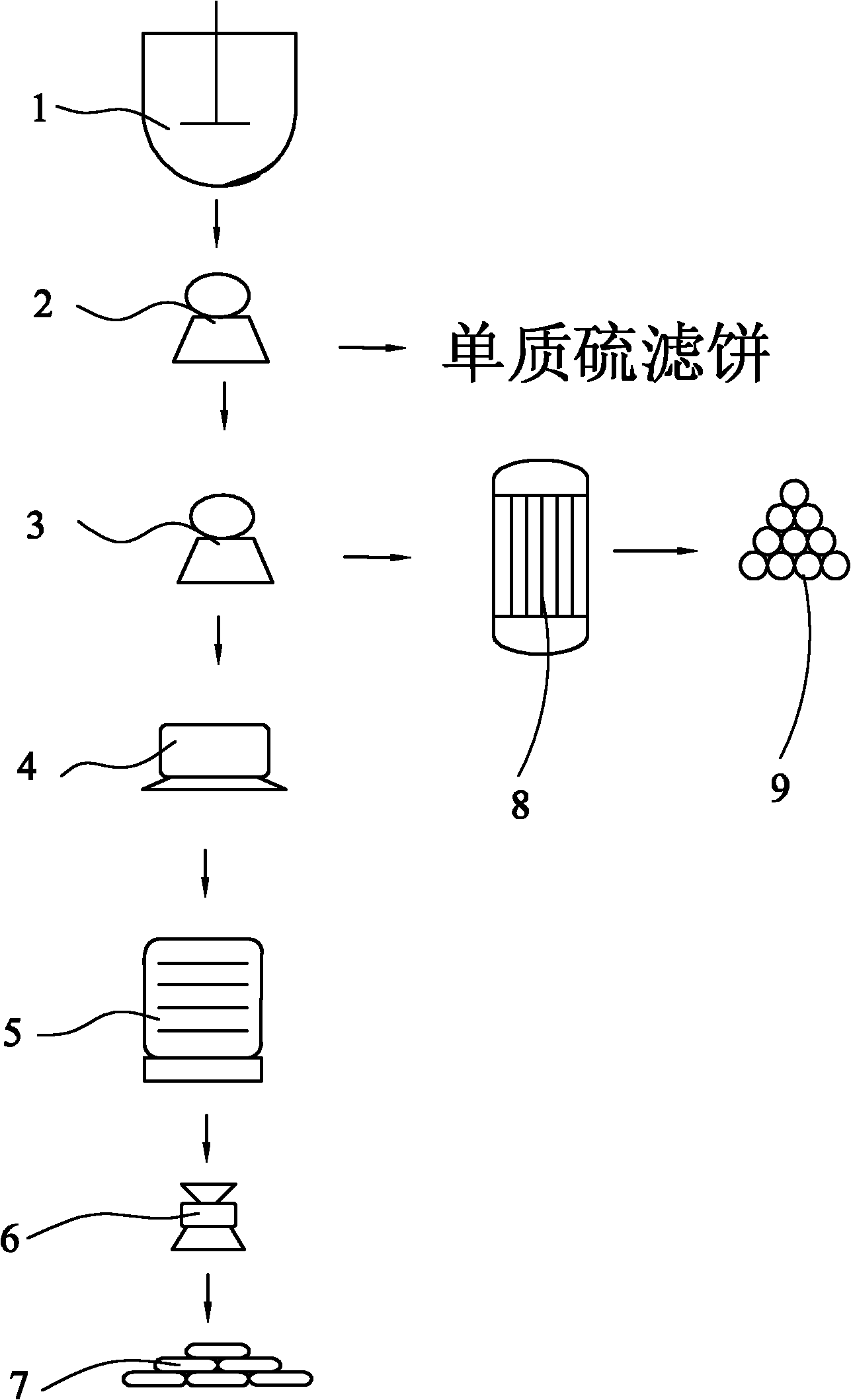
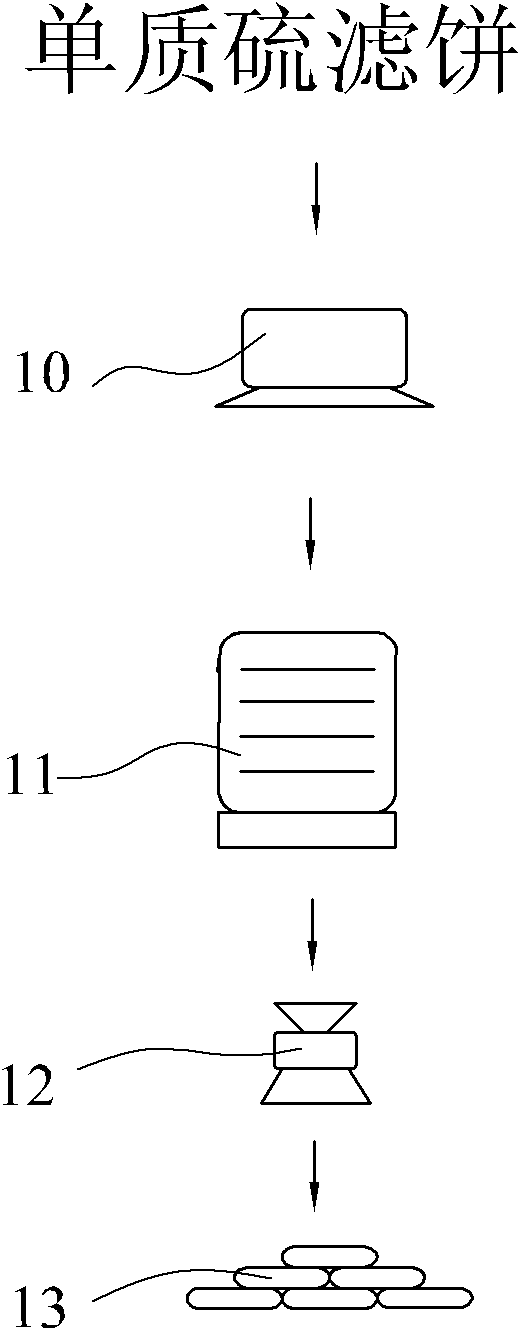
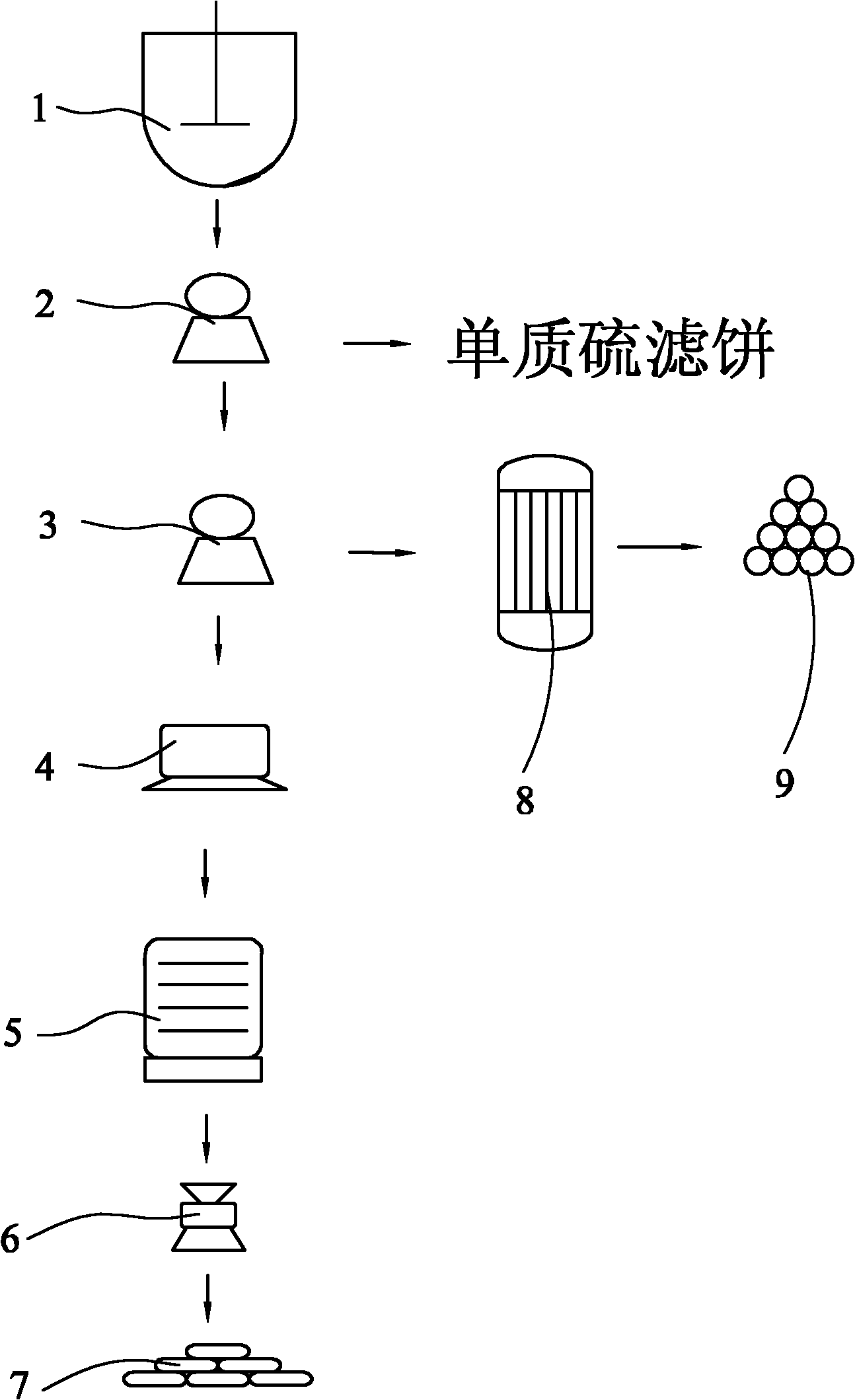
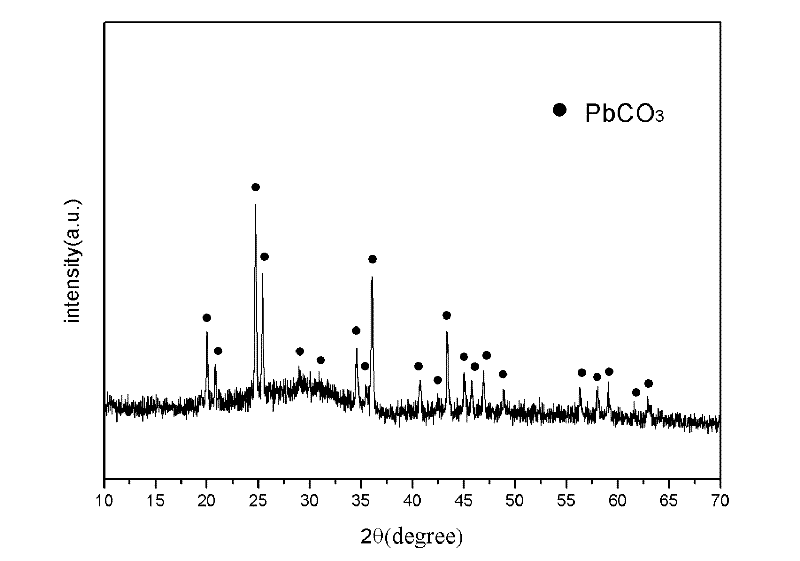
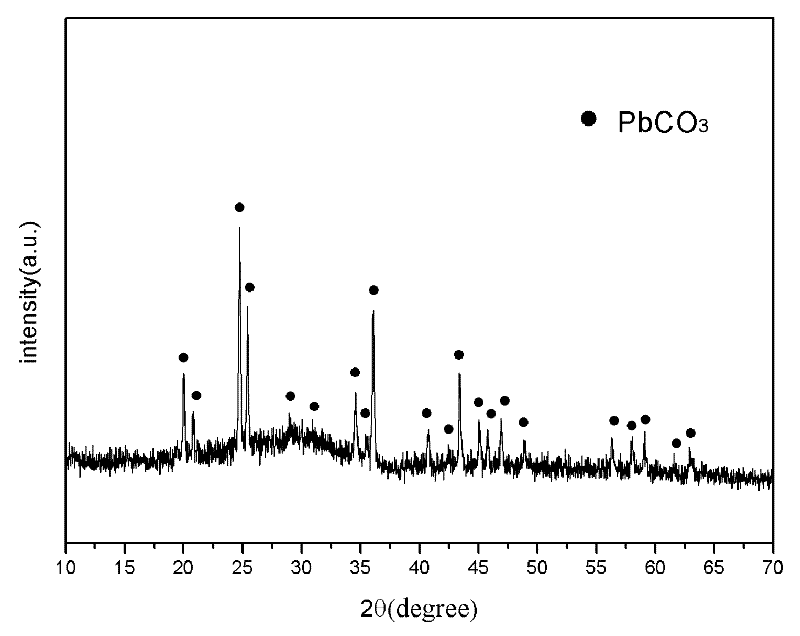
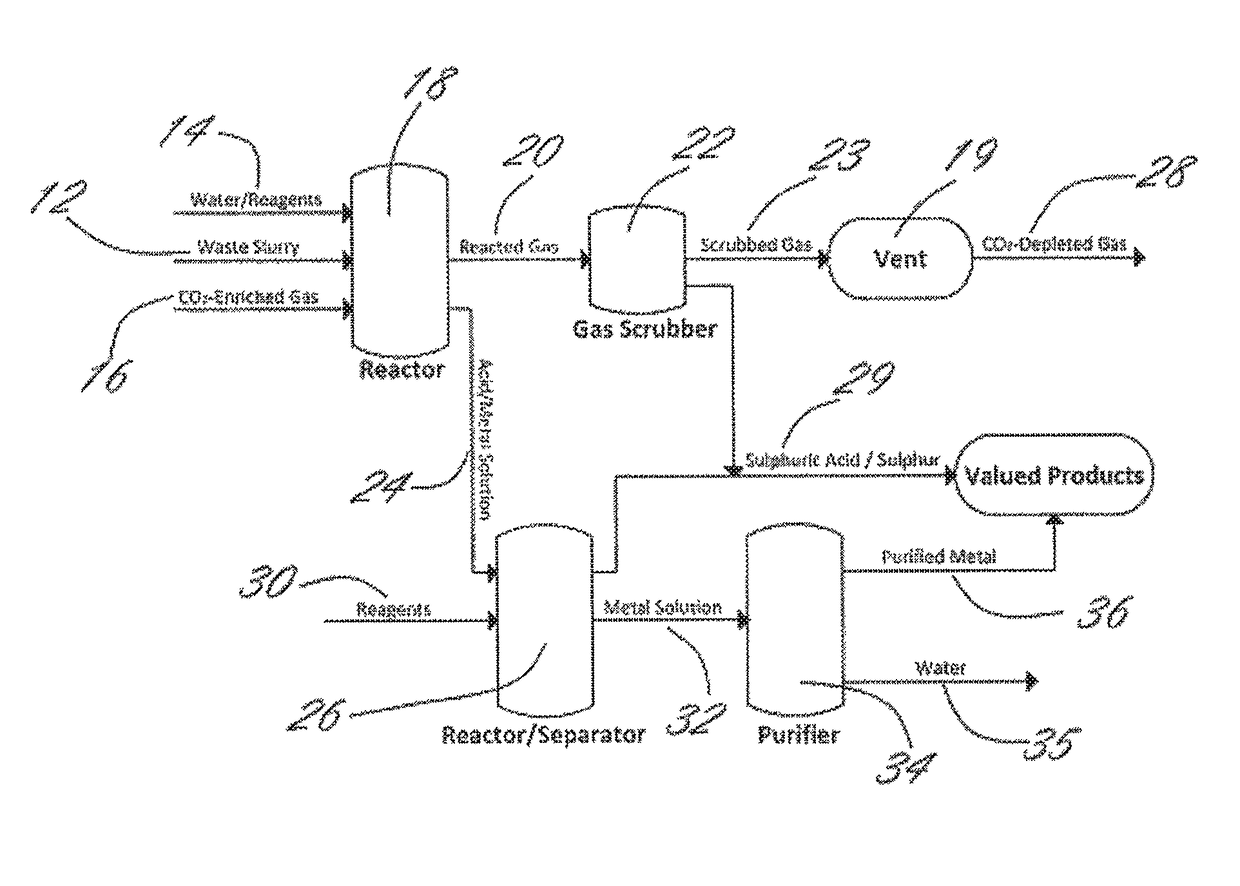
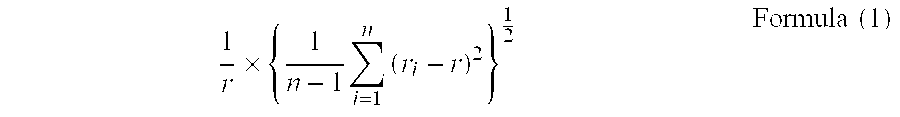Patents
Literature
50results about "Lead carbonates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
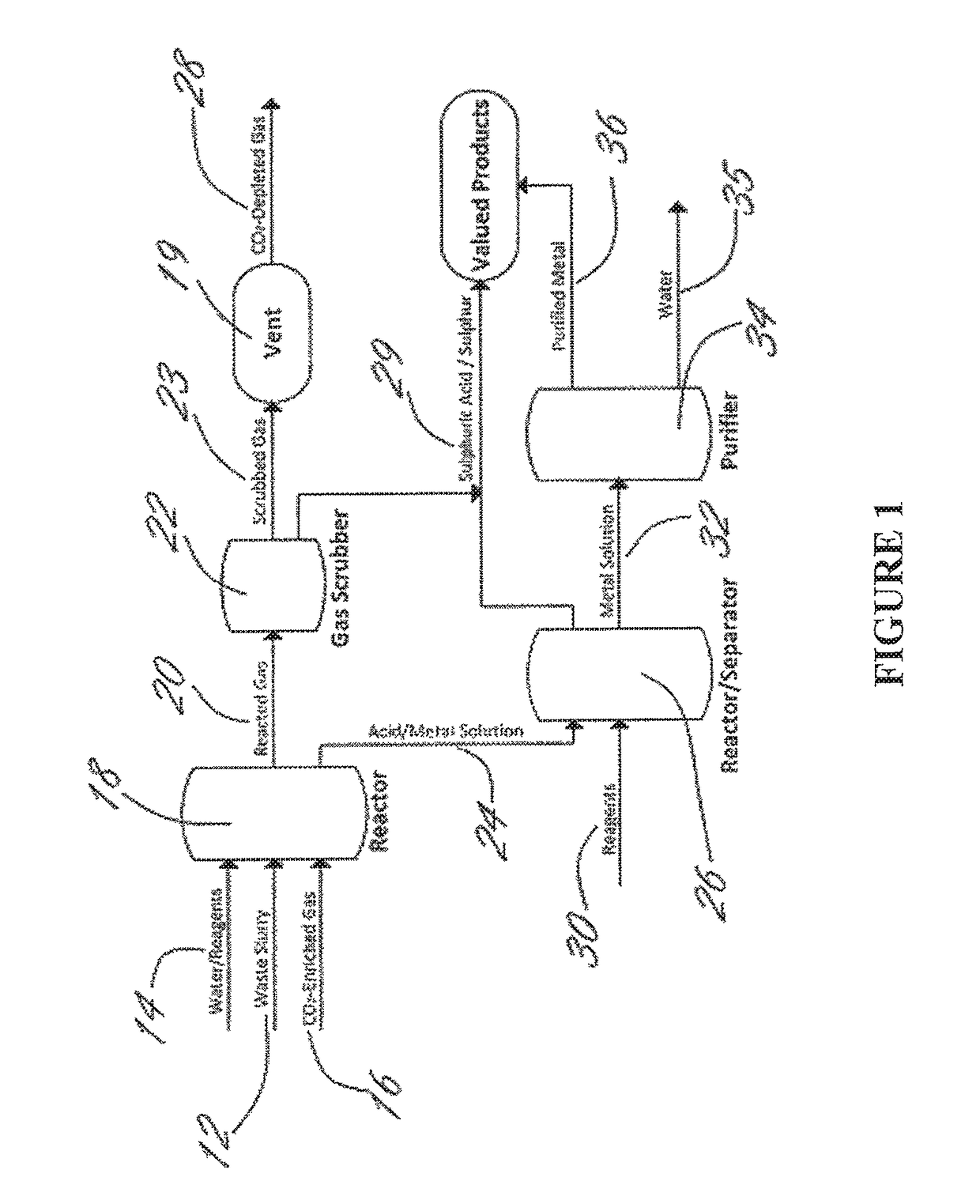
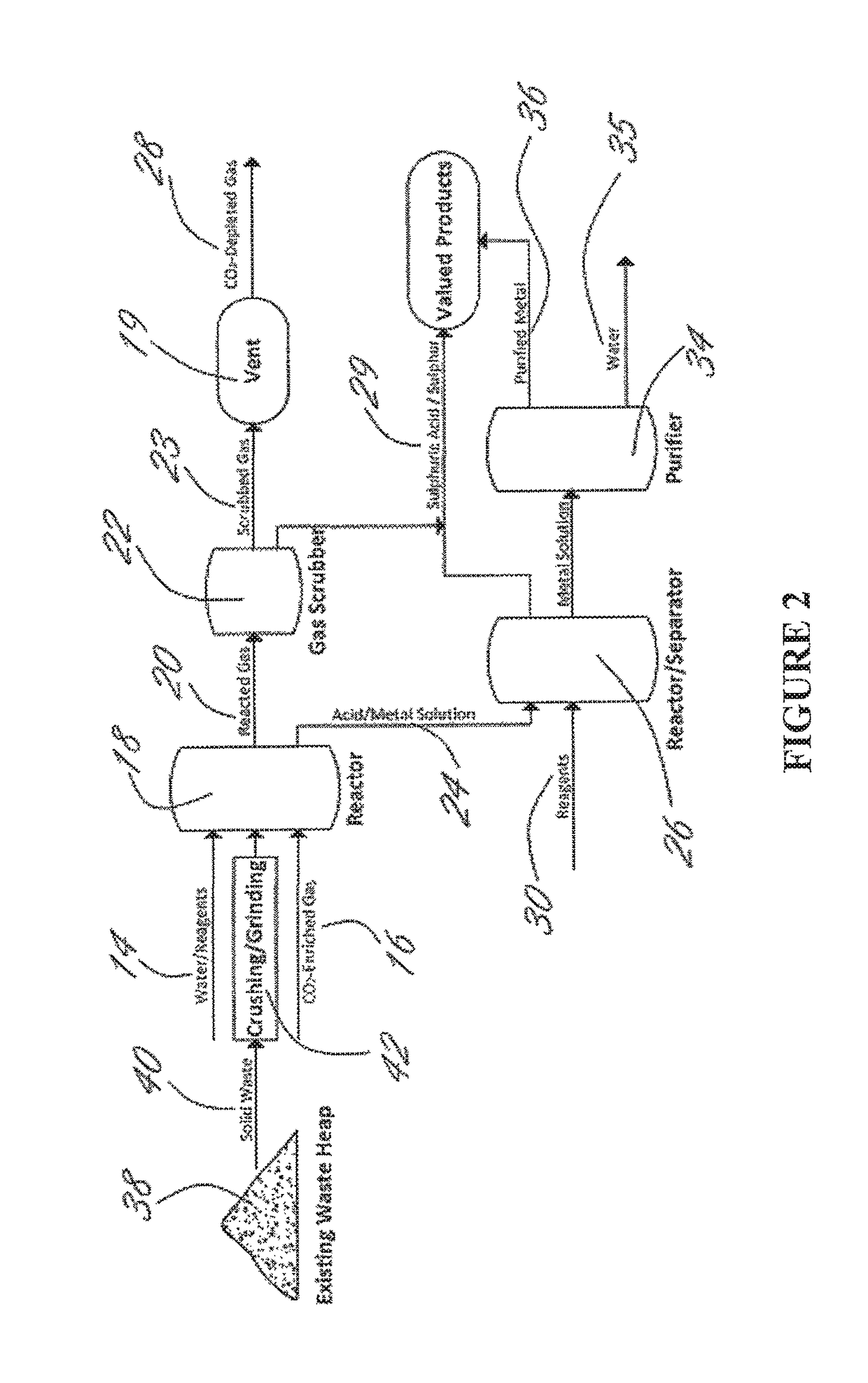
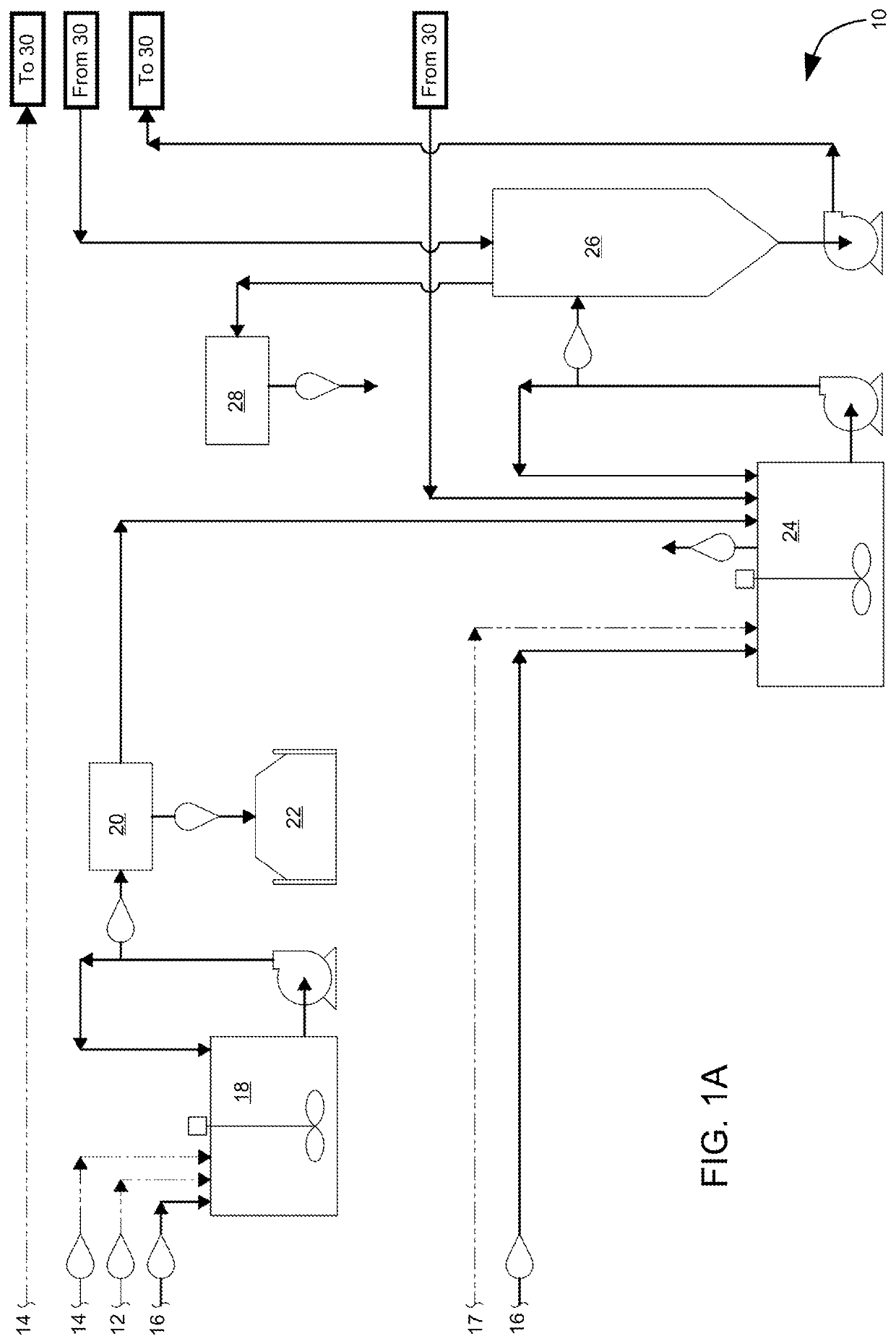
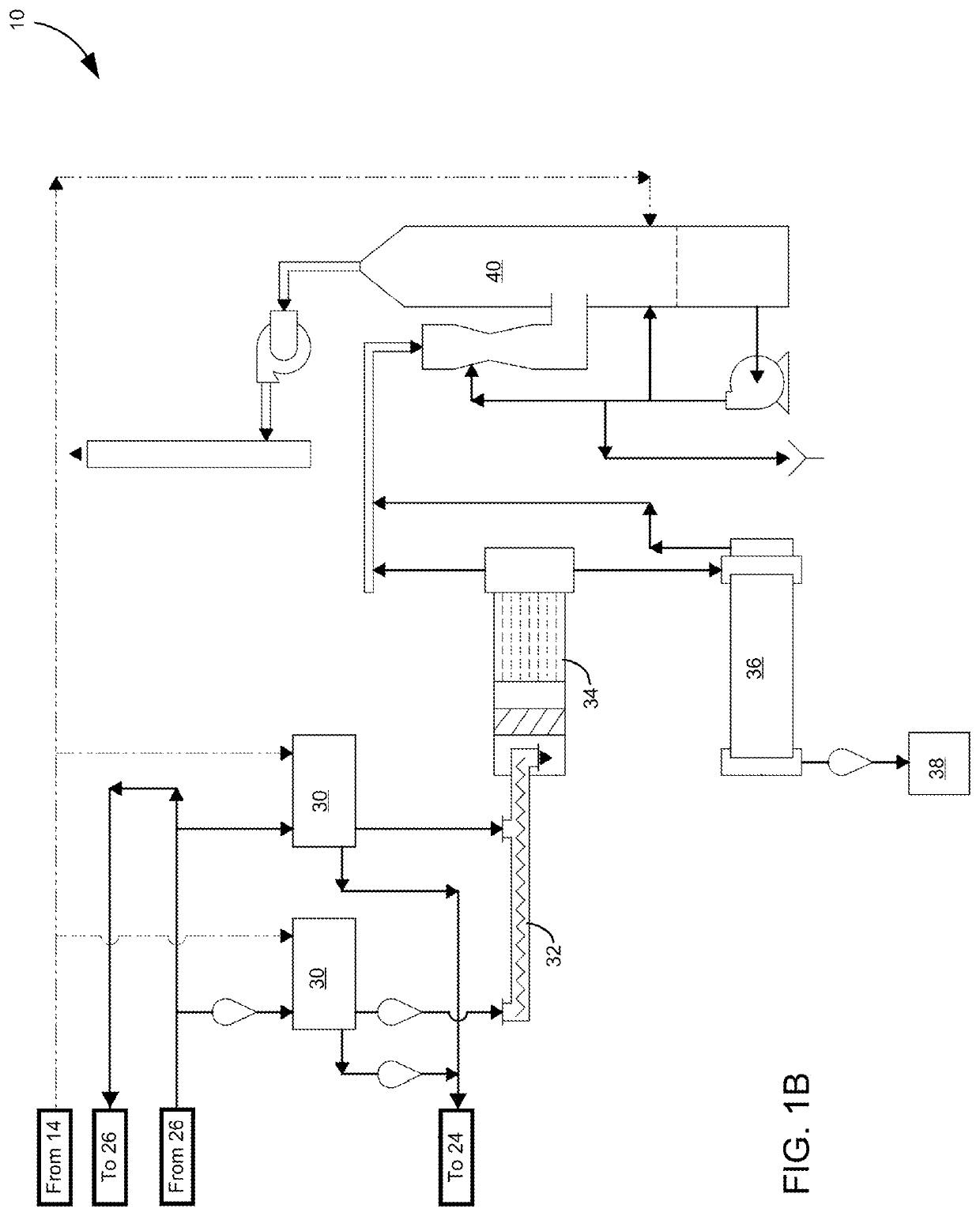
Method for extracting and sequestering carbon dioxide
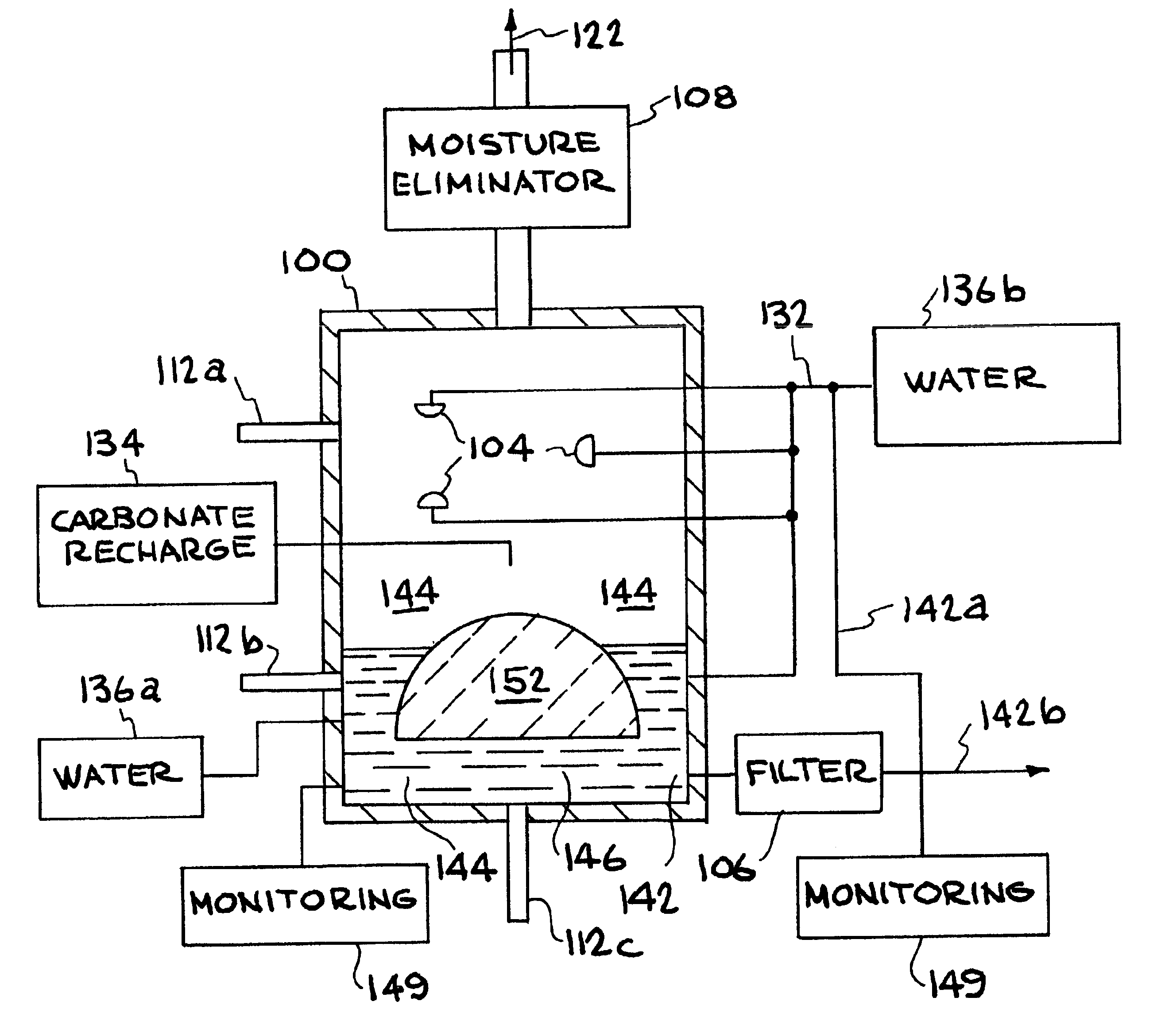
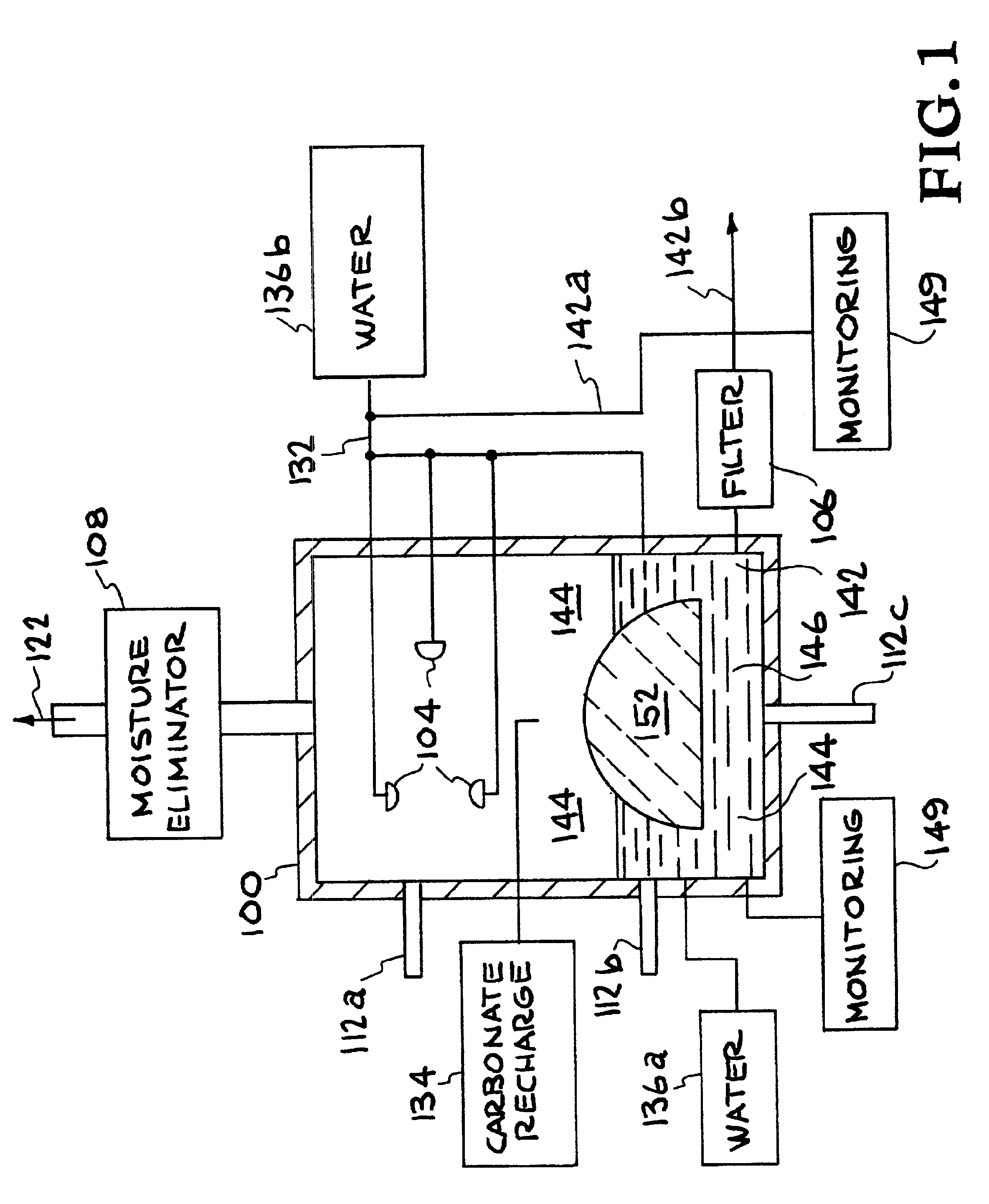
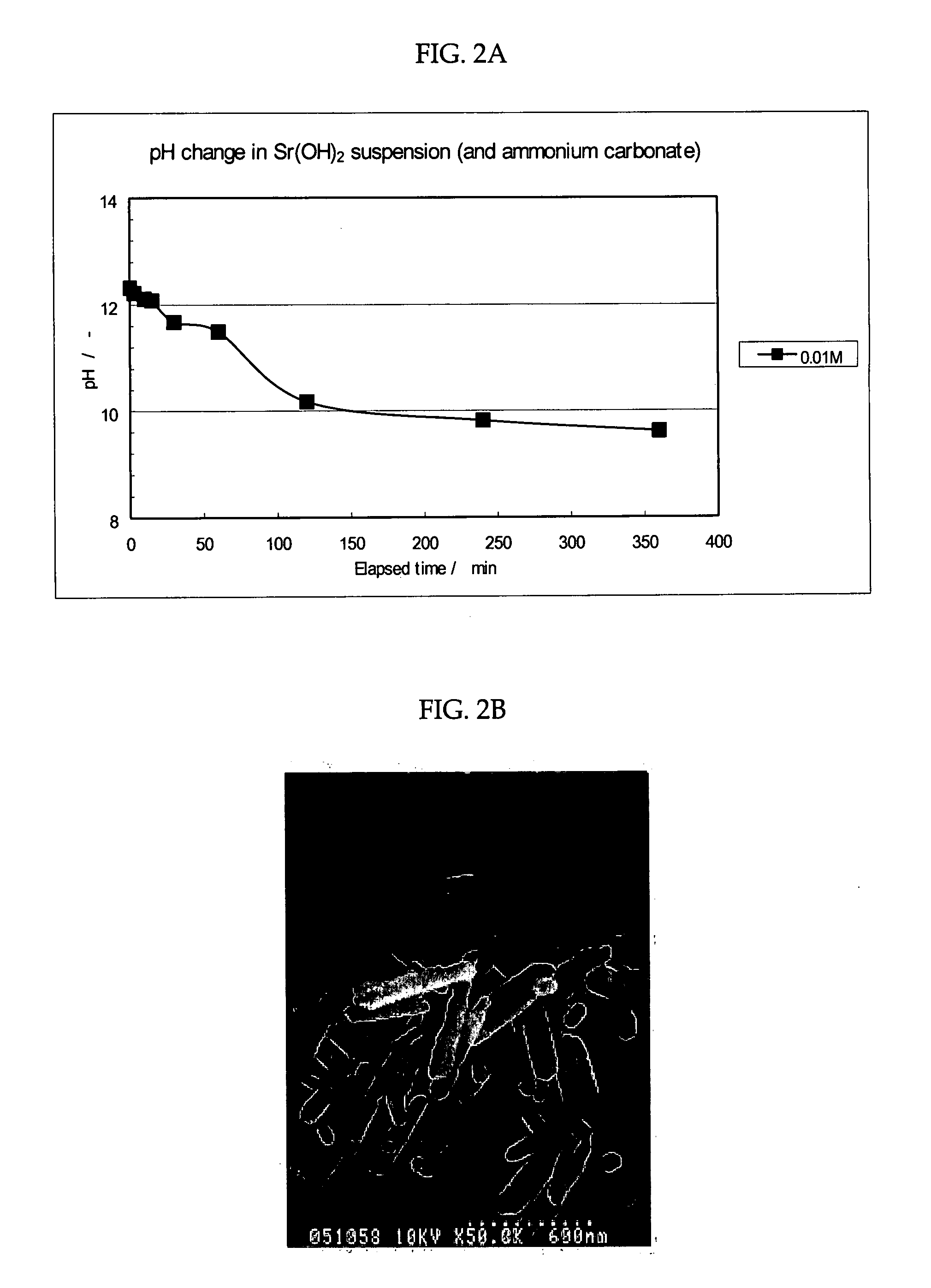
InactiveUS6890497B2Reduce CO burdenWithout significant expenditureCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCombination devicesDicarbonateAlkaline earth metal
A method and apparatus to extract and sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) from a stream or volume of gas wherein said method and apparatus hydrates CO2, and reacts the resulting carbonic acid with carbonate. Suitable carbonates include, but are not limited to, carbonates of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, preferably carbonates of calcium and magnesium. Waste products are metal cations and bicarbonate in solution or dehydrated metal salts, which when disposed of in a large body of water provide an effective way of sequestering CO2 from a gaseous environment.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
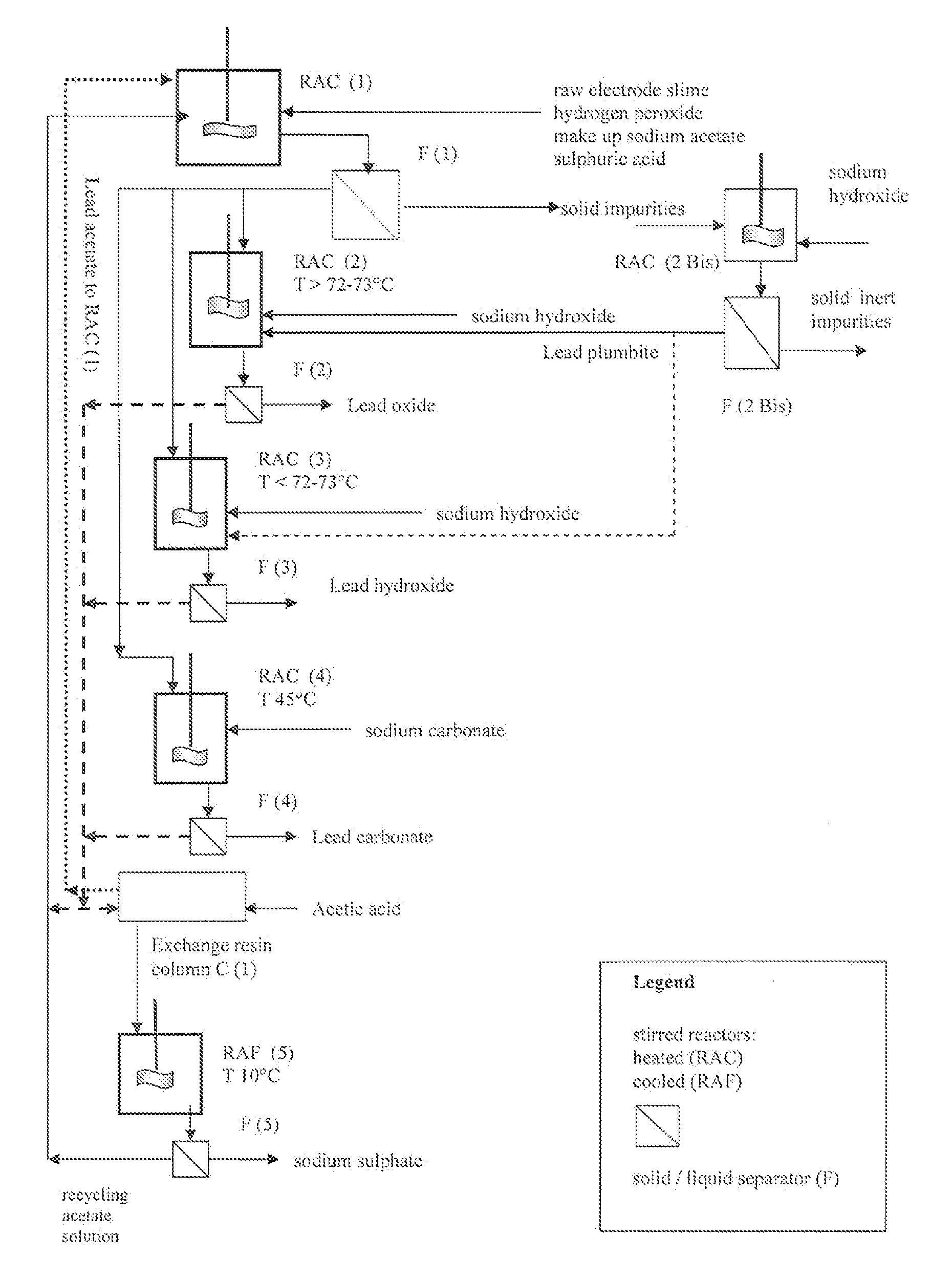
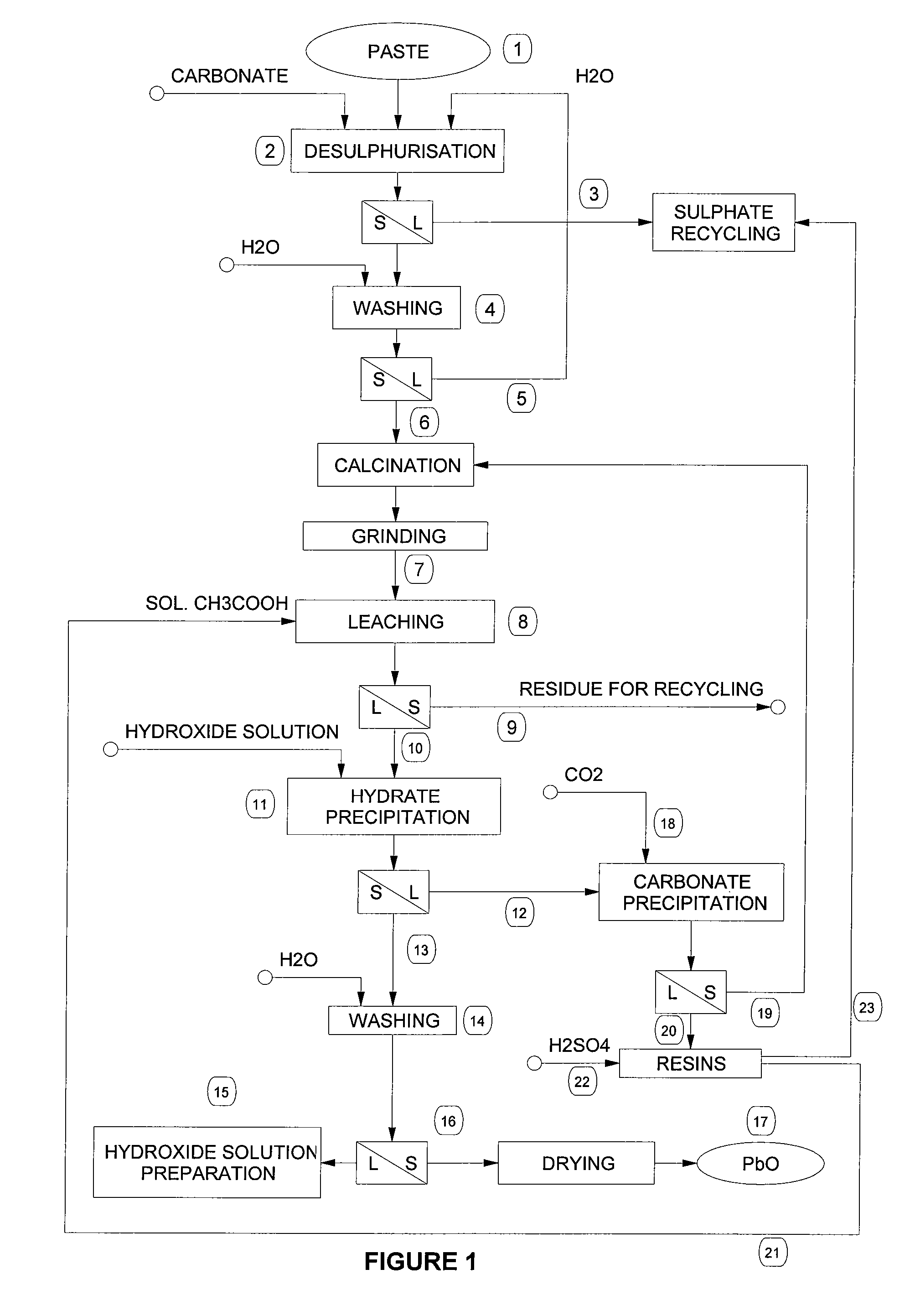
Reclaiming of lead in form of high purity lead compound from recovered electrode paste slime of dismissed lead batteries and/or of lead minerals
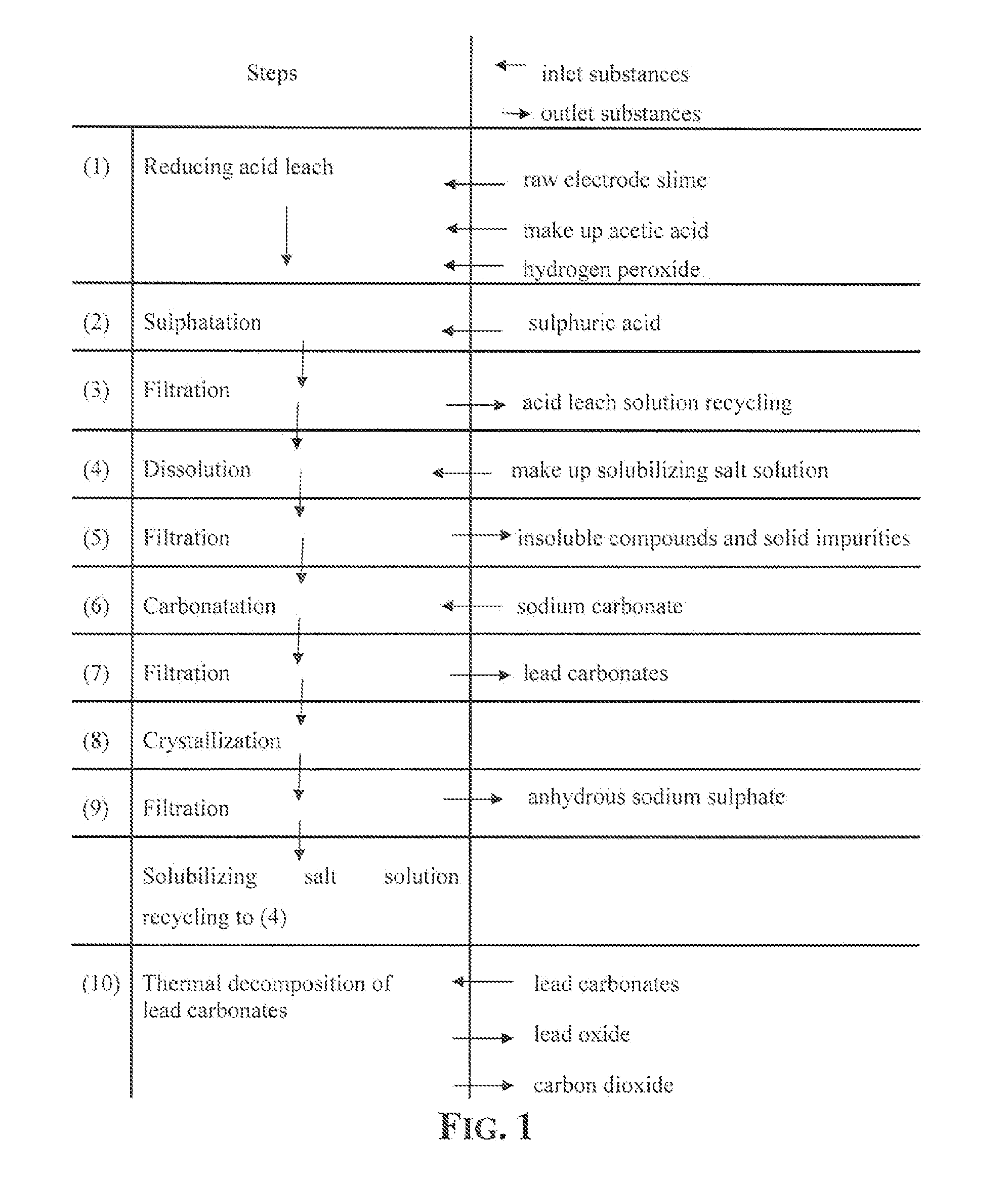
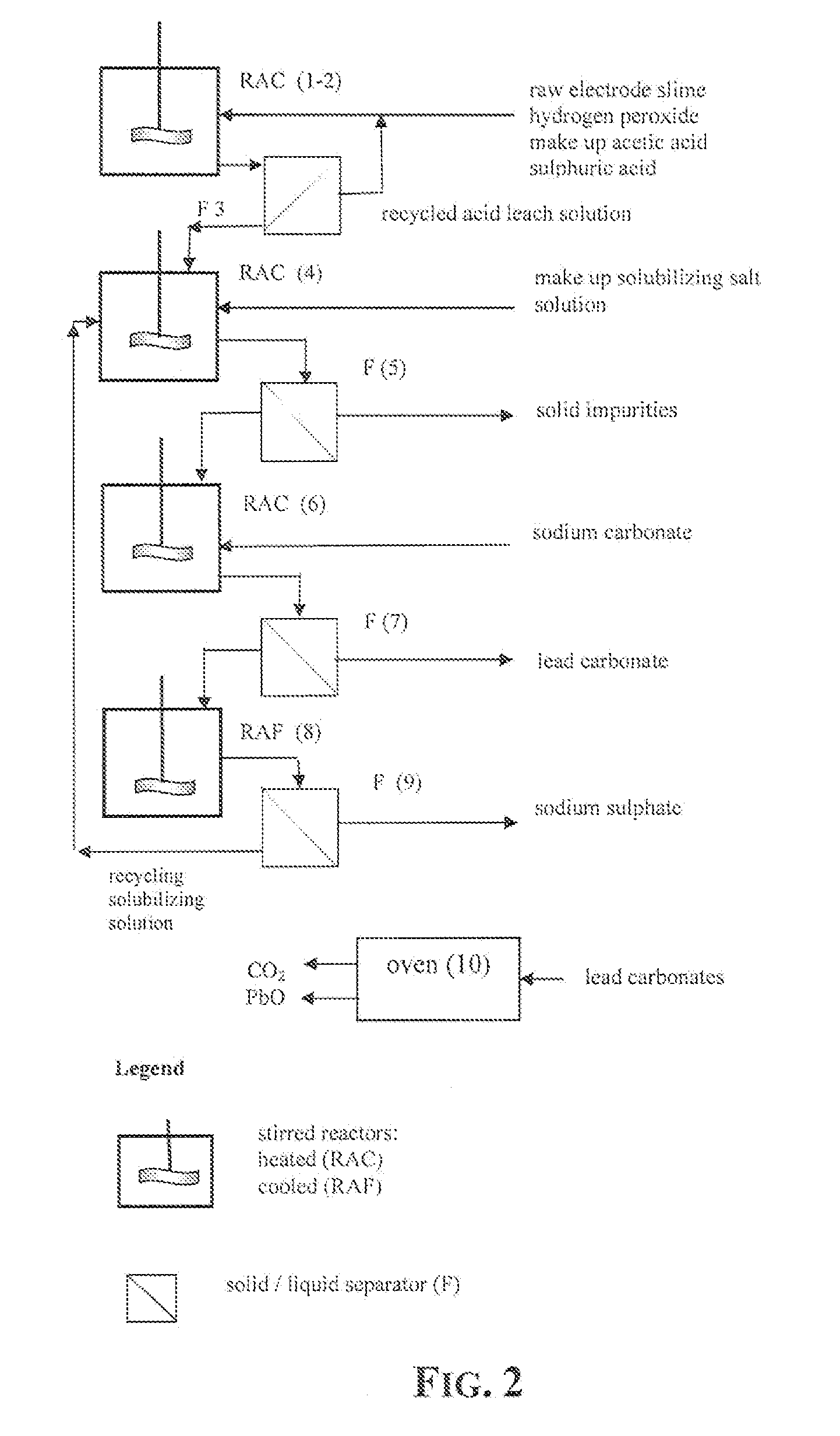
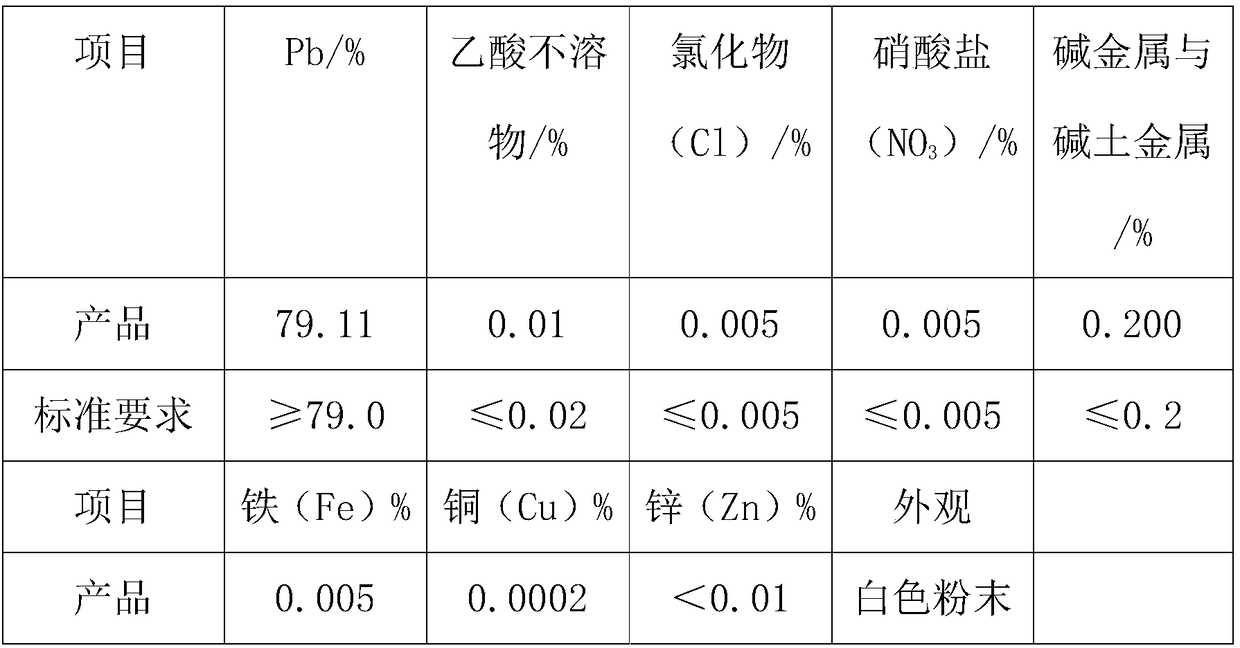
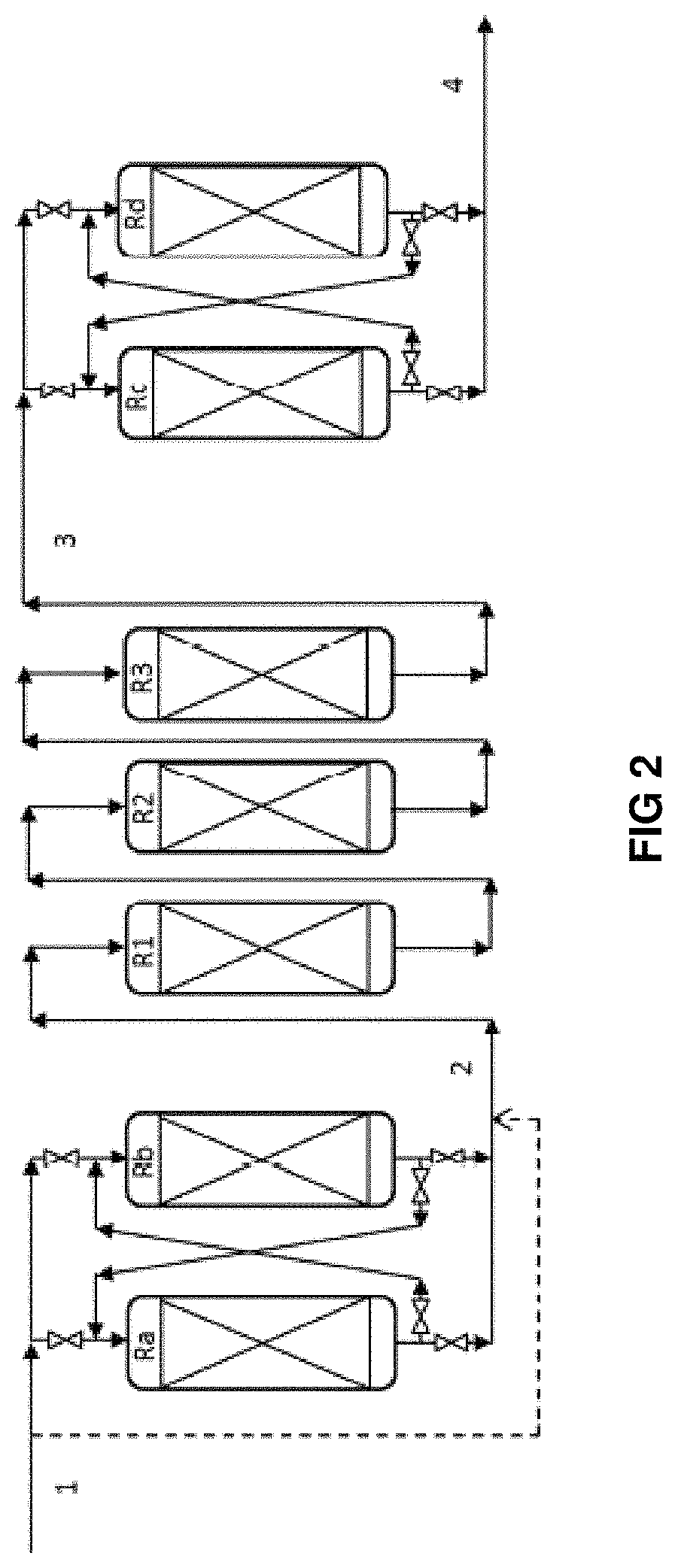
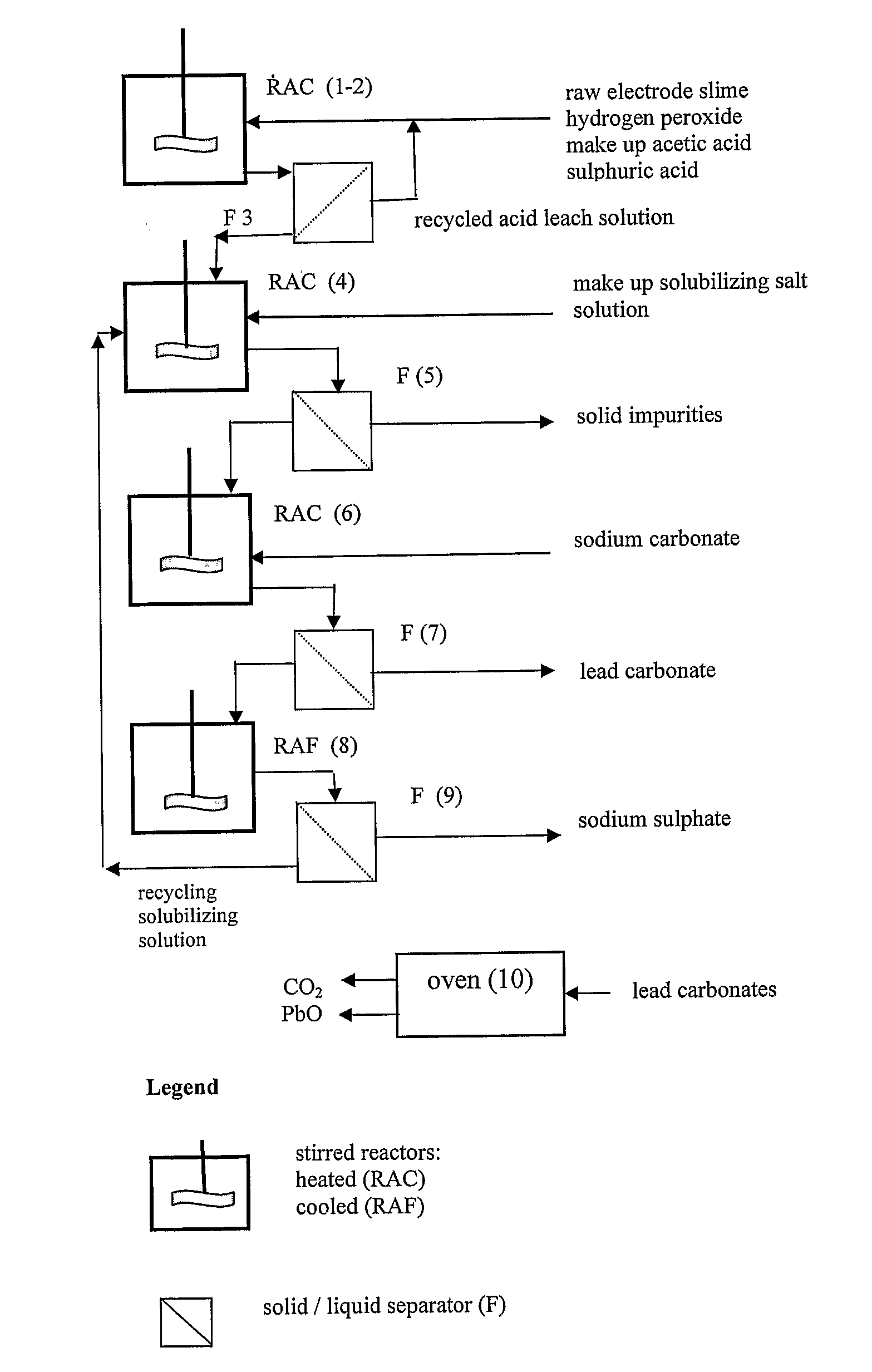
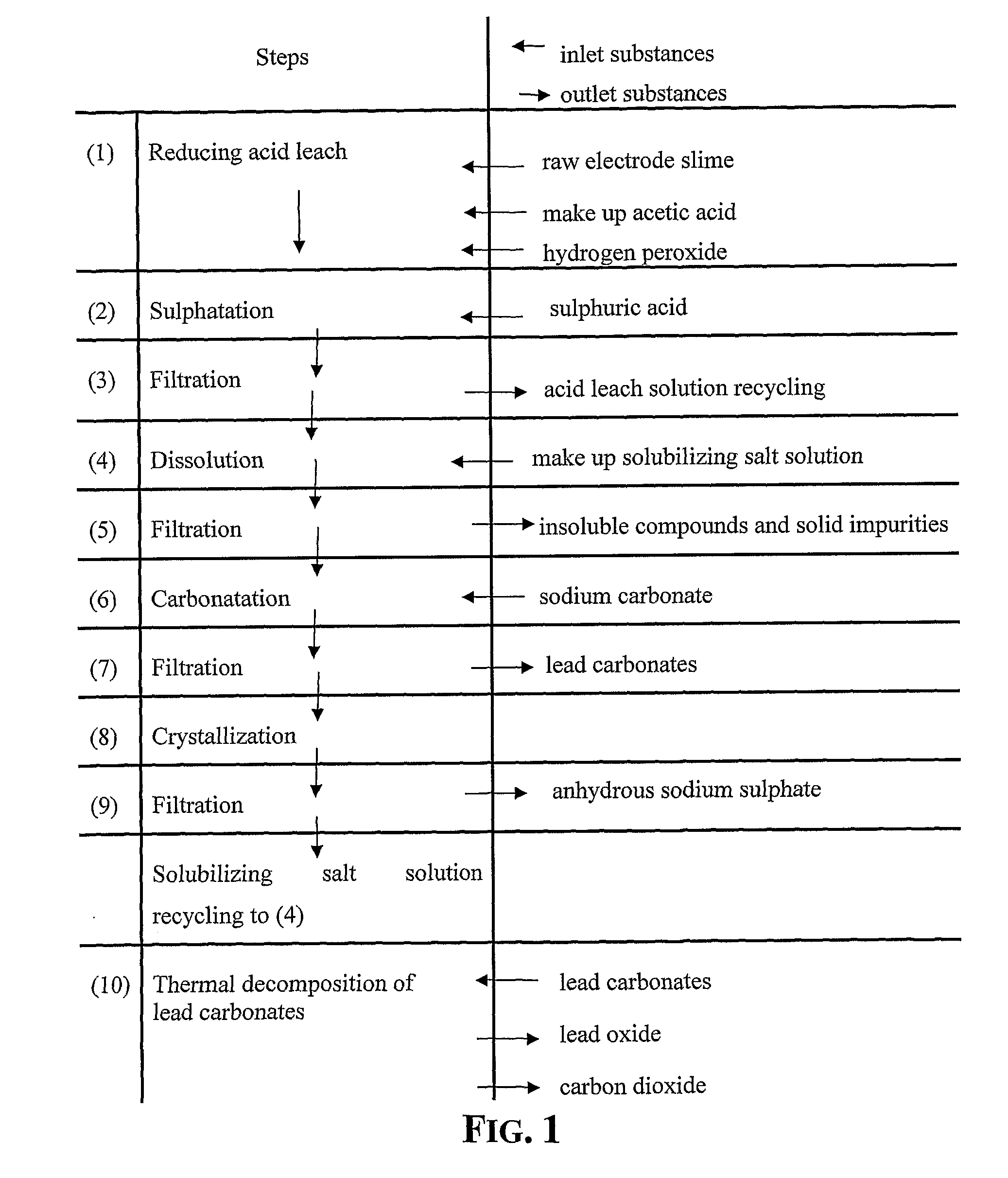
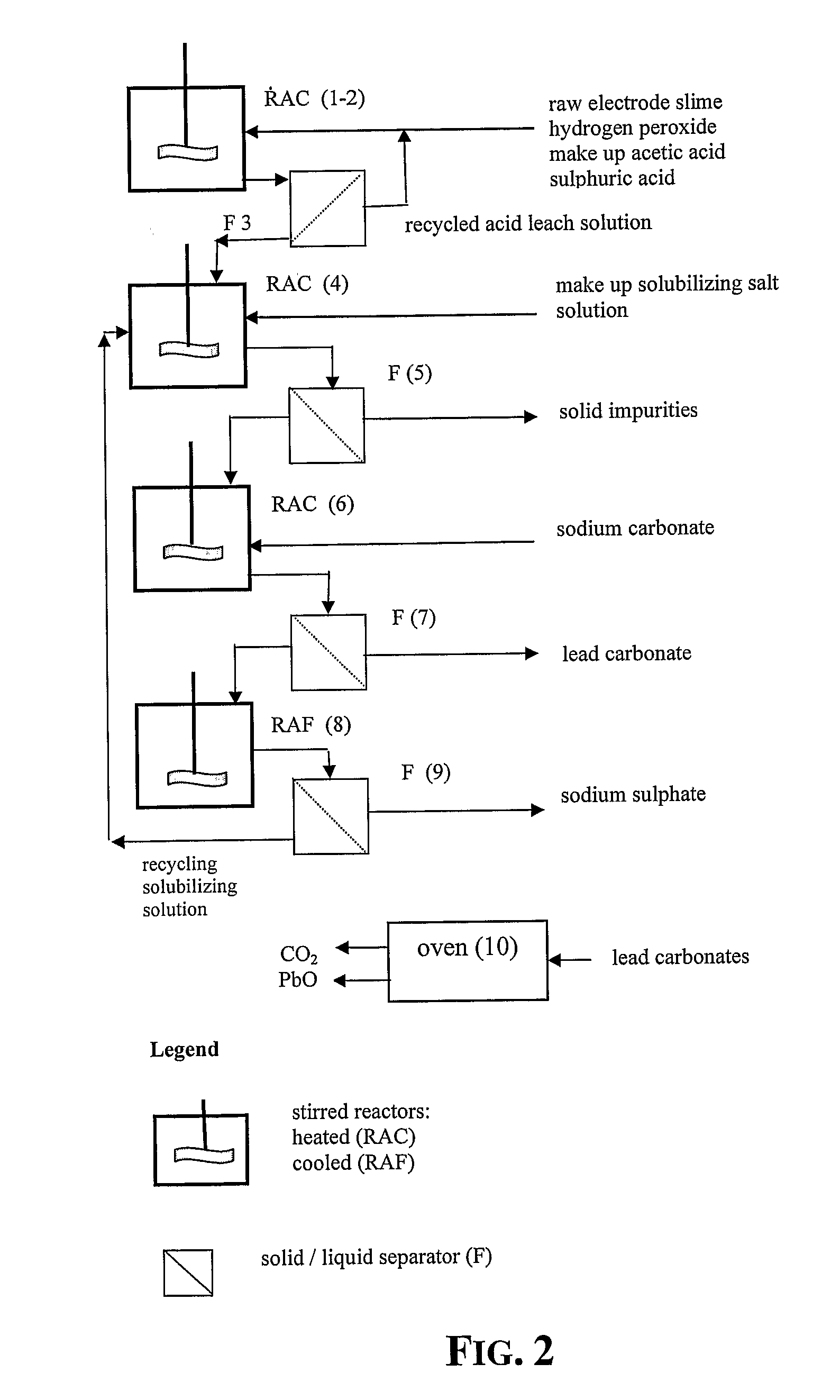
An outstandingly low environmental impact wet process recovers the lead content of an electrode slime and / or of lead minerals in the valuable form of high purity lead oxide or compound convertible to highly pure lead oxide by heat treatment in oven at relatively low temperature, perfectly suited for making active electrode pastes of new batteries or other uses. The process basically comprises the following treatments:a) suspending the impure lead containing material in an aqueous bath containing at least a lead oxide dissolving acid;b) reducing any insoluble lead dioxide to lead oxide by introducing in the suspension either hydrogen peroxide, a sulphite or sulphurous anhydride;c) converting all dissolved lead oxide to lead sulphate in the aqueous bath;d) obtaining a solution of lead sulphate obtained in an aqueous solution containing an acetate salt;e) precipitating and separating a purified lead compound in the form of either carbonate / oxycarbonate or of oxide / or hydroxide by adding to said acetate salt solution a carbonate salt or a hydroxide of the same cation of said acetate salt, respectively.Exemplary flow sheets according to several alternative embodiments and related processing plant diagrams are disclosed.
Owner:MILLBROOK LEAD RECYCLING TECH
Recovery of high purity lead oxide from lead acid battery paste
There is provided a process for recovering high purity litharge PbO from spent lead acid battery paste at low temperatures and the further preparation of highly pure lead oxides and Pb(OH)2.
Owner:RETRIEV TECH
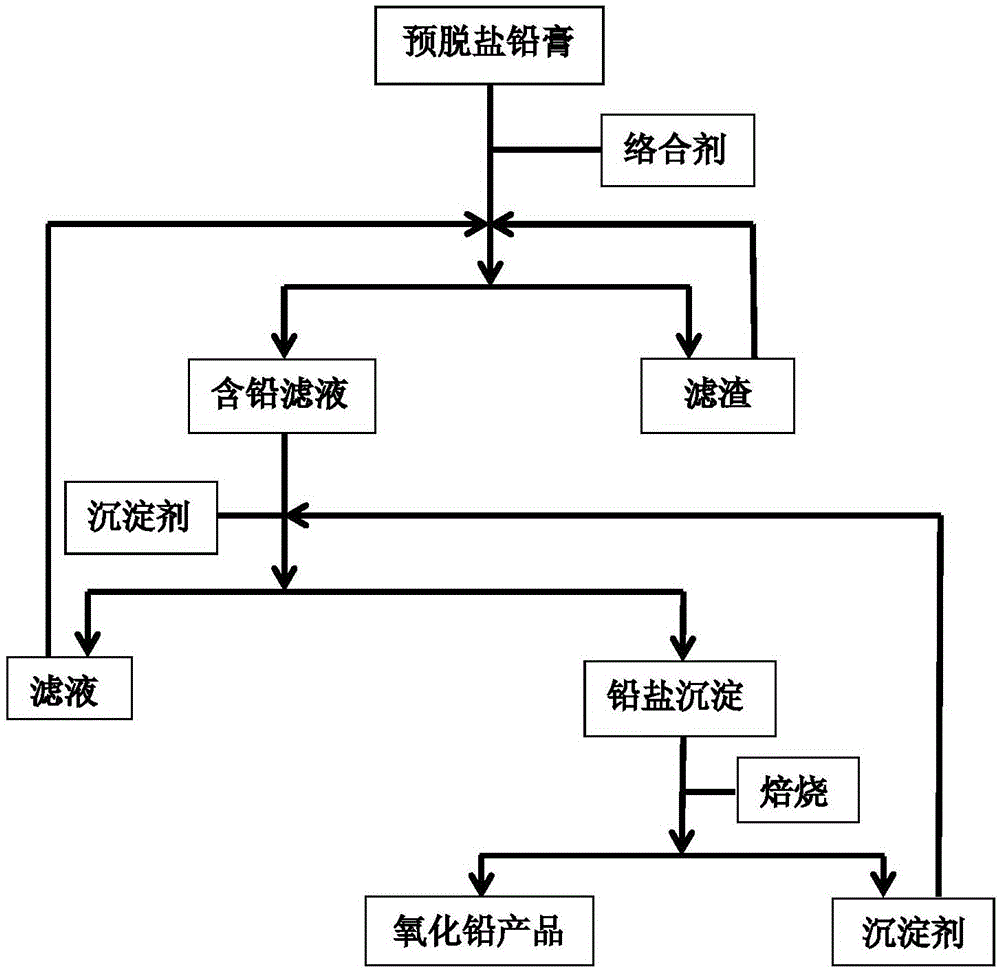
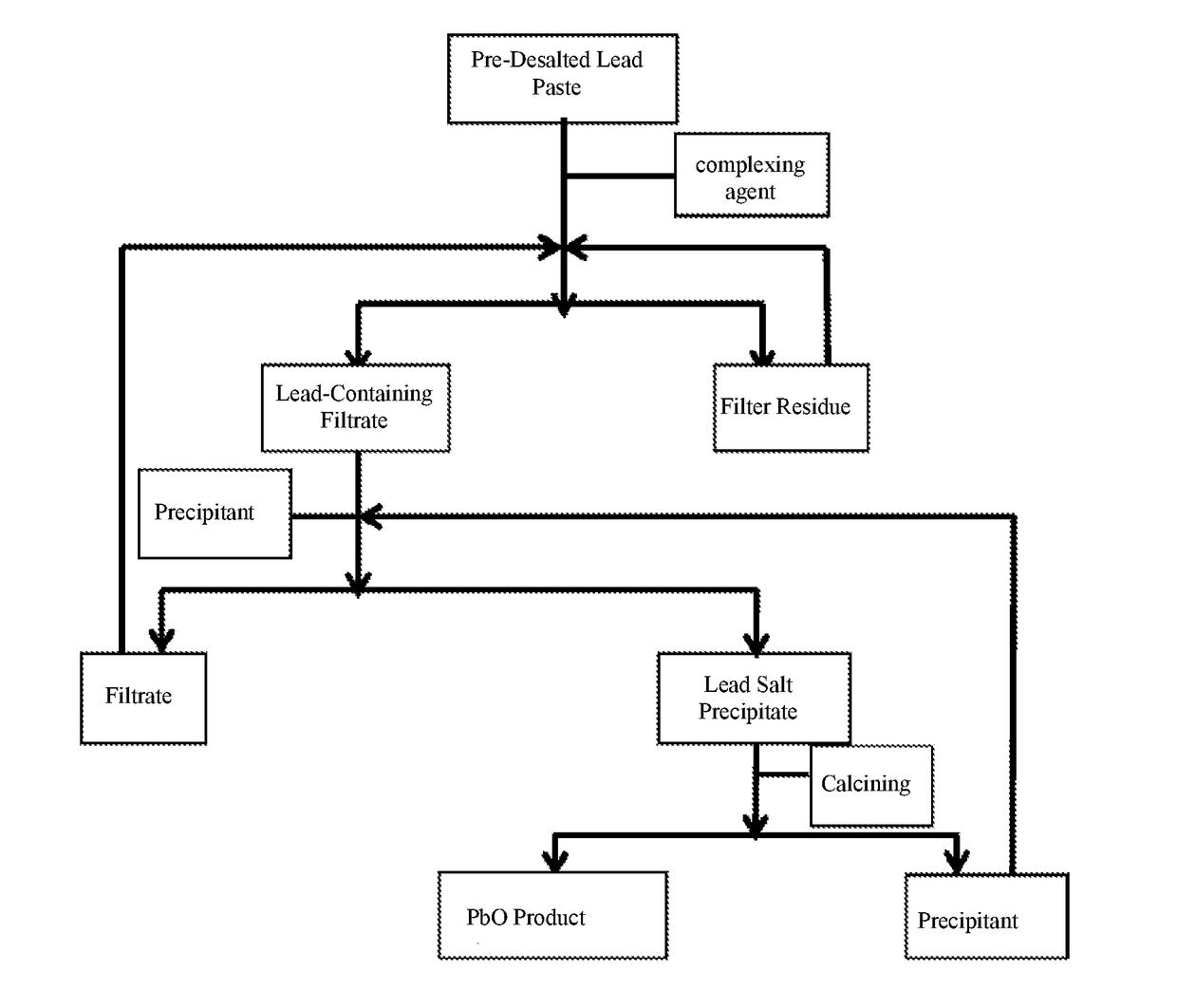
Method for recovering lead oxide from waste lead plaster
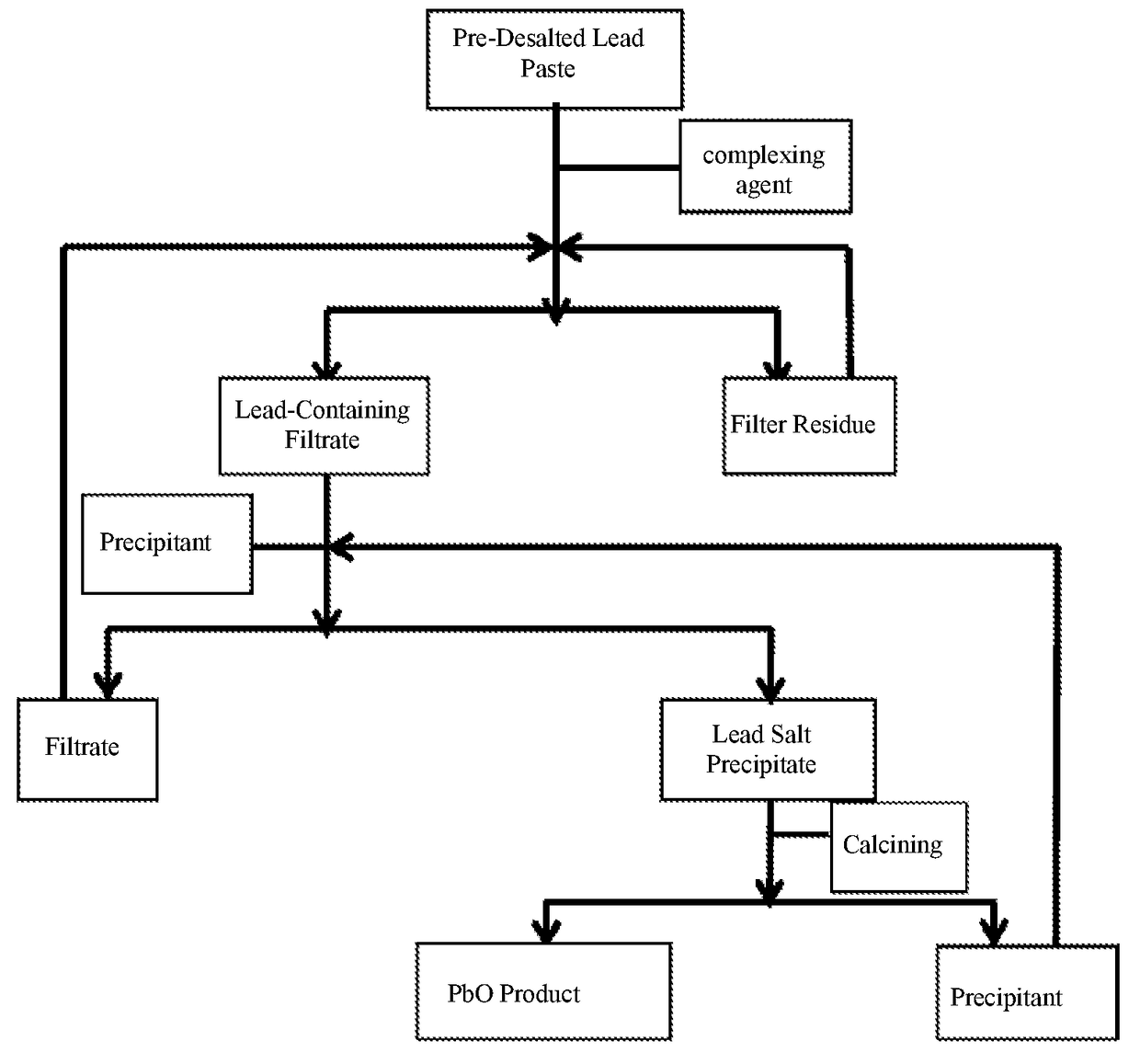
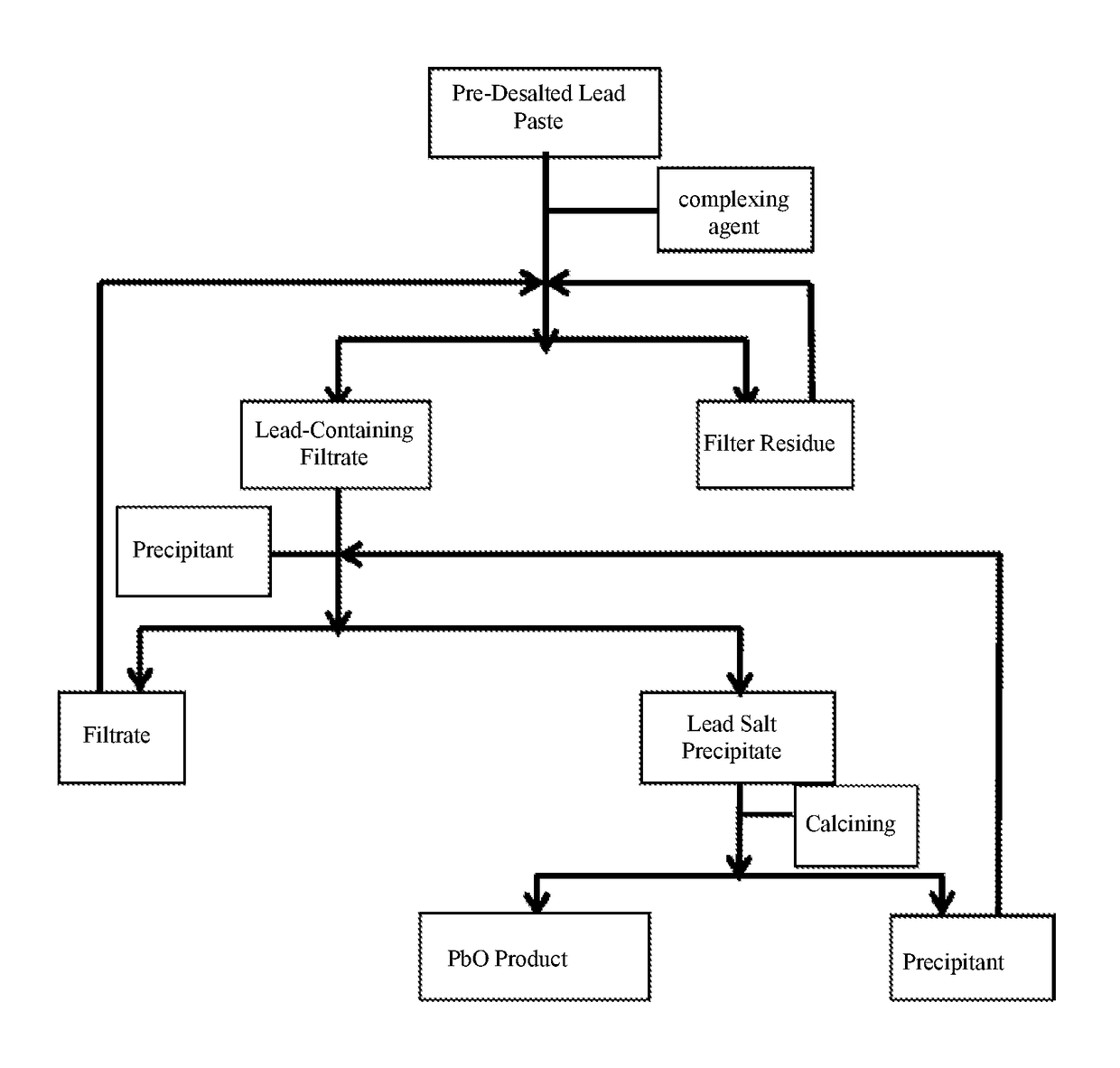
ActiveCN104141045AAtom economy is highIn line with the principles of atom economyLead-acid accumulatorsLead monoxideLead saltLead oxide
The invention provides a method for recovering lead oxide from waste lead plaster. The method comprises the following steps: a, dissolving pre-desalted lead plaster by using a complexing agent solution, and reacting all PbOs with a complexing agent to generate complexing ions so as to obtain a lead-containing solution and filter residues; b, adding a precipitating agent into the lead-containing solution, reacting the precipitating agent with the lead complexing ions to generate lead salt precipitation and the regenerated complexing agent; and c, roasting the lead salt precipitation to obtain lead oxide, and regenerating the precipitating agent. The method can be widely suitable for lead plaster formed by mixing various sources, the process conditions are relatively mild, a process is relatively environment-friendly, and the final recovery rate of lead oxide can reach more than 99%, so that the method has very high application values in the industry of recovery treatment of waste lead-acid batteries.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
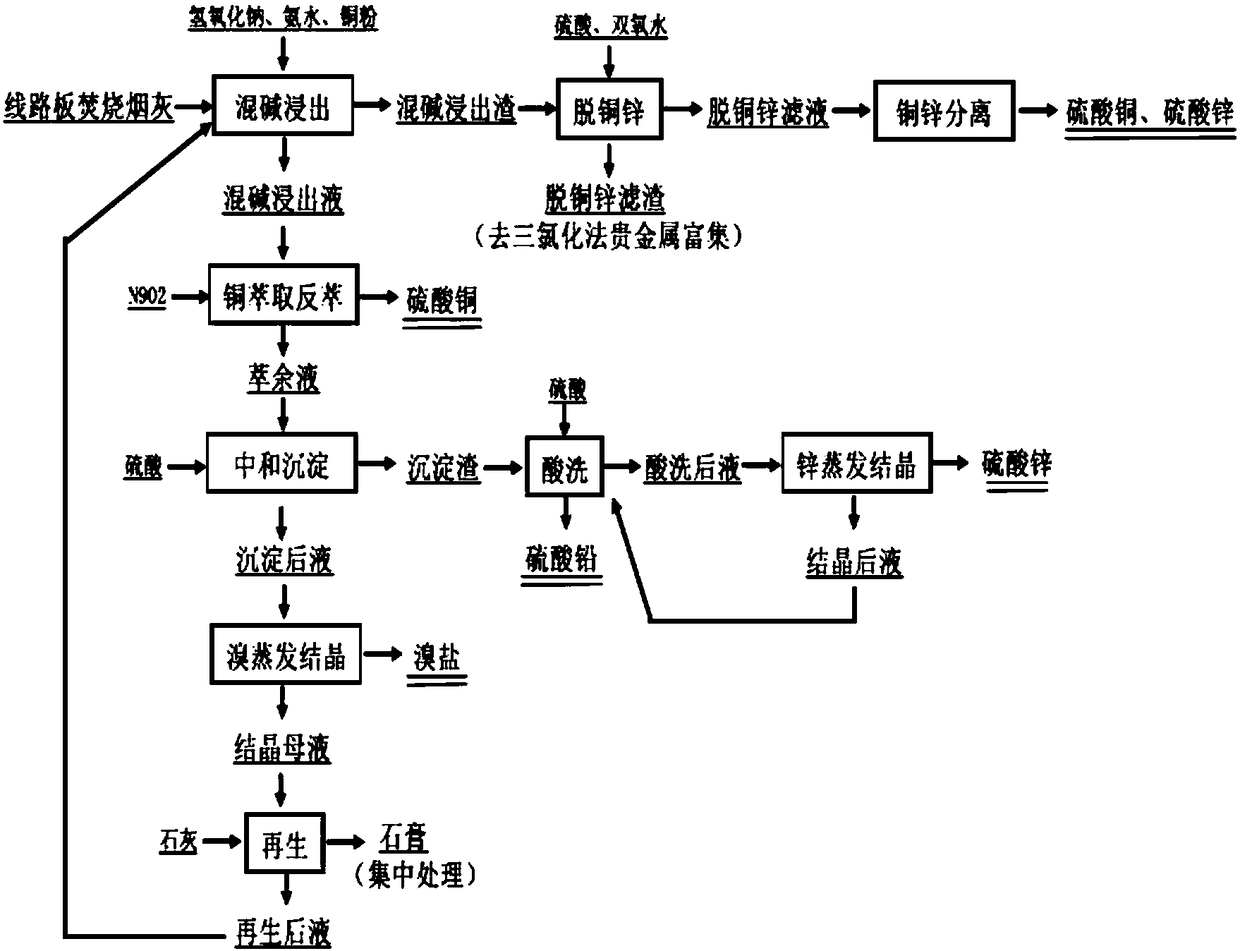
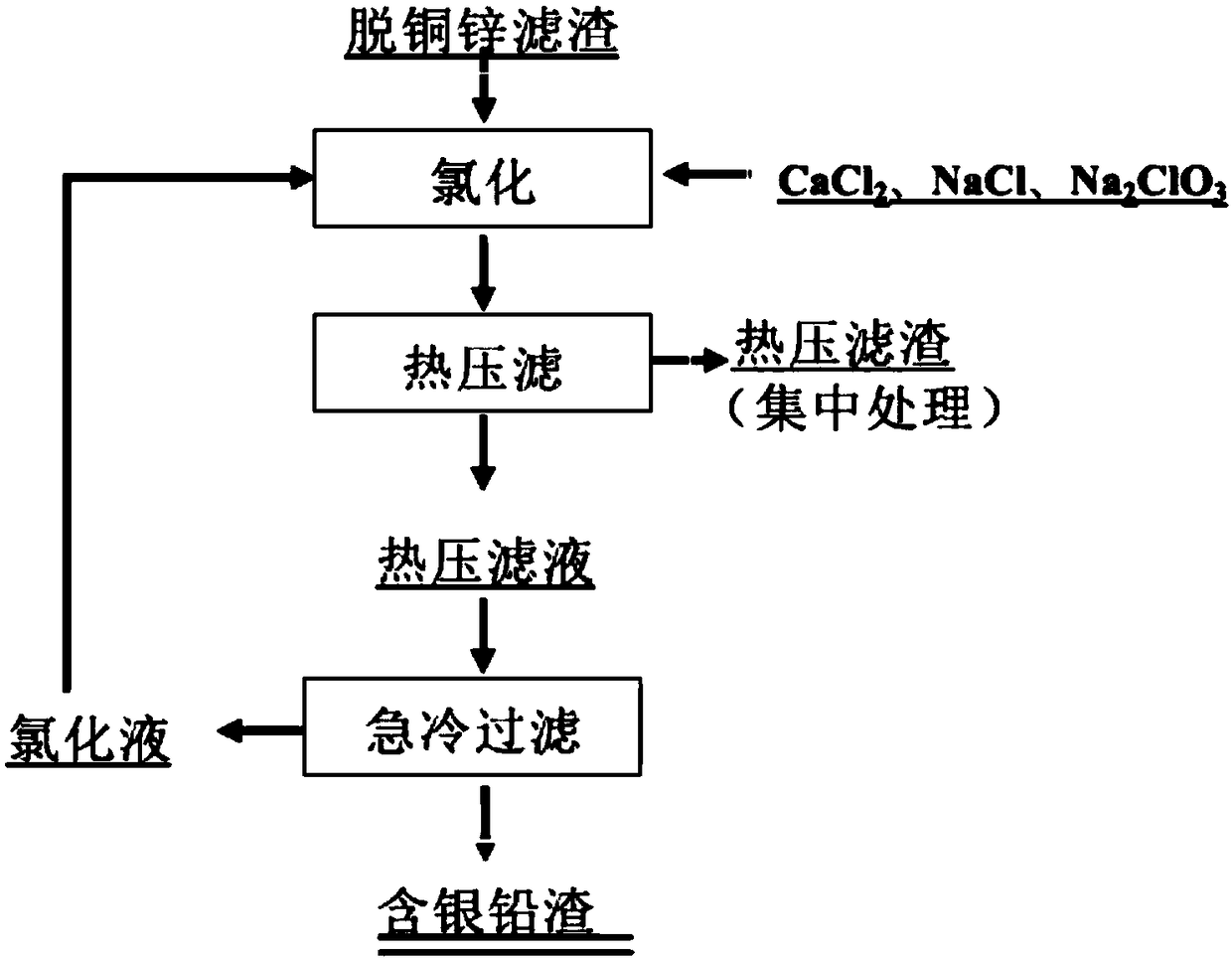
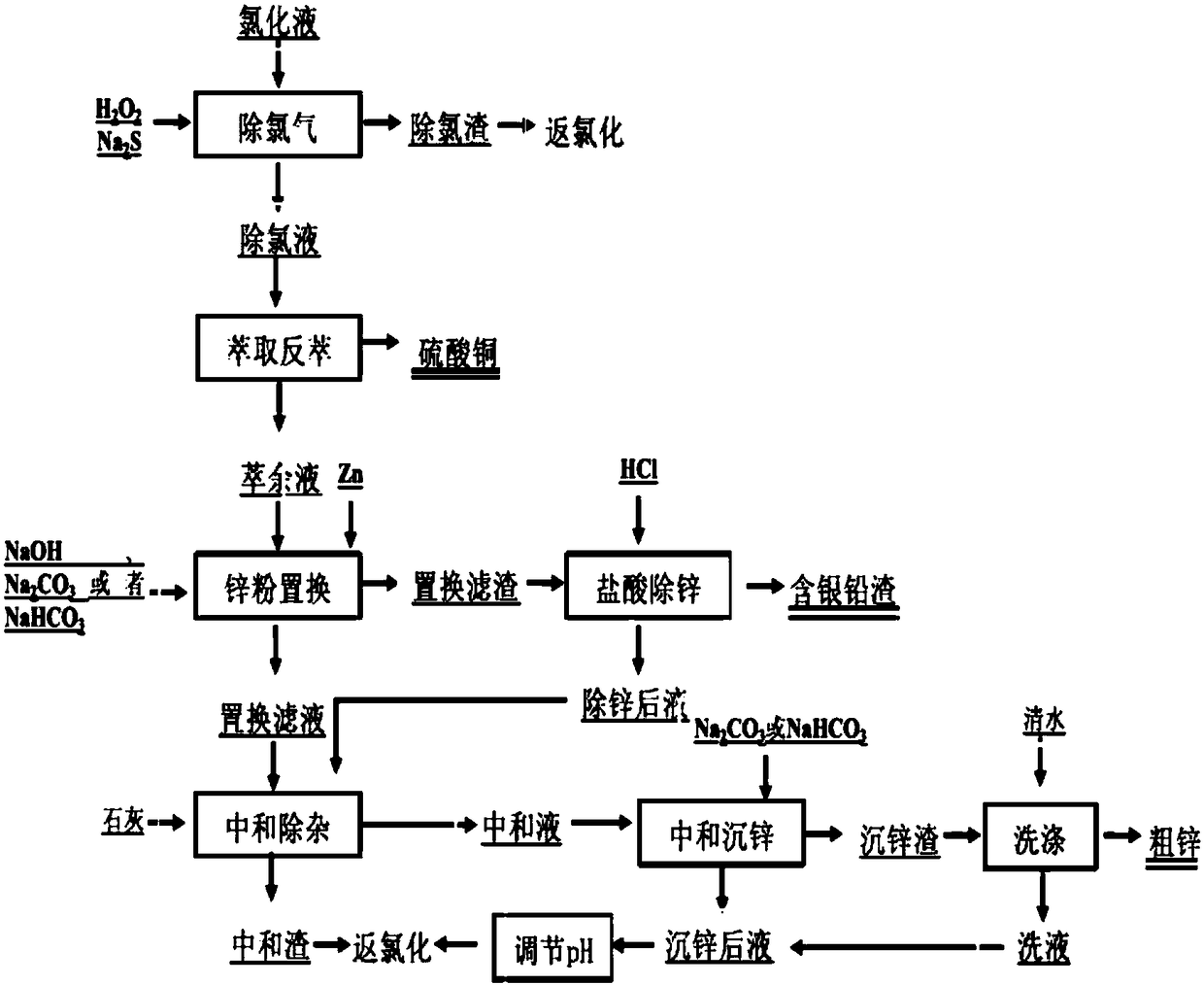
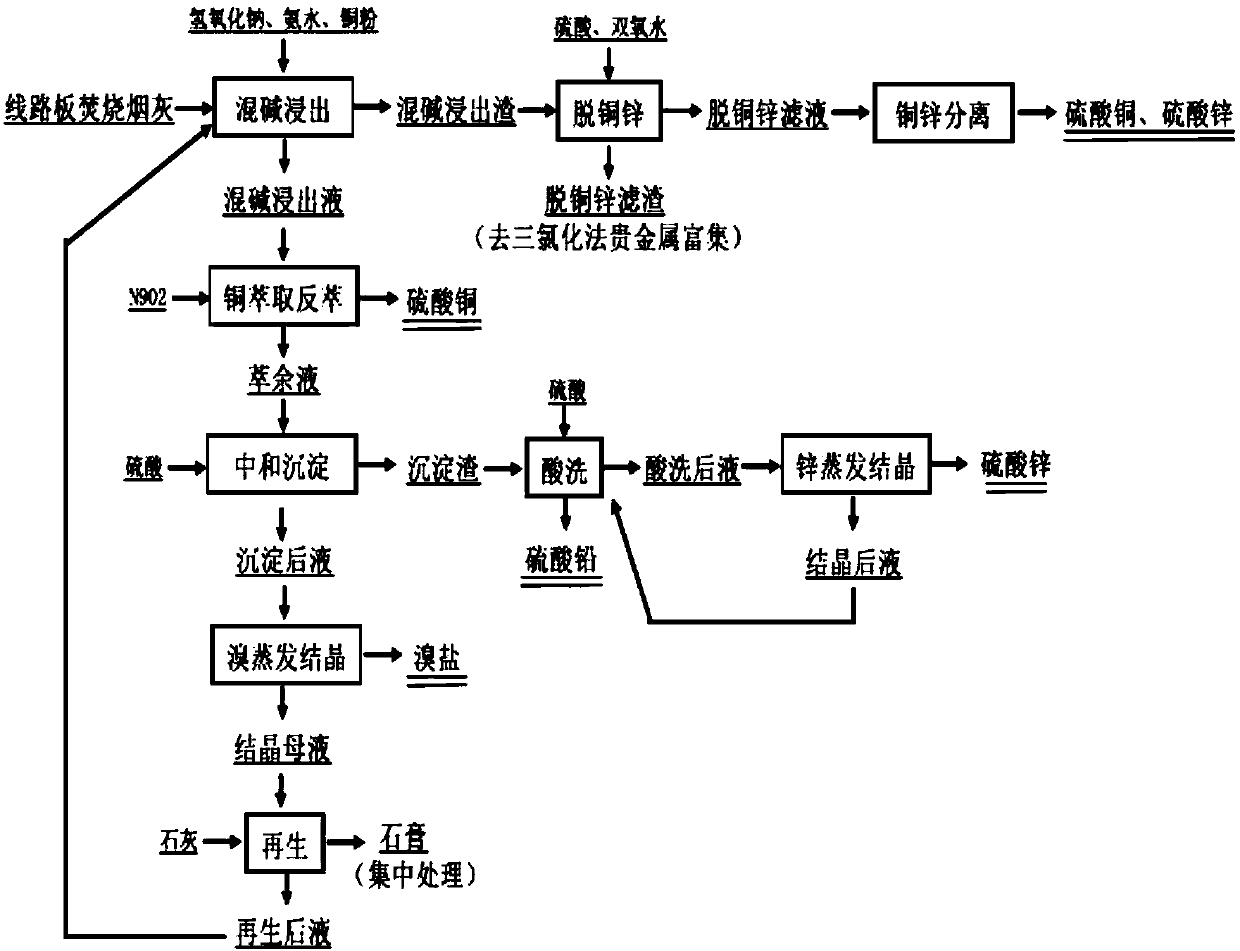
Method for pretreating incineration ash of circuit board and recovering bromine
ActiveCN108118157AEasy to recycleNo emissionsZinc sulatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesRecovery methodBromine
The invention discloses a method for pretreating incineration ash of a circuit board and recovering bromine, belongs to the field of comprehensive recovery of ash whole-wet valuable metal and particularly relates to a method for recovering valuable metal, enriching precious metal and recovering bromine salt in the pretreatment process of incineration ash of the circuit board. The method mainly comprises the steps: extracting mixed alkali; recovering copper by copper extraction and back extraction; carrying out neutralization and precipitation to separate lead and zinc; evaporating and crystallizing bromine; regenerating mixed alkali extracting liquor; removing zinc by acid pickling; evaporating and crystallizing zinc; carrying out zinc and copper removal on mixed alkali extracting residuesand the like. Compared with a traditional ash comprehensive process, the technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages that recovery of valuable metals such as copper, zinc and lead and enrichment of precious metal such as silver in the pretreatment process of the ash is realized to the maximum extent; meanwhile, the bromine salt is separated and recovered; the method has the characteristics of high recovery added value, no tail liquid drainage and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
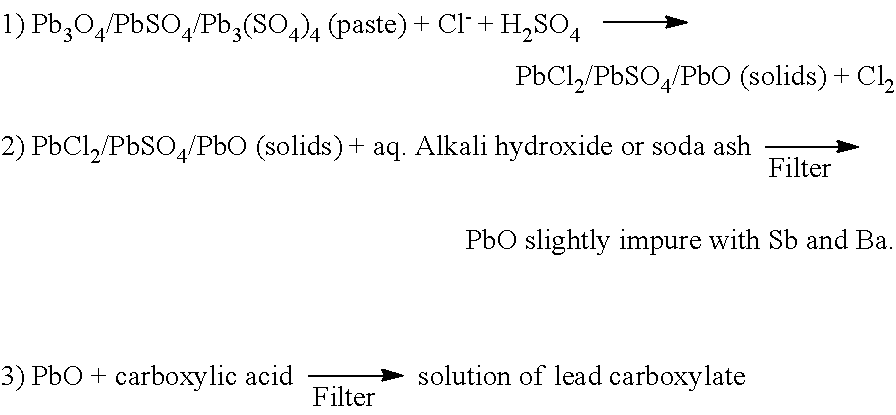
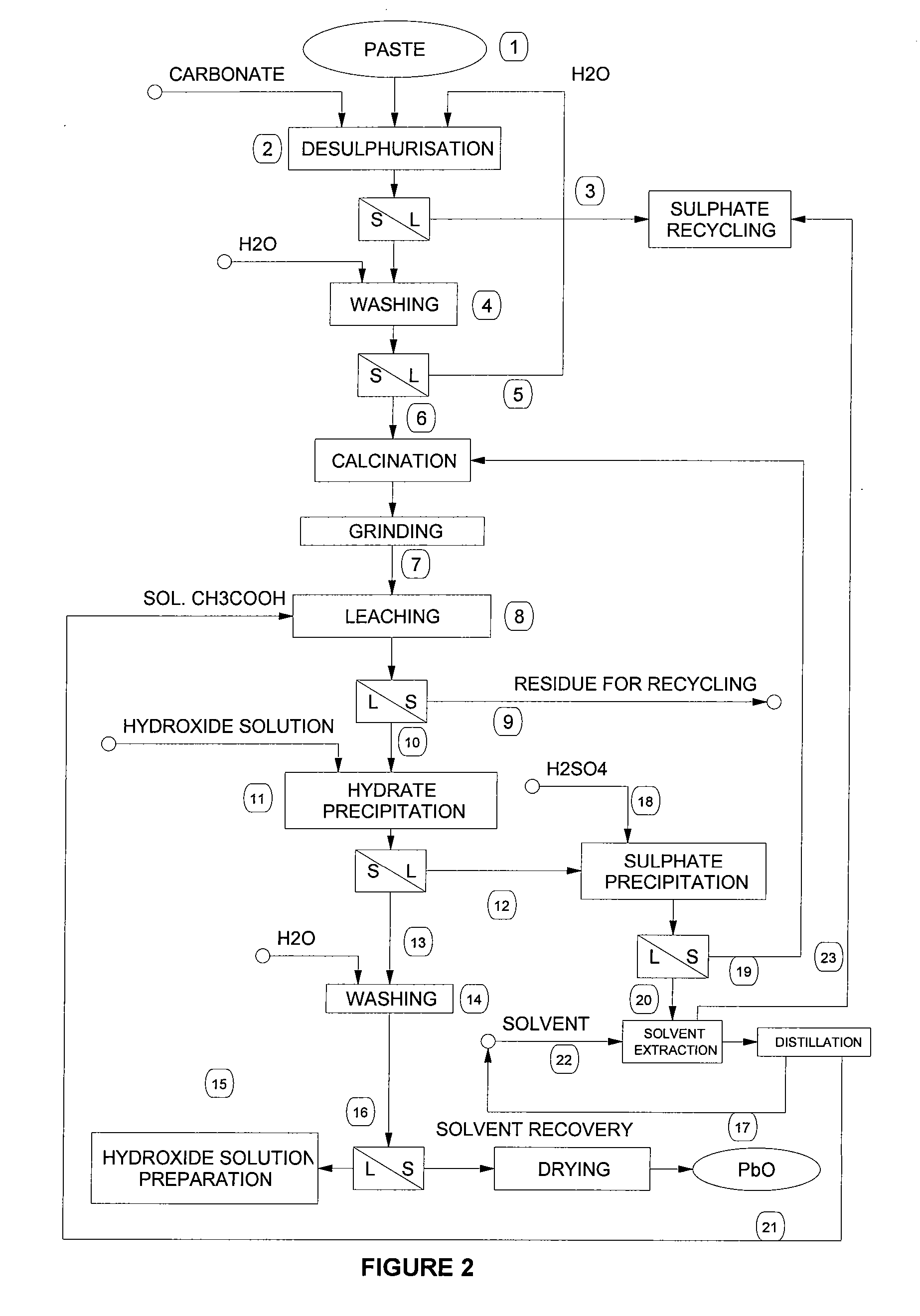
Process for the production of lead hydrate or monoxide of high purity, from materials and/or residues containing lead in the form of sulphates, monoxides and/or other compounds
InactiveUS20060239903A1High purityLead-acid accumulatorsLead monoxideAlkaline earth metalLead(II) acetate
Process for the production of lead hydrate or monoxide of high purity, from materials and / or residues containing lead in the form of sulphates, monoxides and / or other compounds, such as the paste coming from exhaust acid batteries, comprising the following steps of desulphurisation of the material and / or residue containing lead sulphate in an aqueous suspension with a suitable carbonate or hydrate in order to get conversion of the lead sulphate into a carbonate or hydrate, calcination of this desulphurised material and / or residue in order to get impure lead monoxide, followed by cooling and grinding, leaching of the impure lead monoxide by an aqueous solution of acetic acid followed by filtering to separate a solid residue, consisting mainly of non converted lead sulphate, from a lead acetate solution, precipitation of the lead acetate in solution by means of an alkaline hydroxide or alkaline-earth hydroxide, able to obtain soluble acetates, in order to get a precipitate, depending on the precipitation temperature, in the form of either lead hydrate or lead monoxide, followed by filtering of the obtained precipitate, separating a solution, at least one washing cycle and subsequent separation of the washing liquid, drying and optional calcination of the filtered and washed precipitate to get high purity lead hydrate or monoxide depending on the drying temperature.
Owner:STC SRL
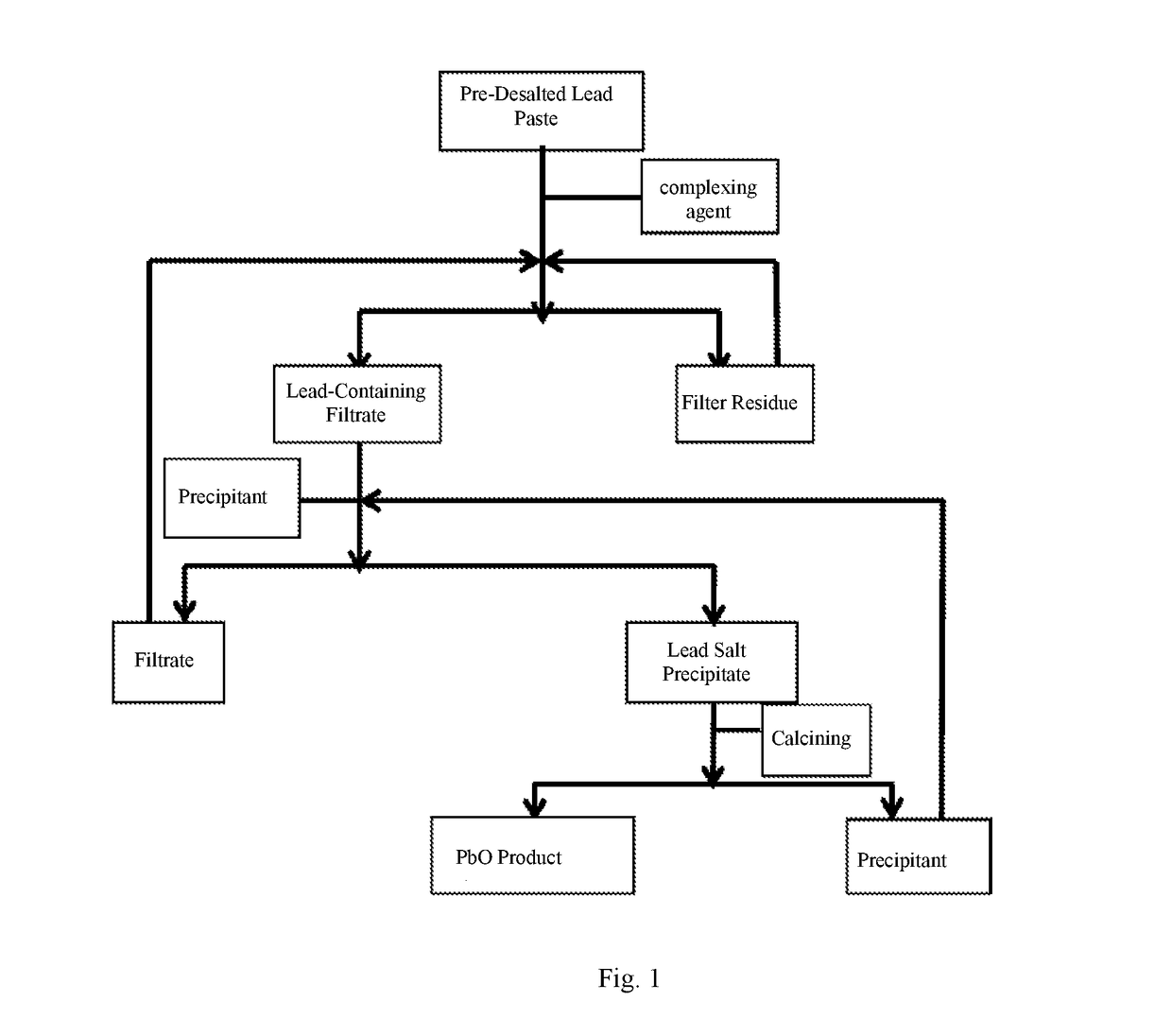
Method for recovering lead oxide from waste lead paste
ActiveUS20170271725A1Reduce decreaseReduction procedureLead-acid accumulatorsLead monoxideLead oxideLead salt
A method for recovering lead oxide from a pre-desalted lead paste, comprising the following steps: a. dissolving the pre-desalted lead plaster by using a complexing agent solution, and making all of PbO therein react with the complexing agent to generate lead complexing ions, obtaining a lead-containing solution and a filter residue; b. adding a precipitant to the lead-containing solution, and then the precipitant reacting with the lead complexing ions to generate a lead salt precipitate and the regenerated complexing agent; c. calcining the lead salt precipitate to obtain lead oxide and regenerate the precipitant. The final recovery rate of lead oxide of the method can reach 99% or more.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
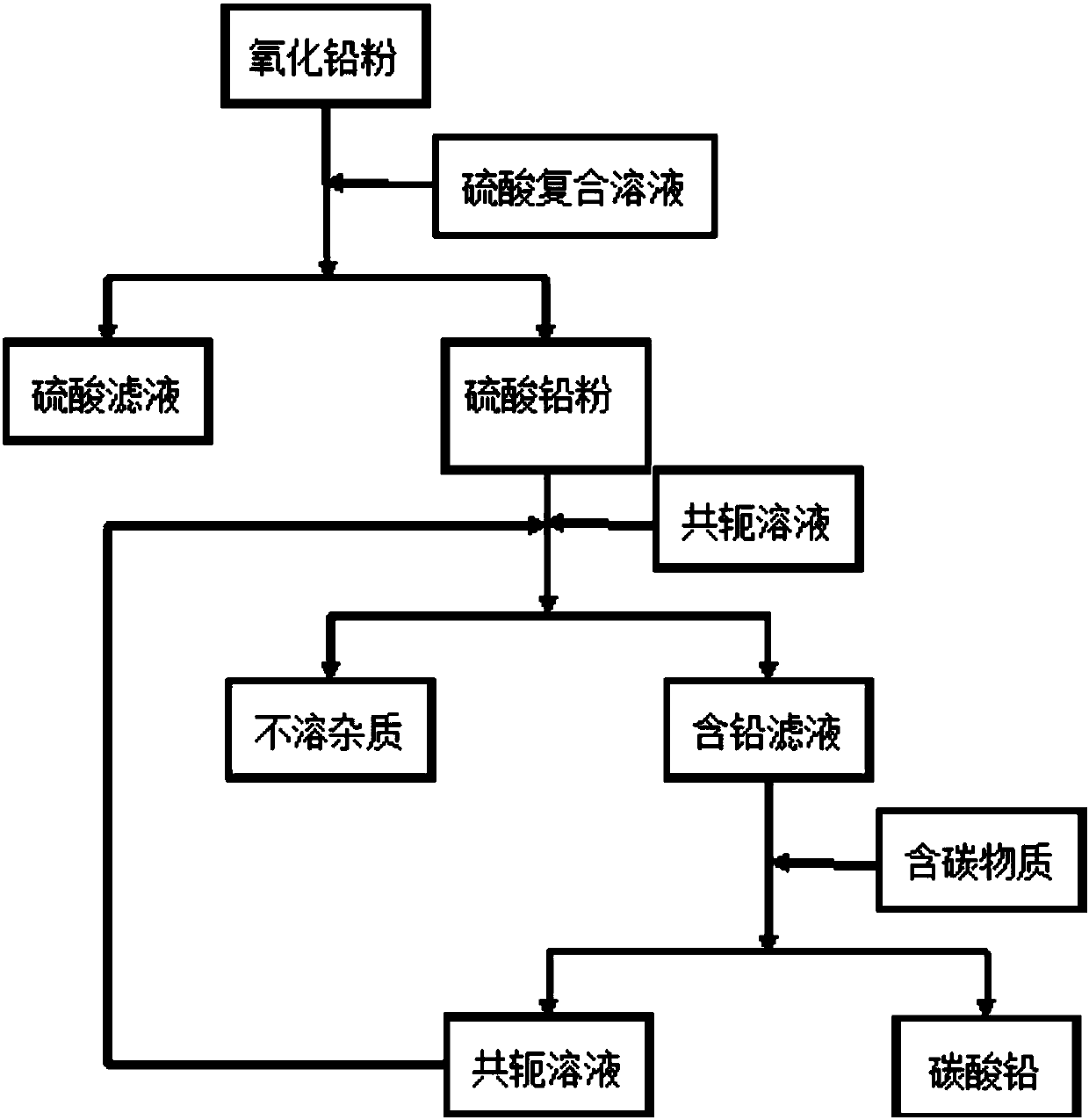
Method for preparing lead carbonate from lead oxide waste
The invention discloses a method for preparing lead carbonate from lead oxide waste and belongs to the field of recycling waste containing lead oxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1) utilizing a sulfuric acid composite solution to convert lead oxide waste into a lead sulfate crude product; (2) dissolving the lead sulfate crude product in the step (1) by an X-Y conjugate solution to dissolve lead sulfate in the crude product and filtering to obtain lead sulfate filtrate and insoluble impurities; (3) adding carbon containing matter into the lead sulfate filtrate obtained in the step (2) and separating to obtain the lead carbonate. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to varieties of sources such as waste lead-acid cell lead plaster, waste generated in lead-acid cell production and lead containing waste in a smelting process and has the advantages of high lead recovery rate, cyclic utilization of a mother solution and the like.
Owner:北京绿色引领环保科技研究院有限公司
Acrylic-fiber finish, acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production, and carbon-fiber production method
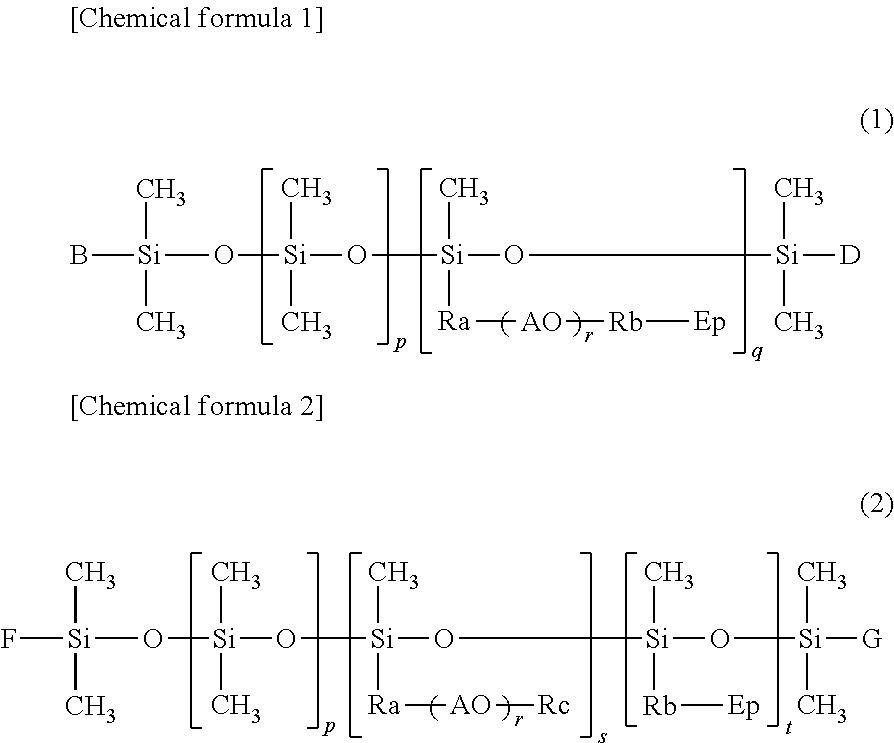
ActiveUS20120021125A1Minimum fiber separationMinimal broken fiberSesquicarbonate preparationFibre typesEpoxyPolymer science
An acrylic-fiber finish for use in carbon-fiber production contributes to high tenacity of resultant carbon fiber. The acrylic-fiber finish for carbon-fiber production includes an epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and a surfactant. The weight ratios of the epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and the surfactant in the total of the non-volatile components of the finish respectively range from 1 to 95 wt % and from 5 to 50 wt %. The carbon fiber production method includes a fiber production process for producing an acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production by applying the finish to an acrylic fiber which is a basic material for the acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production; an oxidative stabilization process for converting the acrylic fiber produced in the fiber production process into oxidized fiber in an oxidative atmosphere at 200 to 300 deg.C.; and a carbonization process for carbonizing the oxidized fiber in an inert atmosphere at 300 to 2,000 deg.C.
Owner:MATSUMOTO YUSHI SEIYAKU
Process for producing basic lead carbonate
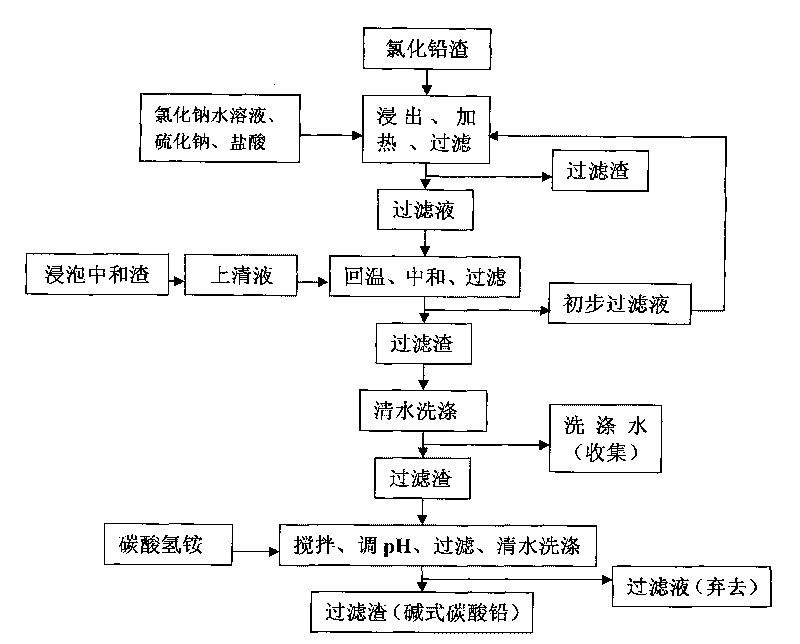
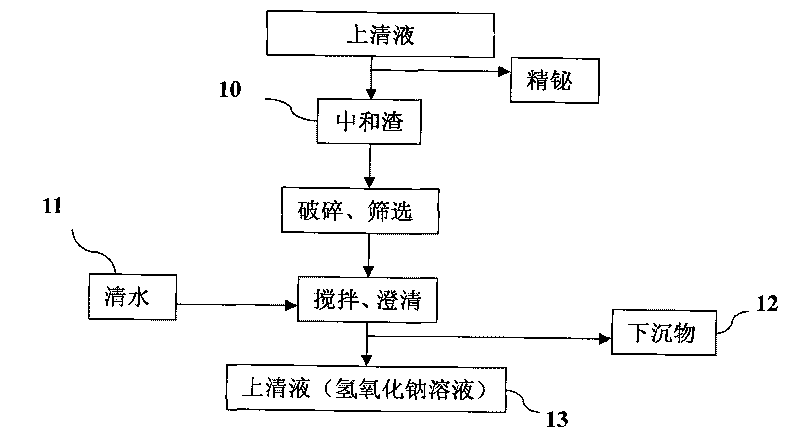
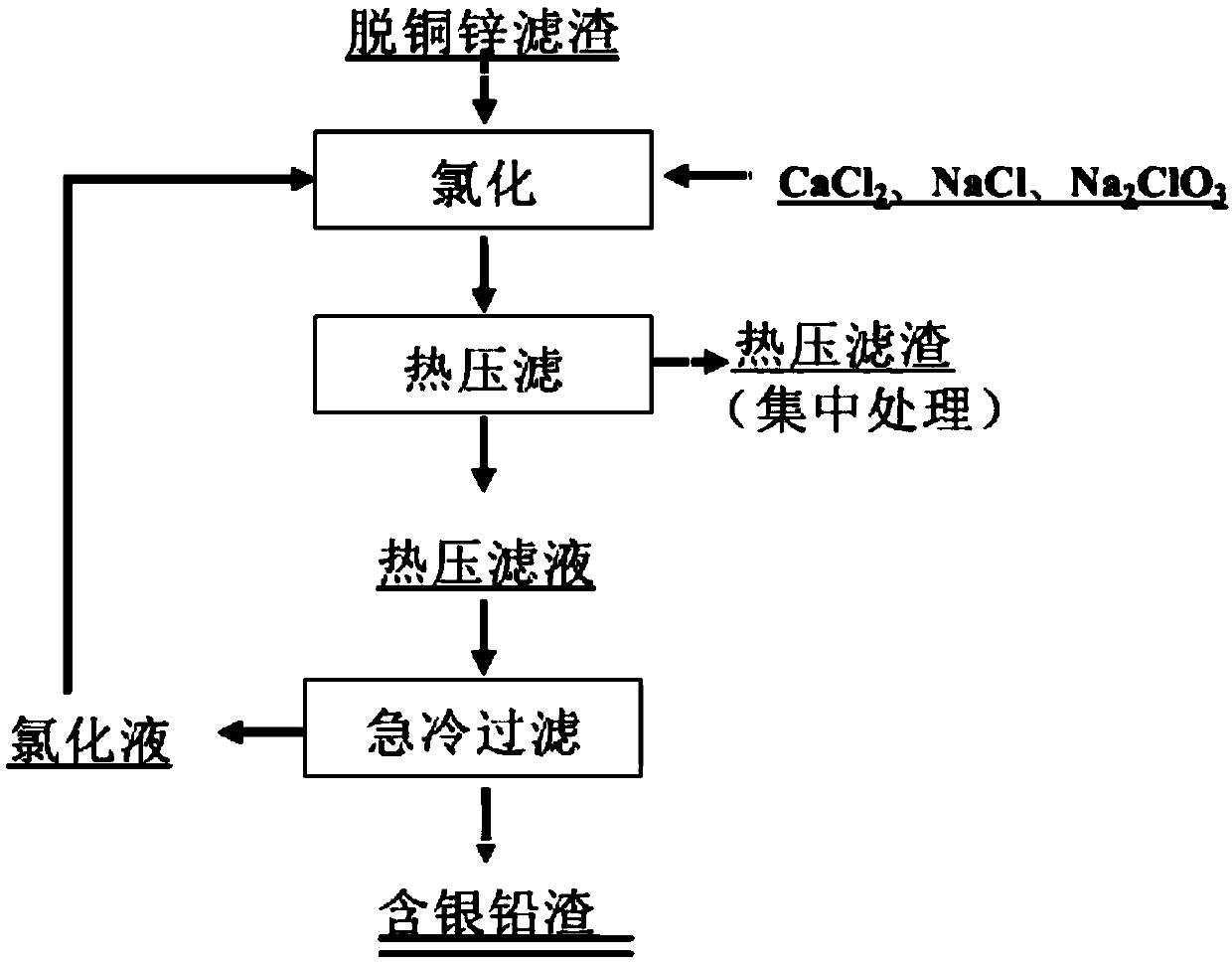
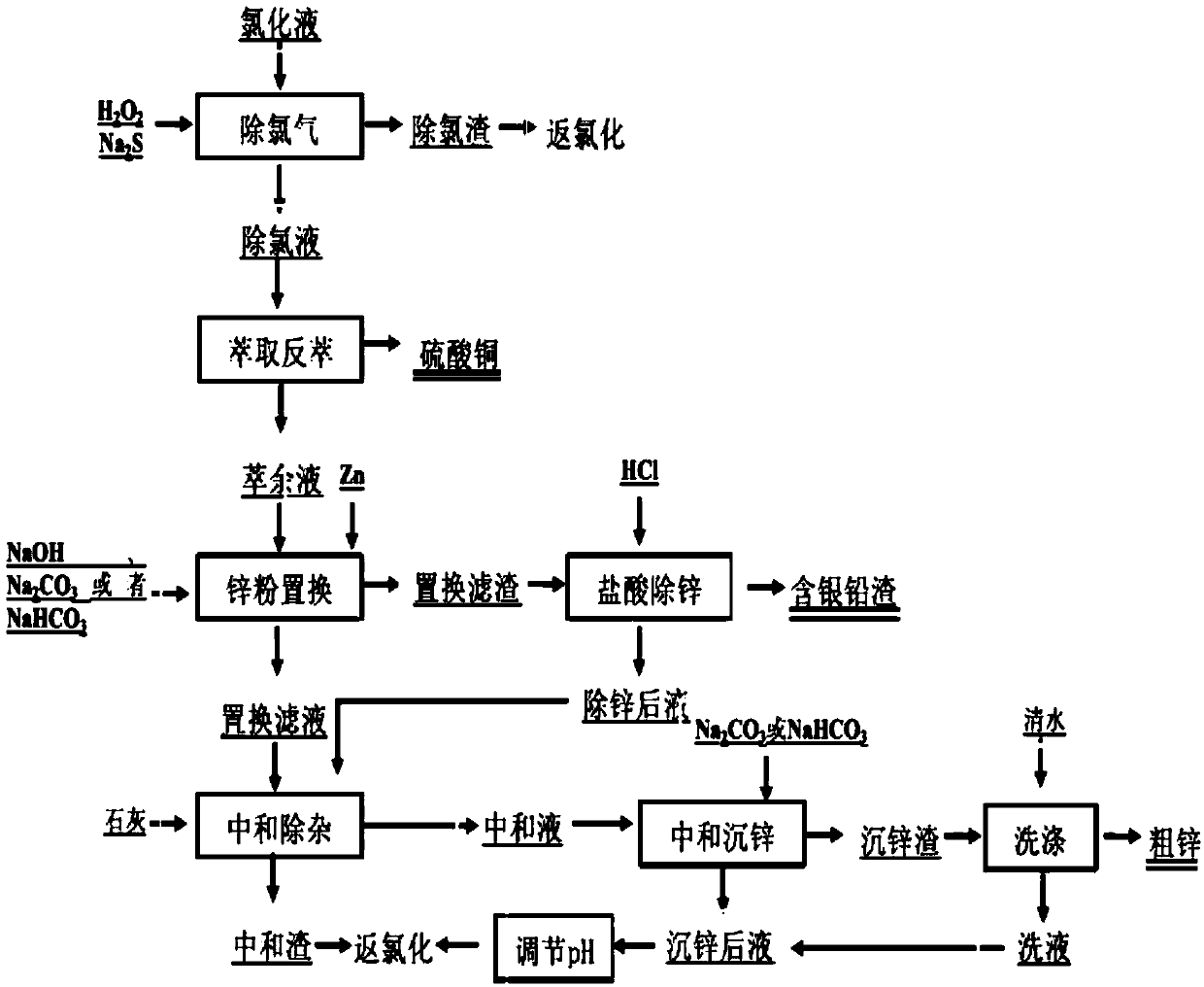
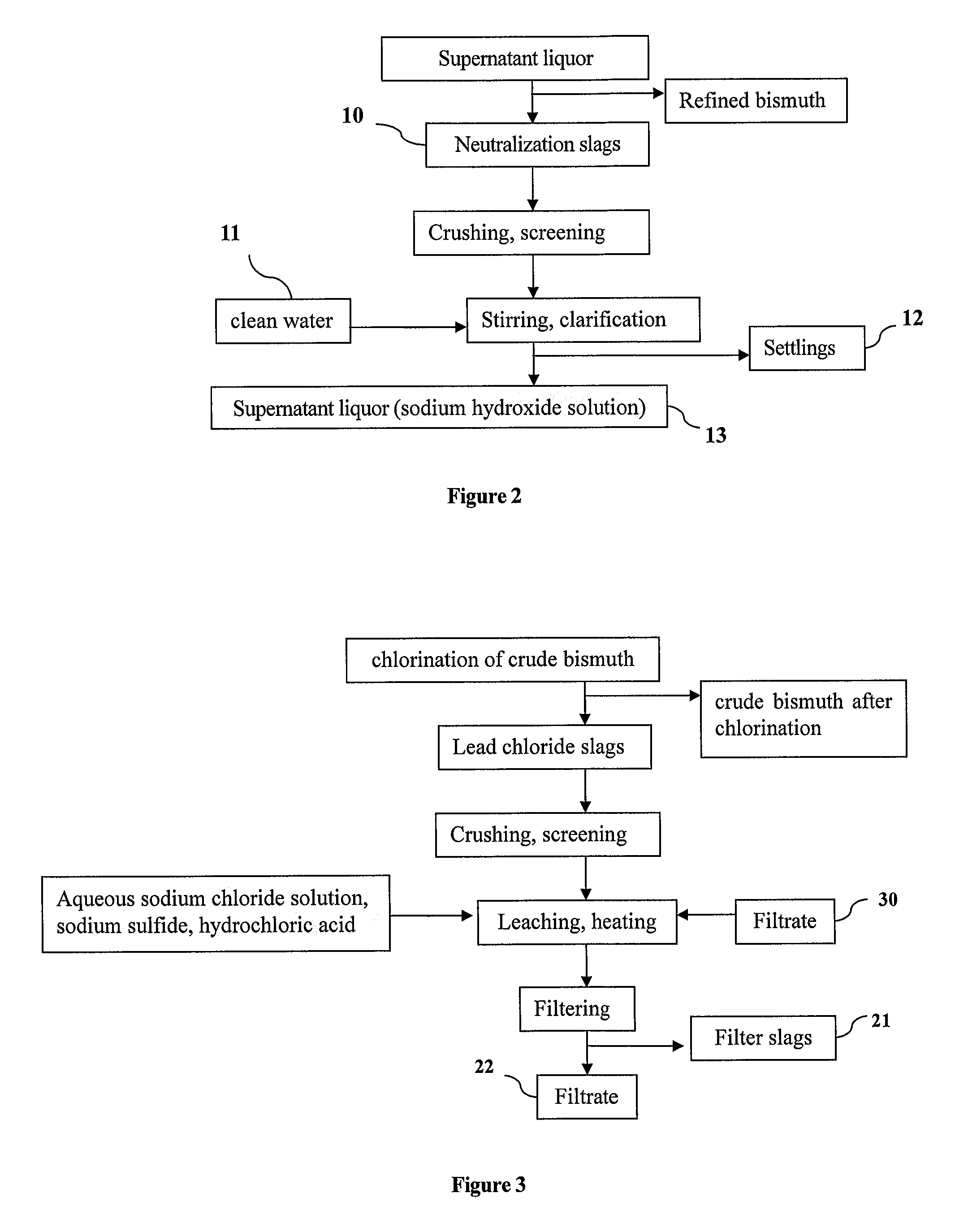
InactiveCN101723440AOptimizing the smelting production processEasy to handleSolid waste disposalLead carbonatesLead carbonateLead bismuth
The invention relates to a process for producing basic lead carbonate, which comprises the following steps: (1) soaking and neutralizing slag to obtain solution of sodium hydroxide, (2) leaching lead chloride slag and filtering, (3) alkali neutralization, filtering and washing, and (4) carbonate conversion, crystallization, filtering and washing. The process uses residual slag of fire refining bismuth as a raw material, optimizes smelting production technology of blast furnace smelting, electrolysis of lead-bismuth alloy, and fire refining to ensure that smelting slag of bismuth can be better treated and utilized, and saves resources. In the process of the invention, lead circulates in a closed system so as to reduce environmental pollution.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP HLDG CO LTD
Process for Producing Carbonate Particles
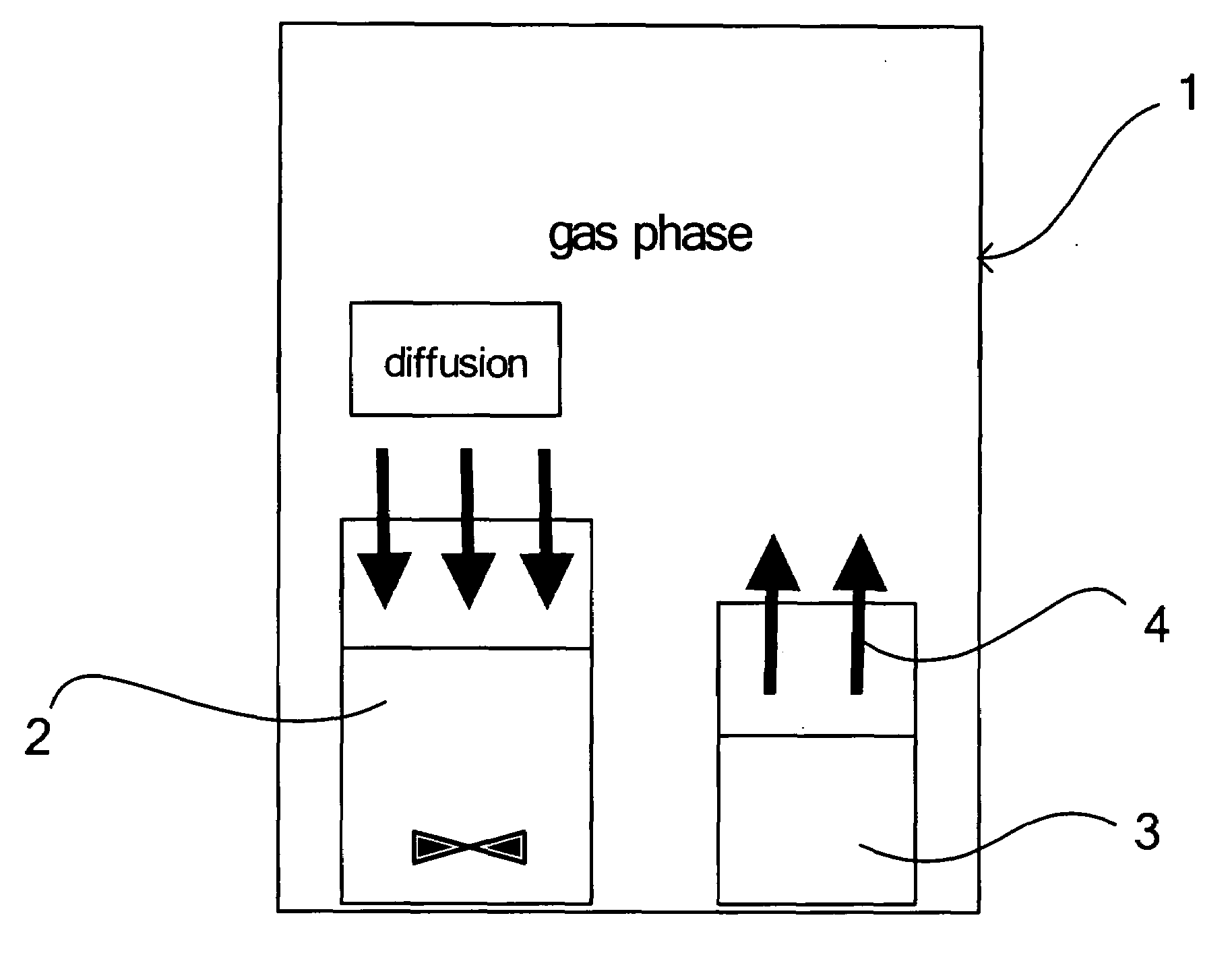
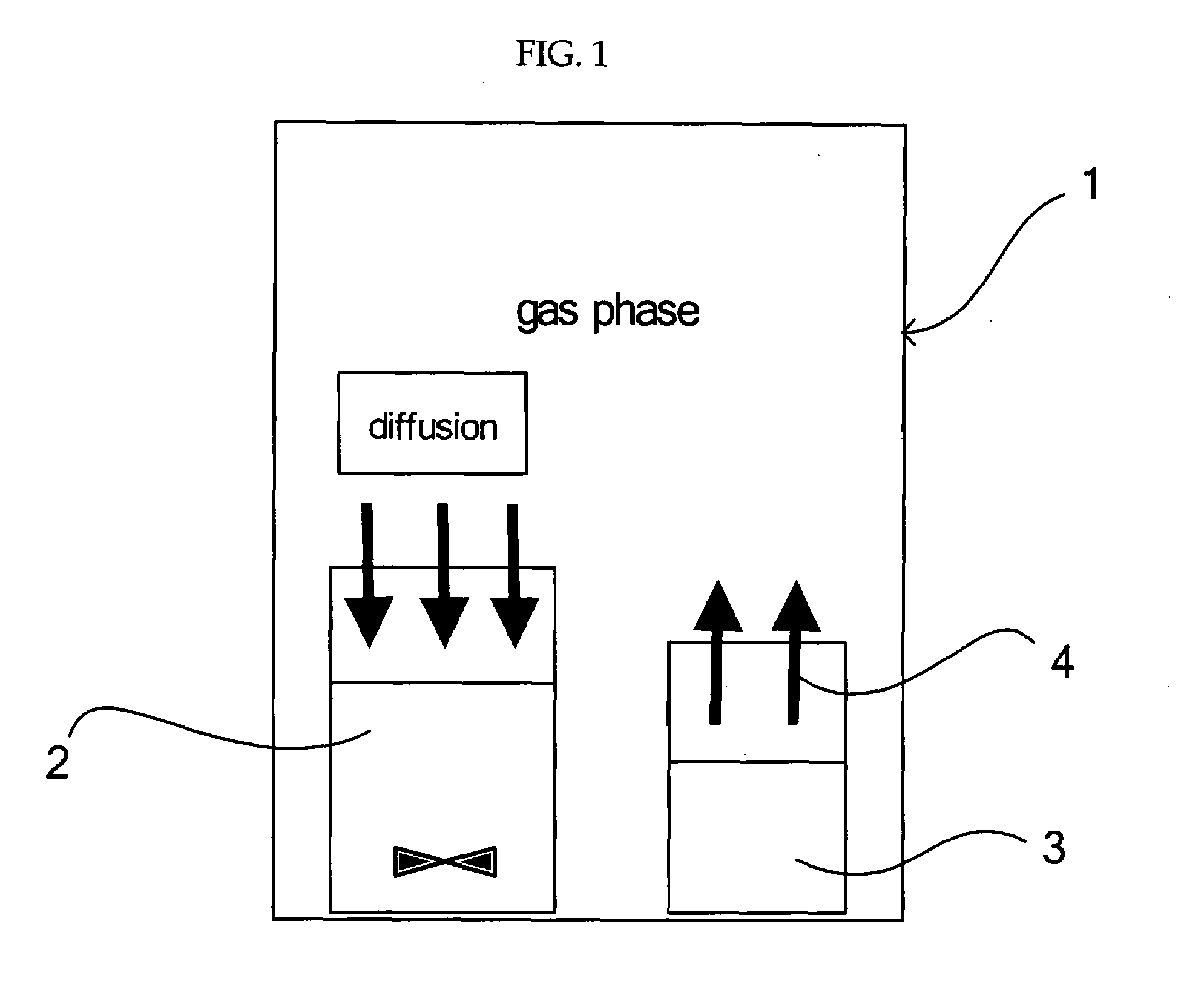
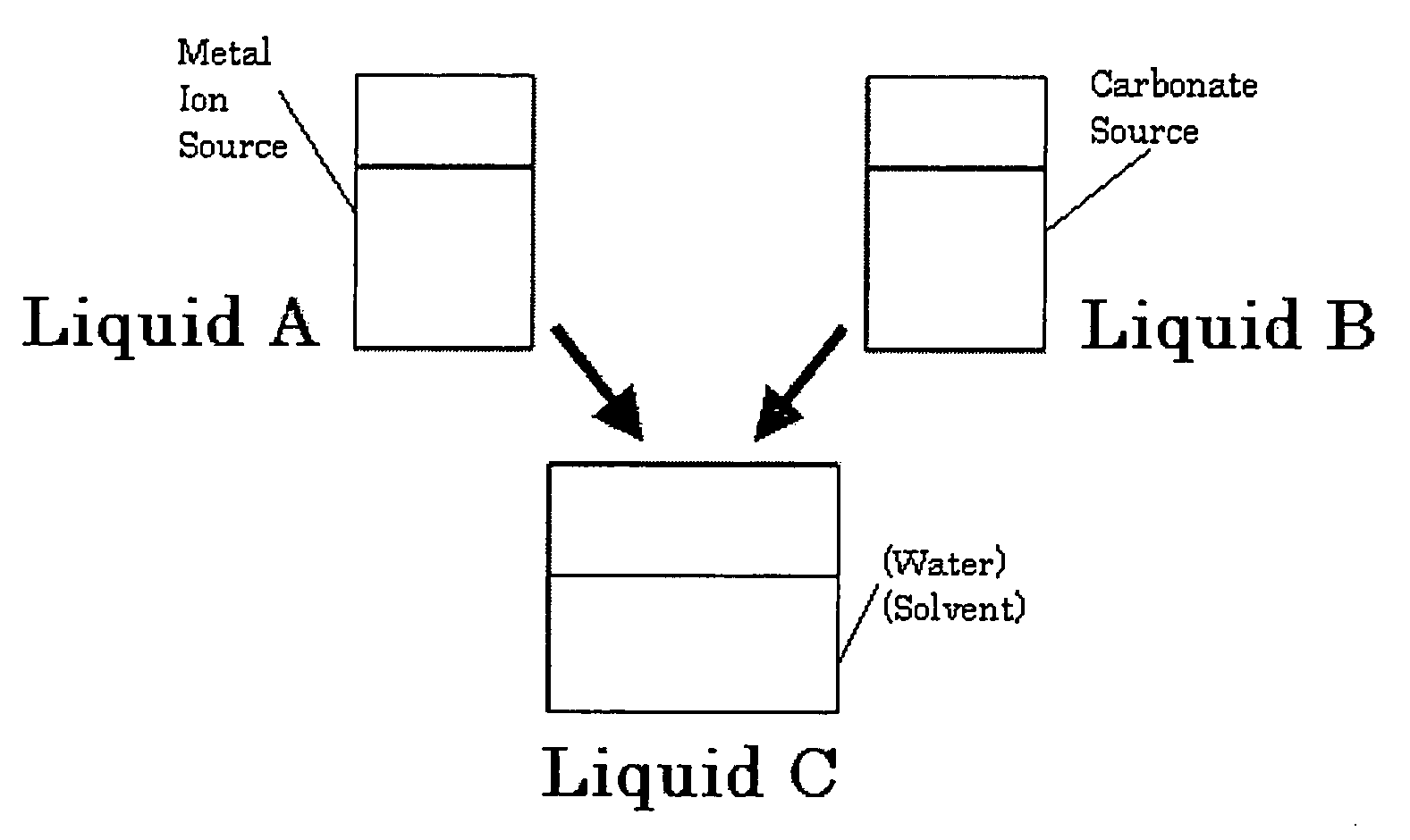
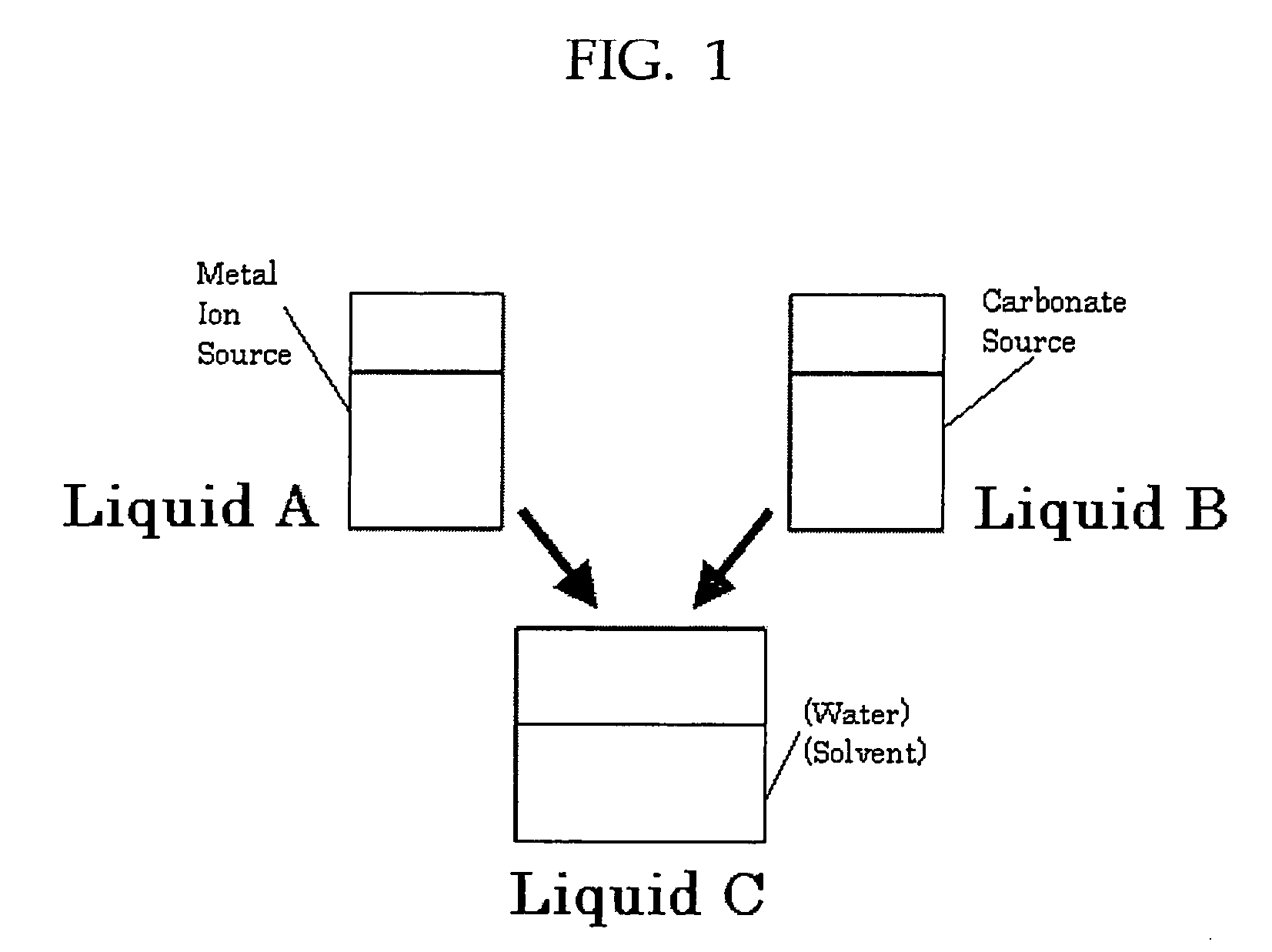
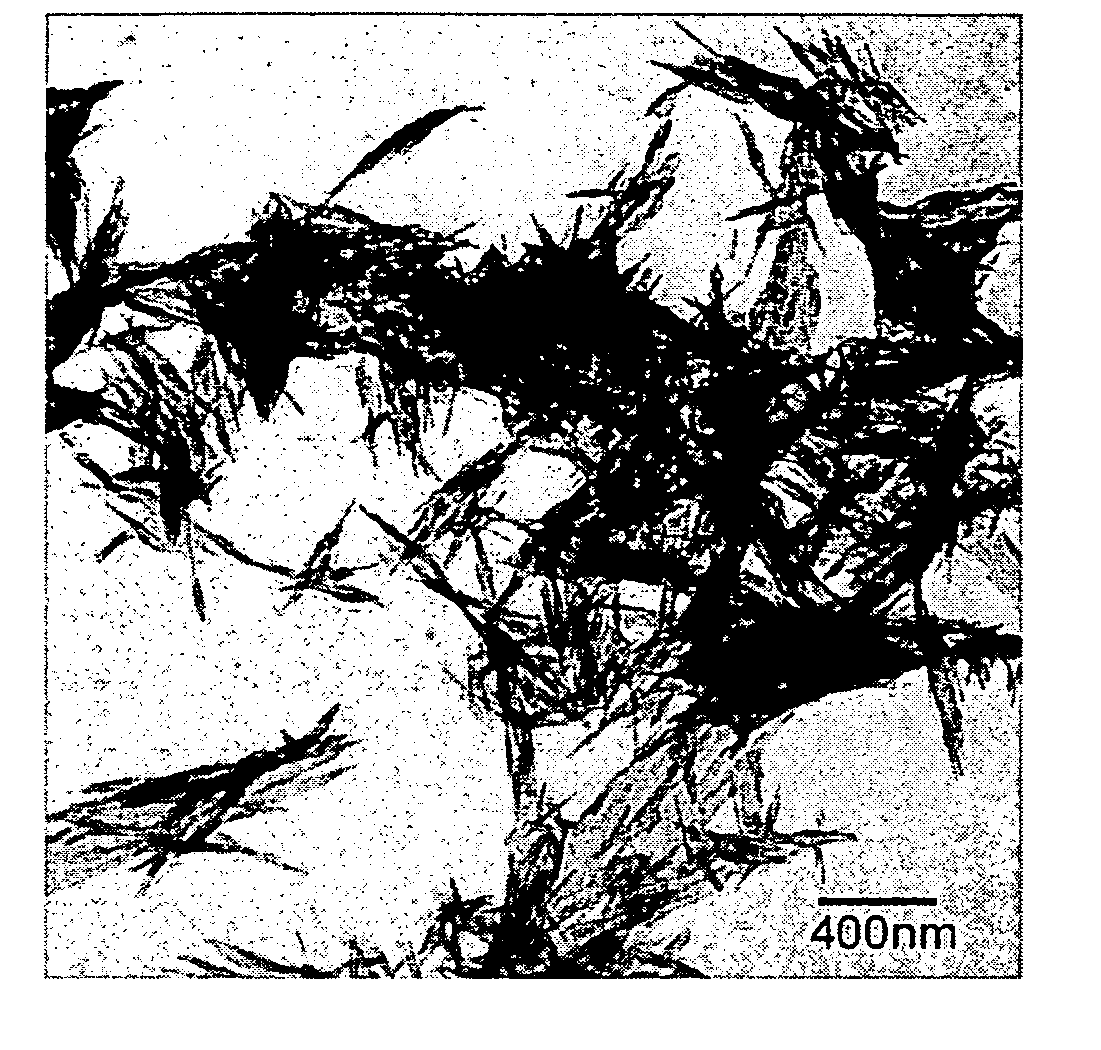
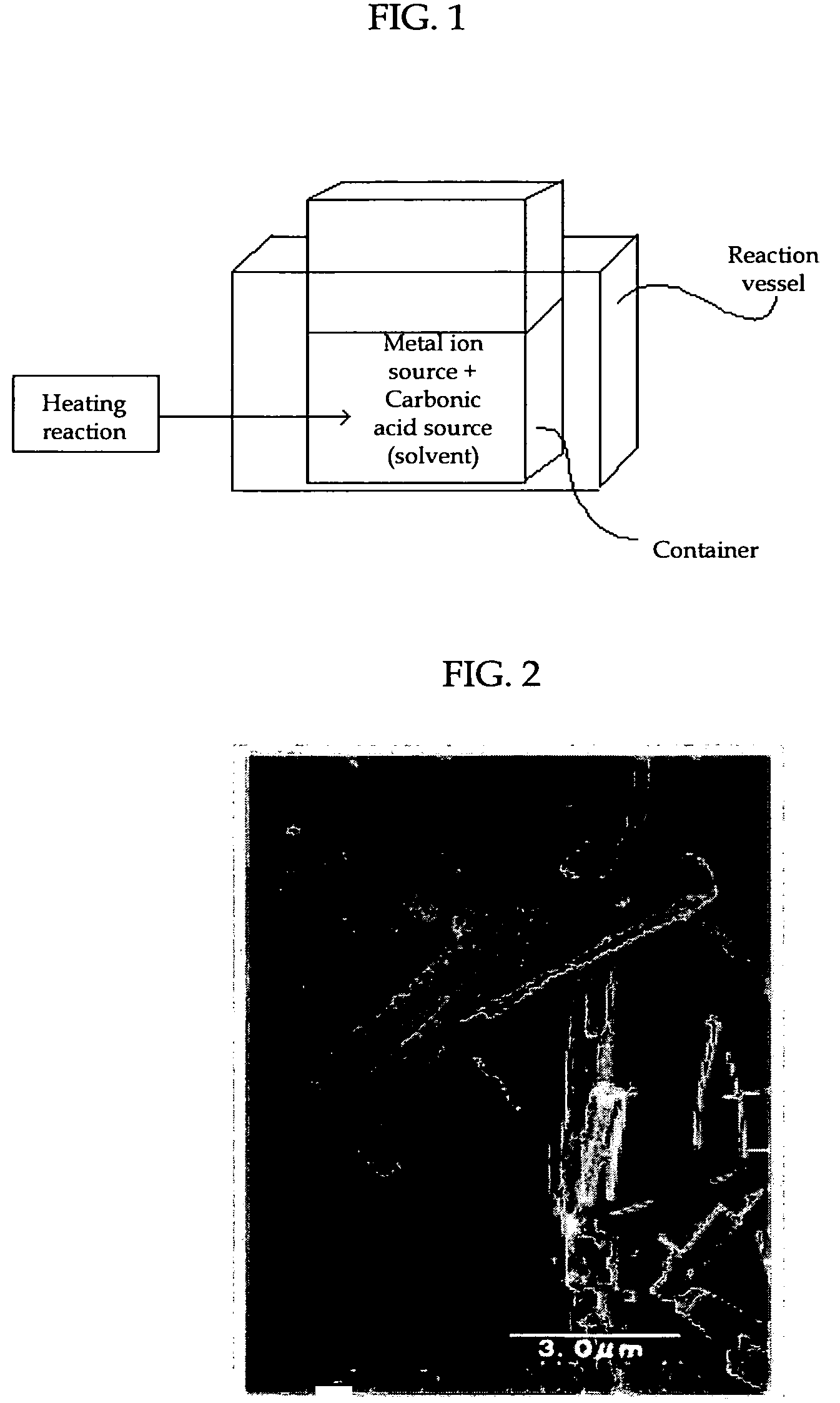
InactiveUS20080260614A1Efficiently and readily formEfficiently and readily produceCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentGas phaseRoom temperature
To provide a process for producing carbonate particles, particularly carbonate particles that are needle- or rod-shaped, which can efficiently and readily form carbonate particles which offer orientation birefringence without heating at approximately room temperature, and can control the particle size. In the process, a carbon dioxide gas from a carbonate source is released into the gas phase and the carbon dioxide gas is dissolved in a liquid containing a metal ion source to produce carbonate particles which have an aspect ratio of greater than 1, wherein the metal ion source contains at least one metal ion selected from the group consisting of Sr2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+. The carbonate particles are preferably needle- or rod-shaped, the metal ion source is a hydroxide of a metal such as Sr, the carbon dioxide gas is released in a closed vessel, and the liquid contains a solvent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
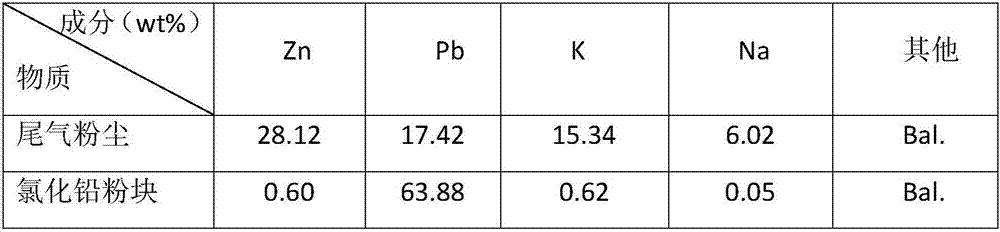
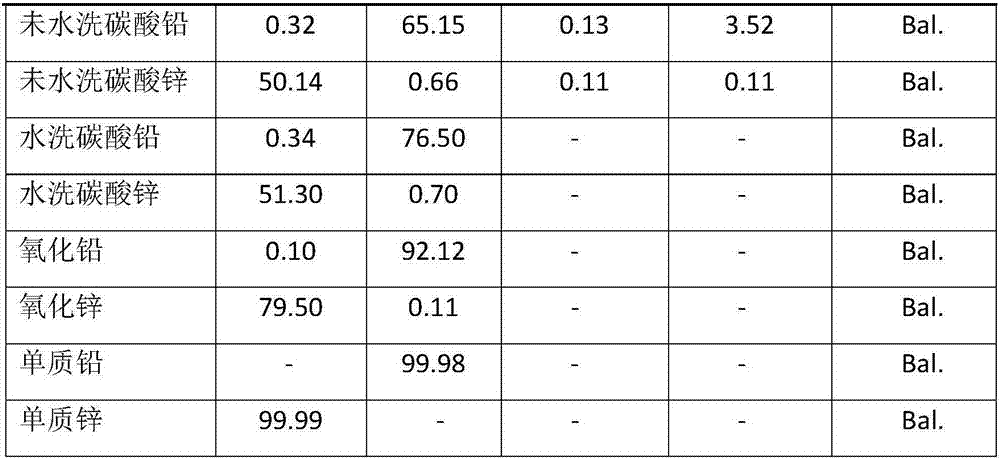
Method for refining lead and zinc from coarse zinc oxide recycled from steelmaking dust
The invention discloses a method for refining lead and zinc from coarse zinc oxide recycled from steelmaking dust and belongs to the technical field of metal recycle. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the coarse zinc oxide is made into spherical particles, and the spherical particles are added into an oxidizing smelting furnace to be heated, oxidized and refined; (2) zinc and lead elements volatilize out of a furnace body in a gaseous form and become dust after meeting oxygen, and the dust containing the zinc and lead is collected through a container; (3) the dust is put into a hydrochloric acid solution to be stirred and dissolved, the zinc component exists in a zinc ion solution form, and the lead component exists in a lead chloride solid form; (4) a sodium carbonate solution is added into the zinc ion solution, zinc carbonate is generated, a sodium carbonate solution is added into the lead chloride, and lead carbonate is generated; and (5) washing and drying are conducted. According to the method, the process is simple, operation is convenient, the purity of PbCO3 and ZnCO3 which are finally obtained can reach 98% or above, the purity of PbO and ZnO reaches 99% or above, and the elementary substances Zn and Pb reach 99.9% or above.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Carbonate Crystal, Manufacturing Method Thereof, And Transparent Optical Resin Composition
InactiveUS20090124744A1Large aspect ratioFormed easily and efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthTransmittanceCarbonate
The object of the present invention is to provide a carbonate crystal, which has oriented birefringence, is needle- or rod-like, and is able to negate the birefringence without sacrificing the light transmittance of a transparent polymeric resin when it exists in the transparent resin; a manufacturing method of the carbonate crystal; and a transparent optical resin composition comprising the carbonate resin. The carbonate crystal has an aspect ratio of two or greater, the average major axis length of 400 nm or shorter, and the variation coefficient expressed in Formula (1) below is 0.40 or less:1r×{1n-1∑i=1n(ri-r)2}12Formula(1)wherein r denotes an average major axis length, n denotes the number of particles used for the measurement of the major axis length, and n denotes the major axis length of the ith particle measured.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for preparing high sodium carbonate type lead carbonate by utilizing lead-containing fly ash
ActiveCN108946795AHigh purityImprove resource utilizationLead carbonatesHigh sodiumChemical industry
The invention provides a method for preparing high sodium carbonate type lead carbonate by utilizing lead-containing fly ash. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving the lead-containing fly ash in a sulfuric acid solution, stirring, filtering and then collecting filter residue; adopting a mixed solution of sodium chloride and calcium chloride for leaching the collected filter residue,thereby acquiring rough lead chloride; refining the acquired rough lead chloride, thereby acquiring high-purity refined lead chloride; converting by dissolving the acquired refined lead chloride intoa sodium carbonate solution, thereby acquiring sodium carbonate type lead carbonate; drying, thereby acquiring an end product of sodium carbonate type lead carbonate. Compared with the prior art, theinvention has the advantages that the lead-containing fly ash is used as the raw material for producing the high sodium carbonate type lead carbonate, the performance meets the chemical industry standard 'basic lead carbonate' HG / T 4835-2015, a reference is supplied for the recycling of lead-containing solid wastes, such as lead slag (ash), the comprehensive utilization of lead-containing fly ashresource is expanded and the additional value of the lead-containing fly ash resource is increased.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
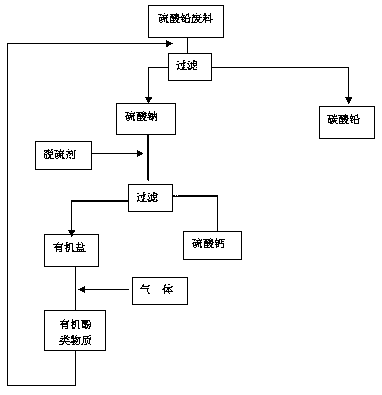
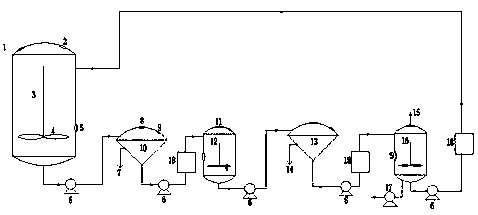
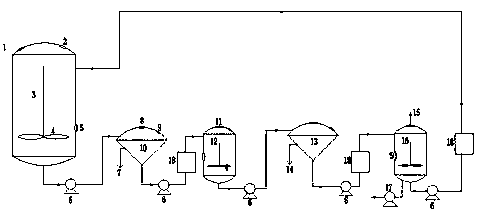
Lead sulfate waste desulfurization device and lead sulfate waste desulfurization process
PendingCN111170351ASpeed up and down convectionWell mixedCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesLead carbonatesCarbonizationProcess engineering
The invention provides a lead sulfate waste desulfurization device and a lead sulfate waste desulfurization process thereof. The device comprises a desulfurization tank, a conversion tank, a carbonization tank, filters, a pump, a liquid storage groove and conveying pipes, wherein the desulfurization tank is connected with a first filter through a conveying pipe, a solution obtained after solid-liquid separation is conveyed into the conversion tank through a conveying pipe, the conversion tank is connected with a second filter through a conveying pipe, a solution obtained after solid-liquid separation is conveyed into the carbonization tank, and the molten liquid in the carbonization tank is pumped into the liquid storage groove through a pump and is to be transferred into the desulfurization tank so as to be recycled. According to the invention, solutions in a desulfurization tank, a conversion tank and a carbonization tank are circularly arranged, so that the reaction efficiency is effectively improved while the conveying pipe of the tank body is blocked due to slurry precipitation or scaling in the tank body is effectively reduced; and a carbonizing agent and organic phenolic substances are regenerated and recycled, so that the desulfurization cost is greatly reduced, the environmental pollution is effectively reduced, the production efficiency is effectively improved, and the desulfurization purpose is thoroughly achieved.
Owner:湖南省金翼有色金属综合回收有限公司
Process for Producing Carbonate Particles
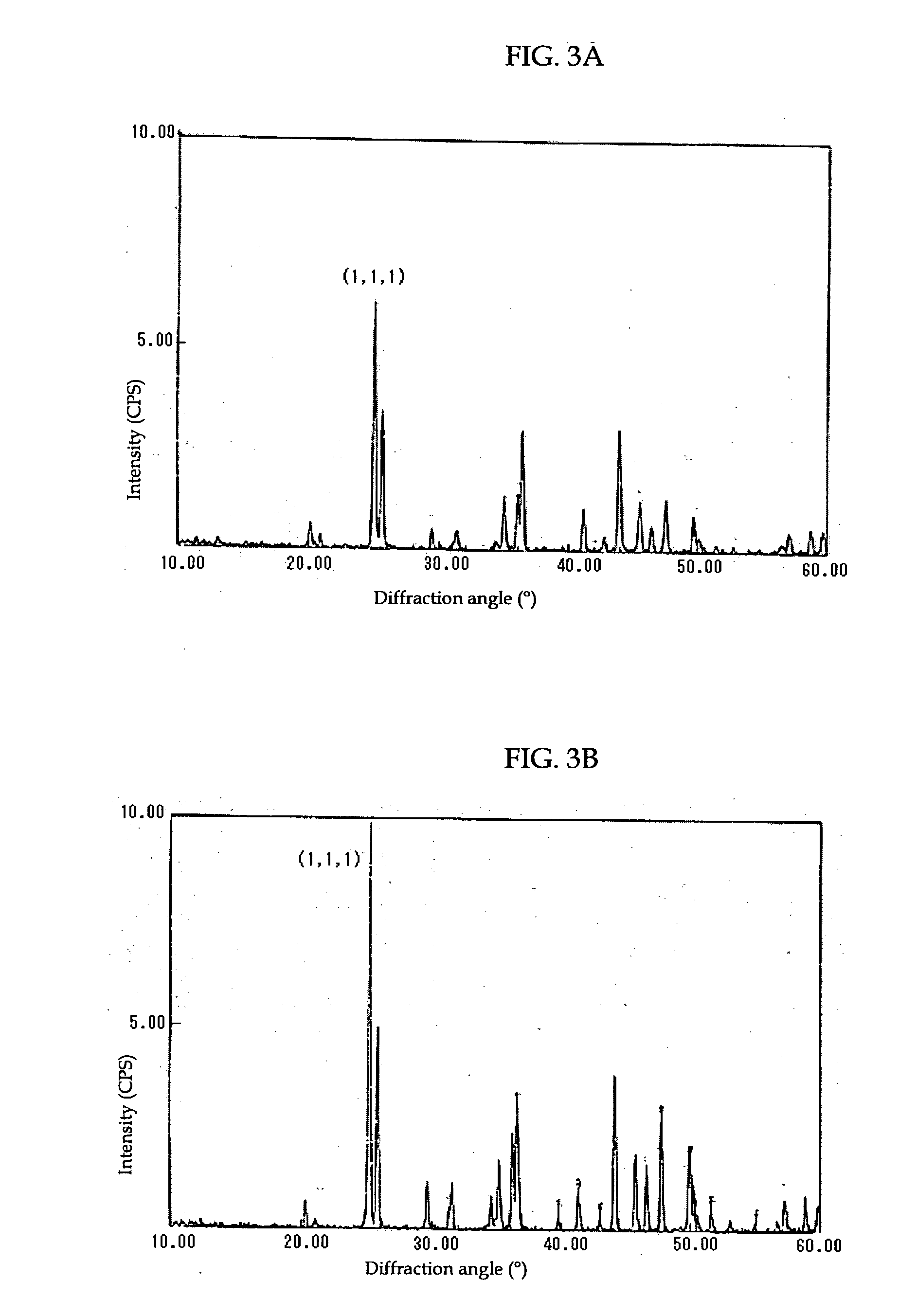
InactiveUS20080267854A1High crystallinityLess-prone to agglomerationStrontium carbonatesMagnesium carbonatesFull width at half maximumX-ray
To provide a process for producing carbonate particles, capable of efficient, easy formation of carbonate particles which have high crystallinity, less prone to agglomeration and offer orientation birefringence, particularly carbonate particles that are needle- or rod-shaped, and of controlling the particle size. In the process a metal ion source and a carbonate ion source are heated together in a liquid of 55° C. or higher for reaction to produce carbonate particles with an aspect ratio of greater than 1, wherein the metal ion source contains at least one metal ion selected from the group consisting of Sr2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+. The carbonate particles are preferably needle- or rod-shaped, pH of the liquid after heating reaction is preferably 8.20 or more, and in its X-ray diffraction spectrum the full-width at half maximum of the diffraction peak corresponding to (111) plane is preferably less than 0.8°.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Conversion process comprising permutable hydrodemetallization guard beds, a fixed-bed hydrotreatment step and a hydrocracking step in permutable reactors
ActiveUS10597591B2Increase the number ofProblematic for quality of productRefining with oxygen compoundsLead carbonatesFixed bedProcess engineering
The invention relates to a process for the treatment of a hydrocarbon-containing feedstock making it possible to obtain a heavy hydrocarbon-containing fraction having a low sulphur content, said process comprising the following stages: a) a stage of hydrodemetallization in permutable reactors b) a stage of fixed-bed hydrotreatment of the effluent originating from stage a), c) a stage of hydrocracking in permutable reactors of the effluent originating from stage b), d) a stage of separation of the effluent originating from stage c), e) a stage of precipitation of the sediments, f) a stage of physical separation of said sediments from the heavy liquid fraction originating from stage d), g) a stage of recovery of the distillate cut used in stage e).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Recovery of lead in form of high purity lead carbonates from spent lead batteries incl. electrode paste
InactiveUS20100034715A1Promote commercializationHigh puritySolvent extractionLead carbonatesSodium acetateLead sulfate
Wet process of low environmental impact recovers the lead content of an electrode slime and / or of lead minerals in the valuable form of high purity-lead carbonates that are convertible to highly pure lead oxide by heat treatment in oven at relatively low temperature, perfectly suited for making active electrode pastes of new batteries or other uses. The process basically comprises the following steps: a) adding sulphuric acid to a different acid leach suspension of the starting impure material for converting all dissolved lead compounds to insoluble lead sulphate; b) separating the solid phase constituted by lead sulphate and undissolved impurities from the acid leach solution; c) selectively dissolving lead sulphate contained in said separated solid phase in an aqueous solution of a lead solubilizing compound comprising preferably sodium acetate; d) separating the solution containing dissolved lead sulphate from the solid phase residue including undissolved impurities; e) adding to the separated solution of lead sulphate a carbonate of the same cation of said dissolving compound for forming insoluble lead carbonate and / or and lead oxycarbonate and a dissolved sulphate of the same cation; f) separating the precipitated carbonate and / or oxycarbonate of lead from the dissolving solution now containing also sulphate of the cation of said solubilizing compound.
Owner:MILLBROOK LEAD RECYCLING TECH
Method for preparing a mixture of lead carbonate and silver carbonate with waste residue gained from lithopone production
InactiveCN102167393AEasy to operateLow investment costLead carbonatesSulfur compoundsLead carbonateSulfur product
The invention provides a method for preparing a mixture of lead carbonate and silver carbonate with waste residue gained from lithopone production. The method comprises making the waste residue gained from the lithopone production react with carbonic acid, to obtain a mixture containing the lead carbonate, the silver carbonate and elemental sulfur; obtaining clarifying fine emulsion and an elemental sulfur filter cake, after coarse filtration of the mixture; obtaining the elemental sulfur product, after deep processing of the elemental sulfur filter cake; obtaining a filter cake containing the lead carbonate and the silver carbonate, and sodium chloride solution, after fine filtration of the obtained clarifying fine emulsion; obtaining a mixed product of the lead carbonate and the silver carbonate, after washing, drying and crashing the filter cake containing the lead carbonate and the silver carbonate; distilling the sodium chloride solution to sodium chloride saturated solution and cooling; and obtaining the sodium chloride product.
Owner:王嘉兴
A kind of preparation method for the lead carbonate combustion catalyst of solid propellant
ActiveCN102259909AThermosynthesisGood dispersionLead carbonatesPressure gas generationLead zirconate titanateDispersity
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lead carbonate combustion catalyst for a solid propellant, which comprises the main step of: directly performing a solvent heating reaction of lead zirconate titanate sol for realizing the sol-solvent heating synthesization of a lead carbonate powder body; firstly, configuring the lead zirconate titanate sol of a certain concentration according to chemical components; then, directly putting the sol into a line of a high-pressure reaction kettle; and performing the solvent heating reaction at high temperature of 120 DEG C to 240 DEG C and highpressure to obtain the lead carbonate powder body. The invention has the advantages of good product crystallization performance, stable quality, high purity, good granule dispersity of powder body, simple technological process, easy control, no pollution, low cost and easy scale production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Lead-carbon metal composite material for electrodes of lead-acid batteries and method of synthesizing same
InactiveUS20180261831A1Inhibition formationImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyLead-acid accumulatorsAlkaline earth metalCarbide
The invention is directed to a radical improvement of the specific electrochemical and corrosive characteristics of a lead-acid battery without a drastic change in the process of battery producing. The lead-carbon metal composite material contains from 0.1 to 10% by weight of carbon, lead is the remainder, while the structure of the material contains carbon allotropic modifications from graphene to graphite. The method for material synthesizing is characterized in that lead or its alloys are melted in a melt of alkaline and / or alkaline earth metal halides containing from 1 to 20 wt. % of metal carbides or non-metals with a particle size of 100 nm to 200 μm, or solid organic substances, for 1-5 hours at a temperature of 700-900° C.
Owner:ELSHINA VARVARA ANDREEVNA
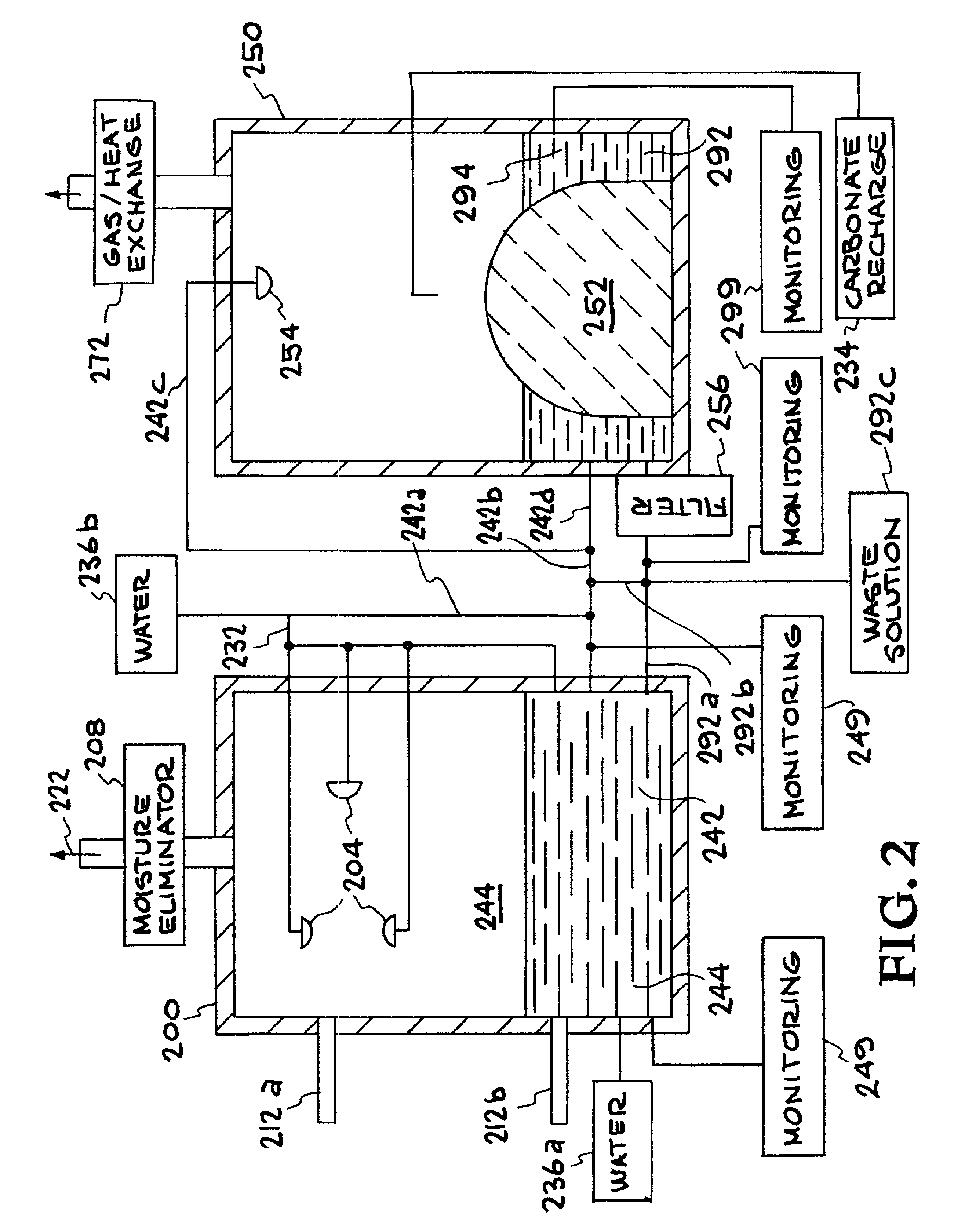
Methods and systems using electrochemical cells for processing metal sulfate compounds from mine waste and sequestering CO2
InactiveUS9695050B2Reduces or eliminates the ARD potential of unreacted sulfateEliminates the metal leaching potentialWaste processingSolid waste disposalPyriteDivalent metal
Systems and methods are provided for processing metal sulfate compounds and sequestering CO2. These systems and processes involve one or more electrochemical cells for producing an alkali-containing catholyte and involve a CO2 absorption reactor operatively connected to the electrochemical cell and to a CO2 source. The CO2 absorption reactor receives the alkali-containing catholyte and CO2 gas for forming an alkaline carbonate solution. The alkaline carbonate solution is directed to a vessel where it reacts with an acidic sulfate solution comprising metal ions resulting in precipitation of solid metal carbonate compounds. The acidic sulfate solution may comprise sulfide leachates from acid mine drainage, sulfide mine tailings and / or reacted pyrite concentrate. The acidic sulfate solution may be circulated through an optional SO2 reduction reactor prior to reaction in the vessel. The SO2 reduction reactor reduces trivalent metal compounds present in the acidic sulfate solution to divalent metal compounds.
Owner:TERRA CO2 TECH HLDG INC
Preparation method of lead oxide
PendingCN112551573ASimple processImprove efficiencyLead-acid accumulatorsFinal product manufactureLead carbonateExhaust fumes
The invention relates to a preparation method of lead oxide, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1. desulfurizing waste lead plaster, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a lead carbonate-containing cured product; and 2, carrying out high-temperature smelting on the lead carbonate-containing cured product to obtain lead oxide and waste gas, inputtingthe waste gas into an ammonia water device to produce a sulfur removal agent containing ammonium carbonate, and using the sulfur removal agent containing ammonium carbonate to desulfurize the waste lead plaster in the step 1. The preparation method of lead oxide is simple in process, high in efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:HANGZHOU QIANLIZHIXING TECH CO LTD
Pretreatment of circuit board incineration soot and recovery method of bromine
ActiveCN108118157BEasy to recycleNo emissionsZinc sulatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesRecovery methodSlag
The invention relates to the pretreatment of circuit board incineration soot and the recovery method of bromine, which belongs to the field of comprehensive recovery of valuable metals by soot full wet method, and particularly relates to the recovery of valuable metals, the enrichment of precious metals and the recovery of bromine salts in the pretreatment process of circuit board incineration soot. It mainly includes mixed alkali leaching, copper extraction and stripping to recover copper, neutralization and precipitation to separate lead and zinc, bromine evaporation and crystallization, mixed alkali leaching solution regeneration, pickling to remove zinc, zinc evaporation and crystallization, mixed alkali leaching slag dezincification of copper and other steps. Compared with the traditional soot comprehensive recovery process, the invented technology maximizes the recovery of valuable metals such as copper, zinc, lead and the enrichment of silver and other precious metals in the soot pretreatment process, and at the same time separates and recovers bromine salts, which has the advantages of recovery High added value, no tail liquid discharge and other characteristics.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
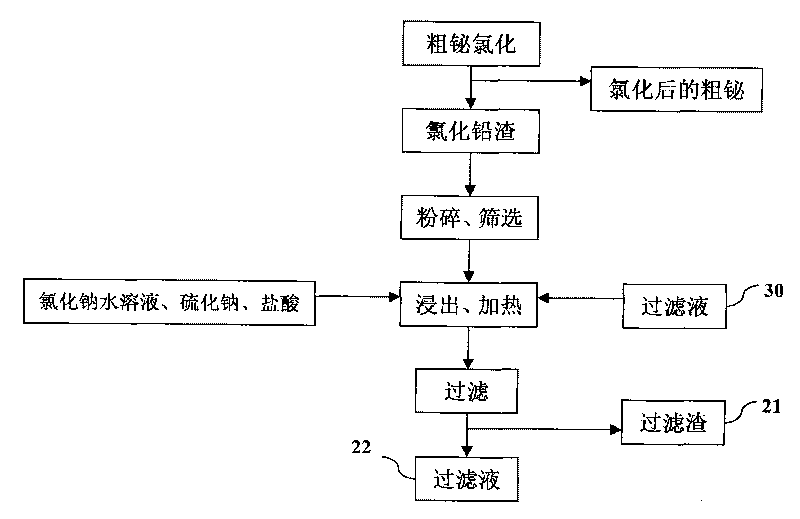
Process for producing basic lead carbonate
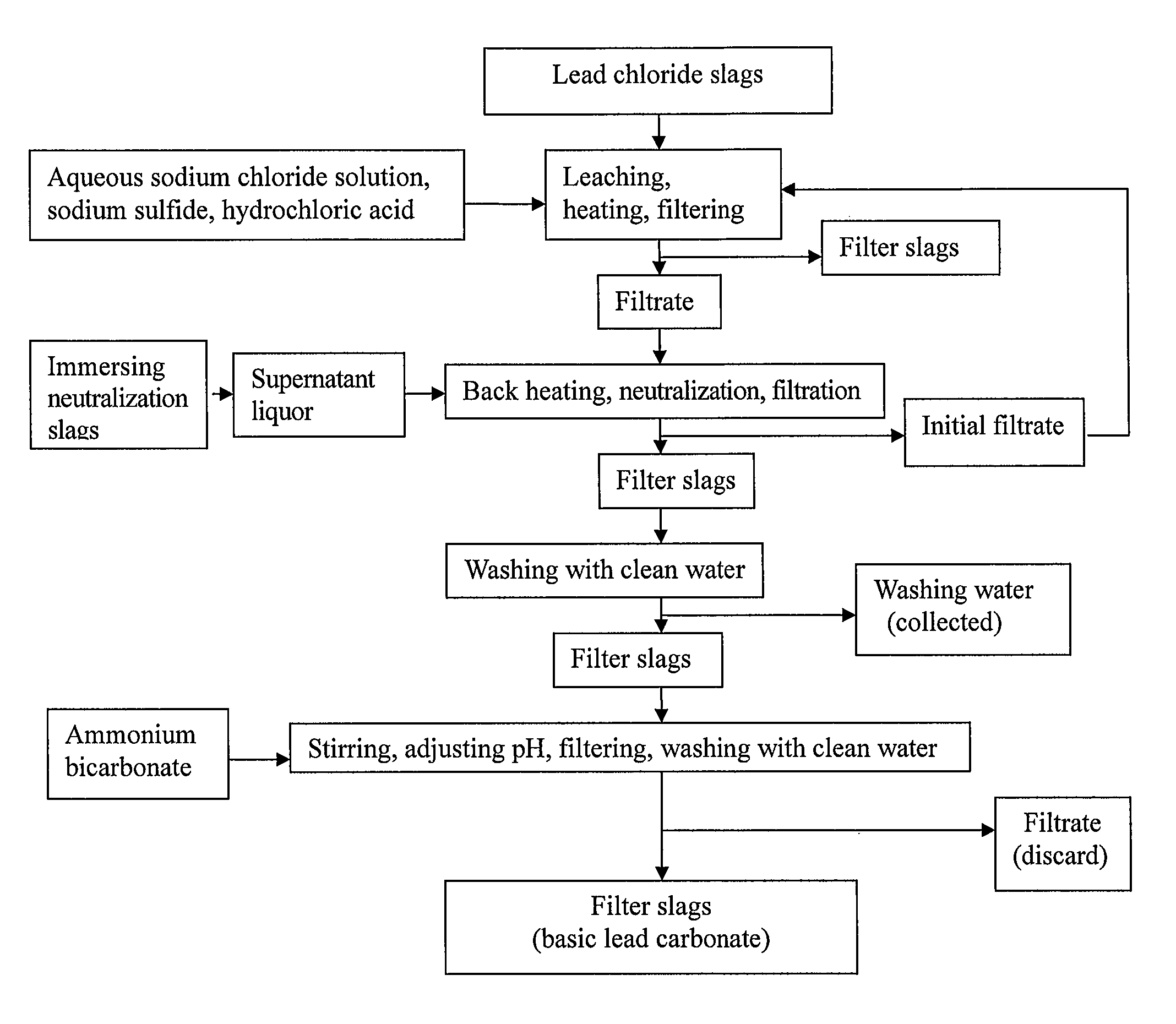
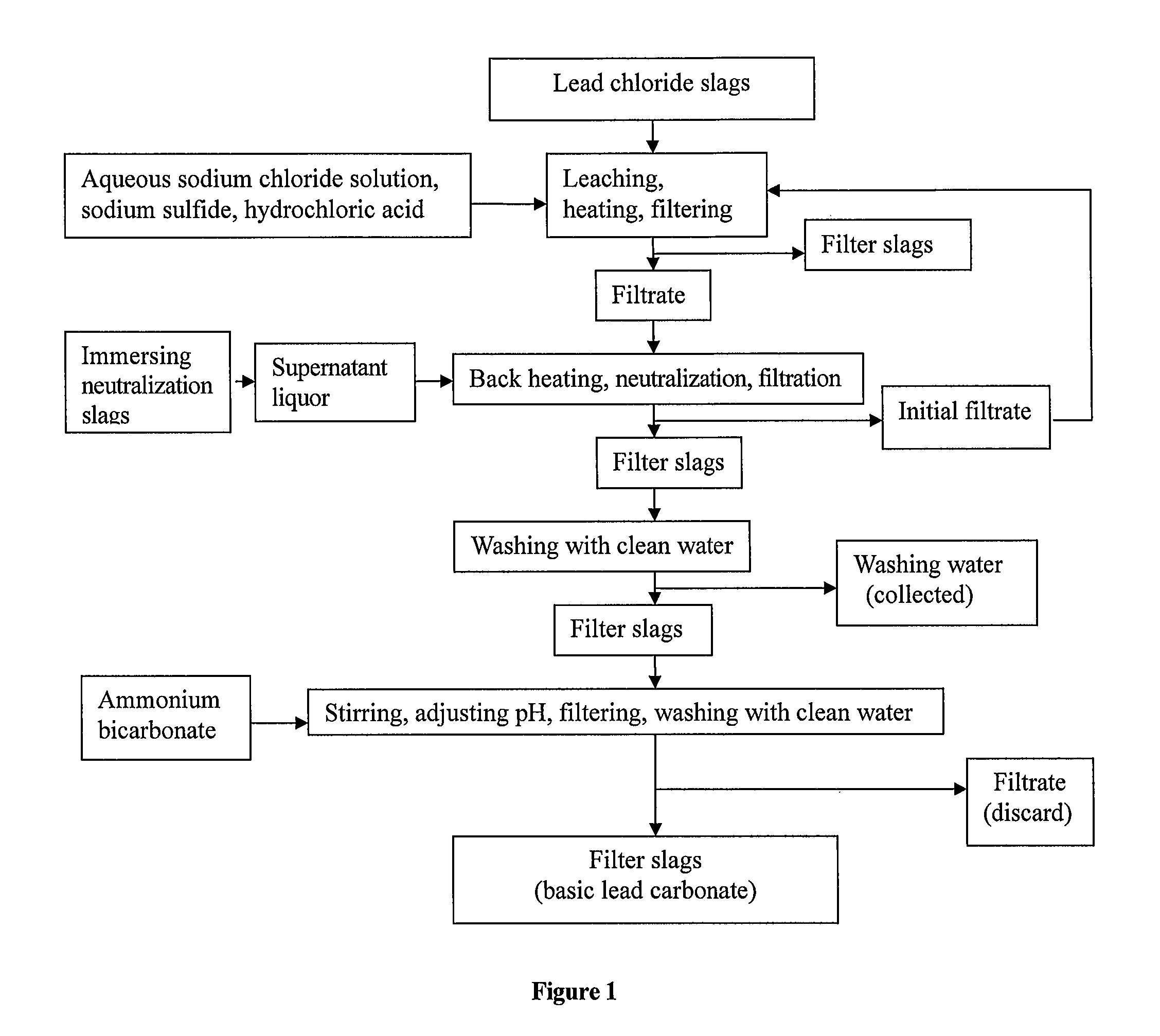
InactiveUS8568670B2Simple processSolve the real problemTin compoundsElectrolysis componentsLead carbonateSlag
A process for producing basic lead carbonate is provided. The process comprises: (1) immersing neutralization slag to obtain sodium hydroxide solution; (2) leaching lead chloride slag with the aqueous solution containing sodium chloride and hydrochloric acid, adding sodium sulfide and filtering; (3) neutralizing the filtrate with sodium hydroxide solution, filtering and washing the precipitate; and (4) converting the precipitate to basic lead carbonate with ammonium bicarbonate, crystallizing and washing. Said neutralization slag and lead chloride slag are the redundant slag from fire refining bismuth. Said process makes better use of the redundant slag from fire refining bismuth, saves resources and reduces environmental pollution.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP
Method for recovering lead oxide from waste lead paste
A method for recovering lead oxide from a pre-desalted lead paste, comprising the following steps: a. dissolving the pre-desalted lead plaster by using a complexing agent solution, and making all of PbO therein react with the complexing agent to generate lead complexing ions, obtaining a lead-containing solution and a filter residue; b. adding a precipitant to the lead-containing solution, and then the precipitant reacting with the lead complexing ions to generate a lead salt precipitate and the regenerated complexing agent; c. calcining the lead salt precipitate to obtain lead oxide and regenerate the precipitant. The final recovery rate of lead oxide of the method can reach 99% or more.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Acrylic-fiber finish, acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production, and carbon-fiber production method
ActiveUS8323743B2Improve toughnessMinimum fiber separationSesquicarbonate preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCarbon fibersPolymer science
An acrylic-fiber finish for use in carbon-fiber production contributes to high tenacity of resultant carbon fiber. The acrylic-fiber finish for carbon-fiber production includes an epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and a surfactant. The weight ratios of the epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and the surfactant in the total of the non-volatile components of the finish respectively range from 1 to 95 wt % and from 5 to 50 wt %. The carbon fiber production method includes a fiber production process for producing an acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production by applying the finish to an acrylic fiber which is a basic material for the acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production; an oxidative stabilization process for converting the acrylic fiber produced in the fiber production process into oxidized fiber in an oxidative atmosphere at 200 to 300 deg.C.; and a carbonization process for carbonizing the oxidized fiber in an inert atmosphere at 300 to 2,000 deg.C.
Owner:MATSUMOTO YUSHI SEIYAKU
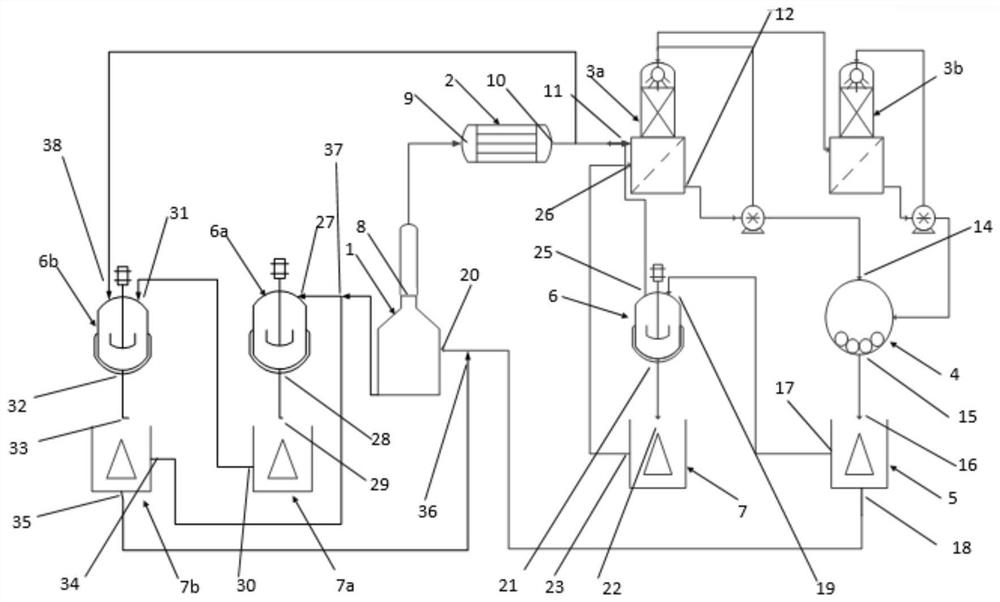
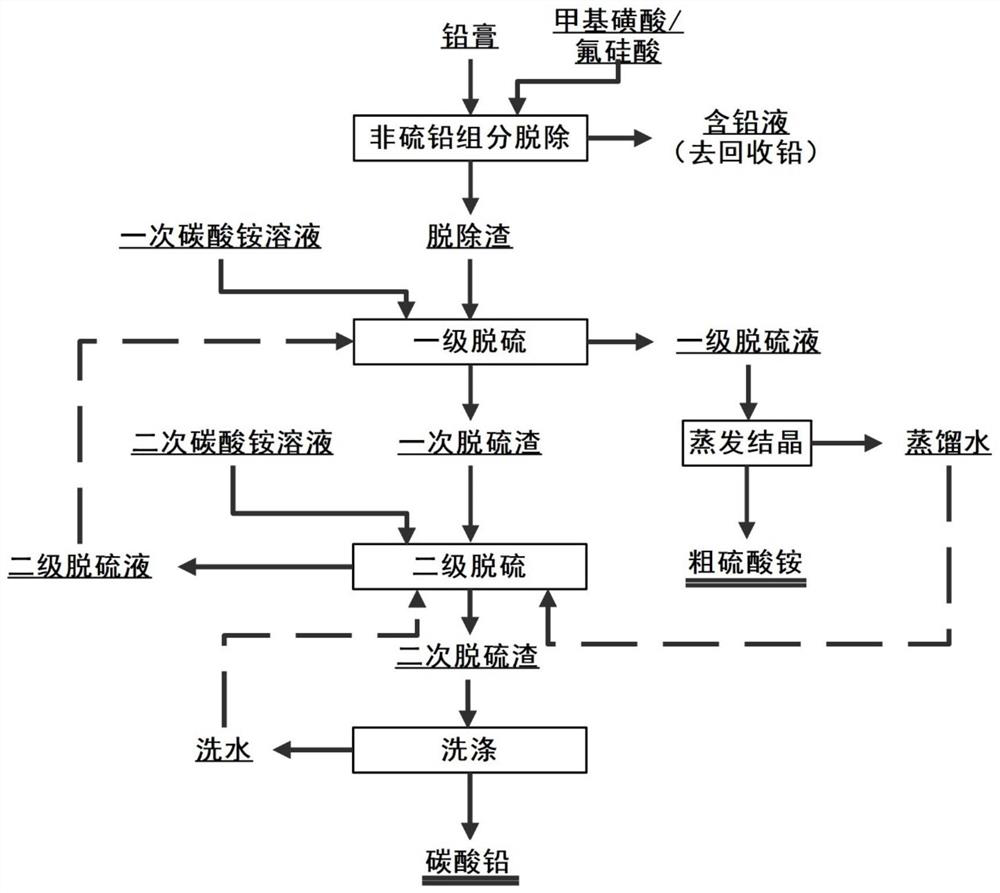
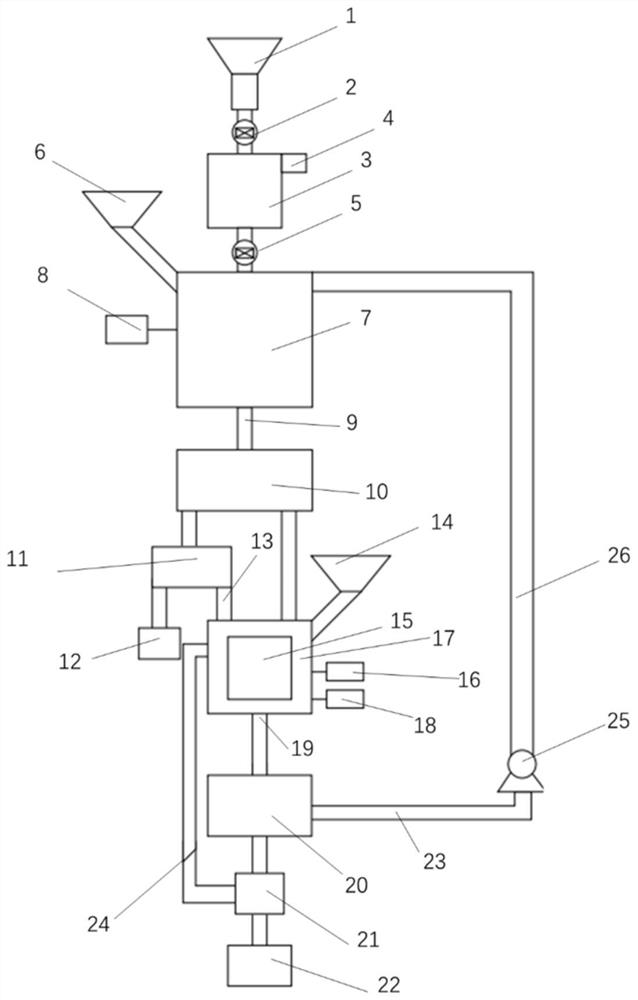
Method and device for two-stage mechanical strengthening desulfurization of waste lead plaster
PendingCN114317947AImprove desulfurization efficiencyReduce desulfurization costLead carbonatesProcess engineeringSlurry
The invention relates to a method and a device for two-stage mechanical strengthening desulfurization of waste lead plaster. The method mainly comprises the steps of non-sulfur lead component removal, primary desulfurization, evaporative crystallization, secondary desulfurization, washing and the like. The invention also discloses a device special for the method. The core components of the device are a primary desulfurization reactor, a secondary desulfurization reactor, a slurry circulating part and a high-efficiency product collecting part. Compared with the prior art, the problems of incomplete product layer coating and reaction in the lead plaster desulfurization process are reduced, and the problems of long desulfurization reaction time, low solid-liquid ratio and the like in the lead plaster desulfurization process are solved. Meanwhile, the modules of graded grinding and desulfurization of lead plaster slurry, efficient collection of products, recycling of desulfurization liquid and the like are integrated, the desulfurization efficiency is further improved, and the desulfurization cost is reduced. The method has the characteristics of cleanness, high efficiency, remarkable energy conservation and emission reduction and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for producing potassium sulfate
ActiveUS20200109090A1Low costEfficient productionLead carbonatesSulfate/bisulfate preparationProcess engineeringEnvironmental engineering
Systems and methods for producing potassium sulfate. Such a method involves providing an industrial waste material that includes at least one metal sulfate or a metal product that has been reacted with sulfuric acid to produce metal sulfates, and then reacting the metal sulfate with potassium carbonate to produce a byproduct that contains potassium sulfate.
Owner:MARSULEX ENVIRONMENTAL TECH LLC
Method for preparing lead carbonate combustion catalyst used for solid propellant
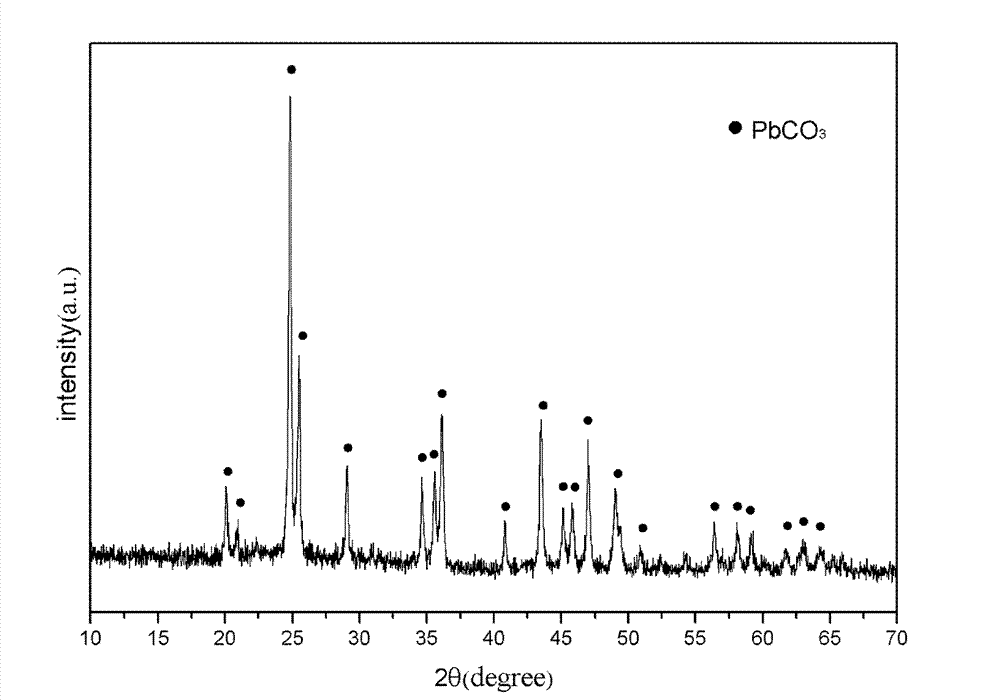
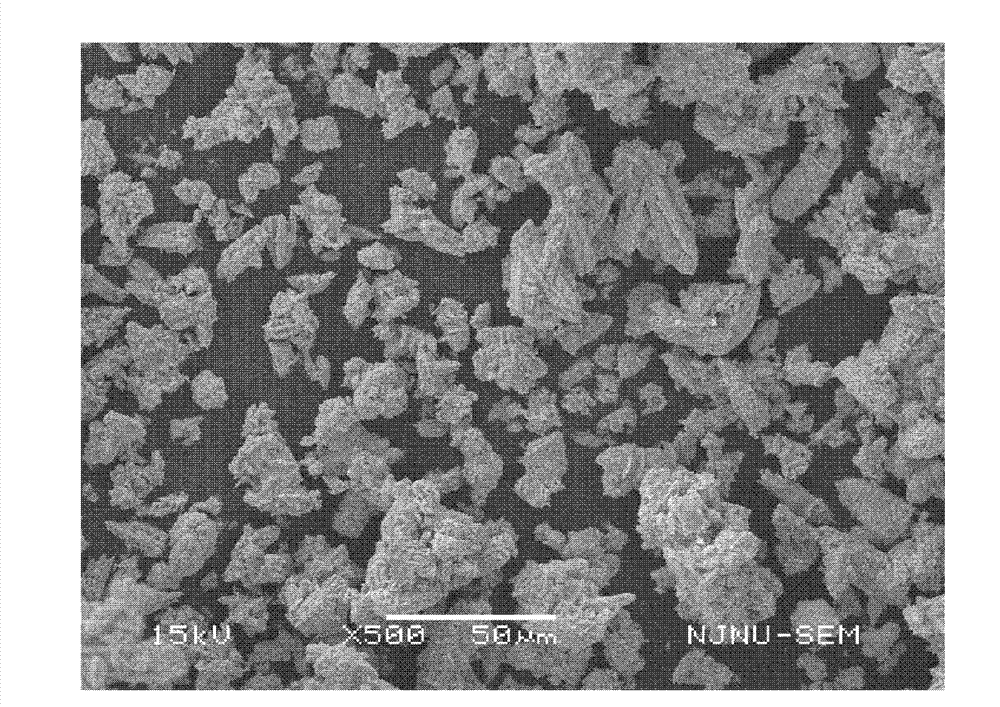
ActiveCN102259908BHigh purityImprove liquidityLead carbonatesPressure gas generationLead carbonatePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a method for preparing a lead carbonate combustion catalyst used for a solid propellant, comprising the following steps of: (1) weighing lead-based oxide, and adding the lead-based oxide into an organic solvent to obtain a lead-based oxide solution; (2) regulating the concentration of lead ions in the obtained solution to be 0.1-1mol / L, and stirring; adding the solution obtained in the step (2) into a high pressure reaction kettle, insulating for 2-32 hours at the temperature of 150-240 DEG C, carrying out solvent heat treatment, and then cooling to room temperature; and taking out a reactant, cleaning with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol sequentially after filtering, and stoving for 6-12 hours at the temperature of 60-100 DEG C to obtain lead carbonatepowder. In the invention, a solvent hot method is adopted to prepare the lead carbonate powder, and the lead-based oxide is directly dissolved into an organic solvent to carry out a hydro-thermal reaction. The technological process in the invention is simple, is easy to control, produces no pollution, has low cost and is easy for mass production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com