Method for comprehensively treating indium-containing lead anode slime through whole wet process
A comprehensive treatment of lead anode slime technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of low yield, small amount of indium-containing anode slime, high recycling costs, etc., to achieve good economic benefits, more valuable recycled metals, tractable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
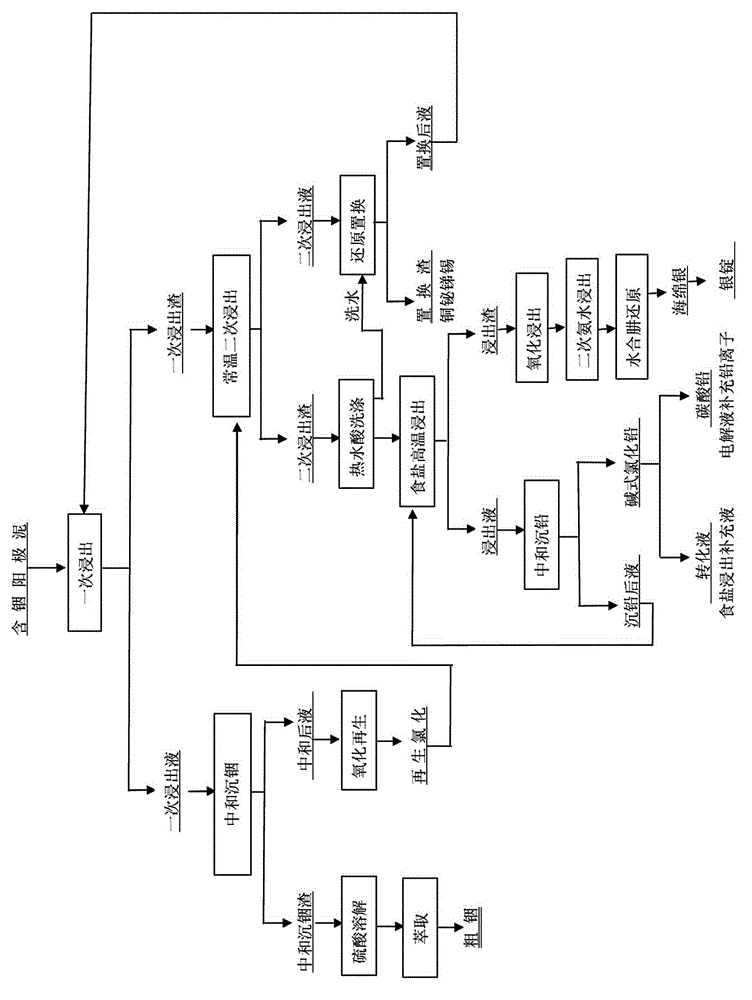
[0010] Example 1: Put in 5.4kg of indium-containing anode slime, grades: Pb8.04%, In9.32%, Ag9.66%, Sn3.45%, Cu2.08%, Bi20.0%, Sb20.0%. 1) Primary chlorine salt heating leaching, leaching conditions: leaching solution: anode slime = 5:1, reaction temperature 80°C, reaction time 80 minutes, final acid pH 2.5, leaching solution plus soda ash for neutralization, control pH 4.8, neutralization slag is The hydroxide of indium is dissolved in sulfuric acid, and the indium is extracted by the traditional extraction process. After neutralization, the liquid is oxidized and regenerated by chlorine gas, and then used as the pre-chlorine salt leaching liquid at room temperature; : chlorine salt heating leaching residue 5:1, stirring at room temperature, reaction time 180min, final acid 41g / L, leaching solution plus reducing agent replacement to obtain copper bismuth slag, the replacement solution is used as the pre-chlorination salt heating leaching solution, and the leaching residue is 8...
Embodiment 2
[0011] Example 2: Input 2.25t of indium-containing anode slime, grade Pb11.26%, In 9.43%, Sb28.71%, Bi 16.52%, Ag 9.98%, Cu2.62%, 1) primary chlorine salt heating leaching, leaching conditions: leachate: anode Mud=6:1, reaction temperature 85°C, reaction time 90min, final acid controlled at 2.5, leaching solution was neutralized with soda ash, control pH=3.0, leaching solution was neutralized with soda ash, control pH=5.1, neutralization slag was hydrogen of indium Oxide, after dissolving with sulfuric acid, the traditional extraction process extracts indium, and after neutralization, the liquid is passed through chlorine gas to oxidize and regenerate, and then it is used as the pre-chlorine salt leaching solution at room temperature; 6:1, stirring at room temperature, reaction time 180min, final acid control 45g / L, leaching solution plus reducing agent replacement to obtain copper bismuth slag. 3) Add sodium chlorate to oxidize the salt leaching residue before ammonia leachi...
Embodiment 3
[0012] Example 3: Put in 15.0kg of indium-containing anode slime, grade: Pb11.26%, In 9.43%, Sb28.71%, Bi 16.52%, Ag 9.98%, Cu2.62%, 1) primary chlorine salt heating leaching, leaching Conditions: leachate: anode slime = 7:1, reaction temperature 85°C, reaction time 100min, final acid pH 2.5, leachate neutralized with soda ash, control pH = 5.0, neutralized slag is indium hydroxide, dissolved with sulfuric acid Finally, the traditional extraction process extracts indium, and the neutralized liquid is passed through chlorine gas to oxidize and regenerate as the pre-chlorine salt leaching solution at room temperature; 2) Secondary chlorine salt leaching at room temperature (leach solution oxidation potential 0.75V) leach solution: chlorine salt heating leaching residue 7:1 , stirring at room temperature, reaction time 180min, final acid 35g / L, leaching solution plus reducing agent replacement to obtain copper bismuth slag, the replacement solution is used as the chlorine salt hea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com