Patents
Literature
342results about "Protein composition from vegetable materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
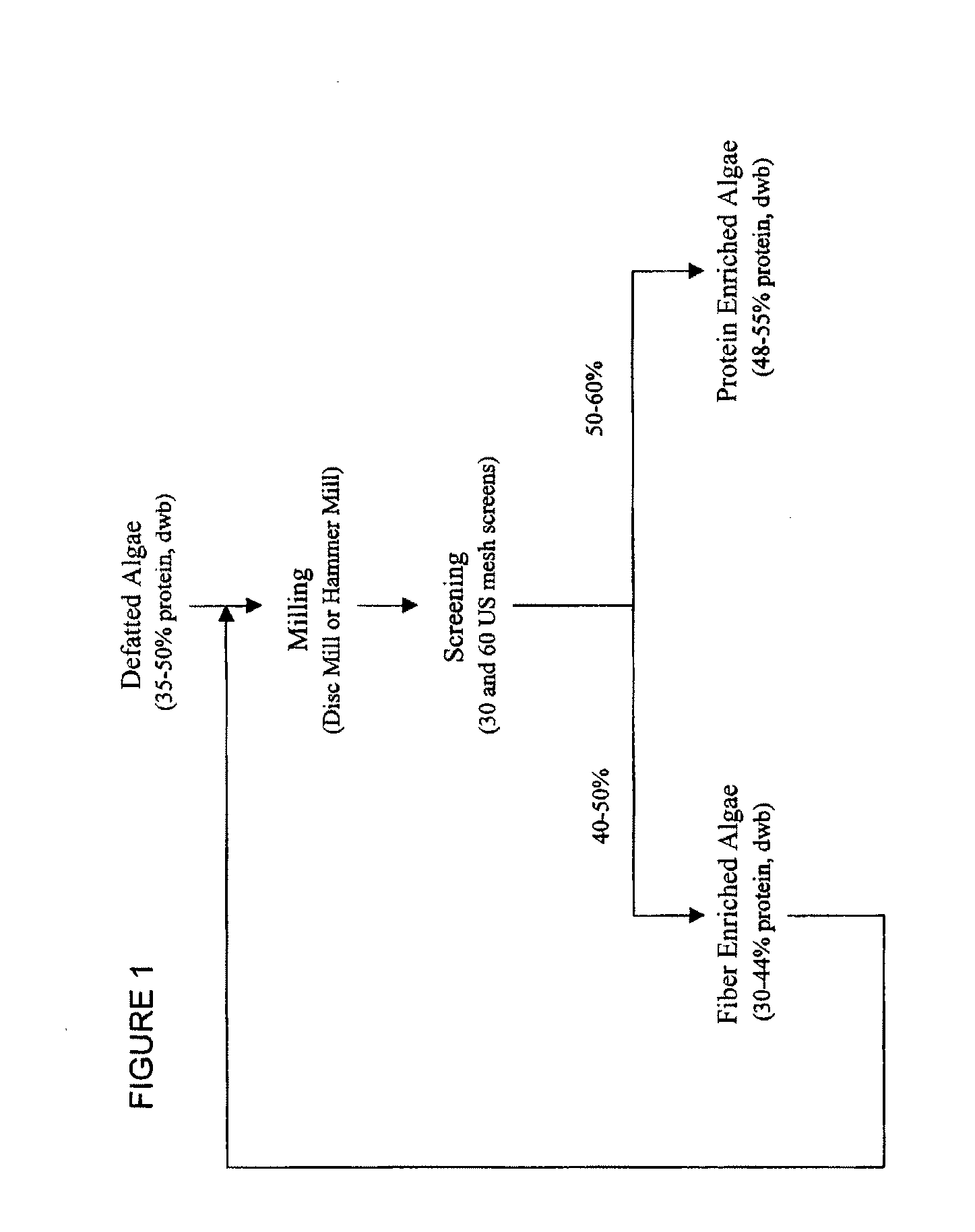
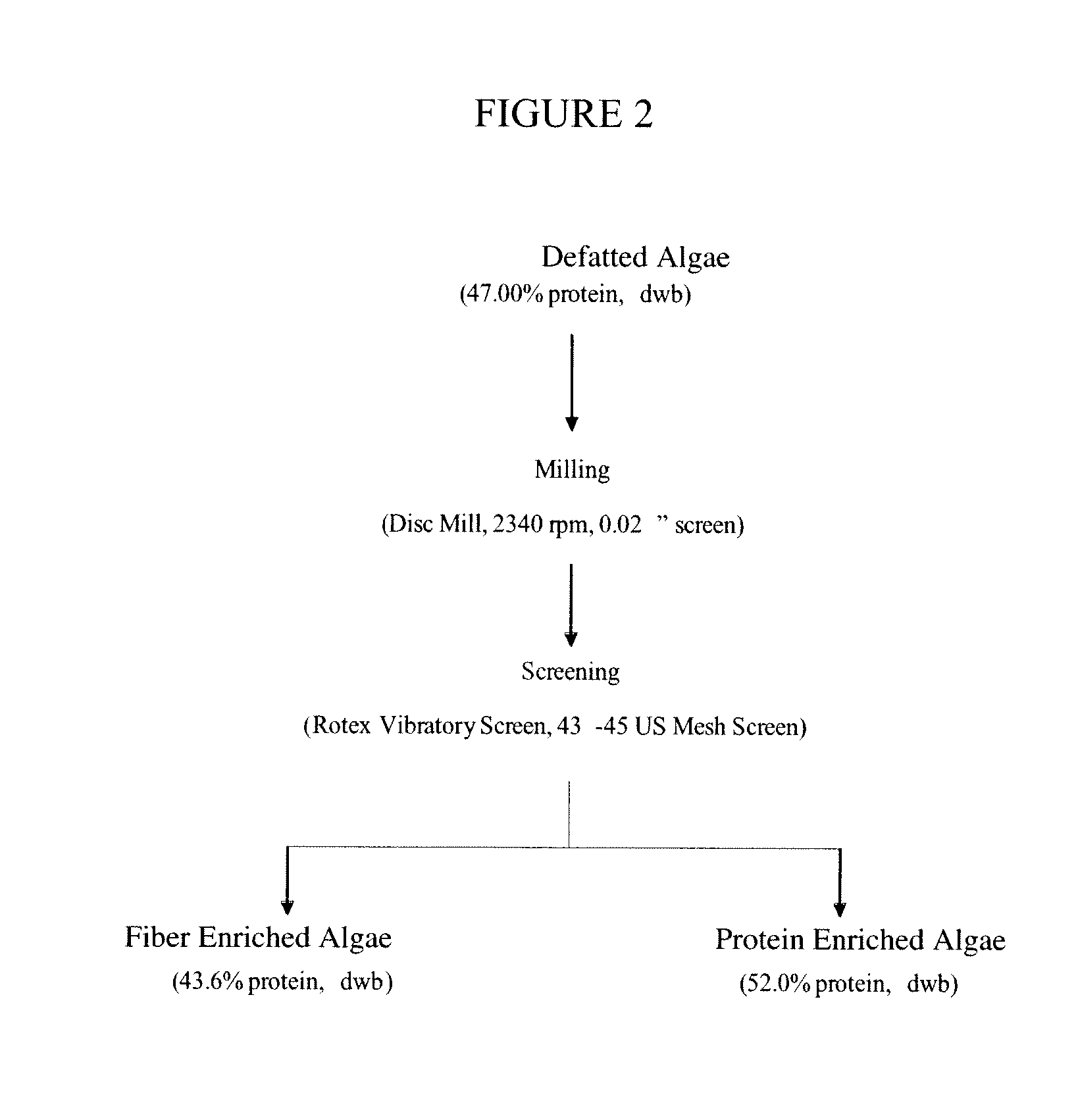
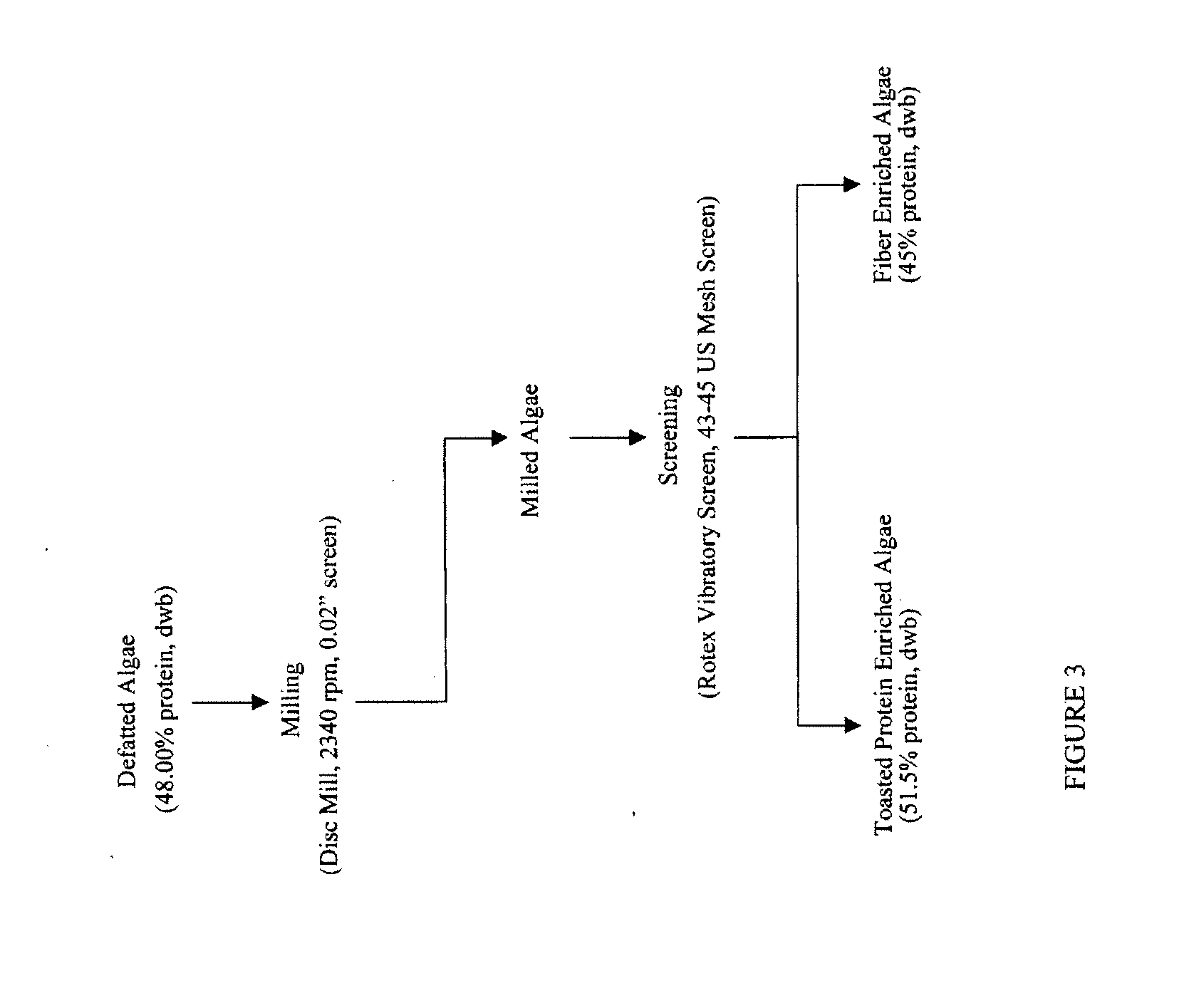
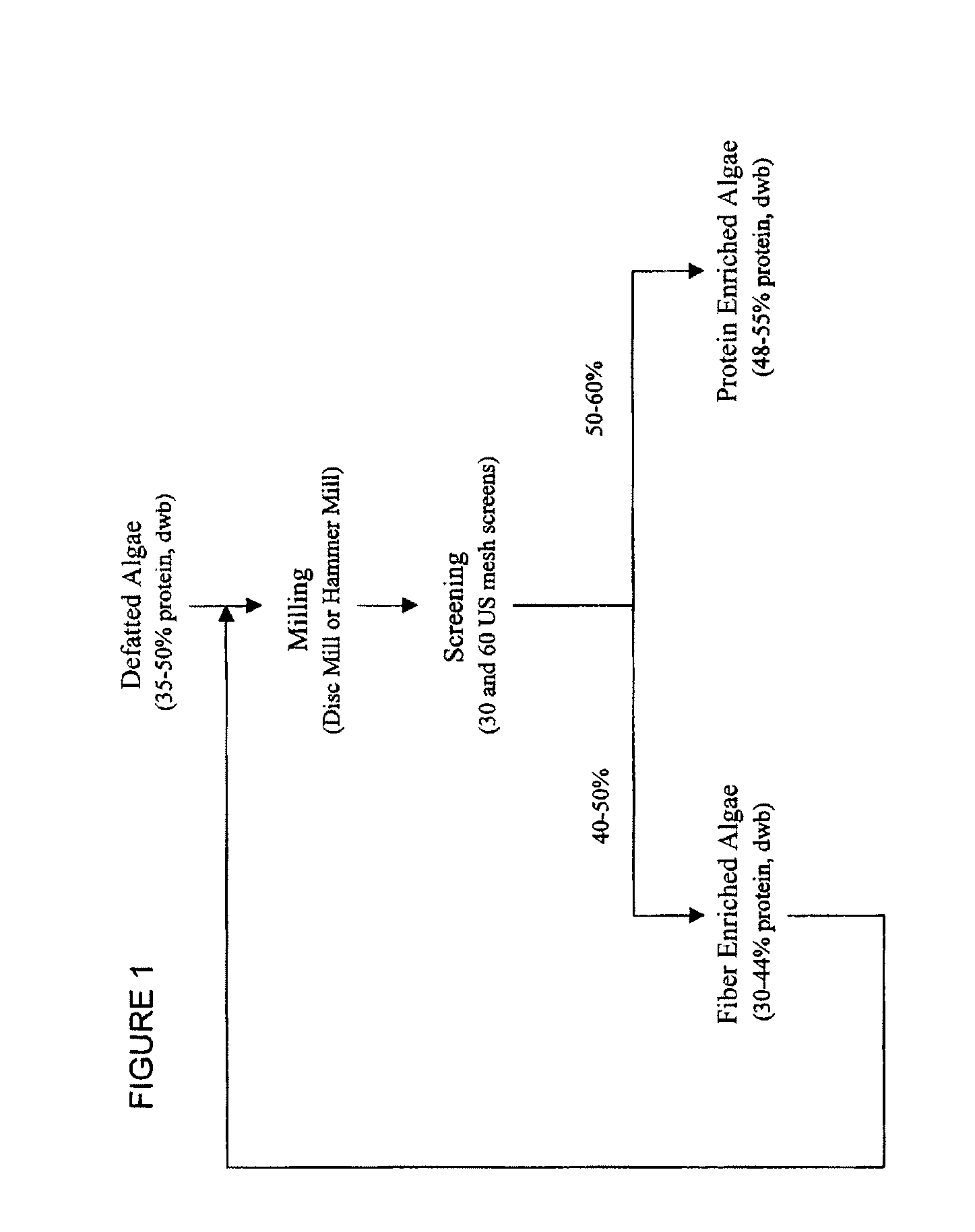
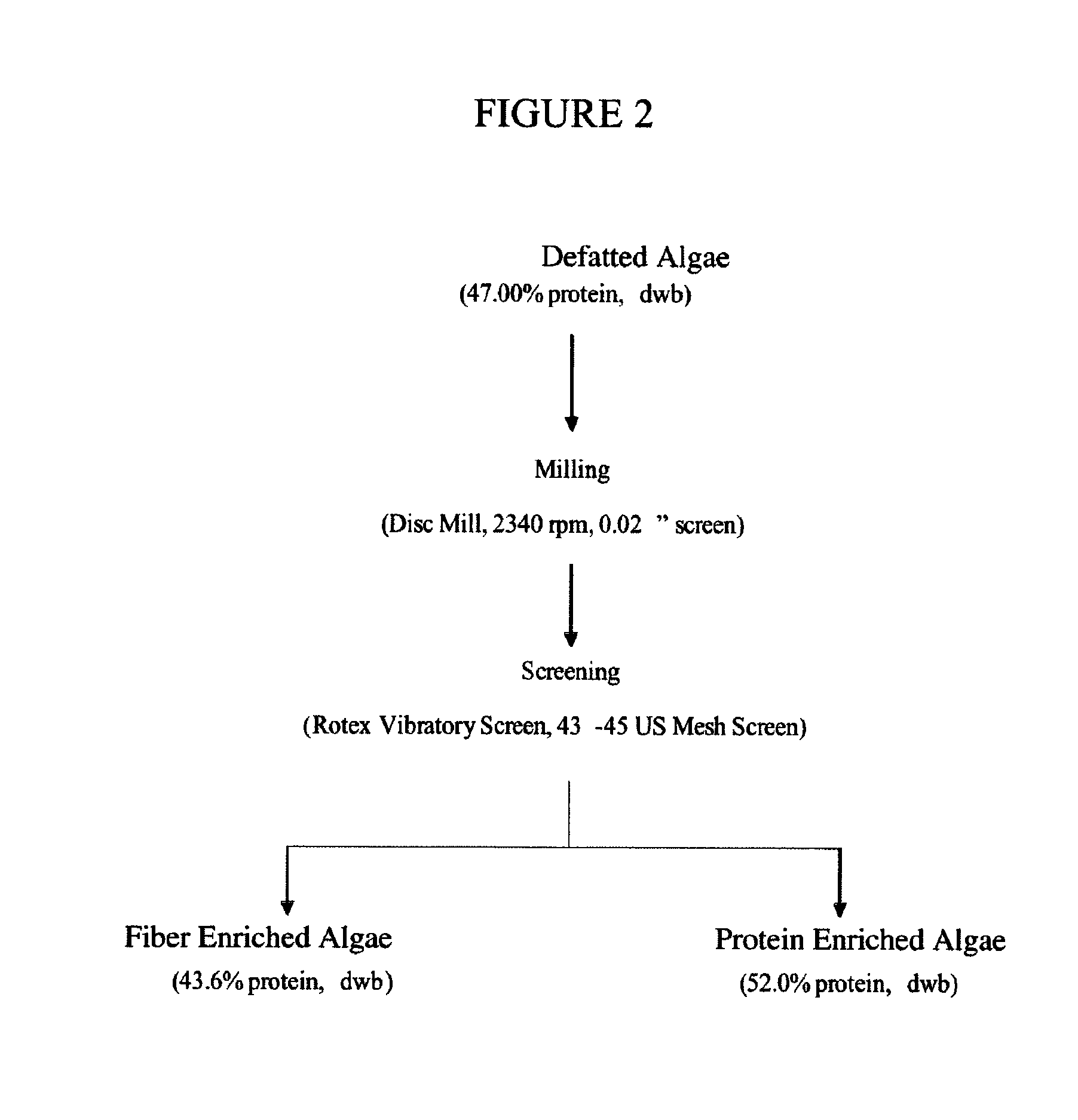
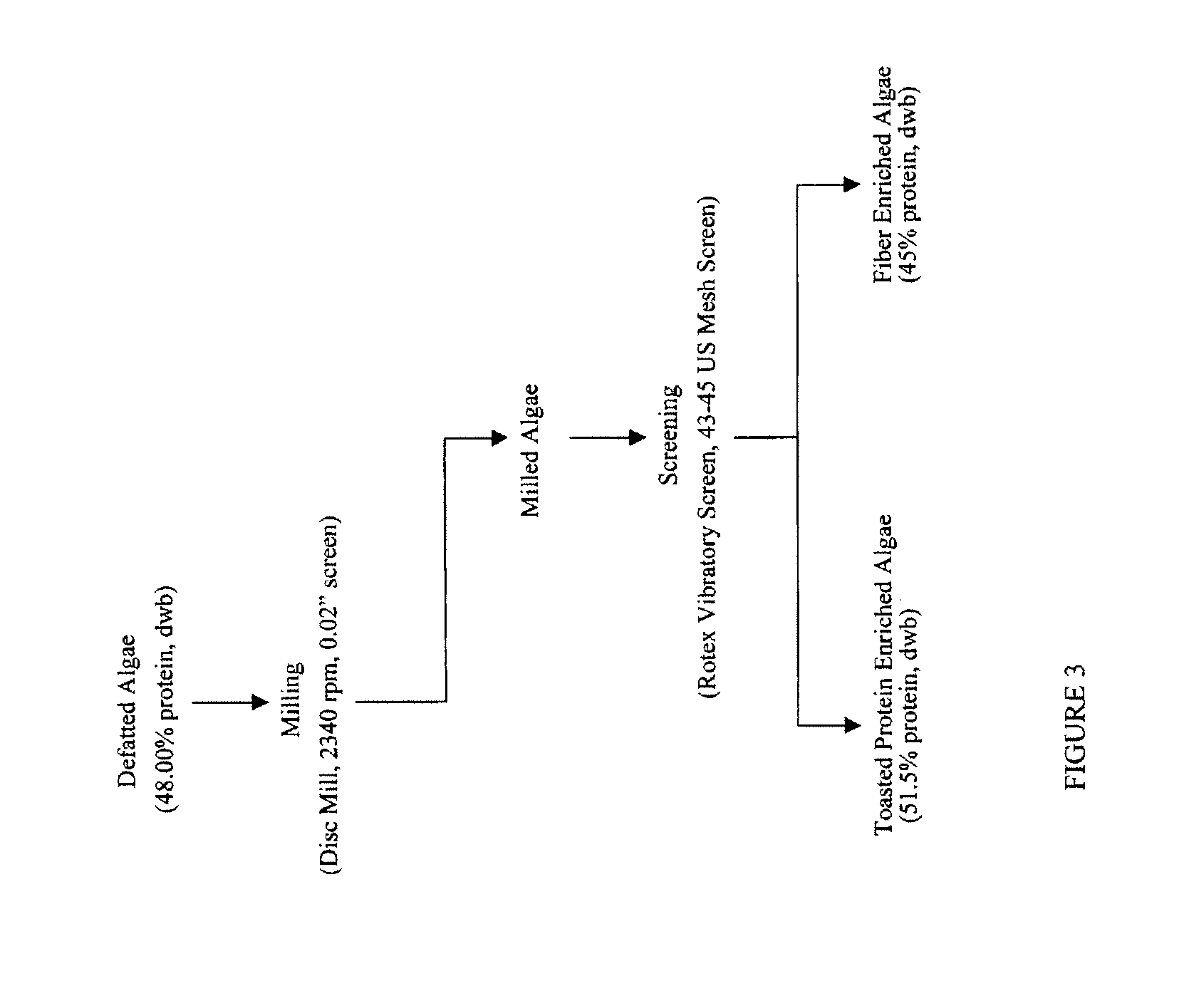
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof from macroalgae and/or microalgae
InactiveUS20120021457A1Quality improvementPeptide preparation methodsFermentationFiberProtein isolate
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
Frozen food product
Plant anti freeze proteins can advantageously be incorporated into frozen confectionery products, provided they have the capability of limiting the growth of ice crystals
Owner:GOOD HUMOR BREYERS ICE CREAM DIV OF CONOPCO
Micro-particle comprising a protein extract from sweet potato for extending satiety and controlling blood glucose and lipid levels
InactiveUS20140356420A1Increase satietyTo promote metabolismPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyLipid formation
The present invention relates to a micro-particle for extending satiety and controlling blood glucose and lipid levels, comprising a core having the protein extract from sweet potato, an active ingredient layer coated on the core, and a protection layer coated over the active ingredient layer as an external layer, wherein the protein extract from sweet potato contains trypsin inhibitor and glycoprotein. The micro-particle comprising a protein extract from sweet potato can effectively extend satiety, control blood glucose and lipid levels and increase metabolism effectively.
Owner:HIMI INVESTMENT HLDG CO LTD
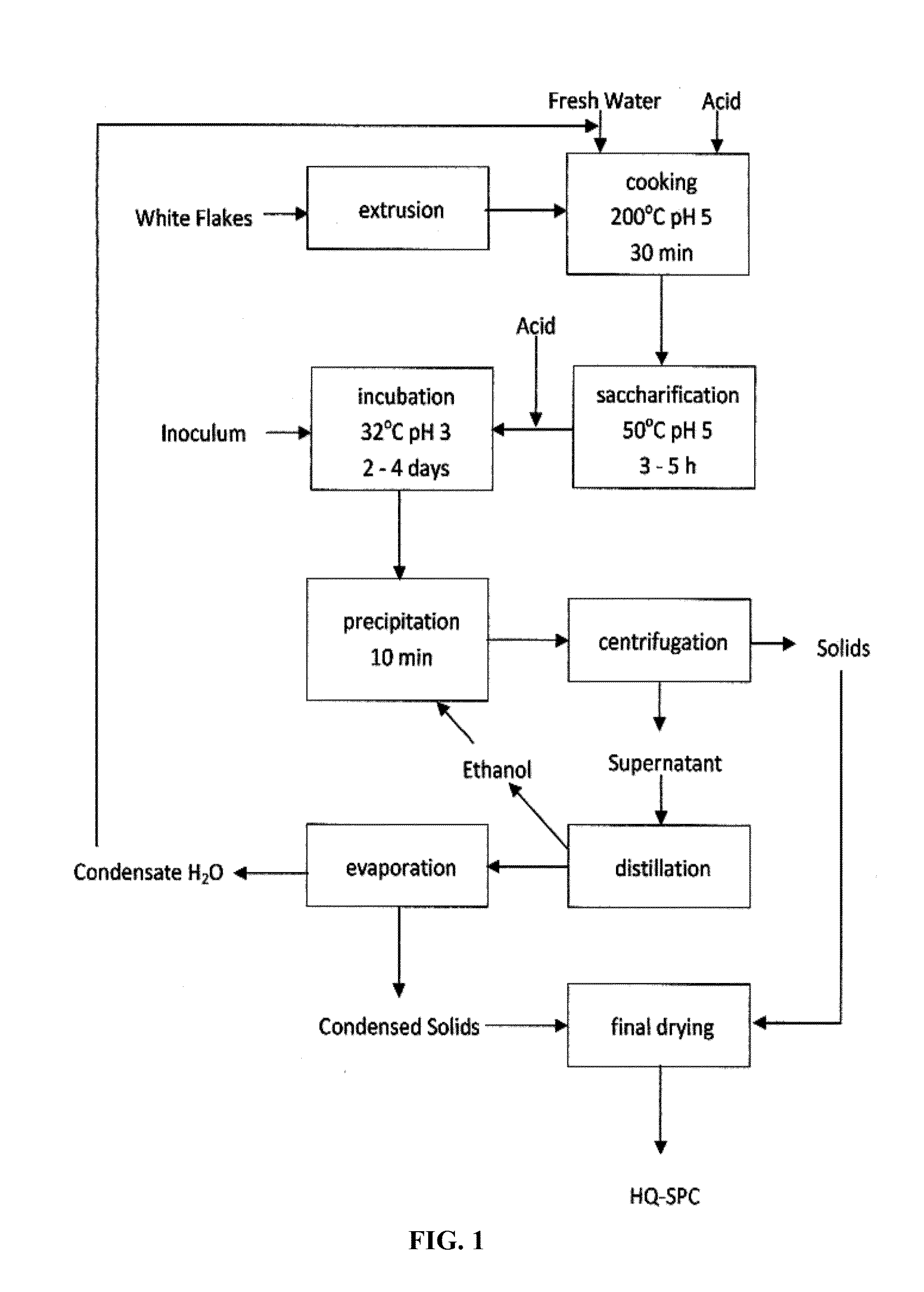
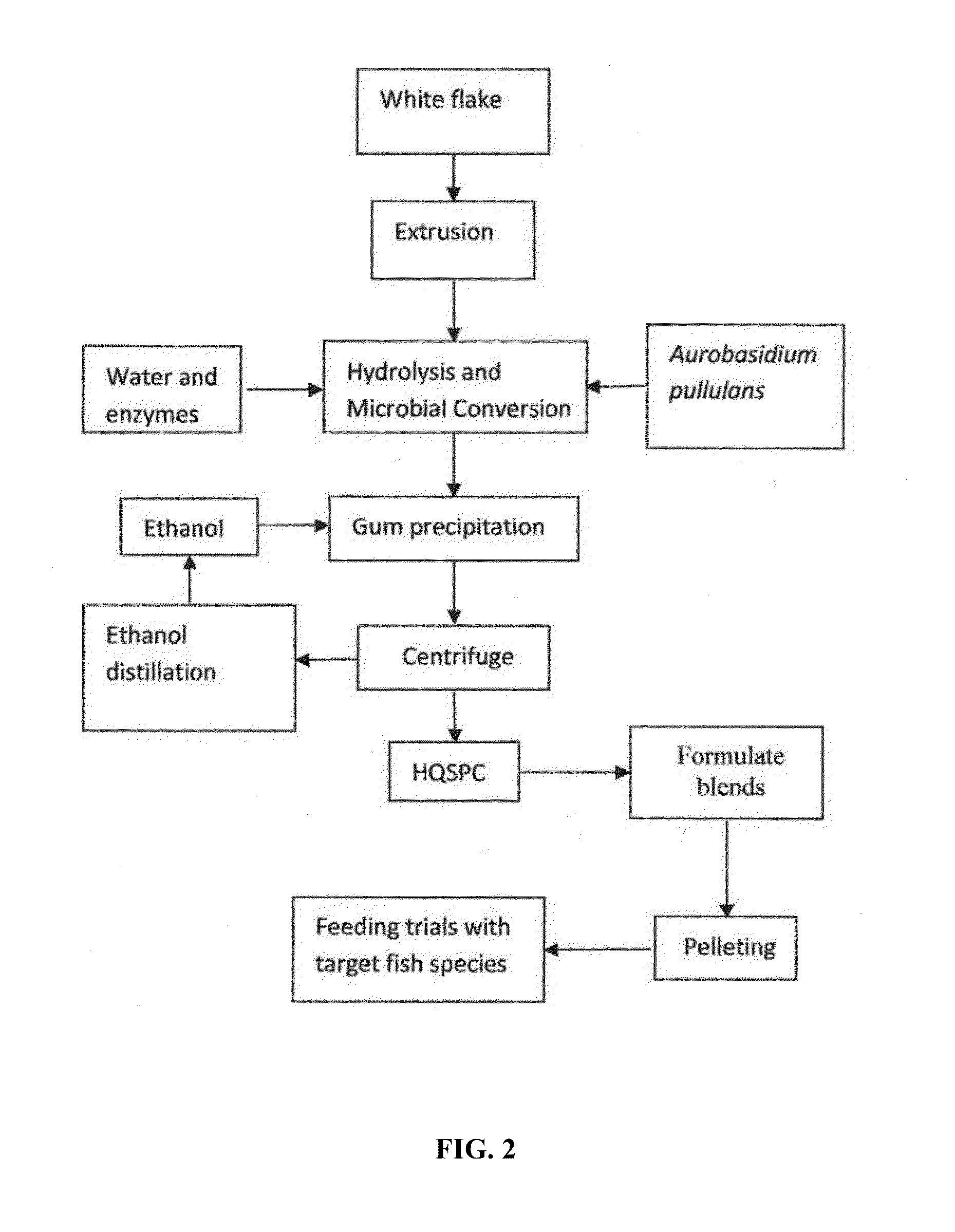
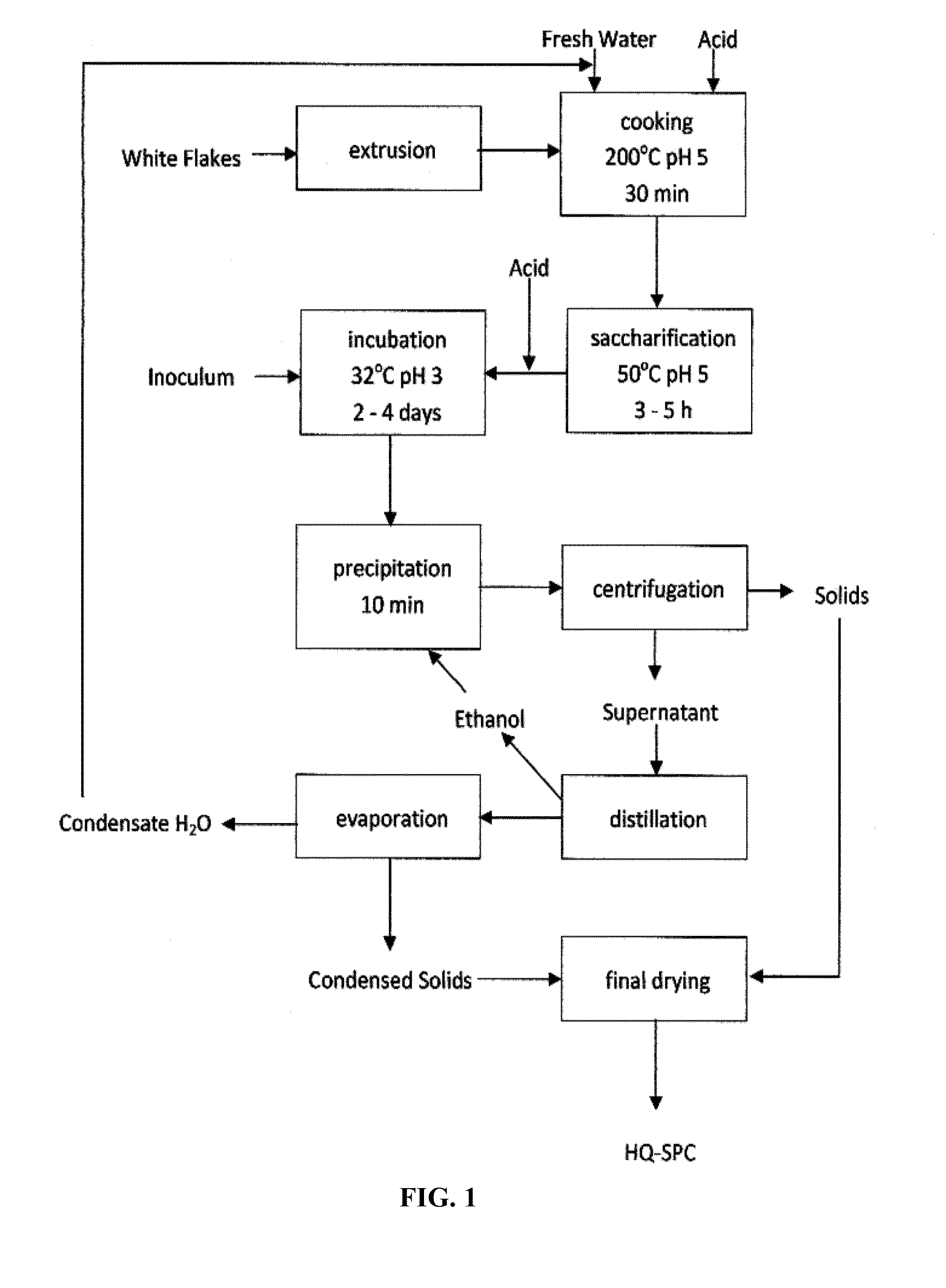
Microbial-Based Process For High-Quality Protein Concentrate
The present invention describes a bio-based process to produce high quality protein concentrate (HQPC) by converting plant derived celluloses into bioavailable protein via aerobic incubation, including the use of such HQPC so produced as a nutrient, including use as a fish meal replacement in aquaculture diets.
Owner:PRAIRIE AQUA TECH LLC +2
Flours produced from fungus myceliated grain
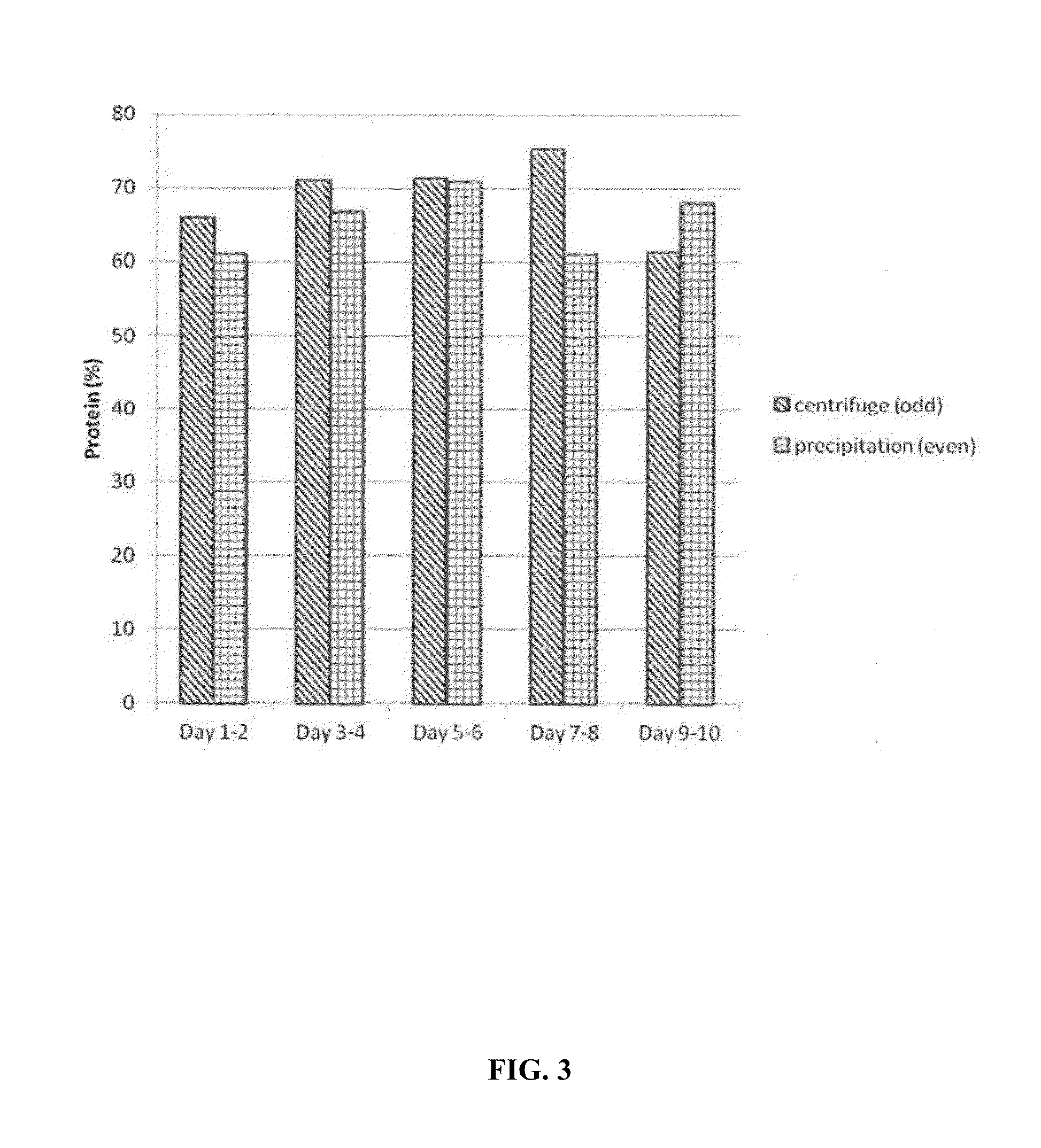
The present patent relates to a method for producing flours from grain myceliated with macroscopic fungi (mushrooms). These flours can be used to prepare food for human consumption, such as bread and biscuits, and for animal consumption, such as fodder. Active principles (ergosterol, beta glucan, linoleic and oleic acids, lectins), enzymes, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, mineral salts, inter alia, can also be extracted from these flours for use in the chemical, foodstuff and cosmetic industries, for producing phytotherapeutic agents, pharmaceuticals, textiles, paper products, pharmaceuticals and fodder for animals.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA +2
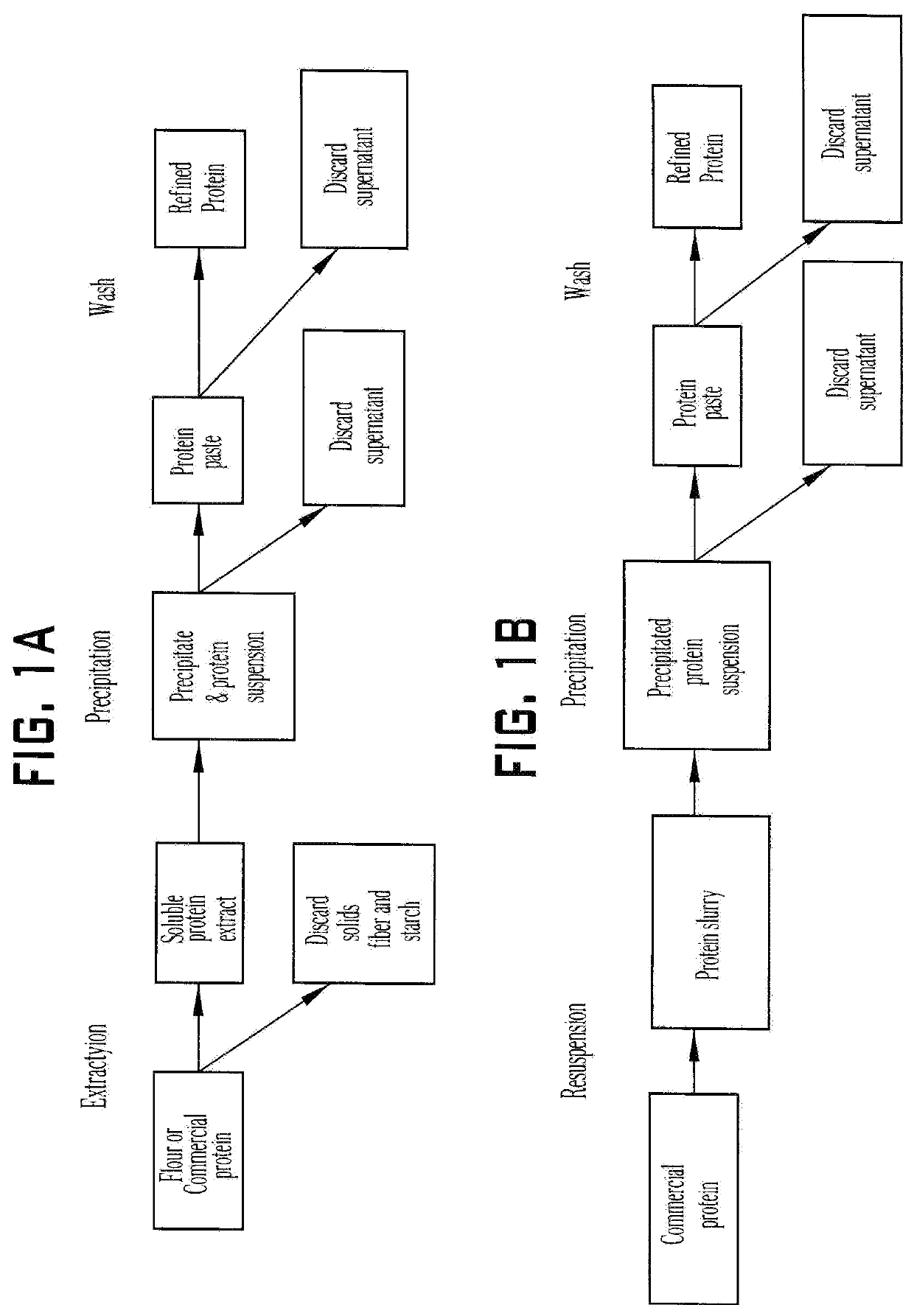
Methods of extracting, concentrating and fractionating proteins and other chemical components
InactiveUS20070054031A1Increase speedHigh extraction rateProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein composition from vegetable materialsPhytochemicalChemical composition
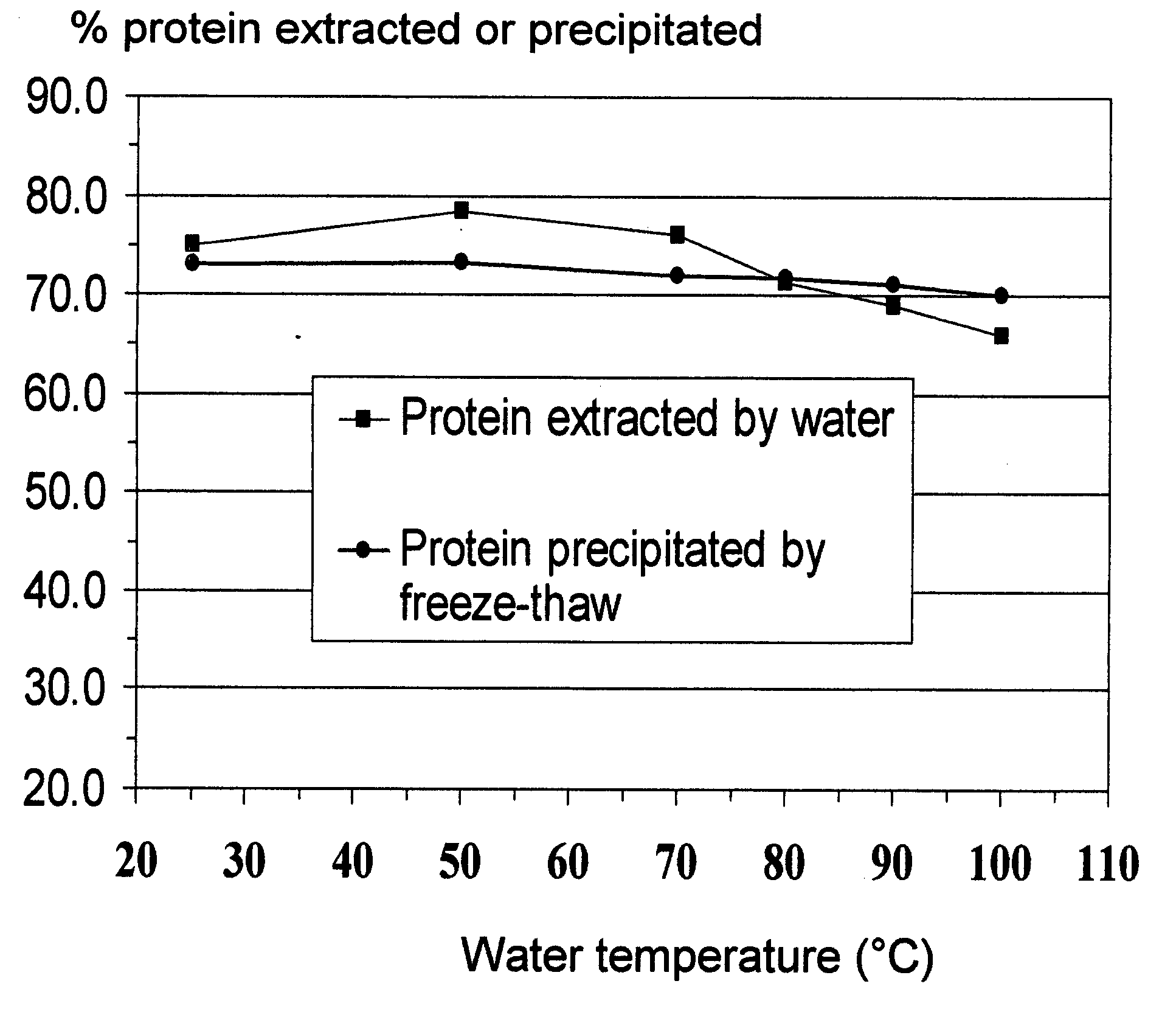
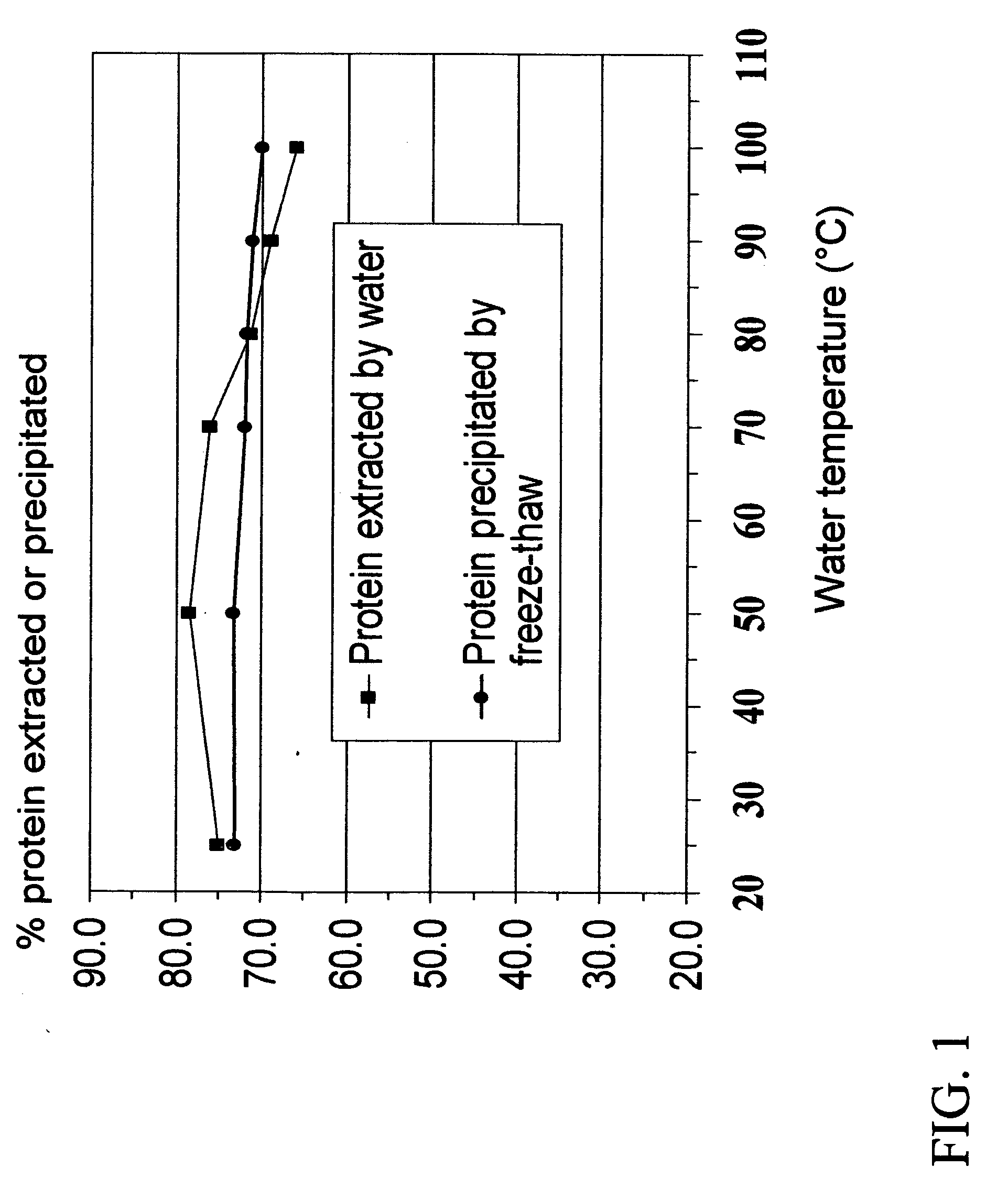
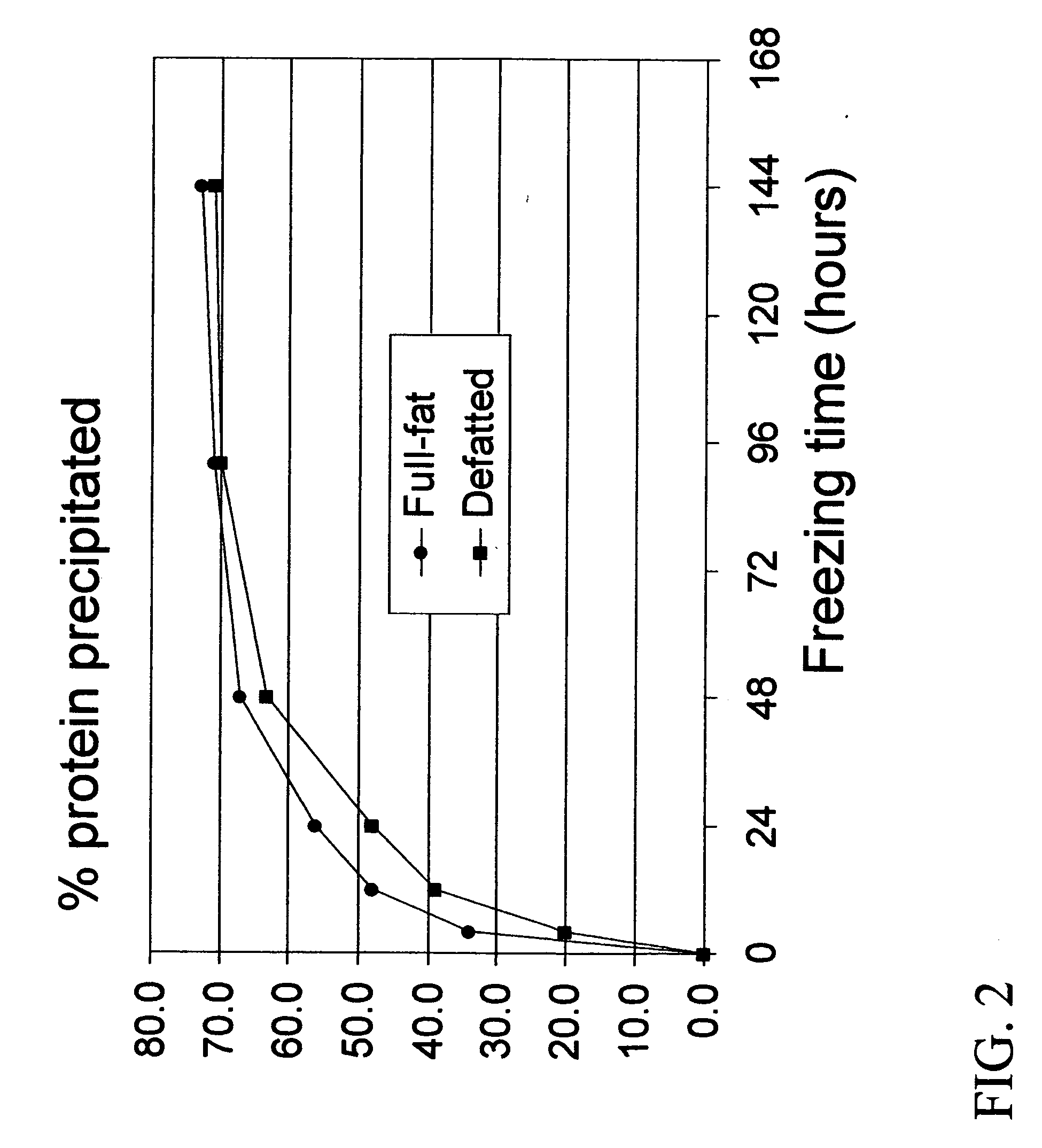
Methods are disclosed herein to extract, concentrate and fractionate proteins and protein-associated complexes with other polymers from soybeans, peanuts, rape, canola, cottonseeds, peas, wheat and other plant materials, based on a principle of cryoprecipitation. The disclosed methods involve no or minimal uses of chemicals, and generate a minimal volume of waste streams. The resulting protein concentrates or isolates have excellent functionality, superior nutritional quality, attractive appearance and mild taste. Based on the sample principle of cryoprecipitation, methods also are also disclosed to extract and concentrate chemical components from living tissues, especially some nutraceutical or phytochemical components from plant materials.
Owner:LIU KESHUN
Methods and compositions for consumables
Provided herein are methods and compositions related to plant based meat substitutes which have properties similar to meat.
Owner:IMPOSSIBLE FOODS
Meat Like Pet Food Chunks
ActiveUS20150320085A1Protein composition from eggsAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates in general to the field of pet food. In particular the present invention relates to a meat like chunk that can be incorporated into a complete pet food. One embodiment of the present invention is a method of using multiple scraped surface heat exchangers and a steam tunnel to produce a meat like chunk. Another embodiment is a composition of meat ingredients, dried egg product, egg whites, and pea protein that results in a meat like chunk having an improved appearance that closely resembles that of actual pieces of meat.
Owner:USPET NUTRITION
Protein product
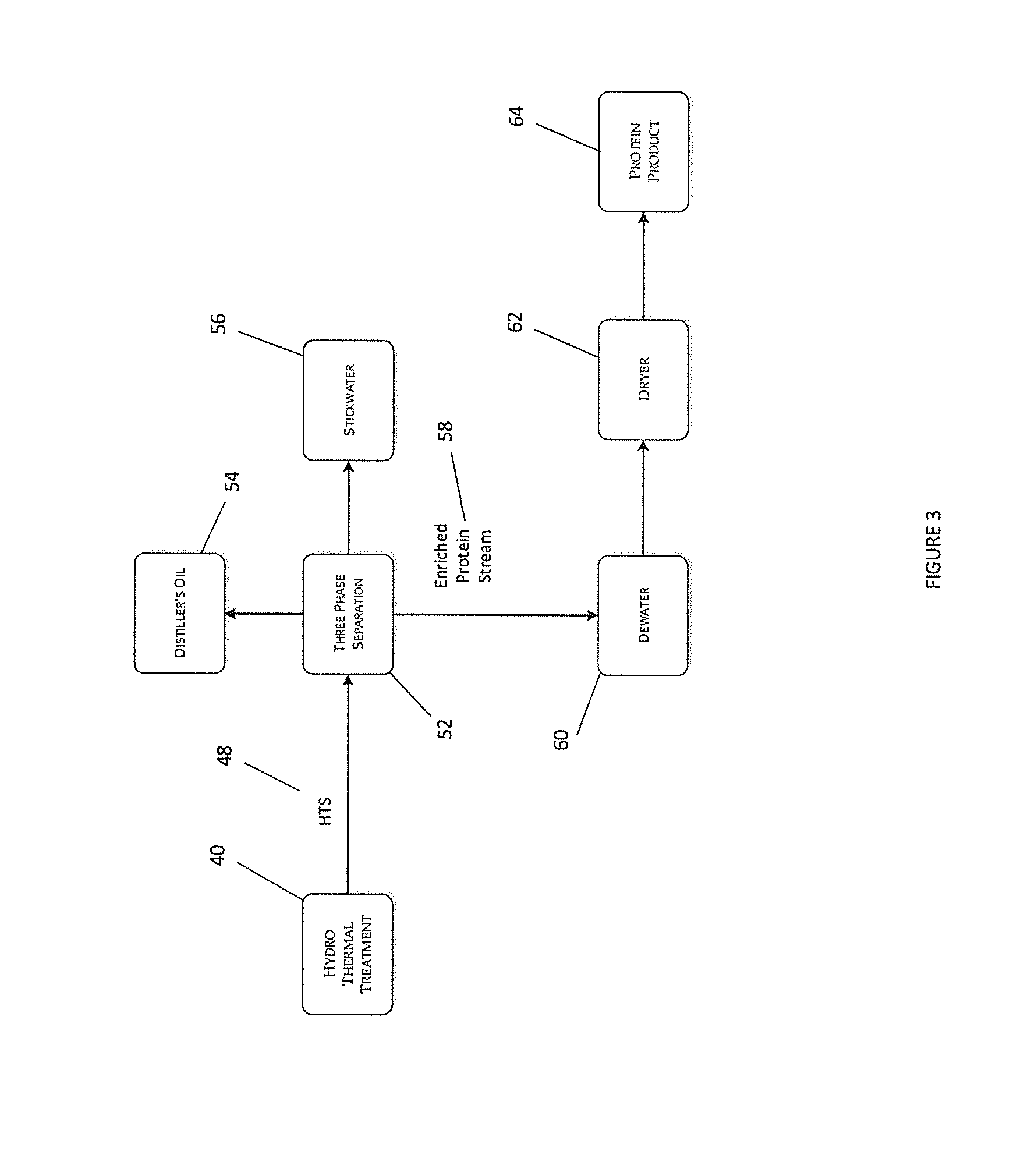
InactiveUS20140343259A1Promote recoveryEasy to separateFermented solutions distillation/rectificationBiofuelsGlycerolChemistry
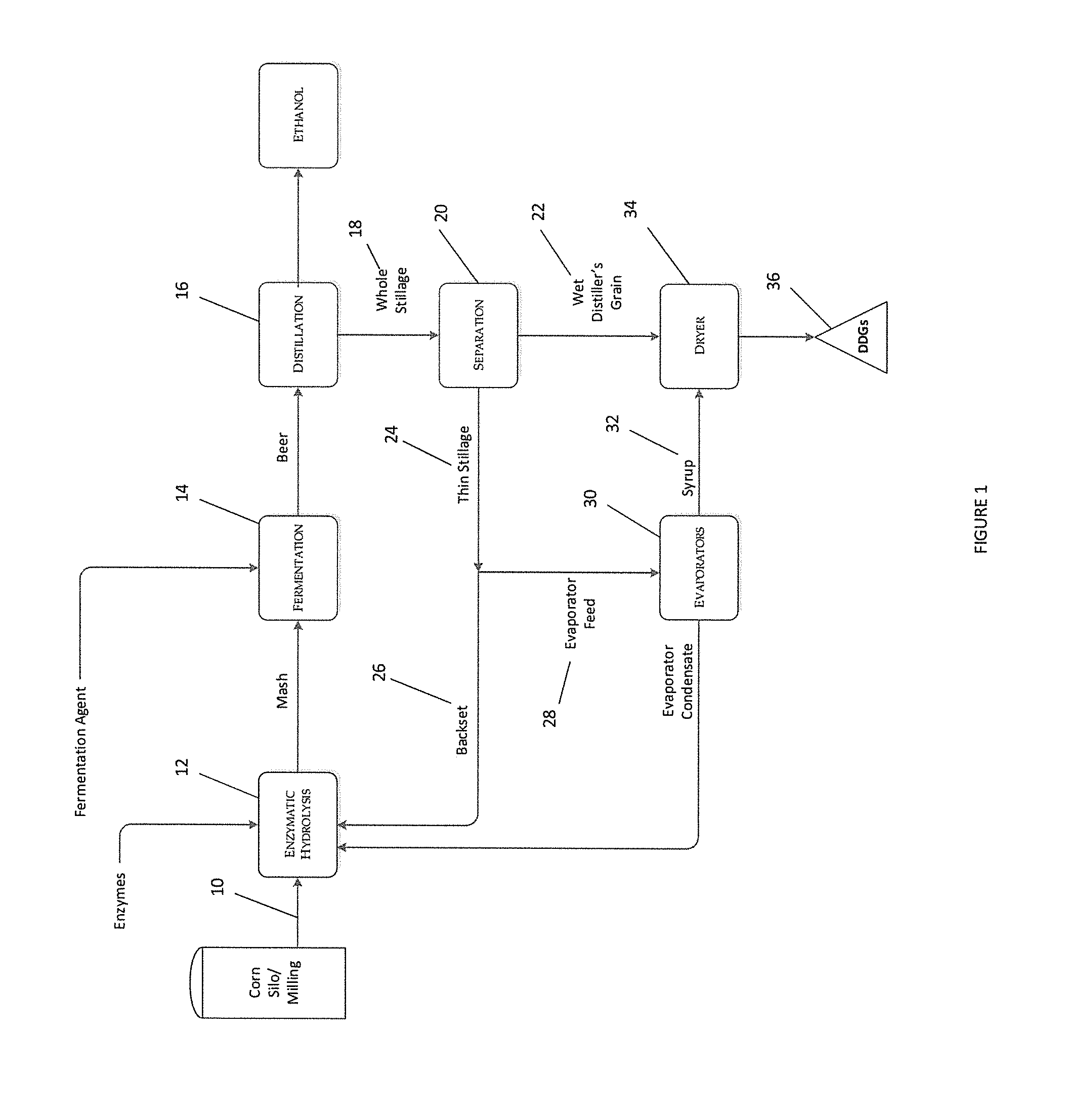
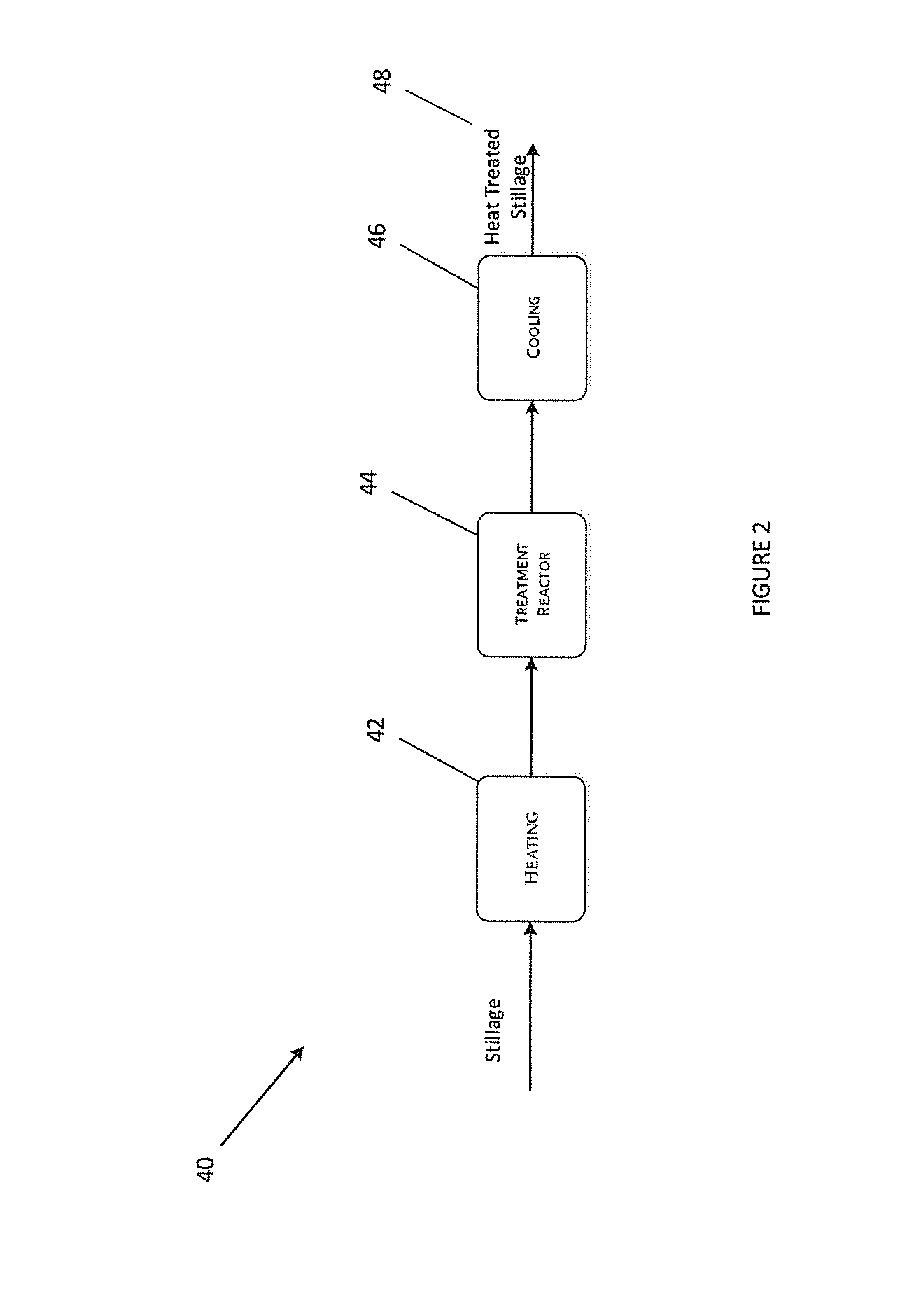
A protein product recovered from a fermentation process including a protein content of 45.0% or more calculated by weight of dry matter, a glycerol content of 1.0% or less calculated by weight of dry matter, and a mineral nutrient content of 6.0% or less calculated by weight of dry matter. A method for recovering a protein product by heating fermentation stillage to 200 degrees F.-350 degrees F., altering the physicochemical properties of the stillage to enable facile separation of the stillage, and separating a phase enriched in protein. Protein products, protein paste, high protein meal, and proteinaceous agglomerates recovered and formed.
Owner:VALICOR
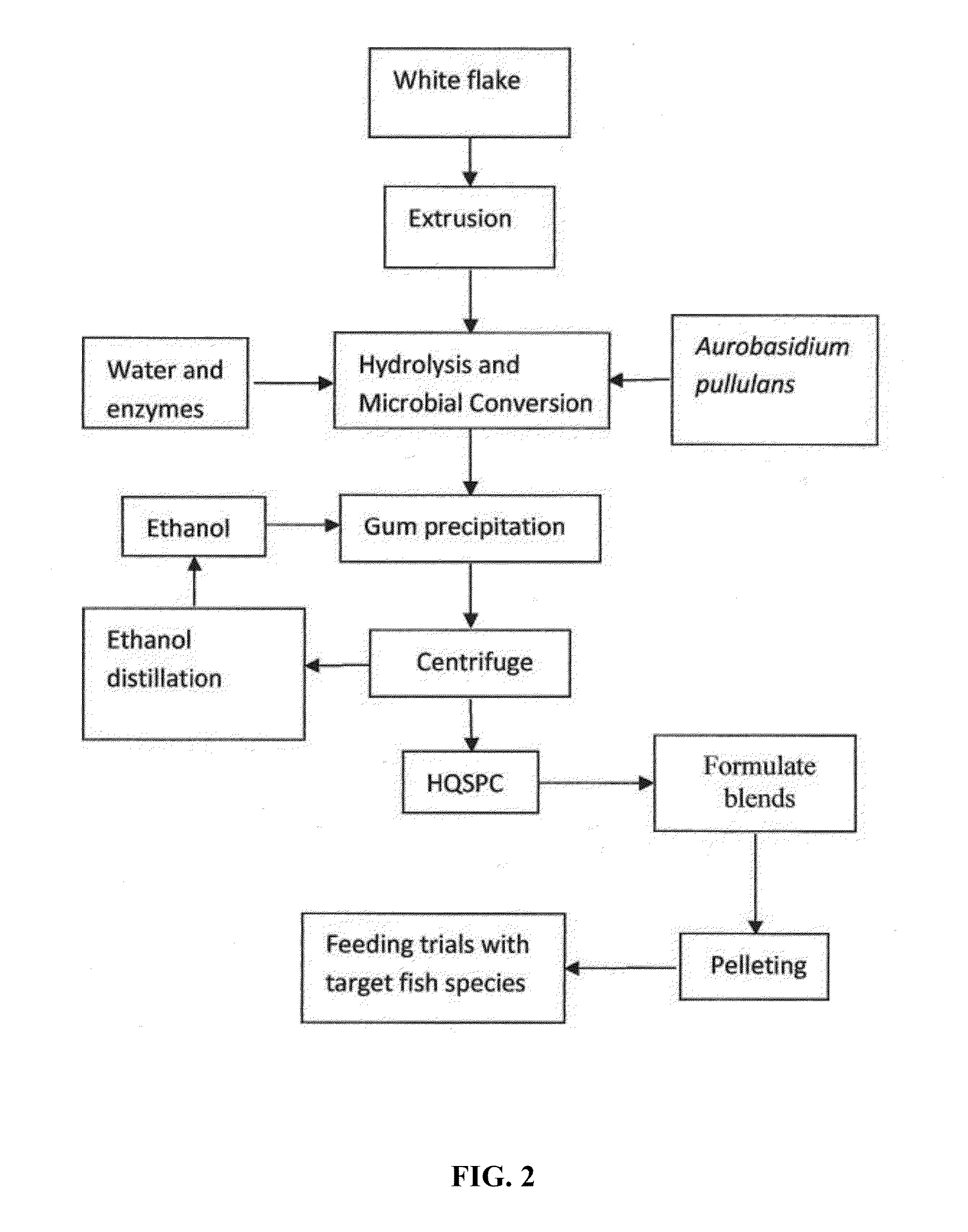
Microbial-based process for high-quality protein concentrate
ActiveUS9370200B2Improve performanceFood processingProtein composition from vegetable seedsCelluloseMicroorganism
The present invention describes a bio-based process to produce high quality protein concentrate (HQPC) by converting plant derived celluloses into bioavailable protein via aerobic incubation, including the use of such HQPC so produced as a nutrient, including use as a fish meal replacement in aquaculture diets.
Owner:PRAIRIE AQUA TECH LLC +2
Glycoalkaloid removal
ActiveUS8486481B2Effective and complete removalSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesSolanum tuberosumChemistry
Owner:COOP AVEBE U A
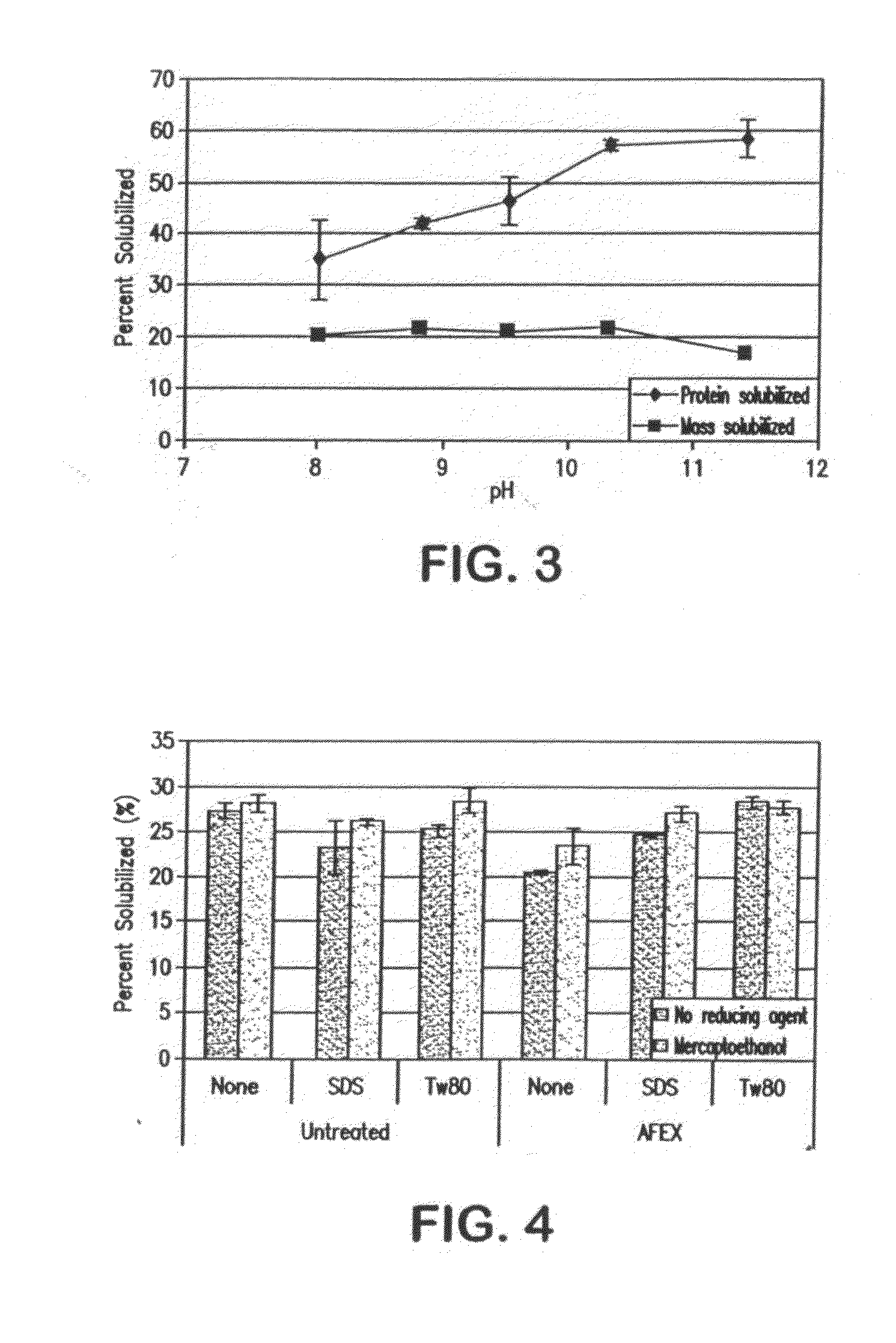
Separation of Proteins from Grasses Integrated with Ammonia Fiber Explosion (AFEX) Pretreatment and Cellulose Hydrolysis
A process for extracting an aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution from a plant biomass after an Ammonia Fiber Explosion (AFEX) process step, is described. The proteins can be separated before or after a hydrolysis of sugar precursors (carbohydrates) from the biomass to produce sugars for fermentation to produce ethanol. The proteins are useful as animal feeds because of their amino acid food values.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for improving solubility of potato protein by combining ultrasound with pH offset
PendingCN111053145AImprove solubilityImprove solubility significantlyMulti-step food processesFood ingredientsBiotechnologyProtein solution
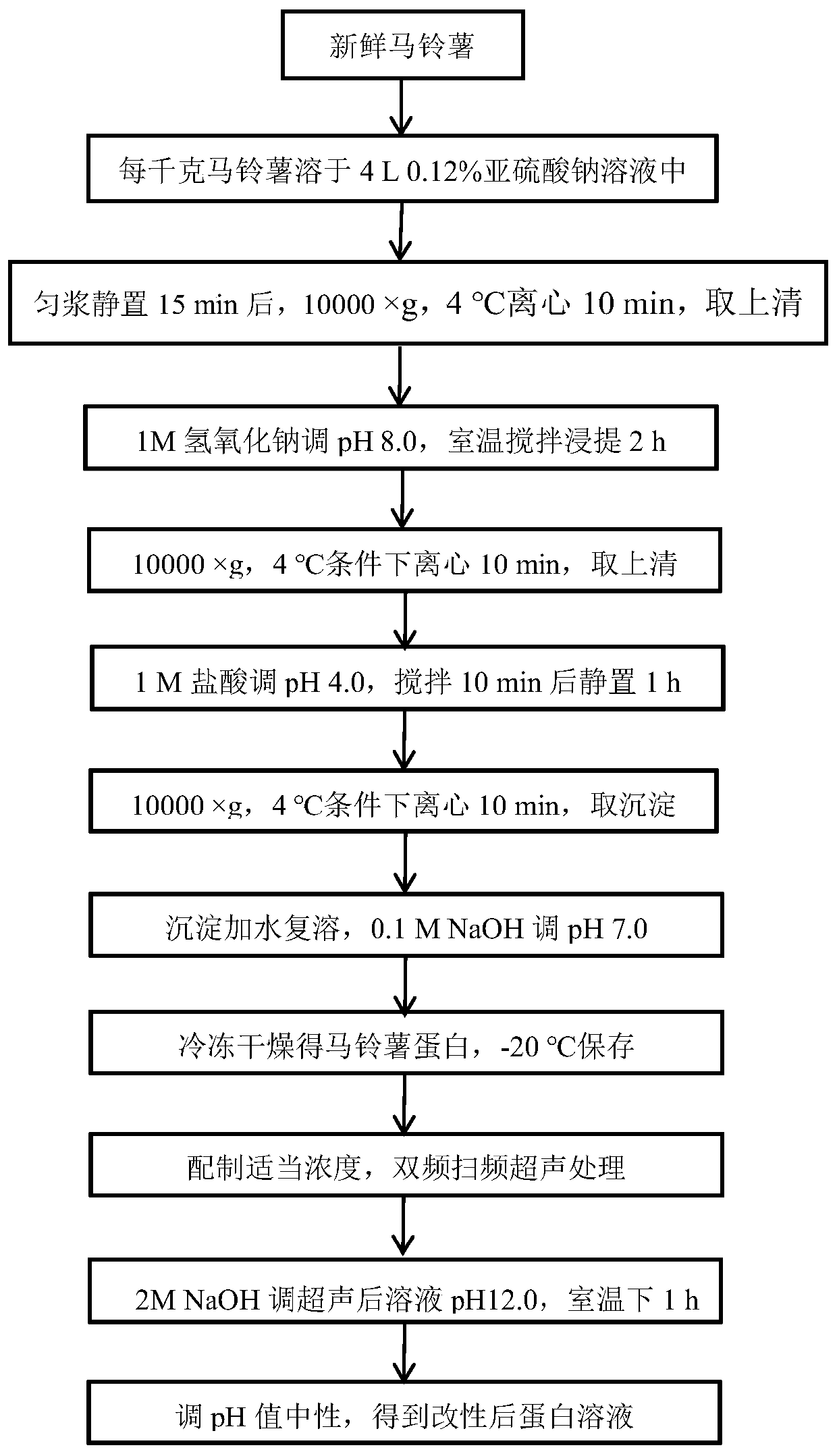
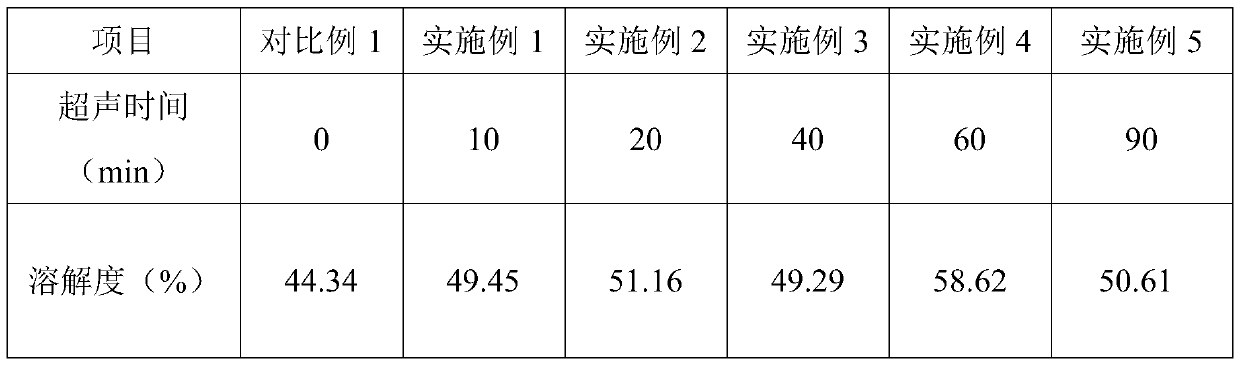
The invention discloses a method for improving the solubility of potato protein by combining ultrasound with pH offset, and belongs to the technical field of protein modification. The method comprisesthe following steps: (1) peeling potatoes, dicing the peeled potatoes, and soaking the diced potatoes in a 0.12% sodium sulfite solution; (2) homogenizing the potatoes and standing for 15 minutes, centrifuging, taking a supernatant, regulating the pH value to 8.0, stirring and extracting at room temperature for 2 hours, centrifuging, taking a supernatant, regulating the pH value to 4.0, standingfor 1 hour, taking a precipitate, adding distilled water, redissolving, regulating the pH value to 7.0, and freeze-drying to obtain potato powder; (3) preparing a proper concentration of the obtainedpotato protein, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment; and (4) adjusting the pH value of the protein solution subjected to ultrasonic treatment in the step (3) to 12.0, maintaining the pH value for 1hour, and adjusting the pH value to 7.0 to obtain a modified potato protein solution. The modification method provided by the invention can greatly improve the solubility of the potato protein, and has very important significance for expanding the application field of the potato protein.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
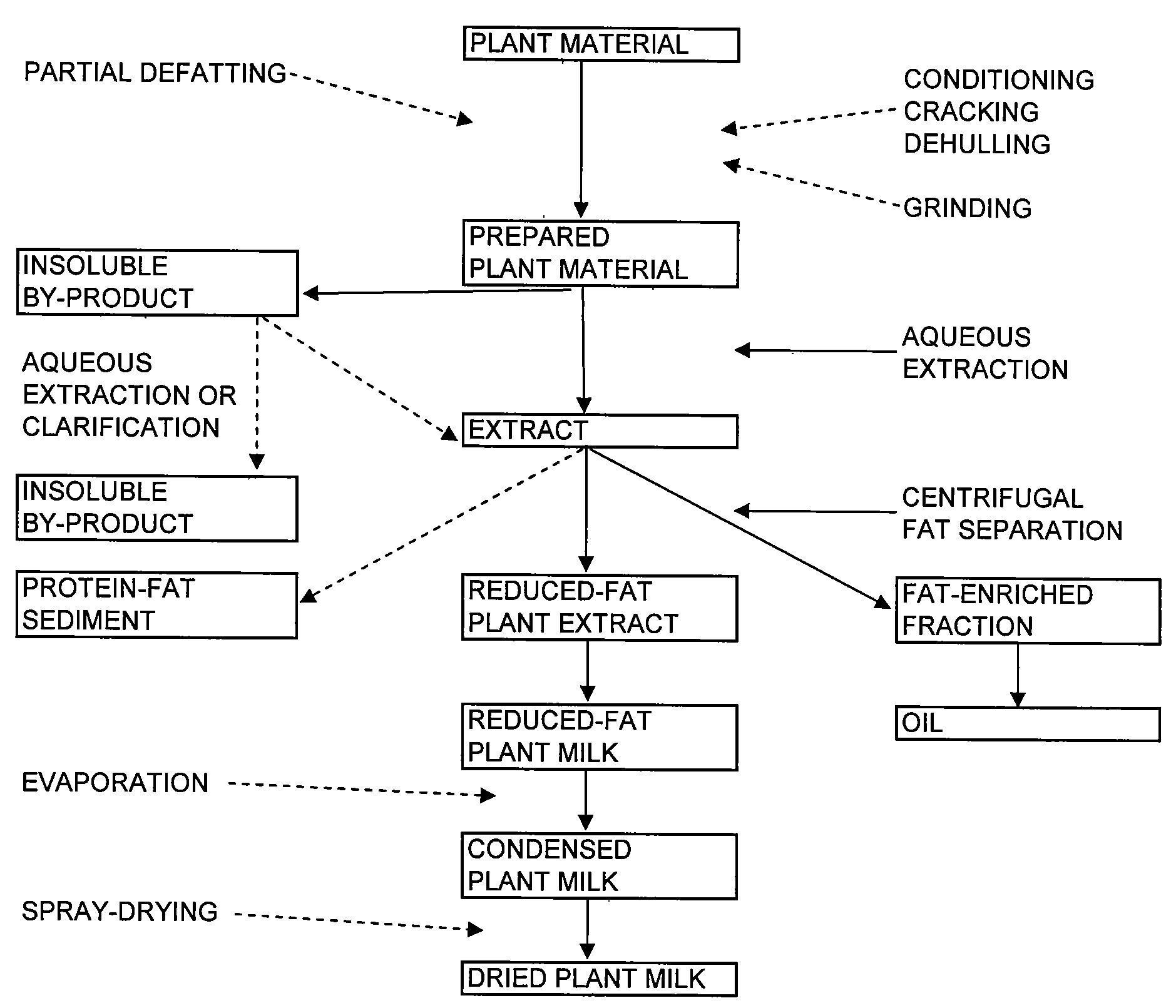
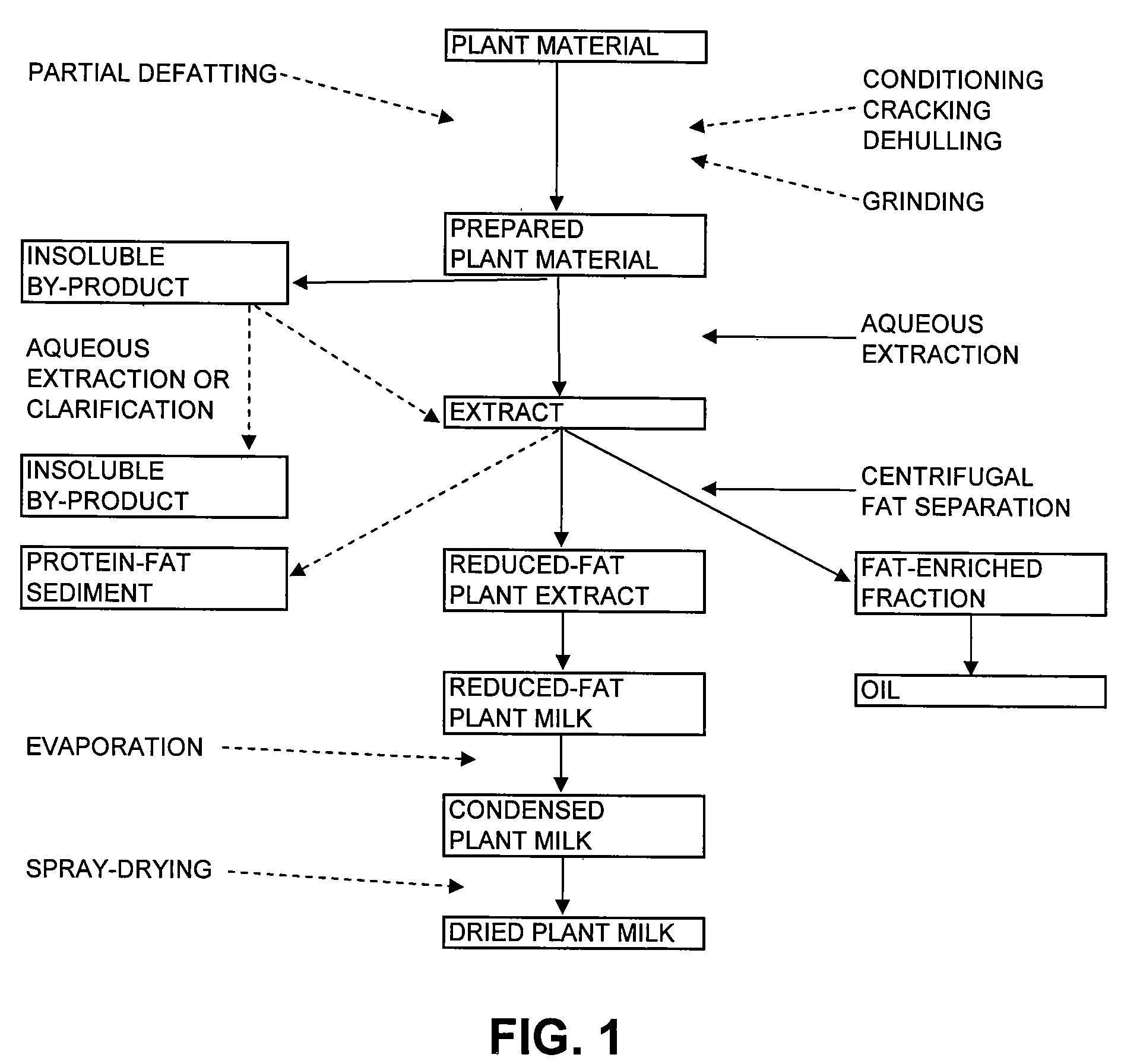
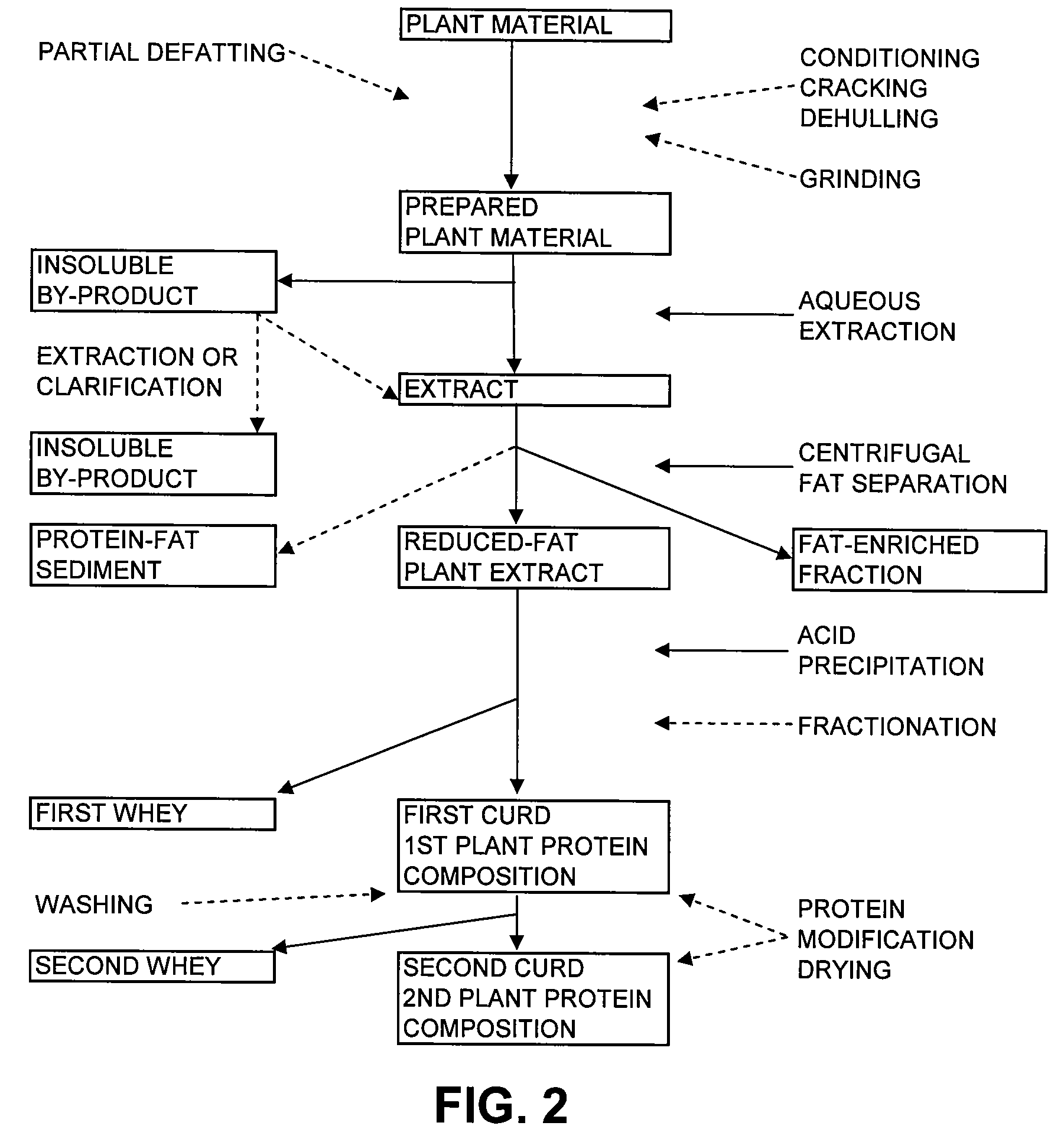
Methods of separating fat from non-soy plant materials and compositions produced therefrom
Disclosed are methods for separating non-soy plant materials to produce a fat-enriched fraction, a reduced-fat plant extract, reduced-fat plant protein compositions, a crude oil, plant gums, a degummed oil and a protein-fat sediment. Also disclosed are food products containing or prepared from the reduced-fat extracts, fat-enriched fraction, gums, oils, protein-fat sediments and reduced-fat protein compositions.
Owner:SPECIALTY PROTEIN PRODRS
Process for preparing white cross-linked protein powder from silkworm pupa
InactiveCN1397192AImprove protectionImprove product qualityProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsCross-linkLinked protein
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Technology for extracting seaweed protein by means of microbial fermentation method
InactiveCN105580975AHigh nutritional valueImprove palatabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMetabolite
In order to overcome the defects in a seaweed protein extracting technology, by means of the microbial fermentation technology, the seaweed protein extracting rate and the water-soluble protein proportion are increased according to seaweed nutritional ingredient changes and the accumulation condition of essential amino acid, lactic acid and other useful metabolites, and therefore the nutritional value of seaweed protein is improved. Seaweed protein is prepared through a technology of compound enzymatic hydrolysis and multi-strain two-step liquid fermentation, multi-bacterium mixed fermentation is adopted, many gene functions in fermentation are added by means of combined strain fermentation, the complex metabolism effect difficult to complete by single strains is completed by combining different metabolic capacities, production efficiency is improved by mean of reciprocity and laterality between microorganisms, and a product is rich in seaweed protein, polypeptide, amino acid, probiotic, vitamin, polysaccharide and other nutritional ingredients.
Owner:QINGDAO HAODA MARINE HEALTH FOOD
Product analogs or components of such analogs and processes for making same
Provided are food products that are derived from non-animal sources that have one or more of the following: color, taste, nutritional content, and other qualities similar to those of dairy products and / or other types of food products. Also provided are processes for production of such dairy-like food products and / or other types of food product analogs.
Owner:RIPPLE FOODS PBC
Method for extracting tea protein product
InactiveCN102302083AHigh purityOvercoming high consumptionProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsBiotechnologyProtein solution
The invention provides a method for extracting a tea protein product. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: 1) pretreating raw materials; 2) preparing tea protein through ultrasonic-assisted alkali extraction; 3) decolorizing a tea protein solution; 4) concentrating a tea protein extracting solution; 5) precipitating the tea protein; and 6) washing the tea protein, refining and drying. The method has the advantages that: tea residue or low-grade tea such as summer-autumn tea and the like is used as a raw material, and a low-frequency ultrasonic circulation technology is used for assisting in extracting the tea protein; by the method, the protein is high in extraction rate and has high purity; the method is low in cost, simple and practicable, and easy to popularize; and the obtained tea protein product has green tea color, and the quality of the product meets food hygienic standard. A novel way of value-added transformation and recycling of tea residue and summer-autumn low-grade tea is provided; and a novel botanical protein product is developed, and the comprehensive utilization and fine and deep processing of tea resources are realized.
Owner:中华全国供销合作总社杭州茶叶研究院 +1
Nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104323342ADough treatmentFood ingredient as taste affecting agentNutritive valuesWhey protein
The invention relates to the food field and particularly relates to nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-15 parts of soybean meal, 1-4 parts of whey protein powder, 0.1-1 part of dried nostoc sphaeroides, 1-5 parts of crude nostoc sphaeroides phycobiliprotein extract powder, 1-3 parts of dry nostoc sphaeroides polysaccharide powder and 1-5 parts of fruit powder. The preparation method of the nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the components and grinding the components into fine powder, passing the powder through a 55-65-mesh sample separating sieve to obtain the nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder. The nostoc sphaeroides nutrition powder which is prepared from nostoc sphaeroides and cereals as raw materials has a very high nutritive value and a health function, and can meet the needs of consumer groups in different age stages and body constitutions. The nutrition powder disclosed by the invention can be independently eaten and also can be applied to the food fields of rice flour, noodles, cakes, biscuits, bread, nutritious foods and the like.
Owner:HUNAN YANDI BIOLOGICAL ENG
Assembly of at least one vegetable protein and at least one dairy protein
ActiveUS20150237885A1Function increaseImprove sensory propertiesFodderFrozen sweetsBiotechnologyVegetable Proteins
Owner:ROQUETTE FRERES SA +2
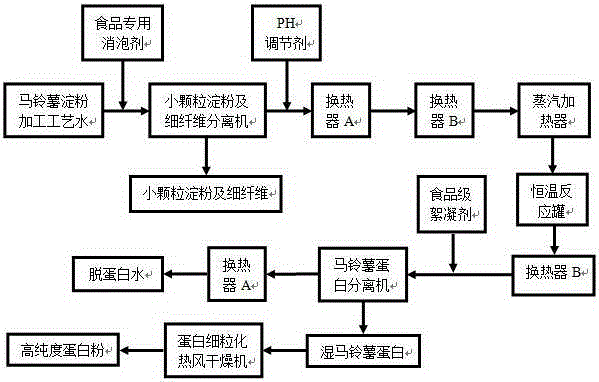
Technology for extracting potato protein through hot flocculence method
InactiveCN105230964AGuaranteed uptimeHigh extraction rateProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsFiberPotato starch
The invention provides a technology for extracting high-purity potato protein through a hot flocculence method. At the significant end of the technology, small-granule starch and a fine-fiber mixture in potato starch processing and separation juice are separated, the purity and quality of the potato protein obtained through flocculence and separation at the final phase are improved, and meanwhile the phenomenon that heat exchange equipment and a pipeline are blocked due to starch dextrinization in the follow-up process is avoided; the potato protein is degenerated and flocculated through the hot flocculence method to be changed from the starch separation juice hydrosol body state into flocculence body solid to facilitate solid and liquid separation, the quality of the extracted protein is ensured, and meanwhile the physical flocculence method and the chemical flocculence precipitation method are used in a combined mode in cooperation with flocculence of chemical auxiliaries, so that the protein extraction rate and the protein separation effect are greatly improved, and the potato protein purity is improved. In addition, resource utilization of the potato protein is performed, more than 50% pollutant loads are reduced for follow-up sewage treatment, and the dual effects of resource utilization and pollutant control are achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for extracting yam mucoproteins from yams
InactiveCN102696852AAvoid harmHigh purityProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsFlocculationOrganic solvent
The invention provides a process for extracting yam mucoproteins from yams and belongs to the field of extracting functional biological macromolecular substances from natural materials to produce functional healthcare food. The extracting process comprises the main steps of (1) material selection; (2) leaching gelatinization; (3) enzymolysis; (4) standing; (5) adjustment of PH value; (6) flocculation; (7) precipitation; and (8) drying. The yield of the yam mucoprotein products prepared by the process is 4 to 5 percent, and the content of yam mucoprotein is 60 to 67 percent. According to the process provided by the invention, the organic solvent extraction in the prior art is replaced by the flocculation and natural precipitation, so the product cost is greatly saved, the environmental pollution is lowered, and the process has great significance for actual production.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Light-yellow odourless degreasing silkworm pupa protein power and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105124131ALow degreasing temperatureShort degreasing timeProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsPROTEIN S HEERLENBiology
The invention relates to light-yellow odourless degreasing silkworm pupa protein power and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, silk reeling silkworm pupae of which the skin and the gland are removed are selected as the raw material, silkworm pupa pretreatment is conducted, and coarse silkworm pupa powder is obtained; the coarse silkworm pupa powder is evenly mixed in degreasing solvent, ultrasonic degreasing treatment is conducted, centrifugal separation is conducted, and degreasing fluid and degreasing coarse pupa protein are obtained; drying and smashing are conducted on the degreasing coarse pupa protein, and the degreasing coarse pupa protein power is obtained; the degreasing coarse pupa protein power is evenly mixed in a sodium hydroxide solution, a silkworm pupa protein extracting solution is obtained, ultrasonic extraction treatment is conducted, macroporous resin is added into the silkworm pupa protein extracting solution, adsorption treatment is conducted, solid-liquid separation is conducted, resin and protein fluid are obtained, the protein fluid pH is adjusted, protein precipitation is collected, and wet silkworm pupa protein is obtained; vacuum drying and smashing are conducted on the wet silkworm pupa protein, and the light-yellow odourless degreasing silkworm pupa protein power is obtained. The light-yellow odourless degreasing silkworm pupa protein power and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the technology is simple, the degreasing efficiency is high, effects of deodorization and decolorization are good, the treatment is low in temperature and short in time, the cost is low, the green and environmental protection is achieved, and the light-yellow odourless degreasing silkworm pupa protein power and the preparation method thereof can be used for industrial production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting yellow mealworm active proteins by using alkali-enzyme method
InactiveCN102048020ASimple processLess investment in equipmentProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsNeutral proteaseActive protein
The invention provides a method for extracting yellow mealworm active proteins by using an alkali-enzyme method, comprising the following steps: drying fresh yellow mealworm larvae to obtain dried yellow mealworm larvae of which the moisture content is lower than 5%, and smashing the dried yellow mealworm larvae; carrying out secondary digestion by taking petroleum ether of which the relative density is 0.64-0.66 as an extraction solvent; carrying out digestion with a 0.08-0.10mol / L NaOH solution; regulating the pH value to 7.0-7.5, carrying out enzymatically hydrolyzed extraction at a temperature of 55-60 DEG C by complex enzyme which is composed of neutral protease and papain at the mass ratio of 1:1-1:1.5; destroying enzyme; and centrifuging and dialyzing to obtain yellow mealworm protein powder. The yellow mealworm protein powder has the advantages of light yellow color and luster, beauty, fragrant odor as well as fine and smooth taste; and the protein content of the yellow mealworm protein powder reaches 94.5% and the extraction efficiency of the yellow mealworm protein powder reaches 75%.
Owner:CHANGSHA SAIBANG BIOTECH
Methods for the production and use of myceliated high protein food compositions
Disclosed is a method to prepare a myceliated high-protein food product, which includes culturing a fungi an aqueous media which has a high level of protein, for example at least 20 g protein per 100 g dry weight with excipients, on a dry weight basis. The fungi can include Pleurotus ostreatus, Pleurotus eryngii, Lepista nuda, Hericium erinaceus, Lentinula edodes, Agaricus blazeii, Laetiporus sulfureus and combinations thereof. After culturing, the material is harvested by obtaining the myceliated high-protein food product via drying or concentrating. The resultant myceliated high-protein food product may have its taste, flavor, or aroma modulated, such as by increasing desirable flavors or tastes such as meaty, savory, umami, popcorn and / or by decreasing undesirable flavors such as bitterness, astringency or beaniness. Deflavoring and / or deodorizing as compared to non-myceliated control materials can also be observed. Also disclosed are myceliated high-protein food products.
Owner:MYCOTECH
Method for extracting macadimia nut proteins
InactiveCN103719531ANot destroyedEasy to separateProtein composition from waste materialsProtein composition from vegetable materialsIsoelectric pointNut Proteins
The invention relates to a method for extracting macadimia nut proteins. The method mainly comprises the following steps of (1) smashing macadimia nuts, and separating oil of the macadimia nuts through infrared treatment and hydraulic cold squeezing; (2) mixing the obtained macadimia nut meal with pure water, treating the mixture through a colloid mill and an alkaline hardening, quenching and homogenizing machine, and then performing dynamic ultrahigh pressure treatment; and (3) adjusting the pH of the fruit meal to an isoelectric point to realize separation, and performing low-temperature spray drying to obtain the macadimia nut proteins. The technology disclosed by the invention is continuous and compact; the product is high in yield and high in quality.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Making method of high-organic selenium cardamine violifolia selenium polypeptide
ActiveCN108157579AHigh protein extraction rateEfficient removalProtein composition from vegetable materialsProtein foodstuffs working-upPectinaseNeutral protease
The invention relates to a making method of a high-organic selenium cardamine violifolia selenium polypeptide. The making method comprises the following steps of: S1, performing pretreatment on a rawmaterial: selecting dried cardamine violifolia powder as a raw material for production, performing soaking with ethano for decolorization, performing filtering for removing impurities, and then performing pretreatment with a mixture of cellulolytic enzymes and pectinase to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysate for standby application; S2, performing double-enzyme composite enzymolysis: firstly adding alkaline protease in a supernatant after pretreatment in step S1 for enzymolysis, performing enzyme deactivation, performing cooling to 50 DEG C, adjusting the pH with hydrochloric acid to 6.0-8.0, adding neutral protease, and performing enzymolysis to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysate; and S3, performing enzyme deactivation and peptide solution separation: boiling over the enzymatic hydrolysate to achieve enzyme deactivation, and performing standing to obtain a clear transparent peptide solution in the lower layer. The making method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the cardamineviolifolia is used a core raw material, and the cellulolytic enzymes and the pectinase are used for pretreatment before enzymolysis, so that the impurities in the cardamine violifolia are effectivelyremoved and the protein extraction rate of the cardamine violifolia is increased; and then a multi-step double-enzyme enzymolysis method is used for enzymolysis, the content of the selenium polypeptide is higher, and the molecular weight of the selenium polypeptide is smaller.
Owner:恩施德源硒材料工程科技有限公司
Preparation method of mulberry leaf protein powder
ActiveCN104543613AHigh extraction rateImprove solubilityFood preservationVegetable proteins working-upSolubilityNitrogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of food, and in particular to a preparation method of mulberry leaf protein powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: raw material pretreatment, superfine grinding, extruding for swelling, enzymatic extraction, alkali dissolution on protein, acid precipitation on protein, enzymolysis solubilizing, and drying to obtain mulberry leaf protein powder with high solubleness. According the preparation method, superfine grinding is combined with the extruding for the swelling, and is assisted by enzymolysis wall-breaking and enzymolysis solubilizing, so that the extraction rate of the protein is increased; the solubleness of the protein is greatly improved; the extraction rate of the protein is over 70%; the content of the protein in the obtained mulberry leaf protein powder is over 75%; the protein is good in solubleness; the nitrogen solubility index (NSI) is over 90%; and the mulberry leaf protein powder obtained by adopting the process disclosed by the invention is good in sensory quality, high in protein content, and good in solubleness, and can be used as a functional food material.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof from macroalgae and/or microalgae
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
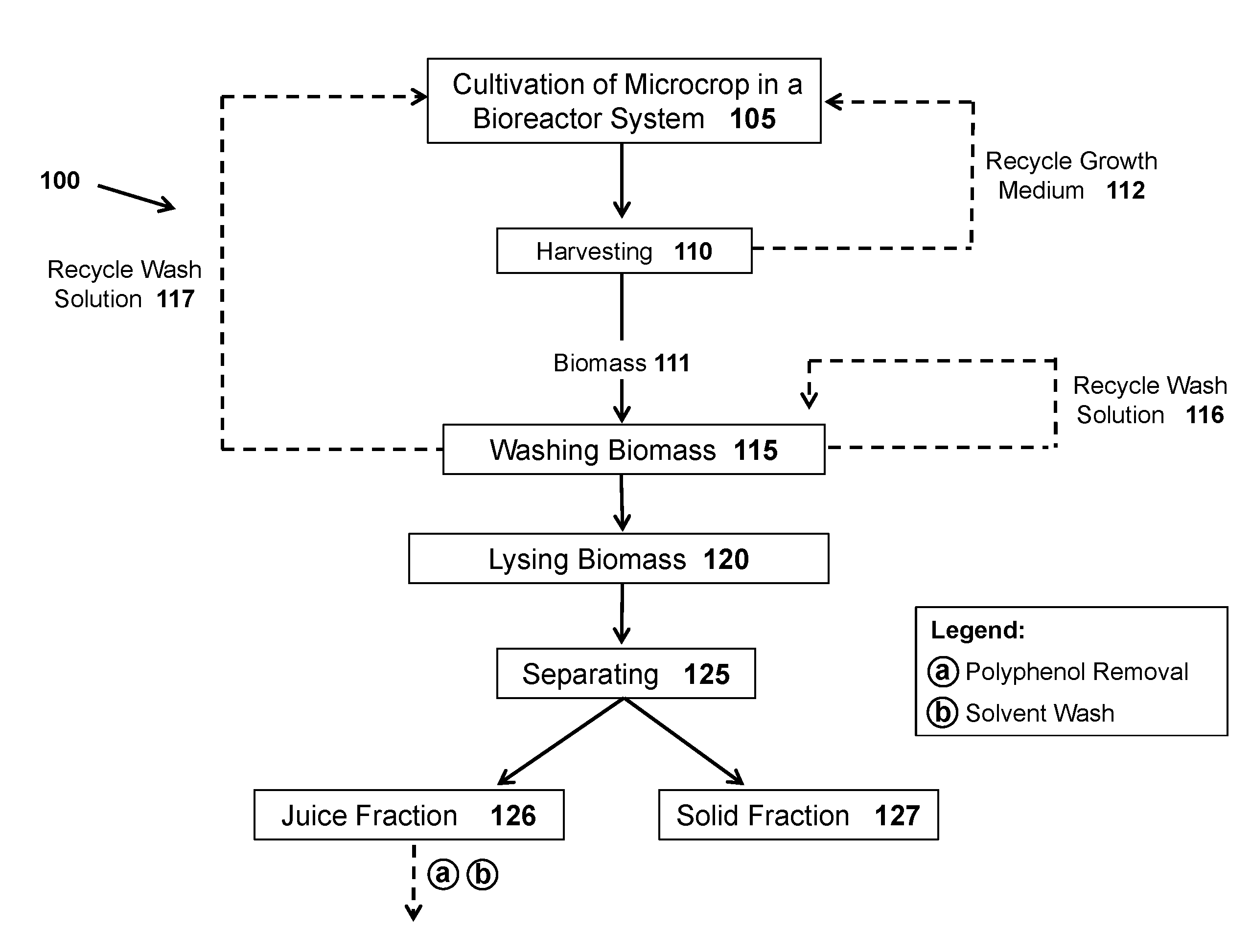
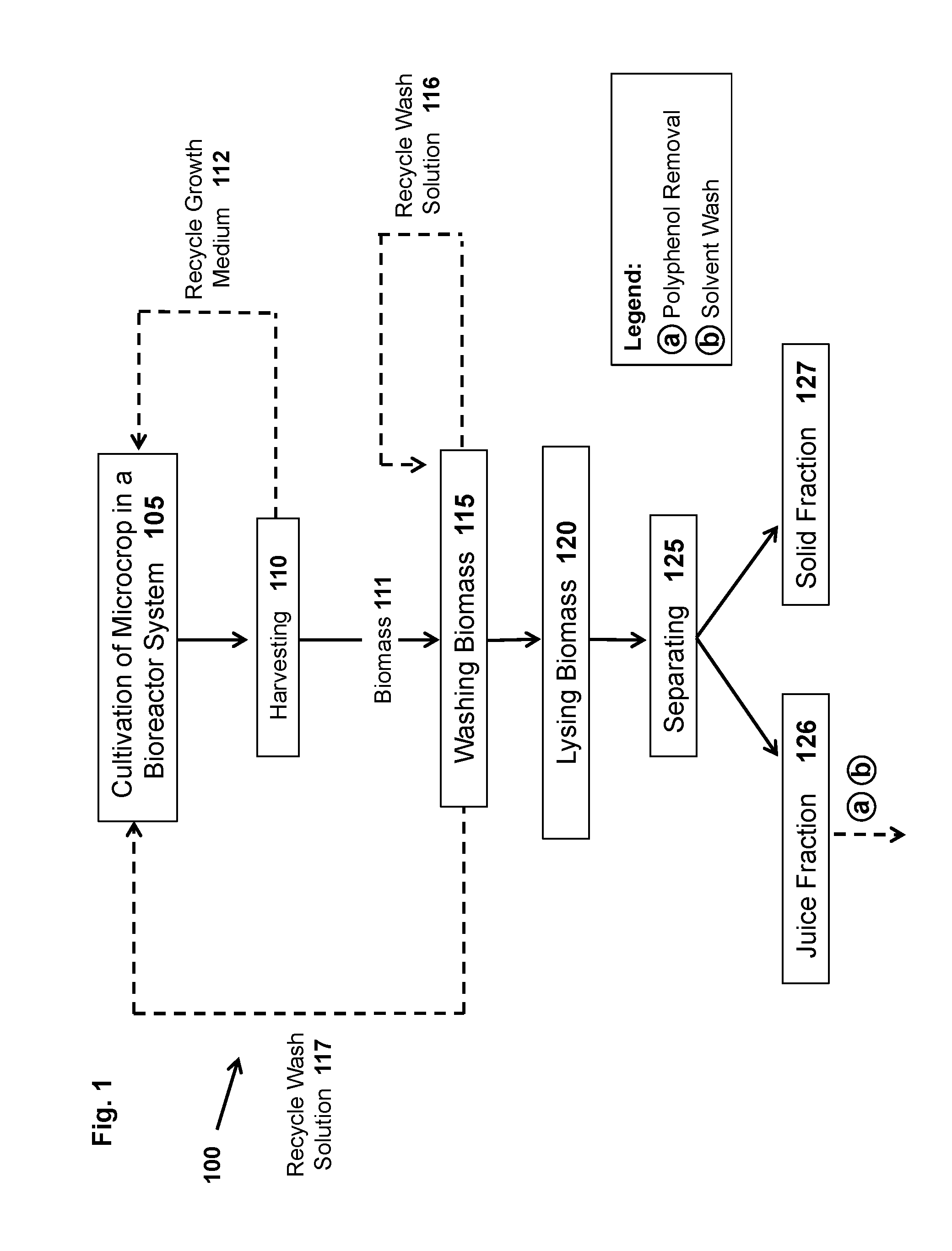
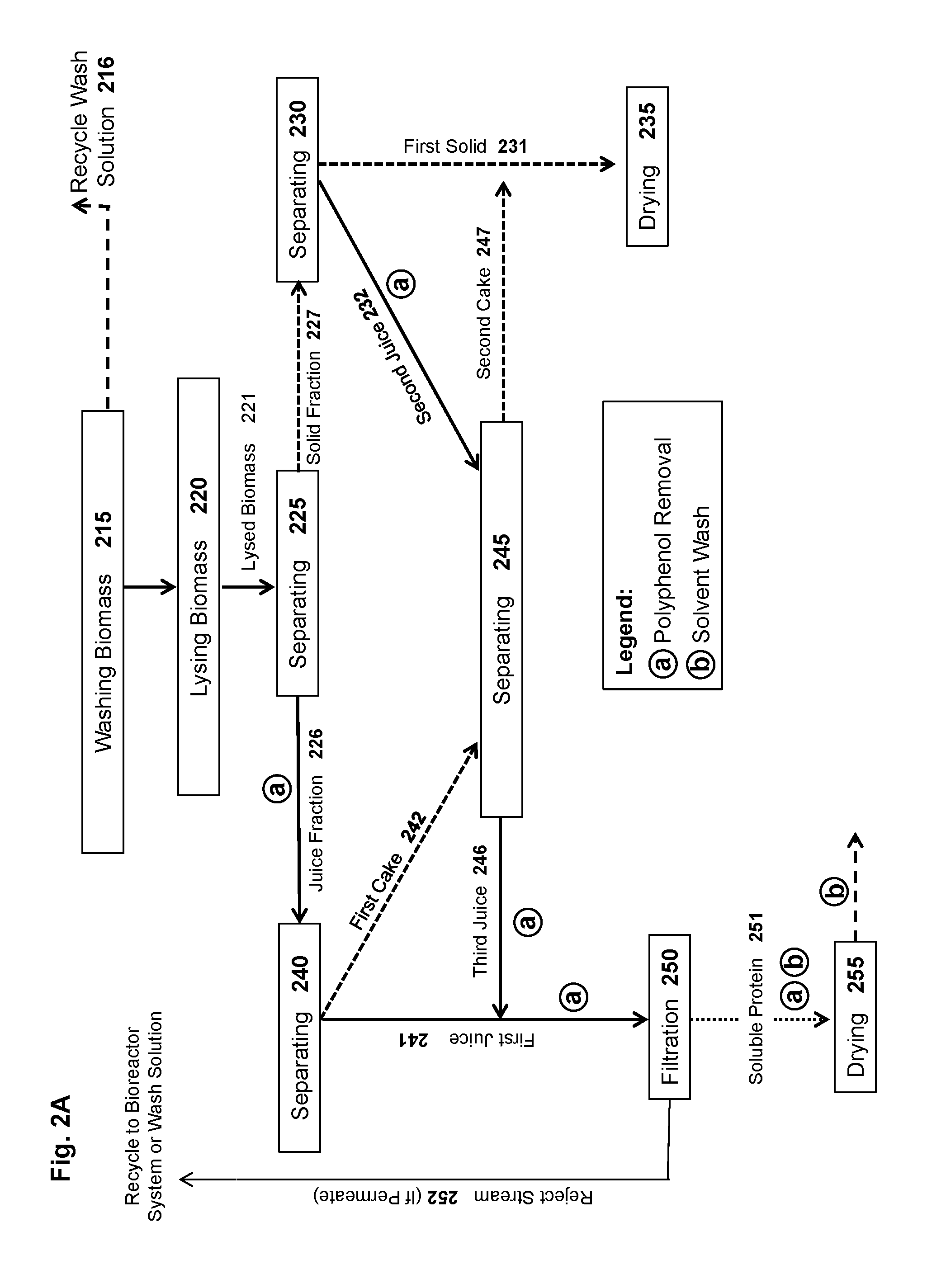
Methods and systems for extracting protein and carbohydrate rich products from a microcrop and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20160360770A1Good dispersibilityImprove integrityMembranesUltrafiltrationFruit juiceAquatic species
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to methods and systems for purifying proteins and carbohydrate rich products from photosynthetic aquatic species and compositions thereof. For example, one embodiment of the present disclosure relates to methods and systems for purifying proteins the present disclosure relates, in some embodiments to methods and systems for extracting proteins, dry biocrude, and carbohydrate-rich meal from Lemna. In some embodiments, a method of treating a biomass comprising a microcrop (e.g., Lemna) to produce a product comprising soluble microcrop protein may comprise: (a) lysing a first portion of the biomass to form a first portion of lysed biomass; (b) separating the first portion of lysed biomass to generate a first portion of a juice fraction and a first portion of a solid fraction; (c) separating the first portion of the juice fraction to generate a first portion of a first juice and a first portion of a first cake, wherein the first juice comprises a soluble microcrop protein; and / or (d) filtering the first portion of the first juice to generate a first portion of the product comprising soluble microcrop protein and a reject stream.
Owner:LEMNATURE AQUAFARMS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com