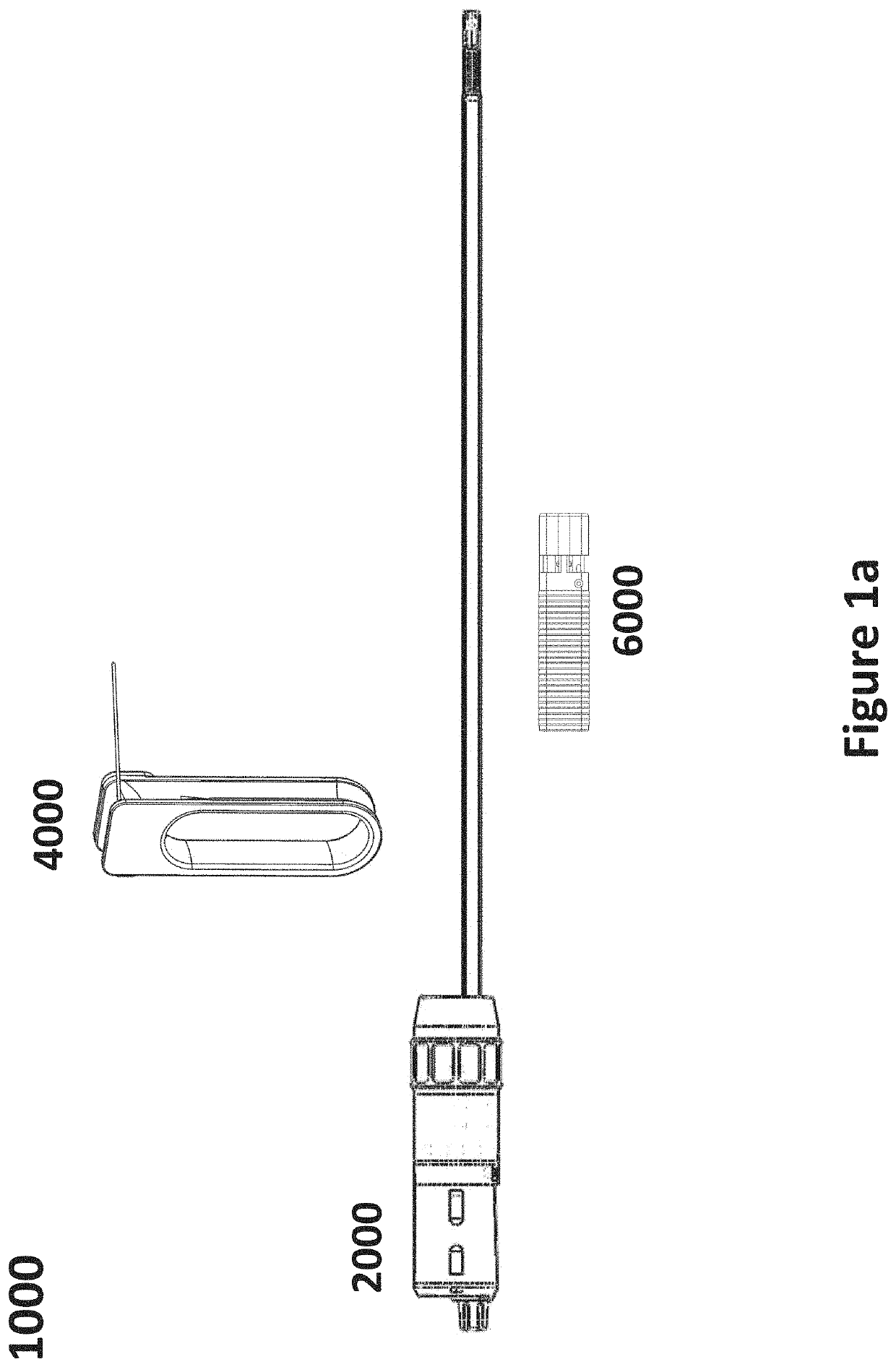
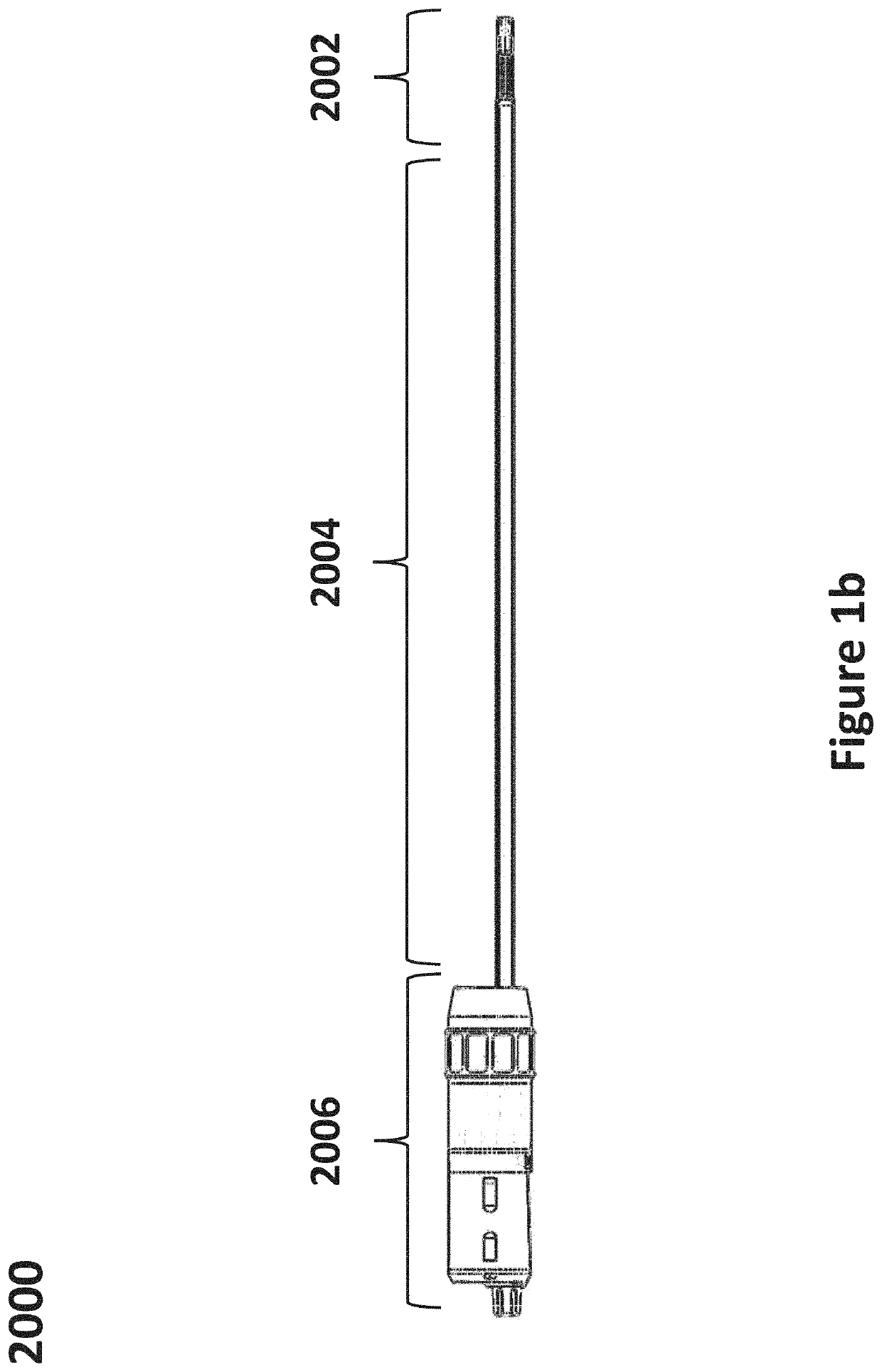
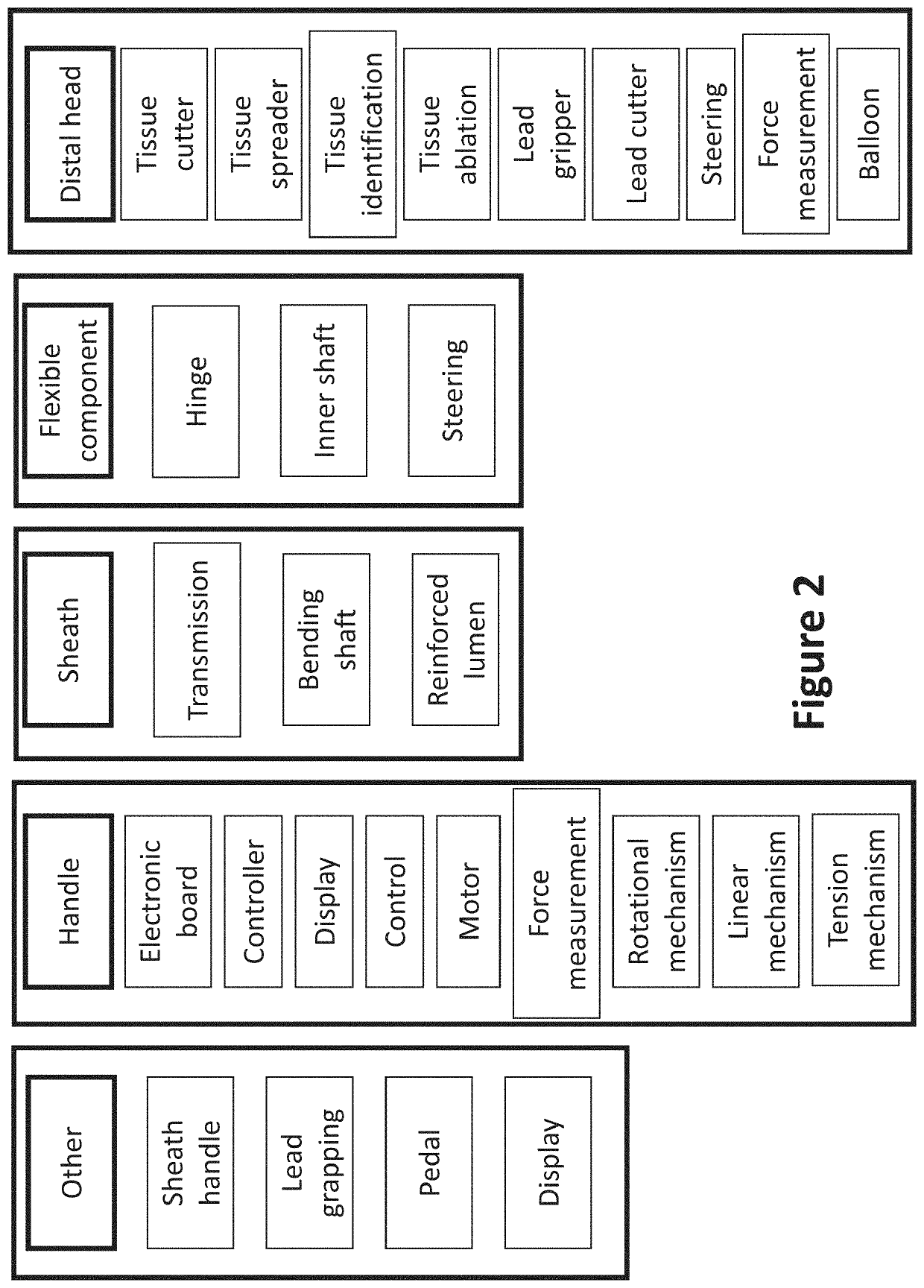
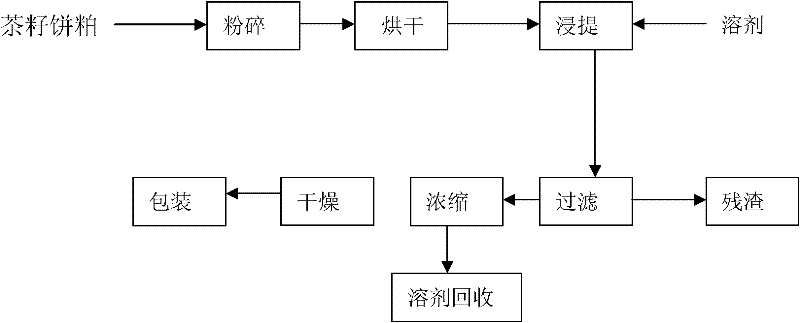
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Lead extraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
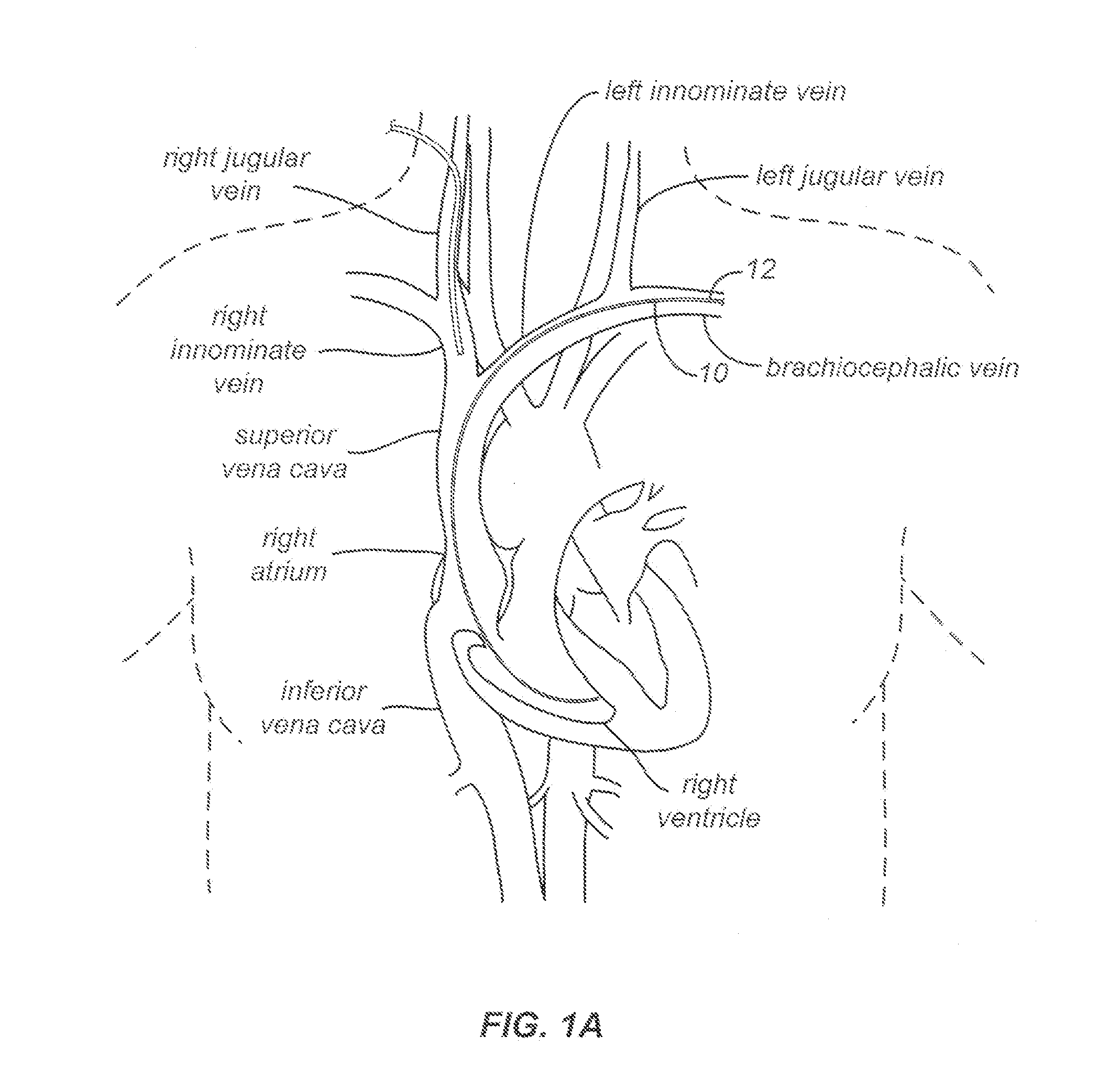
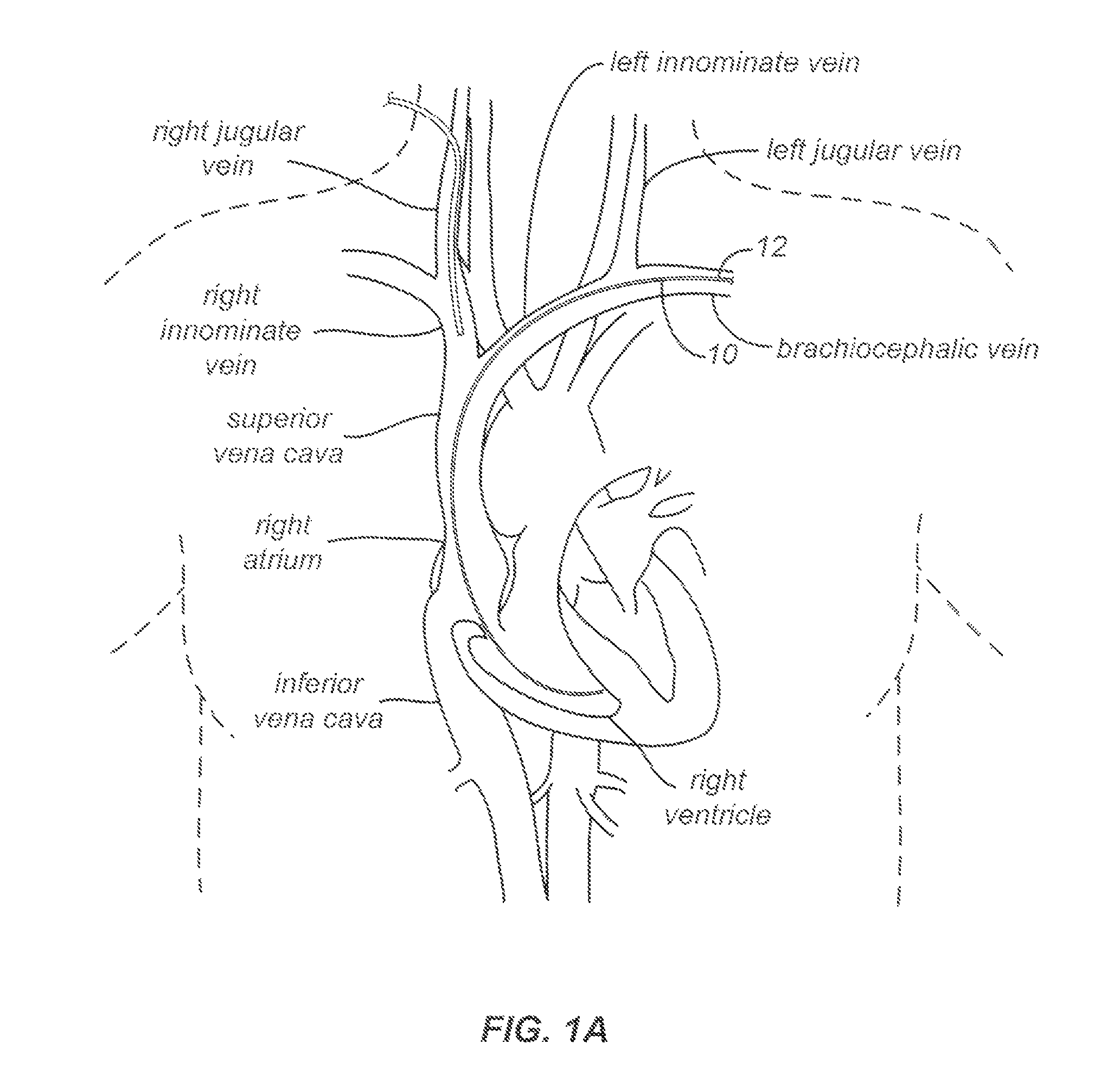
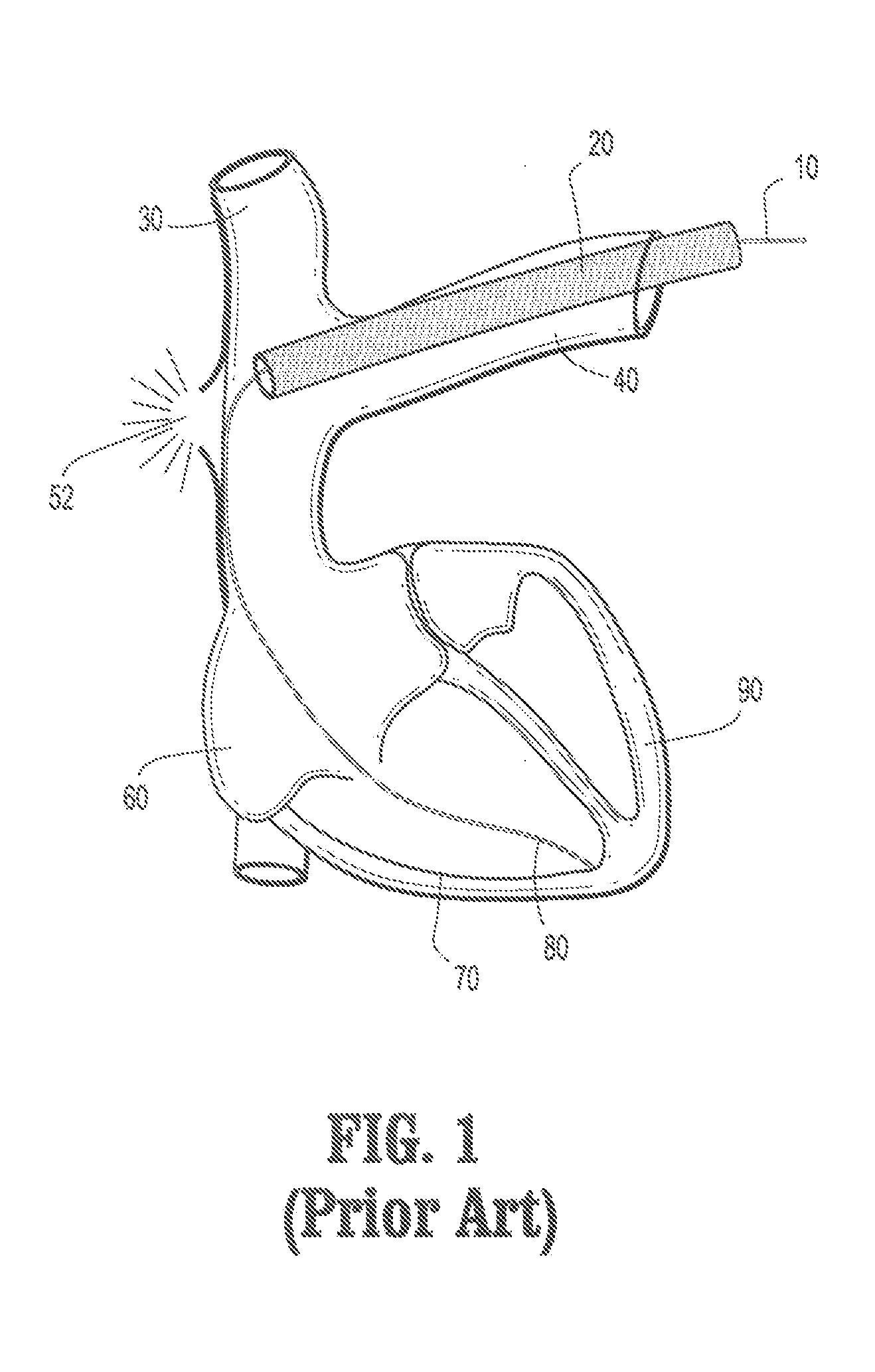
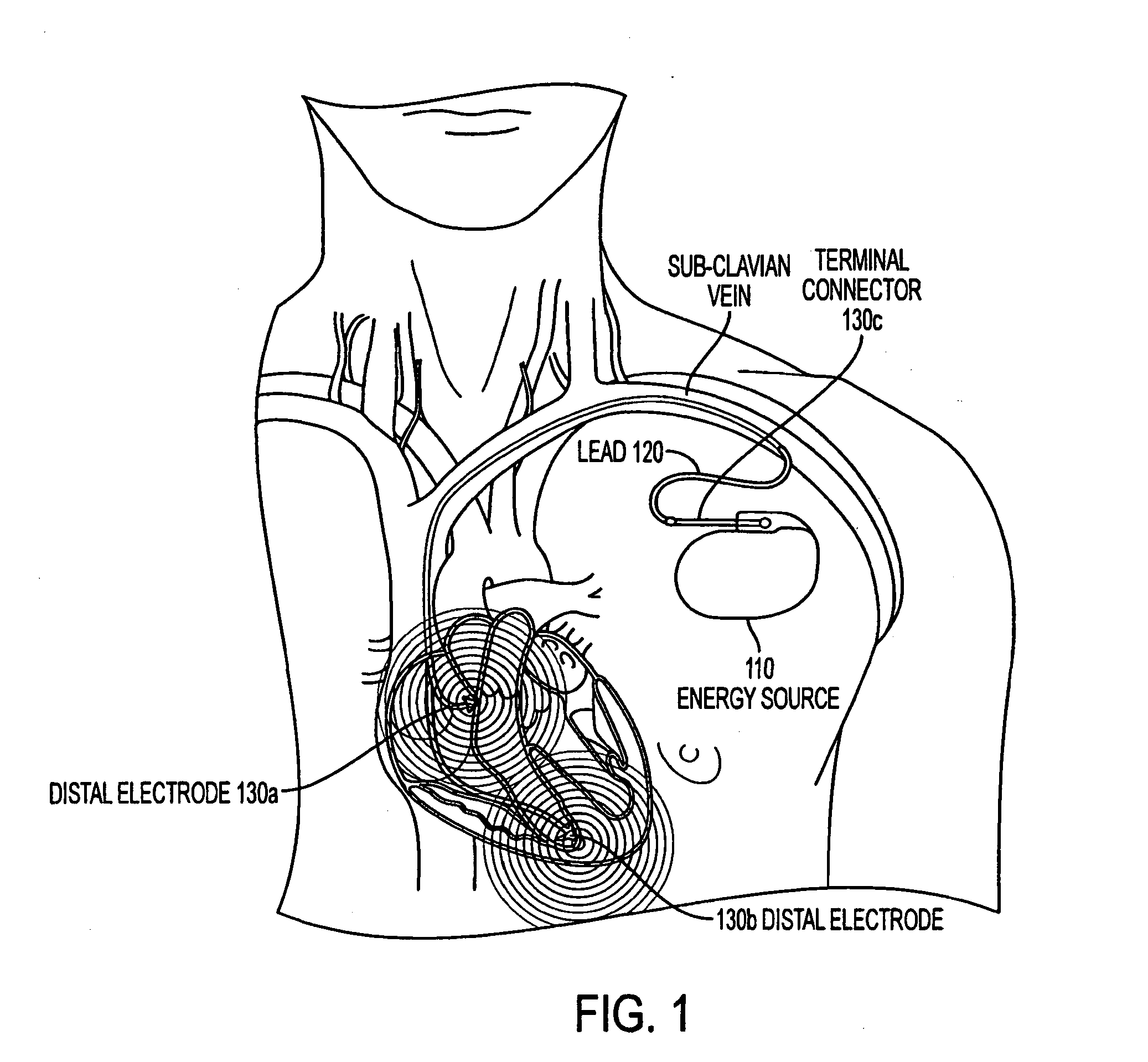
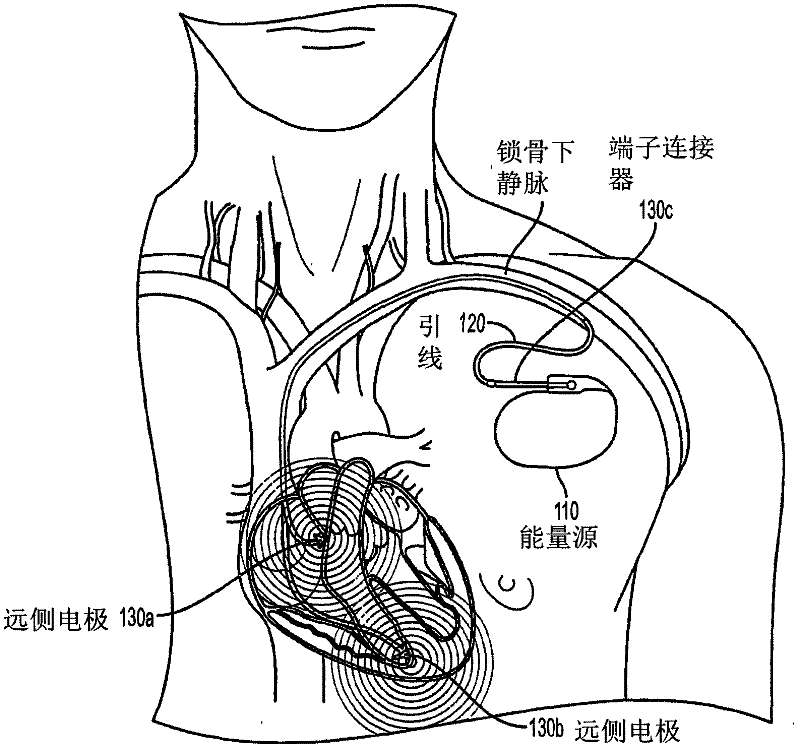
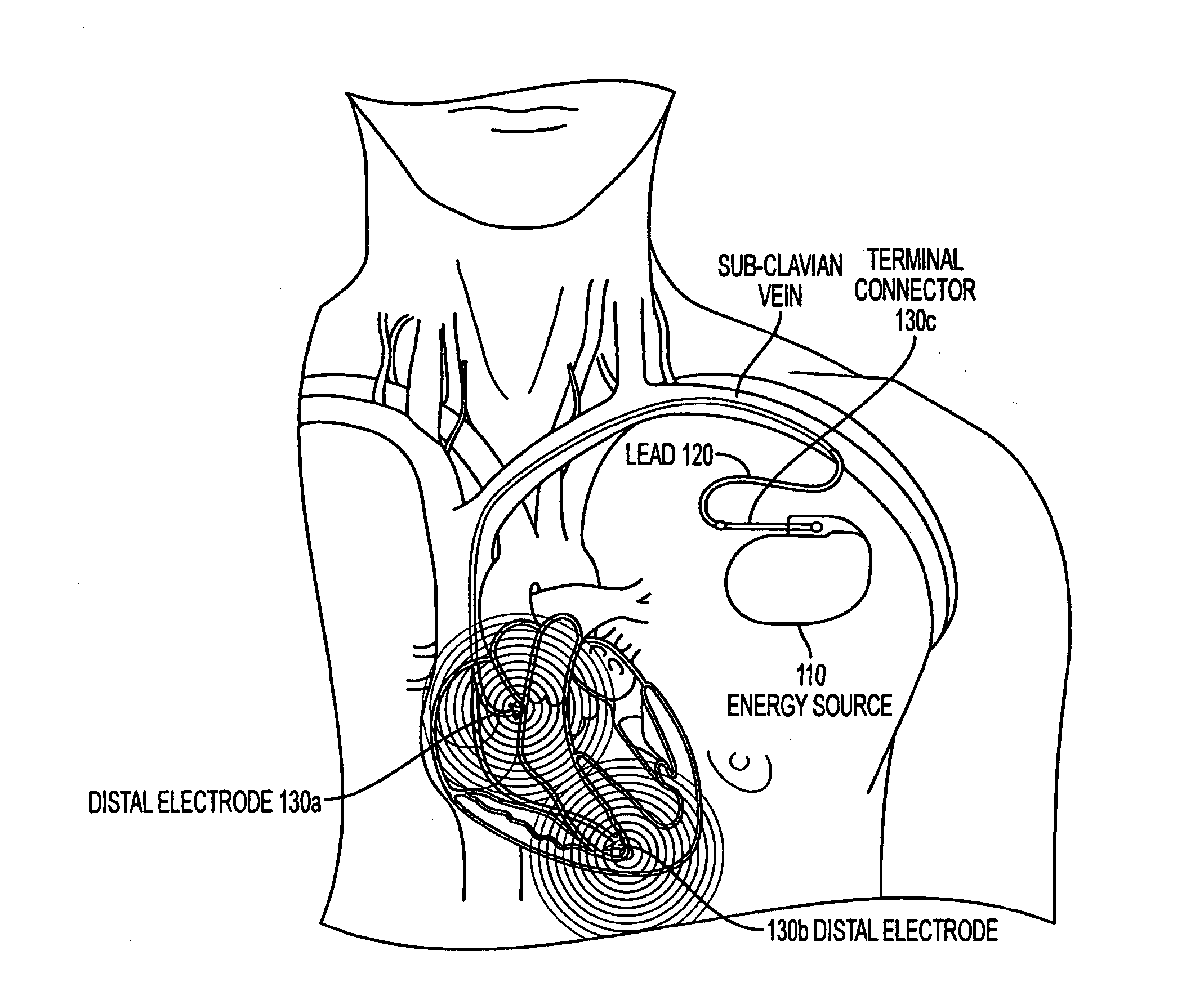
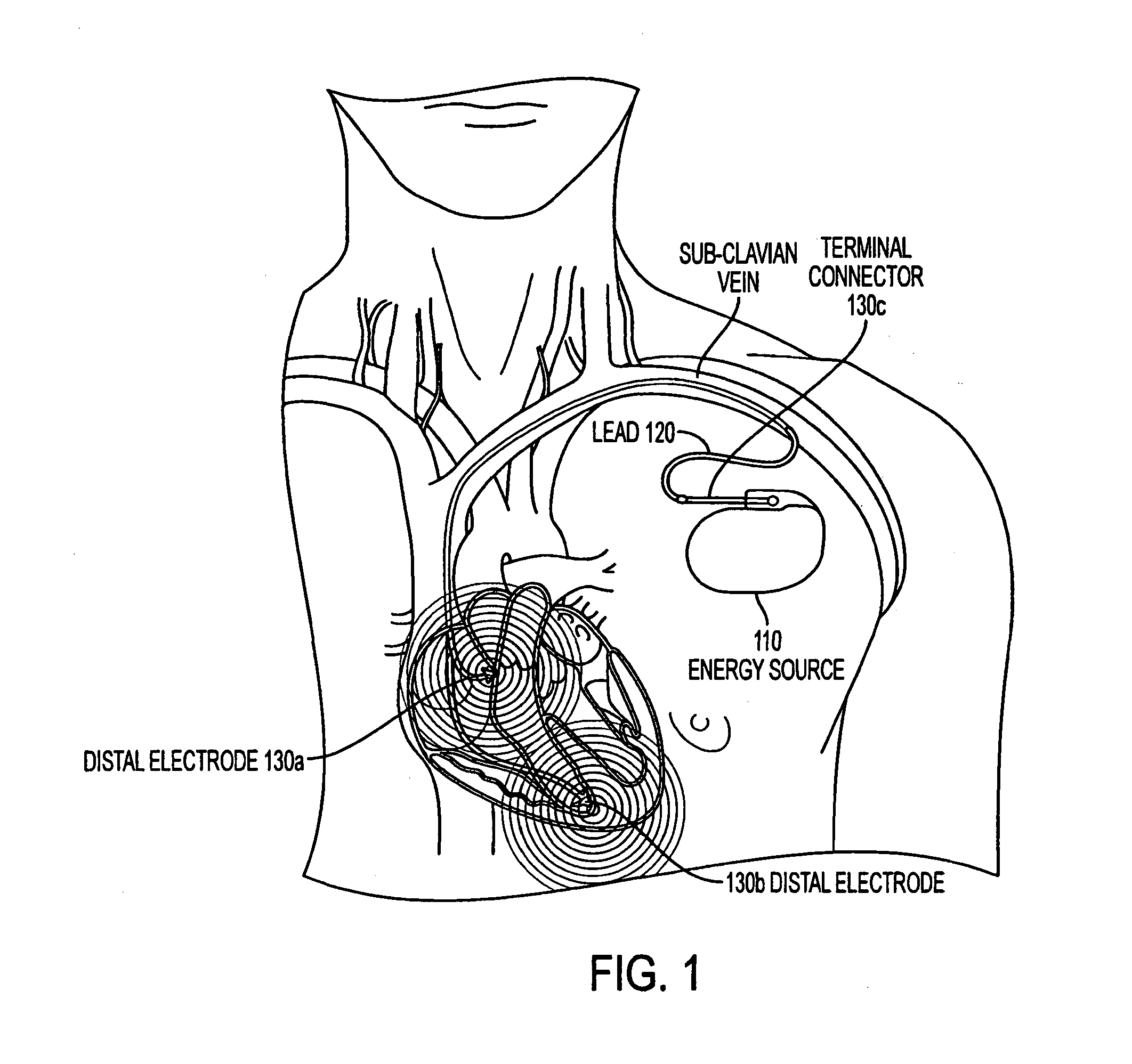
A lead extraction is the removal of one or more leads from inside the heart. Leads that are placed outside the heart during open heart surgery cannot be removed during this procedure.
Deployable medical lead fixation system and method
InactiveUS7107105B2Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesReticular formationLead extraction
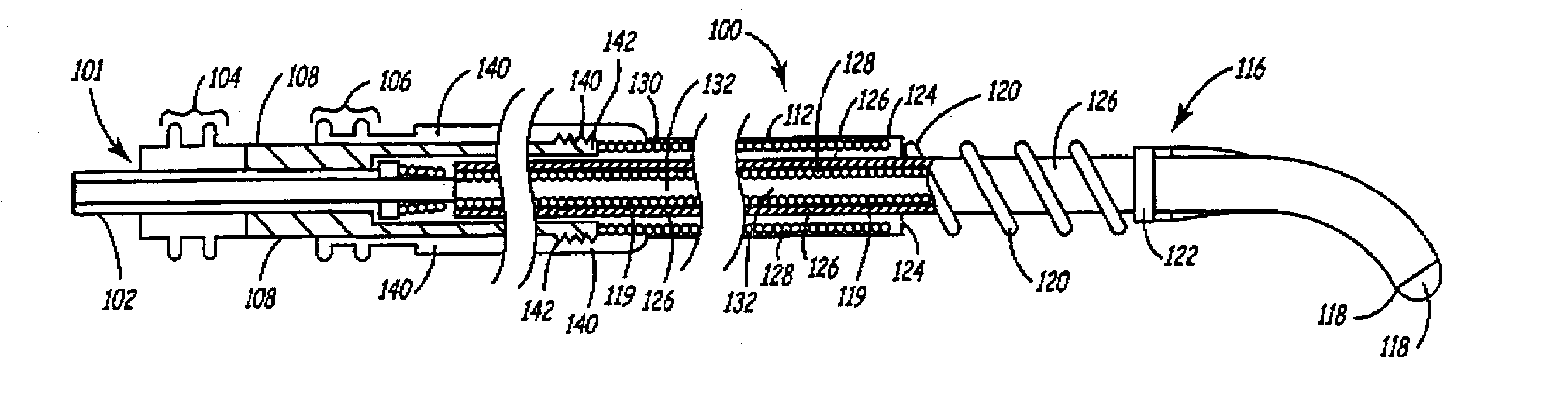
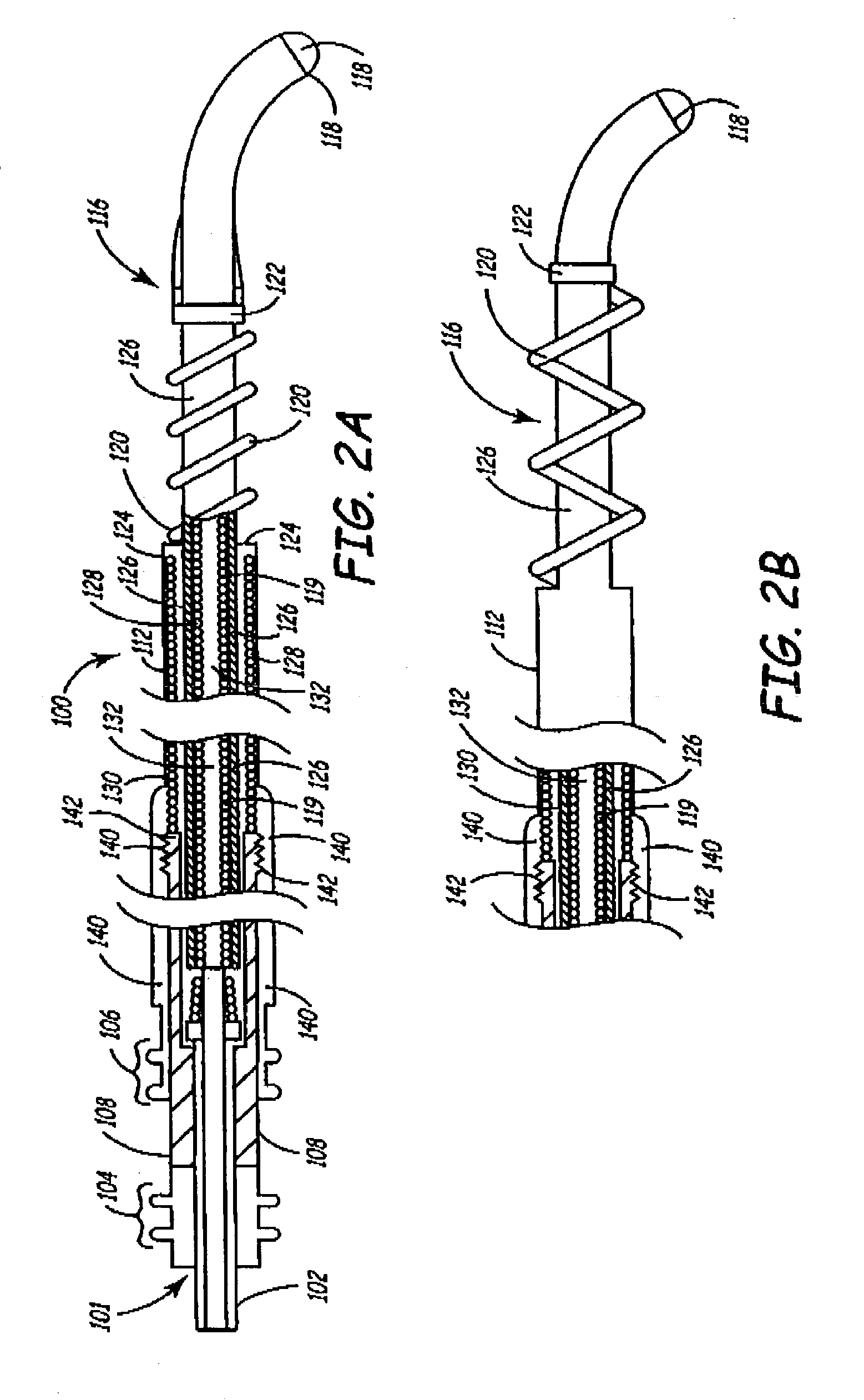
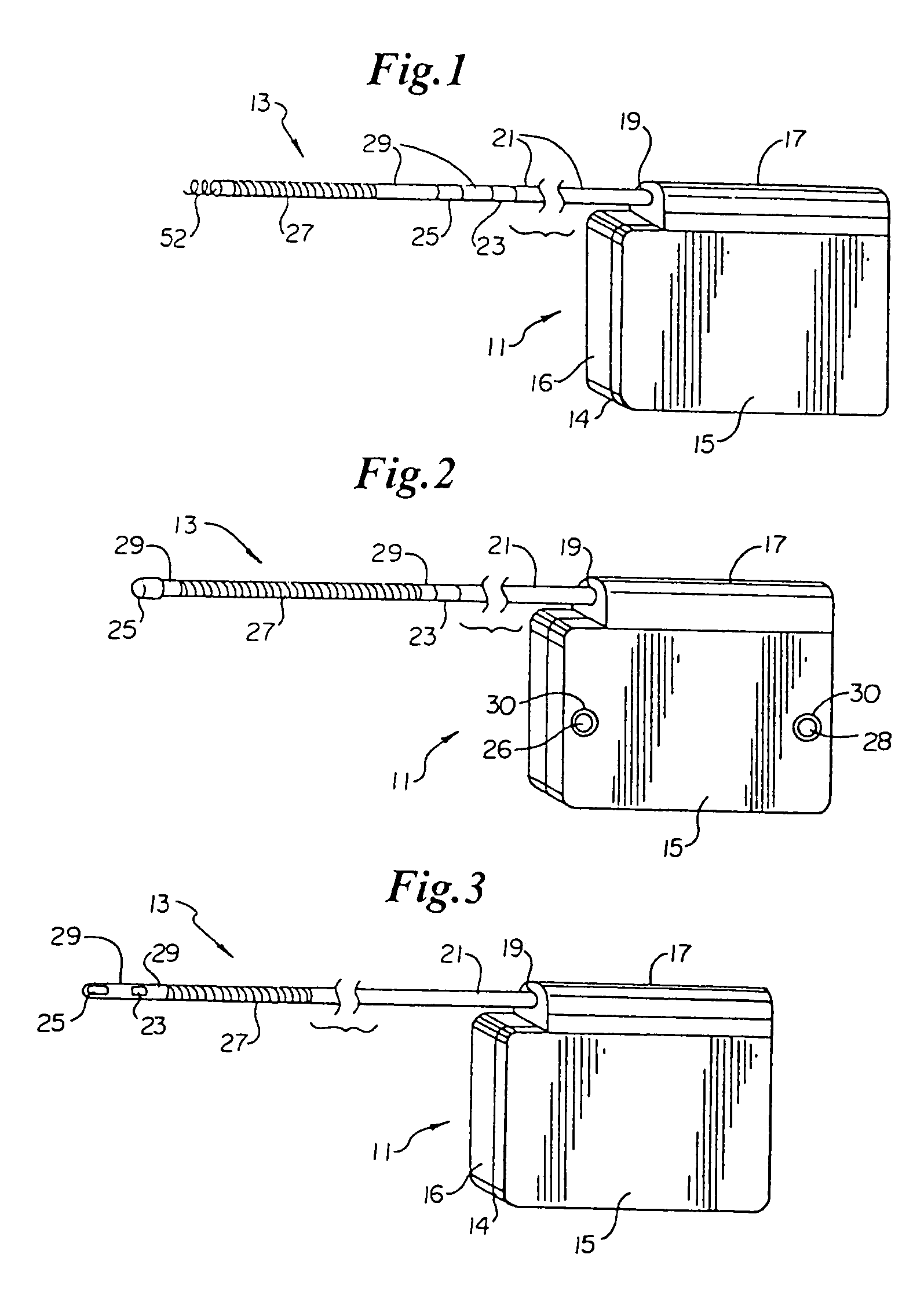
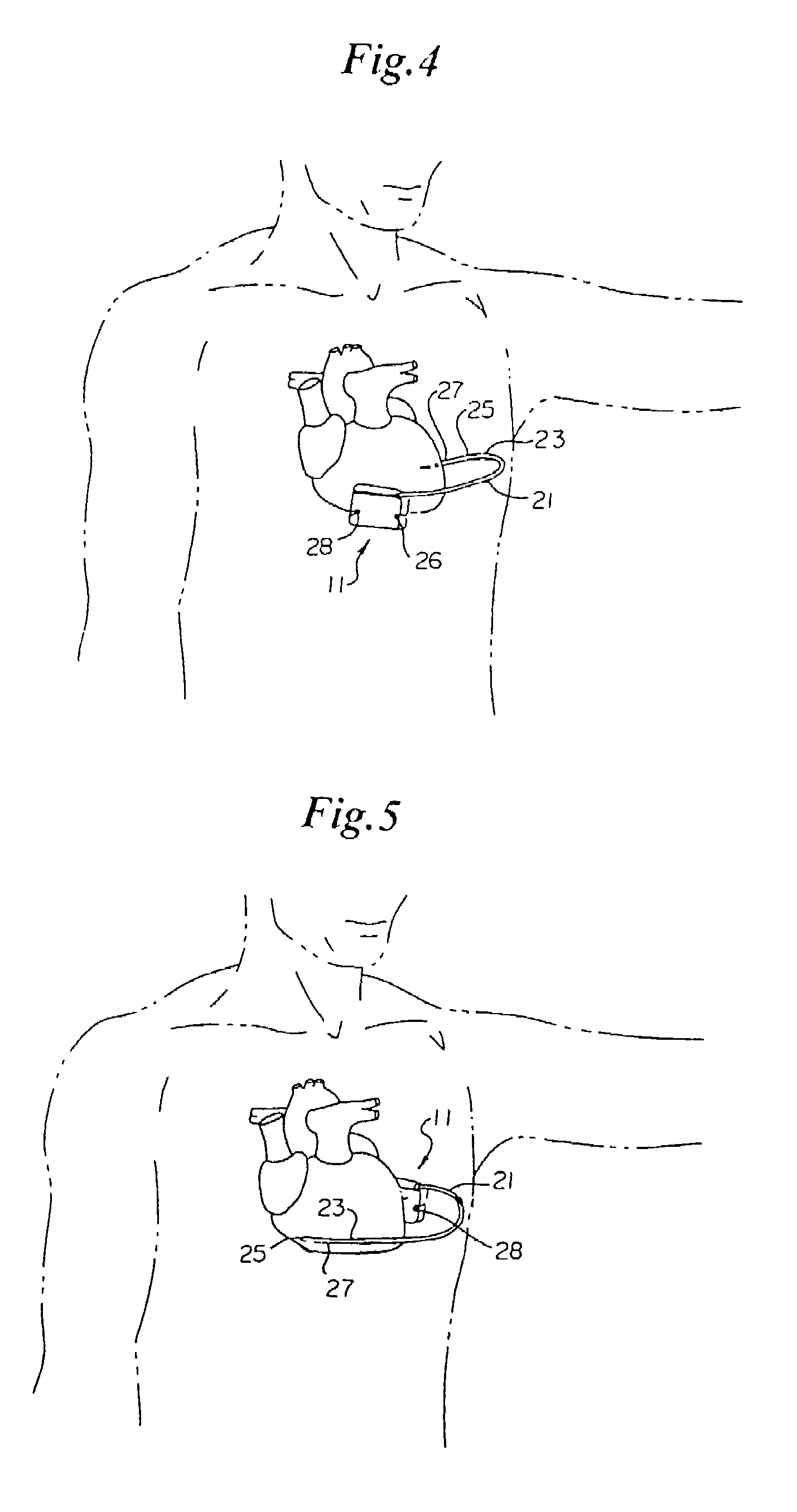
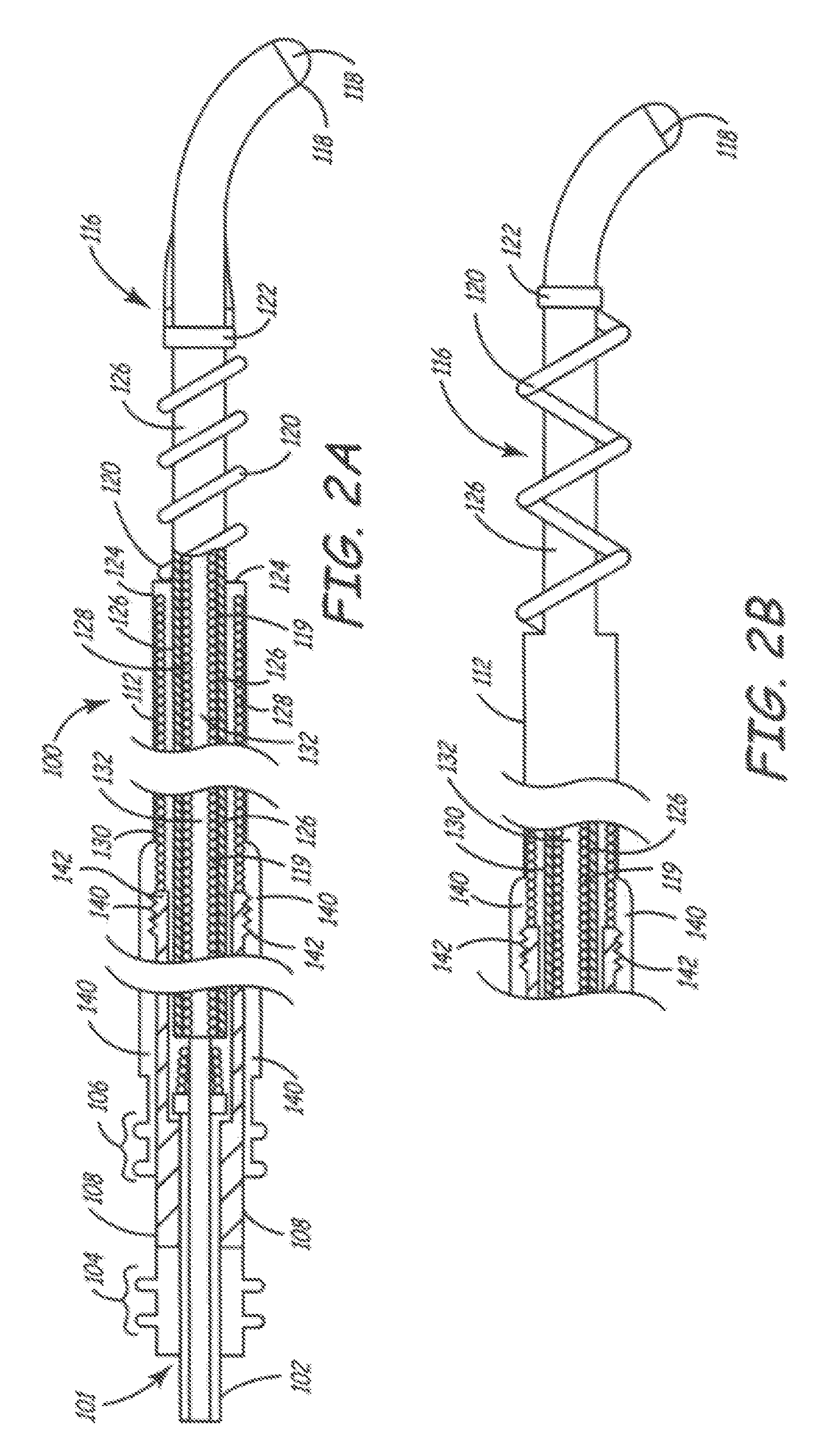
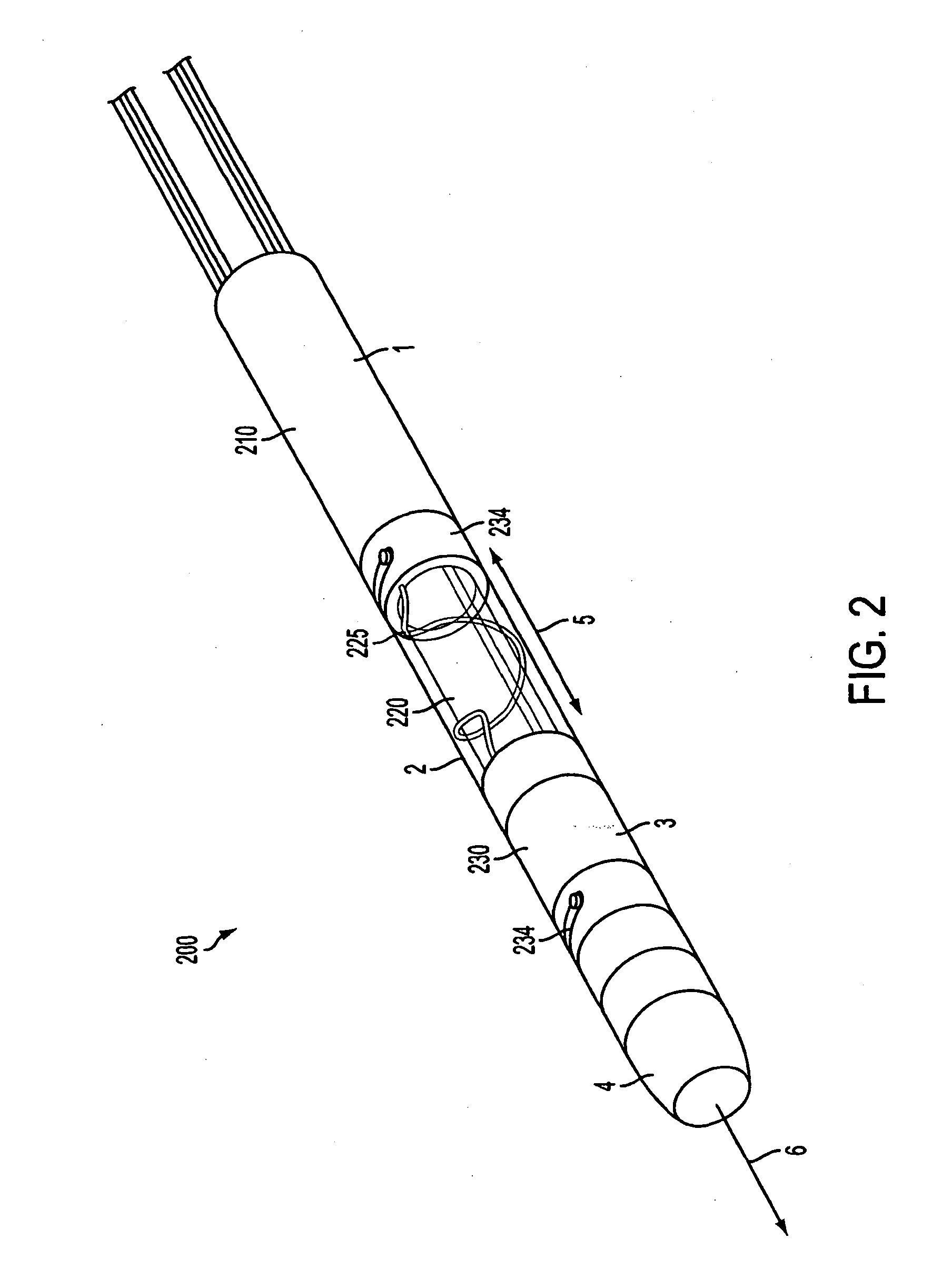
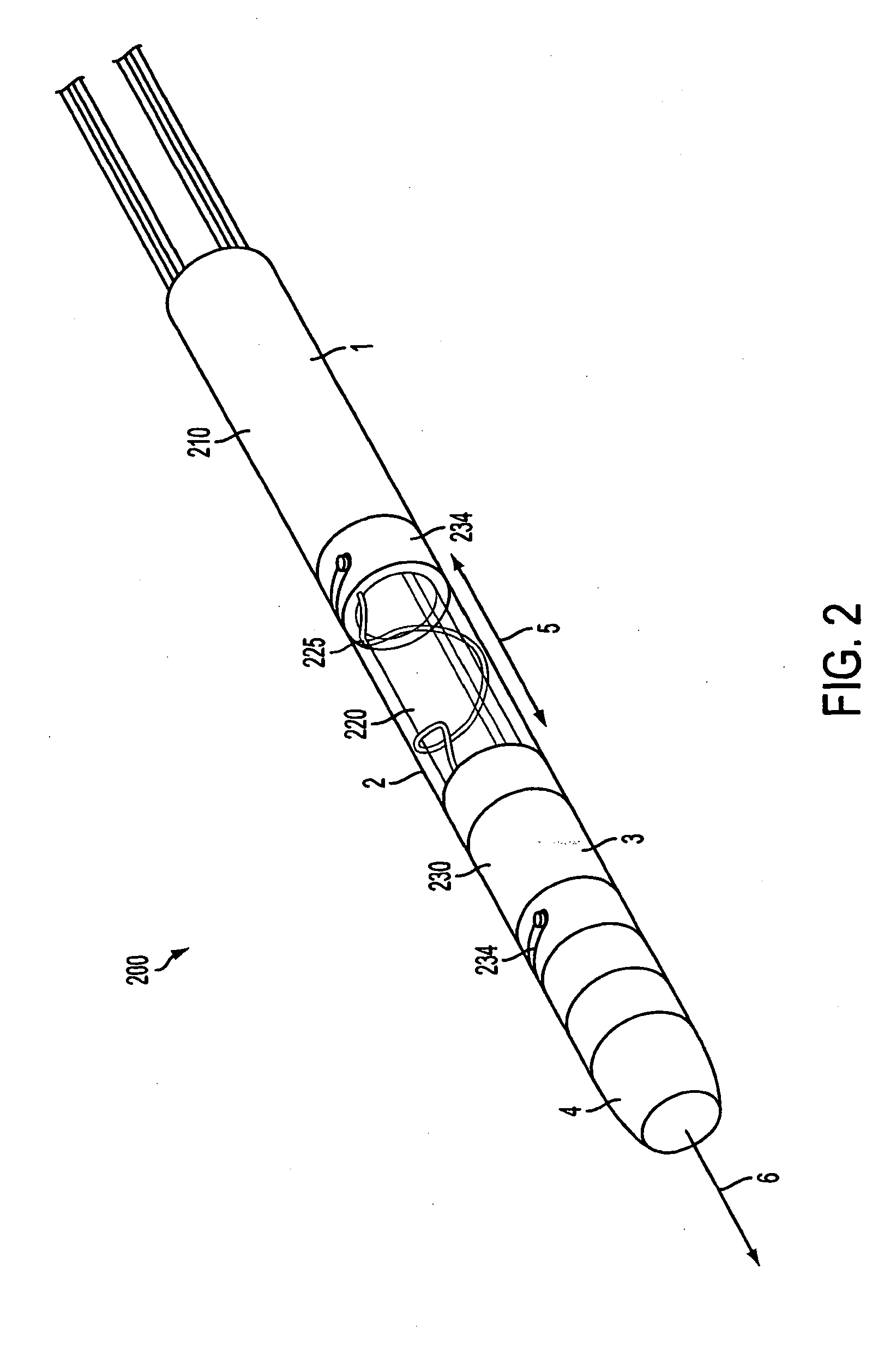
An improved medical lead assembly and method of use is provided. The lead assembly includes a lead body, and a spring member positioned adjacent to the lead body. The spring member may be deployed a selectable amount to maintain the lead body in a fixed location within a patient's body. The spring member may be an expandable coil, a mesh structure that is similar to a stent, or any other similar device that may be positioned in a low-profile state during a lead implant procedure. After the lead is positioned at a target destination, the spring member may be deployed an amount that is selected based on the characteristics of the surrounding tissue, including vessel size. According to one aspect of the invention, the lead assembly may provide means for facilitating chronic lead extraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for extraction of a subcutaneous electrode
A lead assembly is implanted utilizing a lead introducer inserted within an opening of the lead housing. The lead introducer includes an insertion portion and a handle connected to the insertion portion. The lead assembly can be extracted with a lead extractor inserted within an opening of the lead housing. The lead extractor includes an insertion portion having an expandable element, a flexible biocompatible covering around the expandable element, and a handle connected to the insertion portion.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Hybrid catheter for vascular intervention
A catheter for debulking of an undesired deposit from an inner surface of at least one of a blood vessel wall and a stent located in a blood vessel, the catheter having a tip section comprising: circumferentially-directed laser optics; and a circular-action cutter, wherein said circumferentially-directed laser optics is configured to transmit laser radiation for modifying an area of the undesired deposit thereby preparing said area for penetration of said cutter, wherein said cutter is configured to cut through said modified area and thereby debulk at least a part of the undesired deposit. In addition, a catheter for pacemaker and ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) lead extraction is disclosed.
Owner:EXIMO MEDICAL
Method of deployable medical lead fixation
InactiveUS20060292912A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesCoupling contact membersLead extractionFixed position
An improved medical lead assembly and method of use is provided. The lead assembly includes a lead body, and a spring member positioned adjacent to the lead body. The spring member may be deployed a selectable amount to maintain the lead body in a fixed location within a patient's body. The spring member may be an expandable coil, a mesh structure that is similar to a stent, or any other similar device that may be positioned in a low-profile state during a lead implant procedure. After the lead is positioned at a target destination, the spring member may be deployed an amount that is selected based on the characteristics of the surrounding tissue, including vessel size. According to one aspect of the invention, the lead assembly may provide means for facilitating chronic lead extraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
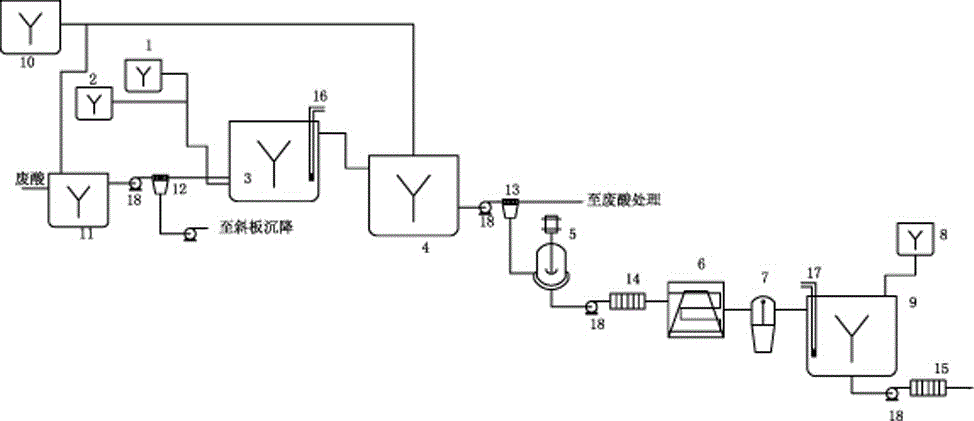
Comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues
ActiveCN105861844AEfficient separation and recoveryWon't break the balanceProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
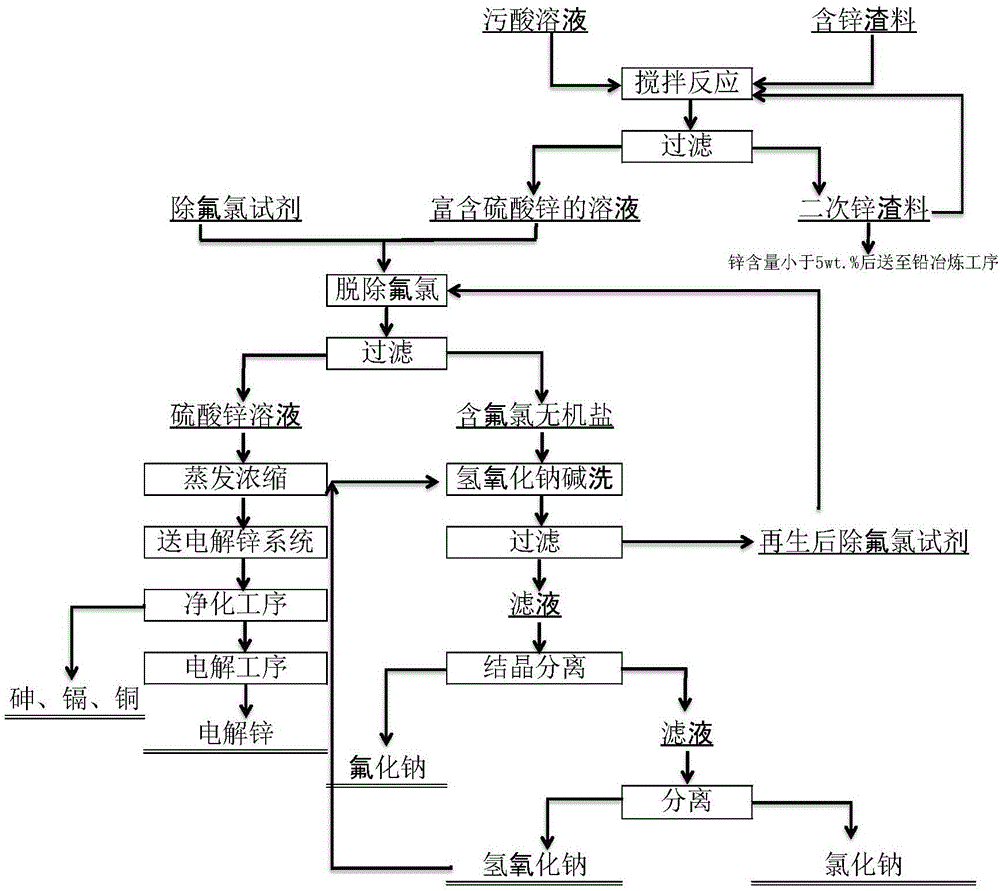
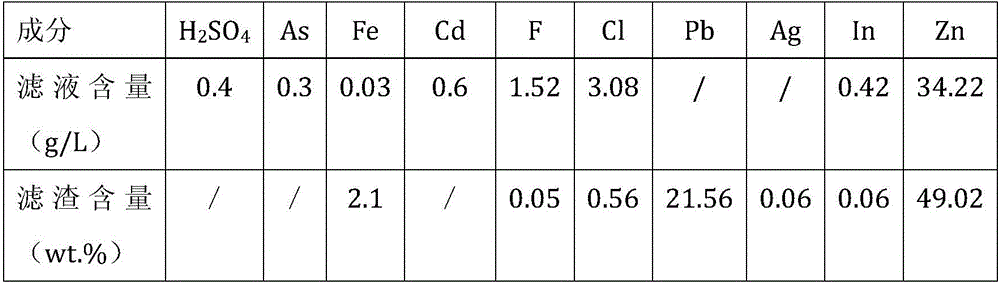
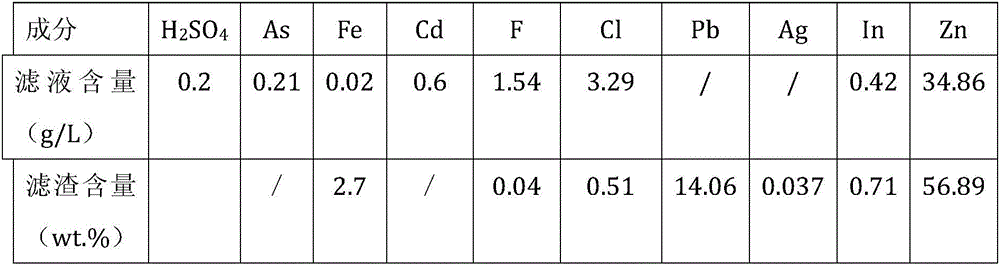
Disclosed is a comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues. The zinc-containing residues generated in the zinc smelting production process serve as an acidic wastewater neutralizer. Liquid obtained after neutralization is subjected to fluorine and chlorine removal and concentrated to meet the requirements for a zinc sulfate solution of a zinc system, and then directly enters the electrolytic zinc system. Valuable metal such as arsenic, cadmium and copper in the acidic wastewater is recycled through an impurity purification procedure of the zinc system. The zinc-containing residues are subjected to a neutralization step to be recycled and fed into a lead extraction procedure after being enriched with lead, silver and other metal. The filter residues with fluorine and chlorine removed are regenerated with a sodium hydroxide solution, the residues obtained after regeneration can be used for the fluorine and chlorine removal procedure repeatedly, and sodium fluoride, sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide in the liquid obtained after regeneration are separated and recycled through efficient evaporative crystallization. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is based on an existing zinc hydrometallurgy system, the balance of original materials in the system is maintained, and an additional heavy metal impurity purification procedure is not added. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is short in process, low in cost, high in valuable metal recycling rate, free of discharging of secondary waste residues and waste water and good in comprehensive economical benefit.
Owner:湖南麓云达环境科技有限公司
Snaring systems and methods
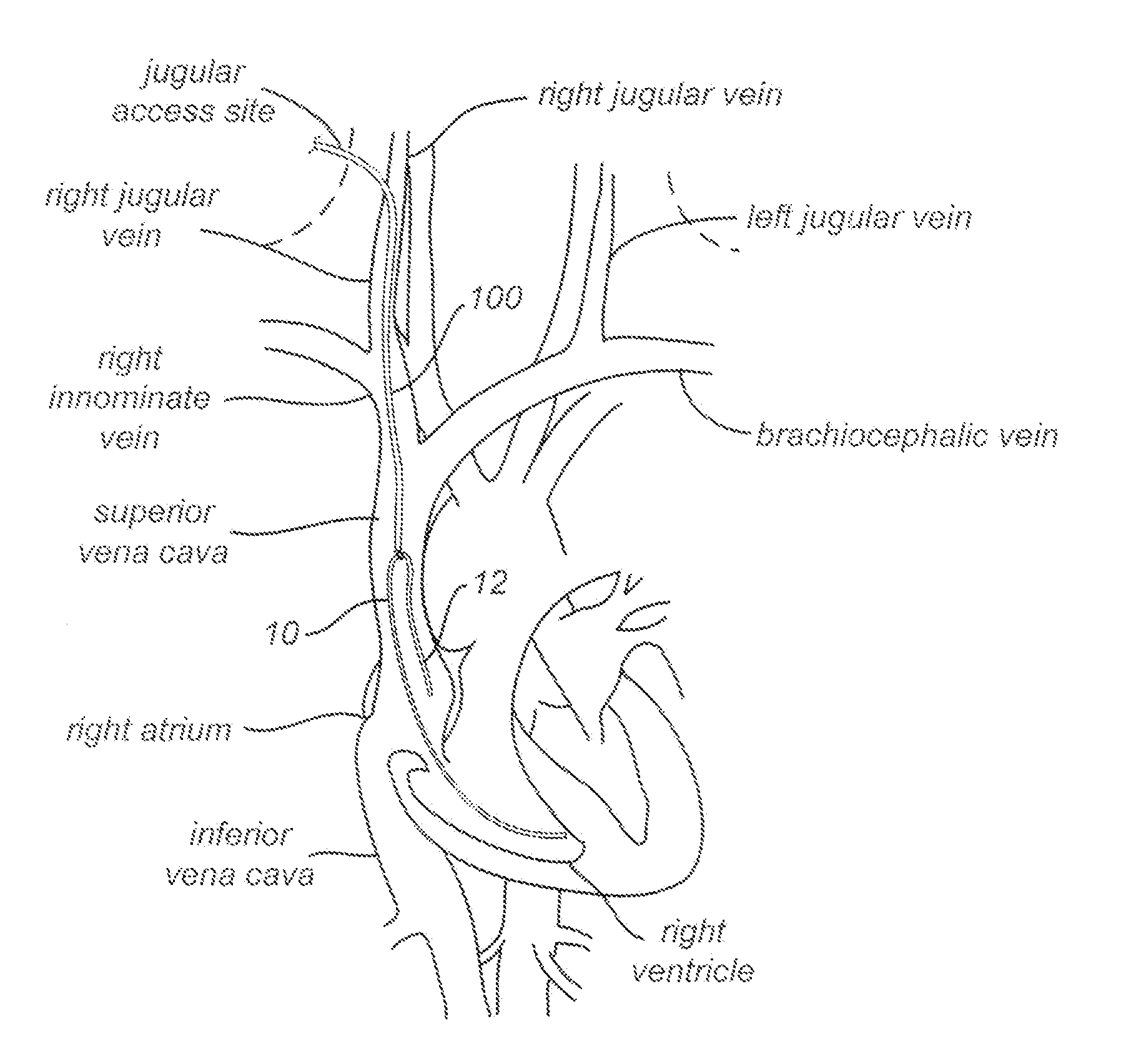
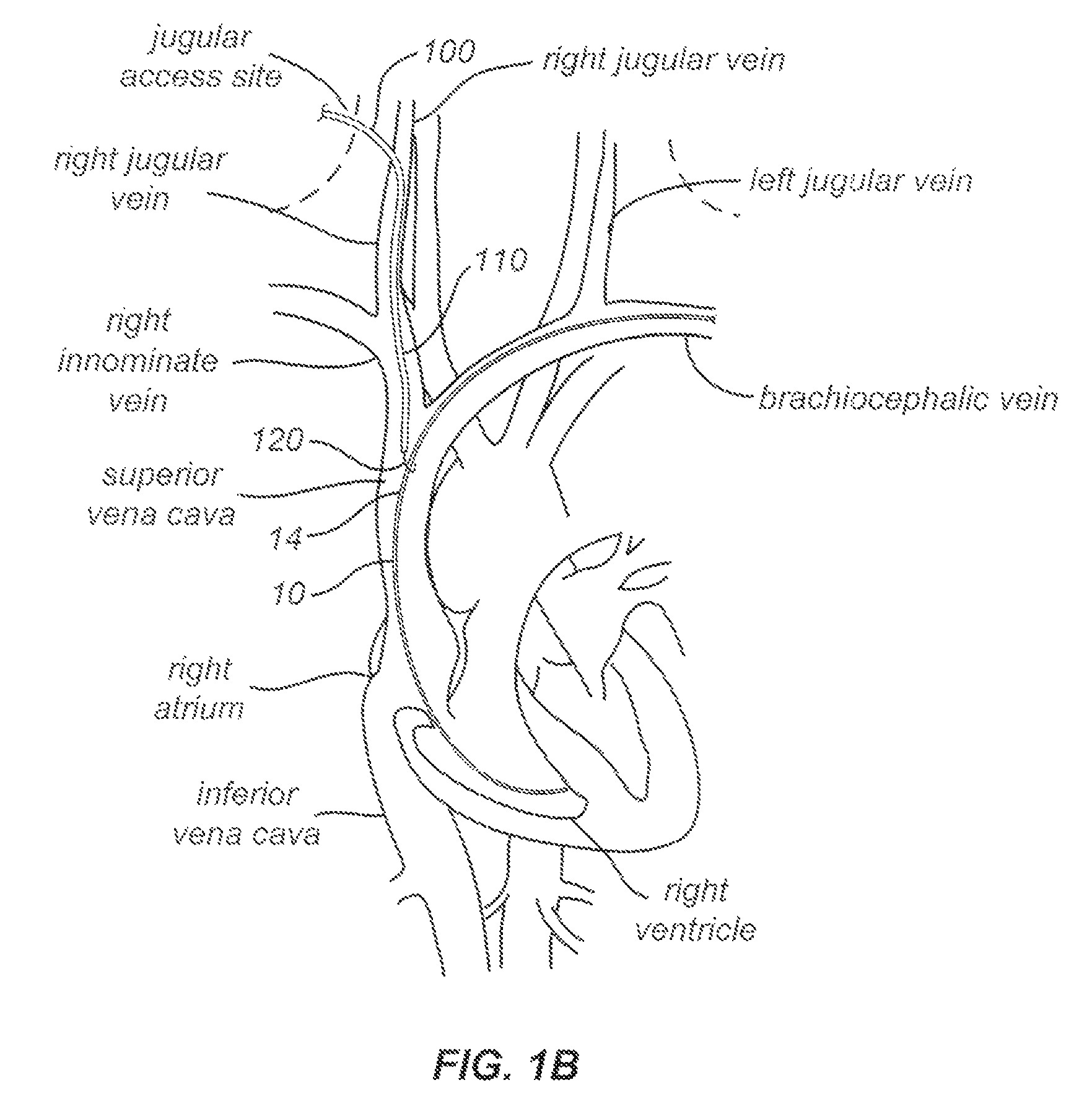
ActiveUS20110098720A1Effective maneuveringEffectively snareDiagnosticsTransvascular endocardial electrodesLead extractionVia jugular vein
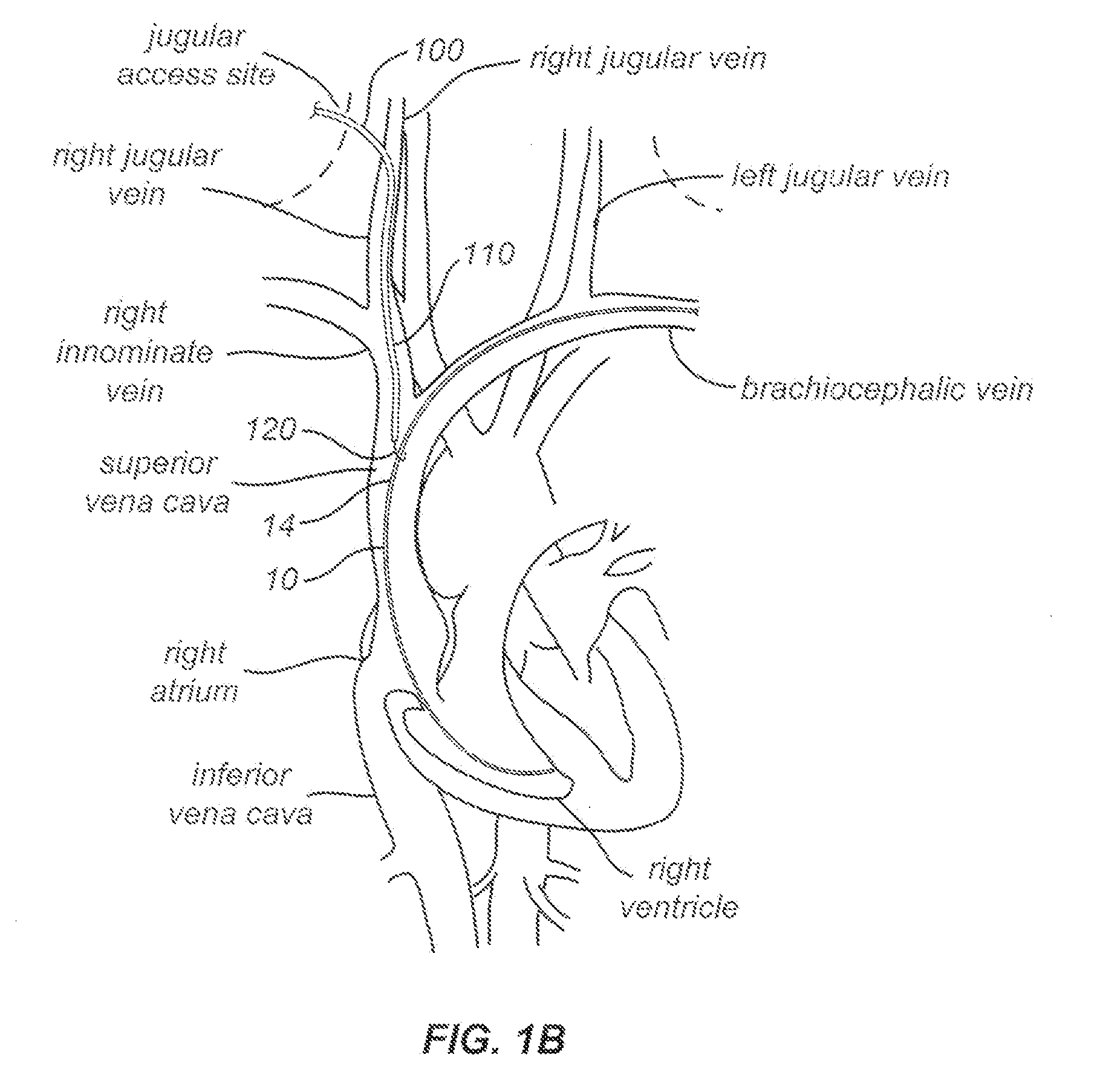
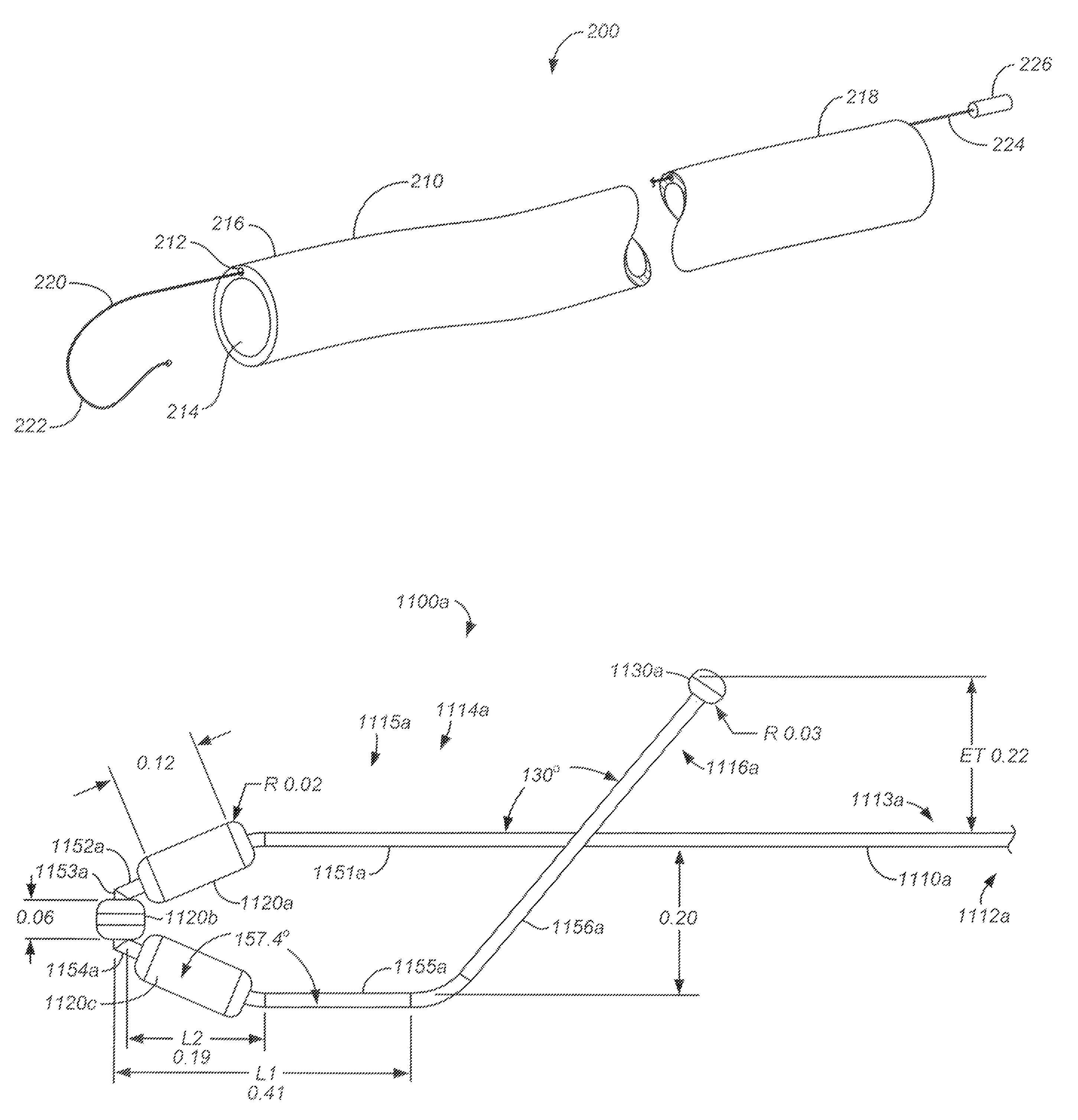
Snaring systems and methods involve engaging objects such as pacemaker pacing leads within a patient. Physicians can use snaring systems having loops, tags, and roller mechanisms to remove a pacing leads from a patient. For example, snaring systems can be inserted through a jugular access site, engaged with a pacemaker pacing lead, and withdrawn through the jugular access site so as to remove a portion of the pacing lead. Lead extraction techniques can be employed to further dislodge the pacing lead from the patient.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Snaring systems and methods
ActiveUS9220523B2Effective maneuveringEffectively snareTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnosticsLead extractionVia jugular vein
Snaring systems and methods involve engaging objects such as pacemaker pacing leads within a patient. Physicians can use snaring systems having loops, tags, and roller mechanisms to remove a pacing leads from a patient. For example, snaring systems can be inserted through a jugular access site, engaged with a pacemaker pacing lead, and withdrawn through the jugular access site so as to remove a portion of the pacing lead. Lead extraction techniques can be employed to further dislodge the pacing lead from the patient.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Process for extracting tea saponin from tea seed cakes or meal
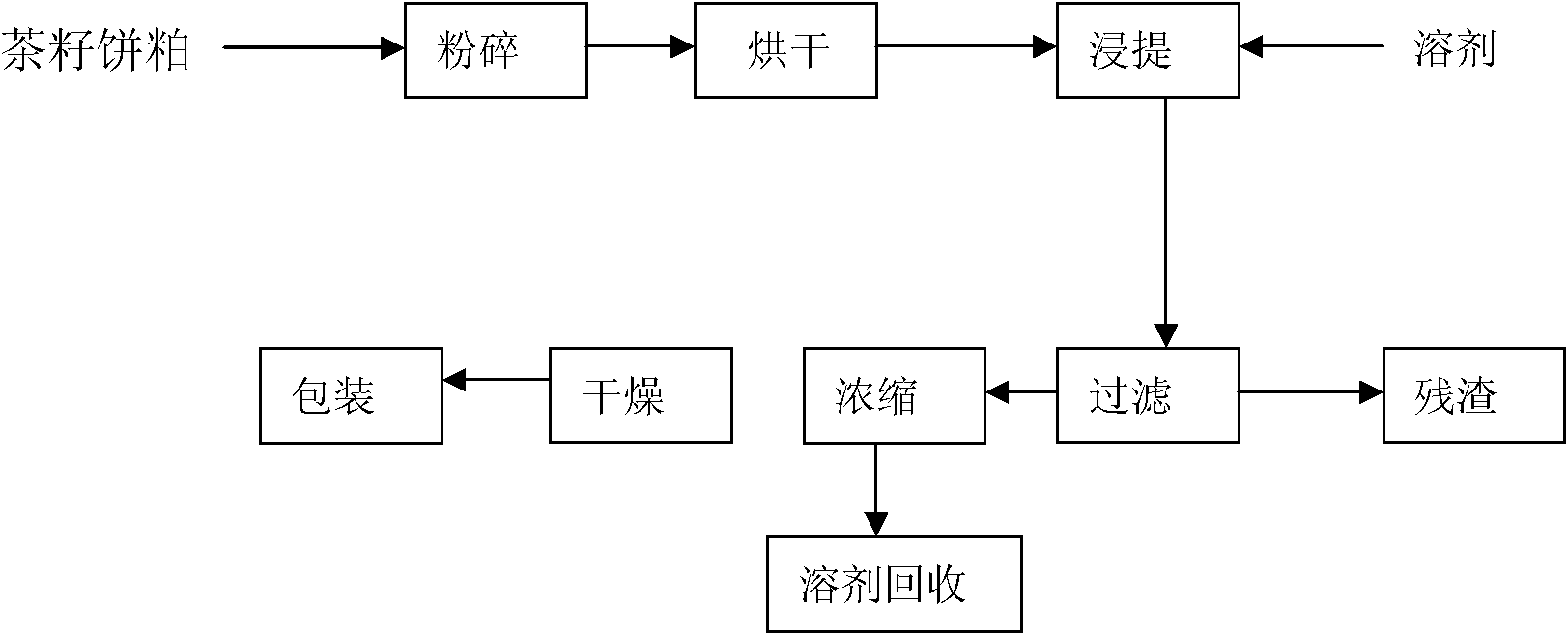
The invention relates to a process for extracting tea saponin from tea seed cakes or meal after oil frying by applying an industrial production device. The process comprises the following steps: crushing the tea seed cakes or the meal (leading the particle size to be 1-3mm), then sending into a steaming and stir-frying cauldron, drying (preventing the water content from exceeding 7%), then leading the material to enter into a material storage cylinder, using a screw conveyor to send the material into a rotocel extractor, and adding a solvent for extraction; carrying out residue-liquid separation (the meal residue can be used as a feed or a fertilizer) after double extraction, leading extraction solution to enter into a long pipe evaporator, removing part of water by double evaporation, and recycling the solvent (which can be recycled); and concentrating the extraction solution via a vacuum concentration tank, then crystallizing and drying, and obtaining a fine saponin finished product for packaging and leaving a factory. A product produced by the process contains 81.5% of active matters, and the pH value is 5.9. Compared with other methods, the process has the advantages of high product purity, light color, high production rate (14%), energy conservation, low consumption, no pollution and environmental protection, and is easy for operation and the like.
Owner:ANHUI YINGSHANHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH
Multi-metal comprehensive recovery process for arsenic-containing smoke dust
ActiveCN103981369AEliminate pollutionEliminate the effects of pollutionProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisHydrometallurgy
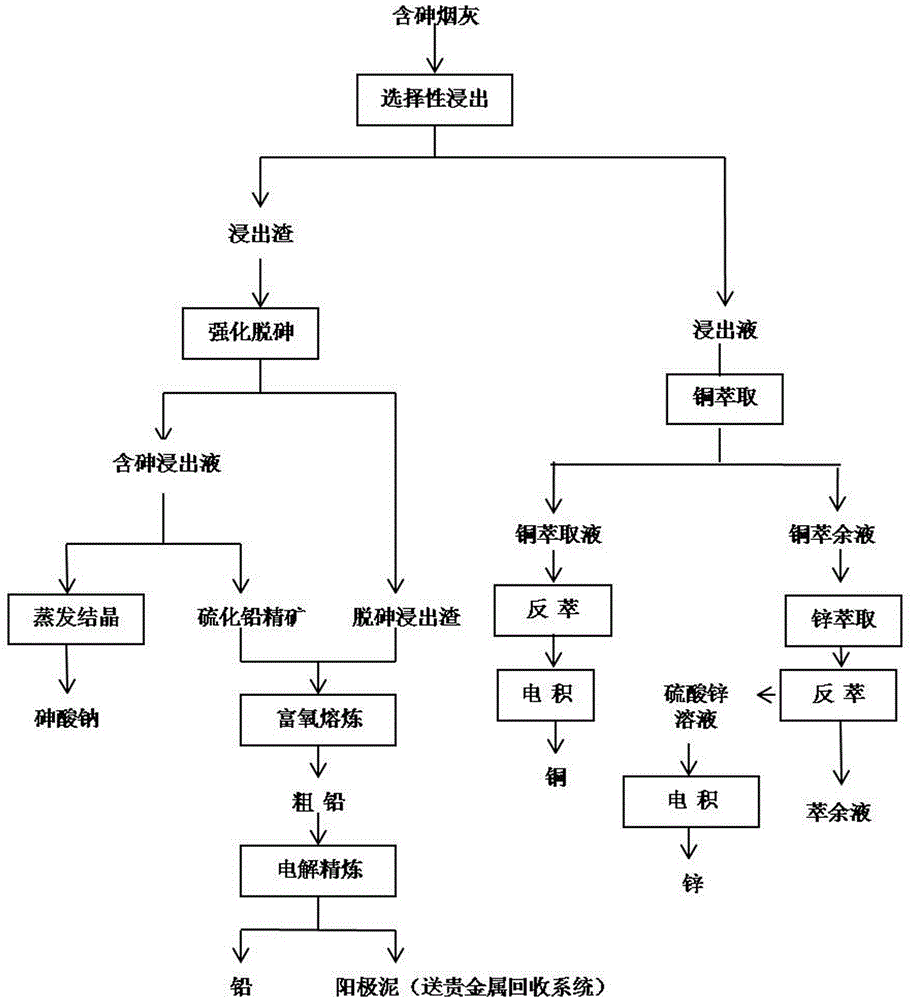
The invention provides a multi-metal comprehensive recovery process for arsenic-containing smoke dust. According to the process, leachate containing zinc and copper and leaching slag containing arsenic and lead are obtained through selective leaching, the leachate is extracted by respectively using a copper extraction agent and a zinc extraction agent, and then reverse extraction and electrodeposition are carried out so as to obtain copper and zinc; the leaching slag is leached with a mixed arsenic removing agent consisting of H2O2 and Na2S2O3 so as to obtain arsenic-containing leachate and lead-containing arsenic-removed leaching slag, the arsenic-containing leachate is concentrated and crystallized so as to obtain sodium arsenate, and the lead-containing arsenic-removed leaching slag is subjected to pyrogenic process lead extraction and electrolytic refining so as to obtain lead. According to the invention, the multi-metal comprehensive recovery process uses combined hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy, comprehensive recovery process and a main smelting system are effectively combined together, seamless butt joint of a part of technology and main process technology is realized, process steps are environment-friendly, metallic copper, zinc and lead are effectively recovered, and resourceful treatment of arsenic is realized.
Owner:甘肃高能中色环保科技有限公司
Endovascular conduit device with low profile occlusion members
InactiveUS20110082465A1Improve securityBalloon catheterEar treatmentCirculatory collapseLead extraction
An endovascular conduit device and method for use during cardiac lead extraction and other vascular procedures is presented. The endovascular conduit device includes an outer-sheath, a conduit member, a lumen member, and an inflation member to control the flow of fluid within the conduit member. The endovascular conduit device may be positioned intravascularly as cardiac lead extraction or other procedures are performed. If necessary, as in the case of a vascular tear, the endovascular conduit device further includes expandable members that are activated to allow blood to be forced into the channel of the conduit member. Blood may then be contained and directed safely to bypass the area of vessel injury. In doing so, a catastrophic circulatory collapse or shock is prevented.
Owner:ATRIAL SYST
Method of deployable medical lead fixation
InactiveUS7736198B2Transvascular endocardial electrodesCoupling contact membersLead extractionFixed position
An improved medical lead assembly and method of use is provided. The lead assembly includes a lead body, and a spring member positioned adjacent to the lead body. The spring member may be deployed a selectable amount to maintain the lead body in a fixed location within a patient's body. The spring member may be an expandable coil, a mesh structure that is similar to a stent, or any other similar device that may be positioned in a low-profile state during a lead implant procedure. After the lead is positioned at a target destination, the spring member may be deployed an amount that is selected based on the characteristics of the surrounding tissue, including vessel size. According to one aspect of the invention, the lead assembly may provide means for facilitating chronic lead extraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
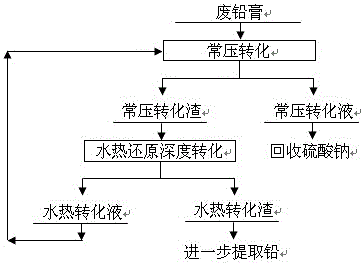
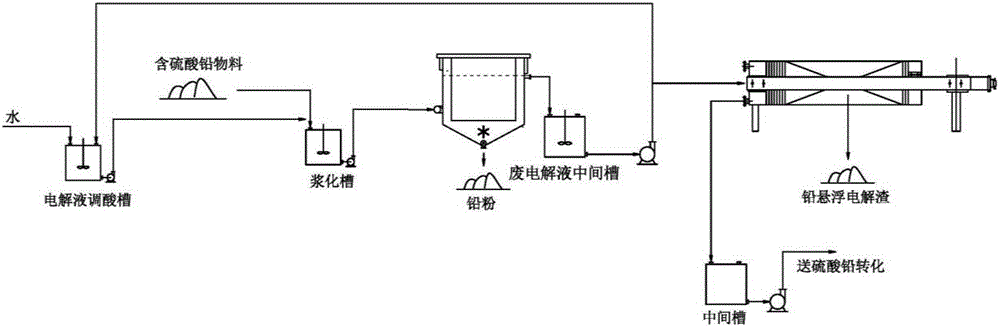
Waste lead-acid battery diachylon hydrothermal reduction dual conversion method
ActiveCN105950872AEasy to operateTechnical indicators are stableWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLead dioxideSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a waste lead-acid battery diachylon hydrothermal reduction dual conversion method. Waste diachylon and alkali solution are firstly converted under normal pressure to remove most sulfate radicals; normal-pressure conversion liquid is fed to recover sodium sulfate; normal-pressure conversion slag and the alkali solution are pulped to feed into a reducing agent to add in a high-pressure reaction kettle for reaction under requested temperature and nitrogen partial pressure, so that residual lead sulfate in the normal-pressure conversion slag is reacted with alkali to deeply remove the sulfate radicals; meanwhile, lead dioxide is reduced as lead monoxide; after the reaction time is reached, the solid-liquid separation is performed; hydrothermal conversion liquid is returned into the normal-pressure conversion process; and lead is further extracted from the hydrothermal conversion slag. The essence of the method is to realize dual purposes of deep conversion desulfurization and reduction conversion of the waste diachylon by using a water heat and reduction combined mode; the desulfurization rate and the lead dioxide reduction rate both reach above 99.0%; and advantageous conditions are created for subsequent lead extraction from conversion slag.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for producing silica white and lead sulfide with waste lead glass tubes as raw material
InactiveCN103172075AOvercoming Process ComplexityOvercoming Process Energy ConsumptionSilicaLead sulfidesDecompositionHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for producing silica white and lead sulfide with waste with lead glass tubes as a raw material, and aims at solving the problems of complicated technology, high energy consumption and easy generation of secondary pollution in the existing lead glass tube lead-extraction technologies. According to the method, firstly waste lead glass tubes are coarsely broken and fine ground to obtain fine ground waste lead glass, and then are added with a potassium hydroxide solution to react for 60-210 minutes under 80-200 DEG C, and leaching residues and lead-silicone contained leaching solution are obtained by filtration; the lead ion concentration in the lead-silicone contained leaching solution is measured, sodium sulfide is added inside based on the mol ratio of Pb / S=1 to react for 30-120 minutes under 60-80 DEG C, and lead sulfide and filtrate are obtained by filtration; the pH value of the filtrate is adjusted to 7-9 by carbon dioxide decomposition or adding acid liquid, so that gel is obtained and then is aged for 60-180 minutes and filtered, and silica white is obtained by drying the filter cake. The method has the advantages of modest reaction conditions, simple process flow, large waste consumption and the like, and is easily suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
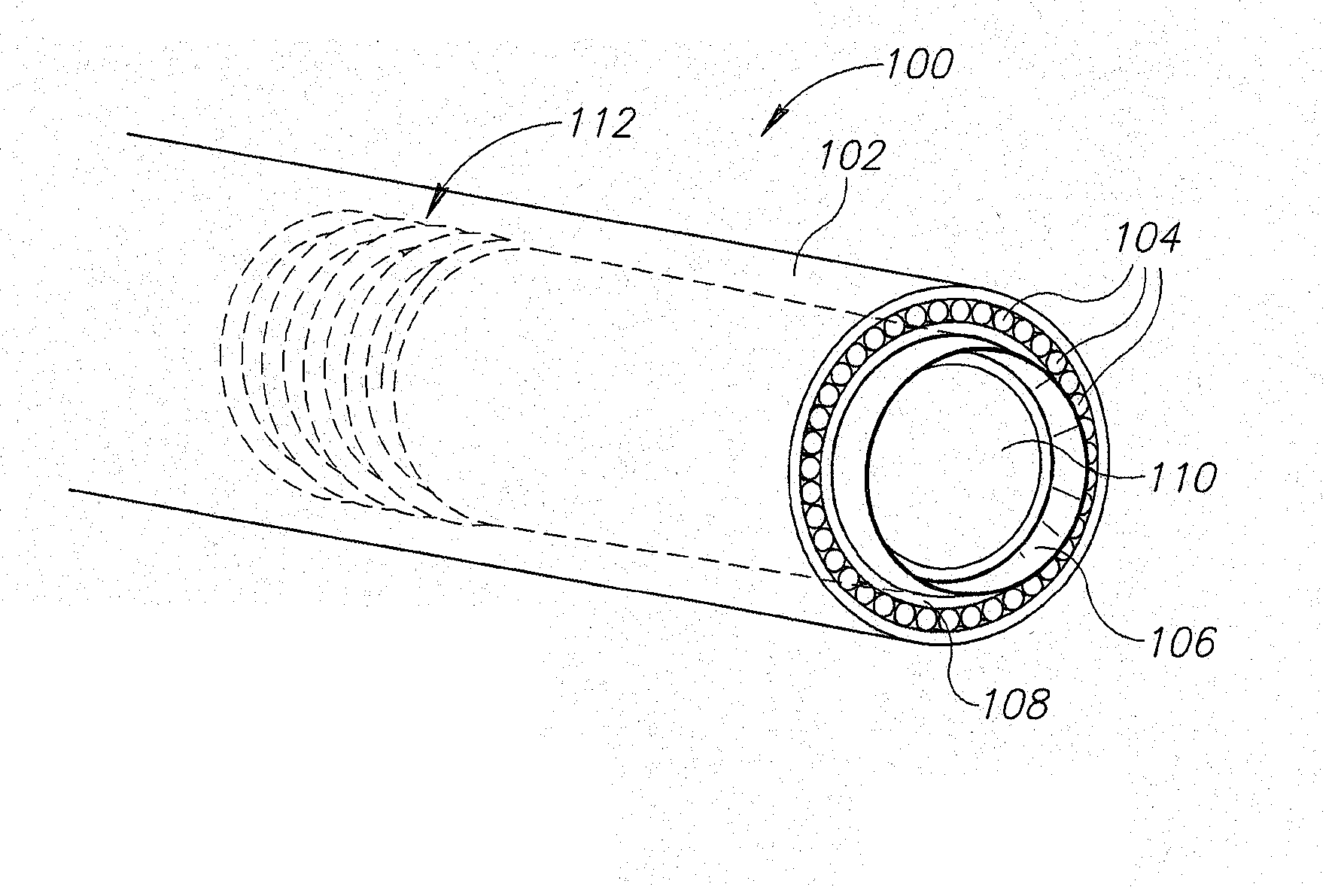
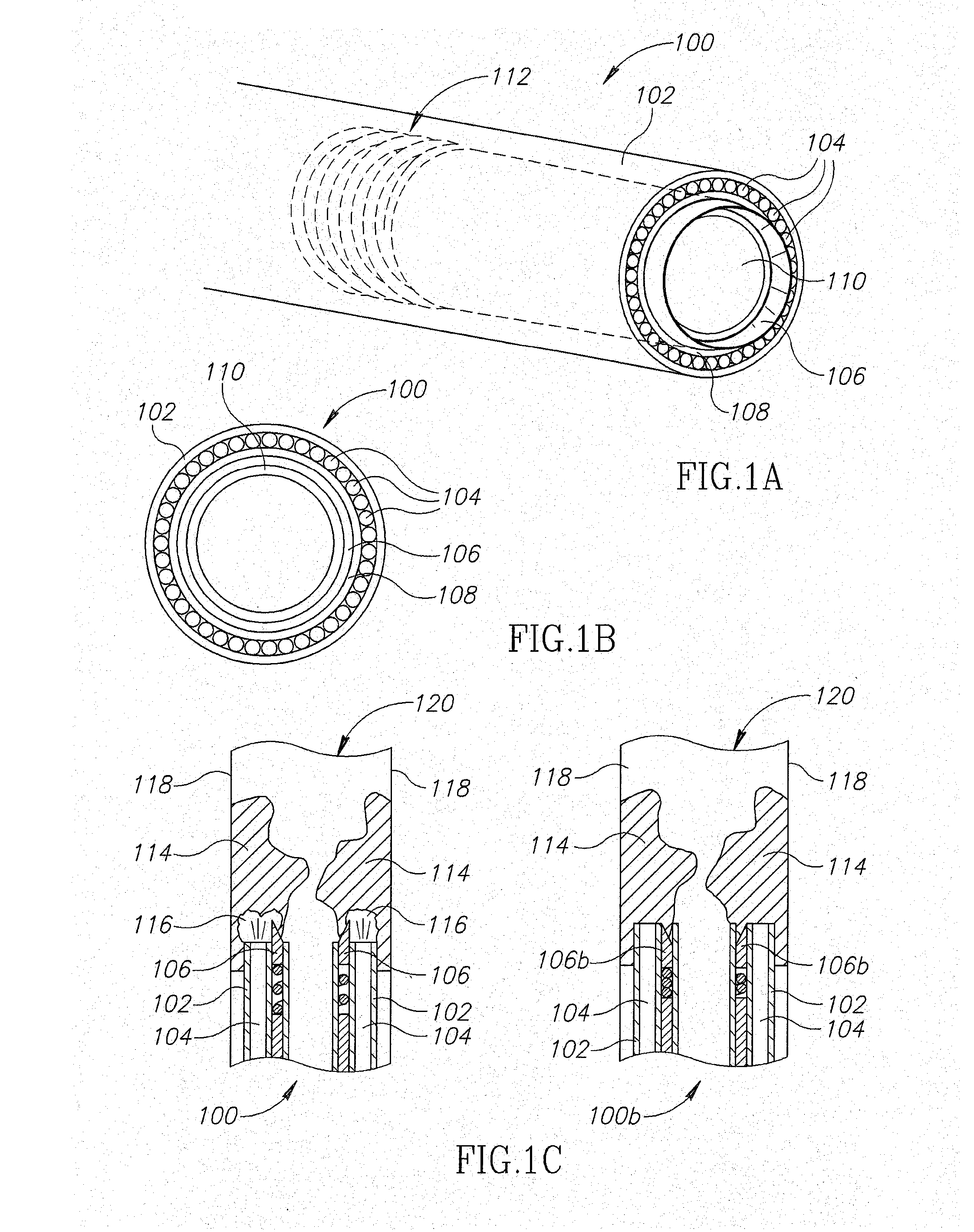
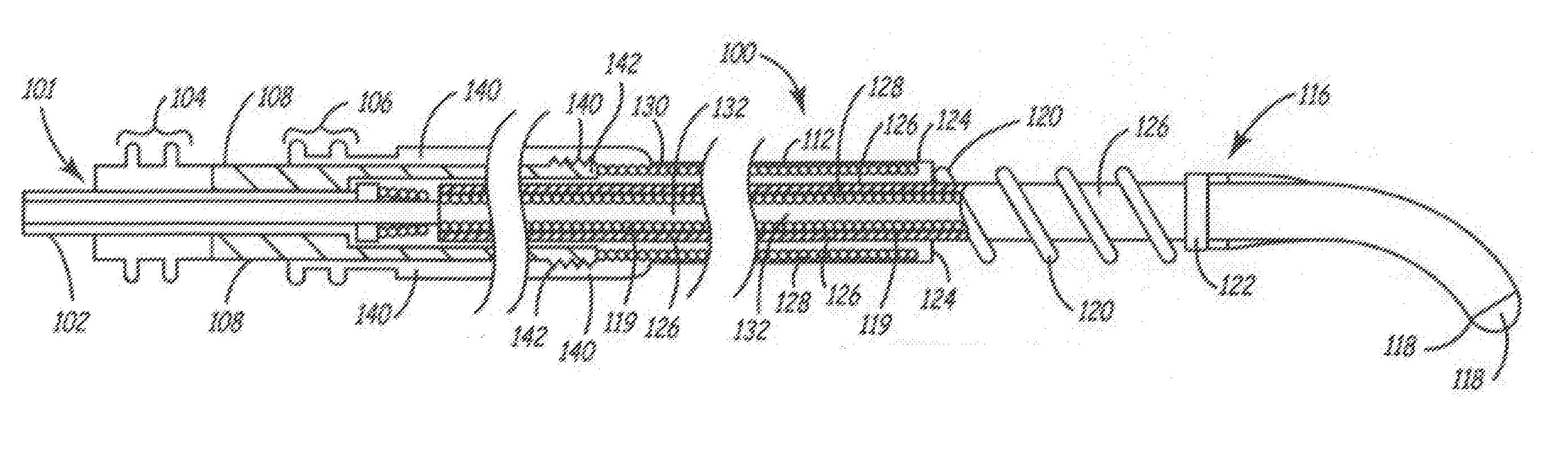
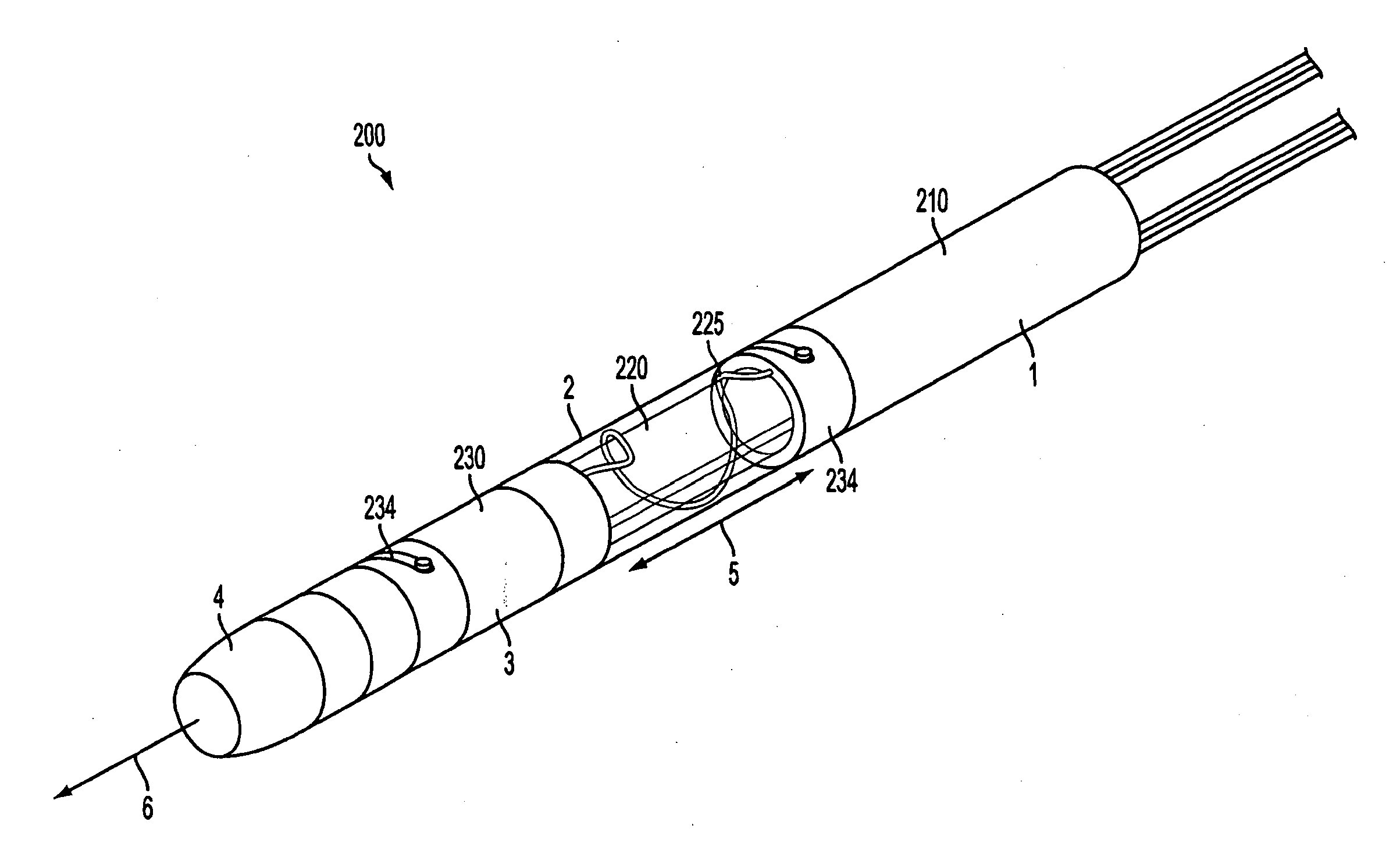
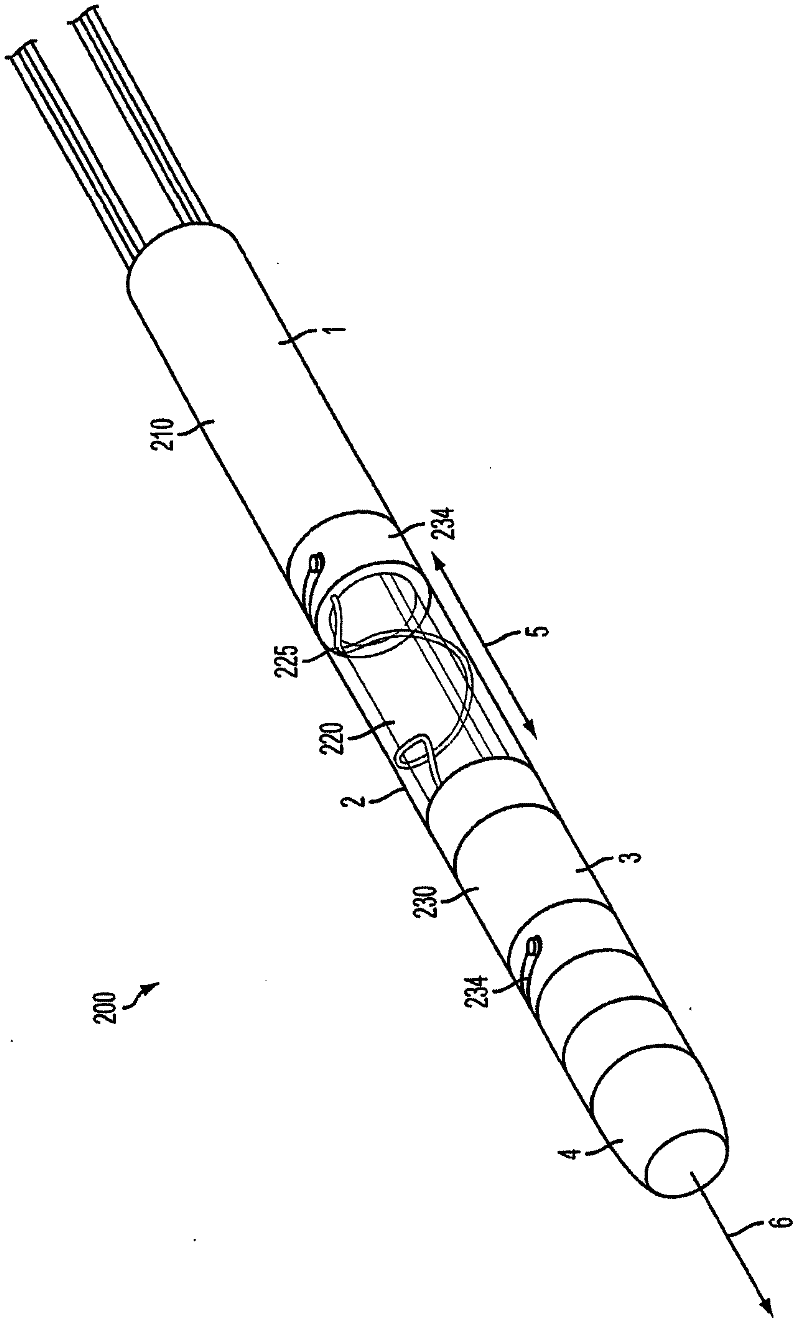
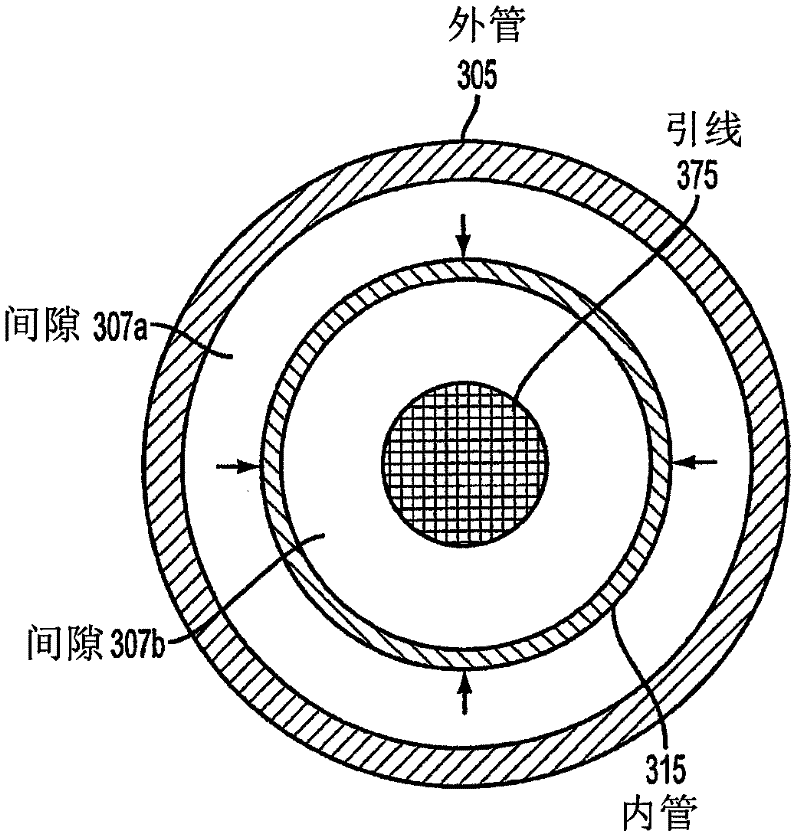
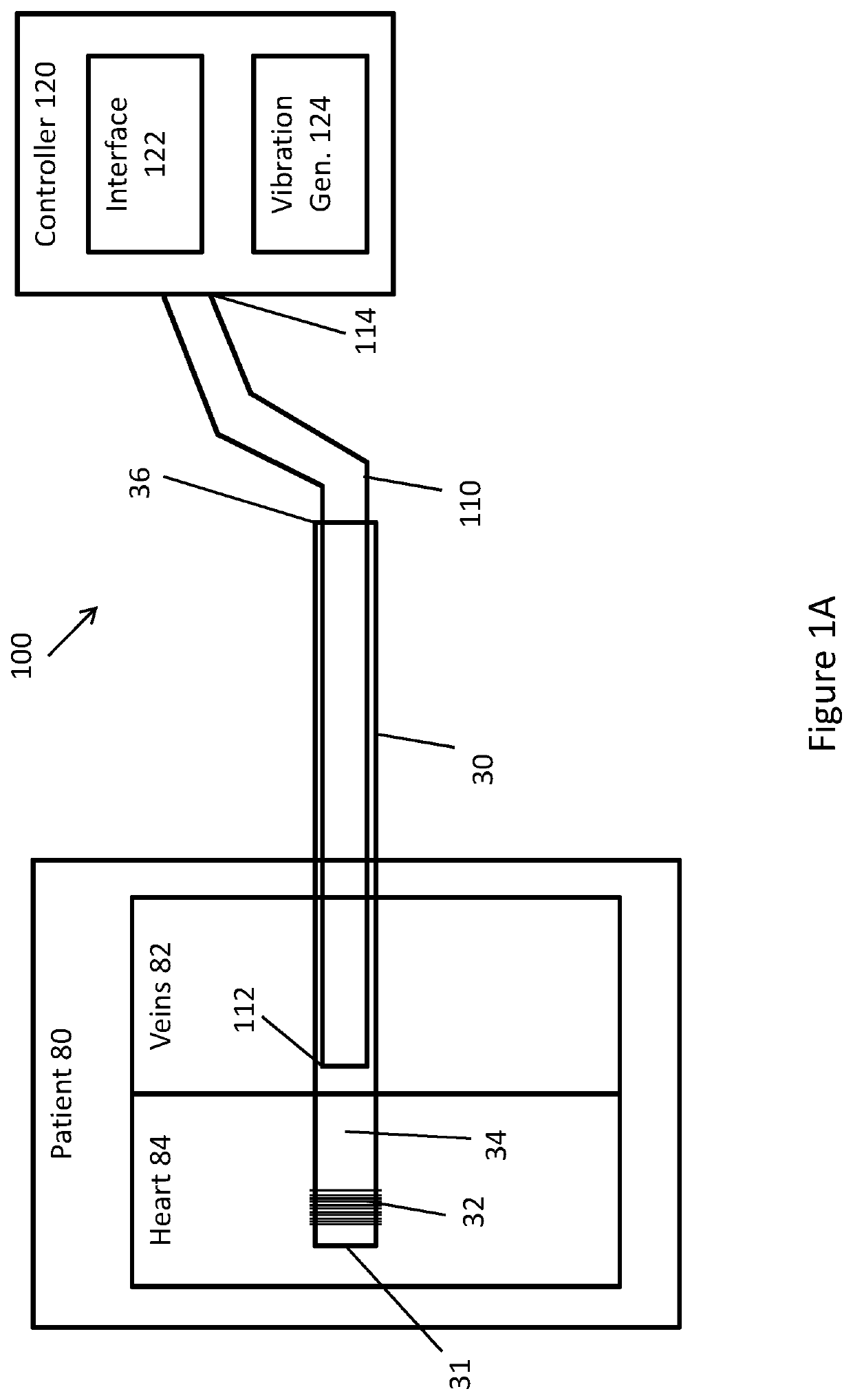
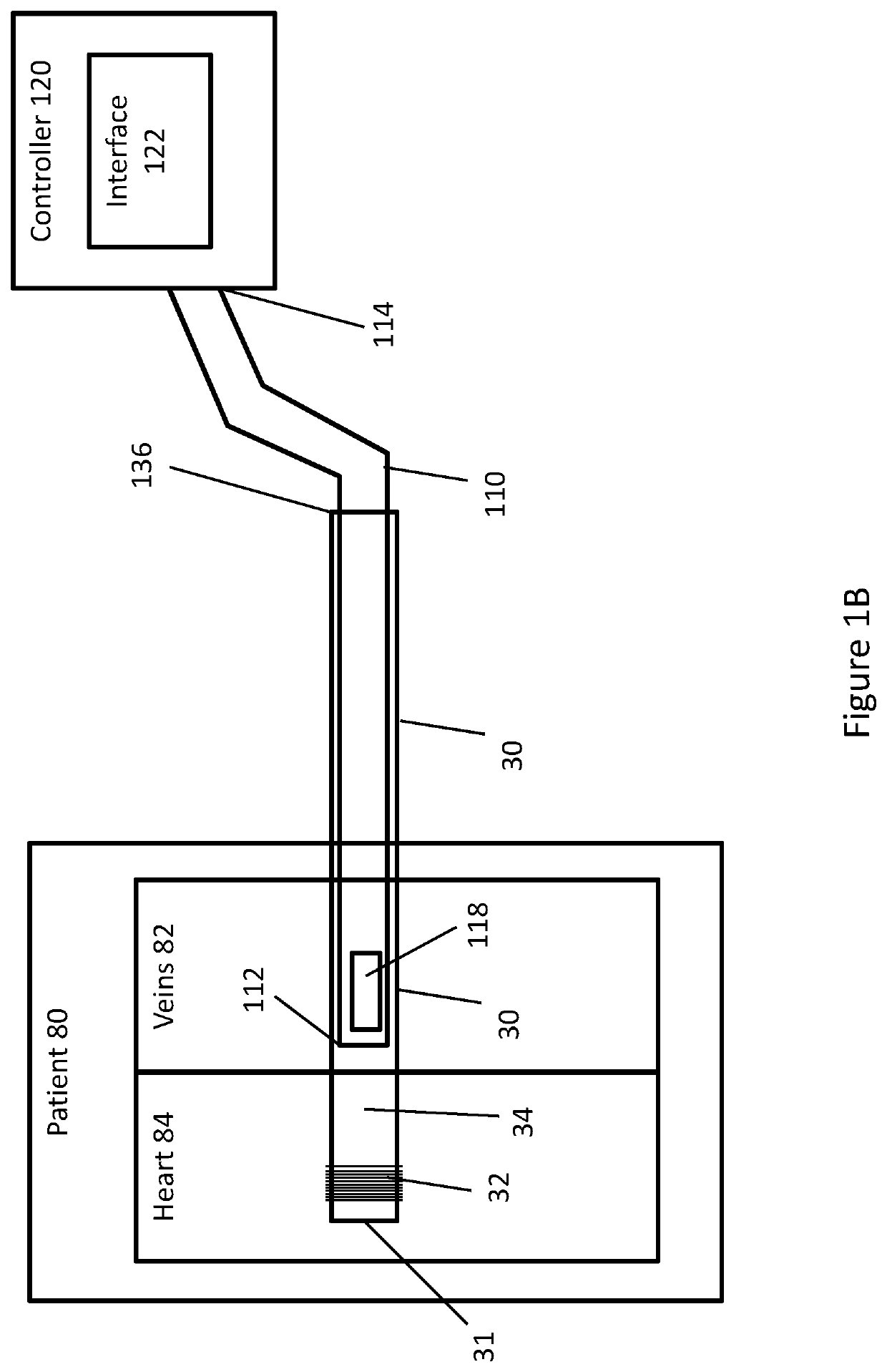
Lead extraction methods and apparatus
An apparatus configured to control a lead extraction tool for assisting in removal of an implanted lead. The apparatus comprises at least one valve configured to control fluid flow to the lead extraction tool. When the at least one valve is open, the at least one valve is configured to allow fluid stored in the apparatus to flow thereby applying, when the apparatus is fluidly coupled to the lead extraction tool, fluid pressure to at least one component of the lead extraction tool. The apparatus further comprises at least one controller configured to control opening and / or closing of the at least one valve.
Owner:LEADEX CARDIAC
Device for medical lead extraction
ActiveUS20180028258A1Easily and safely cutTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical needlesElectricityLead extraction
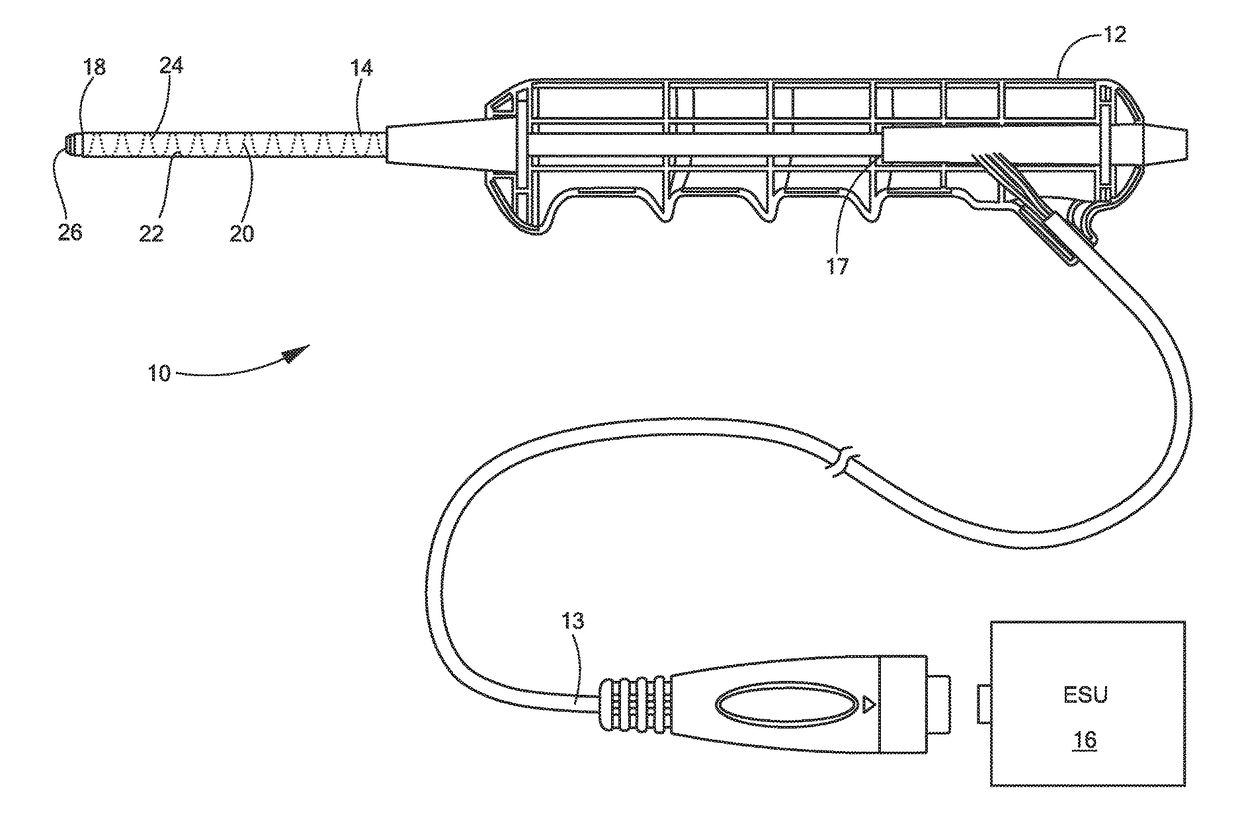
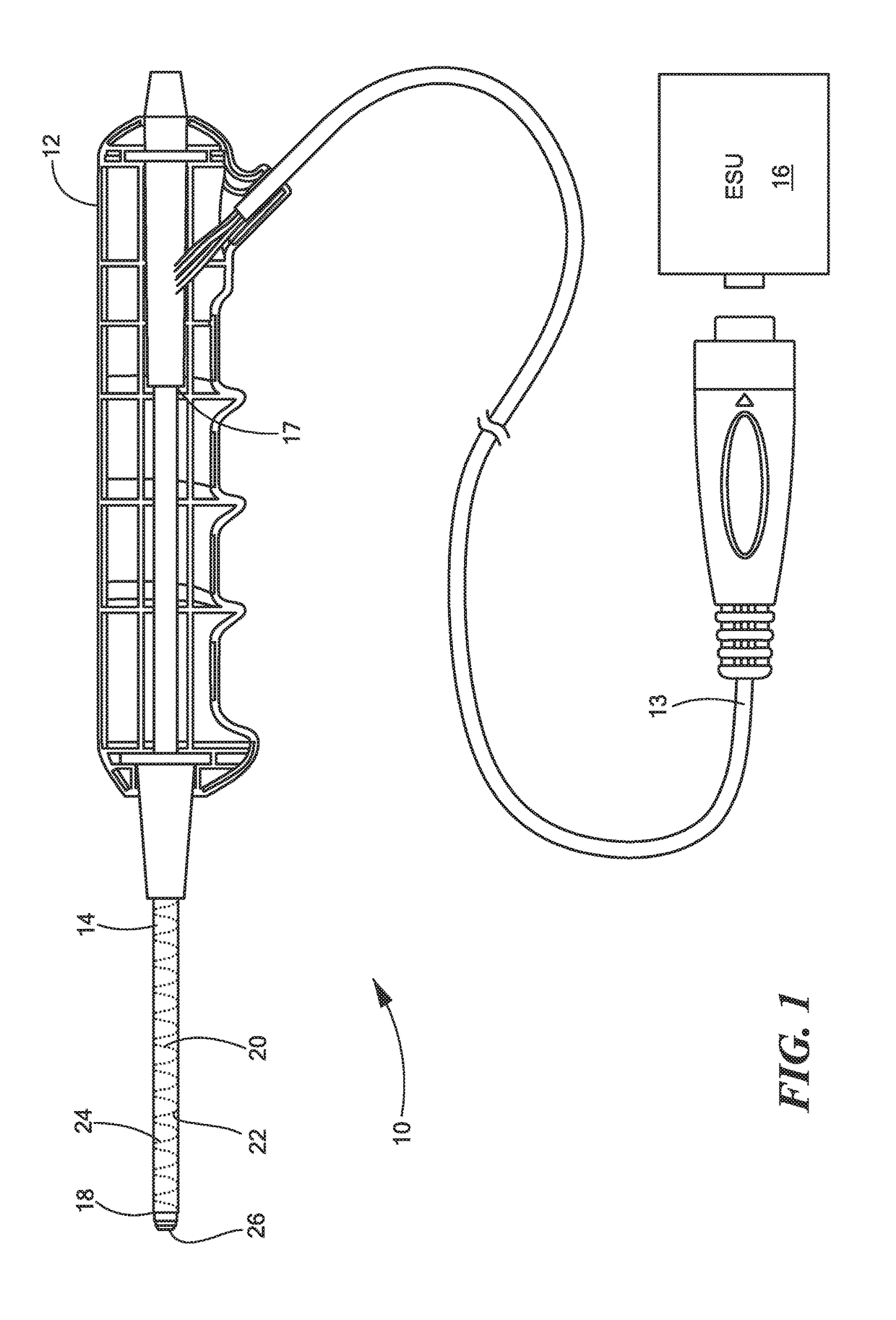
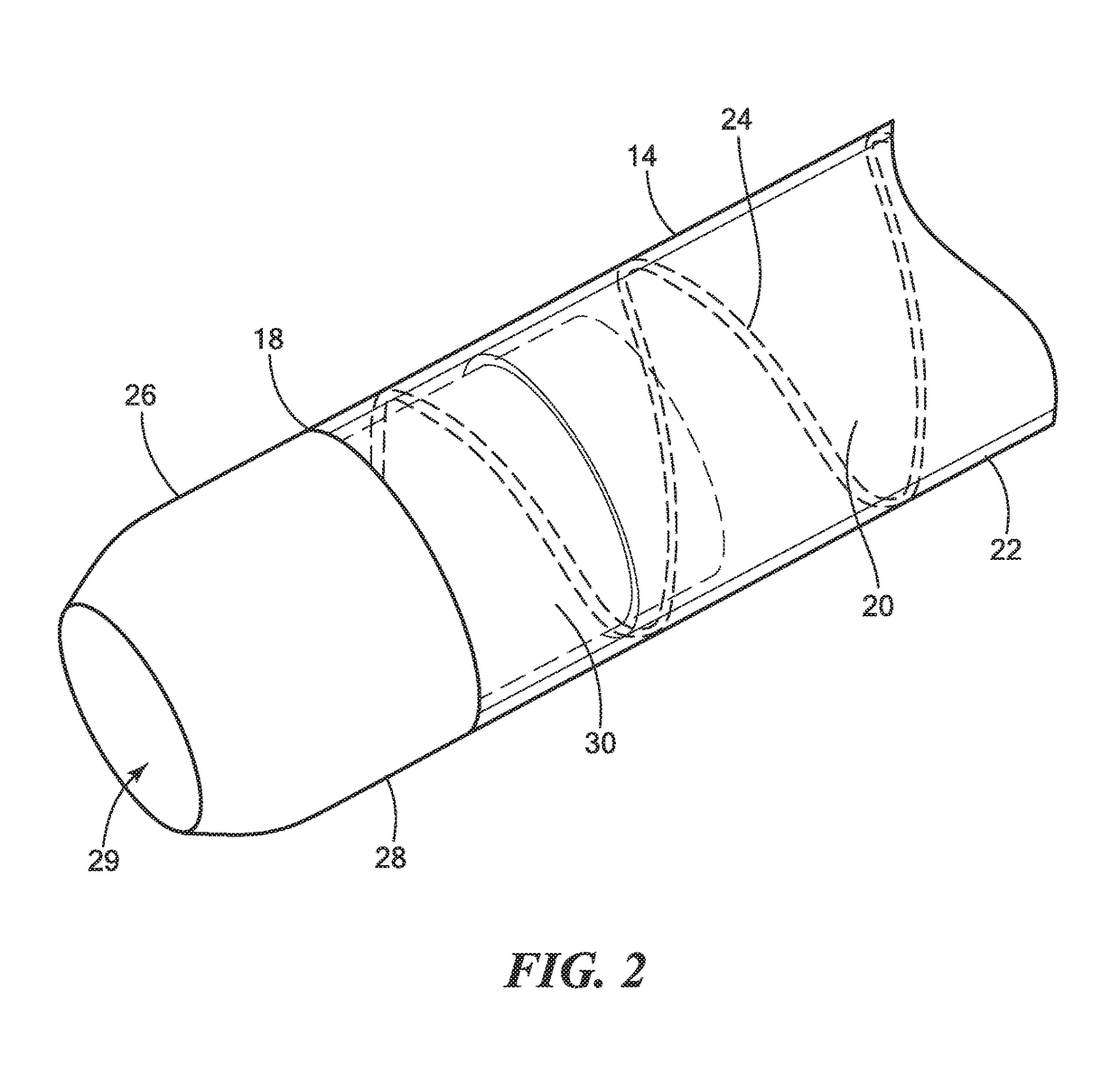
An electrosurgical hand piece device is configured to cut tissue with monopolar RF energy to extract a medical lead submersed in fluid. The device includes an electrode surrounded by an electrically insulating coating that can be exposed from a distal edge of the electrode when power is supplied to the device, thereby focusing the energy at the distal edge and enabling tissue to be more easily and safely cut from around the medical lead while in fluid.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Suspension electrolysis method for lead sulfate
The invention discloses a suspension electrolysis method for lead sulfate, and belongs to the field of wet process lead smelting. For a lead-containing material taking PbSO4 as a principal thing, the invention develops a novel suspension electrolysis method for lead sulfate. The lead sulfate-containing material is continuously added into a suspension electrolysis bath after being pulpified with dilute sulphuric acid, and solid particles in electrolysis slurry are uniformly distributed in the electrolysis bath under the action of stirring paddles; lead powder is directly separated out from lead sulfate particles at a positive pole, and the lead powder is cast into lead bullion after being washed, filtered and briquetted; sulfuric acid and oxygen are generated at a positive pole; the recycling for lead and the sulfuric acid is realized at the same time. The method solves the problems that different solution systems are crossed, the consumption of reagents is high and byproducts cannot be used in a traditional wet process lead extraction technology from the source, thoroughly overcomes the difficulty of clean, economic and efficient recycling for lead in various lead and zinc materials, and can provide support for green and clean utilization of all lead and zinc materials.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
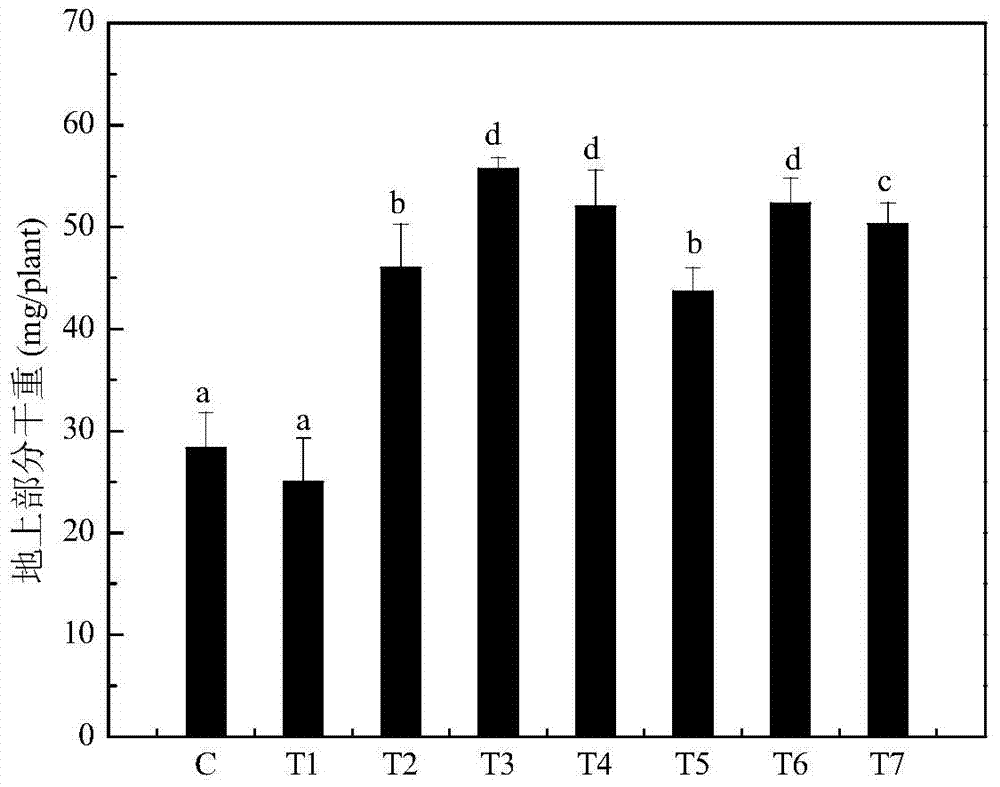
Reinforced restoration method for lead-polluted soil by combining diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)
InactiveCN103586266APromote growthLarge biomassContaminated soil reclamationEthylenediamineAcetic acid
The invention discloses a reinforced restoration method for lead-polluted soil by combining diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), which comprises the following steps: planting ryegrass on the lead-polluted soil, and adding a diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate solution and an EDTA solution in the ryegrass growth process. When the method is used for treating the lead-polluted soil, the added EDTA is beneficial to enhancing the biological effectiveness of lead in soil, and promoting the lead extraction and enrichment of the plants; and meanwhile, the diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate is added to enhance the biomass of the plants, thereby obviously enhancing the restoration effect of the plants on the lead-polluted soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
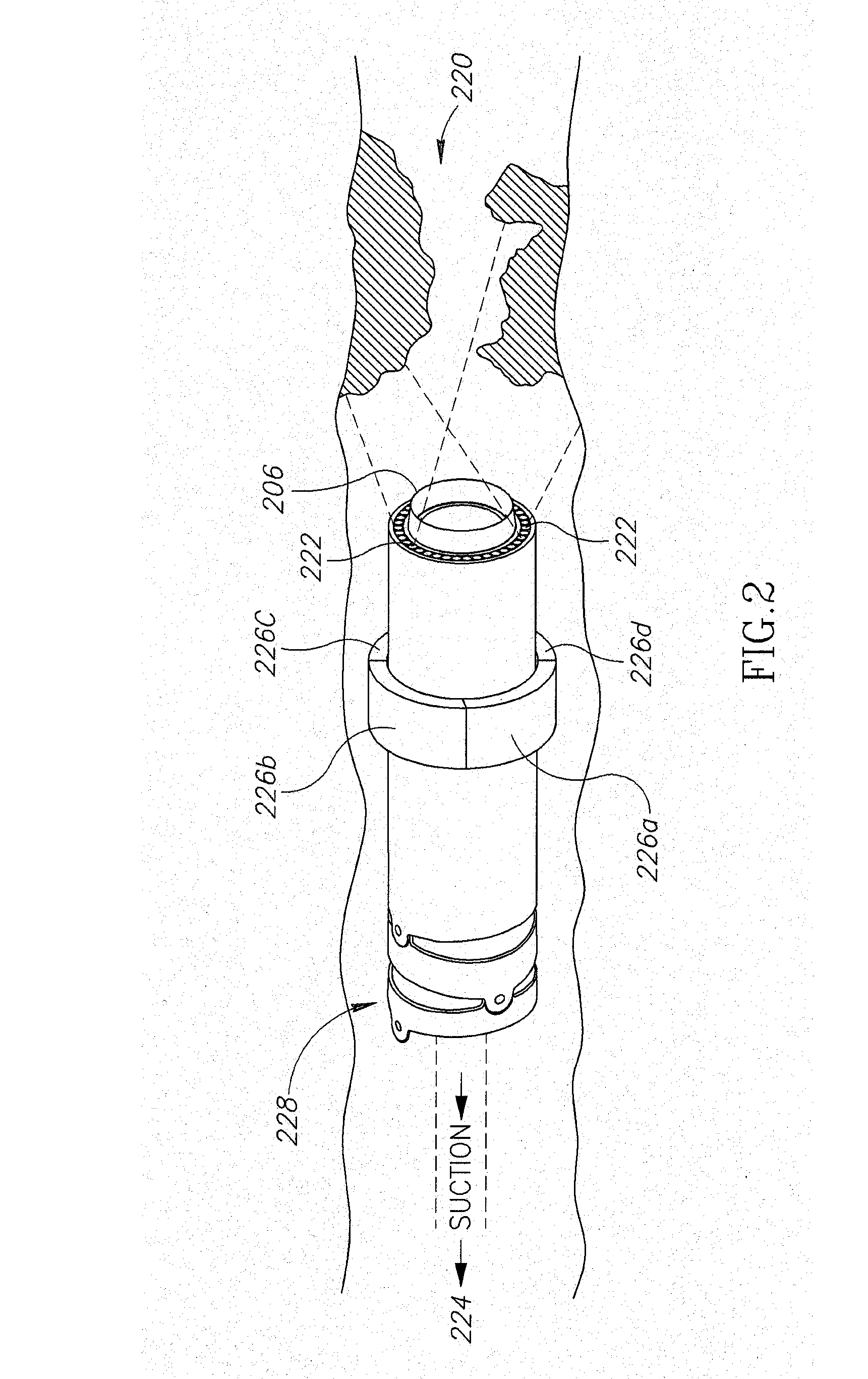
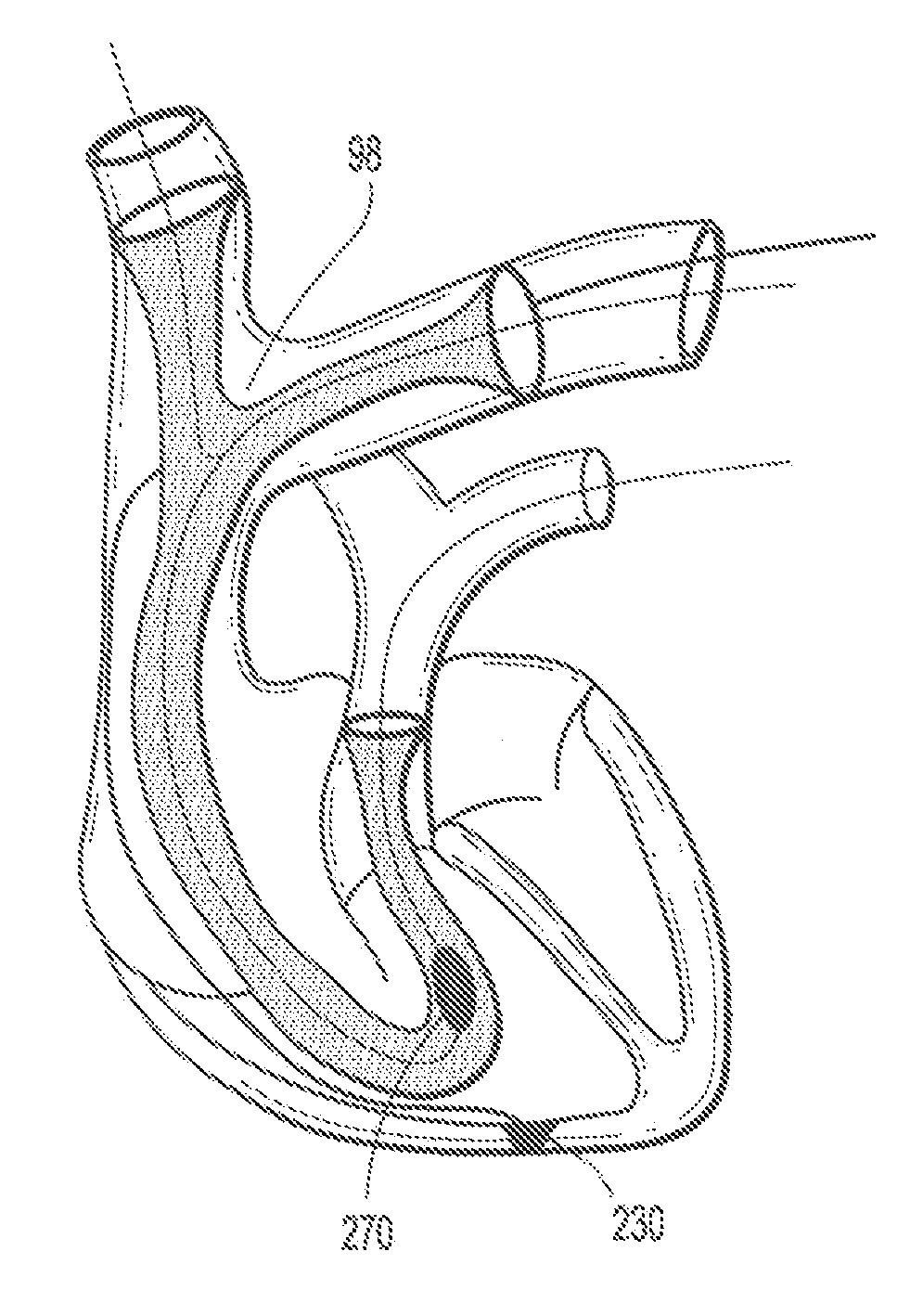
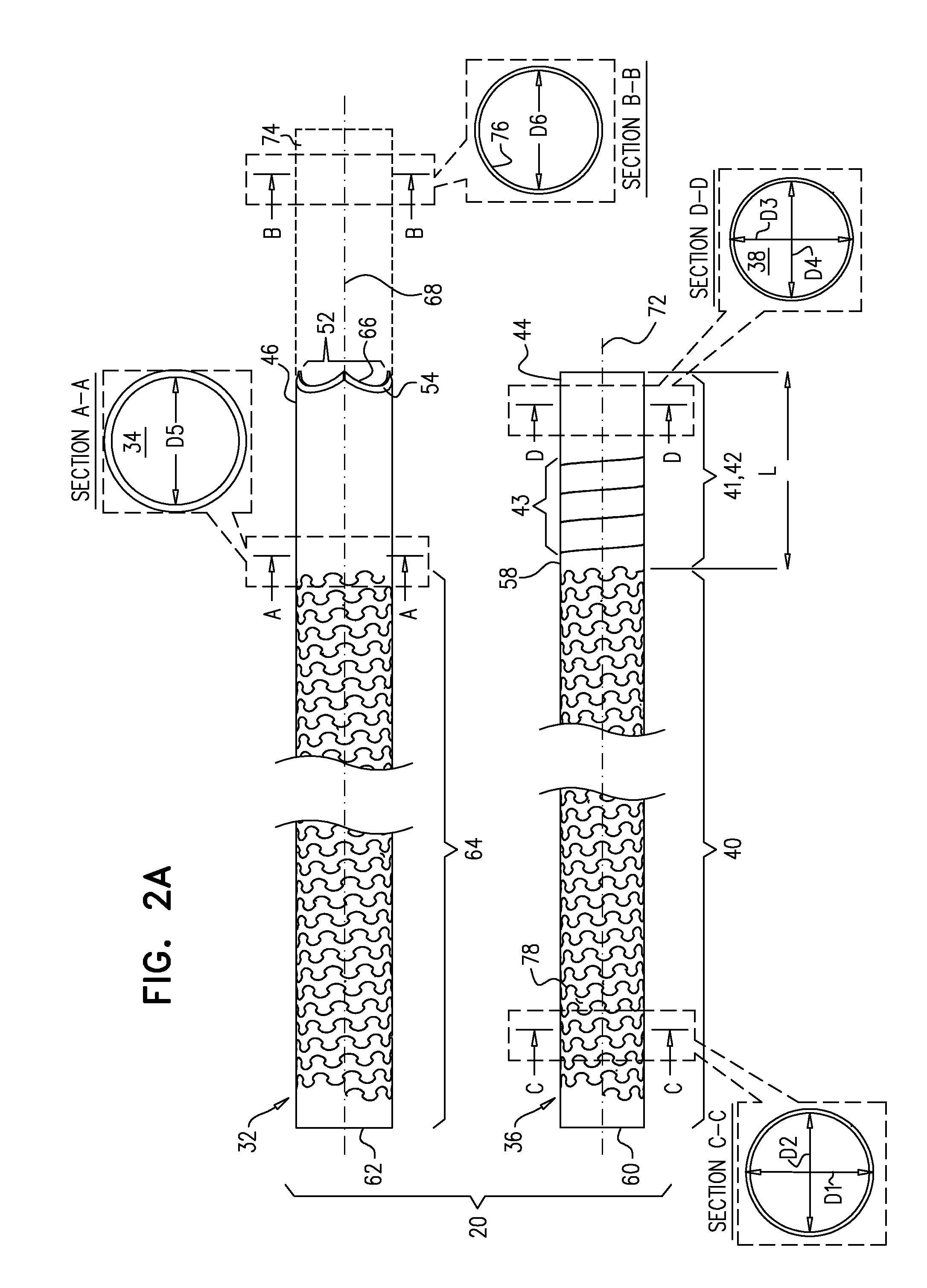
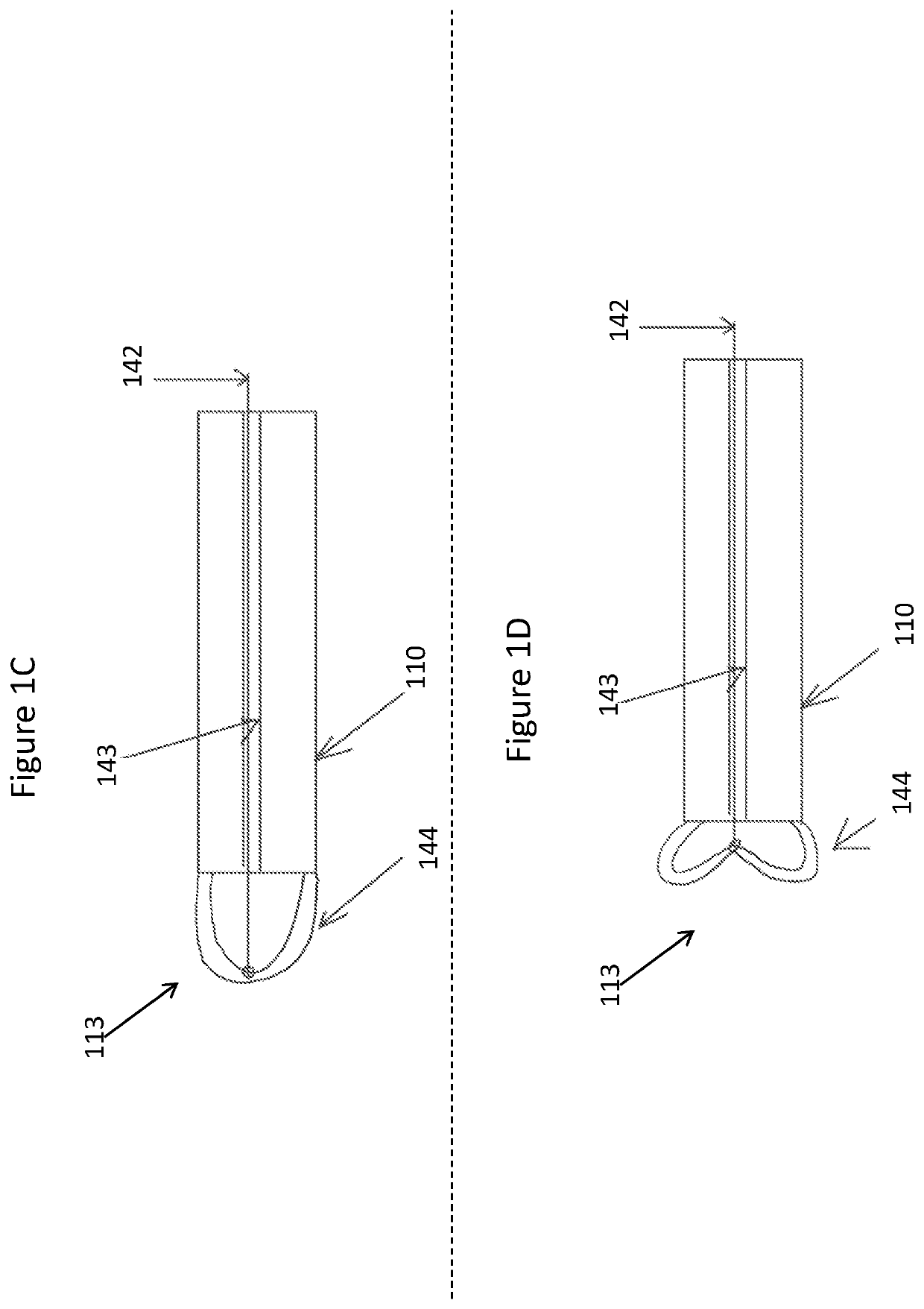
Lead extraction
InactiveUS20150374398A1Reduce the overall diameterReduce second diameterTransvascular endocardial electrodesExcision instrumentsDistal portionLead extraction
Apparatus for removing a lead from a lumen of a subject including a flexible control tube shaped to define a control-tube lumen; and a flexible grasping tube shaped to define a grasping-tube lumen. The grasping tube is disposed within the control-tube lumen and includes a torque-transfer non-distal portion; and a helically-cut distal portion, that is (a) fixed at a distal end thereof to a distal end of the control tube, and (b) rotatable at least at a proximal end thereof with respect to the control tube. The helically-cut distal portion is configured to grasp the lead within the grasping-tube lumen upon the proximal end of the helically-cut distal portion being rotated with respect to the control tube.
Owner:LEADR MEDICAL
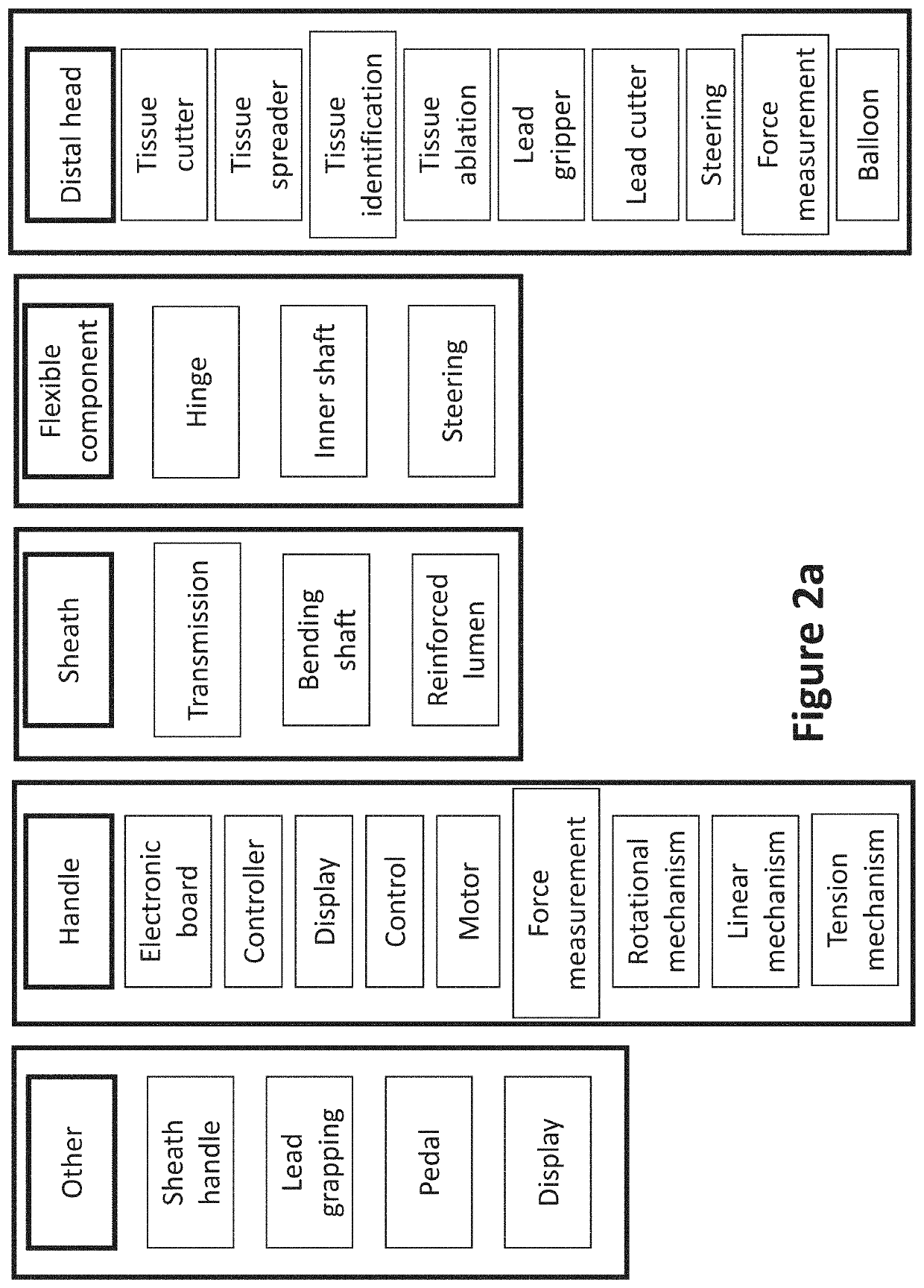
Cardiac lead extraction device
PendingUS20220047292A1Weakening rangeEffective penetrationTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical needlesLead extractionEngineering
The invention relates to a cardiac lead extraction system, comprising: a handle; an elongated body in communication with said handle; a bendable flexible portion in communication with said elongated body, said bendable flexible portion comprising a first lumen sized and shaped to fit over a cardiac lead; said bendable flexible portion being more flexible than said elongated body; an operational distal end in communication with said bendable flexible portion; where said bendable portion is configured to bend to a bending radius of less than 4 cm while keeping said first lumen open; and where said operational distal end comprises at least one lead extraction assistive tool, said operational distal end comprising a second lumen sized and shaped to fit over a cardiac lead, said second lumen being in communication with said first lumen, and said first lumen comprises an inner diameter of from about 1 mm to about 5 mm.
Owner:MDSG INNOVATION LTD
Lead extraction methods and apparatus
InactiveCN102348422ATransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical needlesLead extractionBiomedical engineering
According to one aspect, a device for assisting in removing an implanted lead is provided. The device comprises a body portion having a center adapted to accommodate the lead, a cutting component coupled to the body portion to assist in separating tissue from the lead, and at least one anchoring component disposed at least partially within the body portion, the at least one anchoring component capable of providing pressure on the lead that resists movement of at least part of the body portion along the lead at least in part by applying fluid pressure.
Owner:LEADEX CARDIAC
Efficient and directed nano-light emitting diode, and method for making same
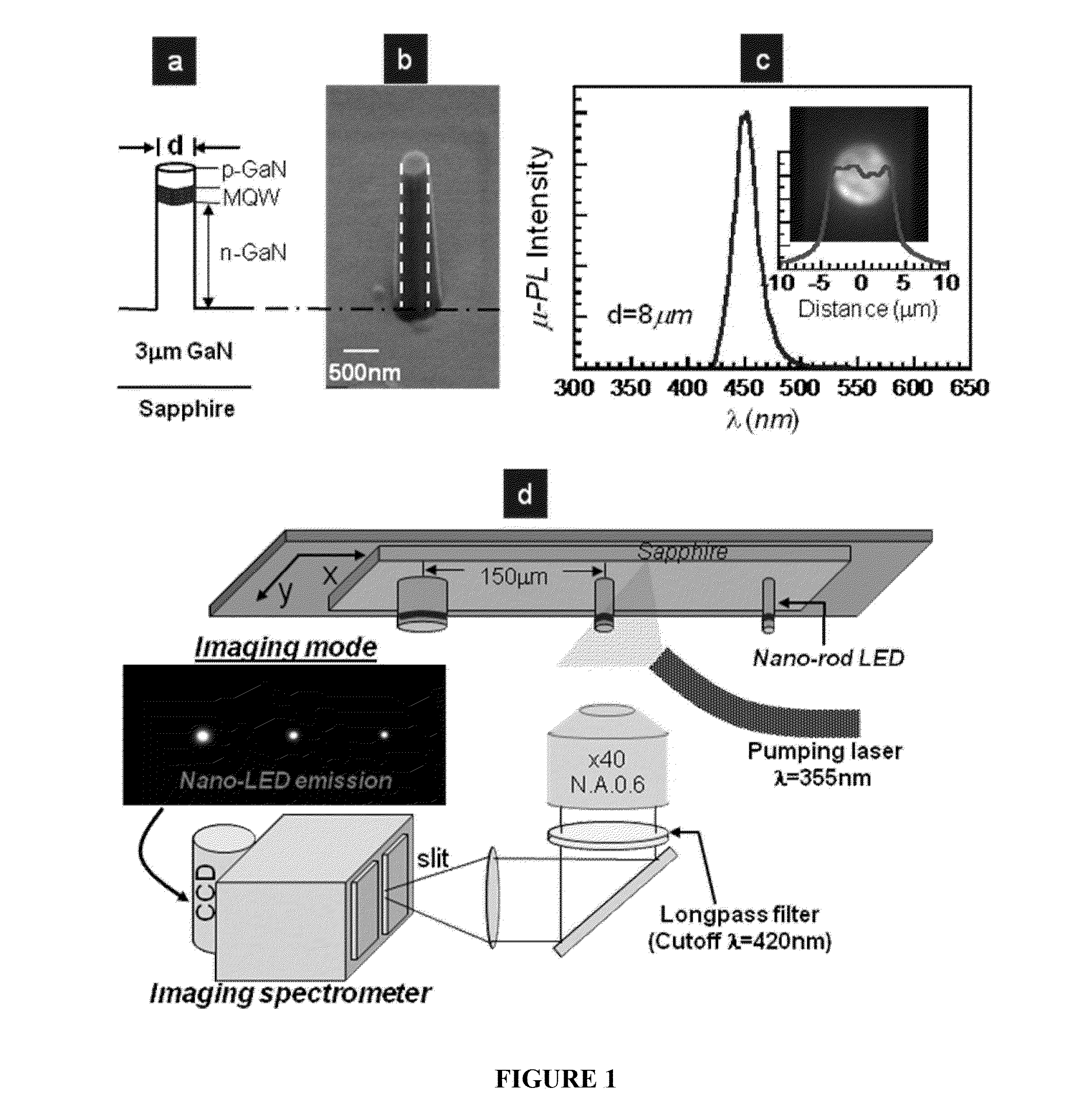
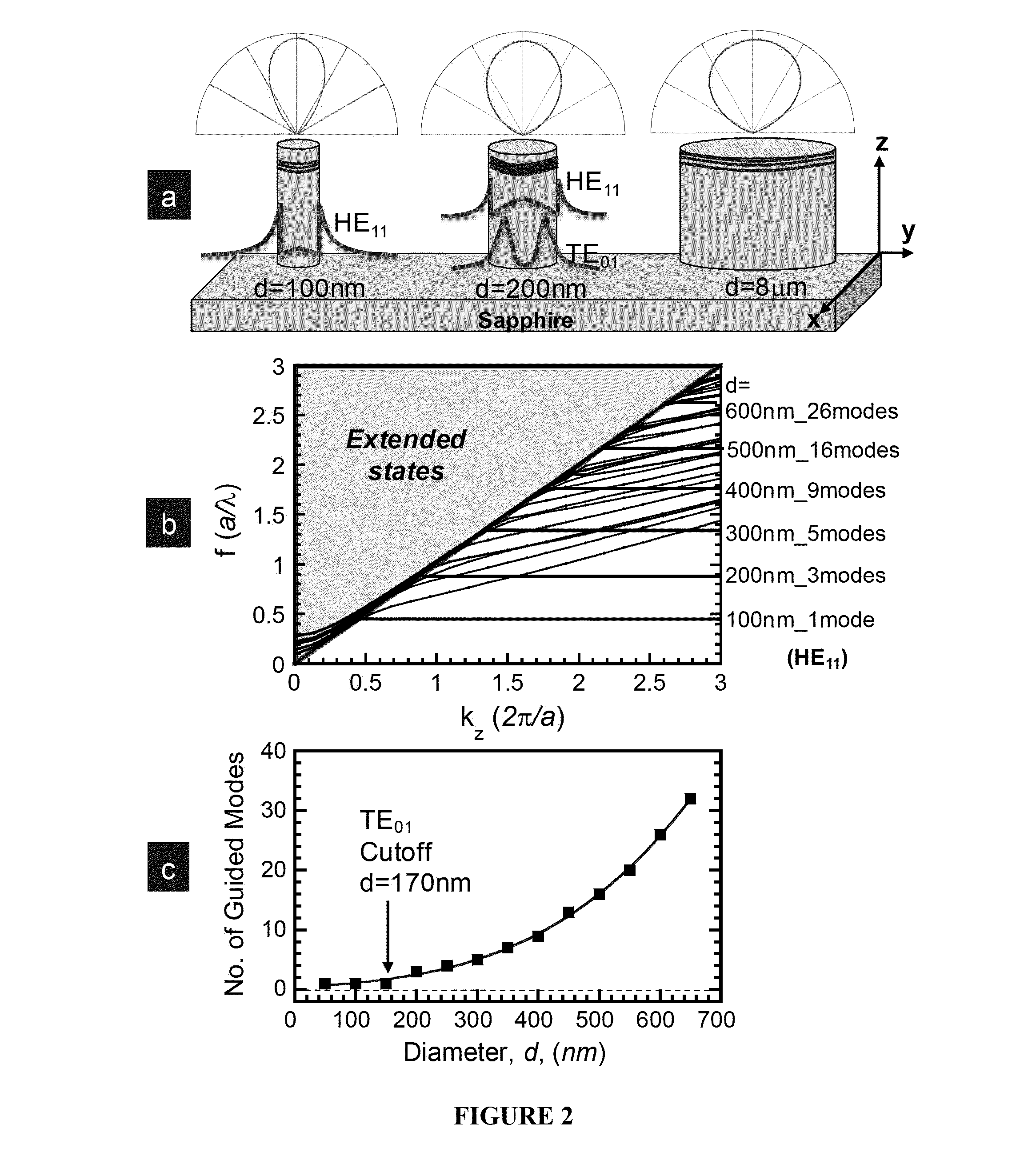
ActiveUS20130221323A1Improve light extractionNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellLead extraction
The invention relates to light-emitting devices, and related components, systems and methods. In one aspect, the present invention is related to light emitting diode (LED) light extraction efficiency. A non-limiting example, the application teaches a method for improving light emitting diode (LED) extraction efficiency, by providing a nano-rod light emitting diode; providing quantum wells; and reducing the size of said nano-rod LED laterally in the quantum-well plane (x and y), thereby improving LED extraction efficiency.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Method for recycling lead-containing waste acid
InactiveCN109626632AHigh recycling valueEfficient separationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPhosphateLead extraction
The invention discloses a method for recycling lead-containing waste acid. The lead-containing waste acid processed by the method is waste hydrochloric acid and includes iron ions and lead ions. The method comprises the following steps of trivalent iron reduction, lead extraction and nitric acid reverse extraction of lead. According to the method, the trivalent iron is reduced into divalent ferricchloride, then, a mixture of di phosphate and dinonylnaphthalene sulfonic acid is adopted as an extracting agent for lead extraction, nitric acid with the specific concentration is adopted as a reverse extraction agent, lead and iron are efficiently and completely separated, the content of lead ions of the recycled ferric chloride solution is lower than 8 ppm, the related standard requirement forthe ferric chloride purifying agent is met, the iron ion recycling rate is also 99% or above, the content of lead ions in the organic extracting agent obtained after reverse extraction is lower than30 ppm, the method is recyclable, the recycling cost is saved, the comprehensive recycling value of the lead-containing waste acid is increased, and the method has the excellent economy and environment-friendliness.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WUJIN YOUBANG WATER PURIFICATION MATERIALS
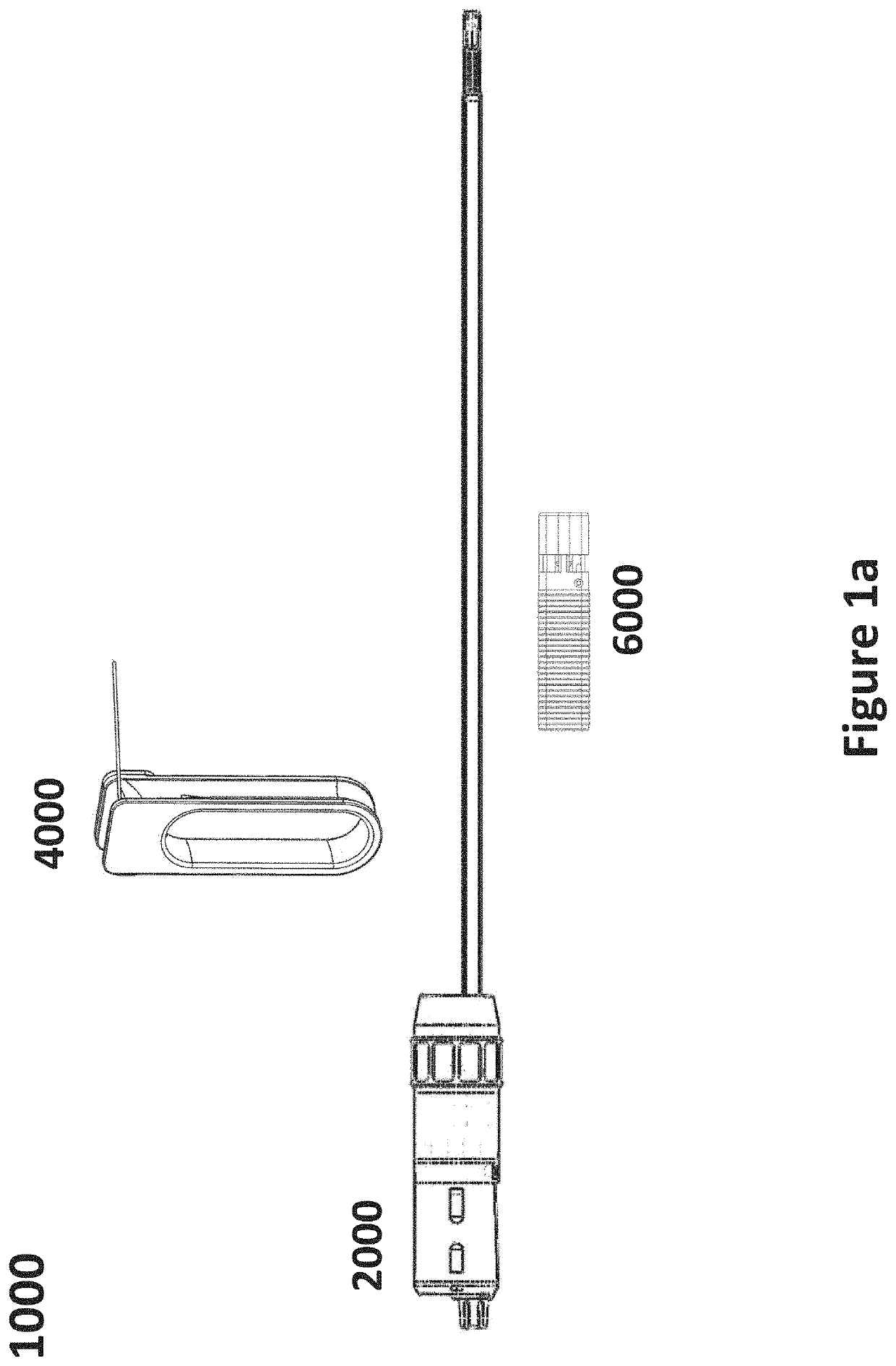
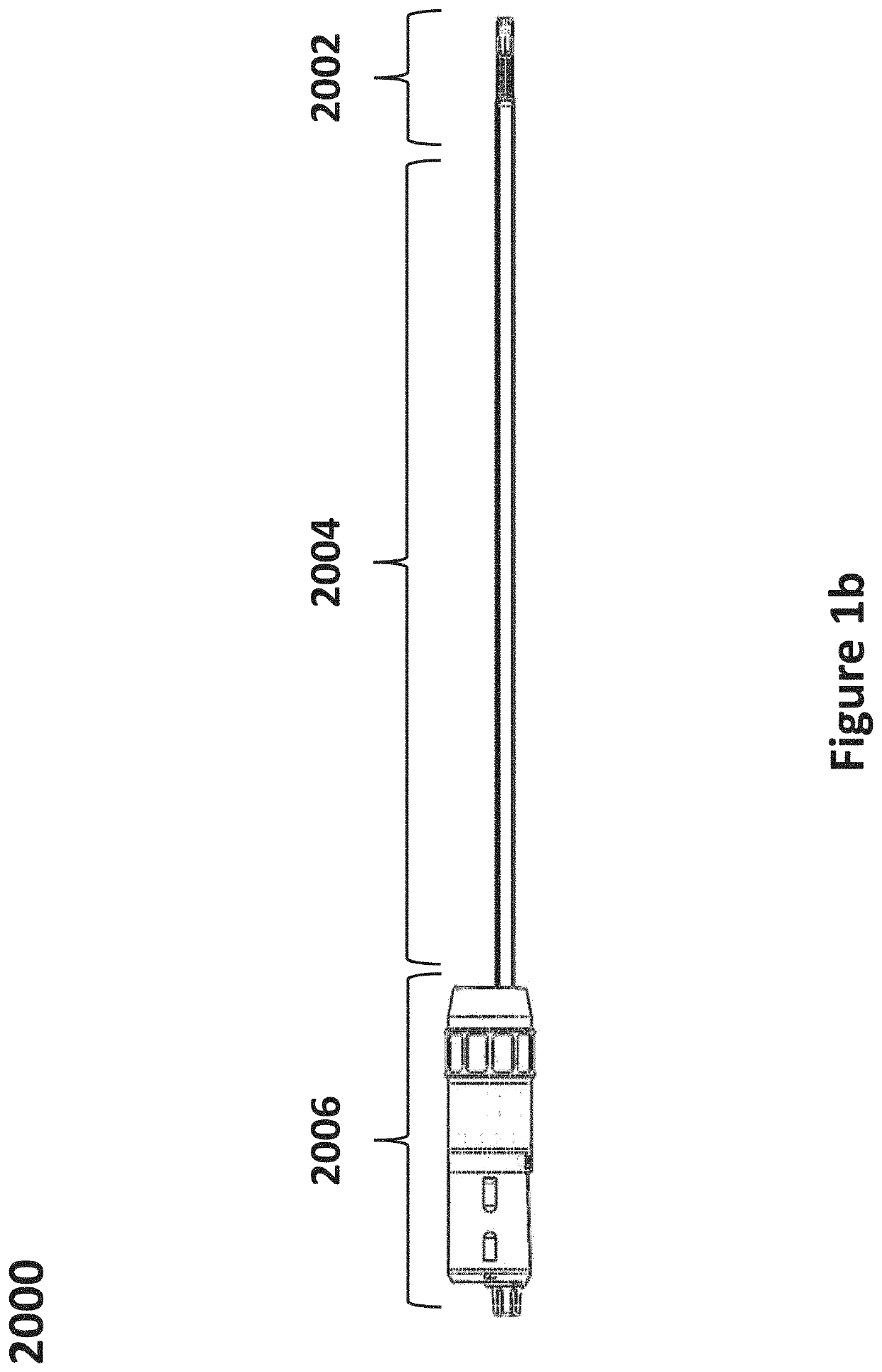
System and method for lead extraction
ActiveUS20210186539A1Overcome deficienciesTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnosticsAnatomyLead extraction
Owner:XTRAC O S LTD
Method for extracting metal lead and coproducing cement raw material from high-lead-content glass
ActiveCN103882233AAvoid generatingIncrease consumptionCement productionProcess efficiency improvementLead extractionIon
The invention discloses a method for extracting metal lead and coproducing a cement raw material from high-lead-content glass. The method comprises the following steps: adding high-lead-content glass into a 4-15 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, adding an impurity remover so that the mole ratio of the Si ions in the high-lead-content glass to the metal ions in the impurity remover is 1:(0.9-3.0), and reacting at 120-300 DEG C for 5-20 hours; after the reaction is finished, filtering, and separating to obtain a solid residue and a filtrate; and by using stainless steel as the cathode and anode materials, electrolyzing at controlled voltage of 1.4-1.7V to obtain the metal lead with the purity of higher than 90% at the cathode. The method overcomes the defects of complex technique, high energy consumption and high tendency to generating secondary pollution in the existing lead extraction technique. The method has the advantages of high waste consumption, simple technical process, high lead extraction rate and the like, can coproduce the cement raw material, changes wastes into valuable substances, and can easily implement large-scale industrial application.
Owner:湖南良田水泥有限公司
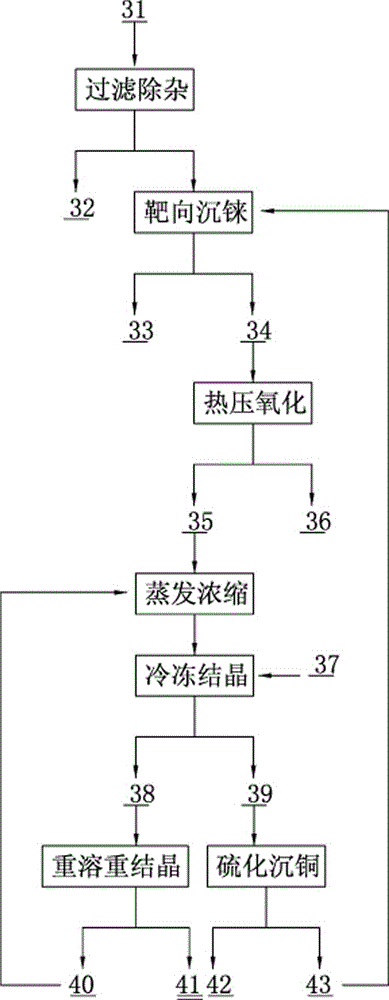
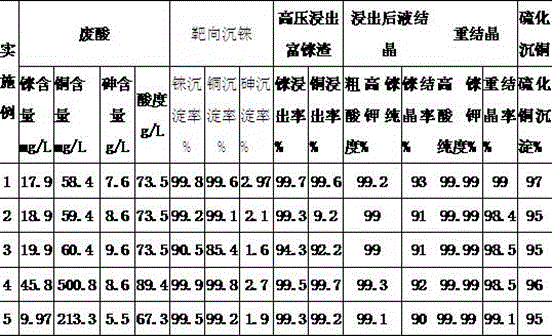
Method for rapidly recovering rhenium, copper and lead from copper smelting waste acid and device for implementing method
ActiveCN105543491AReduce processingImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceAnti-gravity
The invention discloses a method for rapidly recovering rhenium, copper and lead from copper smelting waste acid and a device for implementing the method. According to the method, the copper smelting waste acid is subjected to lead removing through filtering, lead residues with the lead content higher than 55% are obtained and taken as lead extraction raw materials, the lead extraction raw materials are subjected to targeted rhenium precipitation, rhenium-rich residues are obtained and are subjected to hot-pressing oxidizing leaching, a rhenium-rich leaching agent is obtained, the rhenium-rich leaching agent after evaporation and concentration is subjected to KCl rhenium precipitation and recrystallization, potassium perrhenate is prepared, and a liquid obtained after rhenium precipitation is vulcanized for copper deposition. The device comprises a rhenium and copper precipitant storage tank, a precipitation tank, a flocculating agent storage tank, a flocculation reaction tank, a reaction kettle, an evaporation-crystallization device, a centrifugal separator, a waste acid anti-gravity-osmosis filter, a rhenium-rich copper residue anti-gravity-osmosis filter, a filter press, a rhenium and copper precipitation tank steam heating system, a copper precipitation tank steam heating system and a slurry pump. The method and the device have the characteristics of low investment, rapid and short procedures, simple and efficient operation, and high recovery rate, and are clean and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Leaching method for recovering lead from lead oxide ore and leaching agent used in leaching method
InactiveCN104388674AEliminate pollutionEasy to operatePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementOrganic acidChemical industry
The invention belongs to the technical field of mineral metallurgy and particularly relates to a leaching method for recovering lead from lead oxide ore and a leaching agent used in the leaching method. The leaching method comprises the following steps: by mainly using organic acid trichloroacetic acid as the leaching agent, leaching lead from the lead oxide ore at the leaching temperature of 20 DEG C-60 DEG C, wherein the ore having a particle size being less than 60mu m accounts for 70wt%-90wt% and the liquid-solid mass ratio of leaching agent trichloroacetic acid to lead oxide ore powder is (5-20) to 1; and fully stirring for 25 minutes-65 minutes to obtain a lead-containing solution suitable for next lead extraction and electrodeposition treatment. The leaching rate of the used leaching agent is high, the trichloroacetic acid waste generated in pharmaceutical and chemical industries can be utilized; in addition, under the condition of ensuring a high leaching rate of lead, the leaching method does not need high-temperature pressurizing device and is simple to operate and low in process cost.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cardiac lead extraction device
PendingUS20200352552A1Weakening rangeEffective penetrationTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnosticsLead extractionBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a cardiac lead extraction device, comprising: a handle; an elongated body having a first proximal end, a first distal end, and a first lumen extending from said first proximal end toward said first distal end, said lumen sized and shaped to fit over a cardiac lead; a controllable bendable flexible portion more flexible that said elongated body and having a second proximal end, a second distal end and a second lumen extending from said second proximal end toward said second distal end, said lumen sized and shaped to fit over a cardiac lead; said second proximal end interconnected to said first distal end; said second distal end interconnected to an operational distal end; wherein said operational distal end comprises at least one lead extraction assistive tool, said lead extraction helping tool is activated by a motor located at said handle or proximally to said handle.
Owner:MDSG INNOVATION LTD
Process for extracting tea saponin from tea seed cakes or meal
The invention relates to a process for extracting tea saponin from tea seed cakes or meal after oil frying by applying an industrial production device. The process comprises the following steps: crushing the tea seed cakes or the meal (leading the particle size to be 1-3mm), then sending into a steaming and stir-frying cauldron, drying (preventing the water content from exceeding 7%), then leading the material to enter into a material storage cylinder, using a screw conveyor to send the material into a rotocel extractor, and adding a solvent for extraction; carrying out residue-liquid separation (the meal residue can be used as a feed or a fertilizer) after double extraction, leading extraction solution to enter into a long pipe evaporator, removing part of water by double evaporation, and recycling the solvent (which can be recycled); and concentrating the extraction solution via a vacuum concentration tank, then crystallizing and drying, and obtaining a fine saponin finished productfor packaging and leaving a factory. A product produced by the process contains 81.5% of active matters, and the pH value is 5.9. Compared with other methods, the process has the advantages of high product purity, light color, high production rate (14%), energy conservation, low consumption, no pollution and environmental protection, and is easy for operation and the like.
Owner:ANHUI YINGSHANHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH
Lead extraction methods and apparatus
Owner:LEADEX CARDIAC
Leaching method for recovering lead from lead oxide ores, and its leaching agent
InactiveCN104404248AEasy to operateReduce processing costsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementChemical industryGranularity
The invention belongs to the technical field of mineral metallurgy, and concretely discloses a leaching method for recovering lead from lead oxide ores, and its leaching agent. The method is characterized in that 5-sulfosalicylic acid is used as a leaching agent to leach lead from the lead oxide ores with the lead level of 14-75%, the leaching temperature is 20-60DEG C, lead oxide ores with the granularity of below 65[mu]m account for 70-96% of the weight of the lead oxide ores, the concentration of 5-sulfosalicylic acid is 0.1-0.5mol / L, the 5-sulfosalicylic acid leaching agent is mixed with lead oxide ore powder according to a liquid / solid mass ratio of 5-20:1, and the obtained mixture is fully stirred for 20-60min to obtain a lead-containing solution suitable for later lead extraction and electrodeposition treatment. The leaching agent has a high leaching rate and is simple to prepare, and the method uses 5-sulfosalicylic acid wastes generated in the pharmacy and chemical industry; and the leaching method guarantees the high lead leaching rate without high temperature or a pressurizing device, and also has the advantages of simple operation and low process cost.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com