Electrolytic manganese residue harmless treatment and resource utilization method
A technology of harmless treatment and electrolytic manganese slag, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of low ammonia nitrogen leaching rate, inability to effectively remove heavy metals and electrolytic manganese slag, and complicated process, so as to reduce the content of heavy metals and ammonia nitrogen, The effect of shortening the leaching time and increasing the leaching rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
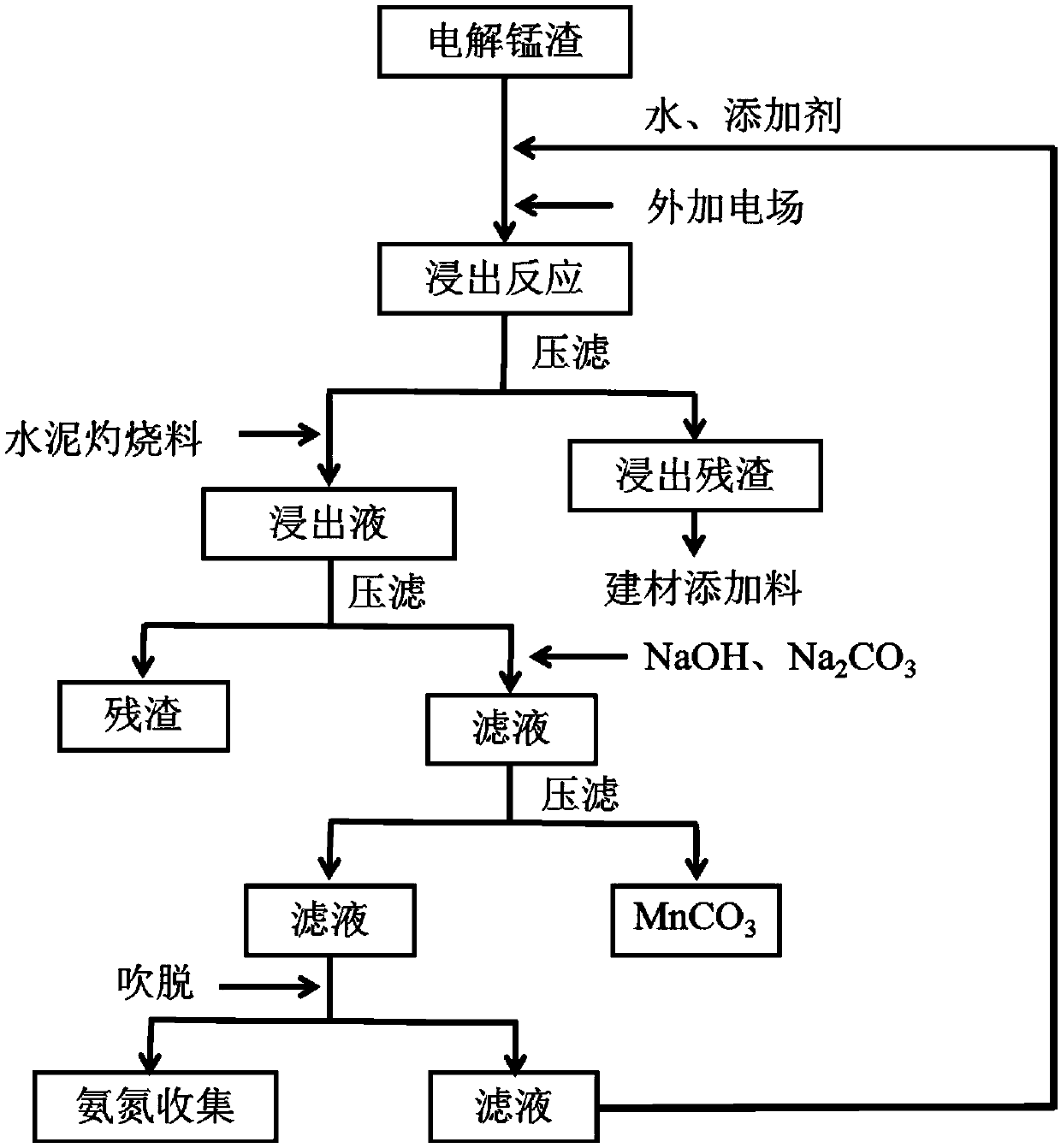
[0024] (1) Accurately weigh 1kg of material I of electrolytic manganese slag just discharged from the filter press workshop with metering equipment, put it into the stirring reaction device, add 5kg of water and corresponding additives (0.09kg Concentrated sulfuric acid, 0.03 kg of hydrogen peroxide) fully mixed to prepare material II;
[0025] (2) Add cathode and anode plates to the reaction device equipped with the material II obtained in step (1), apply a DC electric field, and the current density is 35 mA / cm 2 , carry out the leaching reaction at 40°C for 2 h, and obtain the material III after the leaching reaction;
[0026] (3) Pour the material III obtained in step (2) into the solid-liquid separation device, and obtain the leaching residue I and material IV after separation. The residue I is mainly the leaching residue of electrolytic manganese slag, which can be used in high value-added building material additives and other fields ;
[0027] (4) Add calcium carbonate...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Accurately weigh 1 kg of material Ⅰ of electrolytic manganese slag just discharged from the filter press workshop with a metering device, put it into the stirring reaction device, and add 5 kg of water and corresponding additives by weight to the reaction device using the metering system ( 0.20 kg of concentrated sulfuric acid and 0.12 kg of pyrite) are fully mixed and configured into material II;
[0033] (2) Add cathode and anode plates to the reaction device equipped with the material II obtained in step (1), apply a DC electric field, and the current density is 35 mA / cm 2 , carry out the leaching reaction at 60°C for 2 h, and obtain the material III after the leaching reaction;
[0034] (3) Pour the material III obtained in step (2) into a solid-liquid separation device, and obtain leaching residue I and material IV after separation;
[0035] (4) Add calcium carbonate and calcium oxide additives (0.02 kg calcium carbonate, 0.01 kg calcium oxide) to the material...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Accurately weigh 1 kg of material Ⅰ of electrolytic manganese slag just discharged from the filter press workshop with a metering device, put it into the stirring reaction device, and add 5 kg of water and corresponding additives by weight to the reaction device using the metering system ( 0.09 kg of concentrated sulfuric acid and 0.04 kg of ferrous sulfate) are fully mixed and configured into material II;
[0041] (2) Add cathode and anode plates to the reaction device equipped with the material II obtained in step (1), apply a DC electric field, and the current density is 25 mA / cm 2 , carry out the leaching reaction at 25°C for 1 hour, and obtain the material III after the leaching reaction;
[0042] (3) Pour the material III obtained in step (2) into a solid-liquid separation device, and obtain leaching residue I and material IV after separation;
[0043] (4) Add calcium carbonate and calcium oxide additives (0.023 kg calcium carbonate, 0.013 kg calcium oxide) t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com