Methods and compositions for consumables
a technology of consumables and compositions, applied in the field of consumables compositions, can solve the problems of profound negative environmental impact of animal farming, the largest threat to biodiversity in the world, and the profound negative impact of human consumption of mea
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0387]An exemplary muscle replica composition comprising one or more isolated, purified plant proteins is described herein.
[0388]Protein Purification for Components of the Replica
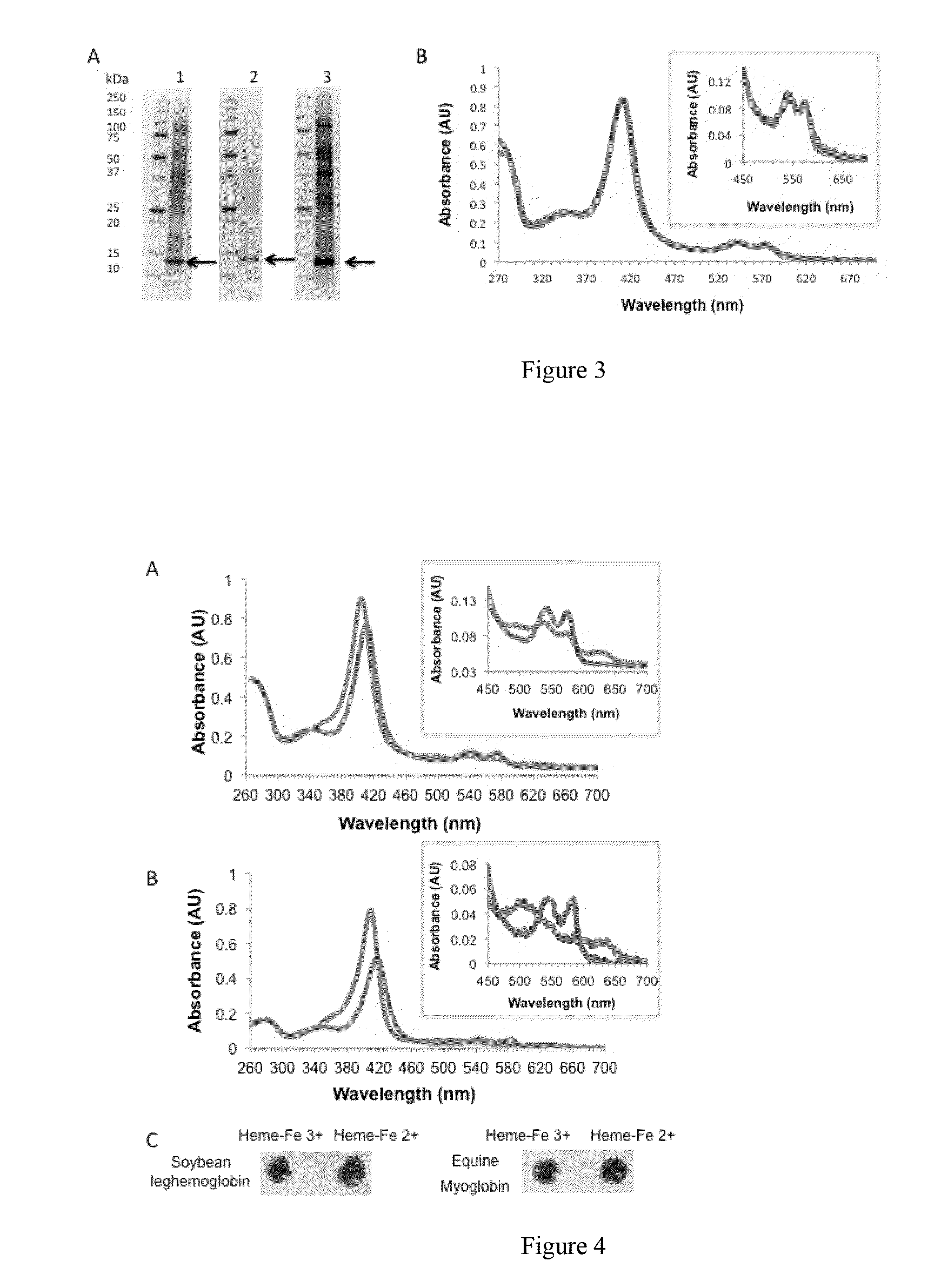
[0389]Moong bean seeds, Green Pea dry seed were purchased as milled flour and used for purification of respective seed storage proteins. Rubsico was purified from fresh alfalfa plant. Protein composition at individual fractionation steps was monitored by SDS-PAGE and protein concentrations were measured by standard UV-VIS and Pierce assay methods.
[0390]Moong bean 8S globulins: Moong bean flour was resuspended in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer pH 7 and 0.5M NaCl at 1:4 (wt / v) ratio, and mixture was incubated for 1 hr. Unsoluble material was separated by centrifugation and proteins in the supernatant were fractionated by addition of ammonium sulfate in 2 steps: 50% (wt / v) followed by 90% (wt / v). Protein precipitated in 90% fraction contained the moong bean 8S globulins and was stored at −20 C until further ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com