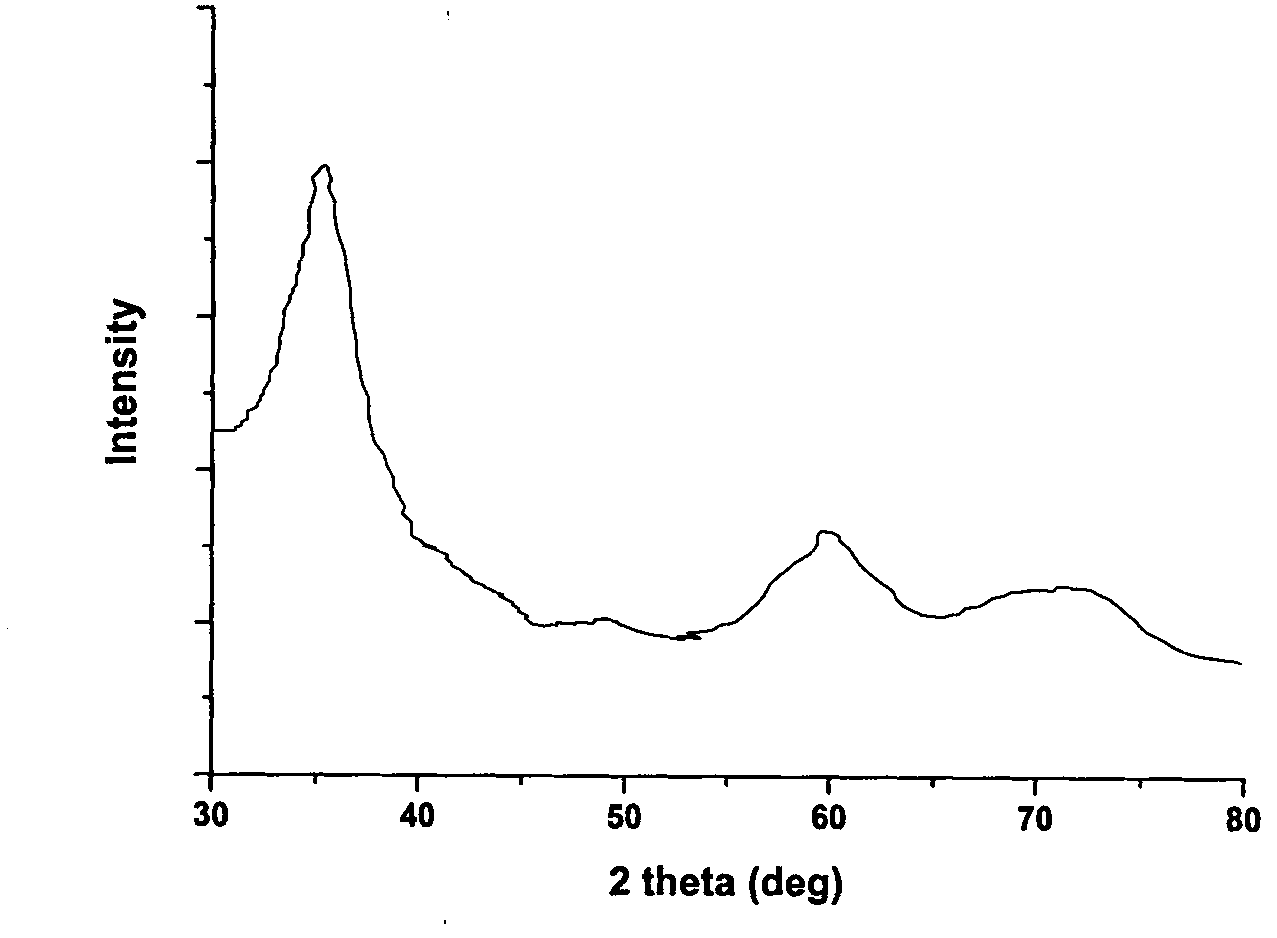
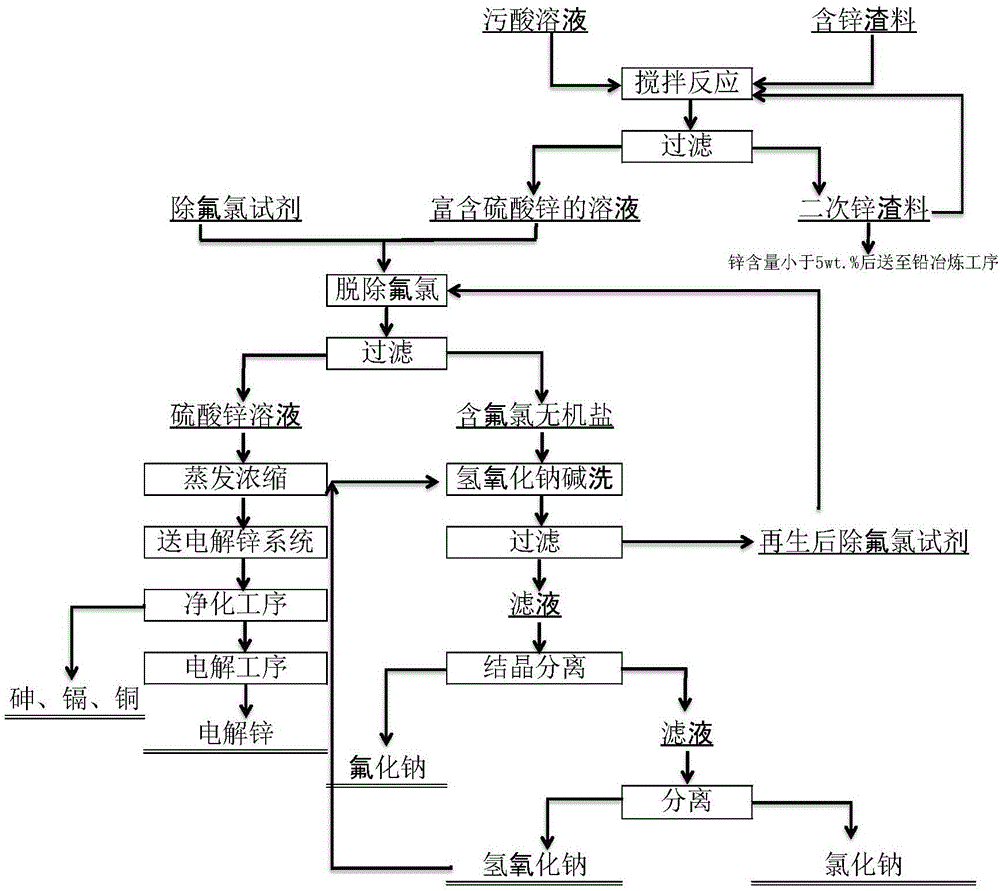
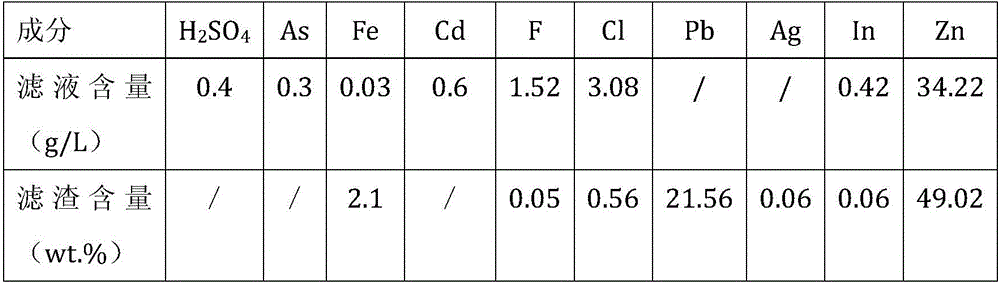
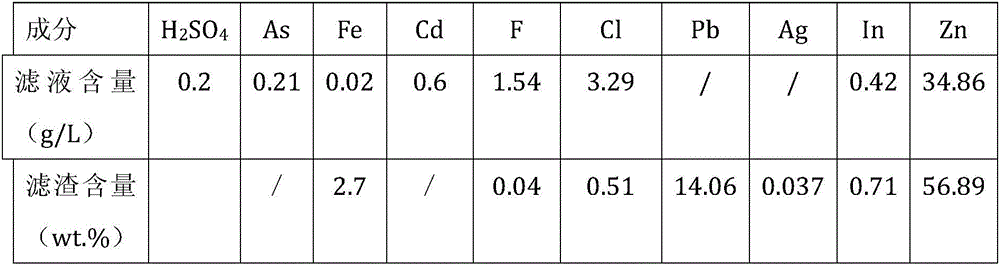
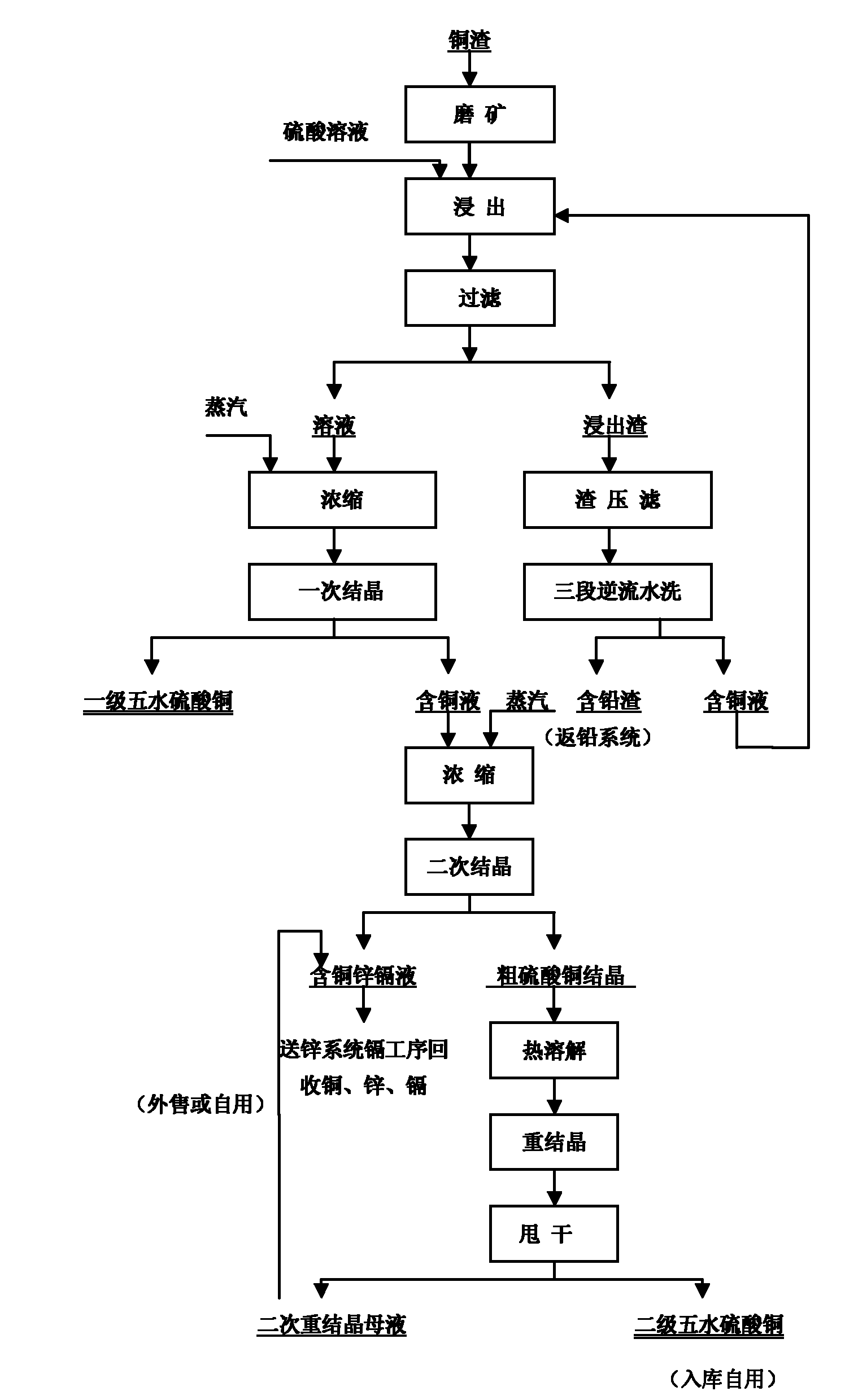
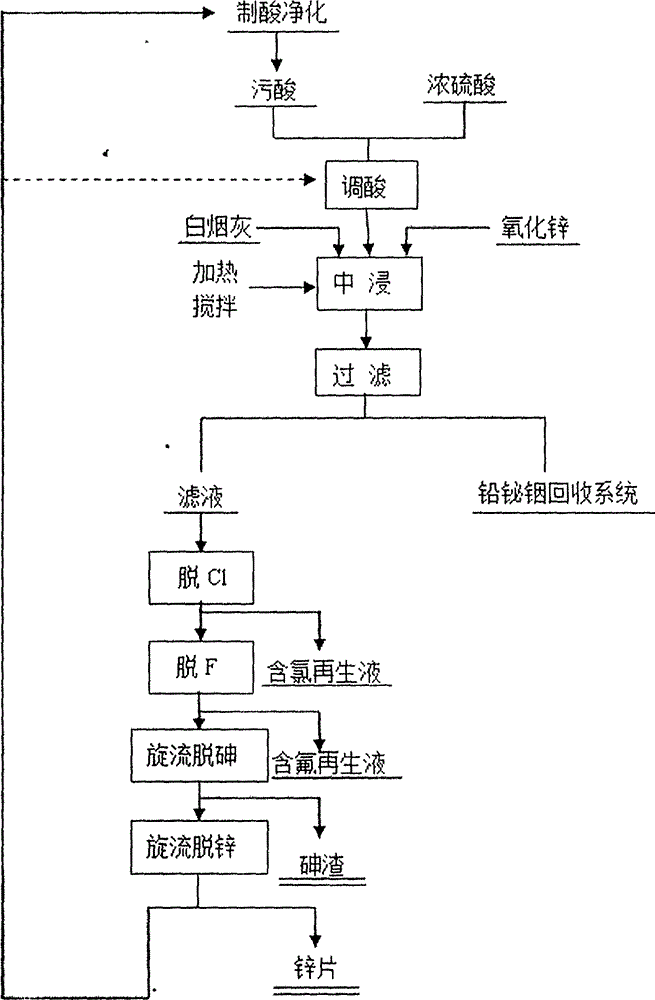
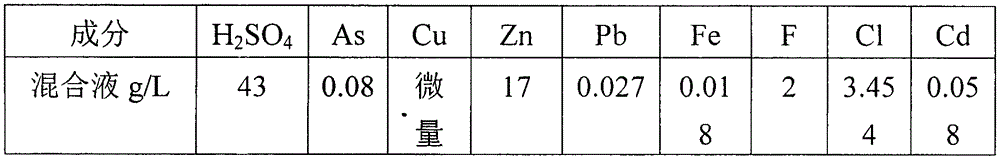
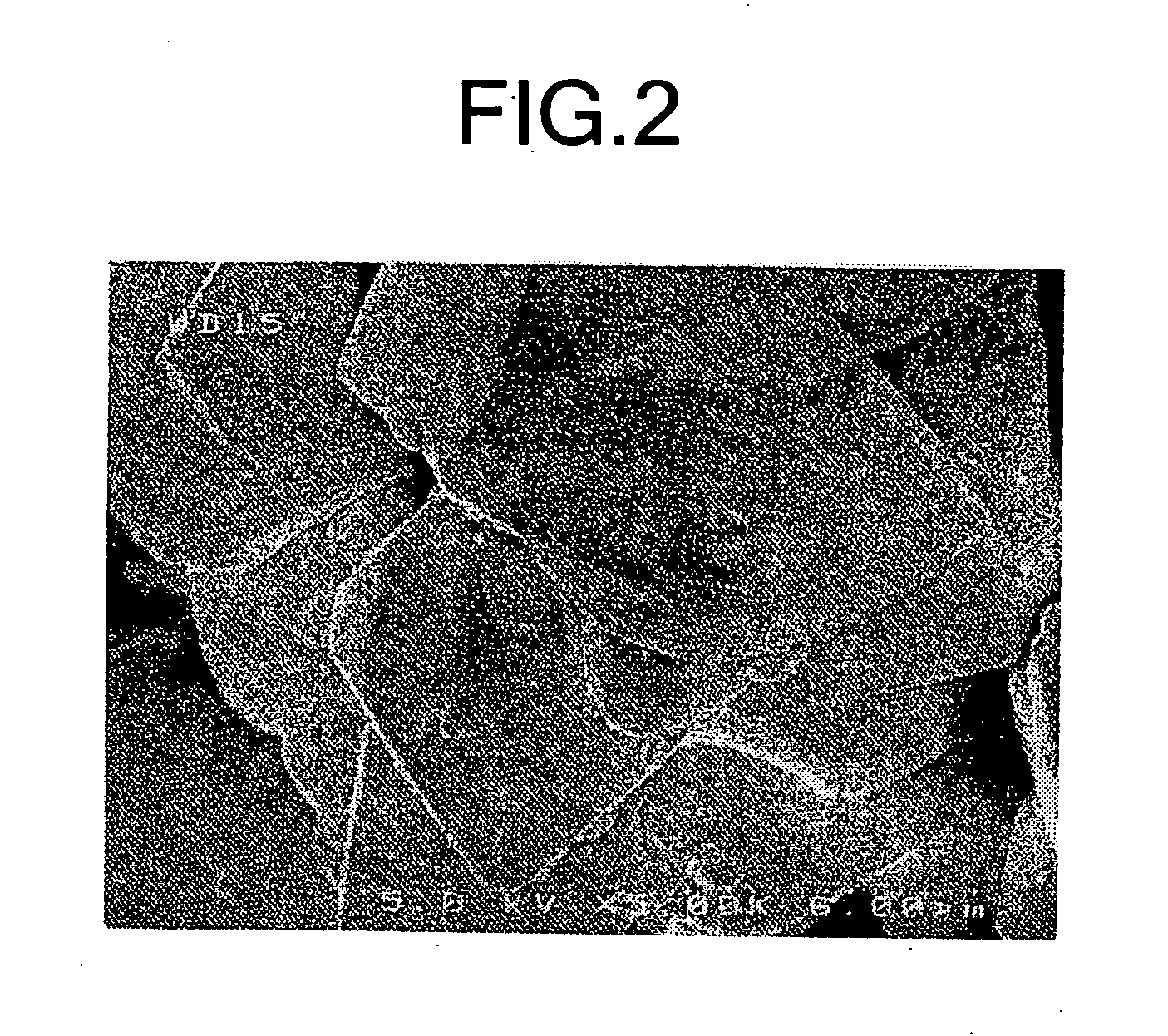
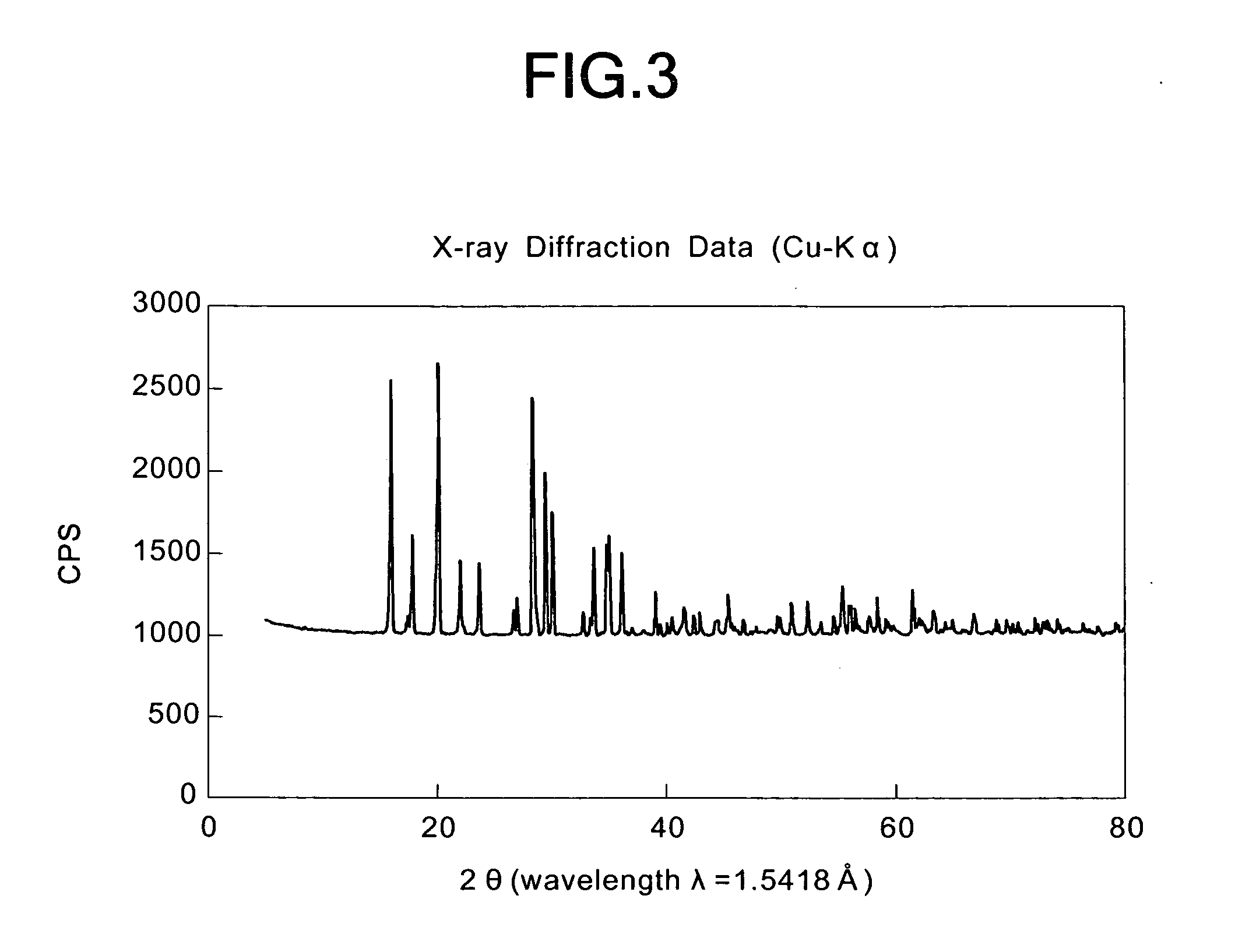
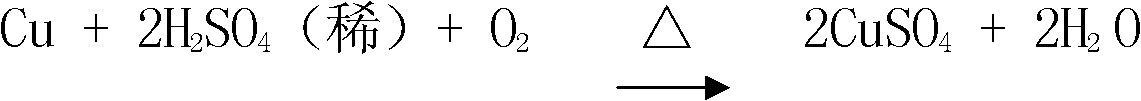Patents
Literature
496 results about "Non-ferrous extractive metallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-ferrous extractive metallurgy is one of the two branches of extractive metallurgy which pertains to the processes of reducing valuable, non-iron metals from ores or raw material. Metals like zinc, copper, lead, aluminium as well as rare and noble metals are of particular interest in this field, while the more common metal, iron, is considered a major impurity. Like ferrous extraction, non-ferrous extraction primarily focuses on the economic optimization of extraction processes in separating qualitatively and quantitatively marketable metals from its impurities (gangue).
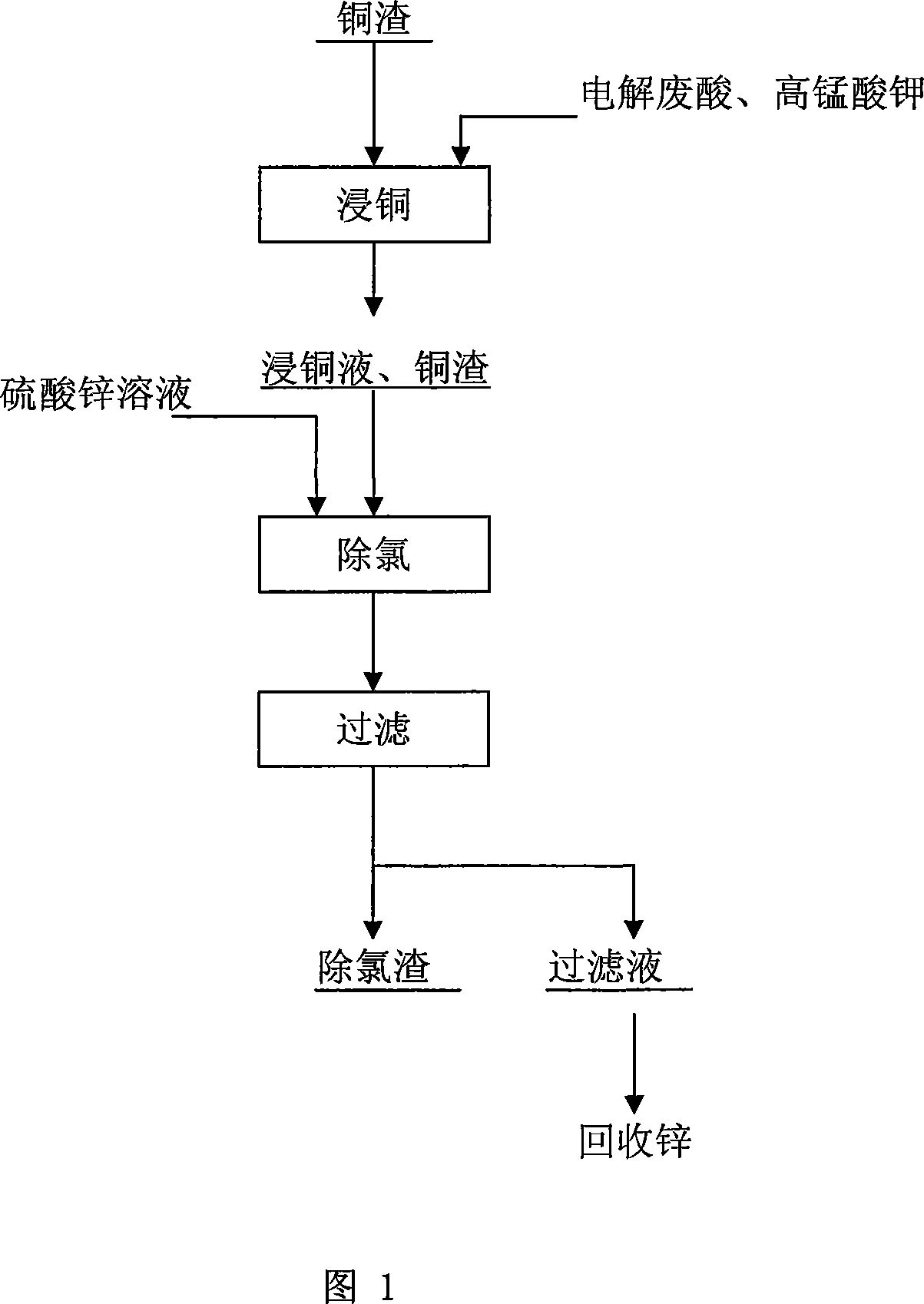
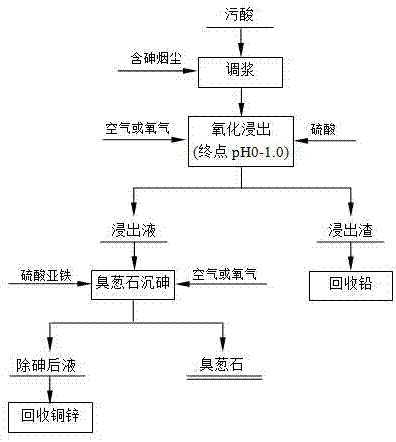
Method for removing chlorine from zinc sulfate solution
InactiveCN101113015ATake advantage ofNo pollution in the processZinc sulatesSulfatePhysical chemistry
A method to remove chlorine from zinc sulfate solution pertains to nonferrous metallurgy. The chlorine in the zinc sulfate solution is removed through elementary copper in copper slug and Cu2+ generated from oxidation of copper slug react with chloride ion to get insoluble CuCl precipitation. The invention makes a further use of copper slug generated from wet zinc melting method, first partial elementary copper in the copper slug is oxidized and then Cu2+ ion is obtained without adding copper sulfate, realizing the effect that elementary copper and Cu2+ ion are both supplied by the slug to involve in chlorine removal reaction. When in the chlorine removal process, no copper sulfate is added and the copper slug is made a full use, therefore, production cost is reduced, operation process is simplified, no waste slug, waste gas and waste water are added and no pollution is done to the environment and as materials involved in the invention are ordinary materials and are not needed and consumed in a large amount, the invention has remarkable economic effect.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
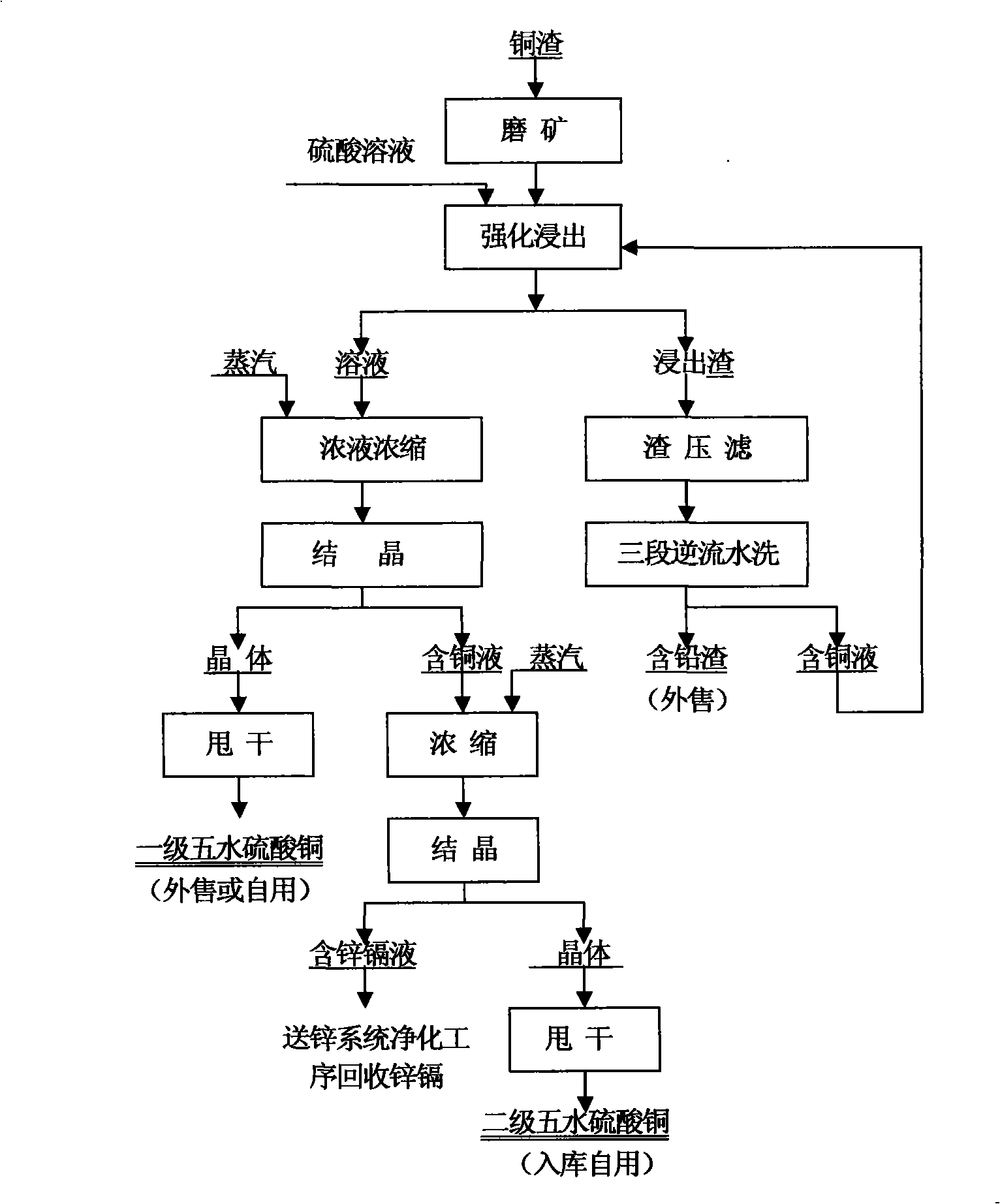
Process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials
InactiveCN101538646AImprove leaching rateImprove product qualityProcess efficiency improvementHigh energyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to a process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials, which has short production flow, low energy consumption, good environment and high metal recovery rate and belongs to the technical field of integrated recovery and utilization of nonferrous metal smelting slag. The process method is mainly characterized in that the copper slag is directly intensifiedly leached, and the oxidation roasting process of the copper slag is replaced by intensified leaching, thereby solving the problems of high energy consumption, great environmental pollution and long process flow of the copper slag during the oxidation roasting process. As the process method intensifies the leaching conditions, the leaching rate of copper is improved to be more than 94 percent, and the leaching time is reduced to 2 hours from the conventional 24 hours, thereby greatly improving the production efficiency of the copper sulfate, effectively reducing the production cost, reducing the production flow of the copper sulfate by one third, and greatly improving the metal recovery rate.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Die-casting method of induction motor copper cage rotor and die casting device thereof
ActiveCN101108416AReduce manufacturing costReasonable workmanshipGearingCylindersMiddle frequencyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to a casting method and casting machine of the induction motor cooper squirrel-cage rotor, which is suitable for the casting of pure copper and high copper content alloy. The invention belongs to nonferrous metal smelting and rolling process technology filed. The casting method comprises module pre-process, copper smelting, liquid casting and forming and quench water cooling. The casting method adopts a casting device which is composed of a casting machine and a smelting furnace, wherein, the smelting furnace comprises an integrated pot and middle frequency induction furnace, the heating efficiency of the middle frequency induction furnace is 0 to 100KW; the casting module comprises a group connection which is connected by a plurality of embedded lump. The invention has reasonable technics and equipment, the product has no defects of breakage on casting piece and surface, poor filling and mold sticking, the shaking present value complies with the R degree provision in IEC34-14(1994), which has the advantages of improving by one degree comparing with the N degree stipulated in Y series motor technology condition.
Owner:云南铜业压铸科技有限公司
Dry-type removing method for sulfur trioxide and heavy metals in nonferrous smelting acid-making flue gas
ActiveCN104841265AEfficient removalReduce contentCombination devicesSorbentNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
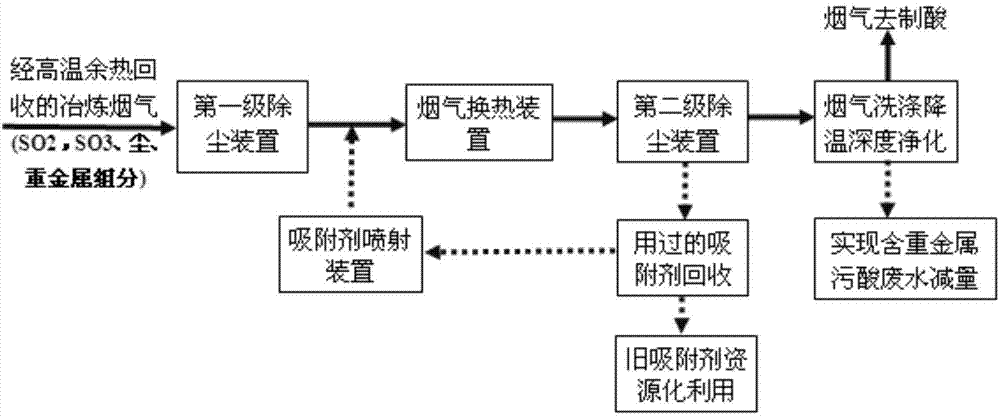
The invention relates to a dry-type removing method for sulfur trioxide and heavy metals in nonferrous smelting acid-making flue gas. The method comprises the following steps: primarily recovering heat of nonferrous smelting flue gas through a high-temperature heat recovery boiler and carrying out first-stage dust removal through a first-stage dust removal device so as to remove more than 90% of gas dust in the flue gas; then directly jetting, from a flue, the powder of an absorbent capable of adsorbing / absorbing SO3 and heavy-metal components into the flue gas having undergone the first-stage dust removal, and carrying out absorption reaction; then cooling the flue gas containing the absorbent by utilizing a flue gas heat-exchange device so as to allow SO3 and heavy metals to be effectively trapped and collected by the absorbent and part of volatile heavy metals to be condensed through induction; and finally, trapping and collecting the absorbent having absorbed SO3 and the heavy metals and granular heavy metals via a second-stage dust removal device. Compared with the prior art, the dry-type removing method provided by the invention can effectively remove the heavy metal components and SO3 in the flue gas from upstream and reduces the concentration of sulfuric acid and the contents of heavy metals in washing wastewater.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Treatment and recycling method of industrial wastewater containing a plurality of heavy metal ions
ActiveCN103819023AHigh recovery rateReduce pollutionWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentIndustrial waste waterFiltration
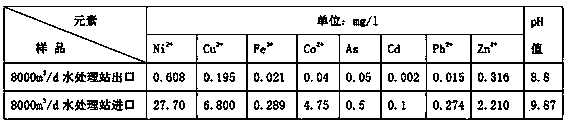
The invention relates to a treatment and recycling method of industrial wastewater containing a plurality of heavy metal ions, and the method can be applied in wastewater treatment and wastewater cyclic utilization of a non-ferrous metal metallurgy manufacturing enterprise. The technology comprises the following steps: wastewater containing a plurality of heavy metal ions, oil separation and desanding, water quality and quantity homogeneous regulation, basic flocculation precipitation reaction, primary precipitation, air floatation and oil removing, sulfuration and flocculation precipitation reaction, secondary precipitation, and filtration. According to the invention, wastewater containing a plurality of heavy metal ions of nonferrous metals and As-containing noble metal ions can be processed, and processed water enters a reclaimed water treatment station to be processed for cyclic utilization. Thus, the pollution of nonferrous metal ions in industrial wastewater to production regions, downtown living environment and surrounding ecological environment is reduced, and recovery rate of nonferrous metal ions is raised. Recovered metal and noble metal have high economic value. Enterprise recycling economy and resource comprehensive utilization are promoted, and reducing discharge and maximum utilization of resources are achieved. Thus, the method provided by the invention has a wide application prospect in the non-ferrous metal metallurgy enterprises.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for preparing white carbon black from secondary carbon component
The twice carbon separating process for preparing silica white includes introducing CO2 gas to sodium silicate solution to lower the pH value to 9-10.5, solid-liquid separating, further introducing CO2 gas to the solution to lower the pH value to 7-8, solid-liquid separating, washing and stoving to obtain coarse silica while product, soaking or boiling in strong acid solution, washing and stoving to obtain silica while product. The present invention may have the sodium silicate solution obtained through soaking high silicon slag from producing aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, ferrous metal and non-ferrous metal and with high impurity content as the material, and the silica while product has high purity, fine granularity and high whiteness.
Owner:PINGSHUO INDAL
Method for low-temperature synthesis of silicon carbide from agricultural wastes
InactiveCN101891195ALow densityImprove adsorption capacitySolid waste disposalSemiconductor materialsNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention discloses a method for low-temperature synthesis of silicon carbide from agricultural wastes. A large quantity of the agricultural wastes such as rice husk, straw, dry branches, fallen leaves and the like generated in China every year are very important undeveloped resources. The method comprises the following simple steps: firstly, heating and decomposing the agricultural wastes into power which comprises main components such as silica and carbon in an inert atmosphere; and mixing the power with a metallic reducing agent, and then calcining the obtained mixture at the temperature of 500-800 DEG C to obtain the silicon carbide. The silicon carbide, as an important semiconductor material, has unique physical and electronic properties and important application prospect in fields such as non-ferrous metal smelting, steel industry, metallurgical ore dressing industry, architectural ceramics, energy conservation, a wave-absorbing material and the like. The method for preparing the silicon carbide from the agricultural wastes provided by the invention has simple process flow, low formation temperature of the silicon carbide and low cost of raw materials, thus being an economical and effective method for utilizing the agricultural wastes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues
ActiveCN105861844AEfficient separation and recoveryWon't break the balanceProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
Disclosed is a comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues. The zinc-containing residues generated in the zinc smelting production process serve as an acidic wastewater neutralizer. Liquid obtained after neutralization is subjected to fluorine and chlorine removal and concentrated to meet the requirements for a zinc sulfate solution of a zinc system, and then directly enters the electrolytic zinc system. Valuable metal such as arsenic, cadmium and copper in the acidic wastewater is recycled through an impurity purification procedure of the zinc system. The zinc-containing residues are subjected to a neutralization step to be recycled and fed into a lead extraction procedure after being enriched with lead, silver and other metal. The filter residues with fluorine and chlorine removed are regenerated with a sodium hydroxide solution, the residues obtained after regeneration can be used for the fluorine and chlorine removal procedure repeatedly, and sodium fluoride, sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide in the liquid obtained after regeneration are separated and recycled through efficient evaporative crystallization. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is based on an existing zinc hydrometallurgy system, the balance of original materials in the system is maintained, and an additional heavy metal impurity purification procedure is not added. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is short in process, low in cost, high in valuable metal recycling rate, free of discharging of secondary waste residues and waste water and good in comprehensive economical benefit.
Owner:湖南麓云达环境科技有限公司
Process method for producing copper sulfate by using copper scale at normal temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN102140581ALow equipment requirementsMinistry of Investment in IndustrializationProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfatesGranularityRoom temperature
The invention discloses a process method for producing copper sulfate by using copper scale at normal temperature and normal pressure, belonging to the technical field of comprehensive recycling of ferrous metal smelting. In the method, under the conditions of normal temperature (to 25DEG C) and normal pressure (to 1.01*10<5>pa, after the ore grinding granularity reaches between -120 and -200 meshes, the copper scale containing 20-60 percent of copper (other components including 1-15 percent of Zn, 5-15 percent of Pb and 1-8 percent of Cd) is mixed with a sulfuric acid solution containing 120-180g.L<-1> of acid and the mixed solution is added in a mechanical stirring groove; and air containing 0.05-0.5m<3>min<-1>.kg<-1> of copper scale is introduced into the groove and sufficient oxidizing atmosphere in the groove is kept. The oxidizing reaction of copper and dilute sulfuric acid is promoted by using the heat released by a neutralization reaction of copper oxide and sulfuric acid and is fully carried out for 18-24h, and then the copper can be better leached to the solution, wherein the leaching rate reaches over 94 percent.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Non-ferrous smelting waste acid purification treatment method
InactiveCN104478140AReduced potential for foulingSolve storage problemsPhotography auxillary processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentIon exchangeNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to a non-ferrous smelting waste acid purification treatment method which comprises the following steps: (1) adding waste acid into concentrated sulfuric acid, adjusting the acidity to 40-50g / L, adding white ash, extracting at 70-80 DEG C, then, adding zinc oxide to enable the pH to 2.5-3.0, reacting under stirring and filtering; (2) removing chlorine from the filtrate by chloride ion exchange resin and removing fluorine from the filtrate by fluorine ion exchange resin respectively; and (3) respectively carrying out spiral electrodeposition on the liquid after ion exchange to remove arsenic and carrying out spiral electrodeposition to recover zinc. Waste acid treated reaches zero discharge, arsenic in the waste acid can be separated and heavy metal zinc can be recovered, so that the piling problem of waste gypsum residues generated in conventional sewage treatment is solved, thereby achieving zero discharge and comprehensive recovery and utilization of sewage and solid wastes of a lead, zinc and copper joint smelting enterprise.
Owner:CINF ENG CO LTD +3
Non-ferrous metal smelting high-arsenic contaminated acid arsenic fixing process
ActiveCN109574319AMild responseSimple processTreatment involving filtrationWaste water treatment from metallurgical processIron sulfateTreatment effect
The invention relates to a non-ferrous metal smelting high-arsenic contaminated acid arsenic fixing process which sequentially includes the steps: pre-neutralization, to be specific, mixing iron-containing slag or iron-containing reagents and smelting contaminated acid, controlling Fe / As molar mole ratio, throwing mixed slurry and the contaminated acid into a pre-neutralization tank, performing reaction, controlling the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of solution, thickening pre-neutralization slag slurry to obtain bottom flow, supernate and gypsum slag, and using the gypsum slag as a cementretarder for sales; oxidation, to be specific, supplementing iron sulfate serving as an iron source reagent as required, heating the pre-neutralized supernate, adding hydrogen peroxide serving as an oxidizing agent for oxidation, controlling oxidation-reduction potential, and completely oxidizing trivalent arsenic into pentavalent arsenic; crystal form iron arsenate precipitation arsenic fixing, to be specific, controlling reaction temperature, adding seed crystals, controlling reaction endpoint pH values by adding lime milk, and conveying bottom flow subjected to two-stage arsenic precipitating reaction to a landfill through filter-pressed crystal form iron arsenate solids. The arsenic fixing process has the advantages of simple process, low cost, good treatment effects, low environmentalpollution risk and the like and is applicable to non-ferrous metal metallurgy industries.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP +1
Technology for zinc wet-process clean smelting and resource comprehensive recycling
InactiveCN102978391AEnhanced leaching processHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of zinc smelting of the nonferrous metal smelting industry, in particular relates to a technology for valuable metal comprehensive recycling and iron element separating and concentrating during a zinc clean smelting process. Zinc calcine which is produced through calcinating zinc concentrate is separated out through neutral leaching and low-acid leaching and is then fed into a wet-process reinforced leaching system to separate acid soluble metals from insoluble substances; the separated zinc and soluble impurity-containing liquid enters a valuable metal separating and concentrating system to separate out indium, gallium, germanium and the like, the separated valuable metal sludge enters a special recycling system; and the liquid enters a zinc and iron separating system to completely separate out zinc and iron, iron is output in a high-grade iron ore concentrate mode, zinc enters the next process in a zinc sulfate mode, and the liquid enters an electrolyzing system after deep purification to output metal zinc. The technology has high metal zinc recovery rate, good valuable metal comprehensive recycling effect, a good environment-friendly effect and high iron content of hematite sludge, the hematite sludge can be treated to be used as a raw material for smelting iron, so that 'non-sludge' smelting is realized, and the smelting process is compact.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
Magnetic biochar quantum dot composite adsorbent as well as preparation method and using method thereof
ActiveCN103920461AImprove adsorption capacityHigh speedOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationSorbentIon exchange
The invention relates to a magnetic biochar quantum dot composite adsorbent as well as a preparation method and a using method of the magnetic biochar quantum dot composite adsorbent. According to the preparation method, an ion exchange nano adsorbent with high adsorption capacity is prepared by means of carrying a sulfide or selenide nano adsorbent on magnetic biochar which serves as a carrier. In use, the ion exchange nano adsorbent is directly immersed in a solution rich in heavy metal ions; by the exchange between the harmless metal ions on the ion exchange nano adsorbent and the heavy metal ions, the heavy metal ions in a liquid phase are adsorbed onto the ion exchange nano adsorbent, so that the aim of removing heavy metal out of the liquid phase is achieved. Compared with the prior art, the ion exchange nano adsorbent has the advantages of high adsorption capacity, high adsorption rate and the like, and is applicable for removing heavy metal out of coal-fired flue gas and non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas, as well as wastewater from other heavy metal industries.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for curing arsenic-containing waste residues through industrial waste residues
ActiveCN105537247AImprove adsorption capacityImprove stabilitySolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingNonferrous metalSlag
The invention discloses a method for curing arsenic-containing waste residues through industrial waste residues. The method includes the following steps that (1) the arsenic-containing waste residues are thrown into a stirring tank, and water is added for slurrying, so that slurry is obtained; (2) an arsenic curing agent is added into the stirring tank for a curing reaction, and the arsenic curing agent is smelting slag or magnetic iron concentrate obtained through ball-milling and magnetic separation of smelting slag; and (3) neutralizing slag is added into the stirring tank for stirring, and finally casting molding and natural curing are conducted, so that solid arsenic products are obtained. According to the method, the waste residues generated by a nonferrous metal smelting plant are utilized, the material cost is basically zero, and meanwhile the excellent effect of dealing with waste by waste can be achieved. Through the method for treatment the arsenic-containing waste residues, the curing rate of arsenic in the arsenic-containing waste residues reaches 94% or more.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Acid recycling and arsenic curing method for acidic waste water
InactiveCN107459166AImprove resource utilizationRealize synchronous processingGas treatmentWater contaminantsNon-ferrous extractive metallurgyOxygen
The invention relates to an acid recycling and arsenic curing method for acidic waste water and belongs to the technical field of the non-ferrous metallurgical industry. The acid recycling and arsenic curing method comprises the following steps: performing size mixing on arsenic soot and acidic waste water, then pumping in air or oxygen to perform oxidation leaching, controlling the pH value of a leaching end point, and performing normal-pressure scorodite arsenic curing on an arsenic-containing leaching agent. According to the acid recycling and arsenic curing method, arsenic-containing soot and acidic waste water mixed size mixing, oxidation leaching and scorodite arsenic curing technologies are adopted to treat acidic waste water, a new thought is provided for recycling of acidic waste water and harmless arsenic treatment of the non-ferrous metallurgical industry, and the acid recycling and arsenic curing method mainly focuses on efficient utilization of acid in acidic waste water and harmless arsenic treatment. Arsenic-containing soot generated in the non-ferrous metal smelting process is taken as a neutralizer, and arsenic-containing soot and arsenic-containing acidic waste water are synchronously treated, so that effective utilization of acid in acidic waste water is realized, meanwhile, obtained scorodite crystals are convenient to pile up, and the characteristics of complete arsenic and acid separation, low treatment cost and the like are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
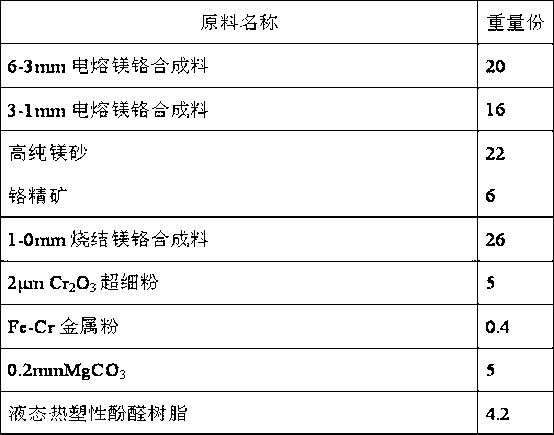
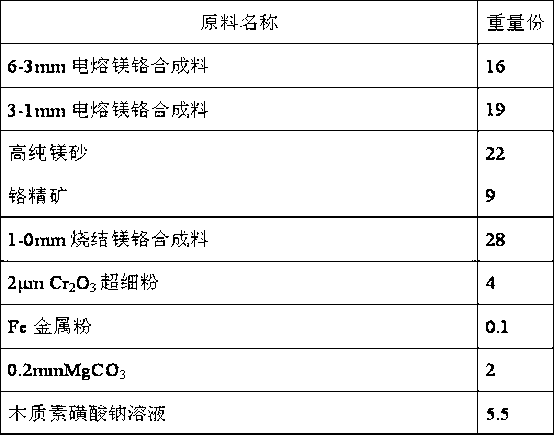
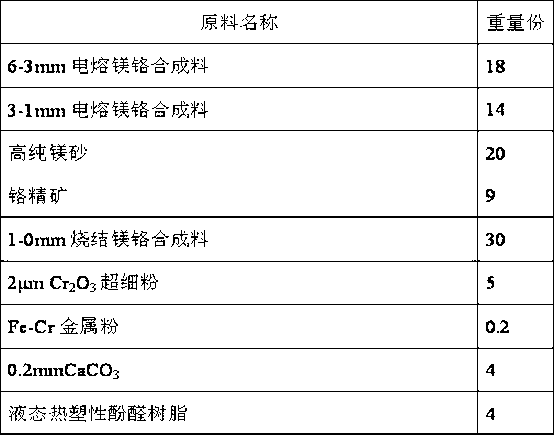
Semi-rebonded magnesite-chrome brick for copper smelter and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a semi-rebonded magnesite-chrome brick for a copper smelter. The brick is prepared by an electric smelting magnesite-chrome synthetic material, high purity magnesia, chrome concentrate, a sintered magnesite-chrome synthetic material, Cr2O3 ultrafine powder, a metal additive, an additive and a bonder. The semi-rebonded magnesite-chrome brick prepared by the invention is high in compactness, low in porosity and high in high temperature resistance, and the cost of the semi-rebonded magnesite-chrome brick is lower than that of rebonded magnesite-chrome brick with equivalent components while the thermal shock resistance and the scouring resistance are superior to those of silicon brick and rebonded magnesite-chrome brick currently used for the copper smelter. The semi-rebonded magnesite-chrome brick can replace the rebonded magnesite-chrome brick in a certain range, can be used for furnace top, slag line, nozzle and other severely corroded parts of the copper smelter, and has the objective economic benefit of lowering the cost and increasing the effect in industry of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, and in particular a copper melting process.
Owner:宜兴新威利成耐火材料有限公司
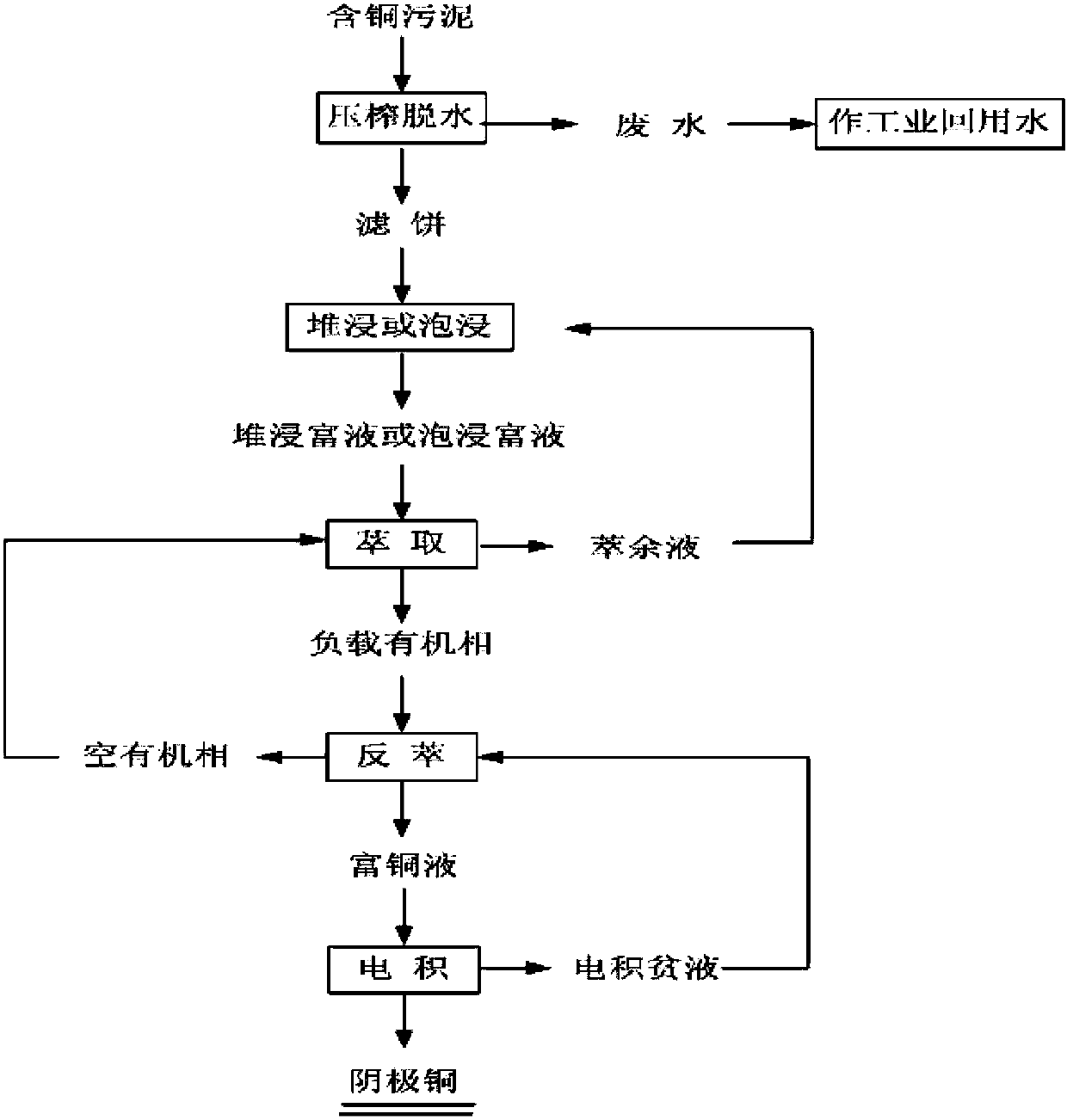
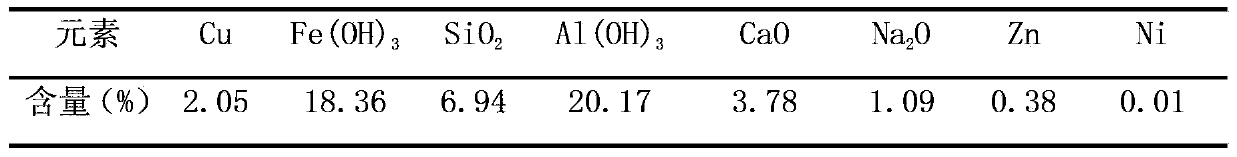
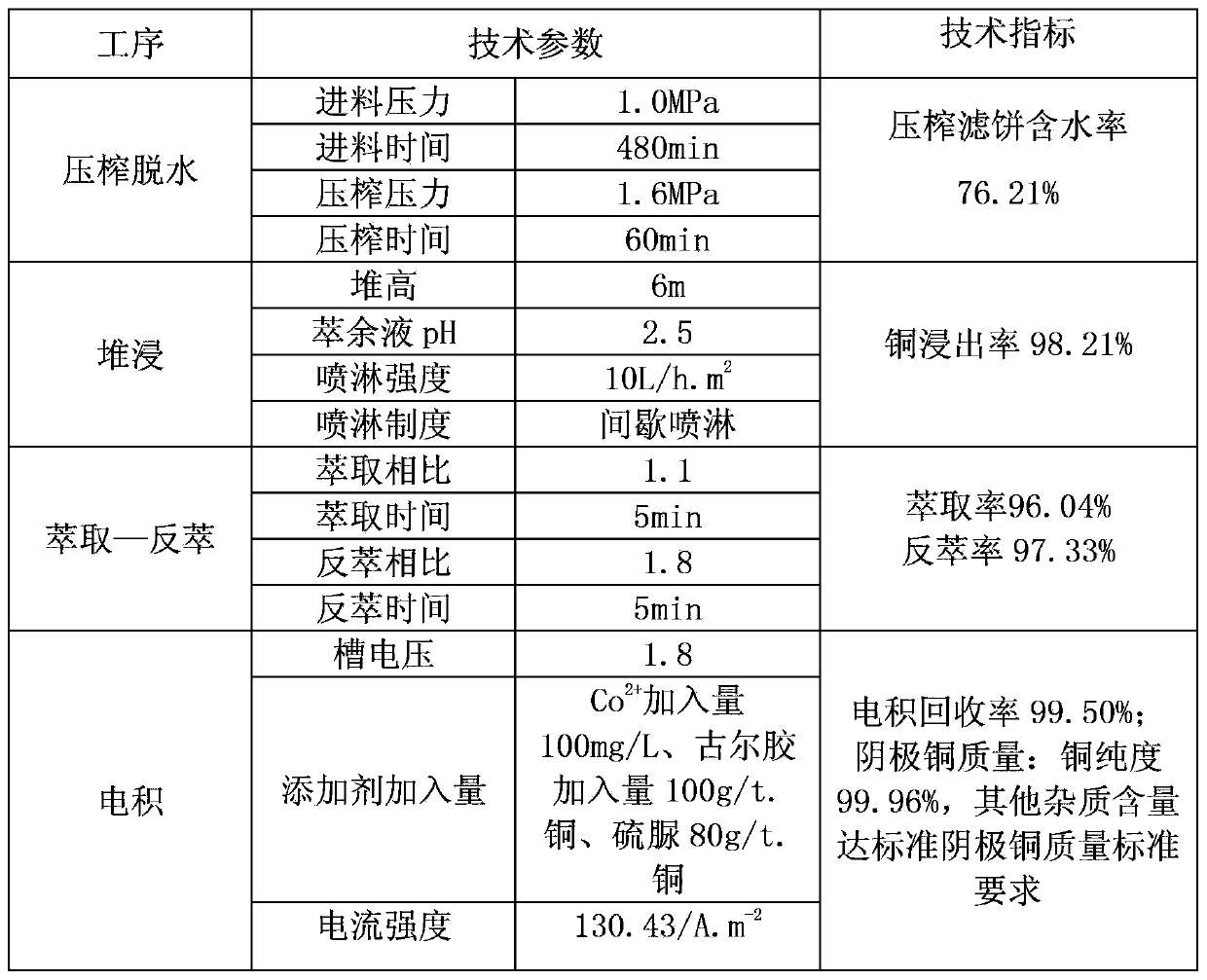
Method for producing tough cathode with cupric sludge
ActiveCN103422119AImprove leaching rateGood washing rateSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningPhotography auxillary processesSludgeMature technology
The invention relates to a method for producing tough cathode with cupric sludge. The method comprises the following processing steps: step 1, squeezing and dewatering: squeezing and dewatering cupric sewage; step 2, heap leaching or pickling: sprinkling acid solution on a columnar heap and feeding obtained heap leaching pregnant solution to an extraction system, or feeding squeezed and dewatered lump sludge to a pickling pool to pickle the squeezed and dewatered lump sludge with acid solution and feeding obtained pickling pregnant solution to the extraction system; step 3, extraction-reverse extraction: performing extraction on the heap leaching pregnant solution or the pickling pregnant solution obtained in the step 2, and performing reverse extraction on obtained loaded organic phase to obtain copper pregnant solution; step 4, electro-deposition: performing electro-deposition on the copper pregnant solution obtained in the step 3 under a copper condition to obtain tough cathode. The method has the advantages of low energy consumption, environmental friendliness, applicability to sludge with a low copper content, easiness in solid-liquid separation, high washing rate, high total recovery rate of copper, mature technology and the like and is applicable to industrial fields such as heavy mineral mining, non-ferrous metal smelting, machining and electroplating.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Technology and device thereof adopting bottom blowing molten bath for antimony reduction and smelting
InactiveCN102758094ASpeed up smeltingEasy to handleProcess efficiency improvementMelting tankMolten bath
The invention belongs to the technical field of antimony smelting in the industry of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, and particularly relates to a technology and a device thereof adopting bottom blowing molten bath for antimony reduction and smelting in the process of antimony smelting, wherein the bottom blowing molten bath smelting technology is adopted, antimonial raw material and burden are uniformly blended according to a suitable proportion and fed into a molten bath antimony smelting furnace for smelting to carry out reduction and slag making reaction; oxygen, nitrogen, natural gas or coal gas are fed into the melt through a gas spray gun from the bottom part or bottom side part of the molten bath antimony smelting furnace; the gas is combusted to release heat, so as to ensure the temperature of the furnace, participate in the oxidation and reduction reaction of the burden, and vigorously blend the melt, as a result, the heat and mass transfer and reaction speed in the smelting furnace can be improved, the burden can be quickly reacted to produce lean antimony slag, crude antimony and flue gas, the antimony can be continuously processed, and the slag type with little corrosion on the refractory material is produced. The technology and the device have the advantages of low investment, energy consumption and cost, high automation degree and environmental protection.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
Magnesium metal reduction process using liquid calcium as reducing agent and device thereof
InactiveCN101117667AReduce manufacturing costReduce energy consumptionReaction temperatureNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The present belongs to the smelting field of nonferrous metal, in particular to a magnesium deoxidation art using liquid calcium as a reducing agent and a magnesium deoxidation device. The present invention is characterized in that the liquid calcium which reacts with magnesia to get magnesium steam is adopted as the reducing agent; the art process is that the solid calcium is added into a reactor and heated to make the solid calcium melt firstly, the added quantity ensures the volume of the melted liquid calcium to occupy 1 / 3 to 2 / 3 of the reactor volume; secondly, the solid calcium and the magnesia powder are mixed according to the proportion of (1 to 2) to 1 and then sent into the reactor, the material is immersed into the liquid calcium; when the temperature reaches to 1090 DEG C, the reaction starts, the magnesium steam is produced, the reaction temperature is controlled between 1150 and 1300 DEG C, and the magnesium steam enters into a crystallizer for cooling through an induced-draft fan. The art has the advantages that the reaction is performed under the atmosphere, the reducing tin is not used, the reaction is the solid-liquid reaction, the reaction speed is fast, and the contact of the reactant is full. The art provides a route of energy conservation and consumption reduction, green production and sustainable development for the magnesium-smelting art.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
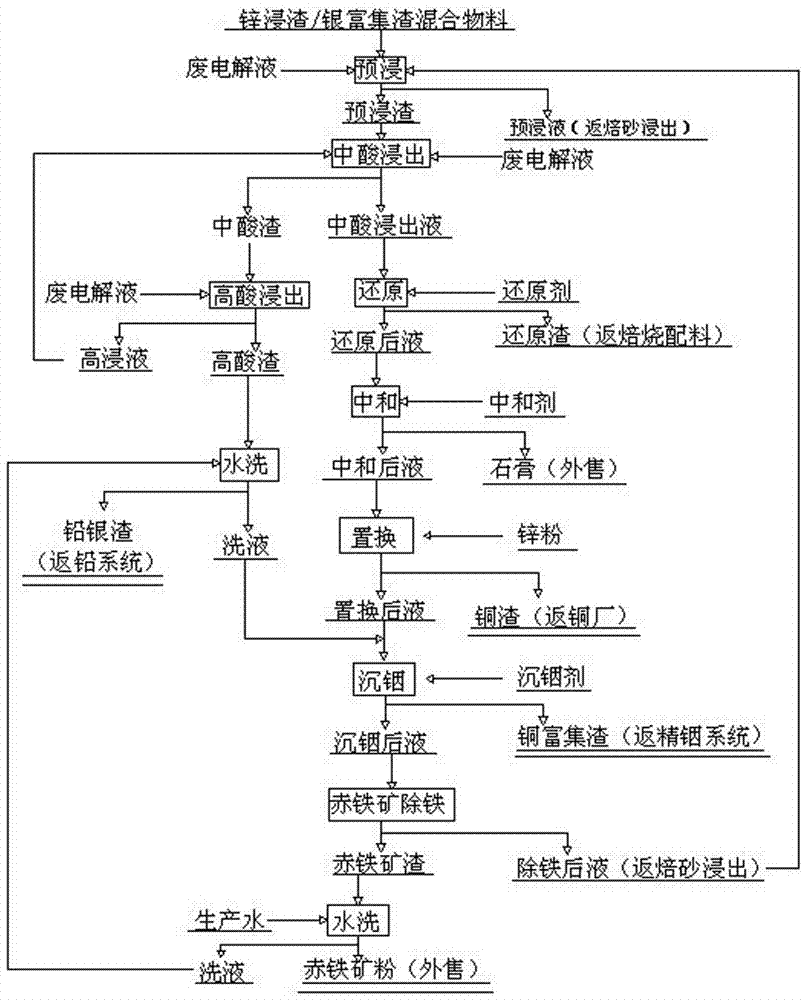
Efficient recovery method of valuable metals in zinc leaching residues
ActiveCN106868306AHigh recovery rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodIndium
The invention belongs to the technical field of zinc smelting in the non-ferrous metal smelting industry, and particularly relates to an efficient recovery method of valuable metals in zinc leaching residues. The efficient recovery method mainly comprises the following steps: high-copper-content and high-silver-content zinc leaching residues and silver-rich residues are mixed uniformly, and an obtained mixture is subjected to preimpregnation, middle-acidity leaching, high-acidity leaching, reduction, neutralization, replacement, indium precipitation and hematite iron removal. The efficient recovery method is applicable to the treatment on the mixture of the high-copper-content and high-silver-content zinc leaching residues and the silver-rich residues, recovery rates of the valuable metals like indium, copper, silver and zinc are high, an iron-zinc separation flow is short, energy conservation and environmental protection are facilitated, the economic benefits are significant, and the recovery method is a clean, environmentally-friendly and efficient new method for comprehensive recovery of high-copper-content and high-silver-content zinc materials.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
Digestion and determination method of heavy metals in waste dust-collecting bag
InactiveCN102313706APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsDust controlNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention discloses a digestion and determination method of heavy metals in a waste dust-collecting bag, and relates to microwave digestion of the waste bags generated by iron and steel smelting and non-ferrous metal smelting (such as lead-zinc smelting and copper smelting). The method comprises the following steps: mixing the waste dust-collecting bag with a digestion acid system composed ofnitric acid, hydrogen peroxide and hydrofluoric acid in a polytetrafluoroethylene-sealed pressurized digestion tank at normal temperature, shaking up and keeping standing overnight; and performing the microwave digestion under certain conditions and then performing heavy metal determination. By adopting the method, the waste dust-collecting bag is made into a digestion solution, and flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is further adopted for determining the content of the heavy metals in the digestion solution.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
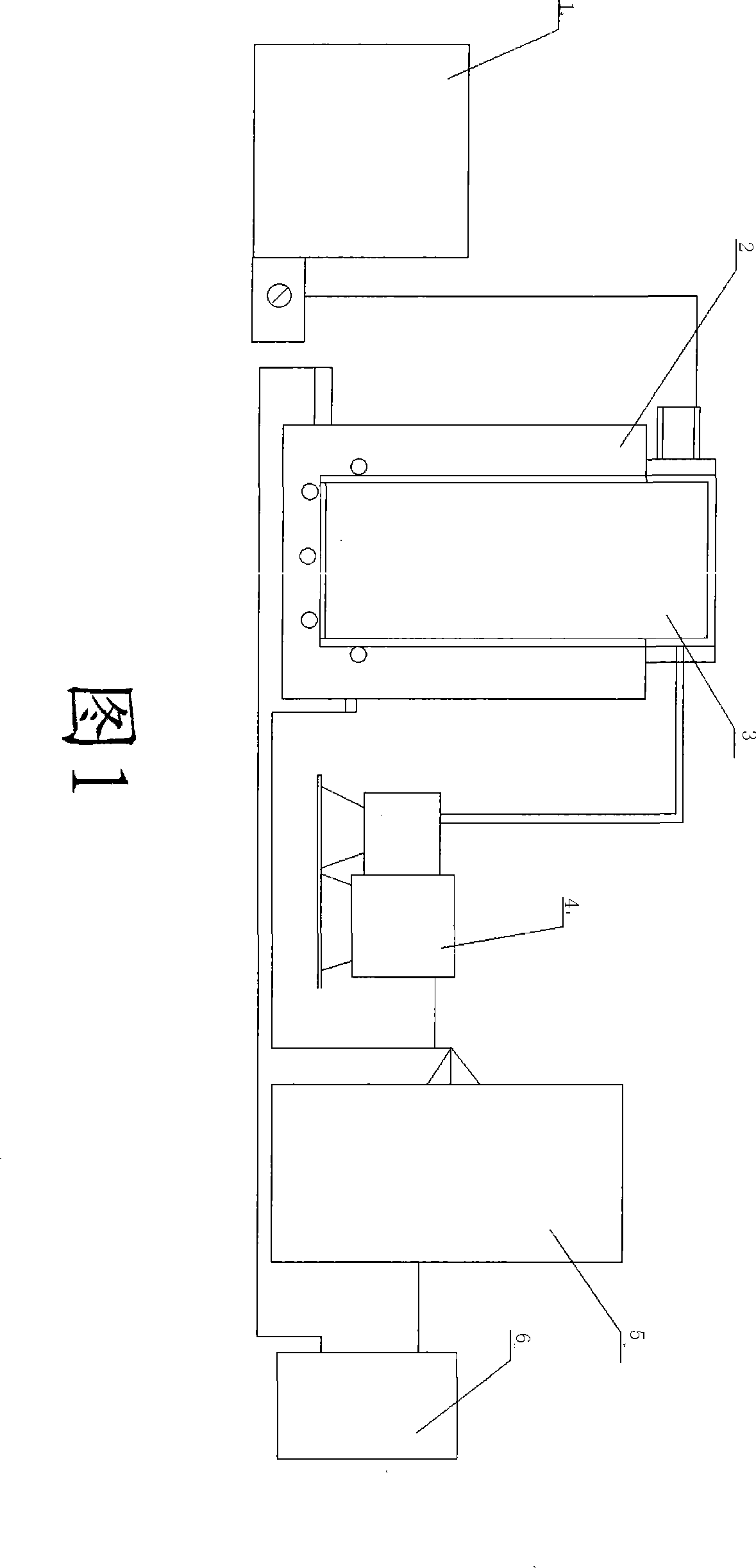
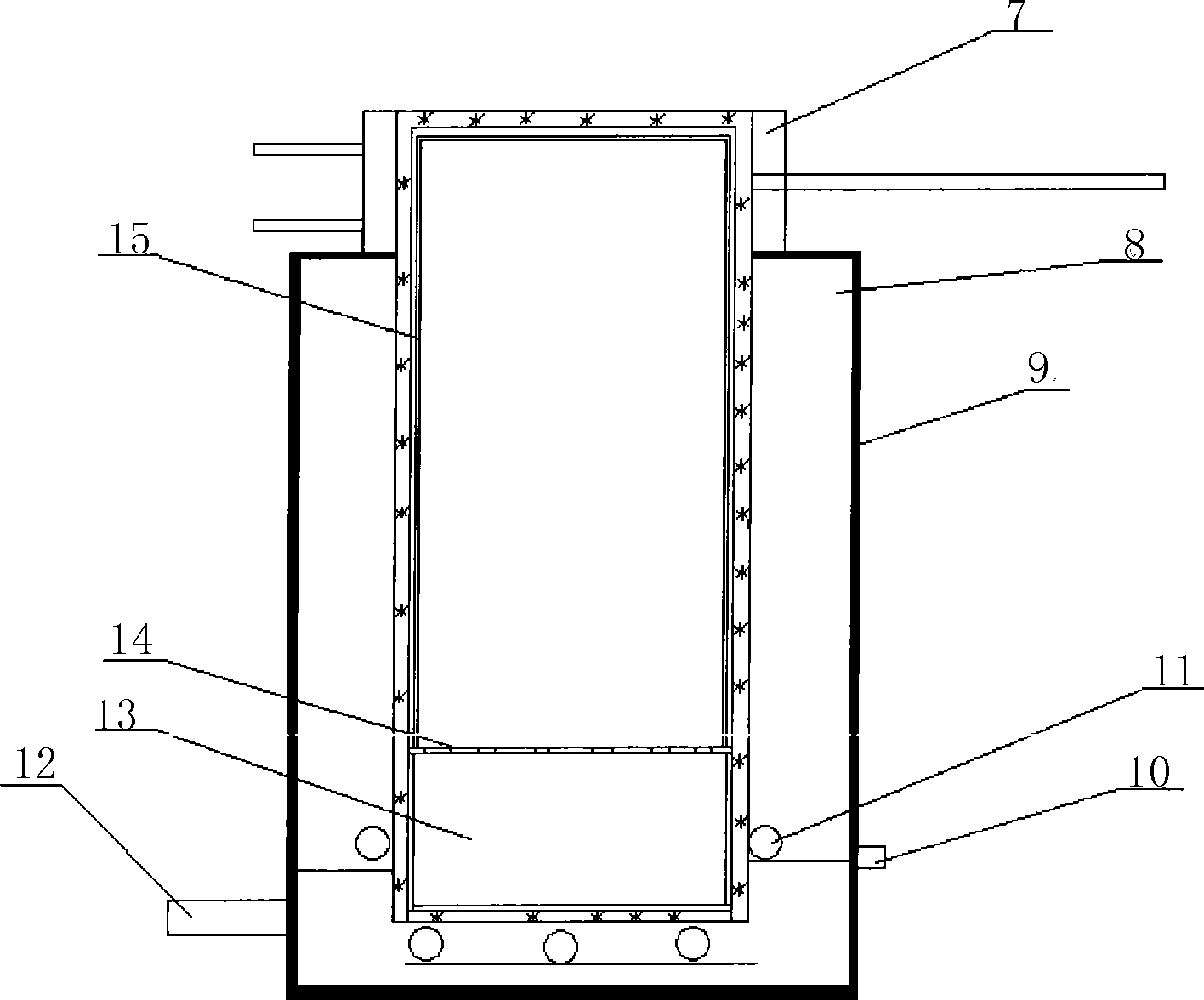
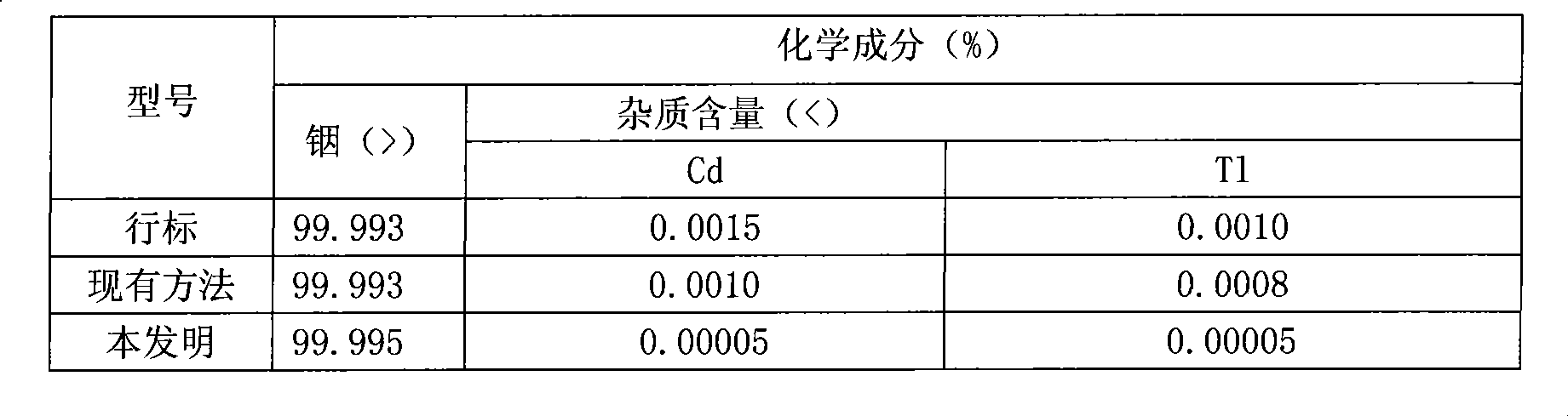
Method and device for removing cadmium and thallium from high purity indium production
The invention relates to a method for removing cadmium and thallium impurities in the process of producing high purity indium and an apparatus thereof, belonging to the smelting field of high purity non ferrous metal in smelting industry. The specific procedures of the invention are as follows: firstly, putting indium into a crucible and loading the crucible in a vacuum tank, disposing a cylindrical titanium plate on the lid of the crucible, covering a titanium sealing sleeve, folding the cover of the vacuum tank, starting up a water cooling system, and launching a vacuum pump; controlling degree of vacuum below 10 Pa; secondly, controlling temperature of the crucible bottom range from 400 to 1000 DEG C, implementing heat preservation for 1 to 5 hours, volatilizing cadmium and thallium impurities completely, and eventually, remaining the high purity indium in the crucible, thus achieving the objective of purification. The invention has the advantages of fast production speed, low power consumption, simple apparatus processing, and is applicable for large-scale production. As the addition of chemical reagents is not required in the production process, purity of the product is high and the production process is free from pollution and discharge of pollutants.
Owner:ZHUZHOU KENENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Method of preparing Mg, Sr alloy by vacuum heat reduction
This invention discloses a method for manufacturing Mg-Sr alloy by vacuum thermal reduction, which comprises the steps of: (1) grinding and mixing calcined MgO, SrO or its precursor, CaO, ferrosilicon (or other silicon alloy, aluminum, or aluminum alloys) and fluorite, (2) pressing into large balls, (3) placing into a reaction kettle for vacuum thermal reduction, and (4) collecting Mg and Sr vapor and condensing to form solid Mg-Sr alloy. Compare with conventional Mg metallurgy by Si-thermal reduction or Sr metallurgy by Al-thermal reduction, the method in this invention can achieve simultaneous vacuum thermal reduction of MgO and SRO to obtain Mg-Sr alloy. The method has such advantages as low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for separating indium and tin from In-Sn alloy by vacuum distillation
InactiveCN101660056AAchieve recyclingImprove direct yieldProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSmelting process
The invention relates to a method for separating indium and tin from In-Sn alloy by vacuum distillation. The method comprises the following steps: adding In-Sn alloy material which includes 40-99% ofIn and 1-60% of Sn into a vacuum furnace, controlling vacuum degree, temperature and distillation time in the furnace, and leading metal indium and tin to separate. The treated objects can be In-Sn alloy, In-Sn slag and the like generated during the non-ferrous smelting process. By vacuum distillation, the content of tin in metal indium is less than 0.5%, the content of indium in metal tin is lessthan 0.5%, and the total recovery efficiency of metal is more than 99%. During the process, any reagent does not need to be added, the technology is simple, the metal recovery efficiency is high, andthe electricity consumption is less than 10KW.h / kg.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
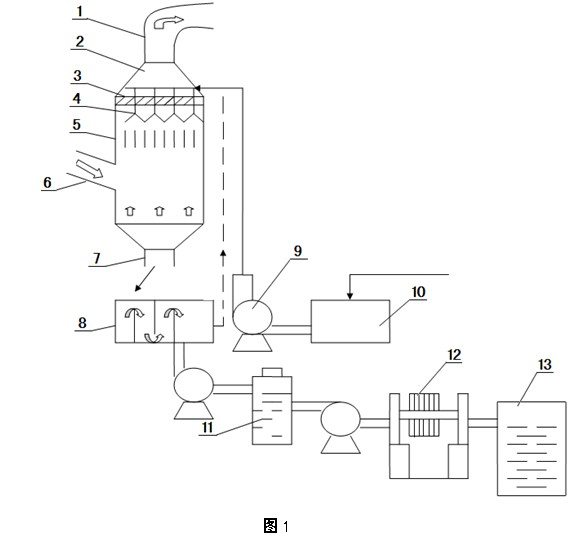
Method for concentrating and purifying dilute acid by using waste heat of smelting flue gas and device thereof
ActiveCN102115045AReduce work stressReduce corrosionEnergy inputSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidNon-ferrous extractive metallurgyNon-ferrous metal
The invention provides a method for concentrating and purifying dilute acids by using the waste heat of smelting flue gas and a device thereof. When the flue gas generated during the smelting of non-ferrous metals is applied to the acid production, a waste dilute acid generated by power waves (with a concentration ranging from 20% to 30%) is delivered to a dilute acid tank, pumped to a concentration tower through a horizontal-type dilute acid pump and sprayed downwards to contact with the smelting flue gas of a temperature ranging from 200 DEG C to 280 DEG C, which oppositely flows from a flue gas inlet pipe; the water is heated to evaporate through the waste heat of the flue gas, so that the dilute acid is concentrated and simultaneously sulfur trioxide (SO3) and dust in the flue gas are washed off; the resulting acid fog is captured by a fog capturing layer and finally falls into the produced concentrated acid; the concentrated acid enters a concentrated acid storage tank through a concentrated acid discharge port; and the dust settles at the front part of the storage tank. The method reduces the working pressure of the power waves and reduces the corrosion to the equipment in the next procedures; achieves the purpose of recovery and reutilization of sulfur resources; doesn't need lime to neutralize the waste acid, so as to avoid the formation of a large amount of gypsum residues and reduce the expenses for waste acid treatment; adapts to the fluctuation of concentration of SO3 in the flue gas, so as to ensure the stability of the dilute acid washing process and improve the washing effect.
Owner:DONGYING FANGYUAN NONFERROUS METALS
Process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on recovery section in process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting
InactiveCN102994764ALow running costAvoid harmProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to the field of nonferrous metal smelting and particularly relates to a process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on a recovery section in the process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting. The soot of a reduction furnace is subjected to a leaching reaction by using arsenic sulfide removal waste acid in the lead smelting industry to generate lead slag to be recovered, and then, the leaching agent is continued to be neutralized by using sodium sulphide and sodium hydroxide to generate high-grade zinc and cadmium slag to be recovered. According to the invention, the waste acid is used for separating the lead, zinc and cadmium in the soot of the reduction furnace for lead smelting, so that the operation cost is low; the problem of production operation damage caused by circulated accumulation of the zinc and cadmium in lead smelting is solved and the pressure of a lead smelting system is relieved under the condition of low cost; and the lead slag which is low in arsenic content and suitable for being treated by a lead system and the zinc and cadmium slag which is suitable for being treated by a zinc system can be generated, and meanwhile, the waste acid is also treated, so that not only is the treatment cost of the waste acid reduced, but also the treatment difficulty is lowered.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
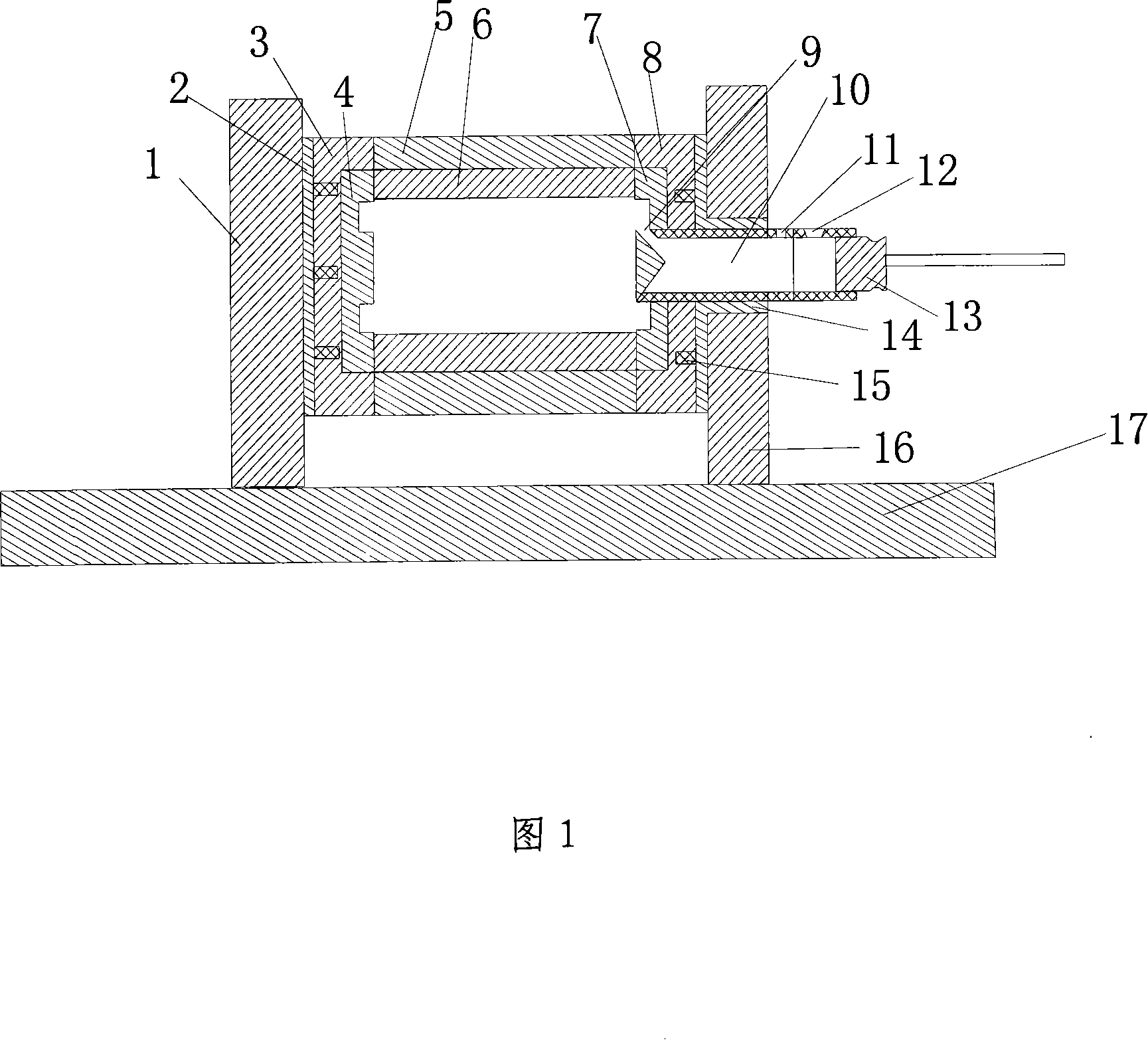
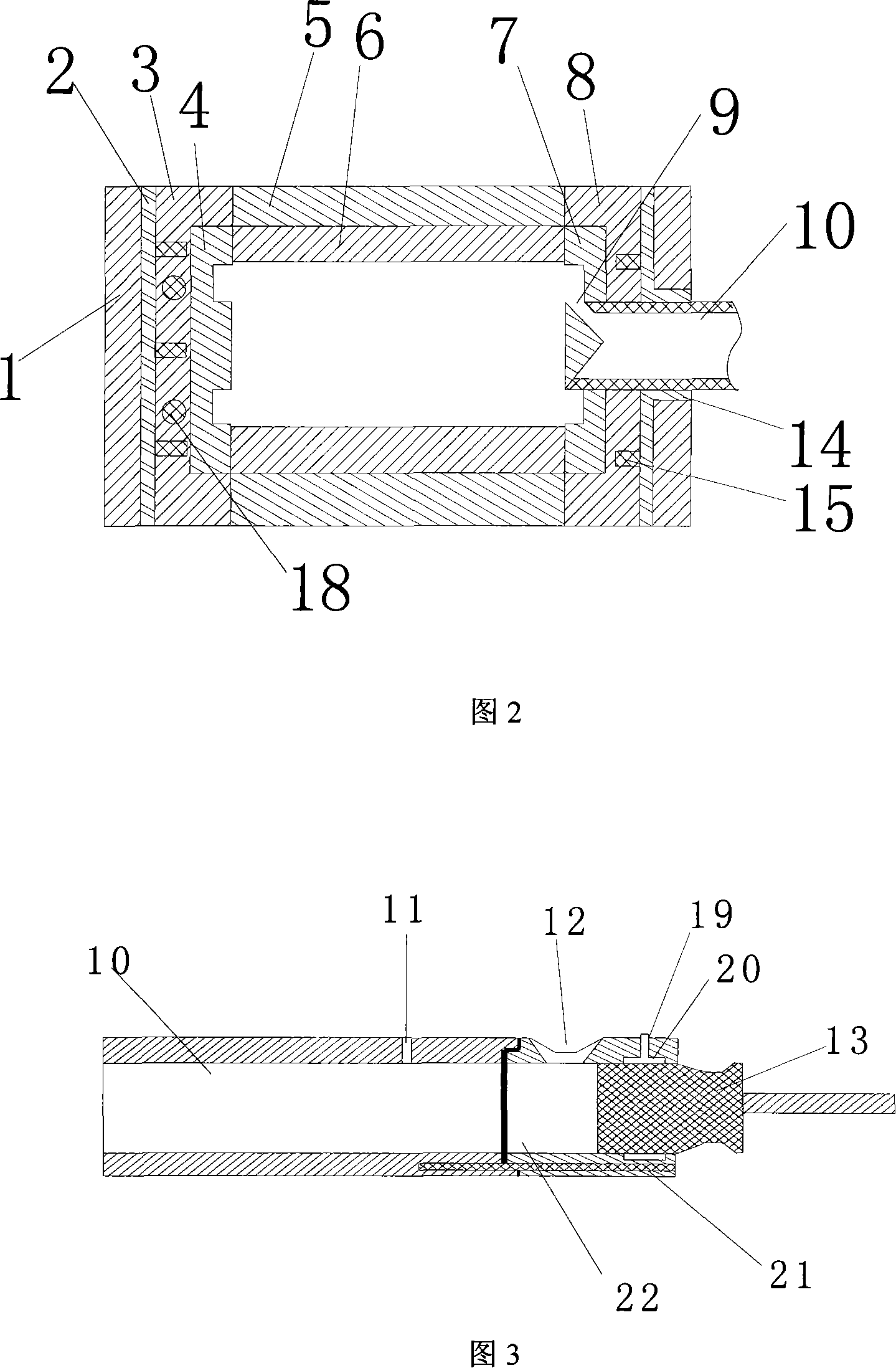
Industrial furnace for non-ferrous metal smelting
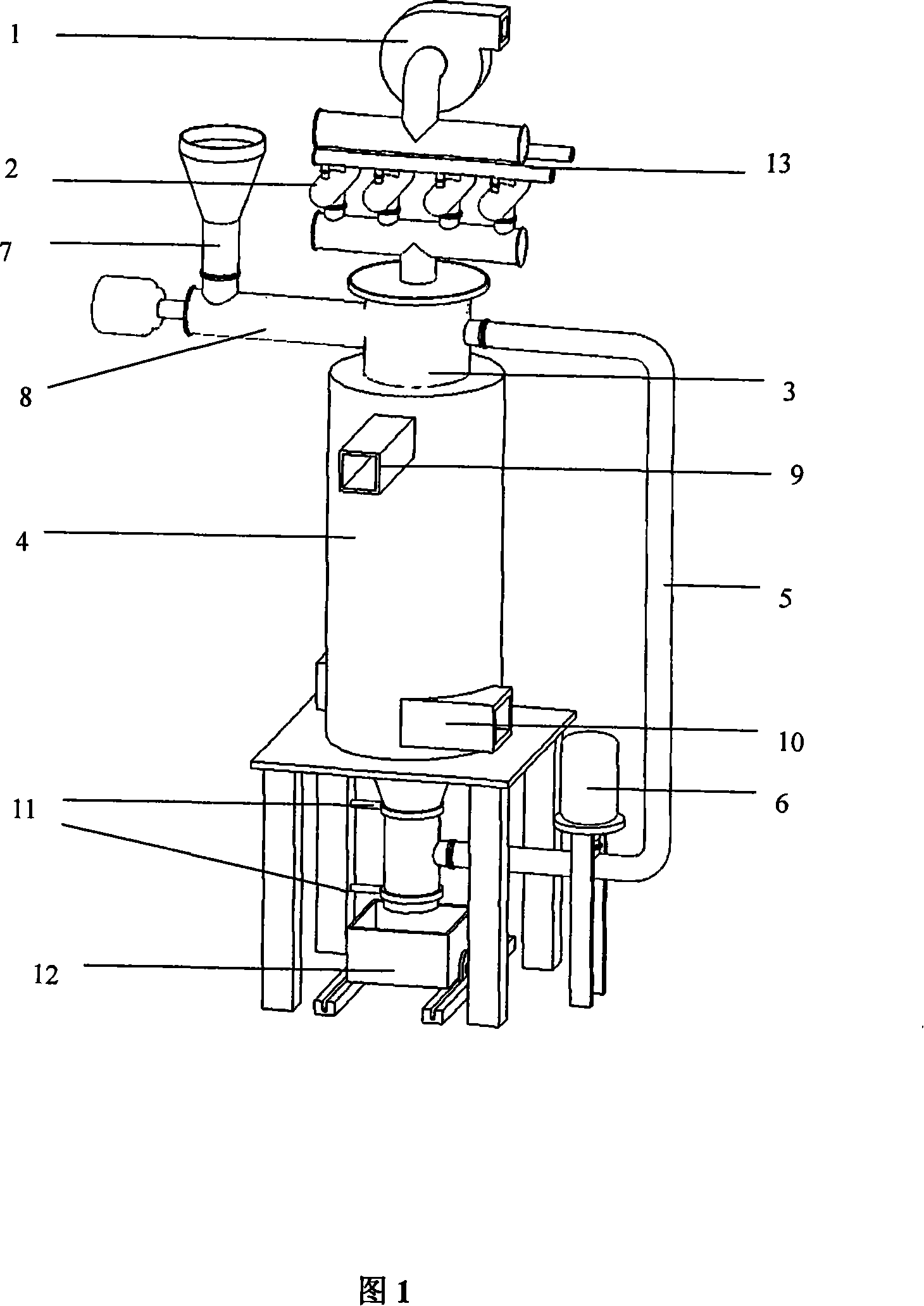
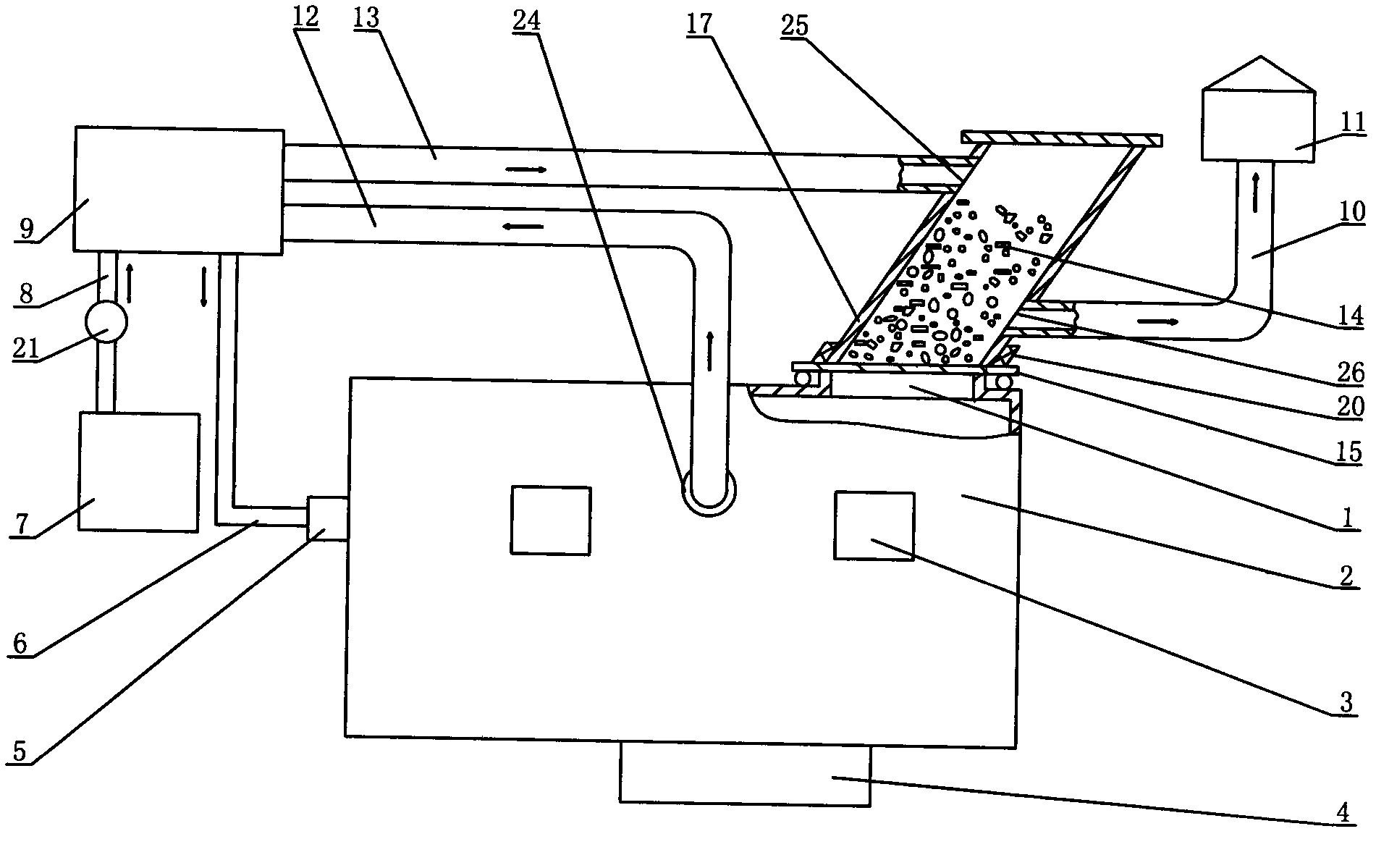
InactiveCN102620554AAvoid getting lostFull conversionPreheating chargesWaste heat treatmentNon-ferrous extractive metallurgyExcess heat
The invention discloses an industrial furnace for non-ferrous metal smelting. The industrial furnace comprises a hearth (2), a feed tube, a combustor (5) and a heat exchanger (9), wherein a low-temperature air pipeline (8) is connected between the heat exchanger (9) and a fan (7), a high-temperature air pipeline (6) is connected between the heat exchanger (9) and the combustor (5), a hearth furnace gas outlet (24) is formed on the hearth (2), the feed tube serves as one part of a heat exchange system, and a furnace gas pipeline connects the hearth furnace gas outlet (24), the heat exchanger (9) and the feed tube into a whole. According to the invention, the feed tube can utilize excess heat of waste furnace gas to preheat furnace materials (14) to be melted, and loading process is performed in a closed space, thereby preventing a great deal of heat in the furnace from being lost and greatly reducing the temperature of the waste furnace gas discharged into the atmosphere, therefore, the preheated furnace materials (14) can be quickly melted in the hearth (2) so as to achieve the aims of high efficiency, low energy consumption and low aluminum loss.
Owner:MEISHAN ZHONGNENG ALUMINUM
Method for comprehensively treating indium-containing lead anode slime through whole wet process
InactiveCN102912143AEfficient separationHigh economic recycling valueProcess efficiency improvementIndiumWater chlorination
A method for comprehensively treating indium-containing lead anode slime through the whole wet process relates to adoption of the whole wet extraction technology for extracting valuable metals such as indium, silver, lead, copper and bismuth, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a chloride solution into anode slime, leaching for the first time at the temperature higher than 80 DEG C, and controlling the final pH value within 2.5-3.0; (2) neutralizing the first leaching solution until the pH value reaches 4.8-5.1, precipitating, then adding sulfuric acid into dregs for dissolution, and extracting to obtain crude indium; (3) oxidizing and chloridizing the neutralized solution of precipitated indium, then leaching the first leached dregs for the second time, and controlling the final acidity within 45-30g / L; (4) the secondary leached dregs are leached at the temperature higher than 90 DEG C, neutralizing the leaching solution for lead precipitation, oxidation leaching the leached dregs, adding ammonia water for leaching, and reducing the ammonia leaching solution by hydrazine hydrate, thereby obtaining silver sponge; and (5) reduction replacing the secondary leaching solution to obtain the valuable metals. The method is low in cost, has higher extraction ratio for the valuable metals, can be used for easily separating the valuable metals, is free from waste liquor and waste residues, and has better economic benefits.
Owner:云南天浩稀贵金属股份有限公司
Method for enriching and recycling cadmium from lead smelting system
ActiveCN103740945AEffective enrichment and separationReduce acidityProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention belongs to a non-ferrous metal metallurgy industry and particularly relates to a method for enriching and recycling cadmium from a lead smelting system. The method comprises the following steps: matching a lead concentrate with auxiliary materials and returned low-cadmium smoke and dust, and adding desulfurization smelting lea of a bottom blowing furnace; circularly enriching the cadmium in electric dust-collection smoke and dust in a form of cadmium sulfate; when the cadmium content of the electric dust-collection smoke and dust is 5%-28%, leaching by using water or dilute sulfuric acid to separate the cadmium; displacing a leaching solution by using zinc powder to produce cadmium sponge and further producing rough cadmium and fine cadmium; and taking a solution obtained by displacing the cadmium as a raw material for producing nano zinc oxide, zinc sulfate monohydrate and zinc sulfate heptahydrate to recycle zinc. The lead is enriched in leached dreg in a leaching process so that the lead can be conveniently returned back to a lead system to be smelted and recycled. According to the method, a bottom blowing smelting technology is adopted; when the lead is smelted, the cadmium in the raw material is efficiently enriched and converted into a water-soluble cadmium salt; a technological process is shortened and conditions for directly enriching, separating and recycling the lead and the cadmium are provided; the dispersion of the lead when the cadmium is recycled by a wet method is avoided and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
Method for treating arsenic containing solution
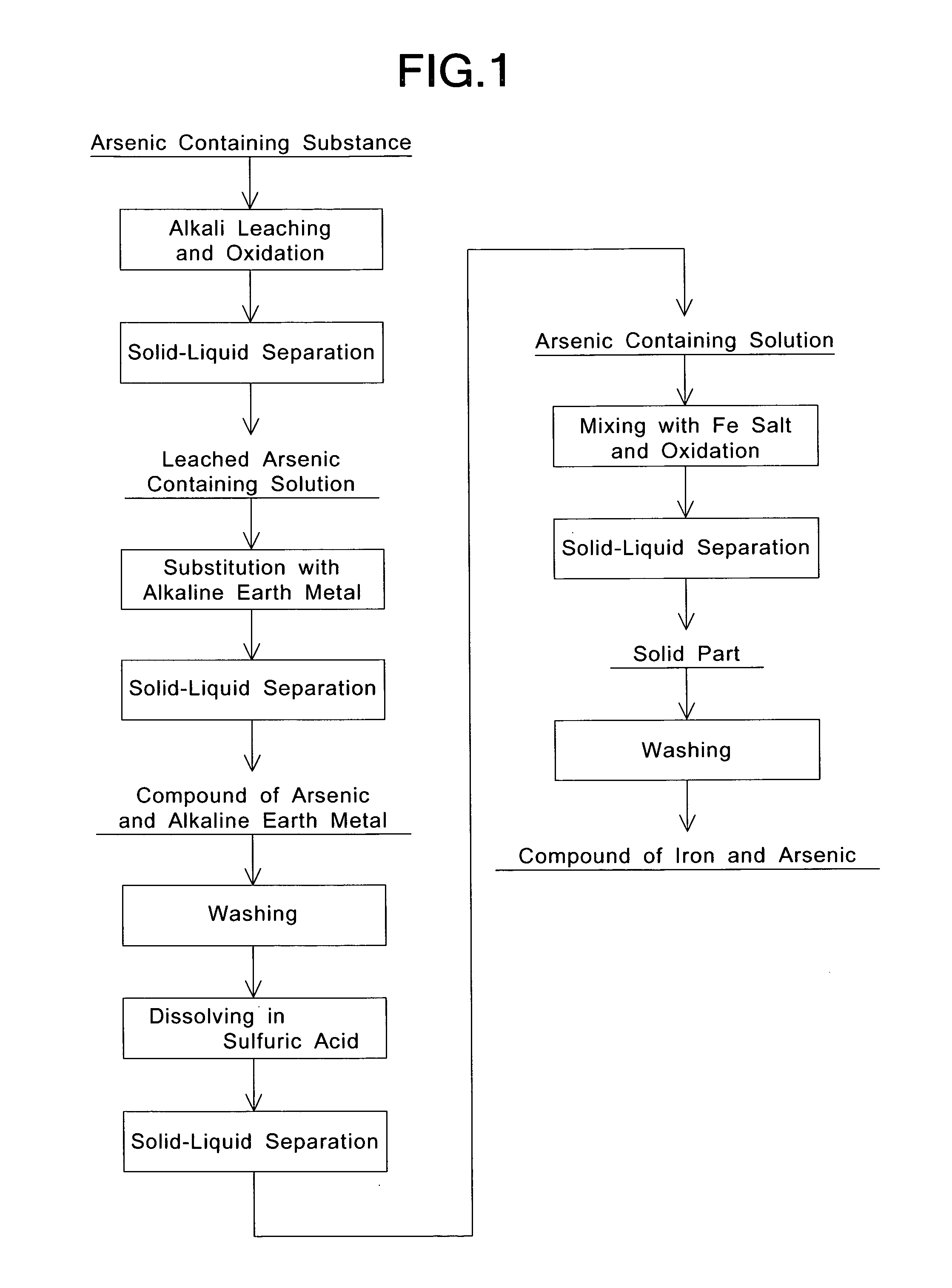
InactiveUS20070253877A1High purityReduce concentrationAntimony compoundsIron compoundsHigh concentrationNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
There is provided a method for recovering a powder of a compound of iron and arsenic, which has a very low concentration of arsenic eluted from the powder, by treating an arsenic containing solution, e.g., a high purity and high concentration arsenic containing solution obtained by treating an arsenic containing substance which contains various elements other than arsenic, such as an intermediate product in a non-ferrous metal smelting or refining process. Ferrous ions are added to an arsenic containing solution, which contains 10 g / L or more of arsenic, so as to cause the ratio (Fe / As) of iron to arsenic in the solution to be not less than 1, and an oxidizing agent is added to the solution to allow a reaction at a temperature of not lower than 70° C. while stirring the solution. Then, a solid-liquid separation is carried out, and a solid part separated by the solid-liquid separation is dried.
Owner:DOWA METALS & MINING CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com