Patents
Literature
377 results about "Ammonia production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonia is one of the most highly produced inorganic chemicals. There are numerous large-scale ammonia production plants worldwide, producing a total of 144 million tonnes of nitrogen (equivalent to 175 million tonnes of ammonia) in 2016. China produced 31.9% of the worldwide production, followed by Russia with 8.7%, India with 7.5%, and the United States with 7.1%. 80% or more of the ammonia produced is used for fertilizing agricultural crops. Ammonia is also used for the production of plastics, fibers, explosives, nitric acid (via the Ostwald process) and intermediates for dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Cellulosic fibers with odor control characteristics
ActiveUS20070077428A1Avoid odorMaintain activityEngine sealsInorganic pigment treatmentBiotechnologyAmmonia production
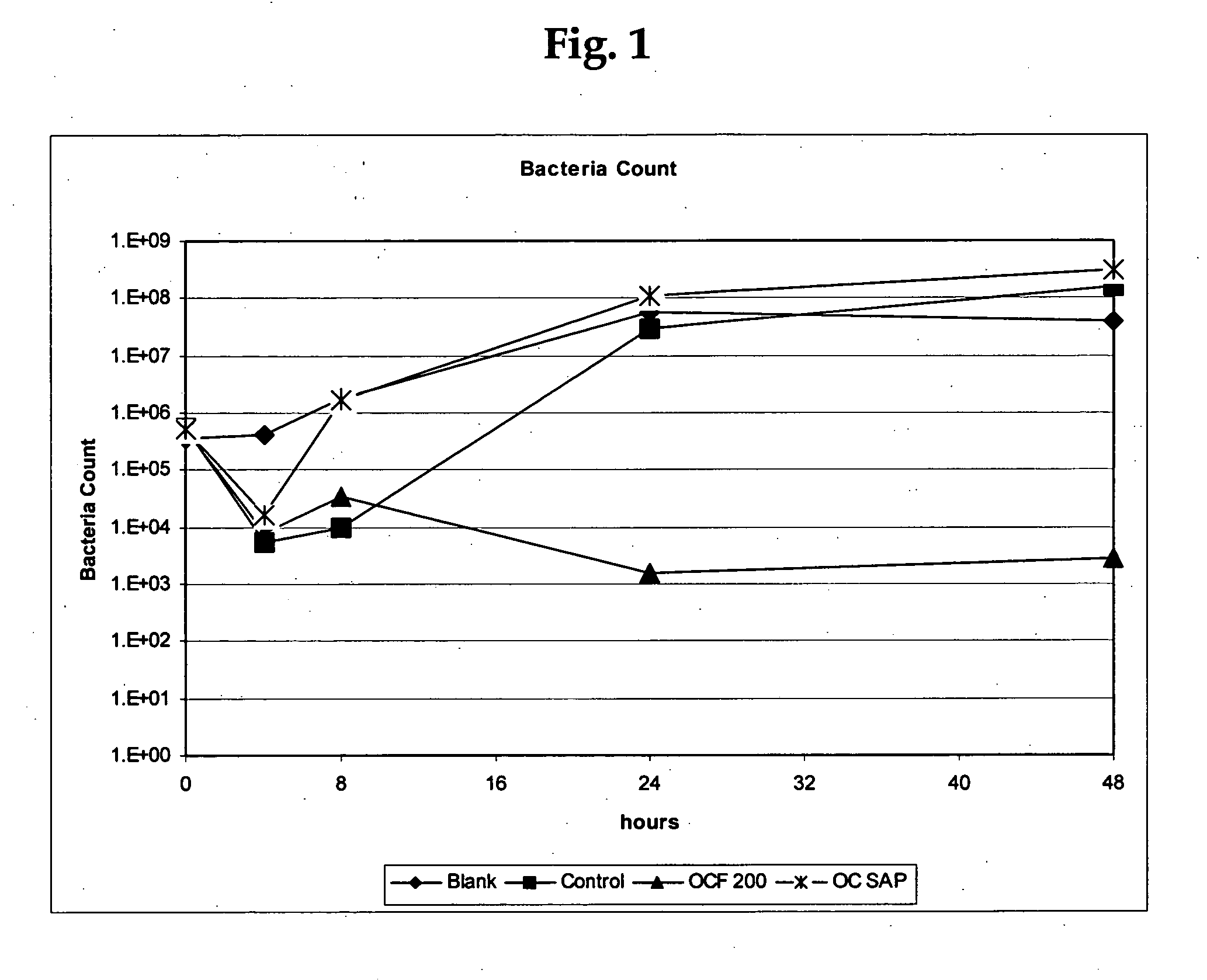
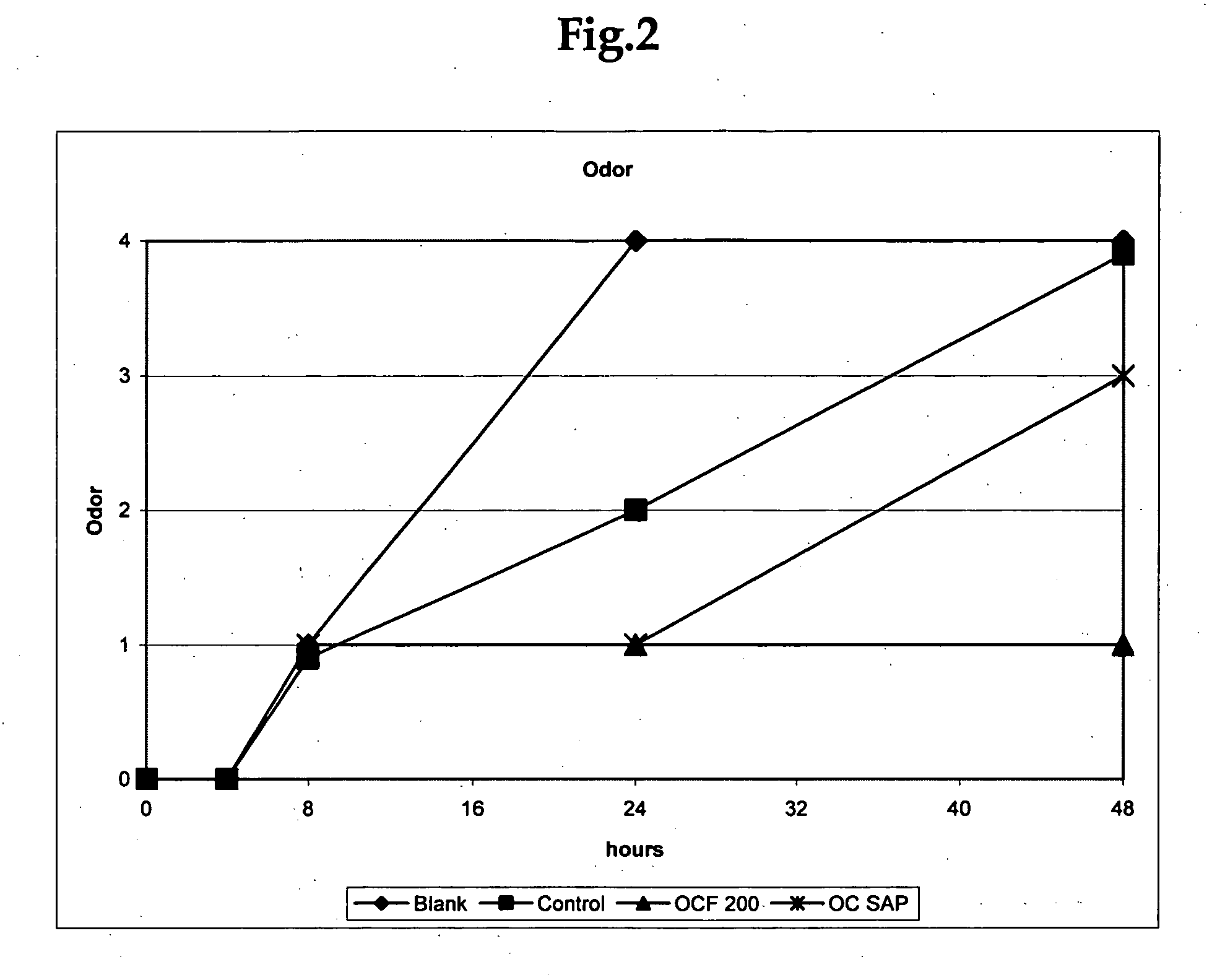
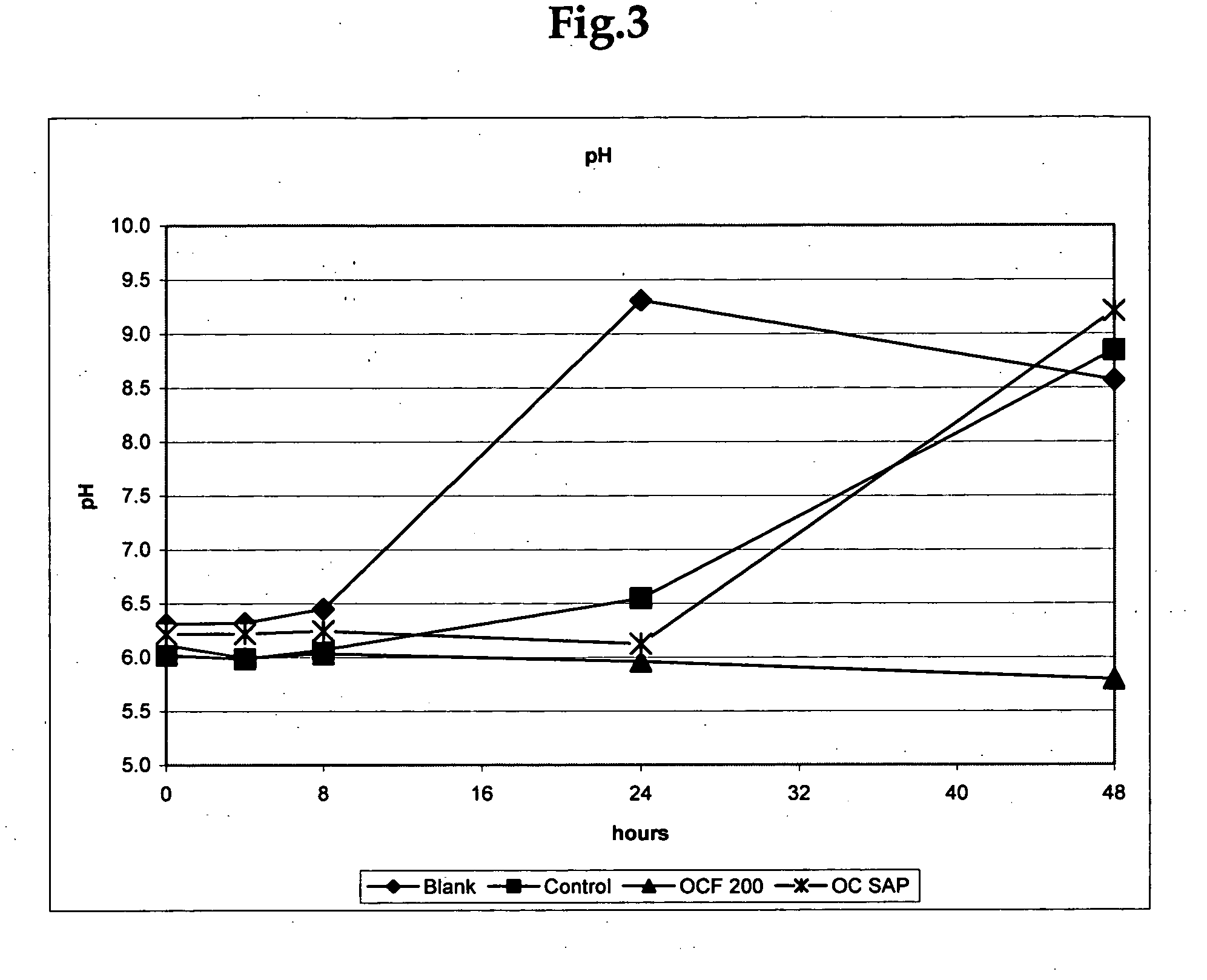
An odor-inhibiting fiber having a cellulosic fiber and an odor-inhibiting formulation. The odor-inhibiting formulation may contain an odor-inhibiting agent, such as a biocide, an enzyme, a urease inhibitor. The odor-inhibiting formulation also may contain a liquid carrier such as a hydrophobic or hydrophilic organic liquid, or a mixture of a hydrophobic and hydrophilic organic liquid. The cellulosic fiber is impregnated with the odor-inhibiting formulation to produce fiber having odor-inhibiting characteristics. The resultant odor-inhibiting fiber is useful in making absorbent articles with odor-inhibiting characteristics. The fiber of the embodiments prevents odor by inhibiting bacteria growth and ammonia production, especially when used in an absorbent article such as a diaper or adult incontinence device.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS
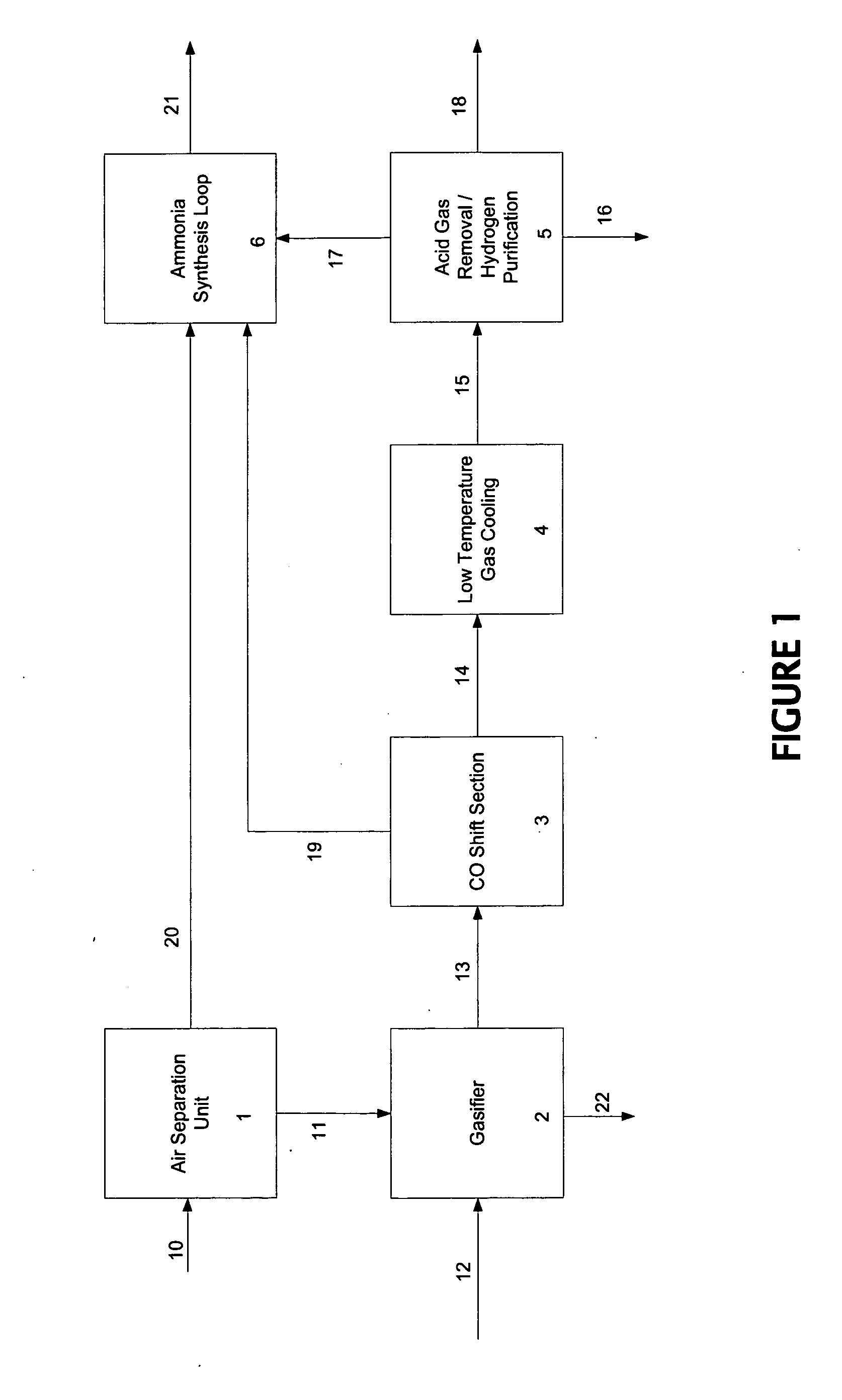
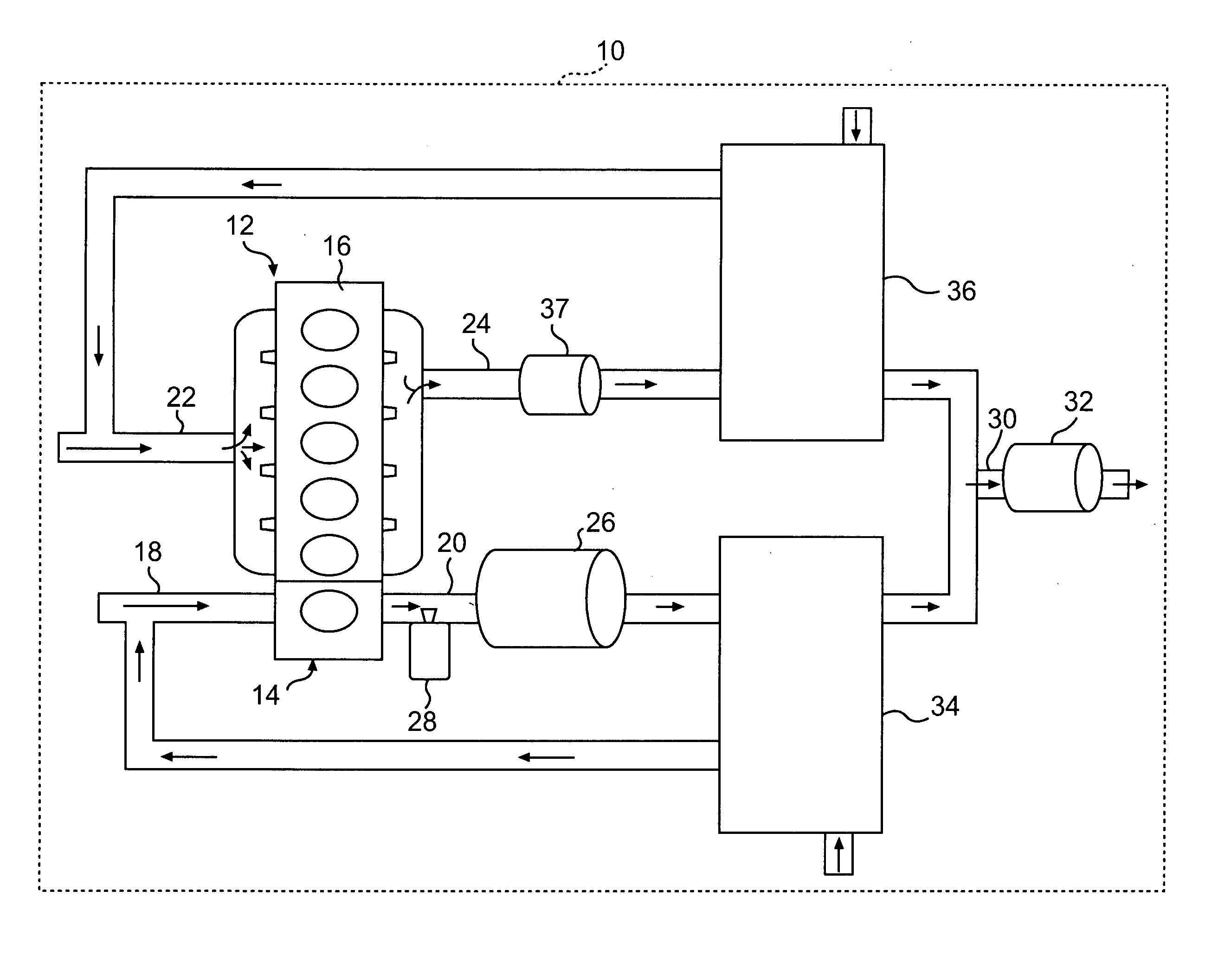
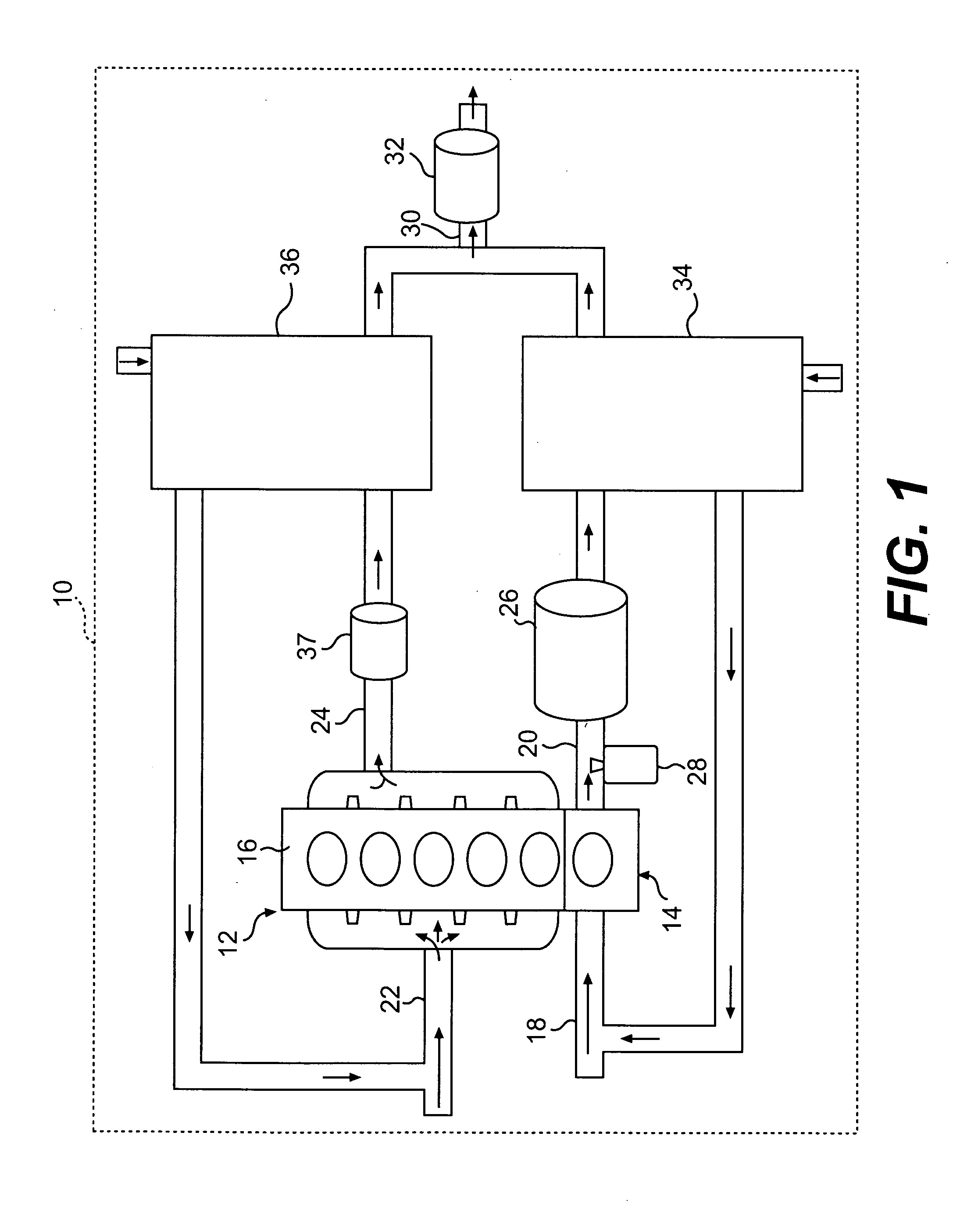
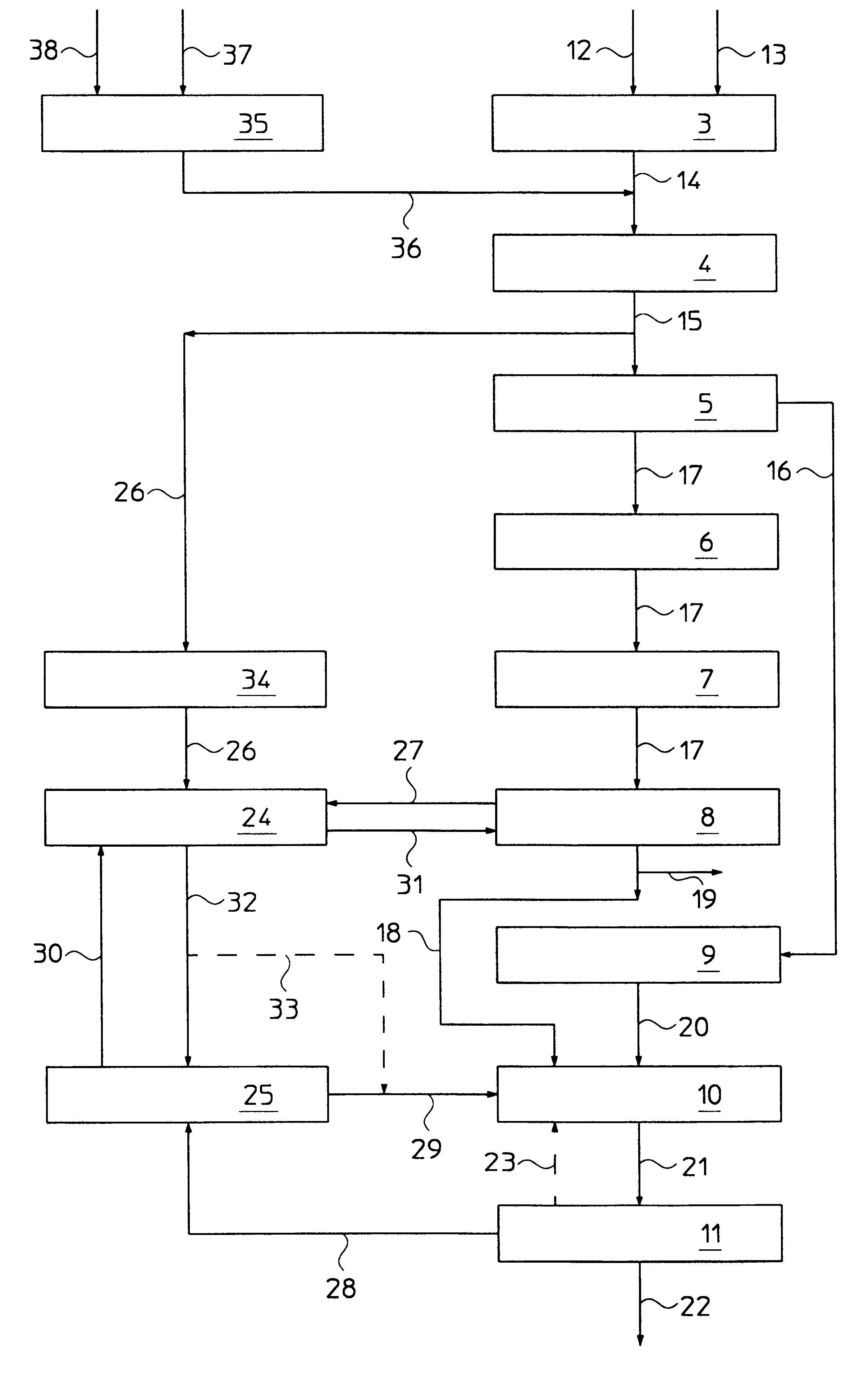
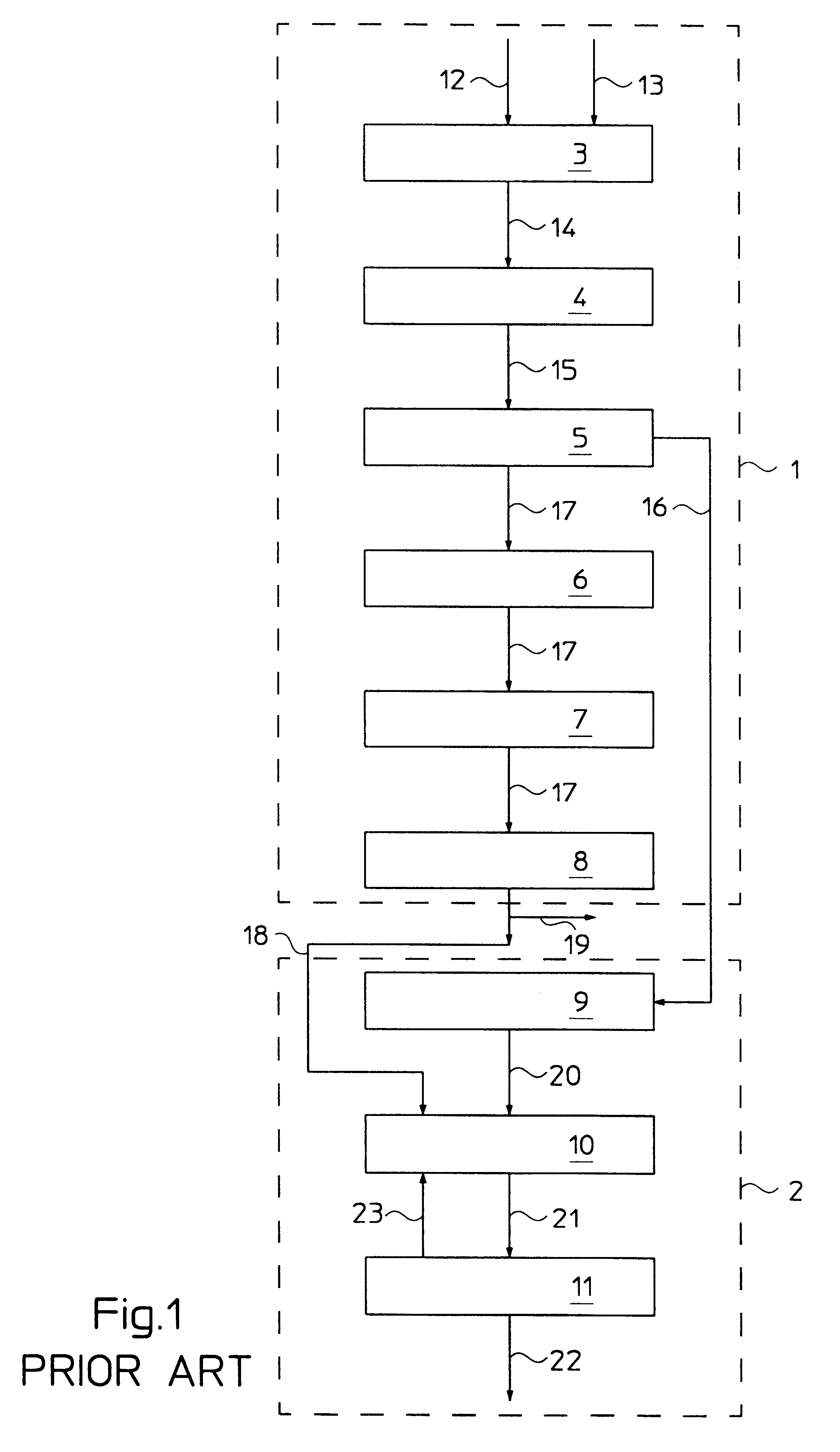
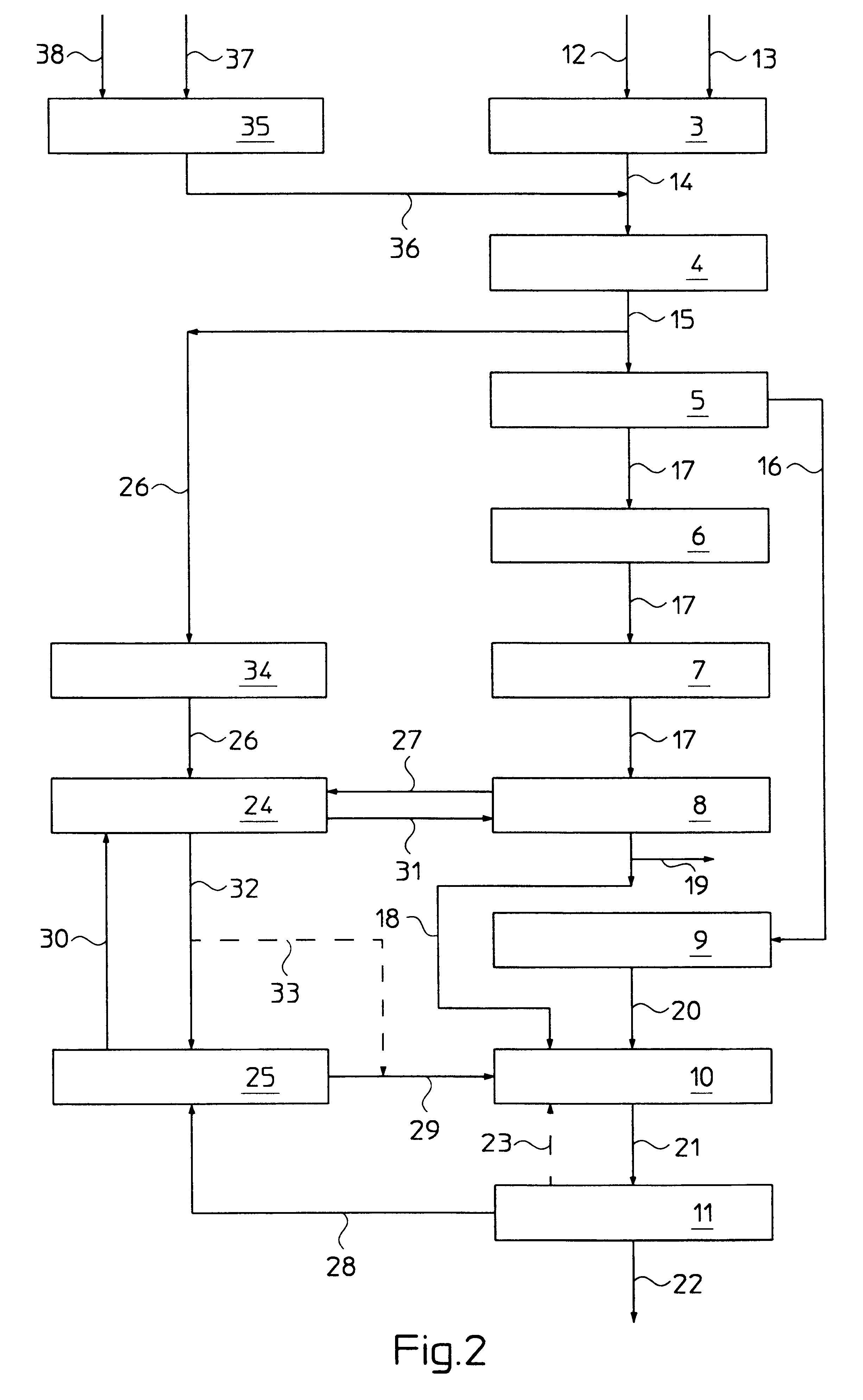
Integration of gasification and ammonia production
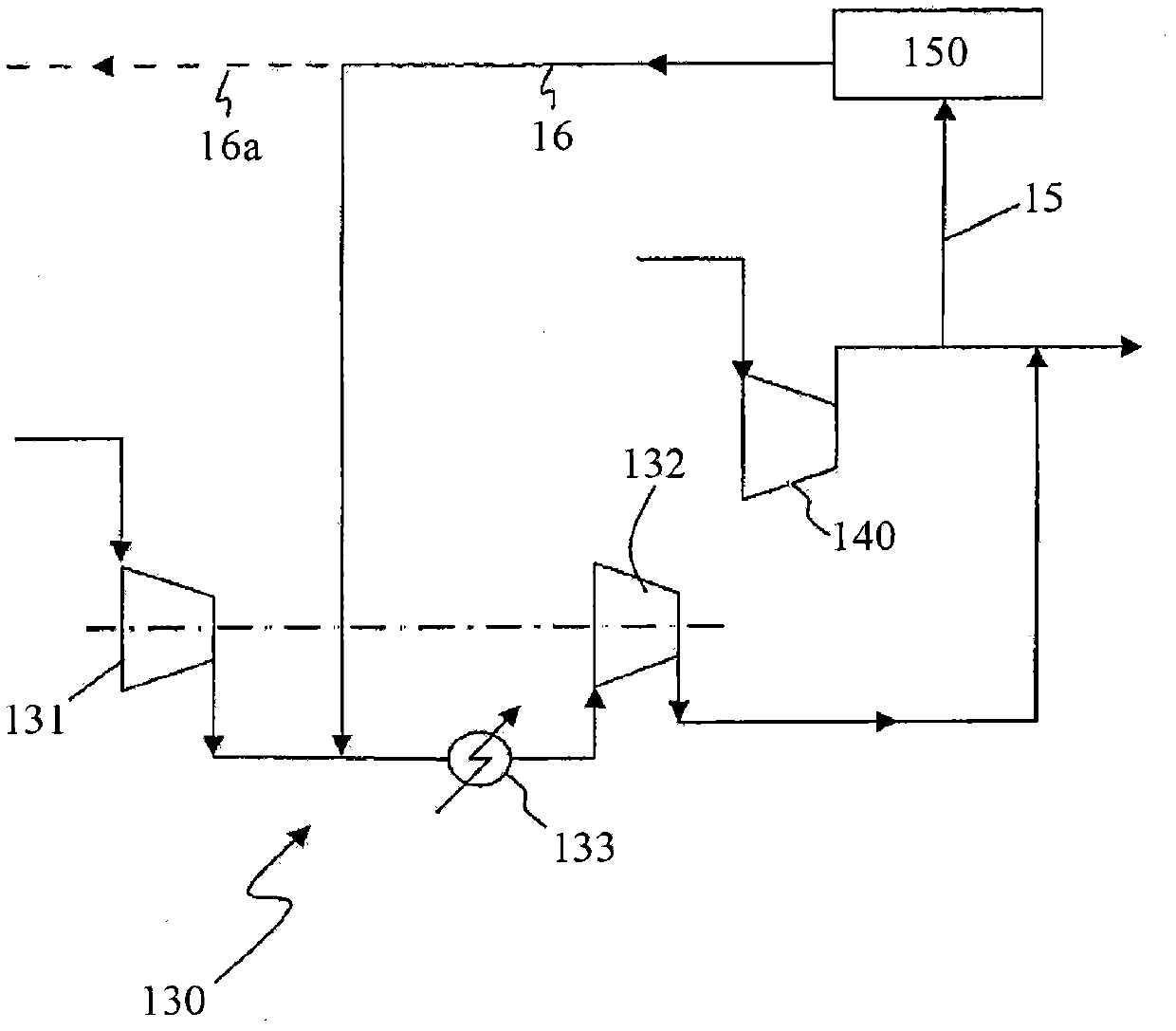
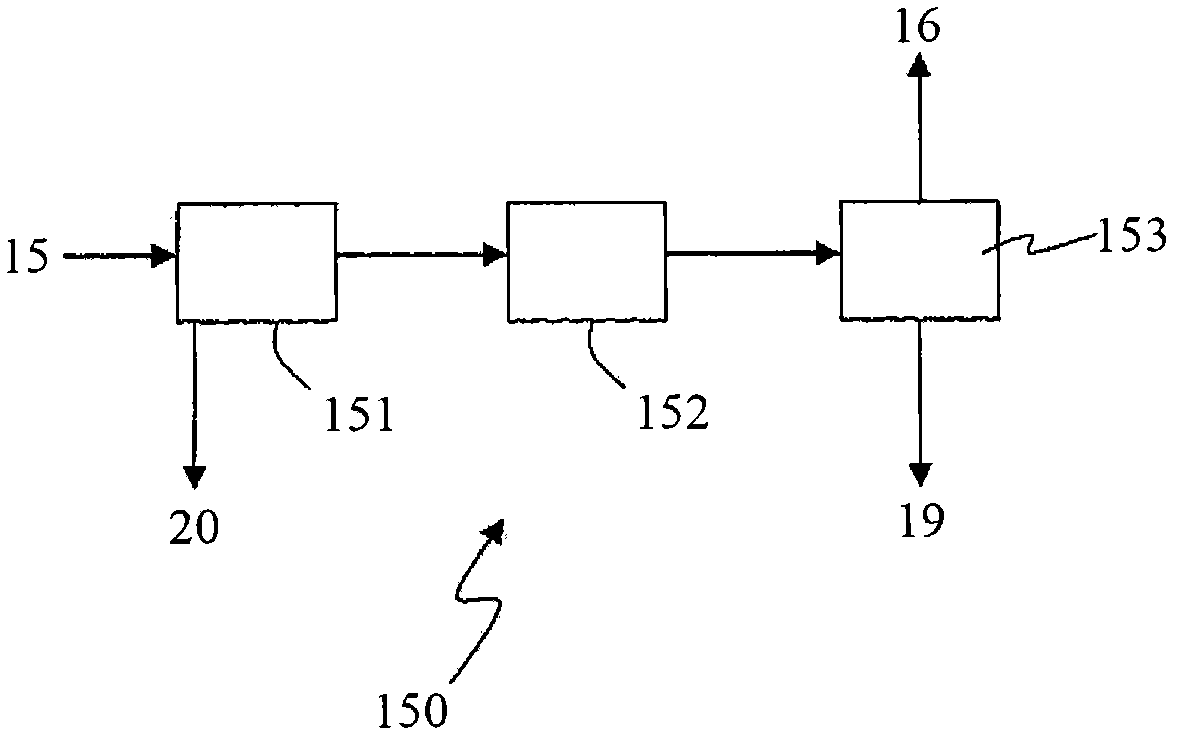
A method and system are described for making ammonia using hydrogen from a gasification process and for integrating the steam systems of the two processes. The gasification process provides high-pressure, purified hydrogen and high-pressure, saturated steam. The high pressure hydrogen lowers the overall compression requirement for the ammonia process. In addition, the high-pressure, saturated steam can be converted into superheated steam by recovering heat from ammonia synthesis and used to power steam turbines for compression and refrigeration needs.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for internal combustion engine, and engine control unit
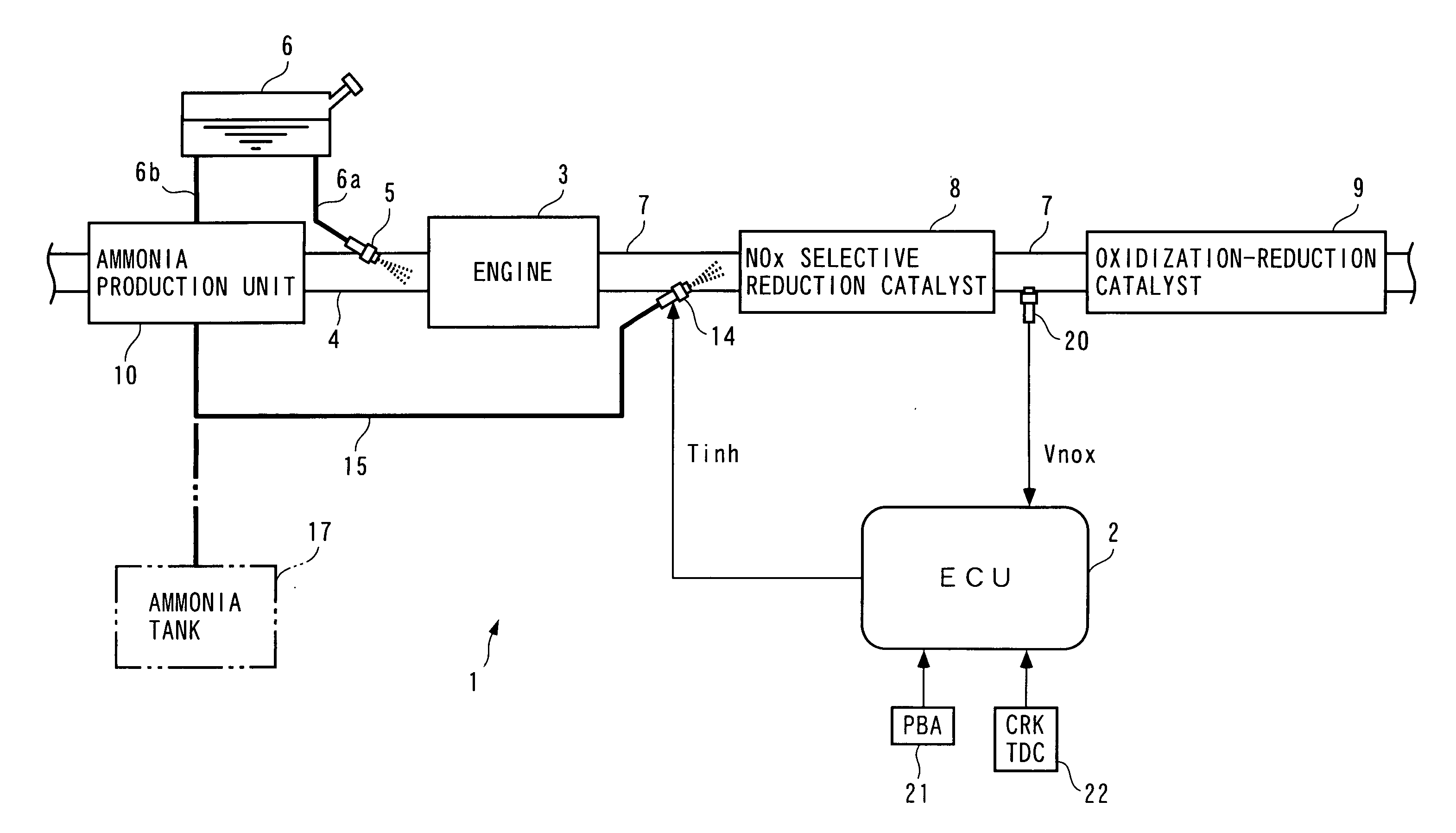
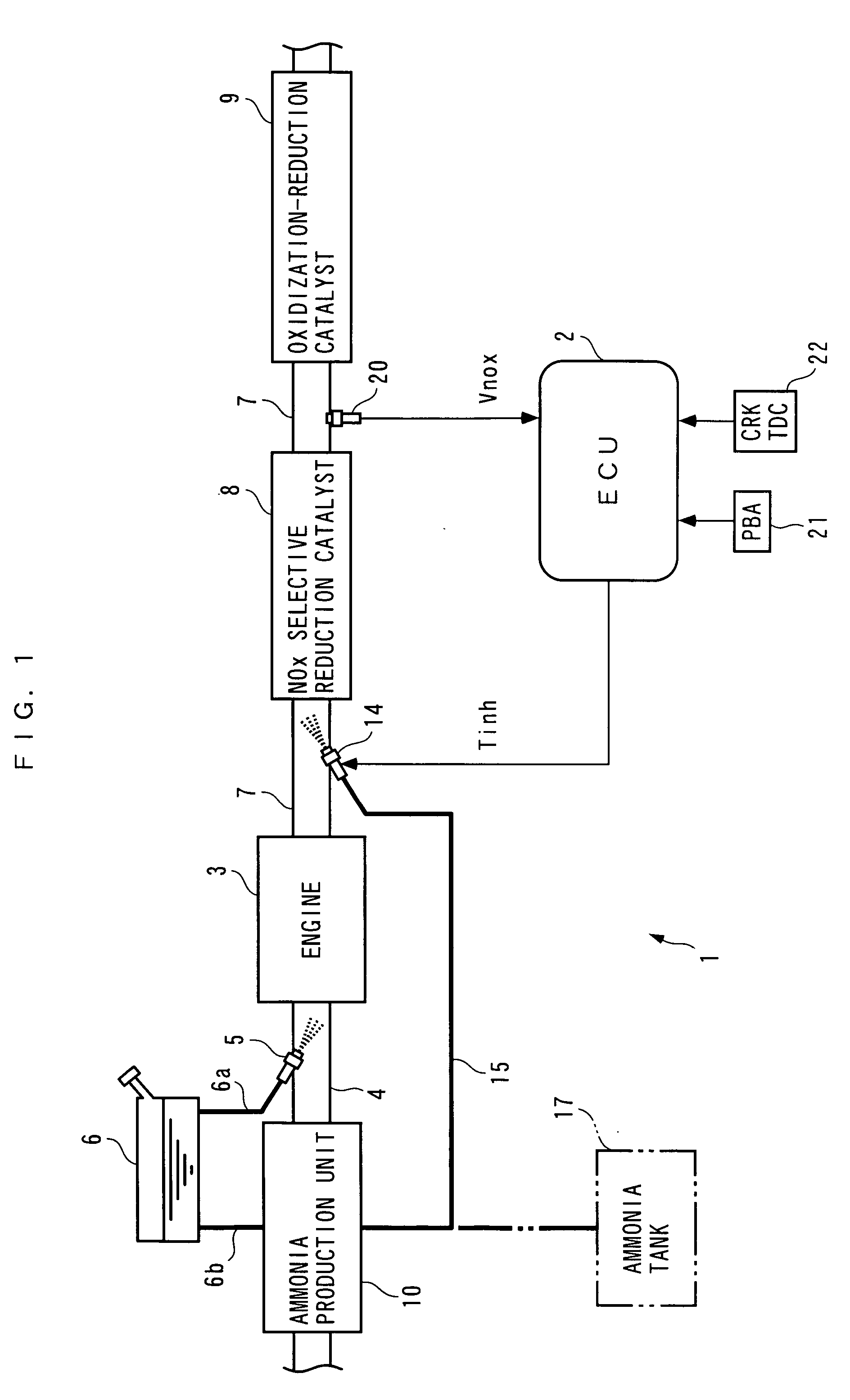
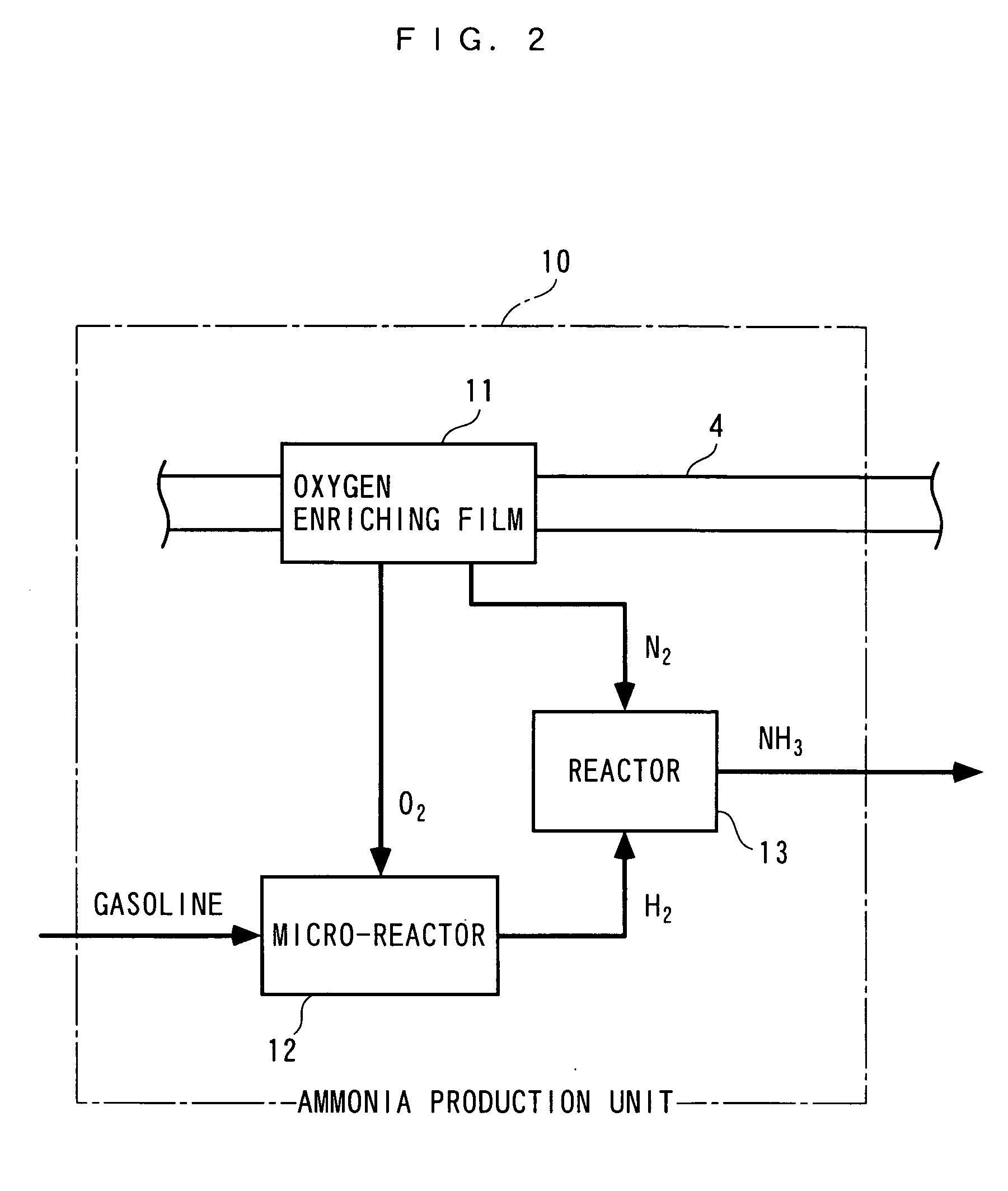
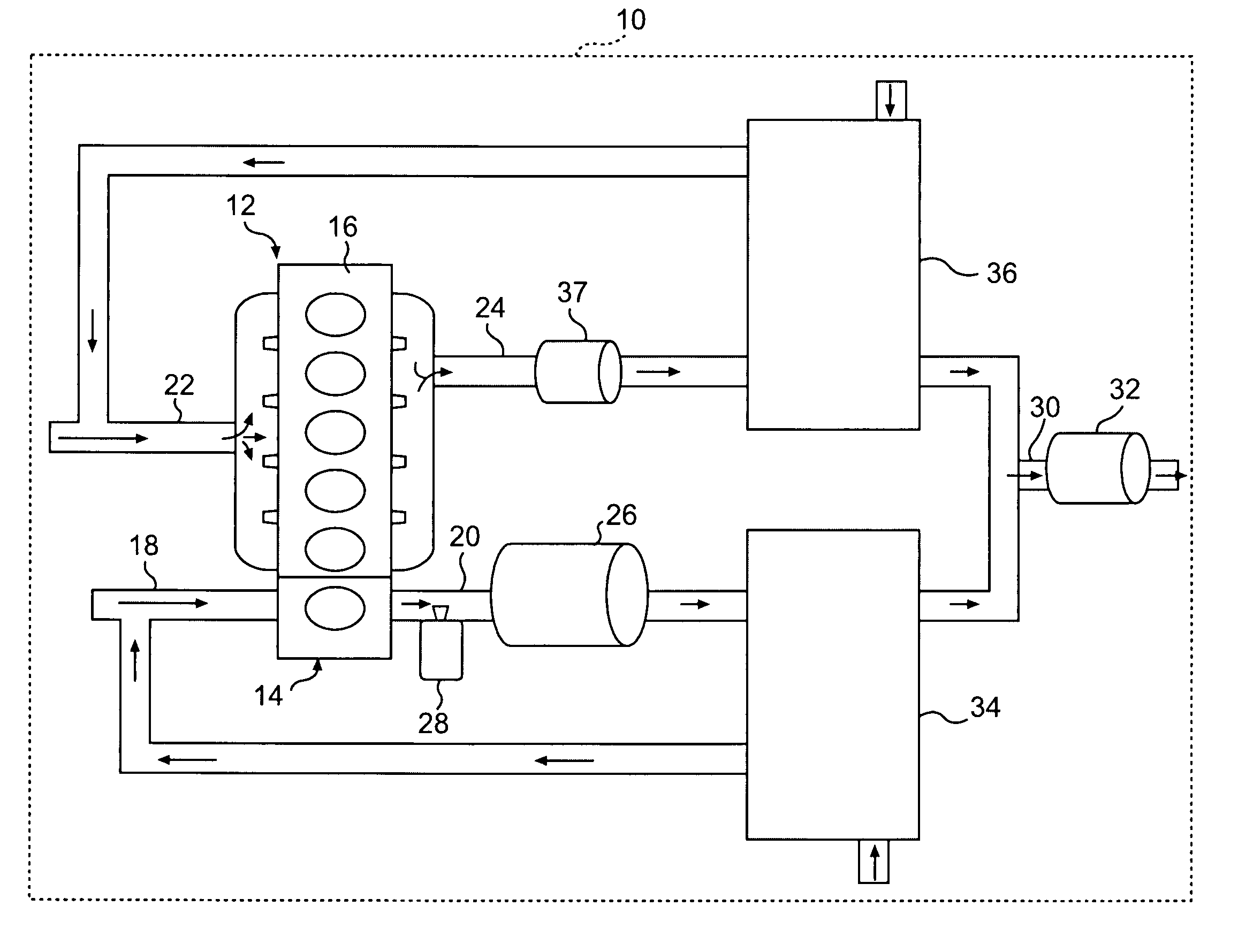
InactiveUS7204081B2Accurate detectionReduce supplyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia productionExhaust fumes
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for internal combustion engine, and engine control unit
InactiveUS20040159096A1Improve performanceImprove featuresInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia productionExhaust fumes
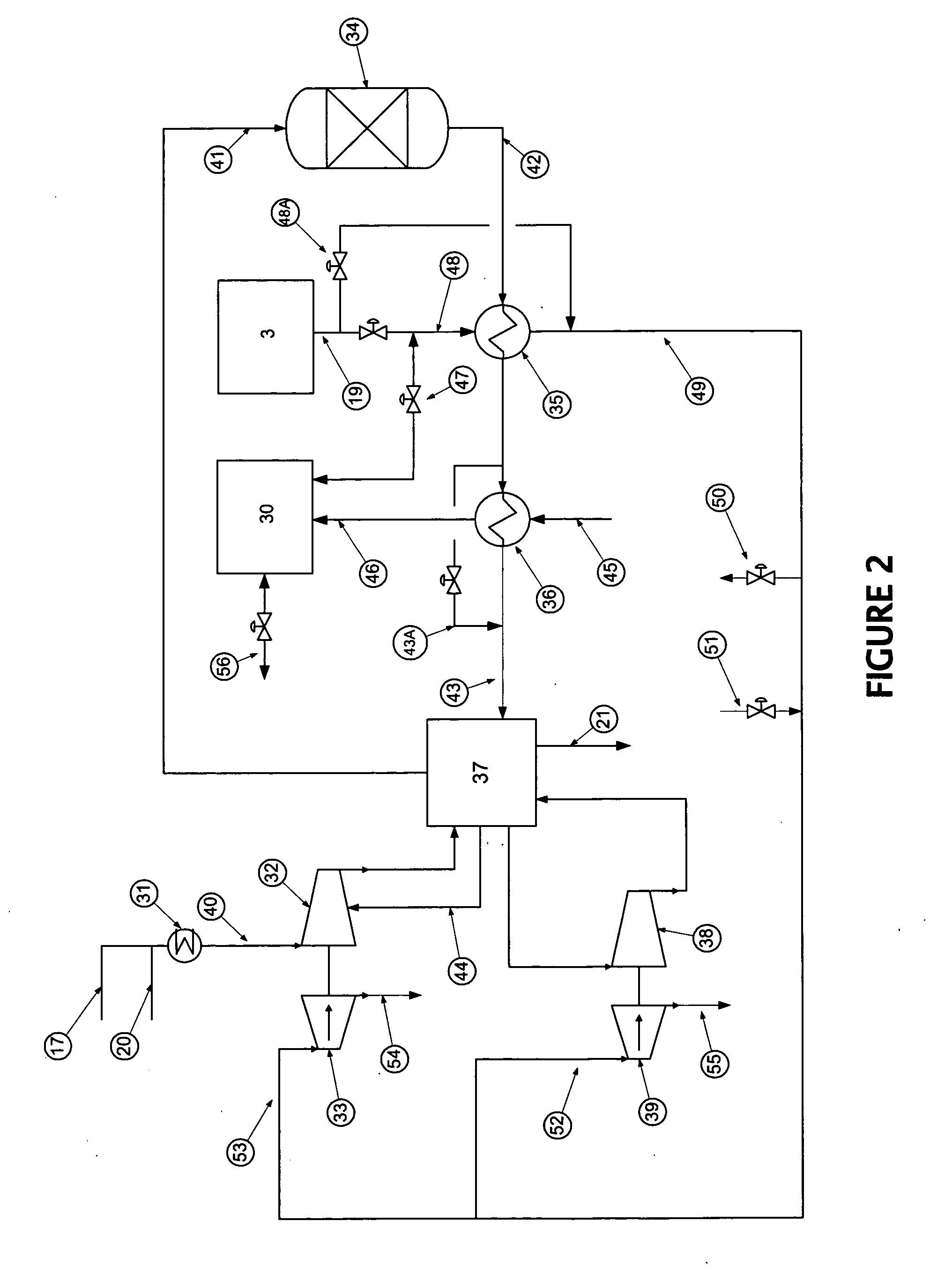
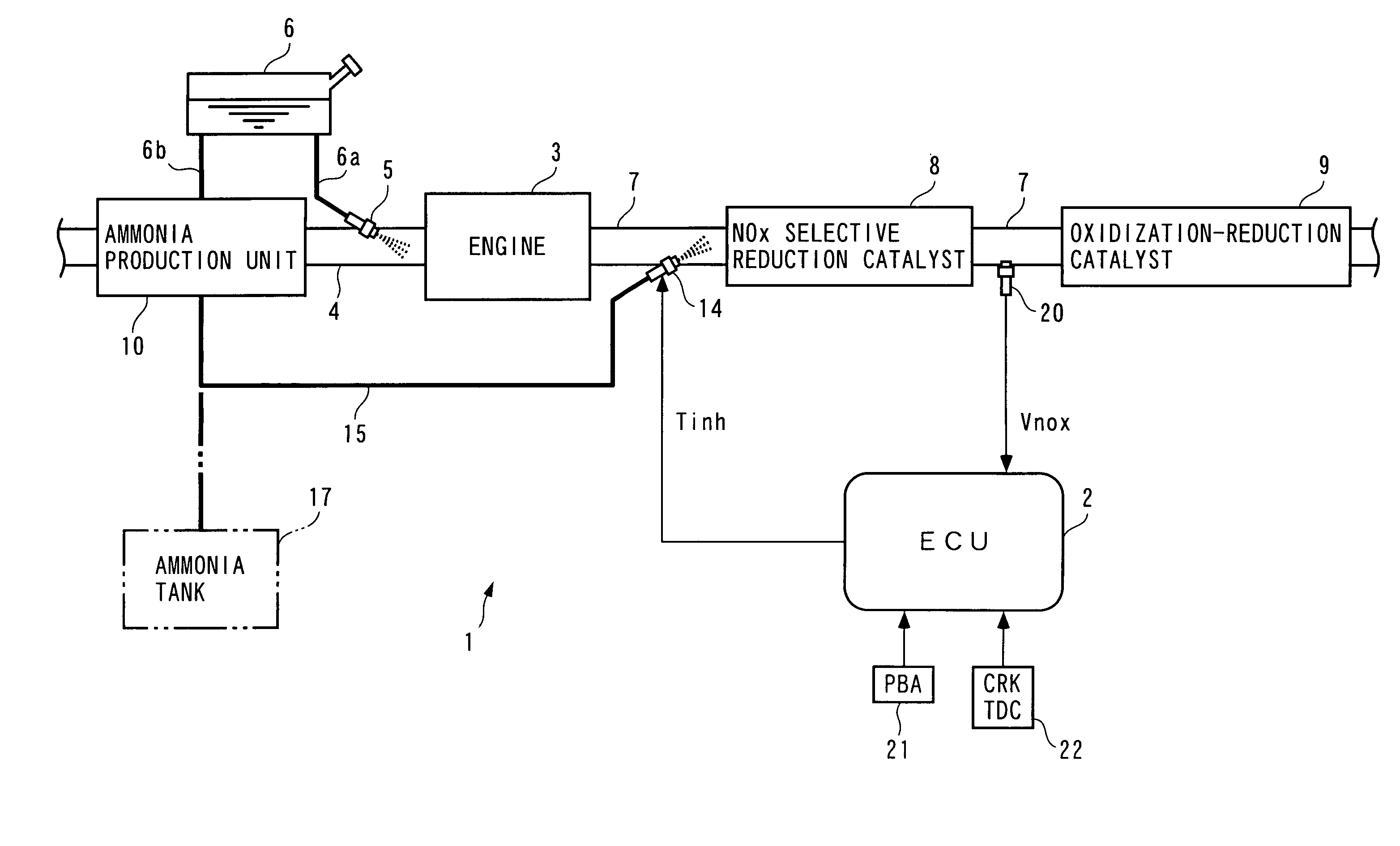
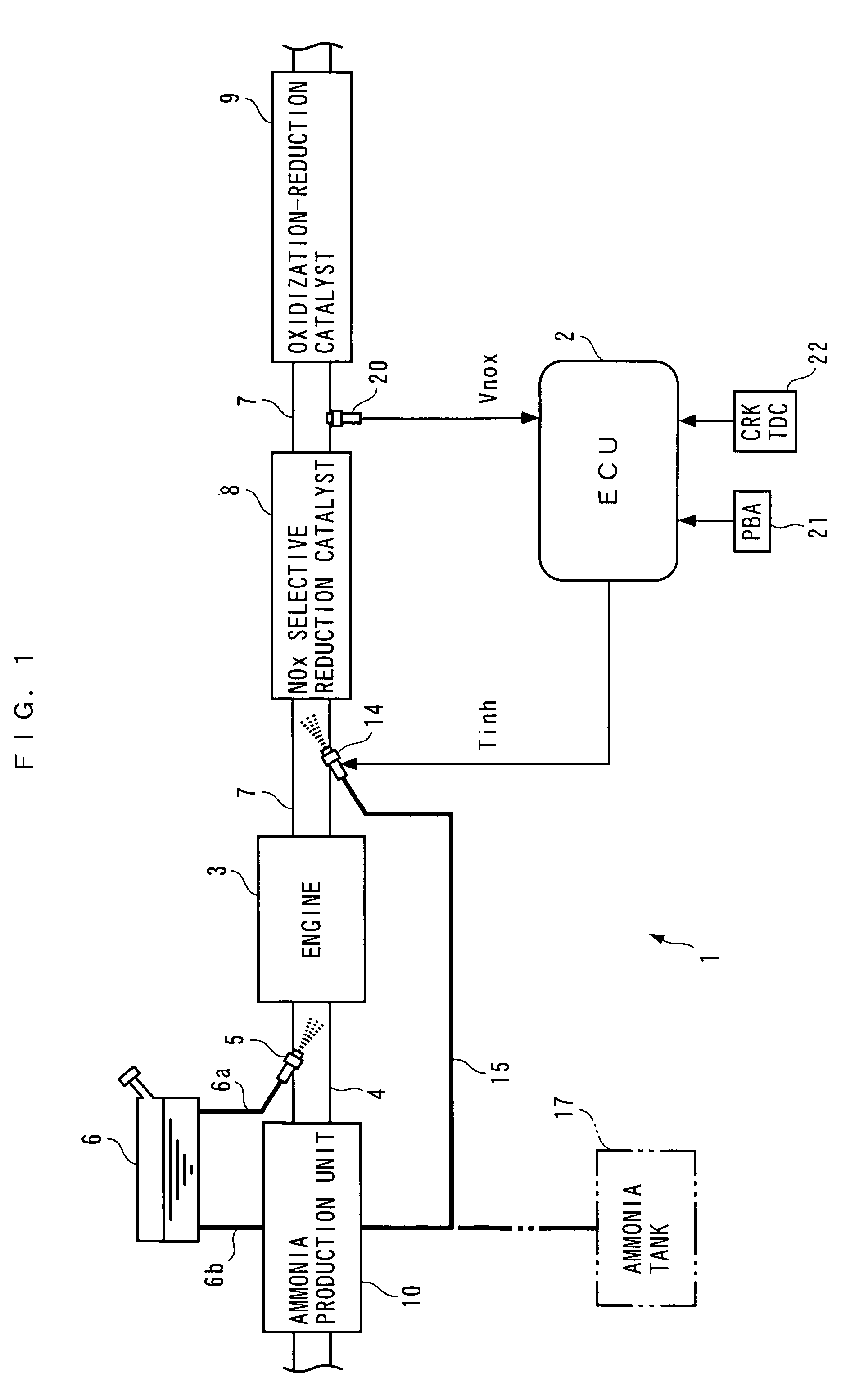
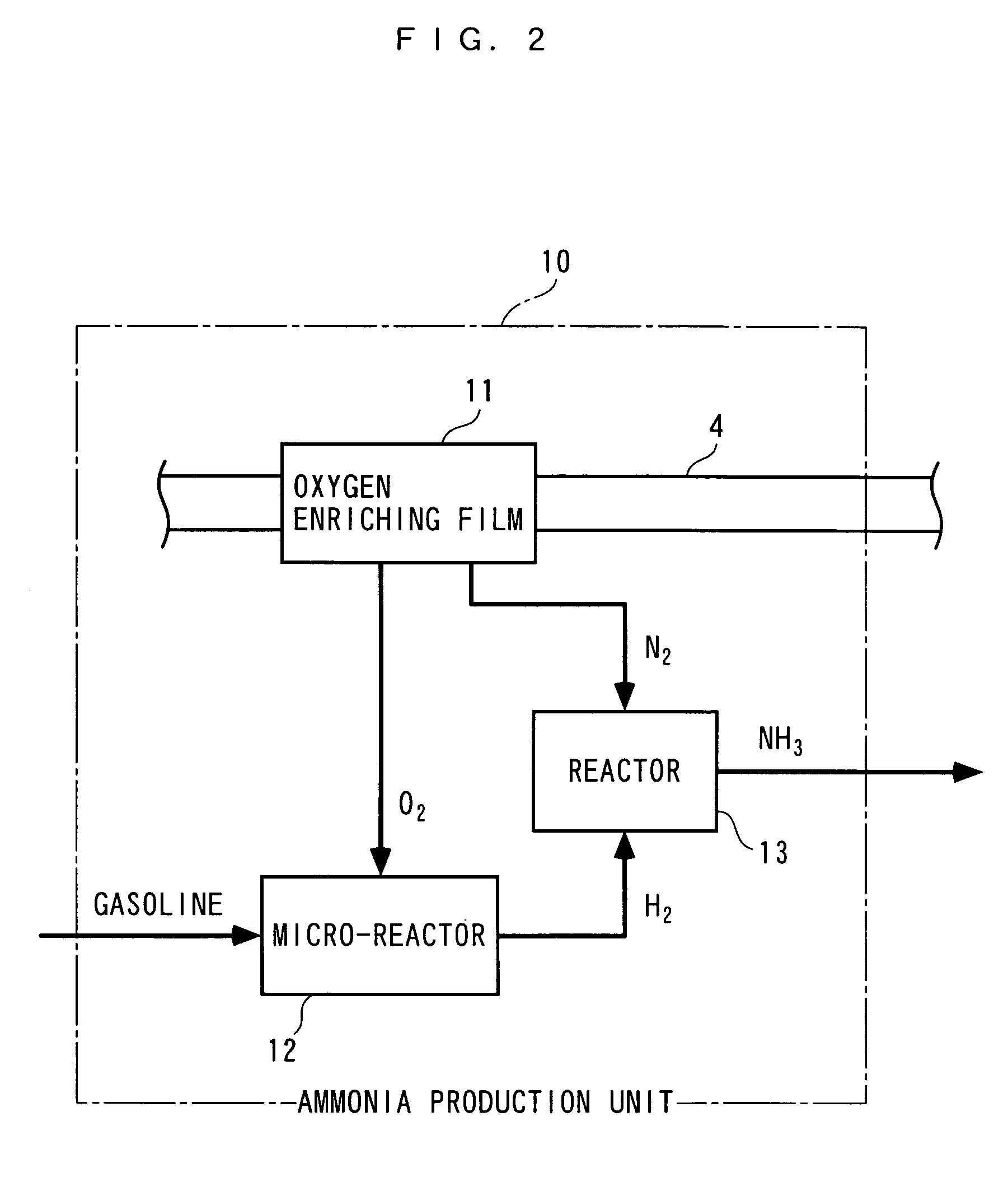
An exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for an internal combustion engine, and an engine control unit are provided for appropriately determining the amount of reducing agent supplied to a NOx selective reduction catalyst to ensure good exhaust gas characteristics. The exhaust gas purifying apparatus comprises an ECU; a NOx selective reduction catalyst for purifying NOx in exhaust gases in an exhaust pipe; a NOx sensor disposed in the exhaust pipe at a location downstream of the NOx selective reduction catalyst for detecting a NOx concentration in exhaust gases; and an injector for supplying the NOx selective reduction catalyst with ammonia produced in an ammonia production unit. The ECU determines the amount of ammonia injected to the NOx selective reduction catalyst by the injector such that an estimate of the NOx concentration detected by the NOx sensor reaches a minimum value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
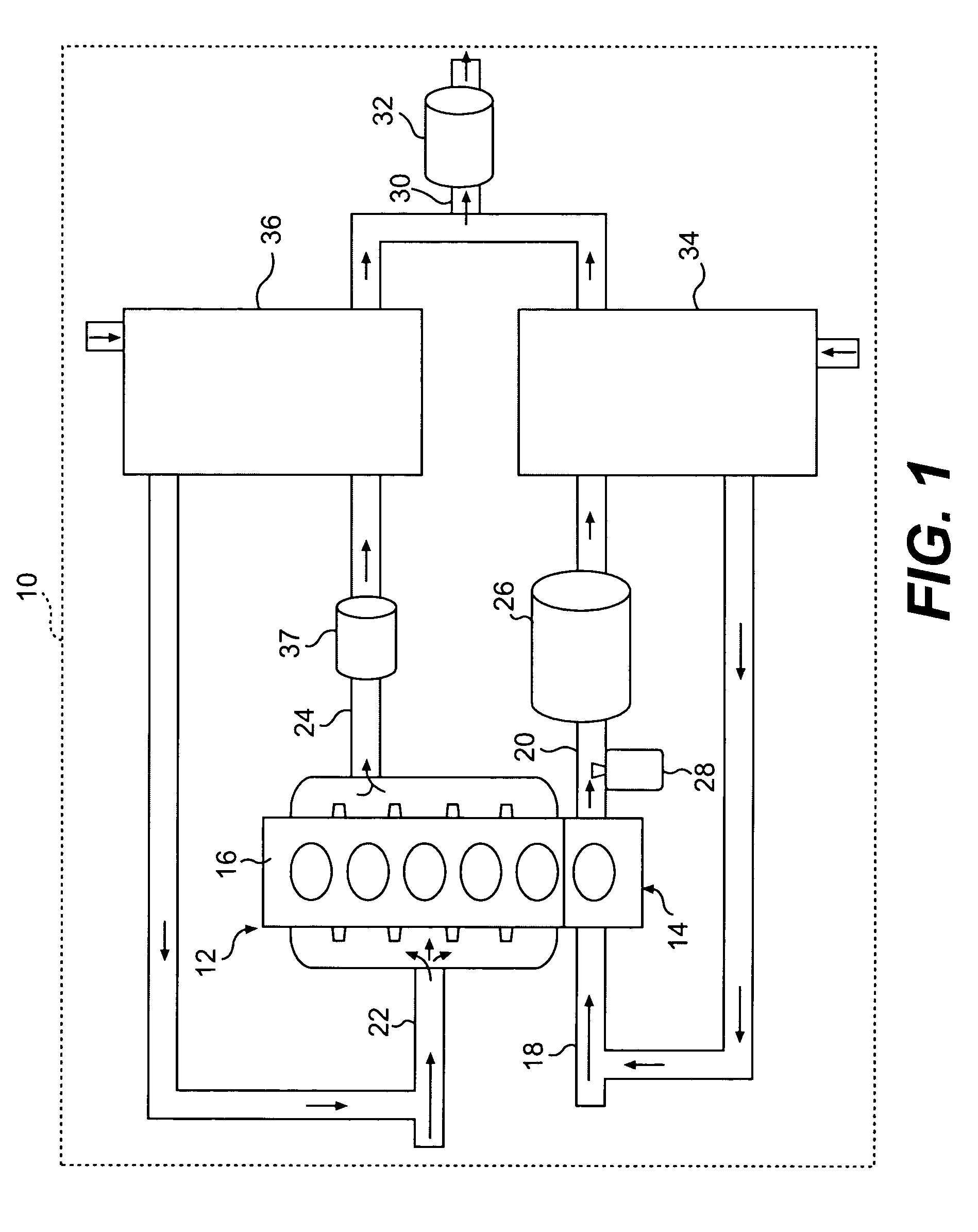
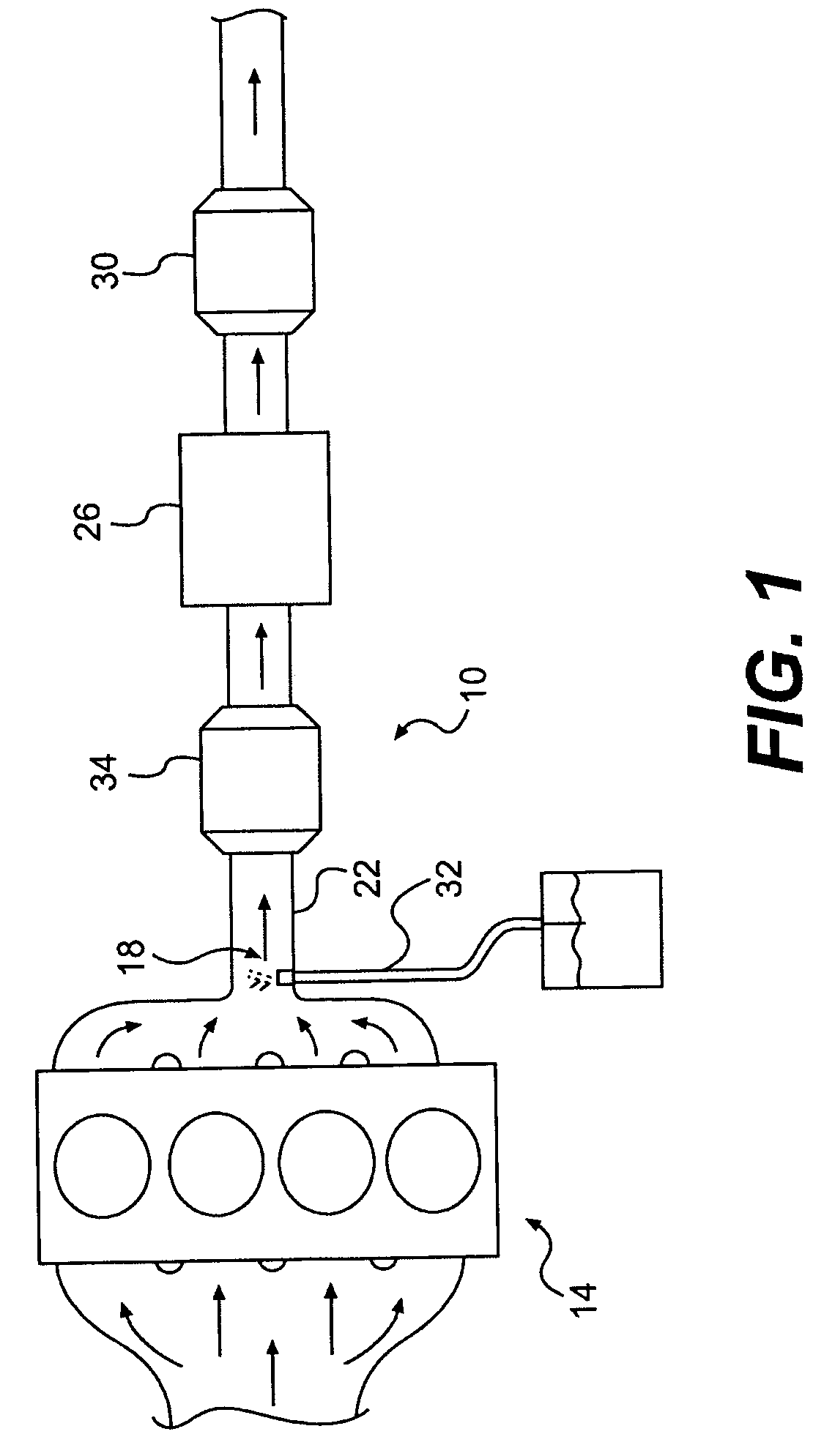
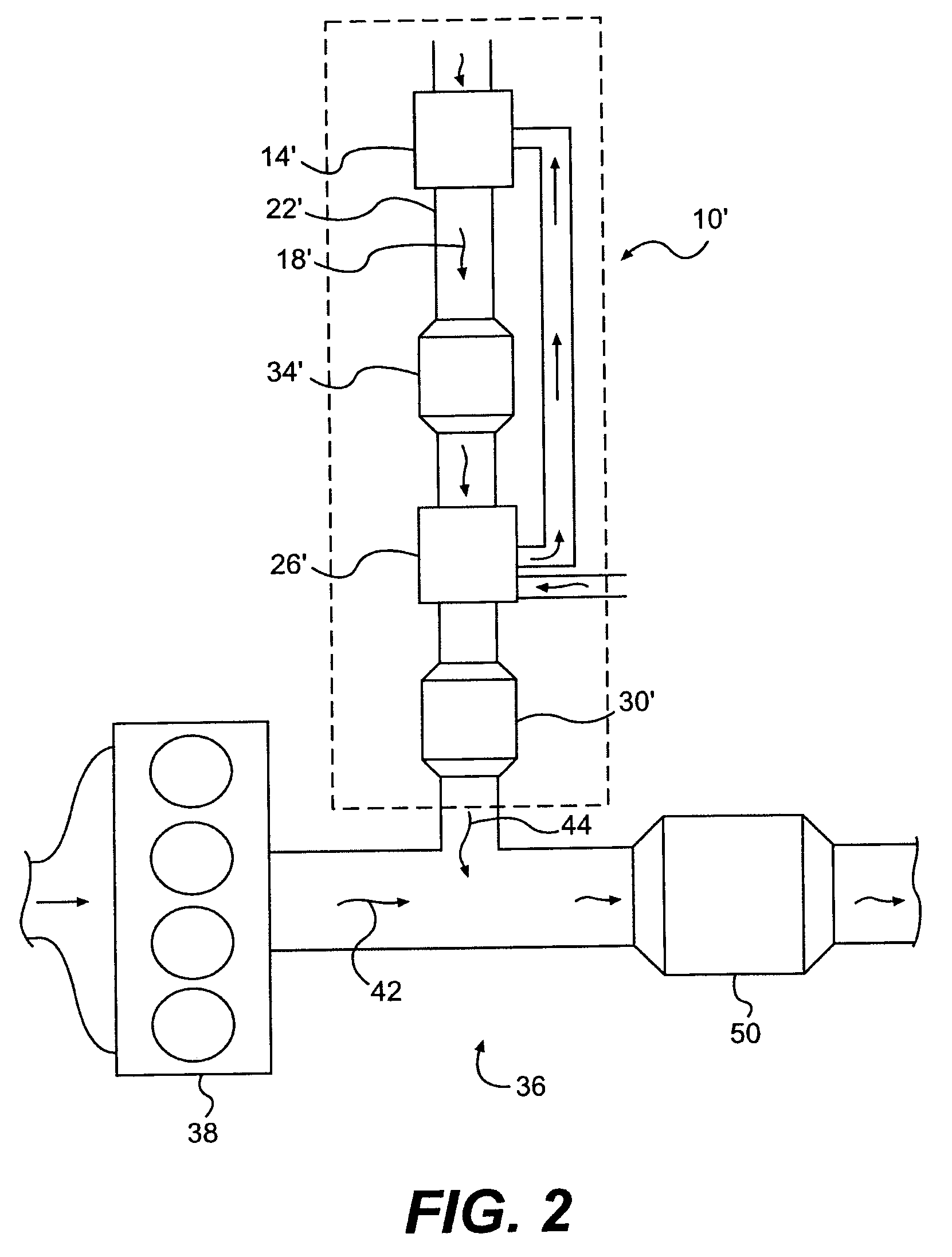
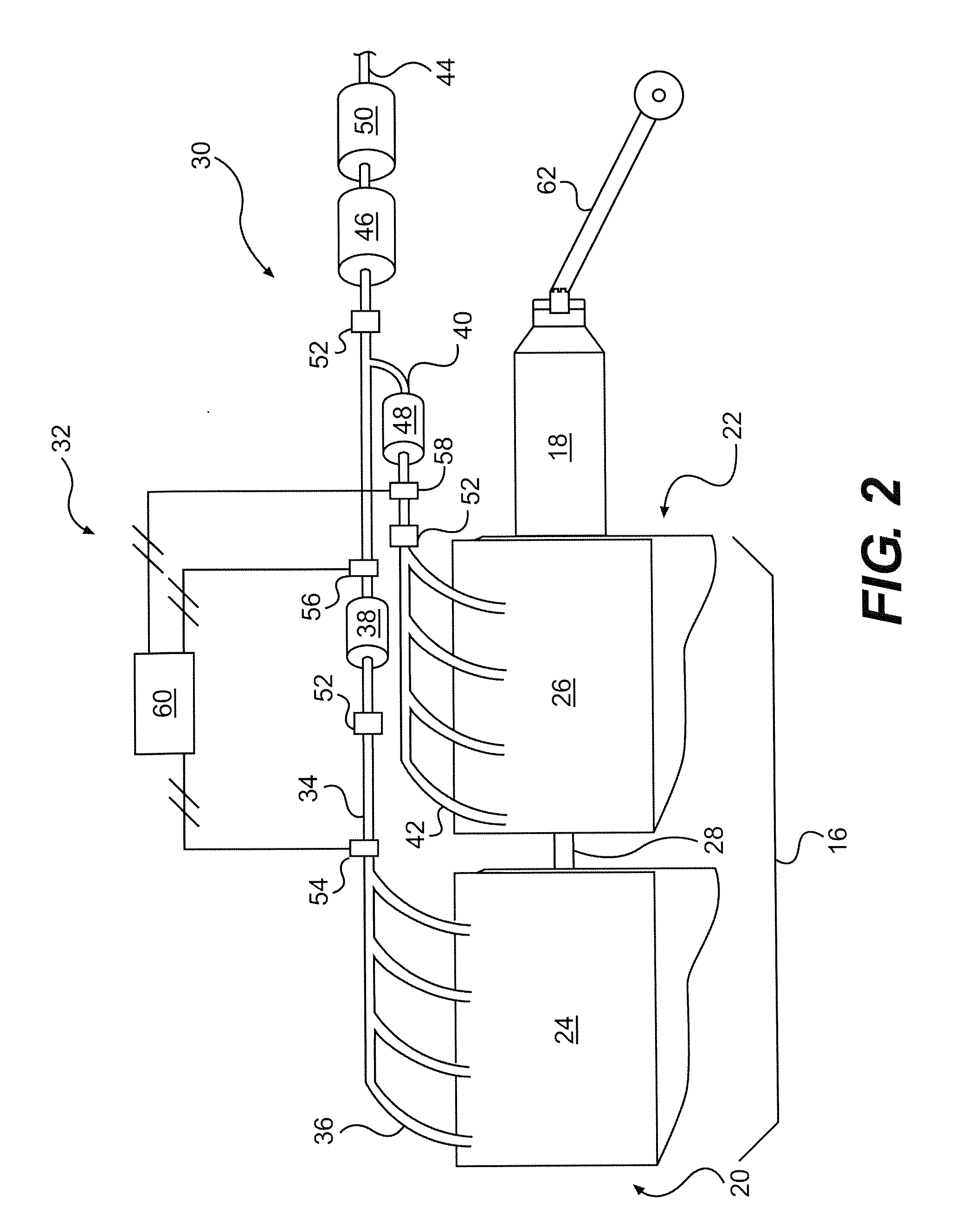
Exhaust purification with on-board ammonia production
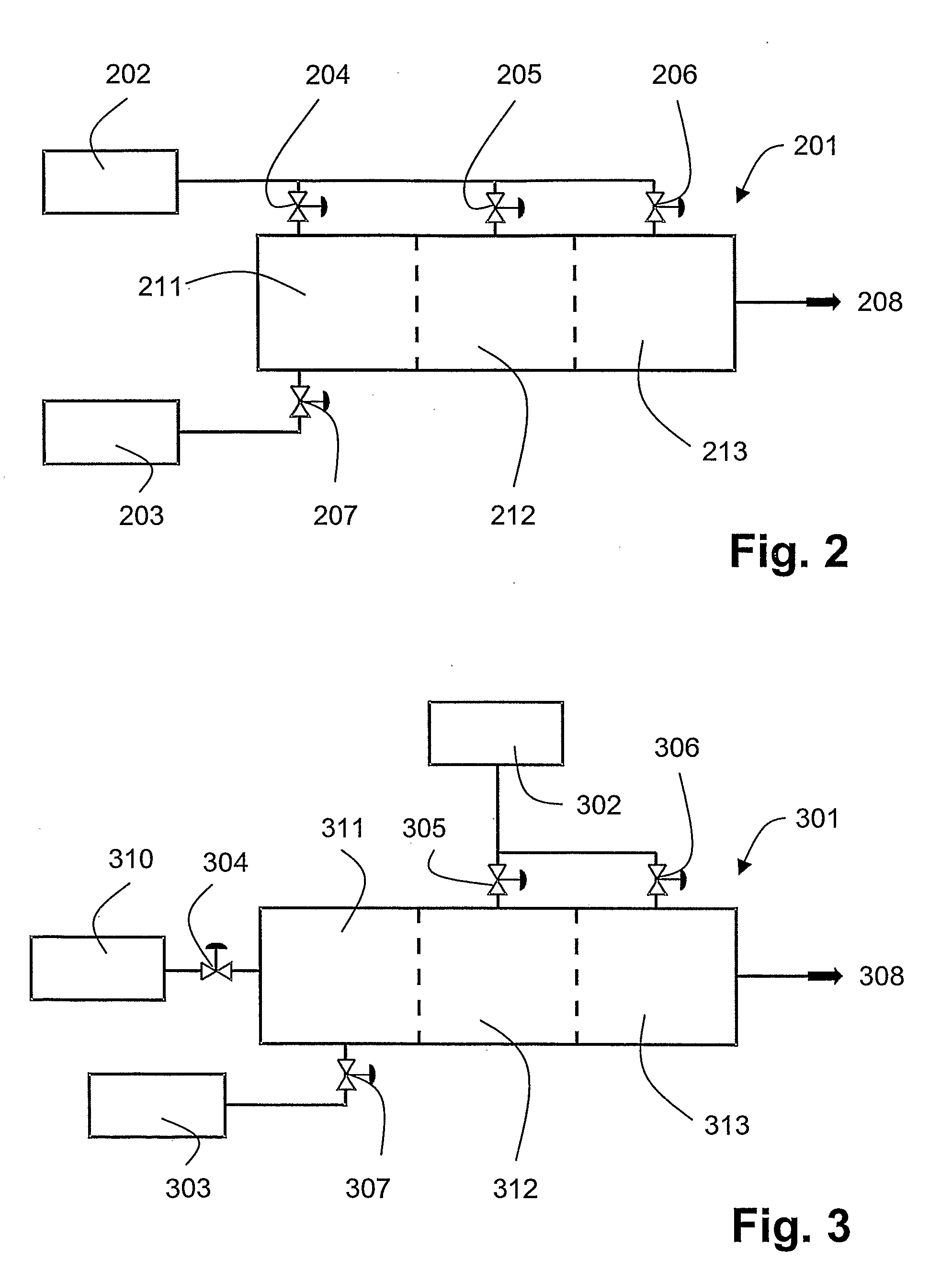
A power source is provided for use with selective catalytic reduction systems for exhaust-gas purification. The power source includes a first cylinder group with a first air-intake passage and a first exhaust passage, and a second cylinder group with a second air-intake passage and a second exhaust passage. The second air-intake passage is fluidly isolated from the first air-intake passage. A fuel-supply device may be configured to supply fuel into the first exhaust passage, and a catalyst may be disposed downstream of the fuel-supply device to convert at least a portion of the exhaust stream in the first exhaust passage into ammonia.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
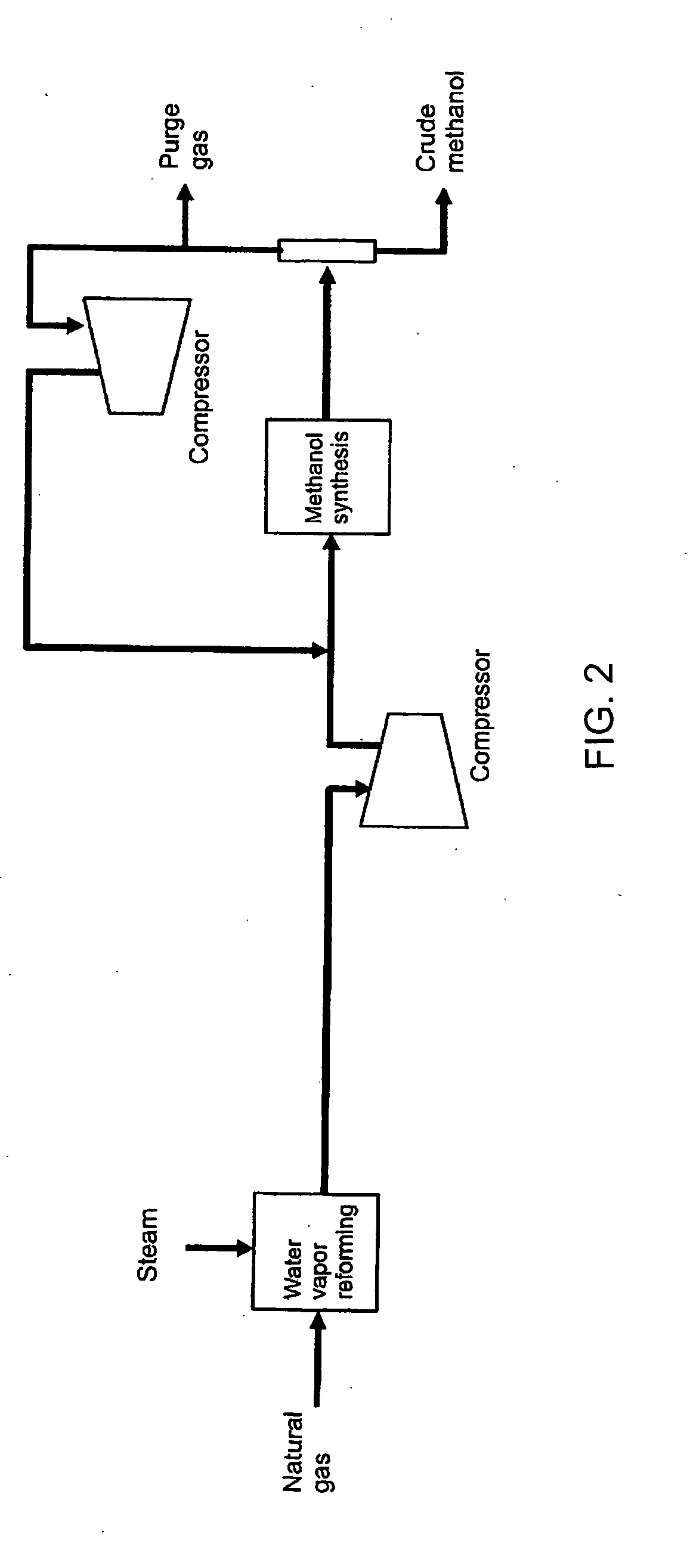
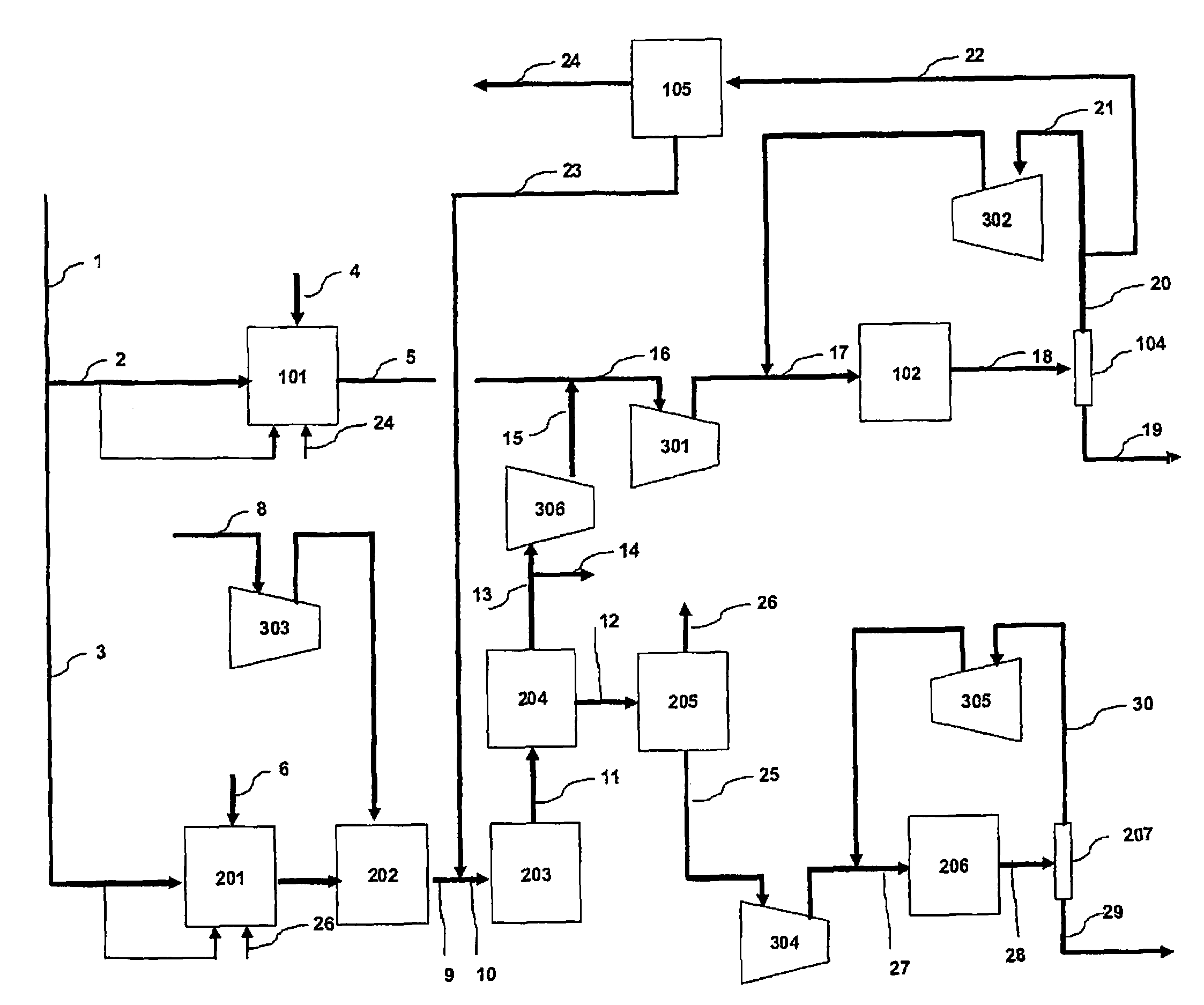
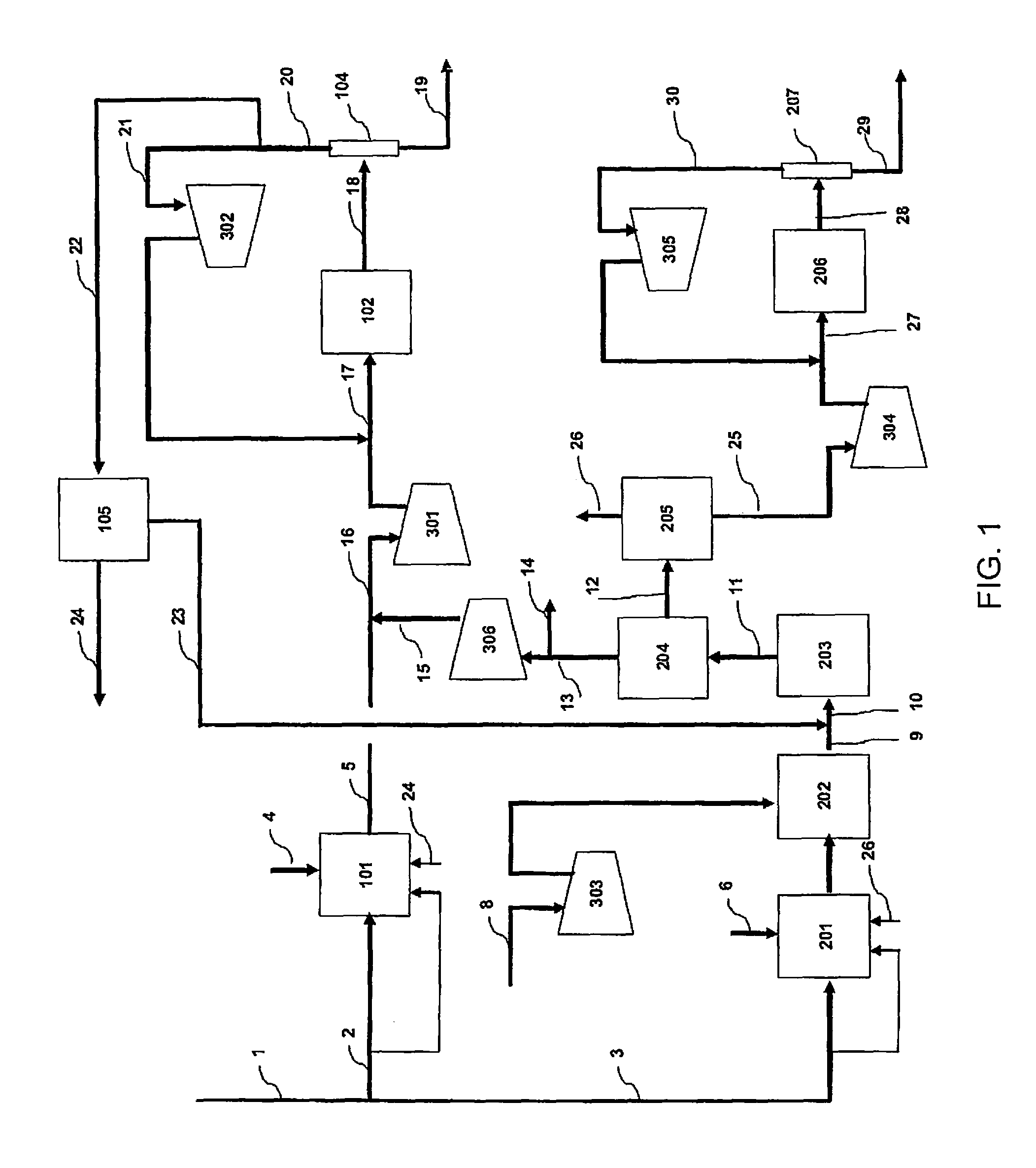
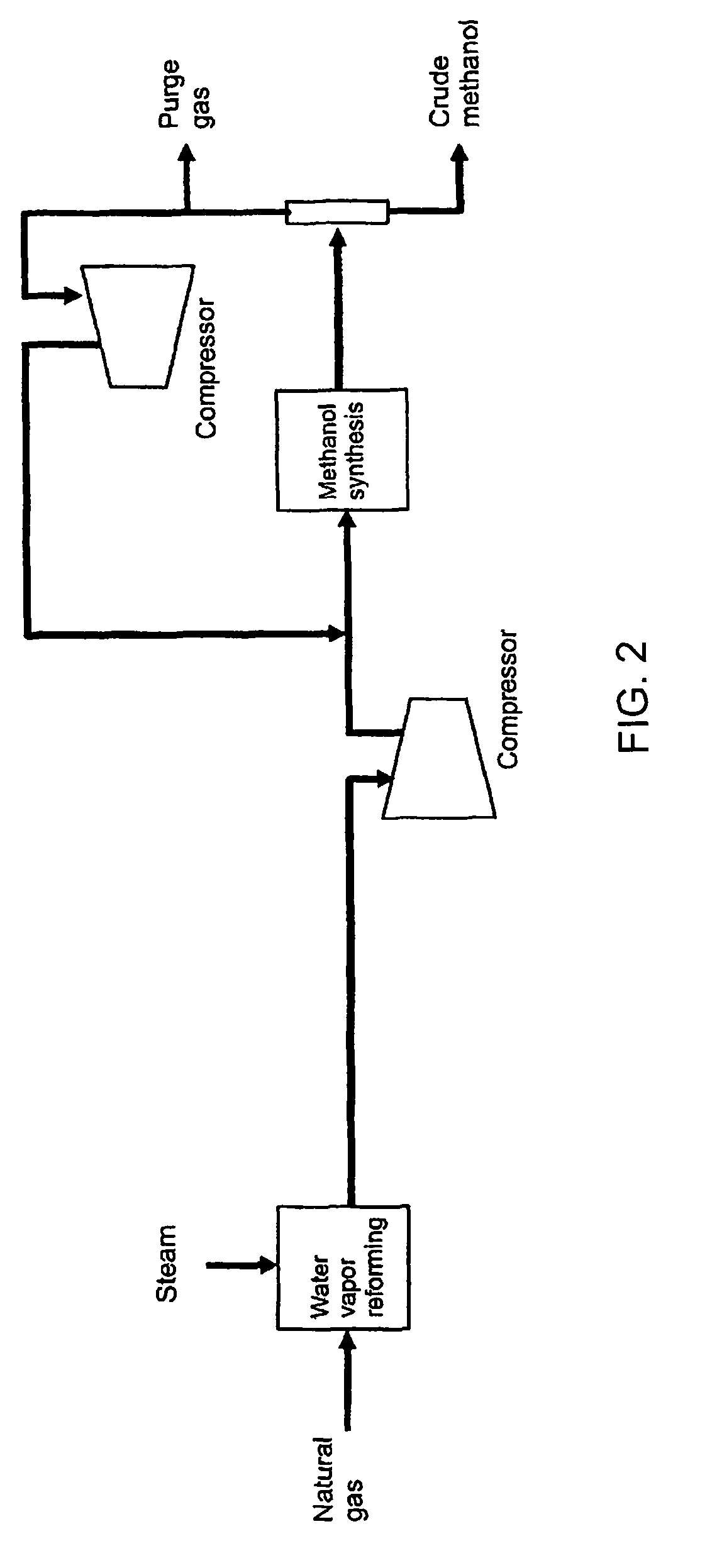
Method of coproducing methanol and ammonia
ActiveUS20100150810A1Efficiently coproduceIncreasing and decreasing specific raw material consumptionCyanogen compoundsHydroxy compound preparationSteam reformingSyngas
The present invention enables the coproduction of methanol and ammonia by using a remarkably smaller amount of raw material, natural gas, as compared with the case of independently producing either of methanol or ammonia. Specifically, the present invention provides a process of coproducing methanol and ammonia by using natural gas, LPG, butane, or naphtha as raw material, having a methanol production process (A) composed of specific steps and an ammonia production process (B) also composed of specific steps, in which (1) directing a gas rich in hydrogen recovered in a hydrogen recoverying step in the methanol production process (A) to a certain step after an air reforming step and before a ammonia synthesis step in the ammonia production process (B) to prepare additional feedstock gas for ammonia synthesis; and also (2) cooling a synthesis gas, formed in a steam reforming step in the methanol production process (A) and separating and removing condensed water from the cooled synthesis gas, mixing the water removed synthesis gas and carbon dioxide obtained by pre-compressing carbon dioxide obtained in a CO2 removing step in the ammonia production process (B), compressing up to the methanol synthesis pressure to be supplied as reactant gas for methanol synthesis to the methanol synthesis step (A-2).
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP
Flue gas desulphurization and denitration method as well as its apparatus
ActiveCN103585867AIncrease temperatureReduce electric heating energy consumptionDispersed particle separationAmmonia productionAtmospheric air
The invention relates to a flue gas desulphurization and denitration method as well as its apparatus, and especially relates to a desulphurization and denitration technology system for flue gas from large-scale mobile facilities such as ships. The method comprises the following steps: flue gas is passed through a heat pipe exchanger and a heat pump in order for increasing temperature of flue gas, and flue gas is selectively passed through an electric heater for heating to the temperature of 340-350 DEG C, an urea solution is used for preparing ammonia gas in a hydrolysis reactor, ammonia gas is diluted by partial high temperature flue gas at an outlet of a SCR reactor and then mixed for injecting flue gas which is undenitrated, the mixed flue gas enters into the SCR reactor for a flue gas denitration reaction, the flue gas after denitration is passed through the heat exchanger, the heat pump and the hydrolysis reactor and cooled, and then enters into a desulfurization tower, flue gas after desulphurization is directly discharged into atmosphere, and an absorption liquid adds alkali and seawater for regeneration and cycle usage. In the method, the heat exchanger and the heat pump are used for recovering waste heat of flue gas, and the energy consumption is greatly reduced. The ammonia production method through hydrolysis is capable of increasing the mixing degree of ammonia and flue gas, so that denitration efficiency can be further increased.
Owner:湖州旧馆頔南污水处理有限公司
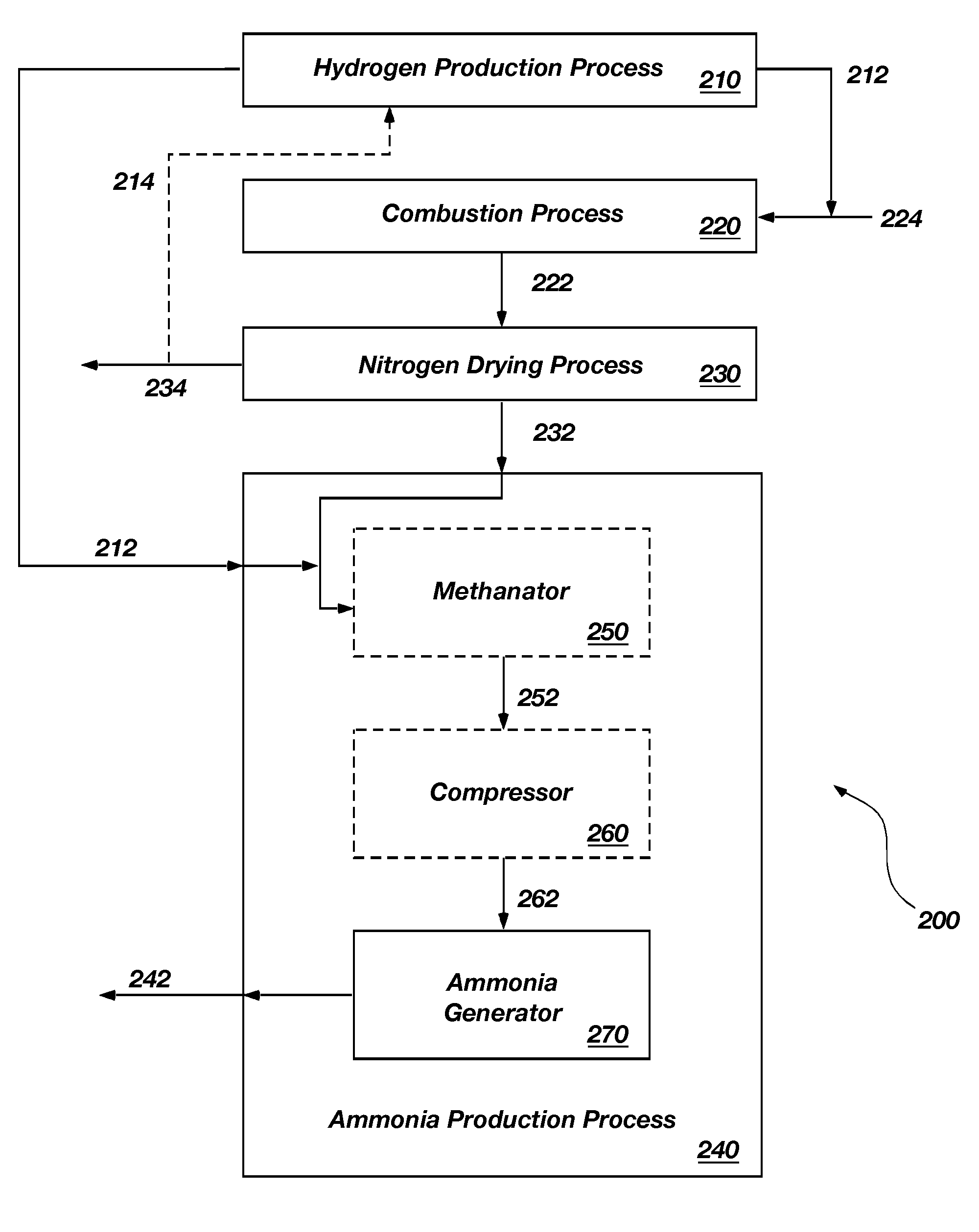
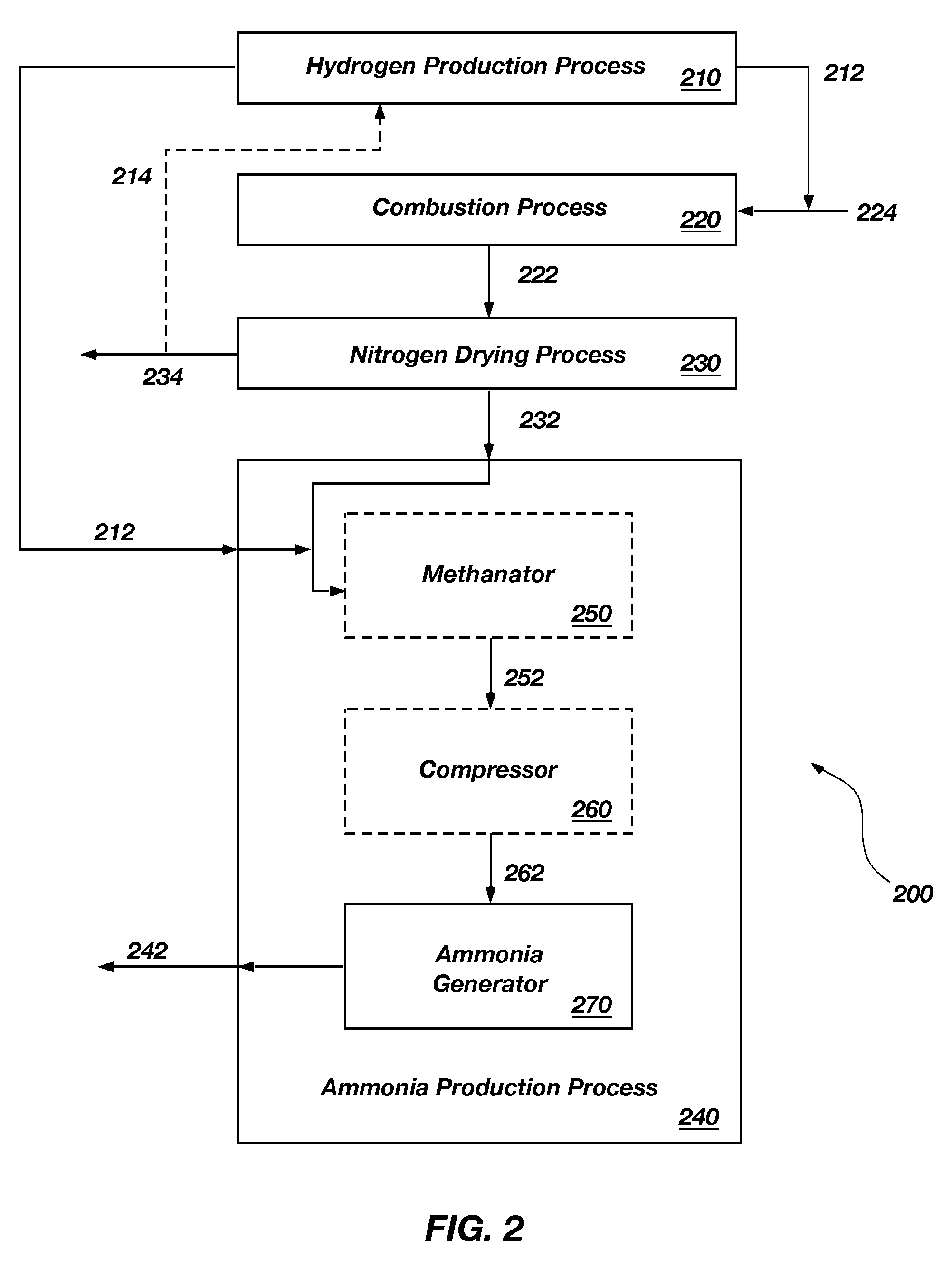
Methods and apparatuses for ammonia production
Processes for the production of ammonia may include the production of nitrogen from the combustion of a stream or slipstream of hydrogen mixed with air. Hydrogen used to produce the nitrogen for an ammonia combustion process may be generated from the electrolysis of water. Hydrogen produced by the electrolysis of water may also be combined with nitrogen to produce ammonia. Apparatuses for the production of ammonia and constituents used to produce ammonia are also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Method and apparatus for anhydrous ammonia production
A method and apparatus for synthesizing anhydrous ammonia utilizing proton conducting electrolyte having a water vapor dissociating electrocatalyst on one side and a nitrogen dissociating electrocatalyst on the other side. A voltage is provided across the proton conducting electrolyte, protons are separated from the water vapor and transferred through the middle of the proton conducting electrolyte to the second side of the proton conducting electrolyte. Nitride ions are formed from nitrogen and the electrons provided by the voltage on the second side of the proton conducting electrolyte. The protons are then reacted with the nitride ions on the second side of the proton conducting electrolyte to produce anhydrous ammonia. A preferred proton conducting electrolyte is barium cerium oxide doped with about 10% ytterbium with a water vapor dissociating electrocatalyst of Ni and Pd, and a nitrogen dissociating electrocatalyst of Co and Ru.
Owner:NHTHREE
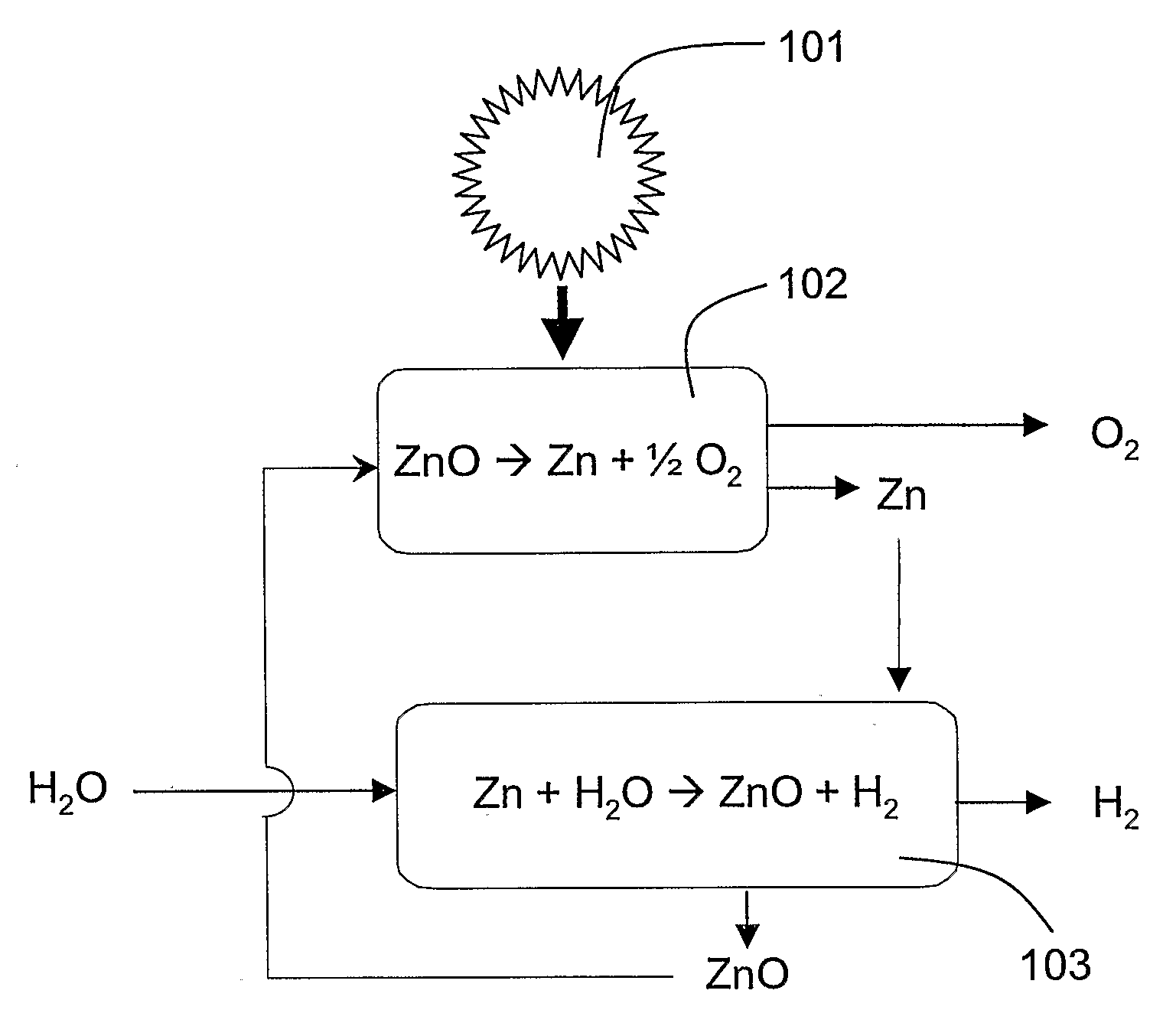
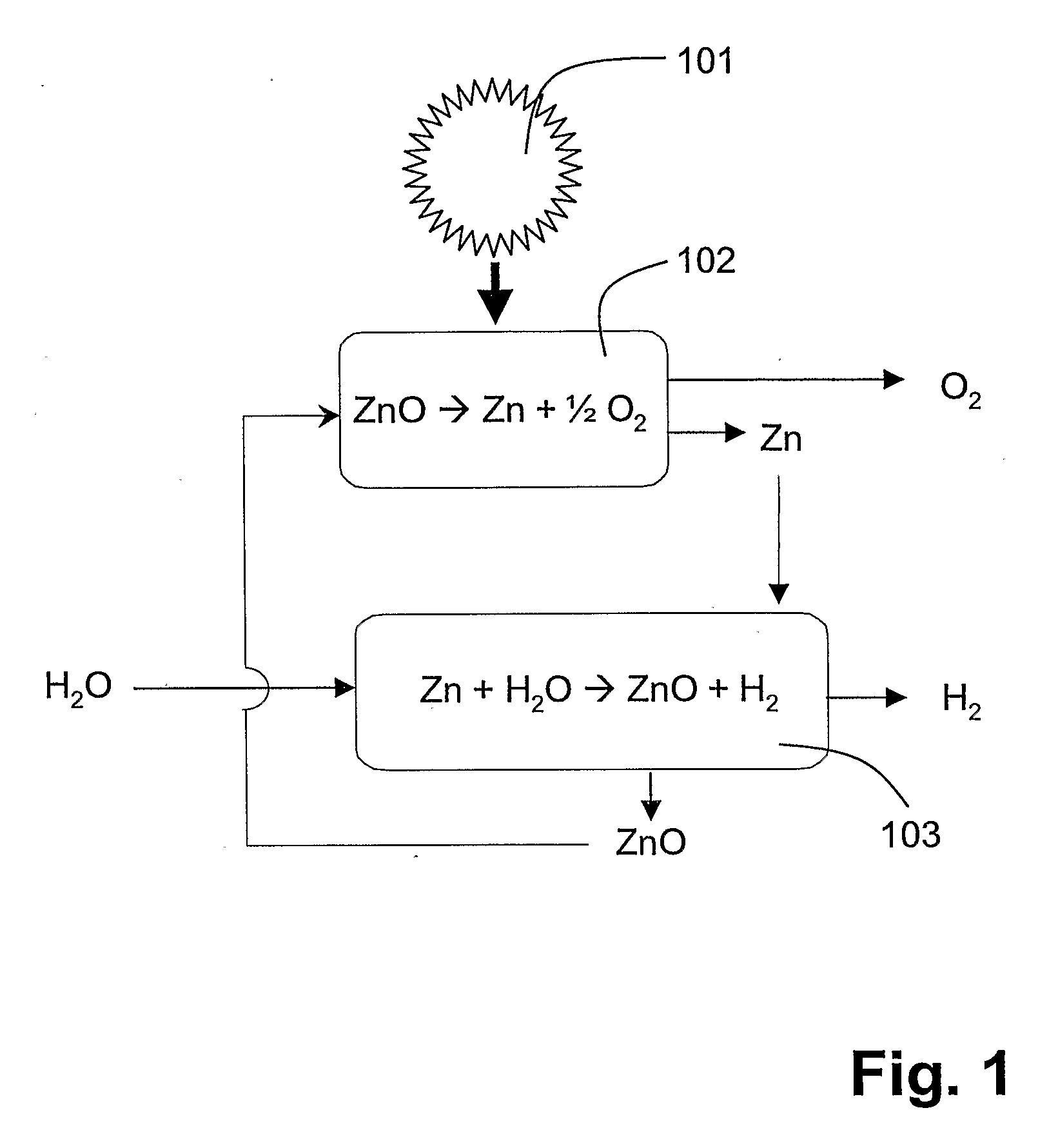
Process and apparatus for prodcing concrrently hydrogen or ammonia and metal oxide nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080019903A1Simple and highly efficient processRapid coolingMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideMetal oxide nanoparticlesAmmonia production
A process for producing hydrogen or ammonia is disclosed. Steam (202) and a metal or a metal-containing compound (in the case of ammonia production, a metal nitride) are provided to a reaction zone (213) and reacted under conditions for obtaining gaseous hydrogen or ammonia, respectively. The metal or metal-containing compound is provided in the form of nanoparticles and / or nanodroplets with a BET surface area of at least 1.0 m2 / g. The nanoparticles and / or nanodroplets may be produced in-situ, either by rapid cooling of a stream of a vapor (203) of the metal or metal-containing compound in a formation zone (212), or by feeding a stream of a precursor into the formation zone (212) and reacting the precursor with a reactant gas in the formation zone to obtain nanoparticles and / or nanodroplets. An apparatus (201) for carrying out the process is also disclosed
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Ammonia synthesis process
ActiveCN101850988AEmission reductionEmission reduction effect is obviousAmmonia preparation/separationSyngasAmmonia production
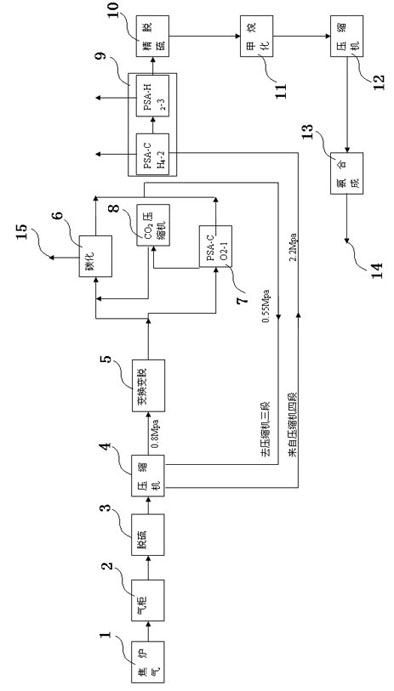
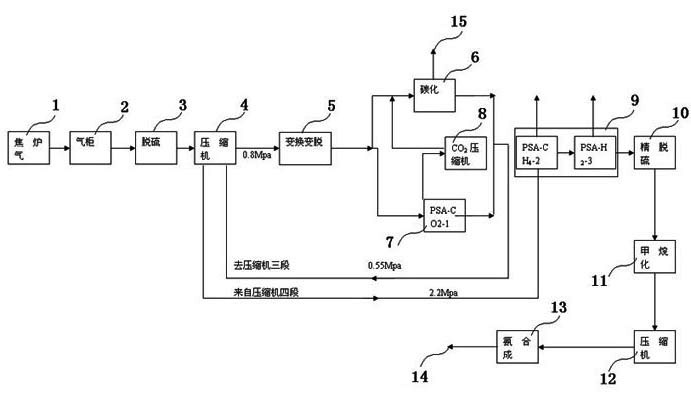
The invention belongs to the field of chemical engineering, in particular to an ammonia synthesis process. The process is characterized in that obtained synthesis gases are conveyed to the ammonia synthesis process by ten steps to produce product ammonia. The invention adopts the process technology that crude gas in a coking plant is used as raw material, nitrogen and methane in the crude gas areseparated and purified by utilizing a PSA (Pressure Swing Absorption) device to greatly reduce atmospheric pollutants, such asH2S, NH3 and the like and the emission of CO2. The invention provides a low-cost low-carbon synthetic ammonia production process which can reduce the atmospheric pollutants, such asH2S, NH3 and the like and lessen the emission of CO2.
Owner:YULIN HONGYUAN ENVIRONMENT FRIENDLY CHEM
Exhaust purification with on-board ammonia production
A system of ammonia production for a selective catalytic reduction system is provided. The system includes producing an exhaust gas stream within a cylinder group, wherein the first exhaust gas stream includes NOx. The exhaust gas stream may be supplied to an exhaust passage and cooled to a predetermined temperature range, and at least a portion of the NOx within the exhaust gas stream may be converted into ammonia.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Multi-engine system with on-board ammonia production
A power system is provided having a first power source including at least one engine configured to combust a first air / fuel mixture and produce a first exhaust stream. The fuel of the first air / fuel mixture may be liquefied petroleum gas. The system also has a first exhaust passageway fluidly connected to the first power source and configured to receive the first exhaust stream. In addition, the system has a second power source including at least one engine configured to combust a second fuel / air mixture and produce a second exhaust stream. Furthermore, the system has a second exhaust passageway fluidly connected to the second power source and configured to receive the second exhaust stream. The system further has a first catalyst disposed within the first exhaust passageway to convert at least a portion of the first exhaust stream to ammonia
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Exhaust purification with on-board ammonia production
InactiveUS20070227143A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAmmonia productionEnvironmental engineering
A first aspect of the present disclosure includes a power source for use with selective catalytic reduction systems for exhaust-gas purification. The power source may comprise a first cylinder group with a first air-intake passage and a first exhaust passage, and a second cylinder group with a second air-intake passage and a second exhaust passage. The power source may further include a first forced-induction system in fluid communication with the first air-intake passage, and a second forced-induction system in fluid communication with the second air-intake passage. A catalyst may be disposed downstream of the fuel-supply device to convert at least a portion of the exhaust stream in the first exhaust passage into ammonia.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
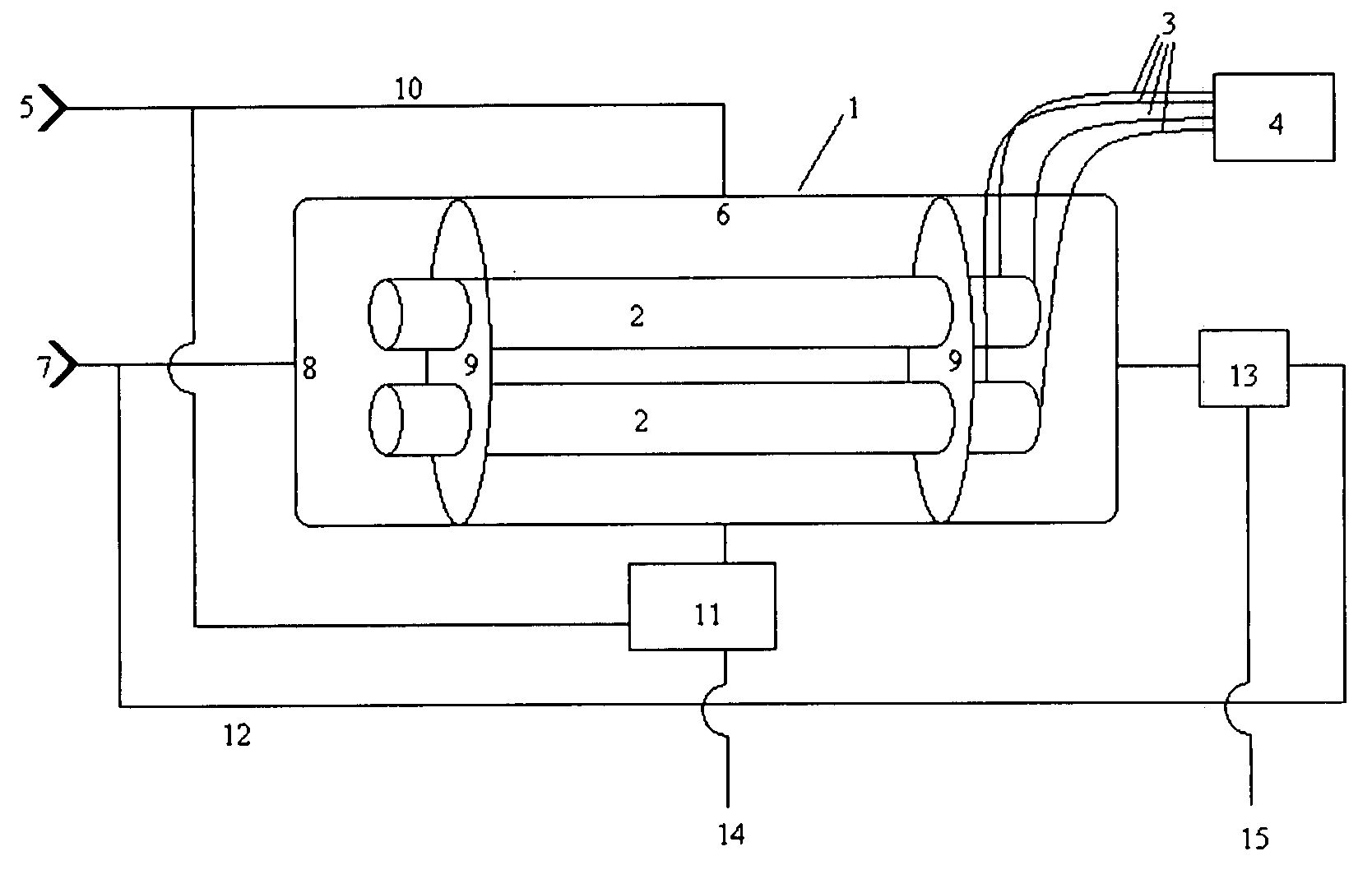
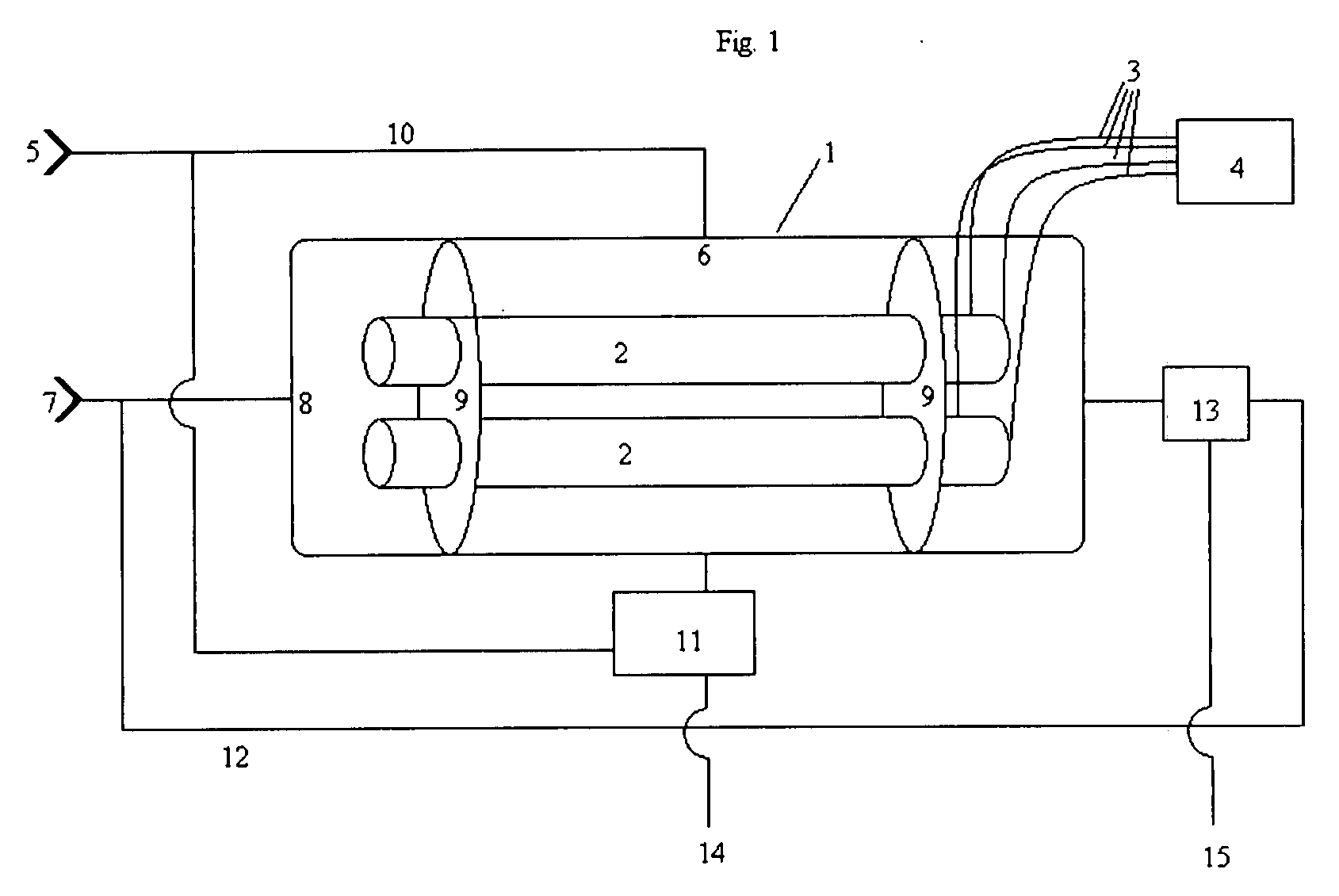
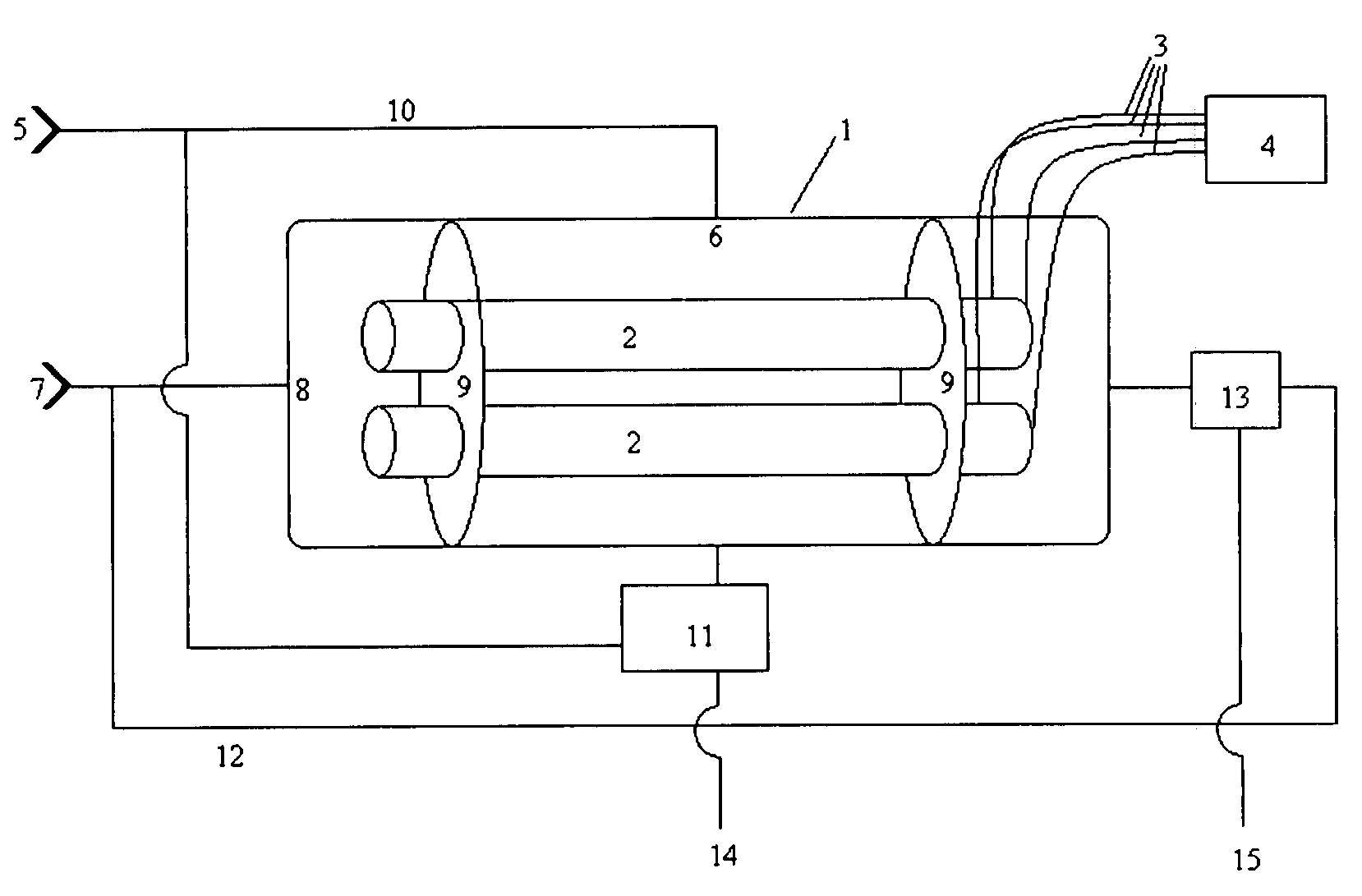
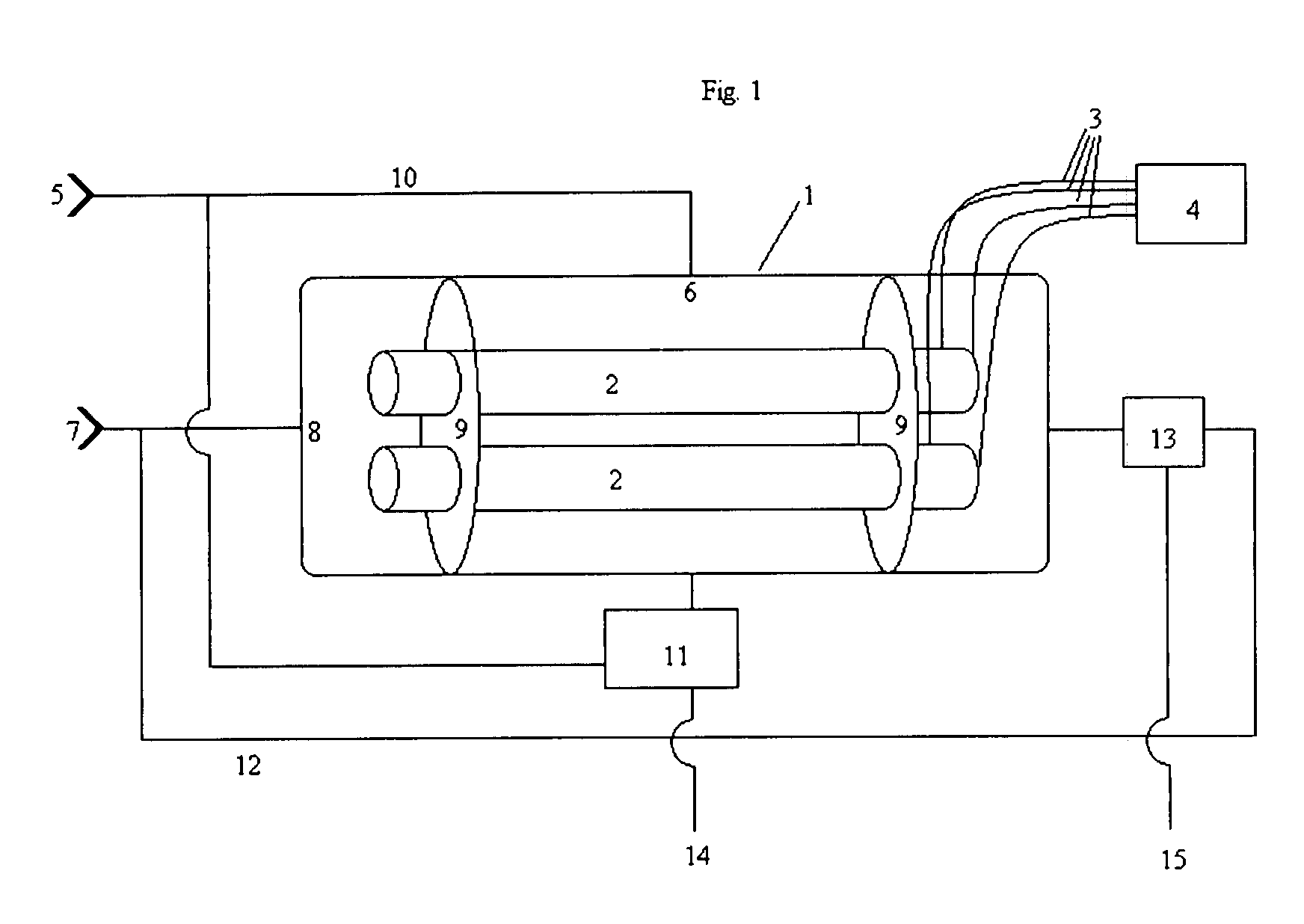
Nested-Flow Heat Exchangers and Chemical Reactors
ActiveUS20160282052A1More cost-effectivelyCost-effectiveUrea derivatives preparationSequential/parallel process reactionsThermal energySingle process
Disclosed is a technology based upon the simple nesting of tubes to provide heat exchangers, chemical reactors or chemical reactors with built in heat exchanger. As a chemical reactor, the technology provides the ability to manage the temperature within a process flow to better control the process for improved performance, control the location of product production to control corrosion issue, or implement multiple steps for a process within the same piece of equipment. As a heat exchanger, the technology can provide large surface areas per unit volume and large heat transfer coefficients. As a combined heat exchanger and chemical reactor, the technology can recover the thermal energy from the product flow to heat the reactant flow to the reactant temperature, significantly reducing the energy needs for accomplishment of a process. Combined heat exchanger and chemical reactor examples for hydrogen production and ammonia production are presented, along with a urea production example that integrates the product formation, resonance time conversion and stripping steps for urea production all within a single process unit.
Owner:BAYOTECH INC
Turbo charged internal-combustion engine for exhaust system with an SCR catalytic equipment
ActiveCN1936286ALow powerSimplify insulationInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusTurbochargerAmmonia production
The invention relates to means of superchargers loaded internal-combustion engine, in particular diesel engine of a vehicle, in whose exhaust strand an exhaust subsequent treatment mechanism with at least one SCR catalyst is intended, ammonia as reducing agent for nitrogen oxide reduction supplyable is characterized, which is generatable in a ammonia reactor from a urea water solution or a solid urea, by the fact that the ammonia reactor (11) outside at the turbine case of the supercharger, whose heat radiation is used for ammonia production.
Owner:MAN NUTZFAHRZEUGE AG
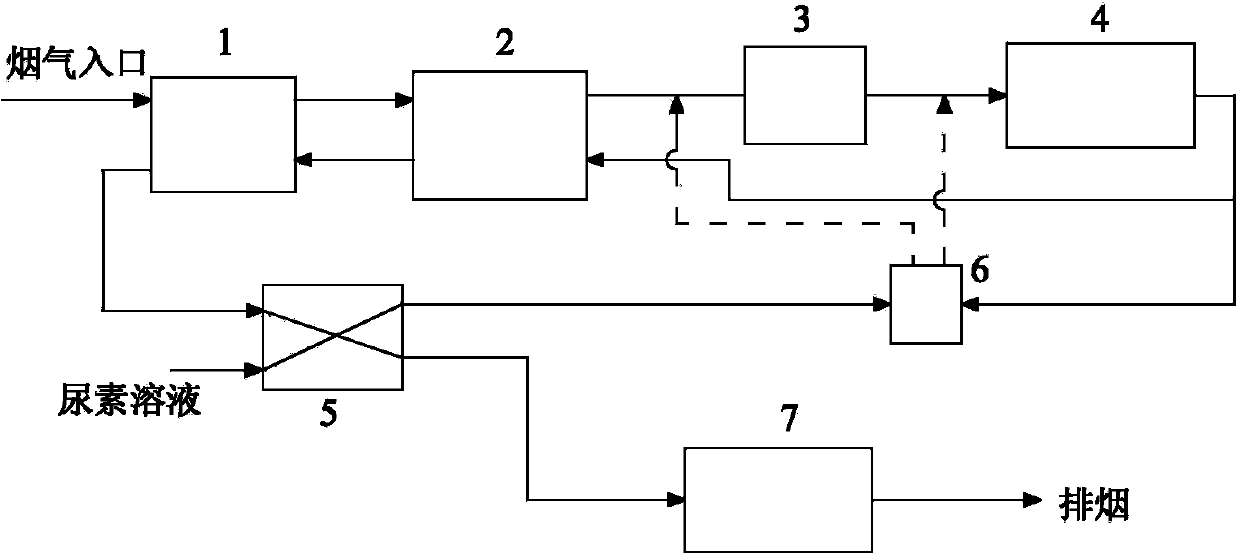
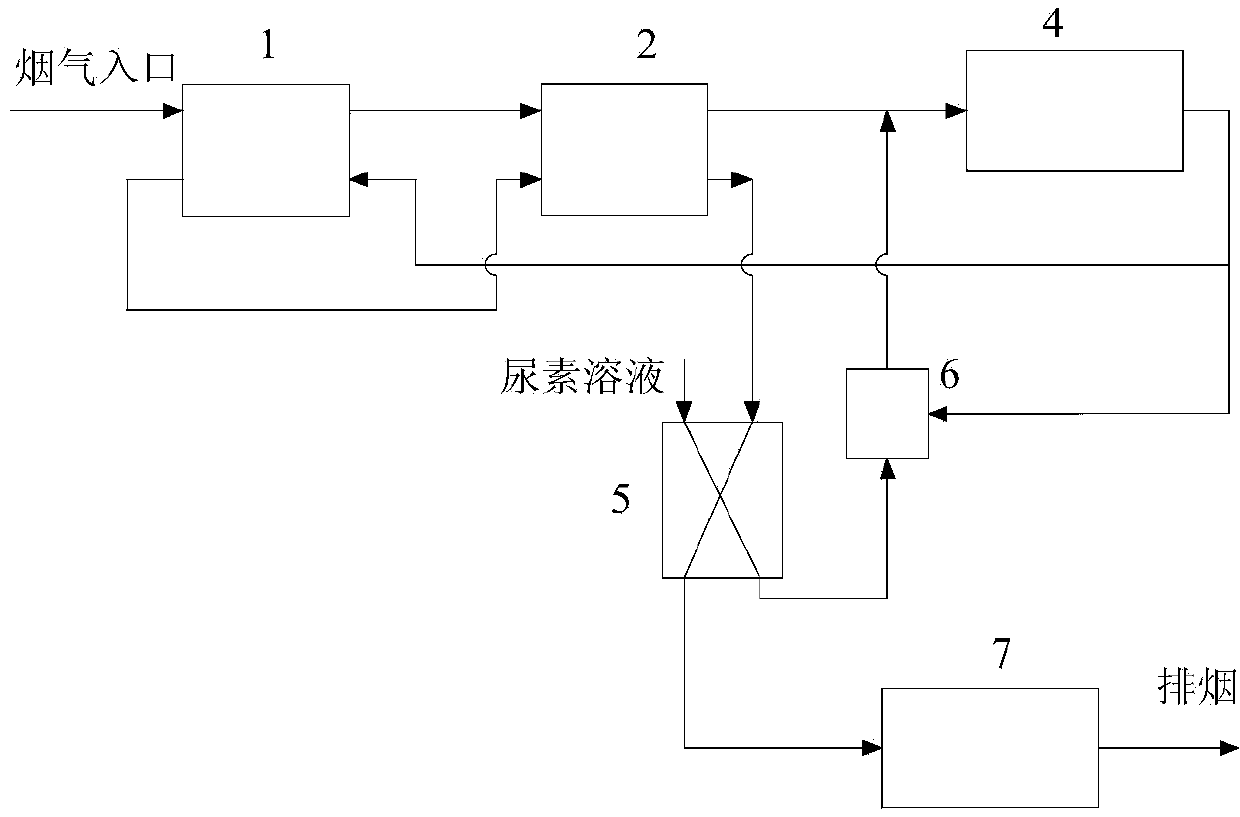
Flue gas SCR denitration urea catalytic hydrolysis ammonia production system and method
ActiveCN105129817AReduce consumptionShort hydrolysis reaction timeAmmonia preparation/separationMolten stateAmmonia production
The invention discloses a flue gas SCR denitration urea catalytic hydrolysis ammonia production system and a method. The system mainly comprises a reaction system, a urea solution supply system, a steam supply system, an ammonia-air mixing system, a sewage discharge and safety system, a catalyst feeding system, a back blow system. By means of the system, fast hydrolysis reaction of molten state urea can be carried out under a temperature of 135-160DEG C and a pressure of about 0.4-0.9MPa. The reaction speed is enhanced by about more than 10 times than that of the traditional hydrolysis method, the response time can be less than 1min, and the energy consumption is about half of the pyrolysis technology. The system and method provided by the invention have the advantages of fast urea hydrolysis rate, small urea consumption, short hydrolysis reaction time, and realization of automation.
Owner:DATANG ENVIRONMENT IND GRP +1
Metallic mesoporous transition metal oxide molecular sieves, room temperature activation of dinitrogen and ammonia production
This invention provides novel stable metallic mesoporous transition metal oxide molecular sieves and methods for their production. The sieves have high electrical conductivity and may be used as solid electrolyte devices, e.g., in fuel cells, as sorbents, e.g. for hydrogen storage, and as catalysts. The invention also provides room temperature activation of dinitrogen, using the sieves as a catalyst, which permits ammonia production at room temperature.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
Exhaust purification with on-board ammonia production
A power source is provided for use with selective catalytic reduction systems for exhaust-gas purification. The power source has a first cylinder group fluidly connected to a first air-intake passage and a first exhaust passage, wherein the first air-intake passage is configured to provide air at a first set of characteristics. The power source also has a second cylinder group fluidly connected to a second air-intake passage and a second exhaust passage, wherein the second air-intake passage is configured to provide air at a second set of characteristics different from the first set of characteristics. An ammonia-producing catalyst may be disposed within the first exhaust passage and configured to convert at least a portion of a fluid in the first exhaust passage into ammonia. Further, a merged exhaust passage may be configured to connect the first exhaust passage and the second exhaust passage downstream of the ammonia-producing catalyst to facilitate a reaction between ammonia and NOx to at least partially remove NOx from the merged exhaust passage.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Procedures for ammonia production
InactiveUS20080213157A1Bulk chemical productionAmmonia preparation/separationPtru catalystAmmonia production
Systems and methods for producing ammonia. In one approach, Li3N is reacted with hydrogen to produce ammonia and is regenerated using nitrogen. Catalysts comprising selected transition metals or their nitrides can be used to promote the reactions. In another approach, supercritical anhydrous ammonia is used as a reaction medium to assist the reaction of hydrogen with nitrogen to produce ammonia, again promoted using catalysts.
Owner:HSM SYST
Poultry farm practices
InactiveUS20150037307A1Improve the environmentEnhanced feedingAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismProduction rate
The present invention relates to methods of improving the environment within a poultry farming facility including reducing ammonia production in a poultry facility, inhibiting urease enzymes in poultry litter, reducing levels of pathogenic bacteria in poultry litter, improving productivity of poultry farms, reducing or preventing pododermatitis in poultry reared in mass production poultry facilities and controlling pests in poultry litter. Compositions, suitable for use in such methods, comprising at least one microorganism of the genus Bacillus and at least one biosurfactant wherein the biosurfactant is present in an amount of 2 mg / L to 7000 mg / L are also described.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOPROTECT IP PTY LTD
Monatomic catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112221528AImprove nitrogen fixationImprove nitrogen fixation capacityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBulk chemical productionPtru catalystAmmonia production
The invention discloses a monatomic catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a high-temperature polymerization reaction on an organic matter which is rich in nitrogen and carbon and is used as a precursor to prepare a block carbon nitride material, and then carrying out stripping treatment to obtain a carbon nitride ultrathin nanosheet; carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on a hydrothermal reaction system containing the carbon nitride ultrathin nanosheet, a transition metal source and a solvent to prepare a transition metal oxide / carbon nitride composite material; and calcining and etching the transition metal oxide / carbon nitride composite material to obtain the monatomic catalyst. According tothe monatomic catalyst as well as the preparation method and application thereof of the invention, transition metal single atoms are loaded on the carbon nitride ultrathin nanosheet, and ammoniationtreatment is further carried out, so that the nitrogen fixation performance of the monatomic catalyst is greatly improved, and the ammonia production efficiency can reach 675mu mol.g <-1> h <-1>.
Owner:江西省纳米技术研究院
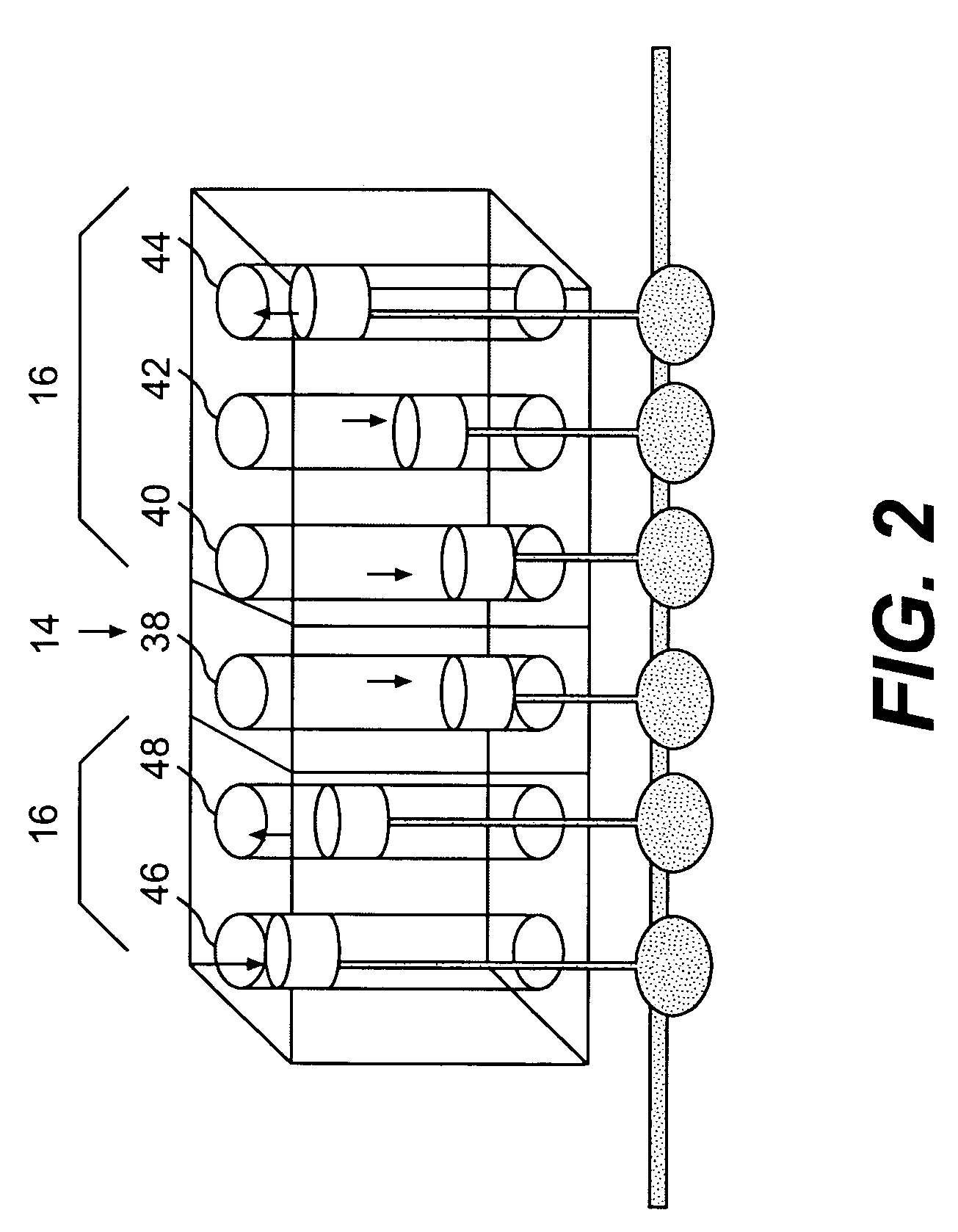
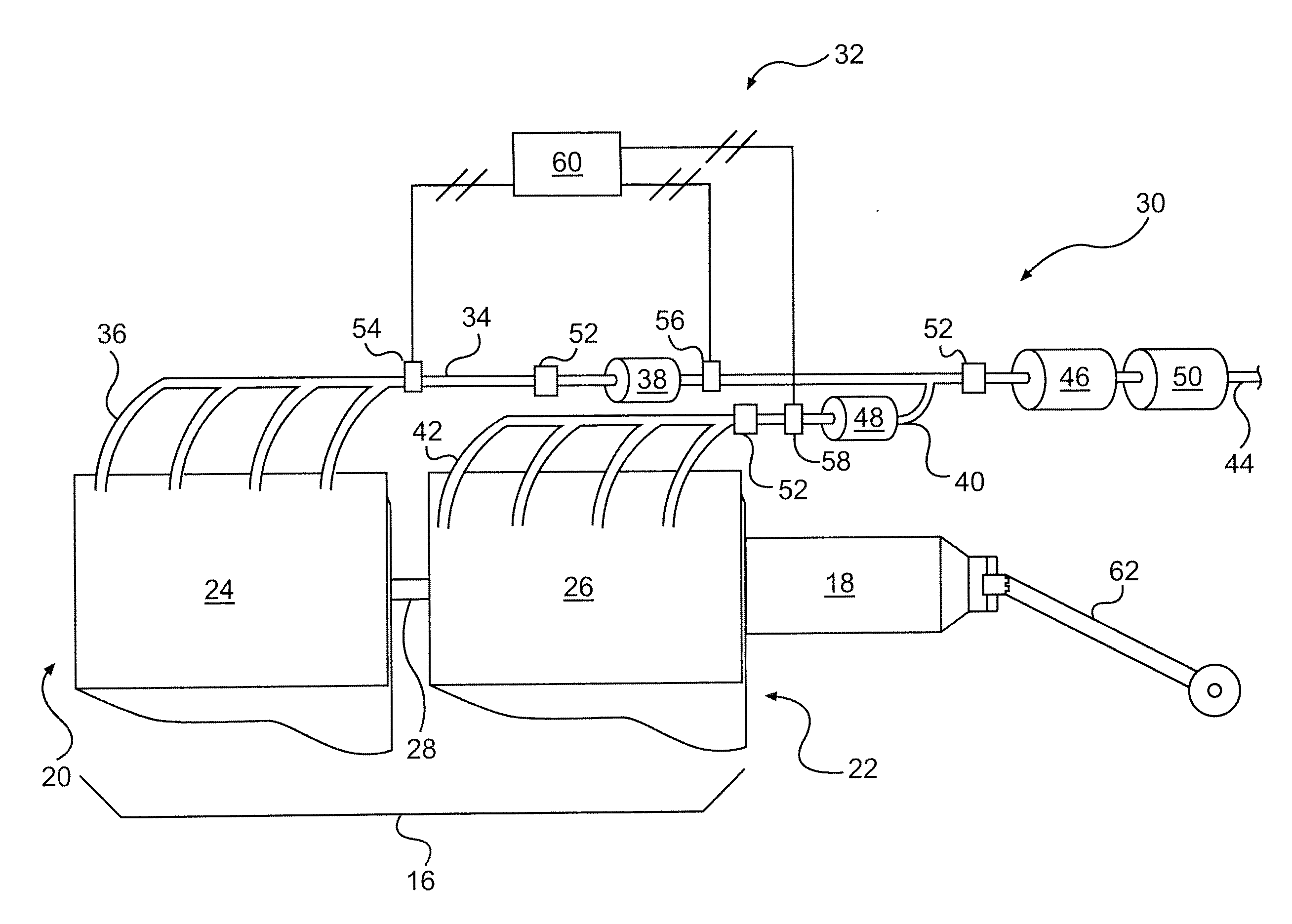
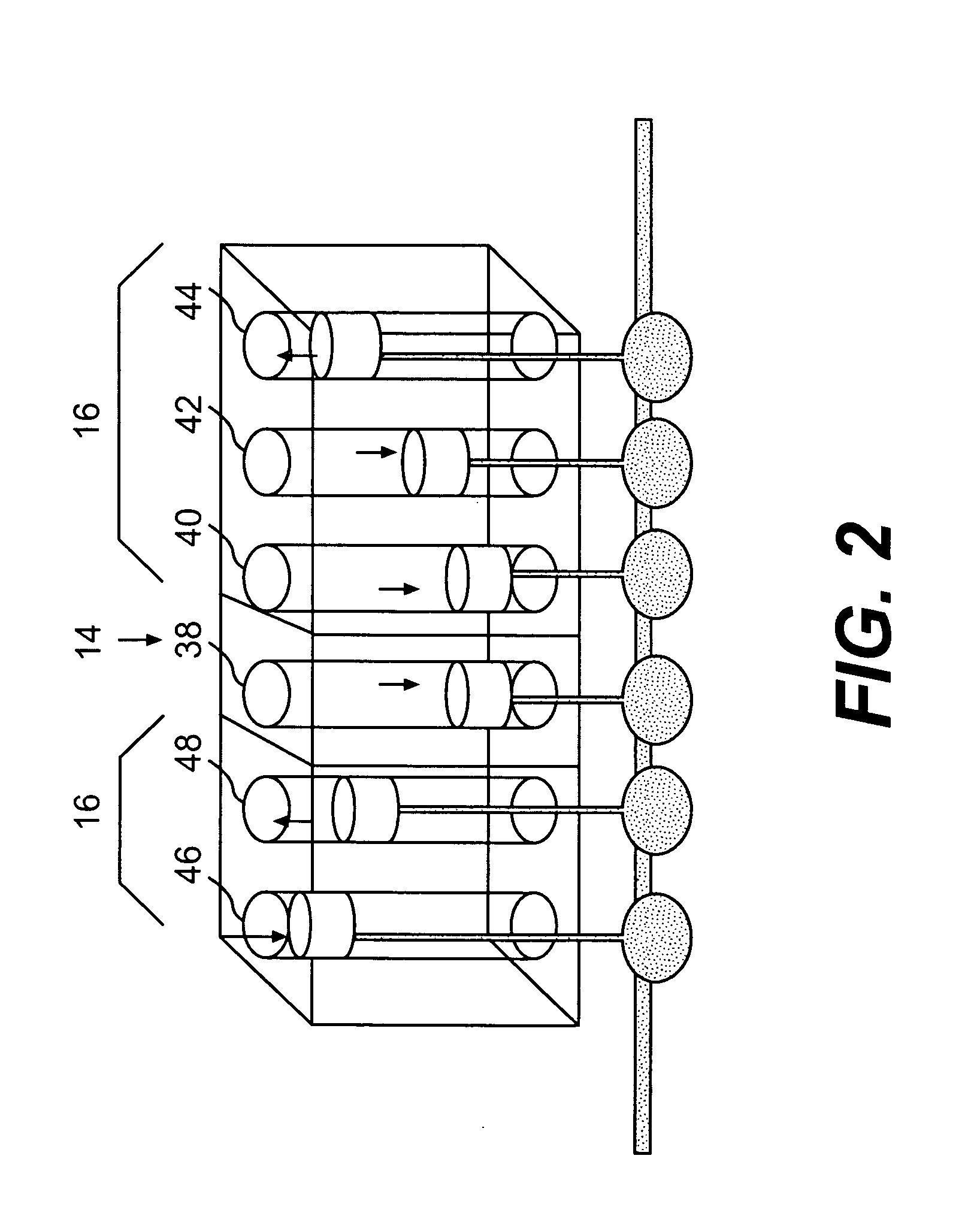
Engine system arrangement with on-board ammonia production and exhaust after treatment system
InactiveUS20070074506A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustion chamberAfter treatment
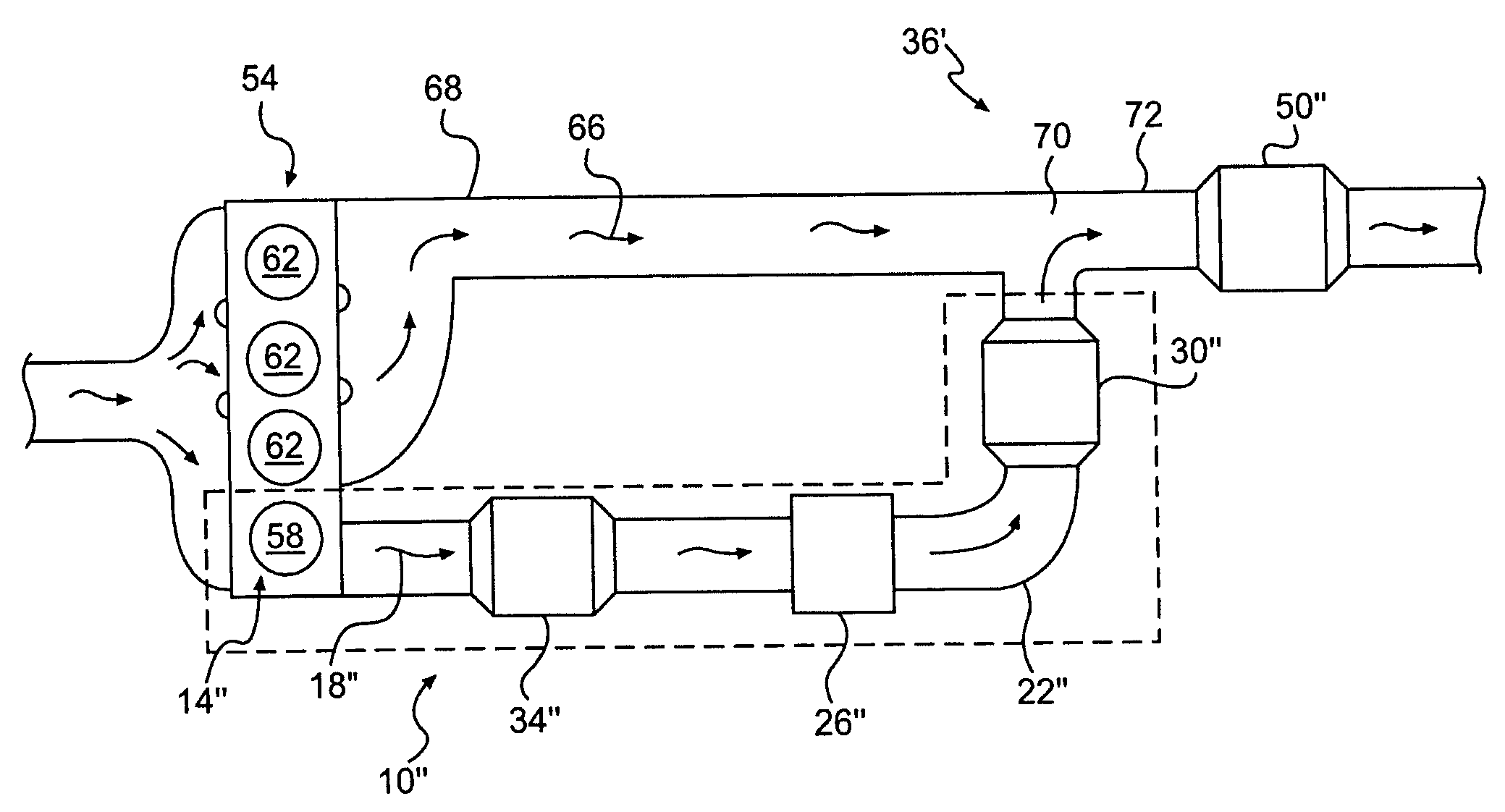
An engine system includes first and second combustion chamber groups that supply exhaust to respective first and second exhaust passages. NOx in the exhaust of the first combustion group is converted to ammonia, such as by enriching the exhaust with fuel and then passing the mixture over an appropriate catalyst. Particles are trapped and continuously oxidized through appropriate placement of one or more particle traps coated with an appropriate oxidizing catalyst. NOx in the second passage from the second combustion group is combined with ammonia produced in the first passage and converted to nitrogen and water in a merged passage before being vented to atmosphere. This conversion is accomplished by passing the merged exhaust over an appropriate selective catalytic reduction catalyst.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
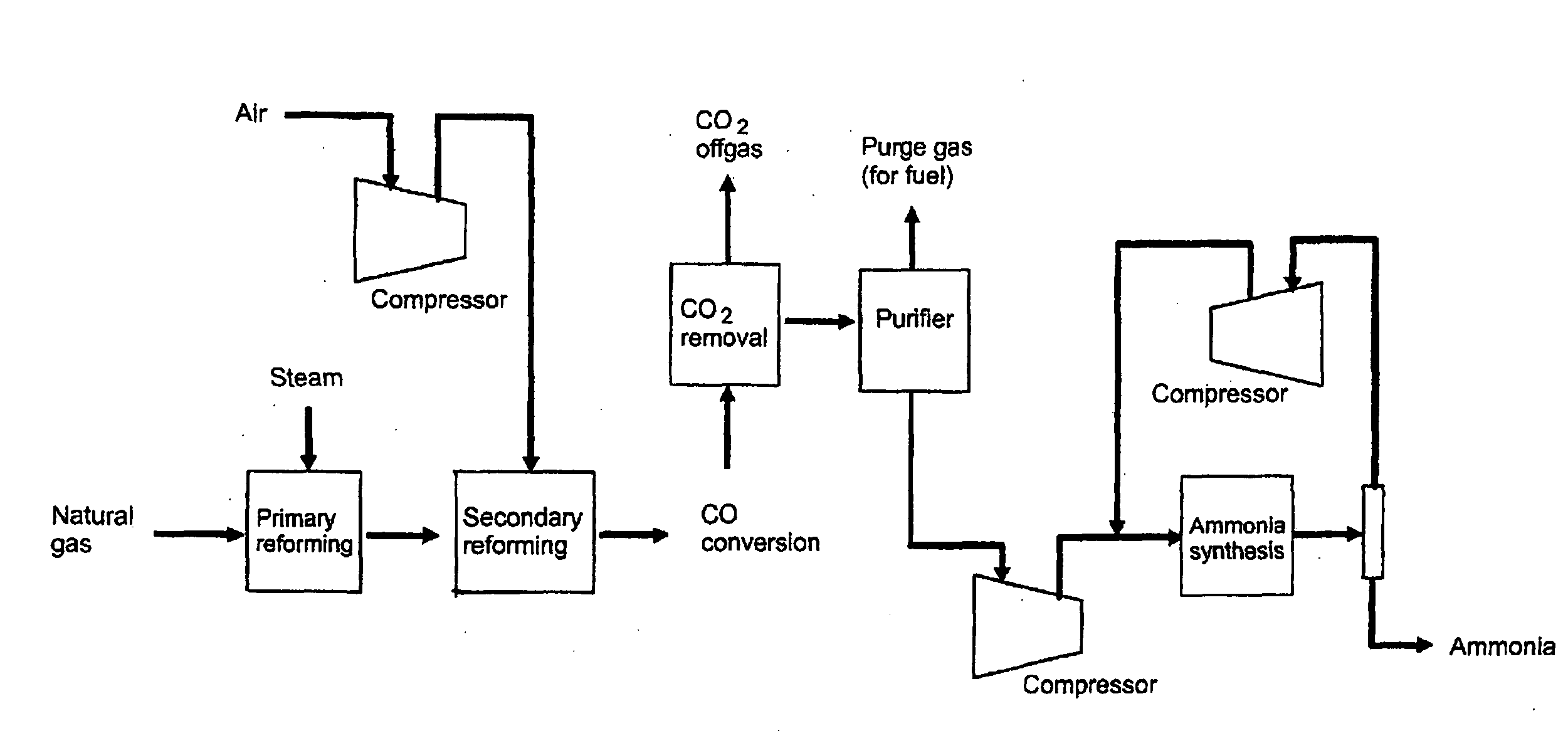
Method for the simultaneous modernization of a plant for ammonia production and a plant for urea production
InactiveUS6340451B1Increase capacityIncrease productionUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCarbamateMethanation
A method for the simultaneous modernization of a plant for ammonia synthesis and a plant for urea synthesis, provides-inter alia-the arrangement of a carbamate synthesis section and a carbamate decomposition section, in order to obtain a predetermined amount of carbamate in aqueous solution and of hydrogen and nitrogen in gaseous phase which are fed to the existing sections for urea synthesis, respectively ammonia synthesis. Thanks to this method of modernization it is possible to remarkably increase the production capacity and at the same time to reduce the energy consumption of the urea and ammonia plants without being forced to replace or anyway overload the existing sections of decarbonation, methanation and compression, in general.
Owner:UREA CASALE SA
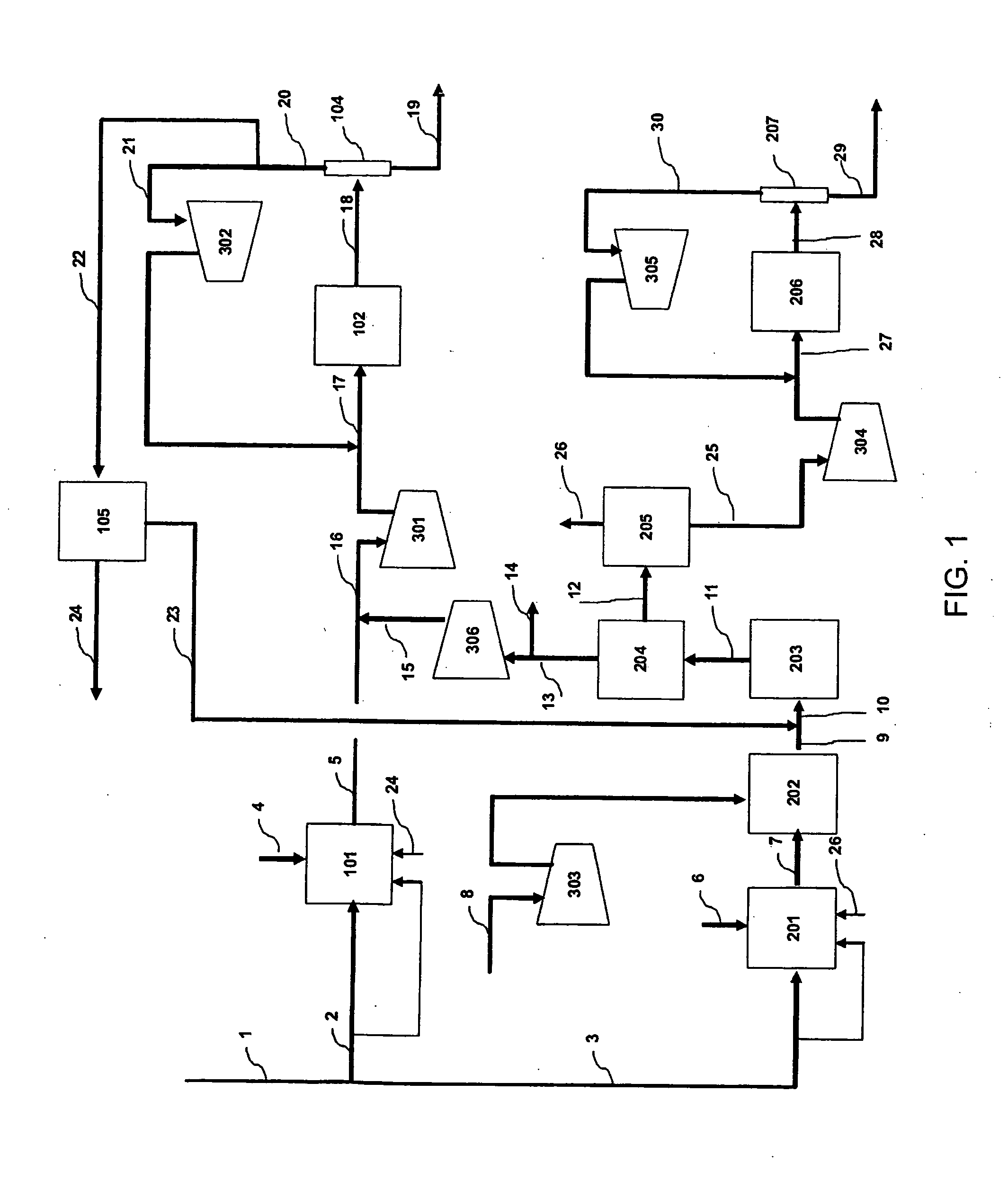
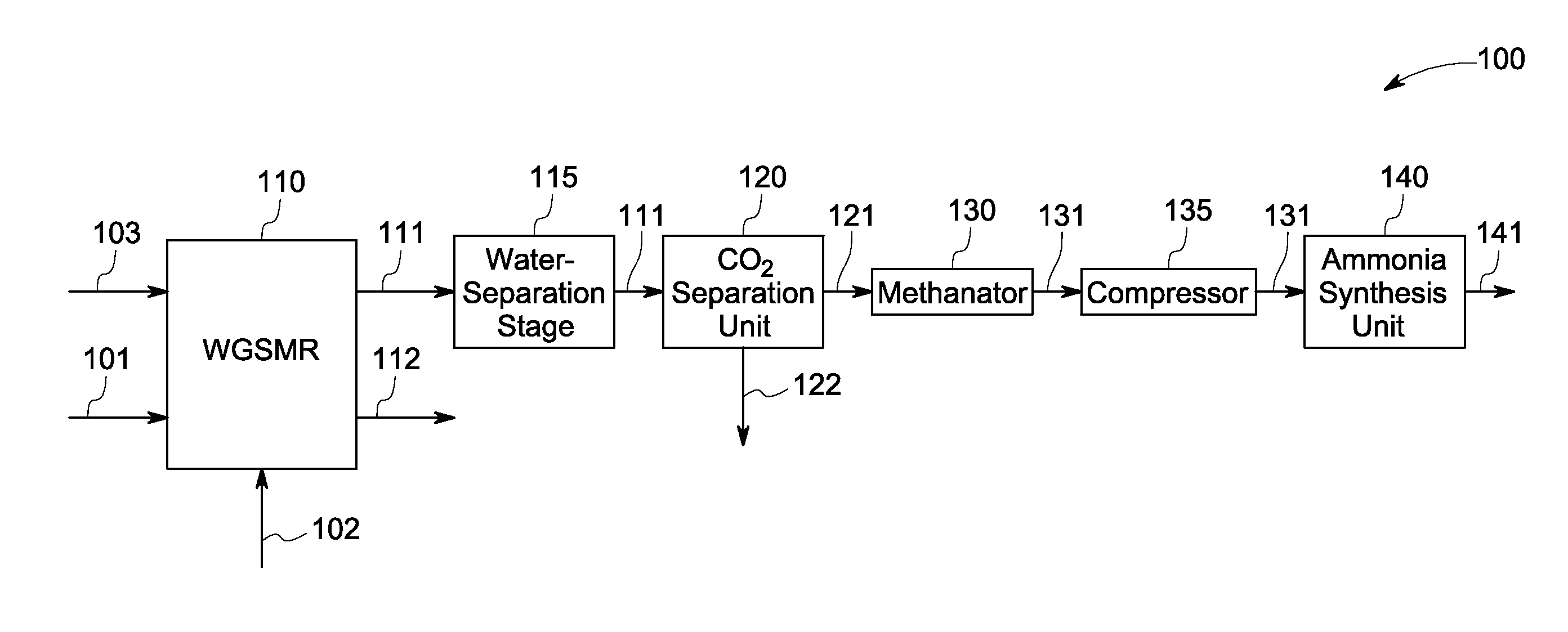
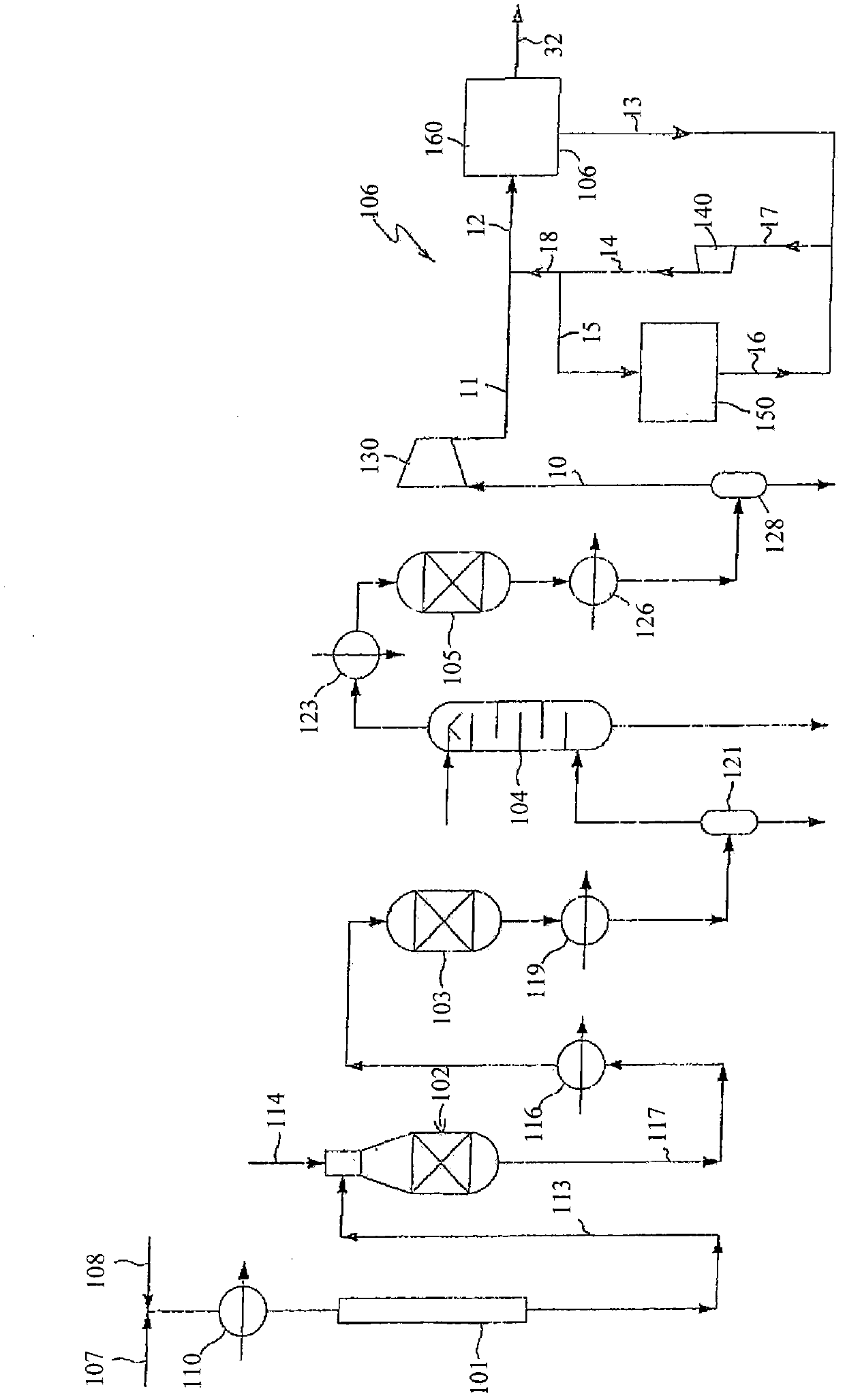
Methods and systems for ammonia production
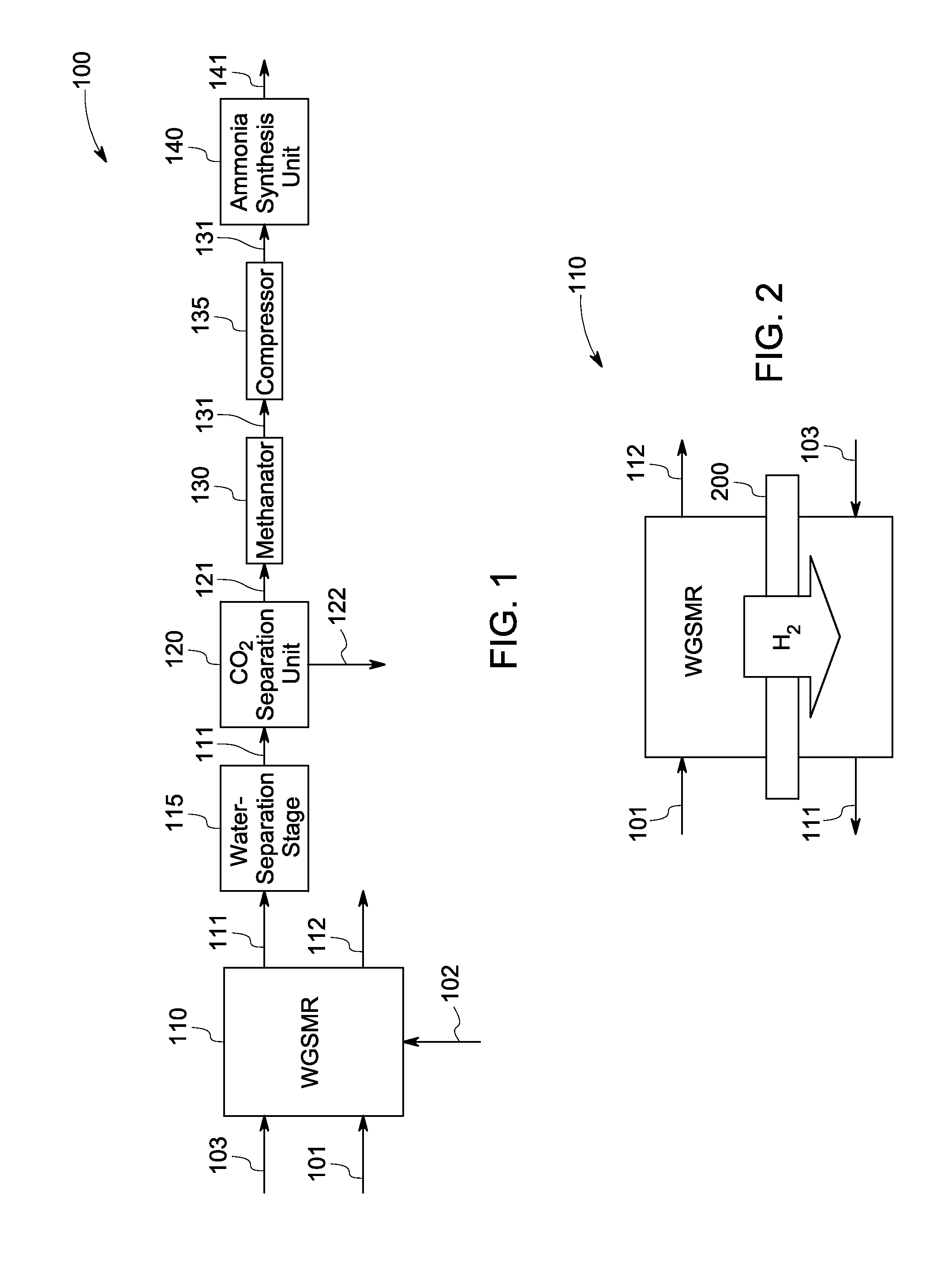
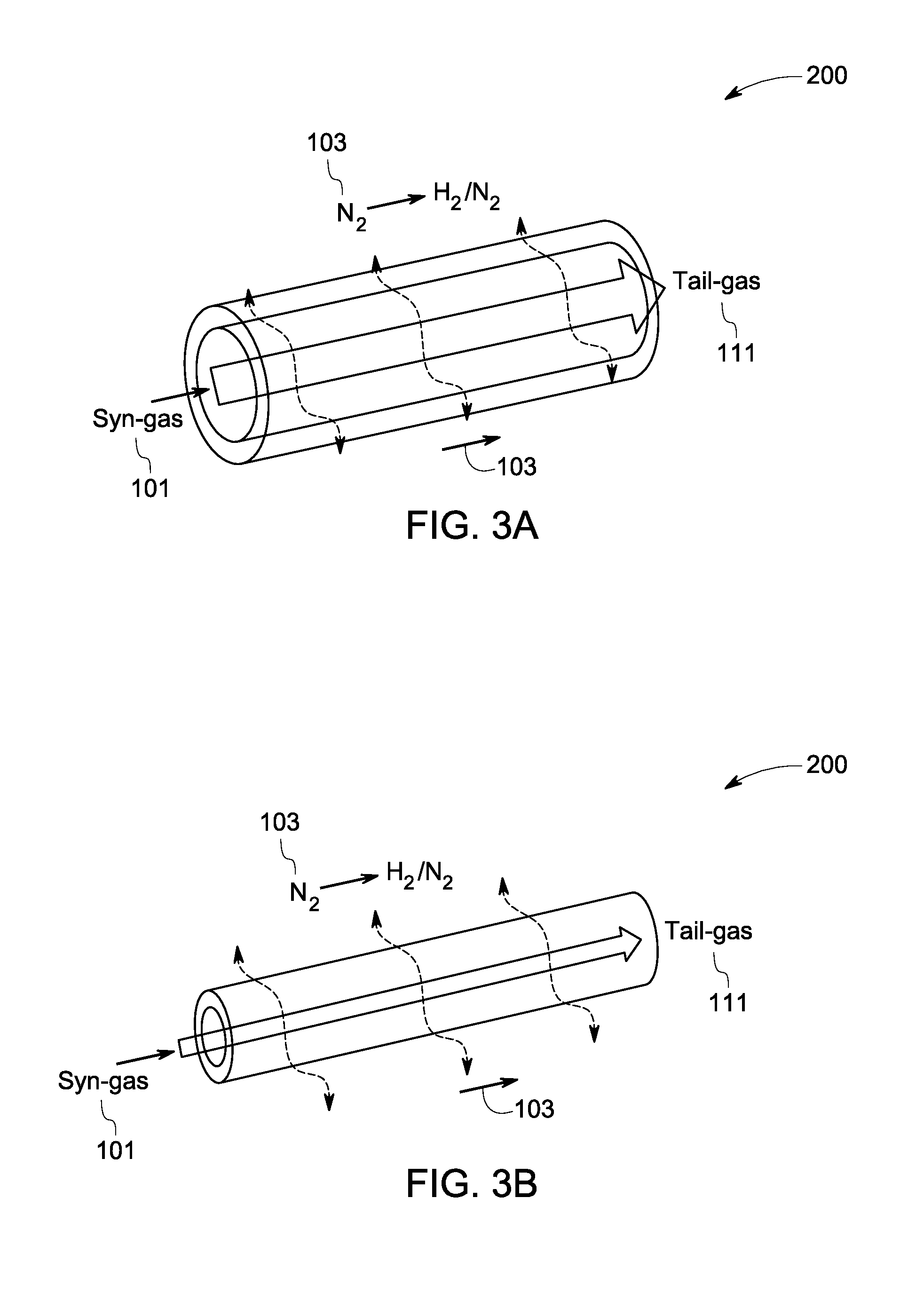
InactiveUS20140120023A1HydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAmmonia productionWater-gas shift reaction
A method for ammonia synthesis using a water-gas shift membrane reactor (WGSMR) is presented. The method includes carrying out a water-gas shift reaction in the WGSMR to form a first product stream and a carbon dioxide (CO2) stream, wherein the first product stream includes nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2), and a molar ratio of H2 to N2 in the first product stream is about 3. The method further includes separating at least a portion of the residual CO2 in the first product stream in a CO2 separation unit to form a second product stream, and separating at least a portion of the residual CO2 and carbon monoxide (CO) in the second product stream in a methanator unit to form a third product stream. The method further includes generating an ammonia stream from the third product stream in an ammonia synthesis unit. A system for ammonia synthesis is also presented.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Integrated process for the manufacture of olefins and intermediates for the productions of ammonia and urea
ActiveUS20110250119A1Improve energy efficiencyReduce carbon dioxide emissionsUrea derivatives preparationCatalytic crackingSteam reformingAmmonia production
An integrated process for the manufacture of olefins and intermediates for the production of ammonia and urea, comprising an FCC reactor, a regenerator, a steam reforming unit, an air-separation unit, an ammonia production unit and a urea production unit, is described. This process makes it possible to minimize CO2 emissions to atmosphere, make use of heavy feedstocks of low added value (AR) for the production of light olefins, in addition to making maximum use of all the flows involved, thus increasing the energy efficiency achieved, all at the same time.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Method of coproducing methanol and ammonia
ActiveUS8247463B2Efficiently coproduceIncreasing and decreasing specific raw material consumptionCyanogen compoundsHydroxy compound preparationNaphthaAmmonia production
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP
Ammonia production process
InactiveCN102596808AHigh hydrogen contentImprove conversion efficiencyEnergy inputBulk chemical productionSyngasMolecular sieve
Owner:AMMONIA CASALE SA
Method for synthesizing ammonia
InactiveCN111217380ALess investmentSuitable for regional productionEnergy inputAmmonia preparation/separationAmmonia productionEnvironmental engineering
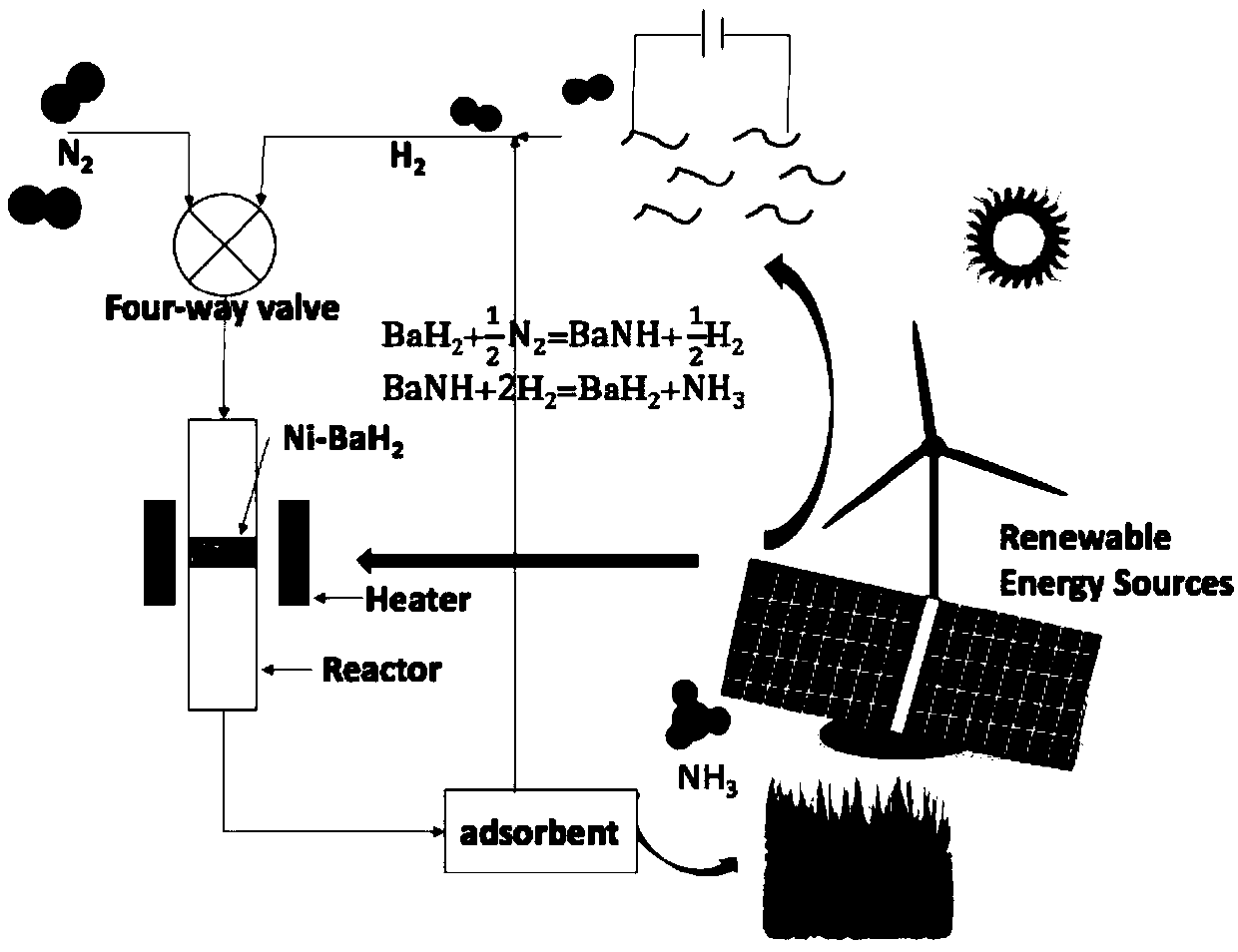
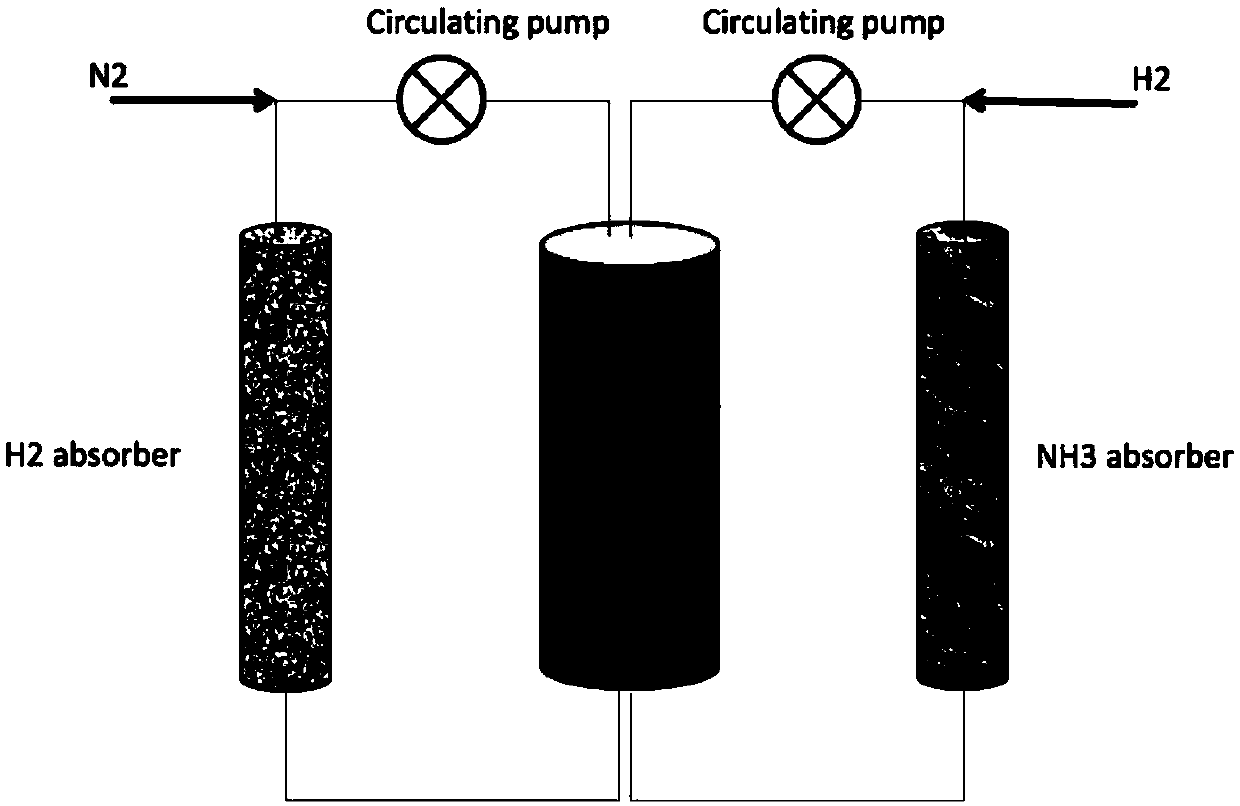
The invention relates to a process for synthesizing ammonia by utilizing renewable energy or nuclear energy under mild conditions. The process is characterized in that clean energy such as solar energy, wind energy, nuclear energy and the like is utilized to produce hydrogen and nitrogen, ammonia is produced through a chemical looping technology, and then an ammonia adsorbent is utilized to absorbammonia. According to the process, renewable energy sources are utilized, CO2 is not generated in the whole process, high pressure is not needed, and the process is an environment-friendly syntheticammonia process. The process is suitable for small-scale regional ammonia production, and the produced ammonia can be used as nearby farmland fertilizers or energy storage media.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com