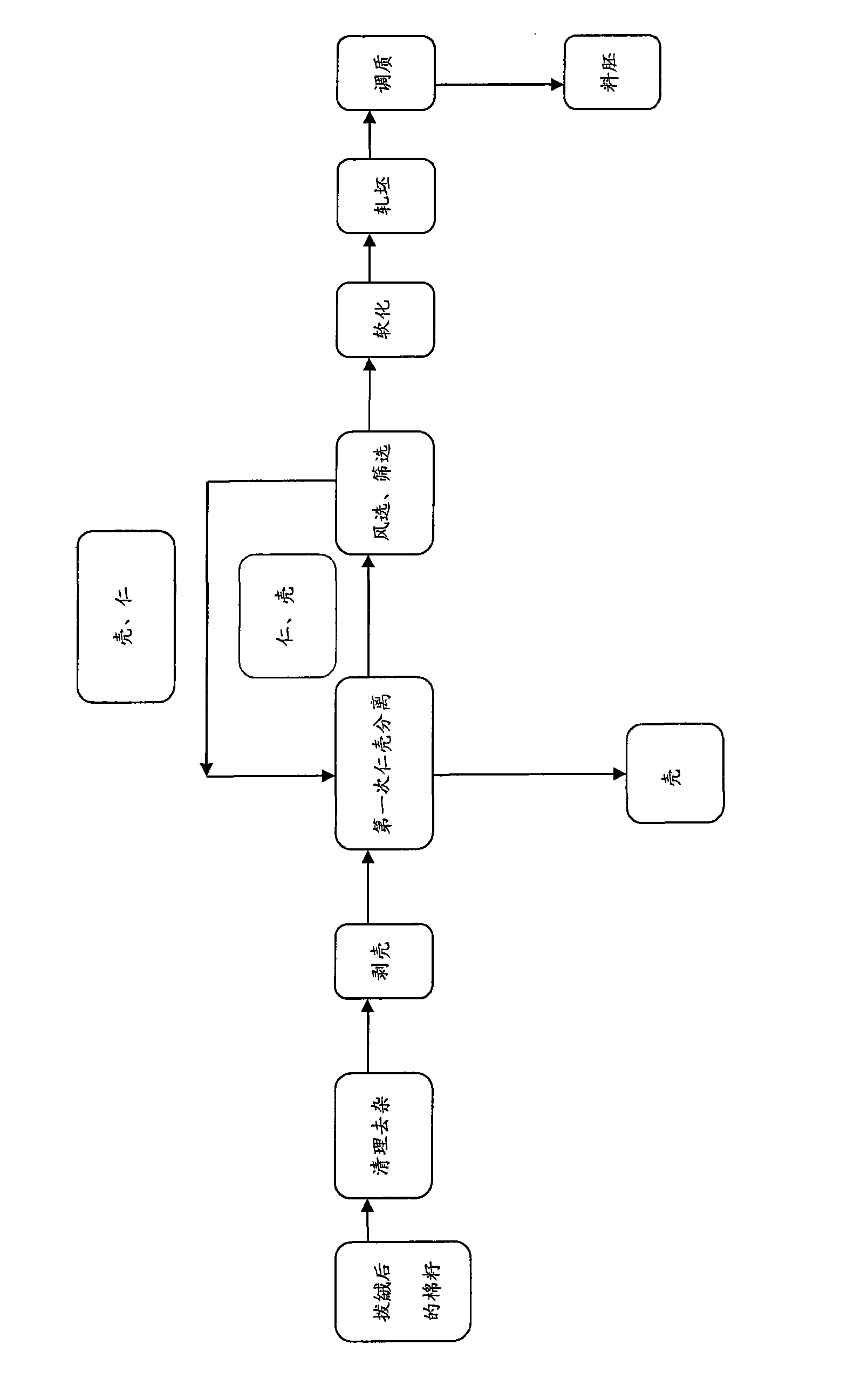Patents
Literature
80results about How to "Short leaching time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
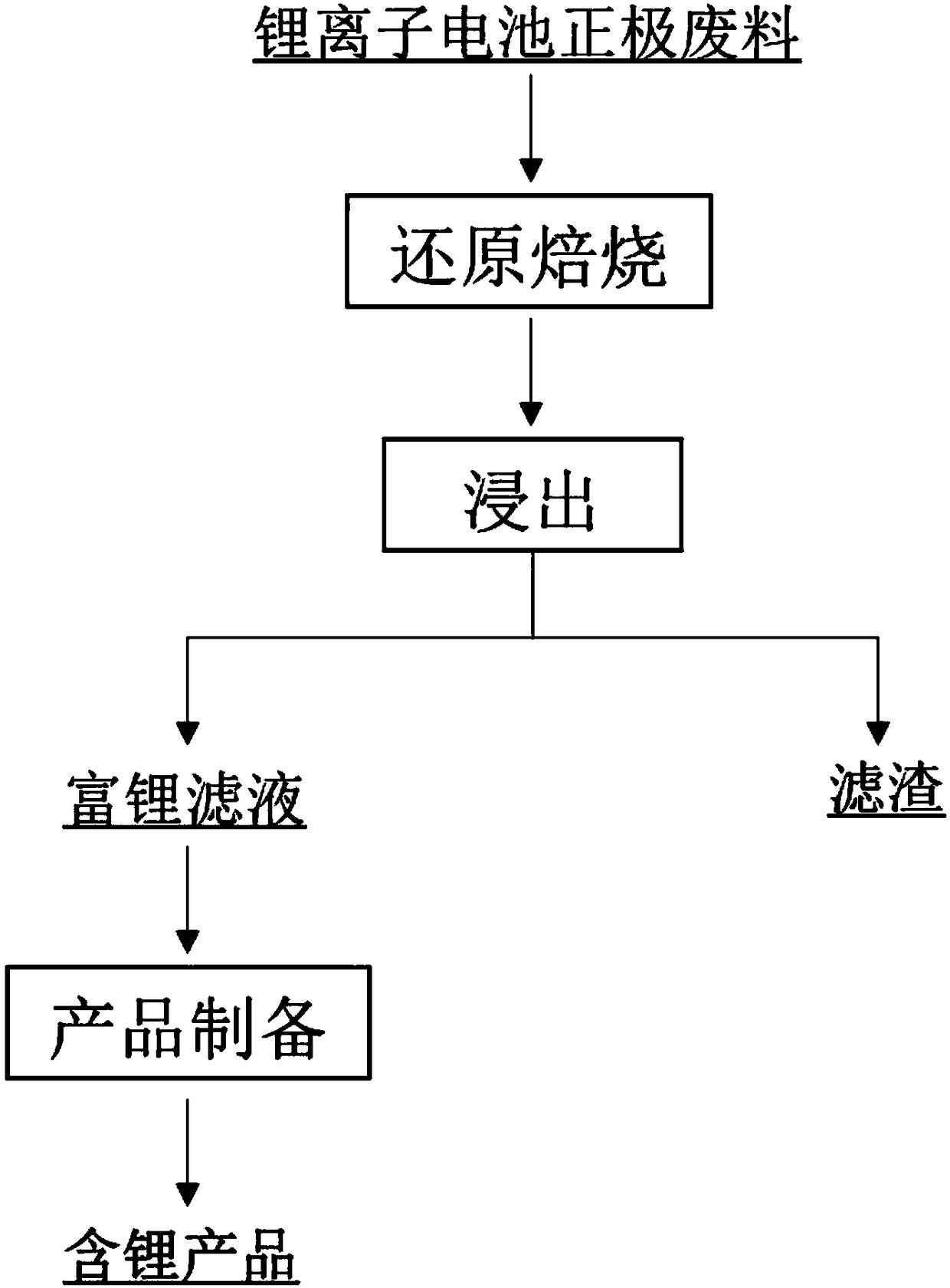
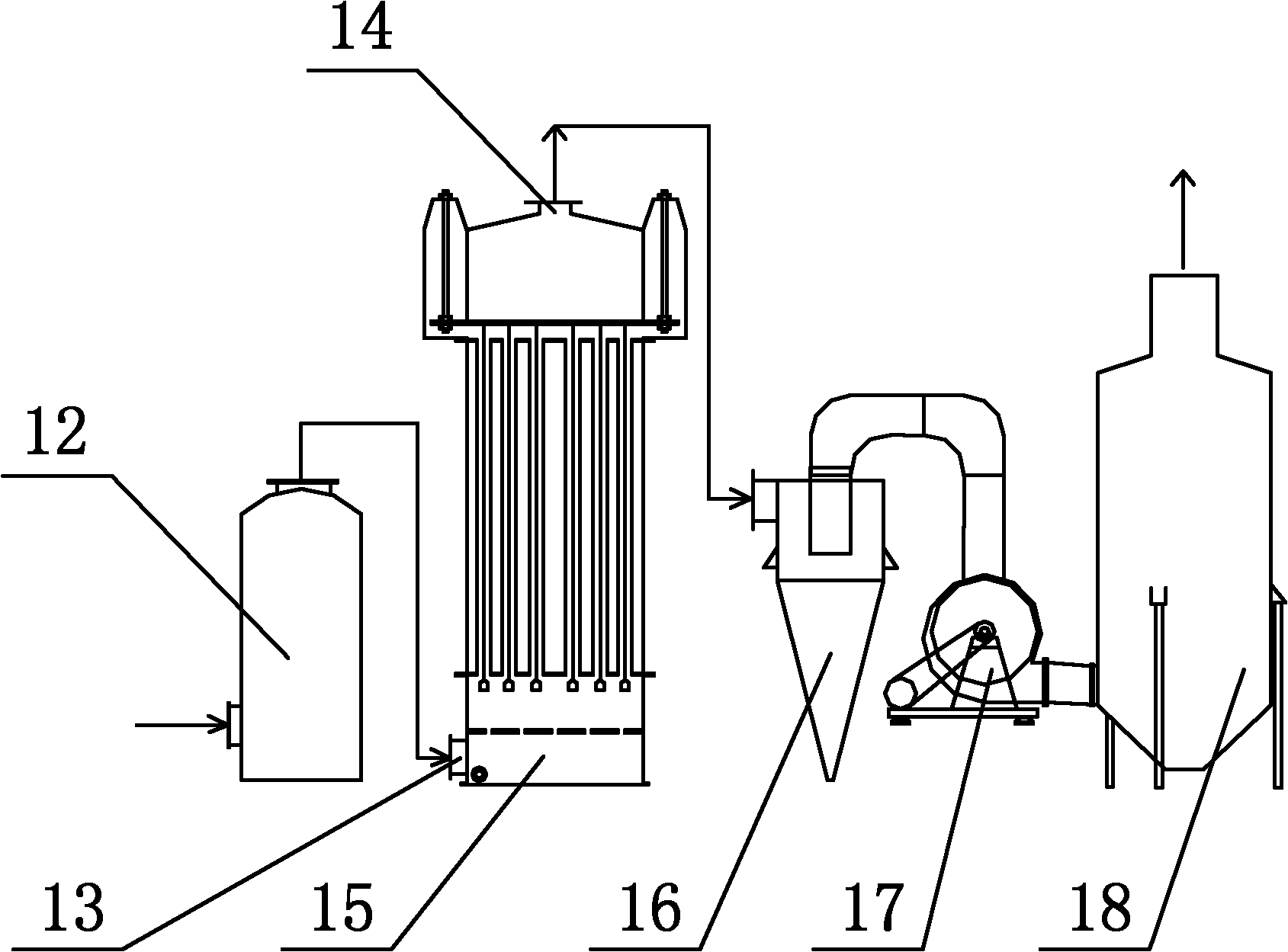
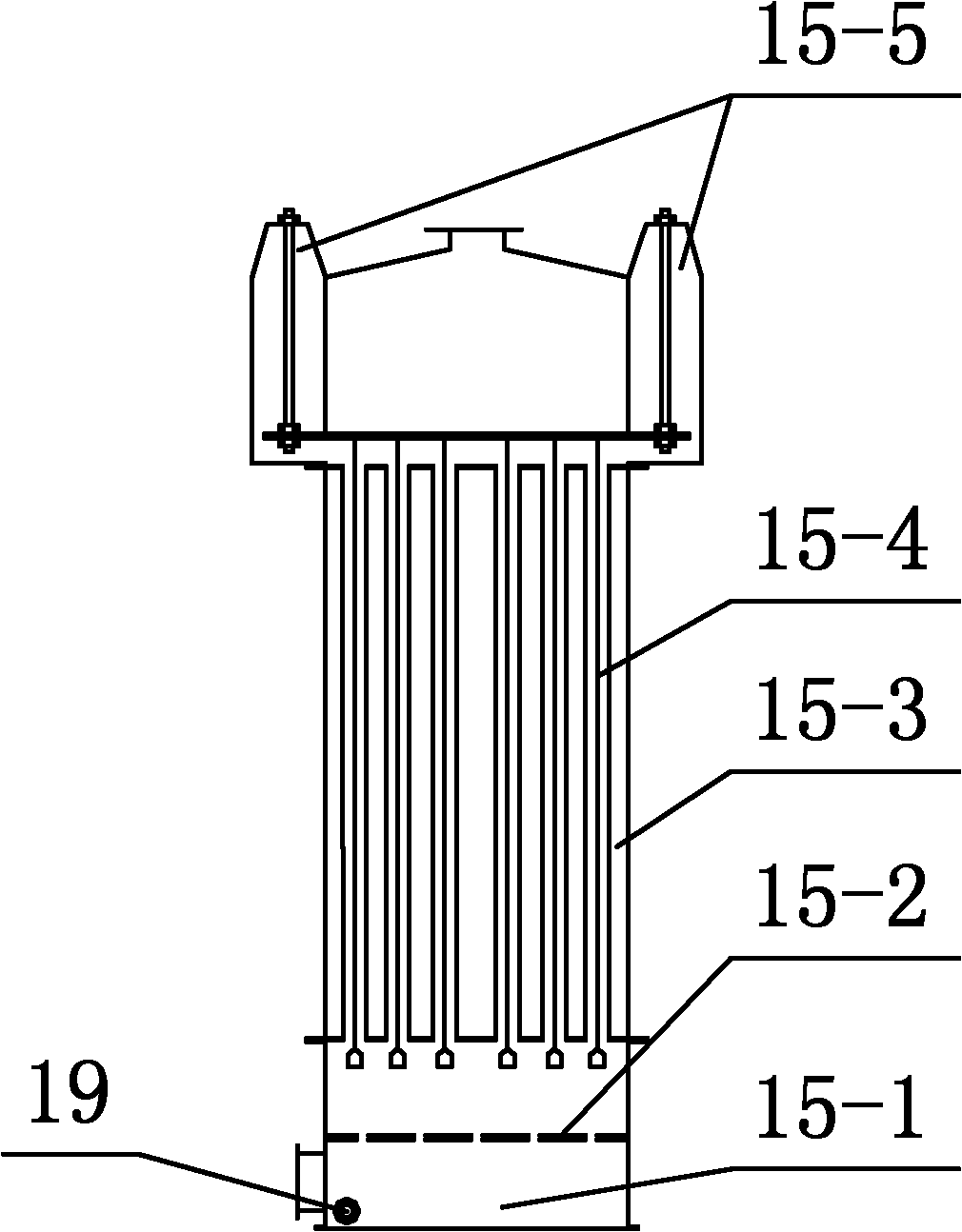
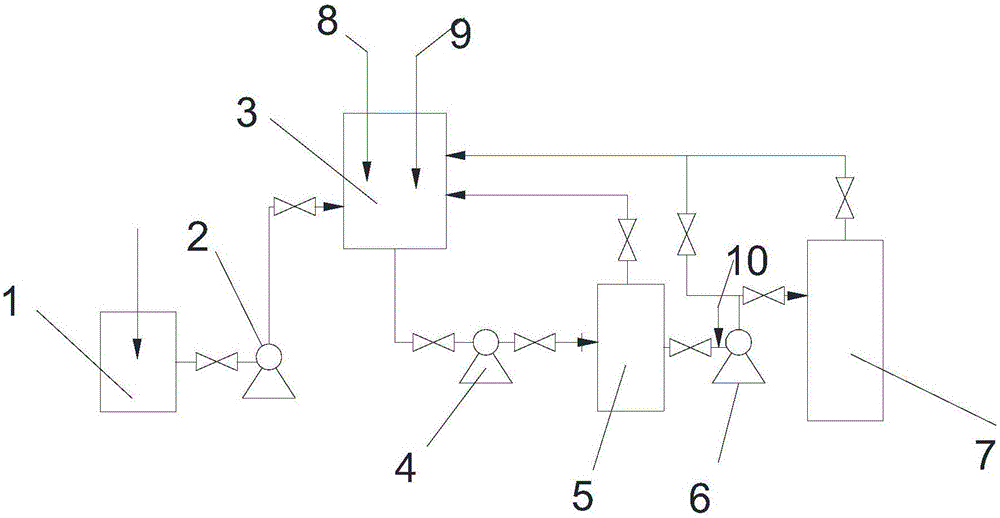
Method for recovering lithium from lithium-containing electrode waste material
InactiveCN108220607AShort leaching timeHigh recovery rateLithium oxides/hydroxidesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSlagScrap
The invention provides a method for recovering lithium from a lithium-containing electrode waste material. The method comprises the following steps of (1) roasting the lithium-containing electrode waste material under a reducing atmosphere, after roasting, cooling under a protective atmosphere to obtain a reduced material, leaching the reduced material through a leaching agent, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a lithium-containing solution and solid slags; (2) preparing the lithium-containing solution in the step (1) into a lithium-containing product. According to the methodprovided by the invention, a reducing gas is adopted for reducing roasting, so that the roasting temperature is low, and the energy consumption is less; and one-step leaching is carried out after reducing, so that high-efficient separation of lithium and other metal elements can be realized, the concentration of the lithium in the leaching agent is high, the recovery rate of the lithium is greatlyimproved, the recovered lithium-containing product has high purity, and in addition, other transition metal elements in the waste electrodes can be further recovered. The method provided by the invention is short in flow, low in cost, and easy to realize industrial application.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
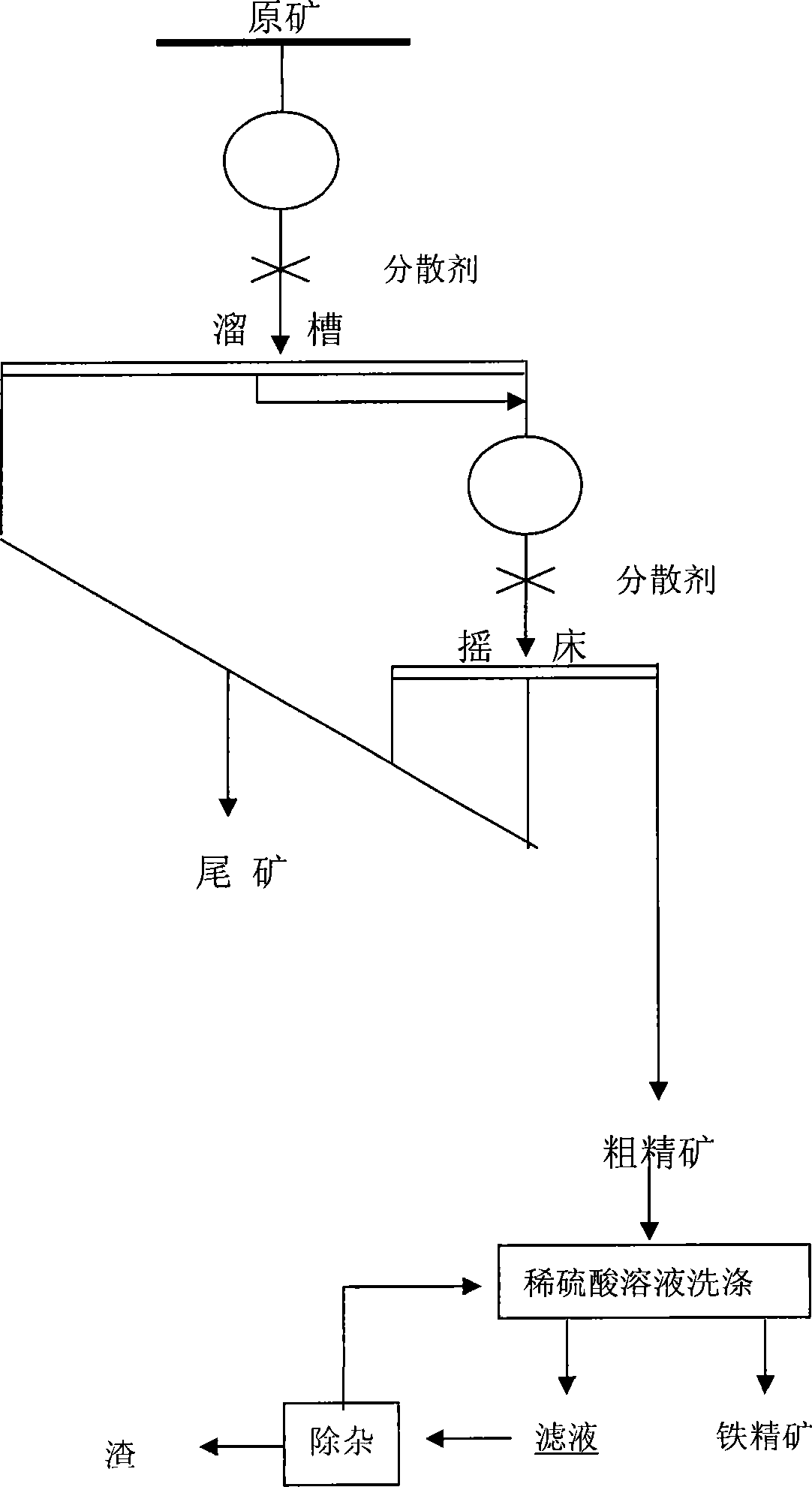
Method forpreparing iron concentrate for making iron from phosphorus-containing oolitic hematite
InactiveCN101054625AAvoid muddyingRaise the gradeProcess efficiency improvementGranularityRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method of producing iron ore concentrate containing roe - like phosphorus hematite for iron manufacture, comprising crashing the roe - like ore, wet grinding until the hematite of granularity < 0.074mm are 40-60 mass% of whole hematite, adjusting the pulp mass percent concentration to 20%-30%, adding the water glass as dispersant of 0.5-1.0kg / t, agitating adequately, selecting by helix shoot, grinding produced ore concentrate until the one with the granularity < 0.074mm are more than 80 mass%, having the water glass as dispersant of 0.2-0.5kg / t, agitating to disperse uniformly, then selecting by shaking table, washing produced iron ore concentrate in room temperature by 0.5%-1.5% dilute sulfuric acid solution for 5-15 minutes, centrifugal separation, in which the solid are iron ore concentrate. The invention treats the roe - like phosphorus hematite to obtain the iron ore concentrate with a tenor of 62%, P content less than 0.06%. The invention can fully and reasonably apply rich roe - like phosphorus hematite resource in our country, has a good effect of dephosphorization and a low cost. And produced iron ore concentrate have a high recovery ratio.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for leaching platinum metals from automobile tail gas spent catalyst by microwave heating and melting
InactiveCN102839287AImprove leaching rateEasy extractionProcess efficiency improvementMicrowaveSodium bisulfate
The invention provides a method for leaching platinum metals from an automobile tail gas spent catalyst by microwave heating and melting, comprising the steps of: crushing and finely grinding the automobile tail gas spent catalyst, uniformly mixing sodium bisulfate serving as a leaching agent with the automobile tail gas spent catalyst, and heating under microwave at the temperature of 300-700 DEG C for 30-150min to obtain sinter; and leaching under water dissolving and stirring at normal temperature for 10-60min, carrying out solid-liquid separation, washing filter residue three times, discarding the filter residue, collecting filtrate and cleaning solution to obtain the solution rich in platinum metals Pd and Rh. According to the method, microwave heating is adopted to simultaneously leach Pd and Rh, the leaching rate of platinum metal Pd reaches 99.97%, the leaching rate of platinum metal Rh reaches 98.91%, and both the leaching rates are improved as compared with that of single wet method or pyrogenic process leaching; and the leaching process is simple, the process flow is short, the reagent is single, the reagent consumption amount is low, the solution contains few impurity elements, the leaching rate is high, the leaching time is short and the energy consumption is low, so that the method has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing manganese sulfate by using sulfur-containing carbonaceous manganese carbonate ore
The invention provides a method for preparing manganese sulfate by using sulfur-containing carbonaceous manganese carbonate ore. The method comprises the following steps: 1, uniformly mixing manganese carbonate ore powder and pyrolusite powder in proportion and carrying out roasting; 2, immersing the roasted ore obtained in step 1 with anolyte, or industrial sulfuric acid or a composition thereof and carrying out filtering so as to obtain a filtrate which is a leachate containing manganese sulfate; and 3, adding ammonia water into the leachate, then adding a vulcanizing agent into the filtrate and carrying out filtering so as to obtain another filtrate which is a manganese sulfate solution meeting requirements for further processing indexes of a manganese salt. According to the invention, reduction roasting of the pyrolusite is carried out by using reductibility of the sulfur-containing carbonaceous manganese carbonate ore which looks like coal, has a low grade of manganese (with manganese content of about 10%) and can hardly be separated by using magnetism, the pyrolusite can be successfully reduced without usage of a reducing agent in the process of roasting, and the integral graded of manganese is improved; and economic benefit assessment results show that cost for reduction roasting of the manganese carbonate ore and the pyrolusite is lower than that for reduction roasting of the pyrolusite and reduction coal and a substantial effect is obtained through reduction roasting of the manganese carbonate ore and the pyrolusite.
Owner:DAXIN MANGANESE MINE BRANCH OF CITIC DAMENG MINING IND
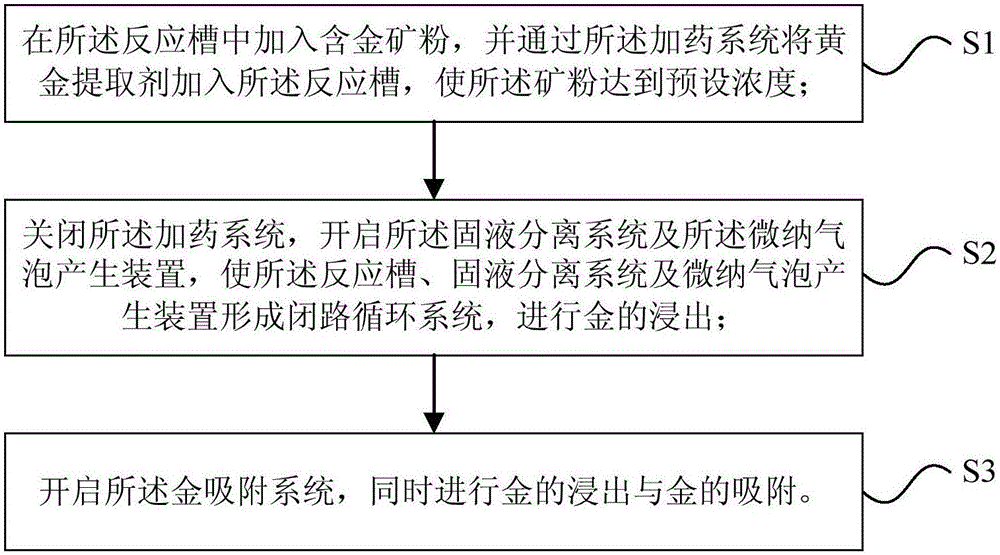
Processing method of trivalent cobalt nickel oxide waste material and waste cobalt nickel alloy
ActiveCN102952954AEasy dischargeShort leaching timeProcess efficiency improvementCobalt nickel alloyHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
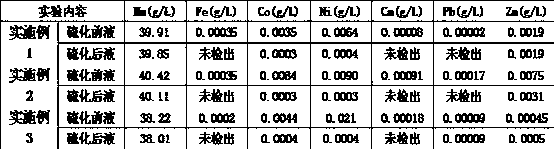
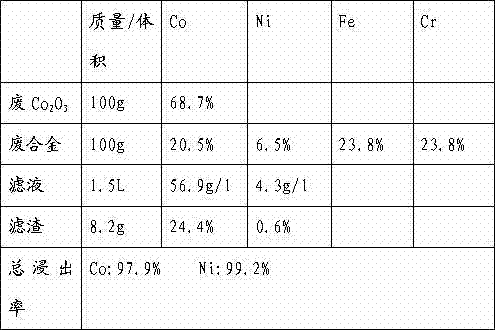
The invention provides a processing method of trivalent cobalt nickel oxide waste materials and waste cobalt nickel alloy, which comprises the following steps: firstly pulpifing trivalent cobalt nickel oxide waste materials by adding an acid solution with a hydrogen ion concentration of 1-2 mol / l, adding the cobalt nickel alloy waste materials under stirring, wherein the mass ratio of the alloy waste materials to the trivalent cobalt nickel oxide waste materials is 1:0.5-4, reacting at a temperature maintained at 80-99 DEG C, filtering, returning the filter residues to the above mentioned steps for leaching, performing chemical preliminary impurity removal and extraction deep purification impurity removal of the filtrate to obtain a high-concentration, pure cobalt nickel solution. The processing method can greatly reduce consumption of auxiliary materials, improve the leaching rate, shorten the reaction time, reduce the generation of toxic and harmful gas, and has great economic benefits and environment benefits.
Owner:GEM CO LTD
Method for preparing puddling iron concentrate by high-alumina iron ore
ActiveCN101037722ATo achieve the effect of dealuminationReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementGranularityLower grade
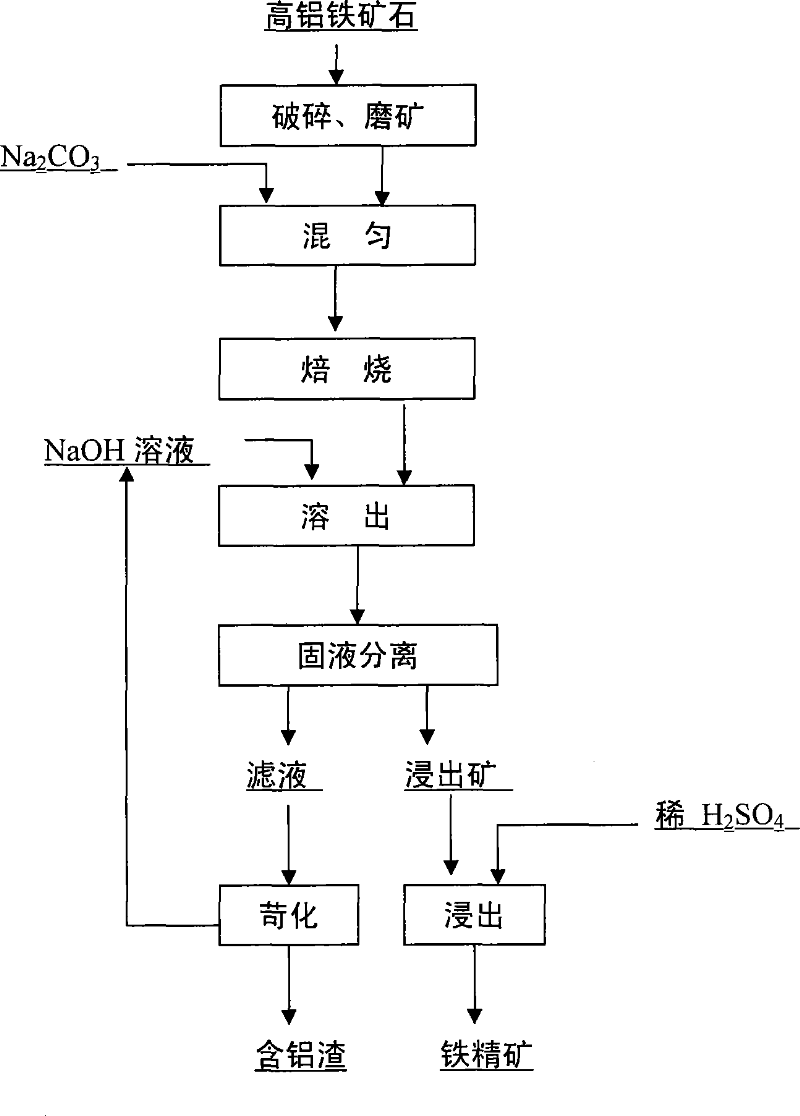
The invention disclosed a method for manufacturing the iron ore concentrate for ironmaking by the high aluminium iron ore, wherein after iron ore is broken to the granularity of less than 1.0mm which is in 40%-60%, it is mixed with Na2CO3 based on the proportion of 10-40 weight percent, and is braked for 10-30 minutes at the temperature of 900-1050 DEG C, then placed in the reactor to be extracted by 100-150 g / l solution at the temperature of 80-150 DEG C based on the liquid-solid quality rate of 3 / 1 -6 / 1 for 5-30 minutes, the filtrate can be extracted by the dilute sulphuric acid of 1.0-15 mass concentration percent at the temperature of 80-120 DEG C after solid-liquid separation for 10-30 minutes, and the solid is the iron ore concentrate after solid-liquid separation. The content of Al2O3 and Na2O in ore concentrate satisfies the requirement of blast furnace ironmaking materials using the invention. The invention can sufficiently and reasonably use existing rich high aluminium low-grade iron ore with good dealuminzation and low cost for reusing the extractive alkali liquor. The invention is suitable for the dealuminzation of each aluminiferous iron ore, in particular, high aluminium iron ore for reducing the close symbiosis and interdigitating of aluminium-containing minerals and iron-containing minerals, the manufactured iron ore concentrate can be used as the blast furnace ironmaking materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for leaching potassium in phosphorus potassium associated ore at low temperature by assisting with microwaves/ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN102864303AHeating fastFacilitate the transfer of substancesProcess efficiency improvementMineralogyUltrasonic assisted
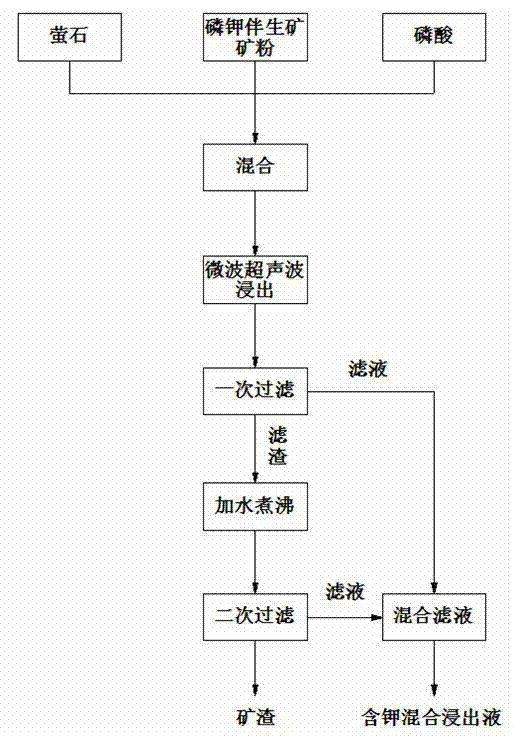
The invention relates to a method for leaching potassium in phosphorus potassium associated ore at low temperature by assisting with microwaves / ultrasonic waves. The method comprises the following steps of (1) mixing materials, taking phosphorus potassium associated ore powder and assistant fluorite to be evenly mixed, and then adding phosphoric acid for soaking to obtain a mixture; (2) conducting microwave and ultrasonic wave leaching; (3) obtaining primary filter residues and primary filter liquor; (4) obtaining secondary filter residues and secondary filter liquor; and (5) mixing a leaching liquid, mixing the obtained primary filter liquor and the obtained secondary filter liquor to obtain the leaching liquid containing potassium. The method has the advantages of substantially shortening heat conduction time, avoiding shortcomings of uneven heating in a traditional heating mode, being energy-efficient due to microwave heating, and almost having no other loss except for temperature rise of materials to be heated. Cavatition of the ultrasonic waves enables liquid to cause a series of movements such as swelling, compression and sinking and the like, and produced chemical effects and mechanical effects can change reaction conditions and quicken reaction speed.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for comprehensively recovering cobalt, copper and iron in cobalt-copper alloy
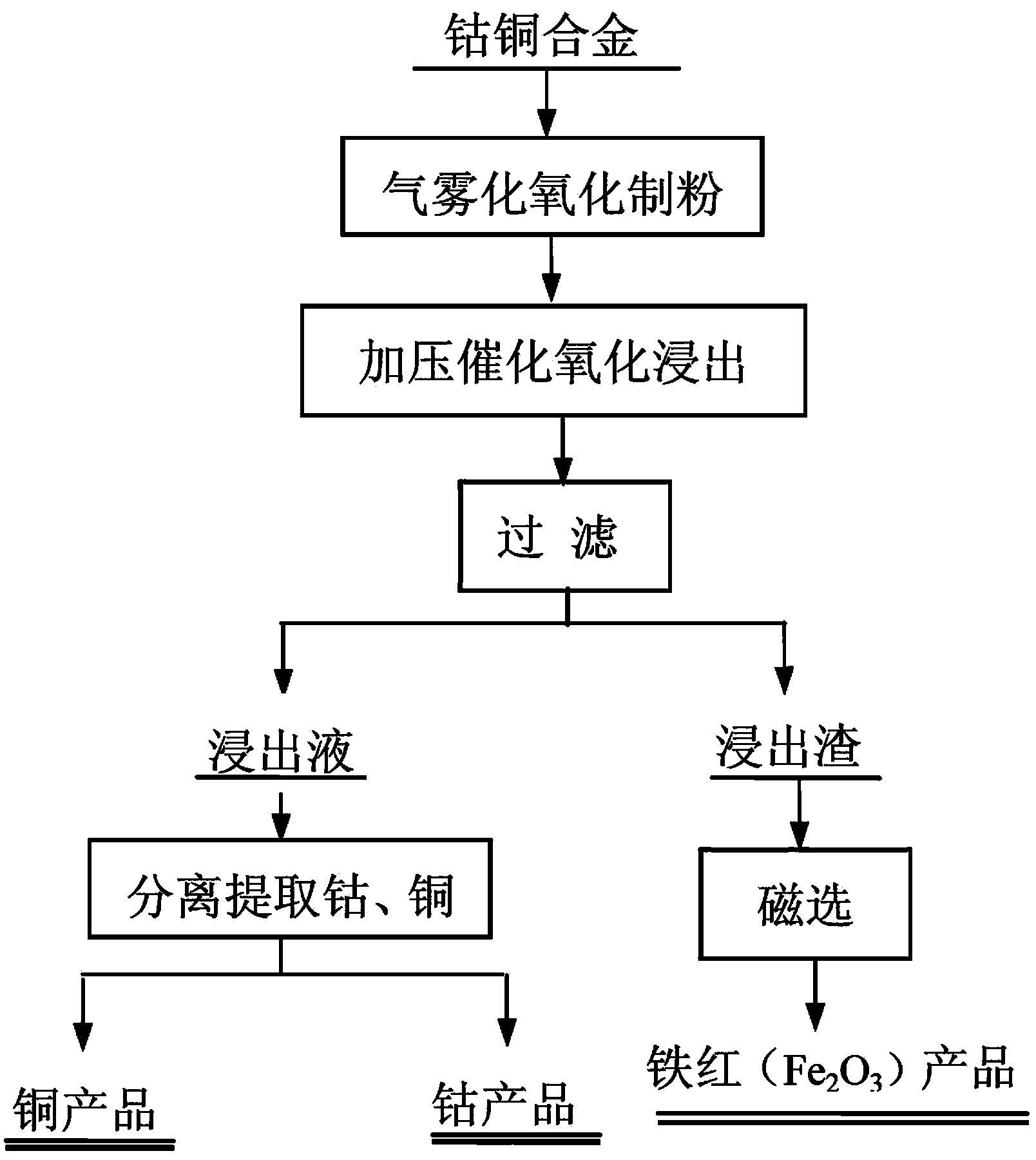
ActiveCN103436708ASmall granularityPowder shape changeFerric oxidesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering cobalt, copper and iron in a cobalt-copper alloy. The method is a full hydrometallurgical process and mainly comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing atomization oxidation on the molten cobalt-copper alloy by adopting high-pressure oxygen or oxygen-rich air to prepare powder; then adding a leaching agent, a catalyst and the cobalt-copper alloy into an autoclave, performing pressurized catalytic oxidative leaching to ensure that cobalt and copper in the cobalt-copper alloy are oxidized and leached out and enter a leach solution in the form of ions, wherein iron in the cobalt-copper alloy is leached, converted and finally remained in leach residues in the form of iron oxide red; finally, separating, purifying and refining the obtained leach solution to respectively obtain a cobalt product and a copper product which meet the international standard, and performing magnetic separation on the leach residues by adopting a strong magnetic separation method to obtain an iron oxide red product meeting the international standard. The method has the advantages of short flow, simplicity in operation, low energy consumption, high metal recovery rate, low cost and the like, and the comprehensive recovery utilization of the high-content iron in the cobalt-copper alloy is realized.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Comprehensive recycling method of platinum-rhenium containing reformed spent catalyst
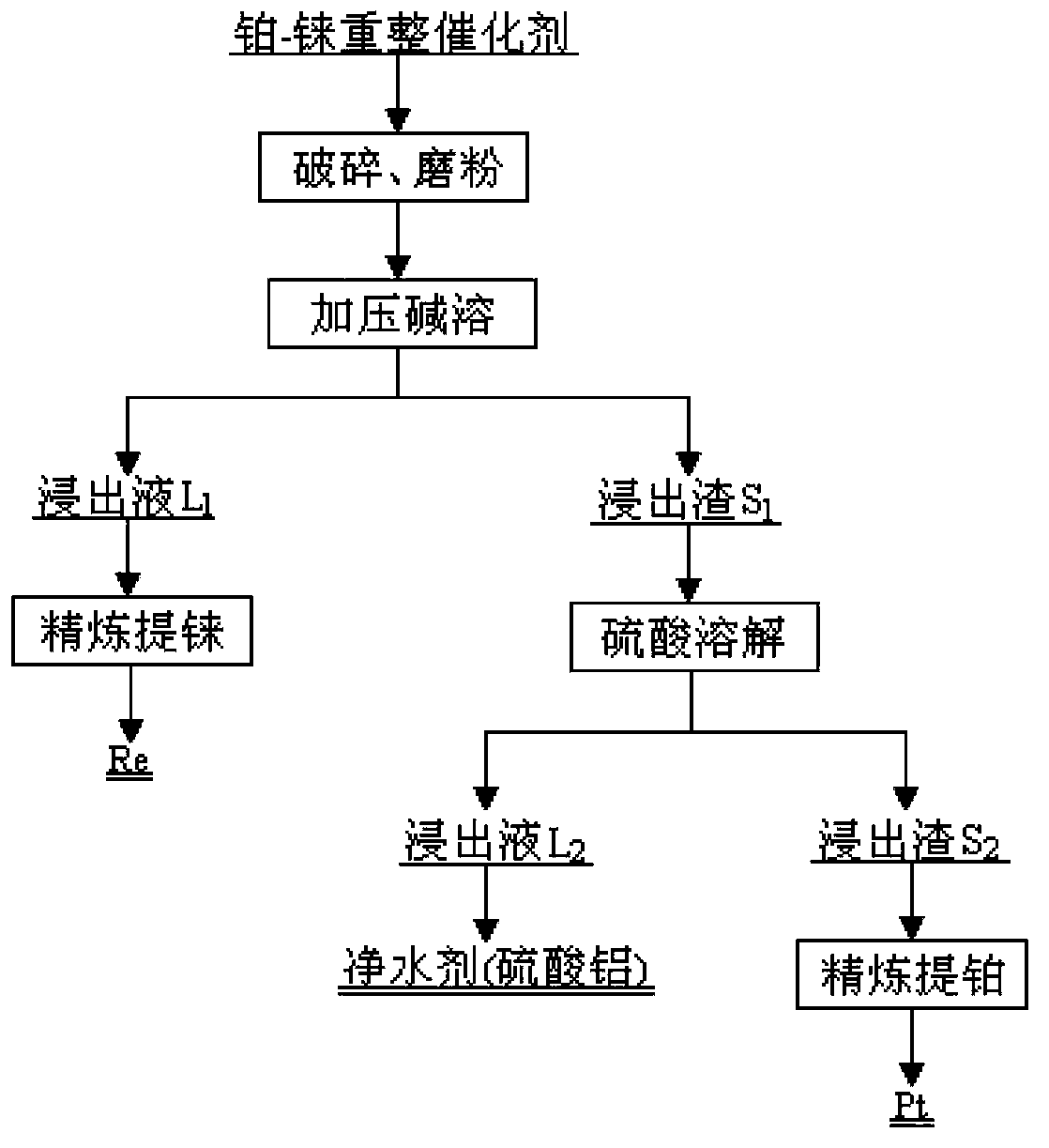
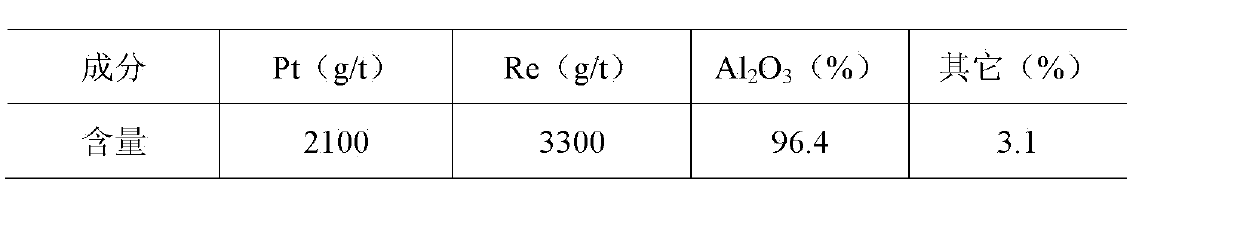
ActiveCN103388077ASimple processHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementChemical recyclingPlatinumPregnant leach solution
The invention relates to a comprehensive recycling method of a platinum-rhenium containing reformed spent catalyst. The comprehensive recycling method is used for leaching rhenium by pressurizing and alkaline-dissolving, is used for enriching platinum by normal-pressure acid dissolving, and is also used for comprehensively recycling aluminum oxide. The main flow comprises: (1), grinding material, namely, grinding the platinum-rhenium containing reformed spent catalyst to obtain powder materials with a grain size of 30-100 meshes; (2), pressurizing and alkaline-dissolving, namely, leaching rhenium by adopting a pressurizing method under an alkaline system to obtain leaching liquor L1 and leaching residue S1; (3), refining and rhenium extracting, namely, adding soluble sylvite to the leaching liquor L1 for refining the rhenium; (4), carrying out acid dissolving, namely, dissolving the leaching residue S1 by using an acid solvent to obtain leaching liquor L2 and leaching residue S2; (5), carrying out platinum refining, namely, refining the platinum in the leaching residue S2 to obtain metal platinum; and (6), carrying out aluminum sulfate recycling, namely, crystallizing the aluminum sulfate in the leaching liquor L2 to obtain a water purifying agent. The comprehensive recycling method of the platinum-rhenium containing reformed waste catalyst is simple in process flow and high in platinum and rhenium comprehensive recovery rate, wherein the platinum comprehensive recovery rate is higher than 99%, and the rhenium comprehensive recovery rate is higher than 92%. Meanwhile, the carrier is comprehensively recycled and utilized, so that the comprehensive recycling method is relatively environment-friendly.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
Device and method for decomposing rare earth ore through sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting
The invention discloses a device for decomposing rare earth ore through sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting, which comprises a sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting kiln, and a high voltage constant-current tail gas liquefying treatment system which is communicated with the sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting kiln and purifies flue gas output by the sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting kiln, wherein the sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting kiln comprises a raw material storage tank, a sulfuric acid storage tank, a double-screw continuous mixer, a kiln body, a material stirring system arranged at the bottom of the kiln body, and a combustion chamber arranged outside the kiln body; and the high voltage constant-current tail gas liquefying treatment system comprises a cooling tower, a high voltage constant-current tail gas liquefying tower, a high-efficiency cyclone separator, an exhaust fan, and a foam tower. The invention also discloses a method for decomposing rare earth ore through sulfuric acid low-temperature dynamic roasting by the device. The device and the method has wide adaptability for decomposing minerals and ensure that the decomposition rate is over 96 percent; and the device and the method can ensure that the materials are fully decomposed and the final tail gas meets the emission standard.
Owner:广西域潇西骏稀土功能材料有限公司
Roasting method for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing shale
InactiveCN102230072AImprove conversion rateAdd lessVanadium compoundsProcess efficiency improvementLeaching rateRise rate
The invention relates to a roasting method for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing shale. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing vanadium-containing shale raw ore with a vanadium-containing shale extraction roasting additive in a ratio of 1:(0.06 to 0.1), feeding the mixture to a roasting furnace, heating to 850 to 1000 DEG C at a temperature rise rate of 400 to 500 DEG C / h, maintaining the temperature for 1 to 2 hours, then adding the roasted product to dilute sulfuric acid with volume fraction of 4 to 10% in a solid-liquid mass ratio of 1:2, and leaching at 90 to 100 DEG C for 0.5 to 1 hour under the condition of stirring. The preparation method of the vanadium-containing shale extraction roasting additive comprises the steps of: preparing Mg compounds, namely NaClO3, Na2CO3 and CaCO3 and mixing uniformly, wherein the mass ratio of NaClO3:Na2CO3:CaCO3 is 1:1:(4 to 8):(6 to 10); and grinding until the particle size is not more than 0.15 mm. The method provided by the invention increases the leaching rate up to 86% to 87% and has the characteristics of high recovery rate, short roasting period, high leaching speed and little roasting pollution.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
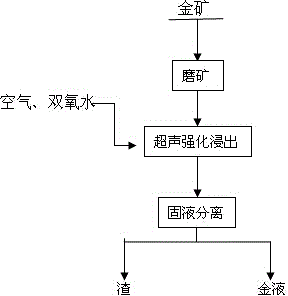
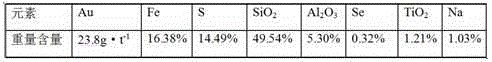
Method for collaboratively leaching gold in refractory gold ores by virtue of ultrasonic enhancement, chlorination and oxidization
InactiveCN104630466AImprove leaching rateShorten the leaching timeProcess efficiency improvementOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The invention discloses a method for collaboratively leaching gold in refractory gold ores by virtue of ultrasonic enhancement, chlorination and oxidization, and belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, crushing gold ores into ore powder, thoroughly mixing the ore powder with sodium hydroxide, sodium hypochlorite and water to obtain ore pulp, introducing air into the ore pulp, and performing ultrasonic enhanced leaching under a stirring condition; periodically adding hydrogen peroxide in the enhanced leaching process. According to the method, at the same time of ultrasonic enhancement, a redox reaction is performed by virtue of the synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide; the synergistic effect of the hydrogen peroxide and the sodium hydroxide is far better than the independent oxidization effect of each of the hydrogen peroxide and the sodium hydroxide. The ultrasonic enhancement is capable of improving the gold leaching effect while shortening the reaction time, and therefore, the reagent cost can be saved and the gold ore leaching efficiency also can be improved; as long as the method is adopted for leaching, the leaching rate can be above 98%; in addition, the sodium hypochlorite is adopted as a leaching agent for the method and no pressure is caused on the environment; besides, the method is capable of realizing one-step enhanced leaching of the gold ores and shortening the leaching steps.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
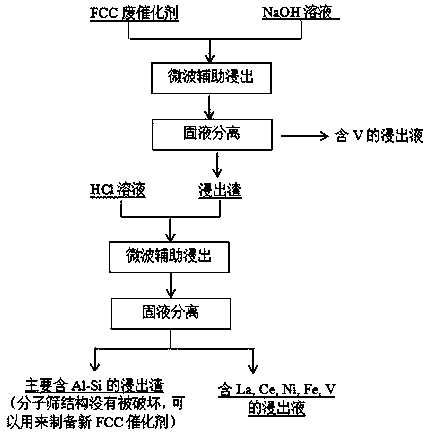
Method for regenerating FCC waste catalyst via microwave assistance
InactiveCN108160109ASimple processEasy to operateMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst regeneration/reactivationRare-earth elementSolvent
The invention relates to a method for regenerating a FCC waste catalyst via microwave assistance, and belongs to the technical field of integrated recycle of secondary resource. The method comprises:taking a sodium hydroxide solution with the concentration being 0.1-0.8 mol / L as a solvent, performing alkali soaking on an FCC waste catalyst for 10-60 min in microwave radiation at 50-100 DEG C to remove a part of vanadium from the FCC waste catalyst and to obtain a soaked residue and a vanadium-containing soaking liquid; and taking a hydrochloric acid solution with the concentration being 1-8 wt% as a solvent, and performing acid soaking on the obtained soaked residue for 10-60 min in microwave radiation at 50-100 DEG C to obtain a soaking liquid which is abundant in rare earth, iron, vanadium and nickel and a soaked residue of a silicon aluminium salt molecular sieve having a crystal structure. According to the method, rare earth elements are recycled, iron, vanadium and nickel are removed, and the most importance is that the molecular sieve structure is kept and can be used for preparing a new FCC catalyst. The method is simple in treatment process and short in operation time, andthe structure of the silicon aluminium salt molecular sieve in the soaked residue is complete.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
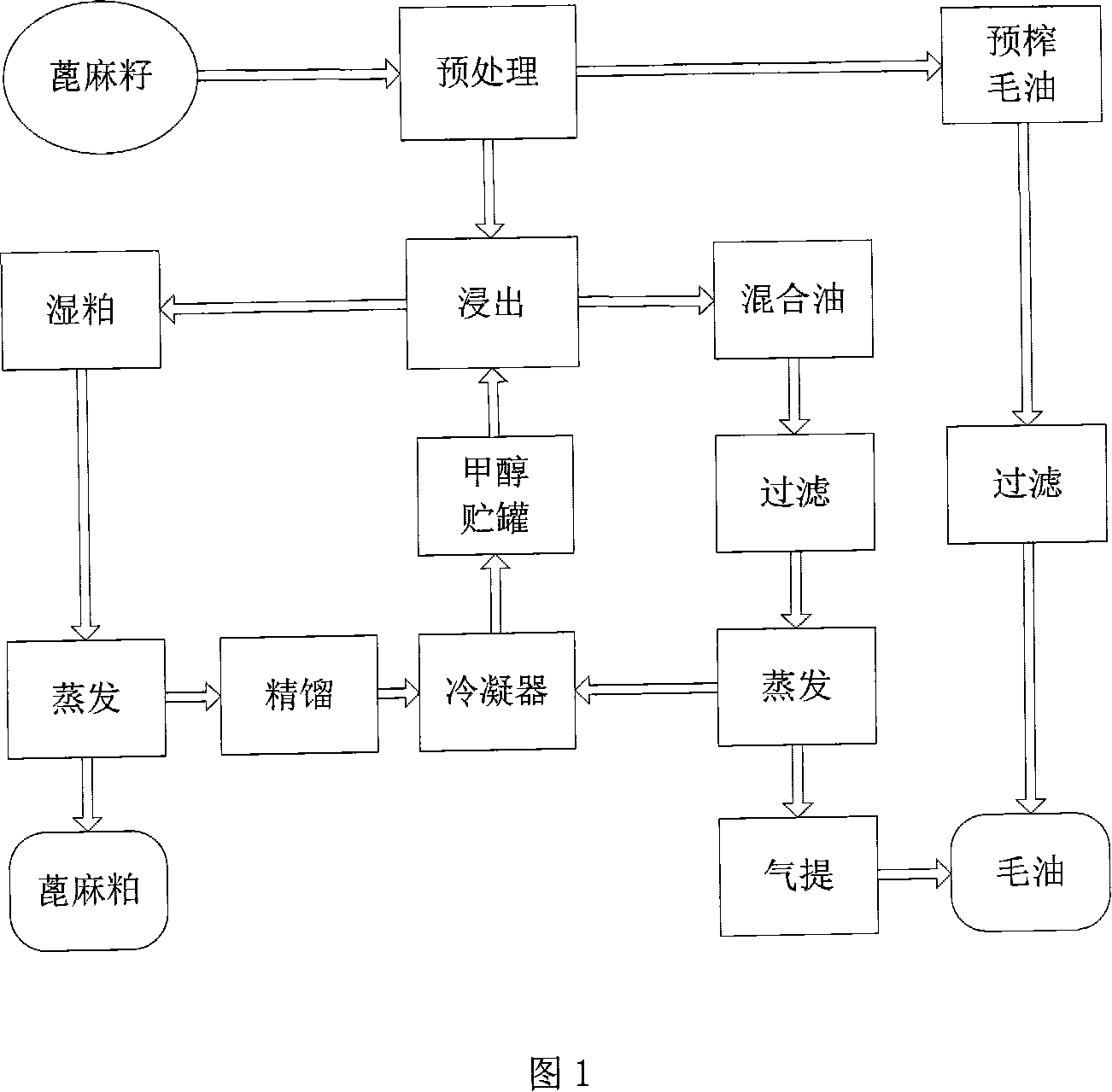
Processing method for solvent extracting ricinus oil with methanol
InactiveCN101108998AShorten the leaching timeReduce dosageFatty-oils/fats productionCastor SeedOil and grease
The invention discloses a methanol leaching castor oil process method. Regulating castor seed choose is done after the cleaning of the castor seeds free from impurity as well as insect damage. The seeds are of shell removal, crush or pre-pressure to make part of castor oil. The castor oil is leached with the ultrasonic or physical field aided condition method. Under the ultrasonic condition, the castor oil is leached by the methanol leaching solute, which improves the existing solute leaching method, greatly shortens the leaching time, decreases the raw material consumption and lowers the experiment cost, thus being the new oil leaching method of the lower cost, short leaching time and high oil production rate. The invention solves the problems that current bio-diesel preparation method has high requirements to the oil, long technique procedure, large consumption of various raw materials, reagents and equipments, serious reagent pollution and high production cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
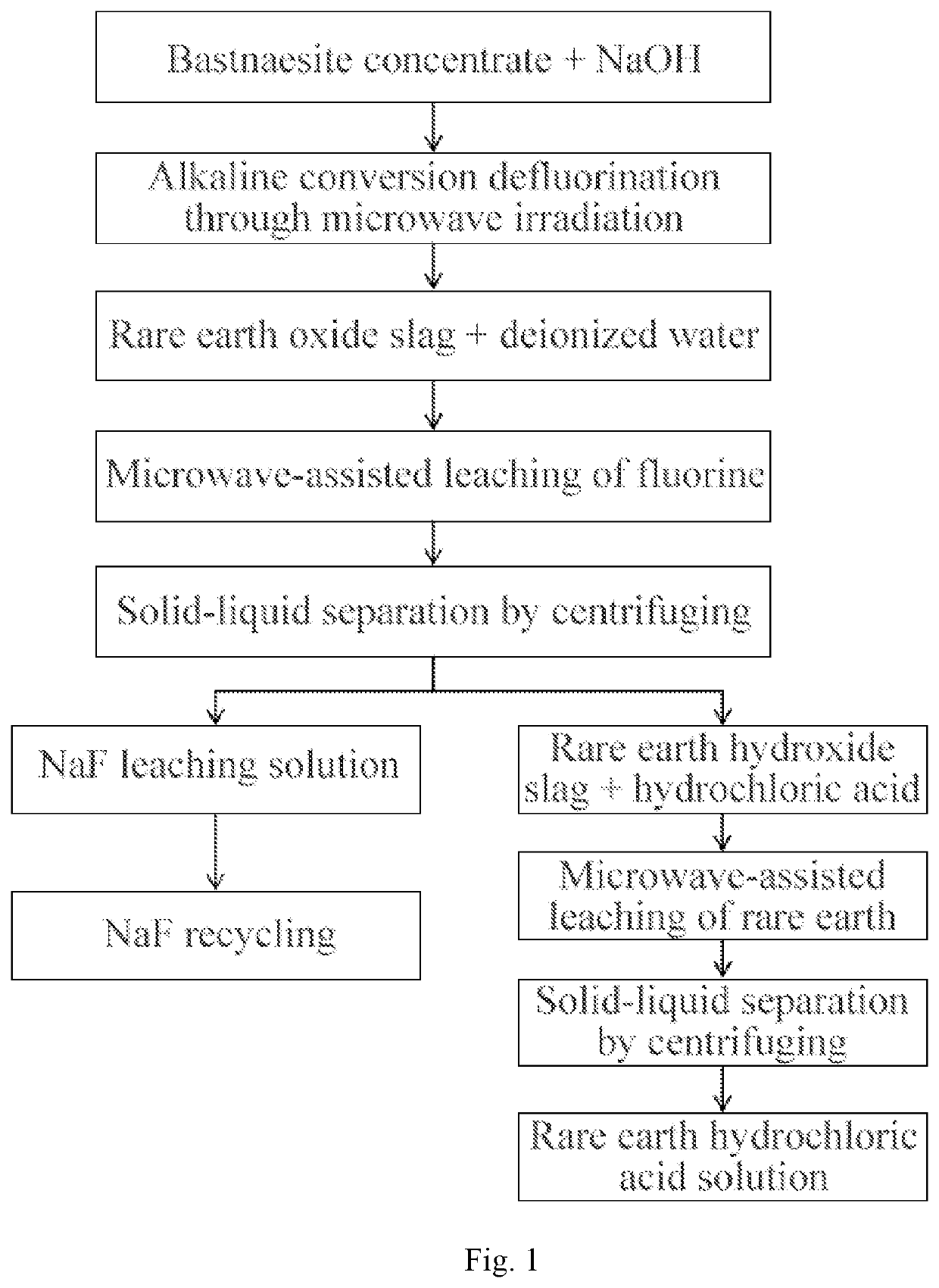
Microwave chemical method for totally extracting fluorine and rare earth from bastnaesite concentrate
PendingUS20210236956A1Short processReduce energy consumptionFluorineProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPhysical chemistry
Disclosed is a microwave chemical method for totally extracting fluorine and rare earth from bastnaesite concentrate, including: alkaline conversion defluorination of bastnaesite through microwave irradiation, microwave-assisted leaching of fluorine, solid-liquid separation of leaching solution and microwave-assisted leaching of rare earth. The rare earth hydrochloric acid solution for leaching contains no fluorine ion, so that the fluorine interference of subsequent processes such as impurity removal can be completely avoided; the fluorine and the rare earth are leached with microwaves, which does not need the stirring, so that the automatic control is easy to implement; the fluorine and rare earth leaching speed is high, the leaching time is short and the complete leaching of fluorine and little residual alkali in the slag can be realized by two-time leaching; and no fluorine-containing waste water is discharged, and the total extraction of the rare earth can be realized by one-time leaching.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
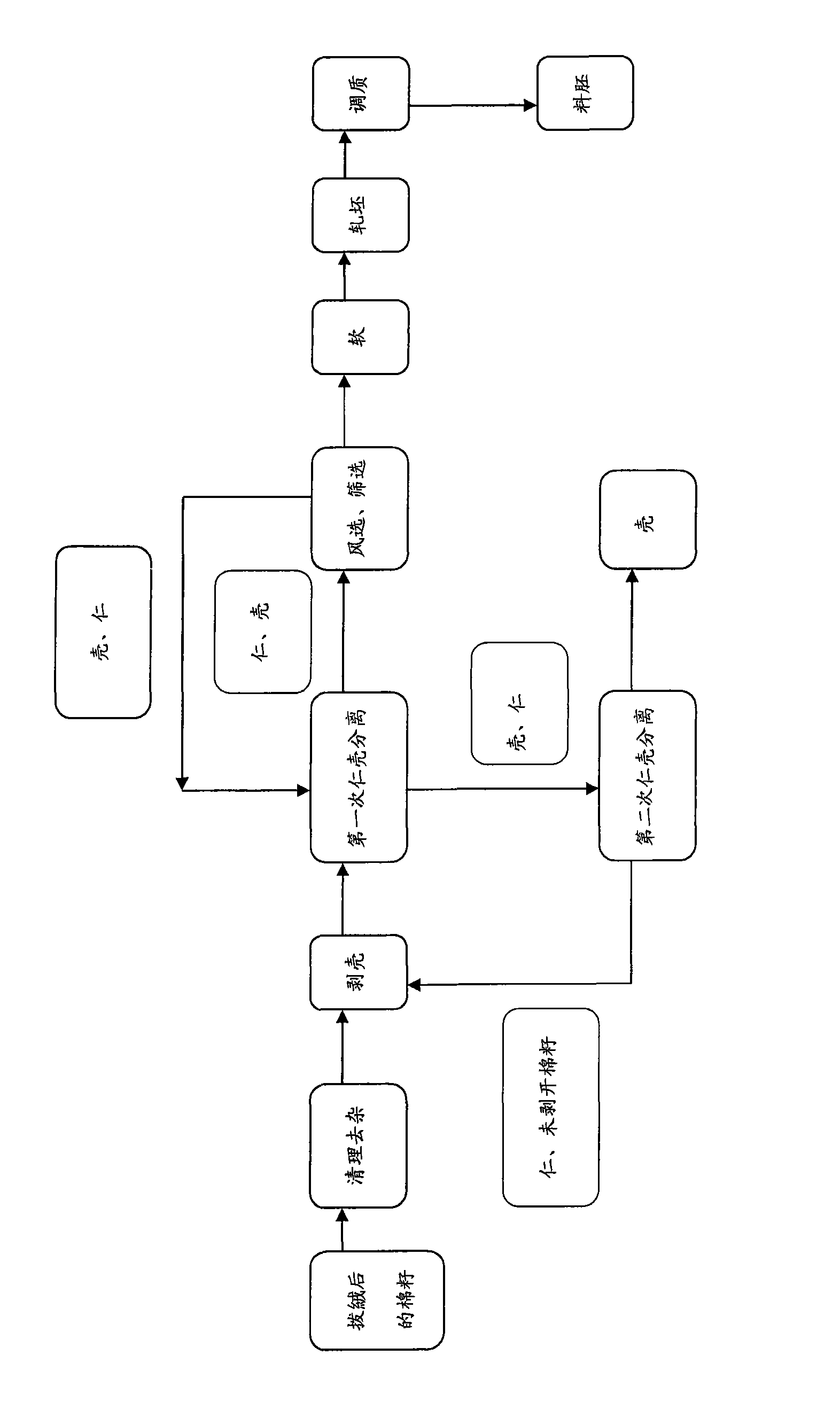
Method for producing cottonseed germ materials used in low-temperature pretreatment production of gossypol-removed cottonseed protein
InactiveCN101664099ADoes not affect nutritional valueGood workmanshipProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsHuskCottonseed oil
The invention provides a method for producing cottonseed germ materials used in low-temperature pretreatment production of gossypol-removed cottonseed protein. The method comprises: cleaning and removing impurities in delinted cottonseeds; husking the cottonseeds after impurity removal; obtaining mixture of cottonseed kernels and cottonseed husks; repeatedly separating the mixture by use of a screening and / or winnowing method; obtaining the cottonseed kernels in which the content of the cottonseed husks is less than or equal to 18 percent; softening the cottonseed kernels at a temperature lower than or equal to 80 DEG C; rolling the cottonseed kernels into germ sheets; adjusting quality at a temperature lower than or equal to 80 DEG C; and obtaining germ materials. The germ materials produced by use of the method have the advantages of good shape, high strength, less breakable property, good permeability during extraction, short seepage time, low content of residual oil and gossypol in meal after oil extraction and gossypol removal, capability of continuous production and capability of maintaining the original nutritional value of protein.
Owner:北京中棉紫光生物科技有限公司 +1
Method for extracting vanadium by roasting vanadium-containing stone coal
InactiveCN106755958ALow firing temperatureShort firing timeProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention relates to a method for extracting vanadium by roasting vanadium-containing stone coal. According to the technical scheme of the method, firstly, vanadium-containing stone coal raw ore and a roasting additive are prepared, evenly mixed and ground till the granularity is smaller than or equal to 0.15 mm, wherein the mass ratio of the vanadium-containing stone coal raw ore to the roasting additive is 1:(0.045-0.115); then the temperature is increased to 700 DEG C to 900 DEG C at the rate of 6 DEG C / min-16 DEG C / min, heat preservation is conducted for 1 h to 1.5 h, and roasted ore is obtained; then the roasted ore is added into dilute sulfuric acid according to the solid-liquid mass ratio of 1:(1.5-2.5), stirring is conducted for 0.5 h to 2 h under the temperature ranging from 90 DEG C to 100 DEG C, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and leaching liquid and leaching slag are obtained; the roasting additive is a mixture of CaO, CaF2 and MnO2, wherein the mass ratio of the CaO to the CaF2 to the MnO2 is 1:(0.55-1):(0.10-0.18); and the volume concentration of the dilute sulfuric acid ranges from 8% to 18%. The method has the beneficial effects of being low in roasting temperature, short in roasting time, high in vanadium leaching rate, high in leaching speed and environment-friendly, and the leaching slag obtained in the method can serve as cement admixture, and comprehensive utilization of solid waste obtained after vanadium extraction is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
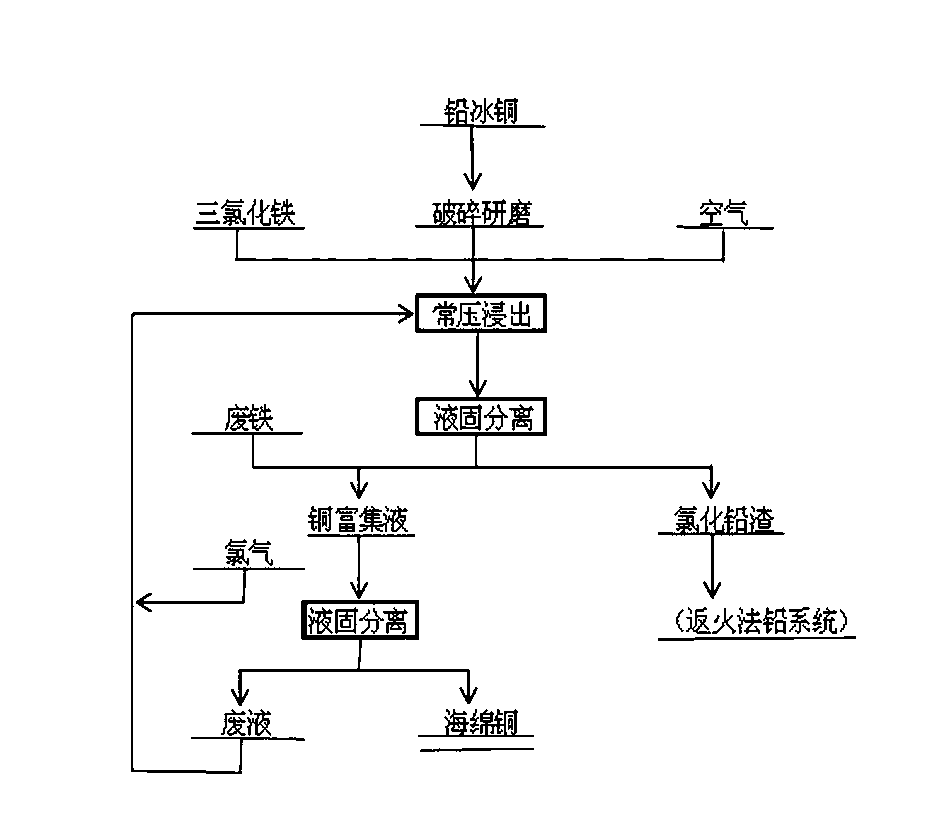
Technology for processing lead copper matte by ferric chloride
InactiveCN102994744AImprove protectionHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention relates to a technology for processing lead copper matte by ferric chloride, and belongs to the wet method field of the non-ferrous metal metallurgy. The technology comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding the lead copper matte, and sieving by a mesh 80 mesh sieve to obtain below 80 mesh particles; and carrying out normal pressure leaching of the ground lead copper matte in a leaching tank at 50-100DEG C for 4-8h, wherein the FeCl3 concentration is controlled between 200g / l and 400g / l, and the liquid-solid ratio is 3-10:1. Air is properly blown and a small amount of hydrochloric acid is added to acidify in order to improve the leaching effect and shorten the leaching time. Trivalent iron ions are utilized as an oxidizing agent to leach sulfides under an acidic condition. In the oxidation leaching process, sulfur in the lead copper matte is oxidized into elemental sulfur which is transferred to slag, copper is oxidized and enters a solution in an ion state, and lead is residual in the slag as lead chloride together with gold and silver; after completing the leaching process, liquid-solid separation of an ore pulp is carried out while hot to realize the preliminary separation of copper and lead; and scrap ion is added to the copper-enrich leaching solution to displace copper in the leaching solution in order to obtain a preliminary product copper sponge.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
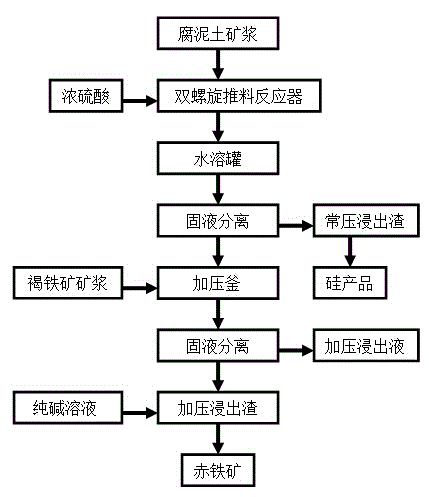
Method for recovering nickel, cobalt, iron and silicon from laterite-nickel ore by combined leaching process
InactiveCN104630500AFast recyclingLess investmentSilicaProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationSlurry
The invention discloses a method for recovering nickel, cobalt, iron and silicon from laterite-nickel ore by a combined leaching process. The method comprises the following steps: adding muck ore slurry and concentrated sulfuric acid after heating into a double-spiral material pushing reactor; dissolving reaction materials in water, then performing solid-liquid separation, and washing filtration residues to obtain normal-pressure leaching residues, a normal-pressure leaching solution and a washing solution; preparing limonite ore slurry from the washing solution and limonite, adding the limonite ore slurry and the normal-pressure leaching solution into a pressurization kettle for pressurization and leaching, hydrolyzing Fe<3+> in the normal-pressure leaching solution to a hematite precipitate, and releasing acid to re-leach the limonite; reducing the temperature, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain pressurized leaching residues and a pressurized leaching solution; removing non-nickel and cobalt impurities in the pressurized leaching solution, and then recovering nickel and / or cobalt by an existing method; washing the pressurized leaching residues with a soda ash solution, and then drying to obtain fine iron powder; and performing screening treatment on the normal-pressure leaching residues to obtain silicon dioxide and fine sand. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of short leaching time, high nickel leaching rate, low acid consumption and effective recovery of iron and part of silicon.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
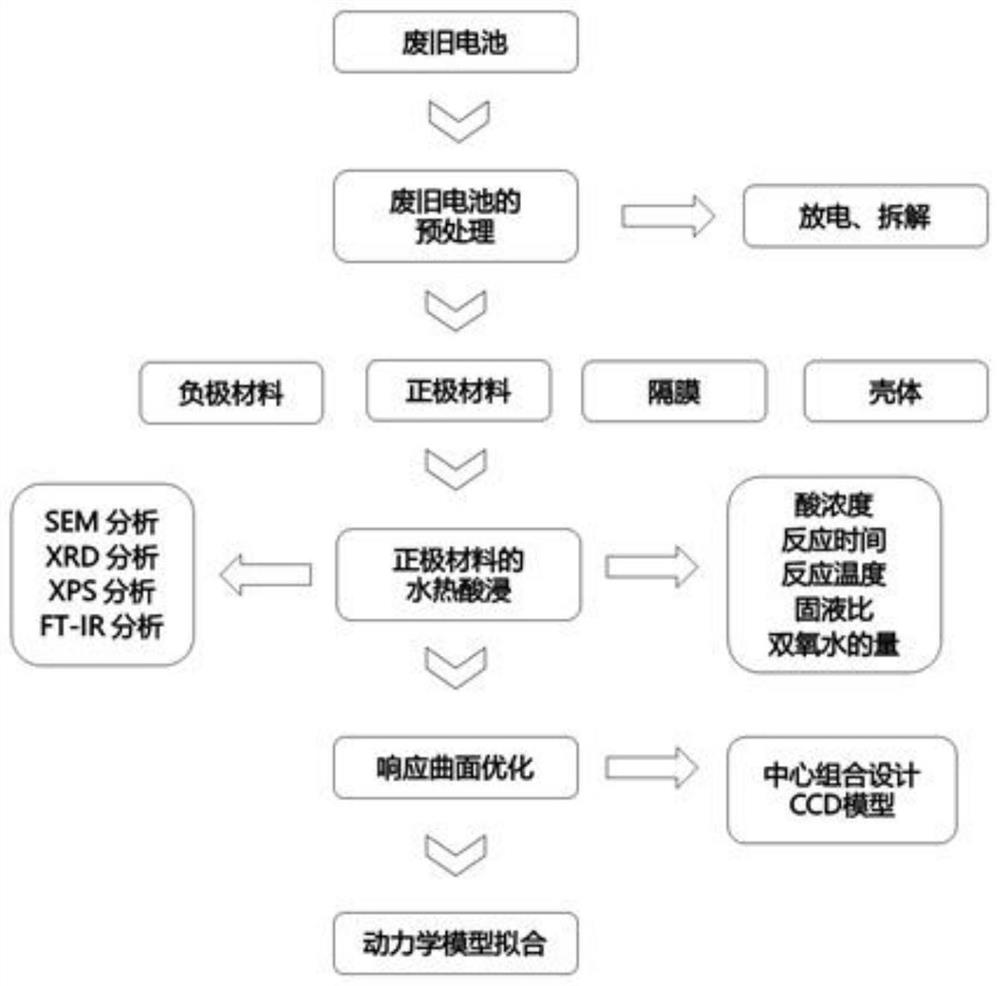
Method for separating Co (cobalt) and Li (lithium) from LiCoO2 (lithium cobalt oxide) of waste lithium batteries to prepare cobaltous phosphate
ActiveCN106395784AEasy to separateEfficient recyclingSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingPregnant leach solutionPhosphate
The invention discloses a method for separating Co (cobalt) and Li (lithium) from LiCoO2 (lithium cobalt oxide) of waste lithium batteries to prepare cobaltous phosphate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) disassembling and peeling the waste lithium batteries to obtain anode and cathode active substances; (2) calcining and grinding the anode and cathode active substances to obtain LiCoO2-containing powder materials; (3) performing leaching on the LiCoO2-containing powder materials by mixed leaching liquid of H3PO4 and H2O2; neutralizing the obtained leaching liquid; performing solid-liquid separation to obtain cobaltous phosphate sediment and a lithium-containing solution. The method has the advantages that the LiCoO2 of typical waste lithium batteries is used as a raw material; the Co and the Li are effectively separated by a roasting and leaching method; the cobalt with high additional values is recovered for preparing the cobaltous phosphate (cobalt violet); the resource recycling and utilization of the LiCoO2 of the waste lithium batteries are realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Cyanide-free extractant and gold extracting method
ActiveCN106191460AShort leaching timeImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementCyanideWastewater
The invention provides a cyanide-free extractant and a gold extracting method. The cyanide-free extractant comprises, by mass percentage, 0.5-2% of amino acid and 0.2-2% of alkali, wherein water serves as a solvent. According to the gold extracting method, the amino acid gold extracting agent free of toxicity to the environment is adopted for leaching of gold, the method is environmentally-friendly, free of toxin, short in leaching time and high in leaching rate, and waste water can be drained after being simply treated. According to the cyanide-free extractant and the gold extracting method, the leaching rate of gold ore easy to leach is high, is larger than 90% and can reach 95%; for traditional gold ore difficult to leach, such as ore which is not pretreated and contains pyrite cyanide arsenopyrite, the leaching rate is high as well and is larger than 85%, and the leaching rate is less than 30% compared with the leaching rate of a traditional cyaniding process of the same type of ore which is not pretreated, so that by the adoption of the cyanide-free extractant and the gold extracting method, the leaching rate of the gold ore difficult to leach can be increased greatly.
Owner:和晶(上海)新能源科技有限公司
Purpose of by-product ammonium thiosulfate generated in steel-making waste water treatment process as complexing agent for leaching silver and its application method
InactiveCN102560098AImprove leaching rateLow leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSilver ionMaterials science
The invention discloses a purpose of a by-product ammonium thiosulfate generated in a steel-making waste water treatment process as a complexing agent for leaching silver and its application method. According to the invention, the by-product ammonium thiosulfate generated in the steel-making waste water treatment process as the complexing agent are reacted with the silver-containing solution for leaching silver; the by-product ammonium thiosulfate generated in the steel-making waste water treatment process is taken as the complexing agent for leaching silver, because thiosulfate radical ion and silver ion can form a stable complex, ammonia ion and silver ion can form stable silver-ammonia complex ion, therefore a better leaching effect is provided to silver chloride, silver oxide, silver sulfide and metal silver, and the ammonium thiosulfate solution possesses high leaching rate to silver under low concentration, the invention has the advantages of short leaching time, high leaching rate, good selectivity, low base metal leaching rate, small environment damage and small hidden trouble in safety production.
Owner:苏州久王环保科技股份有限公司
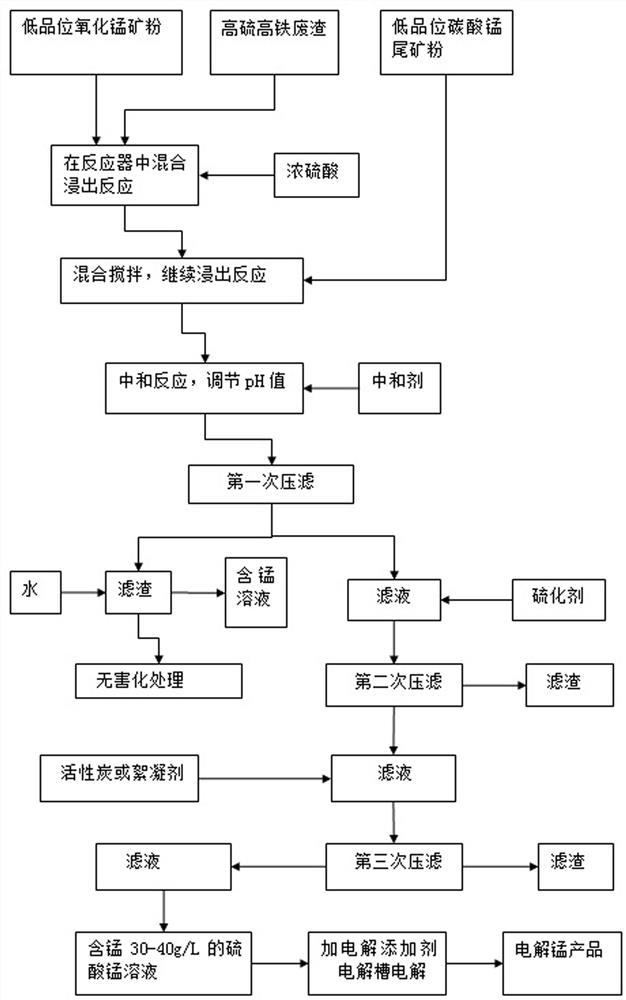
Method for producing electrolytic manganese by using low-grade manganese oxide three-ore method
PendingCN114318417AEliminate pollutionHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsManganese sulphateManganese(II) carbonate
The invention discloses a method for producing electrolytic manganese by using low-grade manganese oxide (lean ore) through a three-ore mixing direct reduction process (called a three-ore method for short), which comprises the following steps of: adding sulfuric acid for leaching without heating by using low-grade manganese oxide mineral powder, low-grade high-sulfur high-iron waste residue and low-grade manganese carbonate tailings as raw materials; and removing harmful impurities through three times of impurity removal and three times of filter pressing to obtain a pure manganese sulfate solution containing 30-40g / L of manganese, adding an electrolytic additive, introducing into an electrolytic bath, and electrolyzing by taking a lead plate as an anode and stainless steel as a cathode to obtain an electrolytic manganese product with the manganese weight content of more than 99.7%. According to the method for producing the electrolytic manganese, the low-grade manganese oxide mineral powder, the low-price low-grade high-sulfur high-iron waste residues and a small amount of low-grade manganese carbonate tailings are used as raw materials, the three kinds of ores are all waste ores without market value, the production cost is greatly reduced, the leaching rate of manganese is high, the reduction conversion rate is high, the environmental pollution is small, and the produced high-purity electrolytic manganese product has good economic benefits. The yield is high and the quality is good.
Owner:赖厚党
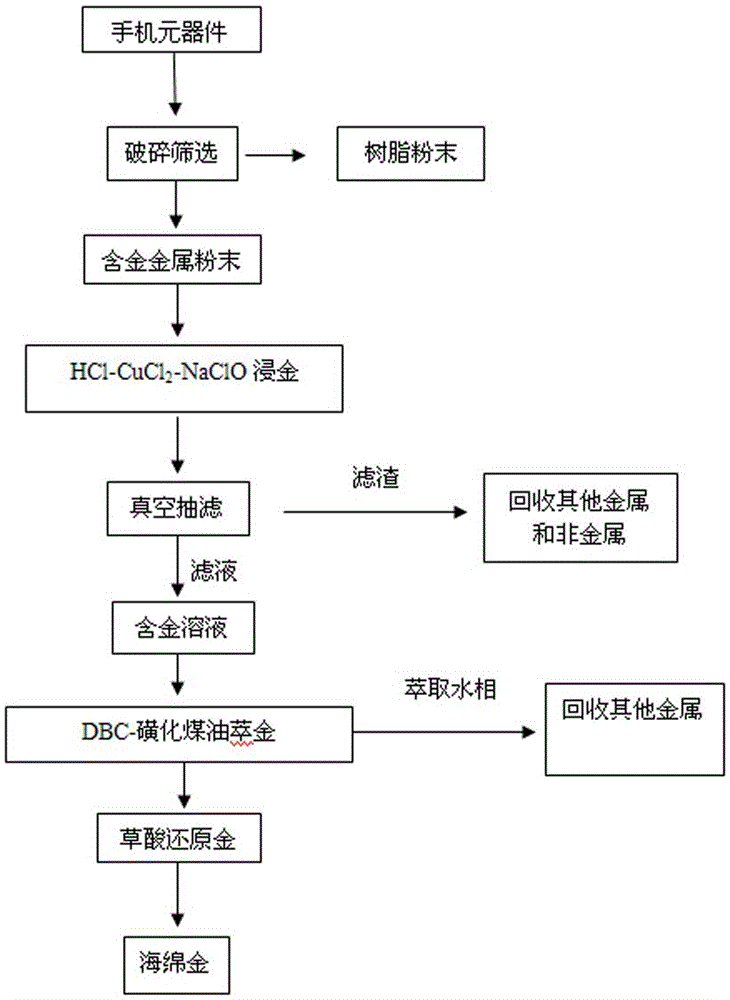
Method for recycling Au from electronic components of waste mobile phone
ActiveCN106148704AAchieve separationImprove enrichment effectProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceDBc
The invention discloses a method for recycling Au from electronic components of a waste mobile phone. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out mechanical crushing on the electronic components of the waste mobile phone into 100 mesh or above; (2) separating non-metallic materials from Pd-containing metallic materials, and grinding the metallic materials into 100 mesh or above; (3) putting metal Au-containing powder into an HCl-CuCl2-NaClO-containging reactor with temperature control and mechanical stirring functions, and leaching Au to obtain an Au-containing solution; (4) carrying out Au extraction on the Au-containing solution through adopting a DBC-sulfonated kerosene system, so as to obtain an enriched Au-containing organic solution; and (5) reducing Au from the Au-containing organic solution through adopting oxalic acid, so as to obtain sponge gold. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, environmental protection, high technological adaptability, high comprehensive resource utilization rate, wide application prospect, and the like, the pollution problem of strong acid acidification recovery is solved, and remarkable economic, environmental and social benefits can be created.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Leaching method of zinc sulfide concentrates
ActiveCN109022770AStrong hydrolysis-oxidationImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagManganese
The invention relates to a leaching method of zinc sulfide concentrates, and belongs to the field of wet metallurgy. Water, an oxidizing agent, the zinc sulfide concentrates, additives and a dispersing agent are added in a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction kettle to obtain a reaction system; under the condition of tightness, the reaction system in the high-temperature and high-pressure reaction kettle is heated and pressurized to reach a supercritical state, is reacted by 10-60 min to obtain a reaction product system, and is cooled to reach the room temperature; the solid / liquid-phase separation is performed to obtain zinc-contained leaching liquid and iron-contained oxide leaching slag; the additives are sulfur-contained additives or nitrogen-contained additives; the temperaturein the supercritical state is 380-500 DEG C; and the pressure is 22.5-40 Mpa. The zinc sulfide concentrates are leached by using supercritical water; and high zinc leaching rate and the deposition ofsuch metal as iron, copper and manganese can be realized at the same time.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering rare noble metals from spent automobile exhaust catalyst
ActiveCN110184465AHigh recovery rateSimple processProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementDissolution
The invention relates to the field of comprehensive utilization of noble metal secondary resources, and in particular relates to a method for recovering rare noble metals from a spent automobile exhaust catalyst. The method for recovering the rare noble metals from the spent automobile exhaust catalyst sequentially comprises the following steps of A, grinding materials; B, carrying out pressurizedacid dissolution; C, granulating; and D, smelting and recovering platinum group metals. The method is simple in process and high in rare-earth elements recovery rate.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
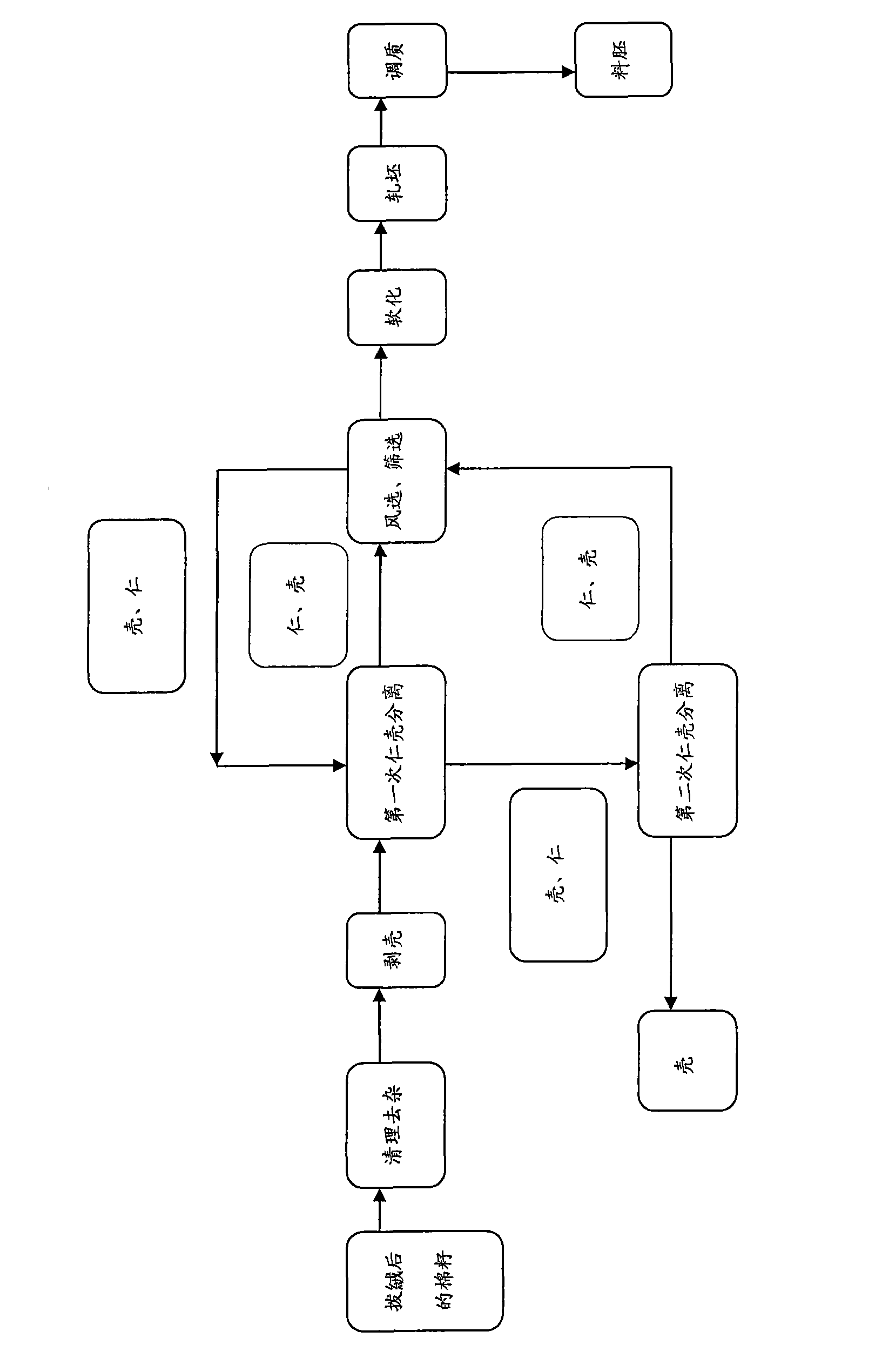
Method for producing cottonseed protein wet dregs by leaching method
InactiveCN101029074AQuality improvementShort leaching timePeptide preparation methodsSolventMethanol
A process for preparing the wet cotton seed protein dregs by leaching-out method includes such steps as loading the raw cotton seed protein material in storage tank, extracting oil in solvent, dephenolizing in methanol, and removing part of solvent.
Owner:北京中棉紫光生物科技有限公司
Method for processing roasted sand containing iron, indium and zinc through hot-pressing selective leaching
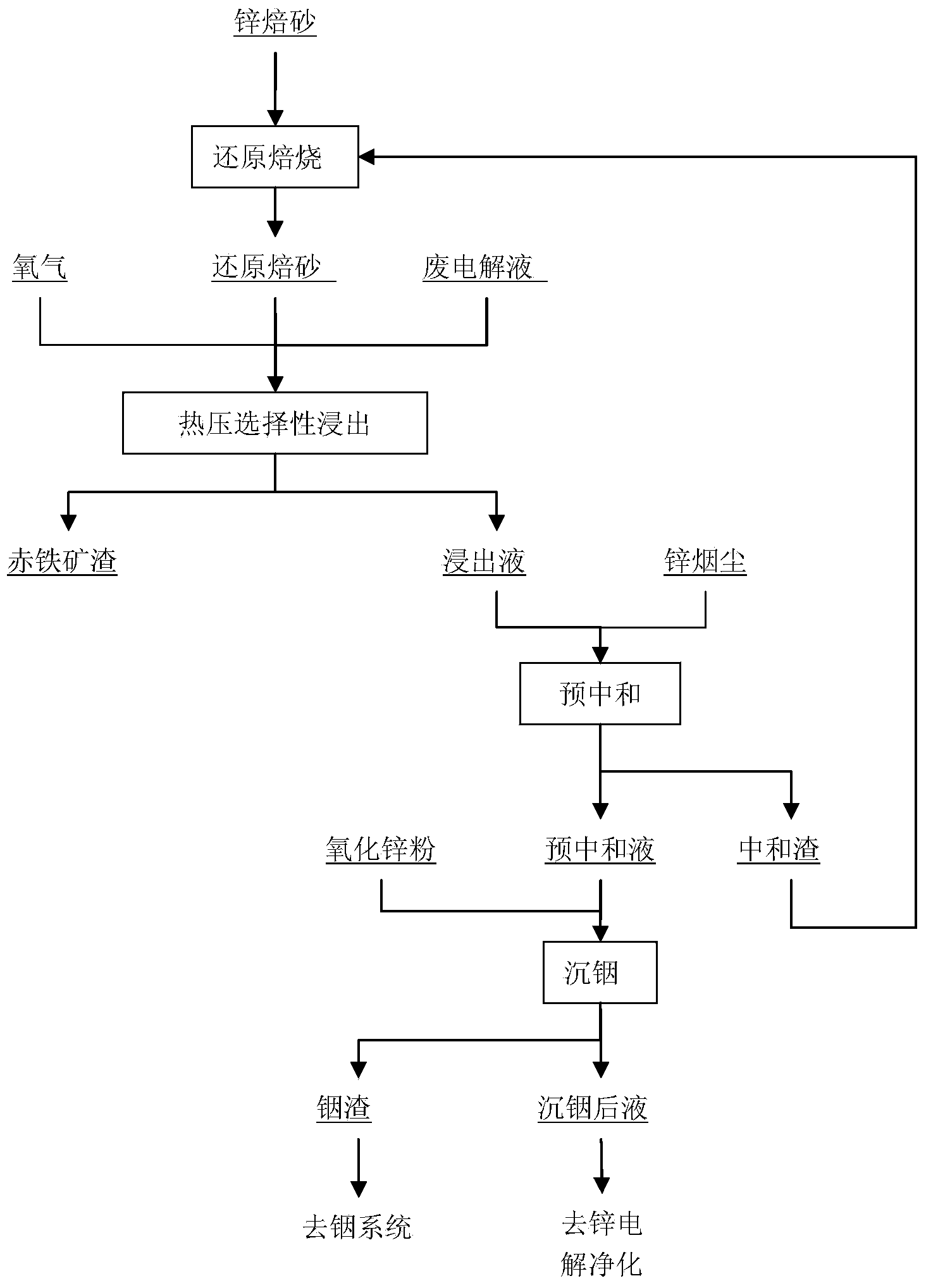
InactiveCN103643036AReducing atmosphere is easy to realizeRaise the gradeProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method of processing a material containing iron, indium and zinc through hot-pressing selective leaching. According to the method, ferric iron in zinc roasted sand is converted into ferrous iron by using reducing roasting; hot-pressing acidic selective leaching is carried out on reduced roasted sand in a autoclave; zinc and indium elements are leached out under high-temperature acidity condition and enter into a solution; since the pH value of the iron becomes negative in the case of hydrolysis in a high-temperature environment, iron is converted into hematite to be retained in leaching residue; leaching liquid is pre-neutralized and precipitates out indium, thus obtaining a zinc sulfate solution and indium residue; neutralization residues return to a rotary kiln to be subjected to reducing roasting together with the zinc roasted sand. By adopting the method, selective leaching of zinc, indium and iron of the roasted sand containing zinc, indium and iron is realized when the roasted sand is leached; the leaching rate of the indium is improved, and the cost of extracting the indium in the zinc roasted sand is reduced. The amount of powdered coal needed in the reducing roasting of the roasted sand is small, and the reducing atmosphere in a reducing roasting process is easily realized. The method can be applied to treatment of indium, zinc and other iron-containing non-ferrous metal materials.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
Method for recycling manganese from positive electrode material of waste zinc-manganese dry battery and application
ActiveCN112259754AImprove leaching effectImprove efficiencyReclaiming serviceable partsDry cellsElectrical batteryResource recovery
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
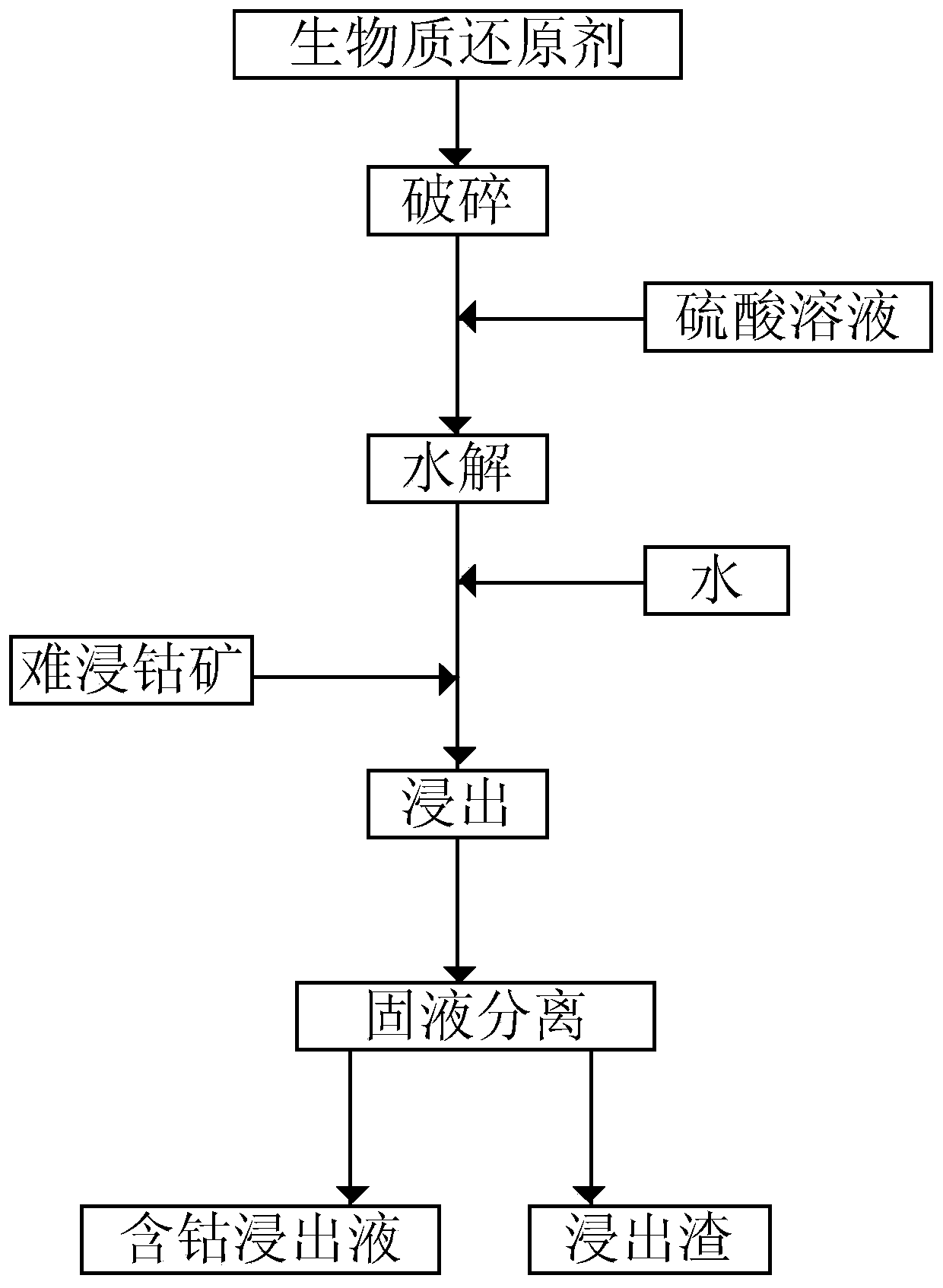
Leaching method of refractory cobalt ore
ActiveCN110184455AWide variety of sourcesLow leaching temperatureRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesRefractoryEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a leaching method of refractory cobalt ore. The leaching method of the refractory cobalt ore comprises the following steps that (1), after a biomass reducing agent is crushed,a sulfuric acid solution is added for hydrolysis, wherein the biomass reducing agent is poplar or straw; (2) a hydrolyzed material is dissolved in water, and then the refractory cobalt ore is placed in for leaching; and (3) the leached material is subjected to solid-liquid separation to obtain a cobalt-containing leachate. In the method, the leaching reducing agent is wide in raw material source,environmentally friendly, low in leaching temperature and short in leaching time. No harmful gas is produced in the leaching process, environmental pollution of enterprises is reduced, the productioncost is reduced, and economic benefits and the yield are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com