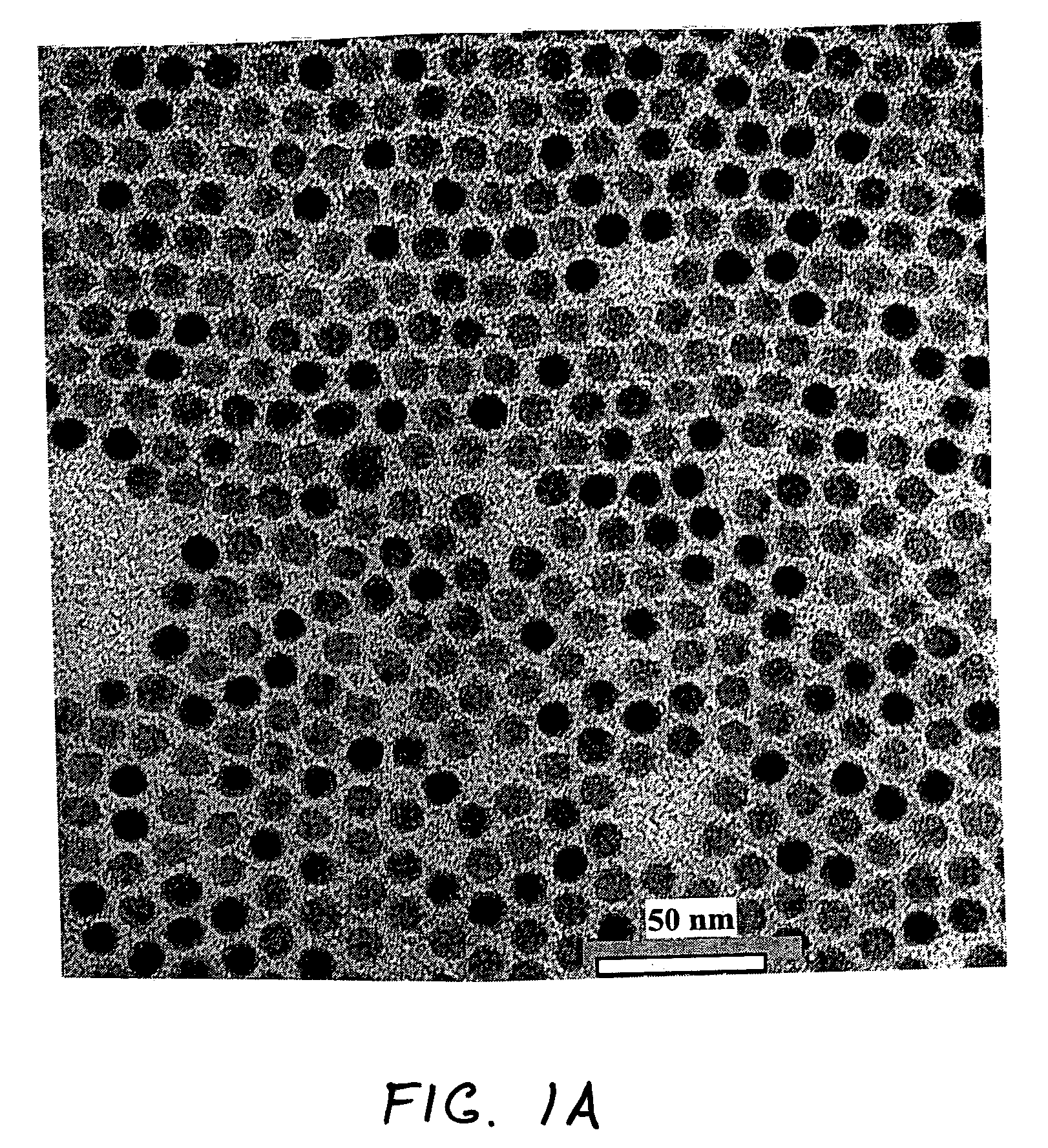
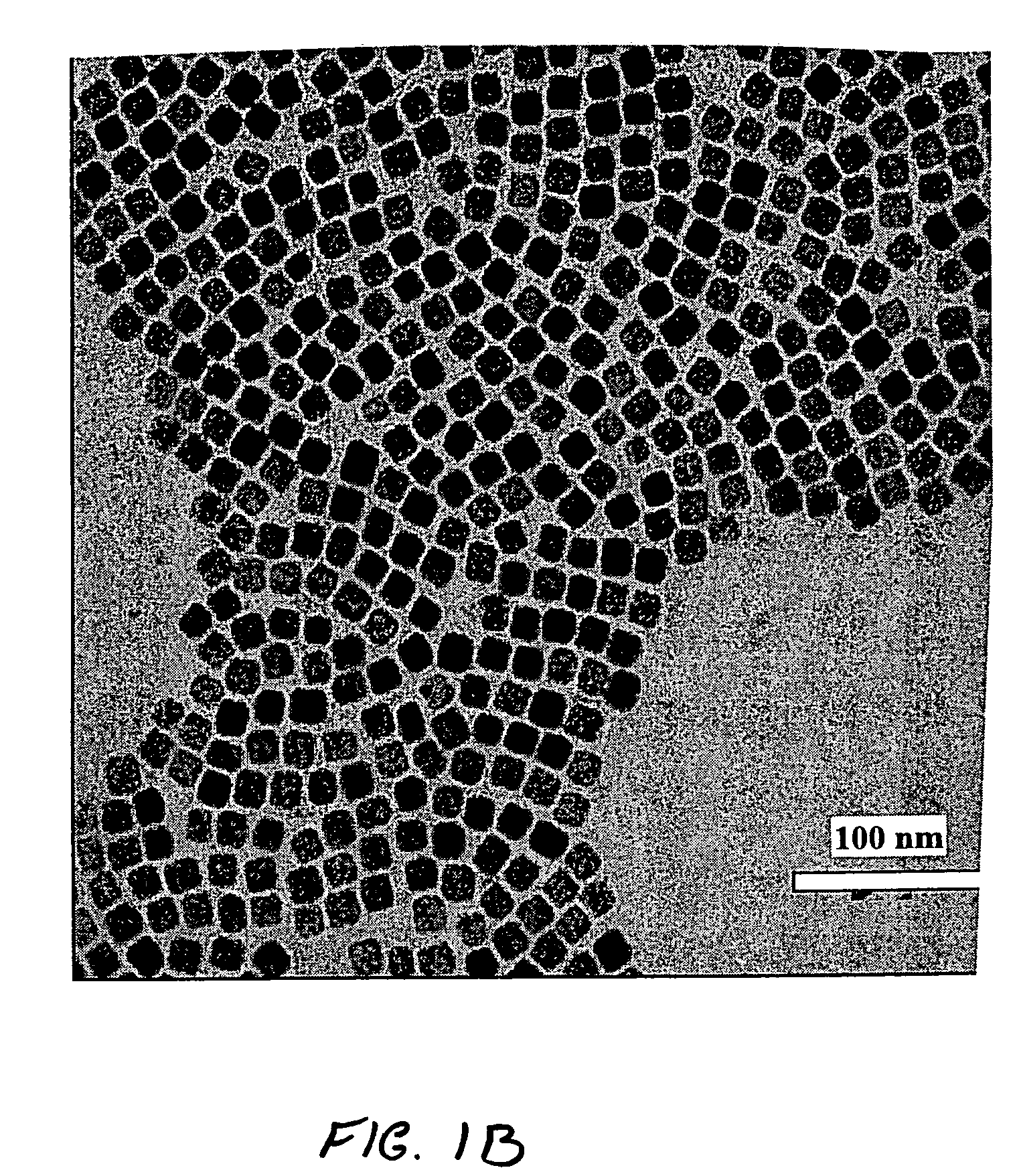
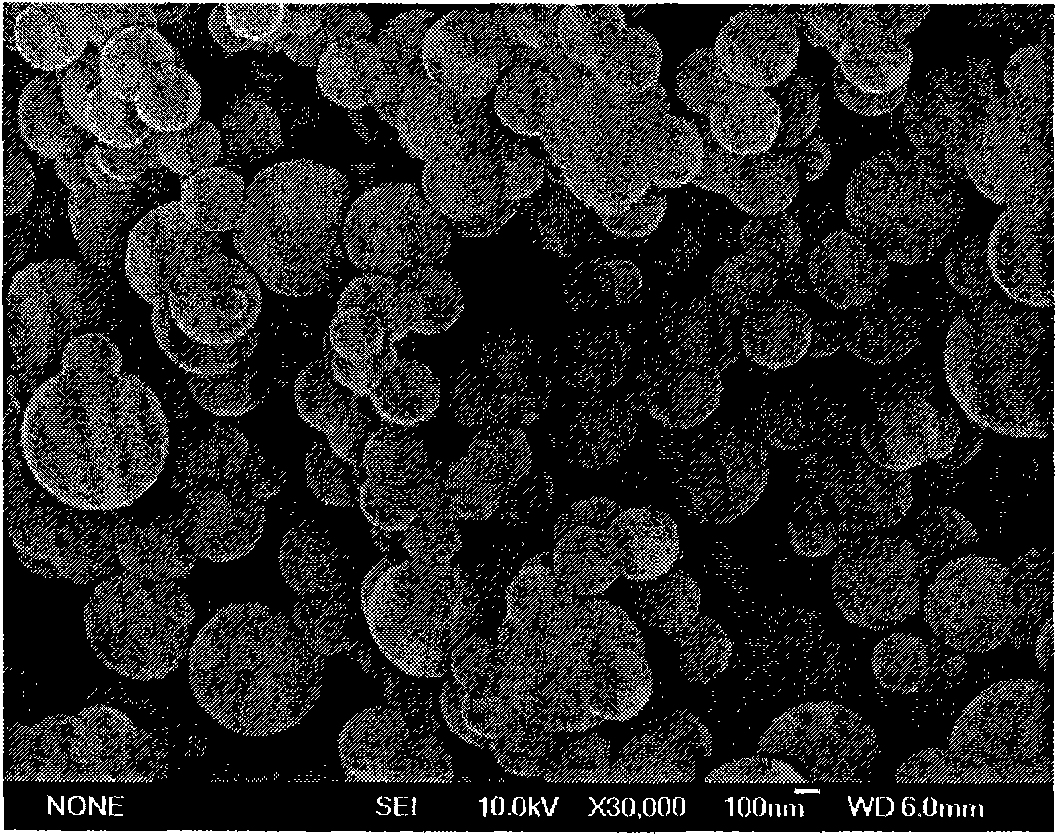
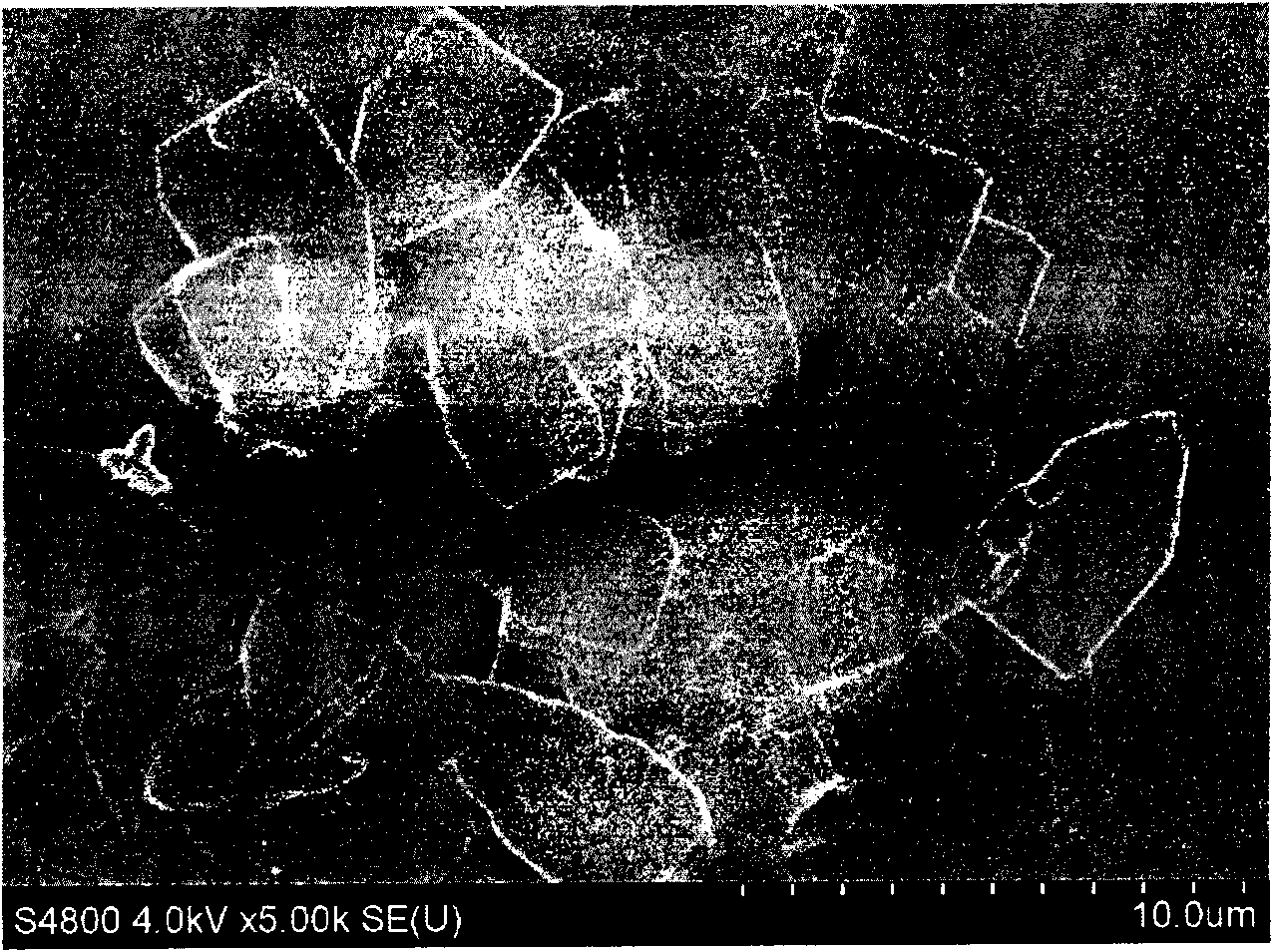
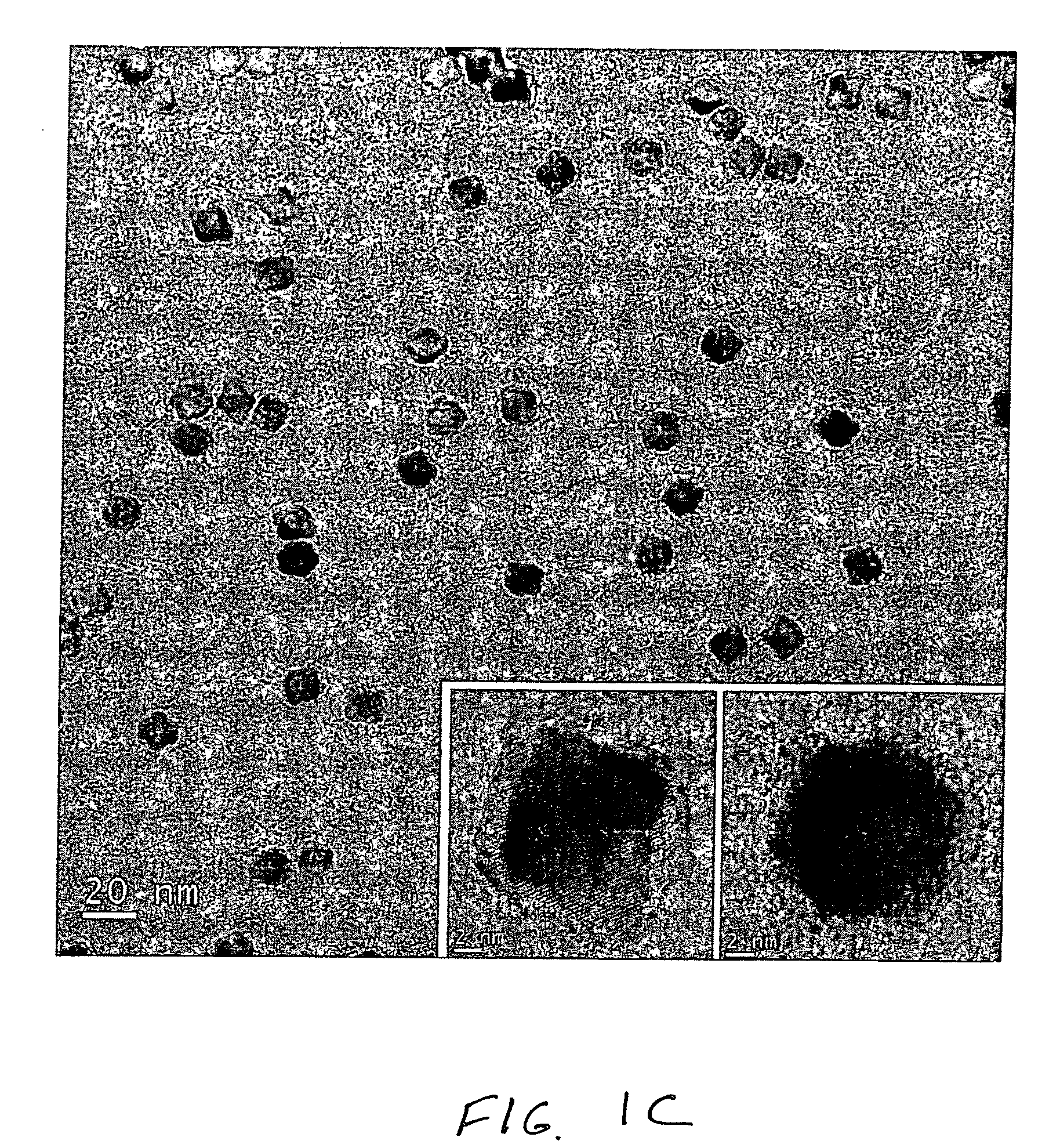
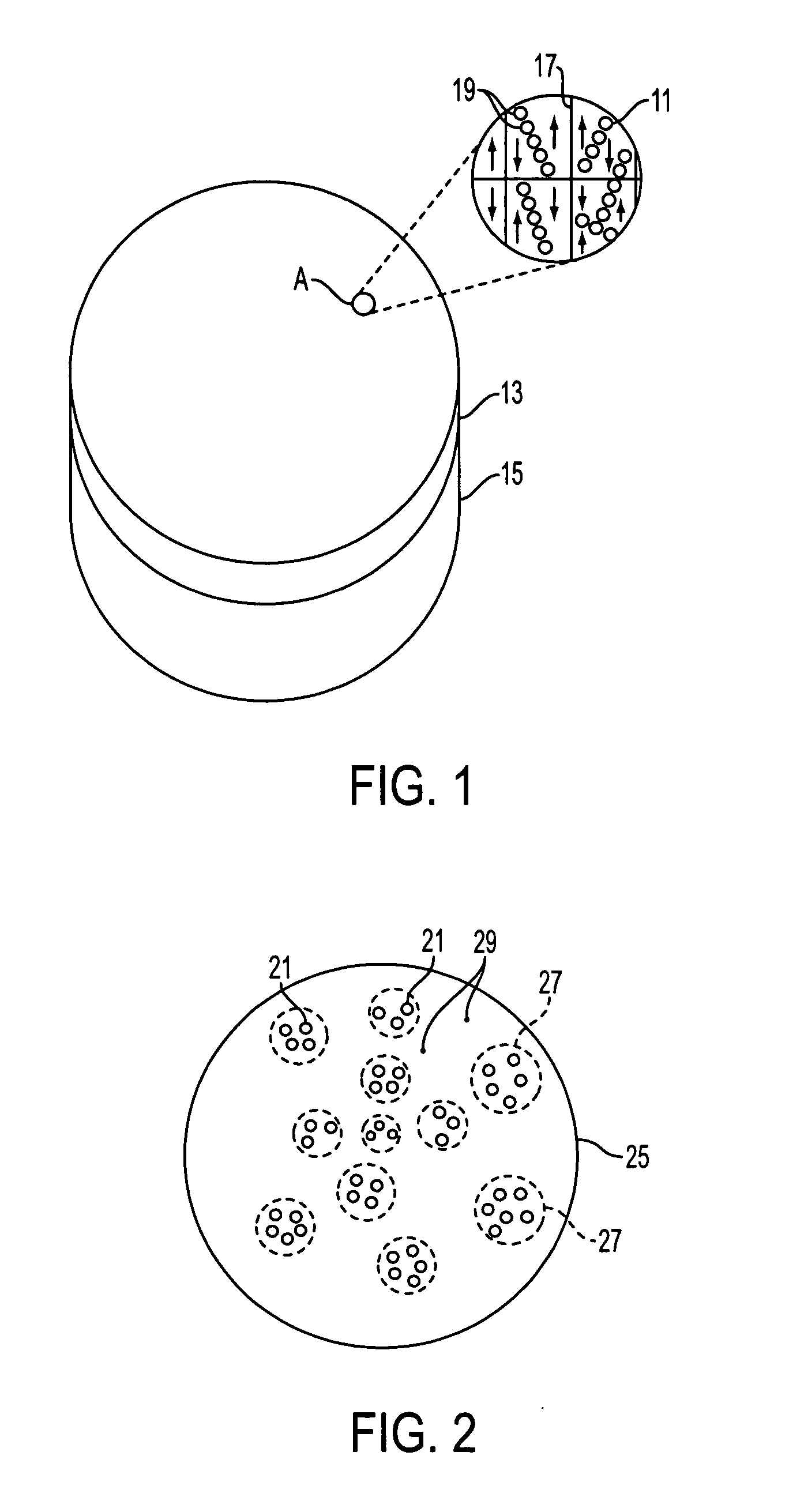
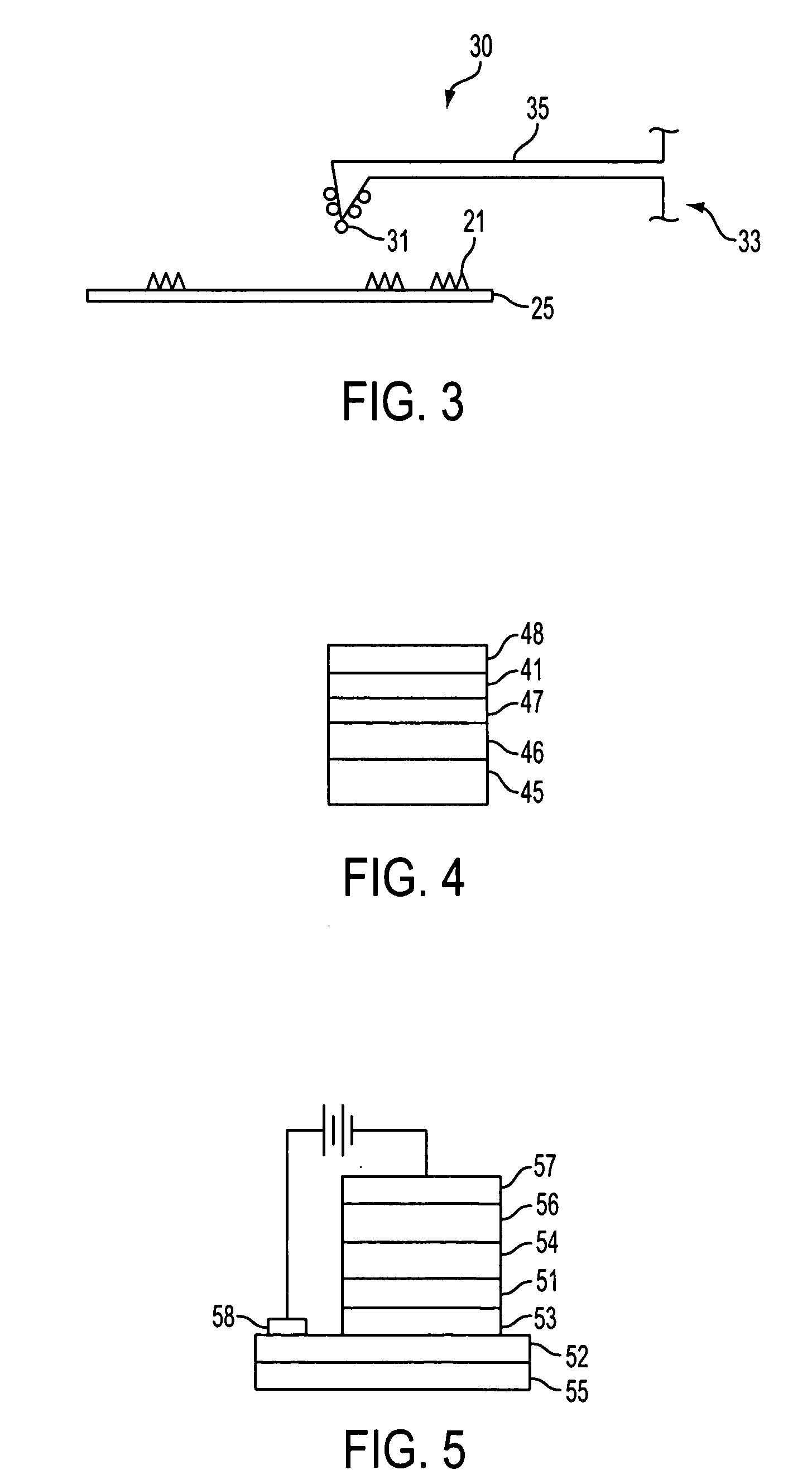
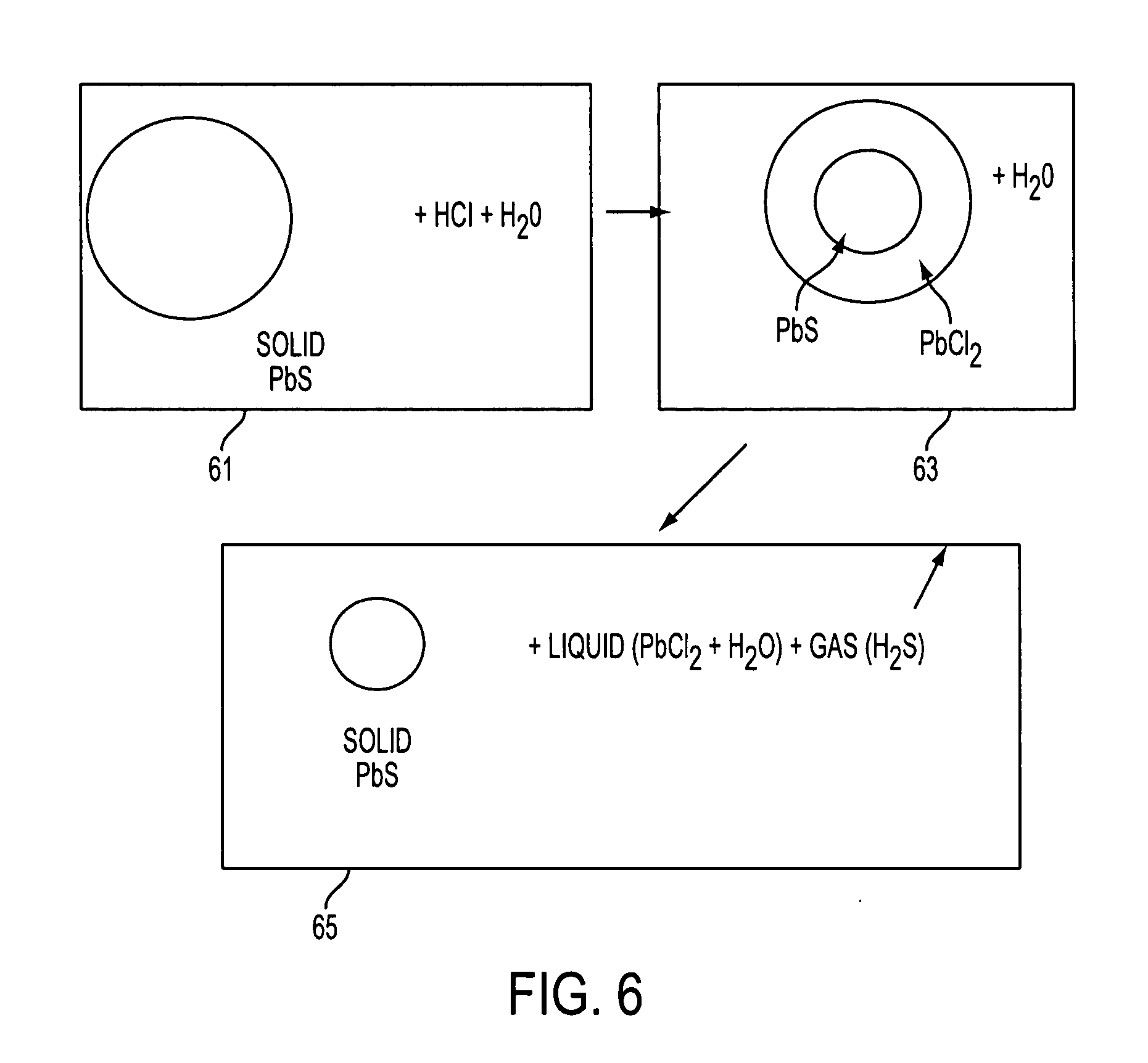
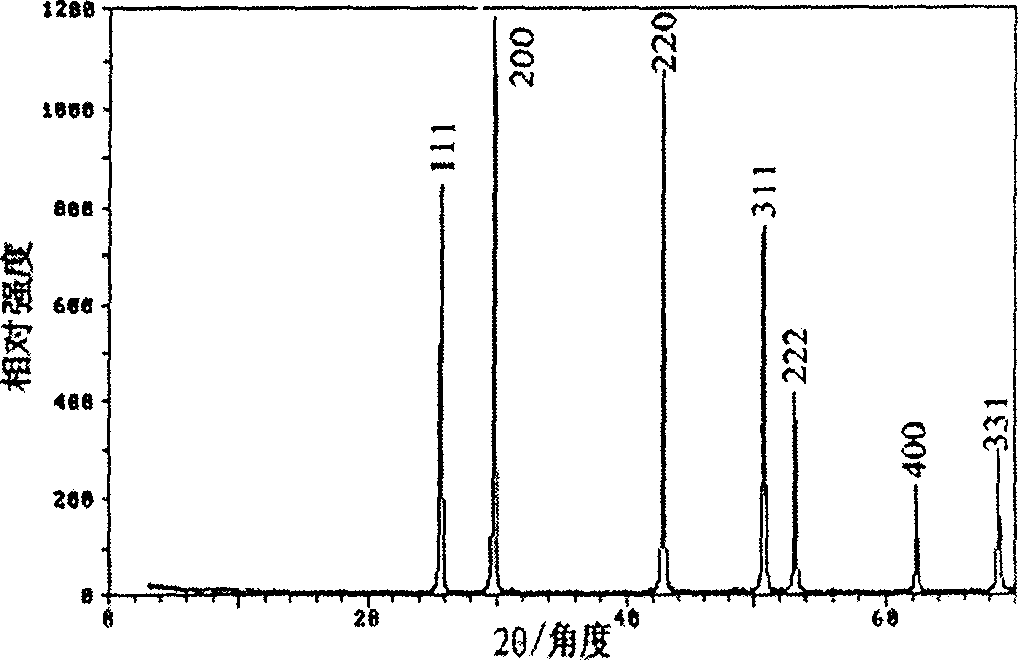
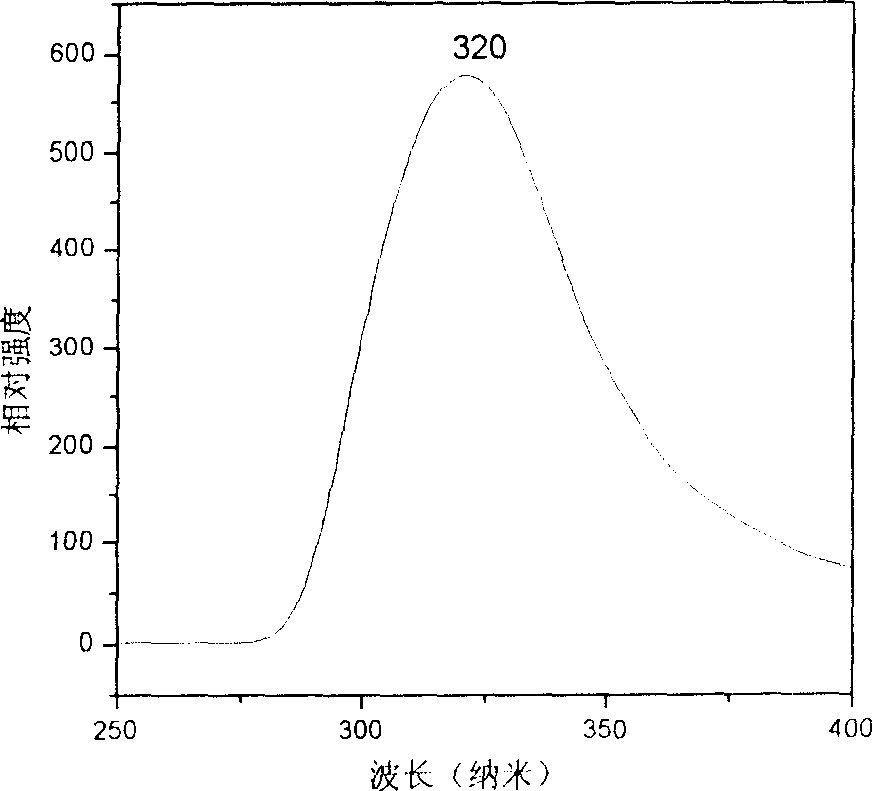
Patents
Literature
232results about "Lead sulfides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
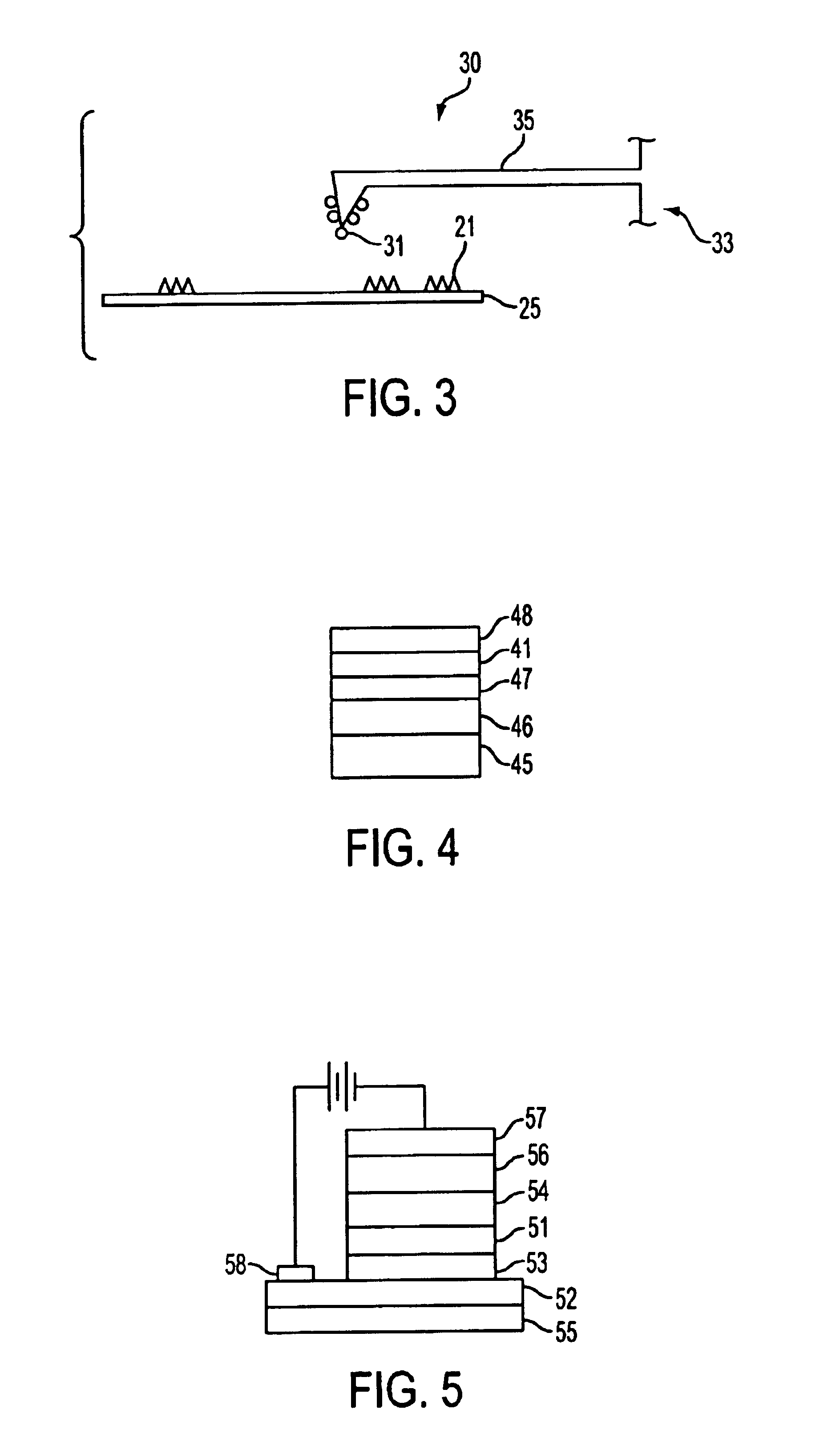
Inorganic Bulk Multijunction Materials and Processes for Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20110220874A1Material nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAlloySemiconductor nanocrystals
A nanostructured composite material comprising semiconductor nanocrystals in a crystalline semiconductor matrix. Suitable nanocrystals include silicon, germanium, and silicon-germanium alloys, and lead salts such as PbS, PbSe, and PbTe. Suitable crystalline semiconductor matrix materials include Si and silicon-germanium alloys. A process for making the nanostructured composite materials. Devices comprising nanostructured composite materials.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
III-V semiconductor nanocrystal complexes and methods of making same
ActiveUS20060001119A1High Luminescence Quantum YieldMaterial nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsLuminescence quantum yieldSemiconductor nanocrystals
A semiconductor nanocrystal complex that is stable and has high luminescent quantum yield. The semiconductor nanocrystal complex has a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a III-V semiconductor nanocrystal material. A method of making a semiconductor nanocrystal complex is also provided. The method includes synthesizing a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a III-V semiconductor nanocrystal material, and forming a metal layer on the semiconductor nanocrystal core after synthesis of the semiconductor nanocrystal core.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Passivated nanoparticles, method of fabrication thereof, and devices incorporating nanoparticles
A plurality of semiconductor nanoparticles having an elementally passivated surface are provided. These nanoparticles are capable of being suspended in water without substantial agglomeration and substantial precipitation on container surfaces for at least 30 days. The method of making the semiconductor nanoparticles includes reacting at least a first reactant and a second reactant in a solution to form the semiconductor nanoparticles in the solution. A first reactant provides a passivating element which binds to dangling bonds on a surface of the nanoparticles to passivate the surface of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticle size can be tuned by etching the nanoparticles located in the solution to a desired size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Semiconductor nanocrystal complexes and methods of making same
ActiveUS20060014040A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsLattice mismatchSemiconductor nanocrystals
A semiconductor nanocrystal complex including a metal layer formed on the outer surface of a semiconductor nanocrystal core after synthesis of the semiconductor nanocrystal core and a method for preparing a nanocrystal complex comprising forming a metal layer on a semiconductor nanocrystal core after synthesis of the semiconductor nanocrystal core. The metal layer may passivate the surface of the semiconductor nanocrystal core and protect the semiconductor nanocrystal core from the effects of oxidation. Also provided is a semiconductor nanocrystal complex with a shell grown onto the metal layer formed on the semiconductor nanocrystal core. In this embodiment, the metal layer may prevent lattice mismatch between the semiconductor shell and the semiconductor nanocrystal core.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
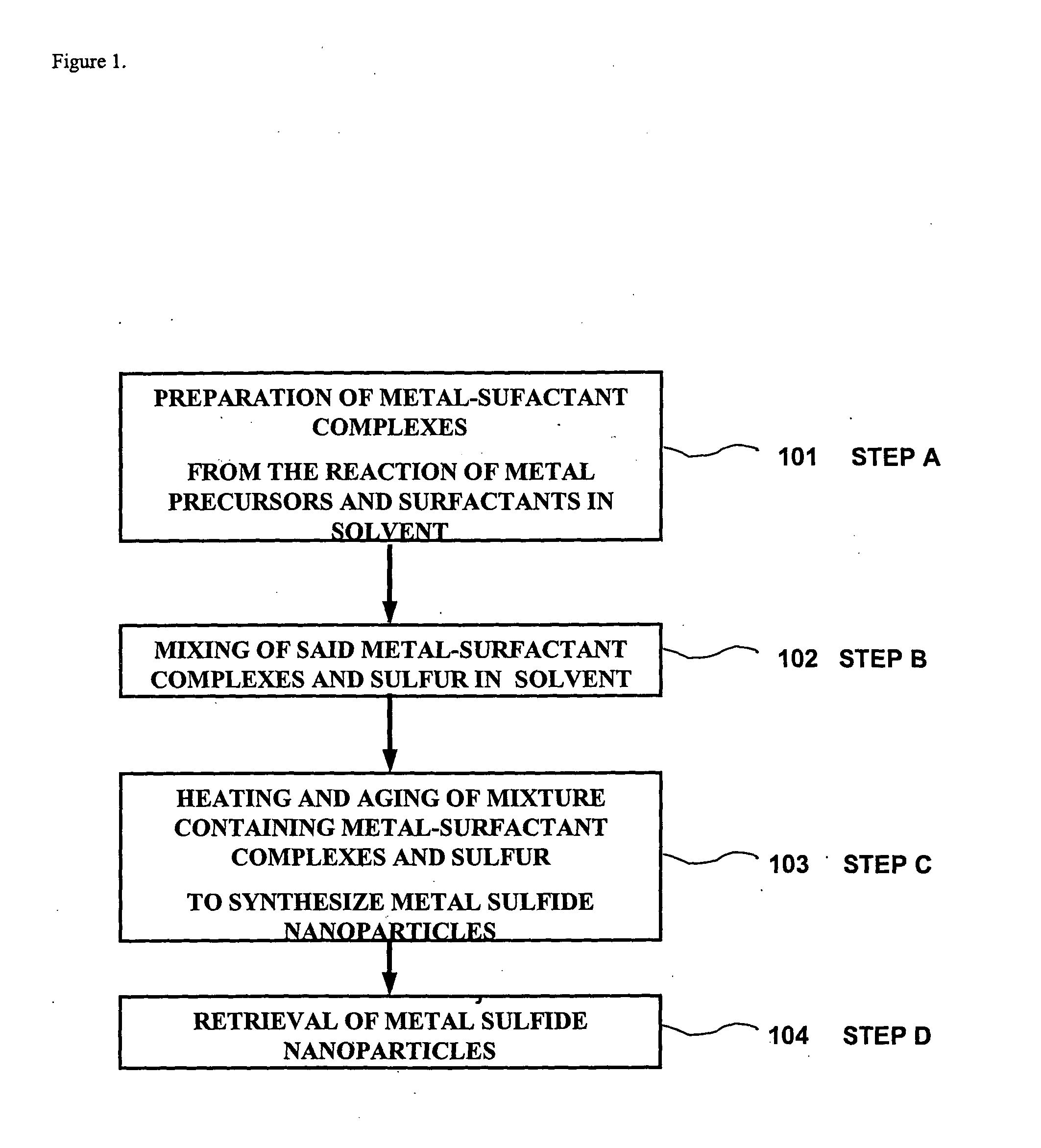
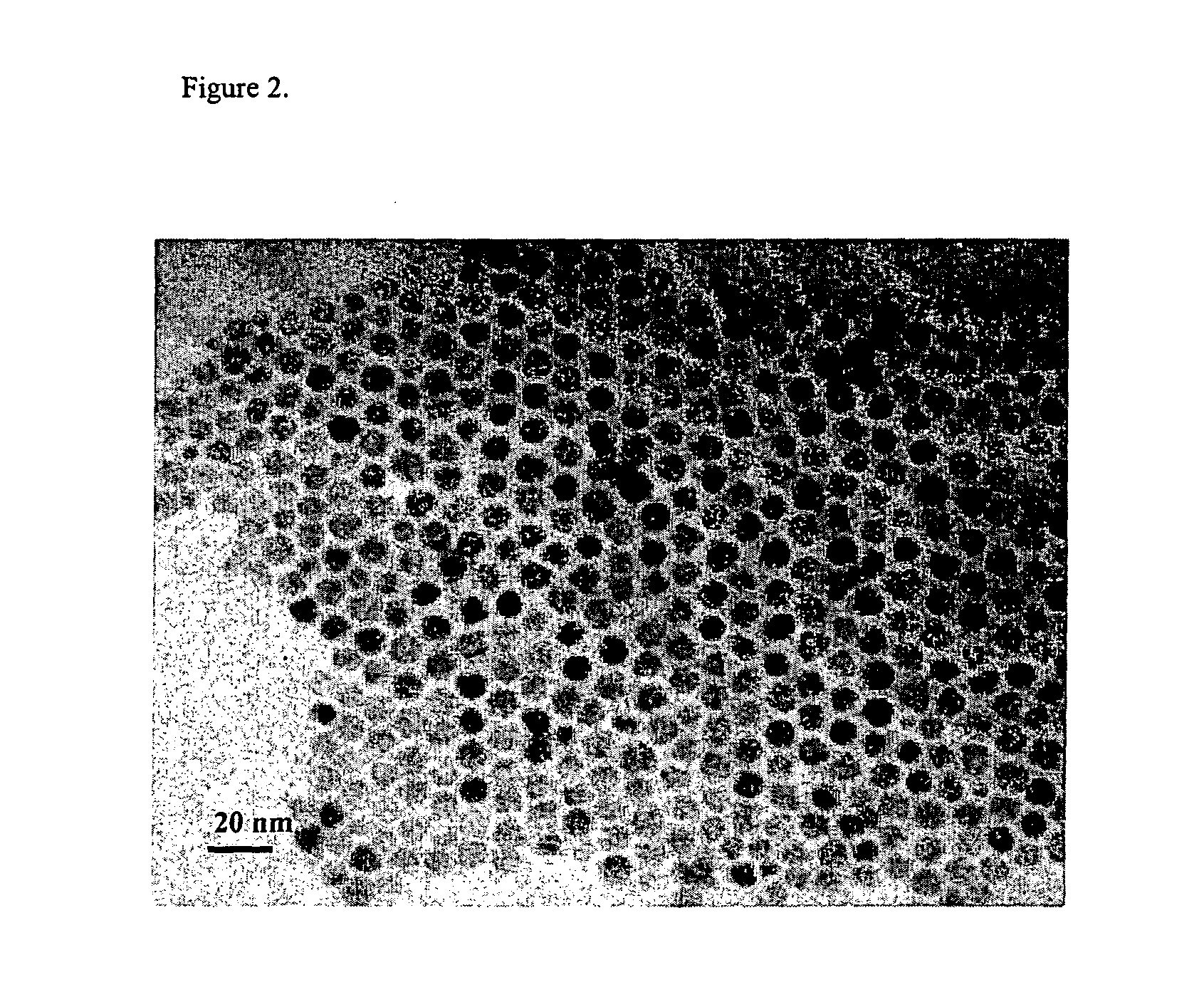
Method for synthesizing nanoparticles of metal sulfides
A synthetic method of fabricating highly crystalline and uniform nanoparticles of metal sulfides, doped metal sulfides, and multi-metallic sulfides disclosed, using no-toxic and inexpensive reagents. A typical synthetic method comprises the steps of, synthesis of metal-surfactant complexes from the reaction of metal precursors and surfactant, addition of sulfur reagent to the solution containing said metal-surfactant complexes followed by heating to high temperature, aging at that temperature to produce metal sulfide nanoparticles and completing the formation of synthesis of nanoparticles metal sulfides and multi-metallic sulfides by adding a poor solvent followed by centrifuging.
Owner:SEOUL NATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Synthesis of nanoparticles by an emulsion-gas contacting process
ActiveUS20050006800A1Easy to controlEasily scaled-upPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyEmulsionGas phase
The present invention is directed to a process for synthesizing nanoparticles. This process involves providing a stable emulsion containing a plurality of droplets suspended in a continuous phase. The droplets, which are encapsulated by an interfacially-active material, contain a first reactant dissolved in a dispersed phase. The process also involves contacting a gas phase containing a second reactant diluted in a carrier gas with the stable emulsion under conditions effective to permit the first reactant and second reactant to react and form nanoparticles. The present invention further relates to nanoparticle-loaded emulsions and their uses in formulations for various purposes.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
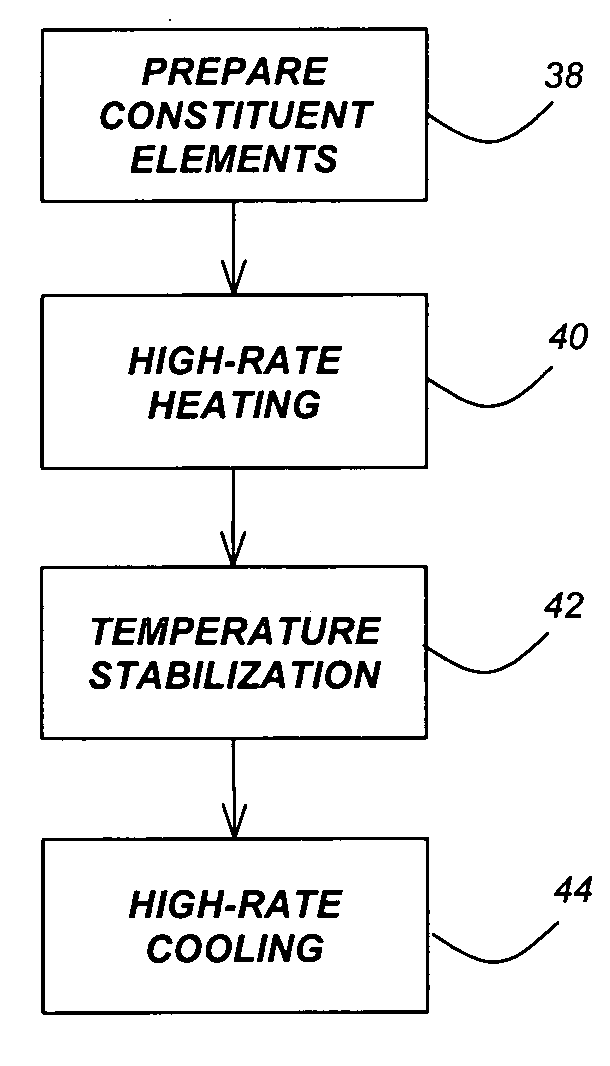
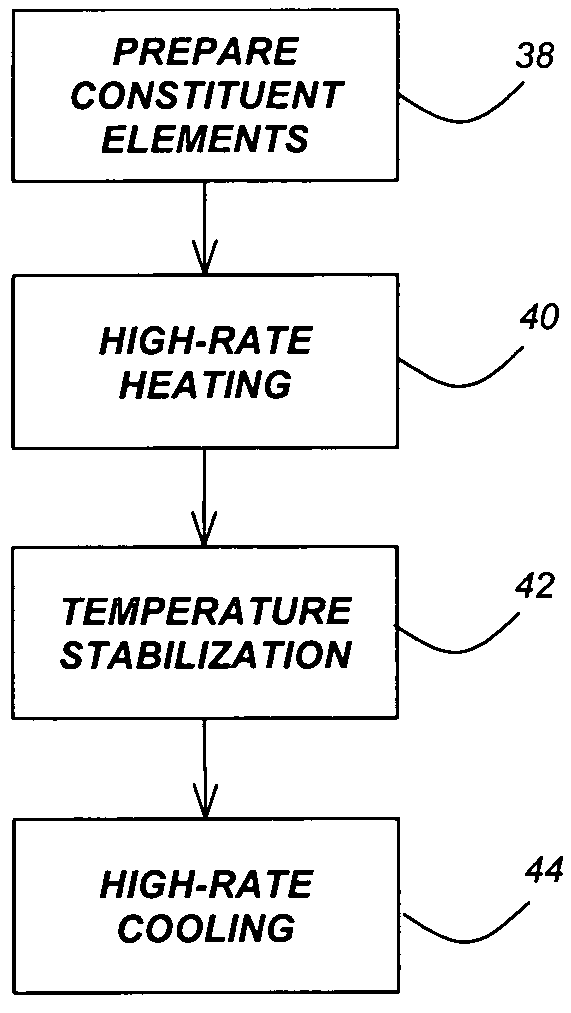
InactiveUS20060060998A1Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for the preparation of IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060110313A1Controlled in sizeControl shapeMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsOrganic solventQuantum dot
A high temperature (on the order of about 90° C. or above) non-aqueous synthetic procedure for the preparation of substantially monodisperse IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles (quantum dots) is provided. The procedure includes first introducing a first precursor selected from the group consisting of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element and a molecular precursor of a Group VI element into a reaction vessel that comprises at least an organic solvent to form a mixture. Next, the mixture is heated to a temperature of about 90° C. or above and thereafter a second precursor which is different from the first precursor and is selected from the group consisting of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element and a molecular precursor of a Group VI element is added into the heated mixture. The reaction mixture is then mixed to initiate nucleation of IV-VI nanocrystals and the temperature of the reaction mixture is controlled to provide substantially monodispersed IV-VI nanoparticles having a diameter of about 20 nm or less.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC +1
Passivated nanoparticles, method of fabrication thereof, and devices incorporating nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050201963A1Material nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentDangling bondSemiconductor Nanoparticles
A plurality of semiconductor nanoparticles having an elementally passivated surface are provided. These nanoparticles are capable of being suspended in water without substantial agglomeration and substantial precipitation on container surfaces for at least 30 days. The method of making the semiconductor nanoparticles includes reacting at least a first reactant and a second reactant in a solution to form the semiconductor nanoparticles in the solution. A first reactant provides a passivating element which binds to dangling bonds on a surface of the nanoparticles to passivate the surface of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticle size can be tuned by etching the nanoparticles located in the solution to a desired size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Continuous flow reactor for the synthesis of nanoparticles
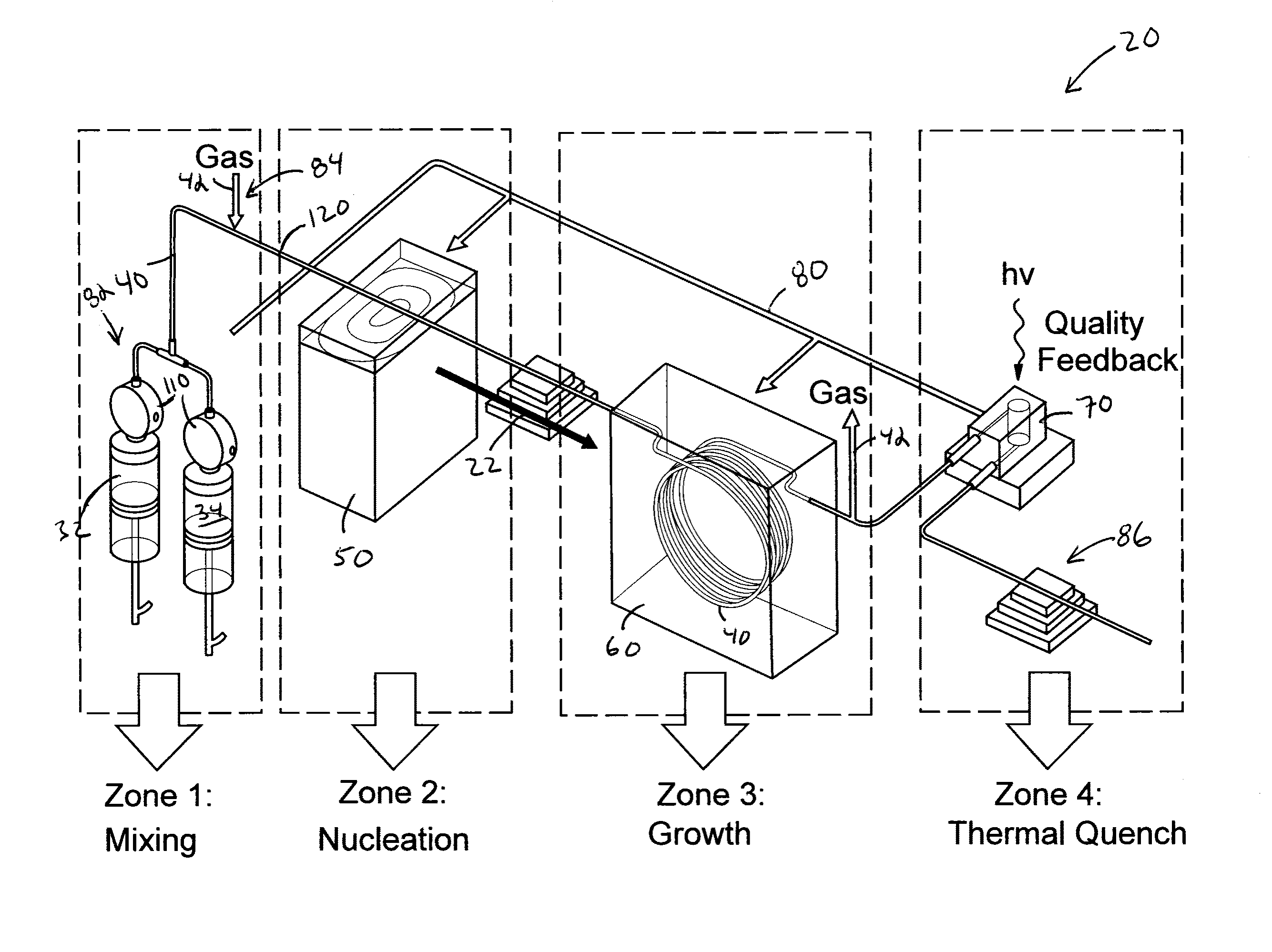
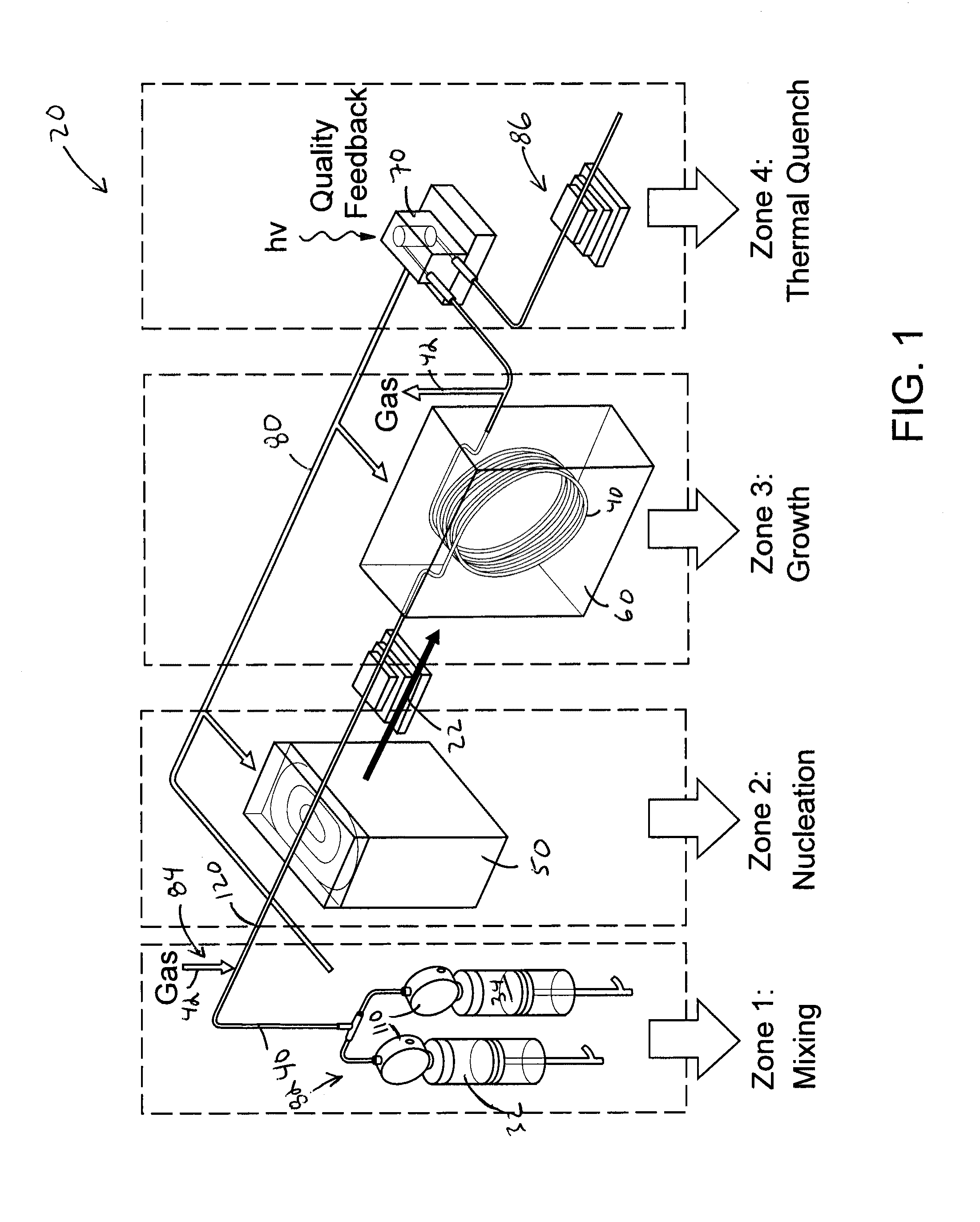
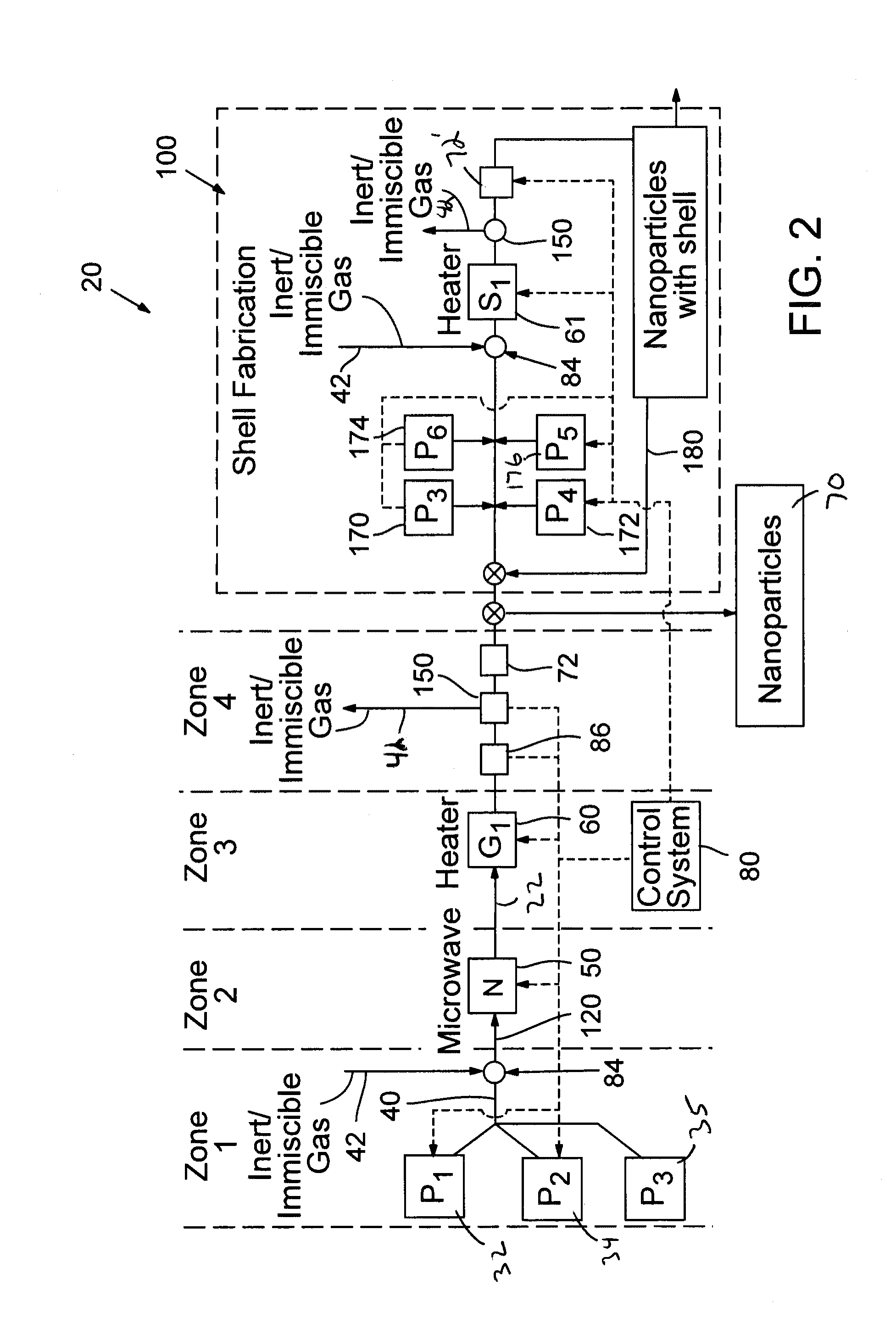
ActiveUS20140264171A1Enhance electronic and optical propertyIncreased durabilityRadiation applicationsCell electrodesEnergy absorptionEngineering
A continuous flow reactor for the efficient synthesis of nanoparticles with a high degree of crystallinity, uniform particle size, and homogenous stoichiometry throughout the crystal is described. Disclosed embodiments include a flow reactor with an energy source for rapid nucleation of the procurors following by a separate heating source for growing the nucleates. Segmented flow may be provided to facilitate mixing and uniform energy absorption of the precursors, and post production quality testing in communication with a control system allow automatic real-time adjustment of the production parameters. The nucleation energy source can be monomodal, multimodal, or multivariable frequency microwave energy and tuned to allow different precursors to nucleate at substantially the same time thereby resulting in a substantially homogenous nanoparticle. A shell application system may also be provided to allow one or more shell layers to be formed onto each nanoparticle.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS7575699B2Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsColloidal nanoparticlesContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of preparing semiconductor nanocrystal compositions
InactiveUS7850777B2High quantum yieldMore and cheapMaterial nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor nanocrystals
A semiconductor nanocrystal composition comprising a Group V to VI semiconductor material and a method of making same. The method includes synthesizing a semiconductor nanocrystal core, where the synthesizing includes dissolving a Group V to VI anion gas in a first solvent to produce a Group V to VI anion precursor, preparing a cation precursor, and reacting the Group V to VI anion precursor with the cation precursor in the presence of a second solvent. The reacting may occur in a high pressure vessel.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
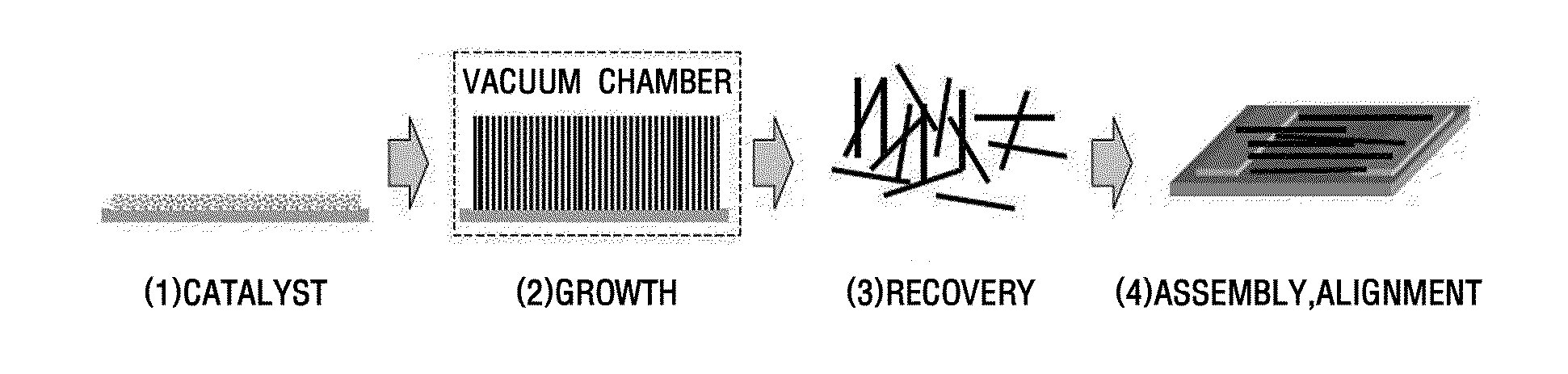
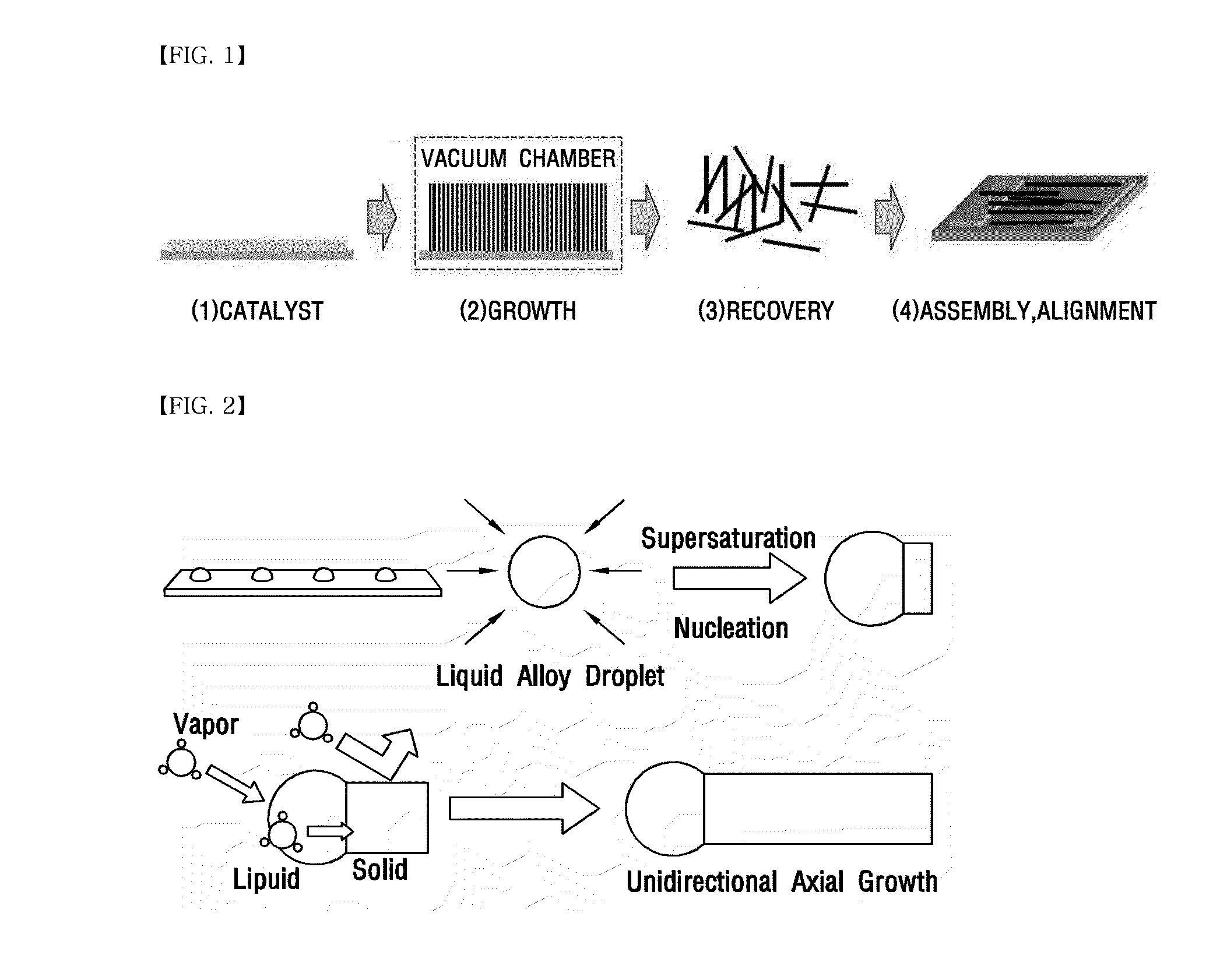
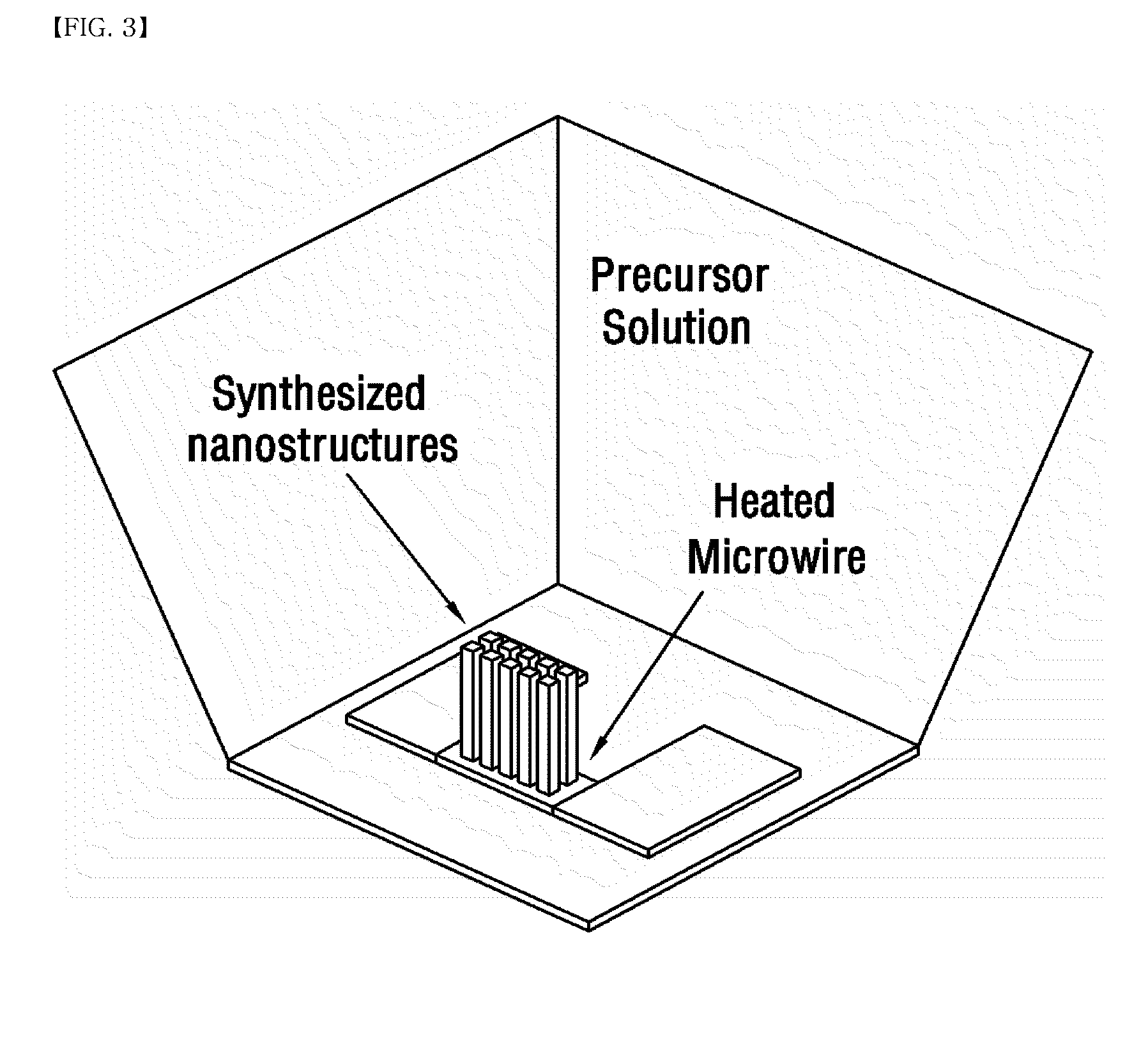
Method for manufacturing nanostructure and nanostructure manufactured by the same
InactiveUS20110008245A1Better cost-efficiencyExcellent cost-effectiveness and safetyFrom normal temperature solutionsCell electrodesVapor liquidCost effectiveness
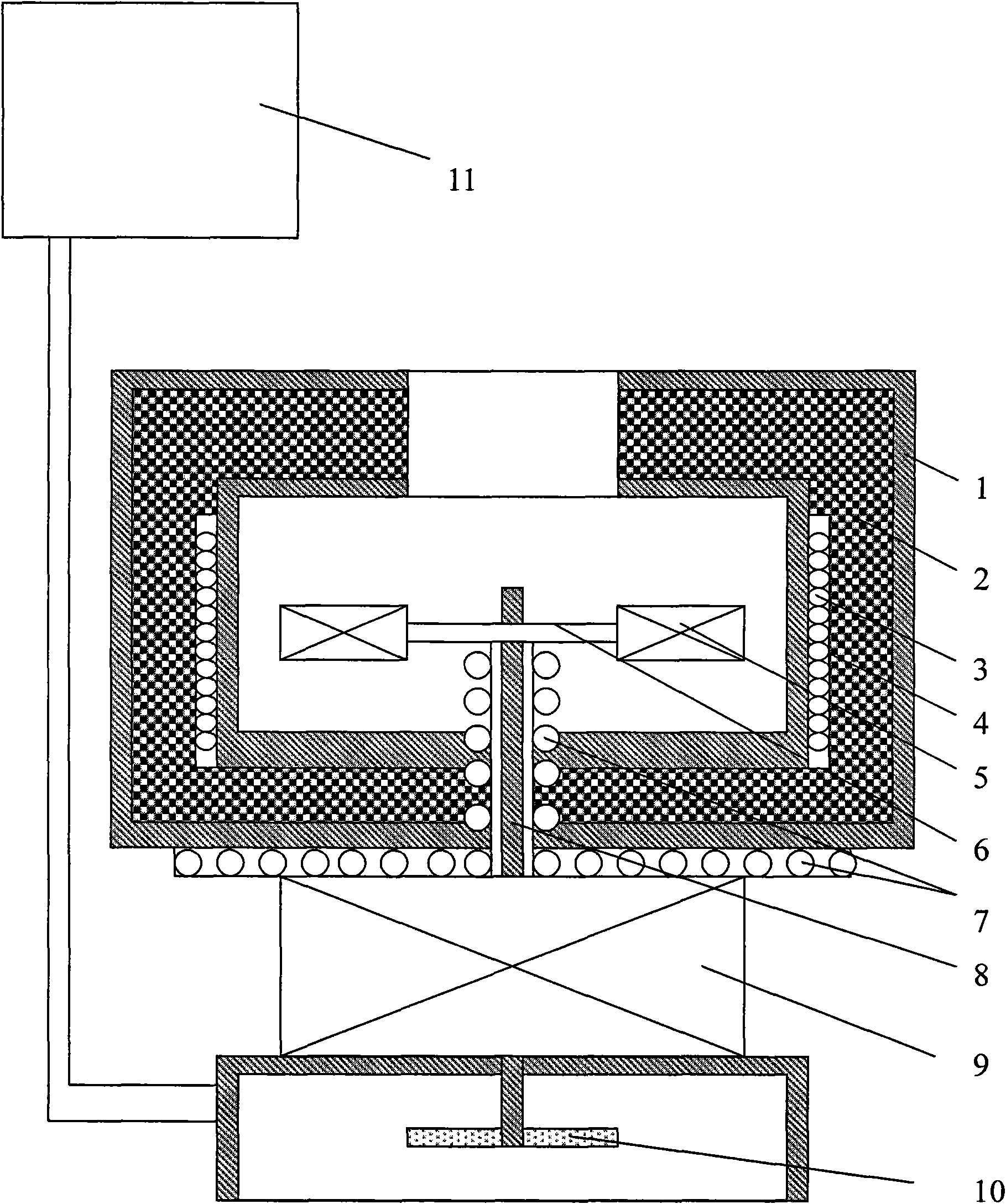
Provided are methods for producing nanostructures and nanostructures obtained thereby. The methods include heating a certain point of a substrate dipped into a precursor solution of the nanostructures so that the nanostructures are grown in a liquid phase environment without evaporation of the precursor solution. The methods show excellent cost-effectiveness because of the lack of a need for precursor evaporation at high temperature. In addition, unlike the vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) process performed in a vapor phase, the method includes growing nanostructures in a liquid phase environment, and thus provides excellent safety and eco-friendly characteristics as well as cost-effectiveness. Further, the method includes locally heating a substrate dipped into a precursor solution merely at a point where the nanostructures are to be grown, so that the nanostructures are grown directly at a desired point of the substrate. Therefore, it is possible to grow and produce nanostructures directly in a device. As a result, unlike the conventional process, it is not necessary to assemble and integrate the nanostructures produced in a sacrificial substrate into a device.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Passivated nanoparticles, method of fabrication thereof, and devices incorporating nanoparticles
InactiveUS7253119B2Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthDangling bondSemiconductor Nanoparticles
A plurality of semiconductor nanoparticles having an elementally passivated surface are provided. These nanoparticles are capable of being suspended in water without substantial agglomeration and substantial precipitation on container surfaces for at least 30 days. The method of making the semiconductor nanoparticles includes reacting at least a first reactant and a second reactant in a solution to form the semiconductor nanoparticles in the solution. A first reactant provides a passivating element which binds to dangling bonds on a surface of the nanoparticles to passivate the surface of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticle size can be tuned by etching the nanoparticles located in the solution to a desired size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
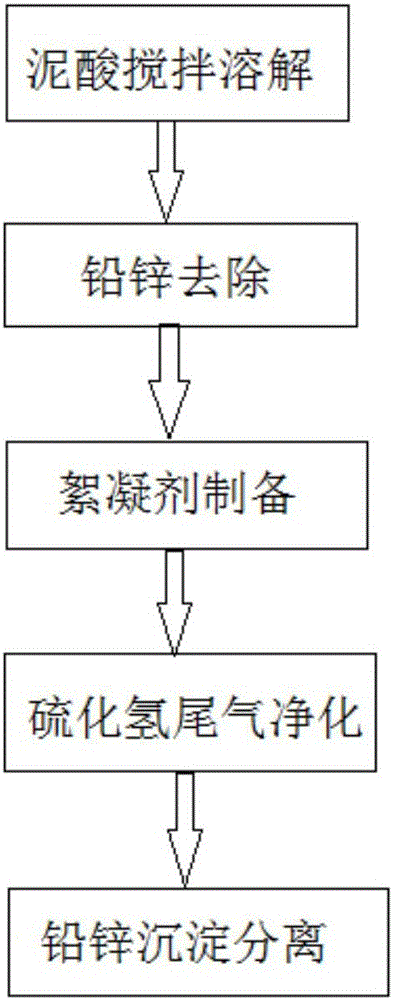
Steel wire rope picking waste acid and high zinc and lead-containing sludge co-disposal system and process
ActiveCN106186445APollution realizedReduce pollutionSludge treatmentOrganic compound preparationSludgeEngineering
The invention discloses a steel wire rope picking waste acid and high zinc and lead-containing sludge co-disposal system and process and belongs to the technical fields of environmental protection and wastewater treatment. The steel wire rope picking waste acid and high zinc and lead-containing sludge co-disposal system disclosed by the invention comprises a mud acid stirring and dissolving device, a lead and zinc removal device, a flocculating agent preparation device, a hydrogen sulfide absorption device and a lead and zinc precipitation separation device, wherein the mud acid stirring and dissolving device is connected with the lead and zinc removal device through a pipeline; and the lead and zinc removal device is connected with the flocculating agent preparation device, the hydrogen sulfide absorption device and the lead and zinc precipitation separation device through pipelines. The steel wire rope picking waste acid and high zinc and lead-containing sludge co-disposal process disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: stirring and dissolving mud acids, removing lead and zinc, preparing polyferric flocculants, purifying hydrogen sulfide tail gas and performing lead and zinc precipitation separation. According to the invention, steel wire rope picking waste acid and high zinc and lead-containing sludge co-disposal can be realized, the elements such as zinc and lead can be effectively removed, and industrial products with high additive values are prepared.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Nanoparticles and production thereof
InactiveUS20070065665A1Good repeatabilityReduce variation in propertyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical propertyNanoparticle
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ultra-small metal chalcogenide compound nano crystal and biological synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN106315663AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyEnergy modified materialsSynthesis methodsFluorescence
The invention discloses an ultra-small metal chalcogenide compound nano crystal and a biological synthesis method and application thereof. In one embodiment, the synthesis method is as follows: a protein with the isoelectric point PI lower than 9.0 and a metal salt are mixed with water evenly to form a mixed solution, the mixed solution is adjusted to alkaline, a reducing agent and a sulfur source are added for reaction to form the ultra-small metal chalcogenide compound nano crystal with the particle size less than 10nm. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, simple operation, direct use of particles without additional surface modification in biological photothermal therapy, and the like, the prepared ultra-small metal chalcogenide compound nano crystal is uniform in size, good in dispersion and high in stability, and the prepared ultra-small metal chalcogenide compound nano crystal has very good bio-compatibility without any surface modification, also has the photothermal effect, and is a great-application-prospect nano material used for photothermal therapy and biological fluorescence imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
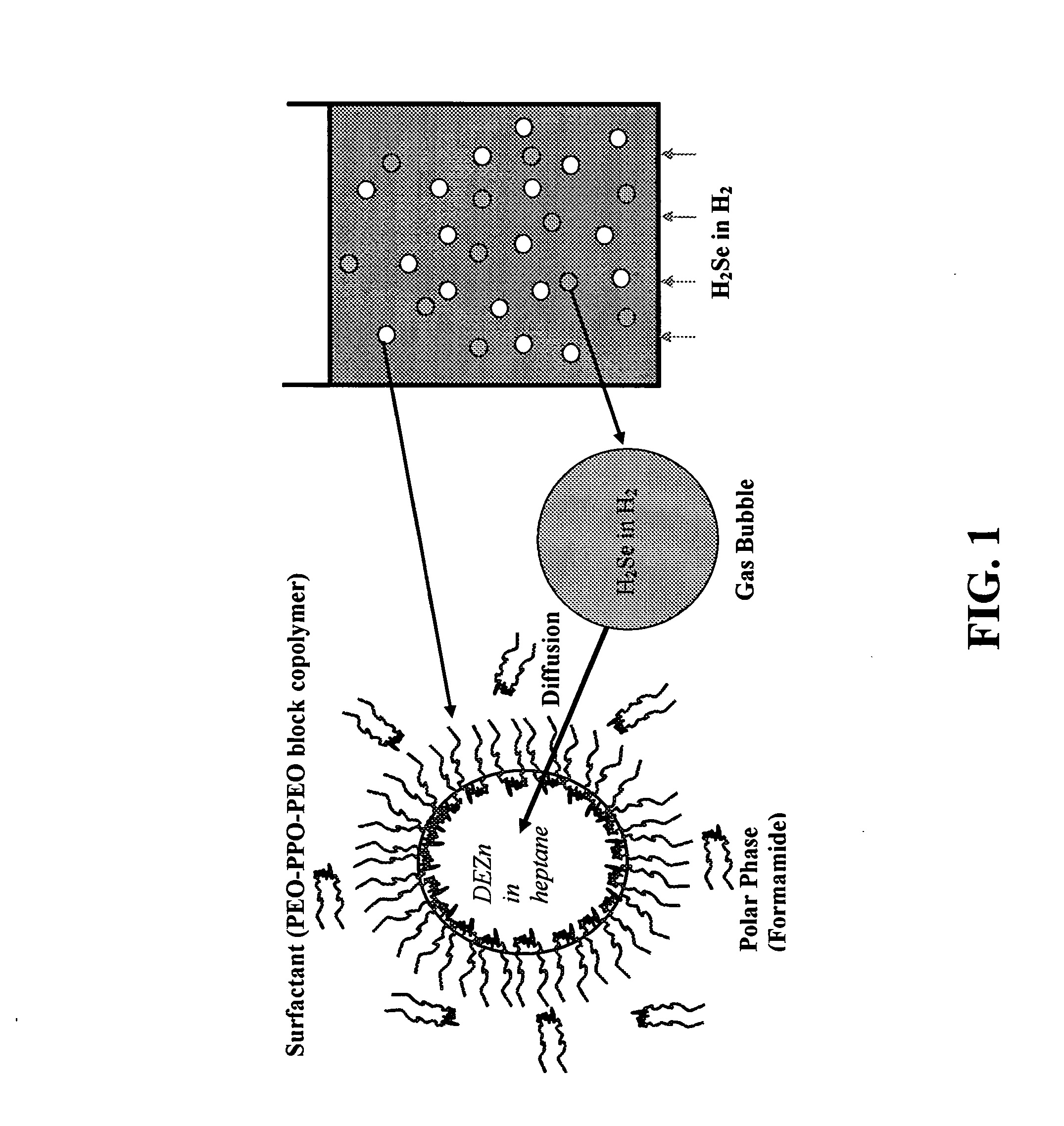
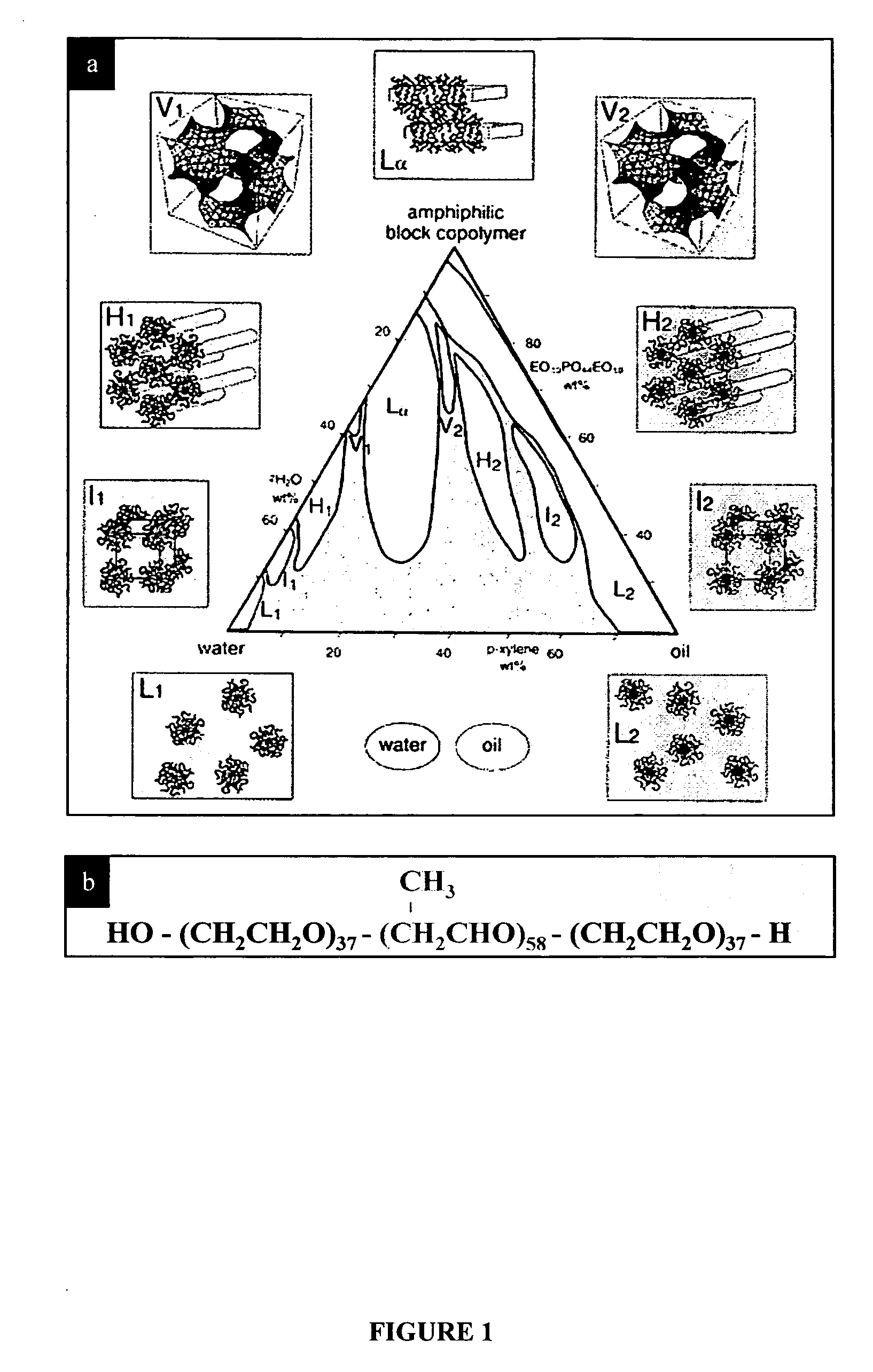
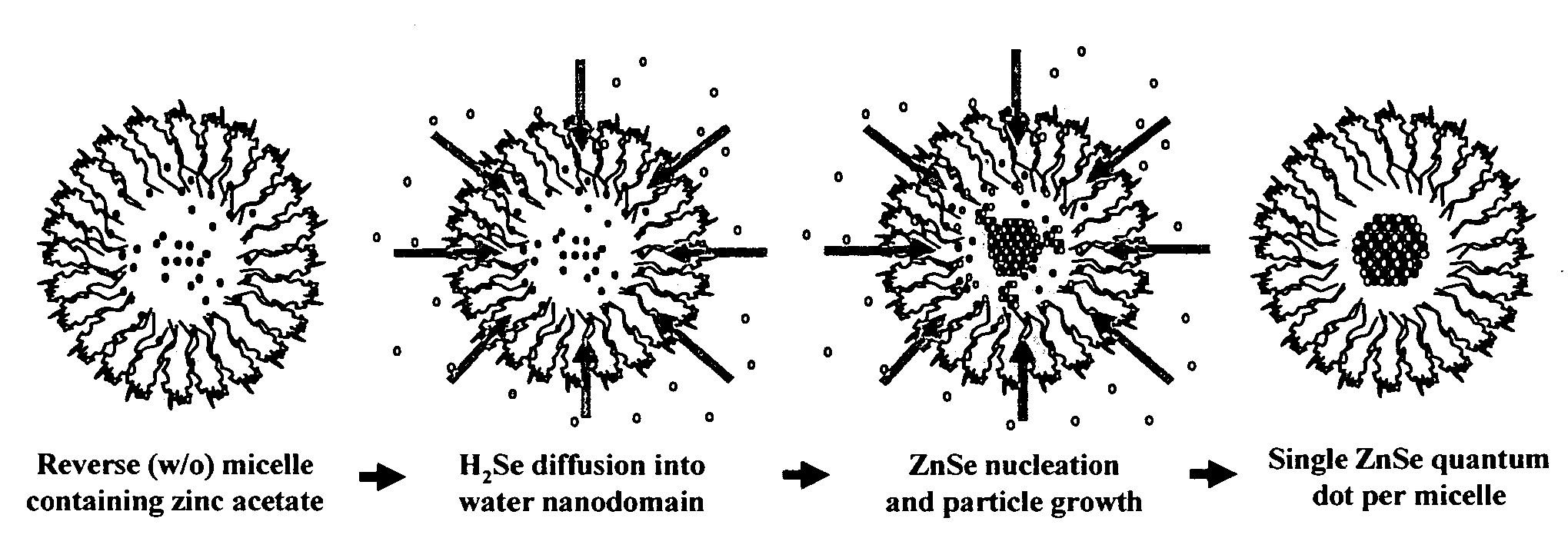
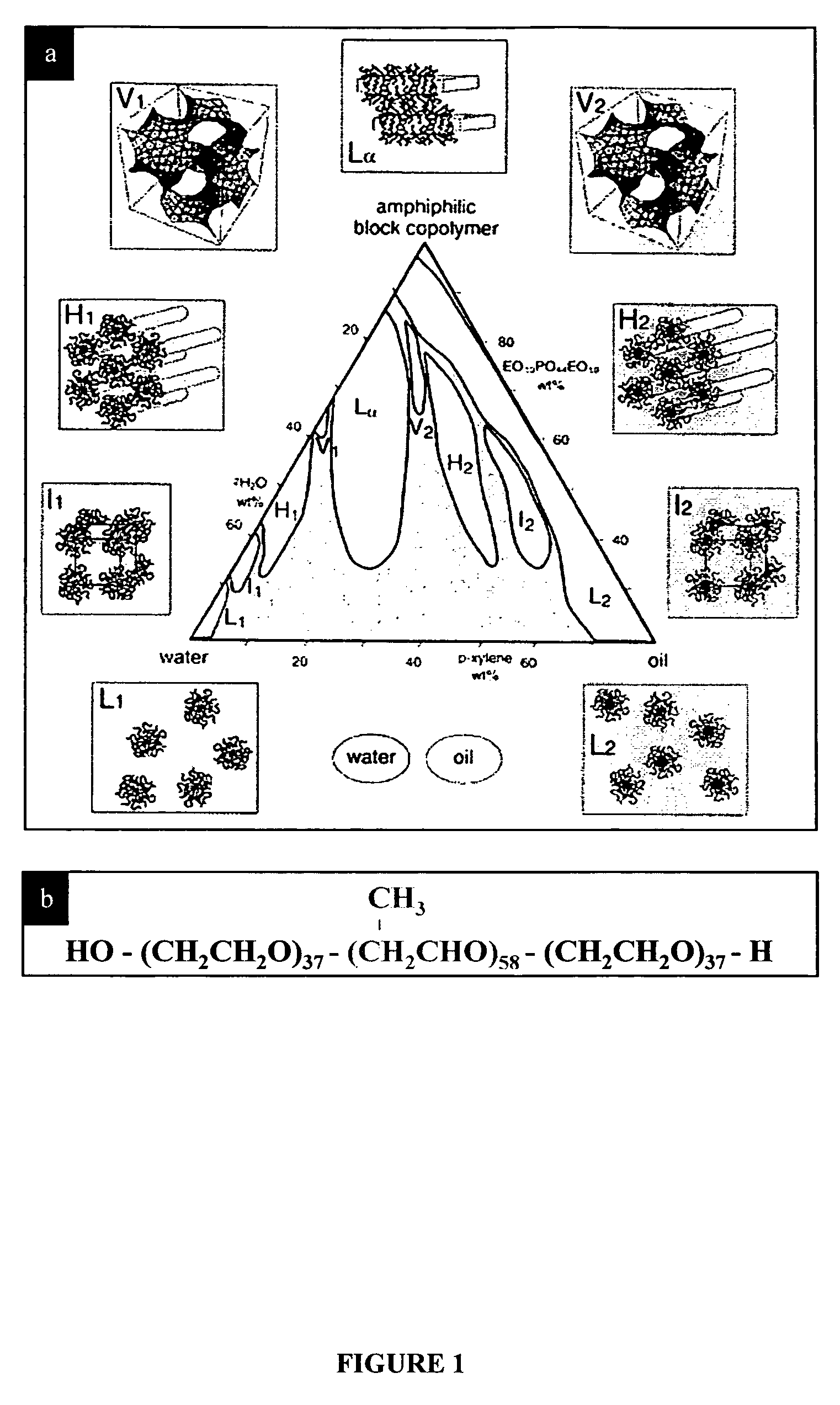
Synthesis of nanostructured materials using liquid crystalline templates
ActiveUS20060275196A1Effectively formMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsCrystallographyLiquid crystalline
A process for synthesizing nanostructures is disclosed. The process involves forming a liquid crystalline template by combining a block copolymer, a first reactant in a polar phase, and a nonpolar phase, then contacting the template with a gas phase composed of a second reactant, under conditions effective to form nanostructures.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
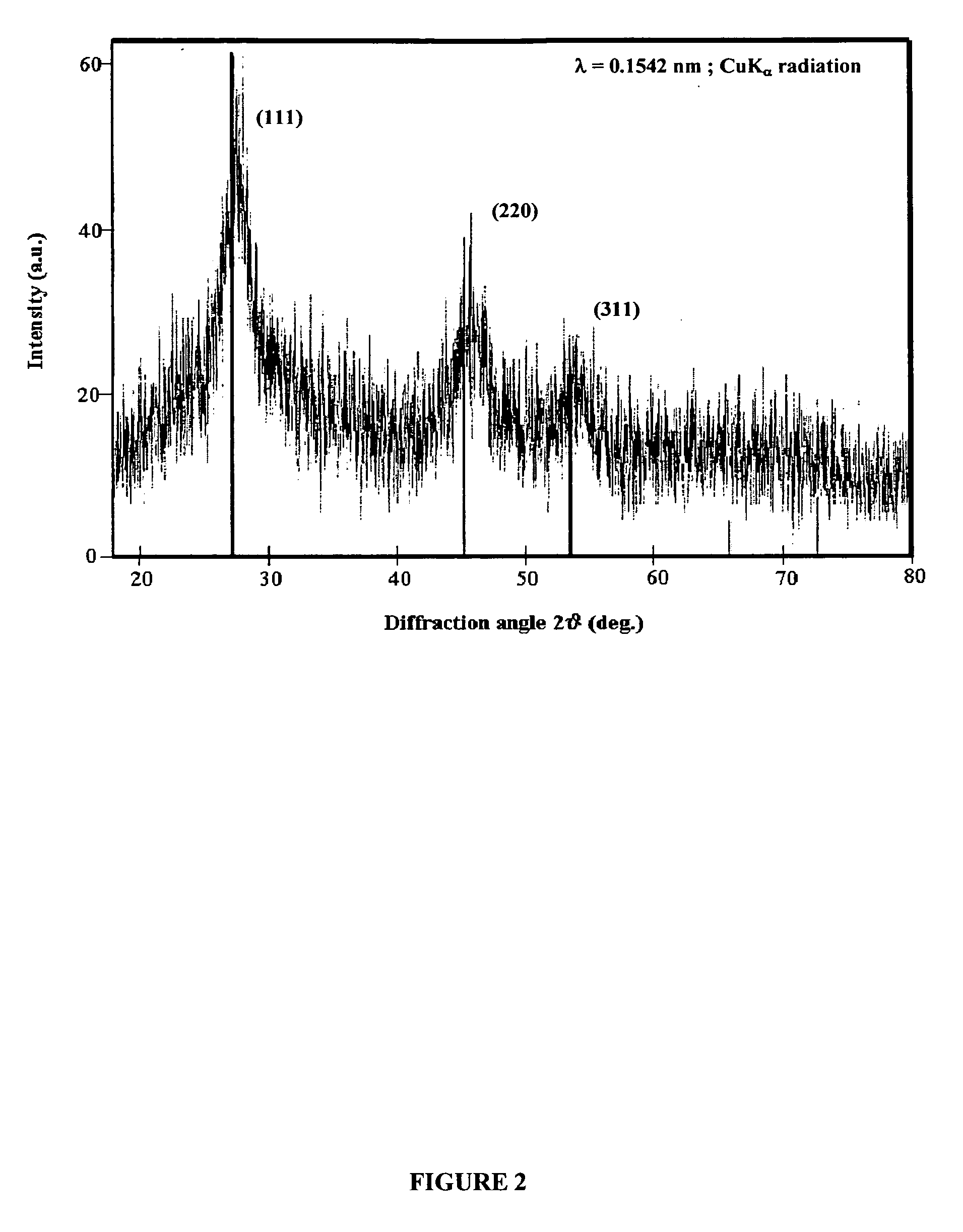
Method for preparing hexagon star-shaped plumbous sulfide nanocrystalline
InactiveCN101117237AEasy to prepareLow reaction temperatureNanostructure manufactureLead sulfidesThioureaReaction temperature
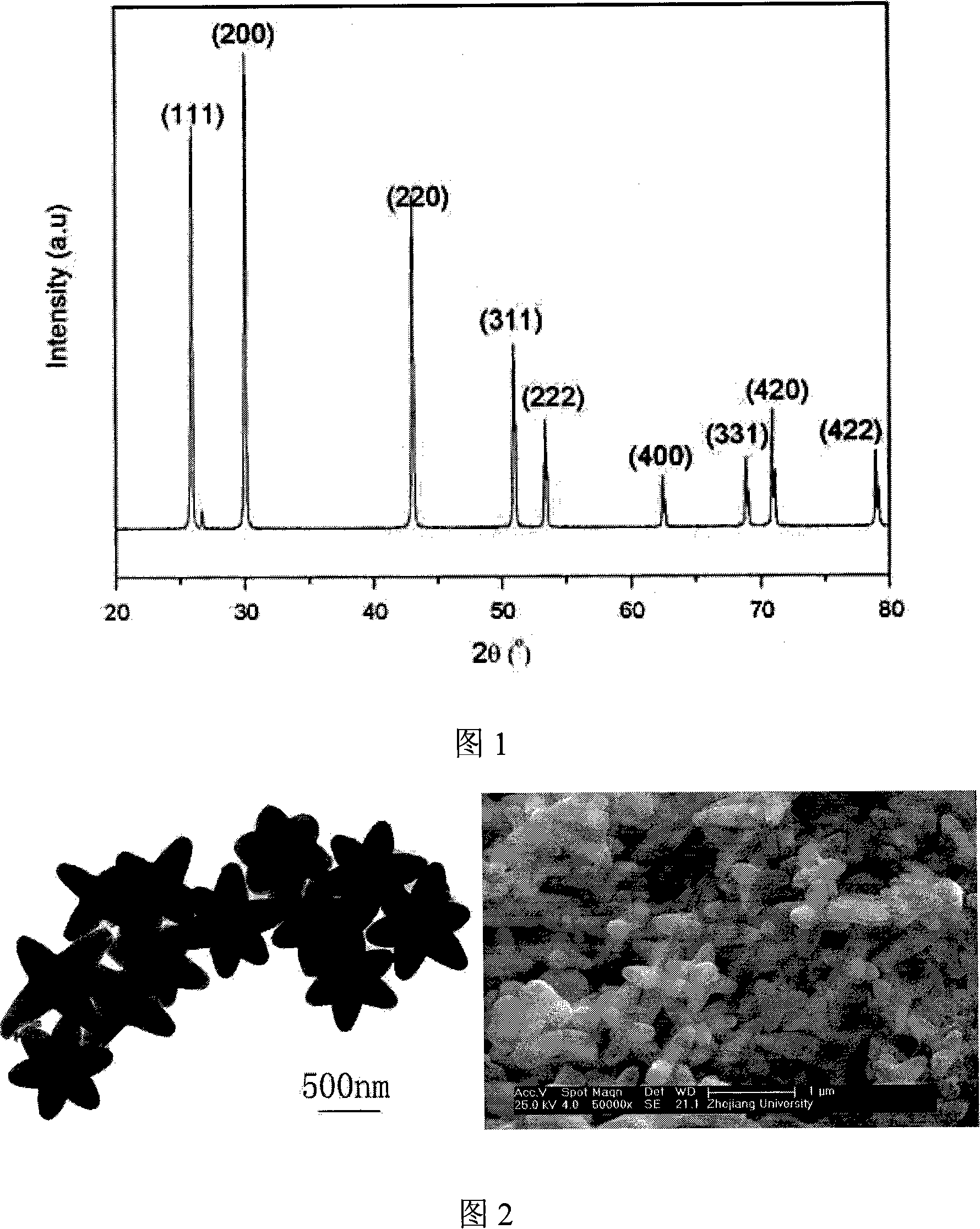
The invention discloses a method preparing hexagram PBS nanocrystal. The process is as follows: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide is added into deionized water, and stirred efficiently to dissolve completely in the water, and then the transparent solution is obtained; lead acetate and thiourea are added into the transparent solution, stirred uniformly, and then added to the hydrothermal reaction kettle; the solution which is in the hydrothermal reaction autoclave keeps the temperature in 80 DEG C to 160 DEG C about 6 to 24 hours; the reaction autoclave is opened until the temperature is reduced to the room temperature through the natural cooling; and the solution is washed by deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol, centrifugally filtrated; the precipitate is dried, and then the final product is obtained. The invention has the advantages of easy preparation, low reaction temperature, less energy consumption and low cost. The invention is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for converting refractory complex lead-zinc oxide ore by low-temporature sul furization
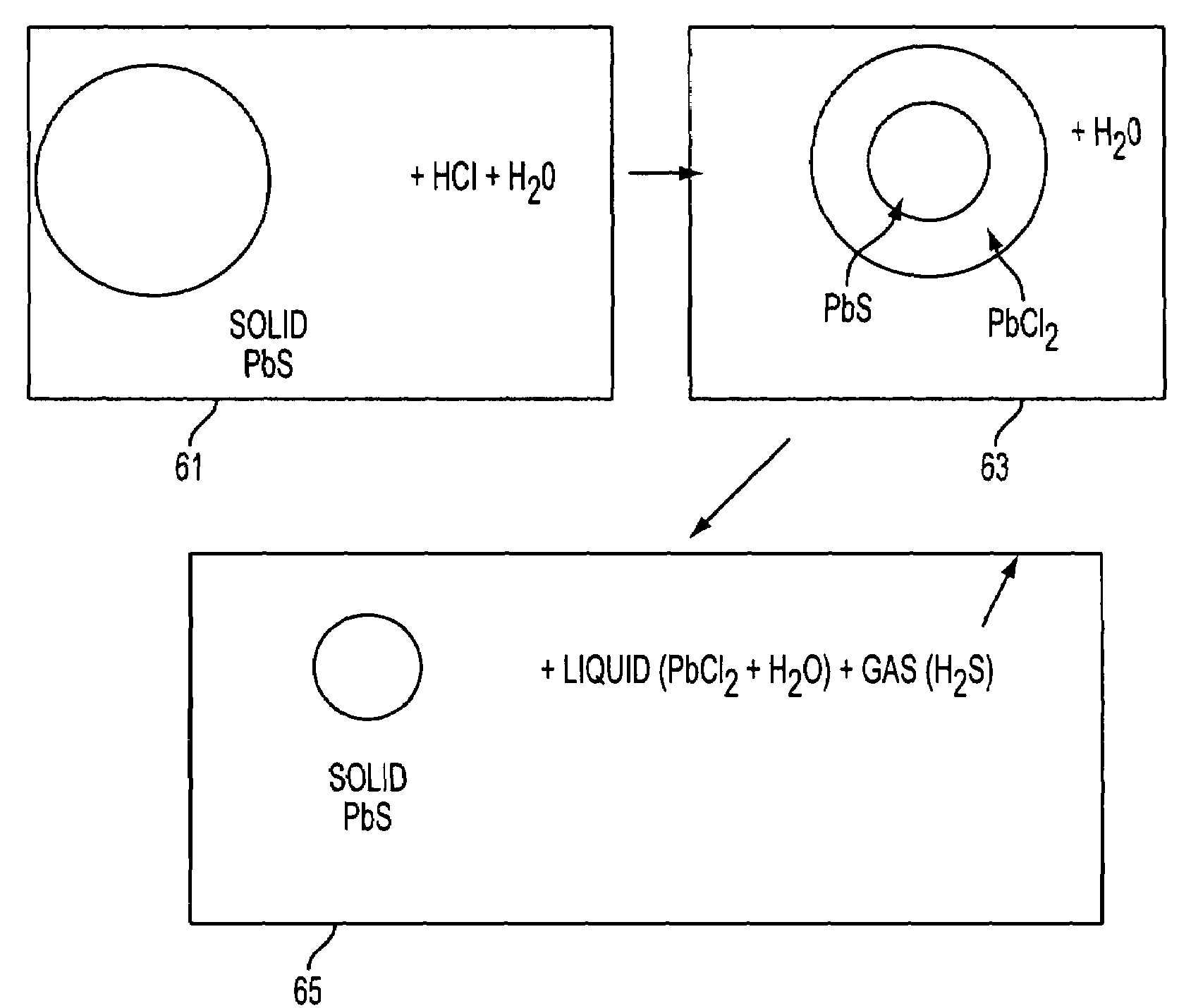
InactiveCN1851009AGuaranteed RecoveryReduce consumptionZinc sulfidesLead sulfidesChemical reactionSlurry
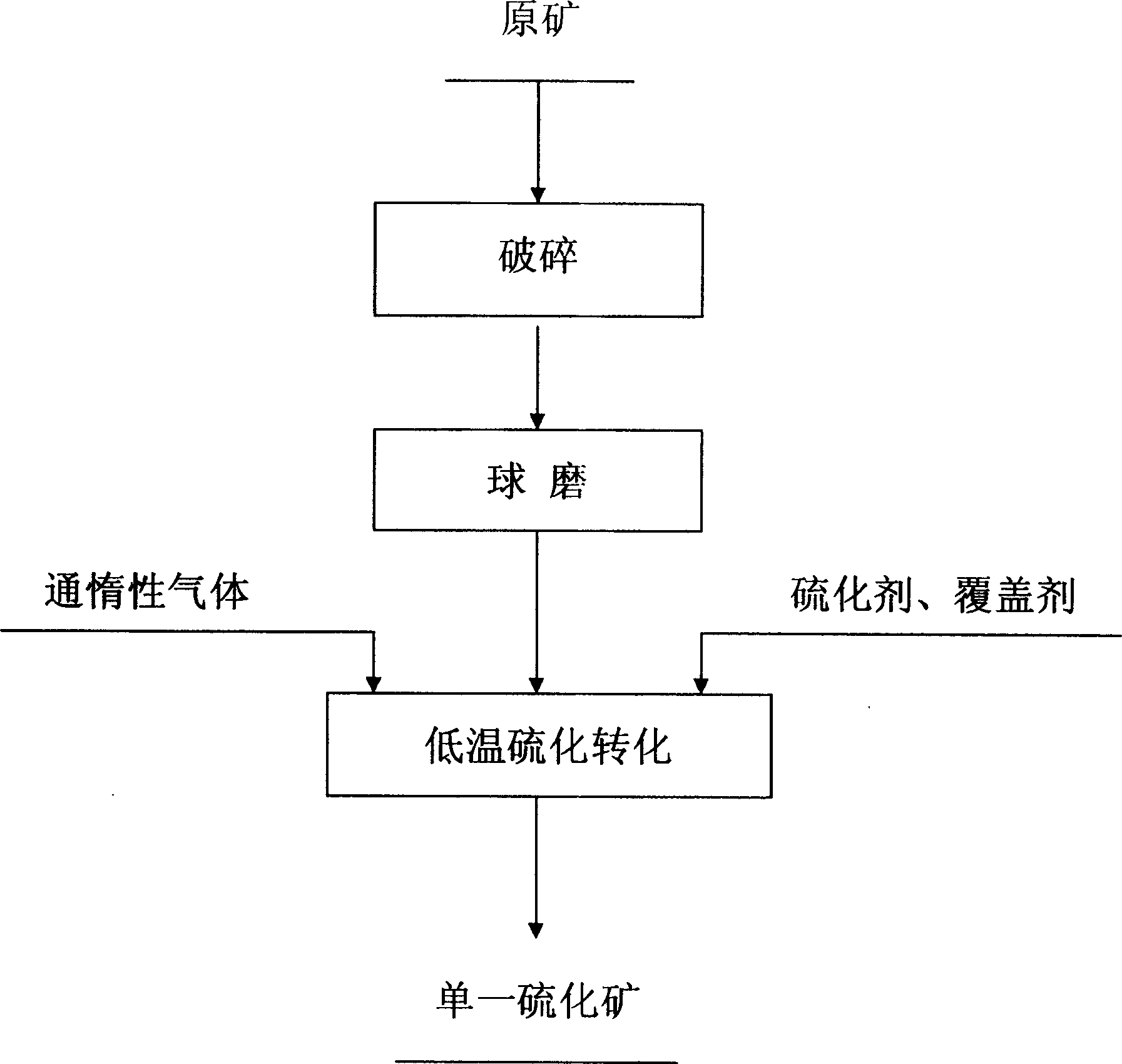
The invention relates to the method of the low temperature sulfuration translating the bad choosing complex oxidation lead zinc mine. The difficult choosing complex lead and zinc mine oxide, the sulfur, the fool's gold and the natrium sulfuration are served for the reagent sulfuration, the joining quantity of the sulfureted reagent is 0.5-10 percentage of the quantity of the difficult choosing complex lead and zinc mine oxide calculating by the element sulfur, the char repeat cover reagent such as the coke, the coke powder, the coal powder and the lead powder are mixing, the inert gases such as the argon gas and the azote gas are severed as the gas medium to add in the heating stove, the temperature keeps 100-900, the inert gas press keeps 0.01-0.1MPa, the lead and the zinc mine oxide is transferred to the sulfureted reagent after 10-180 minutes. On the said circumstance, the added sulfureted reagent can choose the lead, the zinc or the tantalum with the value to act, the single sulfureted reagent is gained, the other gangue factors can hold in the mine slurry without the change. The invention has many merits such as the easy process, the high percentage of reclaim of the metal, separating the lead and the zinc easy, the low wastage of the medicament, the realization of treating the metal with the value in advance.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL GROUP +2
Method for Synthesis of Colloidal Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070264834A1Large-scale, safe, convenient, reproducible, and energy-efficient productionHigh crystallinityDielectric heatingNanoinformaticsSynthesis methodsContinuous flow
A method for synthesis of high quality colloidal nanoparticles using comprises a high heating rate process. Irradiation of single mode, high power, microwave is a particularly well suited technique to realize high quality semiconductor nanoparticles. The use of microwave radiation effectively automates the synthesis, and more importantly, permits the use of a continuous flow microwave reactor for commercial preparation of the high quality colloidal nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Supergravity hydrothermal preparation method of spherical inorganic powder grains
InactiveCN101830497AImprove roundnessReaction is easy to controlCadmium sulfidesZinc sulfidesRare earthReaction temperature
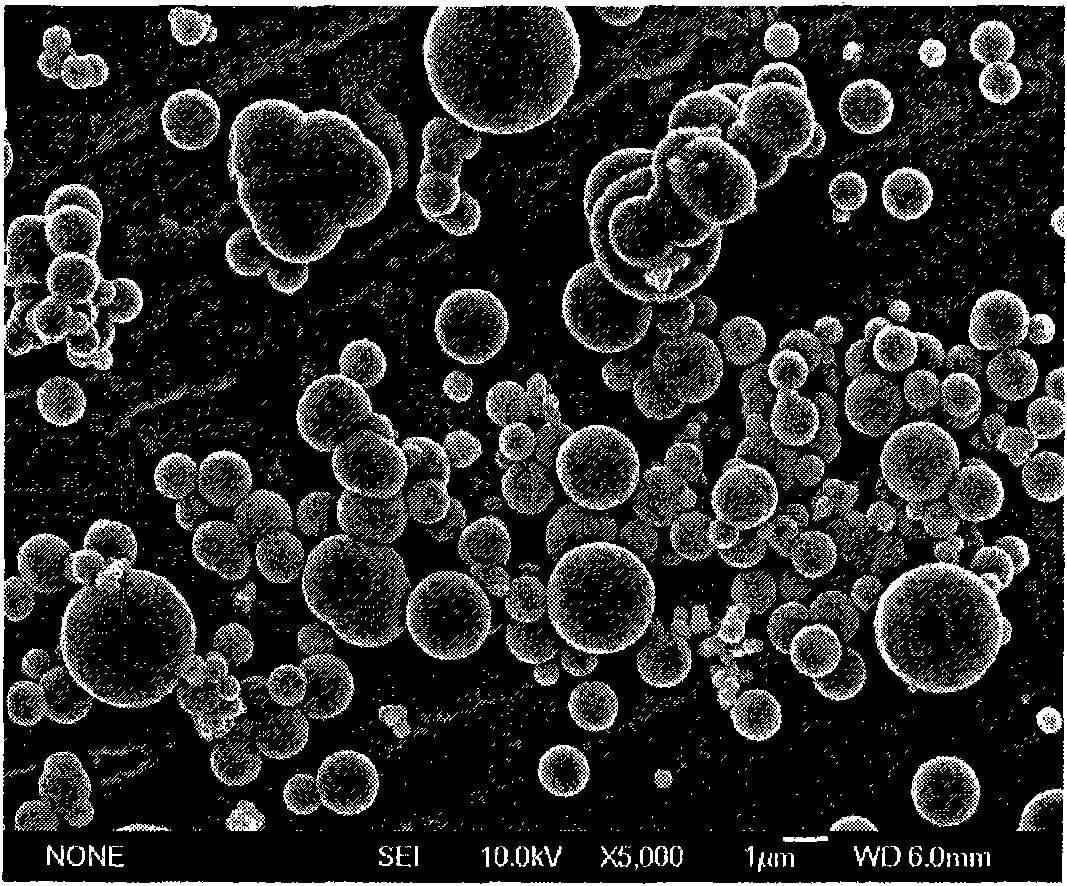
The invention relates to a supergravity hydrothermal preparation method of spherical inorganic powder grains, which comprises the following steps: preparing a metal salt solution at a concentration of 0.001 to 2mol / L; adding a S<2-> chemical reagent into the obtained solution, and adjusting the pH value of the solution to dissolve the S<2-> chemical reagent, wherein the molar ratio of the metal salt ions to the sulfur ions is 1:1 to 1:5; adding an organic solvent or aqueous high polymer compound into the obtained solution, wherein the volume ratio of the organic solvent or aqueous high polymer compound to the metal salt solution is 1:1 to 1:50; pouring the mixed solution into a high-pressure reaction kettle, sealing the high-pressure reaction kettle, fixing the high-pressure reaction kettle on a fixed bracket in a hearth, and performing a hydrothermal reaction in the presence of supergravity at 50 to 250 DEG C for 0.1 to 5 hours under the action of a relative centrifugal force of 100 to 10,000 grams; and filtering the reaction product, washing the reaction product, and drying the reaction product under vacuum to obtain the needed product. The spherical inorganic powder grains prepared by the invention have the characteristics of high roundness, monodispersion and narrow distribution. The inorganic powder prepared by the method of the invention comprises ZnS, CdS, CuS, PbS, and the like. The inorganic powder grains can be used for manufacturing photonic crystals, rare earth luminescent materials, phononic crystals, solar materials, left-handed materials and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Synthesis of nanostructured materials using liquid crystalline templates
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
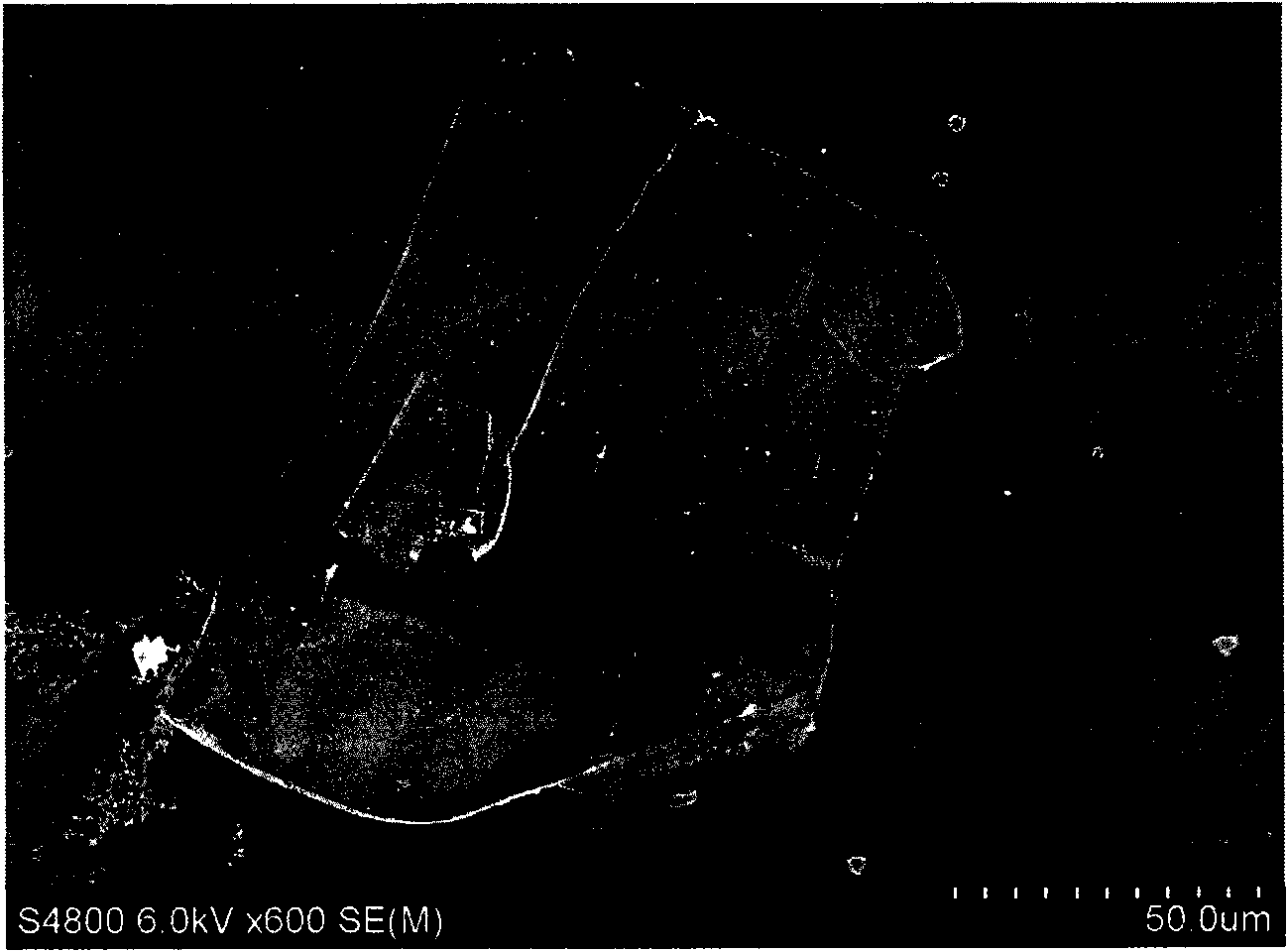
Method for synthesizing lead sulfide (PbS) film through chemical in-situ reaction of solution
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a lead sulfide (PbS) film through the chemical in-situ reaction of a solution. The method comprises the steps of: (1) preparing a precursor solution; (2) preparing the PbS film through carrying out an in-situ reaction: vertically immerging a deposition substrate, of which a lead precursor film is attached to the surface, into a sulfur source anionic precursor solution for carrying out an in-situ chemical reaction, after 10 seconds, pulling the deposition substrate out of the reaction solution at a uniform speed, washing the deposition substrate by using deionized water, then, placing the deposition substrate in a drying box so as to form a PbS reaction deposition layer; and (3) carrying out heat treatment. The invention provides a novel in-situ chemical synthesizing method for the PbS film with high efficiency, convenience, little pollution and low cost, low-toxicity chemical raw materials, such as inorganic salt which serves as a precursor, alcohol ether and alcohol amine which serve as solvents, and the like, are adopted, and the PbS film is synthesized at a lower temperature, so that method for synthesizing the PbS film through the chemical in-situ reaction of the solution has the advantages of good evenness in solution deposition reaction, high degree of crystallizing, and easiness for controlling the thickness of the film.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of porous PbS nano sheet
InactiveCN101805015AControl shapeSimple stepsLead sulfides2-mercaptopropionic acid3-Mercaptopropanoic Acid
The invention provides a preparation method of a porous PbS nano sheet and a porous PbS nano material prepared by the same. The preparation method comprises the steps of reacting inorganic lead salt with an organic molecule to obtain an organic lead source; and reacting the organic lead source with a Na2S solution to obtain the porous PbS nano material, wherein the mol ratio of the inorganic lead salt to the organic molecule is 1:0.5-6; the inorganic lead salt is selected from lead perchlorate, lead chloride, lead nitrate and mixture thereof, preferably the lead perchlorate; the organic molecule is a hydrosulfuryl molecule which is selected from thioglycollic acid, mercaptopropanoic acid, 1,2-dicarboxyl-1-ethanethiol, 1-hydrosulfuryl-2-sodium sulfonate ethane and mixture thereof, preferably the thioglycollic acid or the mercaptopropanoic acid; and the mercaptopropanoic acid is 3-mercaptopropanoic acid or 2-mercaptopropanoic acid. The method has simple steps and easy operation and can effectively control the topography of the porous PbS nano material. The porous PbS nano material obtained by the method has excellent visible light degradation performance.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
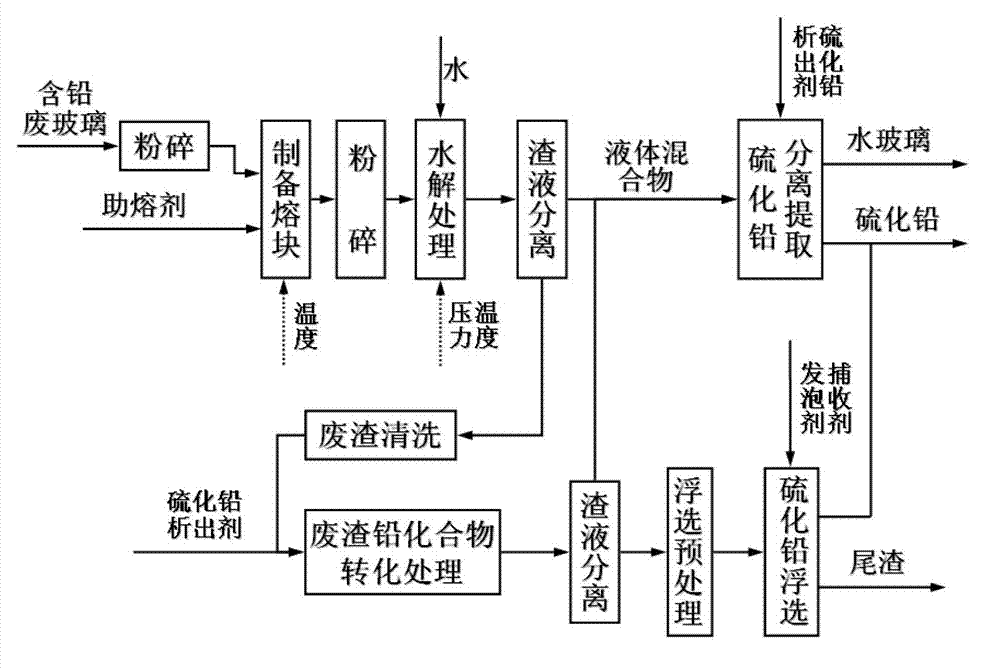
Method for preparing water glass by utilizing waste lead-containing glass and separating lead-containing compound
ActiveCN102826562ASolve refractoryLower melting temperatureAlkali metal silicatesLead sulfidesLead smeltingInorganic Chemical
The invention relates to a method for preparing water glass by utilizing waste lead-containing glass and separating a lead-containing compound. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, making the lead-containing glass of an abandoned cathode-ray tube (CRT) into water glass fusion cake, hydrolyzing the fusion cake, and separating hydrolysate to obtain a water glass solution; then adding an additive to convert lead dissolved in the water glass into lead sulphide, separating and collecting lead sulphide sediment to obtain a lead-free potassium or sodium water glass solution, further treating dissolved residue to convert the lead-containing compound in the residue into lead sulphide, and recycling lead sulphide in the hydrolysis residue by adopting a floatation method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that silicon, potassium and sodium ingredients in the lead-containing glass of the abandoned CRT can be converted into the water glass, recycling of the lead-containing compound is solved; the water glass is a basic inorganic chemical industry product with wide application range; and recycling of the lead-containing compound is solved, the recycled lead-containing compound can be taken as a raw material for lead smelting, and recycling of lead resource is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
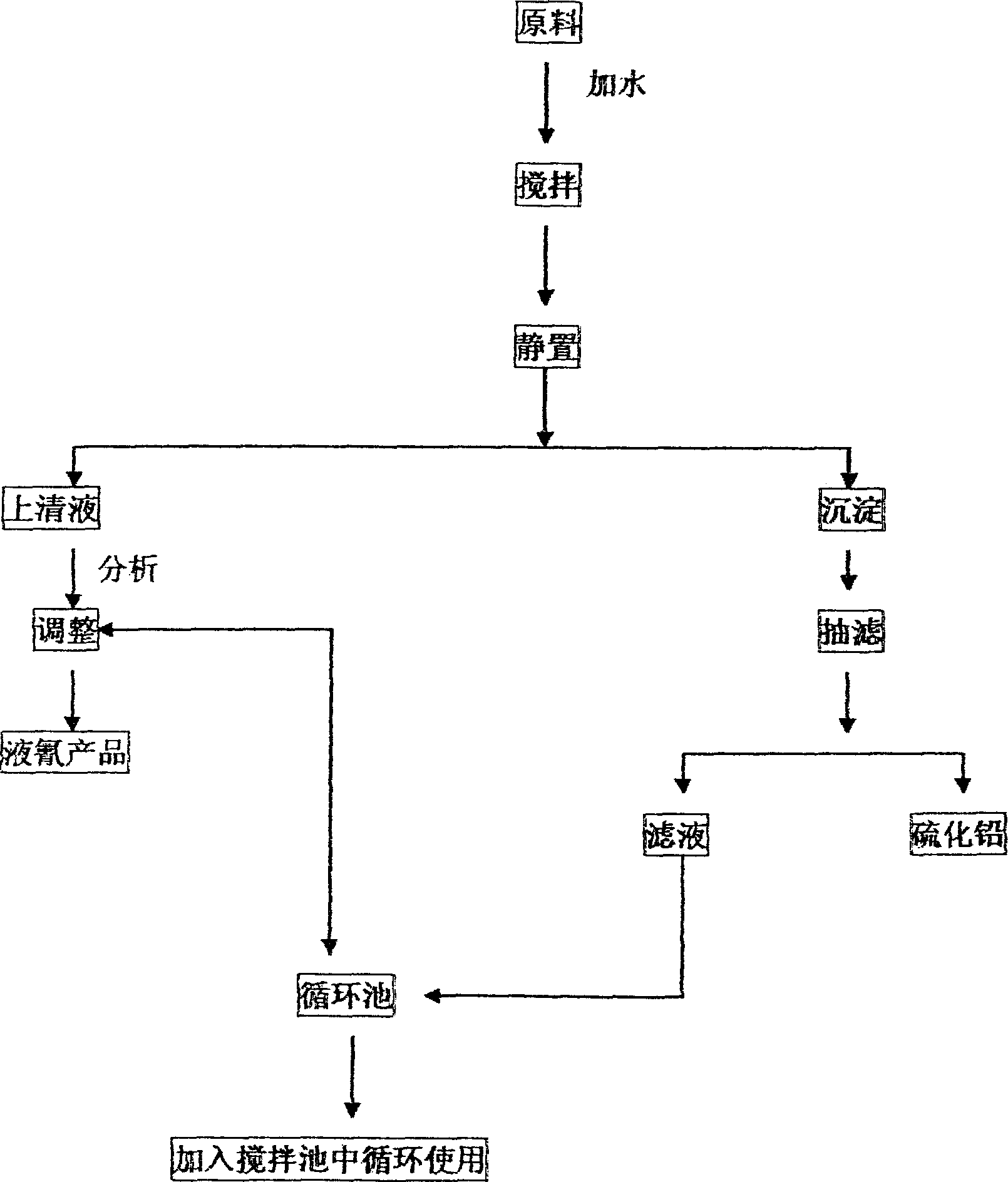
Process of preparing sodium cyanide and lead sulfide for gold ore sorting from waste sodium cyaide desulfurizing dreg
InactiveCN1673082AComplete resourceThe production process is simple and effectiveAlkali metal cyanidesLead sulfidesSodium cyanideLead sulfide
The waste sodium cyanide desulfurizing dreg containing various components with different physical and chemical properties, especially different dissolubility in water, is separated and extracted with water as medium to obtain liquid cyanide product with dissolved sodium cyanide and waste dreg, which is dried as the lead ore product. The said production process is simple and effective, and has no waste produced, no pollution, low cost, high yield and complete utilization of resource.
Owner:安庆盖娅环保科技有限公司
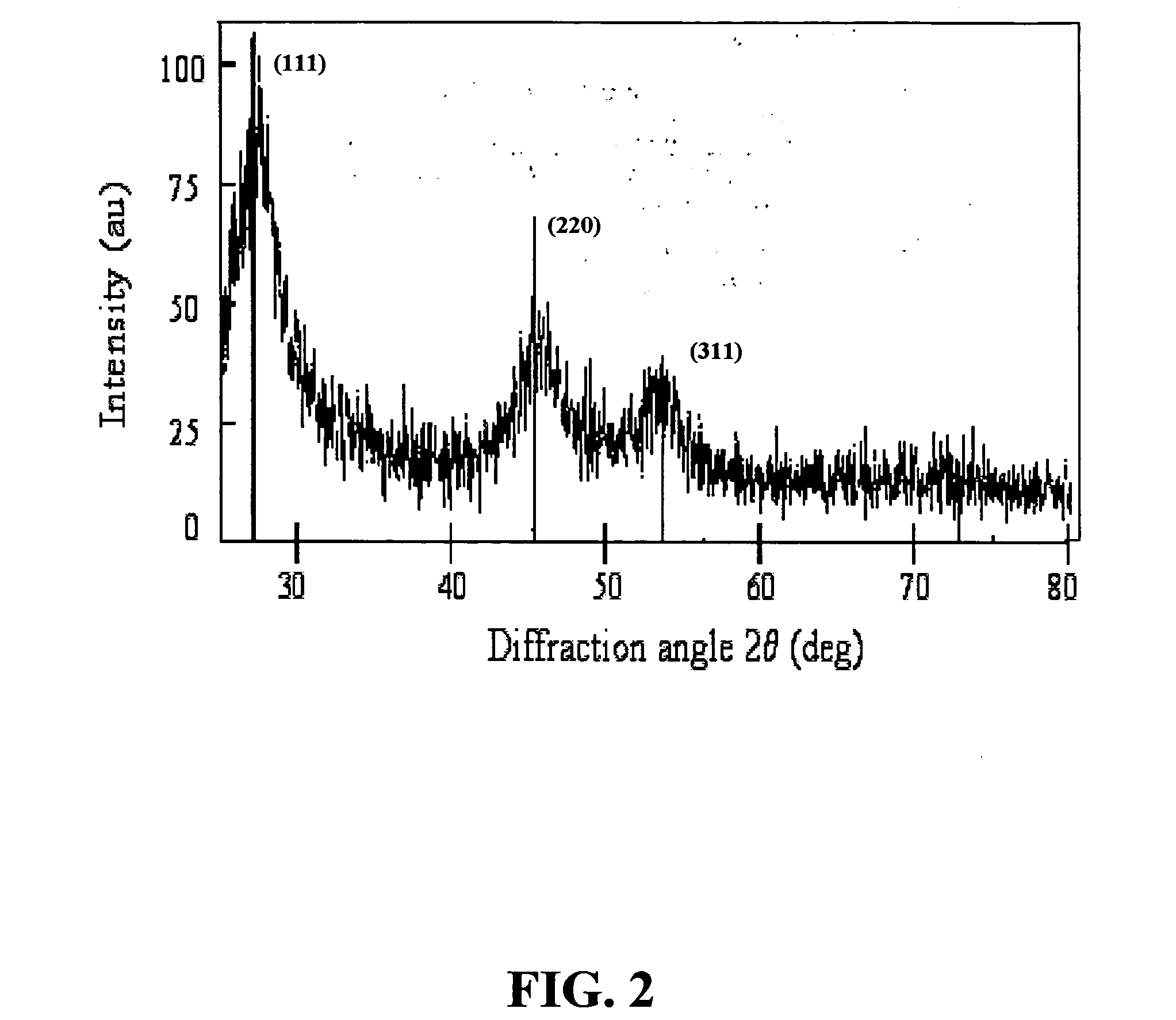
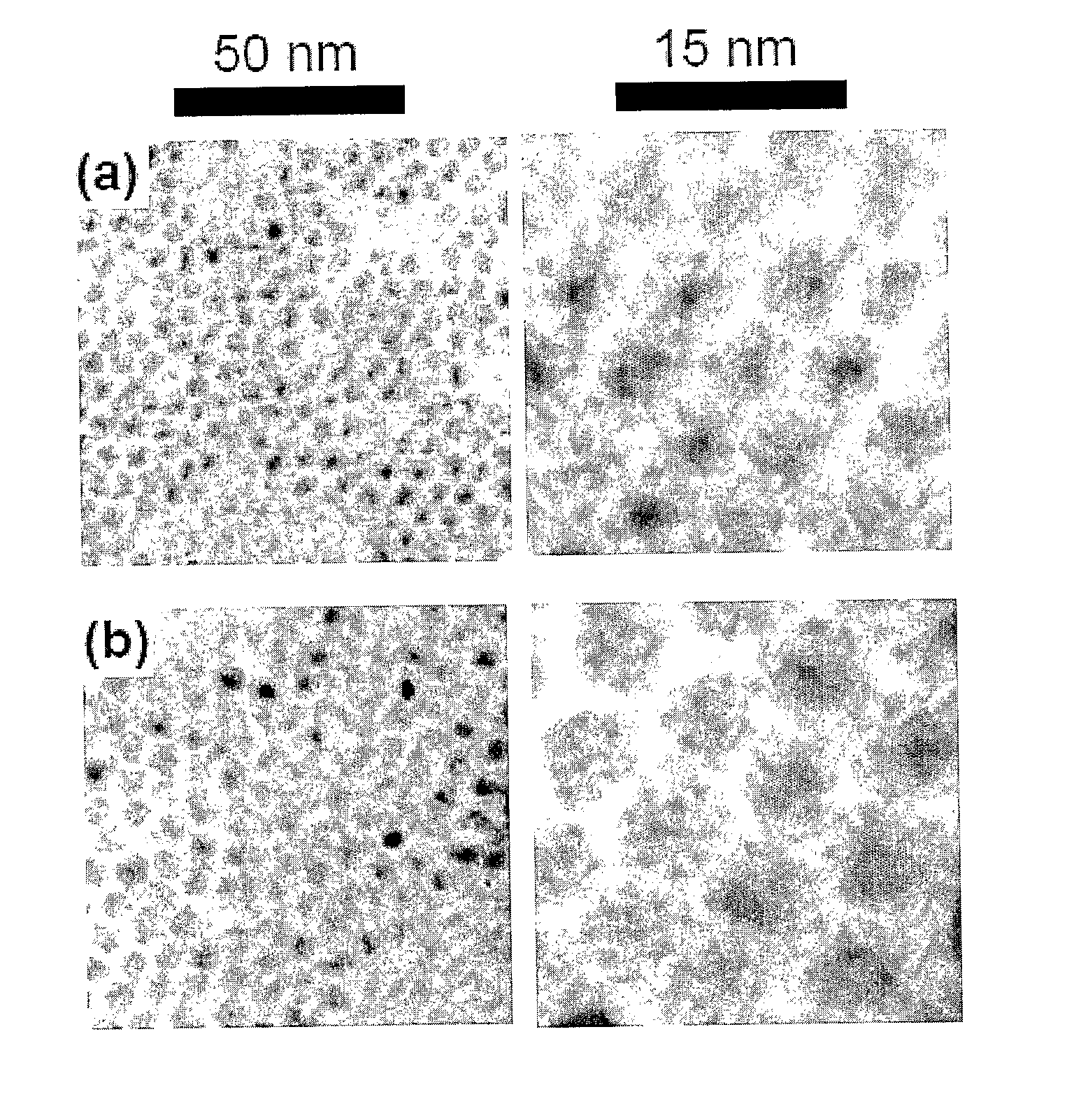
Method for Producing Highly Monodisperse Quantum Dots
InactiveUS20080044340A1Less solventReduce and eliminate needMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureSufficient timeSulfur
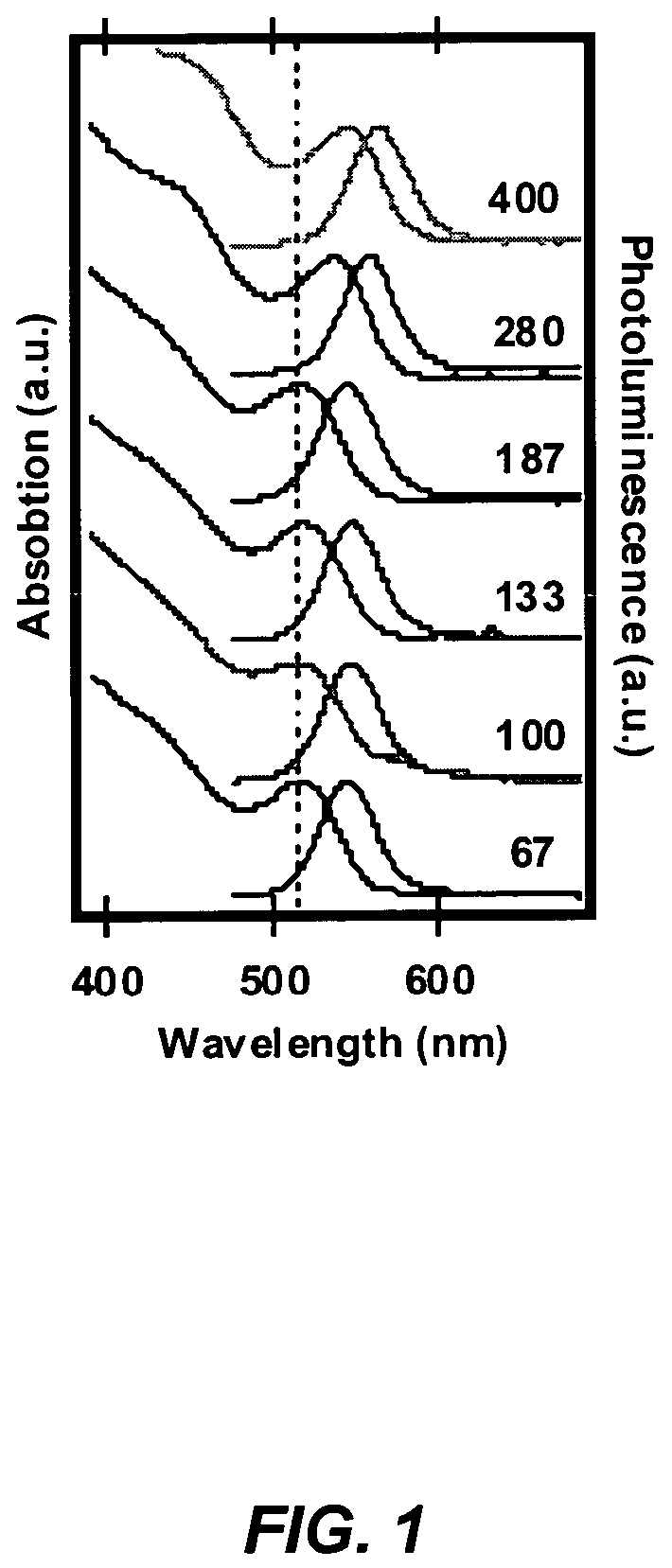
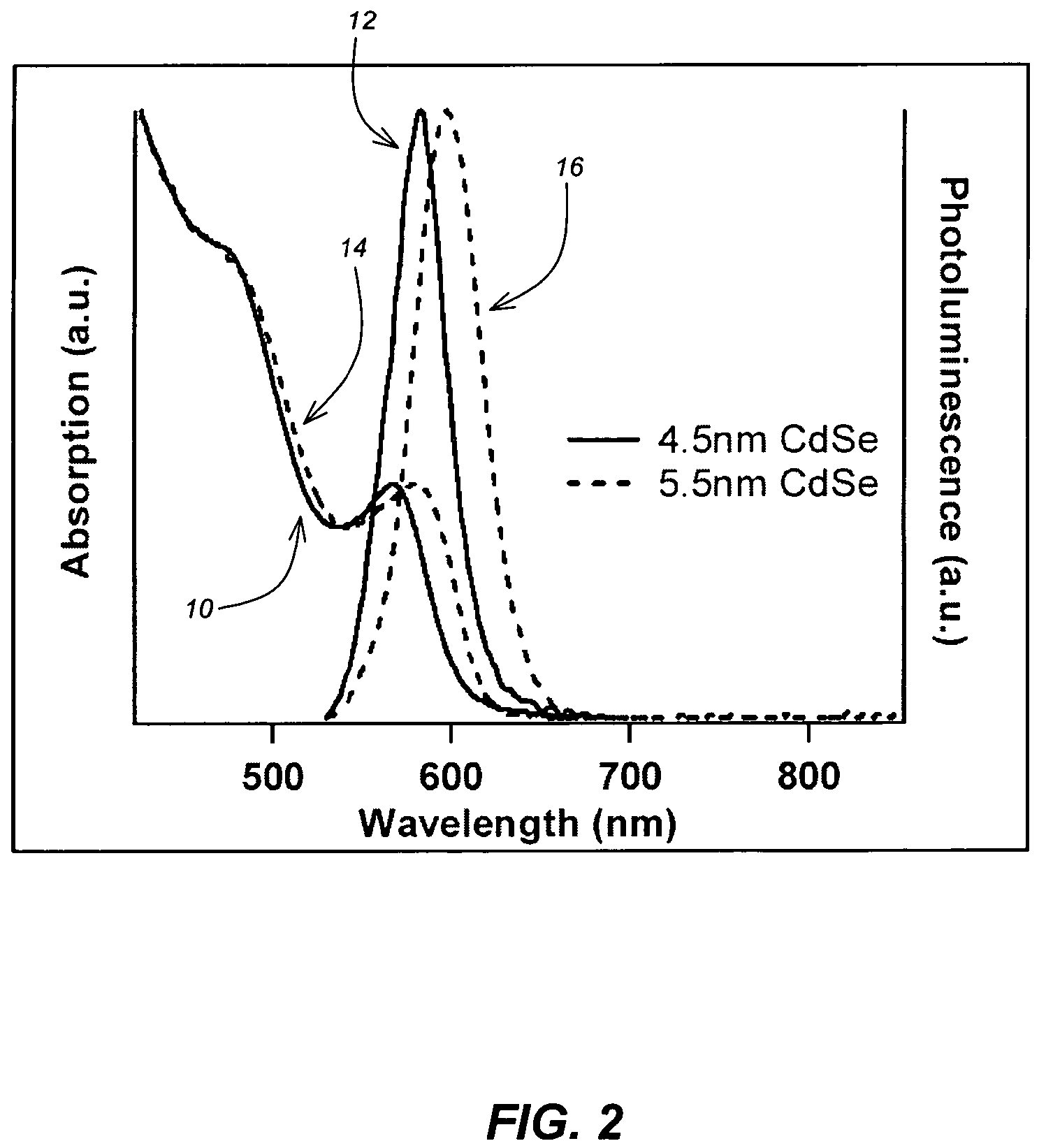
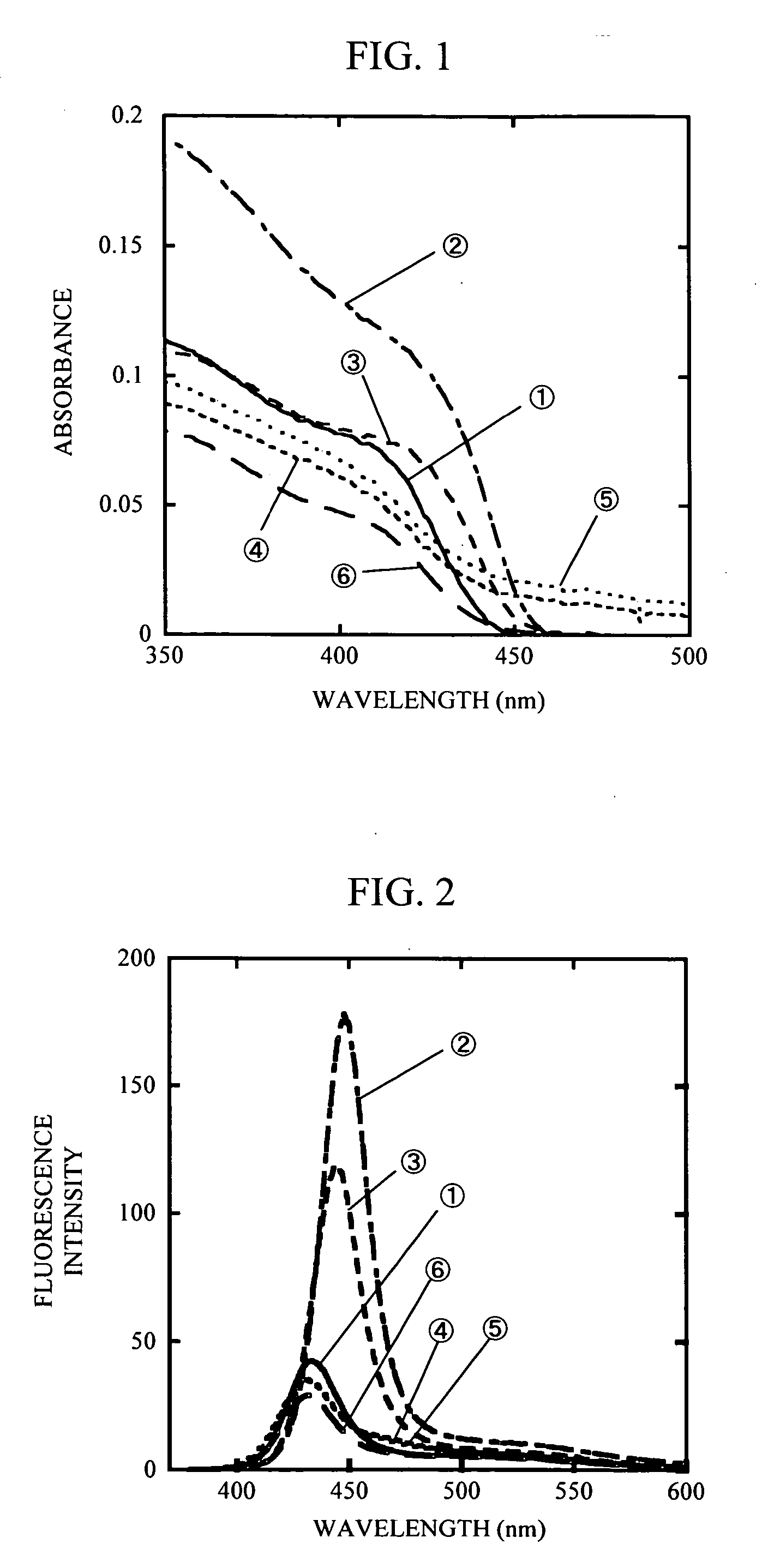
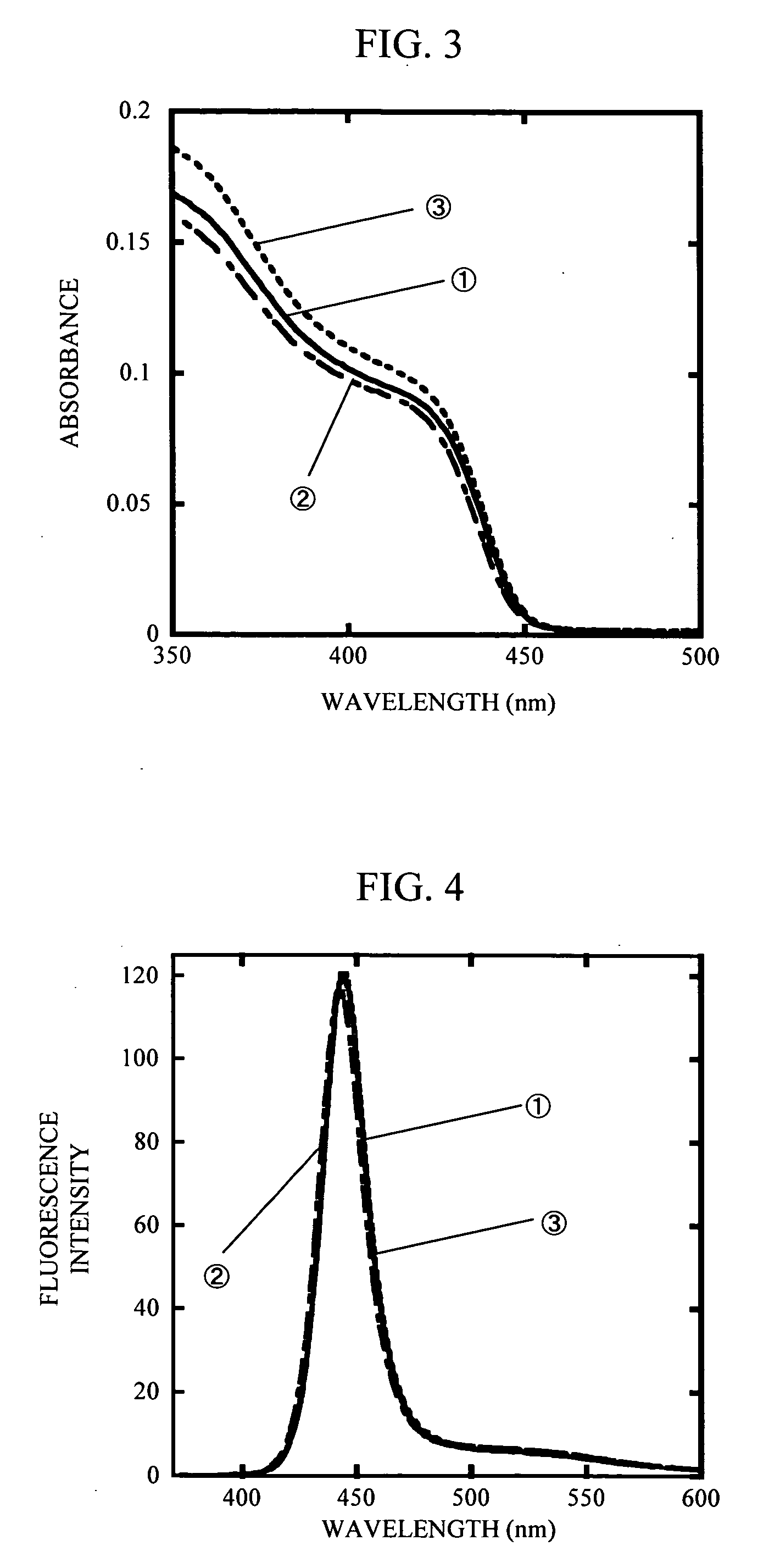
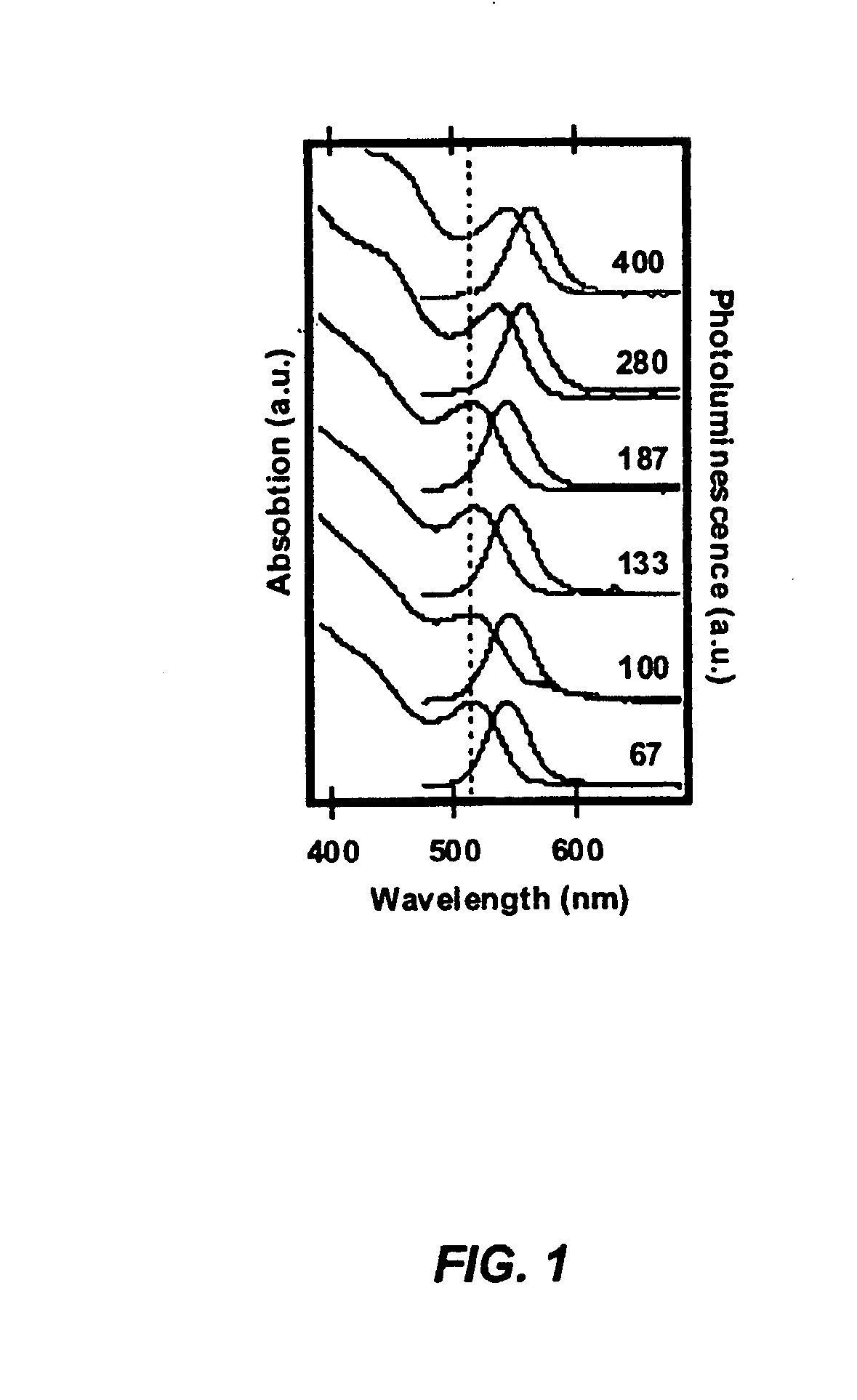
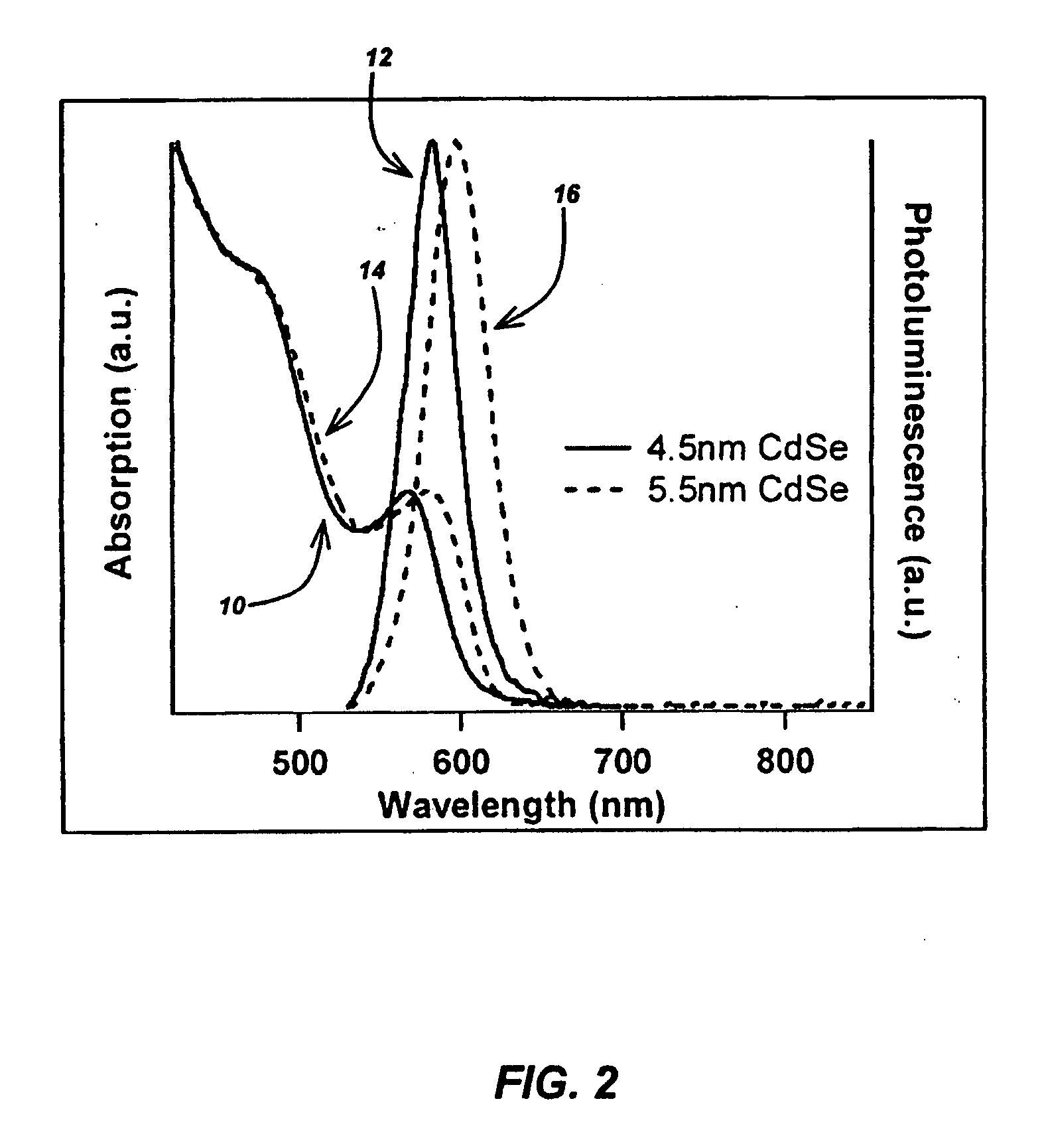
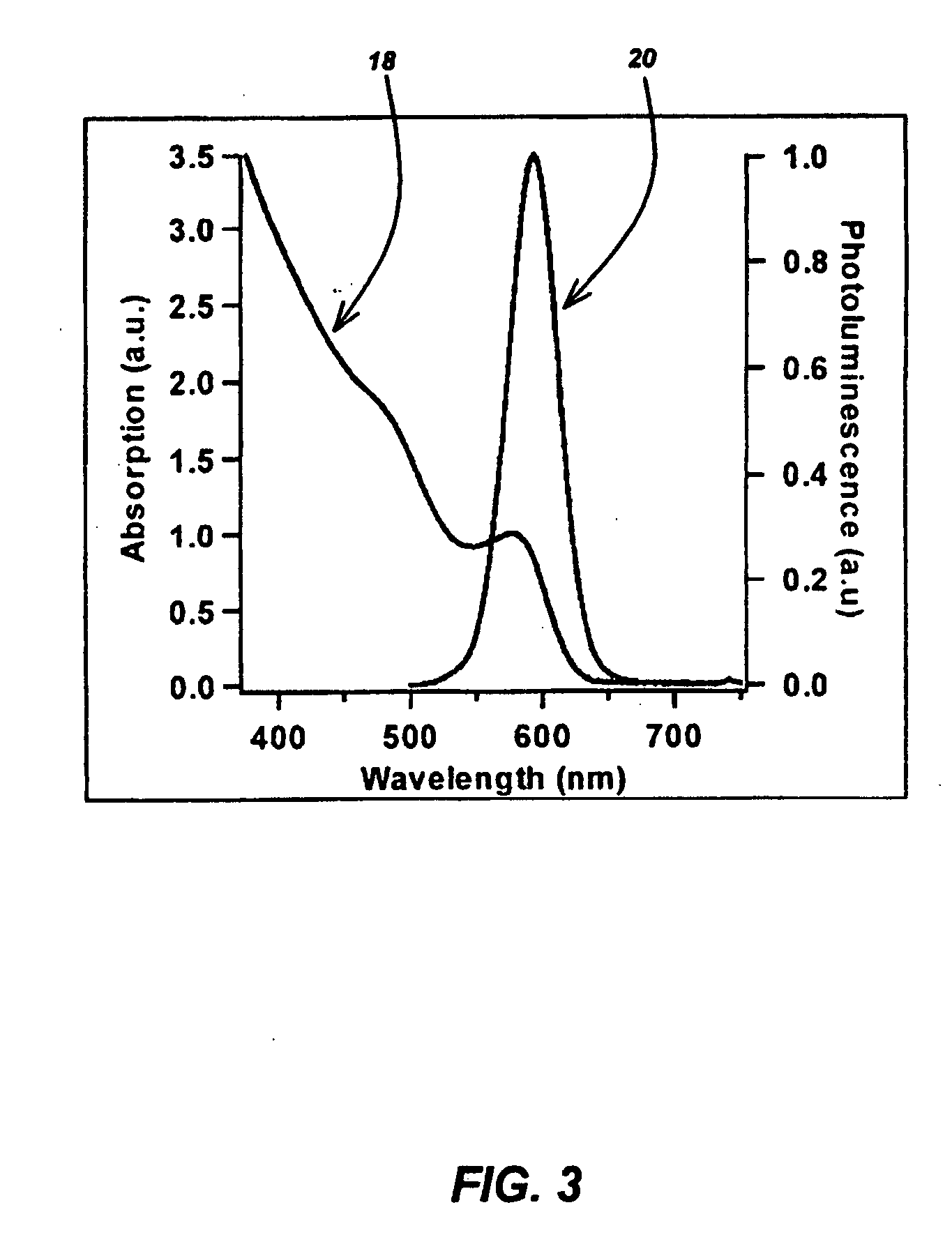
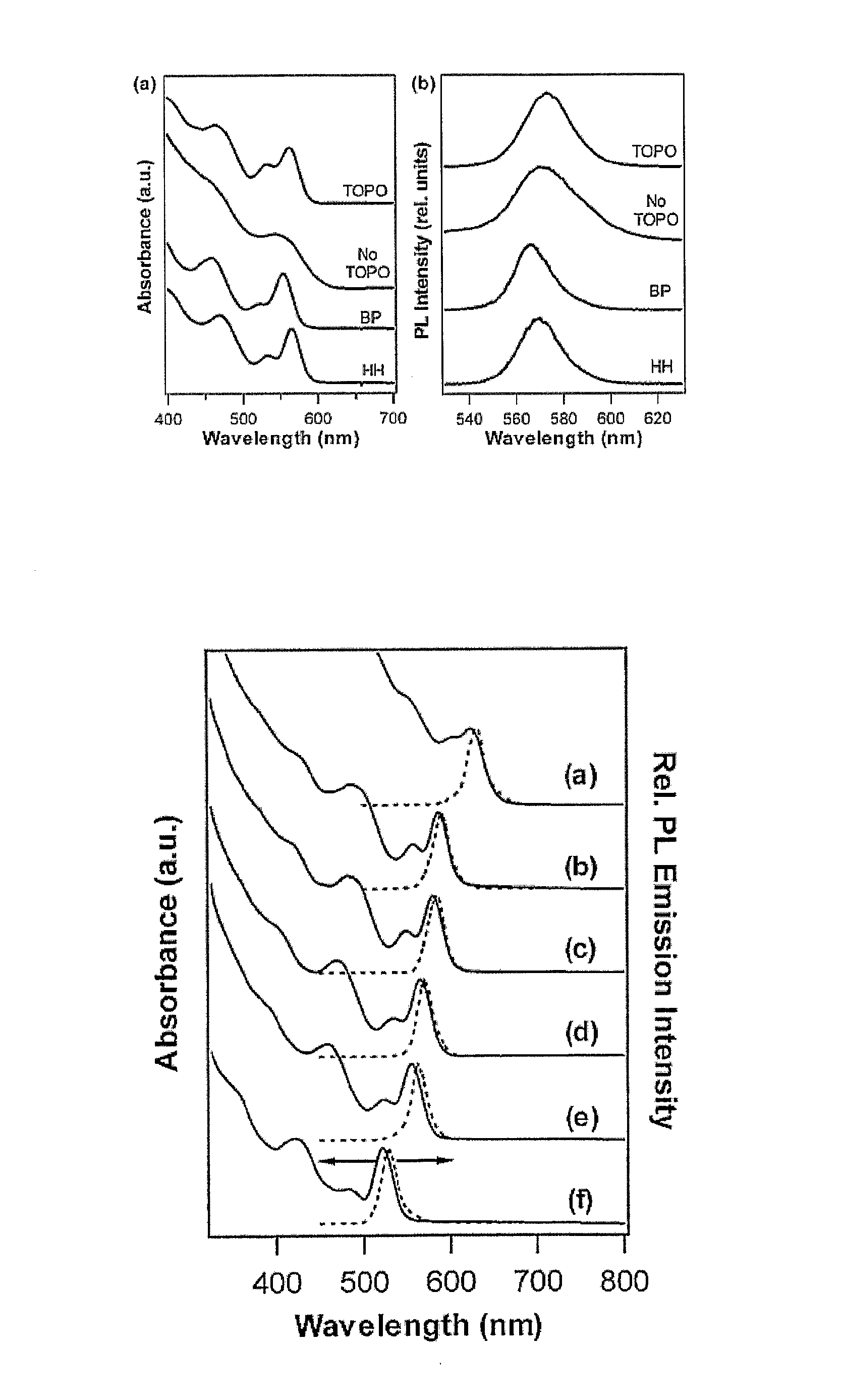
A method for producing highly monodisperse nanocrystals comprising the steps of: a) preparing a precursor comprising a metal ion and a coordinating ligand; b) dissolving the precursor in a solvent mixture comprising coordinating solvent and optionally non-coordinating solvent; c) raising the temperature of the step b mixture into the range from 150° C. to 350° C.; d) adding a chalcogen to the step c heated mixture whereby the chalcogen reacts with the precursor; e) lowering the temperature of the step d mixture to stop the reaction; and e) maintaining the step e cooled mixture for sufficient time at sufficient temperature to narrow the size distribution of the nanocrystals. The methods greatly reduce or eliminate the need for trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO); provide control over particle size, and permits facile production of high quality nanocrystals with very small diameters (<4 nm). CdSe nanocrystals produced via the methods are shown in the Figure.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Method for synchronously realizing water-phase transfer and nucleus targeting of hydrophobic nanoparticles
InactiveCN103011258AWater phase stabilityGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologySelenium/tellurium compundsNanoparticleSurface-active agents
The invention relates to a method for synchronously realizing water-phase transfer and nucleus targeting of hydrophobic nanoparticles, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials. The method comprises the general steps of adding a proper amount of organic solution with the hydrophobic nanoparticles to the aqueous solution containing a surface active agent with a certain concentration; stirring for an appropriate time; and then separating to remove residual surface active agent molecules, wherein the utilized surface active agent molecules contain quaternary ammonium salts at the hydrophobic ends. According to the method, such a surface active agent is adopted and used for modifying the hydrophobic nanoparticles, thus the water-phase transfer of the hydrophobic nanoparticles can be realized, and the nanoparticles show remarkable effect of nucleus targeting without requiring any additional modifications or treatments after the water-phase transfer.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method of preparing sulfide nano material of lead with calixarene adjusting solvent thermal system
InactiveCN1907863ARealize chemical reactionParticle size increases or decreasesNanostructure manufactureLead sulfidesLead nitrateThiourea
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic nanomaterials, and involves a preparation method for sulfur compounds of lead nanomaterial by calixarene in a specific thermal control system solvent. Said method comprises placing lead salt and calixarene in a container, using toluene as solvent, stirring at 70-90DEG C for 0.8-1.5 hours to obtain a mixture, transferring the mixture into a reactor and adding sulfur source, adding toluene to 3 / 5-4 / 5 of the reactor volume and sealing, reacting at 150-200DEG C for 18-30 hours and cooling to room temperature, washing, separating, and drying to obtain the final product. The molar ratio of sulfur source to lead salt is 1 : 1, wherein the lead salt is one of lead nitrate and lead acetate and sulfur source is one of thiourea, sulfur powders, and selenium powders. The raw materials of this invention are easy to get and cheap. This invention also has the advantages of simple operation and equipment, high purity, convenient treatment, and being easy for industrialization. This invention provides a new method for preparing nanomaterials by controlled synthesis.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com