Patents
Literature
4090 results about "Chlorine gas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
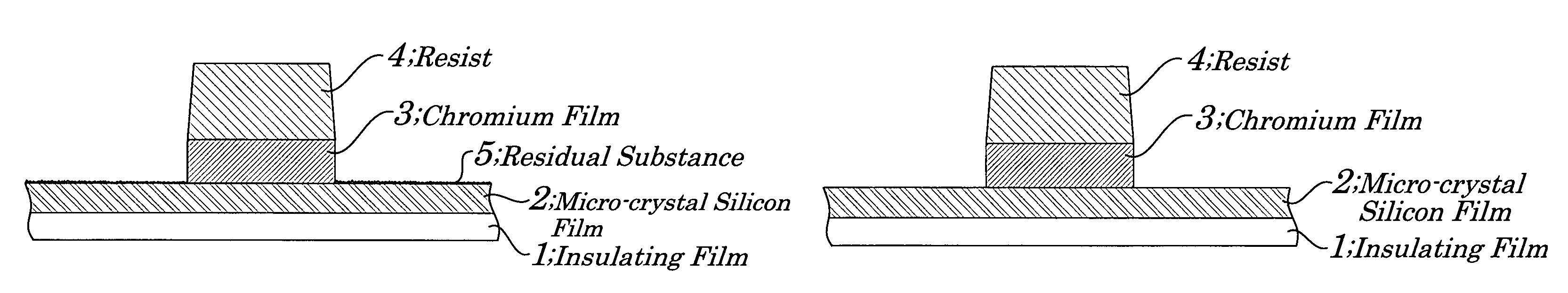
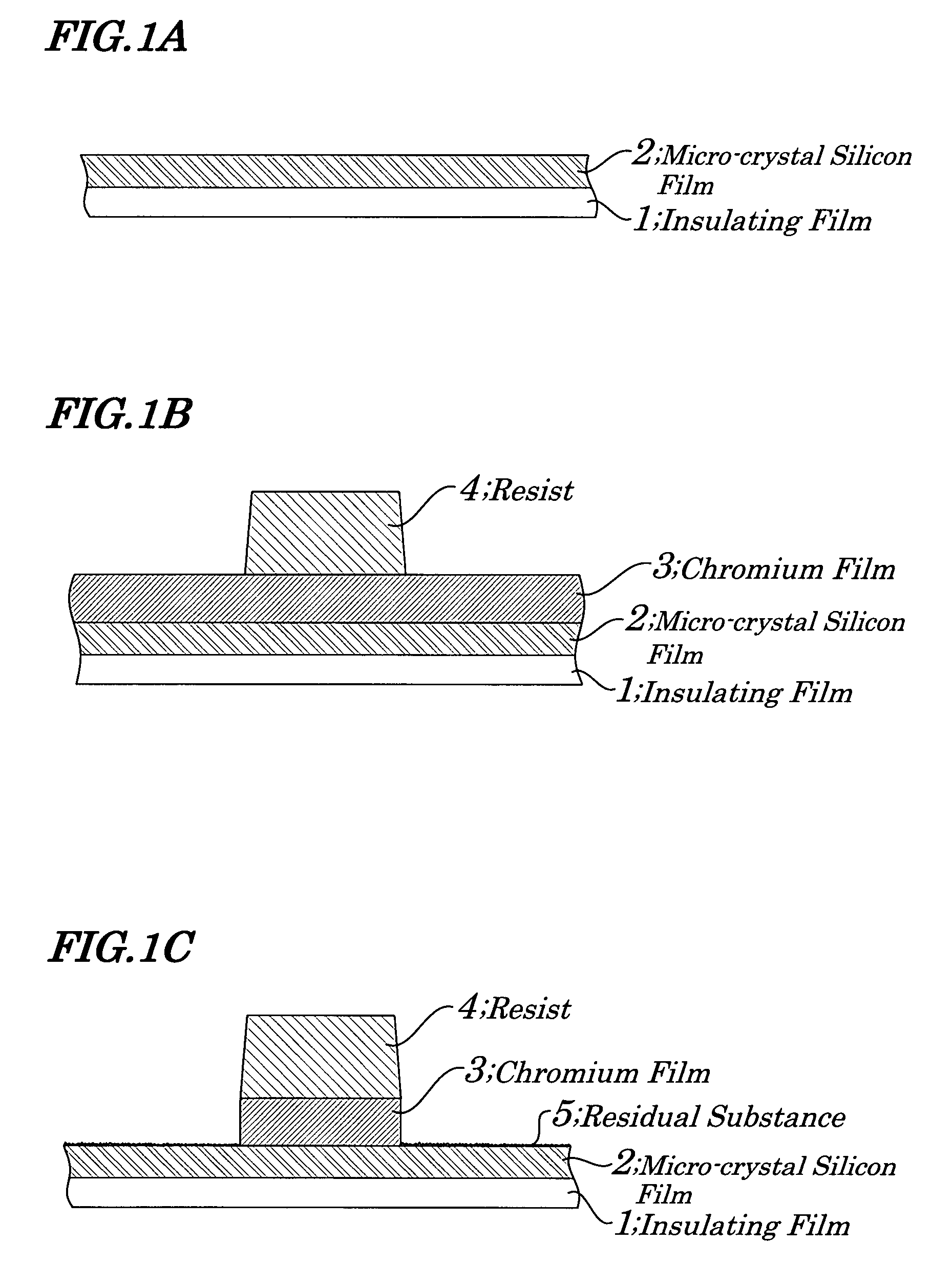
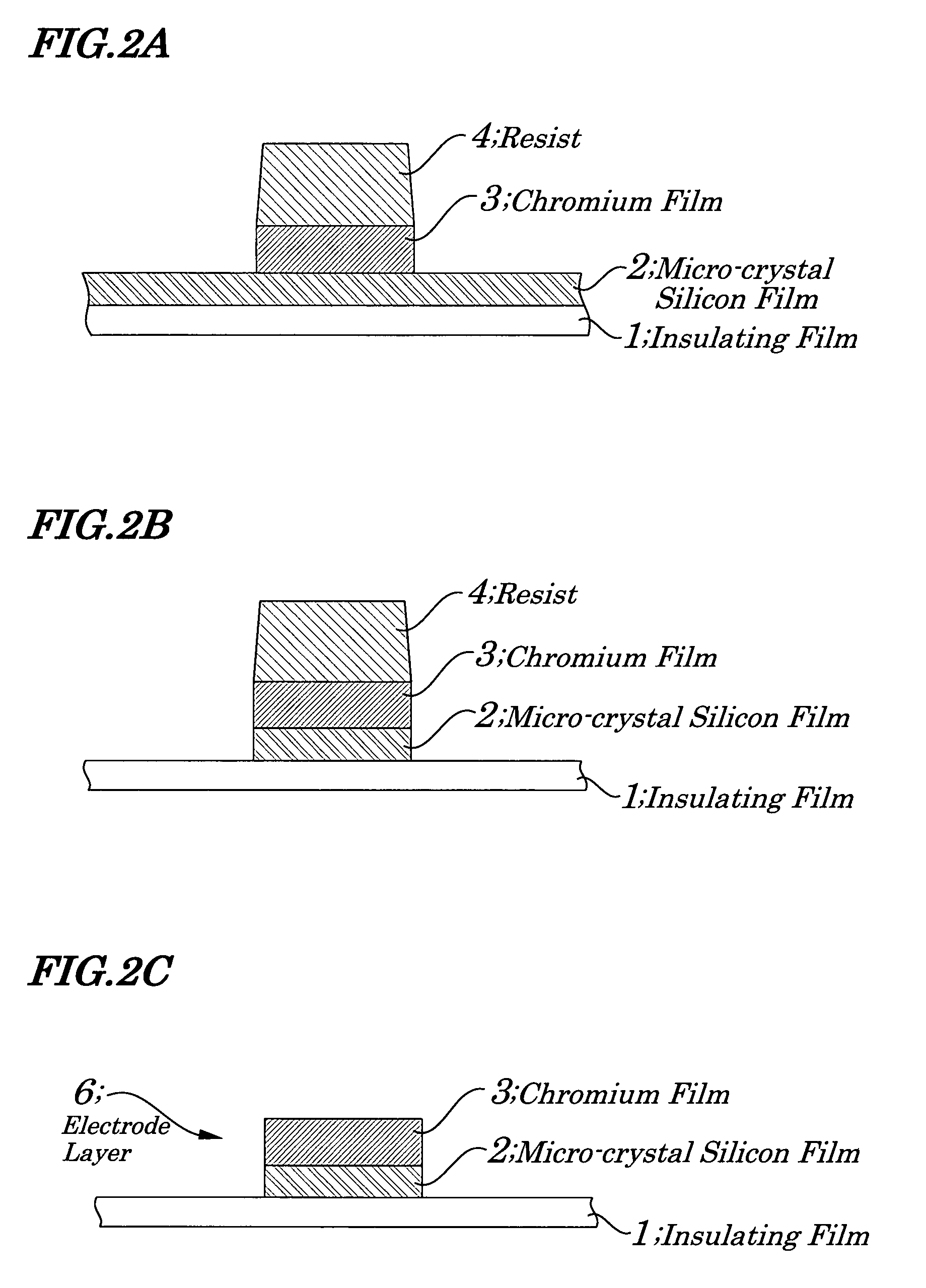
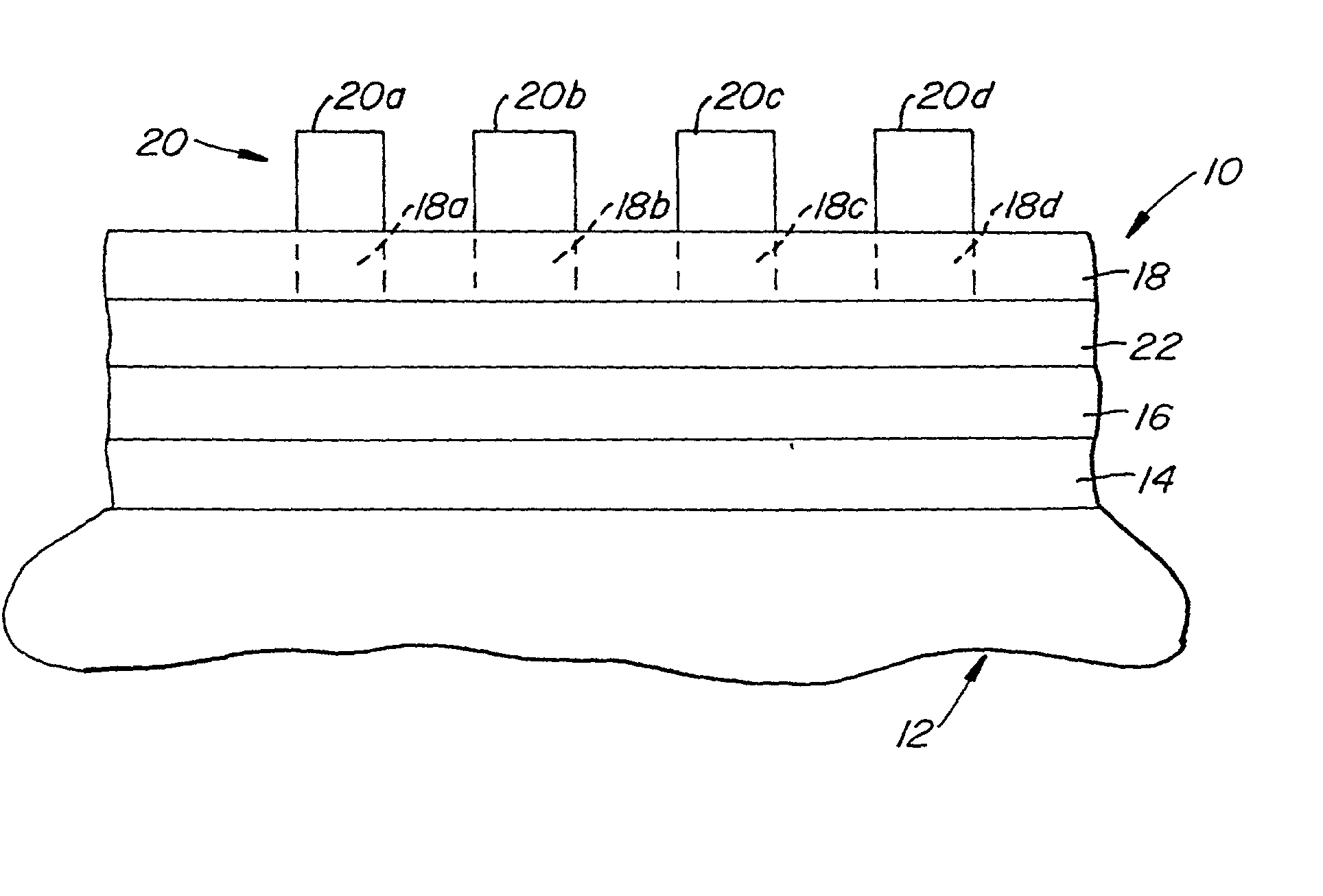
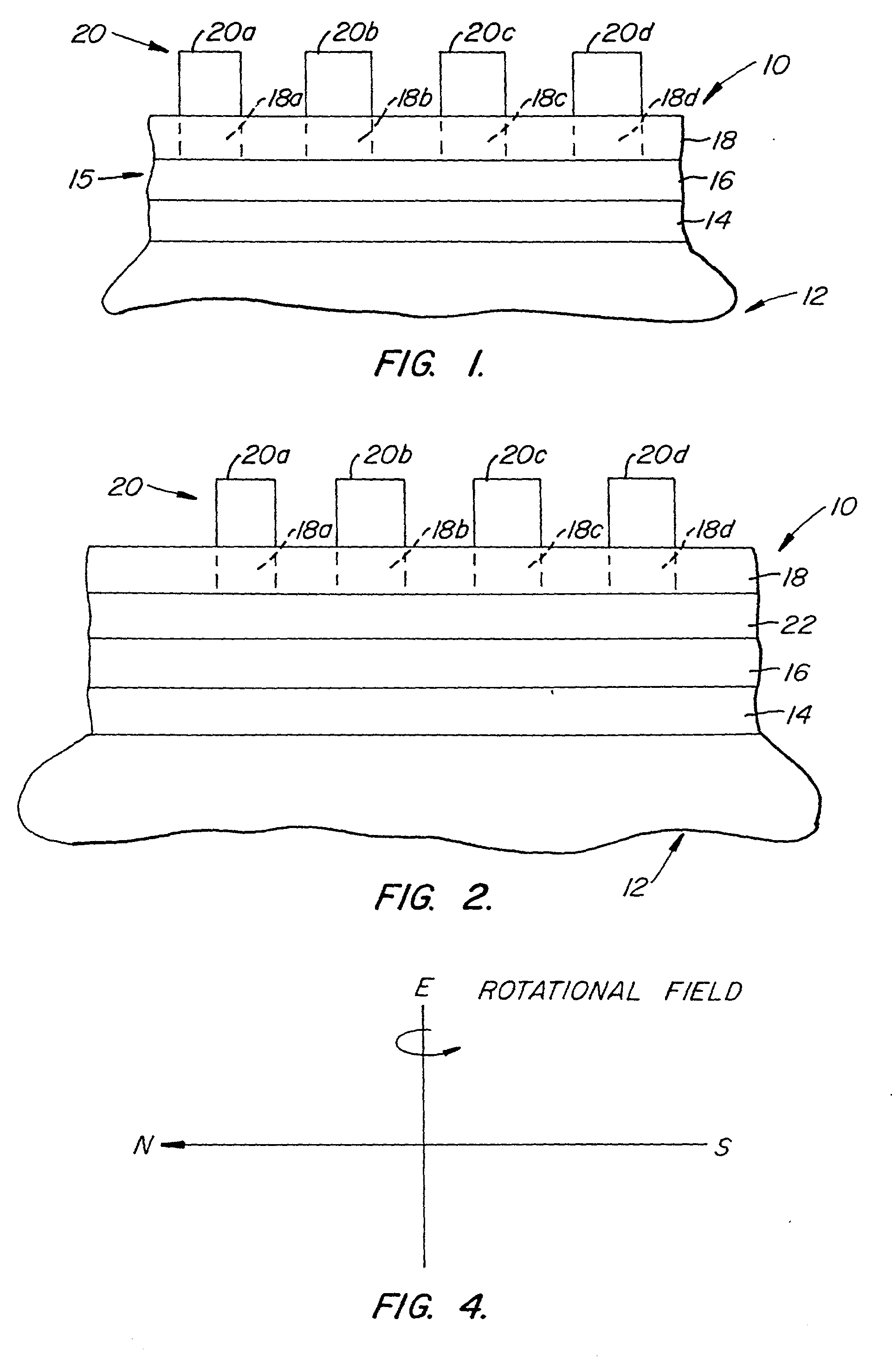
Stacked film patterning method and gate electrode forming method
InactiveUS7723221B2Improve uniformityAvoid it happening againSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistMixed gas
A stacked film patterning method is provided which is capable of reliably removing residual substances remaining after etching of a metal film, improving etching uniformity of a silicon film, and preventing an occurrence of etching residues. A micro-crystal film and a chromium film are sequentially formed on an insulating film serving as a front-end film and the chromium film is etched to be patterned by using a resist as a mask. Next, a micro-crystal silicon film on which the residual substances exist is exposed to plasma of a mixed gas including chlorine gas and oxygen gas to selectively etch the residual substances on a surface of the micro-crystal silicon film. After that, the micro-crystal silicon film is dry etched.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
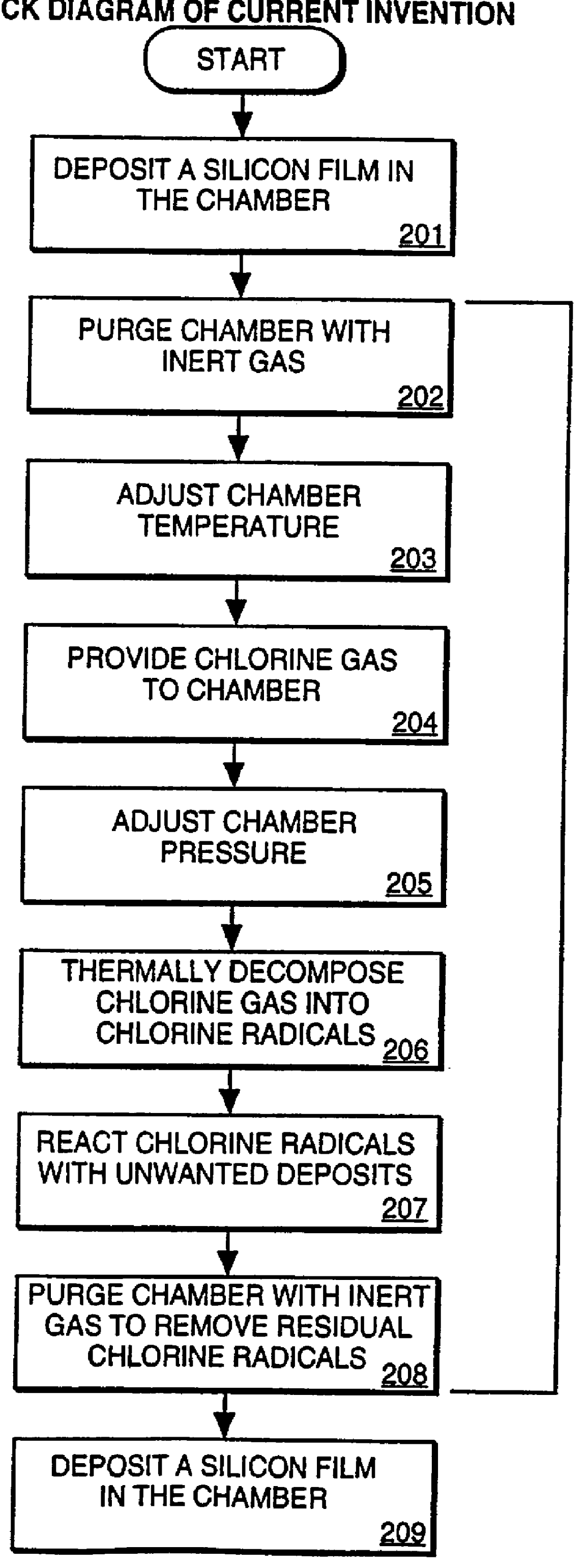
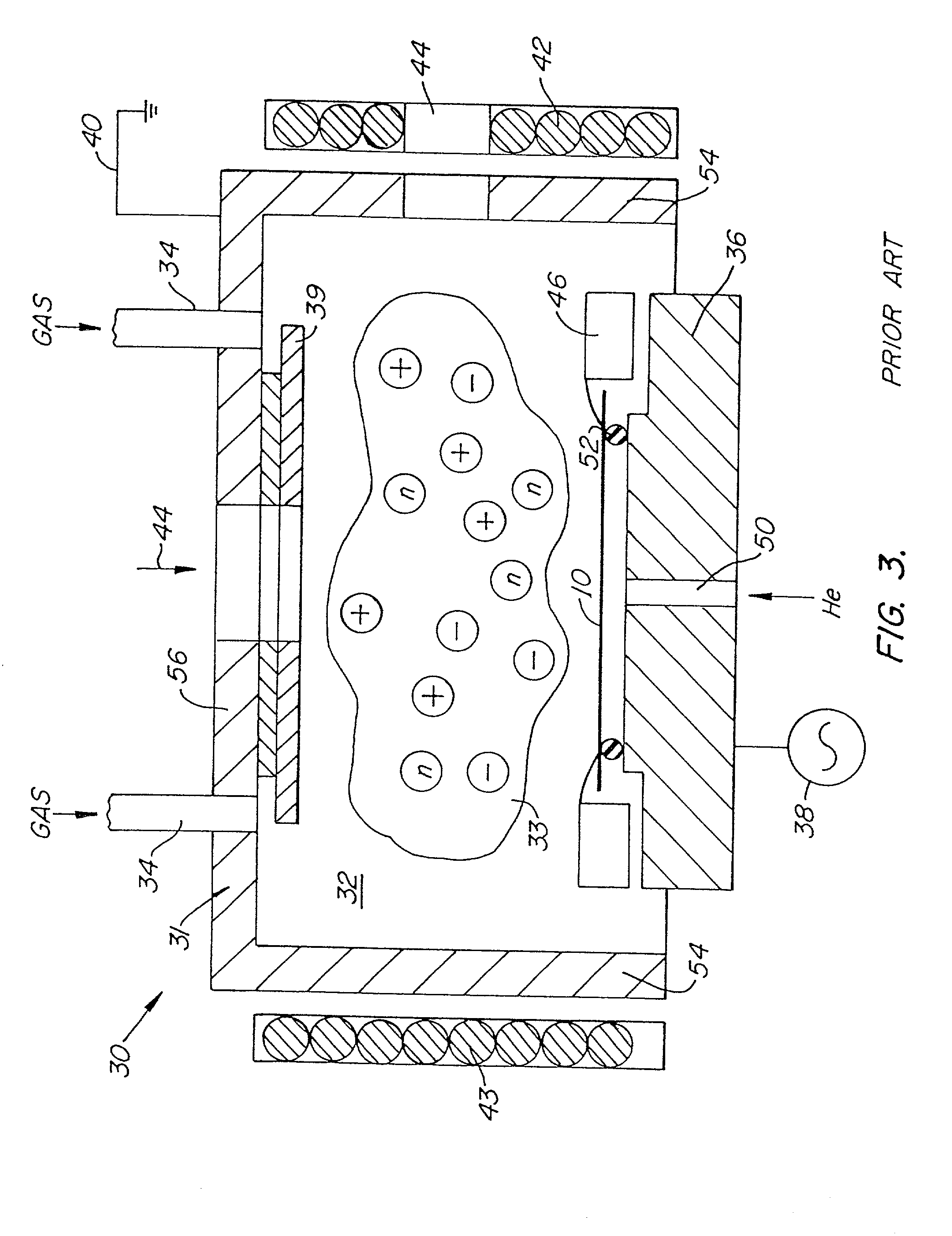
Method of cleaning CVD cold-wall chamber and exhaust lines
InactiveUS6042654APressurized chemical processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemistryChlorine gas
A method of cleaning post deposition deposits from a processing chamber by providing a chlorine gas (Cl2), forming chlorine radicals and reacting the chlorine radicals with the deposits.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
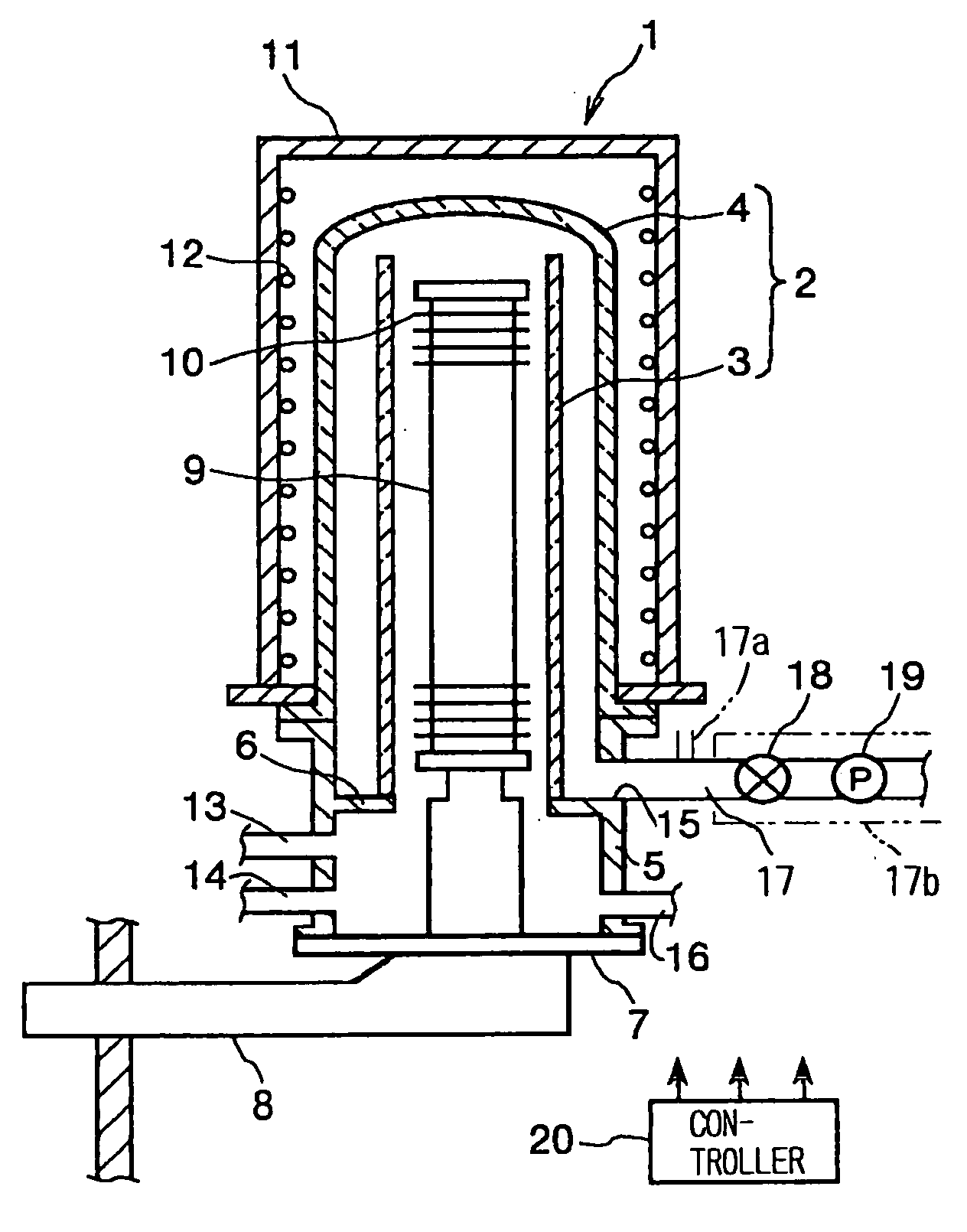
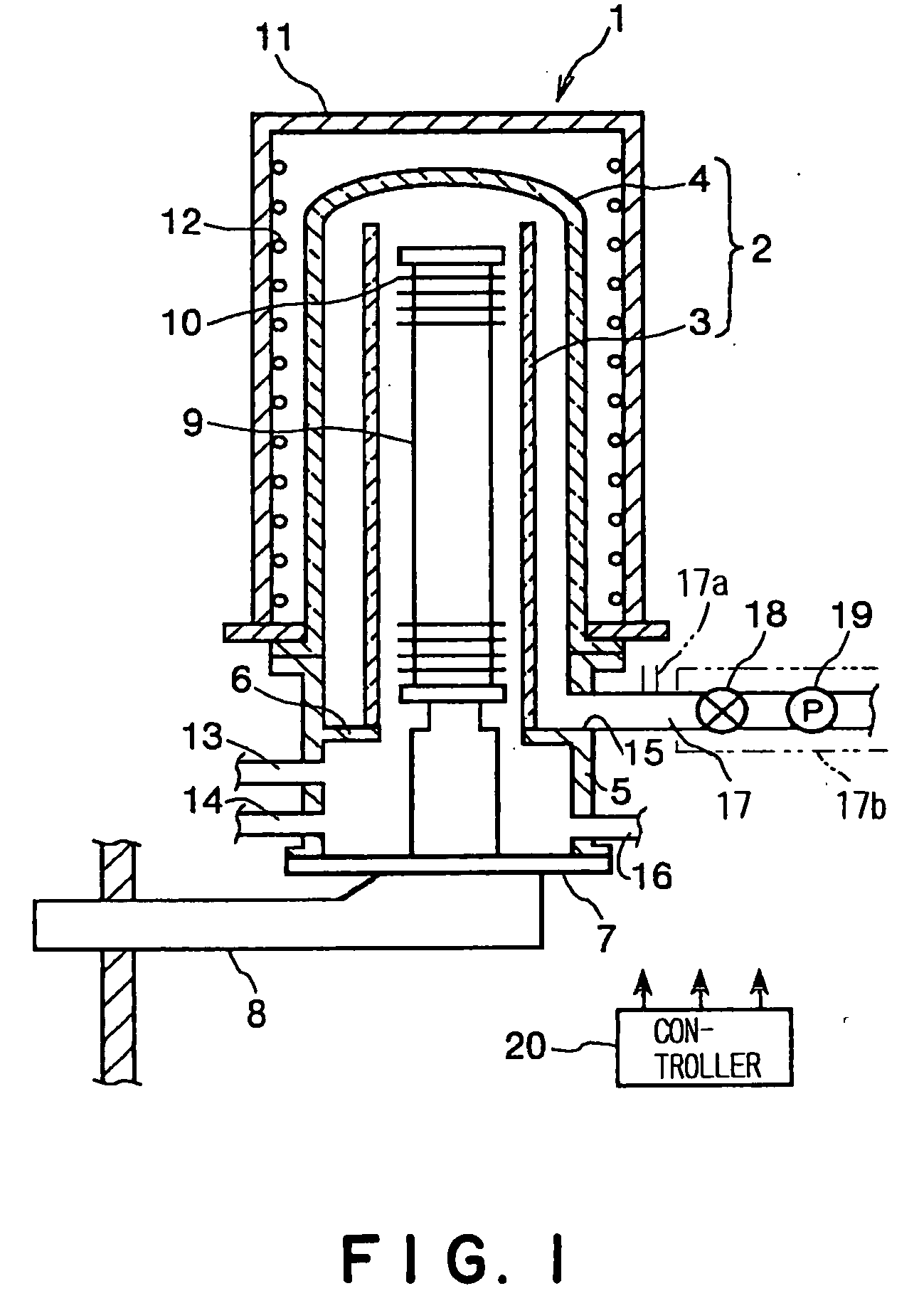
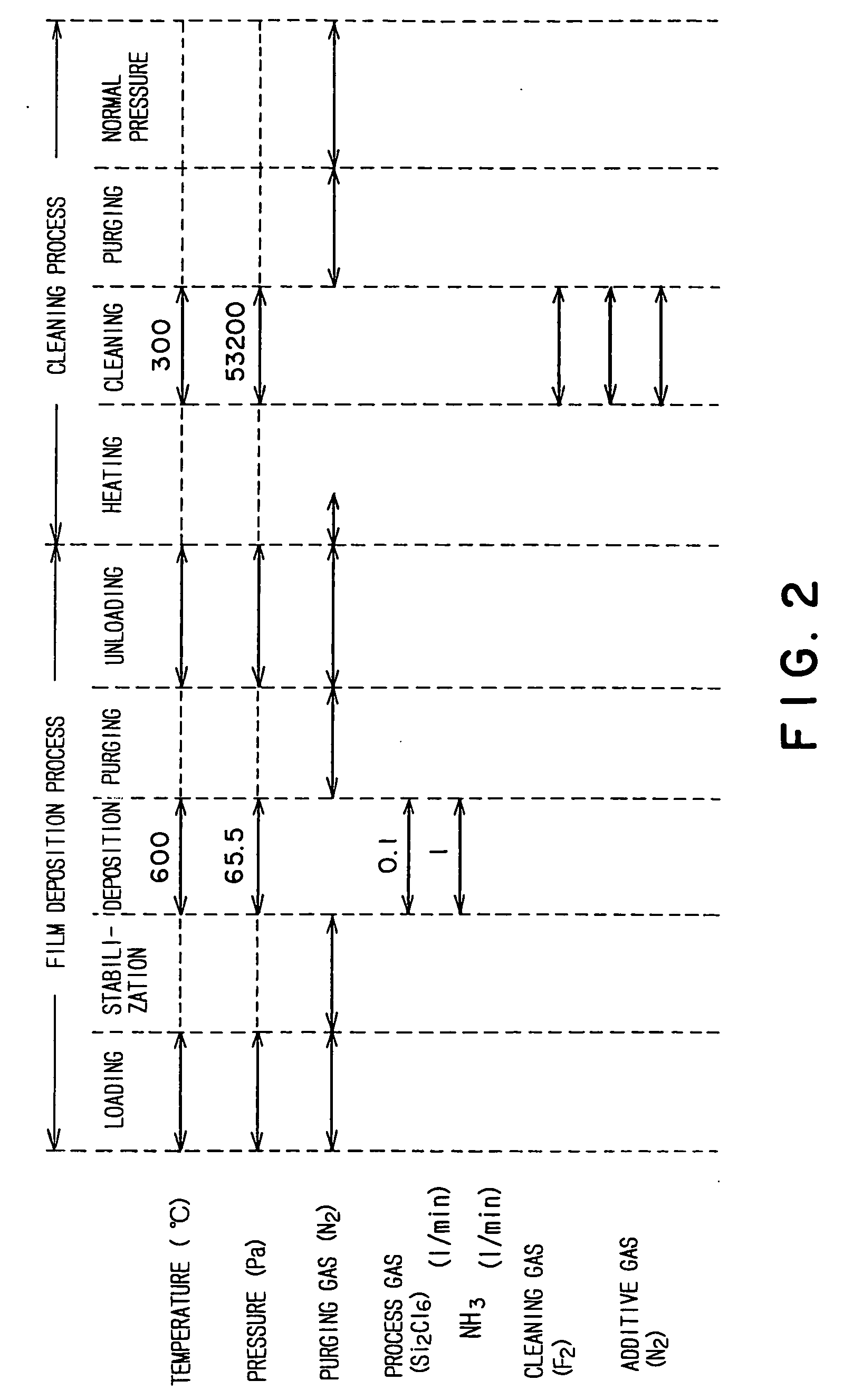
Thin film forming apparatus cleaning method
InactiveUS20050090123A1Inhibit deteriorationIncrease etch rateDrying solid materials without heatSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning methodsNitrogen gas
A cleaning process for cleaning a thermal processing apparatus includes: a heating step of heating an interior of a reaction tube at 300° C., and a cleaning step of removing deposits deposited in the thermal processing apparatus. In the cleaning step, a cleaning gas containing fluorine gas, chlorine gas and nitrogen gas is supplied into the interior of the reaction tube heated at 300° C. to remove silicon nitride so to clean an interior of the thermal processing apparatus.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
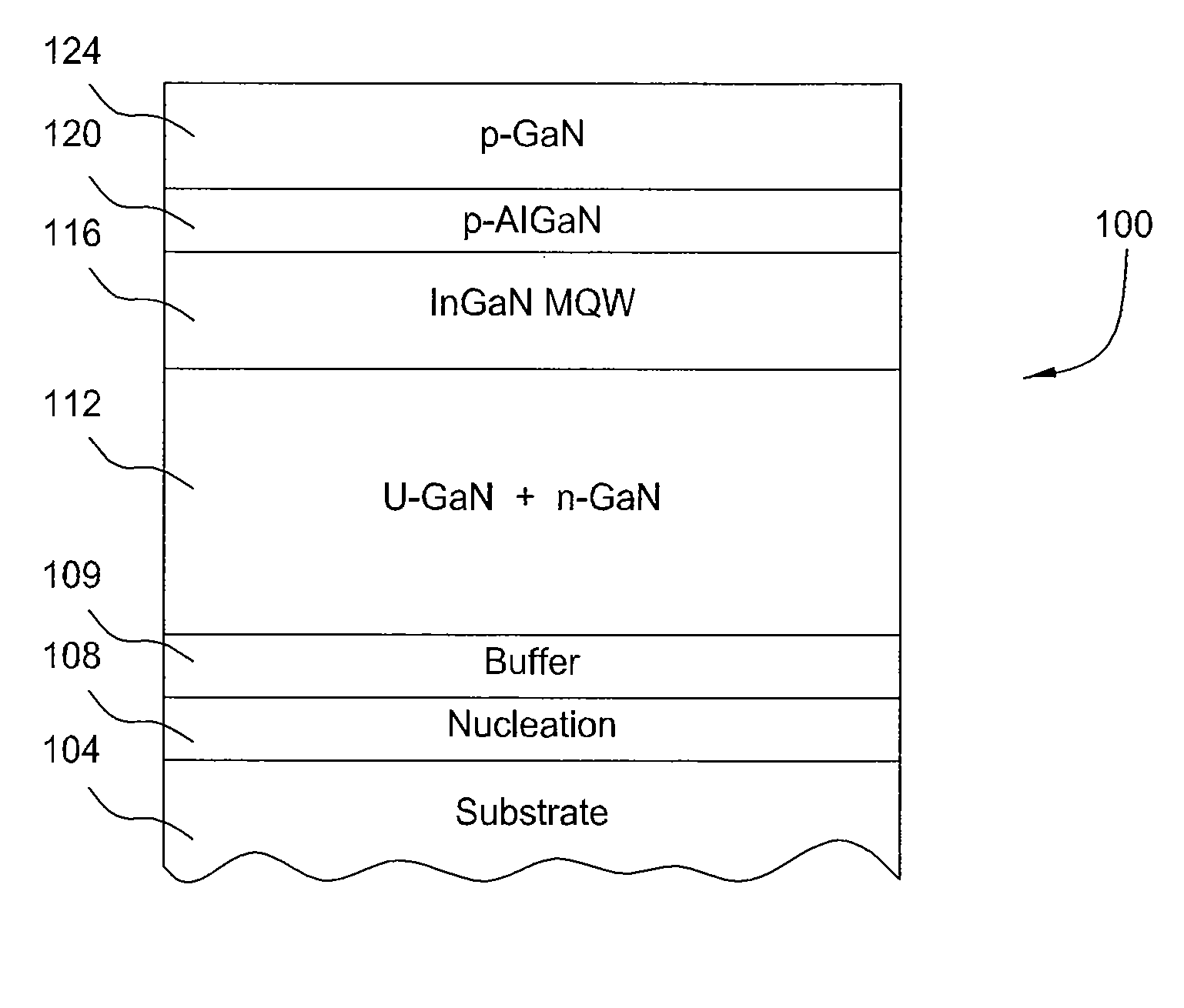
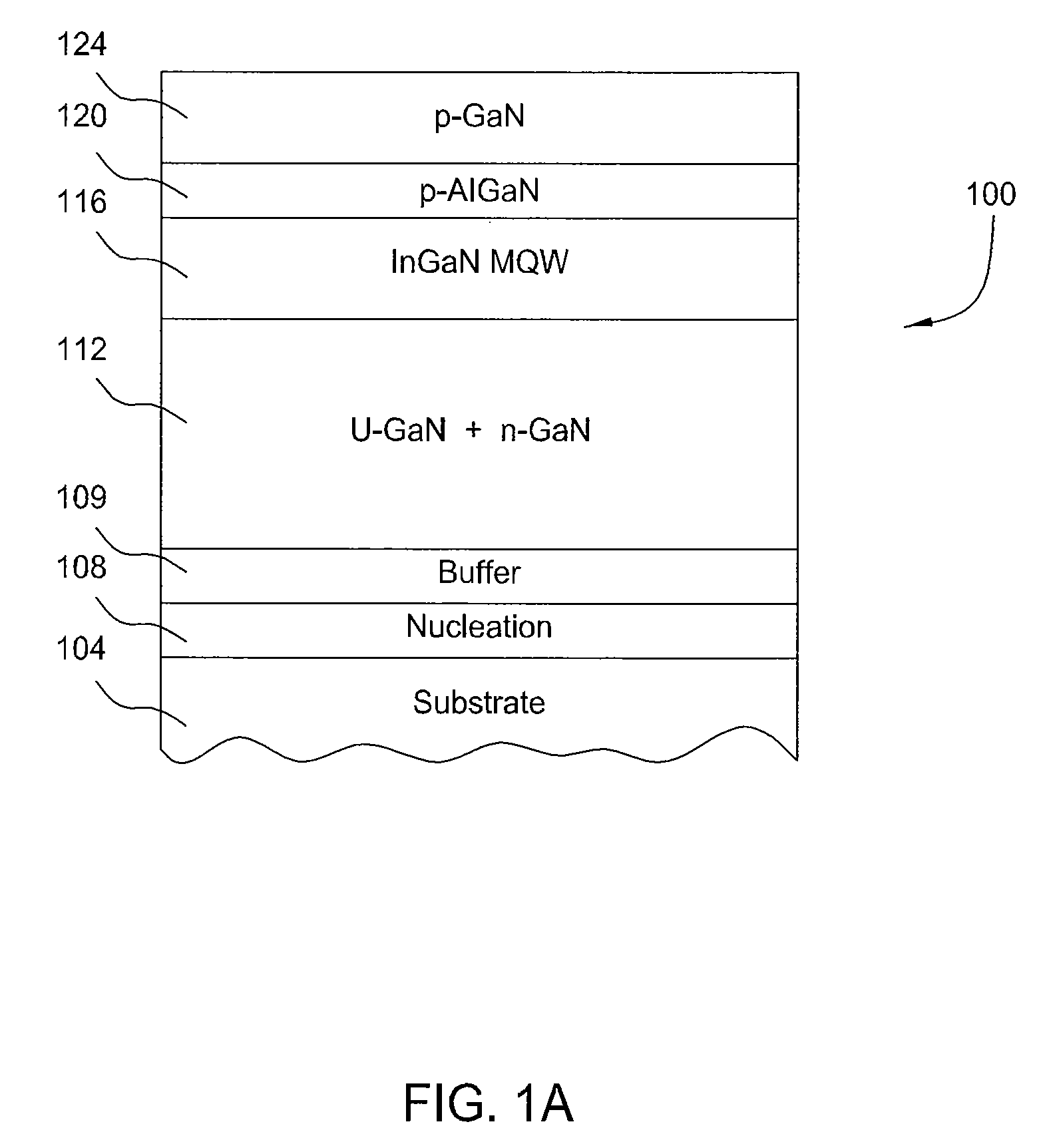
Mocvd single chamber split process for LED manufacturing
InactiveUS20100273290A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorGallium nitride
In one embodiment a method for fabricating a compound nitride semiconductor device comprising positioning one or more substrates on a susceptor in a processing region of a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) chamber comprising a showerhead, depositing a gallium nitride layer over the substrate with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process within the MOCVD chamber by flowing a first gallium containing precursor and a first nitrogen containing precursor through the showerhead into the MOCVD chamber, removing the one or more substrates from the MOCVD chamber without exposing the one or more substrates to atmosphere, flowing a chlorine gas into the processing chamber to remove contaminants from the showerhead, transferring the one or more substrates into the MOCVD chamber after removing contaminants from the showerhead, and depositing an InGaN layer over the GaN layer with a thermal chemical-vapor-deposition process within the MOCVD chamber is provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
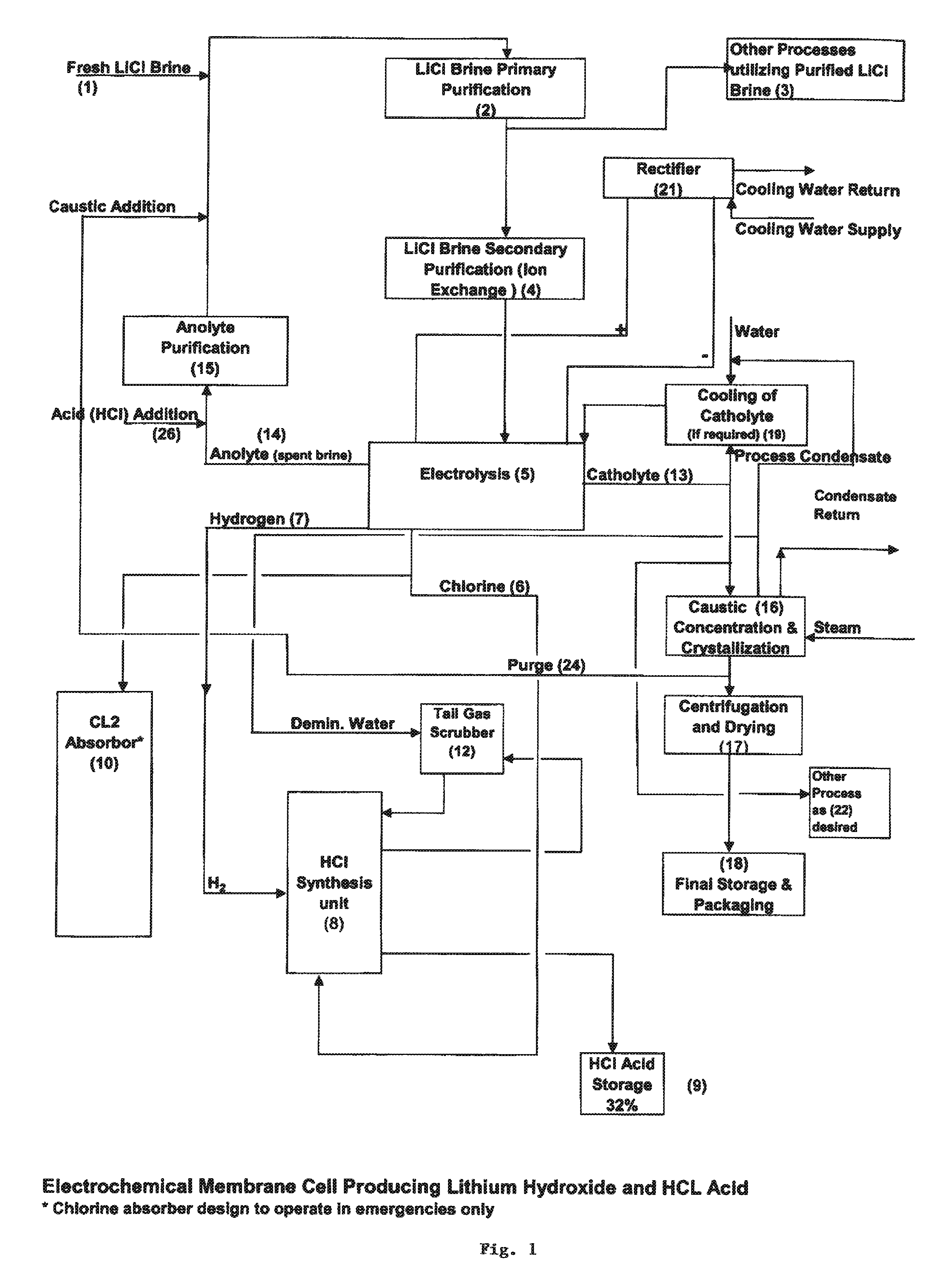
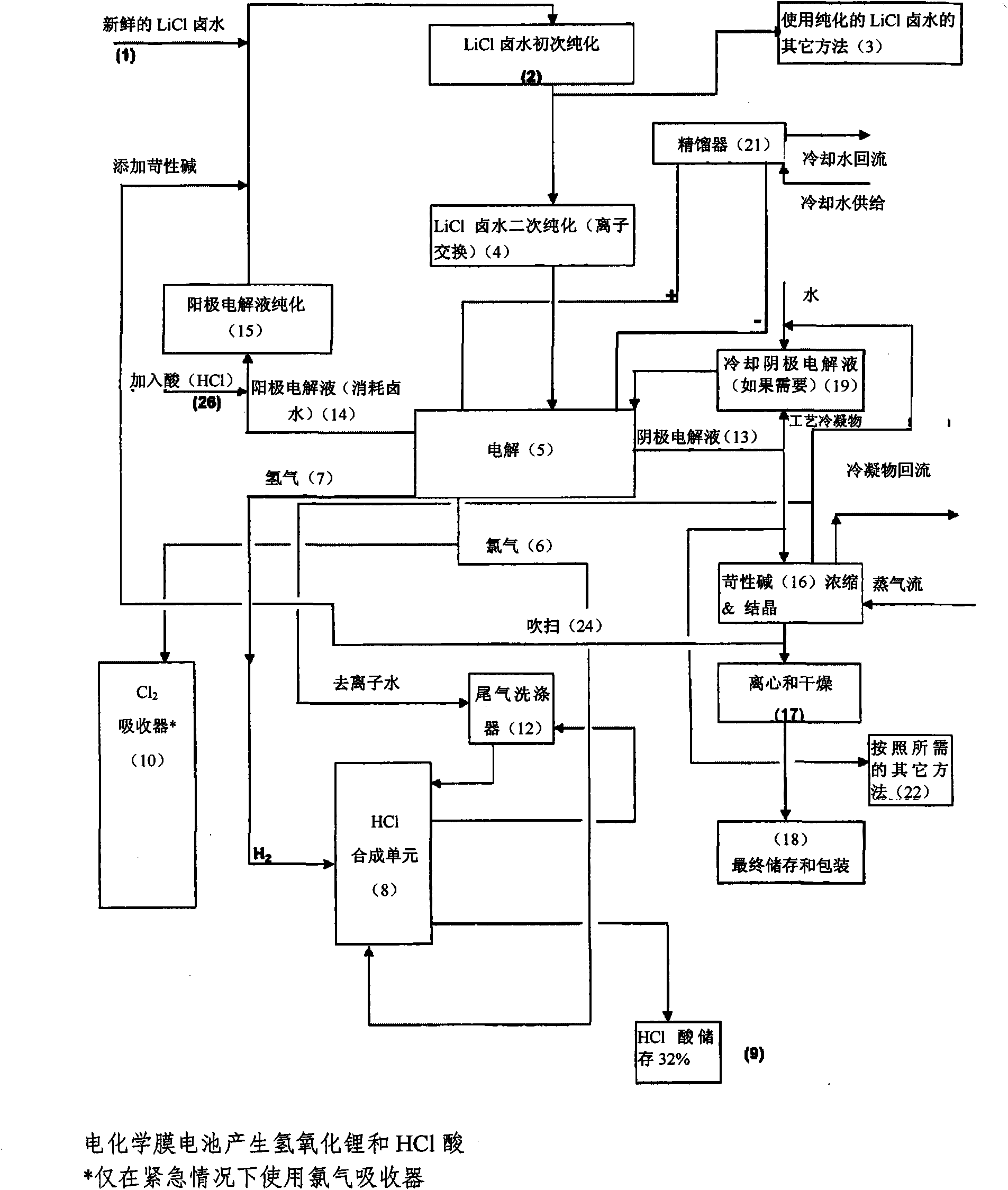
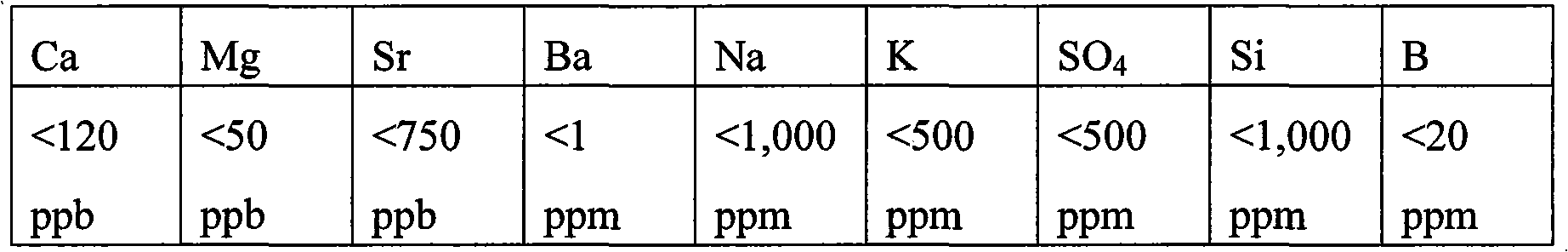
Method of making high purity lithium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
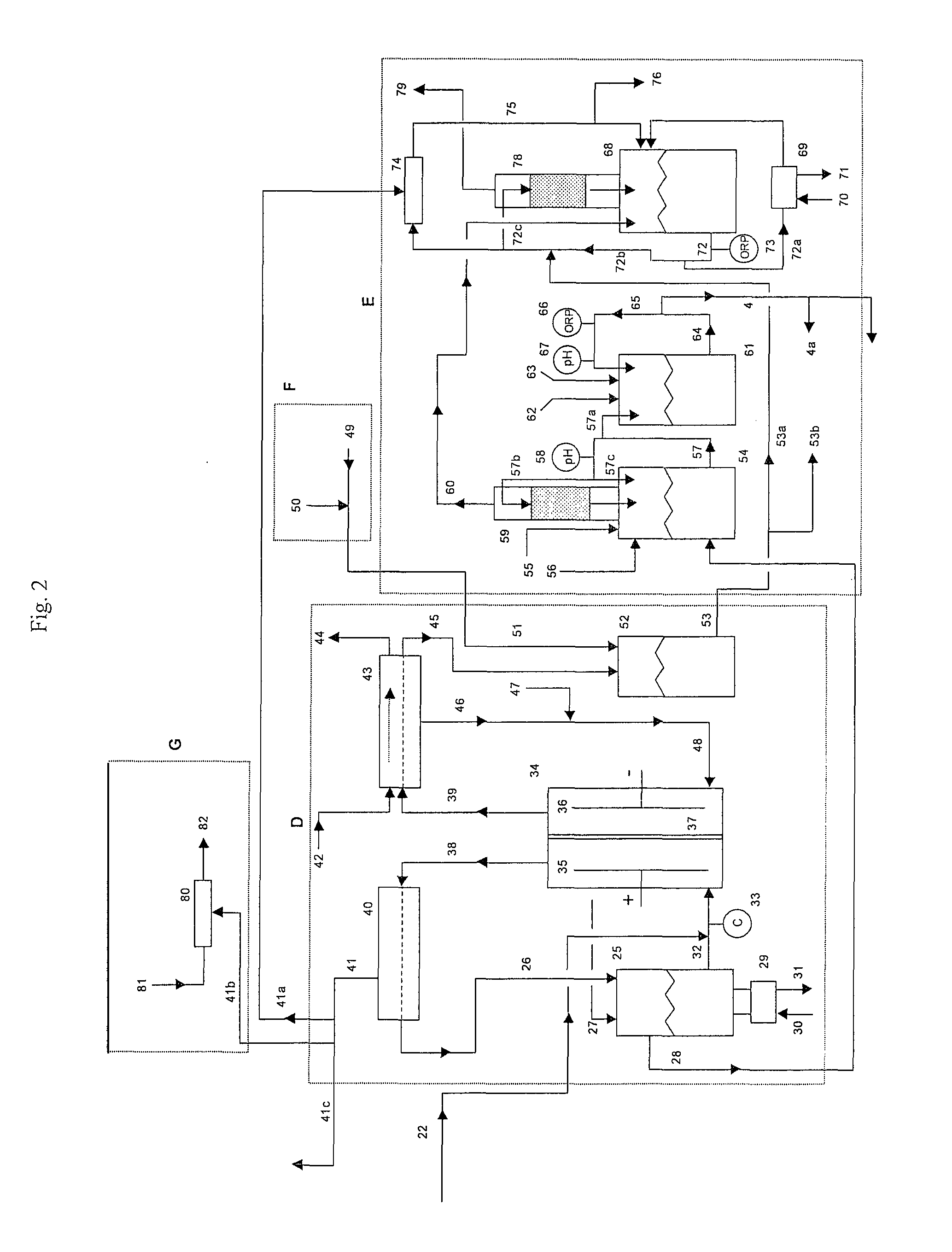
InactiveUS20110044882A1Simple and economical processEasy to convertElectrolysis componentsEnergy inputElectrolysisIon exchange
The present invention relates to a process for producing high purity lithium hydroxide monohydrate, comprising following steps: concentrating a lithium containing brine; purifying the brine to remove or to reduce the concentrations of ions other than lithium; adjusting the pH of the brine to about 10.5 to 11 to further remove cations other than lithium, if necessary; neutralizing the brine with acid; purifying the brine to reduce the total concentration of calcium and magnesium to less than 150 ppb via ion exchange; electrolyzing the brine to generate a lithium hydroxide solution containing less than 150 ppb total calcium and magnesium, with chlorine and hydrogen gas as byproducts; producing hydrochloric acid via combustion of the chlorine gas with excess hydrogen and subsequent scrubbing of the resultant gas stream with purified water, if elected to do so; and concentrating and crystallizing the lithium hydroxide solution to produce lithium hydroxide monohydrate crystals.
Owner:ROCKWOOD LITHIUM INC
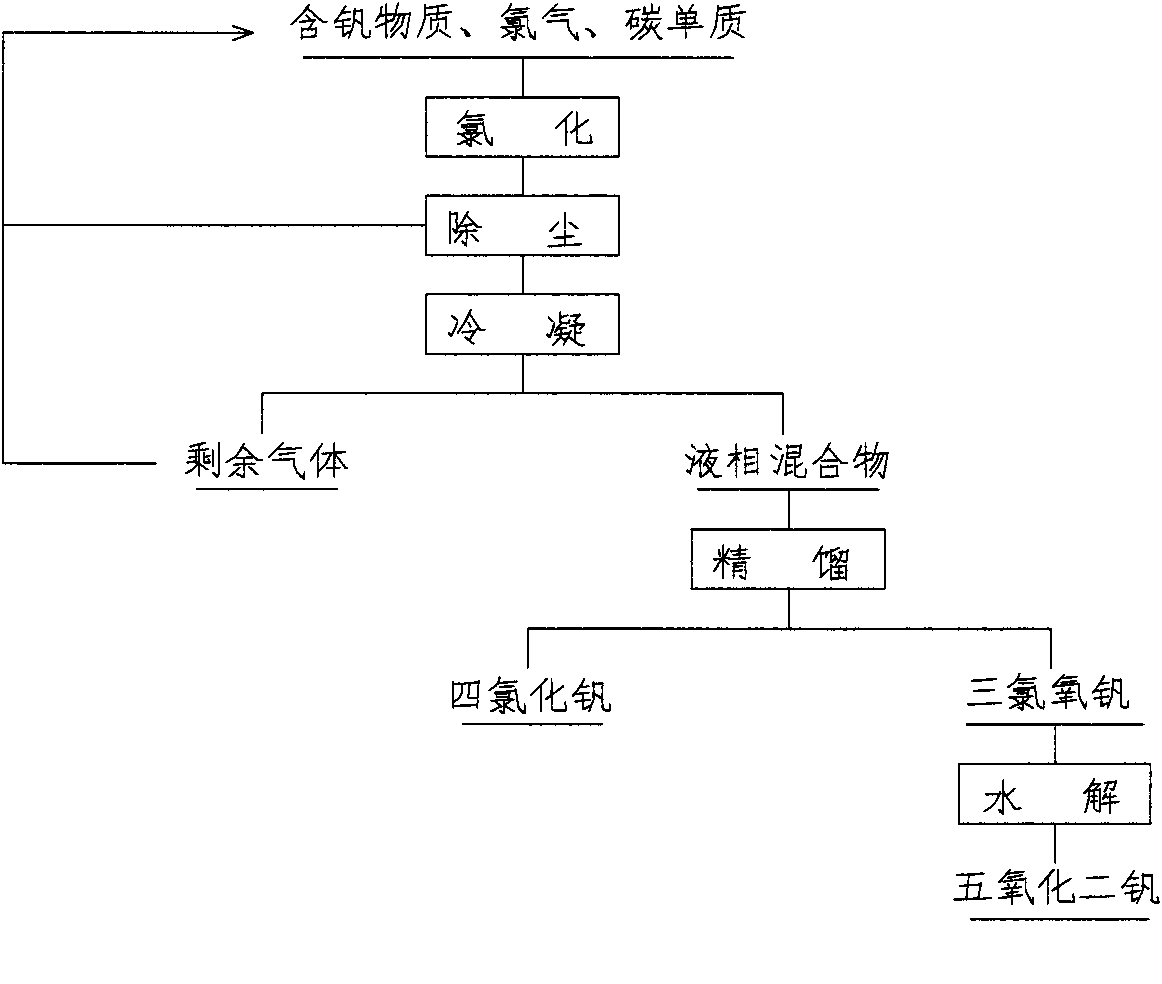
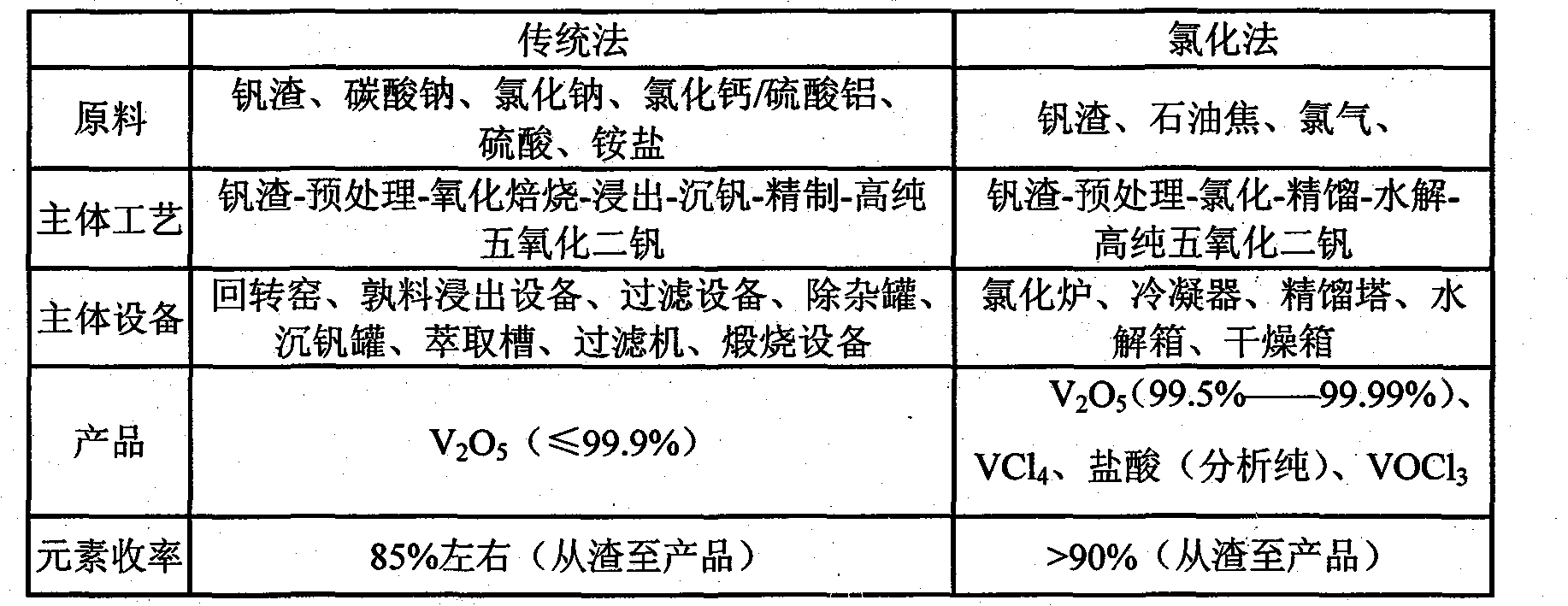
Method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination
The invention discloses a novel method for extracting and converting a substance containing vanadium into high-purity vanadium pentoxide by chlorination. The high-purity vanadium pentoxide process comprises batching, chlorination, dedusting, condensation, rectification, hydrolysis, filtering, drying and postprocessing. Raw materials comprise the substance containing vanadium and a carbon elementary substance and the weight ratio of the substance containing vanadium to the carbon elementary substance is 1: (0.05-0.25). The raw materials are evenly mixed, dried and put in a reactor and the high-purity vanadium pentoxide is obtained through successive chlorination, hydrolysis, postprocessing and the like. The novel method for producing high-purity vanadium pentoxide instead of a traditional method reduces industrial harmful waste water produced during a traditional hydrometallurgy process, and cyclic utilization of chlorine is achieved after the chlorine is processed. The whole production process is easy in process and basically free of produced wastes, and has certain economic benefit and social benefit. The purity of the vanadium pentoxide powder obtained by the method is 99.5%-99.99%.
Owner:刘艳梅
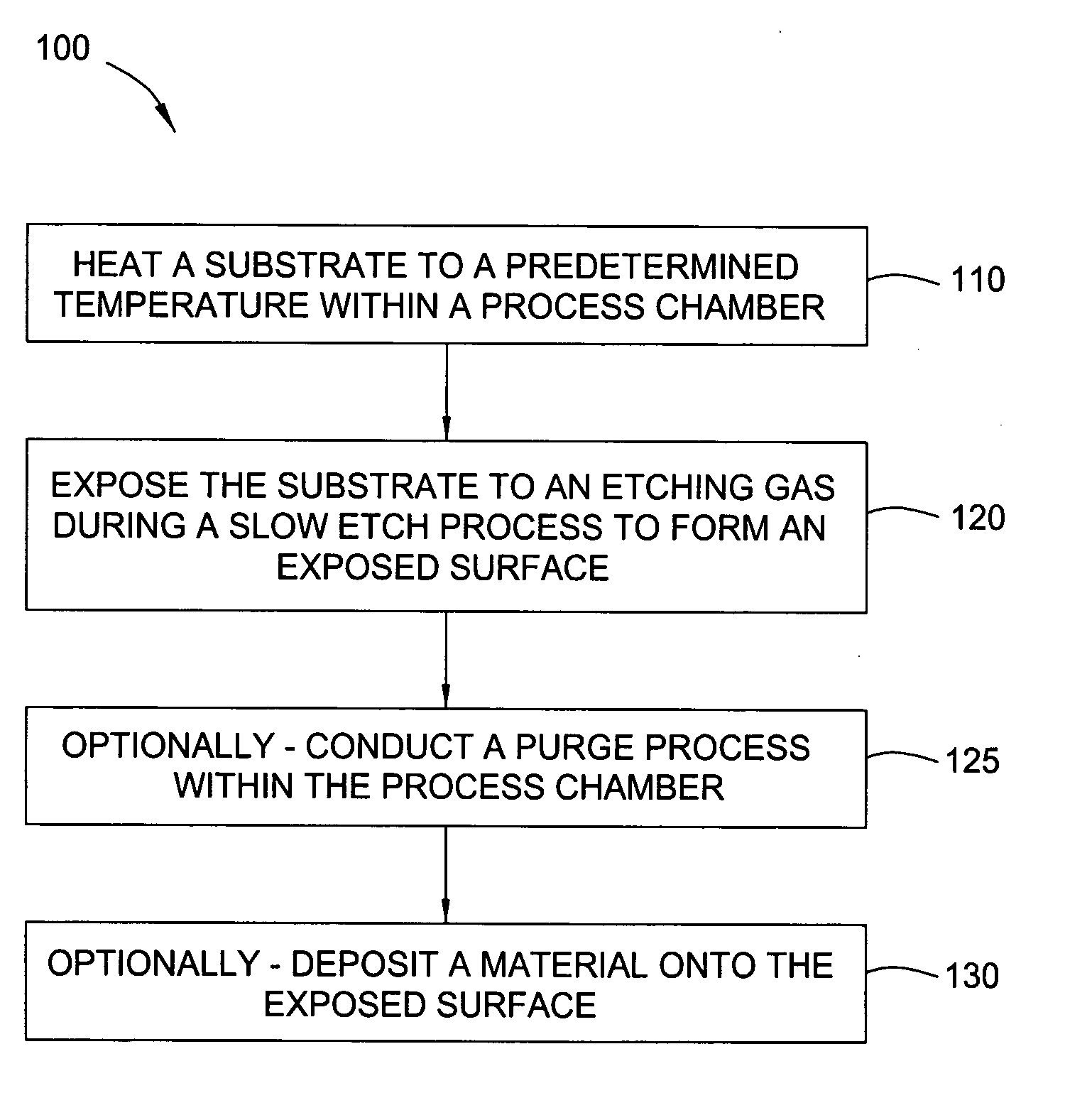
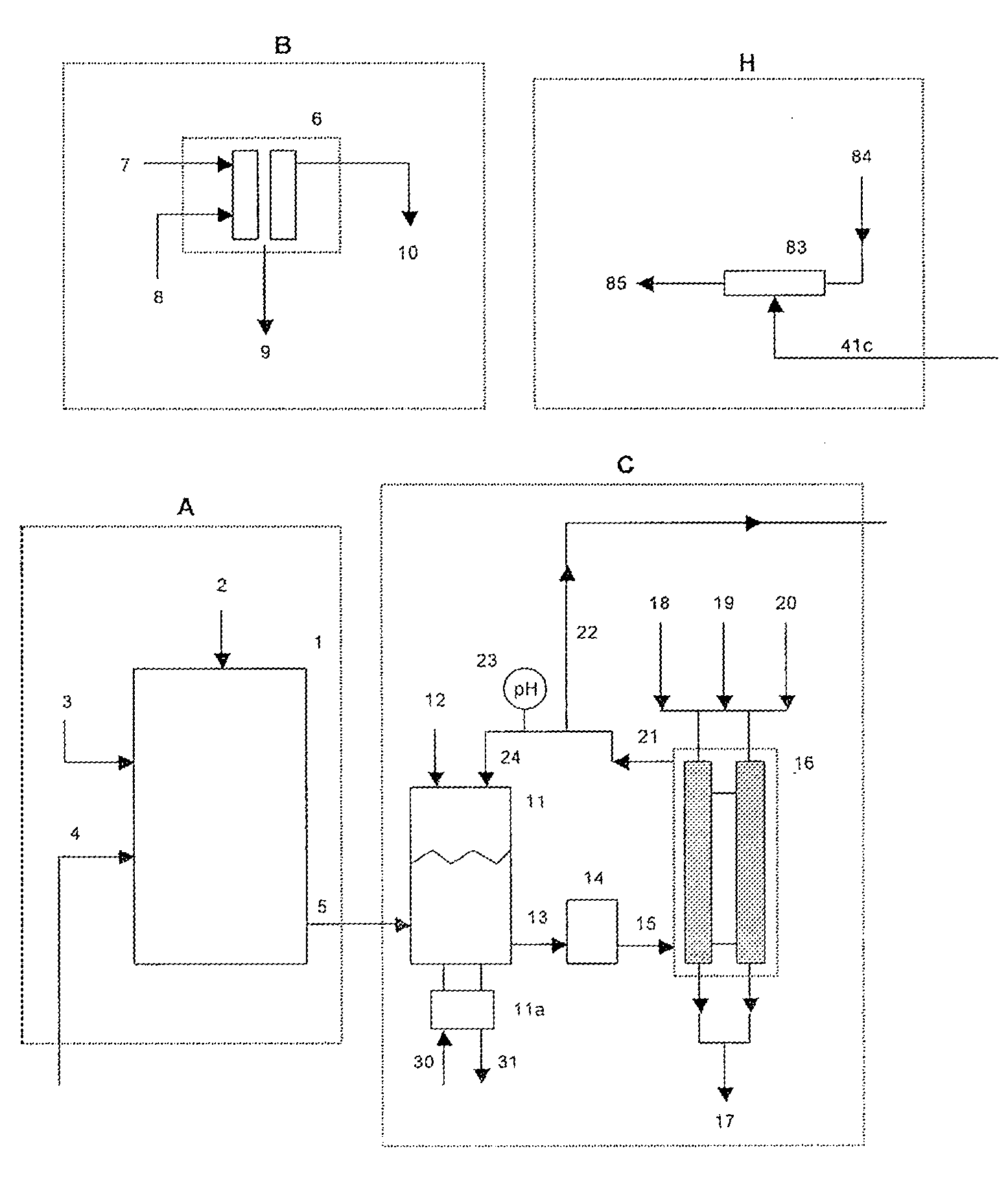
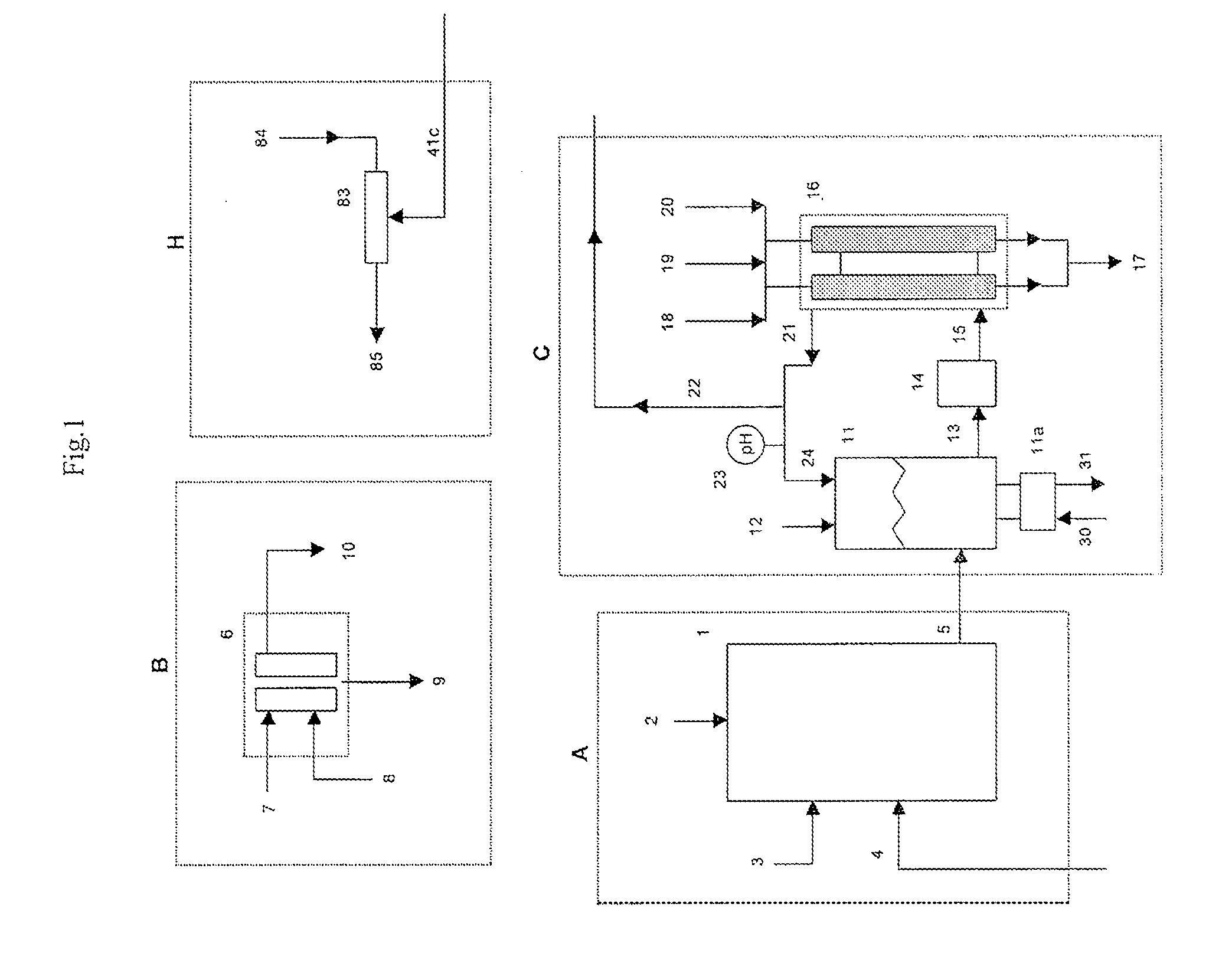
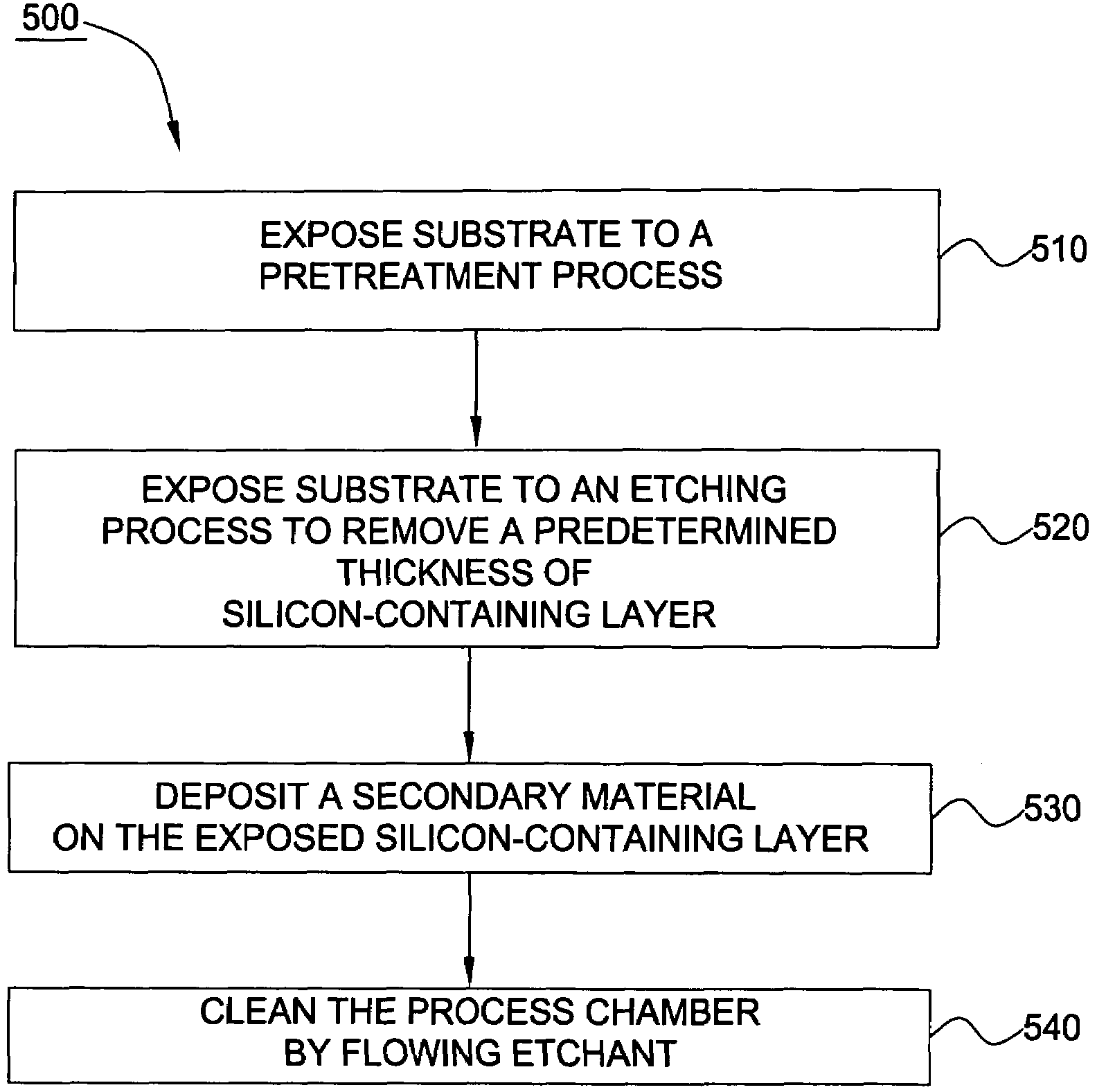
Etchant treatment processes for substrate surfaces and chamber surfaces
ActiveUS20060169669A1Reduce the temperatureFast etch rateDecorative surface effectsElectrostatic cleaningEtchingPhysical chemistry
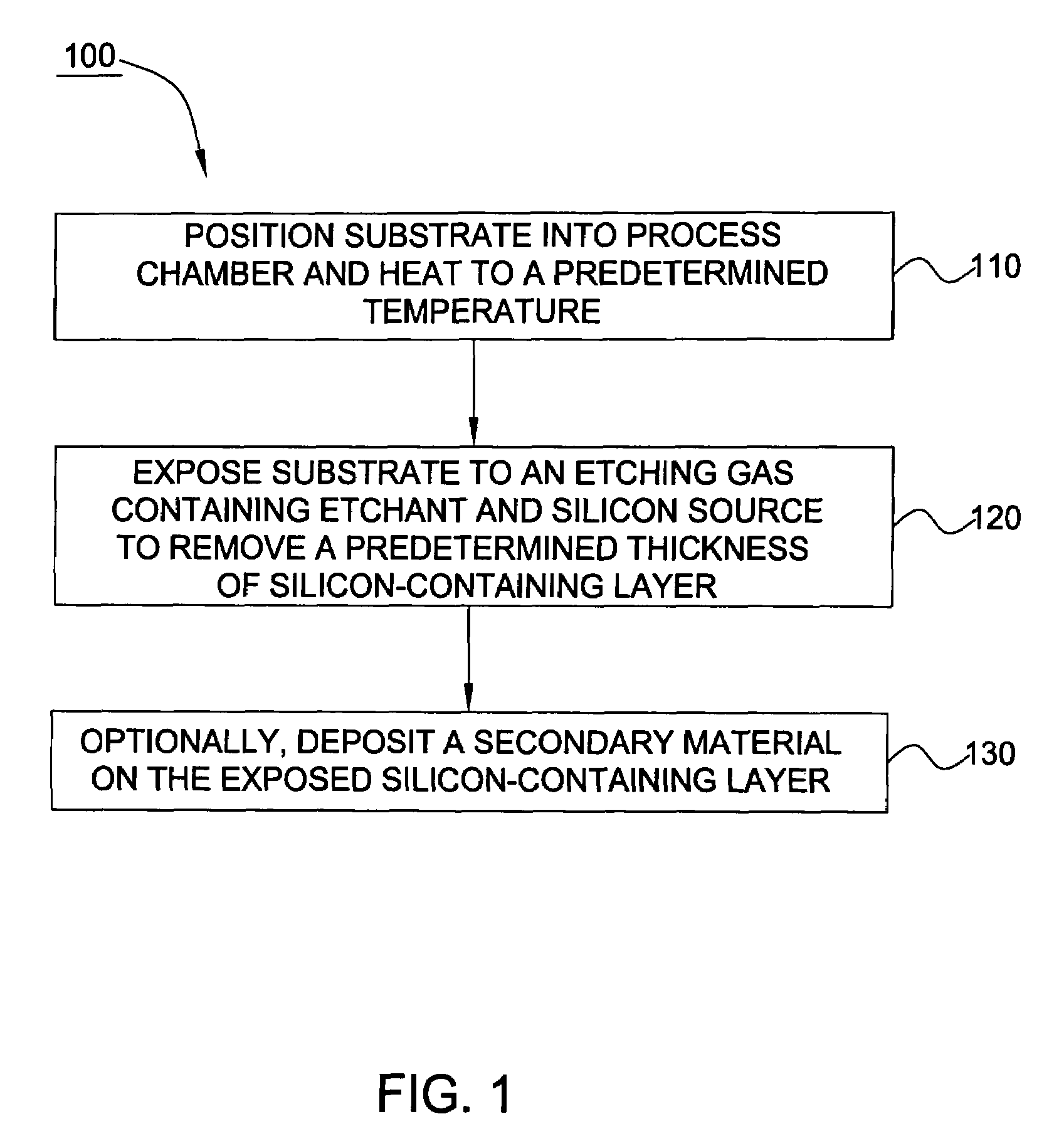
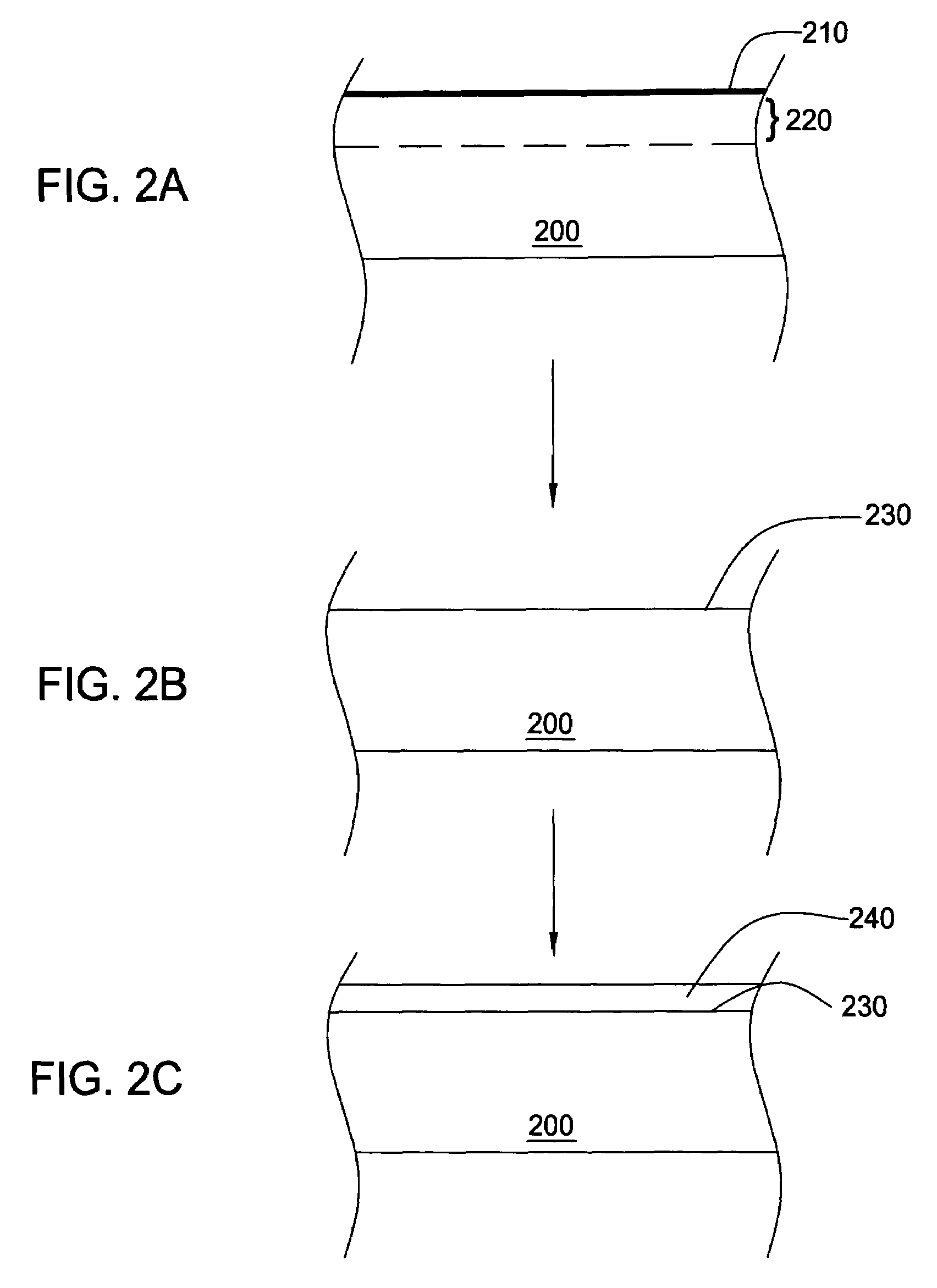
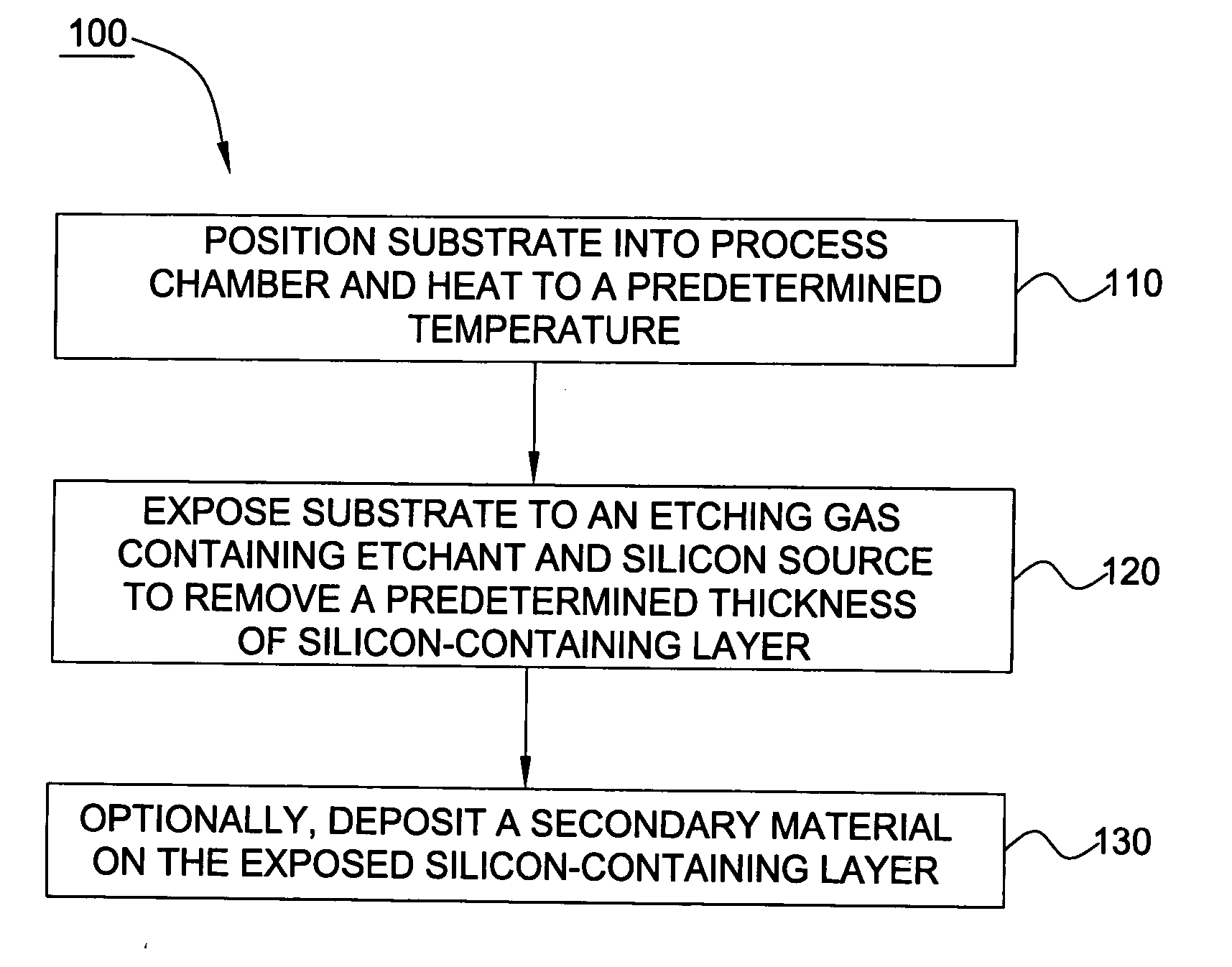
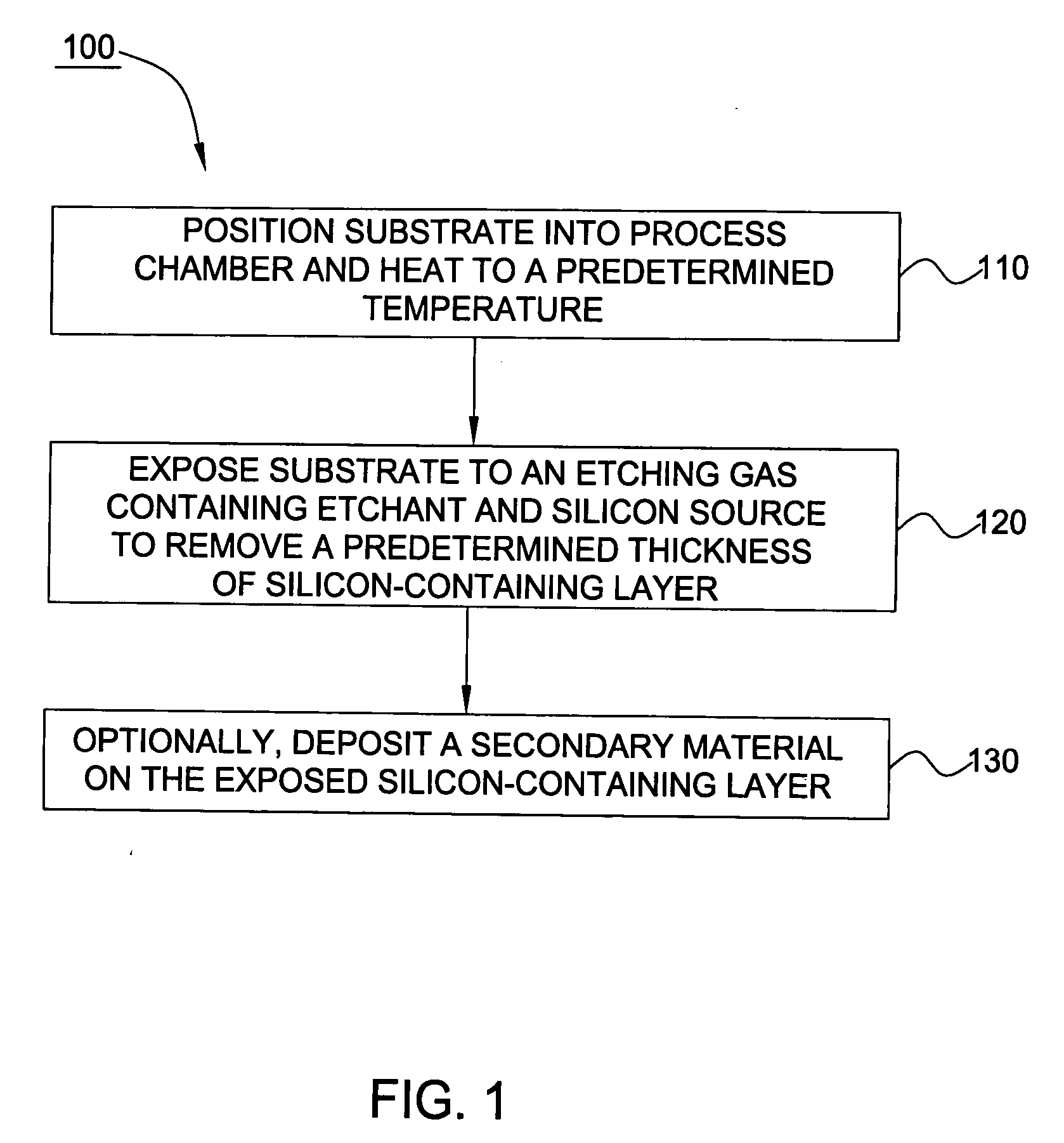
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for finishing or treating a silicon-containing surface is provided which includes removing contaminants and / or smoothing the surface contained on the surface by a slow etch process (e.g., about <100 Å / min). The silicon-containing surface is exposed to an etching gas that contains an etchant and a silicon source. Preferably, the etchant is chlorine gas so that a relatively low temperature (e.g., <800° C.) is used during the process. In another embodiment, a method for etching a silicon-containing surface during a fast etch process (e.g., about >100 Å / min) is provided which includes removing silicon-containing material to form a recess in a source / drain (S / D) area on the substrate. In another embodiment, a method for cleaning a process chamber is provided which includes exposing the interior surfaces with a chamber clean gas that contains an etchant and a silicon source. The chamber clean process limits the etching of quartz and metal surfaces within the process chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reactive formulations for a neutralization of toxic industrial chemicals
InactiveUS7125497B1Efficiently neutralizedHydrogen peroxideLiquid degasificationBoron trichlorideMalathion
Decontamination formulations for neutralization of toxic industrial chemicals, and methods of making and using same. The formulations are effective for neutralizing malathion, hydrogen cyanide, sodium cyanide, butyl isocyanate, carbon disulfide, phosgene gas, capsaicin in commercial pepper spray, chlorine gas, anhydrous ammonia gas; and may be effective at neutralizing hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, formaldehyde, ethylene oxide, methyl bromide, boron trichloride, fluorine, tetraethyl pyrophosphate, phosphorous trichloride, arsine, and tungsten hexafluoride.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Process for the on-site production of chlorine and high strength sodium hypochlorite
ActiveUS20070251831A1Reduce hardnessGuaranteed uptimeCellsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisBleach
The present invention relates to a novel economical on-site electrochemical based membrane cell based process with the capability of producing high strength sodium hypochlorite and / or elemental chlorine gas in any ratio as required by the needs of a water or wastewater treatment plant. The system is compact and modular, using membrane cell based electrolyzers and utilizing novel process modifications and sensors to allow for the unattended control and safe operation of the process. The process allows the operator to produce elemental chlorine gas and sodium hypochlorite in any product ratio, such that 5% to 100% of the total chlorine produced by the process can be converted to high strength bleach. The process has the flexibility to produce stable high quality, low to high strength sodium hypochlorite solutions in concentrations ranging from about 2 to 15% trade as NaOCl.
Owner:ELECTROLYTIC TECH CORP
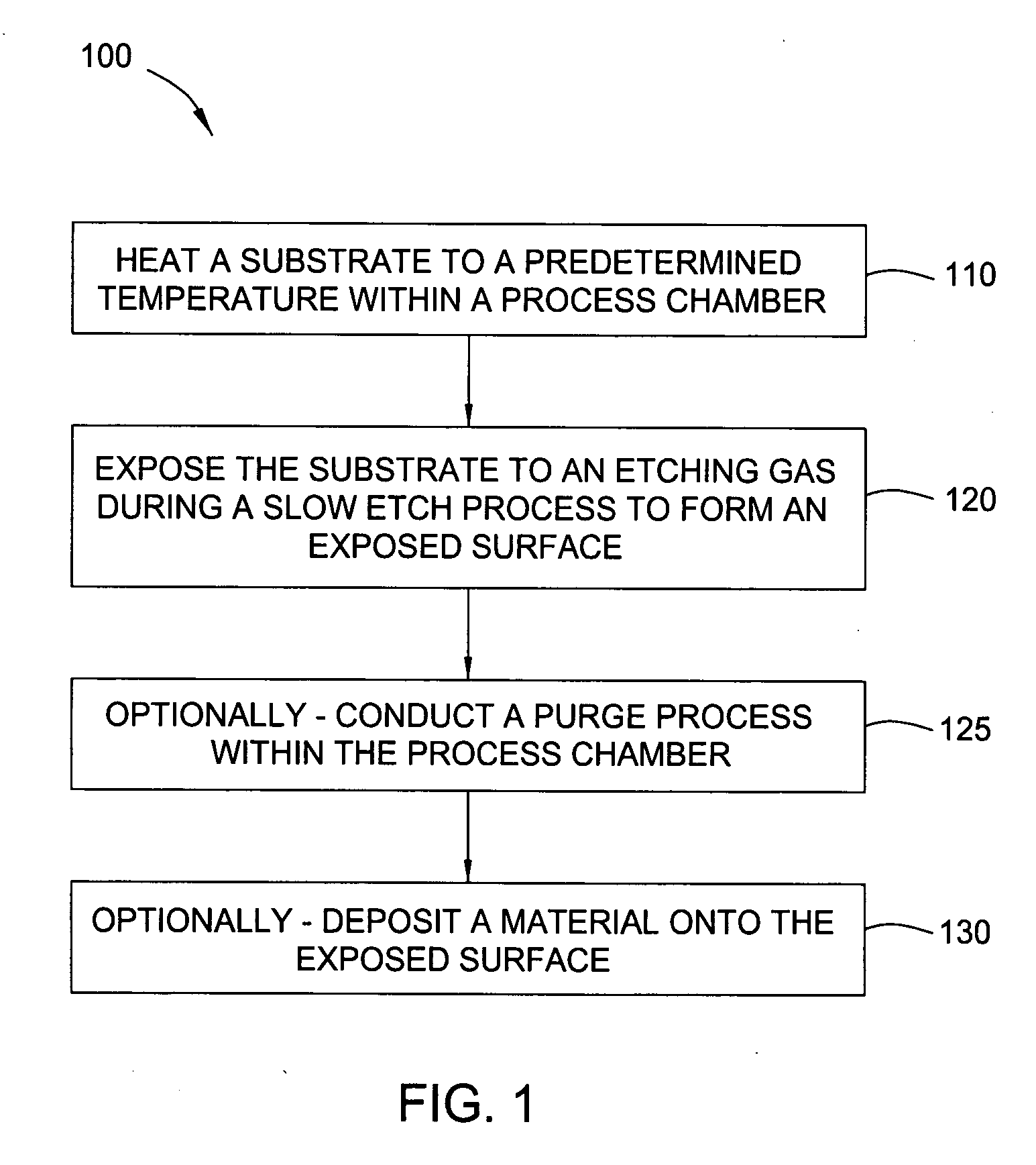
Low temperature etchant for treatment of silicon-containing surfaces
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for finishing or treating a silicon-containing surface is provided which includes removing contaminants and / or smoothing the surface contained on the surface by a slow etch process (e.g., about <100 Å / min). The silicon-containing surface is exposed to an etching gas that contains an etchant, a silicon source and a carrier gas. Preferably, the etchant is chlorine gas so that a relatively low temperature (e.g., <800° C.) is used during etching or smoothing processes. In another embodiment of the invention, a method for etching a silicon-containing surface during a fast etch process (e.g., about >100 Å / min) is provided which includes removing silicon-containing material to form a recess in a source / drain (S / D) area on the substrate. The silicon-containing surface is exposed to an etching gas that contains an etchant, preferably chlorine, a carrier gas and an optional silicon source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature etchant for treatment of silicon-containing surfaces
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for finishing or treating a silicon-containing surface is provided which includes removing contaminants and / or smoothing the surface contained on the surface by a slow etch process (e.g., about <100 Å / min). The silicon-containing surface is exposed to an etching gas that contains an etchant, a silicon source and a carrier gas. Preferably, the etchant is chlorine gas so that a relatively low temperature (e.g., <800° C.) is used during etching or smoothing processes. In another embodiment of the invention, a method for etching a silicon-containing surface during a fast etch process (e.g., about >100 Å / min) is provided which includes removing silicon-containing material to form a recess in a source / drain (S / D) area on the substrate. The silicon-containing surface is exposed to an etching gas that contains an etchant, preferably chlorine, a carrier gas and an optional silicon source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Gas transfer membrane
Porous polymeric membranes formed from a hydrophobic polymer, such as halar having membrane pores of a size sufficient to permit gas and / or vapor permeation 0.05 μm to 5 μm without permitting the flow of a hydrophilic fluid across the membrane. Pore distribution is uniform and porosity is high, in some cases up to 80%. Membranes may be in the form of a flay sheet or hollow fibre for example and can be used in a variety of applications such as stripping HF gas, degassing of caustic solution, chlorine gas / alkaline filtration, degassing tap water to remove dissolved chlorine. Processes used to make such membranes can be carried out using relatively non toxic solvents such as citric acid ethyl ester or glycerol triacetate.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Masking methods and etching sequences for patterning electrodes of high density RAM capacitors
InactiveUS20030059720A1Decorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusDevice materialInductively coupled plasma
A method of etching a noble metal electrode layer disposed on a substrate to produce a semiconductor device including a plurality of electrodes separated by a distance equal to or less than about 0.35 mum and having a noble metal profile equal to or greater than about 80°. The method comprises heating the substrate to a temperature greater than about 150° C., and etching the noble metal electrode layer by employing a high density inductively coupled plasma of an etchants gas comprising a gas selected from the group consisting nitrogen, oxygen, a halogen (e.g., chlorine), argon, and a gas selected from the group consisting of BCl3, HBr, and SiCl4 mixtures thereof. A semiconductor device having a substrate and a plurality of noble metal electrodes supported by the substrate. The noble metal electrodes have a dimension (e.g., a width) which include a value equal to or less than about 0.3 mum and a platinum profile equal to or greater than about 85°. Masking methods and etching sequences for patterning high density RAM capacitors are also provided. The substrate may be heated by a pedestal in a reactor chamber having a dielectric window including a deposit-receiving surface having a surface finish comprising a peak-to-valley roughness height with an average height value of greater than about 1,000Å.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
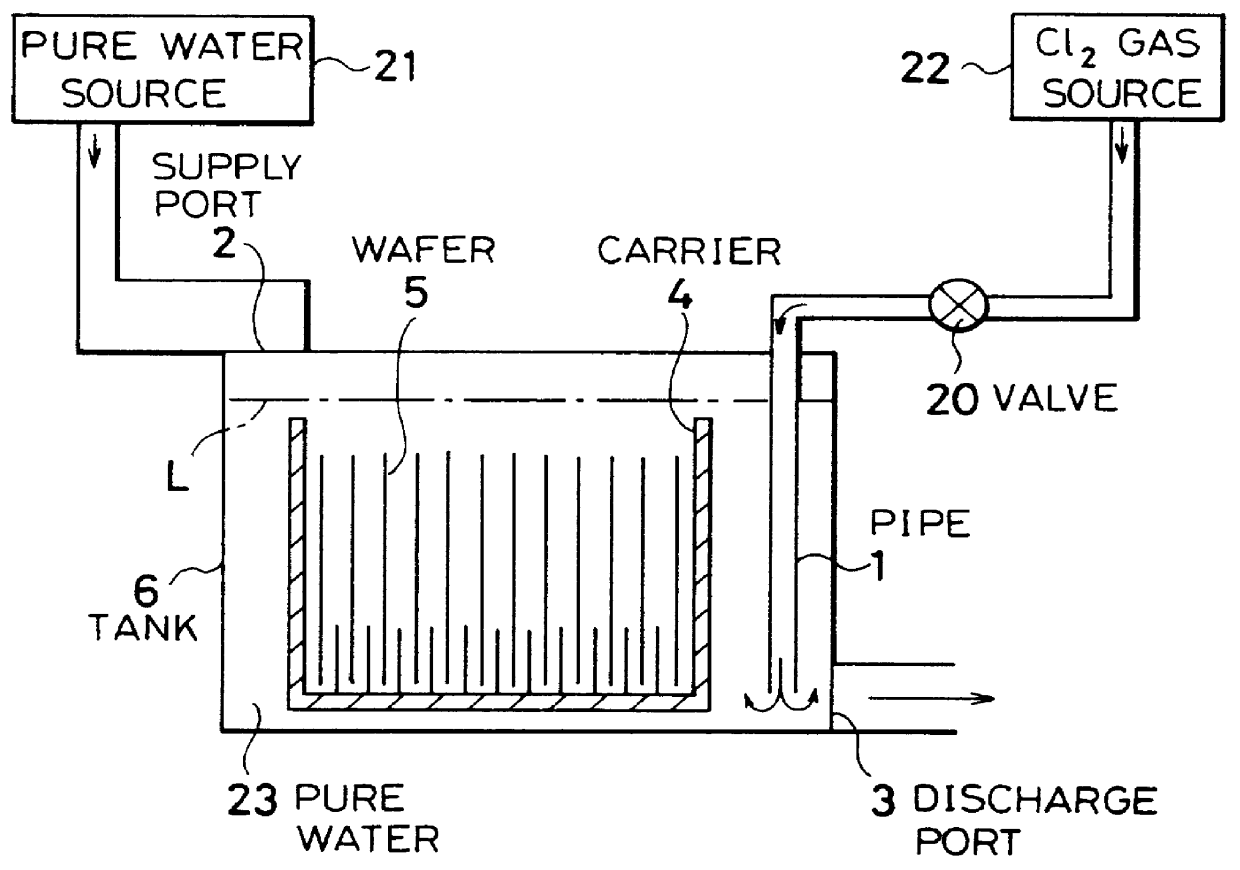
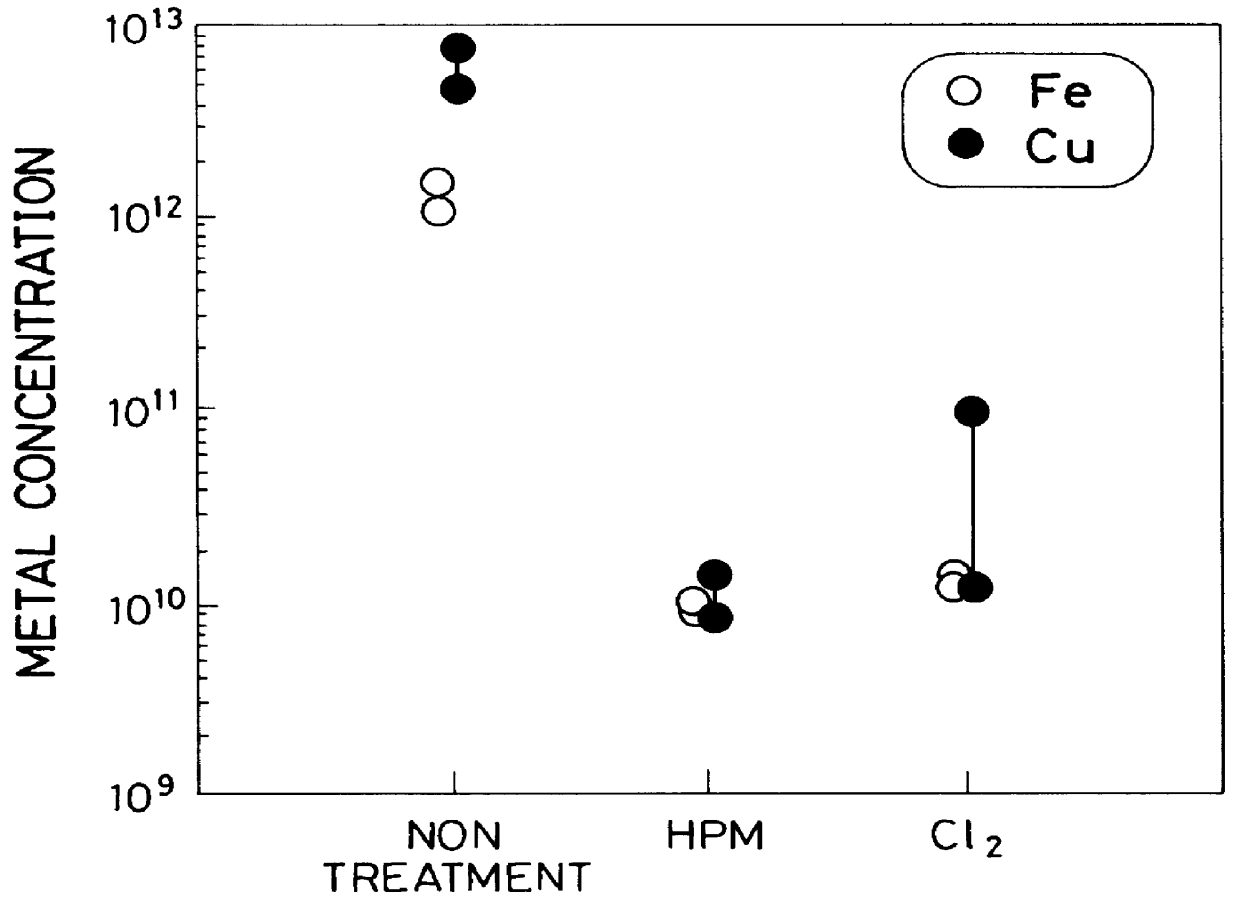
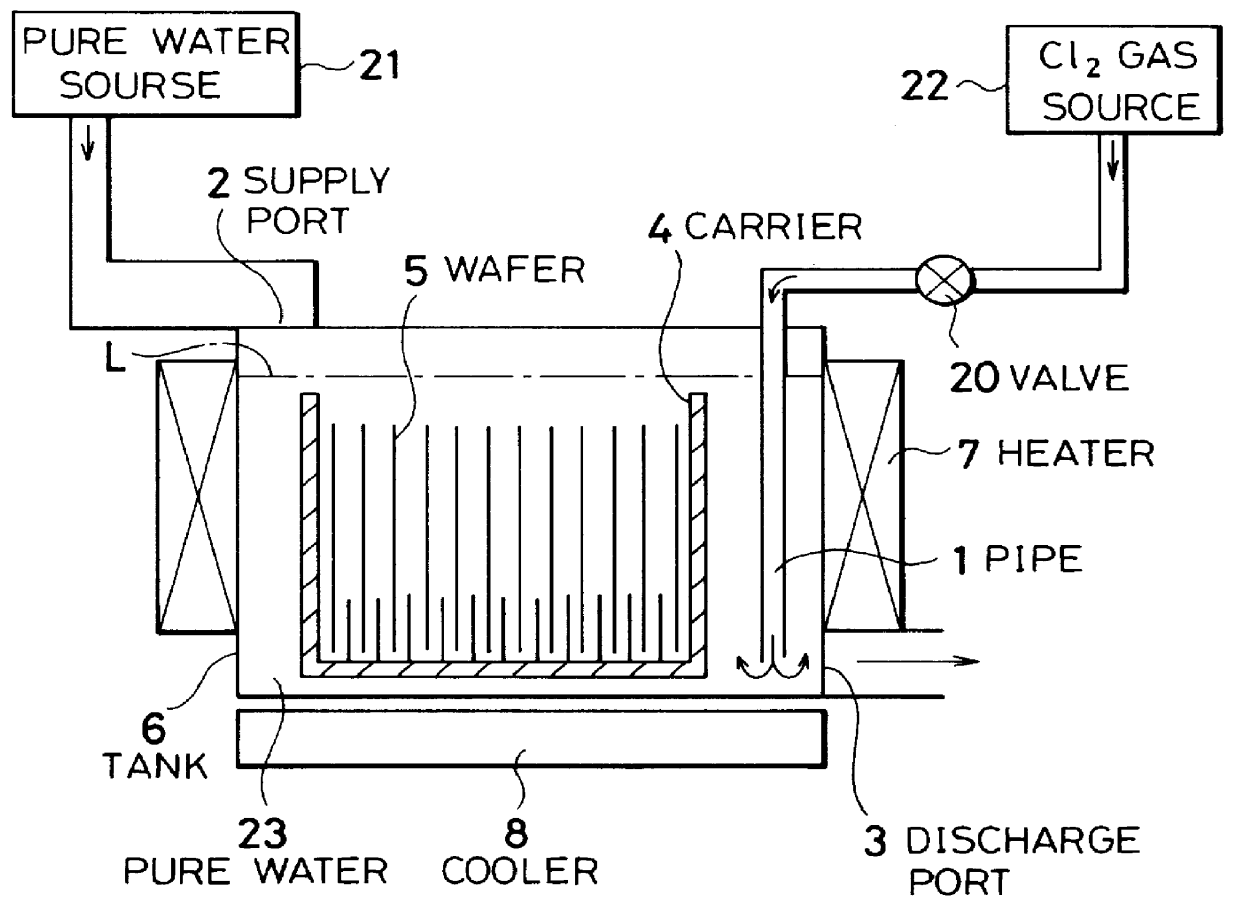
Cleaning method and system of semiconductor substrate and production method of cleaning solution
InactiveUS6116254AMinimize power consumptionReduce adverse effectsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChlorate ionHypochlorite
A cleaning method for a semiconductor substrate is provided. After pure water is supplied to a cleaning tank, a chlorine gas is supplied to the pure water to thereby generate chloride ions, hypochlorite ions, chlorite ions, and chlorate ions in the pure water. Then, a semiconductor substrate is immersed into the pure water containing the chloride ions, hypochlorite ions, chlorite ions, and chlorate ions. The fabrication cost of a semiconductor device and adverse effects on the earth environment can be reduced. The concentration of the dissolved chlorine gas in the pure water is preferably in the range from 0.003 to 0.3% by weight.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Process for preparing metallic titanium and titanium master alloy
The invention relates to the non-ferrous metal metallurgy fused salt electrolysis field, a method mainly comprises the steps of: preparing titanium dioxide, titanium tetrachloride, titanium dichloride and fluotitanate as raw materials, electrolyzing one or a plurality of combinations of TiO2, TiC14 and the fluotitanate in an electrolysis bath, preparing metallic titanium or titanium-based master alloy through an electrolysis method or a thermal reduction-electrolysis combined method, performing the TiO2 and connecting direct current to deoxidize or adopting metal (or metallic compound) for heat reducing the TiO2 beforehand, preparing the metallic titanium which contains oxygen (O) with certain concentration, and then electrolyzing aluminium, alkali metal, alkaline earth, rare earth metal, metallic copper, metallic zinc or metallic lead to deoxidize finally in the electrolysis bath. The purpose of the method is to reduce the production cost of the metallic titanium, simplify the production procedures and lower the environmental pollution in the production process, especially the titanium dioxide taken as the raw materials, the production flow is shortened, the storage and the transportation are convenient, none chlorine gas takes part in the reaction, and green metallurgy of the metallic titanium can be realized.
Owner:曹大力 +1
Method of plasma etching of high-K dielectric materials with high selectivity to underlying layers
InactiveUS20030170986A1Easy to understandSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChamber pressureDielectric permittivity
A method of etching high dielectric constant materials using halogen gas and reducing gas chemistry. An embodiment of the method is accomplished using a 20 to 300 sccm of chlorine and 2 to 200 sccm of carbon monoxide, regulated to a total chamber pressure of 2-100 mTorr to etch a hafnium oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus for producing sterilized water
InactiveUS7416326B2Easy constructionRestrains fluctuation of pressure affecting feedingFlow mixersMixing methodsChlorine dioxideSterile water
Owner:FAMILY LIFE
Formaldehyde scavenging agent
InactiveCN102671335APromote decompositionGood restorativeDeodrantsWood impregnation detailsSodium bicarbonateAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a formaldehyde scavenging agent and relates to a decoration deodorant. The formaldehyde scavenging agent consists of the following ingredients: 34 to 40 percent of plant extract liquid, 9 to 12 percent of sodium bicarbonate, 8 to 12 percent of hydrogen peroxide, 3 to 5 percent of penetrating agents and 35 to 40 percent of purified water. A preparation process of the formaldehyde scavenging agent comprises the steps that: the extract liquid, the sodium bicarbonate, the hydrogen peroxide, the penetrating agents and the purified water are put into a container to be uniformly stirred, and the formaldehyde scavenging agent is obtained. A plant and chemical combination method is adopted, formaldehyde can be fast decomposed in several minutes, high speed and long effect are realized, and the rebound and the secondary pollution are avoided. The formaldehyde scavenging agent has a good restoration effect on floor furniture scratches and can also be diluted to be sprayed onto objects or into the air for odor removal after decoration, and benzene series substances, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, chlorylene, chlorine gas and microorganisms can be decomposed.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUNYOUHUI ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Preparation method of acidic water and alkaline water
The invention discloses a preparation method of acidic water and alkaline water, which includes the steps of: 1) preparation of soft water: preparing soft water through a water softening machine; 2) preparation of a NaCl solution: adding NaCl to the soft water to prepare the NaCl solution; 3) electrolysis: electrolyzing the NaCl solution, wherein the acidic water and alkaline water are formed respectively on a positive pole and a negative pole. In the method, through the electrolysis, H<+> and chlorine gas, which has strong activity, are formed on the positive pole, wherein the chlorine gas can be dissolved in water to form the strong acidic water, which is a colorless and transparent liquid, has a slight chlorine smell, is free of irritation on skin and mucosas and can kill various bacterial vegetative forms. The acidic water can be gradually reduced into common water during contact with air, light and organic substance, so that the acidic water is an excellent green disinfectant.
Owner:康亦健(集团)有限公司
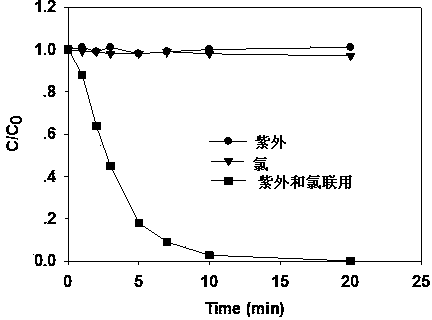
Method for removing micro-pollutants in water via combination of ultraviolet light and free chlorine
InactiveCN103523900AQuick removalAchieve bactericidal effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentHypochloriteLight irradiation
The invention discloses a method for removing micro-pollutants in water via combination of ultraviolet light and free chlorine. The pollutants removed by the method are various pernicious micro-pollutants in water, such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), algal toxin and refractory organics. The method specifically comprises the following steps: adding free chlorine into water containing the micro-pollutants, then performing light irradiation, generating a large amount of hydroxyl radicals and helium atom to attack the micro-pollutants and degrade the micro-pollutants, wherein the feeding amount of the chlorine is determined by the water quality condition and the concentration of the pollutants; the chlorine is fed according to a mole ratio of the chlorine to the pollutants in water being 1:1-100:1; the free chlorine is pypocholoride or chlorine. The method, disclosed by the invention, is simple to operate, obvious in effect and safe to use; the fed chlorine also can be used for the subsequent disinfection; after being processed via the method, the micro-pollutants in water can be completely removed; meanwhile, through the method, other pollutants can be removed synchronously; the synergy of the combination of ultraviolet light and free chlorine for disinfection can be played.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Metal film vapor phase deposition method and vapor phase deposition apparatus
InactiveUS7048973B2Good reproducibilityImprove film qualityVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesHydrogenGas phase
A copper film vapor phase deposition method includes the steps of exposing high-purity copper to a plasma of a gas containing chlorine gas to etch the high-purity copper, thereby generating active CuxCly, wherein x is 1 to 3, y is 1 to 3, gas, and forming a copper film by transporting the CuxCly gas onto the surface of a substrate to be processed. By using inexpensive high-purity copper and inexpensive chlorine, hydrogen chloride, or chlorine and hydrogen as source gases, a copper film containing no residual impurity such as carbon and having high film quality can be formed with high reproducibility.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Method for preparing high-purity ruthenium sputtering target and high-purity ruthenium sputtering target
InactiveUS6284013B1Minimize formation of particleSolve the large leakage currentTransportation and packagingRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsHydrogen atmosphereImpurity
There is provided a high-purity ruthenium sputtering target with a low impurity content, in particular producing extremely few particles, which is suitable for applications such as the formation of semiconductor thin films. The high-purity ruthenium sputtering target is manufactured by feeding crude ruthenium powder into a sodium hydroxide solution; blowing an ozone-containing gas while or after blowing chlorine gas into the solution to form ruthenium tetroxide; absorbing the ruthenium tetroxide in a hydrochloric acid solution or a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and ammonium chloride, and evaporating the solution to dryness; sintering the resultant ruthenium salt in a hydrogen atmosphere to form high-purity ruthenium powder; and hot-pressing the ruthenium powder into a sputtering target.
Owner:NIKKO MATERIALS CO LTD
Continuous production method of chlorinated paraffin
InactiveCN1824737APrevent burning phenomenonAvoid production accidentsPetroleum chemical modificationParaffin oilsChlorinated paraffins
The present invention discloses a method for continuously producing chloroparaffine. Said method includes the following steps: making paraffin oil be passed through paraffin oil inlet and continuously fed into reactor; making chlorine gas be passed through circulation material and chlorine gas feeding device and fed into reactor from bottom portion of said reactor; under the catalysis of UV light making them implement chlorination reaction; making reaction product of the prior-stage be fed into reactor of next-stage to make continuous reaction, making the reaction product of the last reactor be fed into subsequent work-shop section to make refinement; making the reaction product overflowed from upper portion of reactor be fed into inlet of external cooling device, cooled, then passed through circulating pump, conveyed and premixed with chlorine gas, then fed into reactor.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHLOR ALKALI CHEM
Electrolytic process for generating chlorine dioxide
An electrolytic process for generating chlorine dioxide. An aqueous feed stream of an alkali metal chlorite solution is treated with chlorine gas or a mixture of hydrogen chloride and hypochlorous acid formed in an anode compartment from, an aqueous alkali metal chloride solution and subsequently electrolyzed to form a chlorine dioxide effluent.
Owner:NALCO CO +1
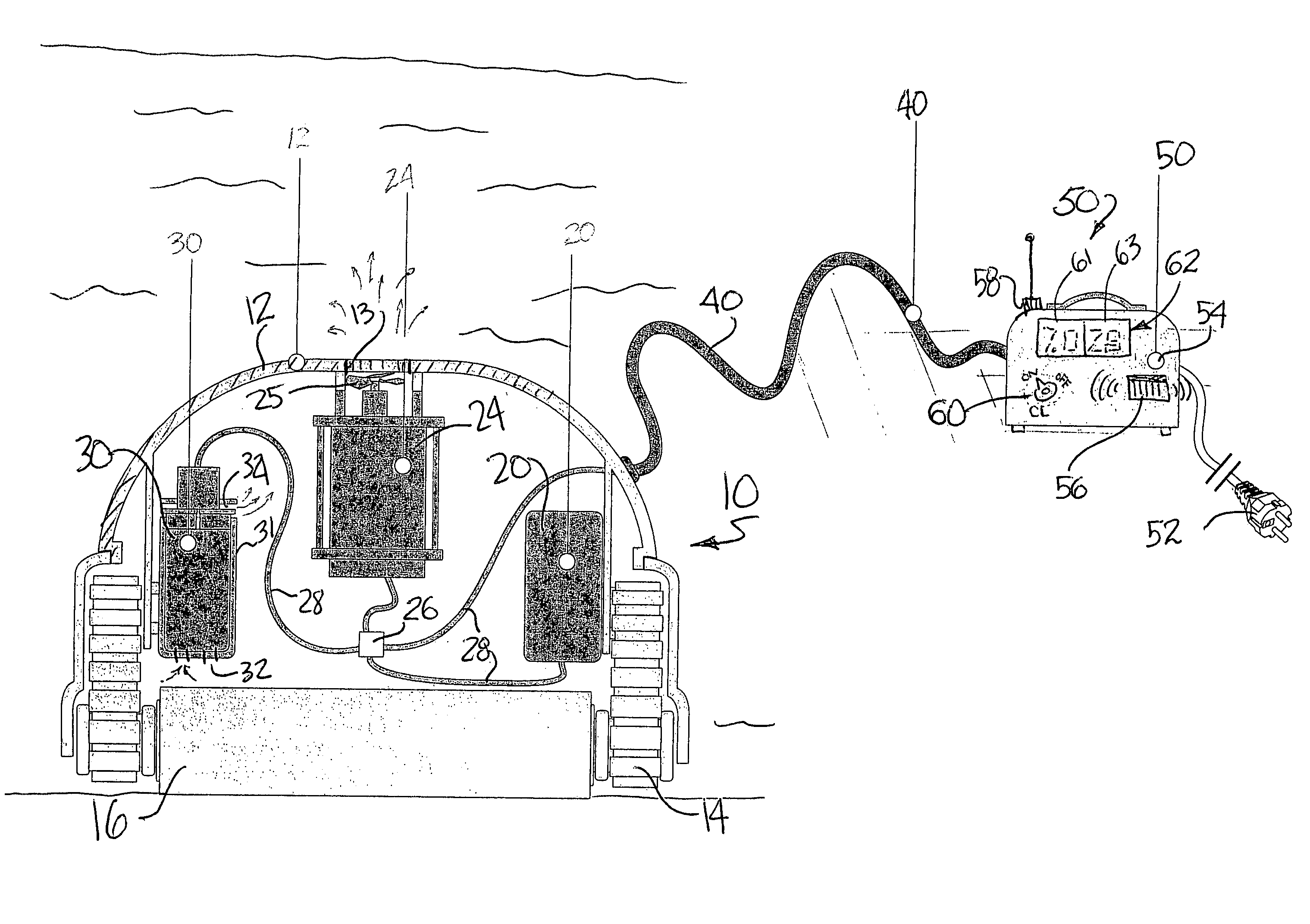
Pool cleaner with integral chlorine generator
InactiveUS20060053572A1Lower requirementWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsOn boardOperation mode
An automated self-propelled robotic pool cleaner having a housing and drive means for moving the pool cleaner over at least the bottom wall of a pool, is provided with an integral on-board electrochemical chlorine generator for producing chlorine from a chlorine compound, e.g., sodium chloride, that is dissolved in the pool water, a source of electrical power operatively connected to the electrochemical chlorine generator, control means for initiating and terminating the operation of the chlorine generator, and an outlet for discharging water containing chlorine ions produced by the electrochemical generator to thereby distribute the chlorine into the water proximate the exterior of the pool cleaner housing as the pool cleaner follows a programmed operational mode across the bottom and / or side walls of the pool. The operation of the chlorine generator is in response to a manually operated switch and / or signals generated by an automated testing probe, which signals are transmitted directly or indirectly to the control means.
Owner:AQUA PRODS
Methods of producing hydrochloric acid from hydrogen gas and chlorine gas
A method of producing HCl from H2 and Cl2 is provided. In some embodiments, the method comprises at least one photochemical chamber placed in fluid communication with at least one source of H2 and at least one source of Cl2. In some embodiments, the photochemical chamber effects the formation of HCl through the use of at least one source of ultraviolet radiation contained therein. In some embodiments, the HCl product may be captured and used as a gas. In some embodiments, the HCl product may be absorbed into water to form an aqueous HCl solution.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
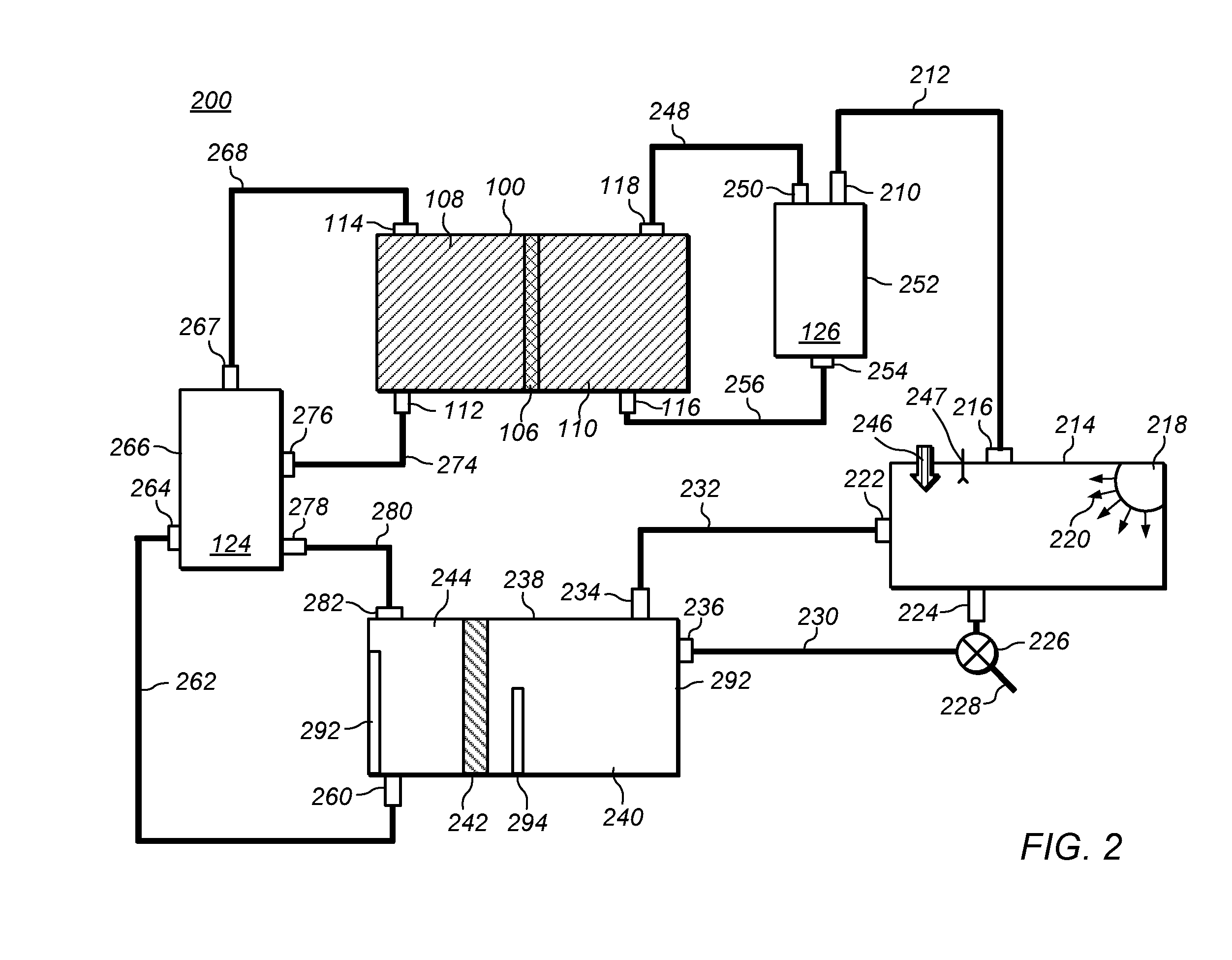
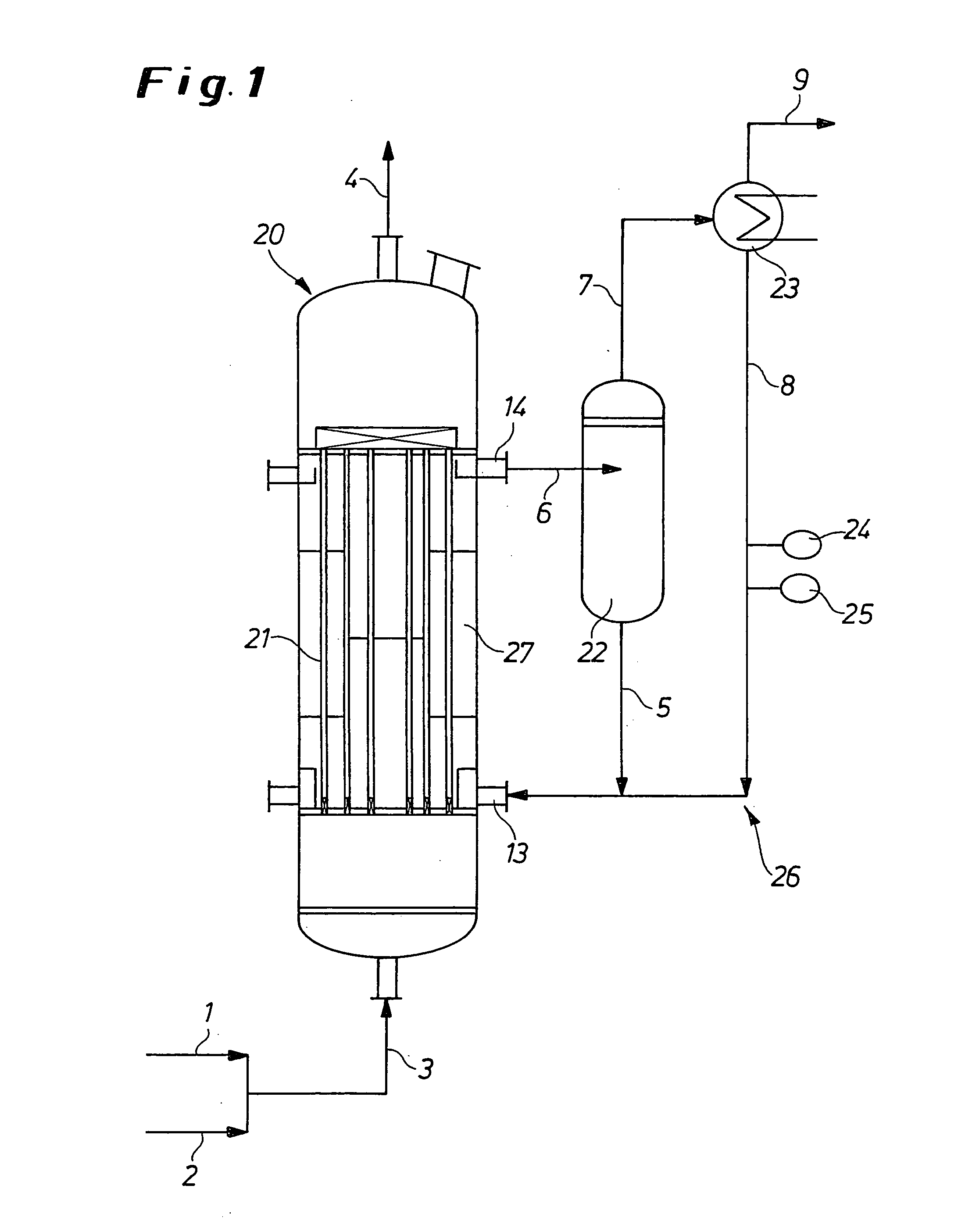
Process and apparatus for the production of phosgene
The invention relates to a process for the production of phosgene, in which chlorine and carbon monoxide are reacted in the presence of an activated charcoal catalyst in a shell-and-tube reactor which contains a plurality of reaction tubes and a coolant space surrounding the reaction tubes, in which a) cooling of the reaction tubes is from the outside through the coolant space with water by evaporative cooling, and b) operation of the reaction tubes is at a pressure above the pressure in the coolant space.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
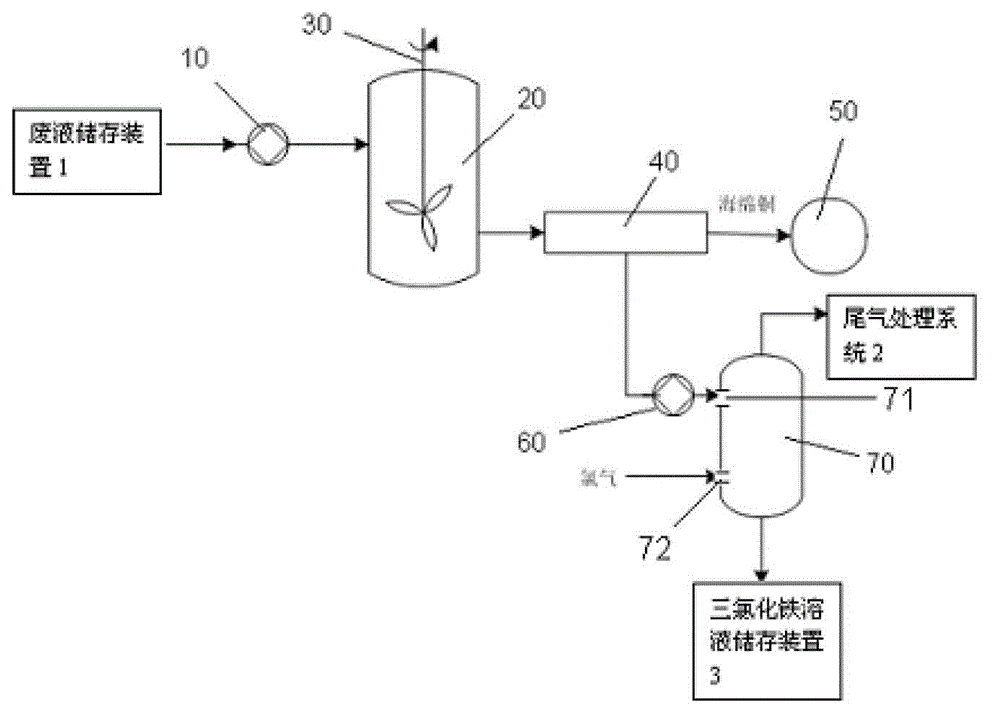
Method for recycling acidic copper-etching waste solution
InactiveCN102912352AAchieving "zero" emissionsShort production processLiquid wastePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for recycling acidic copper-etching waste solution. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, recovering copper form the acidic copper-etching waste solution, filling the acidic copper-etching waste solution in a reaction kettle, adding reduced iron while stirring so as to replace copper ions in the etching solution and separate out spongy copper, and performing solid-liquid separation treatment so as to obtain a spongy copper product having a water content of 50% and the solution containing lots of ferrous ions after the replacement; and step 2, preparing ferric trichloride from the solution after copper extraction: adjusting the solution according to the ferrous ion content and the pH value of the ferrum-containing solution after the replacement in the step 1, and then charging chlorine and reacting the ferrous ions with the chlorine to generate ferric ions, so as to prepare an effluent treatment agent, namely, ferric trichloride. The method disclosed by the invention is short in production flow, simple in process, low in energy consumption, wide in adaptability, capable of reutilizing all the remainder effective cost of the waste solution after the copper extraction while effectively extracting copper powder in the etching waste solution, and capable of realizing zero-discharge of the acidic etching waste solution of a printer circuit board and effectively protecting environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI LVCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method of making high purity lithium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
The present invention relates to a process for producing high purity lithium hydroxide monohydrate, comprising following steps: concentrating a lithium containing brine; purifying the brine to remove or to reduce the concentrations of ions other than lithium; adjusting the pH of the brine to about 10.5 to 11 to further remove cations other than lithium, if necessary; neutralizing the brine with acid; purifying the brine to reduce the total concentration of calcium and magnesium to less than 150 ppb via ion exchange; electrolyzing the brine to generate a lithium hydroxide solution containing less than 150 ppb total calcium and magnesium, with chlorine and hydrogen gas as byproducts; producing hydrochloric acid via combustion of the chlorine gas with excess hydrogen and subsequent scrubbing of the resultant gas stream with purified water, if elected to do so; and concentrating and crystallizing the lithium hydroxide solution to produce lithium hydroxide monohydrate crystals.
Owner:ROCKWOOD LITHIUM INC
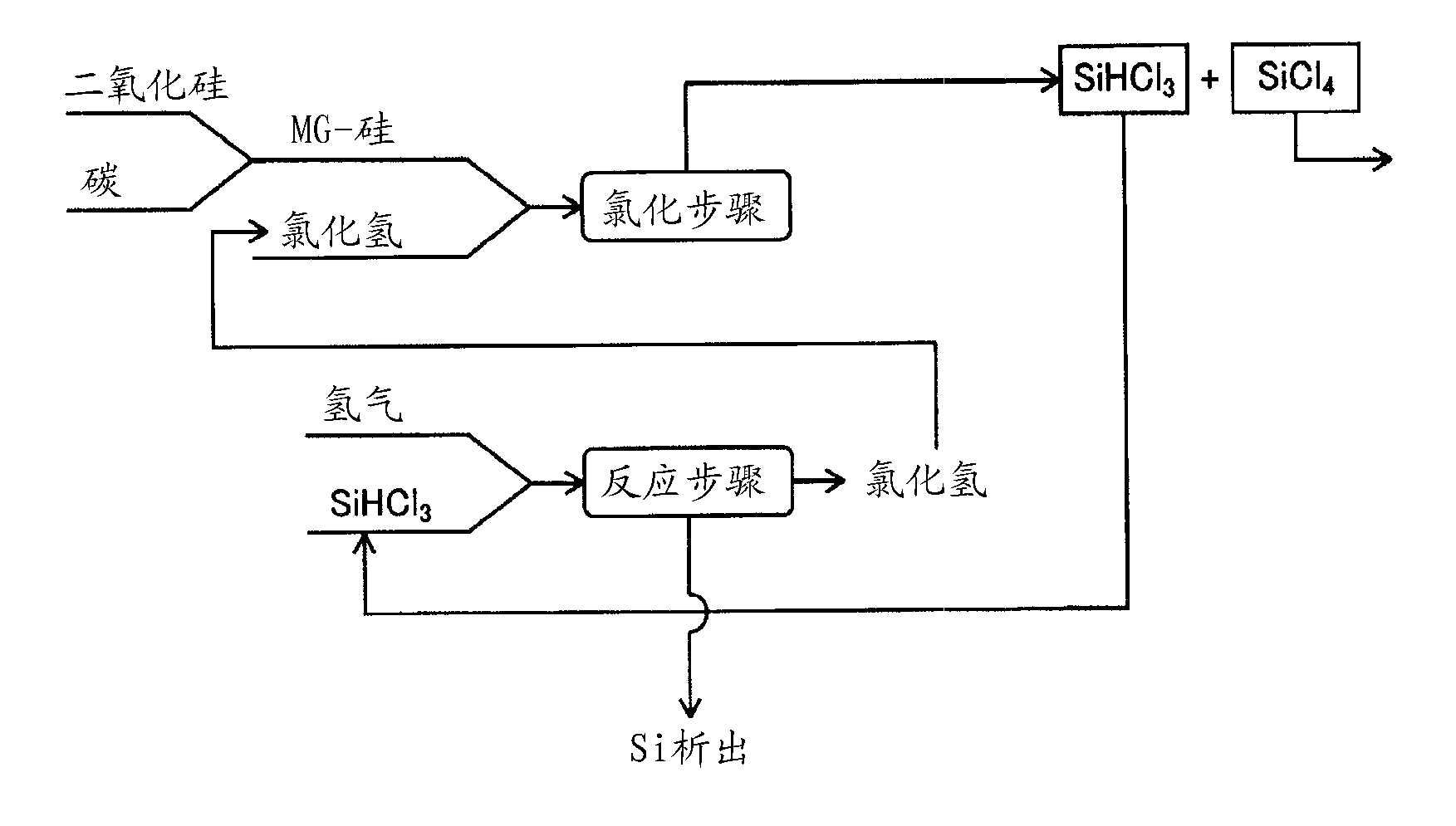
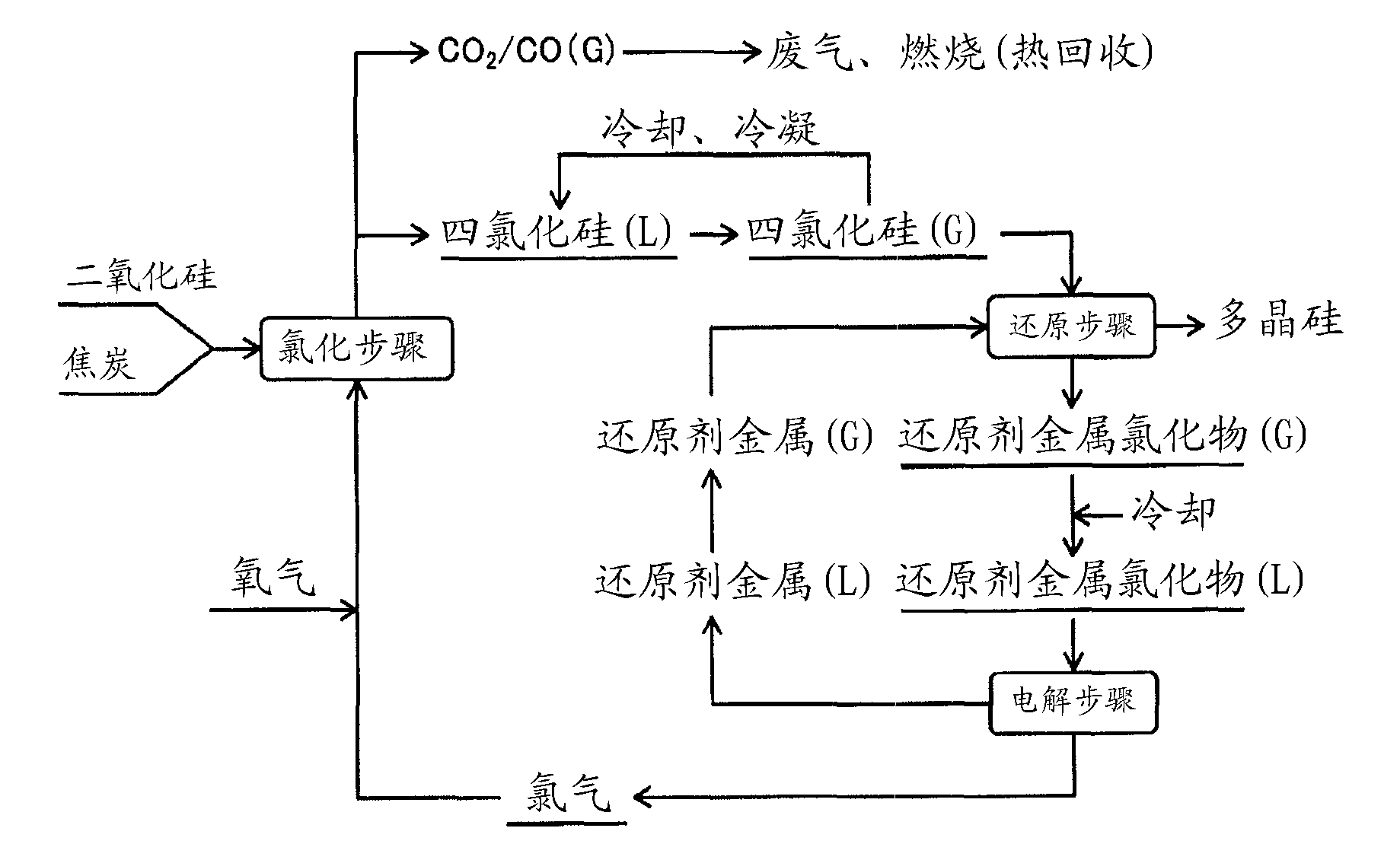
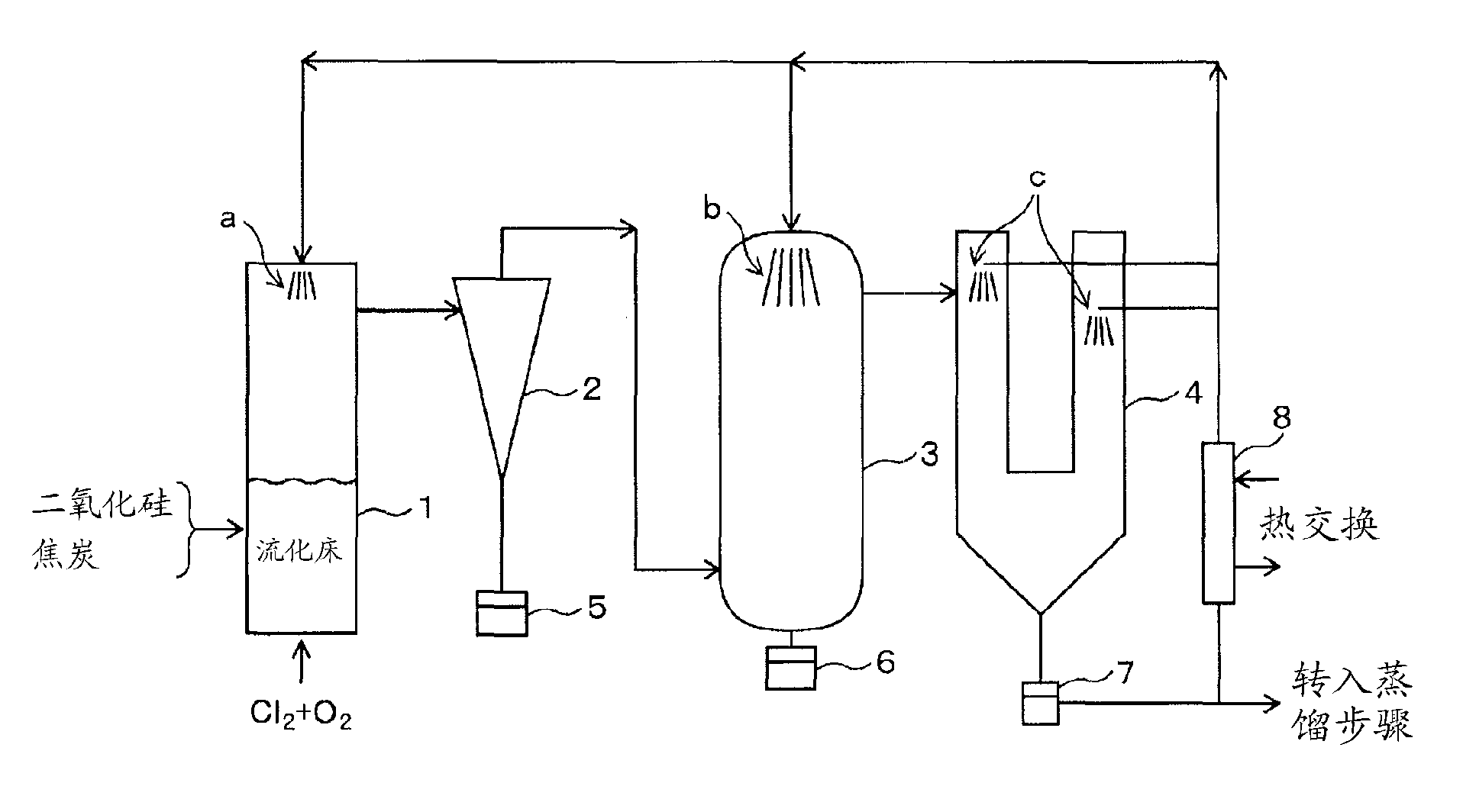
Method for manufacturing polysilicon and method for manufacturing silicon tetrachloride
InactiveCN102686514AEfficient use ofCheap manufacturingSiliconHalogenated silanesElectrolysisSilicon dioxide
Provided is a method for manufacturing polysilicon and silicon tetrachloride. The polysilicon manufacturing process used in said method is energy-efficient and can use an inexpensive raw material, the supply of which is stable. The chlorination reaction in said process proceeds smoothly and post-chlorination impurities are minimized. The provided method comprises: a chlorination step which generates silicon tetrachloride by chlorinating granules comprising silicon dioxide and a carbon-containing substance; a reduction step which generates polysilicon by using a reducing metal to reduce the silicon tetrachloride; and an electrolysis step which generates chlorine gas and a reducing metal by performing molten-salt electrolysis on a reducing metal chloride generated as a by-product from the reduction step. In the chlorination step, chlorine gas is supplied to the silicon dioxide and the carbon-containing substance in the presence of oxygen gas in order to react said substances. The reducing metal generated in the electrolysis step is reused as the reductant for the silicon tetrachloride in the reduction step, and the chlorine gas generated in the electrolysis step is reused in the chlorination step.
Owner:JNC CORP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com