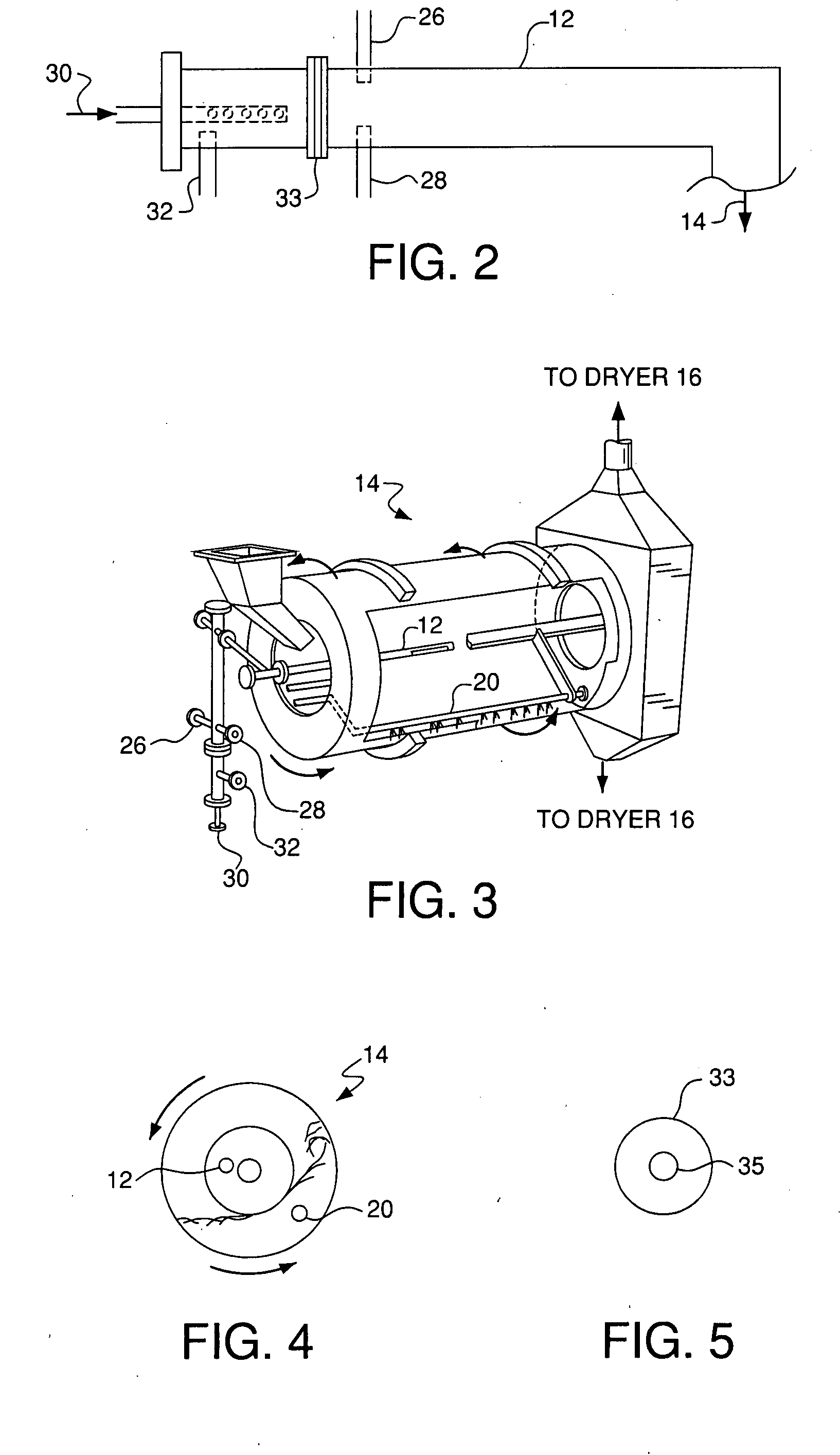
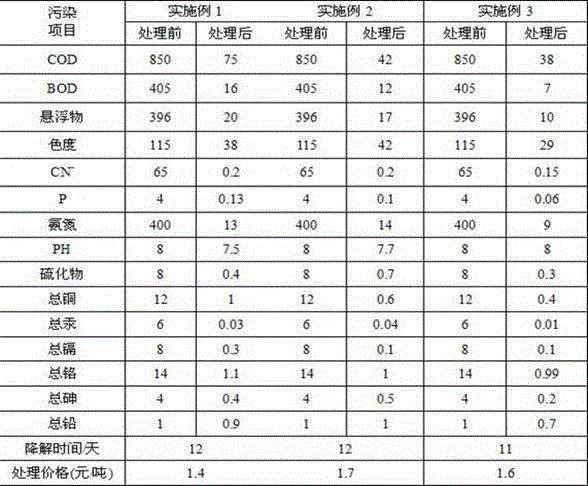
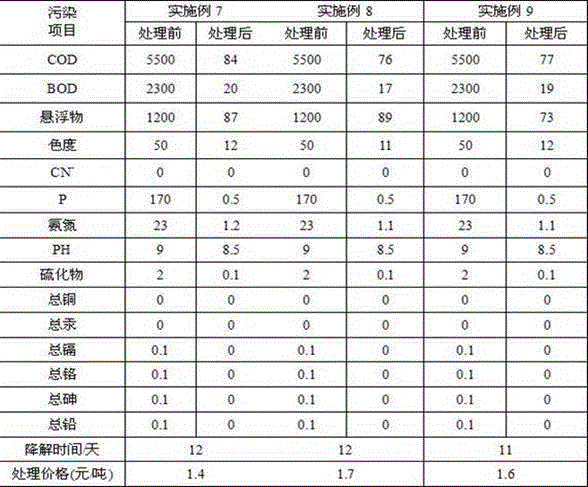
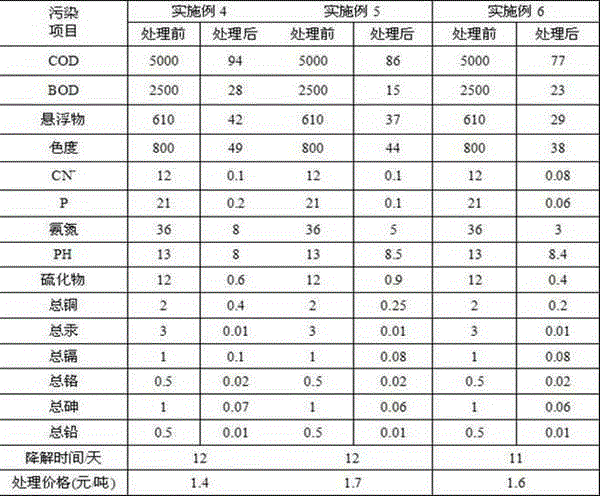
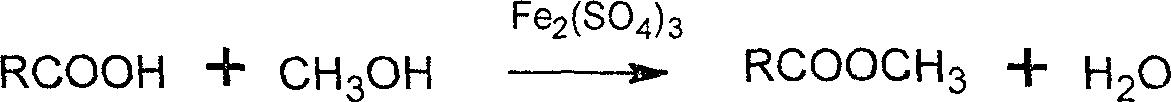Patents
Literature
1519 results about "Iron sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron sulfate may refer to: Ferrous sulfate, Iron sulfate, FeSO₄ Ferric sulfate, Iron sulfate, Fe₂(SO₄)₃
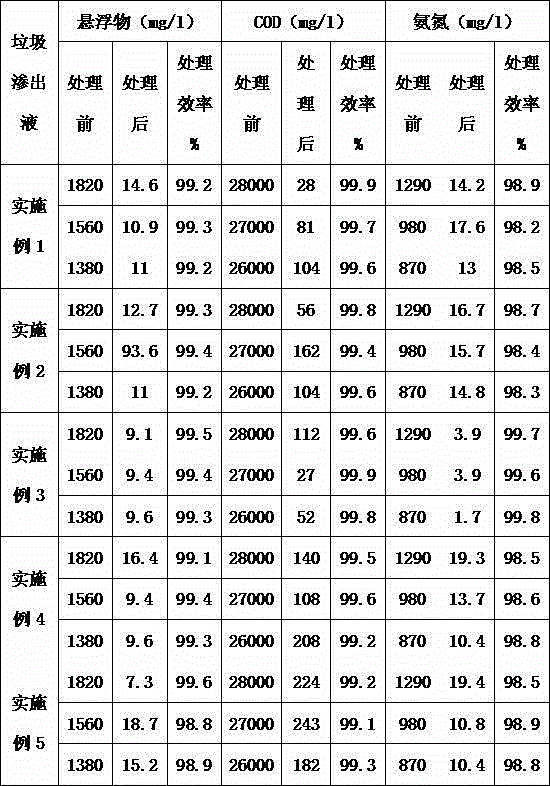
Organic recycling with metal addition
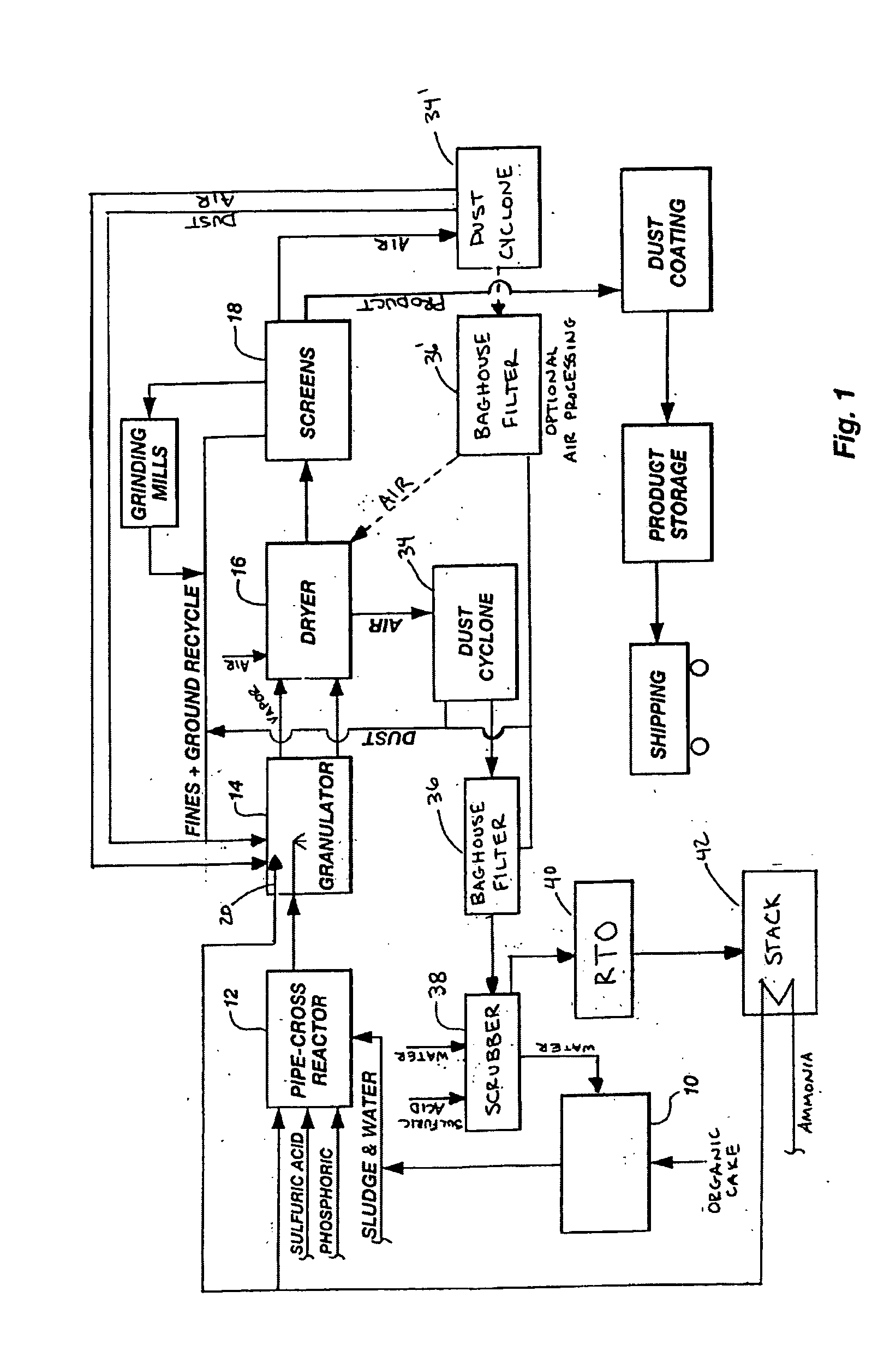
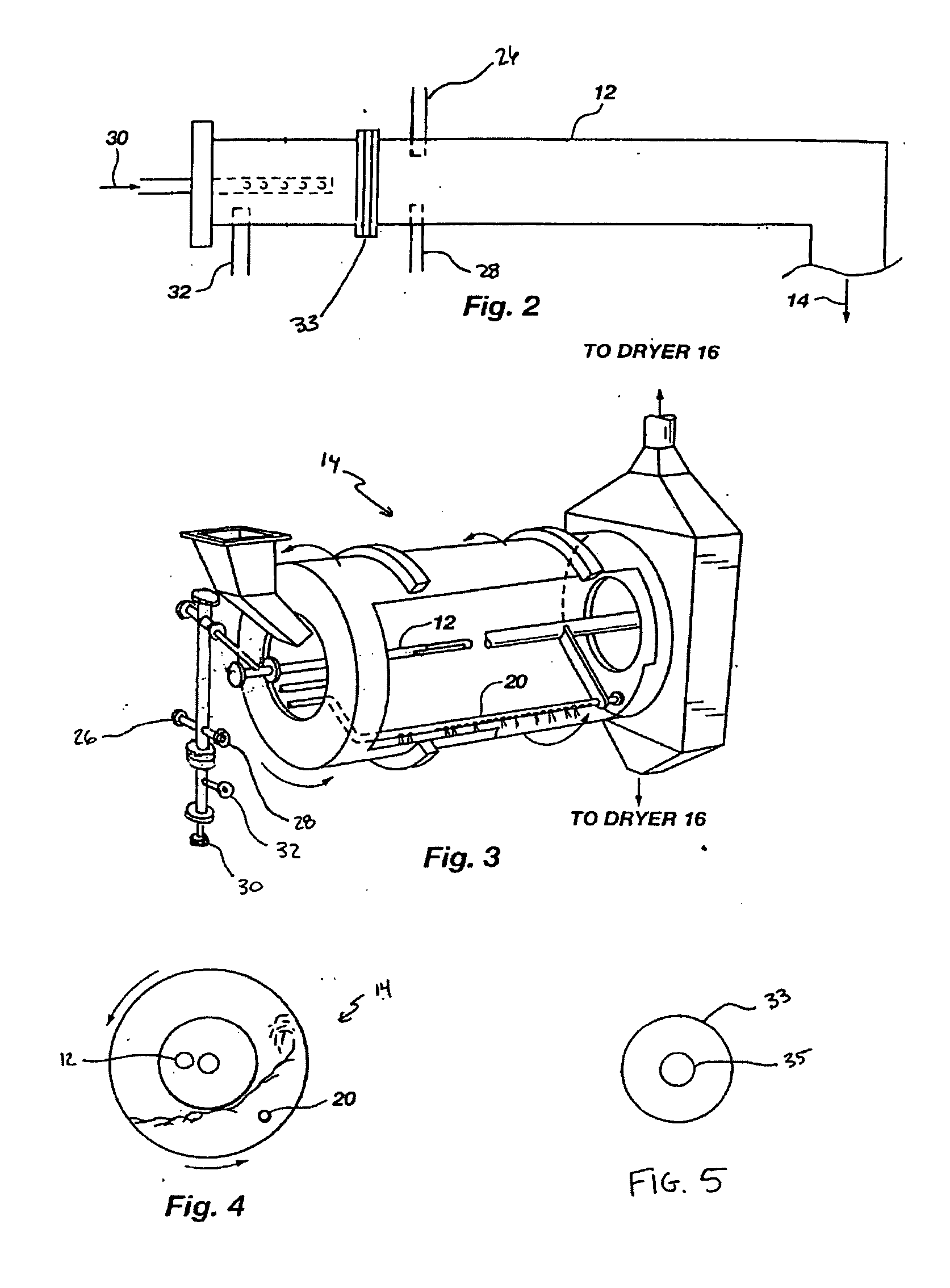
InactiveUS20050039508A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
The invention is directed to methods for producing a granular nitrogen fertilizer from an organic material comprising adding a metallic salt to said organic material to form a slurry. Preferably the organic material comprises dewatered biosolids and contains water from a scrubber. Metallic salts that can be used comprise a salt of iron, zinc, or a mixture thereof. Preferred iron salts comprises ferric sulfate or ferric oxide, and preferred zinc salts comprises zinc sulfate or zinc oxide. Preferably, the metallic salt is mixed with an acid such as sulfuric acid to form an acidified metal salt. Slurry pH ranges from approximately 2-2.5. The acidified metal salt is added to the organic material in sufficient quantity to lower viscosity of the slurry such that the resulting fluid does not hinder fluid flow during operation. When the metallic salt comprises acidified ferric sulfate or ferrous sulfate, sufficient iron can be present to produce a fertilizer product with 0.1 weight percent to 10 weight percent iron sulfate calculated on a dry weight basis. The invention is also directed to fertilizer products made by the methods of the invention. Preferred products are granules and the metallic salt increases product hardness. Fertilizer granules preferably contain metal that is bioavailable to a plant when used as a fertilizer. Solubility of the metal of the product in water is enhanced, and the product is low staining.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP +1
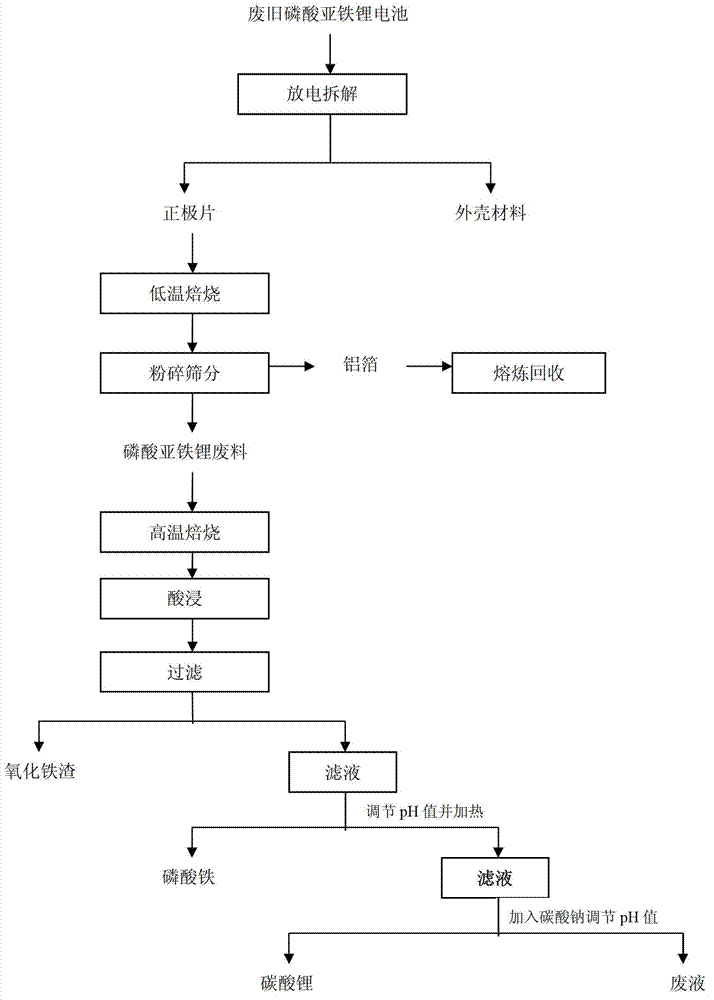
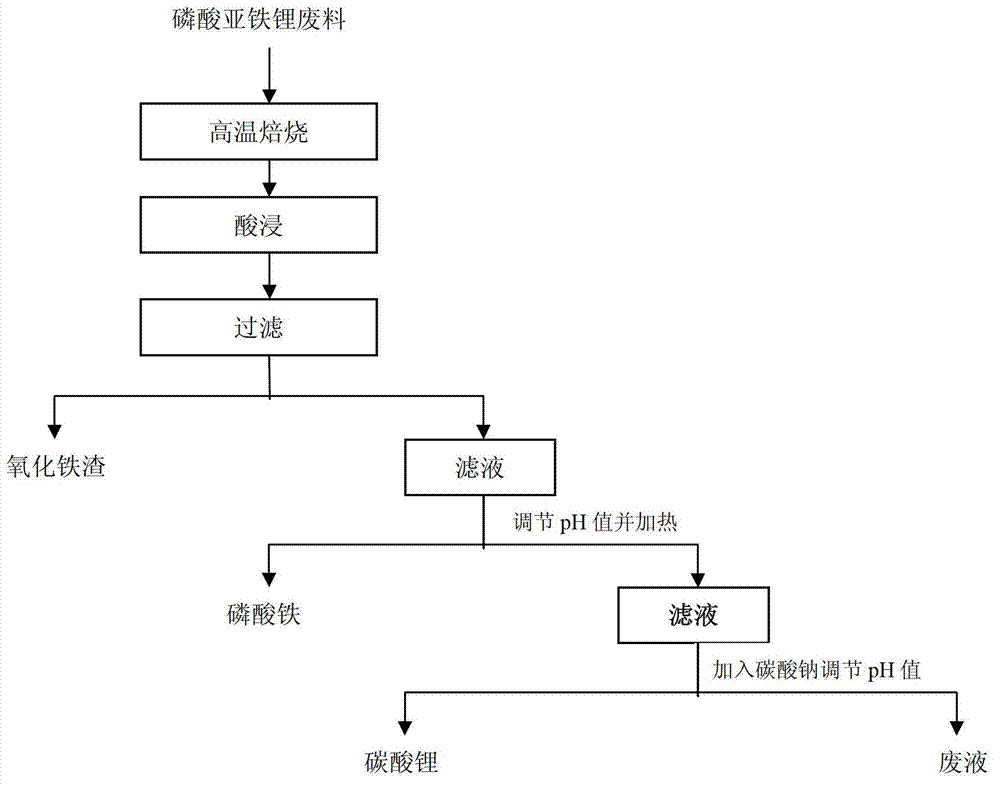
Method for recycling lithium carbonate from lithium iron phosphate waste material
ActiveCN102903985ASolve the problem of resource recyclingSolve your worriesWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingIron sulfateWaste material
The invention relates to a method for recycling lithium carbonate from a lithium iron phosphate waste material, and belongs to the technical field of waste lithium oil battery recycling. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is that a method for recycling lithium carbonate from the lithium iron phosphate waste material is provided. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: roasting the lithium iron phosphate waste material at 500-800 DEG C for 1-4 hours; adding sulfur into the roasted waste material and leaching, and filtering so as to obtain a mixed solution of lithium phosphate, iron phosphate and ferric sulfate; heating the mixed solution to 80-100 DEG C, and adjusting the pH value to 2-2.5, reacting for 1-4 hours, filtering, washing, and drying to obtain iron phosphate; adjusting the pH value of a filtrate obtained by filtering to be 6-7, adding calcium chloride and dephosphorizing, and filtering; and adjusting the pH value of the filtrate obtained by filtering to be 10-12 by sodium carbonate, reacting for 0.5-2 hours, filtering, washing, and drying so as to obtain battery grade lithium carbonate.
Owner:天齐锂业(江苏)有限公司 +2
Iron-base catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and its preparation method
ActiveCN1597105AReduce manufacturing costLow priceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIron sulfatePotassium silicate
A Fe-based catalyst for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis contains Re2O3, Fe3O4, La2O3, CuO, K2O and SiO2. It is prepared through using oxidant to oxidize partially the ferrous sulfate to obtain the mixed solution of iron sulfate and ferrous sulfate, mixing with the mixed solution of lanthanum nitrate and copper salt, fast depositing by alkaline compound, washing the deposited slurry, adding potassium silicate-water glass solution, and spray drying.
Owner:SYNFUELS CHINA TECH CO LTD
Organic recycling with metal addition
InactiveUS20080034822A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER LLC
Method for extracting aurum from difficult-to-handle sulphide ore aurum concentrate by two-segment pressurization leaching method
InactiveCN101876005ADoes not affect the leaching rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementIron sulfateSlag
The invention relates to a method for extracting aurum from difficult-to-handle sulphide ore aurum concentrate by two-segment pressurization leaching method comprising two segments of pressurization oxidation preprocessing and pressurization oxidation aurum leaching. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, pressurizing and oxidizing base metal sulfide such as iron sulfide with sulfuric acid-iron sulfate, wherein most S2- and S22- are oxidized into elemental sulfur; and secondly, pressurizing and leaching the preprocessed slag with thiocyanate so that aurum is selectively dissolved in the solution in the form of aurum-thiocyanic acid compound. Therefore, the pre-oxidation slag can be directly leached without neutralization, the technical process is short, the aurum recovery rate is high, the cost is low and pollution of low-concentration SO2 smoke gas, As2O3 smoke dust, and the like is avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Fire retardant compositions with reduced aluminum corrosivity
InactiveUS6905639B2Reduced-tendency to corrode various metalBroaden applicationFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsBiopolymerFerrous Gluconate
Corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions and methods of making and using the same are provided. The corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions are comprised of at least one fire retardant component, at least one biopolymer having a particle size diameter of less than about 100 microns, and a corrosion inhibiting system. The corrosion inhibiting system is comprised of at least one corrosion inhibiting compound selected from a group of compounds including azoles, insoluble ferric pyrophosphate, soluble ferric pyrophosphate, ferrous oxalate, ferric citrate, ferrous sulfate, ferric ammonium citrate, soluble ferric orthophosphate, insoluble ferric orthophosphate, ferric ammonium oxalate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ferric bromide, ferric sodium oxalate, ferric stearate, ferric sulfate, ferrous acetate, ferrous ammonium sulfate, ferrous bromide, ferrous gluconate, ferrous iodide, ferric acetate, ferric fluoroborate, ferric hydroxide, ferric oleate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous oxide, ferric lactate, ferric resinate and any combination thereof. In a specific embodiment, the corrosion-inhibited fire retardant composition includes a xanthan biopolymer.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
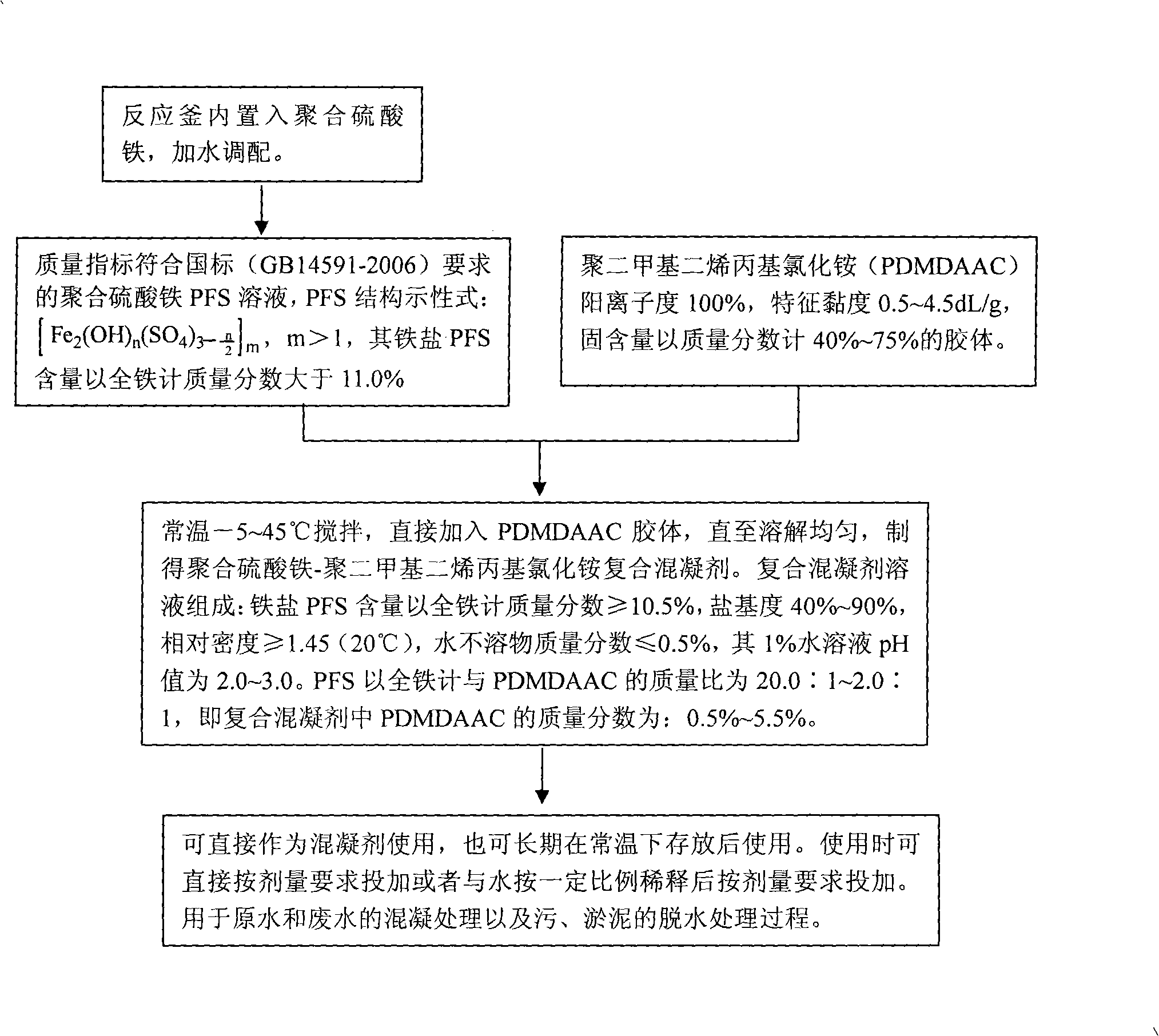
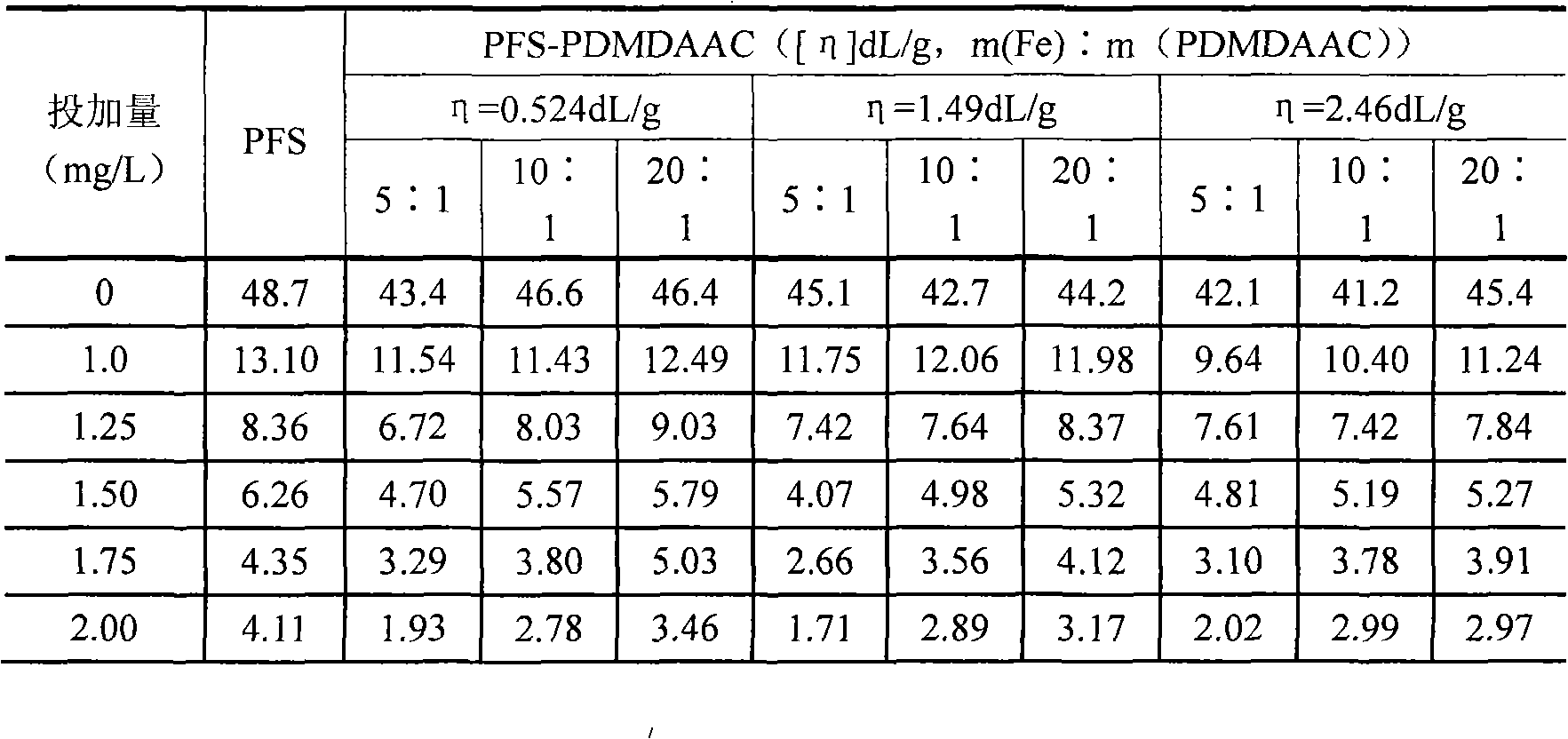
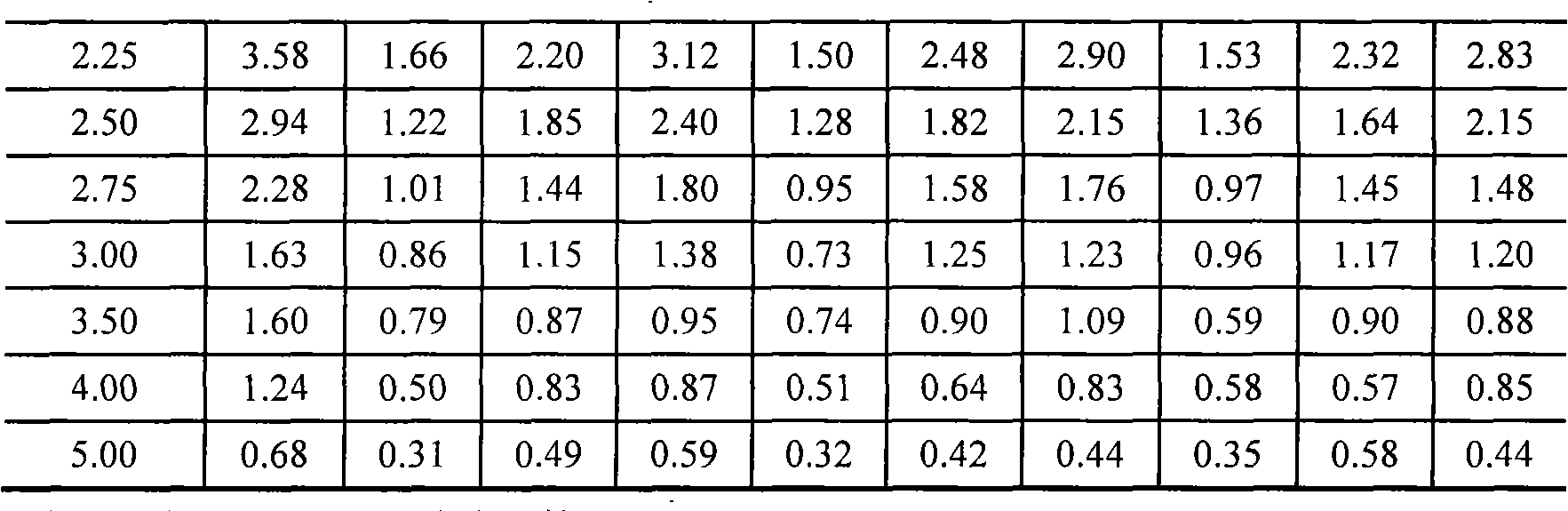
Polymeric ferric sulfate-poly-dimethyl-diallyl-ammonium chloride composite flocculent, preparation and use method thereof
InactiveCN101323472AGuaranteed performanceGuaranteed stabilityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSulfateWater quality
The invention discloses a PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant, a corresponding preparation method and an application method. The PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant is prepared as the following steps: the PFS dry powder or solution is arranged in a mixing reactor, and water is added to obtain a ferric-salt PFS solution which is stirred under normal temperature and a PDMDAAC colloid is added into the solution; the mixed solution is stirred under normal temperature till the PDMDAAC colloid is completely dissolved to obtain a stable PFS-PDMDAAC. The application of the PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant is to adopt the PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant for the coagulation treatment to raw water and waste water and sewage and the dehydration treatment to sludge or silt directly or after dilution with water by any proportion. The component structure and content scope of the invention are distinct to guarantee the capability and stability of the obtained PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant, and the materials on industrial manufacturing are available. The various functions of the PFS-PDMDAAC compound coagulant can be adjusted during water treatment with high adaptability so as to reduce cost, reinforce coagulation effect and dramatically enhance the quality of obtained water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modifying agent for soda-alkalized paddy field soil
InactiveCN102517027AImprove efficiencyLower unit costOrganic fertilisersSoil-working methodsIron sulfateBiology
The invention discloses a modifying agent for soda-alkalized paddy field soil. The modifying agent is prepared by mixing polyferric sulfate with polyaluminum sulfate according to the weight ratio of 1:(0.6-1.4) and is suitable for modifying severe soda-alkalized soil into a paddy field; and the modifying method comprises the following steps of: applying the modifying agent to the paddy field soil of the field prior to soil preparation, wherein the application rate is 5.6-18 tons per hectare of soil; carrying out normal soil preparation; and soaking and leaching the soil after the modifying agent is sufficiently mixed with the soil. Compared with the polyferric sulfate, the unit cost of the modifying agent for the soda-alkalized paddy field soil disclosed by the invention is reduced by 9.4-15% under the condition that the same effect is maintained; and compared with the aluminum sulfate soil modifying agent, the macromolecular polymer of the modifying agent has a better flocculation effect and higher modifying efficiency, and meanwhile, the concentration of activated aluminum of soil is controlled to be in a low-concentration level, which is harmless to crops.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
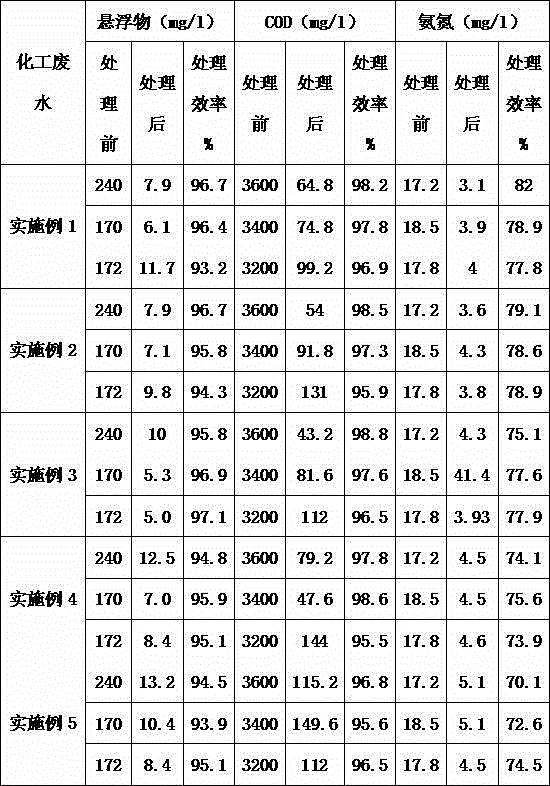
Industrial wastewater treating agent
InactiveCN104591362AGood effectImprove water qualityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSodium bicarbonateIron sulfate
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment and particularly relates to an industrial wastewater treating agent. The industrial wastewater treating agent comprises the following components in parts by mass: 0.8-3 parts of polyacrylamide, 25-35 parts of aluminium polychlorid, 25-55 parts of alums, 3-8 parts of iron trichloride, 0.8-3.4 parts of polymeric ferric sulfate, 1.2-2.5 parts of a coagulant aid, 2-10 parts of plant fiber, 10-30 parts of coal ash, 0.8-2.5 parts of sodium silicate, 2.5-5 parts of sodium sulfite, 0.5-3.5 parts of sodium hypochlorite, 5-10 parts of hydrogen peroxide, 8-15 parts of a sodium carbonate-sodium bicarbonate buffer system and 10-20 parts of sodium-based bentonite. The treating agent has the beneficial effects of wide treated pollutant range, good effect, wide production raw material source, environmental friendliness, no toxicity, good discharged water quality, short process flow, and high process operating safety. The treating agent disclosed by the invention can treat various kinds of wastewater such as chemical wastewater produced in oil fields, mining, steel, electroplating wastewater, dyes, pesticides, wine-making and chemical engineering, and sanitary sewage, papermaking wastewater, river and lake water, rubbish seeping water, leather-making wastewater, and the like; and the treating agent is good in treatment effect.
Owner:湖北源绿高科技节能环保有限公司
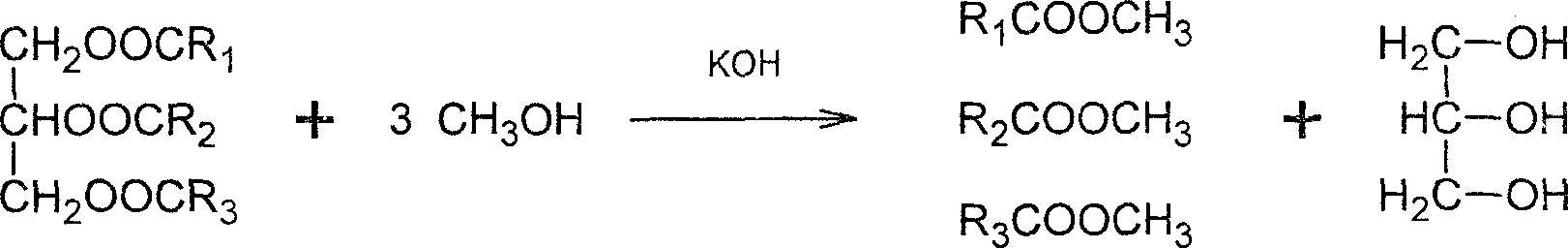
Method for synthesizing biodiesel utilizing swill water oil
InactiveCN1743417AEasy to recycleHigh catalytic activityBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionIron sulfateAlcohol
This invention discloses a method for synthesizing bio-diesel oil by halogenated oil including the following steps: putting halogenated oil, methyl alcohol and catalyst iron sulfate into a reactor to be mixed and reacted for 2-6 hours to separate the iron sulfate from it after the reaction, then, adding KOH into the container to be mixed and heated for 0.5-2 hours, laying it still or centrifugating and laminating it, the upper layer of which contains methyl alcohol and bio-diesel oil, the lower contains glycerin and KOH, discharging the lower layer to get the upper solution to be vacuum distilled to recover the methyl alcohol to be washed by hot water to be centrifugated and separated to get niger and rough diesel oil to be vacuum-distilled to get refined bio-diesel oil.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Polishing composition and method for producing a memory hard disk
InactiveUS6280490B1High cutting rateSmall surface roughnessPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesIron sulfateEthylenediamine
A polishing composition for a memory hard disk, which comprises the following components (a) to (d):(a) from 0.1 to 50 wt %, based on the total amount of the polishing composition, of at least one abrasive selected from the group consisting of silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, cerium oxide, zirconium oxide, titanium oxide, silicon nitride and manganese dioxide,(b) from 0.001 to 10 wt %, based on the total amount of the polishing composition, of at least one iron salt selected from the group consisting of iron nitrate, iron sulfate, ammonium iron sulfate, iron perchlorate, iron chloride, iron citrate, ammonium iron titrate, iron oxalate, ammonium iron oxalate and an iron chelate complex salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid,(c) from 0.01 to 30 wt %, based on the total amount of the polishing composition, of at least one peroxydisulfate salt selected from the group consisting of ammonium peroxydisulfate, potassium peroxydisulfate and sodium peroxydisulfate, and(d) water.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Equipment and method for treating organic waste water through electrocatalysis of cathode in combination with anode
InactiveCN1600699AEase of industrial applicationEasy to zoom inWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationIron sulfateElectrochemical response
In the invention, positive pole is fit at center of reaction casing, negative pole is fit surround inwall of reaction casing, a cyclic microporous aeration unit is fit near negative pole on bottom of the reaction casing, waste water charging pipe intercommunicated with waste water storage tank is fit on bottom part of the reaction casing, water discharging pipe is fit on the super part. In waste water treatment, 0.1-5mM iron sulfate and 1-10g / L sodium sulfate electrolyte are added in waste water, adjusting pH value of waste water is 2.0-5.0, the waste water is pumped from storage tank to electrochemical reactor, at same time, turn on electrochemical DC power and sending gas in, controlling flow of waste water is 10-50ml / s, electric current is 0.1-2A, aeration speed is 1-30ml / s-1.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Selenium-rich nutrient solution for pear and application thereof
InactiveCN103435388ATo promote metabolismImprove disease and stress resistanceFertilizer mixturesIron sulfateDisease
The invention discloses a selenium-rich nutrient solution for a pear. The nutrient solution comprises, by weight, 20 to 30 parts of magnesium sulfate, 5 to 15 parts of zinc sulfate, 10 to 15 parts of copper sulfate, 10 to 25 parts of iron sulfate, 10 to 25 parts of urea, 8 to 15 parts of potassium sulfate, 10 to 15 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 25 to 40 parts of sodium selenite. Through application of the nutrient solution provided by the invention, selenium content of the pear can be substantially increased, production of the pear is promoted, net weight of fruit is increased, resistance of the pear to insect attack is enhanced, and attack by diseases and insect pests is reduced.
Owner:句容市丰之源果品专业合作社
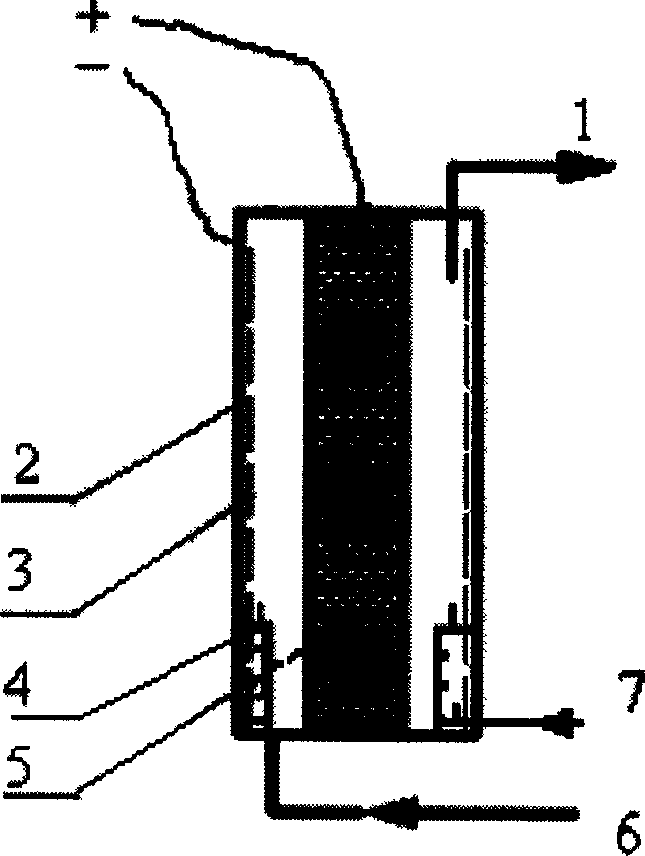
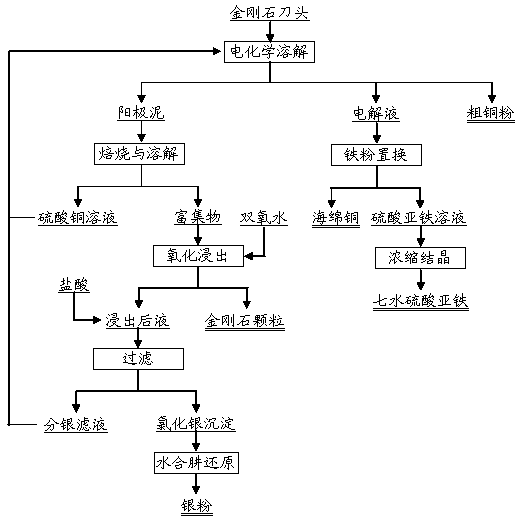
Method for processing waste copper/iron-based diamond tool bit
InactiveCN104046785AEfficient separationRealize closed loopProcess efficiency improvementIron sulfateClosed loop
The invention provides a method for processing waste copper / iron-based diamond tool bit. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, electrochemically dissolving the waste diamond tool bit in a sulfuric acid system so that most part of copper and iron are dissolved into the solution, while silver, diamond and the like are enriched into anode mud; secondly, roasting and oxidizing the anode mud and then adding the oxidized anode mud to the sulfuric acid so that the residual most part of copper is dissolved; next, adding the rest undissolved copper, silver and diamond particles to the sulfuric acid solution of hydrogen peroxide for further oxidizing leaching, recovering the diamond particles which are not dissolved, precipitating the silver in the solution by use of the hydrochloric acid and reducing the hydrazine hydrate to generate simple substance silver powder; finally, after displacing copper with iron powder, concentrating and crystalizing the electrolyte to directly prepare iron sulfate heptahydrate. The recovery rate of the copper is above 96%, while the recovery rate of the diamond particles and the silver is above 99%; the industrial-grade iron sulfate heptahydrate is directly produced, the recovery rate of iron is greater than 98%, closed-loop circulation can be realized, the production labor intensity is low and the method is environmental friendly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Advanced treatment method for urban water of electric power plant
InactiveCN101318747AScale removal and water softeningMultistage water/sewage treatmentIron sulfateWater use
The invention relates to a method for treating municipal intermediate water, in particular to an advanced treatment method for treating the municipal intermediate water which is used as cooling water for a power plant. The method comprises the following specific steps that: water in a municipal sewage treatment plant is introduced into a pool, respectively added with lime hydrate, polymeric ferric sulfate as a coagulant and polyacrylamide as a coagulant aid and clarified; a clarifying solution is added with an disinfectant for disinfection, added with sulphuric acid for adjusting the PH value of the clarifying solution to between 8 and 8.5 and filtered; and intermediate water after filtration is added with a composite scale corrosion inhibitor, evenly mixed and added to circulating water in the power plant. The advanced treatment method solves the relevant technological difficult problems of advanced treatment, disinfection, scale inhibition, anticorrosion, ammonia nitrogen treatment, etc. of the intermediate water recycled by the power plant and provides technological support for the safe and economic use of the intermediate water in the power plant; and the intermediate water in the power plant is used as circulating water and replenishing water for recycling and has remarkable economic, social and environmental benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
High-water absorption humic acid resin with water conserving, water retention and trace fertilizer sustained-release functions
InactiveCN103865002AWith water saving functionHas micro-fertilizer slow-release functionFertilizer mixturesCross-linkIron sulfate
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of multifunctional high-water absorption humic acid resin with water conserving, water retention and trace fertilizer sustained-release functions. The preparation method comprises the following steps of chelating borax, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, ammonium molybdate, iron sulfate and the like by using a chelating agent, mixing the raw materials at the ratio of sodium (or potassium) humate solution to acrylic acid to cross-linking agent to trace fertilizer being (300-400):(80-100):(1-3):(6-10), adding an initiator, and performing reaction to prepare the high-water absorption humic acid resin. The resin has the water conserving, water retention and trace fertilizer sustained-release functions, and can be applied to the industries of agriculture, forestry, gardening and the like to fulfill the aim of increasing both production and income, and the growth and development requirements of crops can be well met.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY +1
Industrial wastewater treating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106630181AWide variety of sourcesThorough treatmentWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsIron sulfateIndustrial waste water
The invention discloses an industrial wastewater treating agent which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15-30 parts of polymeric aluminum silicate-sulfate, 15-30 parts of ferric sulfate, 1-5 parts of polyacrylamide, 1-5 parts of microorganisms, 15-30 parts of potato starch, 3-13 parts of chitosan, 7-17 parts of attapulgite powder, 5-10 parts of tannin, 4-11 parts of kaolin, 20-40 parts of modified vesuvianite, 10-20 parts of calcium hydroxide, 10-20 parts of activated carbon, 5-15 parts of sodium diphosphate, 1-5 parts of sodium hypochlorite and 5-20 parts of lignin. The raw materials of the industrial wastewater treating agent are wide in source, pollutants in the water can be effectively removed, the sewage treatment is thorough, the treatment cost is low, the treating agent does not has toxicity and does not cause pollution, and the treated wastewater meets the national sewage comprehensive emission standard requirements. The preparation method is simple and convenient to produce.
Owner:广西新六合环保有限责任公司
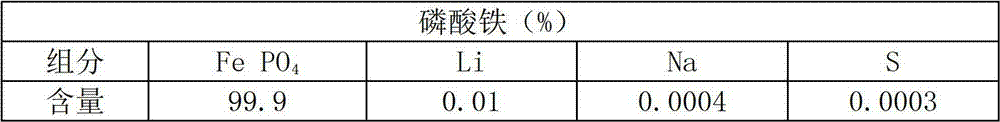
Production method for high-purity ferric phosphate
The invention relates to a production method for high-purity ferric phosphate. Ferrous sulfate solution dissolved by a raw material, i.e., iron sulfate heptahydrate crystal used for producing ferric phosphate or ferrous sulfate solution generated by the reaction of iron and sulfuric acid is subjected to three-time impurity-removal and purification processing; the purified ferrous sulfate solutioncarries out oxidation reaction with hydrogen peroxide to generate ferric sulfate solution; under the condition of emulsifier, phosphate solution is dripped to react to synthesize ferric phosphate precipitates, or phosphoric acid is added into the purified ferric sulfate solution; after evenly mixing, hydrogen peroxide is added for oxidation, emulsifier is added, and ferric phosphate precipitates are synthesized; then, the ferric phosphate precipitates are aged, rinsed, filtered and dried to prepare aqueous or anhydrous high-purity ferric phosphate. The synthesized high-purity ferric phosphatehas an impurity index that potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and manganese are less than 50ppm, titanium and aluminum are less than 20ppm, and heavy metal ions, i.e., cobalt, nickel, zinc, copper,lead, chromium are less than 5ppm. By use of the production method, the problems of low purity and more impurity of a product obtained in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:GUIZHOU DALONG HUICHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Treatment agent of steelmaking waste water
The invention belongs to the technical field of a sewage treatment agent, in particular to a treatment agent of steelmaking waste water. The treatment agent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25 to 45 parts of polyacrylamide, 5 to 15 parts of sodium hydroxide, 2 to 5 parts of sodium carbonate, 5 to 15 parts of magnesium oxide powder, 10 to 20 parts of polysilicon ferric sulfate, 10 to 20 parts of quaternary ammonium salt lignin flocculant, 20 to 30 parts of sodium base bentonite, 0.5 to 2 parts of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid, 5 to 15 parts of pentasodium diethylenetriaminepentaacetate, 10 to 20 parts of polyaspartic acid, and 12 to 25 parts of polyaluminium chloride. The treatment agent of steelmaking waste water disclosed by the invention is good in treatment effect, obvious in corrosion and scale inhibiting effect, capable of reducing scaling and corrosion effectively, lowering the production cost, high in purity, free of toxicity, and has no influence on operating workers and problems such as secondary pollution after treatment.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG
Process for preparing battery-grade high-purity nano iron phosphate
ActiveCN107188149ALow costShort processMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsIron sulfateDistillation
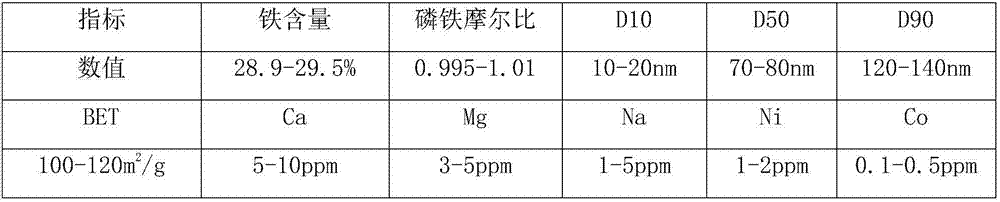
The invention discloses a process for preparing battery-grade high-purity nano iron phosphate. The process comprises the steps that the pH is improved by using a titanium dioxide by-product, impurities are removed and a solution is purified by adding iron powder, then ferrous oxidization is performed to obtain ferric iron, the pH of iron sulfate is regulated, ferric ions in the iron sulfate are extracted by adopting di(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid, a washed organic phase is obtained through 5-6 level counter-current extraction, 5-6 level counter-current acid solution washing and 2-3 level counter-current pure water washing, sulfonated kerosene is distilled out, the organic phase obtained after distillation is mixed with a catalyst, reaction is performed at the temperature of 300-320 DEG C for 3-4 hours, and the material obtained after reaction is washed by adding ethyl alcohol and is dried to obtain the high-purity nano iron phosphate. According to the process for preparing the high-purity nano iron phosphate, the high-purity nano iron phosphate can be prepared through the titanium dioxide by-product, the obtained iron phosphate is high in purity, small in particle size and large in specific surface area, the ferro-phosphorus ratio is 0.995-1.01, and the wastewater production amount is small.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON PHOSPHORUS CHEM
Wastewater treating agent, preparation method and wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN105174500AEasy to handleImprove efficiencyBiocideSpecific water treatment objectivesIron sulfateSodium phosphates
The invention relates to a wastewater treating agent, a preparation method and a wastewater treatment method. According to the oil paint wastewater treating agent, the formula comprising a corrosion inhibitor, a scale inhibitor, a sterilizing agent and a flocculating agent is adjusted, and an auxiliary chemical is added, so that the wastewater treatment process is easy to control, the treatment period is short, and the treatment effect is remarkably improved; the wastewater treating agent comprises the corrosion inhibitor, the scale inhibitor, the sterilizing agent, the flocculating agent and the auxiliary chemical; the corrosion inhibitor comprises sodium polyphosphate, calcium gluconate, alkyl epoxy sodium carboxylate, potassium iodide and gelatin; the scale inhibitor comprises trisodium phosphate, tannin, sodium humate, sulfoacid copolymers and TH-0100 type reverse osmosis scale inhibitors; the sterilizing agent comprises potassium permanganate, didodecyl dimethyl dibenzyltinoammonium chloride and nano-zinc oxide; the flocculating agent comprises lignin, chitosan, quaternary amine type cationic starch, polyaluminum chloride , polymeric ferric sulfate and diatomite earth; the auxiliary chemical comprises polyaspartic acid and alky epoxy carboxylate. An experiment result proves that the wastewater treating agent has an excellent effect.
Owner:上海云火环境科技有限公司
Method for manufacturing nanometer iron
The invention relates to an iron super-micro particle preparation technique, belongs to radiation chemical nanometer material production technique. The technique of the invention is that: nanometer material preparation: obtain iron hydroxide colloid solution by using iron sulfate as raw material and ammonia liquor as precipitant; control the crystal core accumulating speed and the particle size by hydrophilic surface-activator polyvinyl alcohol with isopropyl alcohol as free radical scavenger and in radiation chemistry principles; develop the radiation chemical reaction by the bunch of electrons generated by industrial electron accelerator; the radiated solution produces nanometer triple iron quadoxide which deoxidated with high purity hydrogen to obtain nanometer iron powder. The advantages of the invention are that: simple technical processes, short production cycle, non-pollution, the obtained particles are of uniform diameter and finely divided. The nanometer iron produced in above ways is of higher satiating hard magnetism and coercive force which is applicable on high intensity magnetic recording material..
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Denitration catalyst for wide temperature window under high sulfur condition and preparation method thereof
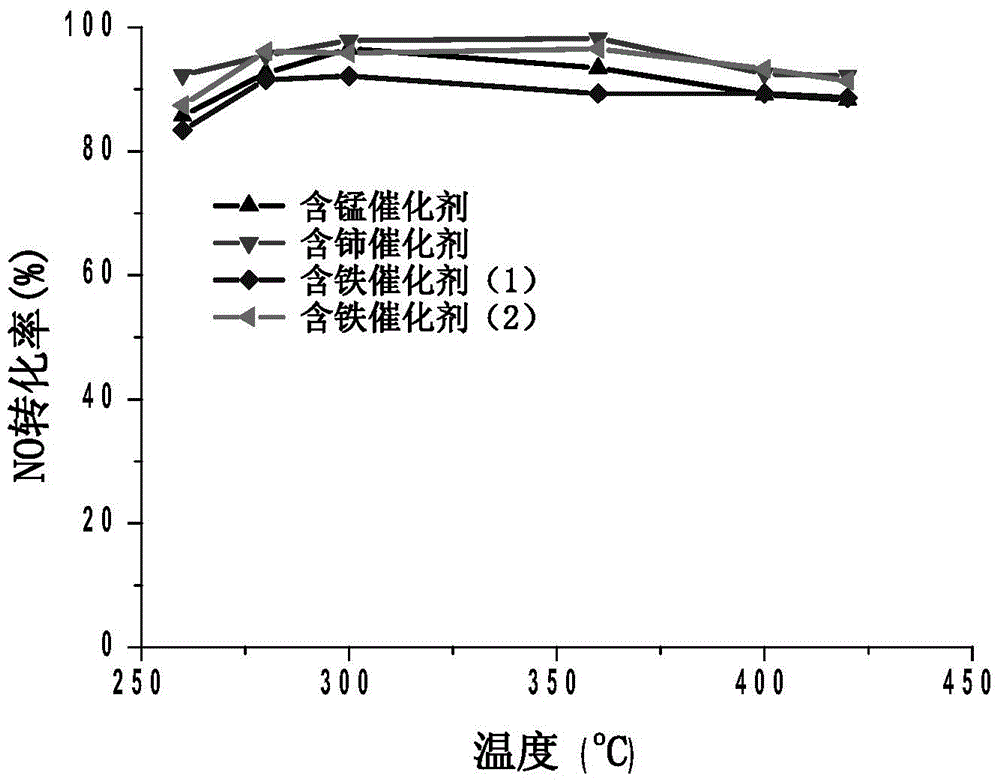
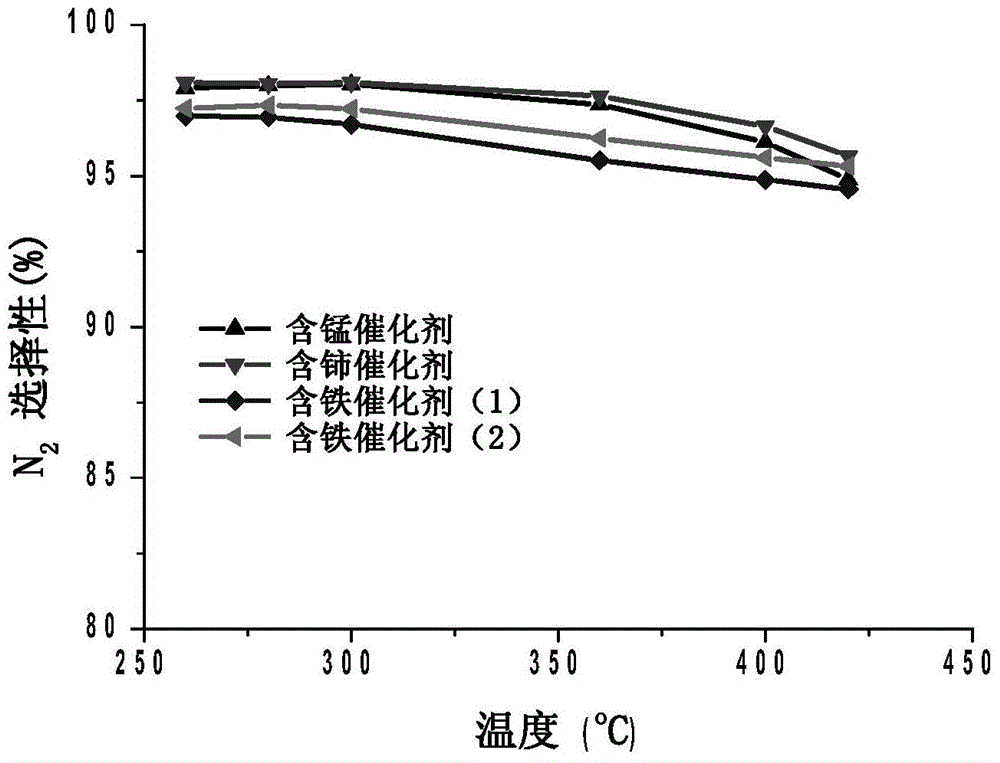
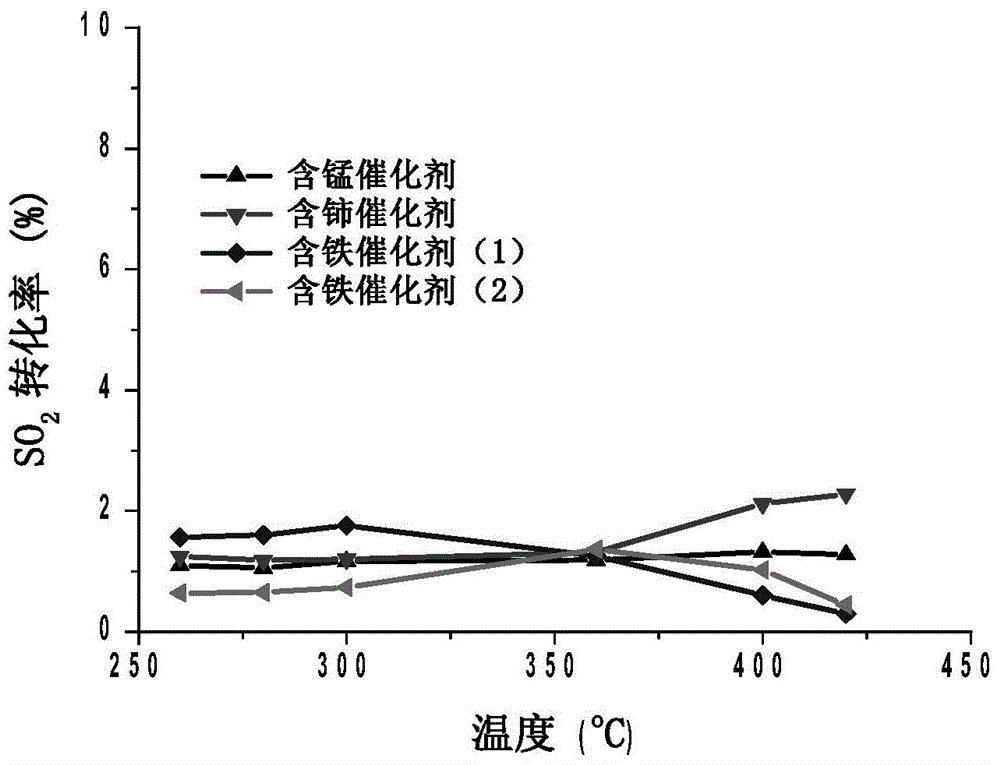
ActiveCN104525216ASimple processImprove denitrification activityDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMANGANESE ACETATERare earth
The invention discloses a denitration catalyst for a wide temperature window under a high sulfur condition and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight of the denitration catalyst: 1wt% of vanadium pentoxide, 6wt% of tungsten trioxide, 5wt% of one of manganese oxide, cerium oxide, ferric oxide without sulfur or ferric oxide with sulfur, and the balance of titanium dioxide. The preparation method comprises the following step: adjusting a commercial V2O5-WO3 / TiO2 catalyst by adding traditional metals iron and manganese and rare earth cerium, specifically, in the preparation process of the catalyst, adding ferric nitrate, ferric sulfate, manganese acetate or cerous nitrate to obtain the highly active catalyst which has good SO2 poisoning resistance and has the denitration activity over 80% under the condition that the temperature is 260-420 DEG C in a relatively wide high-temperature region and the SO2 concentration is high (1000ppm).
Owner:江苏中创清源科技有限公司
Novel sludge dehydrating agent
InactiveCN104829088AGood dehydration synergyReduce dosageSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningAluminium chlorideSodium Bentonite
The present invention discloses a novel sludge dehydrating agent, a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the sludge treatment field, wherein poly aluminium chloride, calcium oxide, ferric sulfate, bentonite, starch, and polyacrylamide are mixed according to a certain ratio, and then drying is performed for 20-40 min at a temperature of 80-100 DEG C to prepare the novel sludge dehydrating agent. According to the present invention, the novel sludge dehydrating agent has the good dehydrating effect, the water content of the dehydrated sludge is 40-50%, the polyacrylamide content is low, the environmental pollution is low, the preparation process is simple, the cost is low, and the novel sludge dehydrating agent is suitable for large-scale sludge dehydrating treatment.
Owner:唐国萍
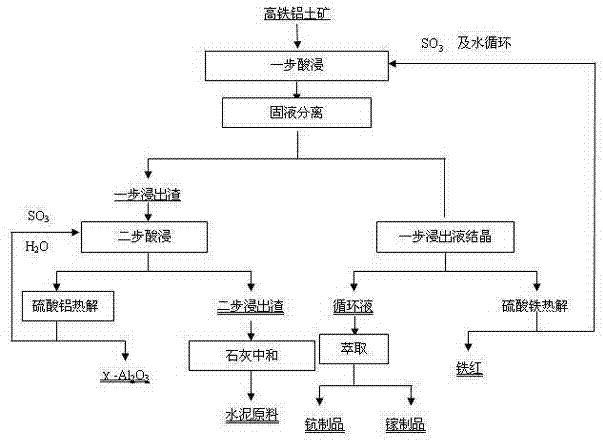
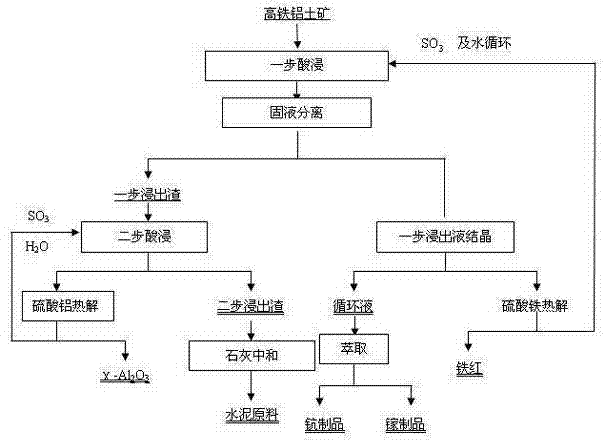
Method for extracting valuable metals from high-iron bauxite with step-by-step acid leaching
ActiveCN102643985ANo emissionsMeet environmental protection requirementsProcess efficiency improvementIron sulfateSlag
The invention belongs to the field of mineral processing, and specifically relates to a method for extracting valuable metals from high-iron bauxite with step-by-step acid leaching. The technical scheme of the invention is to extract multiple valuable metal elements in minerals with a step-by-step acid leaching method by taking high-iron bauxite as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, leaching the elements of scandium, gallium, iron and the like in the minerals at low temperature by use of low-concentration sulfuric acid; adding the aluminum-containing mineralphase into the first-step leached slag, and crystallizing the first-step leached liquid to obtain ferric sulfate; in the second-step leaching, extracting aluminum in the first-step leached slag underthe pressure leaching condition by use of the first-step leached liquid after iron removal and acid supplement; crystallizing the second-step leached liquid to obtain the aluminum sulfate product, and returning the second-step leached liquid after the crystallization to the first-step leaching for circular use; and after multiple times of circular enrichment of the elements of scandium, gallium and the like in the leached liquid, separating by an extraction method to obtain the scandium and gallium products. In the invention, the comprehensive utilization, acid and water circulation and zero discharge of wastes of the valuable elements in high-iron bauxite are realized through a step-by-step extraction method.
Owner:DONGDA NONFERROUS SOLID WASTE TECH RES INST LIAOLING CO LTD
Leaching of mineral ores
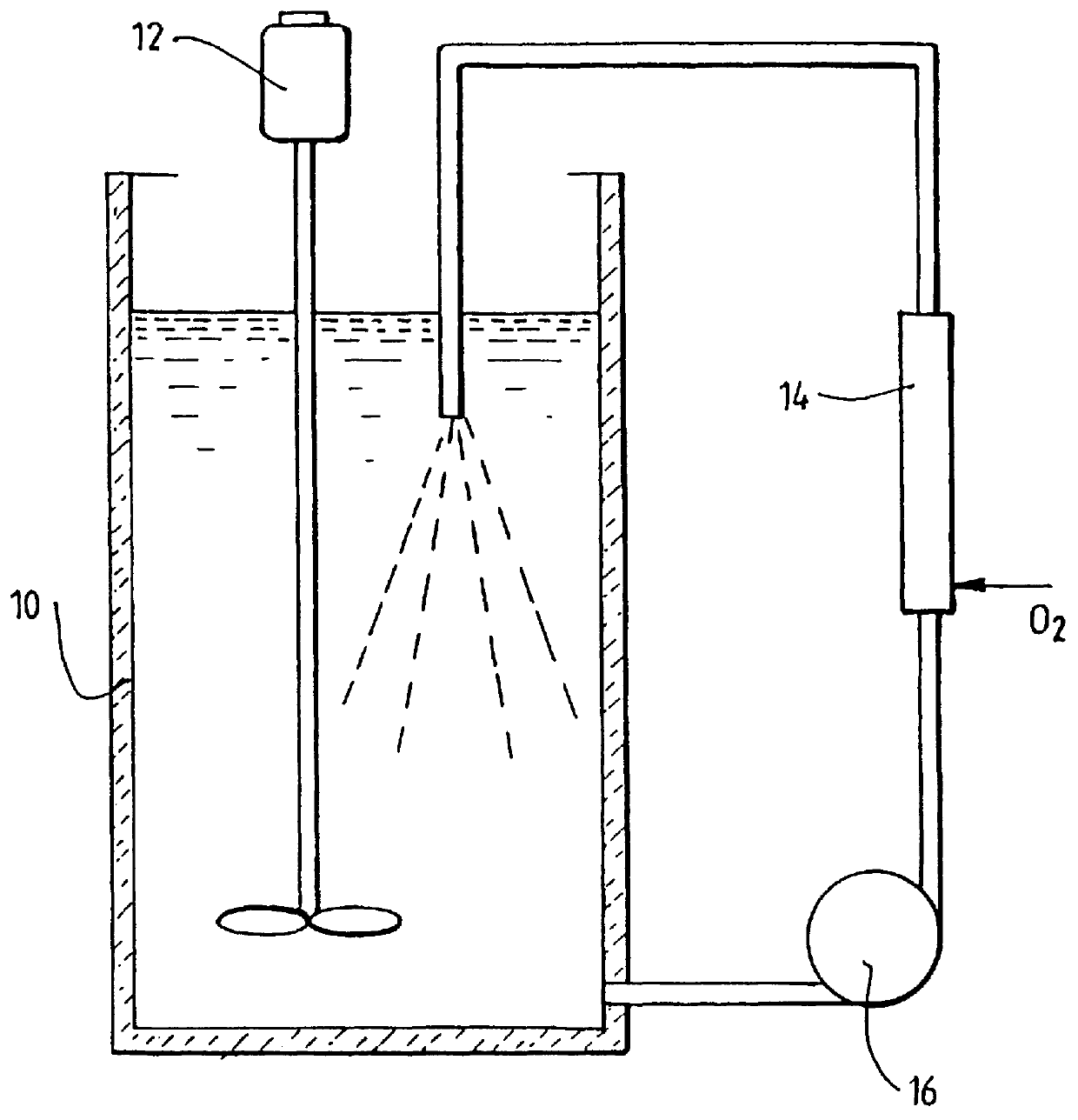
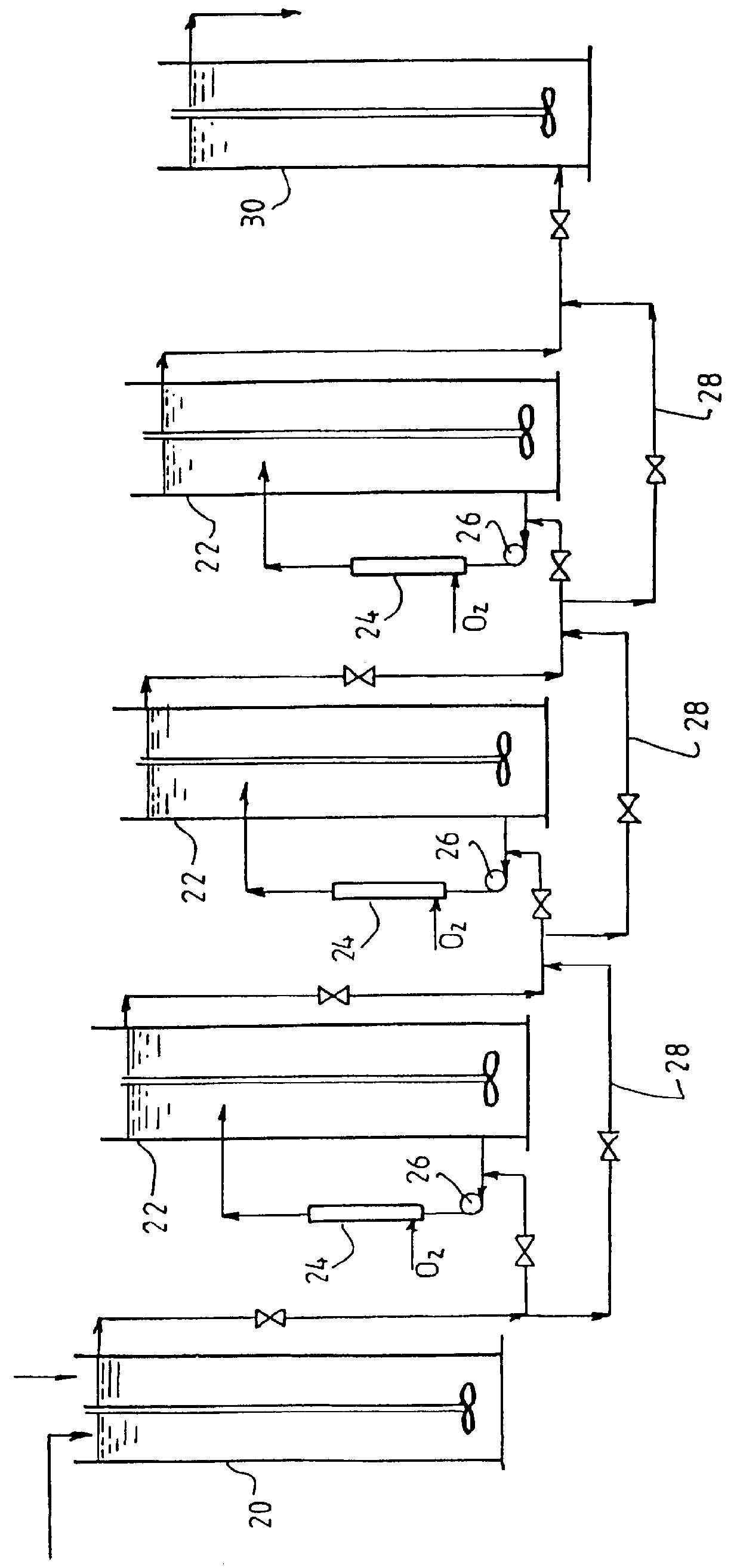
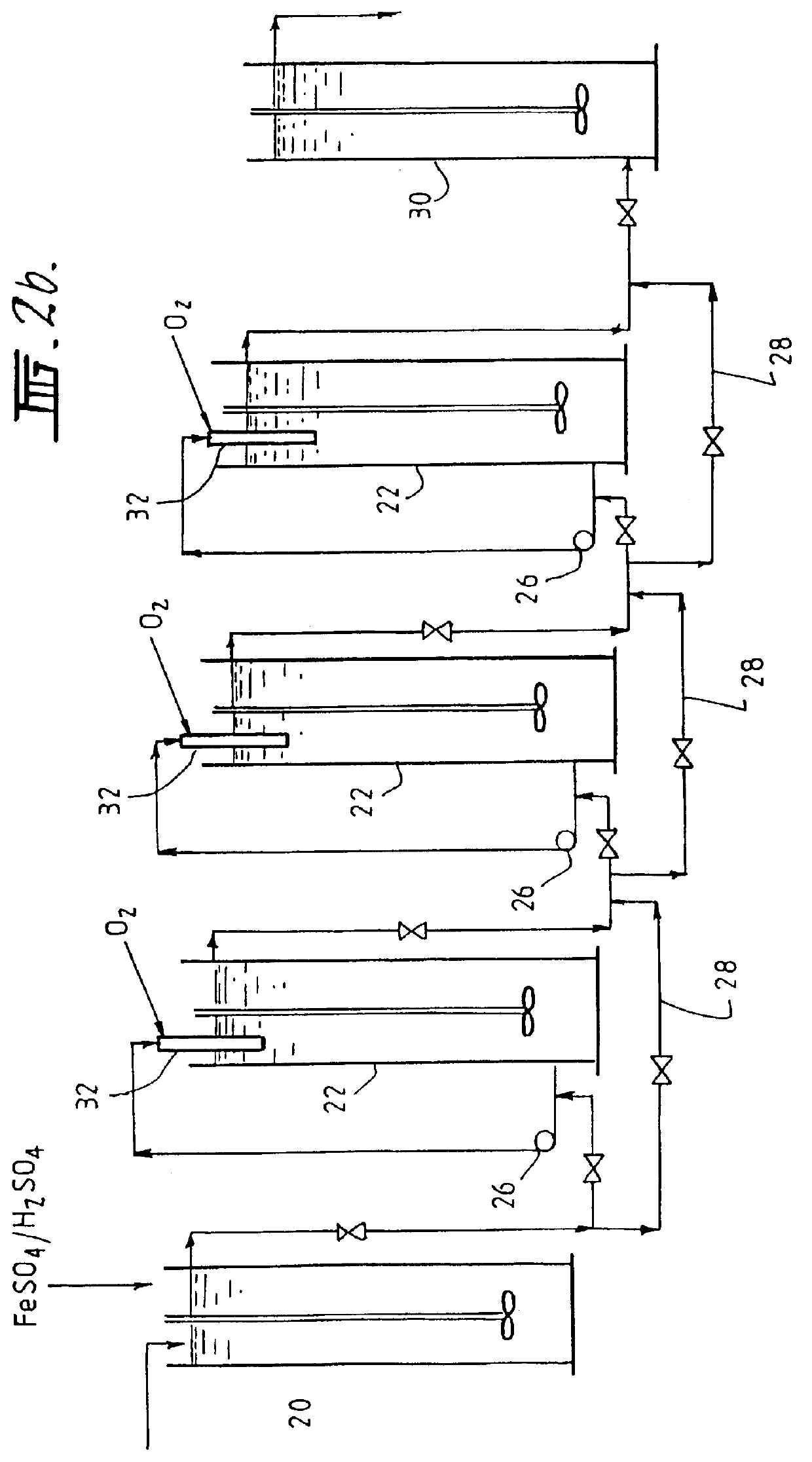
A process for oxidation of ferrous ions in solution, and more particularly a process for improved base metal and / or uranium leaching from ores, concentrates or tailings using ferric ion as an oxidizing agent. A reaction vessel (10) holds a ferrous ion-containing solution, for example, a copper sulphide leach slurry or concentrate. An agitator (12) may be provided to promote leaching of the base metal into solution. Some of the ferrous ion-containing solution is drawn off from the reaction vessel (10) and pumped through an in-line mixer (14) via a feed pump (16). Oxygen is injected into the reactor (14) to facilitate oxidation of the ferrous sulphate to form ferric sulphate. The ferric ion-containing solution is then recirculated back to the reaction vessel (10) where the ferric ions are reused in the dissolution of copper sulphide into soluble copper sulphate. The two processes of ferrous oxidation and metal leaching can be conducted either simultaneously or sequentially to effect recovery of copper, other base metals or uranium from ores, concentrates or tailings.
Owner:ATOMAER
Method for removing arsenic from sulfate acidic wastewater
ActiveCN105417767AAdvantages of the treatment methodReduce arsenic levelsWater contaminantsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesHigh concentrationIron sulfate
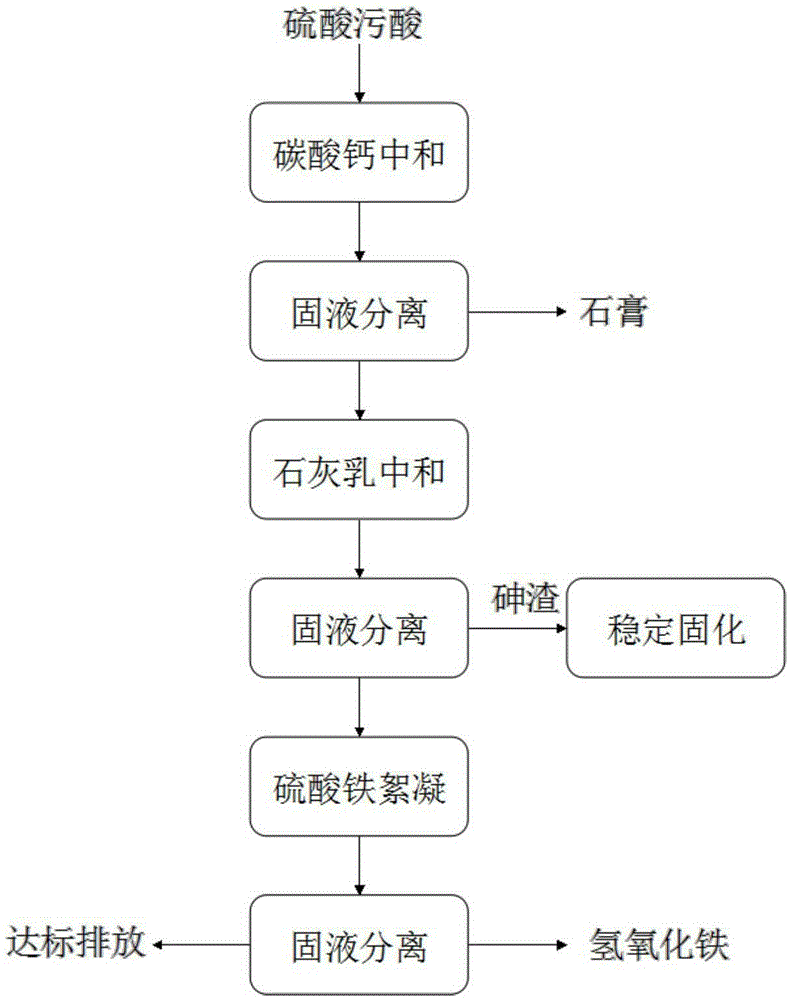
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment, and particularly discloses a method for removing arsenic from sulfate acidic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sulfate acidic wastewater is neutralized through a calcium carbonate suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, and solid-liquid separation is conducted after neutralization is conducted; 2, neutralized filtrate is neutralized again through a lime milk suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and more than 98% of the arsenic is removed in the process; 3, ferric sulfate or polymeric ferric sulfate flocculent settling is conducted, and flocculent settling is conducted on the filtrate in the second step to remove the residual arsenic. The method for removing the arsenic from the sulfate acidic wastewater is low in treatment cost and simple in operation condition, and the treated wastewater can reach a corresponding national emission standard; meanwhile, high-concentration arsenic residues can be obtained, and resource recycling or stabilizing or curing of the arsenic is facilitated.
Owner:湖北金润德环保技术有限公司
Non-ferrous metal smelting high-arsenic contaminated acid arsenic fixing process
ActiveCN109574319AMild responseSimple processTreatment involving filtrationWaste water treatment from metallurgical processIron sulfateTreatment effect
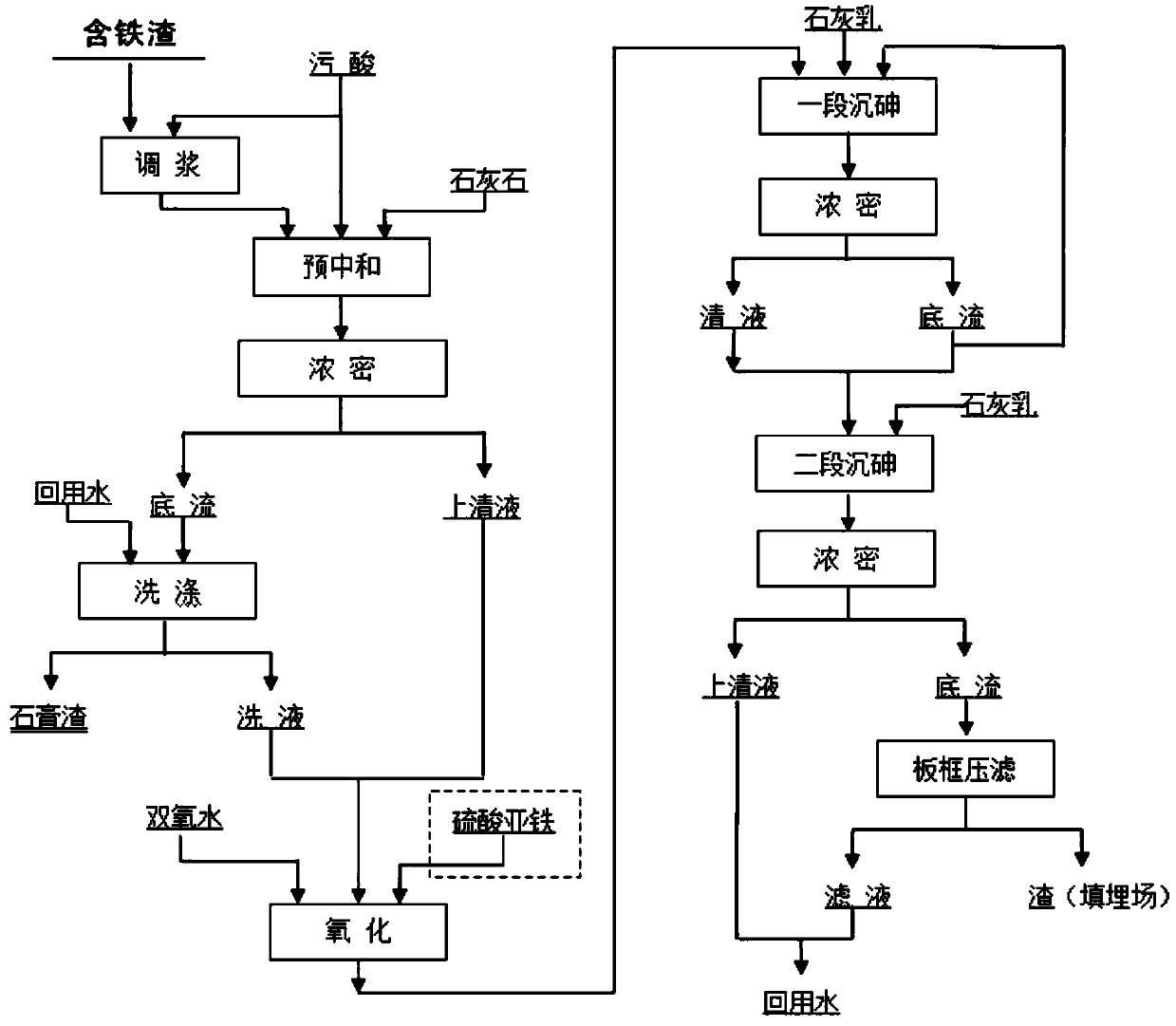
The invention relates to a non-ferrous metal smelting high-arsenic contaminated acid arsenic fixing process which sequentially includes the steps: pre-neutralization, to be specific, mixing iron-containing slag or iron-containing reagents and smelting contaminated acid, controlling Fe / As molar mole ratio, throwing mixed slurry and the contaminated acid into a pre-neutralization tank, performing reaction, controlling the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of solution, thickening pre-neutralization slag slurry to obtain bottom flow, supernate and gypsum slag, and using the gypsum slag as a cementretarder for sales; oxidation, to be specific, supplementing iron sulfate serving as an iron source reagent as required, heating the pre-neutralized supernate, adding hydrogen peroxide serving as an oxidizing agent for oxidation, controlling oxidation-reduction potential, and completely oxidizing trivalent arsenic into pentavalent arsenic; crystal form iron arsenate precipitation arsenic fixing, to be specific, controlling reaction temperature, adding seed crystals, controlling reaction endpoint pH values by adding lime milk, and conveying bottom flow subjected to two-stage arsenic precipitating reaction to a landfill through filter-pressed crystal form iron arsenate solids. The arsenic fixing process has the advantages of simple process, low cost, good treatment effects, low environmentalpollution risk and the like and is applicable to non-ferrous metal metallurgy industries.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP +1
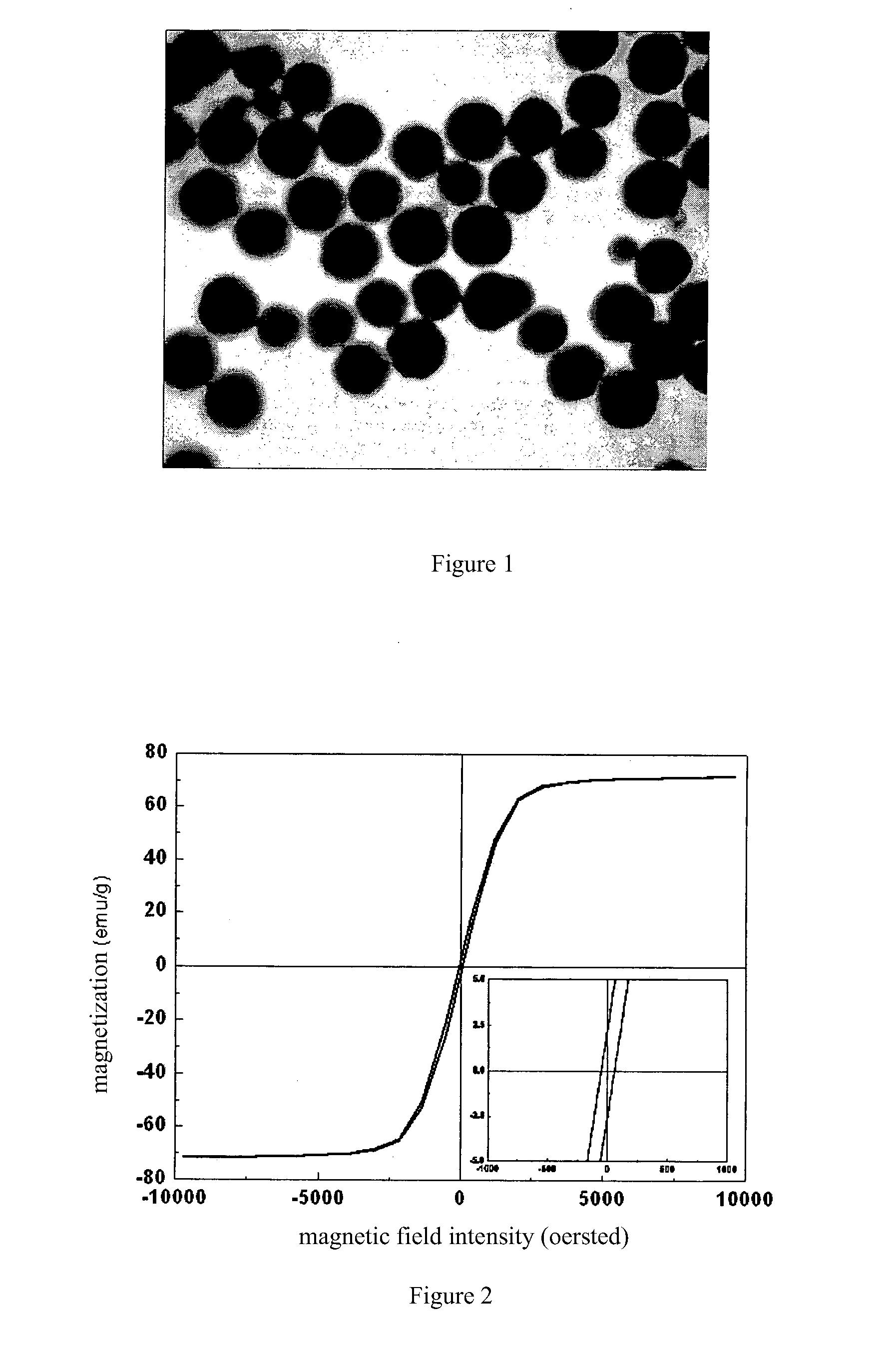
Preparation Method of Ferroferric Oxide Magnetic Nanospheres
ActiveUS20110318261A1Uniform particle sizeGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismDispersityIron salts
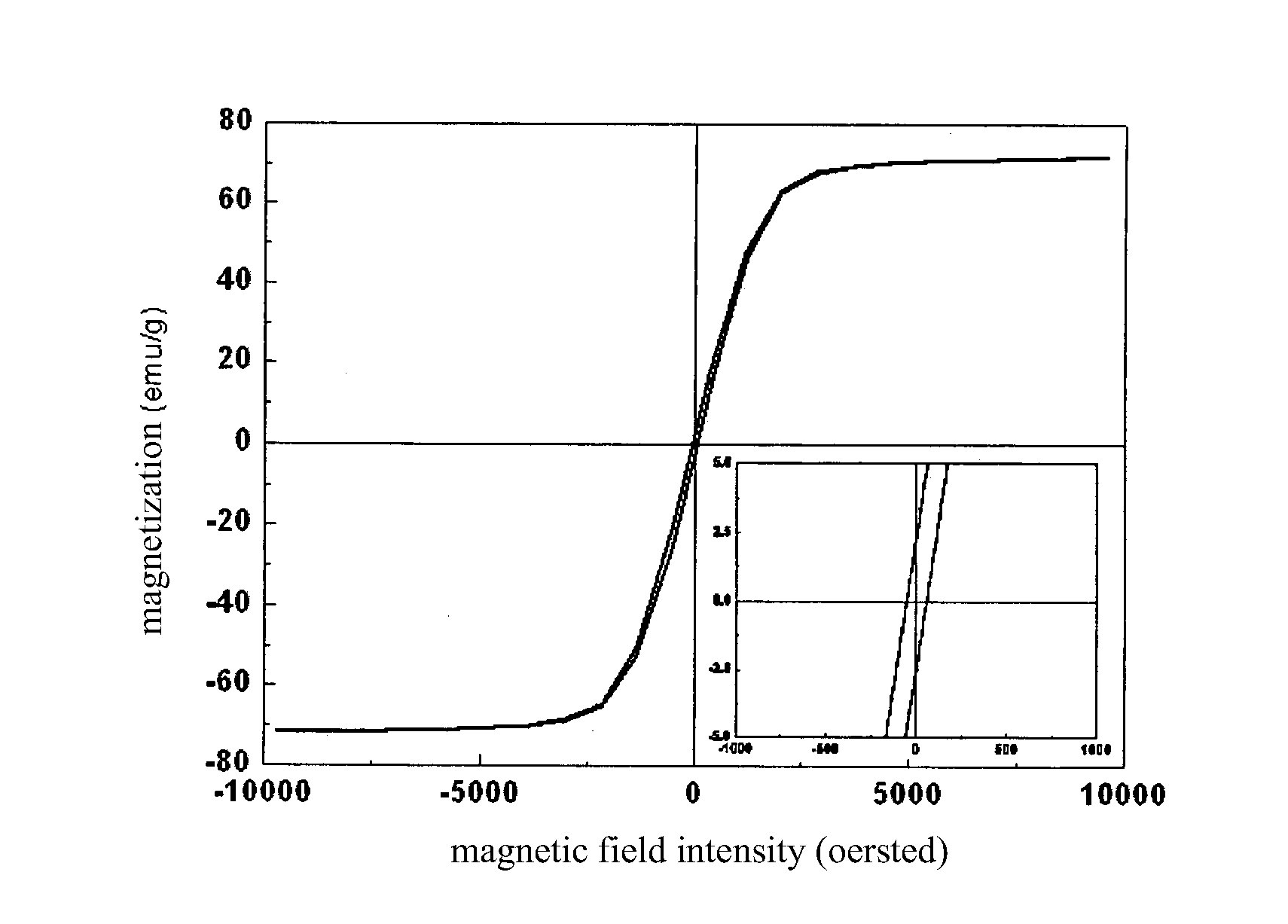
Disclosed is a process of preparing magnetite nanoparticles, comprising the following steps: 1) preparing a ferric salt mixed system, wherein a soluble ferric salt is dissolved in glycol at ambient temperature, and then urea and polyethylene glycol are added and mixed homogeneously to obtain the trivalent iron salt mixed system, the mass ratio of glycol to the trivalent iron salt being 15:1 to 60:1, glycol to urea being 20:1 to 100:1, and glycol to polyethylene glycol being 20:1 to 100:1; 2) reacting, wherein the trivalent iron salt mixed system is transferred into a reaction autoclave, sealed and placed into a heating device to react at a temperature of 200 to 300° C. for 8 to 72 hours; and 3) washing, wherein after the reaction system is naturally cooled down to ambient temperature, the product is taken out, and washed with anhydrous ethanol and water in turn to obtain the magnetite nanoparticles. The soluble iron salt includes ferric chloride, ferric sulfate, ferric acetate and ferric nitrate. The obtained nanospheres exhibit a uniform distribution of the particle diameter with a good dispersity in water. The nanospheres have superparamagnetism, and their particle diameter can be controlled by varying the reaction time as desired.
Owner:XIAN GOLDMAG NANOBIOTECH
Multielement composite foliar fertilizer
InactiveCN104591845AFast absorbencyQuick conversionMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserIron sulfatePlant growth
The invention relates to the field of fertilizers, and concretely relates to a multielement composite foliar fertilizer. The multielement composite foliar fertilizer is composed of the following substances in percent by mass: 10-20% of urea, 5-7% of diammonium phosphate, 3-5% of potassium sulfate, 0.05-0.15% of ferric sulfate, 0.02-0.04% of zinc sulfate, 0.03-0.05% of sodium molybdate, 0.1-0.3% of borax, 0.03-0.05% of magnesium sulfate, 0.07-0.09% of potassium chloride, 0.07-0.09% of iodoacetic acid, and 1-3% of a plant-growth regulator.
Owner:YANTAI NAKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com