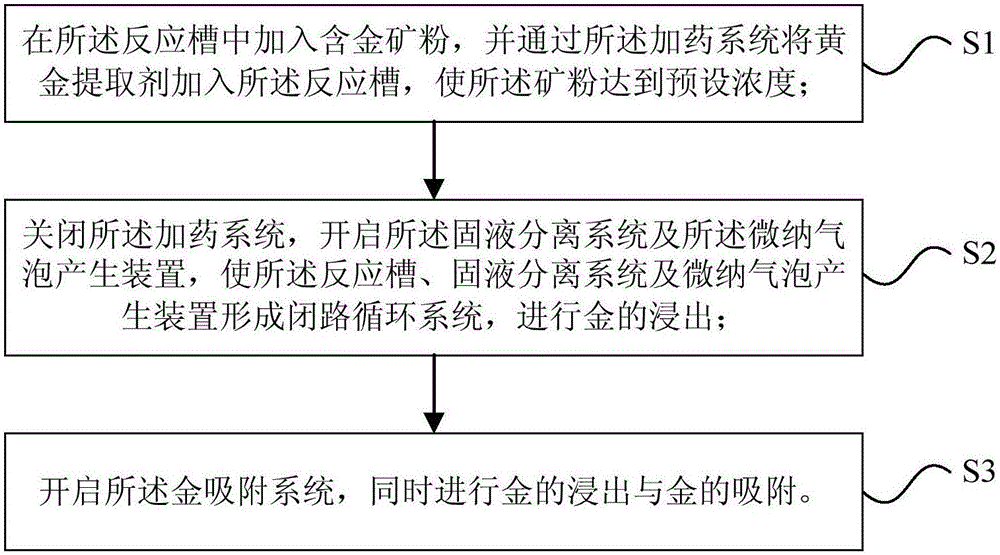
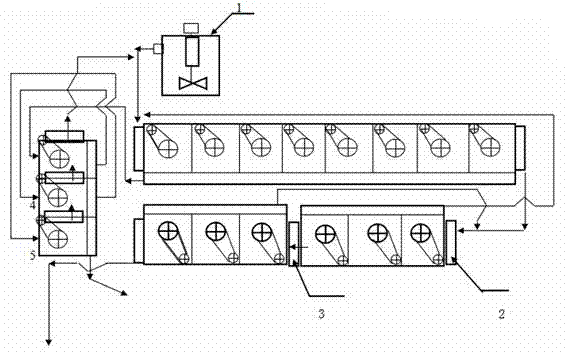
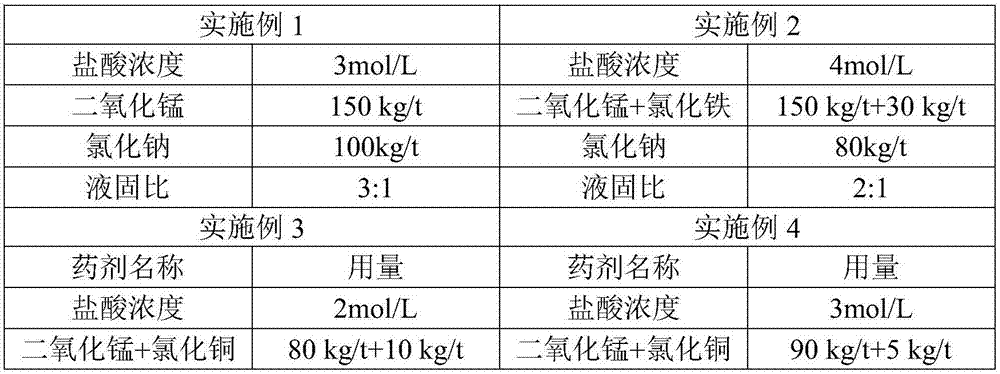
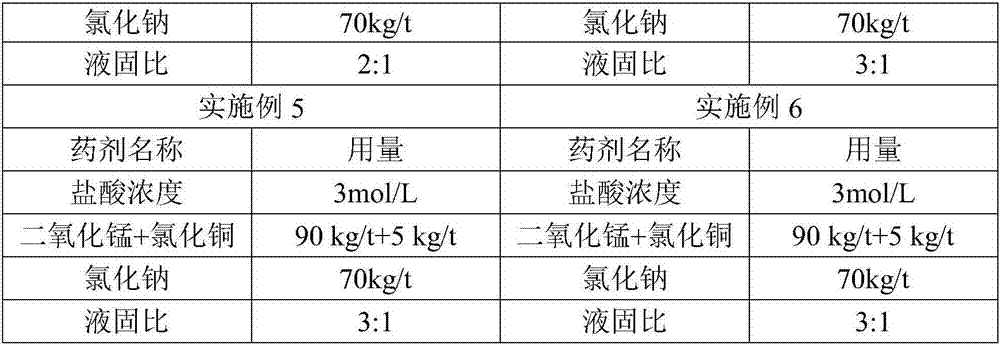
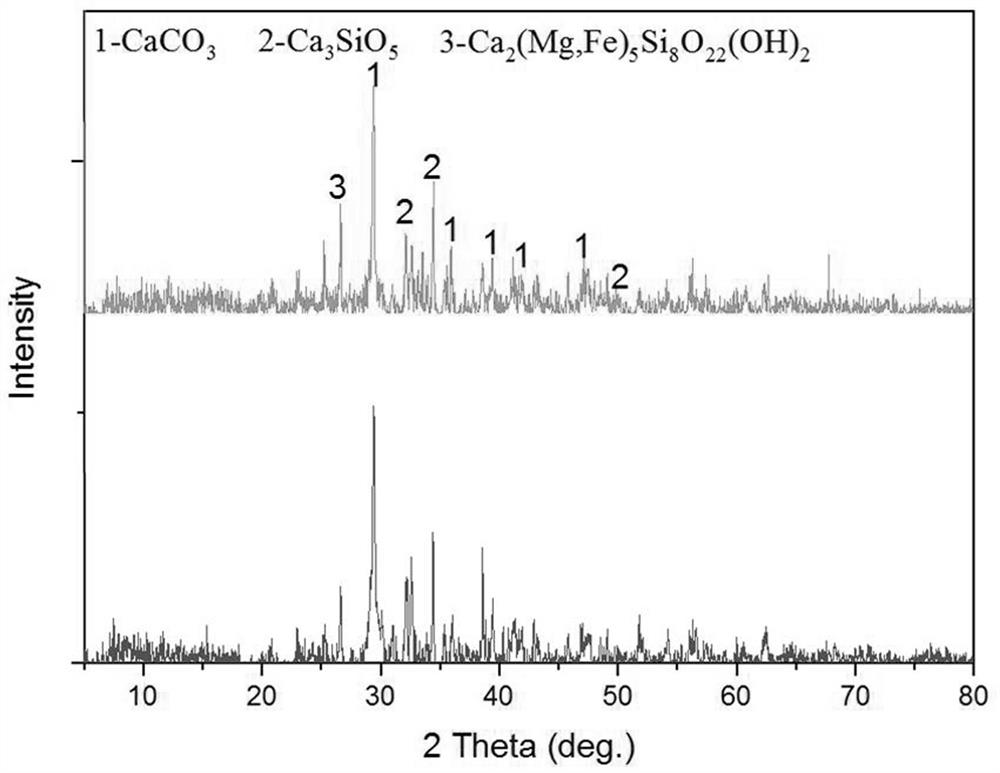
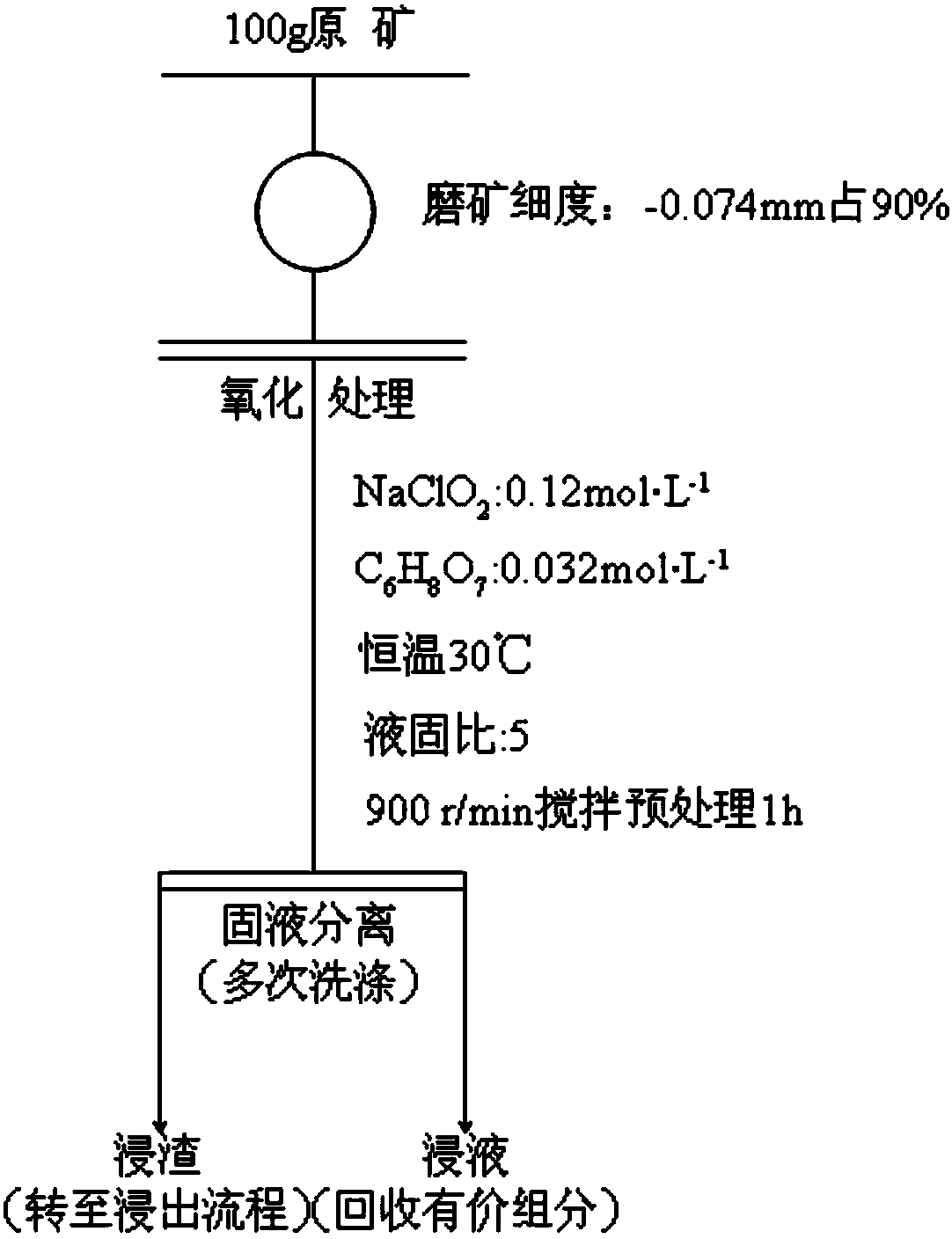
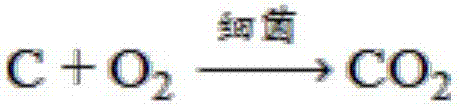Patents
Literature
81 results about "Arsenopyrite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
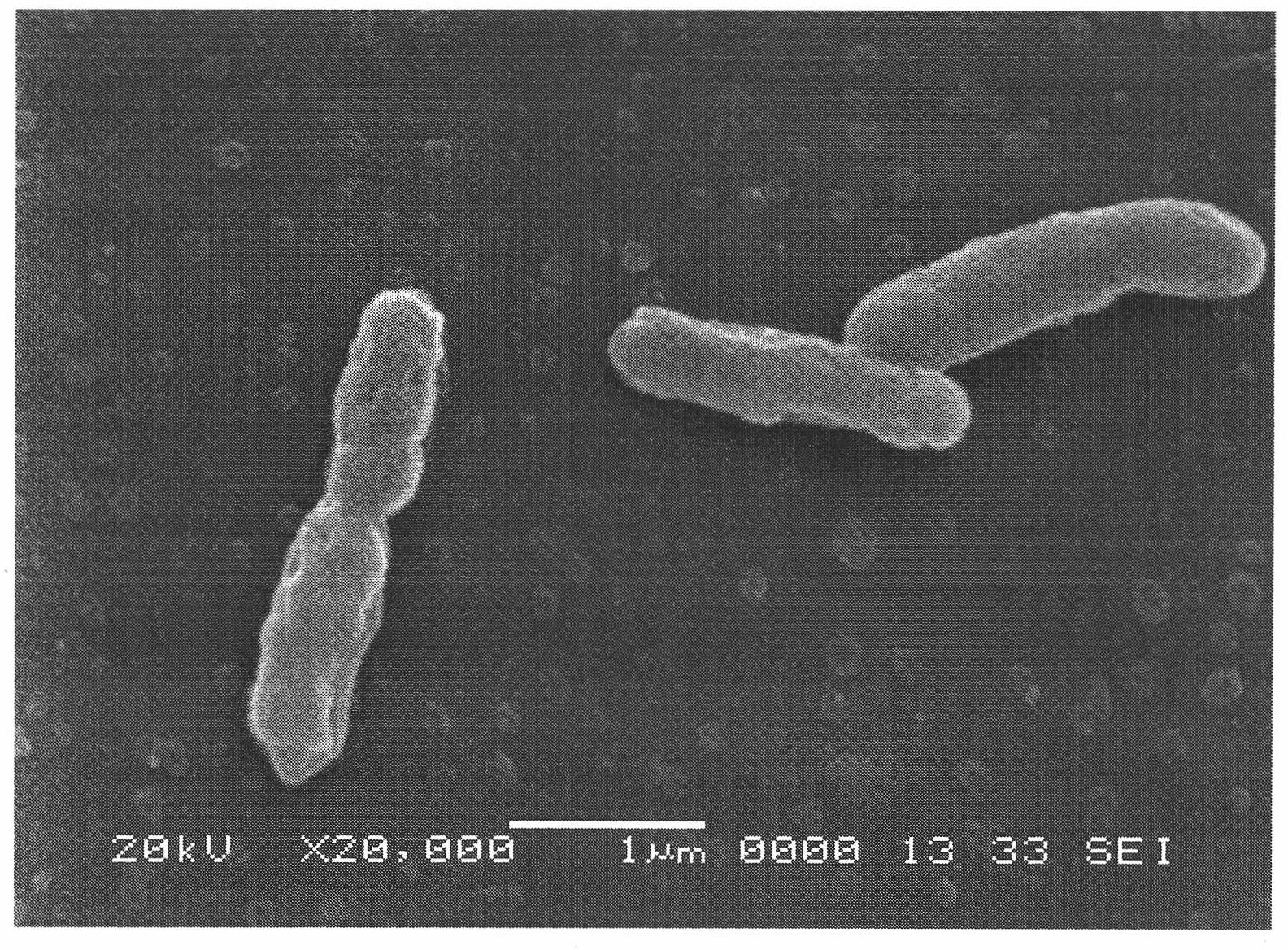
Arsenopyrite is an iron arsenic sulfide (FeAsS). It is a hard (Mohs 5.5-6) metallic, opaque, steel grey to silver white mineral with a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1. When dissolved in nitric acid, it releases elemental sulfur. When arsenopyrite is heated, it produces poisonous sulfur and arsenic fumes which can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. With 46% arsenic content, arsenopyrite, along with orpiment, is a principal ore of arsenic. When deposits of arsenopyrite become exposed to the atmosphere, the mineral will slowly oxidize, converting the arsenopyrite into an iron arsenate, a relatively stable compound. Arsenopyrite is generally an acid consuming sulfide mineral unlike iron pyrite which can lead to acid mine drainage.
Five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method
ActiveCN107363083AAvoid pollutionReduce penetrationSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSolubilityReaction layer
The invention provides a five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method, and belongs to the technical field of mine environment ecological restoration. A five-layer structure involved in the method particularly comprises a non-pollution new soil layer, a clay sealing layer, a biomass reduction sealing layer, a main reaction layer and an original tailing layer. The method comprises the steps that organic matter in biomass on the main reaction layer is taken as the reducing agent, arsenic in a high oxidation state is reduced into arsenic in a low oxidation state or in a reduced state under the effect of anaerobic bacteria, and sulphur in a high oxidation state is reduced into sulphur in a reduced state, so that the minerals of realgar, orpiment and the like are formed again; and meanwhile, a large amount of iron is reduced to form iron pyrite, arsenopyrite, pyrrhotite and other minerals with the low solubility, and the heavy metals of Pb<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Hg<2+>, Cd<2+>, Sb<3+> and the like form galena, blende, copper pyrites, cinnabar, greenockite, stibnite and other sulfide minerals with the extremely low solubility, so that mine heavy metal pollution in-situ mineralization restoration is achieved.
Owner:北科蕴宏环保科技(北京)有限公司
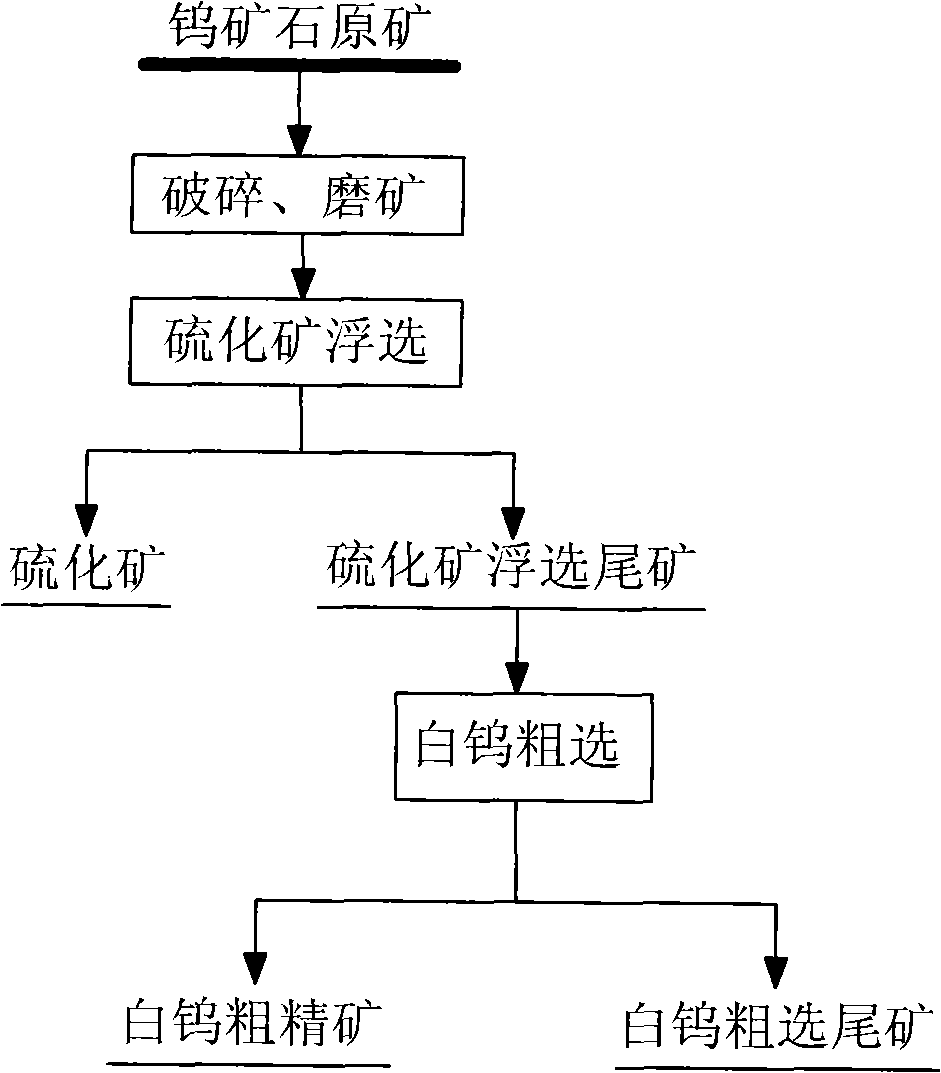
Beneficiation method for recycling scheelite from tungsten ore rich in mispickel
InactiveCN101269353AReduce dosageImprove rough selection indexFlotationSodium silicateMaterials science
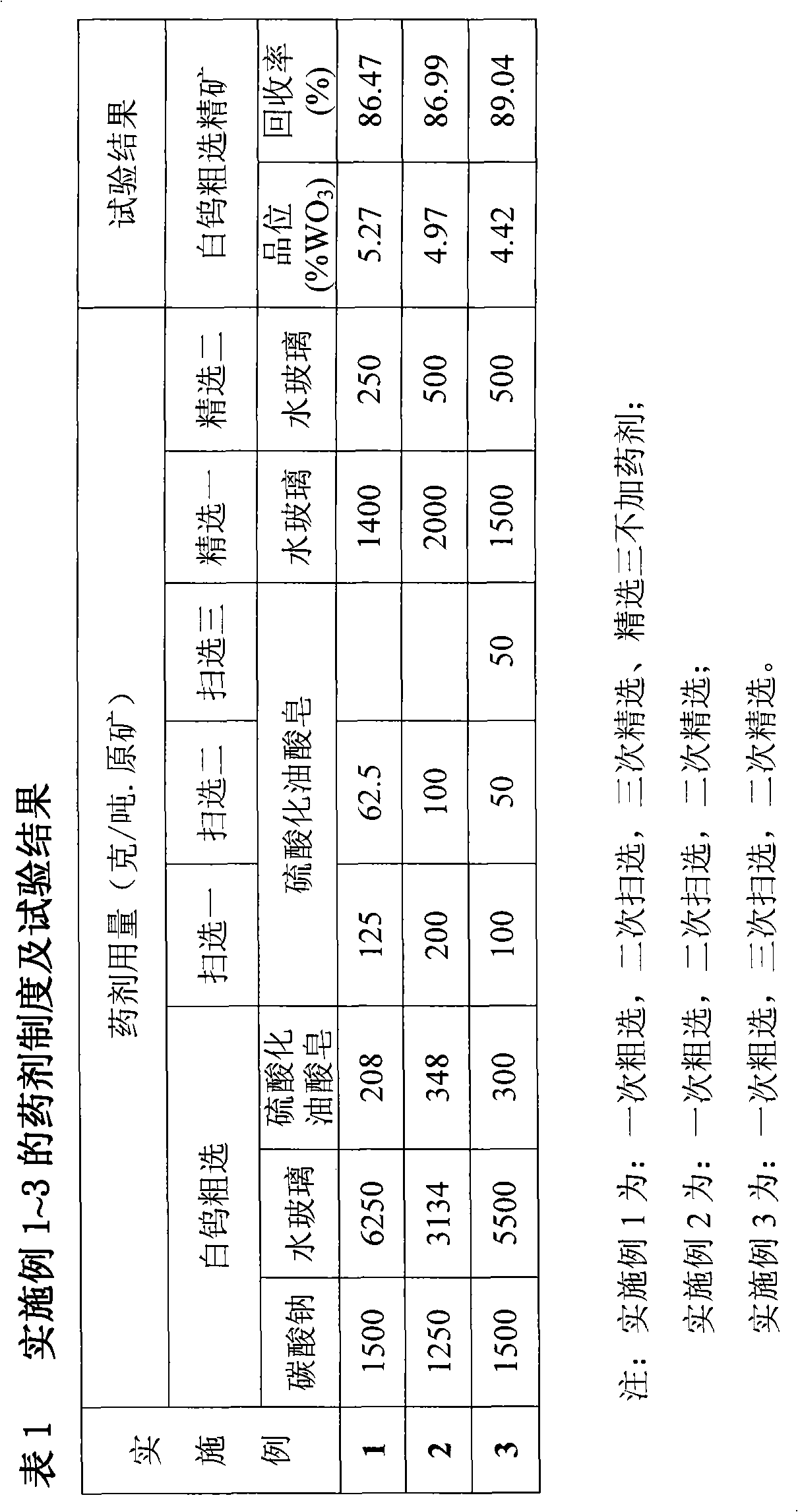
The invention relates to an ore dressing method for recycling scheelite from tungsten ore which is rich in arsenopyrite. The method is characterized in that: (1) the flotation of sulphide ore is performed: the tungsten ore is crushed, ground and floated so as to obtain the sulphide ore and sulphide ore flotation tailing which are mainly composed of arsenopyrite; (2) the rough flotation of scheelite is performed: the sulphide ore flotation tailing is mixed with sodium carbonate and sodium silicate, then is added with a collector, namely, sulfating nascent soap; the scheelite concentrate and the coarse ore and the scheelite coarse flotation tailing are obtained by stirring, rough flotation, fine flotation and scavenging. The method provided by the invention is characterized in that the process is simple, the beneficiation reagent has low cost, the recovery rate of tungsten is high, and scheelite concentrate and coarse ore with the recovery rate of tungsten ranging from 80 to 90 percent and containing WO3 which accounts for 4 to 10 percent is obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
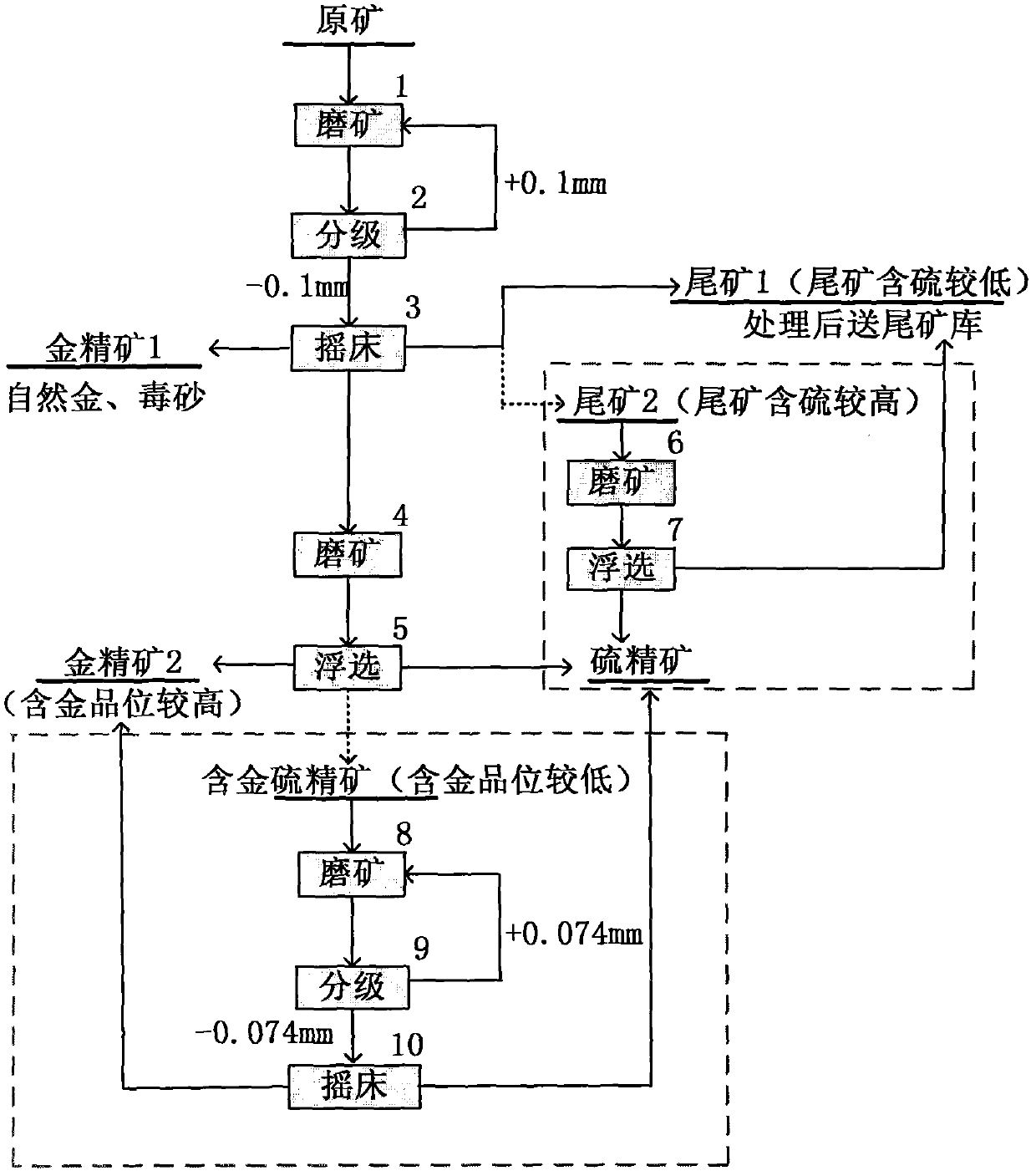
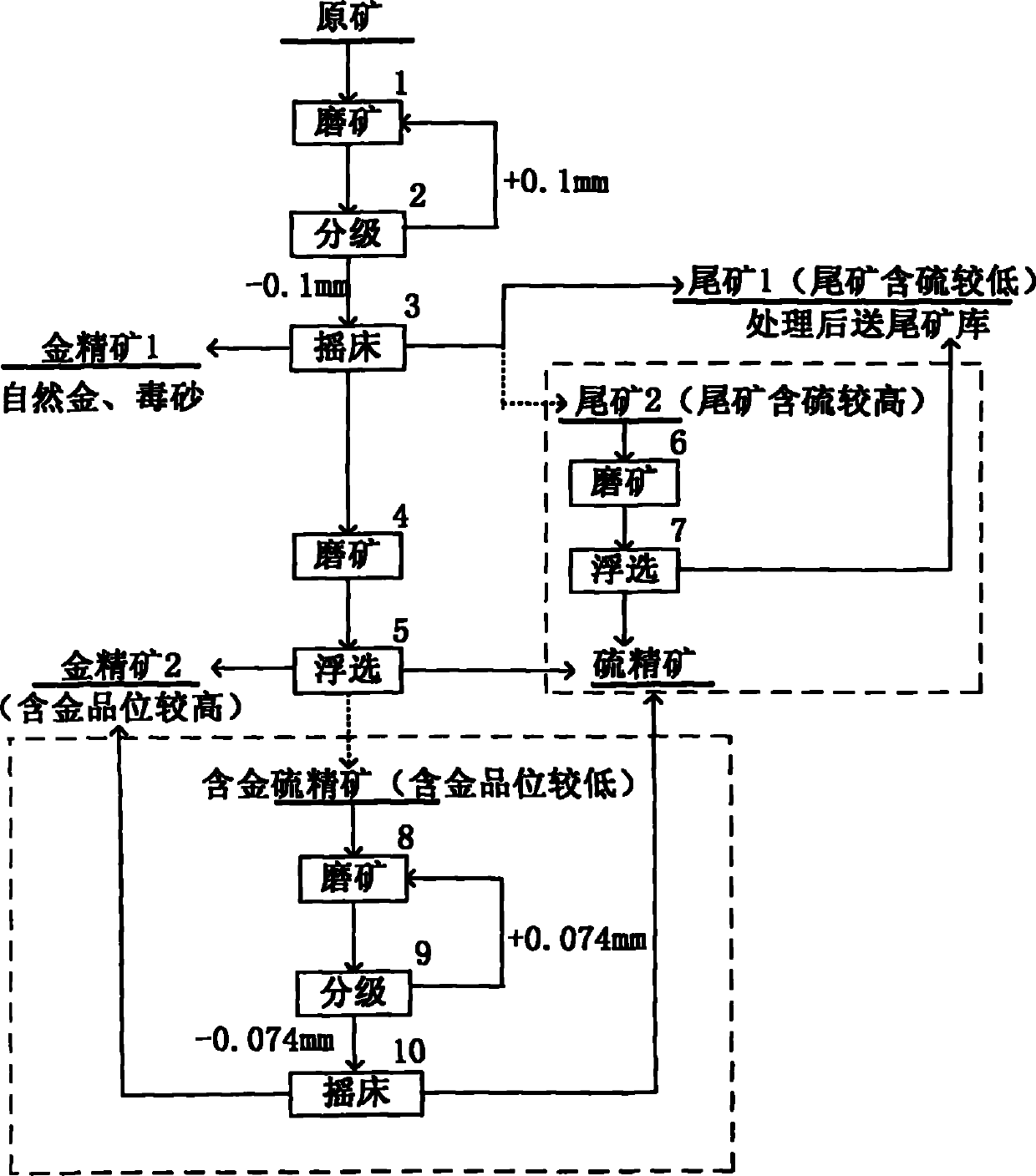
Process for recycling gold from high-arsenic and high-sulfur difficultly treated gold ore
The invention relates to a process for recycling gold from a high-arsenic and high-sulfur difficultly treated gold ore. The process comprises the following steps of: separating natural gold and arsenopyrite from a raw ore through an ore grinding and grading table to obtain gold concentrate 1, tailings 1 or tailings 2; wherein when the content of sulfur in the tailings is low, the tailings 1 are obtained, processing the tailings 1, and directly conveying the tailings 1 to a tailing warehouse; when the content of sulfur in the tailings is high, the tailings 2 are obtained, performing ore grinding floatation on the tailings 2 to obtain sulfur concentrate and the tailings 1; further performing sulfur fine grinding floatation on the ore in the table, wherein the floatation tailings are sulfur concentrate, and the flotation concentrate is gold concentrate 2 or gold-containing sulfur concentrate; when the gold-containing grade of the flotation concentrate is relatively high, obtaining the gold concentrate 2; and when the gold-containing grade of the flotation concentrate is relatively low, obtaining the gold-containing sulfur concentrate, and after ore grinding and grading, further collecting through the table to obtain the gold concentrate 2, wherein the tailings are sulfur concentrate. The grade of the gold concentrate is greatly improved in a processing way that repeated selectionand floatation are combined in the new process; and a large amount of arsenic is collected into the gold concentrate simultaneously, so the utilization rate of sulfur is improved. When an ore sample of which the pyrite grade is relatively high and gold with a large amount is distributed in the pyrite is treated, qualified gold concentrate with certain amount can be still obtained.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method for separating and recovering sulfur and arsenic from sulfur and arsenic containing materials
InactiveCN102240600ASimple processEasy to separateFlotationMagnetic separationEconomic benefitsSulfur containing
The invention relates to a method for separating and recovering sulfur and arsenic from sulfur and arsenic containing materials, comprising the following steps of: firstly inhibiting arsenopyrite and pyrrhotite by adopting an inhibitor to obtain sulfur ores a mainly containing pyrites through floatation; and then separating the pyrrhotite and the arsenopyrite from flotation tailings by adopting magnetic separation so as to obtain arsenic ores and sulfur ores b mainly containing the pyrrhotite. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, effectiveness for separation and recovery of the sulfur and the arsenic, good economic benefit and higher popularization value.
Owner:厦门紫金矿冶技术有限公司
Floatation separation method for pyrites from arsenopyrites
InactiveCN101844108AIncrease oxygen contentElectrochemical conditions for stable flotationFlotationMineral flotationElectrochemistry
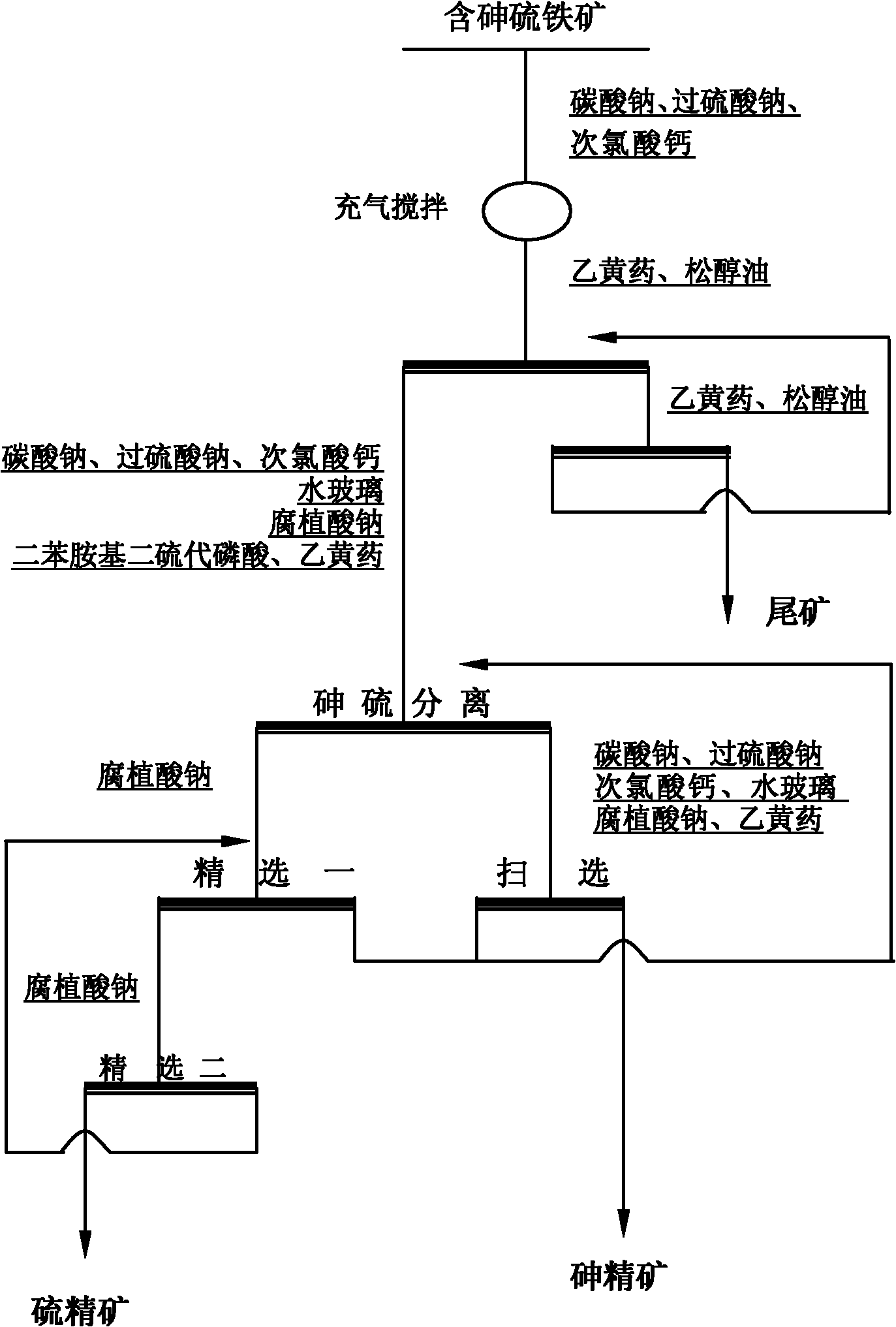
The invention aims at floatation separation of arsenic from sulfur in arsenic-containing pyrites. The floatation separation comprises the following steps of: adjusting an ore pulp to keep the pH value of the pulp between 9 and 10; adjusting the potential of the ore pulp to between 350 and 380 millivolts by adding oxidant medicaments of sodium persulfate and calcium hypochlorite; introducing air to increase oxygen content in the ore pulp; and stabilize electrochemical conditions of mineral floatation. During the floatation separation of the pyrites from the arsenopyrites, the potential of the ore pulp is stabilized by adding the oxidant medicaments of sodium persulfate and calcium hypochlorite; the arsenopyrite is suppressed by using a new collector of dianilino dithiophosphoric acid, and regulators of sodium silicate and sodium humate according to a principle of an electrochemical floatation process to make the pyrites such as arsenopyrites, iron pyrites, pyrrhotites and the like acted with a medicament selectively in the subsequent floatation process; and the floatation separation of the pyrites from the arsenopyrites is performed so as to form a sulfur concentrate with low arsenic content.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Preparation method and application of non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor. The preparation method for the flotation and separation inhibitor comprises the step of enabling phosphorus pentasulfide and alkaline compounds to react with water-soluble macromolecules, and thus the flotation and separation inhibitor can be obtained. According to the preparation method for the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor, operation is easy, the process conditions are mild, the raw material cost is low, and the industrial production requirements are met; and moreover, the prepared product directly serves as the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral inhibitor applied to flotation and separation of molybdenum sulfide minerals and non-molybdenum sulfide minerals, the molybdenum sulfide minerals and the non-molybdenum sulfide minerals can be effectively separated, the grade of molybdenum concentrates is improved, and the flotation and separation inhibitor is particularly suitable for flotation and separation of molybdenite, copper sulfide ore, galena, pyrite, jamesonite, arsenopyrite, bismuth sulfide ore and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
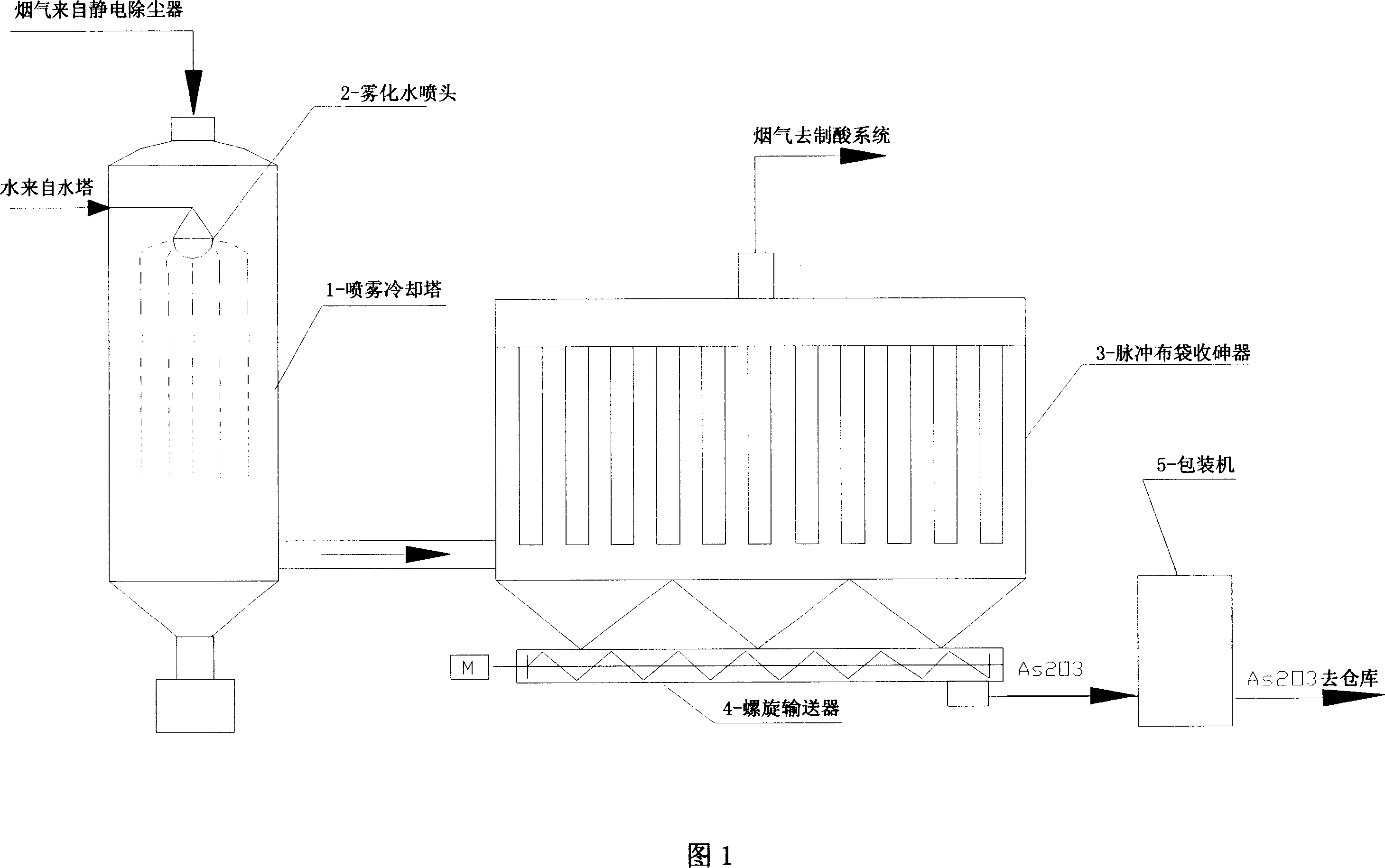
Process for purifying arsenic-containing mineral burned fume
InactiveCN1994531AAchieve the purpose of purificationMeet the technical requirements of the acid production processCombination devicesArsenic compoundsGas coolerEngineering
The invention relates to a method for purifying the burning smoke of arsenic mineral, especially the method for recycling As2O3 from the burning smokes of arsenic aurin mine, arsenic brass, and arsenopyrite, wherein the invention is characterized in that: it uses gas cooler, cyclone dust collector, statistic dust collector, atomizing cooler, pulse bag arsenic collector, ejection tubular washer, stuff tower washer, statistic defroster to treat the smoke to remove the dust, As2O3, SeO2, etc. The invention can produce continuously, with simple and stable operation.
Owner:SHANDONG GUODA GOLD
Separation of copper minerals from pyrite using air-metabisulfite treatment
ActiveUS9346062B2Improve efficiencyIncrease sulfoxy reagent consumptionEvaporationFlotationCopperMaceral
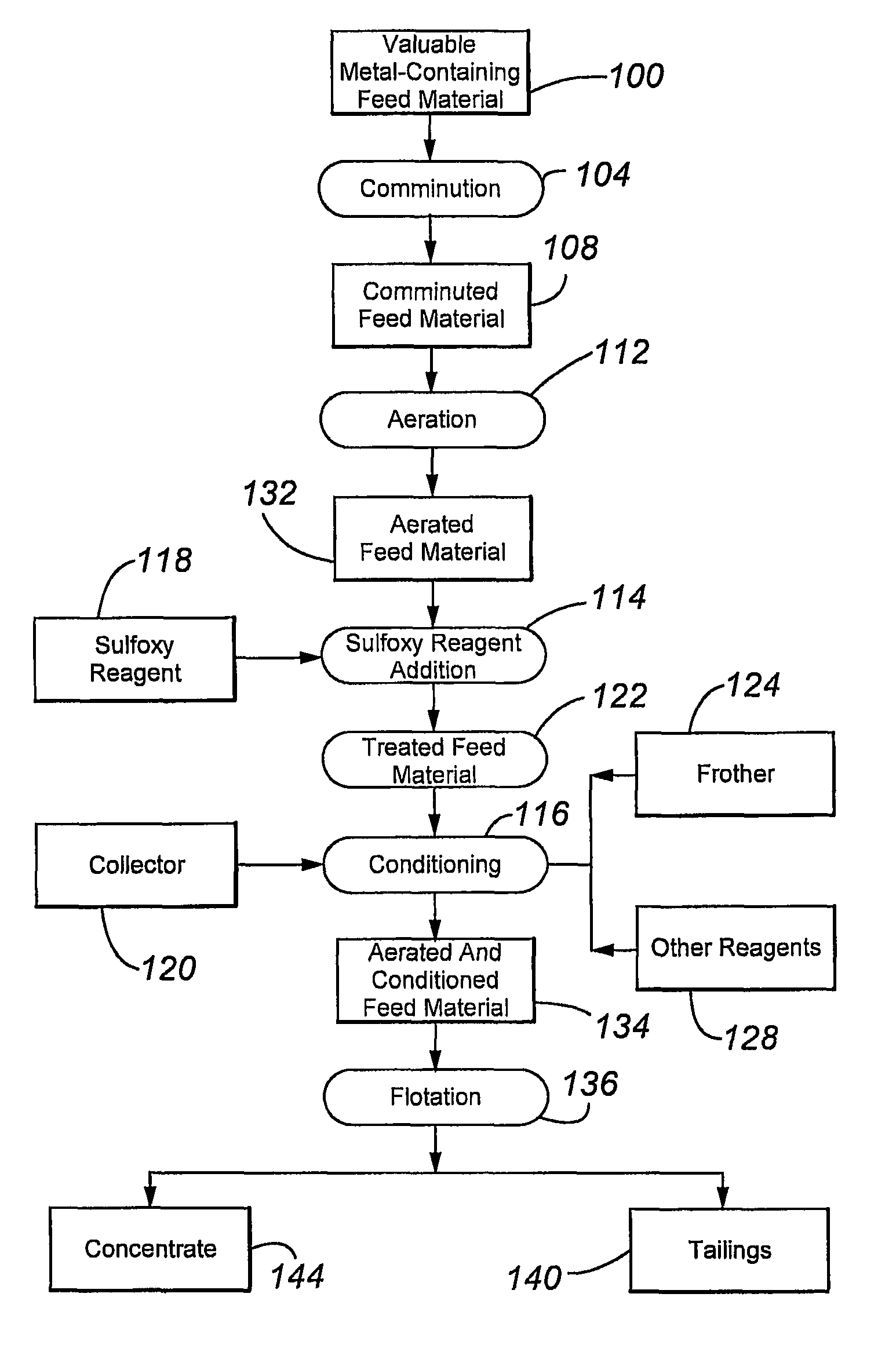
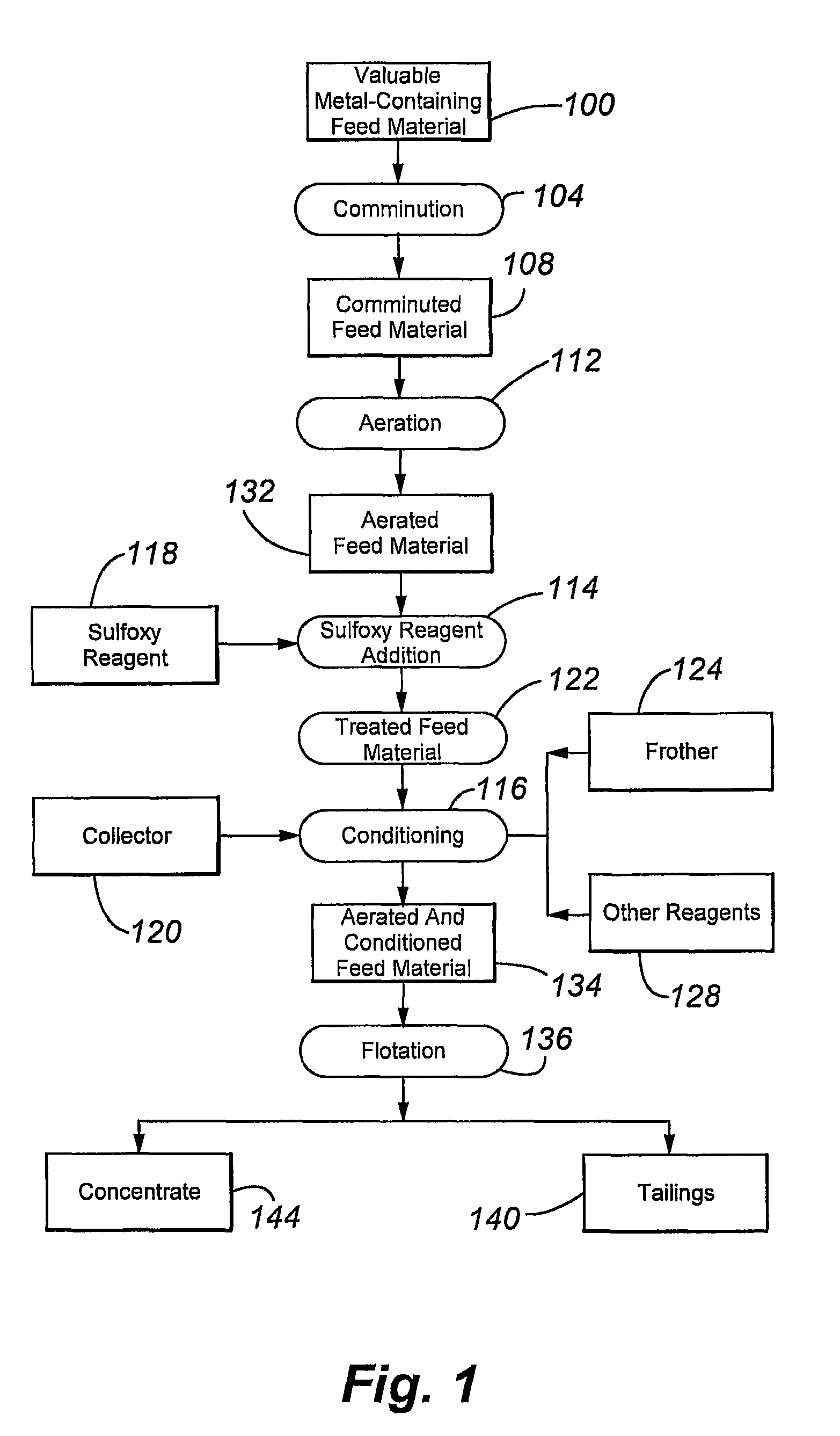
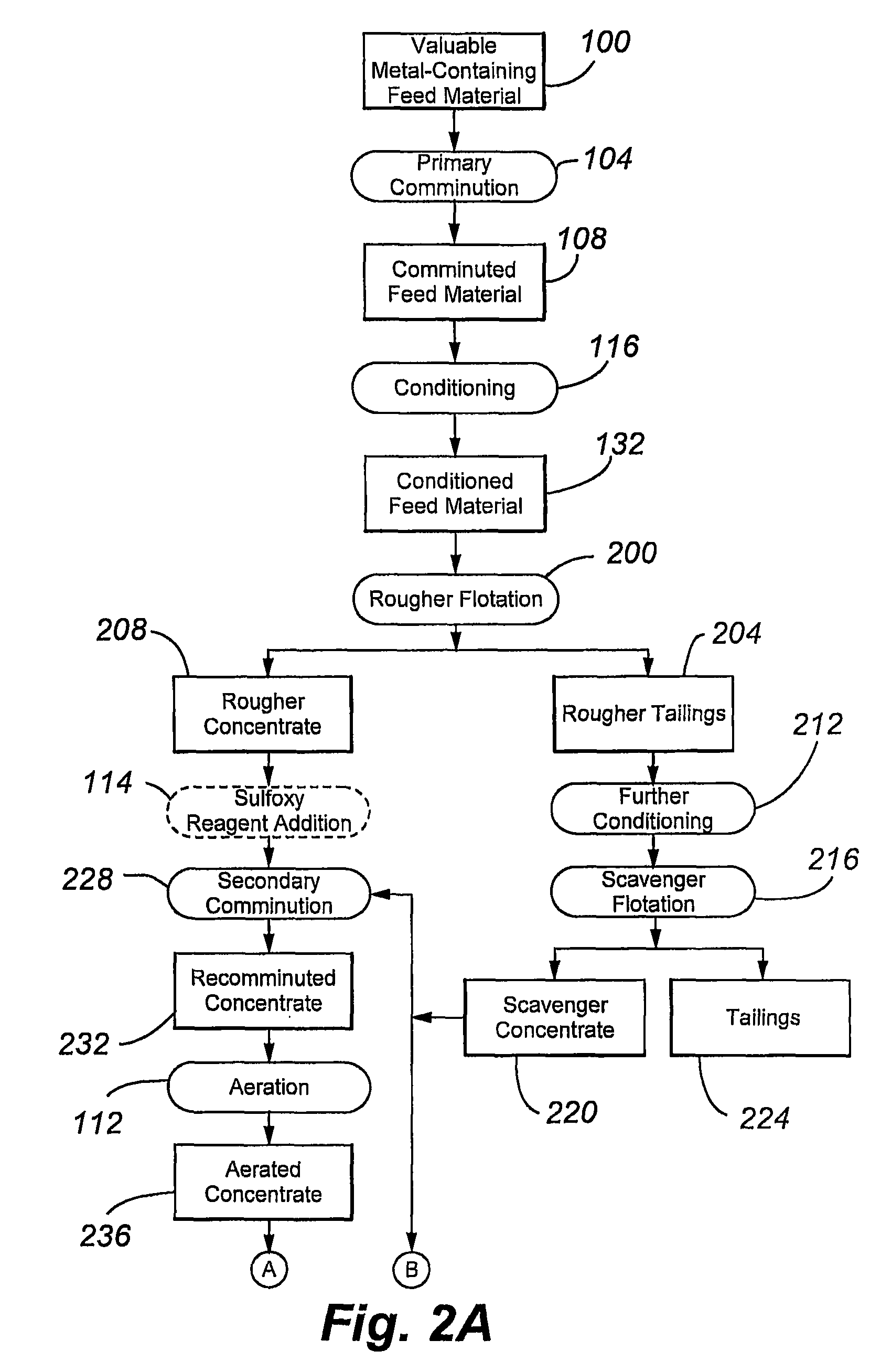
The present invention relates to flotation of sulfidic copper- molybdenum- and gold-containing minerals. More specifically, the invention relates to sulfoxy reagent-assisted flotation for separating of sulfides of copper, molybdenum and gold from pyrite, marcasite, pyrrhotite, arsenopyrite, and other gangue minerals following aerating by an oxidizing gas and contacting by a sulfoxy reagent. To promote collection and flotation the feed mineral materials are preferably not contacted with an externally generated non-oxidizing gas to lower the dissolved molecular oxygen content prior to flotation.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
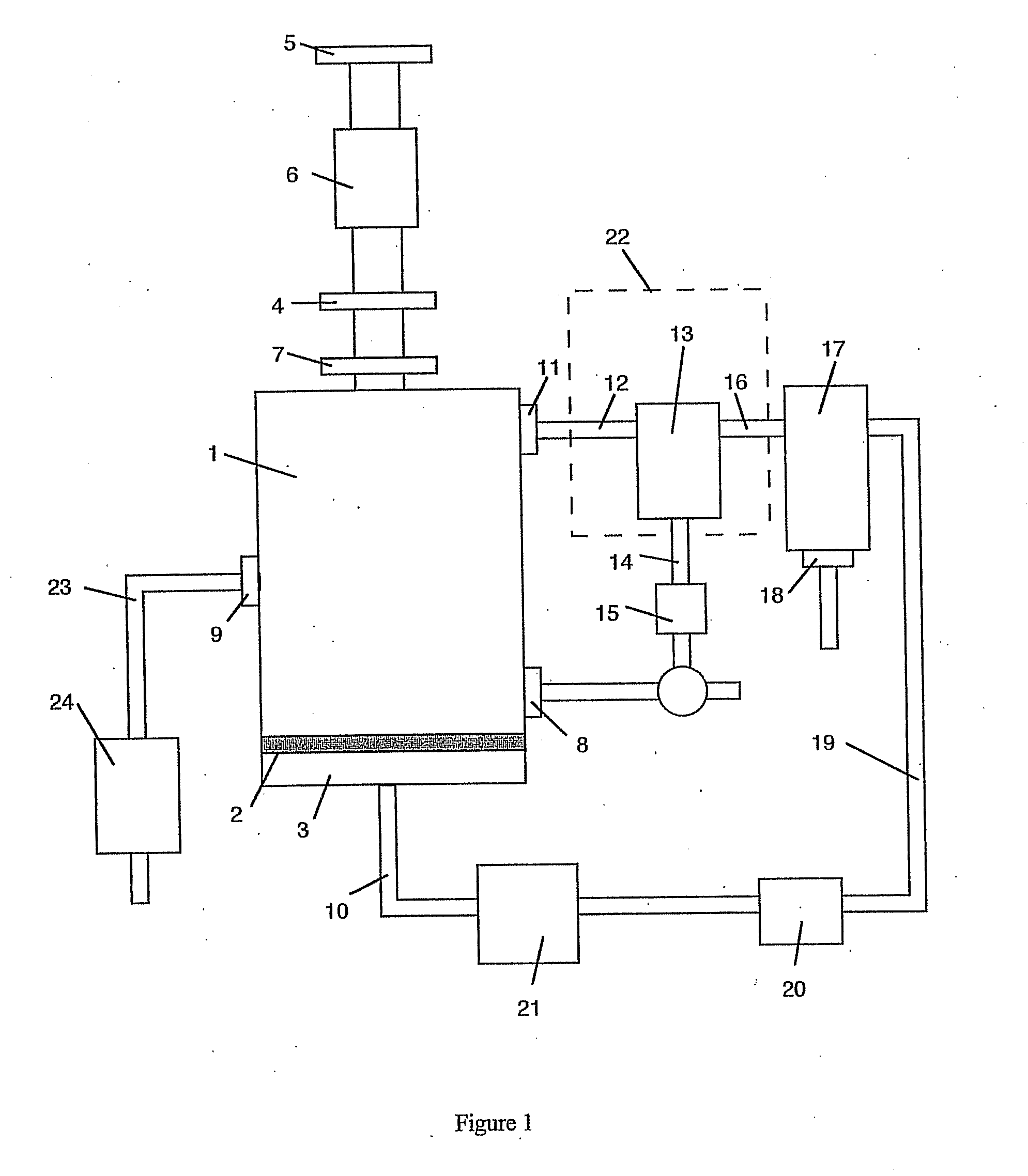
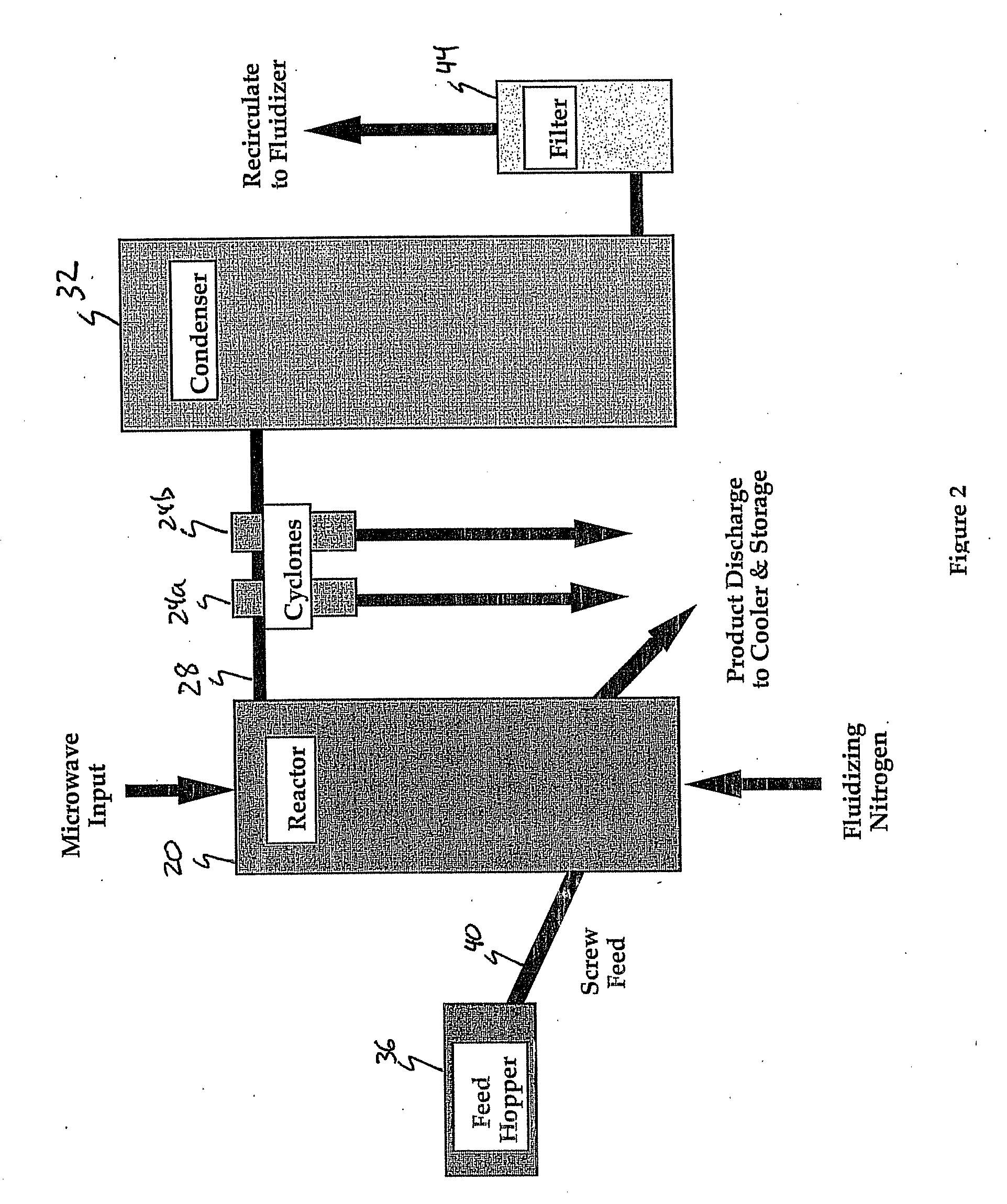
Method and apparatus for microwave induced pyrolysis of arsenical ores and ore concentrates
A method is provided that includes the steps of passing microwave energy through a sulfidic material comprising arsenopyrite and pyrite to reduce at least most of the arsenopyrite to arsenic sulfide and form a calcine, the material being positioned in a reaction chamber of a reactor vessel and removing the arsenic sulfide from the calcine.
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
Application of additive in enhancing oxidization of arsenical gold mineral by bacteria
ActiveCN102634661AOxygenPromote oxidationProcess efficiency improvementBiological oxidationGold deposit
The invention provides an application method of an additive in enhancing oxidization of arsenical gold mineral by bacteria. The additive is ammonium persulfate, and the dosage is 20-50% of total amount of the arsenical gold mineral. Two adding modes are adopted, the first adding mode is adding to a leaching system together with bacteria liquid, and the second adding mode is adding to the leachingsystem after bacterial leaching for a certain period of time. When the first adding mode is adopted, the additive mainly contains oxidized arsenical pyrite, the dosage of the additive is increased to50% from 0%, and the oxidation rate of the arsenical pyrite is increased to 95% from 8.7%. When the second adding mode is adopted, the additive mainly contains As(III) in oxidizing solution, the dosage of the additive is increased to 50% from 0%, and the oxidation rate of As(III) is increased to 91.12% from 4.9%. Reproduction and activity of the bacteria are not affected after the additive is added; the oxidation of the arsenical pyrite or As(III) can be obviously enhanced in an oxidization process; the problem of toxicity of a biological oxidation product can be solved, and the application method becomes an important measure for increasing the speed of oxidizing the arsenical gold mineral by the bacteria.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
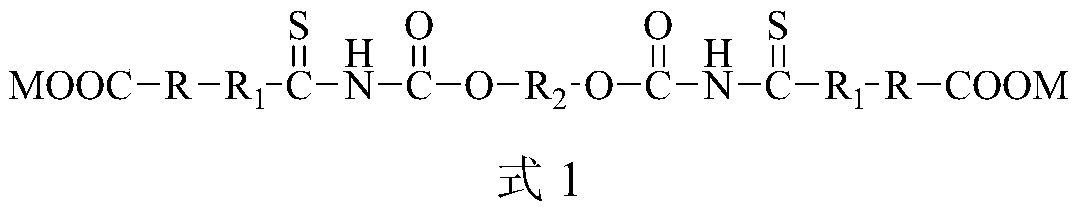
Ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105801458ASpecial molecular structureHas surfactant propertiesOrganic chemistryFlotationChloroformateNickel sulfide
The invention provides an ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or an ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular structure of the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative contains a large quantity of thioamide or thiourea or thioacid amide ether or other lipophilic groups and carboxyl hydrophilic groups. The preparation method includes the steps that bis-chloro-carbonic ester and thiocyanate are subjected to a substitution reaction, an intermediate product containing bis-acyl bis-isothiocyanate is generated, the intermediate and an alcohol compound or an amine compound or a phenol compound are subjected to an addition reaction, and then the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative is obtained. The preparation method is simple, the prepared product directly serves as a non-molybdenum sulphide ore inhibitor, and floatation separation of molybdenum sulfide ore and the non-molybdenum sulphide ore can be effectively achieved. The preparation method is especially suitable for separation of molybdenite and copper sulphide ore, galena, sphalerite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, jamesonite concentrate, nickel sulfide ore, bismuth sulfide ore and the like, and the grade of molybdenum concentrate is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for reinforcing bacterial preoxidation of arsenic-containing gold ore
The invention provides a method for reinforcing bacterial preoxidation of an arsenic-containing gold ore. Two additives (separately silver nitrate and ferric sulfate or ferric nitrate) are added. When being in use, a chloride-free 9K solution is prepared with the concentration of Ag(I) and Fe(III) reaching 0.005-0.05 g / L and 1-10 g / L respectively; then the arsenic-containing gold ore is added to the solution; and finally, a certain amount of a bacterium liquid is inoculated to the system for bacterial preoxidation. Under the synergistic effects of Ag(I) and Fe(III), the bacterial oxidation rate of the arsenic-containing gold ore can reach higher than 90%; and oxidation time is greatly shortened. On one hand, the synergistic reinforcement of Ag(I) and Fe(III) accelerates the dissolution of the arsenopyrite; on the other hand, toxicity of As (III) in the system toward to the bacteria is lowered, so that the bacterial oxidation of the arsenic-containing gold ore is reinforced; and important theoretical and technical guidance for increasing efficiency bacterial preoxidation-cyanide gold leaching process of the gold ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
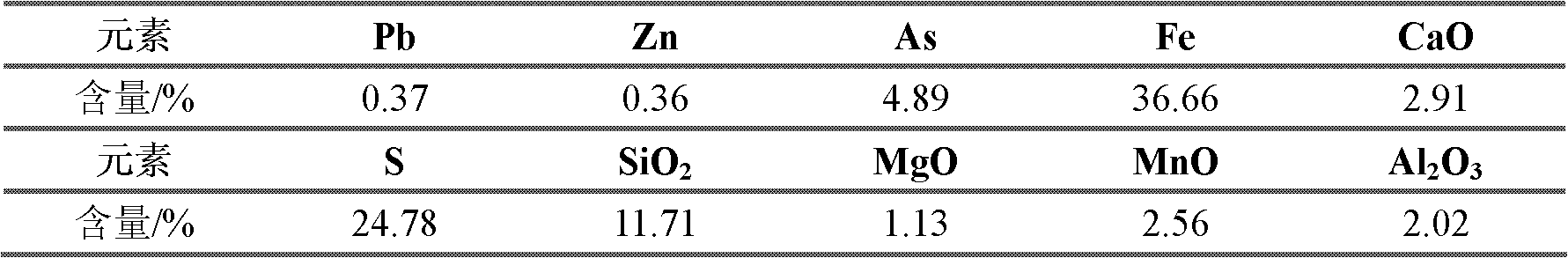
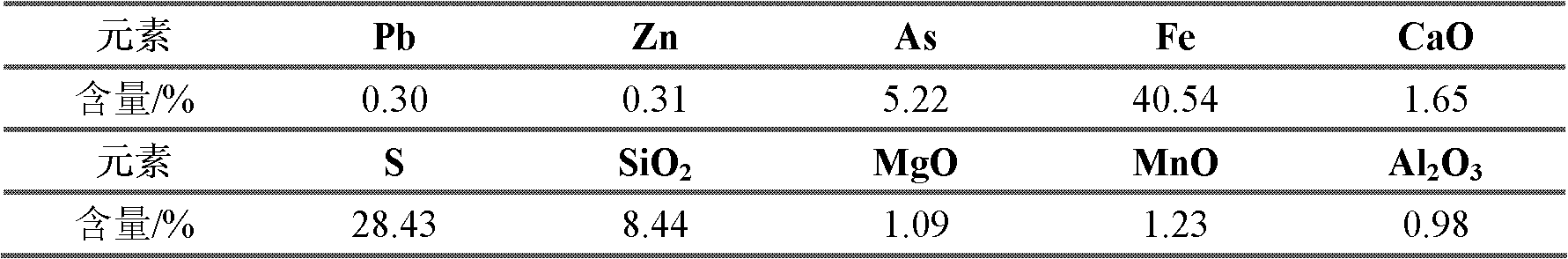
Arsenic-reducing mineral processing process for high-arsenic sulfur concentrate rich in tin copper associated sulphide minerals
The invention discloses an arsenic-reducing mineral processing process for high-arsenic sulfur concentrate rich in tin copper associated sulphide minerals. The arsenic-reducing mineral processing process comprises the following steps: grinding minerals and scrubbing to remove reagents after carrying out concentration dehydration on the high-arsenic sulfur concentrate rich in the tin copper associated sulphide minerals, adding an arsenic-reducing inhibitor to re-inhibit arsenopyrite minerals, feeding the high-arsenic sulfur concentrate to a full-floating arsenic-reducing mineral processing process of primary roughing, secondary scavenging and primary concentration after size mixing, wherein a low-arsenic high-sulfur sulfur concentrate product is produced by adding a combined arsenic-reducing inhibitor; carrying out gravity separation by a shaking table on tailings subjected to secondary scavenging, thereby obtaining arsenic and tin mixed minerals and total tailings; and separating the arsenic and tin mixed minerals, thereby obtaining an arsenic concentrate product and a tin rough concentrate product. The arsenic-reducing mineral processing process is good in separating effect of sulfur and arsenic in the tin copper associated sulphide minerals, and is high in sulphide mineral recovery rate, so that valuable minerals are comprehensively recycled and utilized, and the reagent cost is low; and the method is simple, and is easy to operate.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN
Bacterial oxidation pretreatment and cyanidation gold extraction method of arsenopyrite and realgar type refractory gold ores
The invention relates to a bacterial oxidation pretreatment and cyanidation gold extraction method of arsenopyrite and realgar type refractory gold ores, comprising the following steps of: inoculating a mixed bacterial solution containing CCTCC NO: M209074 and CCTCC NO: M207215 to a 9K culture medium for culturing; adding ore powder to a bacterial culture solution; carrying out bacterial oxidation pretreatment at the temperature of 44-60 DEG C, wherein pH is 0.8-2.5; charging air and stirring for 4-8 days, wherein the aeration rate is 0.1-0.3m3 / h and the stirring rate is 600-1400 turns / min; adding water to bacterial oxidation slag and blending into a slag slurry; regulating the pH value of the slag slurry to 9.0-12; then adding sodium cyanide, wherein the pH value in the cyanidation process is 9.0-12, and the cyanidation time is 24-48 hours. The leaching rate of gold is greatly increased and can reach by more than 94 percent after cyanidation leaching is carried out on the bacterial oxidation treated bacterial oxidation slag, and the economic benefit is extremely remarkable.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
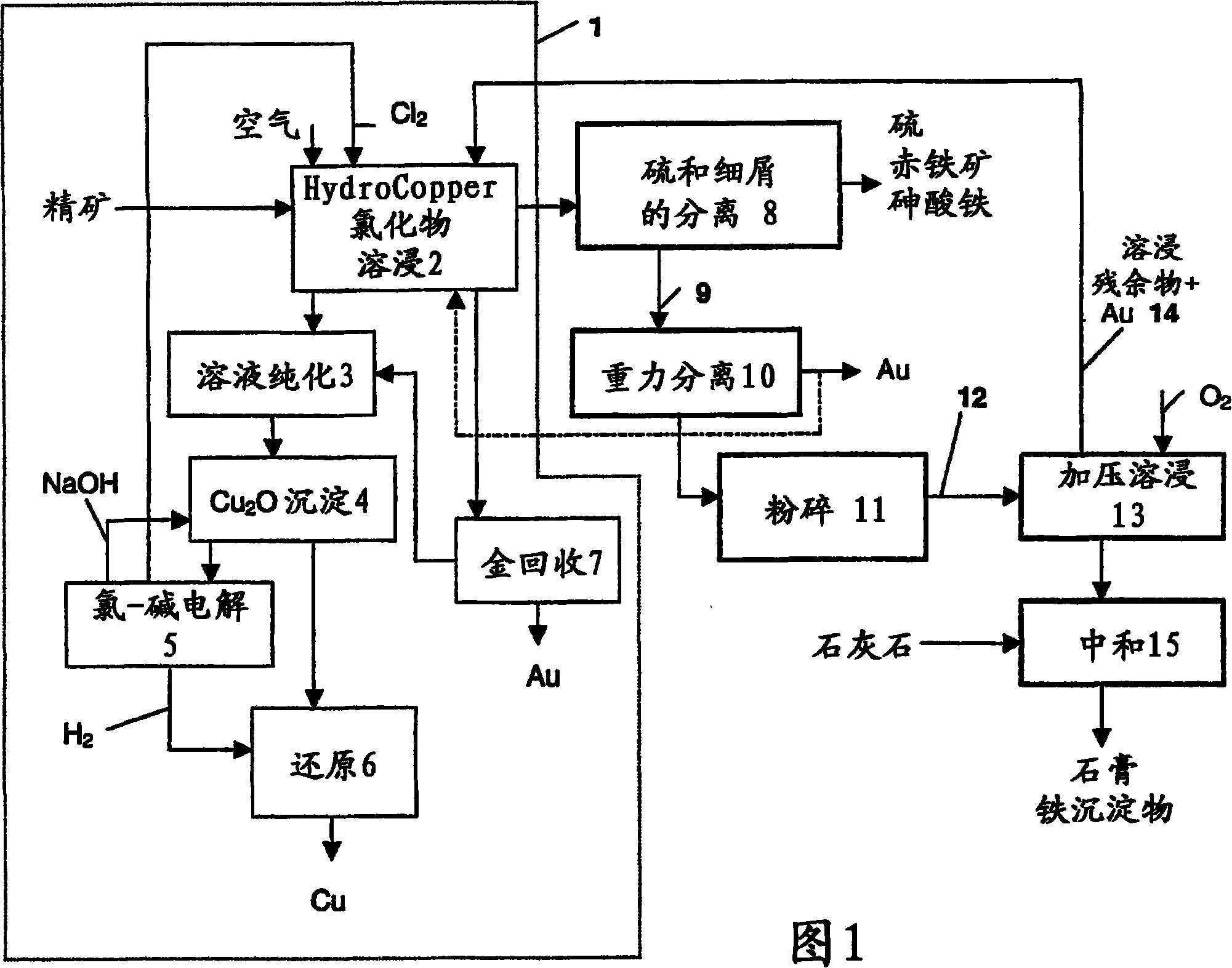
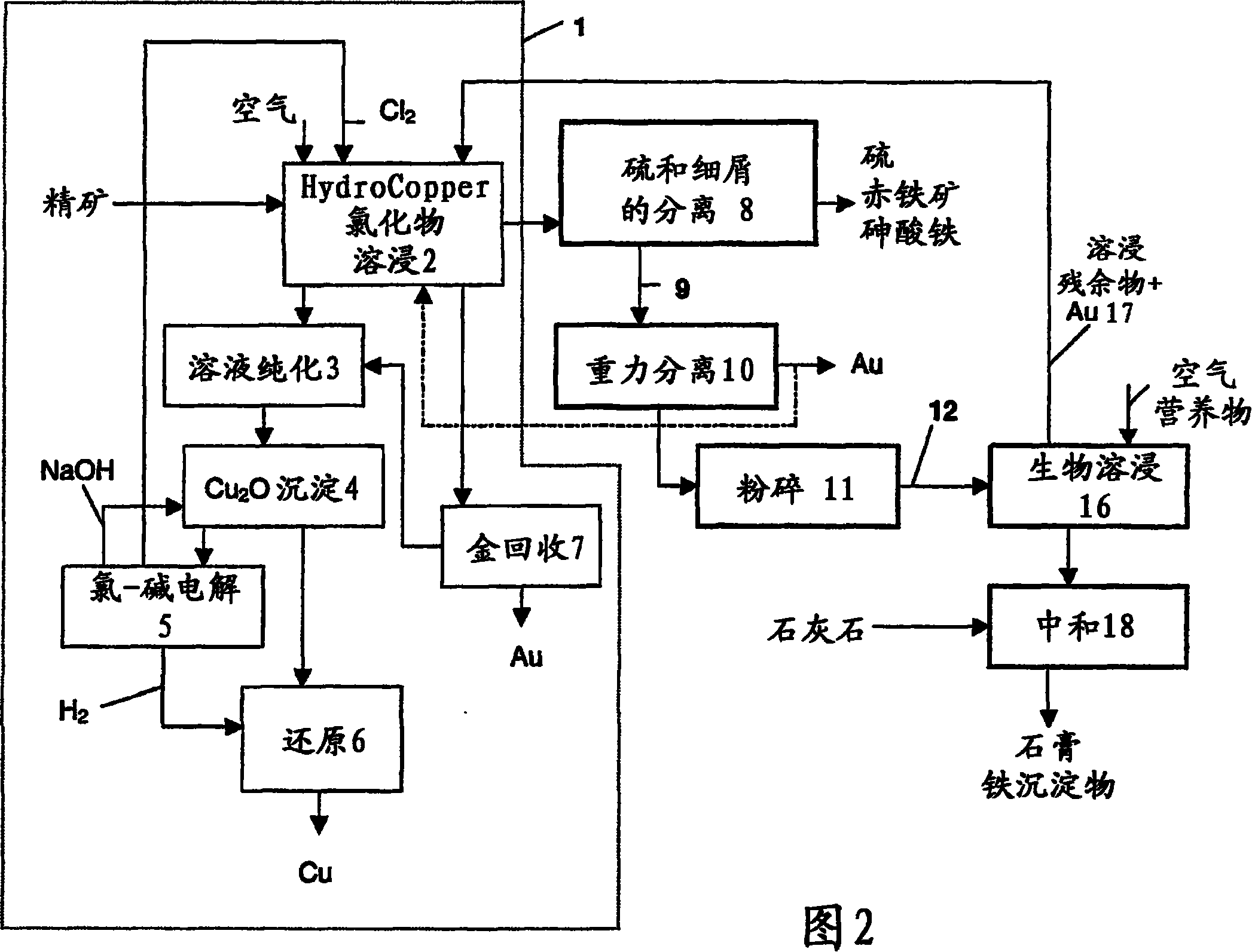
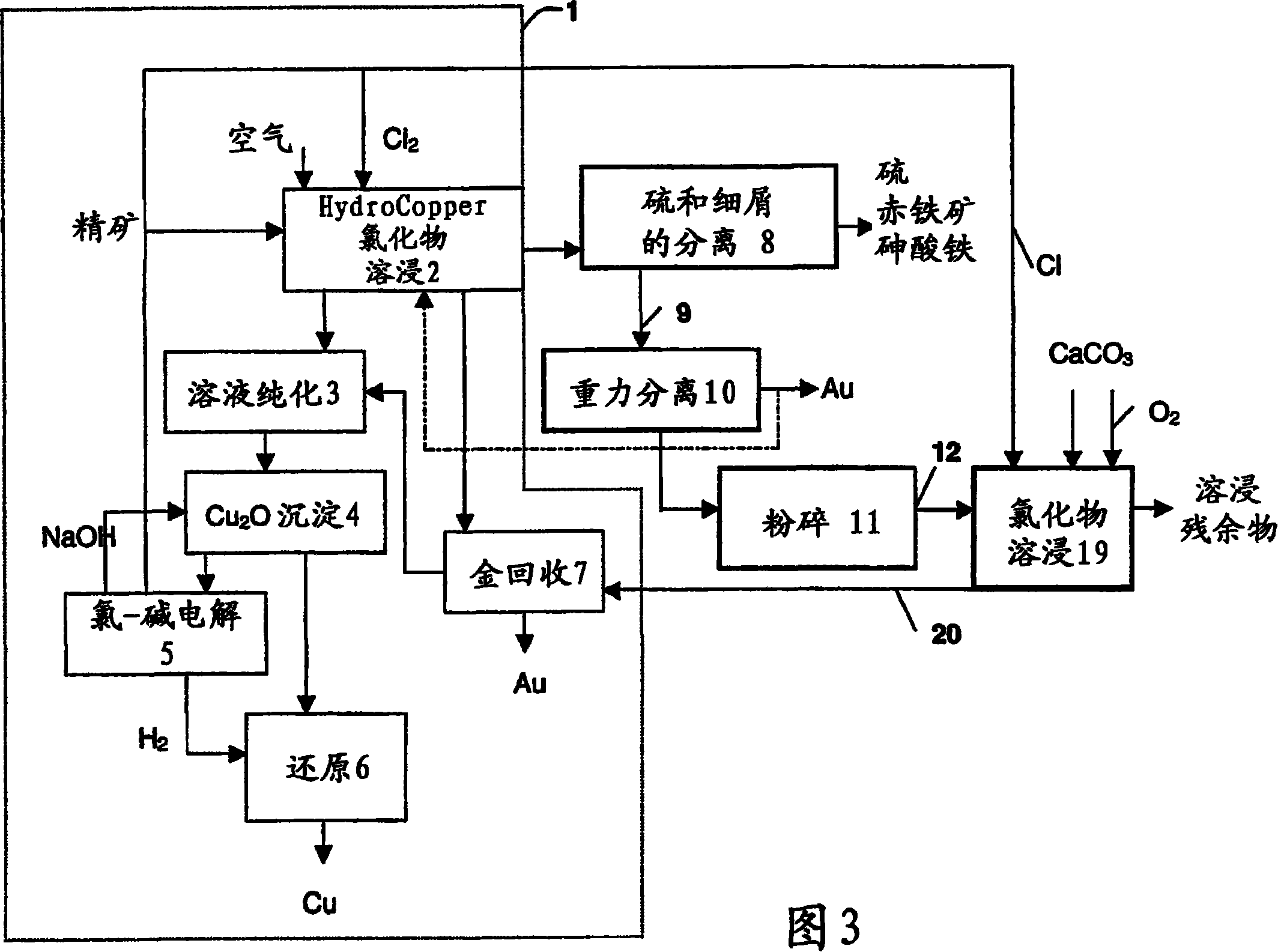
Method for the recovery of gold from sulphide concentrate
InactiveCN101120106AThe leaching rate is acceleratedLess investmentProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgySulfide minerals
The invention relates to a method for recovering gold from a sulphidic concentrate, particularly one containing arsenopyrite and / or pyrite, hydro- metallurgically. The concentrate is first subjected to leaching with a concentrated solution of alkali chloride and copper (II) chloride, by means of which the copper minerals and some of the gold in the concentrate are made to dissolve. Elemental sulphur and precipitated iron and arsenic compounds are separated from the leaching residue using physical separation methods, whereby the first intermediate is obtained, which contains gold- bearing sulphide minerals and gangue minerals as well as the gold that remains undissolved. The free gold that remains undissolved is separated by means of gravity separation methods. After gravity separation, additional comminution is carried out, after which the sulphide minerals are decomposed and the gold-containing solution or residue is routed to the concentrate leaching circuit.
Owner:OUTOTEC OYJ
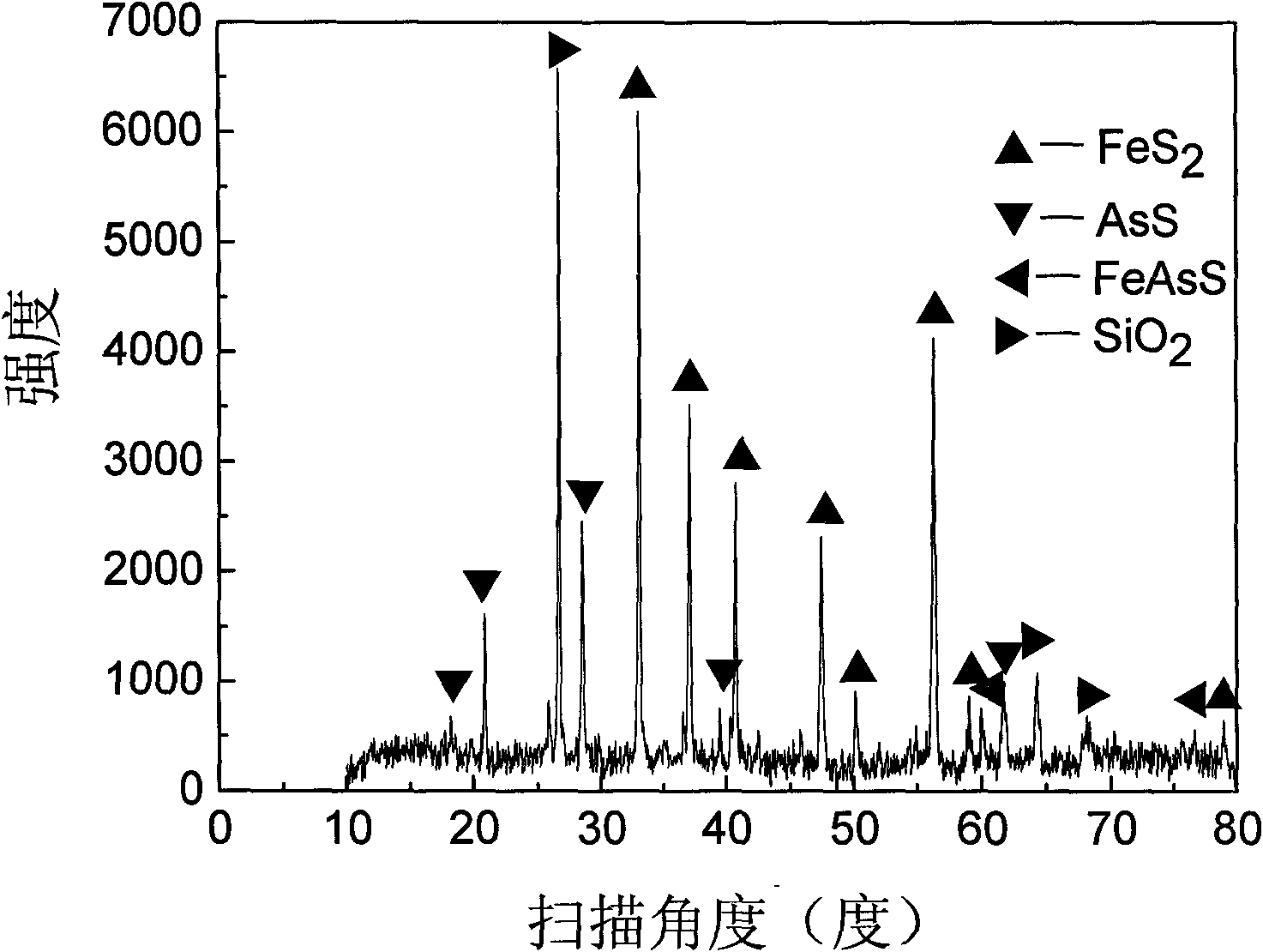
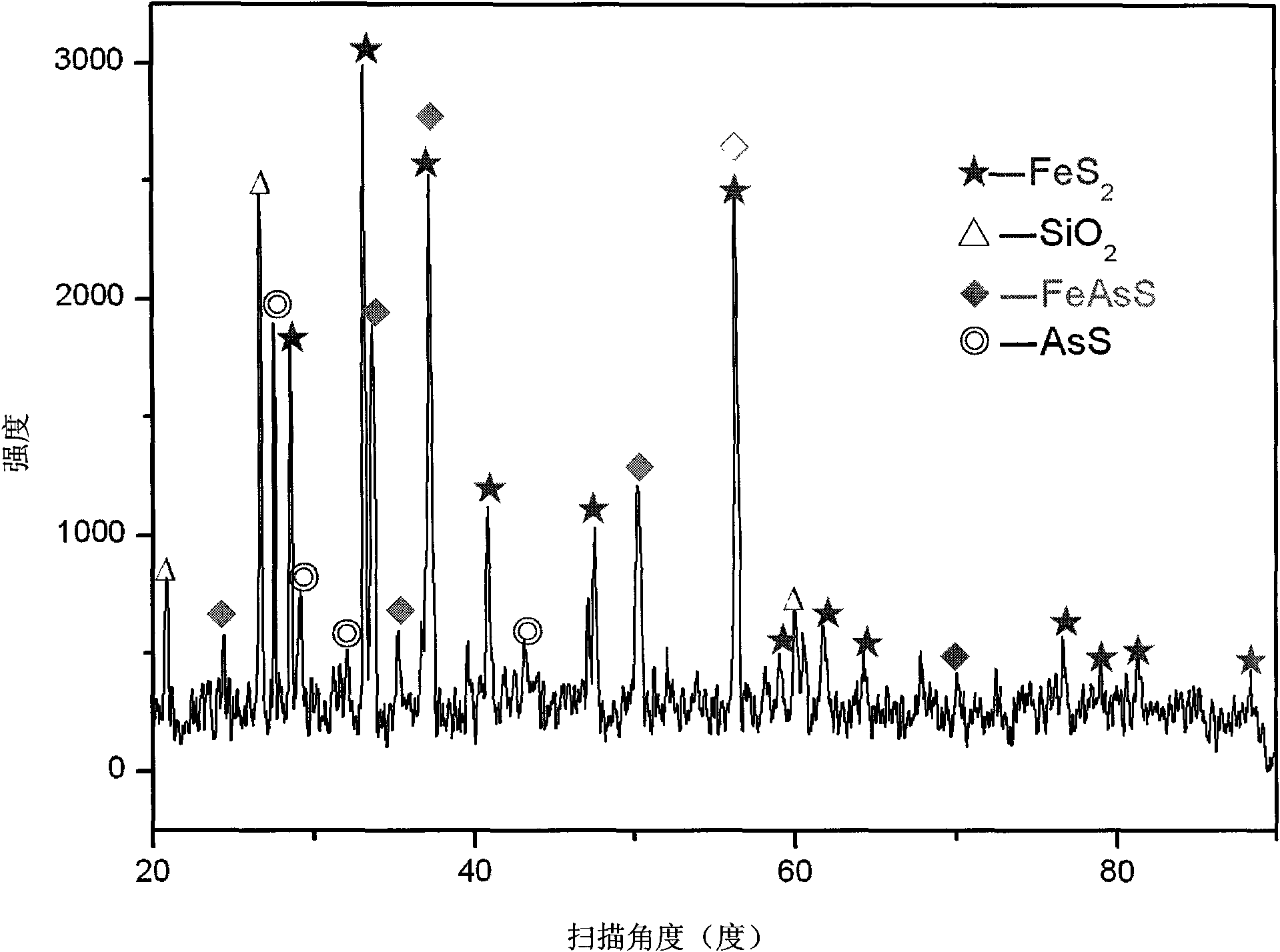
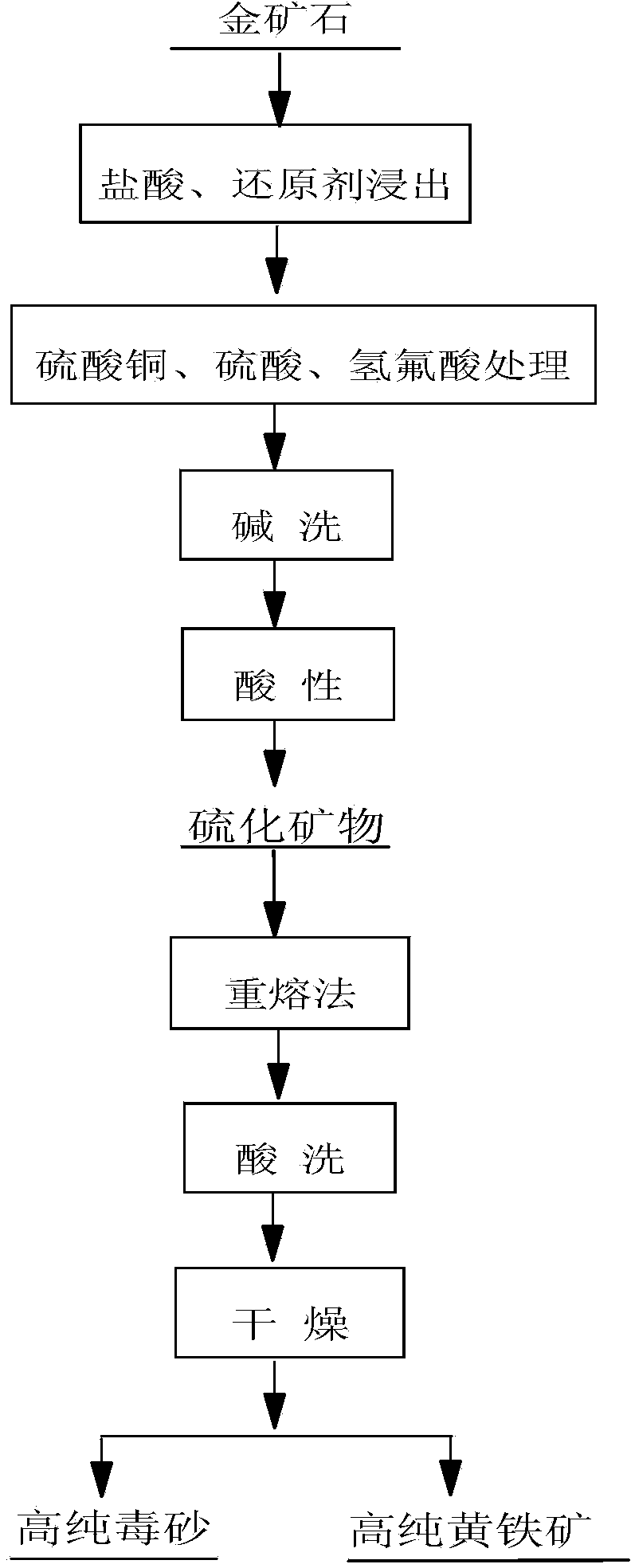
Method for extracting high-purity pyrite and arsenopyrite from carlin-type gold deposit
The invention relates to a method for extracting high-purity pyrite and arsenopyrite from carlin-type gold deposit. The method comprises the following steps of: selectively leaching other minerals from ore containing pyrite and arsenopyrite by using chemical agents, recycling the pyrite and arsenopyrite, and then separating pyrite from arsenopyrite using silver iodide-silver nitrate in a melting state. The method is simple in process, and is not limited by the particle size and dissociation degree of minerals. The obtained gold-bearing pyrite and arsenopyrite have high purity of minerals, less impurity, and regular surface, and are basic materials used in the basic research field such as surface structure, flotation reagent, oxidation and the like which are related to ore dressing, metallurgy, thereby solving the problem for preparing single-mineral raw material of the high-purity gold-bearing pyrite and arsenopyrite which are researched.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Flotation process for arsenic-containing pyrite
InactiveCN103212481ASimple systemSulfur and arsenic separation effect is goodFlotationHydrogenSulfur
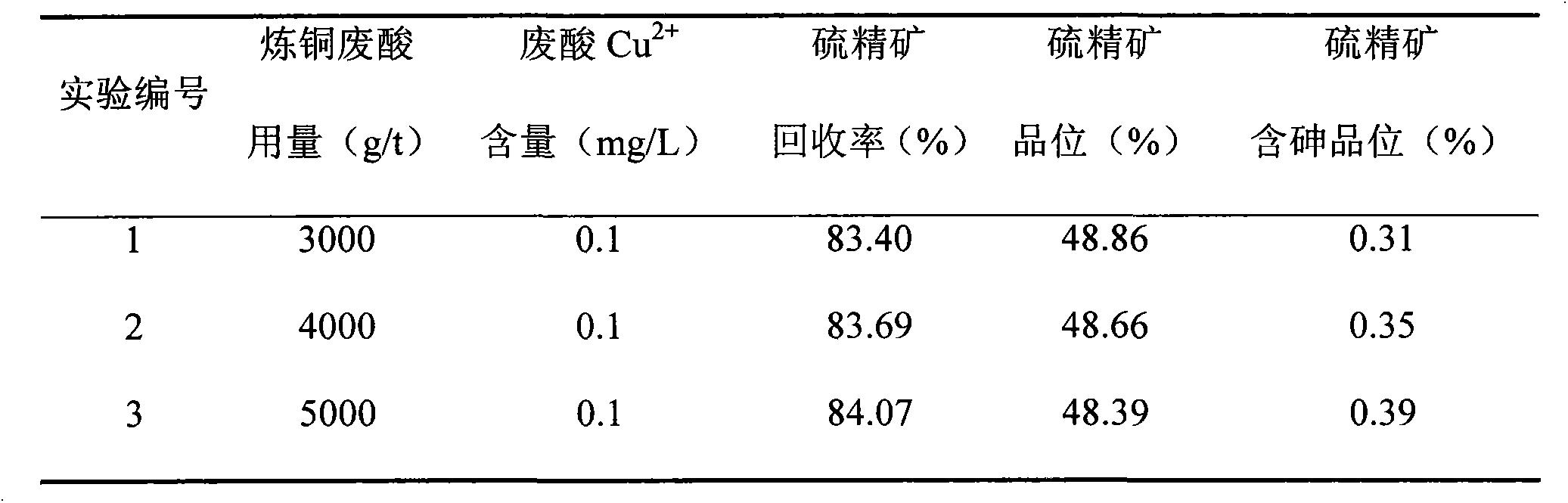
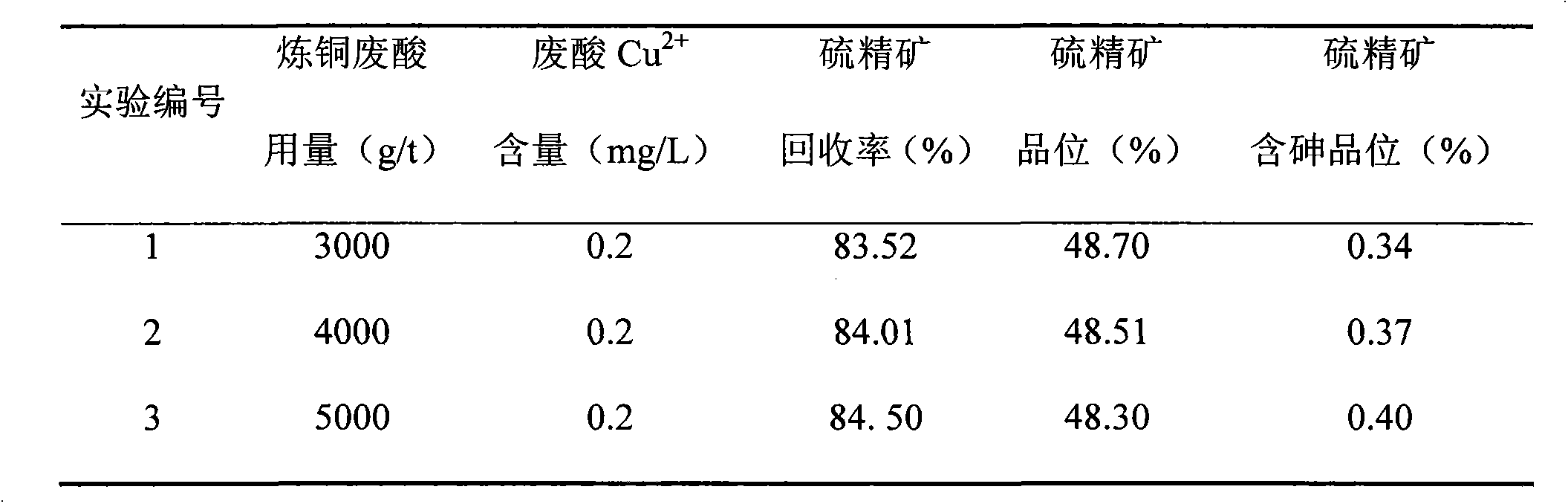
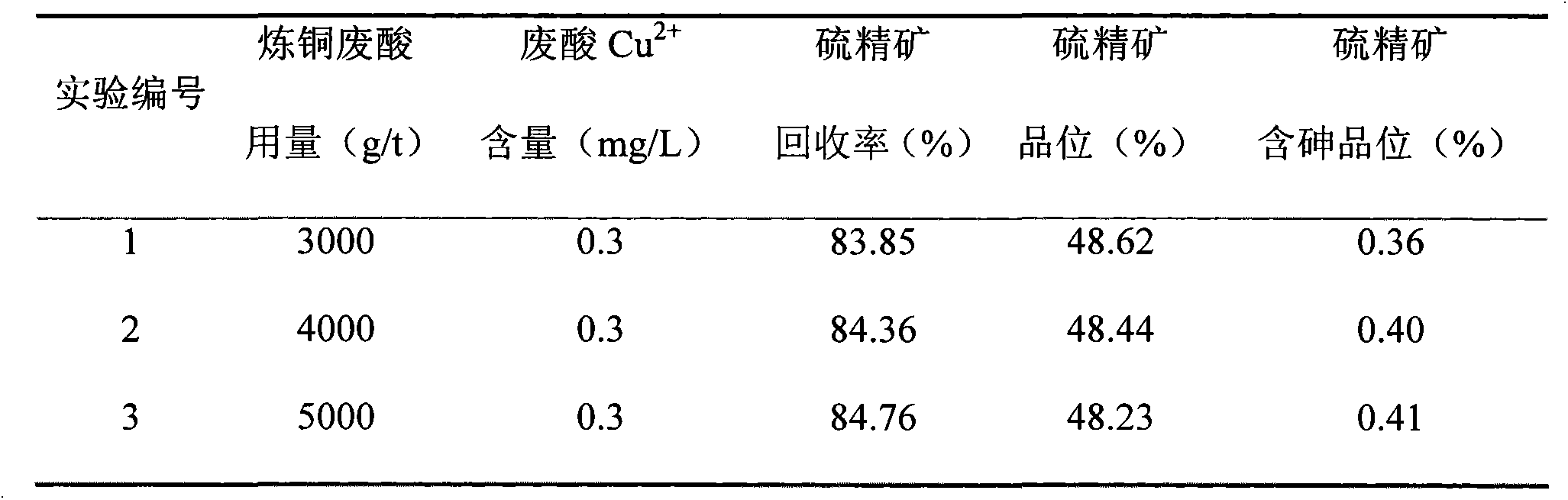
The invention relates to a flotation process for arsenic-containing pyrite. The method comprises the following steps: grinding ore through an ore mill until monomer separation and then entering a flotation process; adding copper smelting waste acid as an activator of pyrite; adjusting the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value to be 6-7; and adding an arsenopyrite inhibitor, a collector and pine oil to perform pyrite flotation so as to obtain low-arsenic sulfur concentrate. The copper smelting waste acid adopted by the flotation process is waste acid stock solution of a copper smelting plant, and the using amount is 3,000-5,000 g / t; and Cu<2+> included in the copper smelting waste acid is 0.1-0.3 mg / L. The process has the advantages of simple flow, low medicament cost, capability of recycling the copper smelting waste acid of the copper smelting plant, low-arsenic high-sulfur sulfur concentrate can be obtained by the process, and the process has good industrialapplicationprospect.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for breeding and separating high arsenic oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to a method for breeding and separating mineral leaching bacteria from an environmental sample, wherein the mineral leaching bacteria have high arsenic resistance and can efficiently oxidize arsenious sulfide ore, particularly arsenopyrite. The sample is made into turbid liquid, a culture medium 1 is inoculated in the turbid liquid, first-generation richment is obtained by means of shake culture at the temperature of 30 DEG C, a culture medium 2, a culture medium 3 and a culture medium 4 are sequentially added in the first-generation richment, three generations of richment are continuously cultured under the same conditions, and finally fourth-generation richment is obtained. The fourth-generation richment is continuously diluted and separated at the same temperature, and finally, dilution 4 is obtained, namely purified high arsenic oxidizing bacterial strains are obtained. Gold concentrate with containing 19.2% of arsenic is pre-oxidized, the arsenic content of oxidizing slag can be reduced by 93.02%, and the weight of the oxidizing slag can be reduced by 51.24%. Gold extraction experiments indicate that the gold leaching rate of the oxidizing slag reaches 95.78% and is five times that of the gold concentrate not pre-oxidized by the bacteria.
Owner:INST OF BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES JIANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Sunlight greenhouse seedling-raising method for improving Chinese angelica germination rate
InactiveCN104396485AImprove germination rateBudding stimulationSeed and root treatmentGrowth substratesCotton clothControllability
The invention discloses a sunlight greenhouse seedling-raising method with which a Chinese angelica germination rate can be improved. The method comprises the steps of: (1) seed treatment; (2) seedbed preparation; (3) greenhouse controllability improvement; (4) sowing; (5) stem cutting and root insertion; and (6) seedling hardening. The method is characterized in that in the step (1), seeds are scrubbed by using arsenopyrite for removing seed wings, and are sprayed by using sterile water; the seeds are wrapped by using white cotton cloth for 1-2 days for regaining moisture; the seeds are subjected to ultrasonic processing for 30-50min; 0.35-0.40% alpha-sodium naphthylacetate is used for spraying, and the seeds are flatly paved in one layer on a filter paper; the seeds are wrapped by using the filter paper and are buried in composite nutritive soil for germination-promotion for 5-10 days; after germination-promotion, the seeds are sterilized by using 0.1g / L mercuric chloride for 5-6min, and are sterilized by using 0.1g / L sodium hypochlorite for 2-3min. In the step (5) stem cutting and root insertion, when seedlings grow to a height of 3-5cm, 1-1.5cm of aerial stems are cut, and the incisions are sterilized by using 0.1g / L mercuric chloride for 5-6min; the cut stem segments are adopted as female parents, and are transplanted into a germination medium for seedling-raising; and the stem cutting and root insertion seedling-raising step is circulated 2-3 times.
Owner:定西市农业科学研究院
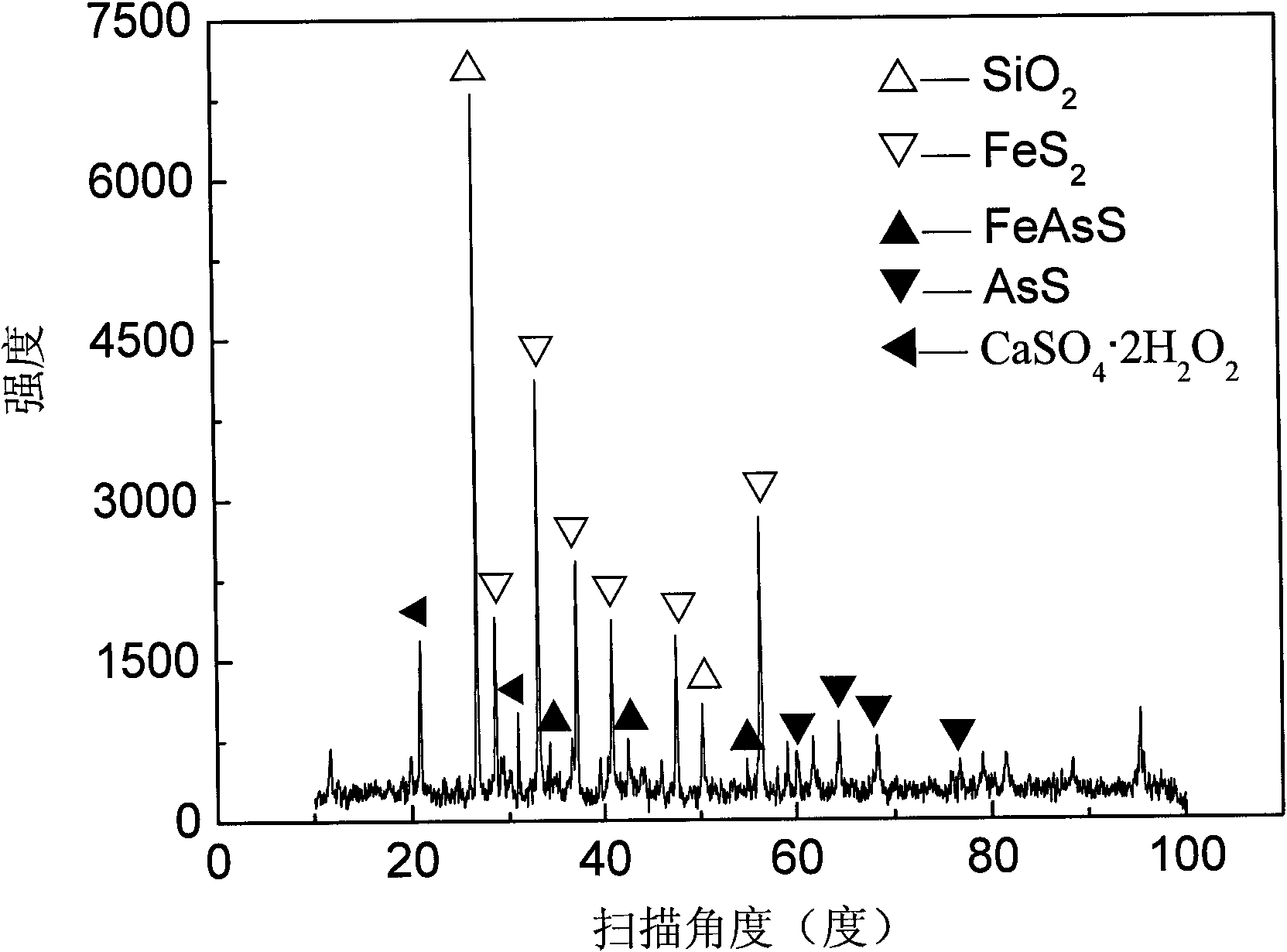
Preparation method of inhibitors for arsenic-containing sulfide minerals in copper tailings
The invention discloses a preparation method of inhibitors for arsenic-containing sulfide minerals in copper tailings. According to the method, for the characteristic that the surfaces of arsenopyrite and pyrites in the copper tailings have been oxidized, the inhibitor with the electrochemistry reducibility is used for eliminating oxidation products on the surfaces of the arsenopyrite and the pyrites in the copper tailings; and meanwhile, by adding the inhibitor which can generate the selective inhibition effect on the arsenopyrite, the surfaces of the arsenopyrite are oxidized to generate precipitate, and therefore separation of the arsenopyrite and the pyrites in the copper tailings is achieved. The method includes the following steps that a solution A, a solution B and a solution C are prepared, and concentration and crystallization are conducted. According to the preparation method, through the inorganic and organic compound reaction, a product with the complicated complexing structure and the electrochemistry reducibility is formed, and arsenate on the surfaces of the arsenopyrite and sulfite on the surfaces of the pyrites can be removed; and meanwhile, by means of the reducibility and coordination capacity of thiourea groups and benzene ring quinone groups, inhibition on the surfaces of the arsenopyrite is achieved.
Owner:JIANGXI YIYUAN REGENERATION RESOURCE CO LTD
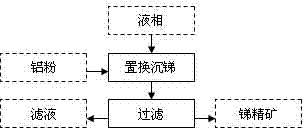
Method for gold separation by means of removing antimony
InactiveCN103203281AEliminate negative effectsSimplified process conditionsWet separationSulfidationSulfide minerals
A method for gold separation by means of removing antimony is used for treating refractory gold and antimony ores by a leaching antimony removing process, so that the antimony in an ion state is turned into a liquid phase, and the gold in a crystalline state remains in a solid phase. The refractory gold and antimony ores at least comprise elementary gold and gold-carrying minerals; the elementary gold includes visible gold and invisible gold; the gold-carrying minerals at least include gold-carrying oxygenic salt minerals and gold-carrying sulfide minerals; the oxygenic salt minerals at least include carbonate minerals and silicate minerals; and the sulfide minerals at least include antimony glance and (or) iron pyrite and (or) arsenic pyrite. An antimony removing gold separation dressing and smelting technology for implementing the method for gold separation by means of removing the antimony is characterized by comprising 1), treating the refractory gold and antimony ores by the leaching antimony removing process so that the antimony in the ion state is turned into the liquid phase and the gold in the crystalline state remains in the solid phase; 2), performing solid and liquid separation for ore pulp obtained after leaching, and generating a liquid phase and a solid phase; 3), treating the liquid phase by a displacement antimony settling process so that the antimony is turned into a crystalline state from the ion state; and 4), treating the solid phase by a floatation process so that the elementary gold and the gold-carrying sulfite minerals are separated from gangues.
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
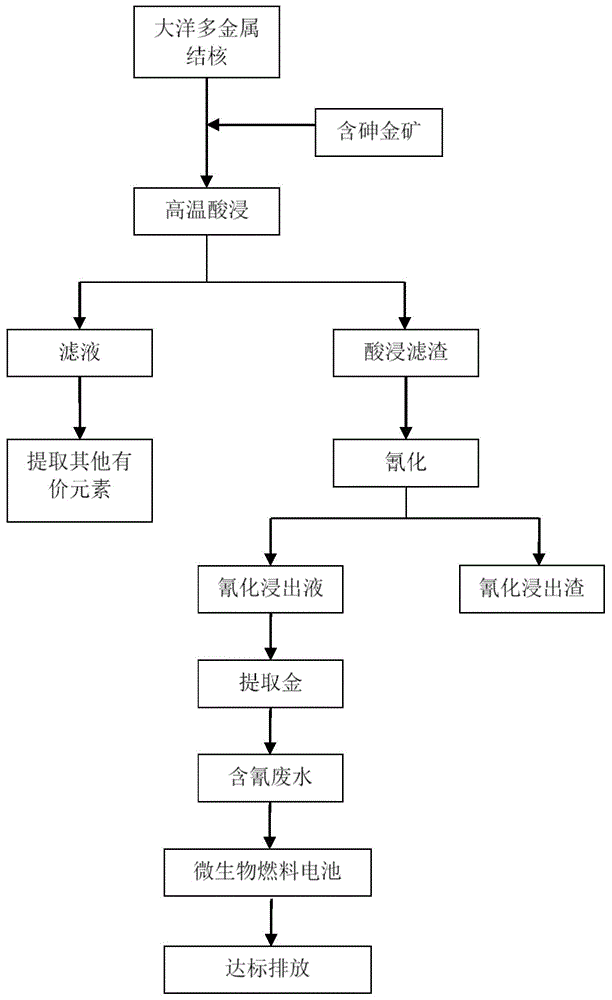
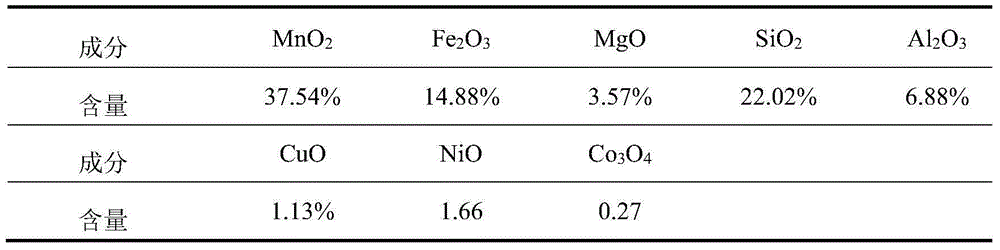
Ocean polymetallic nodule and arsenious gold ore mixing pretreatment method
InactiveCN104928468AImprove leaching rateHigh extraction rateWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsProcess efficiency improvementPretreatment methodGold particles
The invention discloses an ocean polymetallic nodule and arsenious gold ore co-utilization method. Ocean polymetallic nodules and arsenious gold ore are utilized together through mixed acid leaching by means of the oxidability and reducibility of main minerals in ocean polymetallic nodules and arsenious gold ore. In the process, manganese dioxide is reduced, and ions like cobalt ions, nickel ions and copper ions are released; meanwhile, ultrafine gold particles wrapped in arsenopyrite are exposed, and the gold leaching rate of follow-up cyanide leaching is increased. According to the method, waste water containing cyanogens and heavy metal can also be treated by means of the microorganism electrochemical method to achieve closed circulation. The process is simple, the extraction rate is high, environment friendliness is realized, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
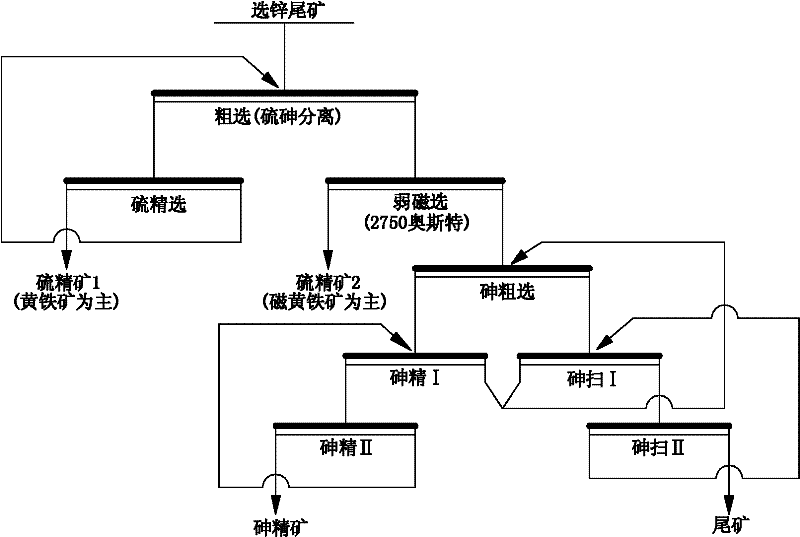
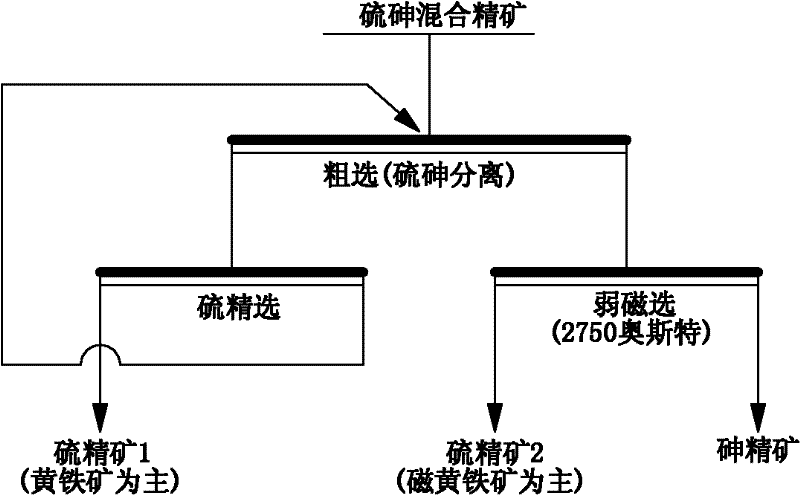
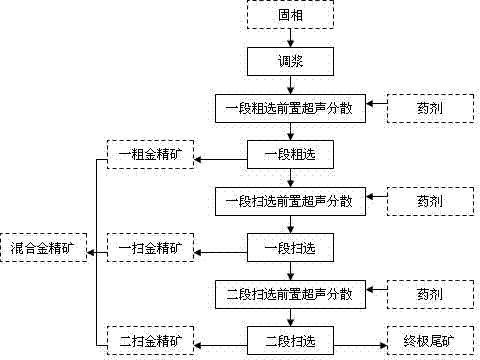
Method for using microbial flotation method to separate pyrites from arsenopyrites
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Cyanide-free extractant and gold extracting method
ActiveCN106191460AShort leaching timeImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementCyanideWastewater
The invention provides a cyanide-free extractant and a gold extracting method. The cyanide-free extractant comprises, by mass percentage, 0.5-2% of amino acid and 0.2-2% of alkali, wherein water serves as a solvent. According to the gold extracting method, the amino acid gold extracting agent free of toxicity to the environment is adopted for leaching of gold, the method is environmentally-friendly, free of toxin, short in leaching time and high in leaching rate, and waste water can be drained after being simply treated. According to the cyanide-free extractant and the gold extracting method, the leaching rate of gold ore easy to leach is high, is larger than 90% and can reach 95%; for traditional gold ore difficult to leach, such as ore which is not pretreated and contains pyrite cyanide arsenopyrite, the leaching rate is high as well and is larger than 85%, and the leaching rate is less than 30% compared with the leaching rate of a traditional cyaniding process of the same type of ore which is not pretreated, so that by the adoption of the cyanide-free extractant and the gold extracting method, the leaching rate of the gold ore difficult to leach can be increased greatly.
Owner:和晶(上海)新能源科技有限公司
Floatation reagent used for separating gold from antimony
The invention discloses a floatation reagent used for separating gold from antimony. The floatation reagent comprises sulfite, humic acid salt and potassium permanganate, wherein the mass ratio of the sulfite to the humic acid salt to the potassium permanganate is 40-50:25-30:25-30. The floatation reagent restrains iron pyrite and arsenical pyrite, but weakly restrains antimony glance, and can obviously increase the floatability difference between the antimony glance and the iron pyrite and the arsenical pyrite, and compared with traditional floatation, the reagent can improve the effect of separating the gold from the antimony by above 30%.
Owner:新疆星塔矿业有限公司
Mineral oxidation acid production inhibition method based on sulfide mineral surface in-situ rapid film formation
ActiveCN113522931AGood value for moneyEasy to getSolid waste disposalPriming paintsMicroorganismSulfidation
The invention discloses a mineral oxidation acid production inhibition method based on sulfide mineral surface in-situ rapid film formation. The method comprises the following steps of sequentially and uniformly spraying a first hydrophobic film solution and a second hydrophobic film solution on the surface of a target sulfide mineral, so that a hydrophobic double-layer passivation film is formed on the surface of the target sulfide mineral in situ, and oxidation acid production of the target sulfide mineral is effectively inhibited. According to the method, the hydrophobic double-layer passivation film can be rapidly formed on the surface of the sulfide mineral such as pyrite, pyrrhotite and arsenopyrite in situ, contact between moisture, air and microorganisms and the surface of the sulfide mineral is avoided through the isolation effect of the hydrophobic double-layer film, and therefore the oxidation effect of the sulfide mineral under the effects of the microorganisms, the air, the moisture and the like is inhibited; and the acid mine wastewater can be eradicated from the source. According to the method, the hydrophobic double-layer passivation film can be rapidly generated in situ in the environment of a tailing pond and a tailing slag storage yard, generation of the acid mine wastewater is eradicated from the source, and the method has important significance on tailing treatment and environmental protection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
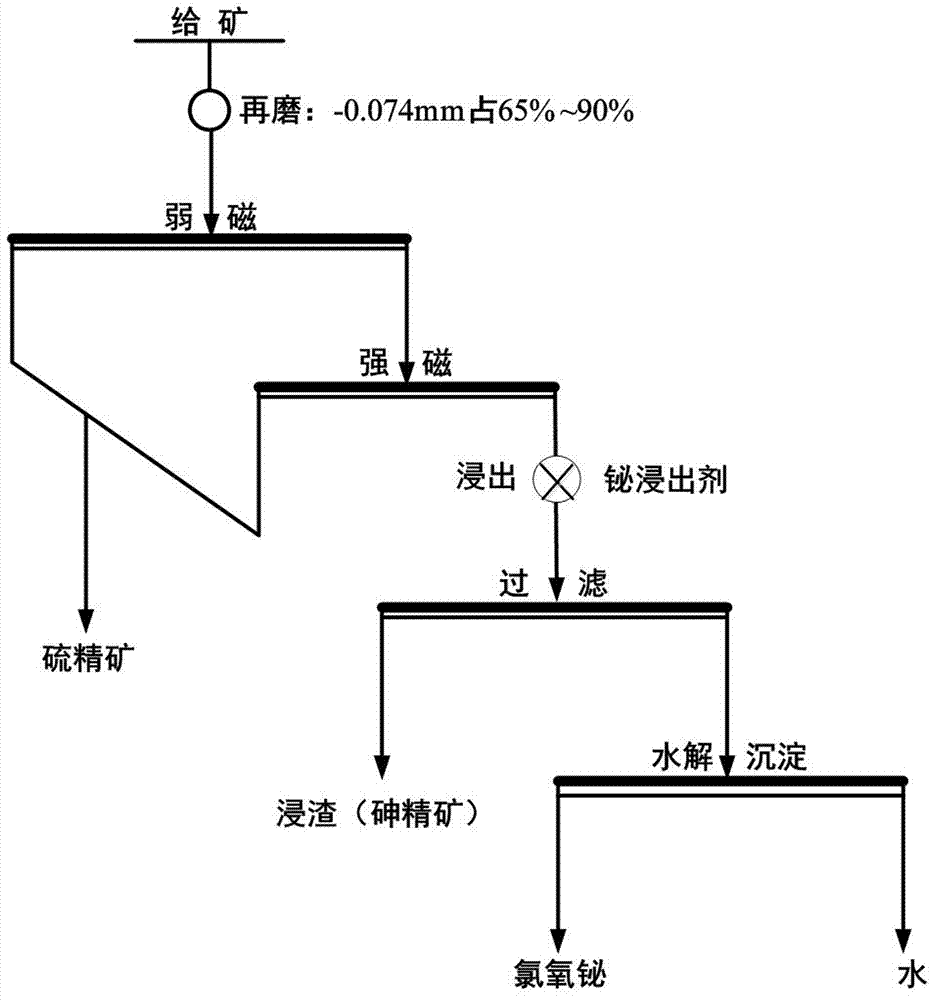
Method for separating bismuth from arsenic in high-bismuth and arsenic sulfur concentrate
The invention discloses a method for separating bismuth from arsenic in high-bismuth and arsenic sulfur concentrate. According to the method, firstly, pyrrhotite with relatively high magnetism is sorted out through low intensity magnetic separation in advance; and then, pyrrhotite with relatively low magnetism is sorted out through strong magnetic separation, the pyrrhotite with relatively high magnetism and the pyrrhotite with relatively low magnetism are combined to form the sulfur concentrate mainly with the pyrrhotite, effective removing of the pyrrhotite is achieved through the action ofthe magnetic separation, preconcentration of bismuth is achieved through the scientific control of a magnetic separation condition, the handling capacity of following bismuth leaching is effectively reduced, the leaching rate of the bismuth is increased, the in-leaching grade of the bismuth is remarkably improved, a bismuth leaching agent is reasonably added in magnetic separation of tailings so that normal temperature and normal pressure leaching of the bismuth can be carried out, the chemical stability of arsenopyrite is utilized by creating conditions, the thorough separation of the bismuthfrom the aesenic is achieved, the bismuth leachate is obtained, the leachate is further hydrolyzed, a chlorine, oxygen and bismuth product is obtained, and leaching residue is arsenic concentrate.
Owner:INST OF RESOURCES UTILIZATION & RARE EARTH DEV GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI +1
Low-cost method for solidifying arsenic by using multi-element solid waste cementing material for underground filling
The invention discloses a low-cost method for solidifying arsenic by using a multi-element solid waste cementing material for underground filling, and belongs to the technical field of heavy metal pollution treatment and solid waste treatment. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing cement, metakaolin, blast furnace slag and desulfurized gypsum to obtain a mixture A; and uniformly mixing the mixture A and arsenopyrite to obtain a mixture B, uniformly stirring the prepared sodium silicate excitant C and the mixture B to obtain a mixture D, pouring the mixture D into a mold, molding, demolding, and curing in a curing box for 28 days. The rich aluminosilicate cementing material is formed through full reaction of the multi-element solid waste, the cement and the sodium silicate exciting agent, the requirements for low leaching rate and strength of underground filling of heavy metal arsenic are met, and the purposes of green low-carbon, low-cost filling, short technological process, waste treatment with waste and arsenic solidification are achieved. The 7 d strength of the solidified body reaches 25 Mpa or above, the arsenic leaching concentration of the solidified body is less than 5 mg / L, and the solidified body can be used as a low-cost underground filling gelling agent for stably solidifying arsenic.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Method for curing arsenic by using red mud/metakaolin-based multi-component solid waste geopolymer
PendingCN113511846AAchieve reductionRealize harmless disposalSolid waste managementCement productionAluminiteSlag
The invention discloses a method for solidifying arsenic by using a red mud / metakaolin-based multi-component solid waste geopolymer. According to the invention, industrial solid waste consisting of red mud, metakaolin, blast furnace slag and desulfurized gypsum are used as raw materials to prepare a backfill material for underground filling, so cost is low, and the strength and arsenic leaching concentration of the backfill material both meet national-standard requirements on leaching in China. The method is a comprehensive utilization method which applies the industrial solid waste such as red mud, metakaolin, blast furnace slag and desulfurized gypsum to curing and stabilizing of arsenic solid waste so as to treat the waste with the waste; the multi-component solid waste and an alkali activator are fully reacted to form rich ettringite to solidify arsenic in red mud and arsenopyrite; and meanwhile, due to the three-dimensional structure of a rich aluminosilicate cementing material in the geopolymer, the waste is treated by the waste, and arsenic immobilization efficiency is improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chlorine dioxide preoxidation method of sulfur-contained gold ores
ActiveCN108103310AImprove leaching rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementChlorine dioxideGalena
The invention belongs to the technical field of gold ore mineral processing, and in particular, relates to a chlorine dioxide preoxidation method of sulfur-contained gold ores. Chlorine dioxide is used as an oxidizing agent for redox reaction with such sulfides as stibnite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, galena, blende and chalcopyrite in refractory gold ores, so that gold surrounded by the sulfides is released, the contact probability of gold with gold leaching medicament is increased, the gold recovery rate in subsequent leaching flow is increased, and the consumption of the gold leaching medicamentis reduced. The used oxidizing agent-chlorine dioxide is safe and nontoxic, and has higher environmental protection advantage. Chlorine dioxide is prepared by direct reaction of binary solid medicament in pulp, is prepared when being needed, is not needed to store, and is high in conversion efficiency. The method is performed under the conditions of low temperature, normal pressure and no need ofcontrolling acidity; reaction conditions are mild; and requirements on a reaction container are low. In conclusion, the method is a new method for metal sulfide ore wet oxidation pretreatment with environmental protection, high efficiency and prominent economical benefit.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com