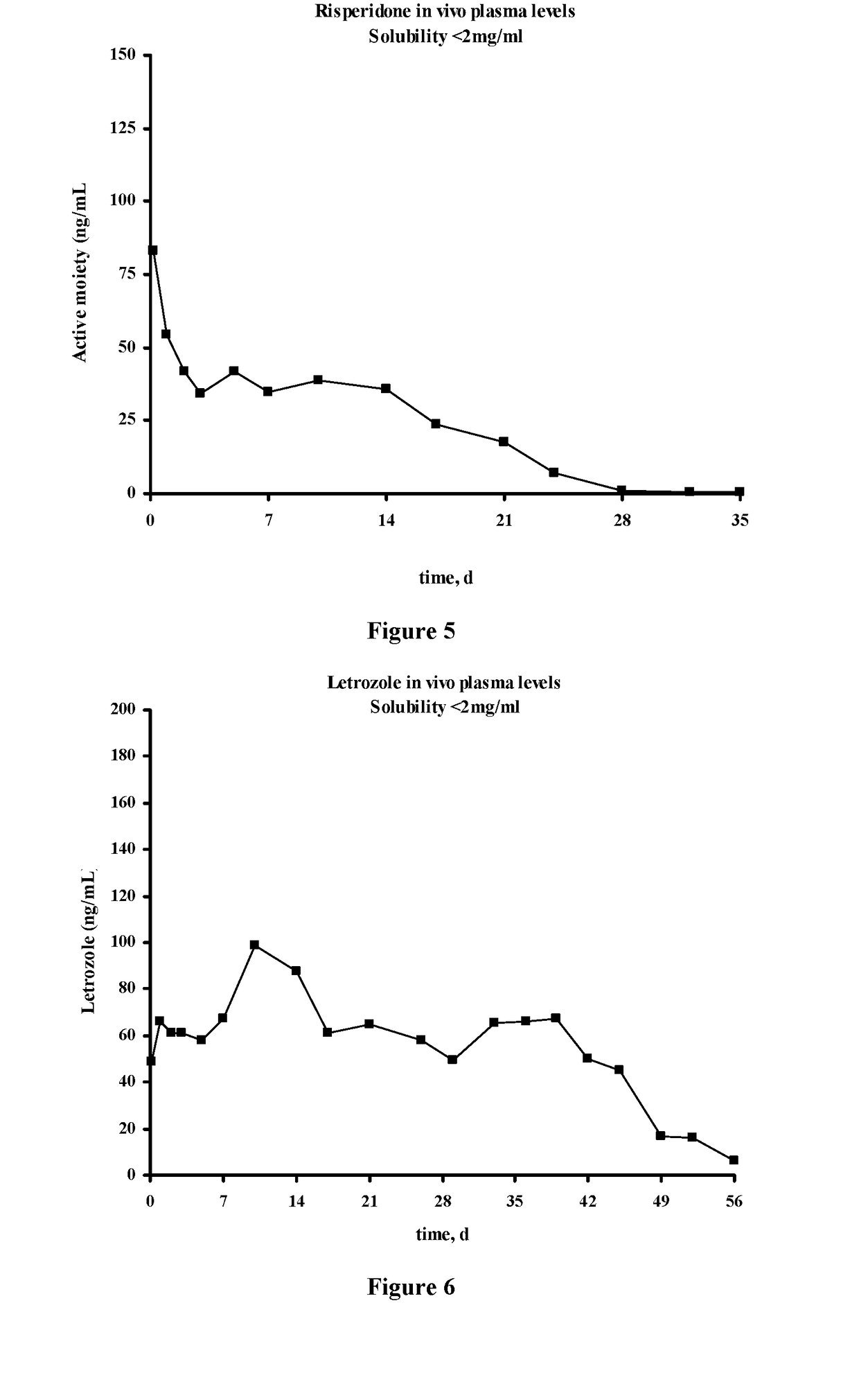
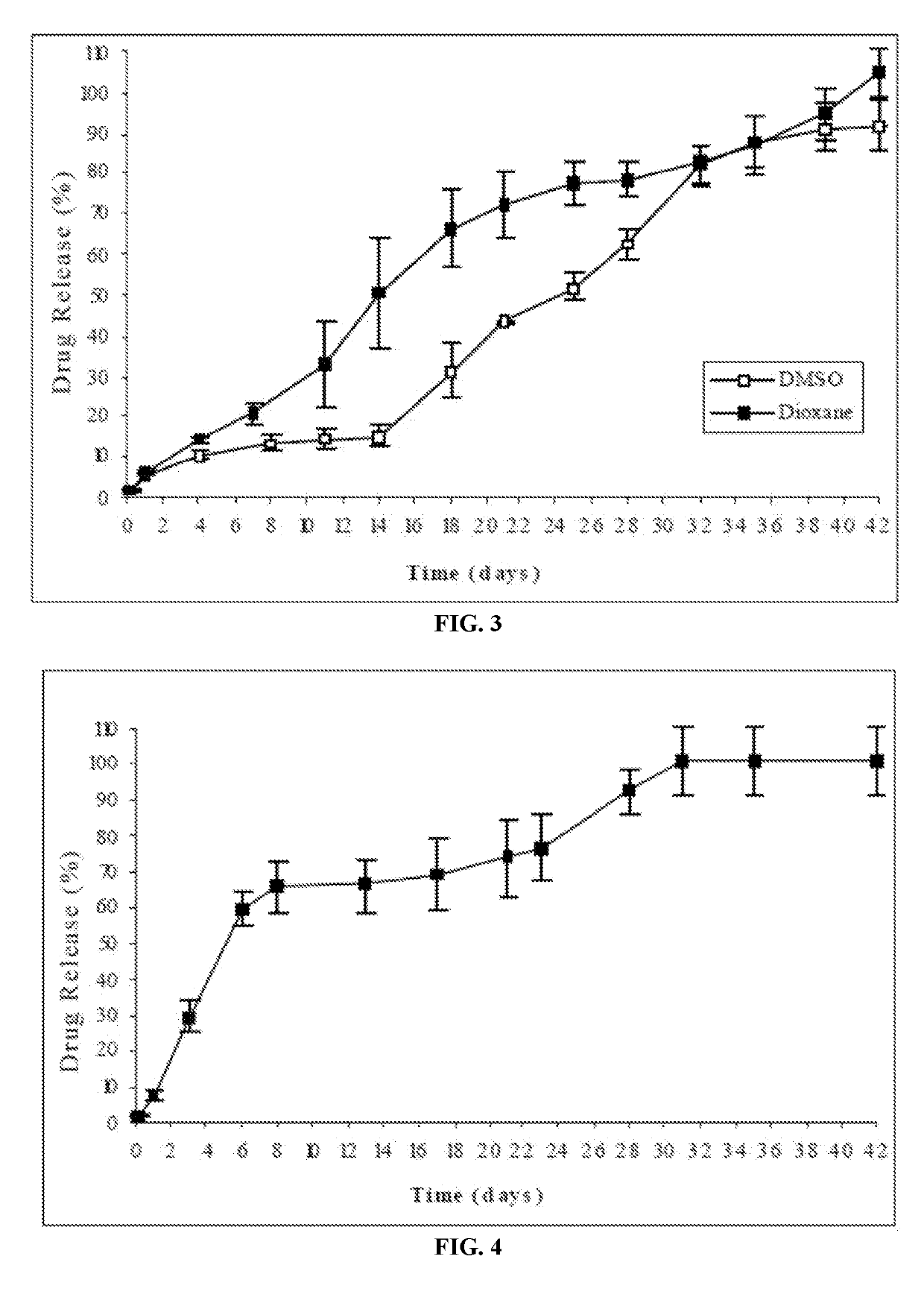
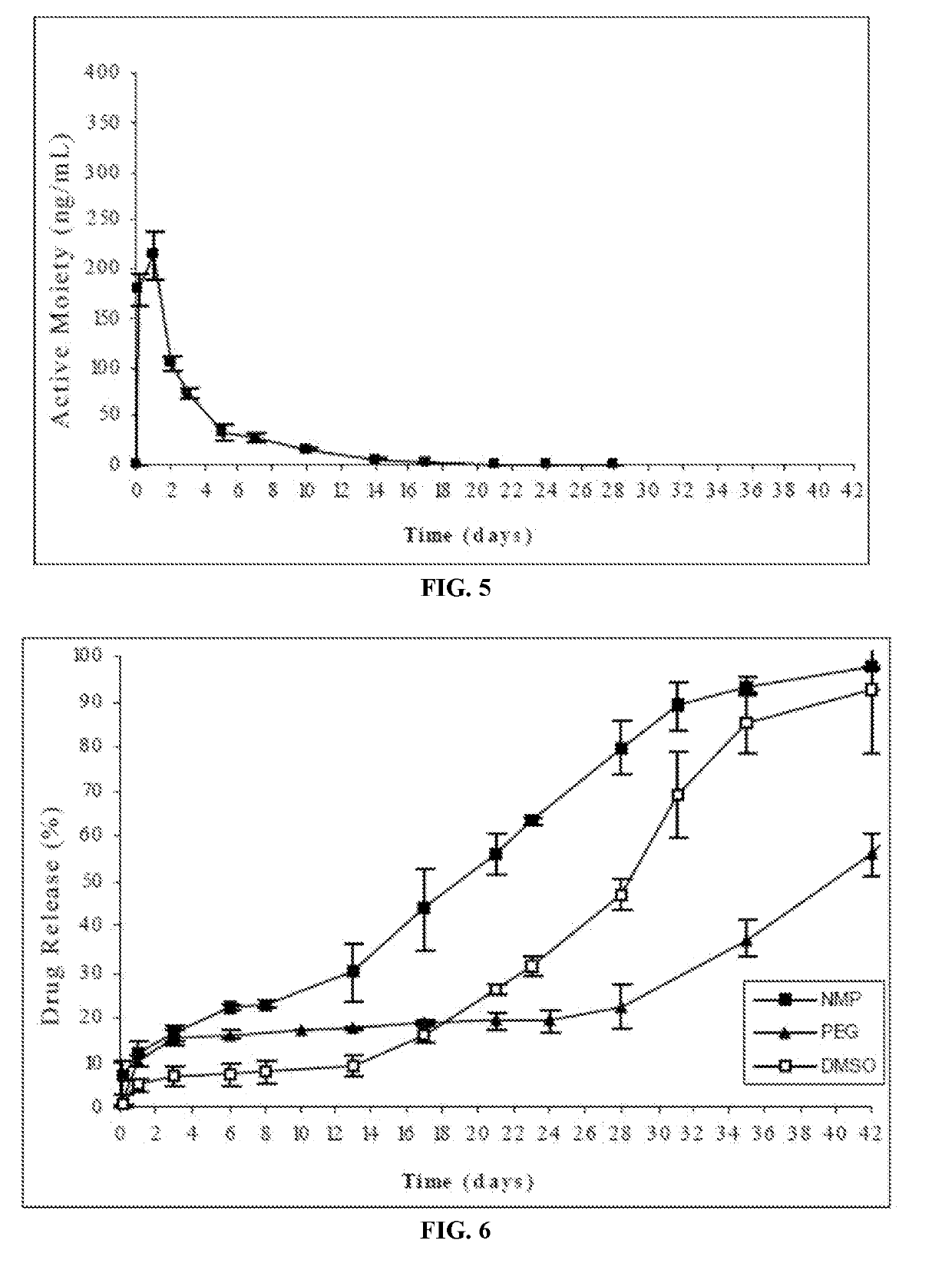
Injectable depot compositions, comprising a biocompatible polymer which is a polymer or copolymer based on lactic acid and / or lactic acid plus glycolic acid having a monomer ratio of lactic to glycolic acid in the range from 48:52 to 100:0, a water-miscible solvent having a dipole moment of about 3.7-4.5 D and a dielectric constant of between 30 and 50, and a drug, were found suitable for forming in-situ biodegradable implants which can evoke therapeutic drug plasma levels from the first day and for at least 14 days.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Fiber-reinforced, porous, biodegradable implant device
InactiveUS7524335B2Promote regenerationProvide strengthBone implantLaminationArticular cartilageInorganic particle
A fiber-reinforced, polymeric implant material useful for tissue engineering, and method of making same are provided. The fibers are preferably aligned predominantly parallel to each other, but may also be aligned in a single plane. The implant material comprises a polymeric matrix, preferably a biodegradable matrix, having fibers substantially uniformly distributed therein. Inorganic particles may also be included in the implant material. In preferred embodiments, porous tissue scaffolds are provided which facilitate regeneration of load-bearing tissues such as articular cartilage and bone. Non-porous fiber-reinforced implant materials are also provided herein useful as permanent implants for load-bearing sites.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
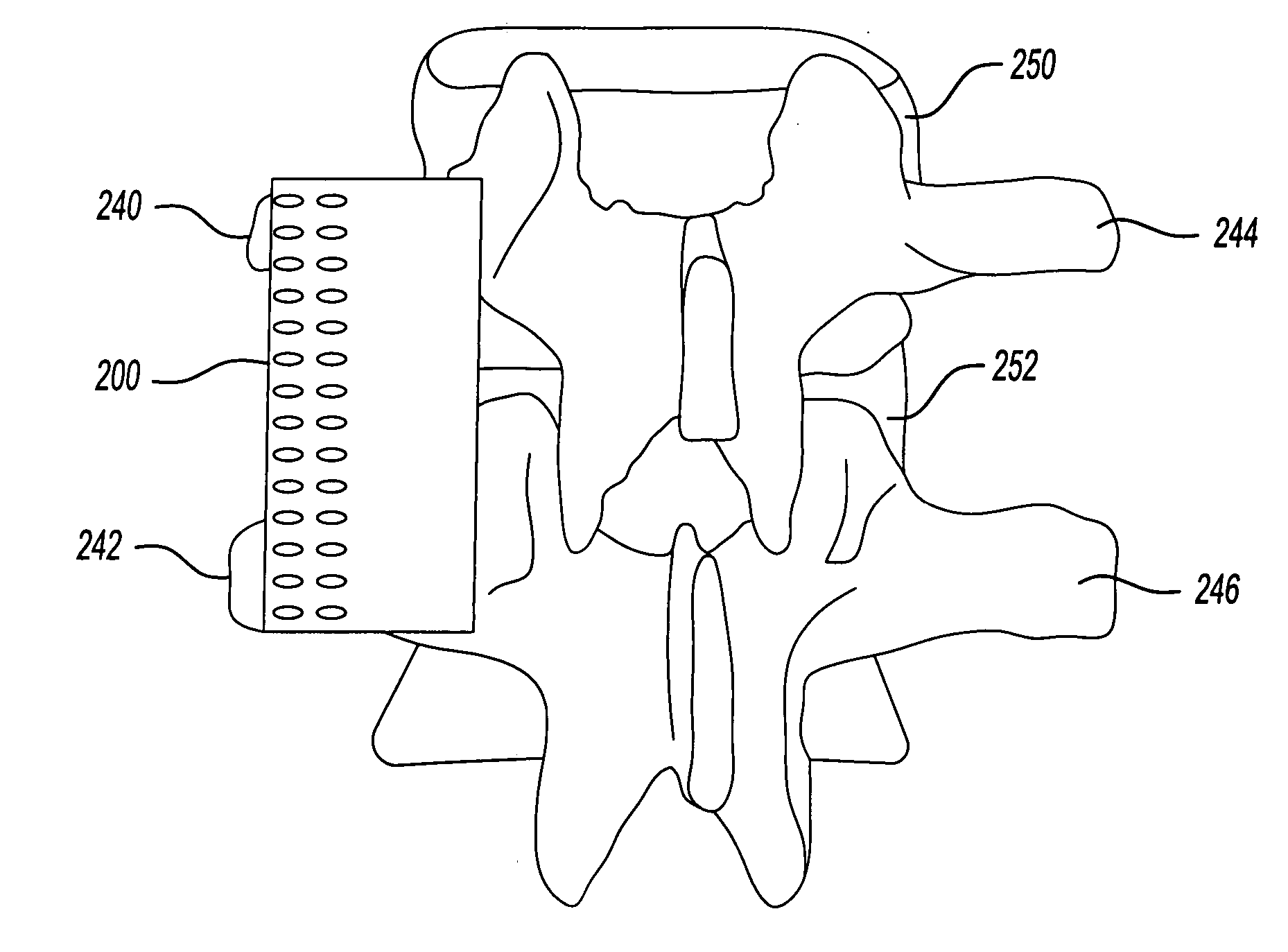
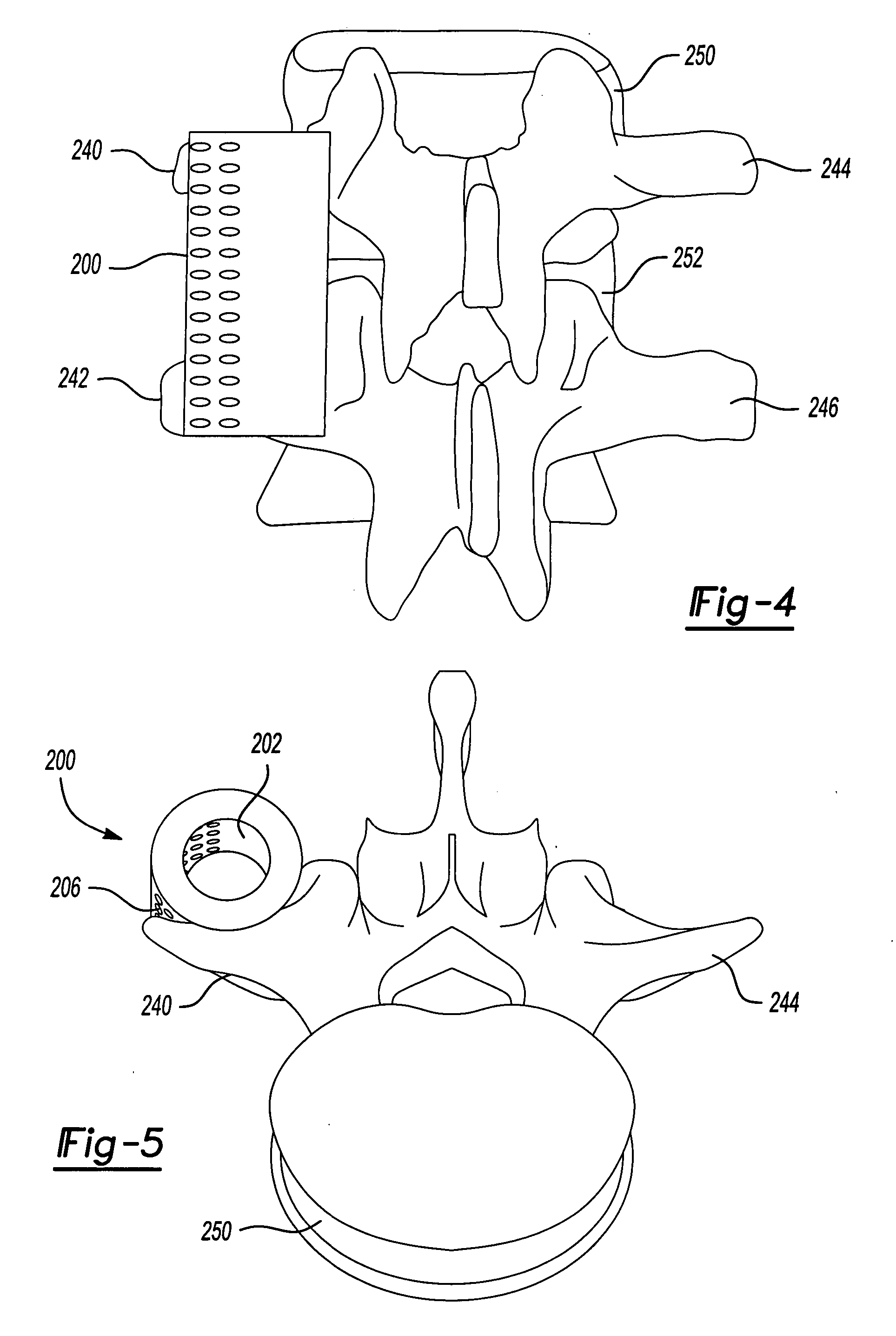
Biodegradable implant for intertransverse process fusion
A biodegradable implant for use in intertransverse process spinal fusion having an absorbable matrix having a bone generating material disposed therein. A molded biodegradable case being made of bioabsorbable polymer can at least partially surround the absorbable matrix to carry a substantial portion of compression force relative to said absorbable matrix.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Biodegradable implant and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120035740A1Reduce biodegradationBetter presentBone implantSpecial surfacesManganeseBiodegradable implants
This invention relates to a biodegradable implant including magnesium, wherein the magnesium contains, as impurities, (i) manganese (Mn); and (ii) one selected from the group consisting of iron (Fe), nickel (Ni) and mixtures of iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), wherein the impurities satisfy the following condition: 0< / (i)≦5, and an amount of the impurities is 1 part by weight or less but exceeding 0 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the magnesium, and to a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:U & I INC
In-vivo biodegradable medical implant
InactiveUS9119906B2The implementation process is simpleReduce internal stressSuture equipmentsBone implantMetallic materialsEngineering
In-vivo biodegradable medical implants, containing at least in part at least partially fine-grained metallic materials that are strong, tough, stiff and lightweight, are disclosed The in-vivo biodegradable implants are used in a number of stent applications, for fracture fixation, sutures and the like. The in-vivo biodegradable medical implants enable the reduction of implant size and weight and consequently result in reducing the release of implant degradation products into the body.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Intraocular drug delivery systems
Biodegradable implants sized and suitable for implantation in an ocular region or site and methods for treating ocular conditions. The implants such as microsheres provide an extended release of an active agent at a therapeutically effective amount for a period of time between 10 days and one year or longer. The active is selected from estradiols such as 2-methoxyestradiol or alpha2-adrenergic agonists such as brimonidine and its derivates or prostagladin analogis.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
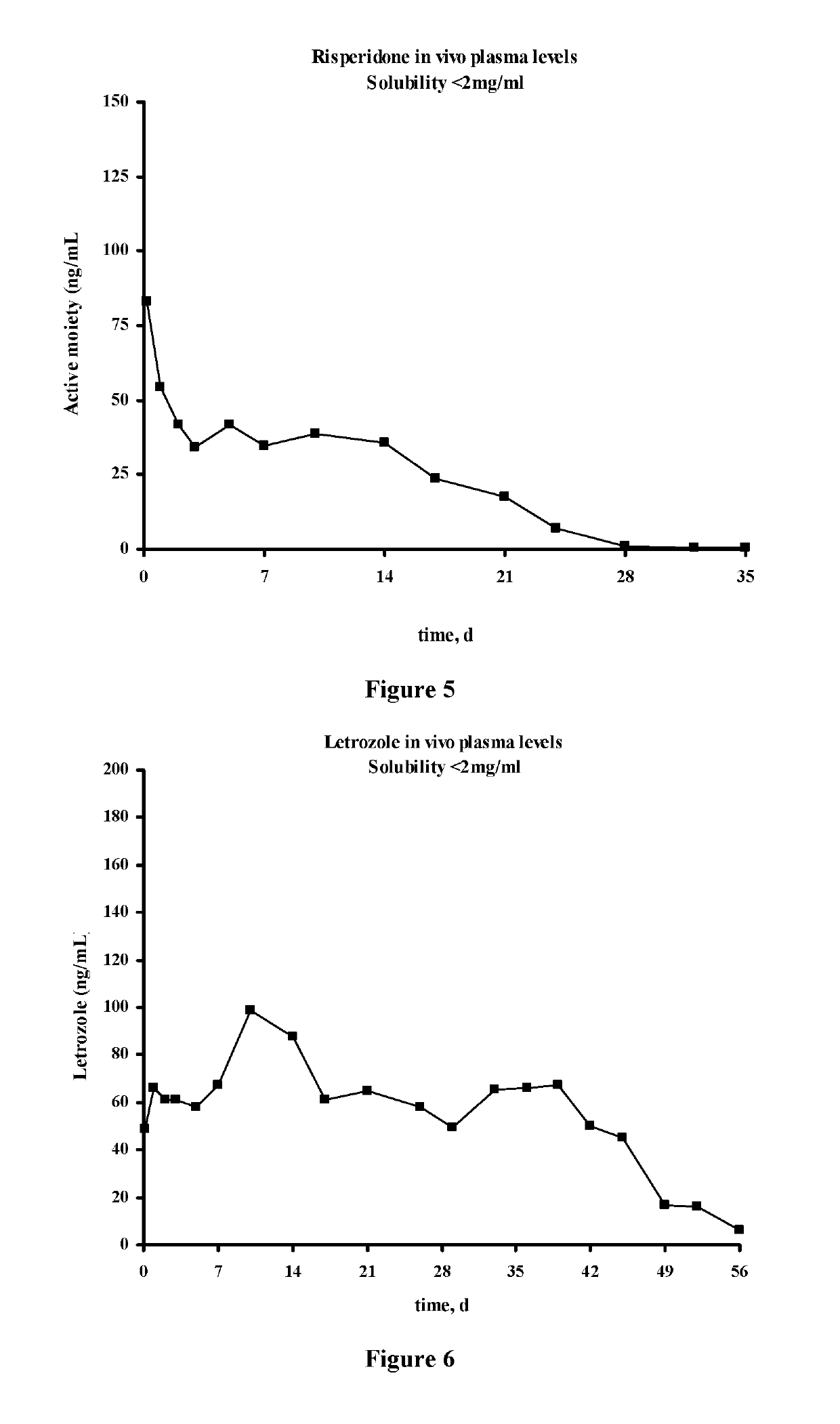
Antipsychotic Injectable Depot Composition
ActiveUS10463607B2Simple methodAvoiding irregular initial burst release of drugOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineSolvent
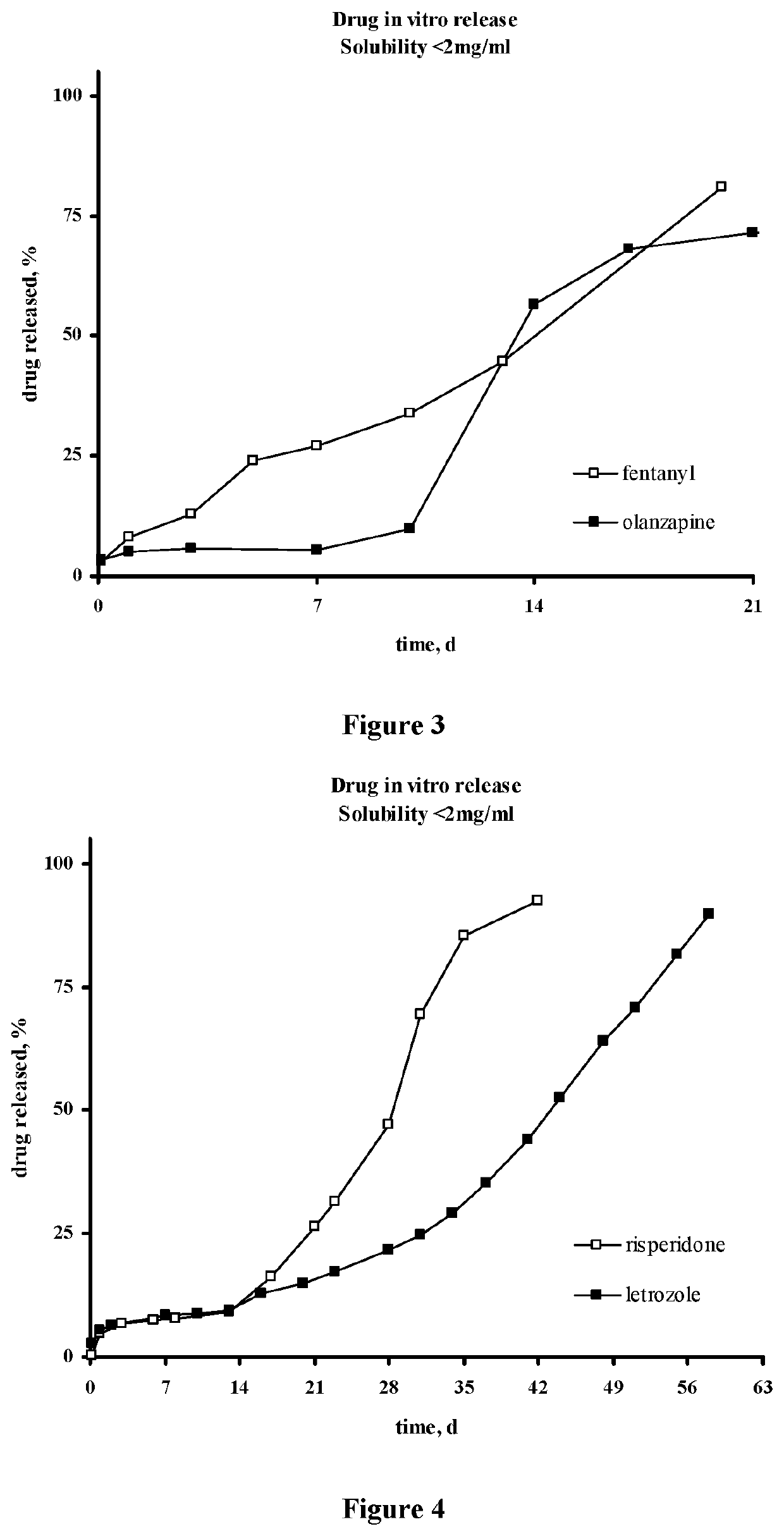
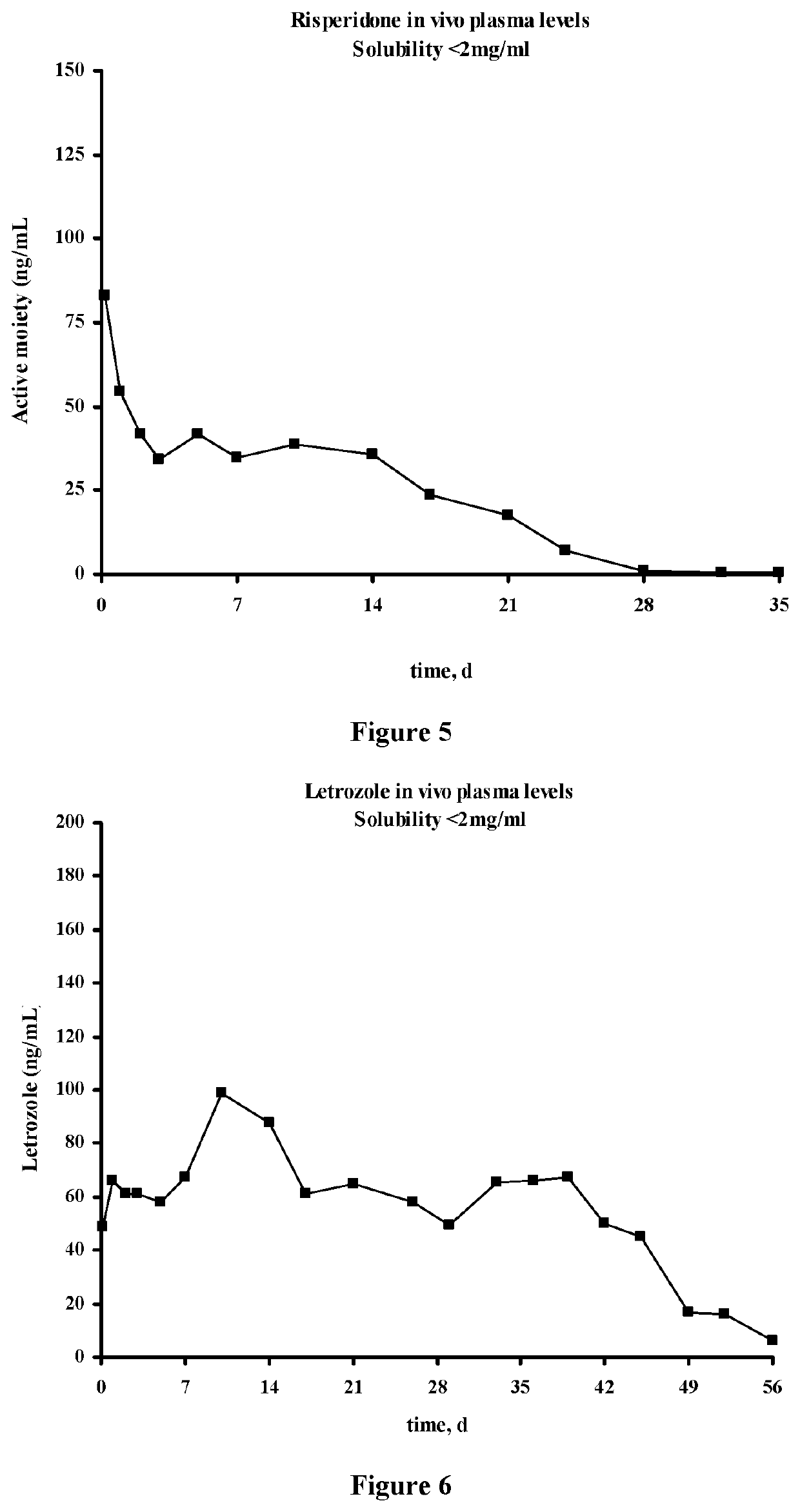
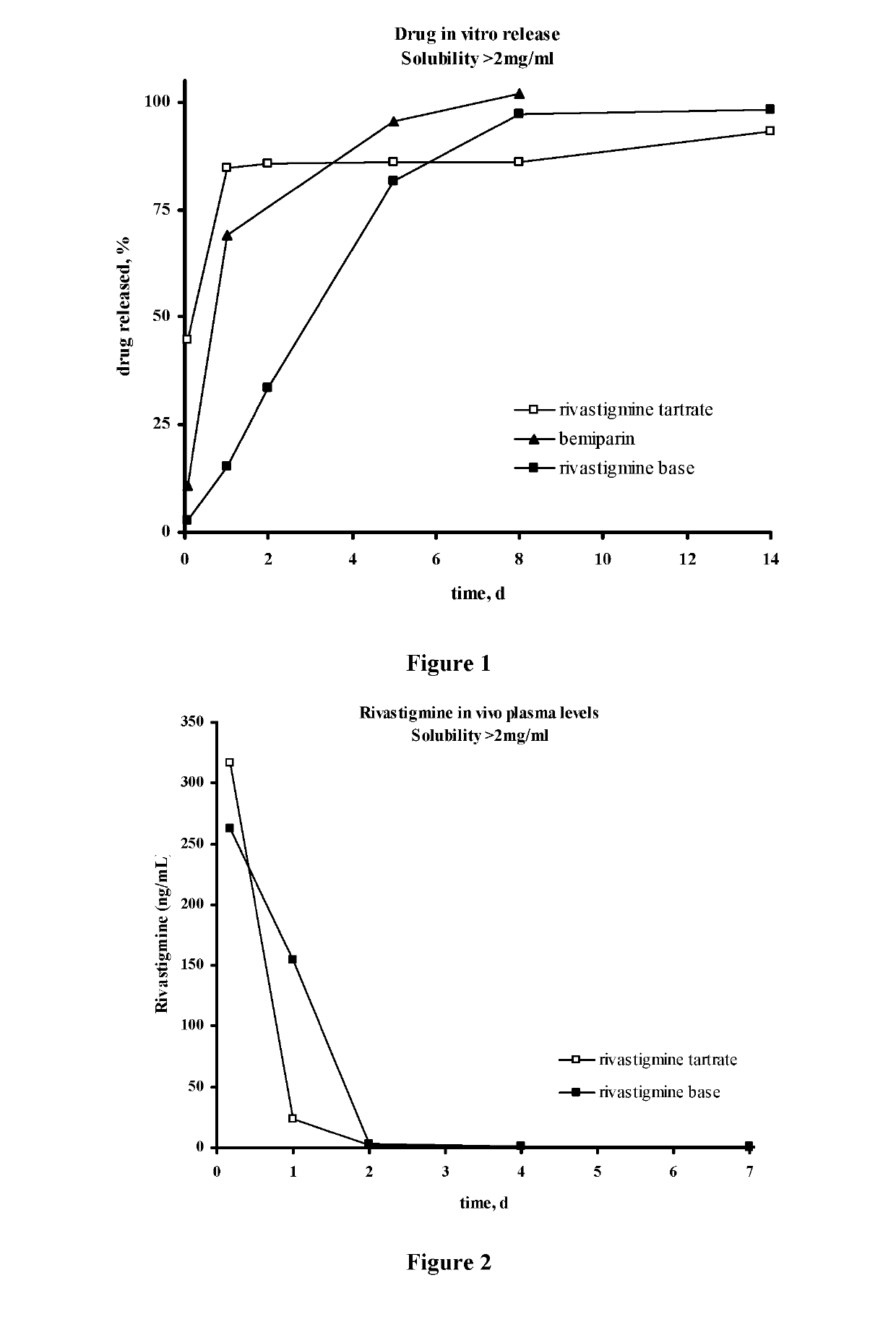
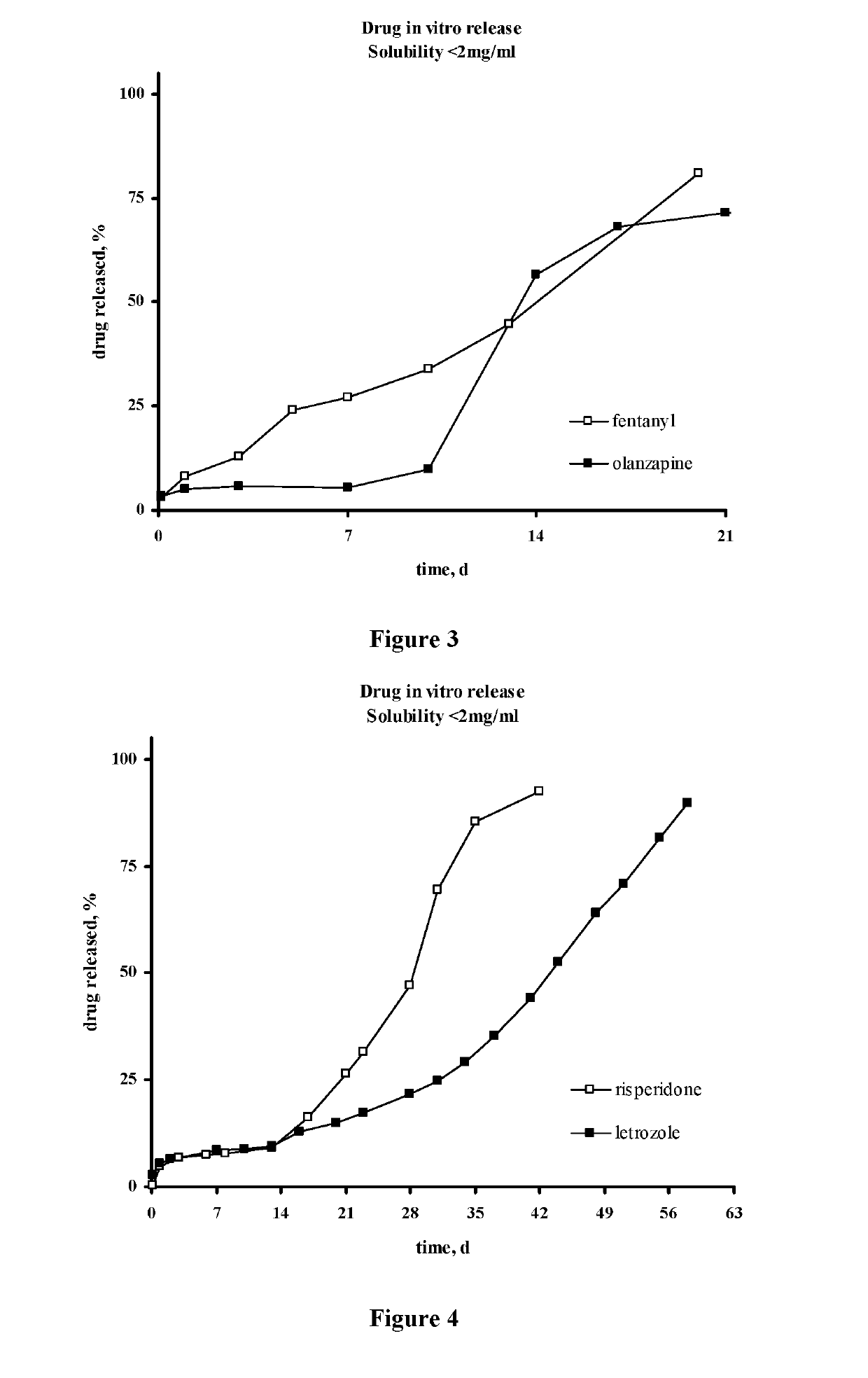
The present invention is directed to a composition that can be used to deliver an antipsychotic drug such as risperidone, paliperidone or a combination thereof, as an injectable in-situ forming biodegradable implant for extended release providing therapeutic plasma levels from the first day. The composition is in the form of drug suspension on a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer or copolymers solution using water miscible solvents that is administered in liquid form. Once the composition contacts the body fluids, the polymer matrix hardens retaining the drug, forming a solid or semisolid implant that releases the drug in a continuous manner. Therapeutic plasma levels of the drug can be achieved from the first day up to at least 14 days or more even up to at least four weeks.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
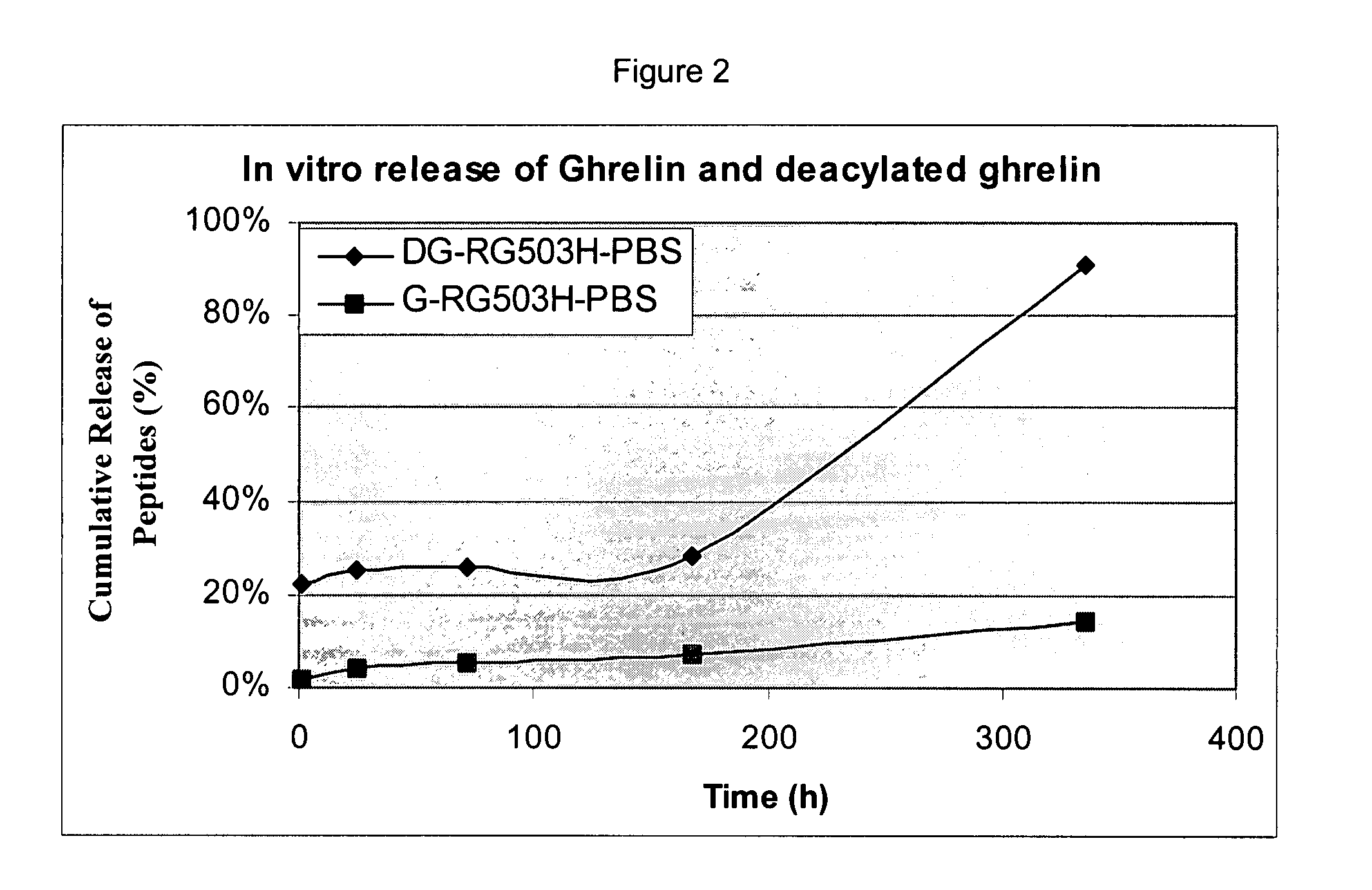
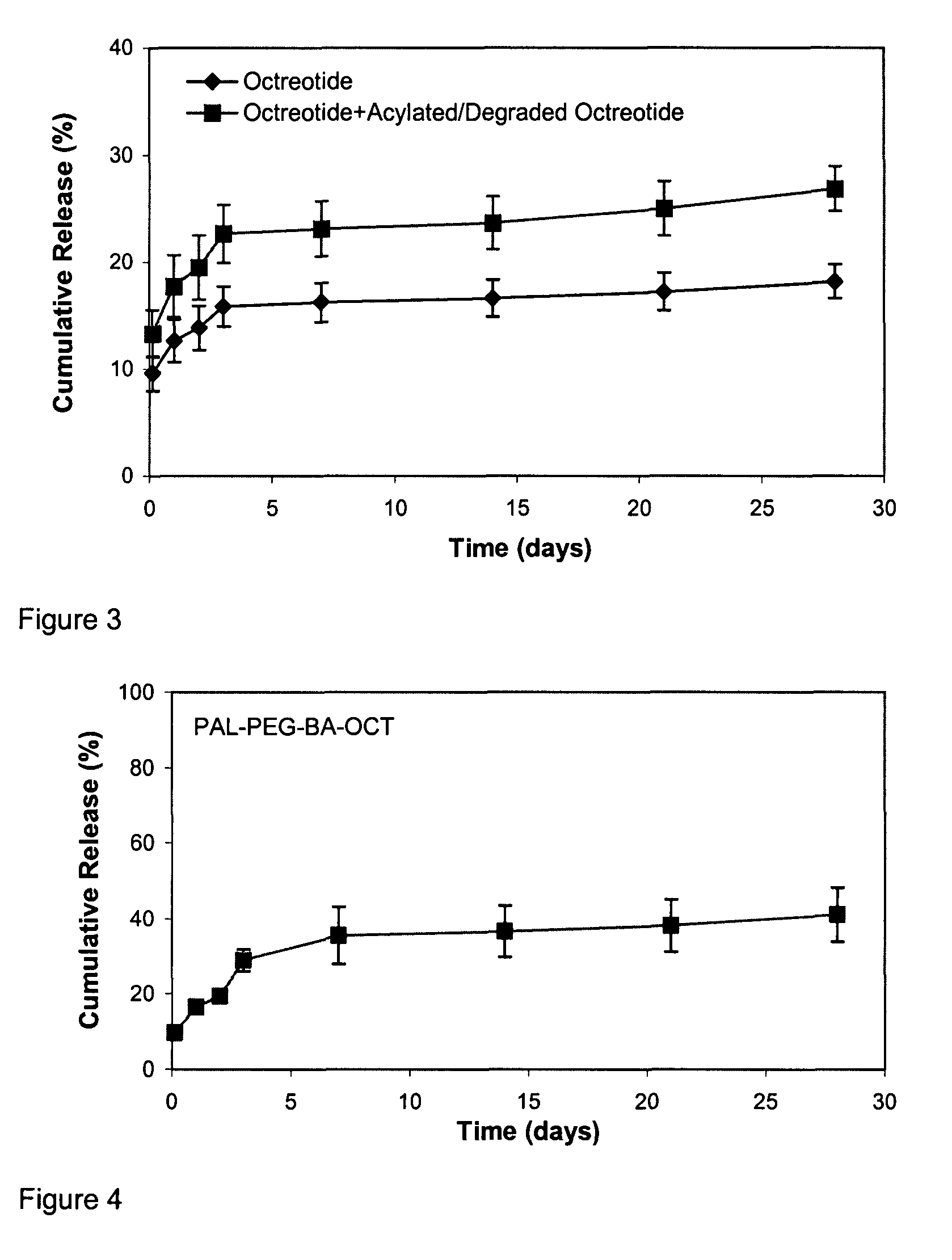
Pharmaceutical compositions for sustained release delivery of peptides
ActiveUS8206735B2Reduce undesired initial burst releaseImproved profileAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiocompatibilityPharmaceutical Substances
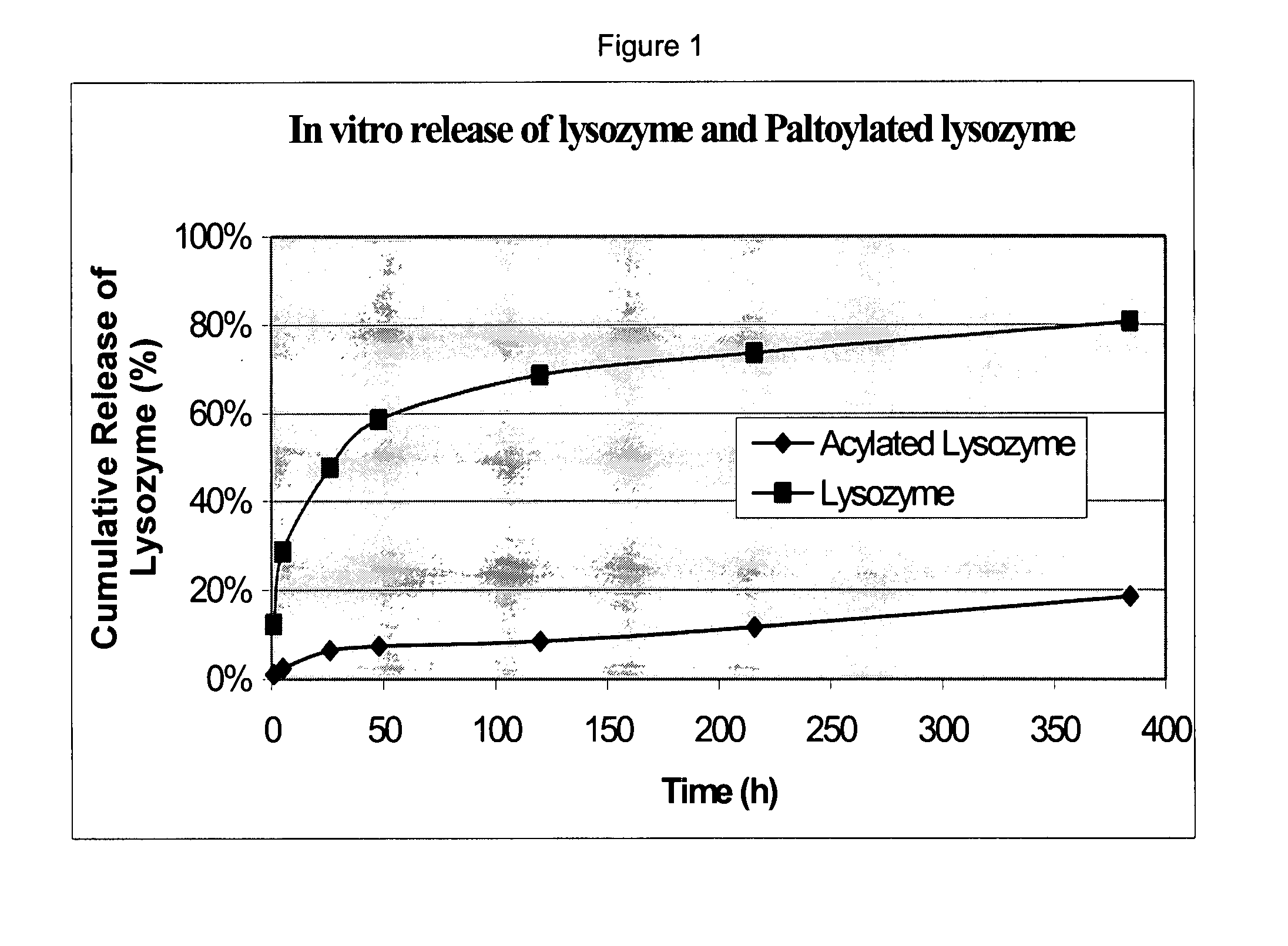
The present invention provides methods of forming a solid, biodegradable implant in-situ in a body by administering a liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising an effective amount of a biocompatible, water-insoluble, biodegradable polymer and an effective amount of a therapeutic peptide covalently modified with one or more lipophilic or amphiphilic moieties, which are dissolved or dispersed in a biocompatible, water-soluble organic solvent. This invention also provides related compositions and methods.
Owner:FORESEE PHARMA CO LTD
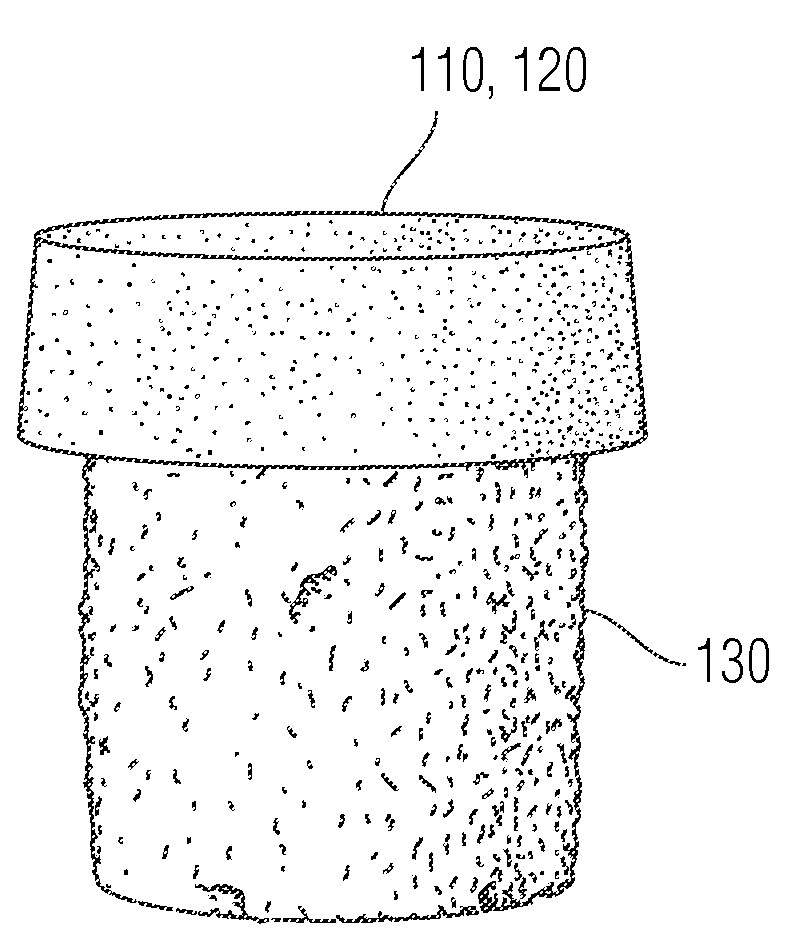
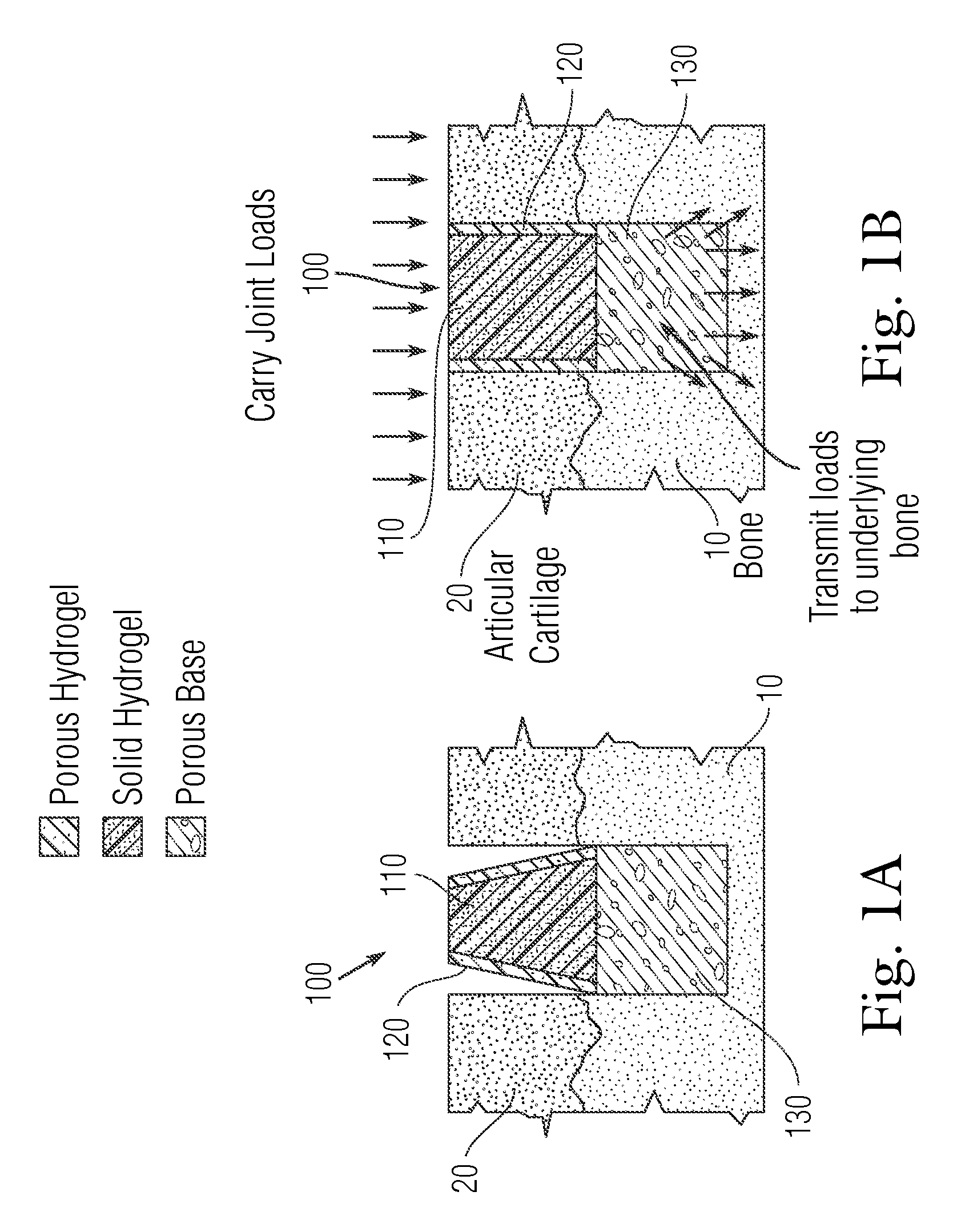
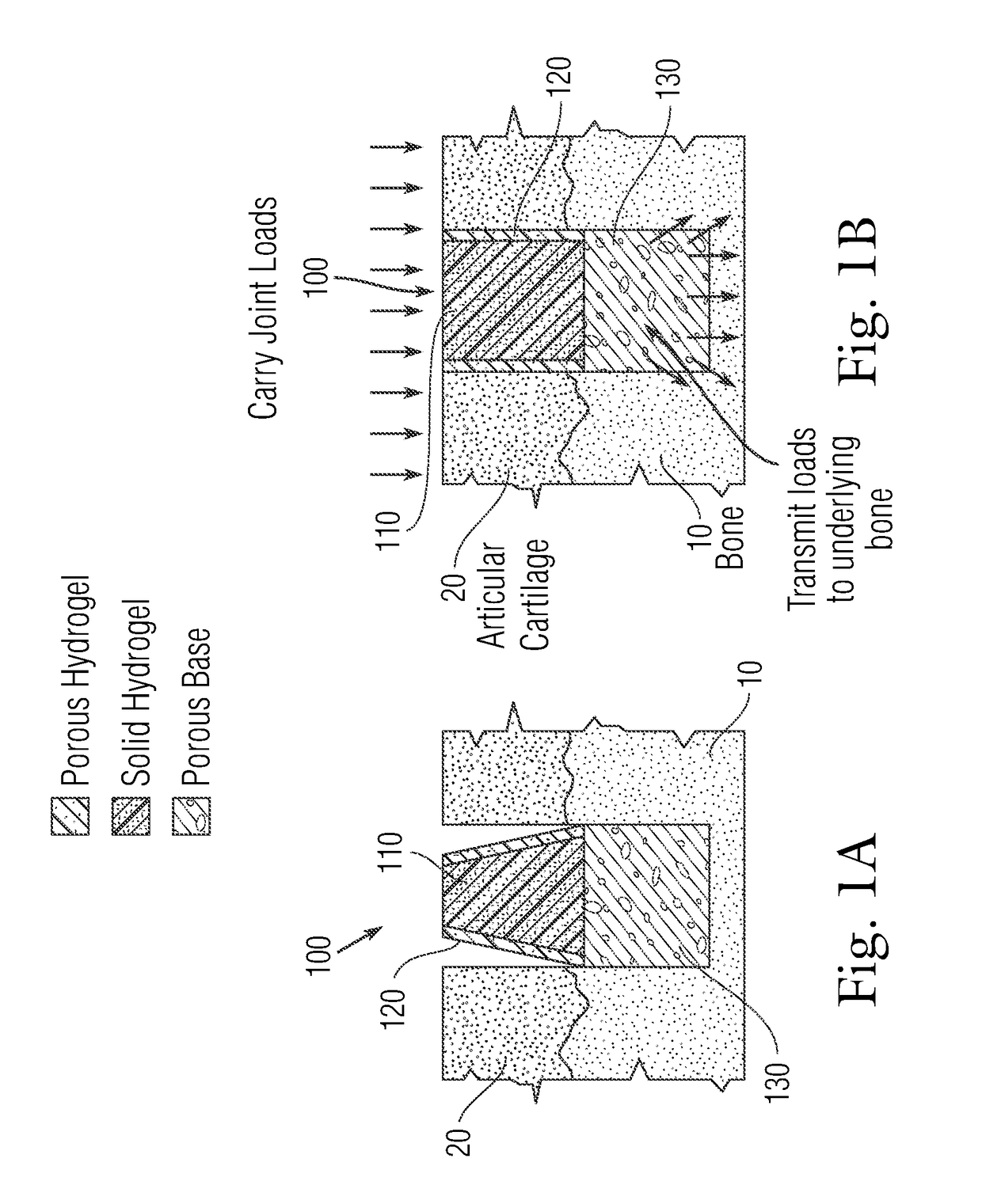
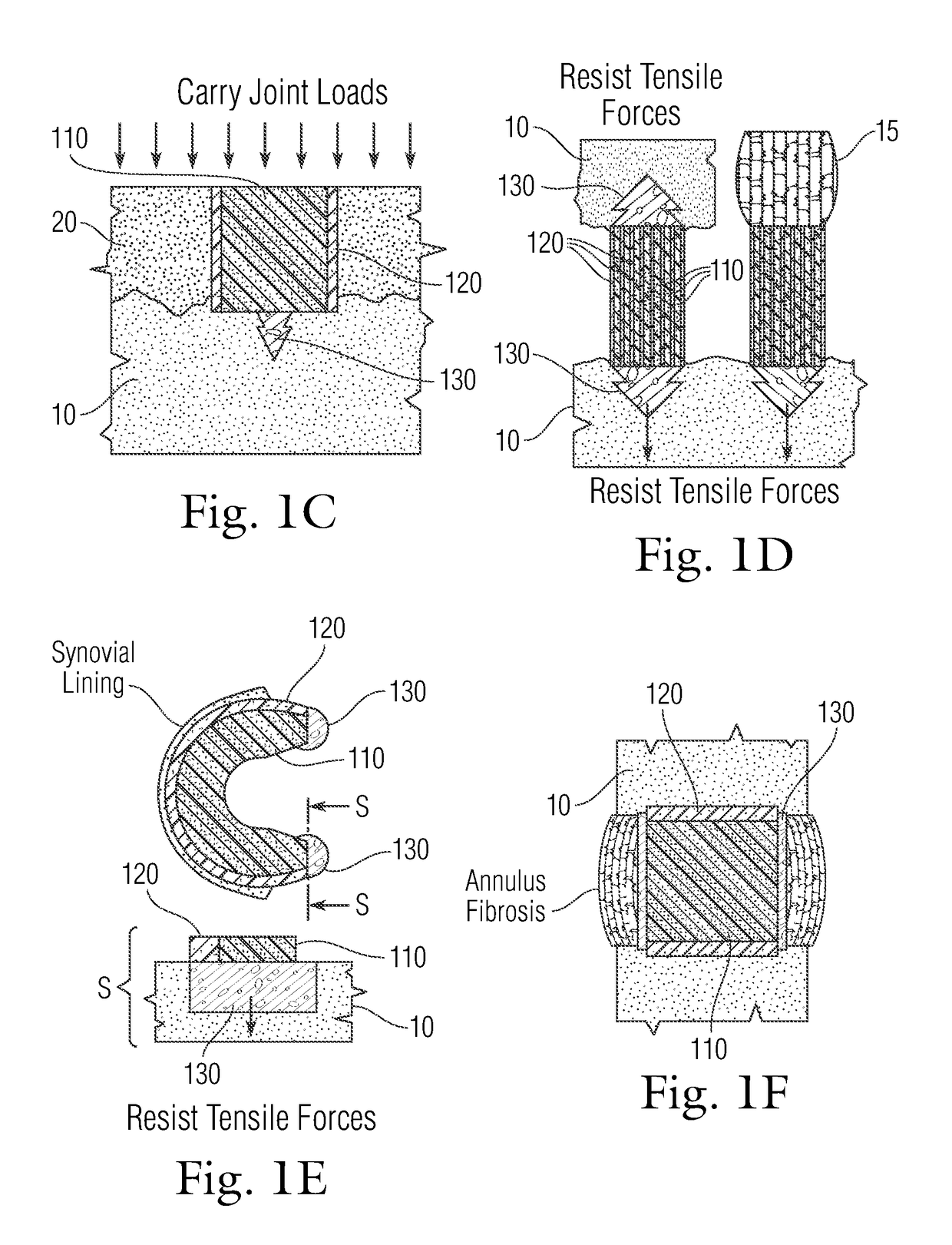
Multi-component non-biodegradable implant, a method of making and a method of implantation
ActiveUS9545310B2Maximizes integrationHigh and low viscosityBone implantSurgeryBiodegradable implantsBiomedical engineering
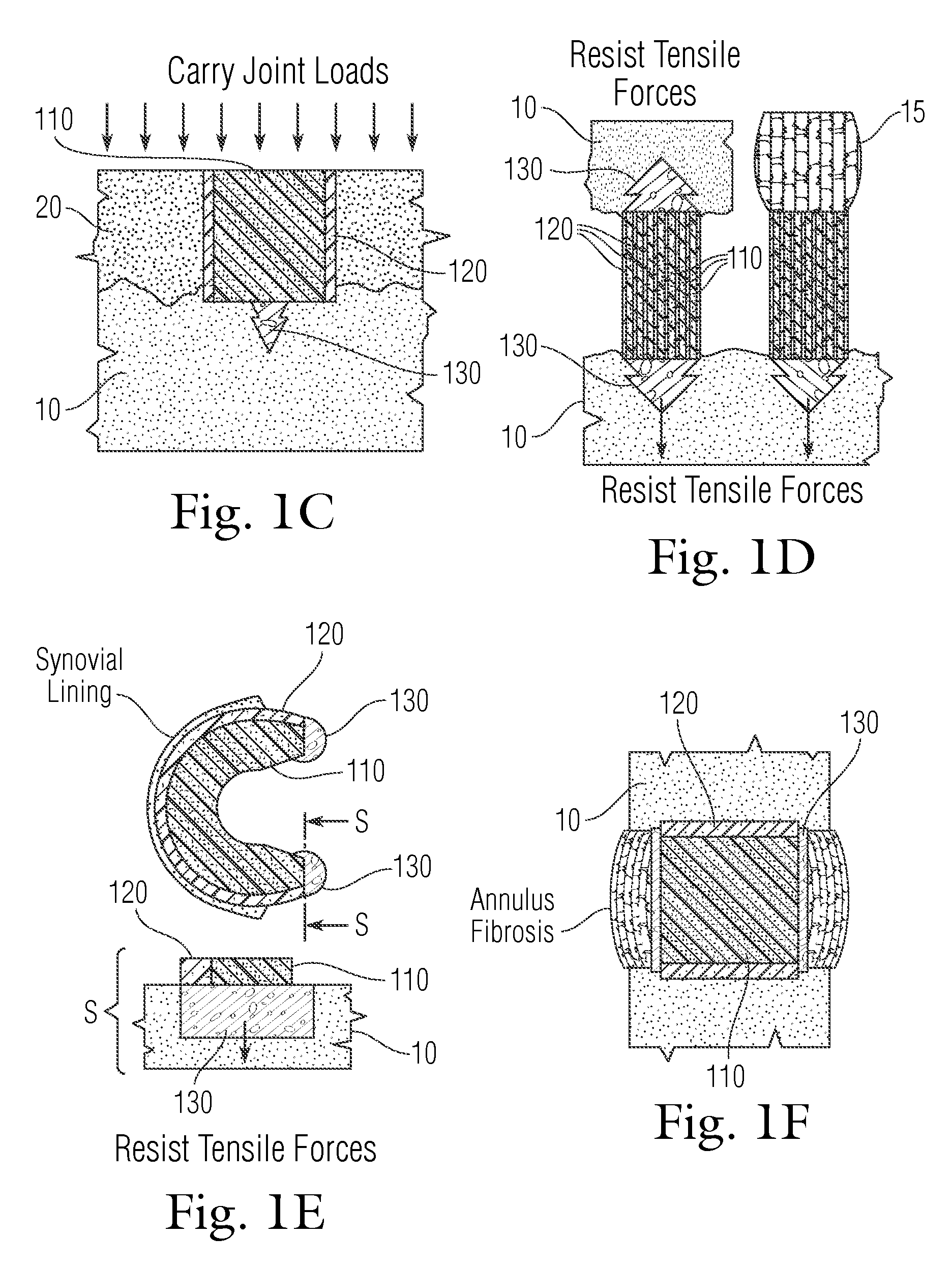
An implant having at least three components, namely, a solid hydrogel, a porous hydrogel adjacent to or surrounding the solid hydrogel (together considered “the hydrogel”), and a porous rigid base. The solid hydrogel and porous rigid base carry joint load, and the porous hydrogel layer and the porous rigid base allow for cellular migration into and around the implant. The invention is also a novel method of manufacturing the implant, a novel method of implanting the implant, and a method of treating, repairing or replacing biological tissue, more preferably musculoskeletal tissue, with the implant.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Methods for the preparation of injectable depot compositions
ActiveUS10881605B2Simple methodAvoiding irregular initial burst release of drugOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineGlycolic acid
Injectable depot compositions comprising a biocompatible polymer which is a polymer or copolymer based on lactic acid and / or lactic acid plus glycolic acid having a monomer ratio of lactic to glycolic acid in the range from 48:52 to 100:0, a water-miscible solvent having a dipole moment of about 3.7-4.5 D and a dielectric constant of between 30 and 50, and a drug, were found suitable for forming in-situ biodegradable implants which can evoke therapeutic drug plasma levels from the first day and for at least 14 days.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Porous biocompatible implant material and method for its fabrication
ActiveUS8153148B2Reduce lossesPromote growthSurgical adhesivesLigamentsBiological bodyPolymer coatings
A biocompatible and biodegradable implant for a cavity in a bone of a living organism is made of biocompatible and biodegradable granules. The biocompatible and biodegradable granules are provided with a coating, which includes at least one layer of a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer. The biocompatible and biodegradable implants are obtained by fusing together the polymer-coated granules through polymer-linkage of the polymer coatings of neighboring granules.
Owner:COLLAGEN MATRIX
Antipsychotic Injectable Depot Composition
ActiveUS20180221272A1Simple methodConstant effectiveNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSolventBlood plasma
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Methods for the Preparation of Injectable Depot Compositions
ActiveUS20180318208A1Easy to controlConstant effectiveOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineGlycolic acid
Injectable depot compositions, comprising a biocompatible polymer which is a polymer or copolymer based on lactic acid and / or lactic acid plus glycolic acid having a monomer ratio of lactic to glycolic acid in the range from 48:52 to 100:0, a water-miscible solvent having a dipole moment of about 3.7-4.5 D and a dielectric constant of between 30 and 50, and a drug, were found suitable for forming in-situ biodegradable implants which can evoke therapeutic drug plasma levels from the first day and for at least 14 days.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Biodegradable implant for intertransverse process fusion
A biodegradable implant for use in intertransverse process spinal fusion having an absorbable matrix having a bone generating material disposed therein. A molded biodegradable case being made of bioabsorbable polymer can at least partially surround the absorbable matrix to carry a substantial portion of compression force relative to said absorbable matrix.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Antipsychotic Injectable Depot Composition
ActiveUS20190117554A1Simple methodConstant and effective plasma levelOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSolventBlood plasma
The present invention is directed to a composition that can be used to deliver an antipsychotic drug such as risperidone, paliperidone or a combination thereof, as an injectable in-situ forming biodegradable implant for extended release providing therapeutic plasma levels from the first day. The composition is in the form of drug suspension on a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer or copolymers solution using water miscible solvents that is administered in liquid form. Once the composition contacts the body fluids, the polymer matrix hardens retaining the drug, forming a solid or semisolid implant that releases the drug in a continuous manner. Therapeutic plasma levels of the drug can be achieved from the first day up to at least 14 days or more even up to at least four weeks.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Methods for the Preparation of Injectable Depot Compositions
ActiveUS20190151230A1Simple methodAvoiding irregular initial burst release of drugOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineGlycolic acid
Injectable depot compositions comprising a biocompatible polymer which is a polymer or copolymer based on lactic acid and / or lactic acid plus glycolic acid having a monomer ratio of lactic to glycolic acid in the range from 48:52 to 100:0, a water-miscible solvent having a dipole moment of about 3.7-4.5 D and a dielectric constant of between 30 and 50, and a drug, were found suitable for forming in-situ biodegradable implants which can evoke therapeutic drug plasma levels from the first day and for at least 14 days.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Multi-component non-biodegradable implant, a method of making and a method of implantation
ActiveUS20170209624A1Maximizes integrationHigh and low viscosityBone implantSurgeryEngineeringBiodegradable implants
An implant comprising at least three components, namely, a solid hydrogel, a porous hydrogel adjacent to or surrounding the solid hydrogel (together considered “the hydrogel”), and a porous rigid base. The solid hydrogel and porous rigid base carry joint load, and the porous hydrogel layer and the porous rigid base allow for cellular migration into and around the implant. The invention is also a novel method of manufacturing the implant, a novel method of implanting the implant, and a method of treating, repairing or replacing biological tissue, more preferably musculoskeletal tissue, with the implant.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Biodegradable implantation controlled-release microsphere using vibration membrane technique
InactiveCN101416946AResistant to degradabilityNot easy to failPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrosphereOil phase
The invention relates to a biodegradable implanting controlled release microsphere prepared by adopting a vibrating diaphragm technology, and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to the filed of pharmacy. The invention aims at overcoming the technical problems that parts of the existing target area have low controlled release drug-load rate and a crude drug is easy to be degraded and become ineffective during the preparation process, and providing a new preparation method of the biodegradable implanting controlled release microspheres. The preparation method adopts the physical method of the vibrating diaphragm technology, evenly spreads the crude drug with the particle diameter of 10nm to 50nm in a carrier to prepare nano-particles with the particle diameter of 10 nanometers to 200 nanometers. The biodegradable implanting controlled release microsphere has the drug-load rate reaching about 20 percent to 40 percent; the use and residual of various toxic organic solvents are reduced during the preparation process; meanwhile, the transferring process from oil phase and aqueous phase of the crude drug does not exist, thereby avoiding crude drug loss; furthermore, low-temperature grinding is adopted during the preparation process, thereby preventing the crude drug from degrading and becoming ineffective during the preparation process and being capable of realizing the scale and target of industrialized production.
Owner:王剑
Use of plasma-synthesised pyrrole-derived polymers for the neuroprotection and reconnection of the central nervous system
The purpose of the present invention is to demonstrate that semiconducting and non-biodegradable implants made with polypyrrole and polyethylenglycol copolymers and iodine-doped and plasma-synthesized pyrrole polymers, have a neuroprotector effect and induce the reconnection of the spinal cord after an injury; this effect was proved in a model involving a complete section of the spinal cord in rats; the results o the functional evaluation demonstrated 5 times greater recovery in animals implanted with the polypyrrole-polyethylenglycol copolymer compared with the control group which only underwent a complete section of the spinal cord; in addition, the functional recovery of the group with iodine-doped polypyrrole was ten times greater compared to the control group; in the histological study various inflammatory and immune cells were identified at the injury site in the three experimental groups with and without implants and the integration of the polymers in the nervous tissue of the spinal cord was also observed; finally, no respiratory, renal or skin infections, adverse effects or rejection of the biomaterials were found in any of the animals.
Owner:UNIV AUTONOMA METROPOLITANA +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com