Making method of high-organic selenium cardamine violifolia selenium polypeptide
A high-organic technology of crushed cinnabar leaves, which is applied in the field of preparation of selenium polypeptides of cinnabar leaves, can solve the problems of hair and nail shedding, toxicity, and reduction, and achieve the effect of improving protein extraction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] S1. Raw material pretreatment: Select the dry powder of broken rice chestnut with a protein content of more than 15% and a selenium content of 2000ug / g as the production raw material, soak it in ethanol for 20-30min, filter and remove impurities, and then pass cellulase and pectin Obtain the enzymatic hydrolysis product after the pretreatment of the enzyme mixture, and set aside;
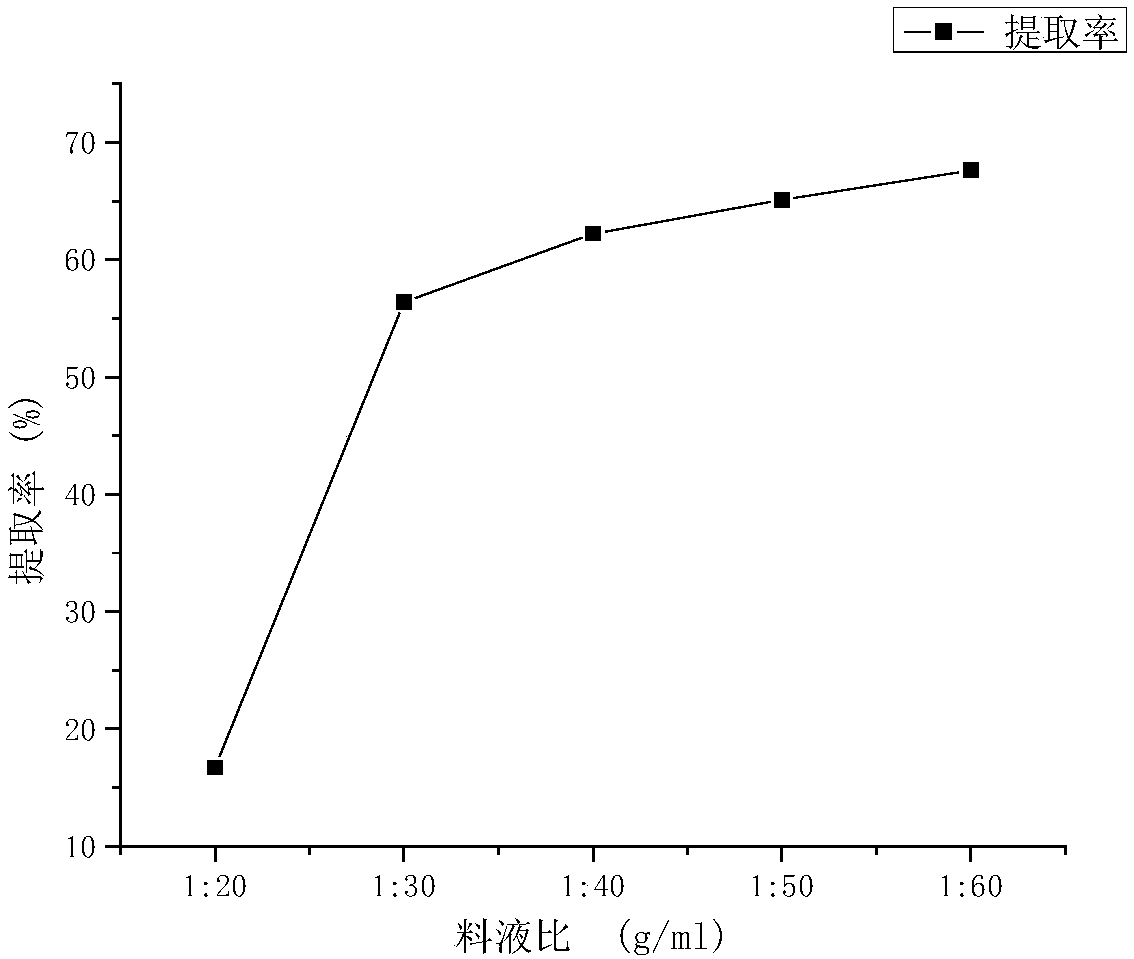
[0038] S11. Weigh cellulase and pectinase in equal proportions and mix them, and then put the mixture into the raw material for removing impurities at 50°C (for the raw material after removing impurities, first mix the dry powder of rice chestnut and water at a ratio of 1:20~ 1:40g / mL ratio mixes, then puts cellulase and pectinase mixture), obtains mixed solution A, makes the total mass of cellulase and pectinase account for 1% of mixed solution A quality; Enzymolyze for 1 hour under the condition of 6.0, then adjust the pH to 7.0, add water, and mix the enzymolyzed product obtained at this t...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Adopt embodiment one scheme to do three groups of tests respectively,
[0045] The difference from Example 1 is that:
[0046] Group A, adopt the method of Example 1 (that is, in step S2, use alkaline protease alone for enzymatic hydrolysis, without subsequent neutral protease enzymatic hydrolysis process)
[0047] Group B, using the method of Example 1 (that is, in step S2, neutral protease is used alone for enzymatic hydrolysis, and there is no pre-ordered alkaline protease enzymatic hydrolysis process)
[0048] Group C, using the method of Example 1 (that is, in step S2, acidic protease is used alone for enzymolysis, and alkaline protease and alkaline protease are not used for enzymolysis)
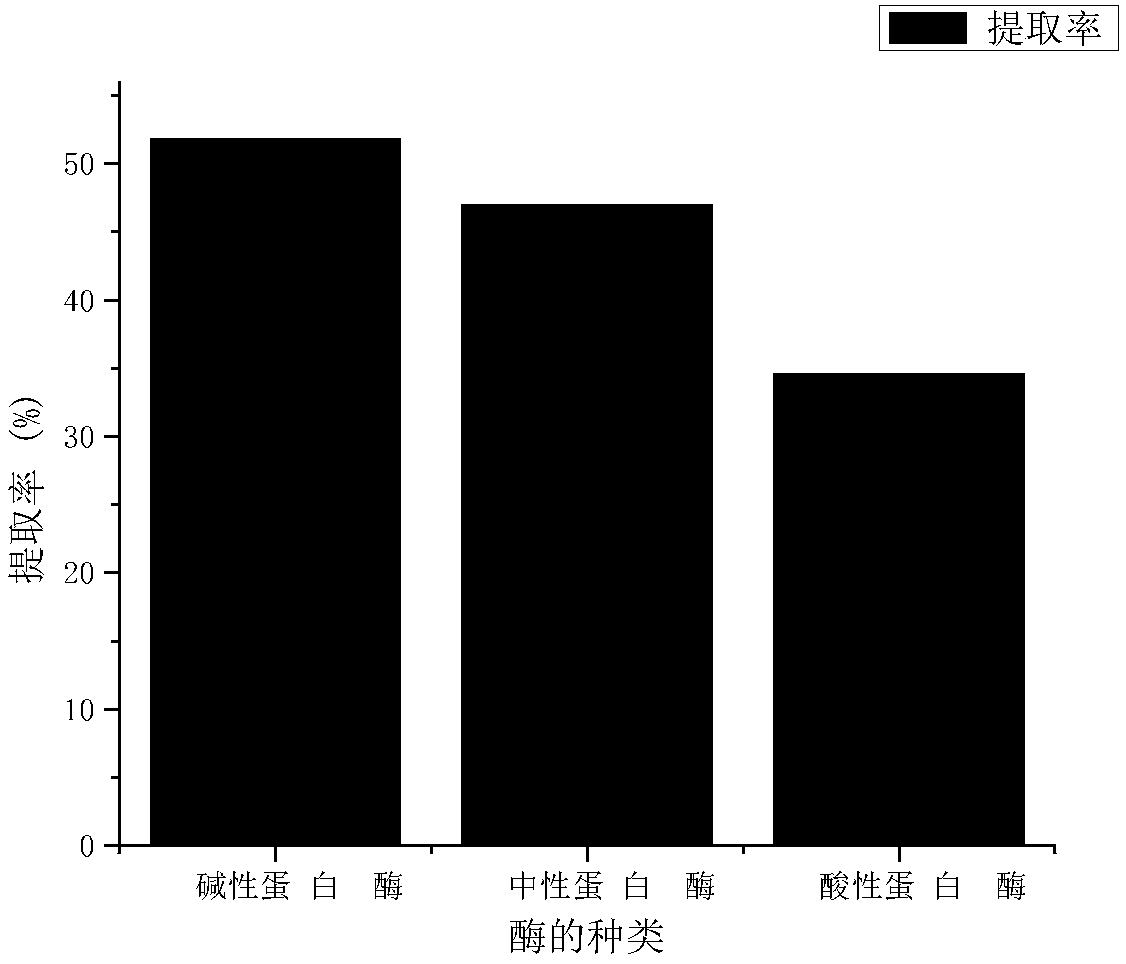
[0049] Subsequently, adopt routine method to detect respectively the amount of broken rice sheath protein in three groups of obtained materials, after group A, group B, group C extract, extraction rate is respectively 51.8%, 47.0%, 34.6% (as figure 1 Shown), it can be seen that...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The difference from Example 1 is:
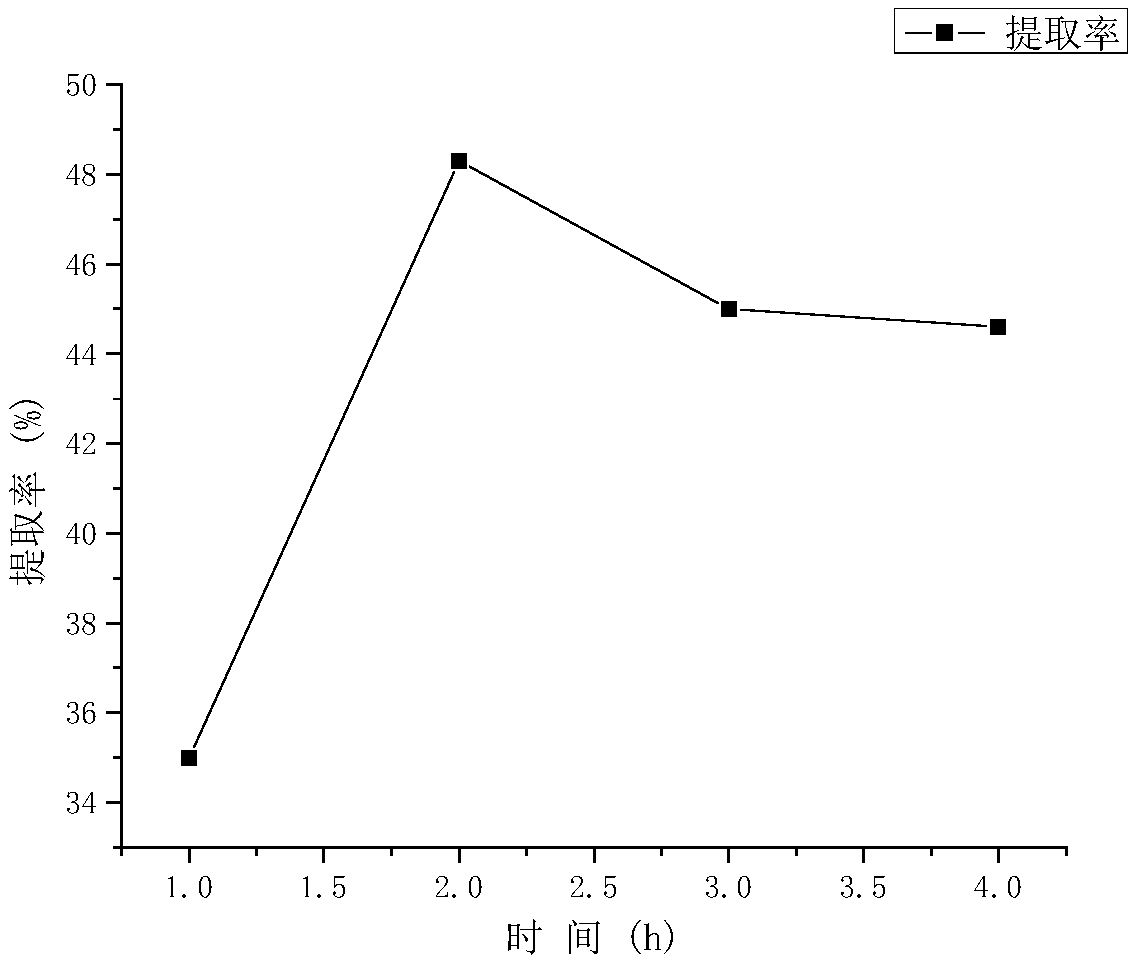
[0052] In step S2: the enzymatic hydrolysis time of alkaline protease is divided into four groups of 1, 2, 3, and 4 hours in turn for experiments to determine the influence of different enzymatic hydrolysis times on the protein extraction rate in step S2
[0053] Extract results such as figure 2 As shown, within 1-2 hours of adding alkaline protease, the extraction rate increased rapidly with the increase of time, and the extraction rate gradually decreased after 2 hours. The extraction rate decreased due to the excessive hydrolysis of alkaline protease, and the extraction rate remained unchanged after 3 hours. , due to the gradual inactivation of alkaline protease, so the optimal extraction time is preferably 2 hours for the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com