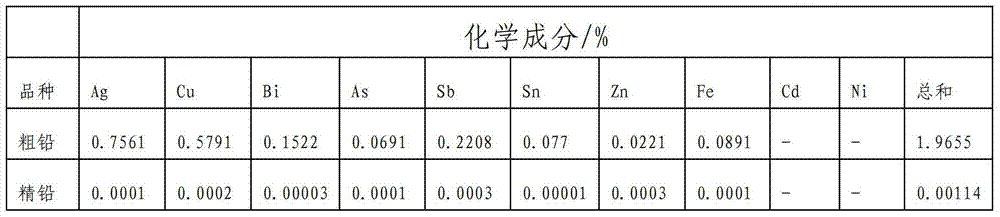
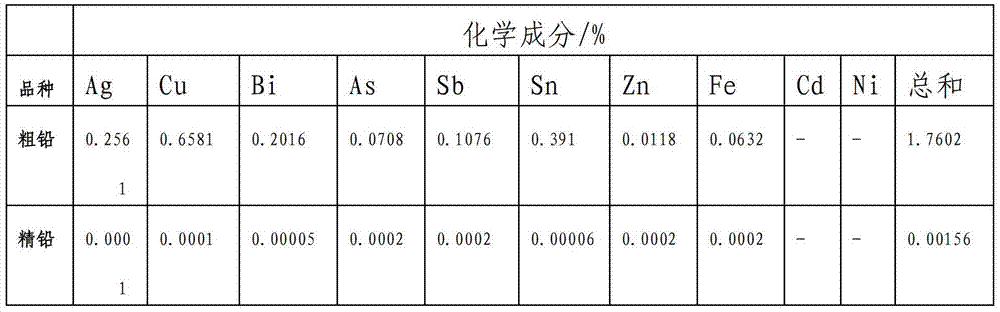
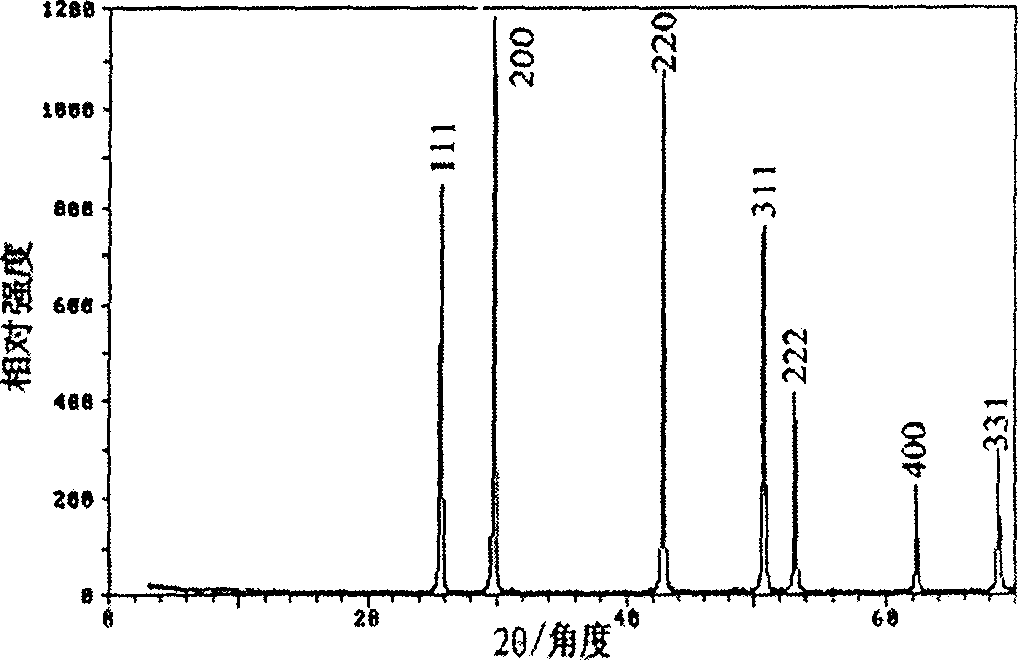
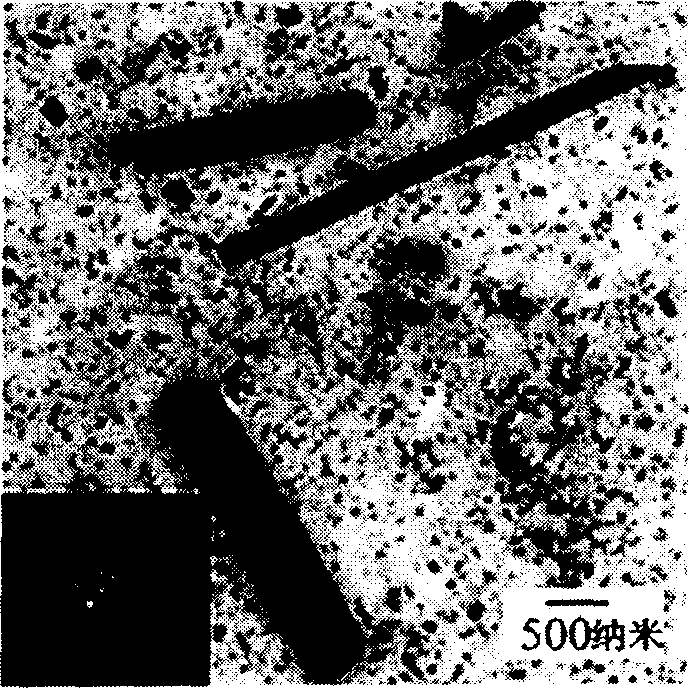Patents
Literature
67 results about "Compounds of lead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compounds of lead exist in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.
Process for recovering lead oxides from exhausted batteries
ActiveUS7507496B1Speed up the processObtained inexpensivelySolvent extractionPrimary cell maintainance/servicingLead dioxideLead oxide
A process for recovering lead oxides from the spent paste of exhausted lead acid batteries. The process provides heating the spent paste with an alkali hydroxide solution at elevated temperatures prior to calcinations. Calcination is at various temperatures so that either lead mono-oxide, lead dioxide or red lead is obtained as the principal product. There is also provided the use of the lead oxide to prepare the paste for positive and negative electrodes or other lead compounds.
Owner:RETRIEV TECH +1
Reclaiming of lead in form of high purity lead compound from recovered electrode paste slime of dismissed lead batteries and/or of lead minerals
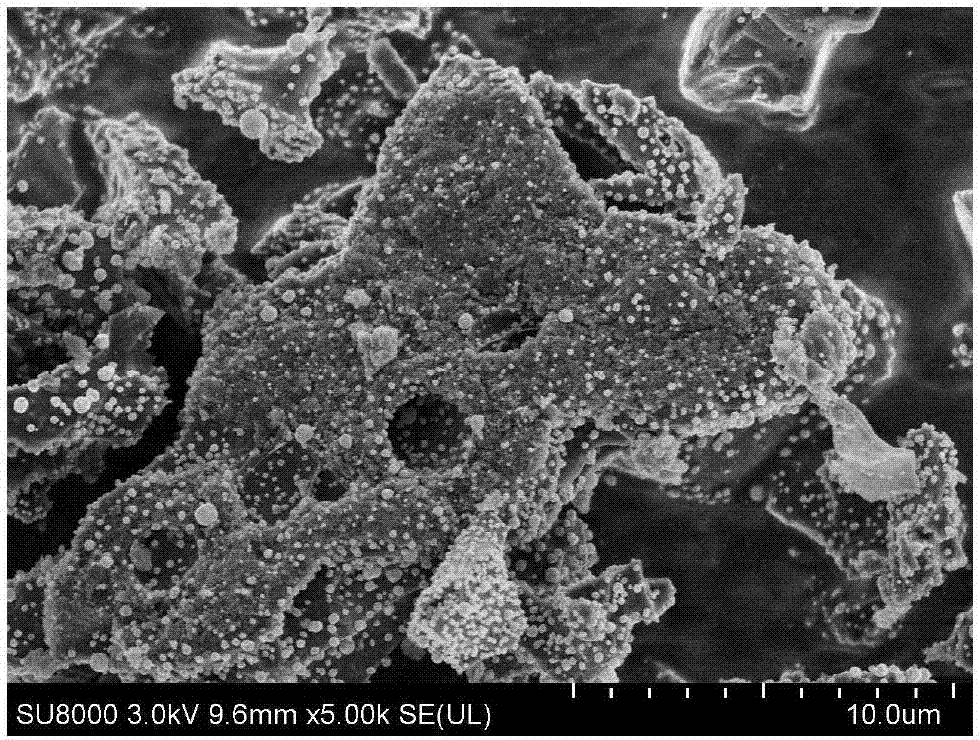
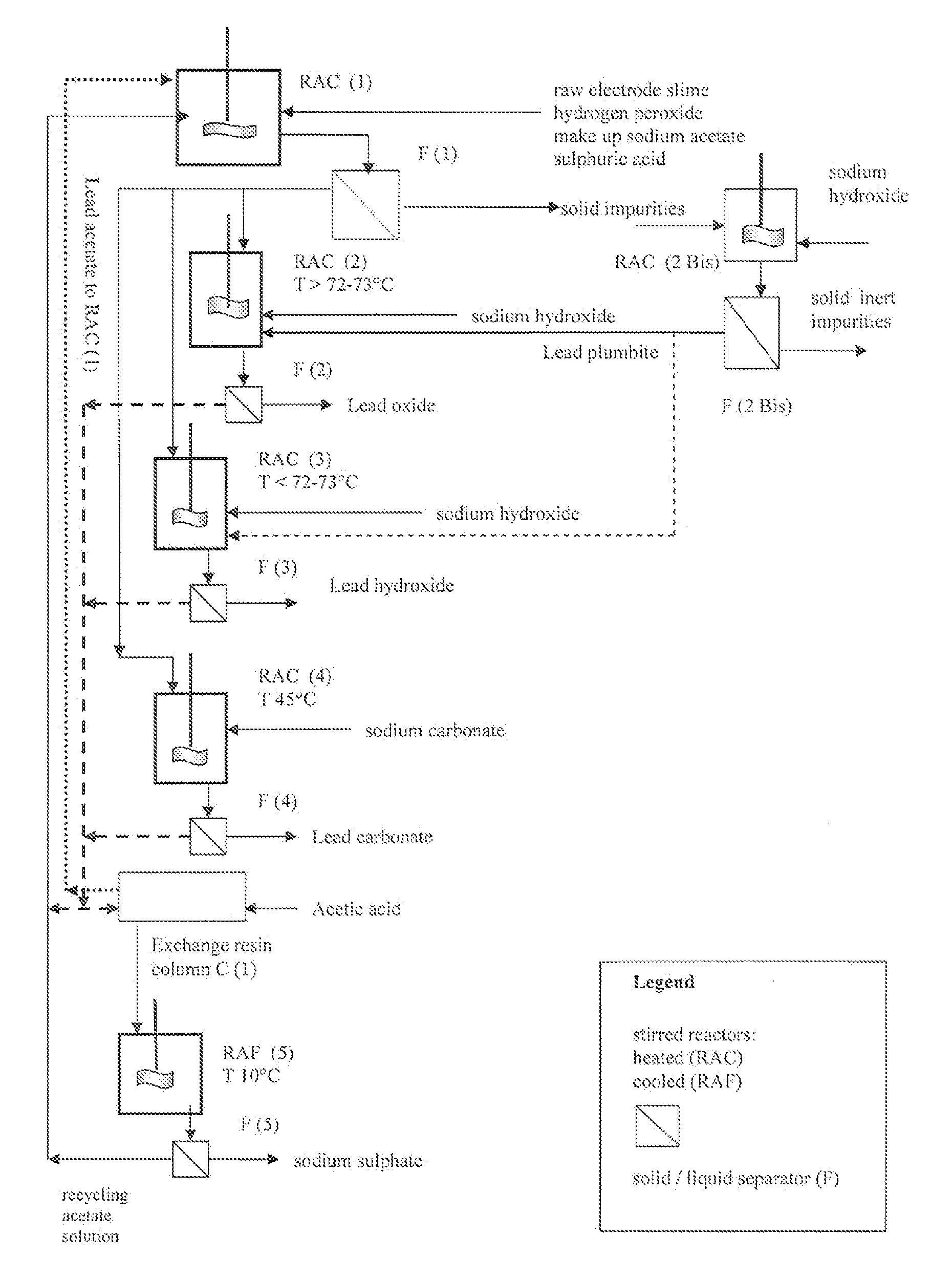
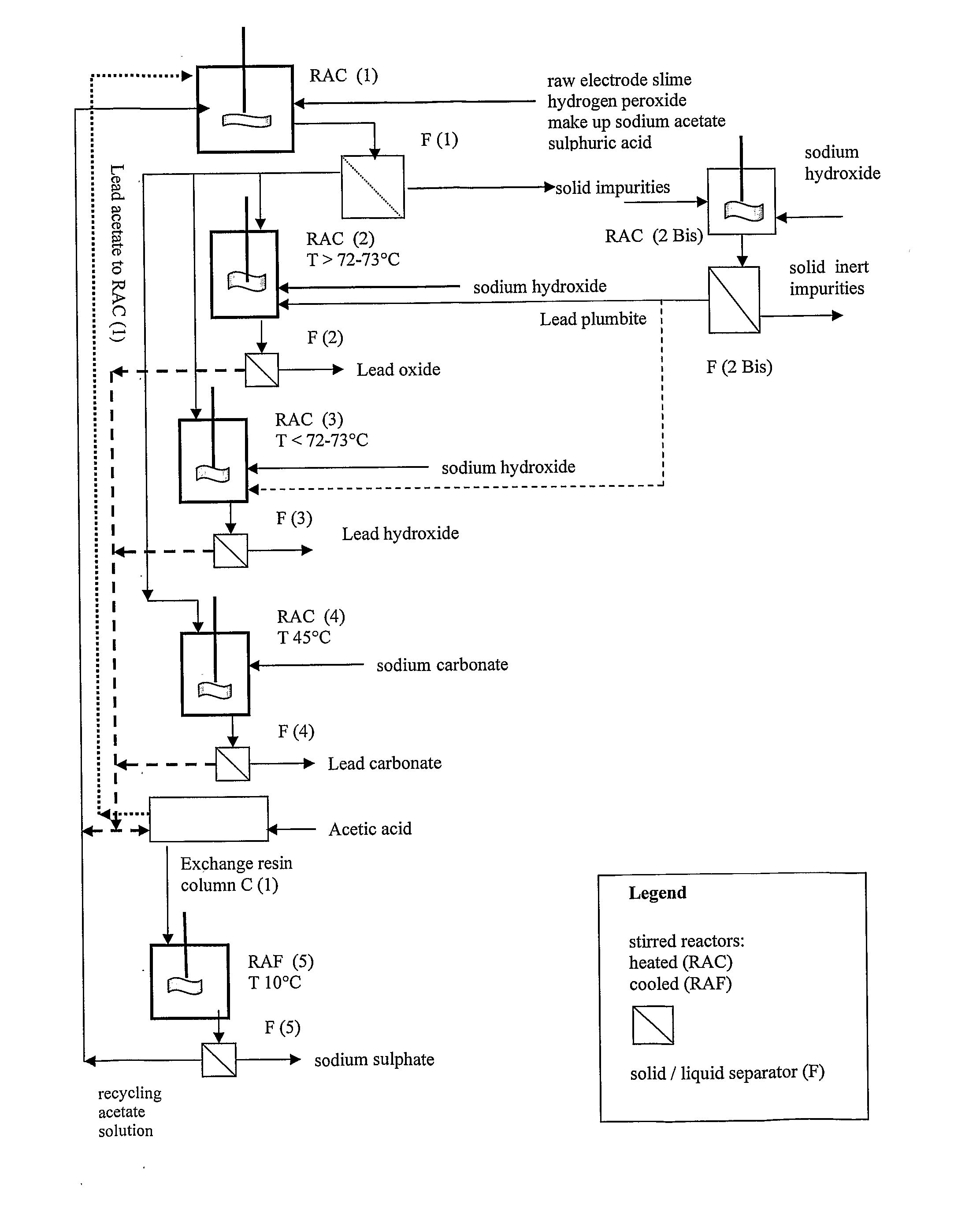
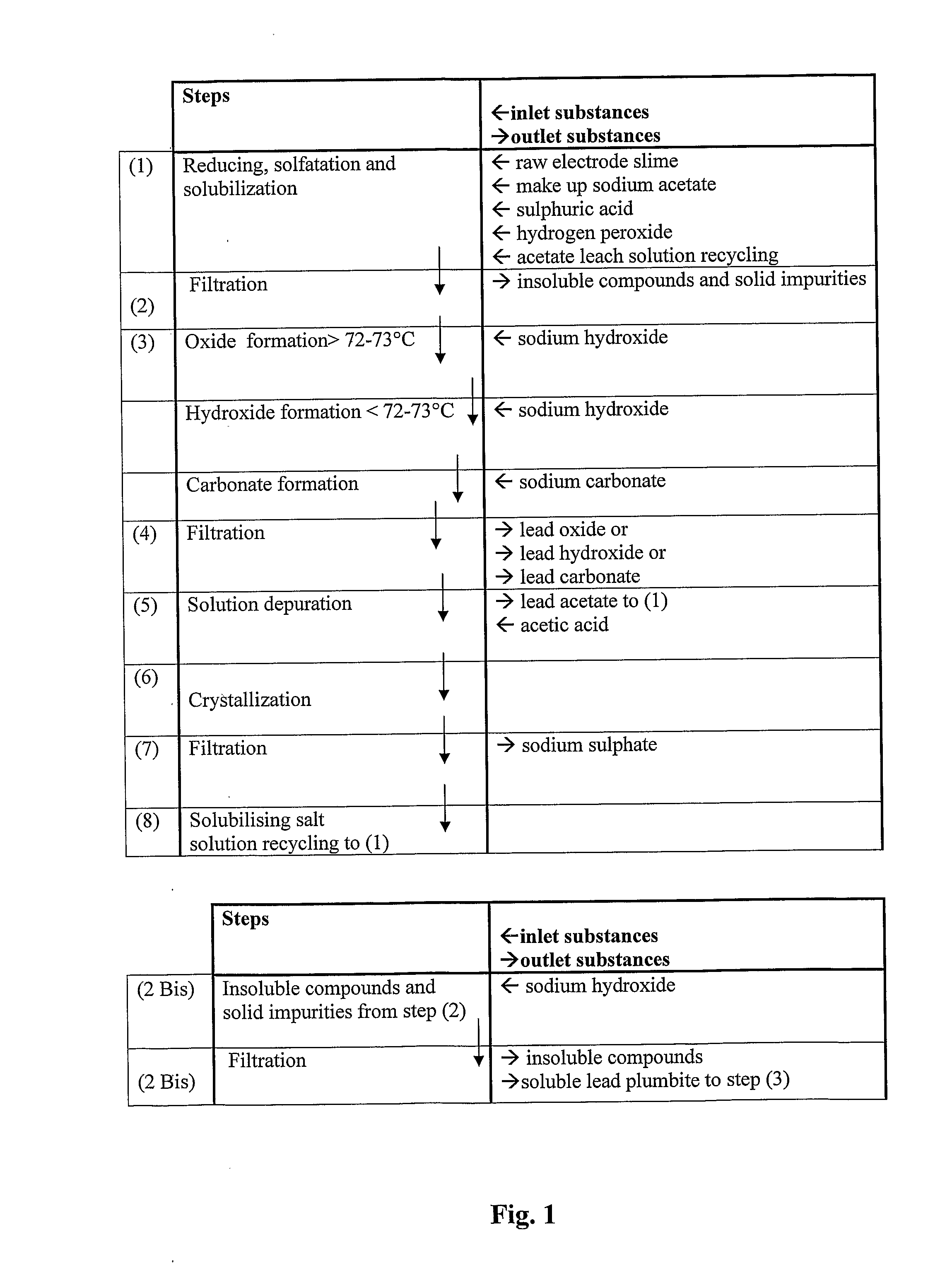
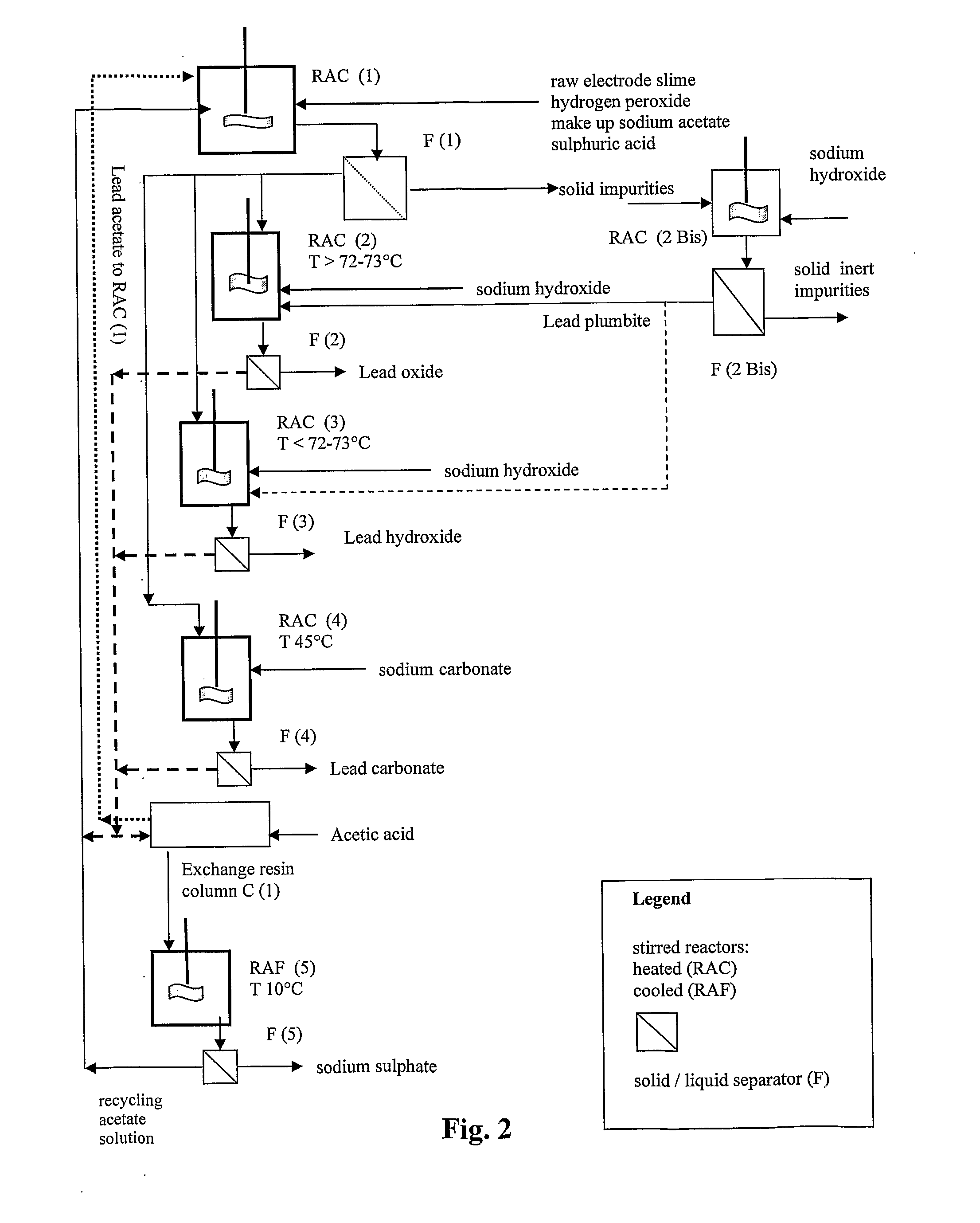
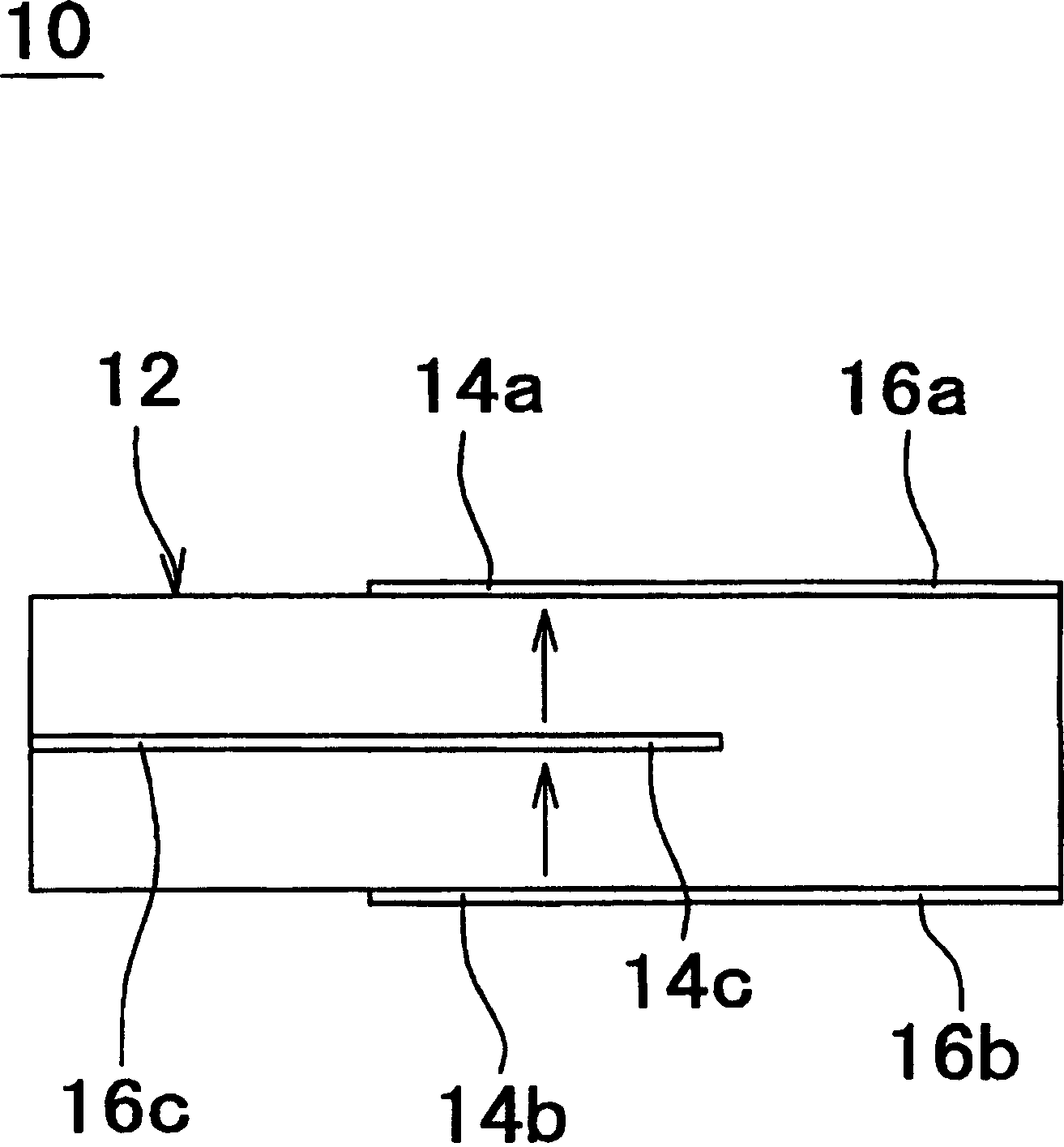
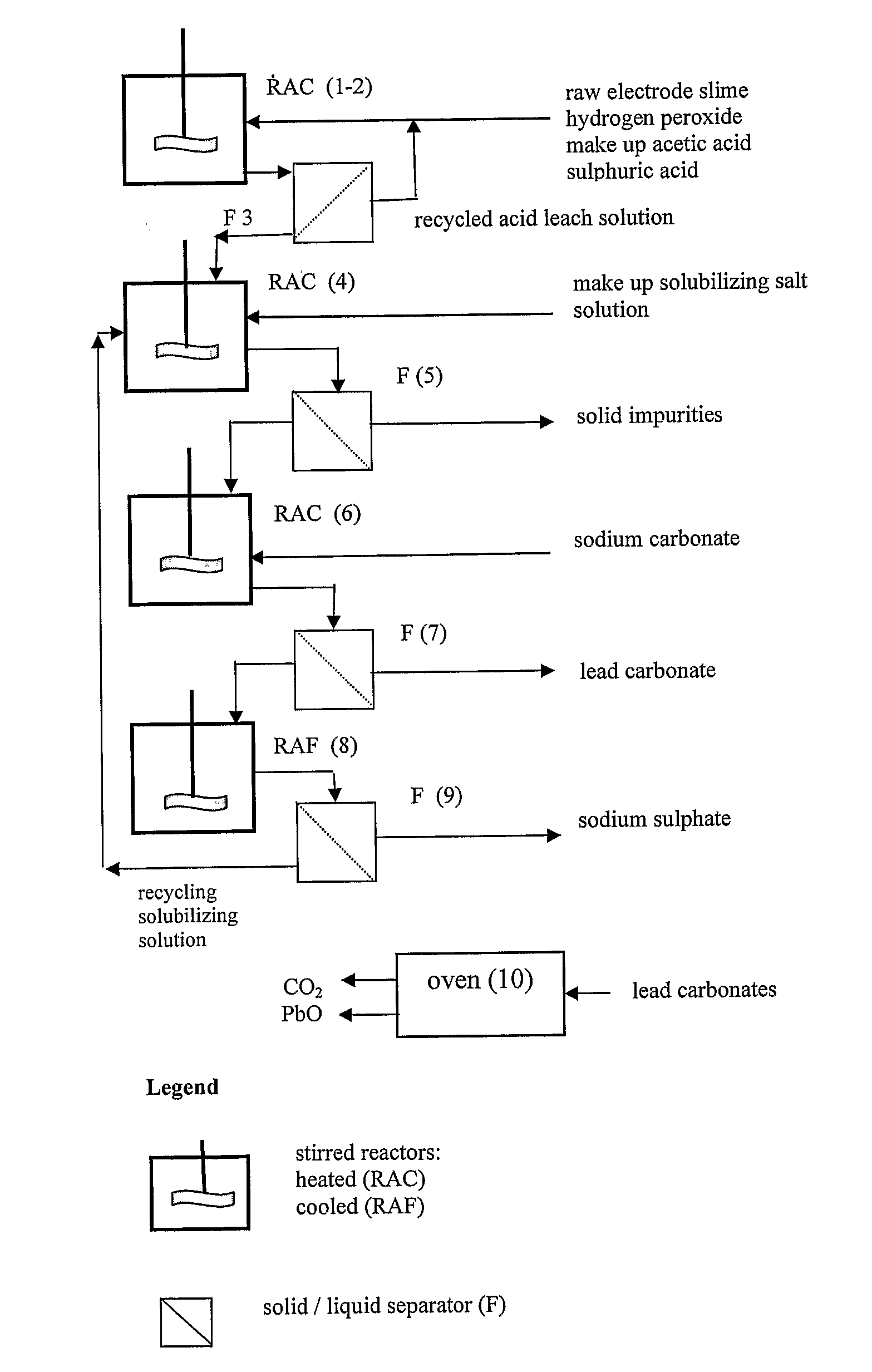
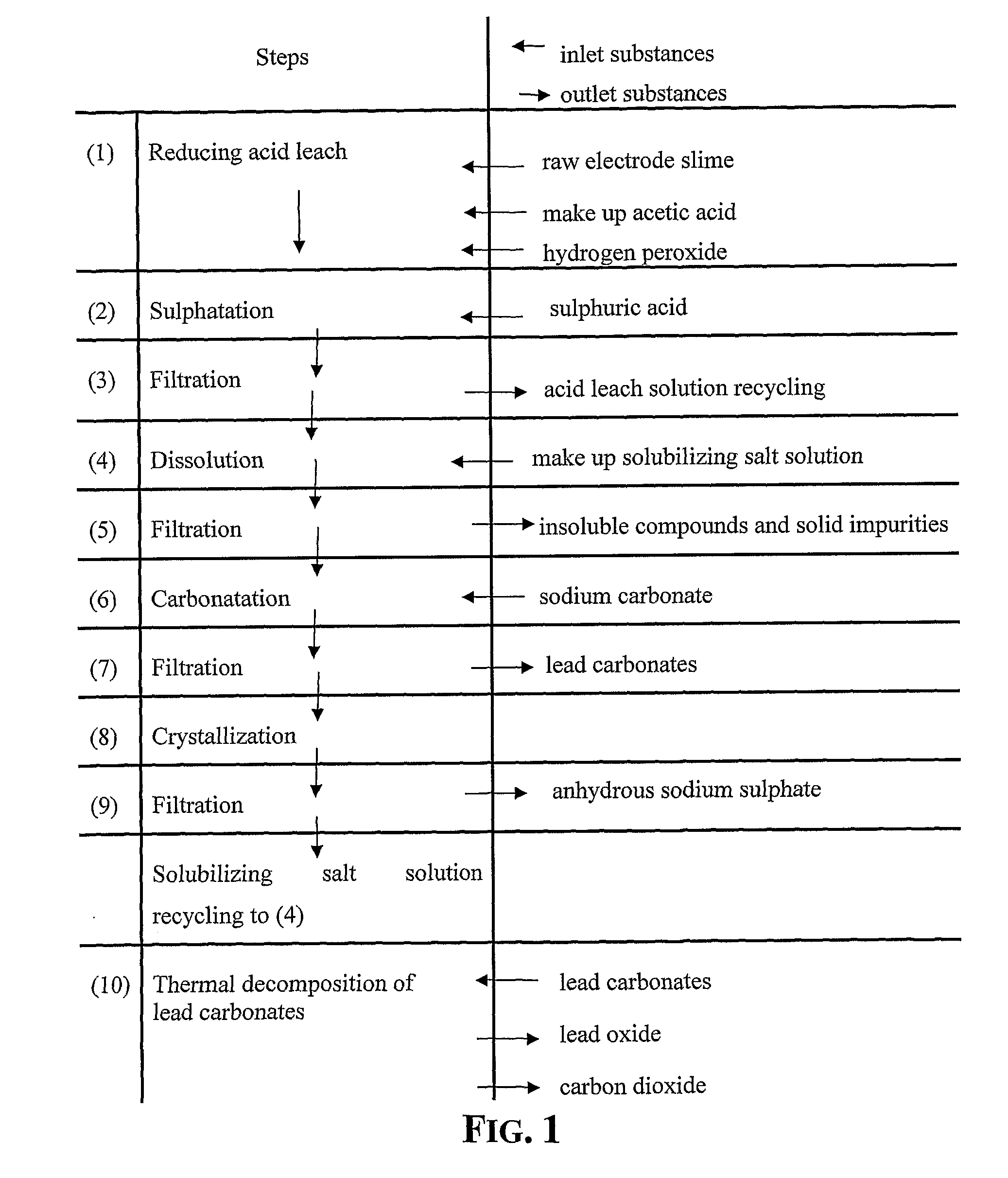
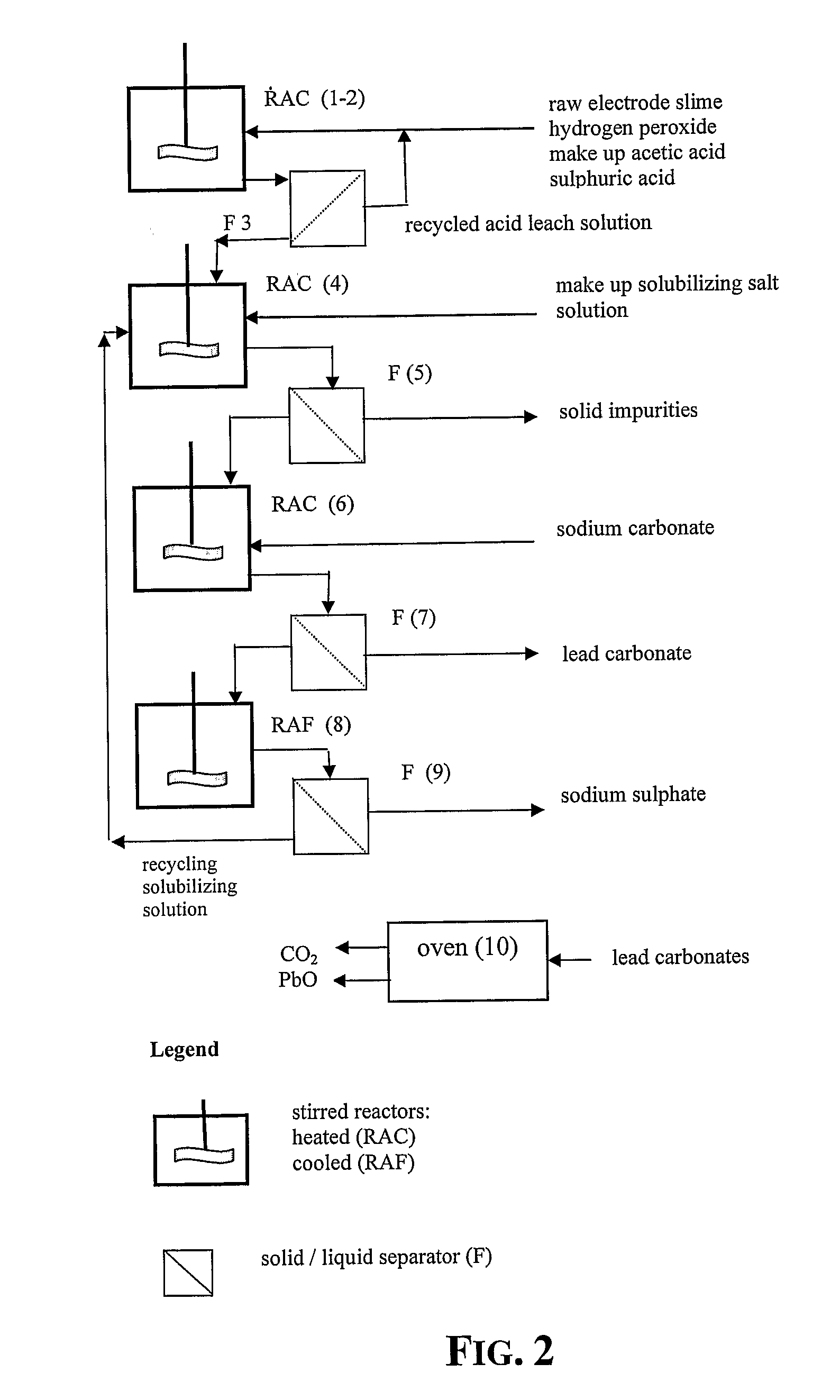
An outstandingly low environmental impact wet process recovers the lead content of an electrode slime and / or of lead minerals in the valuable form of high purity lead oxide or compound convertible to highly pure lead oxide by heat treatment in oven at relatively low temperature, perfectly suited for making active electrode pastes of new batteries or other uses. The process basically comprises the following treatments:a) suspending the impure lead containing material in an aqueous bath containing at least a lead oxide dissolving acid;b) reducing any insoluble lead dioxide to lead oxide by introducing in the suspension either hydrogen peroxide, a sulphite or sulphurous anhydride;c) converting all dissolved lead oxide to lead sulphate in the aqueous bath;d) obtaining a solution of lead sulphate obtained in an aqueous solution containing an acetate salt;e) precipitating and separating a purified lead compound in the form of either carbonate / oxycarbonate or of oxide / or hydroxide by adding to said acetate salt solution a carbonate salt or a hydroxide of the same cation of said acetate salt, respectively.Exemplary flow sheets according to several alternative embodiments and related processing plant diagrams are disclosed.
Owner:MILLBROOK LEAD RECYCLING TECH
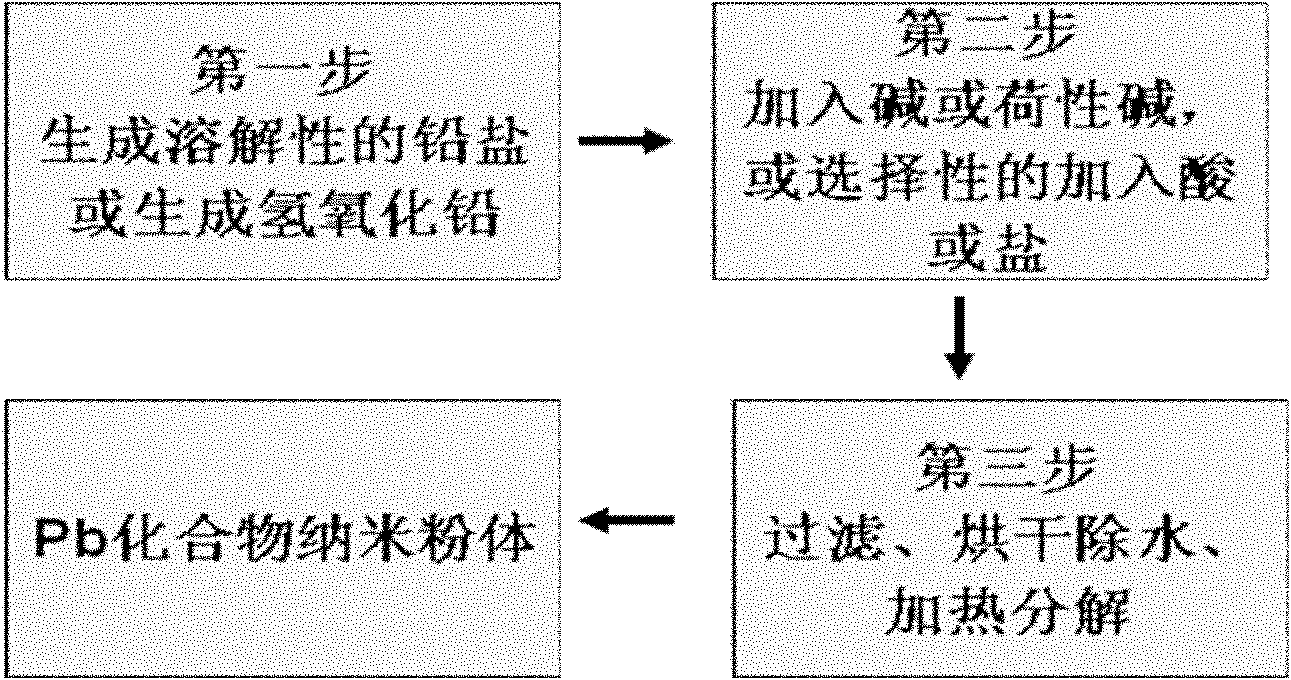
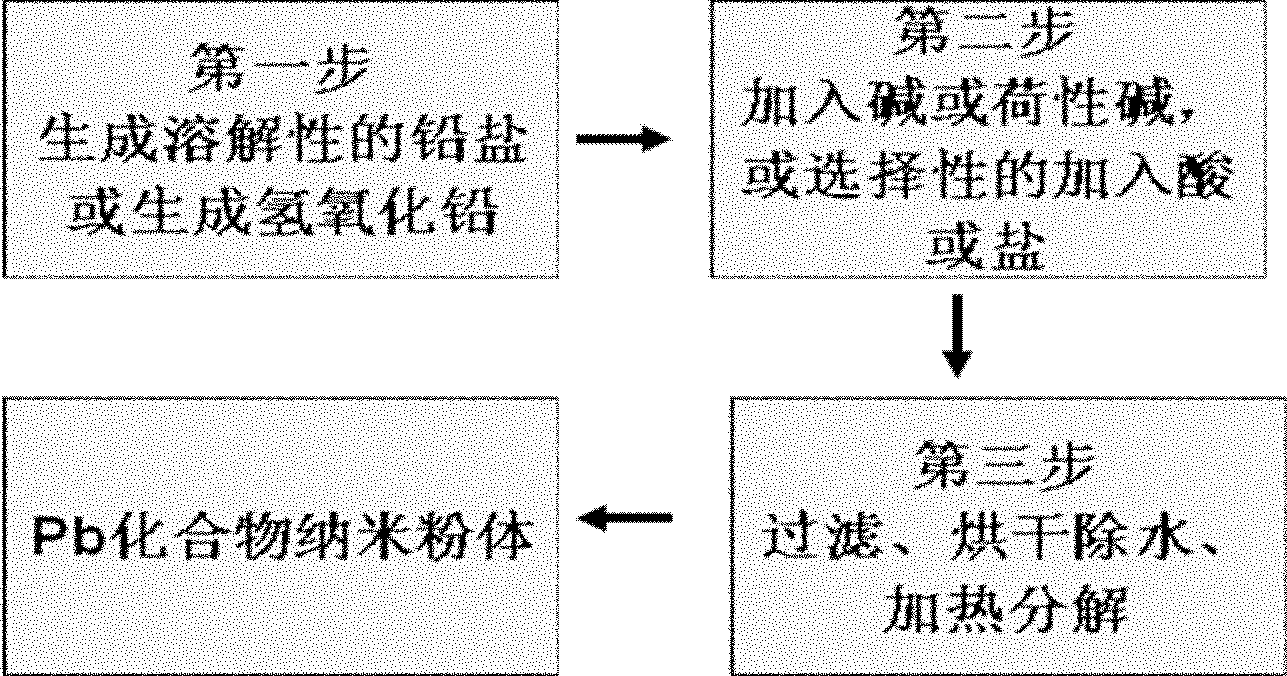
Lead compound nano-powder preparation method for recovery and manufacture of lead-acid battery
ActiveCN102689922AEnvironmental recyclingEnvironmental productivityLead monoxideNanotechnologySolubilityLead salt
The invention discloses a lead compound nano-powder preparation method for recovery and manufacture of lead-acid battery. The lead compound nano-powder preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, lead, a lead salt or waste lead-acid battery lead paste reacts with one or more organic or inorganic compounds to produce a soluble lead salt solution or a lead hydroxide solution; 2, one or more alkalis or caustic alkalis are added into the soluble lead salt solution, or a part or excess amount of H2CO3 or CO2, sulfuric acid, one or more organic acids or their salts are added into the lead hydroxide solution, and 3, lead oxide or lead hydroxide precipitates obtained by the step 2 are filtered and are subjected to drying and pyrolysis to form the lead compound nano-powder. The lead compound nano-powder preparation method realizes environmentally friendly recovery and production, has low energy consumption, greatly reduces a production cost, and shortens a production period. The lead compound nano-powder obtained by the lead compound nano-powder preparation method is conducive to improvement of technical product performances.
Owner:杨春晓
Preparation method of leadless glass powder for electronic slurry
A process for preparing lead-free glass powder used for electronic paste, which comprises: firstly uniformly mixing silicon dioxide or sodium silicate, barium oxide or barium carbonate, boron oxide or boric acid, bismuth oxide or bismuth sulfate, aluminum oxide, aluminum sulfate or aluminum silicate, zinc oxide or zinc carbonate, sodium oxide, sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate, potassium oxide or potassium carbonate and titanium dioxide, then heating the mixed raw materials to melt, cooling the melted mixture, then grinding into power by a ball grinder, sieving by a sieve of 100-400 eye and lastly drying glass powder to obtain the lead-free glass powder. Because the glass power of the invention does not contain lead oxide (PbO) or compounds of lead oxide (PbO), the invention is harmless in the manufacture process of paste, simultaneously is beneficial for environmental protection, and is convenient for recycling and reusing electronic product modules containing the electronic paste.
Owner:IRICO
Channeled polymer fibers as stationary/support phases for chemical separation by liquid chromatography and for waste stream clean-up
ActiveUS20050023221A1Reduce back pressureWide rangeSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesWaste streamCell culture media
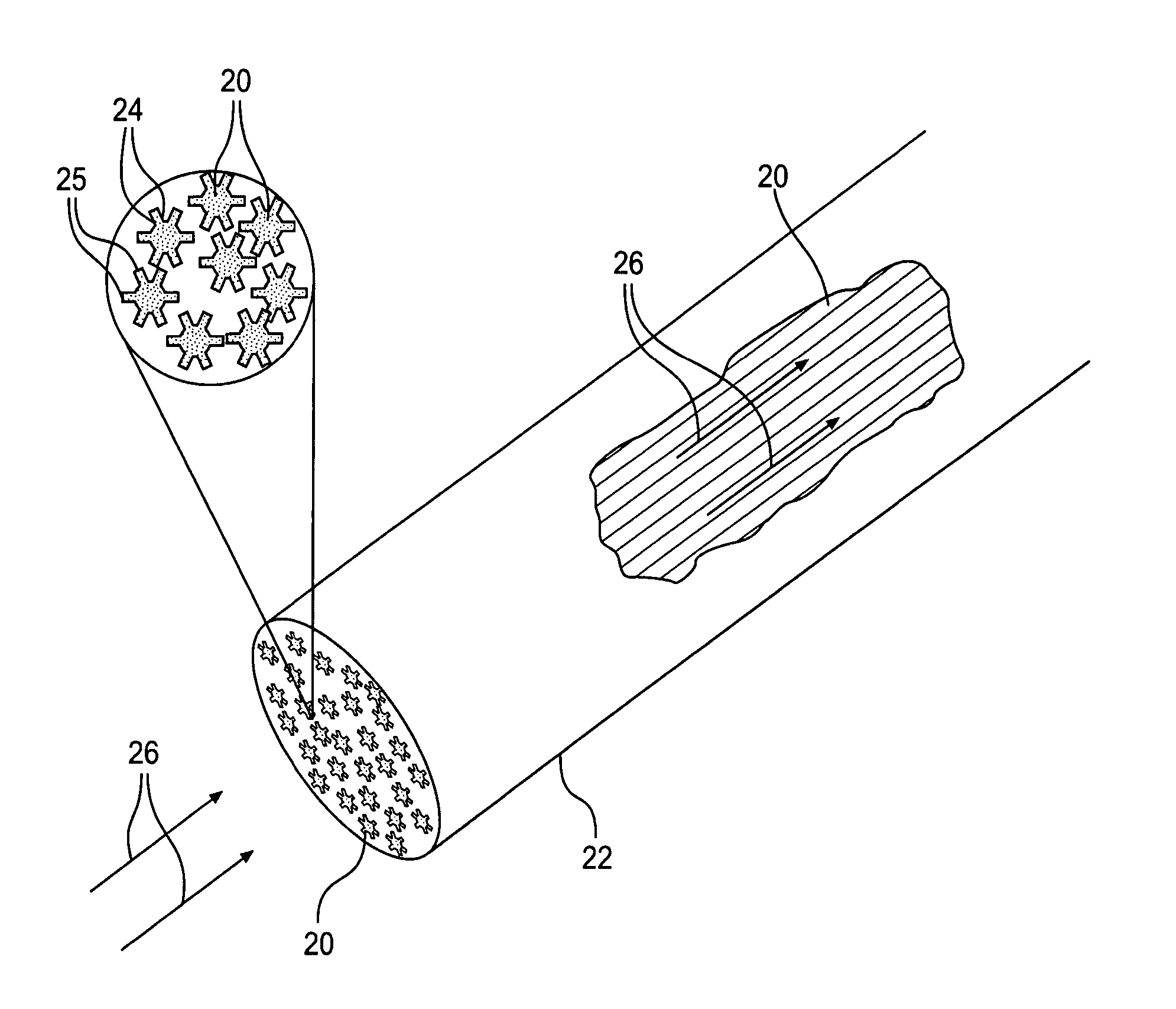
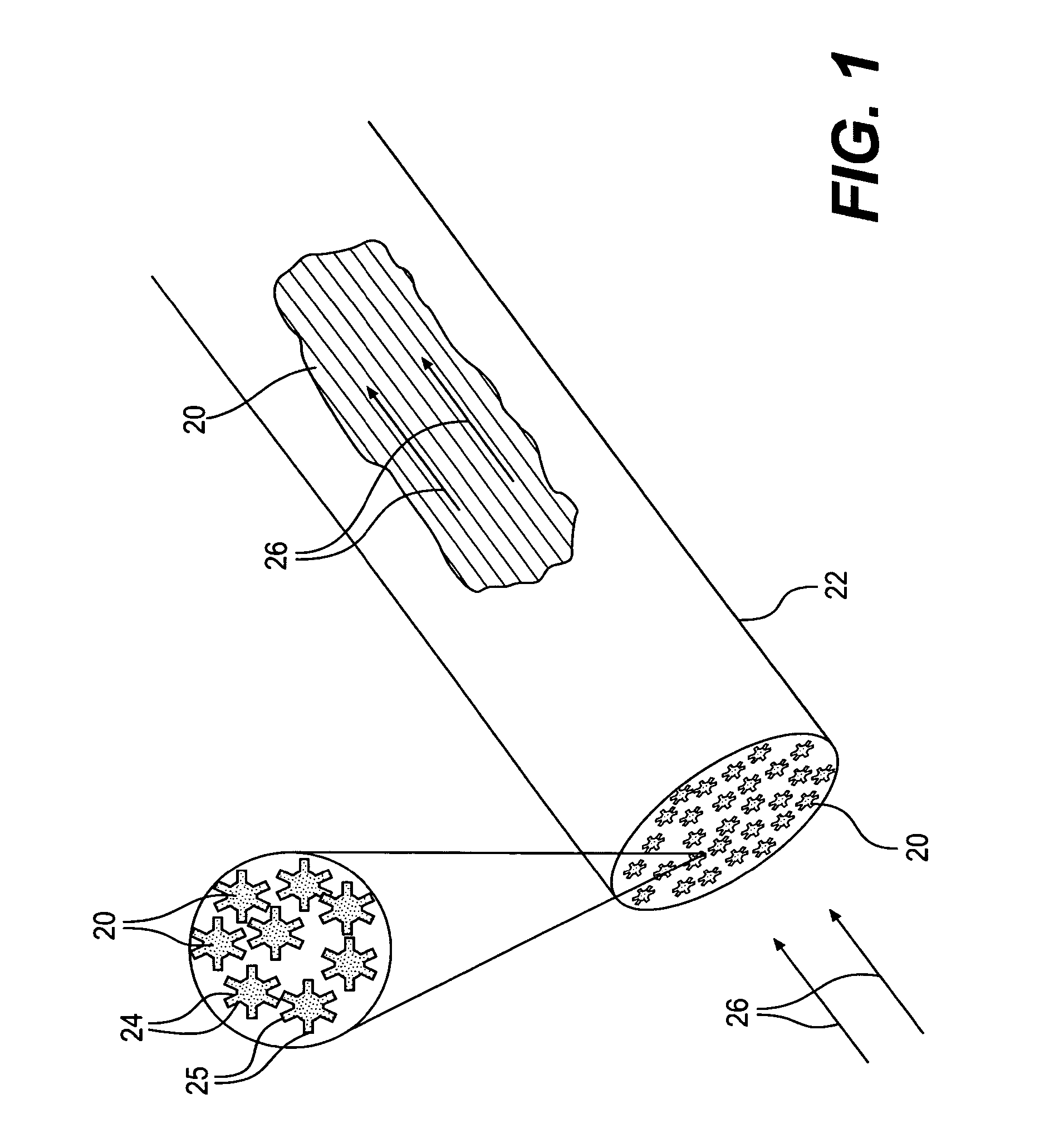
Polymer fibers having a novel cross-sectional geometry are used as stationary phase materials for liquid chromatography separations. Fibers of 20 to 50 micrometer diameters have surface-channel structures extending their entire lengths. Bundles of fibers having this novel cross-sectional geometry are packed in columns. Different polymer compositions permit the “chemical tuning” of the separation process. Channeled fibers composed of polystyrene and polypropylene have been used to separate mixtures of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Pb-containing compounds and fatty acids. Use of channeled fibers allows a wide range of liquid flow rates with very low backing pressures. Applications in HPLC, cap-LC, prep-scale separations, analytical separations, single fiber separations, waste remediation / immobilization, extraction of selected organic molecules / ions from solution, purification of liquid streams (process waste, drinking water, pure solvents), selective extraction of cell matter and bacteria from growth media, and immobilization of cell matter and bacteria are envisioned.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
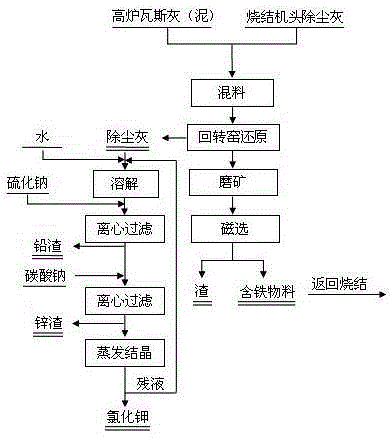
Method for comprehensively utilizing electric field dust-removal ash at head end of sintering machine and blast furnace gas ash
InactiveCN104532007AEfficient recyclingEfficient use ofProcess efficiency improvementAlkali metal chloridesRecovery methodEnvironmental resistance
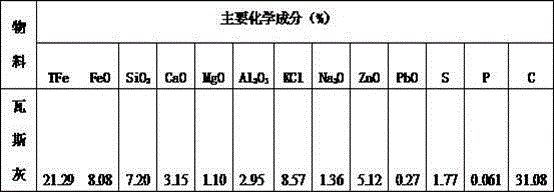
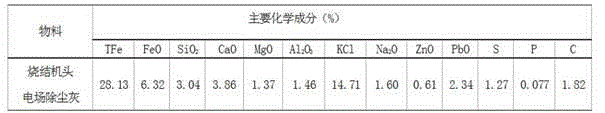
The invention belongs to the field of ferrous metallurgy and environmental protection and particularly relates to a method for comprehensively utilizing electric field dust-removal ash at a head end of a sintering machine and blast furnace gas ash. By-products generated in two metallurgical production processes, namely, electric field dust-removal ash at an electrical dust remover located at the head end of the sintering machine and blast furnace gas ash have different contents of potassium salt, iron metal compounds, carbon nonmetal elementary substance, heavy metal compounds of lead and zinc, however, the chemical compositions of the by-products are complementary, by virtue of scientific and reasonable combination and matching of two materials, certain process conditions and recovery methods, iron-containing compounds and potassium salt in the two iron and steel smelting by-products are recovered, heavy metal compounds of lead and zinc are separated so as to achieve the efficient recycling and comprehensive utilization of multiple elements in two solid wastes and meet the requirements of resourceful treatment of the solid wastes, energy conservation and emission reduction.
Owner:ANYANG IRON & STEEL
Anticorrosive Coating Compositions
InactiveUS20080000383A1Good storage stabilityAnticorrosive ability equalPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSingle substanceRust
It is an object of the present invention to provide an anticorrosive coating composition which uses a pollution-free (heavy metal-free) rust preventive pigment and exhibits anticorrosive performances equal or superior to those of lead compounds or chromic acid compounds even if the pigment is blended in various binder resins and also to provide an anticorrosive coating composition having excellent storage stability. The present invention relates to an anticorrosive coating composition comprising a binder resin and a pollution-free (heavy metal-free) rust preventive pigment containing a condensed calcium phosphate produced by baking a single substance or mixture of a calcium component and a phosphorous component in the following atomic ratio (Ca / P=m): 0.50<m<1.00, at 180 to 350° C.
Owner:DAI NIPPON TORYO CO LTD
Recovery of high purity PbO
ActiveUS7785561B1High purityTin compoundsPrimary cell maintainance/servicingLead oxideMetal particle
A process for producing high purity lead oxide from impure lead compounds particularly from waste lead battery paste which includes an oxidation-reduction step. The process results in a reduction of impure lead compounds to the +2 valence state and metal particle contaminants are oxidized to the +2 state.
Owner:RETRIEV TECH +1
Reclaiming of lead in form of high purity lead compound from recovered electrode paste slime of dismissed lead batteries and/or of lead minerals
InactiveUS20120186397A1Reduce recycling costsEffective simplificationFinal product manufactureWaste accumulators reclaimingInorganic lead compoundSolid phases
An all-wet process for reclaiming the lead content of impure electrode paste or slime from discarded lead batteries and / or lead minerals, in form of high purity lead compound, comprises a) suspending the impure lead containing material in a lead sulphate dissolving aqueous solution of a salt belonging to the group composed of the acetates of sodium, potassium and ammonium; b) adding to the suspension sulphuric acid in an amount sufficient to convert all lead oxides to lead sulphate soluble in the acetate salt solution and slowly adding to the suspension either hydrogen peroxide or a sulphite or bubbling sulphurous anhydride through it, in a measure adapted to reduce any lead dioxide to lead oxide converted eventually to soluble lead sulphate by the sulphuric acid; c) separating a limpid acetate salt solution containing dissolved lead sulphate from a solid phase residue including all undissolved compounds and impurities; d) adding to the separated solution of lead sulphate either carbonate or hydroxide of the same cation of the acetate salt of the lead sulphate dissolving solution for precipitating highly pure lead carbonate / oxycarbonate or lead oxide or hydroxide, respectively, while forming sulphate of the cation, soluble in the acetate salt solution; and e) separating the precipitated high purity lead compound from the acetate salt solution now containing also sulphate of the same cation of the acetate salt. The acetate salt solution containing also sulphate of the same cation of the acetate salt separated from the precipitated compound of lead is re-cycled to step a) and the content of sulphate of the same cation in the solution is maintained below saturation limit by continuously or periodically cooling at least a portion of the solution separated from the precipitated lead compound to cause selective crystallization of sulphate salt of the same cation of the acetate salt and removing it as a by-product. Optionally, the separated solid phase comprising insoluble compounds of lead and / or undissolved concretions of lead compounds is treated in hot concentrated hydroxide of the same cation of the selected acetate salt and converting these compounds of lead and / or undissolved concretions of lead compounds to soluble plumbites, and the separated lead containing alkaline liquor may be added to the limpid acetate solution for precipitating all reclaimable lead in form of high purity lead oxide or hydroxide.
Owner:MILLBROOK LEAD RECYCLING TECH
Remediation method of stabilization/solidification of lead-polluted soil
The invention discloses a remediation method of stabilization / solidification of lead-polluted soil. According to the method, a FeSO4 solution is added to the heavy metal lead-polluted soil, so that H+is generated through oxidization of the Fe2+, thus reducing pH value of soil, and promoting the conversion of instable lead in the soil into an effective state; then biochar and phosphate are added to the heavy metal lead-polluted soil, so that through adsorption, complexness, kation exchange, precipitation and the like between the biochar and phosphate and lead ions, the lead of effective stateis further converted into a lead compound in a stable residue state, thereby reducing the bio-availability of the heavy metal, reducing the content of the heavy metal in effective state in soil, and achieving adsorption and stabilization treatment of lead. The remediation method can reduce the leaching concentration of a leachate from the lead-polluted soil to lower than type III water quality standard (0.01 mg / L) according to the Quality Standard for Ground Water GBT 14848-2017.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Channeled polymer fibers as stationary/support phases for chemical separation by liquid chromatography and for waste stream clean-up
ActiveUS7374673B2Reduce back pressureIon-exchange process apparatusSemi-permeable membranesCell culture mediaChemical separation
Polymer fibers having a novel cross-sectional geometry are used as stationary phase materials for liquid chromatography separations. Fibers of 20 to 50 micrometer diameters have surface-channel structures extending their entire lengths. Bundles of fibers having this novel cross-sectional geometry are packed in columns. Different polymer compositions permit the “chemical tuning” of the separation process. Channeled fibers composed of polystyrene and polypropylene have been used to separate mixtures of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Pb-containing compounds and fatty acids. Use of channeled fibers allows a wide range of liquid flow rates with very low backing pressures. Applications in HPLC, cap-LC, prep-scale separations, analytical separations, single fiber separations, waste remediation / immobilization, extraction of selected organic molecules / ions from solution, purification of liquid streams (process waste, drinking water, pure solvents), selective extraction of cell matter and bacteria from growth media, and immobilization of cell matter and bacteria are envisioned.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Metal electrolytic method in alkaline solutions
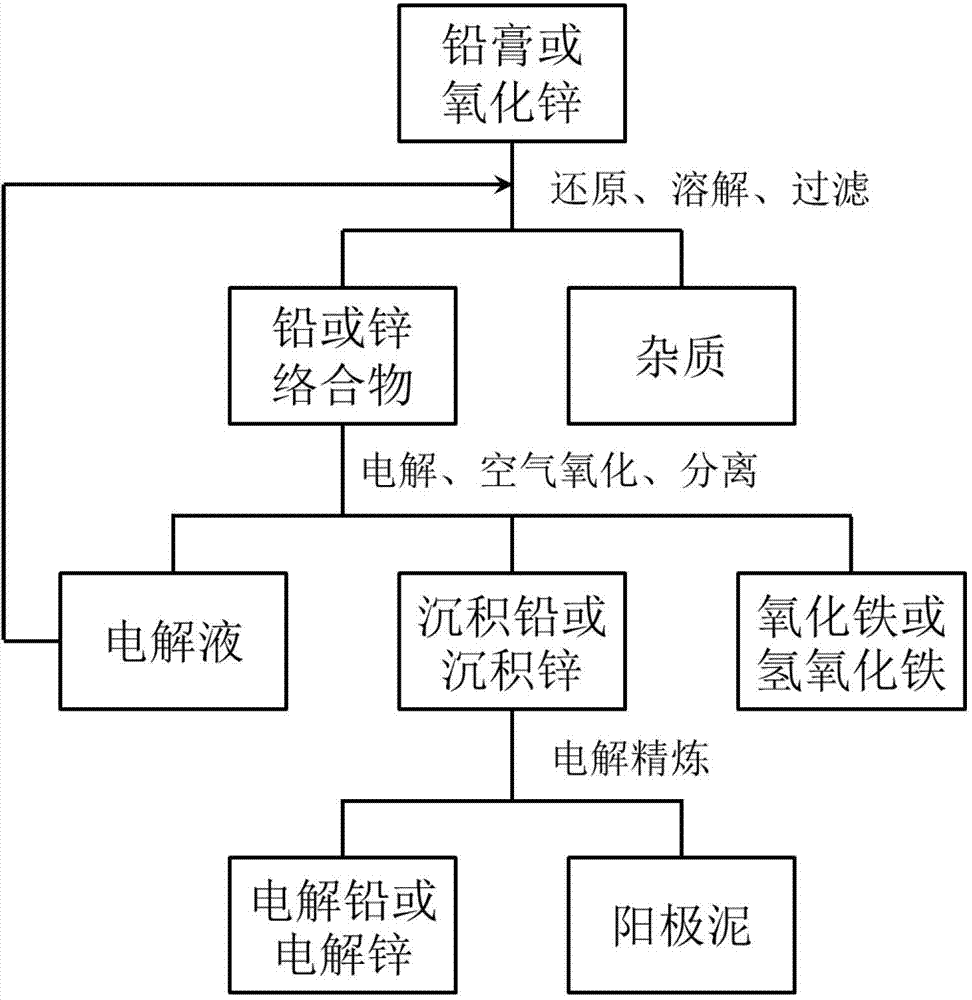
ActiveCN103540954AReduce oxidationHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesFerric hydroxideZinc compounds
The invention discloses a metal electrolytic method in alkaline solutions, which comprises the following steps: casting deposited lead or deposited zinc or commercially available crude lead or crude zinc to a 0.2-6 cm thick anode plate, and preparing a lamelliform cathode through pure lead, pure zinc or an inert electrode; electrolytic refining in alkaline electrolyte, and finally obtaining high-purity electrolytic lead or electrolytic zinc on the cathode, wherein the metal electrolytic method further comprises: 1) dissolving a lead compound or a zinc compound into the alkaline electrolyte, and adding a reducing agent to reduce lead dioxide existing in the lead compound or the zinc compound to a soluble lead complex; and 2) selecting the lamelliform cathode prepared by the pure lead, pure zinc or inert electrode in the electrolysis process, selecting the anode as iron with purity larger than 94%, and finally obtaining the deposited lead or deposited zinc on the cathode. According to the metal electrolytic method disclosed by the invention, the lead compound or the zinc compound is dissolved under an alkaline condition through a complexing agent, the electrolytic lead or electrolytic zinc is obtained by electrolyzing the cathode, and a byproduct ferric oxide or ferric hydroxide is obtained by separation.
Owner:北京中金瑞丰环保科技有限公司
Method of preparing sulfide nano material of lead with calixarene adjusting solvent thermal system
InactiveCN1907863ARealize chemical reactionParticle size increases or decreasesNanostructure manufactureLead sulfidesLead nitrateThiourea
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic nanomaterials, and involves a preparation method for sulfur compounds of lead nanomaterial by calixarene in a specific thermal control system solvent. Said method comprises placing lead salt and calixarene in a container, using toluene as solvent, stirring at 70-90DEG C for 0.8-1.5 hours to obtain a mixture, transferring the mixture into a reactor and adding sulfur source, adding toluene to 3 / 5-4 / 5 of the reactor volume and sealing, reacting at 150-200DEG C for 18-30 hours and cooling to room temperature, washing, separating, and drying to obtain the final product. The molar ratio of sulfur source to lead salt is 1 : 1, wherein the lead salt is one of lead nitrate and lead acetate and sulfur source is one of thiourea, sulfur powders, and selenium powders. The raw materials of this invention are easy to get and cheap. This invention also has the advantages of simple operation and equipment, high purity, convenient treatment, and being easy for industrialization. This invention provides a new method for preparing nanomaterials by controlled synthesis.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
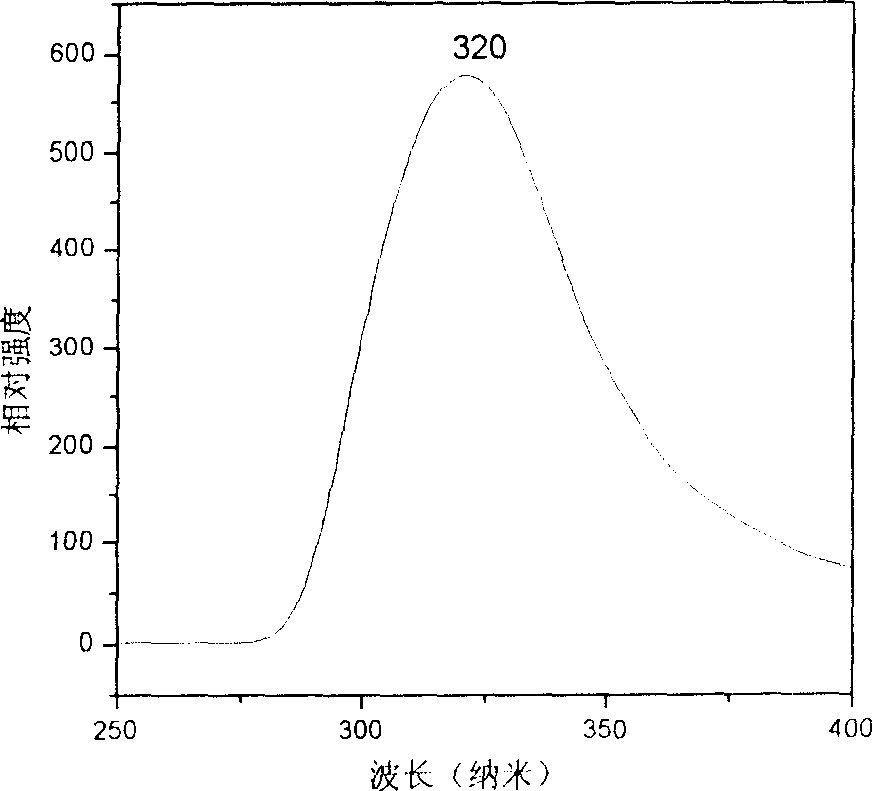
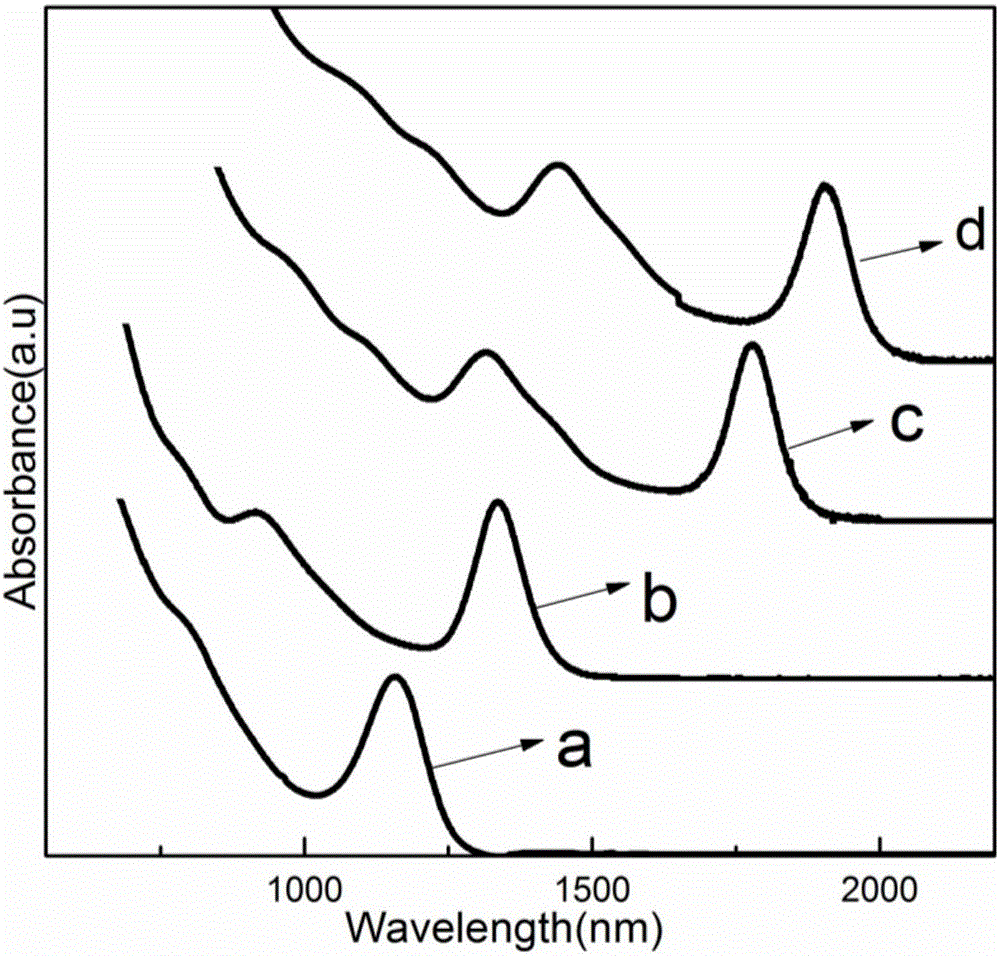
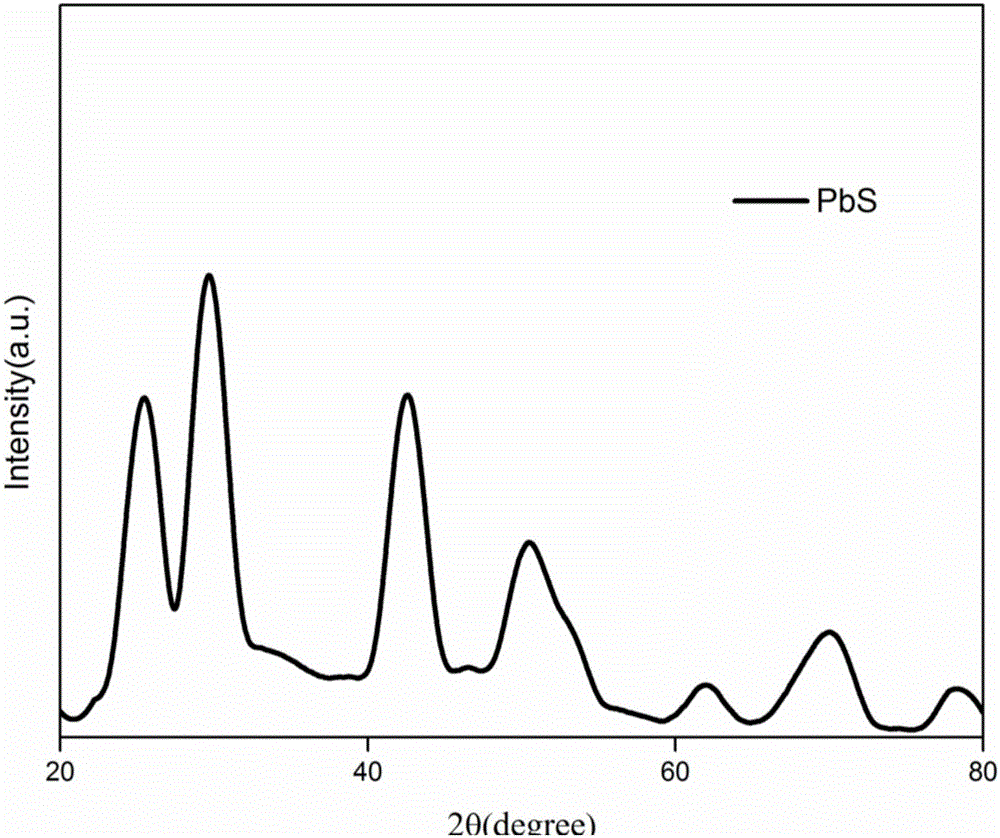
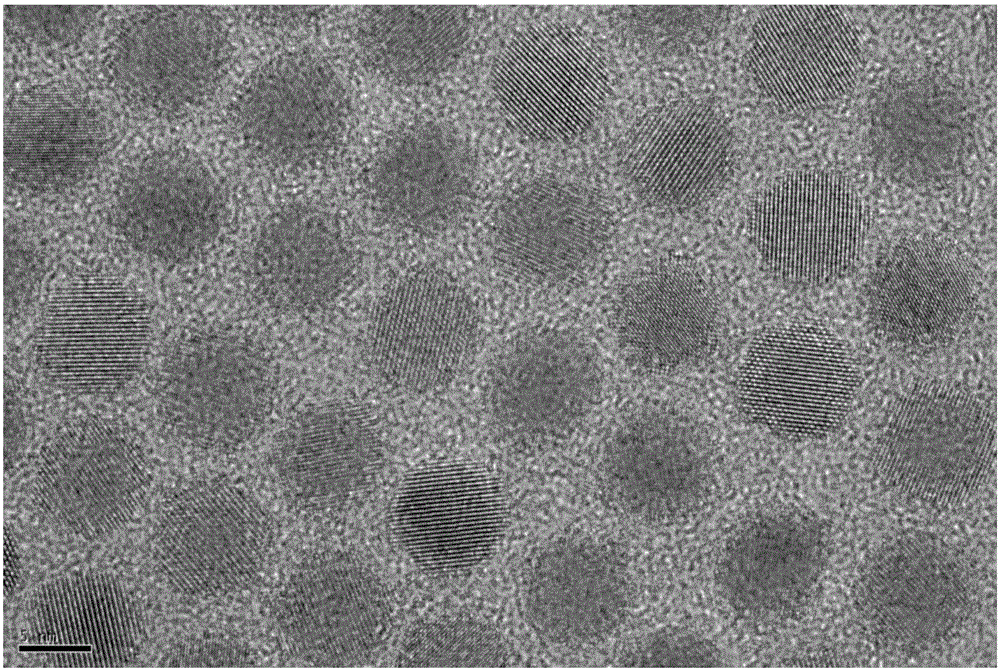
Preparation method of PbS quantum dots
The invention discloses a preparation method of PbS quantum dots. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) mixing a halogen compound of lead with oleylamine to form a mixture, heating the mixture to 80-150 DEG C in an inert atmosphere, and carrying out heat preservation to obtain an oleylamine solution of lead halide; and (2) injecting a ZnS nano-rod solution prepared in advance into the oleylamine solution of the lead halide, and reacting at a temperature of 80-190 DEG C to obtain a reaction product comprising the PbS quantum dots. Through modification of the critical preparation method principle and the reaction conditions of various steps, compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the problems that the preparation method of the PbS quantum dots is complicated and high in cost can be effectively solved, and prepared nanoparticles have the characteristics of high crystallinity, size uniformity and stability and good optical characteristics and are very beneficial to development of various characteristics of the PbS quantum dots.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
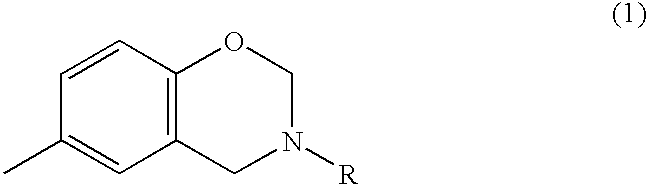
Coating composition containing benzoxazine compound
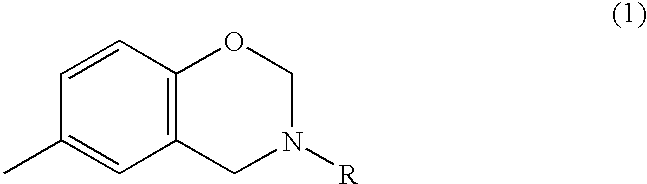
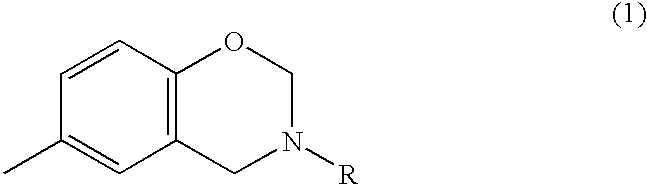
InactiveUS6905590B2Remarkable effectIncrease resistanceElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementEpoxyCompound a
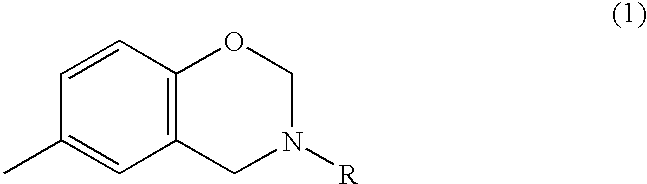
A cationic electrodeposition coating composition containing no heavy metal-based anticorrosive agents such as lead compounds, and which is capable of forming a coating film with a high corrosion resistance. The composition contains 0.5 to 20% by weight of a compound having an N-substitued benzoxazine ring represented by formula (1), relative to a resin solid matter, and an unsaturated hydrocarbon group-containing sulfide-modified epoxy resin as a base resin: wherein R is a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CO LTD
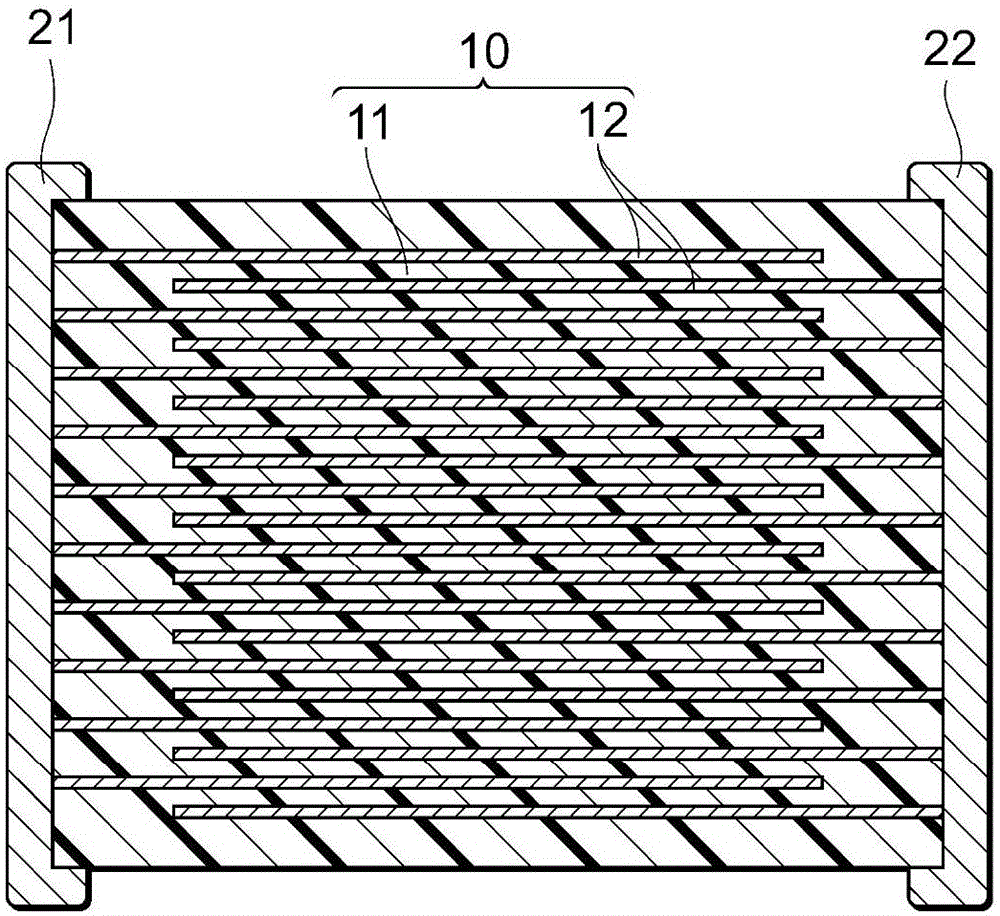
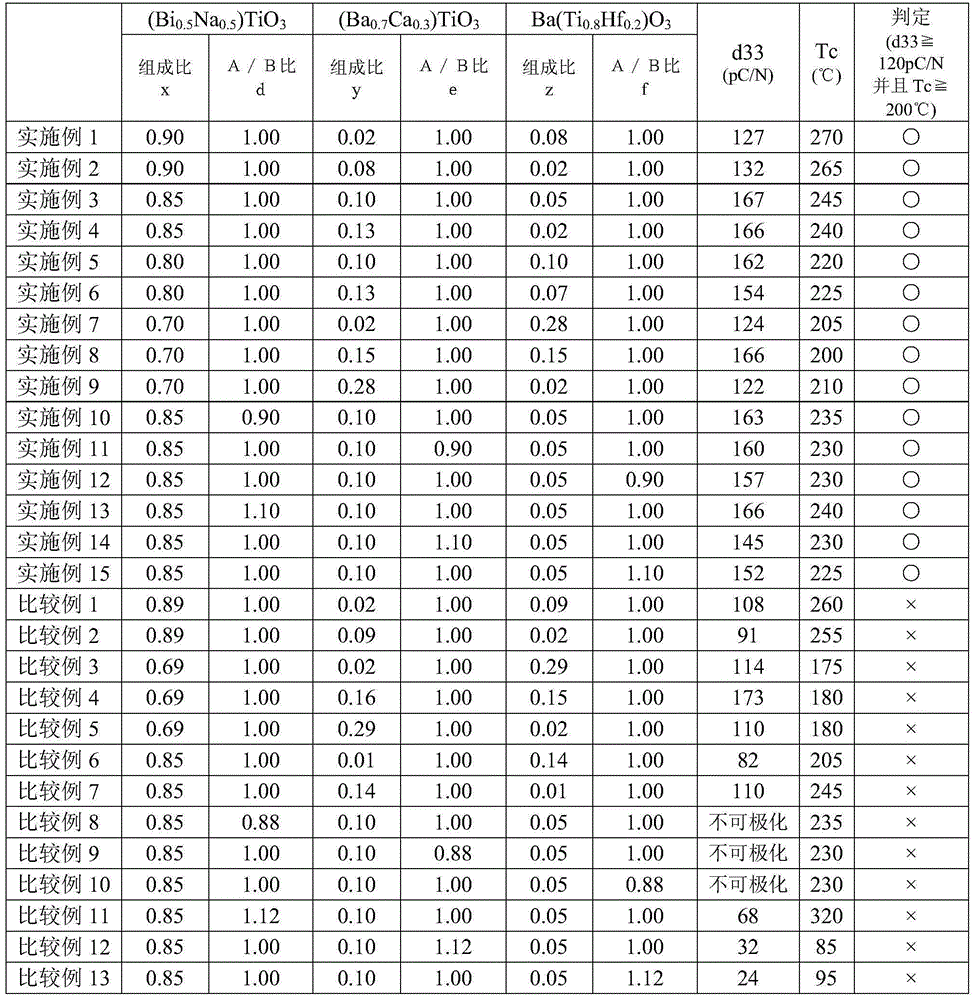
Piezoelectric composition and piezoelectric element
ActiveCN105390607AWide range of practical temperatureHigh sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Electroless displacement gold plating solution and additive for use in preparing plating solution
InactiveUS20050031895A1Improve adhesionSmooth appearanceLiquid surface applicatorsRecord information storageNickel compoundsThallium
An object of the present invention is to provide an electroless displacement gold plating solution, an additive for use in preparing the plating solution, and a metal composite material obtained by treatment with the plating solution. The present invention provides an electroless displacement gold plating solution containing a water-soluble gold compound, a complexing agent, and a water-soluble silver compound, and optionally a water-soluble thallium compound, a water-soluble lead compound, a water-soluble copper compound or a water-soluble nickel compound, or any combination thereof. The plating solution has good stability and, even not only immediately after the preparation but also after a lapse of a certain time period from the preparation, can be used for production of a metal composite material exhibiting a even plated appearance and also having a thick gold coating film.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
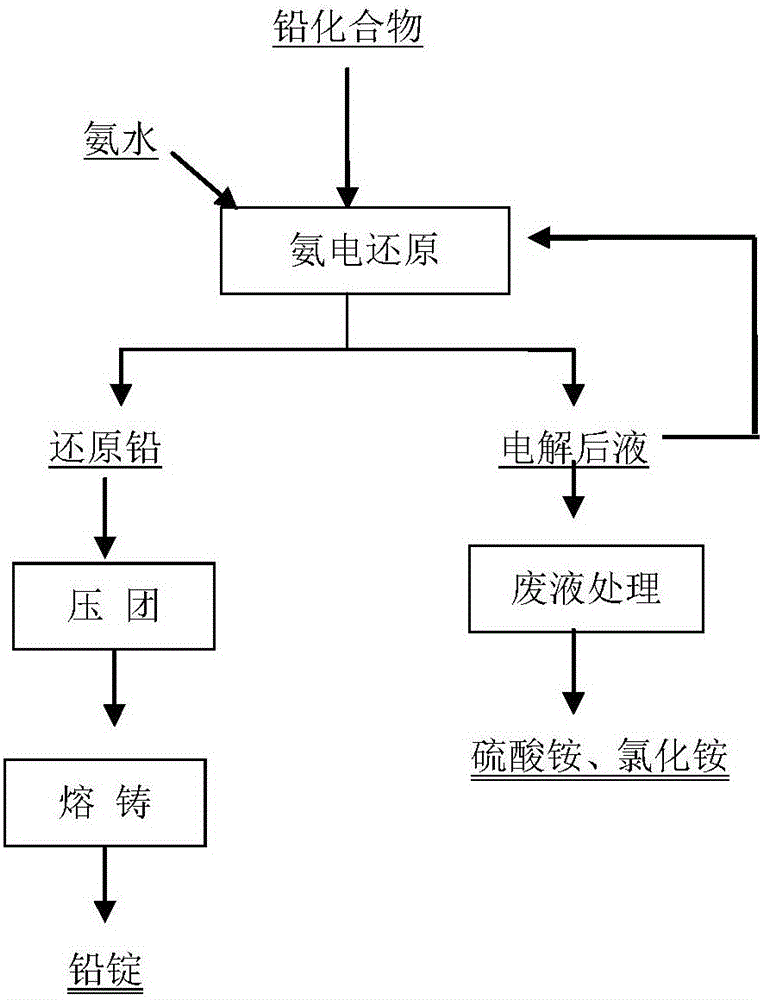
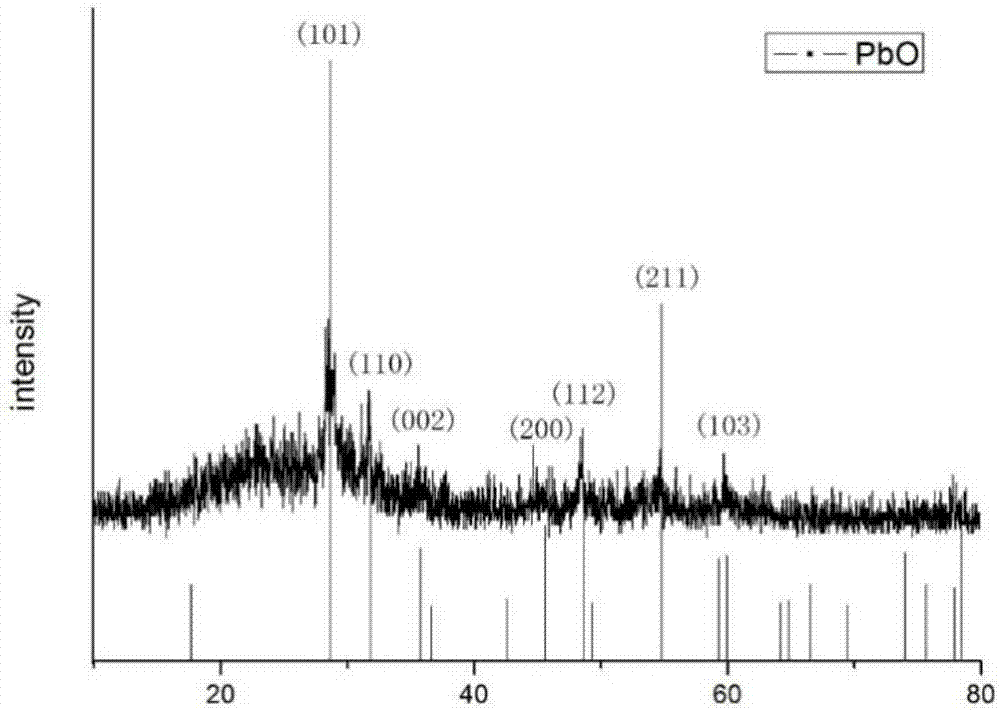
Process for preparing lead by ammonium sulfate through ammonia power reduction
ActiveCN106065485ANo pollution in the processShort processPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsLead dioxideAmmonia production
The invention belongs to a wet metallurgy process, and relates to a process for reducing a lead compound as metal lead in ammonium sulfate water solution. Ammonium sulfate water solution is used as electrolyte; the lead compound is used as a raw material; titanium is used as an anode; stainless steel or lead is used as a cathode; a direct-current electric field is applied in an electrolytic cell; the lead compound obtains electrons at the cathode to reduce as the metal lead; ammonia is oxidized as nitrogen for emission at the anode, and meanwhile, H+ ions are generated; sulfates and chlorine ions in the compound enter the solution to generate ammonium sulfate and ammonium chloride with added ammonia water; lead monoxide and lead dioxide in the lead compound are reduced as the metal lead; and meanwhile, H+ ion combination generation water generated by OH+ and the anode is released. The lead compound includes such materials as lead sulfate, lead monoxide, lead dioxide, lead chloride and mixtures thereof as waste lead accumulator paste. The process is different from traditional electrolysis and electrodeposition process; electrolyte contains no lead; and the lead compound is directly reduced as the metal lead at the cathode.
Owner:杨云婷
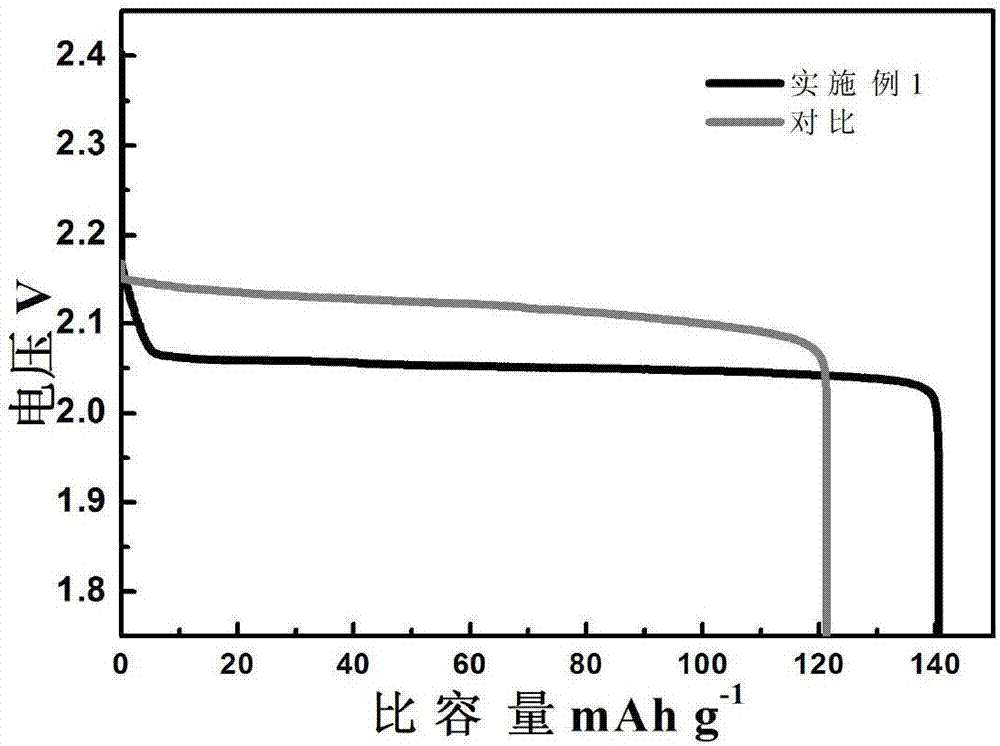
Preparation method of carbon-based composite material for cathode of lead-carbon battery
The invention relates to a preparation method of a carbon-based composite material for a cathode of a lead-carbon battery, which can prepare a carbon-based lead compound composite material with a controllable proportion, wherein the lead compound uniformly distributes on the surface of carbon material and maintains the original structure character of the carbon material. The preparation method isas follows: the carbon material and a lead ion solution are uniformly mixed in a reaction vessel, a precipitant is slowly dropped, the lead ions are completely deposited on the surface of the carbon material, then filtered, washed and dried to obtain a precursor, and the composite material is obtained through high temperature treatment, and mass ratio of lead compounds is between 1% to 90%. The composite material and the active substances of cathode of lead-acid battery can be better combined by the lead oxide particles on the surface, while the cathode capacity of the cathode of the battery prepared by using the composite material additive is obviously increased, the hydrogen evolution of the cathode is reduced, cathode active material utilization rate is also greatly improved, and the cycle life of high-rate charge-discharge of partial charge state of the cathode is significantly prolonged.
Owner:吉林省凯禹电化学储能技术发展有限公司
Coating composition containing benzoxazine compound
InactiveUS20030038031A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove surface smoothnessElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCompound aSolid matter
A novel method for improving the coating film smoothness and a cationic electrodeposition coating composition containing no heavy metal-based rust prevention agents such as lead compounds and capable of forming a coating film with a high corrosion resistance are provided. A coating composition forming a coating film under heating, which comprises, relative to a resin solid matter, 0.5 to 20% by weight of a compound having an N-substituted benzoxazine ring represented by the following general formula (1): in the formula, R is a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CO LTD
Preparation method for large-area homogeneous organic-inorganic perovskite thin film and product and application of large-area homogeneous organic-inorganic perovskite thin film
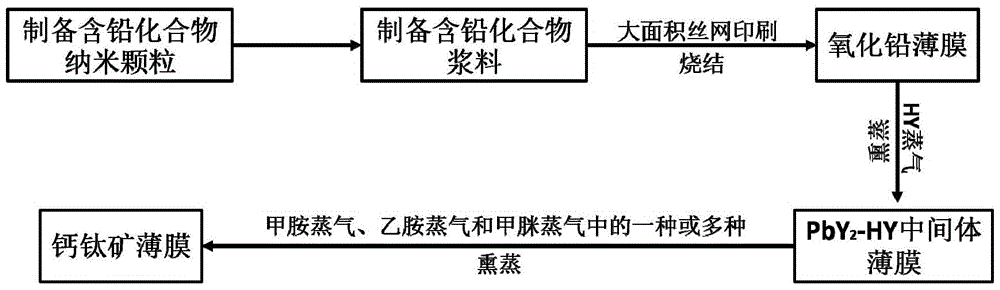
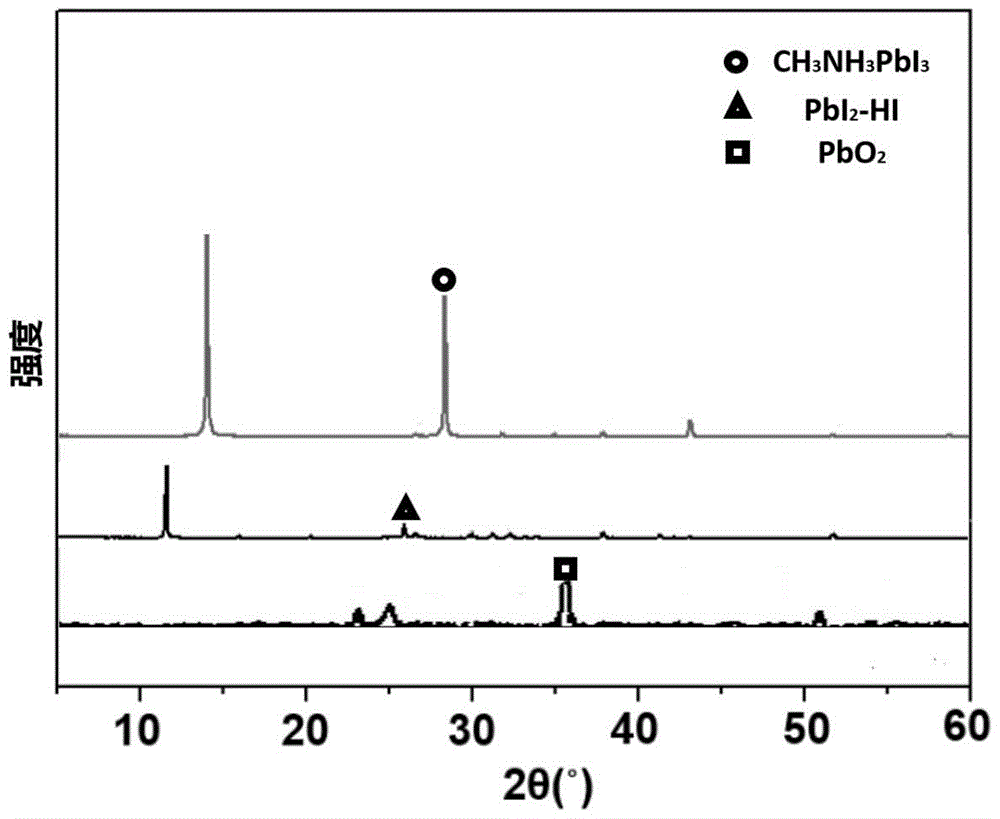
ActiveCN105789450AImprove uniformityControllable areaFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesScreen printingCompound (substance)
The invention relates to a preparation method for a large-area homogeneous organic-inorganic perovskite thin film and a product and application of the large-area homogeneous organic-inorganic perovskite thin film. The method comprises the following steps of 1) preparing lead-containing compound paste; 2) arranging a conductive substrate, silk-screen printing the lead-containing compound paste on the conductive substrate, and sintering the conductive substrate to obtain a uniform lead oxide thin film on the conductive substrate; and 3) respectively placing the lead oxide thin film in first steam and second steam for fumigation to prepare the uniform perovskite thin film. According to the method, a lead oxide precursor is prepared by a silk-screen printing method, and the homogeneous organic-inorganic perovskite thin film with high uniformity and controllable area is obtained by a series of simple fumigation chemical processing; and moreover, the process is simple, the repetitive rate is high, the cost is low, raw material is saved, and a large-area solar cell device with excellent and stable performance can be acquired.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHONGNENG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Method, chemistry, and apparatus for high deposition rate solder electroplating on a microelectronic workpiece
The present invention is directed to an improved electroplating method, chemistry, and apparatus for selectively depositing tin / lead solder bumps and other structures at a high deposition rate pursuant to manufacturing a microelectronic device from a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer. An apparatus for plating solder on a microelectronic workpiece in accordance with one aspect of the present invention comprises a reactor chamber containing an electroplating solution having free ions of tin and lead for plating onto the workpiece. A chemical delivery system is used to deliver the electroplating solution to the reactor chamber at a high flow rate. A workpiece support is used that includes a contact assembly for providing electroplating power to a surface at a side of the workpiece that is to be plated. The contact contacts the workpiece at a large plurality of discrete contact points that isolated from exposure to the electroplating solution. An anode, preferably a consumable anode, is spaced from the workpiece support within the reaction chamber and is in contact with the electroplating solution. In accordance with one embodiment the electroplating solution comprises a concentration of a lead compound, a concentration of a tin compound, water and methane sulfonic acid.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
Crystal glass having refractive index higher than 1.53 without a content of compounds of lead, barium and arsenic
This invention relates to a crystal glass having a refractive index higher than 1.53 and a high mechanical strength, free of any content of compounds of lead, barium and arsenic and guaranteeing maximum safety for health, which consists in that it comprises by weight: 55-70% SiO2, 0.05-3.5% Li2O, 2-15% Na2O, more than 3% and less than 5% or more than 15% and less than 19% K2O, 5 to 10% CaO, more than 1% and less than 4% or more than 7% and less than 8% ZnO, 0.1-3.5% B2O3, 0.1-3.5% Al2O3, 0.1-3.5% TiO2, less than 3.5% ZrO2, 0.05-1.5% Gd2O,3 0.05-1% P2O5, 0.1-1% Sb2O3,
Owner:PRECIOSA AS
Optical glass and optical element
ActiveUS20050233890A1Low TgExcellent devitrification resistanceOptical beam guiding meansGlass reforming apparatusRefractive indexOptical glass
Optical glass which is suitable for press molding does not substantially contain a compound of lead or arsenic, and has intermediate refractive index, low dispersion properties, low Tg and small gravity. Concretely, the optical glass includes the glass components of SiO2: 20 to 45%, B2O3: 15 to 40%, Al2O3: 4 to 15%, MgO: 0 to 10% (including 0), CaO: 13 to 25%, MgO+CaO: 13 to 25%, Li2O: 12.5 to 25%, Na2O: 0 to 10% (including 0), K2O: 0 to 10% (including 0), Li2O+Na2O+K2O: 12.5 to 25%, SrO: 0 to 10% (including 0), BaO: 0 to 5% (including 0), and Sb2O3: 0 to 1% (including 0).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Method for recovering valuable metals
Owner:METSO OUTOTEC (FINLAND) OY
Piezoelectric ceramic compact and piezoelectric ceramic device
InactiveUS6488864B2Impedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionOxygenLead compound
A piezoelectric ceramic compact is provided as an effective material for forming piezoelectric ceramic devices and the like, and is primarily composed SrBi2Nb2O9 containing no lead nor lead compounds or containing a little amount thereof, and has a maximum value Qmax improved to a level suitable for practical use. In the piezoelectric ceramic compact primarily having a bismuth-based layered compound containing Sr, Bi, Nb and oxygen, when the molar ratio of Sr, Bi and Nb contained as primary components in the bismuth-based layered compound is represented by a: b: c, the relationships represented by 0.275<=a / c<0.5 and 4<=(2a +3b) / c<=4.5 are satisfied.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Piezoelectric ceramic composition and piezoelectric ceramic device composed of same
InactiveCN1572751AHigh curie pointReduce piezoelectric effectConveyorsImpedence networksBismuth compoundOxygen
A piezoelectric ceramic composition that is based on a layered bismuth compound composed of Sr, Bi, Nb, oxygen, contains an additional monovalent metallic element. The piezoelectric ceramic composition has an elevated Curie point, is highly reliable at higher temperatures, that is, minimizes the reduction in the piezoelectric effect, and is useful as a material for piezoelectric ceramic devices that contain little or no lead or lead compounds. The layered bismuth compound contains not more than about 0.125 mol and more than 0 mol of the monovalent metallic element for 1 mol ofNb.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Recovery of lead in form of high purity lead carbonates from spent lead batteries incl. electrode paste
InactiveUS20100034715A1Promote commercializationHigh puritySolvent extractionLead carbonatesSodium acetateLead sulfate
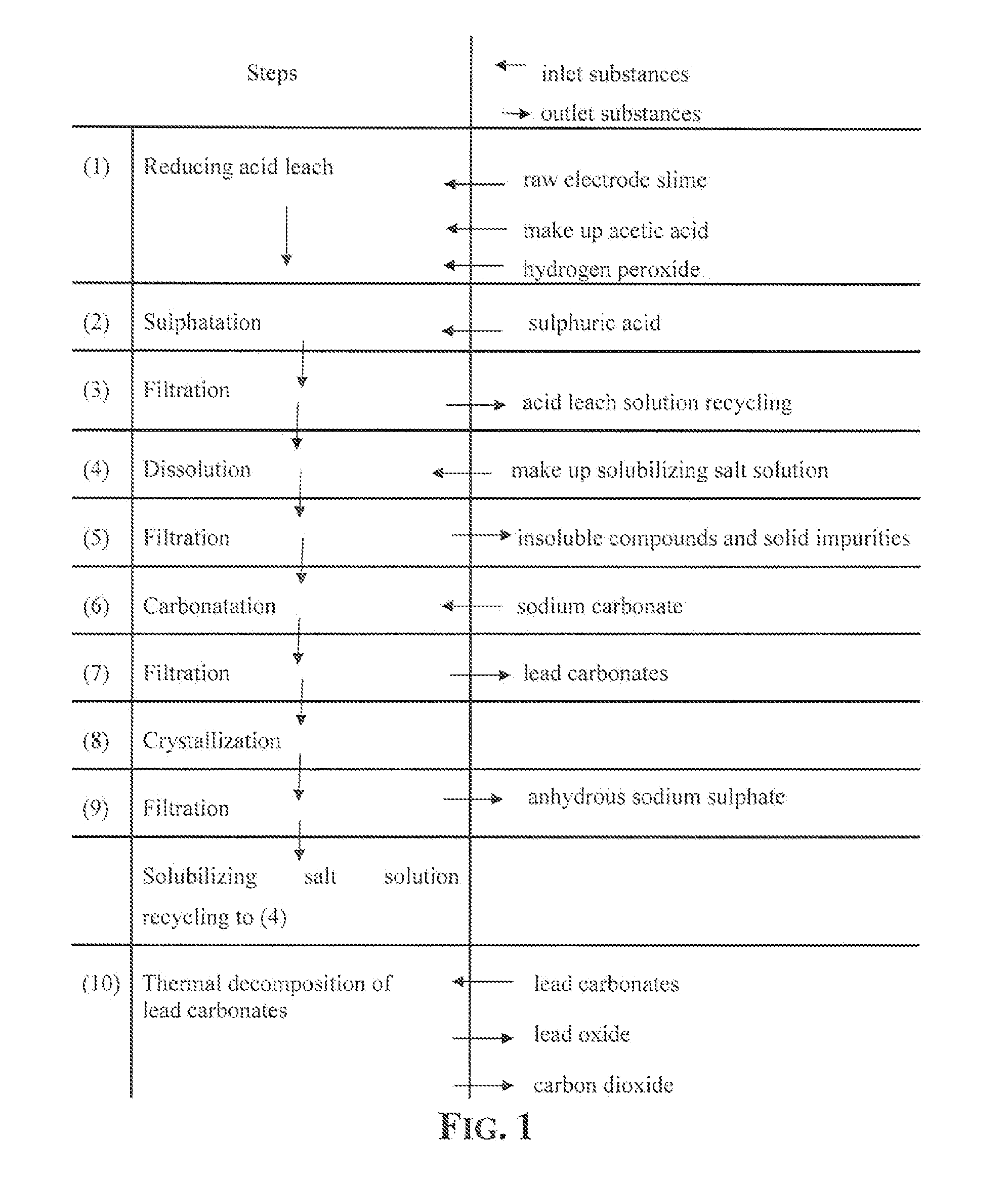
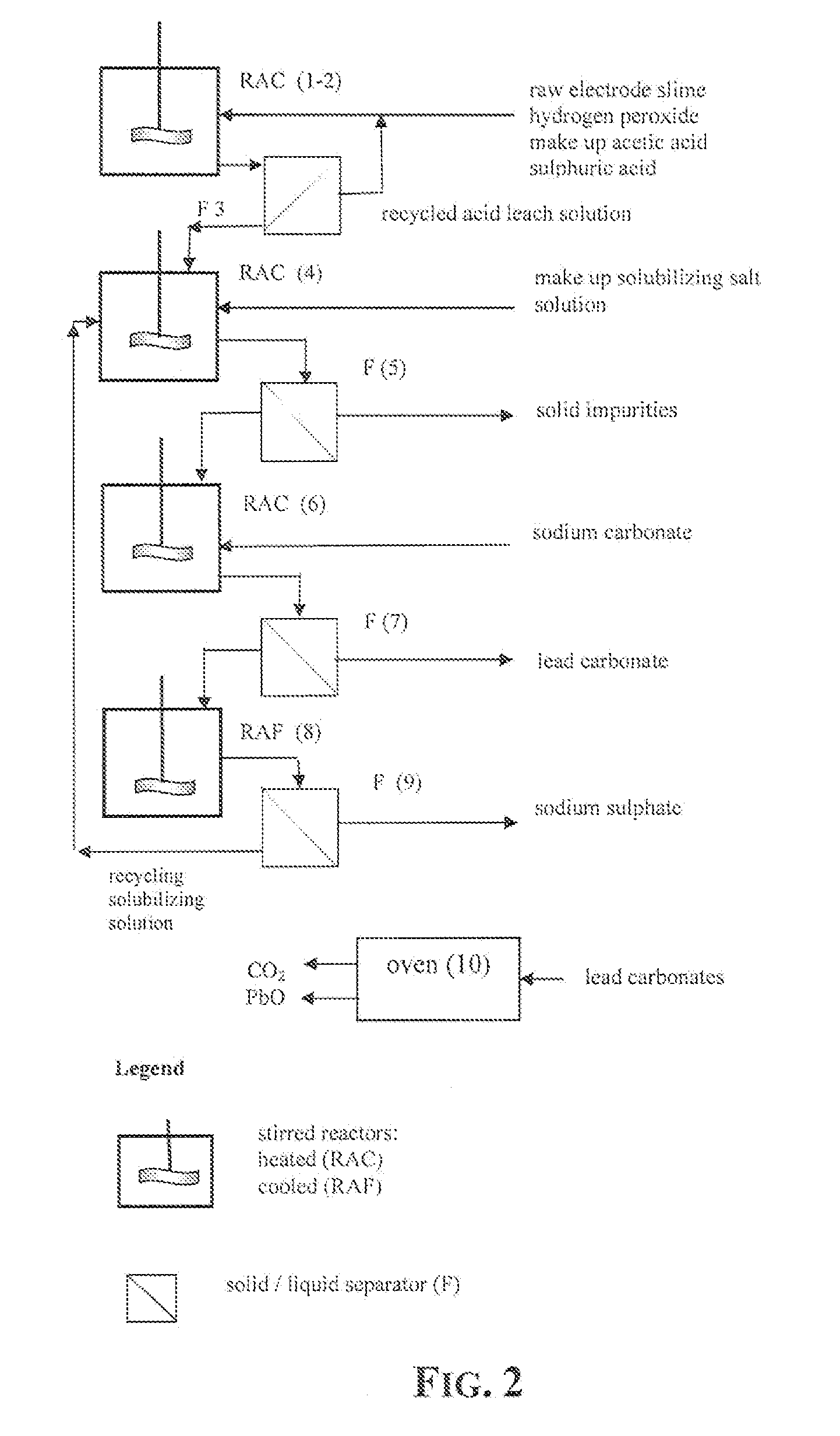
Wet process of low environmental impact recovers the lead content of an electrode slime and / or of lead minerals in the valuable form of high purity-lead carbonates that are convertible to highly pure lead oxide by heat treatment in oven at relatively low temperature, perfectly suited for making active electrode pastes of new batteries or other uses. The process basically comprises the following steps: a) adding sulphuric acid to a different acid leach suspension of the starting impure material for converting all dissolved lead compounds to insoluble lead sulphate; b) separating the solid phase constituted by lead sulphate and undissolved impurities from the acid leach solution; c) selectively dissolving lead sulphate contained in said separated solid phase in an aqueous solution of a lead solubilizing compound comprising preferably sodium acetate; d) separating the solution containing dissolved lead sulphate from the solid phase residue including undissolved impurities; e) adding to the separated solution of lead sulphate a carbonate of the same cation of said dissolving compound for forming insoluble lead carbonate and / or and lead oxycarbonate and a dissolved sulphate of the same cation; f) separating the precipitated carbonate and / or oxycarbonate of lead from the dissolving solution now containing also sulphate of the cation of said solubilizing compound.
Owner:MILLBROOK LEAD RECYCLING TECH
Igniting agent composition and ignitor using same
InactiveCN1285547CBelt retractorsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementNitrate saltsPhysical chemistry
An igniting agent composition substantially free of a lead compound, characterized in that it comprises a metal power and one or more selected from the group consisting of nitrate salt, basic nitrate salt, a metal oxide and a basic carbonate salt; and an igniter using the igniting agent composition. The igniting agent composition shows no delay in ignition time and no reduction in igniting capability, as compared to conventional lead-containing composition.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Preparing method for lead-sulfide nanocrystalline material
ActiveCN107720807AGood application prospectSimple methodRaman scatteringNanotechnologyMicrowaveOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a preparing method for a lead-sulfide nanocrystalline material. The preparing method for the lead-sulfide nanocrystalline material is characterized by including the following steps that a lead compound and sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate are added into pure water and stirred and then subjected to ultrasonic for 30 min to 40 min, suction filtration, washing and drying are carried out, and a lead-source precursor is obtained; the lead-source precursor is added into an organic solvent, the mixture is fully stirred and mixed and subjected to ultrasonic washing for 20 min to30 min, and precursor reaction liquid is obtained; under the ultrasonic stirring power of 100 W to 400 W, the precursor reaction liquid is subjected to gradient microwave heating, wherein gradient microwave heating is heated to be 110 DEG C to 120 DEG C, first reaction liquid is obtained, and the heating temperature gradient is 35 DEG C / min to 40 DEG C / min; the heating temperature is 130 DEG C to180 DEG C, heat preservation is carried out for 4 min to 6 min, second reaction liquid is obtained, and the heating temperature gradient is 2 DEG C / min to 30 DEG C / min; the second reaction liquid is naturally cooled to the room temperature, centrifuged, precipitated and washed, and the lead-sulfide nanocrystalline material is obtained.
Owner:INST OF NEW MATERIALS & IND TECH WENZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com