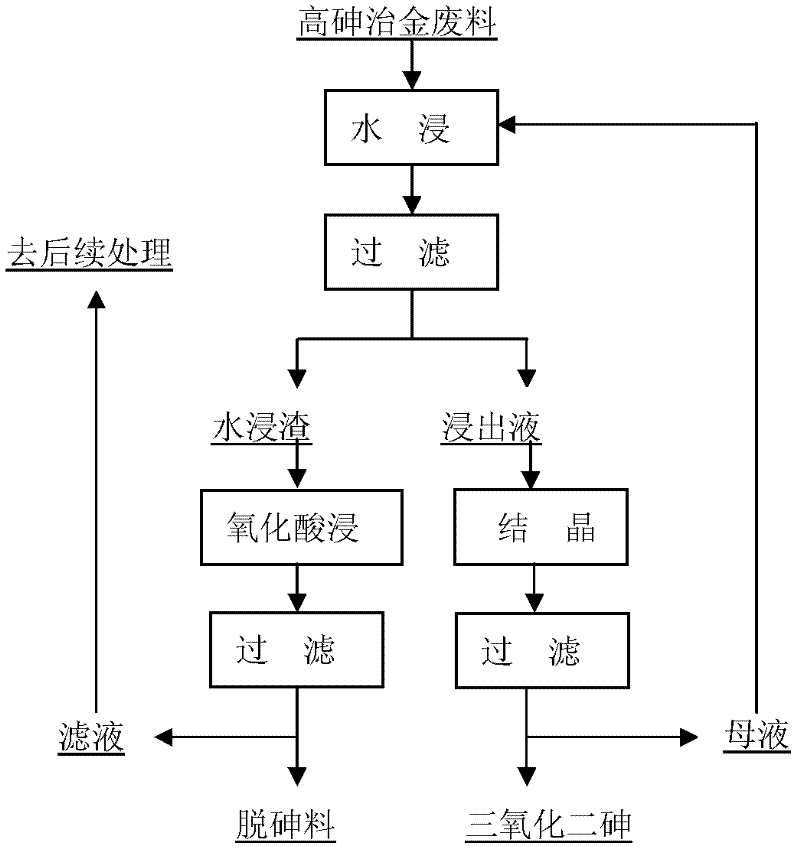
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Arsenic sulfide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arsenic sulfide may refer to: .
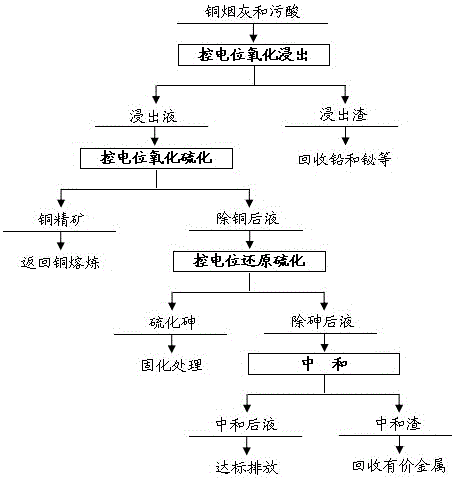
Method for innocent treatment of arsenic sulfide residues
InactiveCN105963902ARealize harmless treatmentReduce arsenic leaching concentrationChemical protectionRoom temperatureArsenic sulfide
The invention discloses a method for harmless treatment of arsenic sulfide slag, which comprises the following steps: adding water to arsenic sulfide slag at room temperature, mixing to obtain mixture I, adding sodium sulfide to react to obtain mixture II, and then Add oxidant to carry out oxidation reaction to obtain mixture III, then add iron salt or aluminum salt for reaction to obtain mixture IV, and then add cement. The invention has the advantages of being able to effectively reduce the arsenic leaching concentration of the arsenic sulfide slag, the treated arsenic sulfide slag meets the requirements for hazardous waste landfill, simple process flow, small volume increase, strong operability, short stirring time, and low consumption.
Owner:云南大地丰源环保有限公司
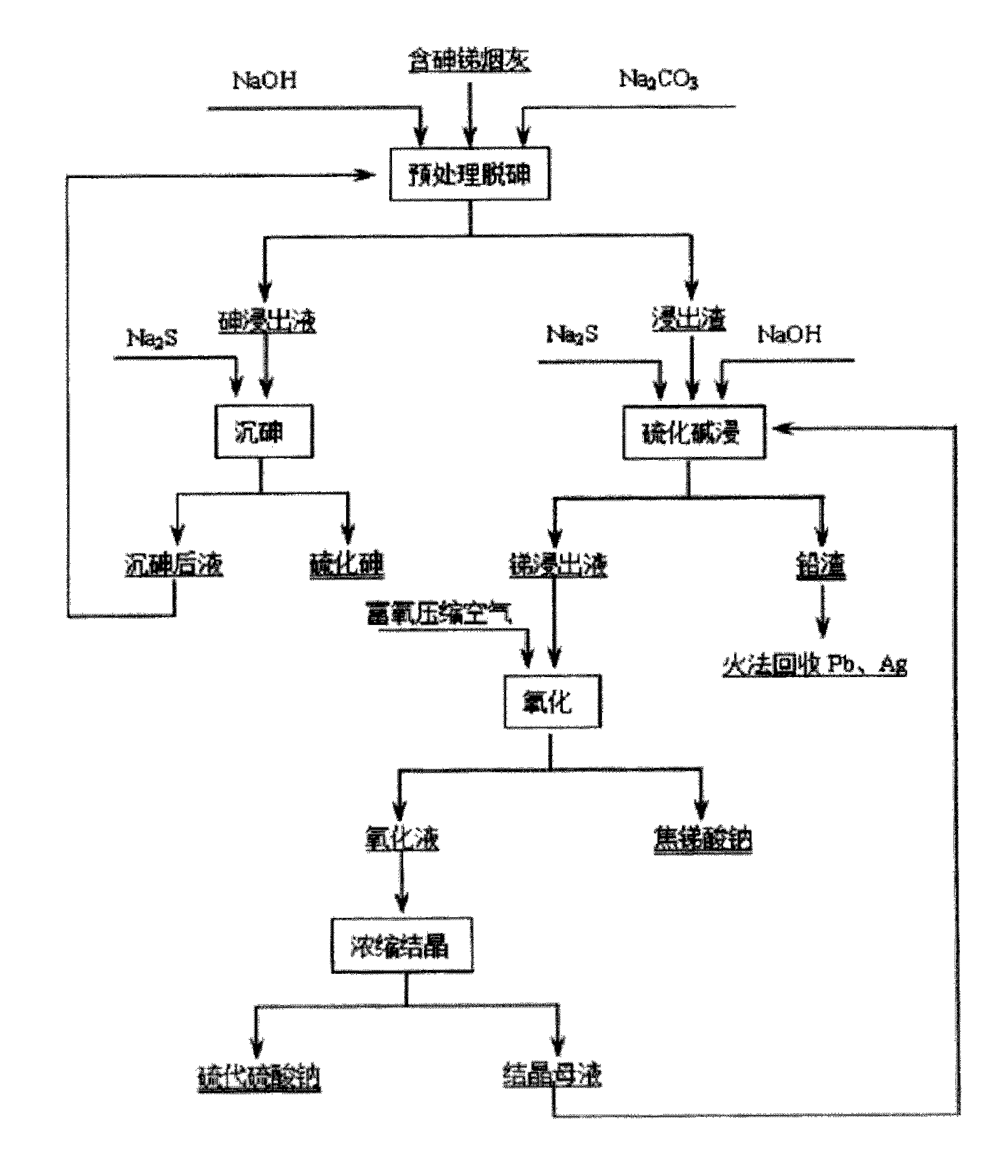
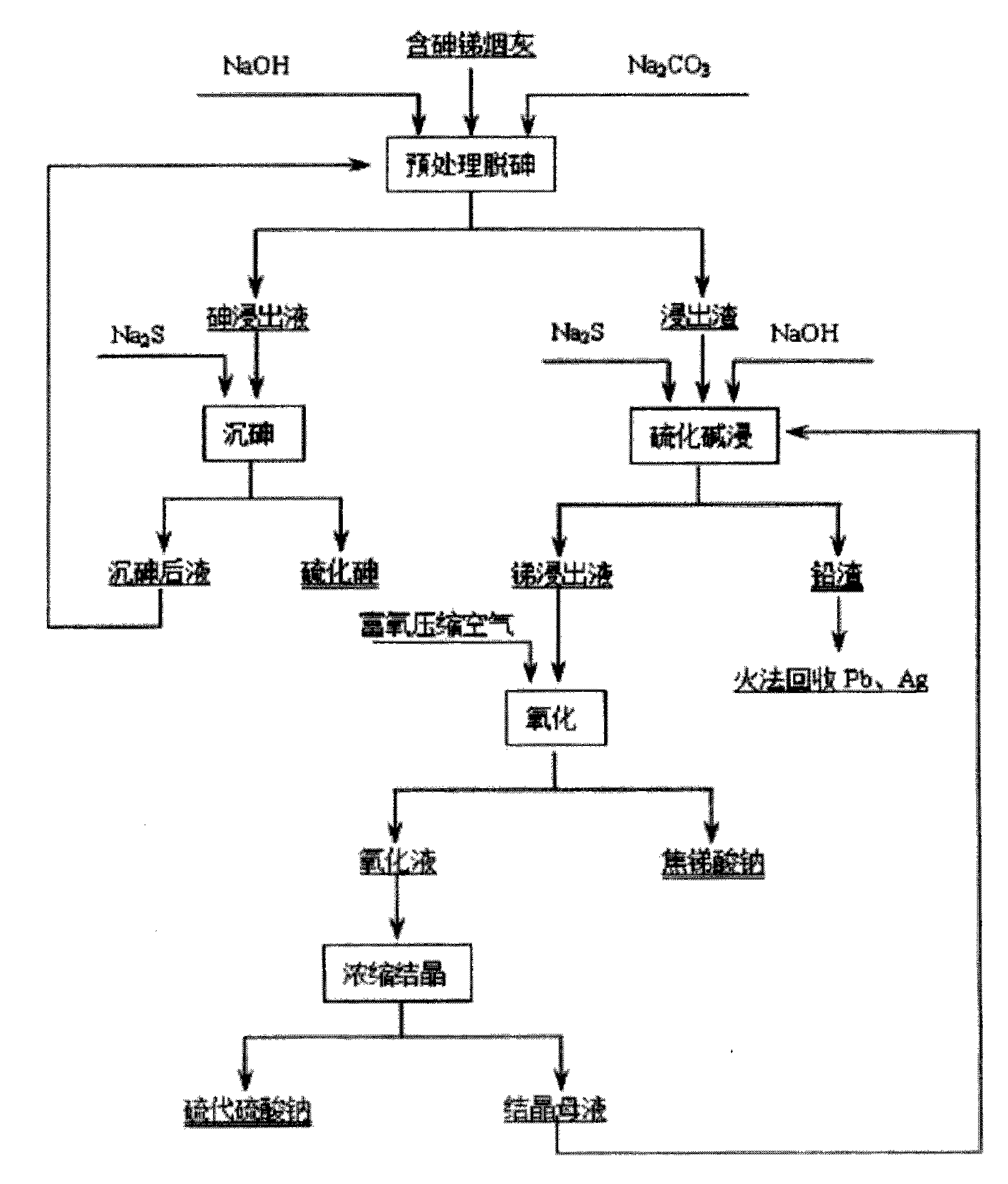
Process for preparing sodium pyroantimonate from arsenic- and stibium-containing smoke ash
ActiveCN102031381AEfficient separationSolve processing problemsProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyArsenic sulfide
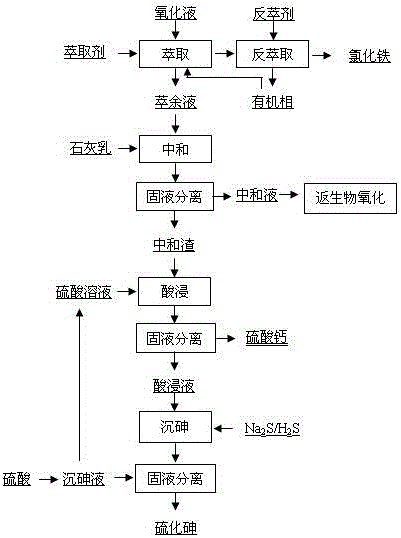
The invention discloses a process for preparing sodium pyroantimonate from arsenic- and stibium-containing smoke ash and belongs to the field of wet-process metallurgy. The production process for preparing the sodium pyroantimonate is characterized by comprising the following steps of: using NaOH and Na2CO3 or mixing the NaOH and Na2CO3, and performing wet-process pretreatment to remove arsenic; precipitating arsenic in arsenic-containing leaching liquor by using Na2S to obtain an arsenic sulfide byproduct; leaching arsenic- and stibium-containing leaching residues by mixing the Na2S and NaOH, returning lead residue, smelting, and recovering lead, silver and other valuable metals; blowing oxygen-rich compressed air into stibium-containing leaching liquor to prepare a sodium pyroantimonateproduct; and concentrating and crystallizing oxidized liquor to prepare Na2S2O3. The process has the advantages of no environmental pollution, simple equipment, low investment, high comprehensive utilization rate, low cost, suitability for industrial production, and the like.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
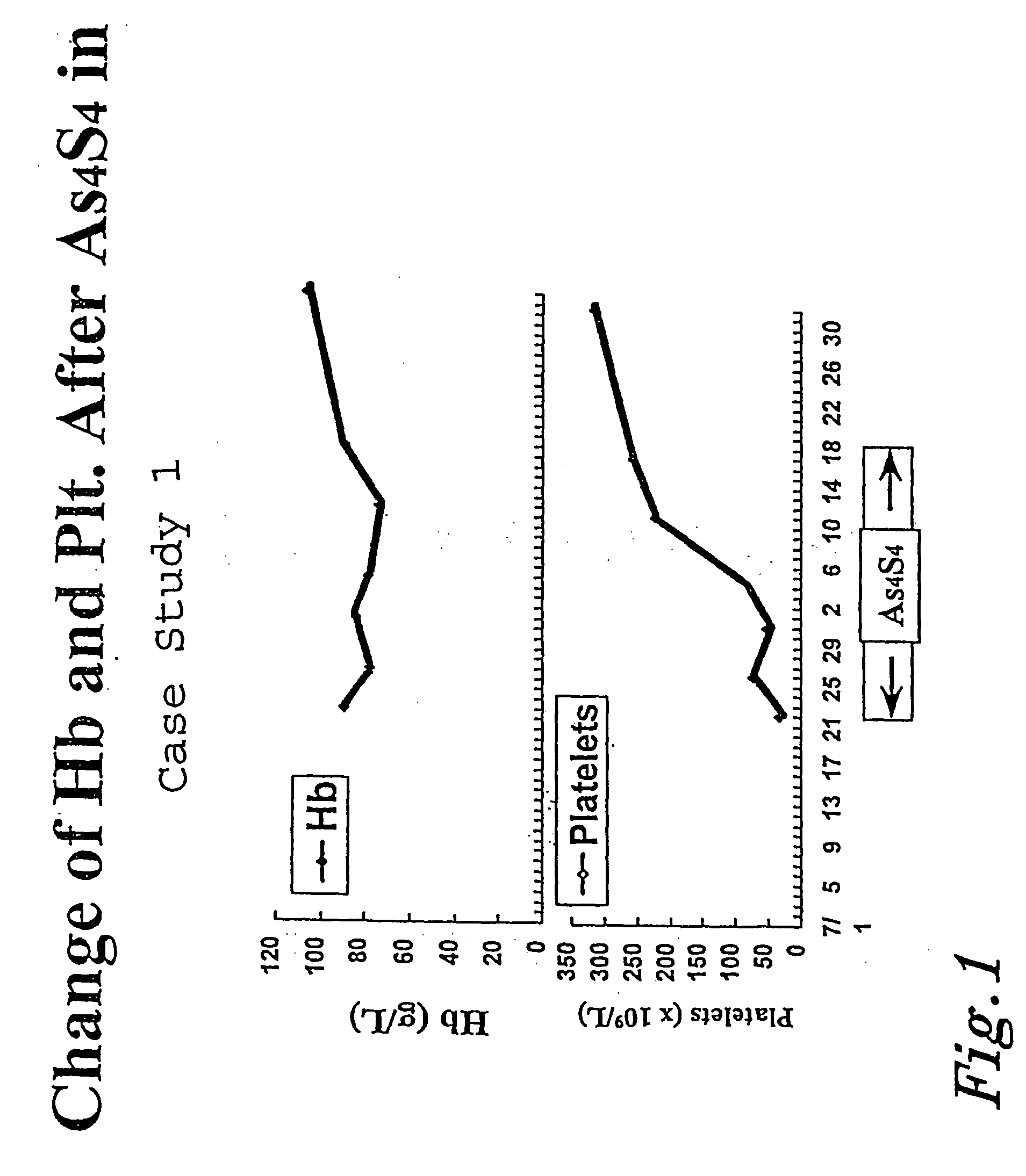
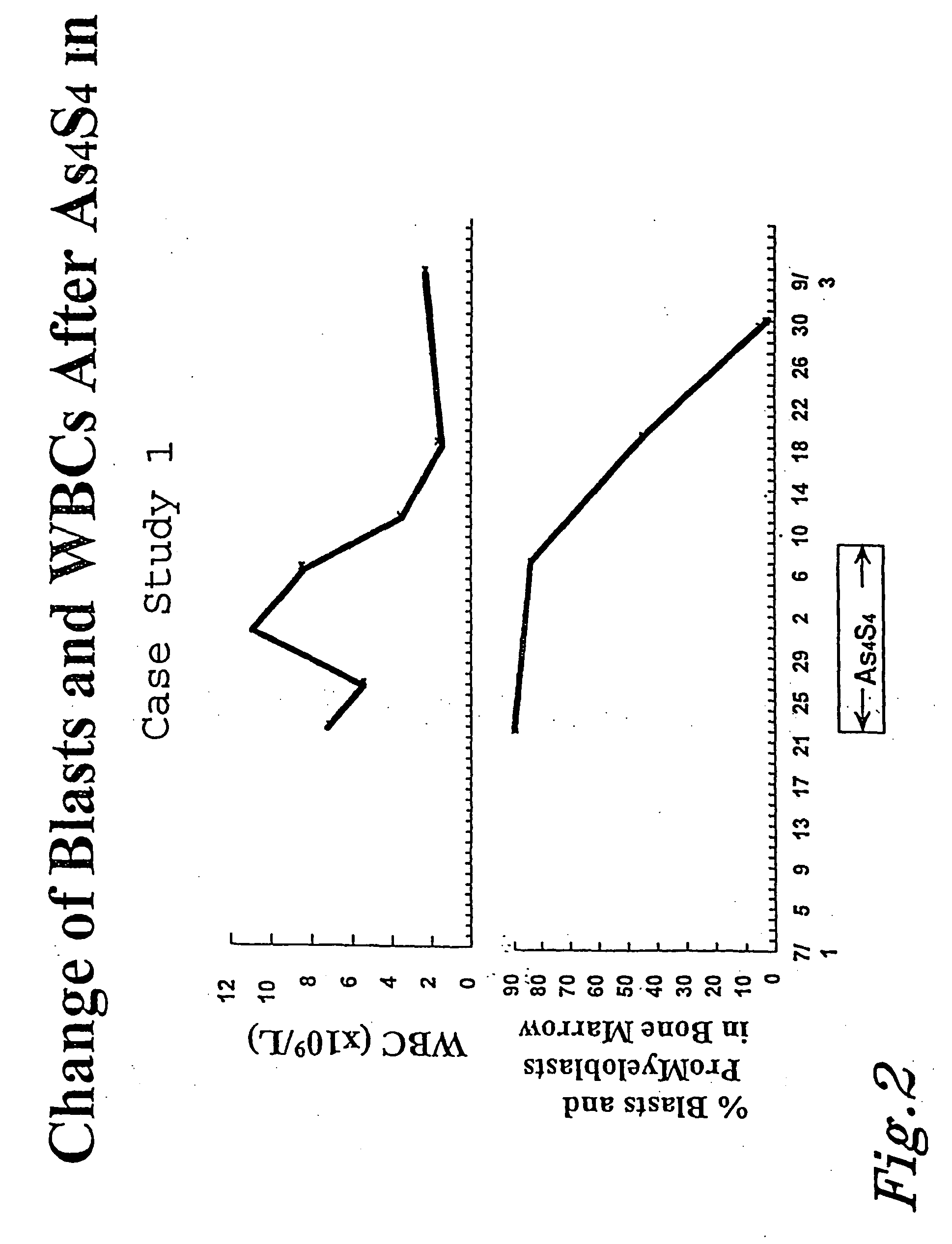
Arsenic sulfide compounds and derivatives thereof for the treatment of malignancies
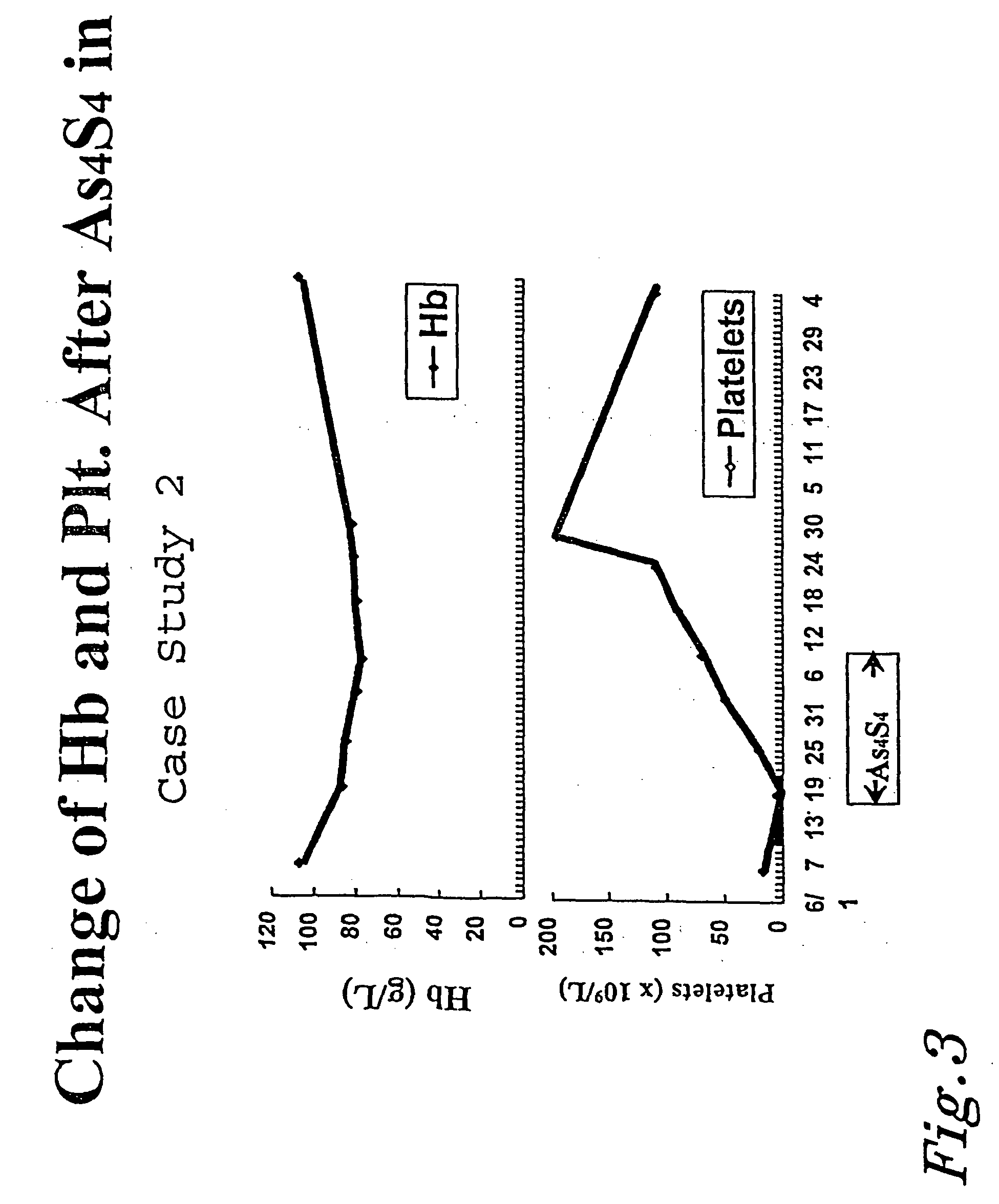
The present invention relates to arsenic sulfide compounds. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions useful for treating cancer, such as leukemia or lymphoma, which comprises an arsenic sulfide compound. The present invention further relates to methods for treating cancer, such as leukemia or lymphoma, using an arsenic sulfide compound. Finally, the present invention relates to processes for producing arsenic disulfide (As4S4).
Owner:LU DAOPEI
Method for metallic arsenic production directly through reducing sulfur-fixed roasting of arsenic sulfide residues
ActiveCN106756113AEfficient arsenic removalShort processProcess efficiency improvementDistillationCopper sulfide
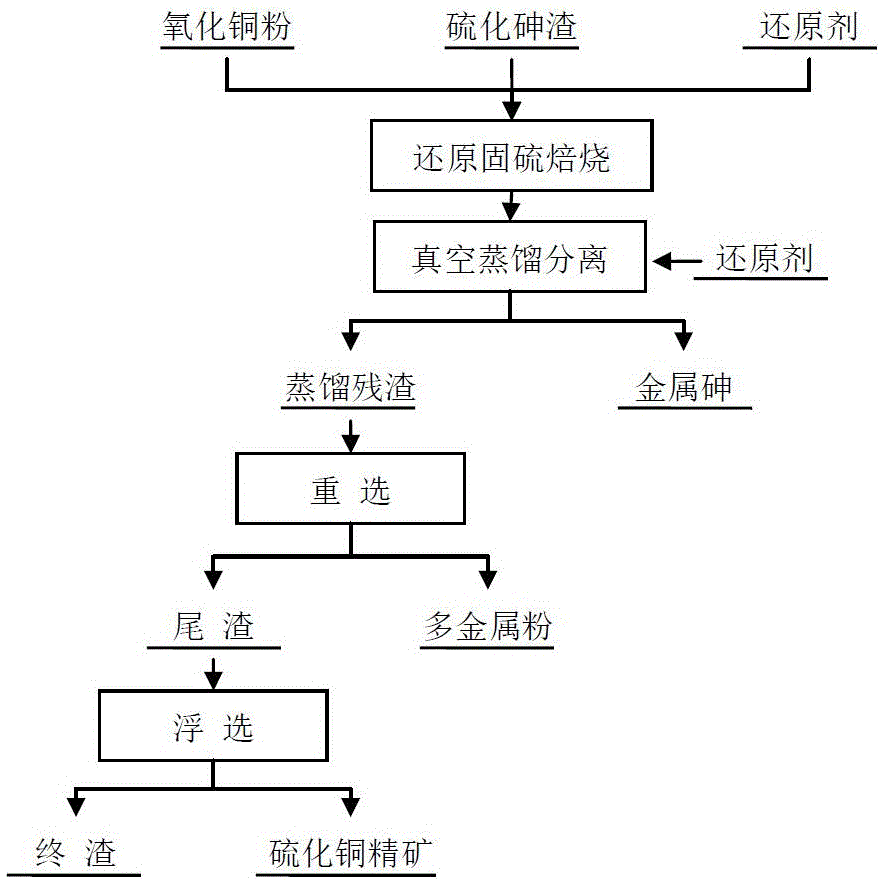
The invention discloses a method for metallic arsenic production directly through reducing sulfur-fixed roasting of arsenic sulfide residues. The arsenic sulfide residues produced in the acidic wastewater purifying working procedure of a copper smelting plant serve as a raw material, meanwhile cupric oxide powder and a reducing agent are added, low-temperature reducing sulfur-fixed roasting is conducted after metallurgy calculation and ingredient mixing are conducted, and volatility of arsenic is utilized to enable roasted products to be subjected to vacuum separation in the reducing atmosphere so that the crude metal arsenic and distillation residues can be obtained; and distillation residues are subjected to a reselection technique for separation to obtain multi-metal powder and tailings, and the tailings are subjected to a flotation technique to obtain final residues and copper sulfide concentrates. According to the method for metallic arsenic production directly through reducing sulfur-fixed roasting of the arsenic sulfide residues, efficient arsenic removal of the arsenic sulfide residues can be achieved, harmless high-value products of the arsenic are directly produced, the process is short, energy consumption is low, the process is clean, and the direct recovery rate of the metal arsenic reaches up to 96.45%; and meanwhile, recovery of valuable metal existing in the arsenic sulfide residues is completed, and the cupric oxide powder is recovered in a high-quality copper sulfide concentrate mode finally.
Owner:广西河池鑫银环保科技有限公司
Hydrothermal stabilized curing treatment method of arsenic sulfide residue water
ActiveCN106823238AReduce operating expensesEasy to operateChemical protectionReaction temperatureHigh pressure
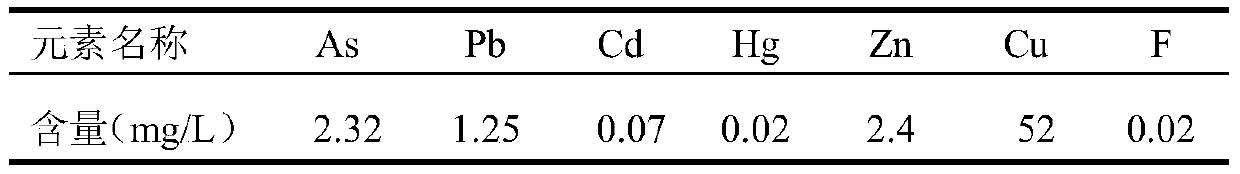
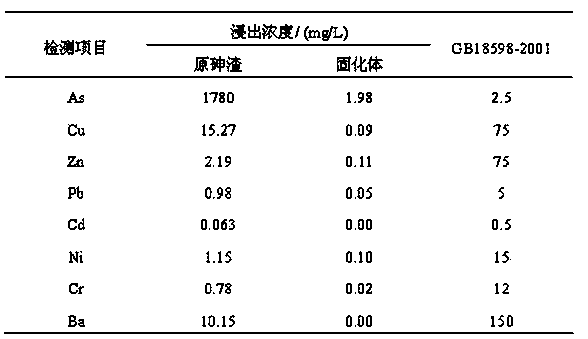
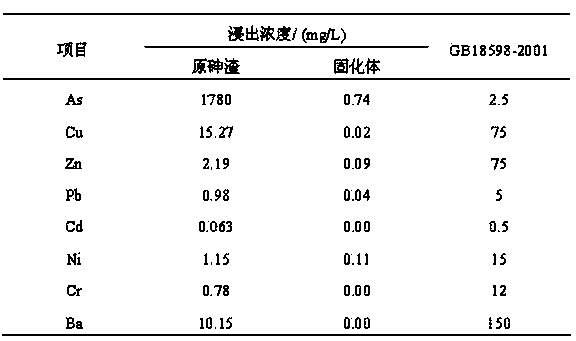
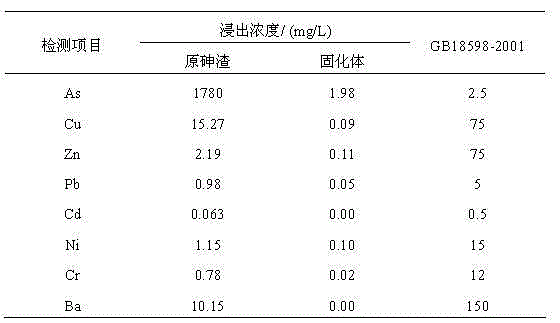
The invention provides a hydrothermal stabilized curing treatment method of arsenic sulfide residue water. According to the method, the liquid-solid ratio, pH and redox potential of arsenic sulfide residues are adjusted, then the arsenic sulfide residues enter a high-temperature and high-pressure hydrothermal reaction kettle for a curing reaction, and hydrothermal stabilized curing of the arsenic sulfide residues is realized by controlling the reaction temperature, reaction pressure, stirring rate, reaction time, cooling rate and cooling manner. The method is simple in treatment process and low in cost and has obvious economic and environment benefits. The arsenic sulfide residues produced in acid arsenic wastewater sulfidizing in smelting, electroplating, fertilizer (phosphate fertilizer) production, chemical engineering and other industries are used as the object, after hydrothermal stabilized curing treatment, the arsenic leaching toxicity (see sulfuric acid and nitric acid method, the leaching method in HJT 299-2007) concentration can be decreased to 1 mg / L or below, the compressive strength can reach 10 MPa or above, the specification of solid waste identification standard-leaching toxicity identification (GB5085.3-2007) is conformed, and the hazardous waste landfill pollution control standard (GB18598-2001) can be met.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing arsenic trioxide from arsenic sulfide waste
InactiveCN102115166ALow costNothing producedSolid waste disposalArsenic compoundsSolubilityArsenic sulfide
The invention provides a method for preparing arsenic trioxide from arsenic sulfide waste. The arsenic sulfide waste is soaked in a sodium hydroxide solution to extract arsenic sulfide, arsenic sulfide mixes with an excessive amount of arsenic acid, and the mixture reacts at a temperature ranging from 40 DEG C to 95 DEG C for 0.5 to 3 hours, to produce a mixture containing arsenous acid and elemental sulfur; the mixture containing arsenous acid and elemental sulfur mixes with 2 to 5 times (by mass) of water and then oxygen gas is introduced so that arsenous acid is oxidized into arsenic acid, and the reaction product is filtered to remove elemental sulfur and thus to produce an arsenic acid solution; and the arsenic acid solution is reduced by sulfur dioxide gas to arsenous acid with a lower solubility, the reaction liquid is distilled under a reduced pressure to produce a saturated solution of arsenous acid, the saturated solution of arsenous acid is cooled so that arsenous acid is crystallized and then filtered to produce a filter cake of arsenous acid, and the filter cake of arsenous acid is dried and pulverized to obtain an arsenic trioxide product. The method has a short process flow, increases the recovery rate of arsenic, avoids the production of secondary pollutants, adopts simple equipment, greatly reduces the cost of arsenic recovery and is worthy to be widely applied.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGKE MACHINERY
Method for recovering elementary substance arsenic from arsenic sulfide slag
The invention belongs to the field of comprehensive utilization and processing technologies for arsenious waste slag, and particularly discloses a method for recovering elementary substance arsenic from arsenic sulfide slag, namely a desulphurization oxidation extract-acidification reduction technology. The method comprises steps of adding the arsenic sulfide slag in a water bath and heating to a certain temperature, adding an alkaline substance and controlling pH to be 8-9, and adding hydrogen peroxide slowly to react for 6h; and filtering to obtain an arsenic-rich solution, adding concentrated hydrochloric acid, adding stannous chloride for reduction to obtain the elementary substance arsenic, and drying to obtain the arsenic having a purity of higher than 98%. The method has advantageous of short technological process, easily controllable operation conditions, capability of convert arsenic from the arsenic sulfide slag into elementary substance arsenic, arsenic recovery rate of 99%, simple equipment, largely reduced cost for arsenic recovery, and significant economic benefit and environmental protection benefit.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Gradient arsenic removing method for high-arsenic metallurgical wastes
ActiveCN102409165AReduce manufacturing costChoose good dissolutionProcess efficiency improvementPotassiumOxidizing acid
The invention provides a gradient arsenic removing method for high-arsenic metallurgical wastes, which is generally suitable for comprehensive arsenic removing treatments of high-arsenic smoke dust generated in the smelting process of lead, zinc, antimony, copper, tin and the like, high-arsenic anode mud generated in the electrolytic process of wet lead, silver, copper and the like and other metallurgical wastes. The method comprises two stages of water leaching arsenic removal and oxidizing acid leaching arsenic removal and specifically comprises the following steps of: first, selectively dissolving out free arsenic trioxide and water soluble arsenate (like sodium arsenate and potassium arsenate) through water leaching; and then further leaching out indissolvable arsenate and arsenic sulfide in the water leaching residue as well as little incomplete arsenic trioxide dissolved out by water by using a mixed leaching liquor of acid and water soluble oxidizing agent. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low consumption of acid and alkali, high arsenic removing efficiency, safety, environment friendliness and suitability for arsenic removing treatment of various arsenic contained metallurgical wastes, in particular for arsenic removing treatment of the smoke dust with high content of free arsenic trioxide.
Owner:HUNAN ZHANTAI NON FERROUS METALS
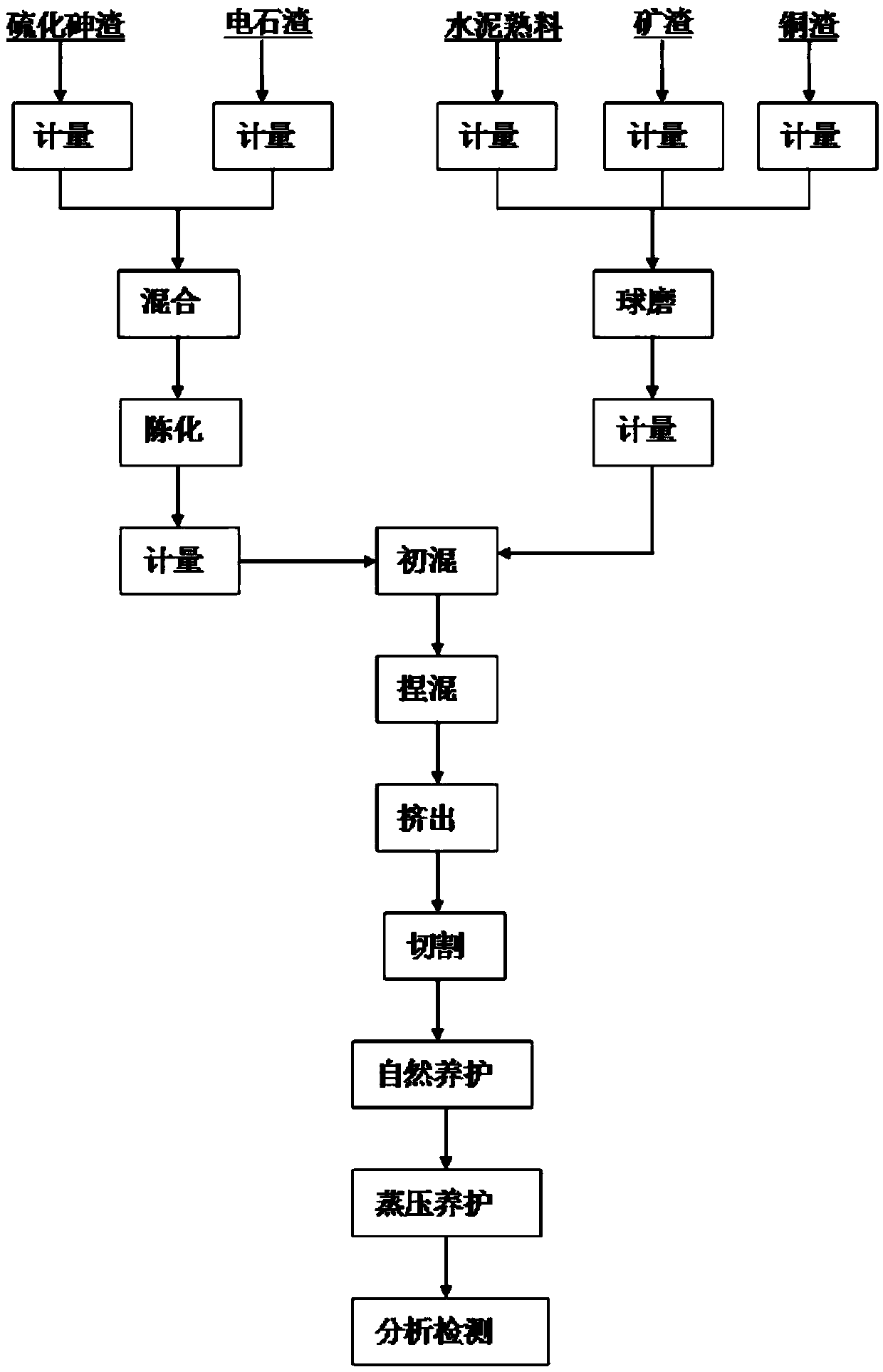
Stabilizing treatment method for sulfide arsenic-removed dregs
The invention discloses a stabilizing treatment method for sulfide arsenic-removed dregs. The stabilizing treatment method comprises the following steps: mixing cement clinker, mineral slag and copper slag in a ratio of parts by mass being (25-30) to (60-70) to (5-10), carrying out ball-milling on the materials, and enabling the materials to pass through a 180-mesh square hole sieve with weight of screen residues being 5wt%, thereby preparing a gel material; mixing arsenic sulfide slag and carbide slag in a dry-weight mass ratio being 1 to (1.0-1.2), and ageing and pre-treating the arsenic sulfide slag and carbide slag for 24 hours; preparing the pre-treated arsenic sulfide slag and the self-made gel material in a ratio of parts by mass being (25-35) to (65-75), adding calcium chloride with gel material amount being 0.4-0.5wt% or a mixture of calcium chloride and sodium chloride as an additive, controlling moisture content of materials to be 20-22wt%, mixing the materials on a horizontal type stirrer to macroscopically homogenize the materials, putting the homogenized materials into a continuous kneading extruder to forcibly mix, extrude, cut, naturally cure and carry out steam curing for 10 hours under pressure of 0.8-1.0MPa, and carrying out a toxicity leaching test on a solidified body according to GB5085.3-2007 to enable the solidified object to meet stock-piling or filling requirements.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for recovering simple substance arsenic from arsenic sulfide slag
InactiveCN101386915ASimple processOperating conditions are easy to controlProcess efficiency improvementCopper chlorideSlag
The invention relates to a method for reclaiming simple substance arsenic from arsenic sulfide slag. The method comprises the following steps: the arsenic sulfide slag is immersed in an acidic solution containing copper chloride to obtain an arsenic-rich solution; the arsenic-rich solution is cooled to the room temperature and is precipitated with a As2O3 crystal; the As2O3 crystal is added with concentrated hydrochloric acid and SnCl2 and is oxidized and reduced to the simple substance arsenic; and the simple substance arsenic is subjected to dehydration, pickling, drying and purification to obtain the simple substance arsenic with the arsenic content of more than or equal to 90 percent. The method has simple process flow, is easy to control the operating condition, can convert arsenic in the arsenic sulfide slag into the simple substance arsenic, has the arsenic reclaiming rate reaching 99 percent and has remarkable economic benefit and environmental benefit.
Owner:湖南宏大锑铅有限公司
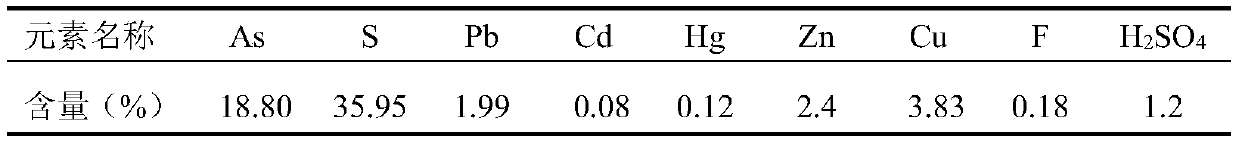
Stable curing method of strongly acidic arsenic sulfide waste residues
ActiveCN104174634AReduce leachingReduce contentSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingCalcium hydroxideSludge
The invention discloses a stable curing method of strongly acidic arsenic sulfide waste residues. The stable curing method comprises the following steps: (1) adding heavy-metal sludge to to-be-treated strongly acidic arsenic sulfide residues, and stirring, so as to obtain muddy materials; (2) adding calcium hydroxide powder to the muddy materials obtained in the step (1) in the state of stirring, and continuing to stir until all yellow substances in the muddy materials disappear; (3) adding yellow sand and cement to the materials obtained after stirring in the step (2); (4) cooling the stirred materials obtained in the step (3) to room temperature, transferring to a forming die, taking out from the die after forming, and curing at room temperature, so as to obtain solidified bodies which conforms to the landfill standard. According to the stable curing method, the heavy-metal sludge is used as an arsenic stabilizer, so as to control waste by waste; sources of the materials such as the heavy-metal sludge, the lime, the cement and the yellow sand required for treating the strongly acidic arsenic sulfide waste residues are wide, and additionally, other drugs do not need to be added; compared with other methods, the stable curing method has the advantage of low treatment cost.
Owner:扬州杰嘉工业固废处置有限公司
Process of extracting arsenic from arsenic sulfide waste residue by adopting whole wet method
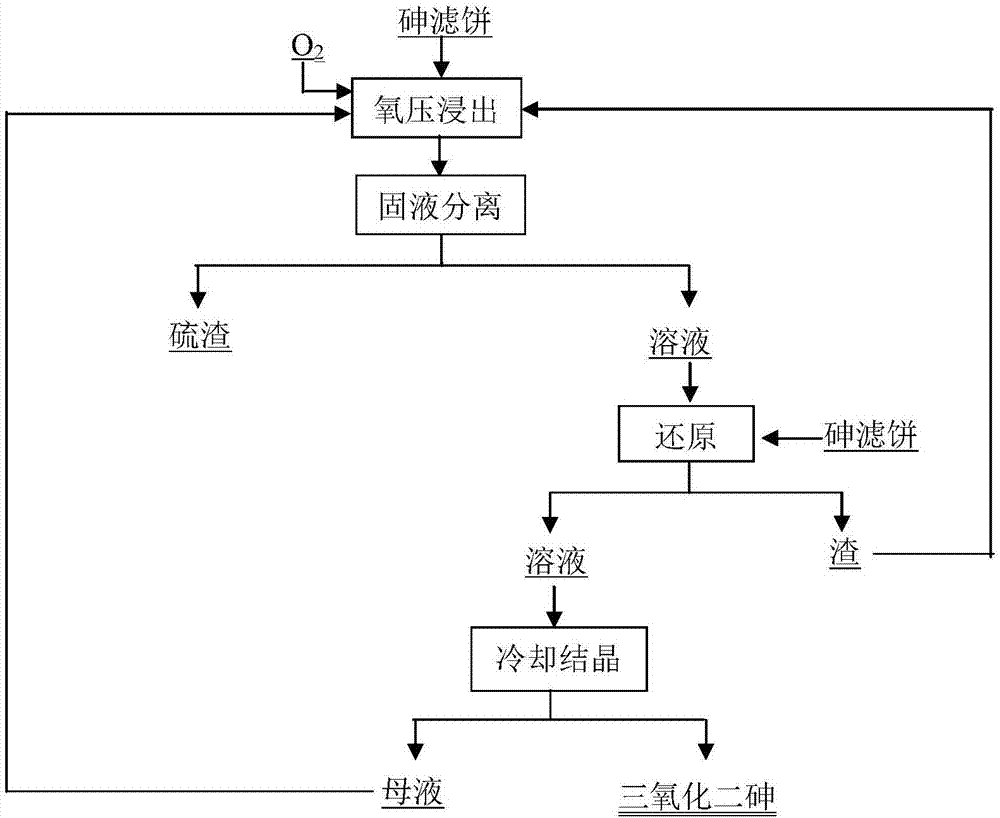
The invention discloses a process of extracting arsenic from arsenic sulfide waste residue by adopting the whole wet method. The process comprises the following steps: arsenic sulfide waste residue is subjected to oxygen pressure leaching and solid-liquid separation to obtain sulfur slag and an oxygen pressure leach solution containing pentavalent arsenic and H2SO4; arsenic sulfide waste residue is taken as a reducing agent to obtain pentavalent arsenic by reduction, and solid-liquid separation is carried out, so as to obtain a solution containing trivalent arsenic and a slag phase; the solution containing trivalent arsenic is subjected to cooling crystallization and drying to obtain a opaque glass product, and the slag phase is returned to be subjected to oxygen pressure leaching. The process has the advantages of being short in process flow, economic and practical, good in operating environment and capable of realizing closed circulation of the solution; arsenic and sulfur are recovered in the forms of a arsenic trioxide product and sulfur, the problem that the conventional SO2 reduction causes acid swelling is solved, and the industrial popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:郴州金铖环保科技有限公司
Method for recovering elementary substance arsenic from arsenic sulfide slag
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method for leaching and simultaneously stabilizing arsenic sulfide slag
InactiveCN105967232AImprove stabilityFacilitate solid-liquid separationArsenites/arsenatesSlagCulture mediums
The invention relates to a method for leaching and simultaneously stabilizing arsenic sulfide slag. The method comprises the following steps: preparing ore pulp from arsenic sulfide slag under the acid condition, adding ferrous sulfate, thermophilic iron oxide microbial strains and microbial culture medium salt, filling air and stirring, oxidizing and leaching arsenic sulfide slag under the temperature of 70-95 DEG C and a pH value of 0-2.0 by taking trivalent iron generated by microbial ferrous oxide, simultaneously adsorbing iron and arsenic by using microbial cell surface and accelerating generation of scorodite crystals. The method is simple in process flow and low in cost; the concentration of arsenic leached by the generated scorodite crystals meets the stipulation of solid waste identification standard which is leaching toxicity identification (GB5085.3-2007); the arsenic can be safely piled and stored; the leaching solution can be reused.
Owner:SCI RES ACADEMY OF GUANGXI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
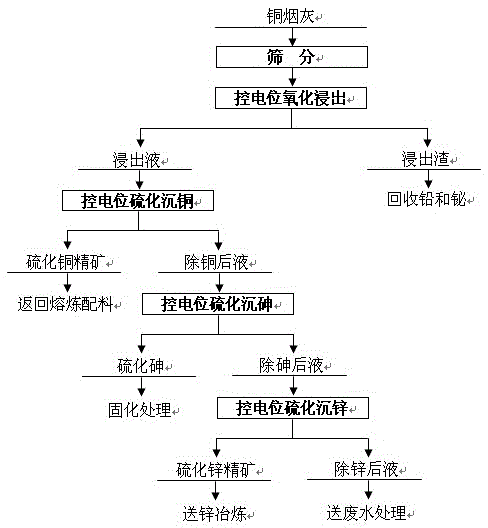
Method for potential controlled selection separation of copper refinery ash
InactiveCN105567984AIncrease sedimentation rateEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementSlurryCopper sulfide
The invention relates to a method for potential controlled selection separation of copper refinery ash. The copper refinery ash is screened and then subjected to oxidizing leaching in a sulfuric acid system. An oxidizing agent is added to control the metal ion mixed potential of slurry, copper, arsenic, zinc and other metal are dissolved into a solution, and lead, bismuth and other metal precipitate and enter leaching residues. The metal ion mixed potential and the pH value of a leachate are simultaneously controlled, so that copper sulfide concentrate is produced through precipitation. The metal ion mixed potential and the pH value of copper-removed liquid are simultaneously controlled, so that arsenic sulfide products are produced through precipitation. The metal ion mixed potential and the pH value of arsenic-removed liquid are simultaneously controlled, so that zinc sulfide concentrate is produced through precipitation. Zinc-removed liquid is subjected to wastewater treatment and then discharged after reaching the standard. According to the method, the potential controlled oxidizing leaching and potential controlled sulfide precipitation ways are simultaneously adopted for recovering valuable metal step by step, the selection separation effect, which cannot be achieved by independently using the ways, of the valuable metal in the copper refinery ash is achieved, and the leaching rates of copper, arsenic and zinc are larger than 98.0%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
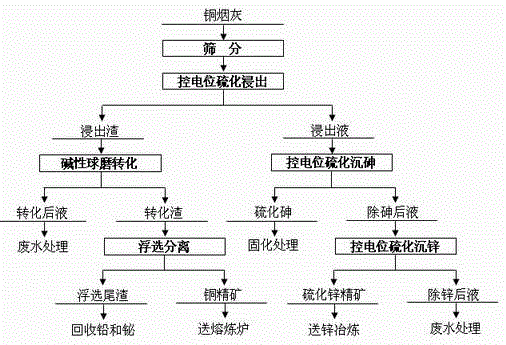
Copper soot smelting and separation combined treatment method
InactiveCN105624412AEasy to separateEasy to controlProcess efficiency improvementArsenic compoundsSlagFiltration
The invention discloses a copper soot smelting and separation combined treatment method. Copper soot is leached in water solution after ball milling to a requested particle size; sodium sulfide is added to control the metal ion mixed potential of whole pulp at a requested numerical value; meanwhile, sulfuric acid is added to adjust the pH value of the pulp to keep at a requested numerical value; after the solution potential is stabilized, and the stirring is continued by a period of time, the filtration is performed; the leaching liquid controls the metal ion mixed potential and the pH value; arsenic sulfide and zinc sulfide precipitates are respectively prepared to send to waste water for treatment; and leaching slag directly performs flotation to prepare copper concentrate and flotation tailing after alkaline ball milling conversion. The method recovers valuable metal step by step by using a control potential vulcanization leaching and beneficiation combined method; the processes are tightly associated; and single process cannot achieve the desired effect of selection and separation of the valuable metal in copper soot. The leaching rates of arsenic and zinc both reach above 95.0%; and the direct recovery rate of copper reaches above 98.0%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
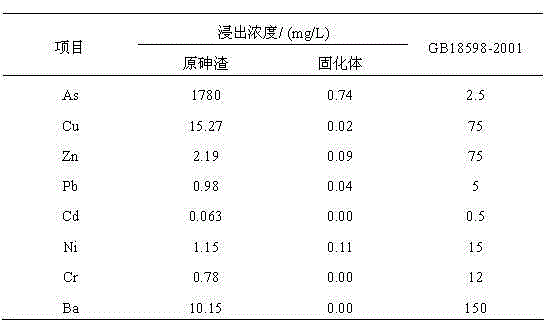
Stable curing method of arsenic sulfide waste slag
ActiveCN105215047AReduce leachingReduce contentSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingCalcium hydroxideSlag
The invention discloses a stable curing method of arsenic sulfide waste slag. The method comprises the following steps: (1) heavy metal sludge is added in arsenic sulfide slag to be treated for stirring to obtain a slurry material; (2) calcium hydroxide powder is added in the slurry material obtained in the step (1) in the stirring state for continuous stirring until red substances in the slurry material are all disappeared; (3) yellow sand and cement are added in the material obtained by stirring in the step (2); and (4) the stirring material obtained in the step (3) is cooled to the normal temperature, is transferred to a forming mold for molding, is taken out from the mold, and is maintained at the normal temperature to obtain a curing body accordant with the landfill standard. The method uses the heavy metal sludge as an arsenic stabilizing agent for treating wastes by wastes; the sources of such materials as heavy metal sludge, lime, cement and yellow sand needed to treat the strong-acid arsenic sulfide waste slag are wide; other medicaments are not needed to be added; and compared with other methods, the method is lower in treatment cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU JIEJIA IND SOLID WASTE HANDLING CO LTD
Combined treatment method for copper smelting soot and polluted acid
InactiveCN105950874AEasy to separateAvoid consumptionProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfideSoot
The invention discloses a combined treatment method for copper smelting soot and polluted acid. The method includes the steps that after the copper smelting soot and the polluted acid are mixed for pulp conditioning, an oxidizing agent is added for controlled-potential oxidization leaching, so that copper, arsenic, zinc and other metal in the copper soot are dissolved to enter leachate, and lead, bismuth and other metal are precipitated to enter a reaching residue; then an oxidizing agent is added into the leachate so that As(III) in the solution can be completely oxidized into As(V); afterwards, sodium sulphide is added, so that the copper in the solution is precipitated in the form of copper sulphide to produce copper concentrate, and a reducing agent is added into the copper-removed solution so that the As(V) in the solution can be completely reduced into As (III); then sodium sulphide is added so that the arsenic in the solution can be precipitated in the form of arsenic sulfide; and finally the arsenic-removed solution is neutralized with alkaline and then is discharged after reaching the standard. By the adoption of the combined treatment method, controlled-potential oxidization leaching, controlled-potential oxidization sulfurization and reduction sulfurization are simultaneously combined to be used for step-by-step separation and recovery of valuable metal in the copper smelting soot and polluted acid, and therefore waste in the system can be recycled, and the purpose of using waste to treat waste is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
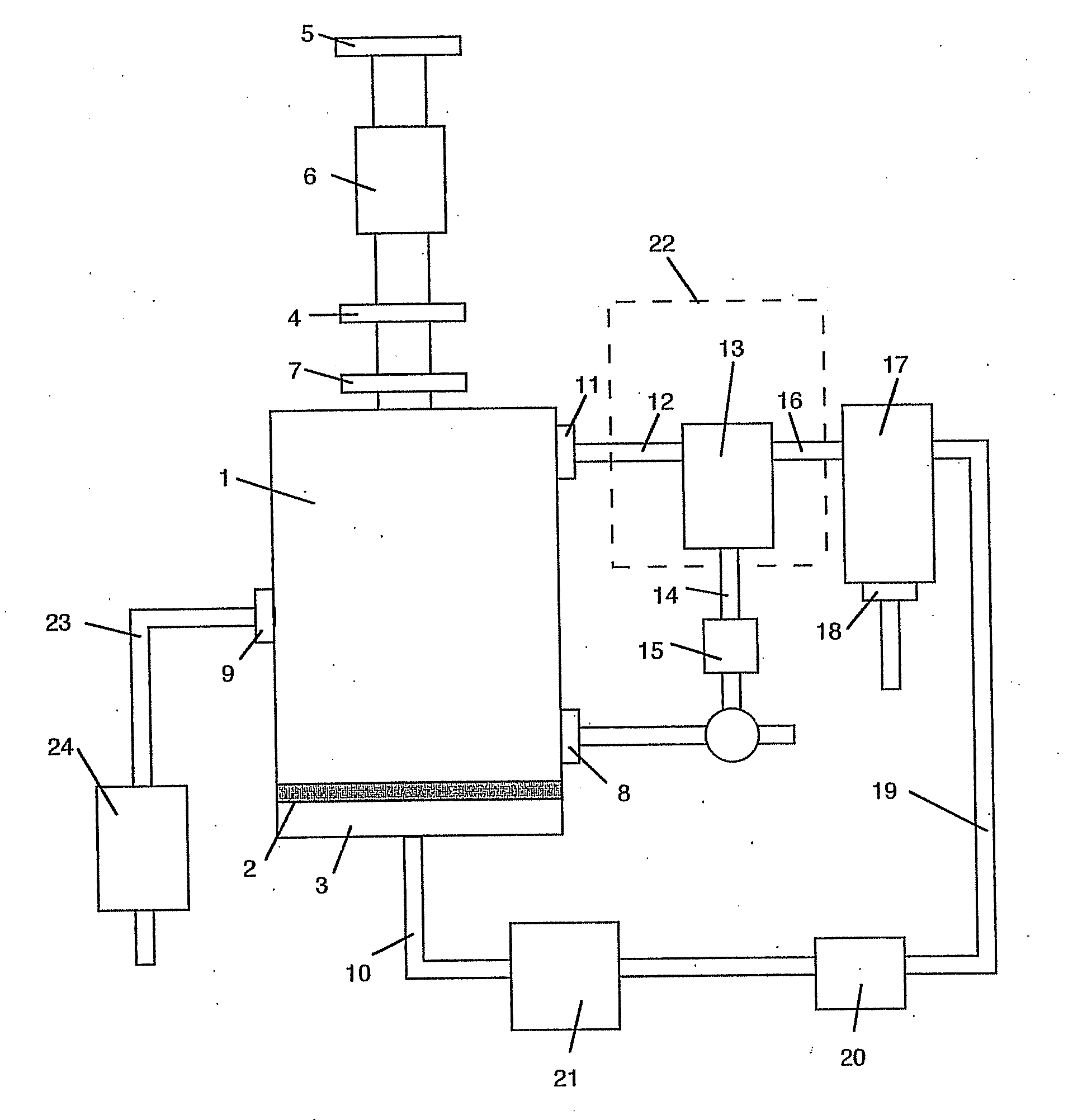
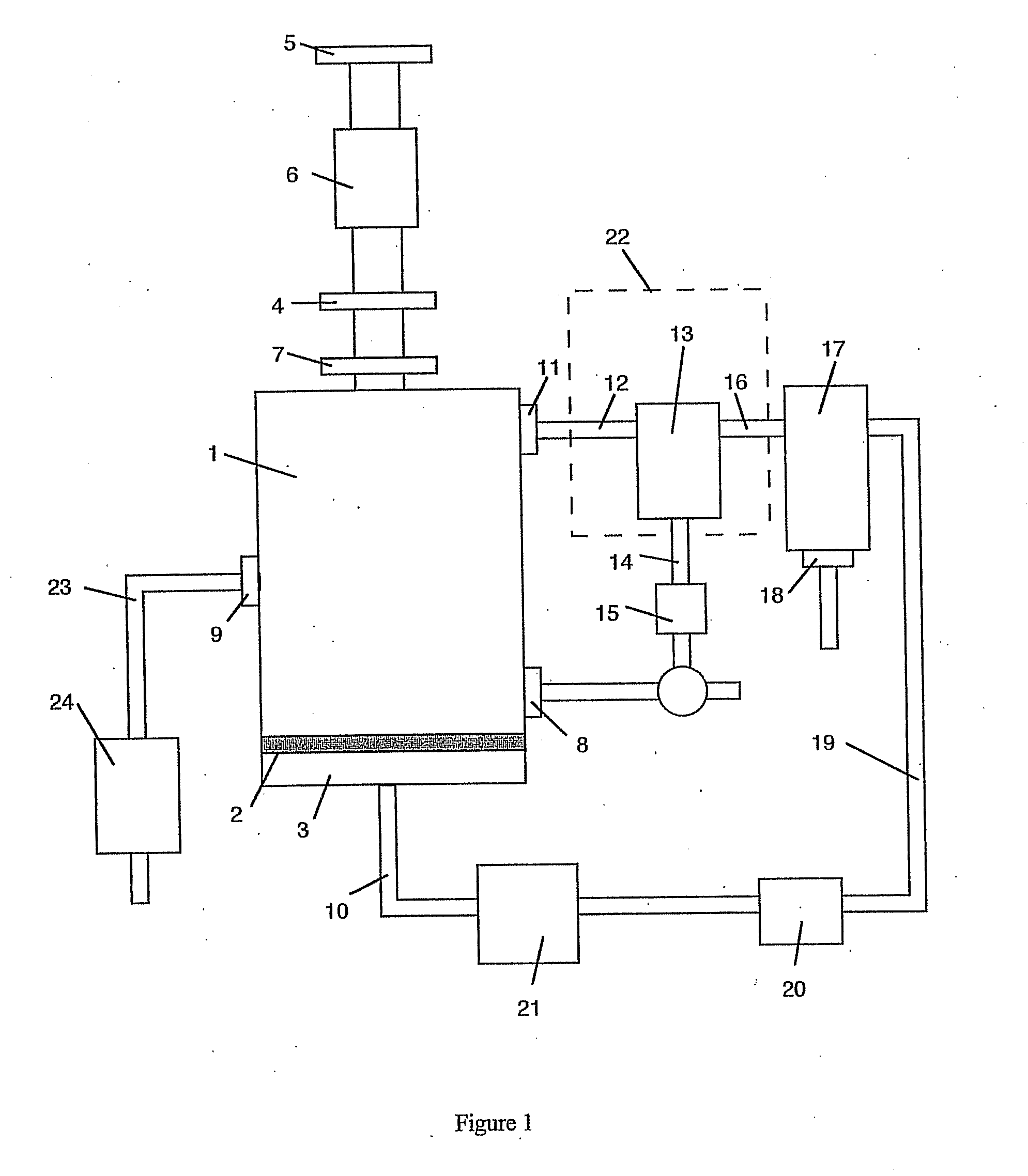
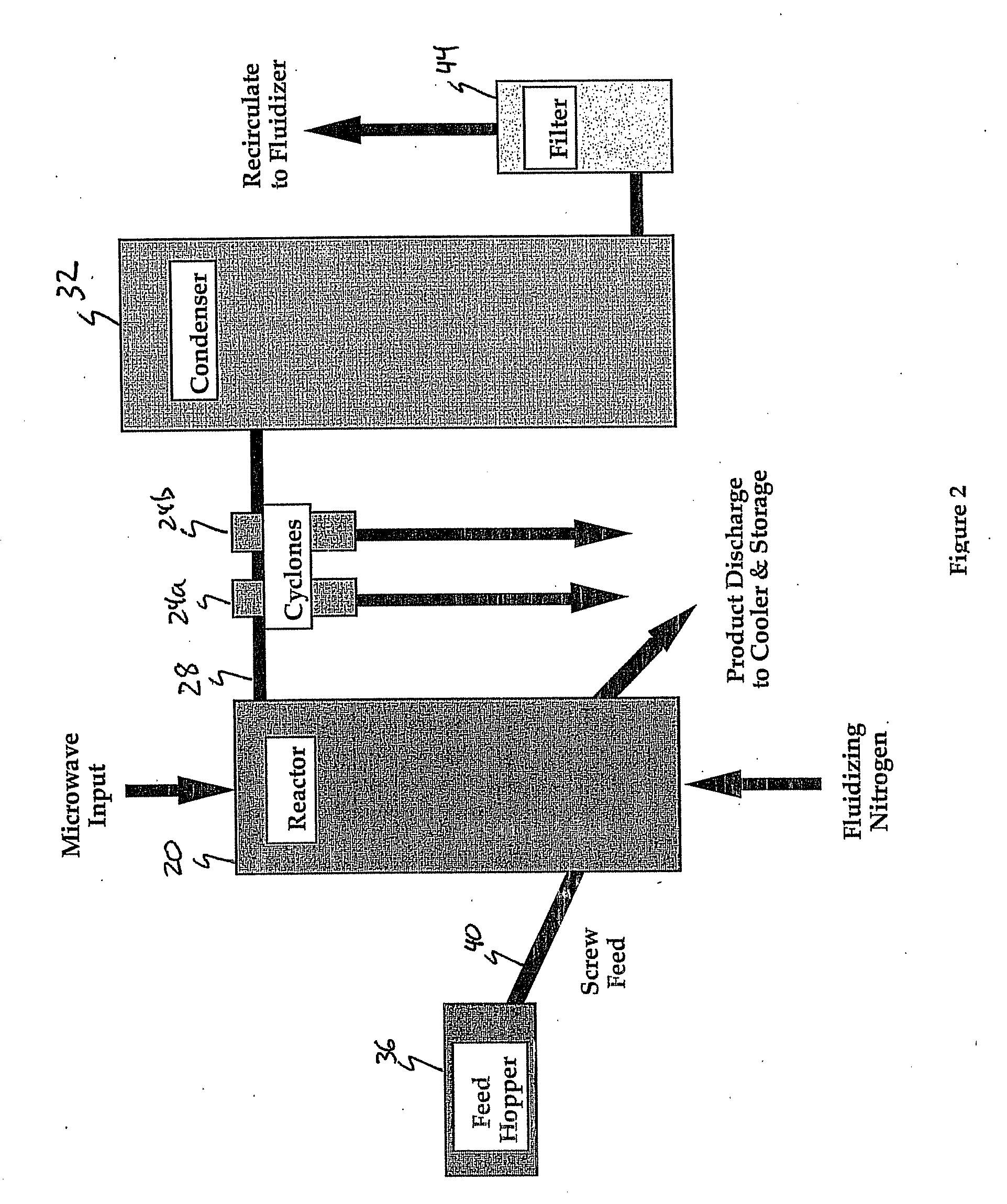
Method and apparatus for microwave induced pyrolysis of arsenical ores and ore concentrates
A method is provided that includes the steps of passing microwave energy through a sulfidic material comprising arsenopyrite and pyrite to reduce at least most of the arsenopyrite to arsenic sulfide and form a calcine, the material being positioned in a reaction chamber of a reactor vessel and removing the arsenic sulfide from the calcine.
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
Method for recycling valuable elements in acidic biological oxidation solution containing arsenic, iron and sulfur
ActiveCN106521162AEasy to storeAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyArsenic sulfide
The invention relates to a method for recycling valuable elements in an acidic biological oxidation solution containing arsenic, iron and sulfur and belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: performing three-stage counter-current extraction on the oxidation solution and an extracting agent so that iron ions in the oxidation solution can turn into an organic phase so as to be separated and recycled; adding a precipitator to the iron-removed raffinate, and concentrating the elements such as arsenic, sulfur and a trace amount of copper, lead, zinc and iron in neutral dregs; leaching the ions of arsenic, copper, lead, zinc, iron and the like from the neutral dregs obtained after solid and liquid separation by using a sulfuric acid solution, and then performing solid and liquid separation to obtain a calcium sulfide product; adding sodium sulfide to a sulfuric acid leaching solution, precipitating arsenic ions in the solution in the form of arsenic sulfide and recycling arsenic in the form of a arsenic sulfide product after solid and liquid separation; and adding sulfuric acid to the arsenic-precipitated acidic solution, and repeating the step of leaching the arsenic in the neutral dregs. The method has the advantages that the used raw materials are easy to get and low in price; the technological process is simple and practical; comprehensive recovery rate of the valuable elements is high; and zero emission of wastes is realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
Process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on recovery section in process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting
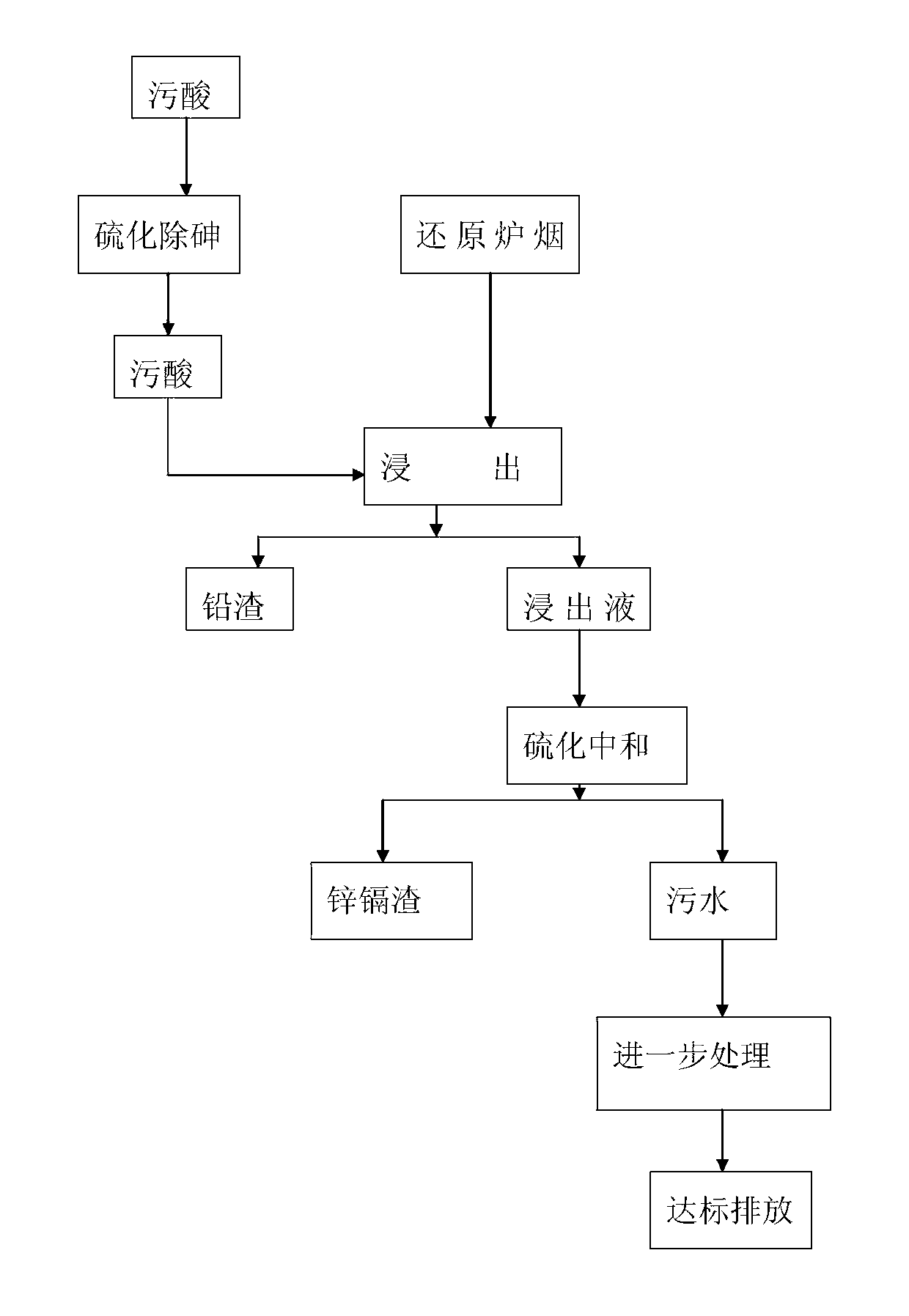
InactiveCN102994764ALow running costAvoid harmProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to the field of nonferrous metal smelting and particularly relates to a process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on a recovery section in the process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting. The soot of a reduction furnace is subjected to a leaching reaction by using arsenic sulfide removal waste acid in the lead smelting industry to generate lead slag to be recovered, and then, the leaching agent is continued to be neutralized by using sodium sulphide and sodium hydroxide to generate high-grade zinc and cadmium slag to be recovered. According to the invention, the waste acid is used for separating the lead, zinc and cadmium in the soot of the reduction furnace for lead smelting, so that the operation cost is low; the problem of production operation damage caused by circulated accumulation of the zinc and cadmium in lead smelting is solved and the pressure of a lead smelting system is relieved under the condition of low cost; and the lead slag which is low in arsenic content and suitable for being treated by a lead system and the zinc and cadmium slag which is suitable for being treated by a zinc system can be generated, and meanwhile, the waste acid is also treated, so that not only is the treatment cost of the waste acid reduced, but also the treatment difficulty is lowered.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
Method for purifying and recovering valuable metal by copper electrolyte
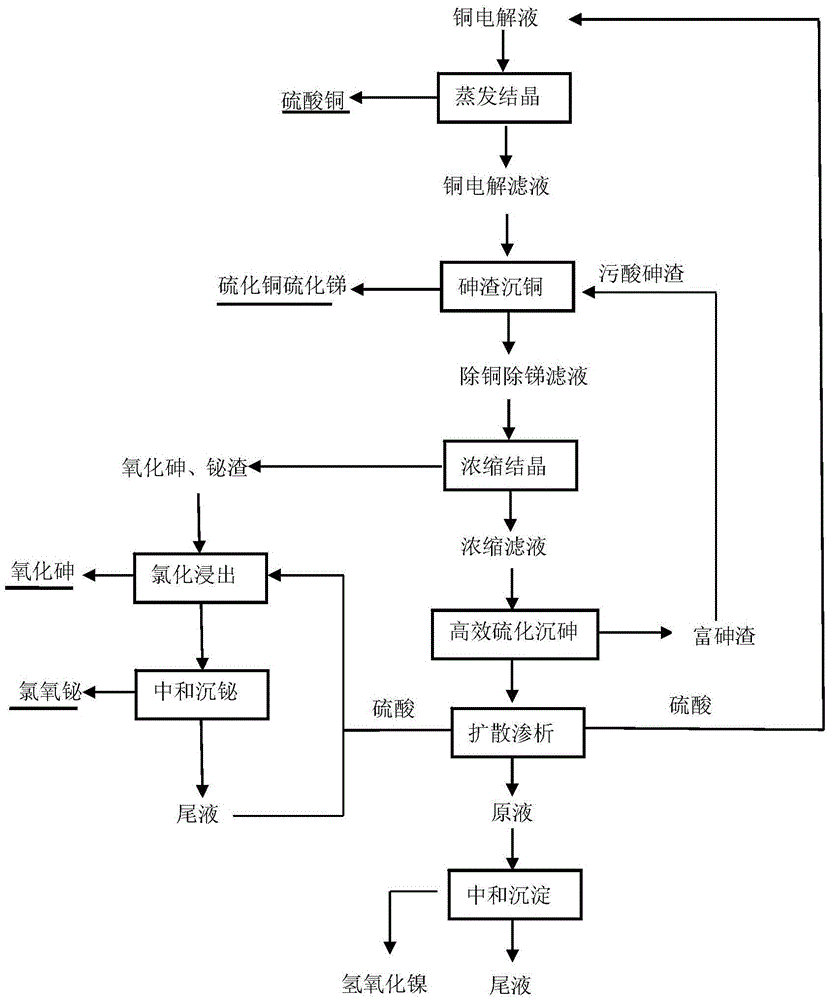
ActiveCN105603190AReduce manufacturing costSimple processProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention discloses a method for purifying and recovering valuable metal by copper electrolyte. The method comprises the following steps: (1) evaporating, crystallizing and filtering the copper electrolyte to recover copper sulfate; (2) adding arsenic sulfide slag into copper electrolysis filtrate, and filtering to recover copper sulfide and antimony sulfide after a reaction is finished; (3) evaporating, crystallizing and filtering the copper electrolysis filtrate to separate arsenic oxide and bismuth oxide; (4) selectively leaching and recovering bismuth in the step (3); (5) efficiently vulcanizing the copper electrolysis filtrate for deep arsenic removal; (6) performing diffusion dialysis on the copper electrolysis filtrate to separate and recover sulfuric acid; (7) recovering nickle in a diffusion dialysis stock solution by adopting a neutralization precipitation method. The method adopts a wet method in the whole process, is efficient, environment-friendly and energy-saving, and has better application value.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
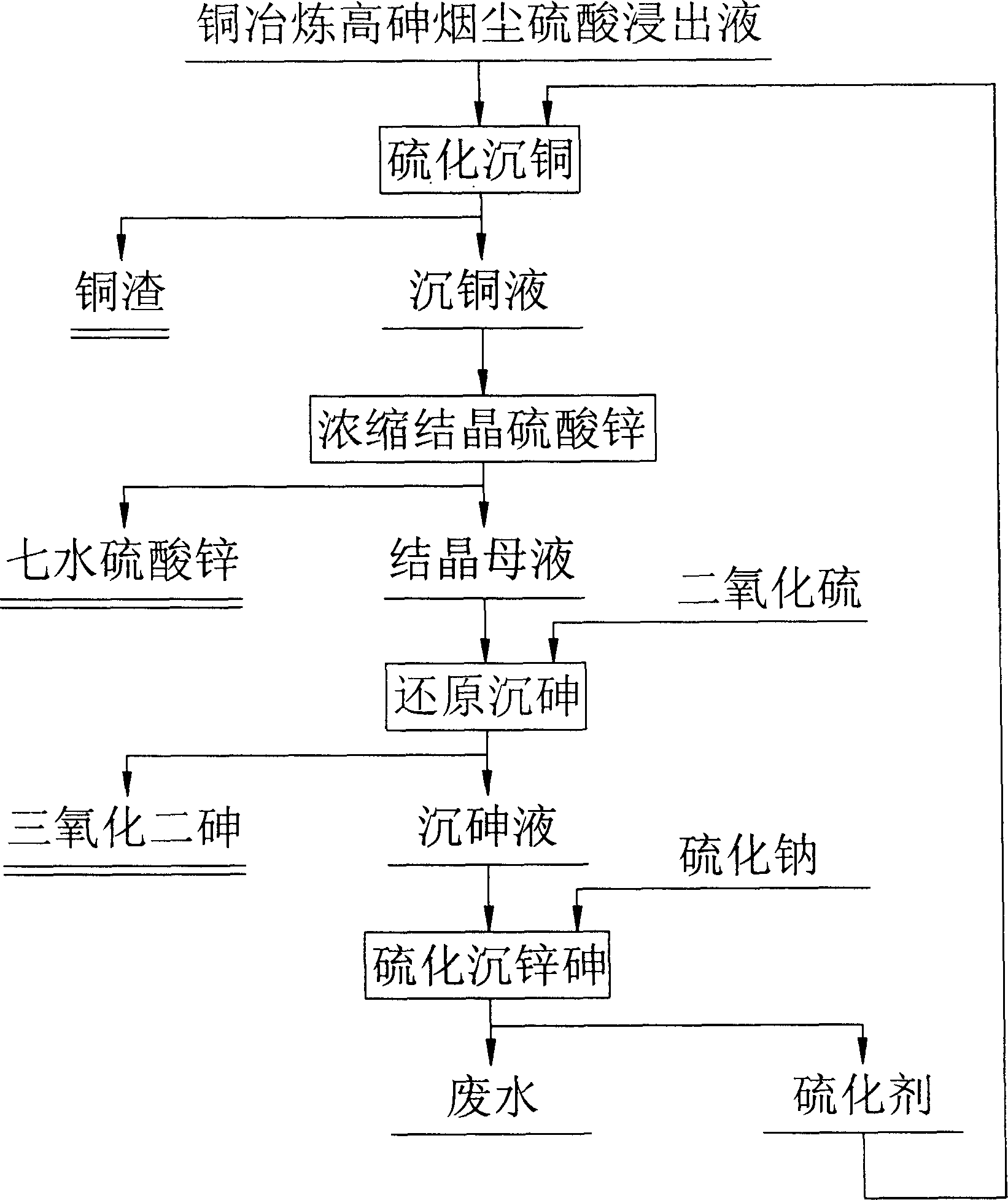
Method for separating copper, arsenic and zinc from copper-smelting high-arsenic flue dust sulphuric acid leach liquor
InactiveCN1789445AHigh recovery rateEffective pollution controlProcess efficiency improvementSulfideZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
The invention relates the method of separating copper, arsenic and zinc from copper smelting high arsenic fog sulfuric acid leachate, comprising the following steps: adding vulcanized agent (zine sulfide and arsenic sulfide) into the leachate to make copper precipitate, separating and getting the copper scale and copper liquid; concentrating the liquid and cooling, getting the zinc sulphate heptahydrate and crystallization mother liquid; adding sulfur dioxide into the crystallization mother liquid and getting arsenious oxide and the arsenic liquid; adding sodium sulfide aqueous solution into the arsenic liquid and getting the zine sulfide and arsenic sulfide which can be used as vulcanized agent to precipitate copper. The core technology of the invention is copper precipitation by sulfidization. At the process of the copper precipitation there is not other impurity substances and the vulcanized agent is made by the flow process. The invention realizes the segregation of copper, arsenic and zinc and effectively harnesses the arsenic contamination.
Owner:朱永文
Method for reduction, self vulcanization and dearsenification of refractory high-arsenic high-sulphur gold ore
The invention discloses a method for reduction, self vulcanization and dearsenification of refractory high-arsenic high-sulphur gold ore. The method includes the steps that the high-arsenic high-sulphur gold ore is roasted on the condition of the medium and low temperature in the presence of a reduction agent; and the obtained roasted ore is isolated from air cooling, so that the gold ore product with arsenic removed is obtained. By means of the method, arsenic and sulphur in the high-arsenic high-sulphur gold ore are volatilized and removed as arsenic sulfide; since the arsenic sulfide is low in toxicity, and no external sulphur source or other additives is needed in the roasting process, compared with an existing oxidation roasting method, the method has the advantages of being economical and environmentally friendly. Besides, the technical process is short, practicability is high, and the method can be applied and popularized advantageously.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biological production method of photoconductive arsenic-sulfide (As-S) nanotube and strain used for the same
InactiveUS20090155876A1Improve convenienceHigh potential utilityBacteriaUnicellular algaeArsenateBiochemistry
Disclosed is a biological method for preparing arsenic sulfide (As—S) compounds. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for production of nanotubes based on As—S compounds including As2S3 by reacting thiosulfate S2O32− with arsenate As5+ through mediation of Shewanella sp. strain.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Hot-pressing sintering curing method for arsenic sulfide slag
ActiveCN108580513AReduce energy consumptionDoes not affect the effectSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingSulfurSlag
The invention provides a hot-pressing sintering curing method for arsenic sulfide slag. The hot-pressing sintering curing method comprises the following steps that firstly, the pH value of the arsenicsulfide slag is adjusted to be 1-7; the arsenic sulfide slag subjected to a neutralization reaction is dried and dehydrated; then sulfur powder is added, and after even stirring and mixing are conducted, vibrating compaction and briquetting forming are conducted; and finally, a formed arsenic sulfide slag block is placed in a hot-pressing sintering curing reaction device to be subjected to hot-pressing sintering curing so as to obtain the arsenic sulfide slag hot-pressing sintered block. According to the arsenic sulfide slag hot-pressing sintered block obtained by treating through the hot-pressing sintering curing method, the leaching toxicity of arsenic can be reduced by 90% or above, and the compressive strength of the cured block can reach 10 MPa or above. The hot-pressing sintering curing method is simple in treatment technology, low in cost and obvious in economic benefit and environmental benefit.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Copper smelting hazardous waste co-processing and valuable metal comprehensive recovery method
PendingCN112359213ALarge amount of processingIncrease consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagCopper sulfide
The invention provides a copper smelting hazardous waste co-processing and valuable metal comprehensive recovery method which comprises the following steps of firstly, carrying out atmospheric pressure-pressurization two-stage countercurrent leaching on copper smelting smoke to obtain atmospheric pressure leachate and lead-silver-bismuth slag, and carrying out electrodeposition pre-copper removalon the atmospheric pressure leachate to obtain electrocoppered and pre-decoppered liquid; then adding arsenic sulfide slag into the pre-decoppered liquid for replacement and copper precipitation to obtain copper sulfide concentrate and copper precipitation post-liquid; and introducing SO2-containing flue gas into the copper precipitation post-liquid for reduction and arsenic precipitation, and obtaining arsenic trioxide and arsenic precipitation post-liquid. According to the copper smelting hazardous waste co-processing and valuable metal comprehensive recovery method provided by the invention, the waste residue recycling and harmless processing degree is high, the valuable metal comprehensive recovery effect is good, no waste acid, waste water or hazardous solid waste is generated in thewhole process, a new path is provided for copper smelting hazardous waste co-processing, and wide application prospects are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Resource utilization process for high pressure oxygen continuous leaching of arsenic sulfide slag
ActiveCN106086426AHigh recovery rateNo pollution in the processProcess efficiency improvementSlagResource utilization
The invention discloses a resource utilization process for high pressure oxygen continuous leaching of arsenic sulfide slag. The arsenic sulfide slag is treated through high pressure oxygen and then is reduced and extracted so that refined arsenic trioxide, copper sulfate and ammonium rhenate can be obtained; meanwhile, obtained waste acid liquid can be recycled for slurrying of the arsenic sulfide slag; and the whole process is high in recycling rate and free of pollution and is a novel and environment-friendly arsenic sulfide slag recycling process.
Owner:郴州金铖环保科技有限公司
On-chip integrated arsenic sulfide microdisk cavity and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN105731352AHigh quality factorImprove performanceSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsArsenic sulfideMaterials science
An embodiment of the present invention discloses an on-chip integrated arsenic sulfide microdisk cavity and a method for manufacturing the same. The microdisk cavity includes: a microdisk and a supporting structure stacked from top to bottom; wherein the size of the microdisk is greater than that of the supporting structure. According to the on-chip integrated arsenic sulfide microdisk cavity and the method for manufacturing the same provided in the embodiment of the present invention, the quality factors of the on-chip integrated arsenic sulfide microdisk cavity can be increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing arsenic trioxide by arsenic-containing waste water
InactiveCN102115165AHigh recovery rateLow costSolid waste disposalArsenic compoundsCopper sulfateArsenic sulfide
The invention provides a method for preparing arsenic trioxide by arsenic-containing waste water, which comprises the steps of: mixing arsenic sulfide waste residue with water, and extracting arsenic sulfide by sodium hydroxide solution; mixing the obtained arsenic sulfide with the water with 2-5 times of the weight of the arsenic sulfide to be sizing agent, and reacting with copper sulfate solution to obtain arsenous acid and copper sulphide-containing precipitate and sulfuric acid solution; mixing the arsenous acid and copper sulphide-containing precipitate with the water to feed the oxygen, oxygenizing arsenious acid to generate arsenic acid which is easy to dissolve in water, and filtering to obtain arsenic acid solution and copper sulphide precipitate; restoring the obtained arsenic acid to be arsenious acid by sulfur dioxide to obtain arsenious acid; and distilling the arsenious acid, concentrating, filtering and drying to obtain an arsenic trioxide product. The method is short in technological process, high in arsenic recovery rate, free of the generation of secondary pollutant, simple in equipment, and extremely lower in arsenic recovery cost, thereby being a method which is worth to popularize and apply.
Owner:马艳荣
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com