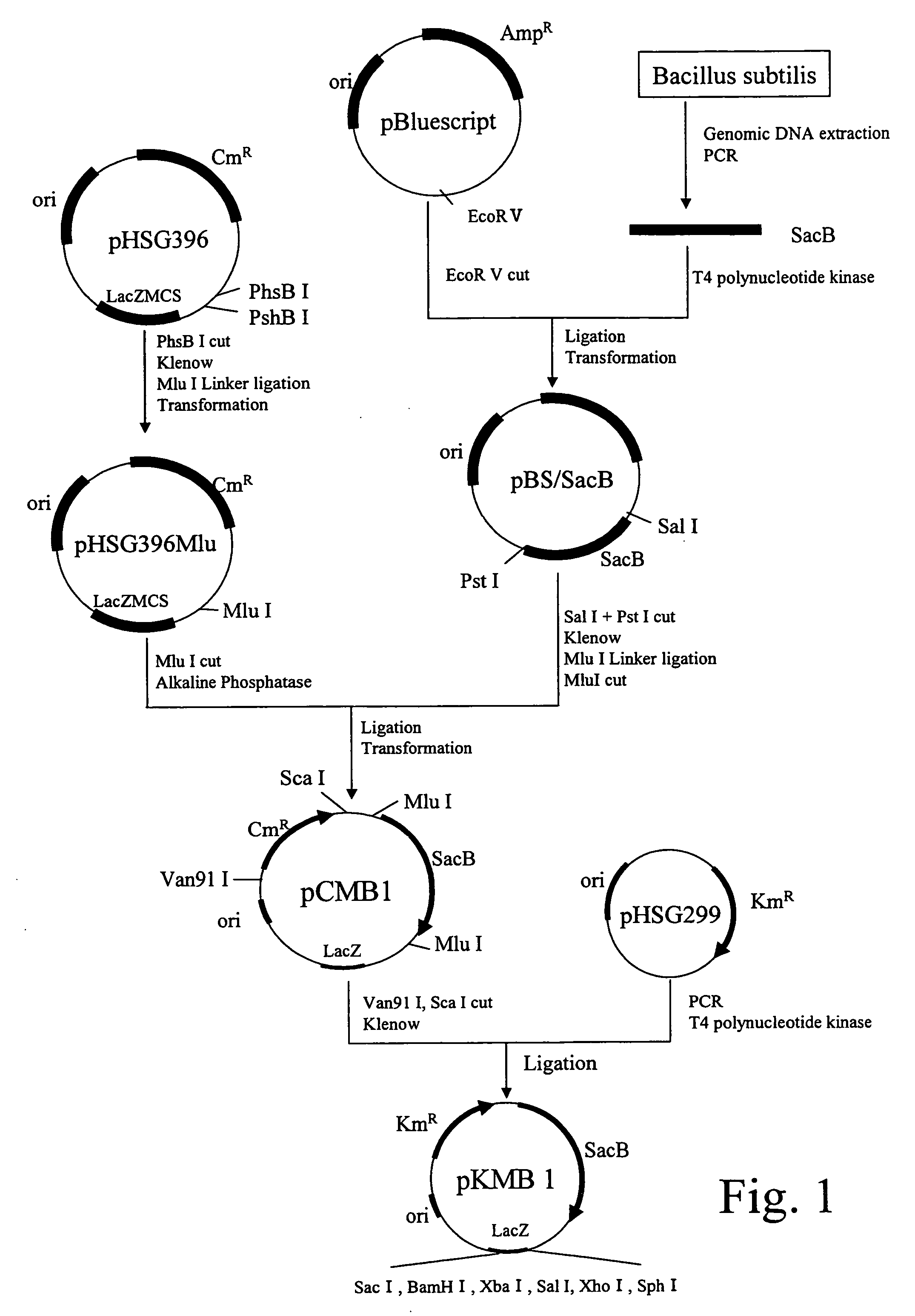
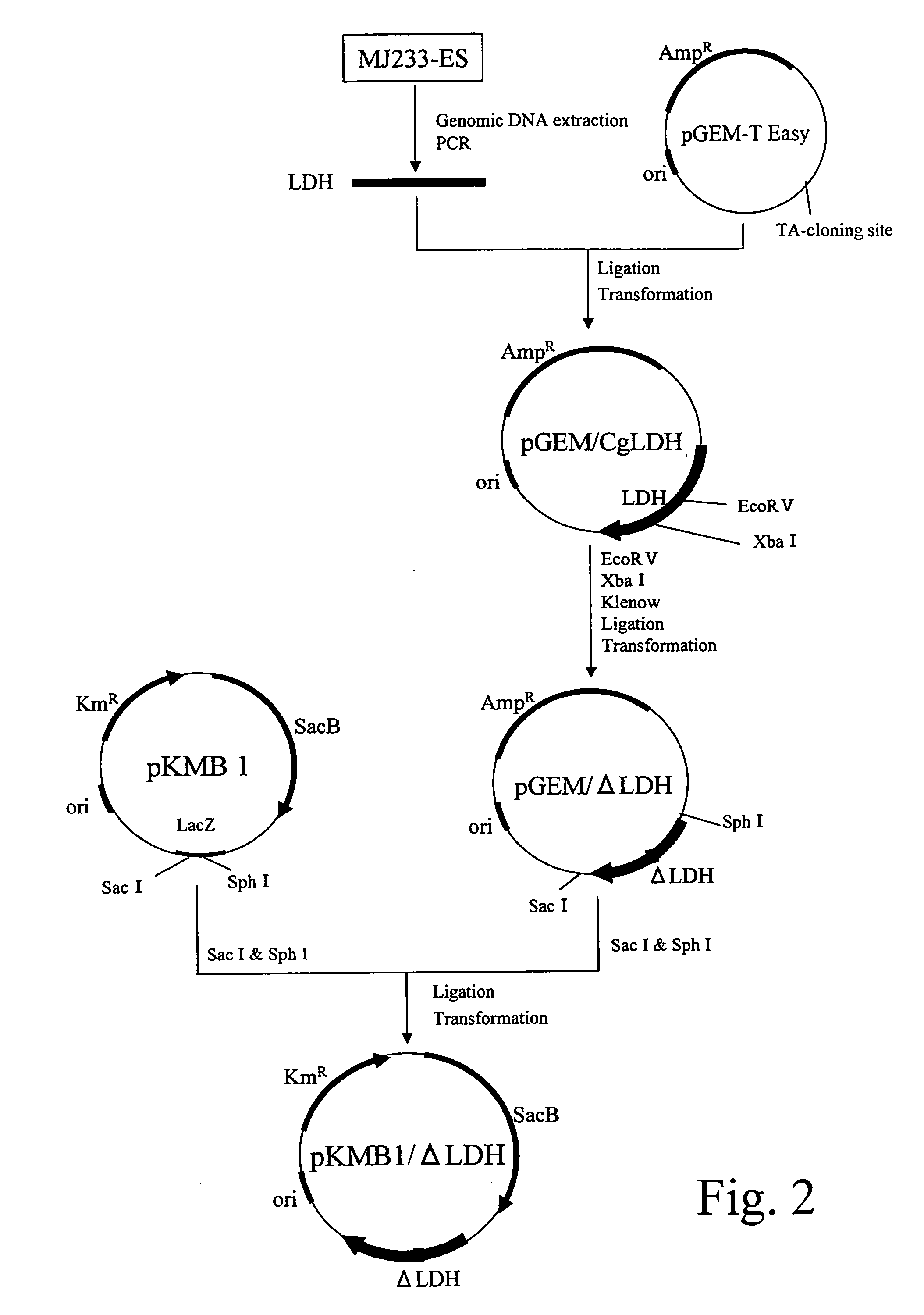
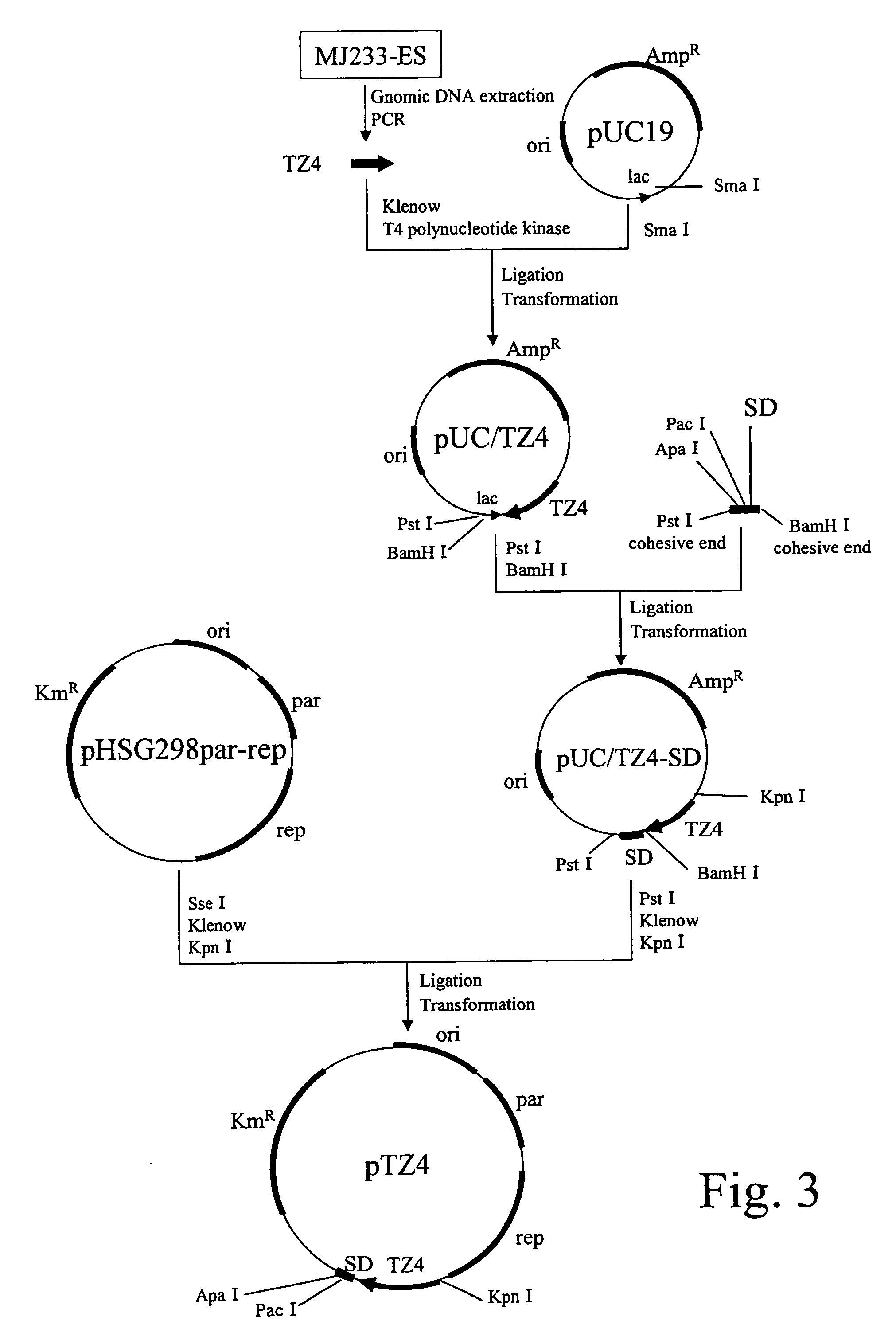
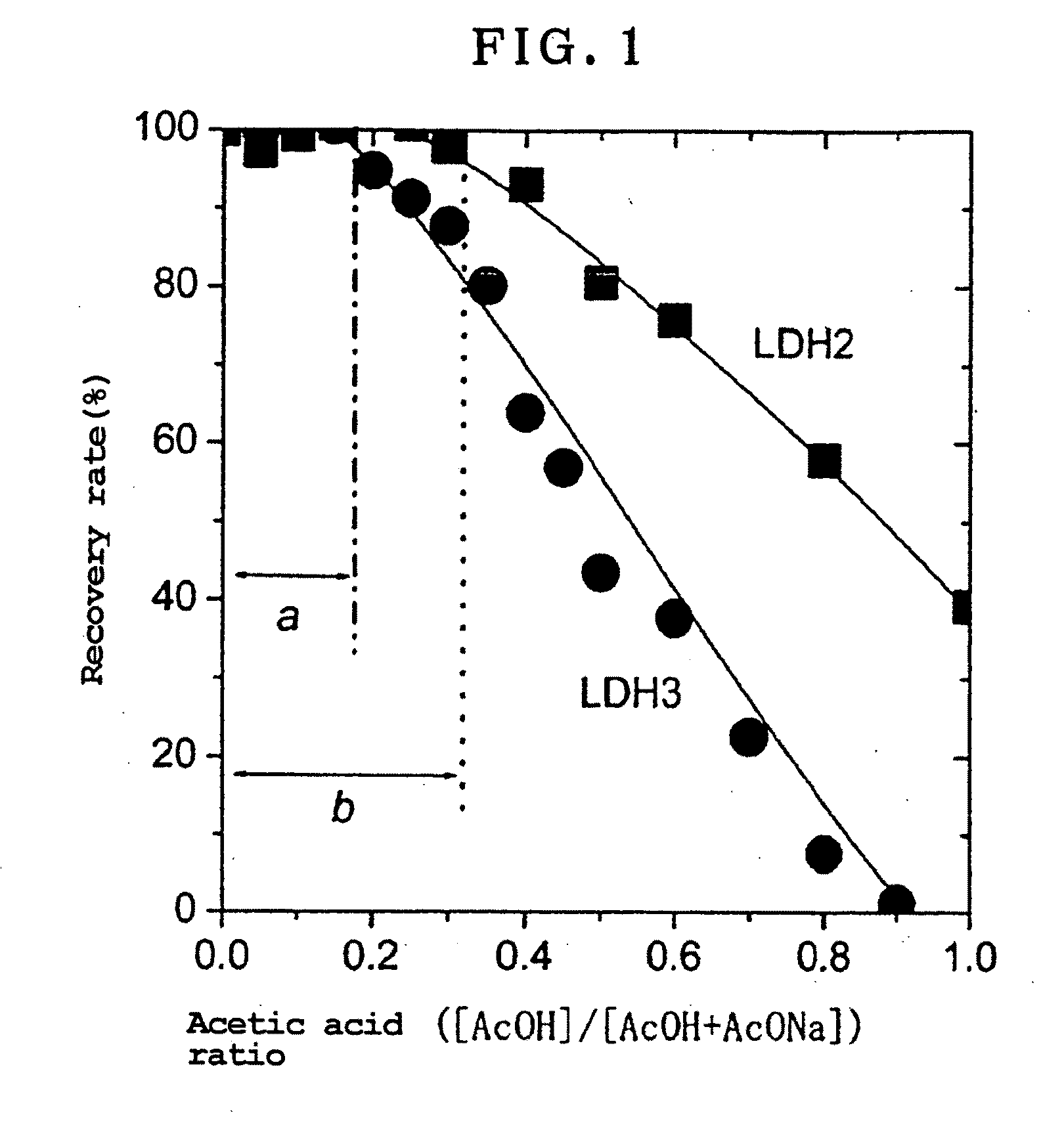
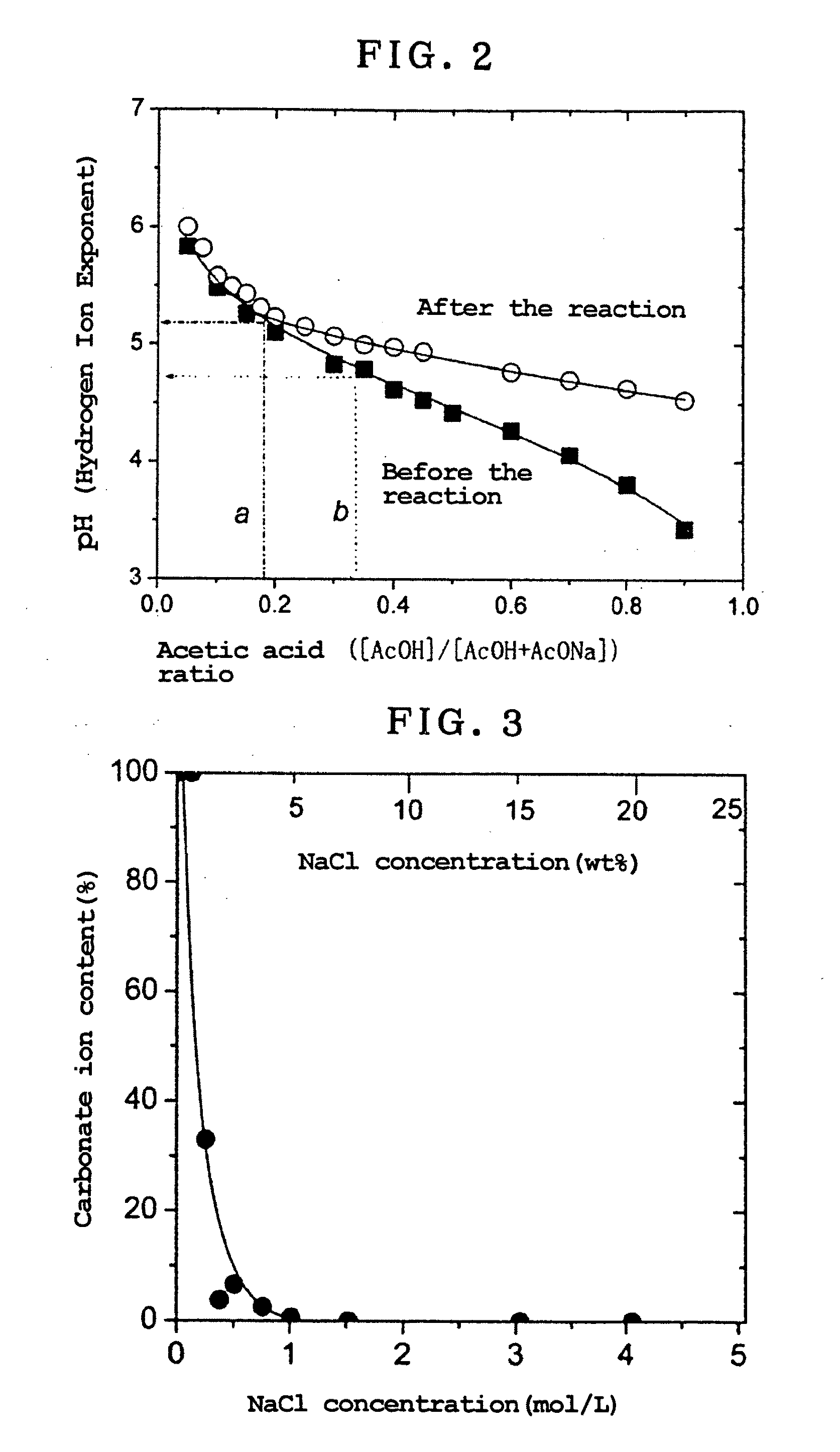
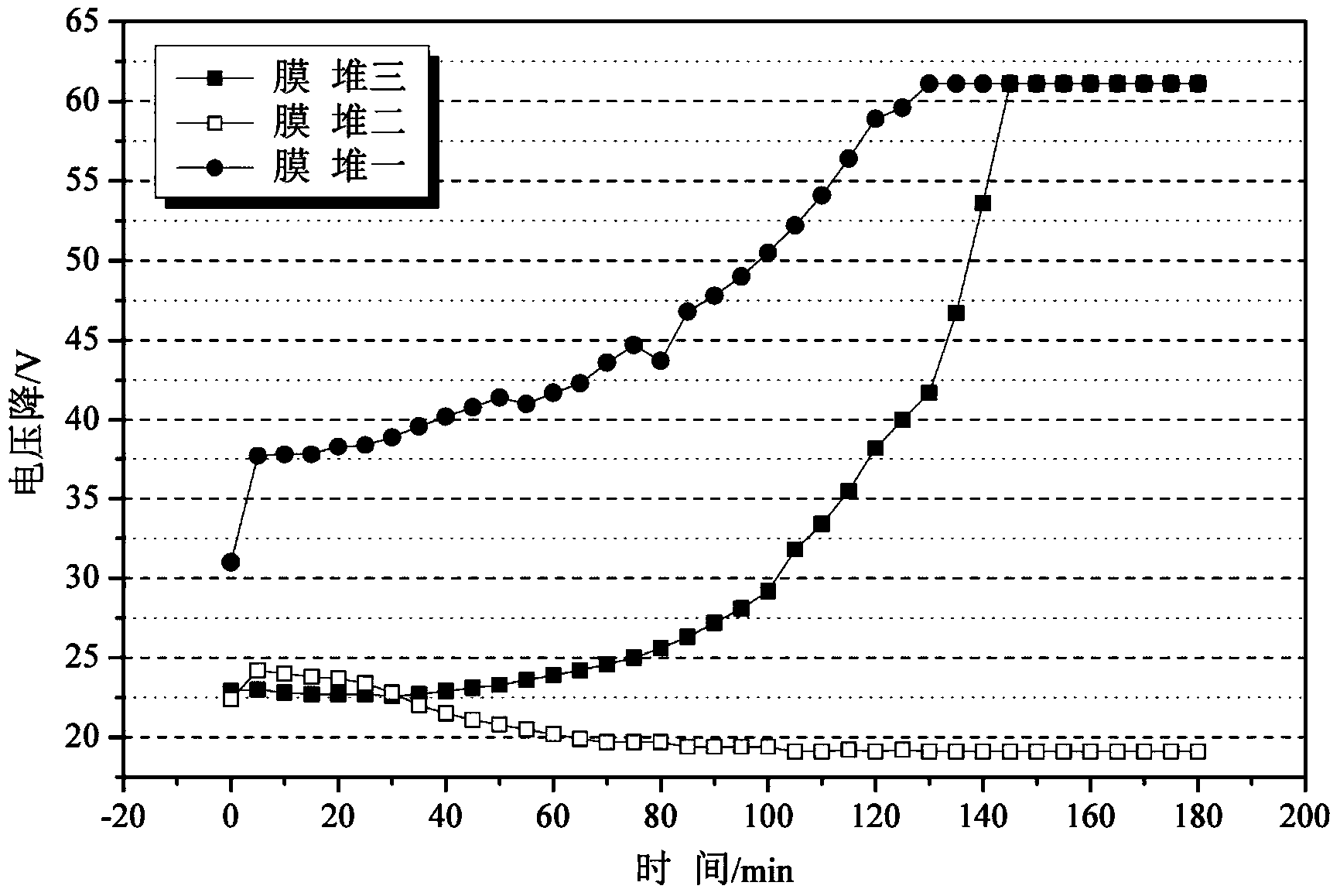
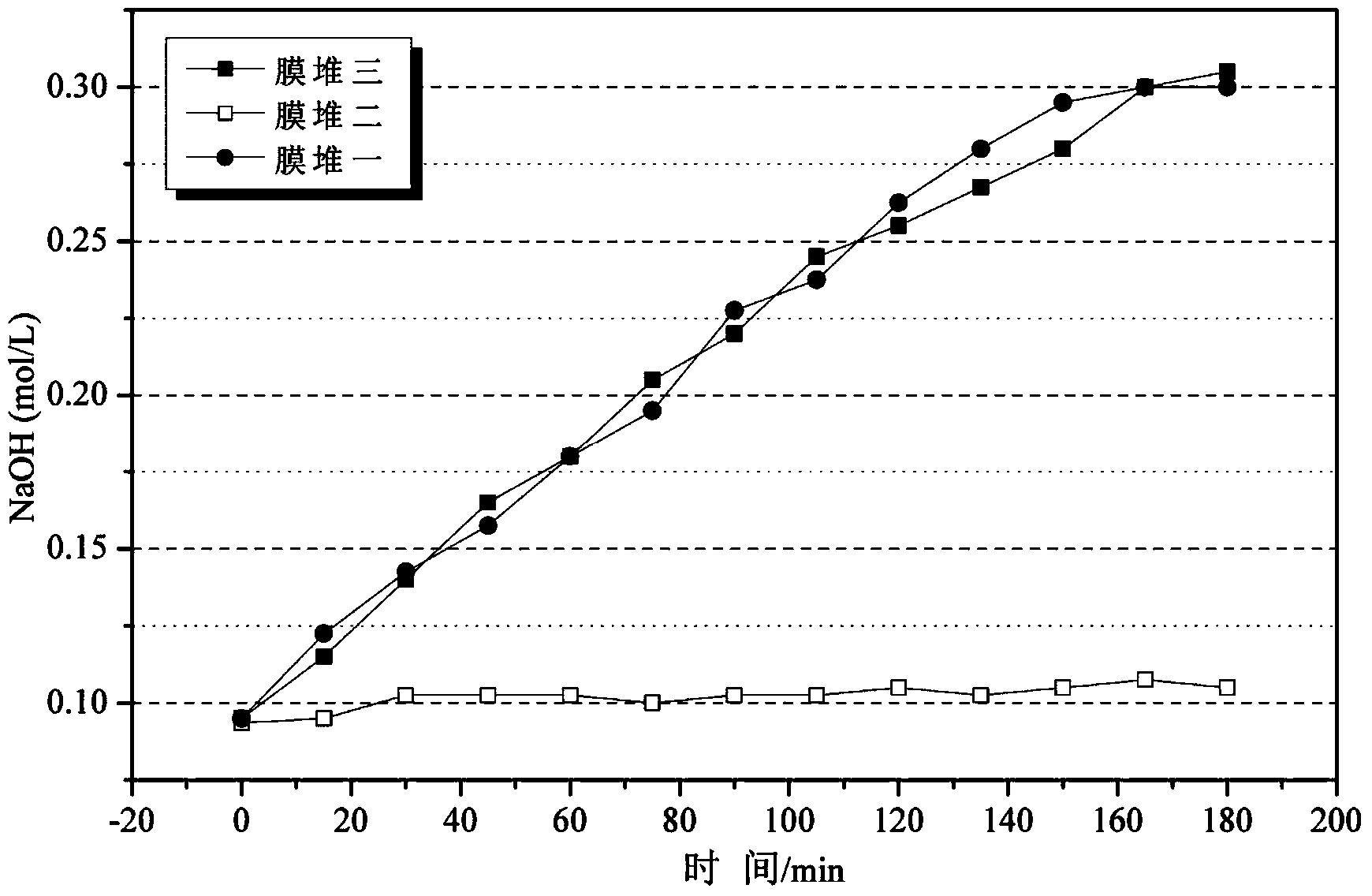
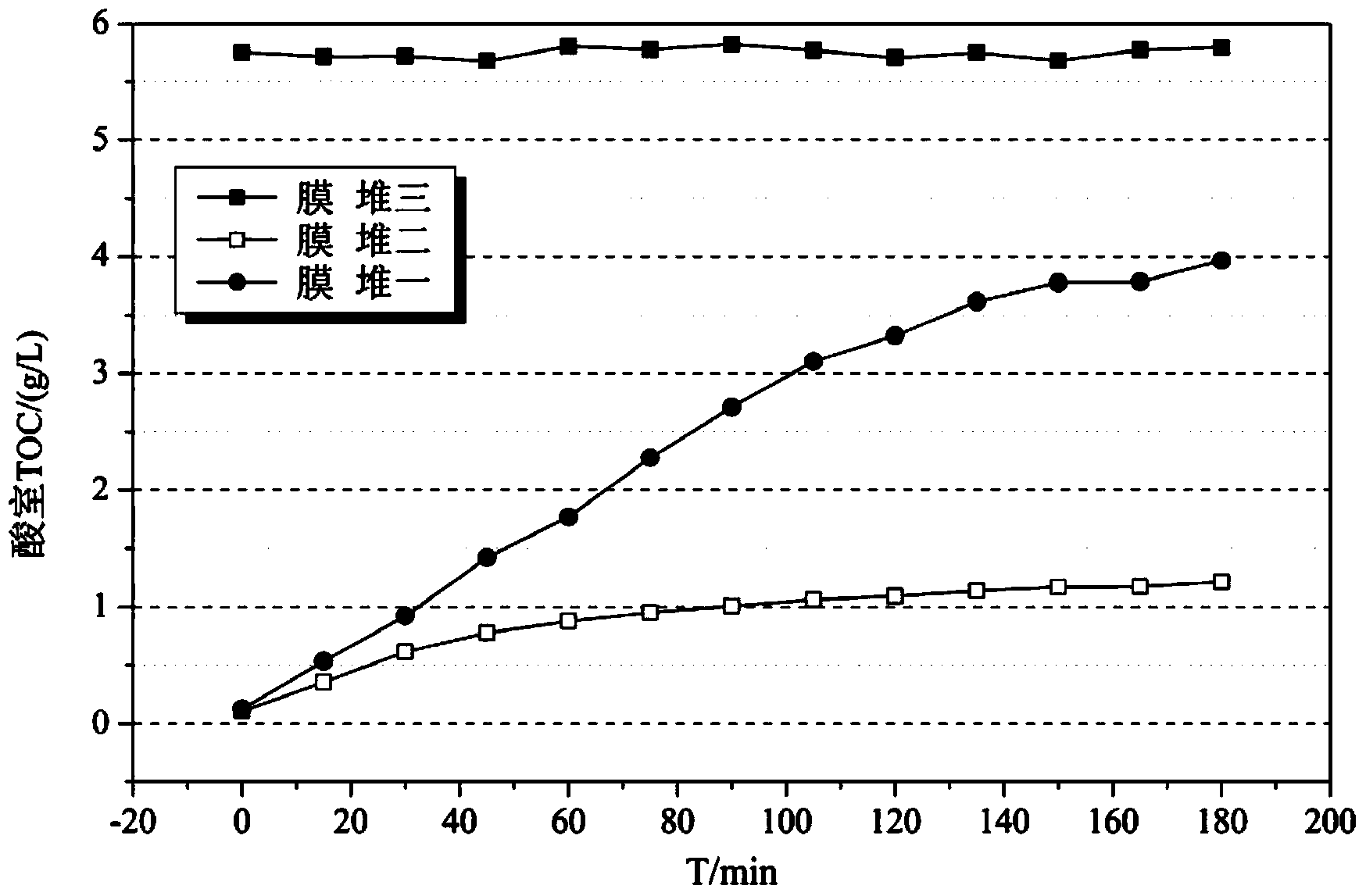
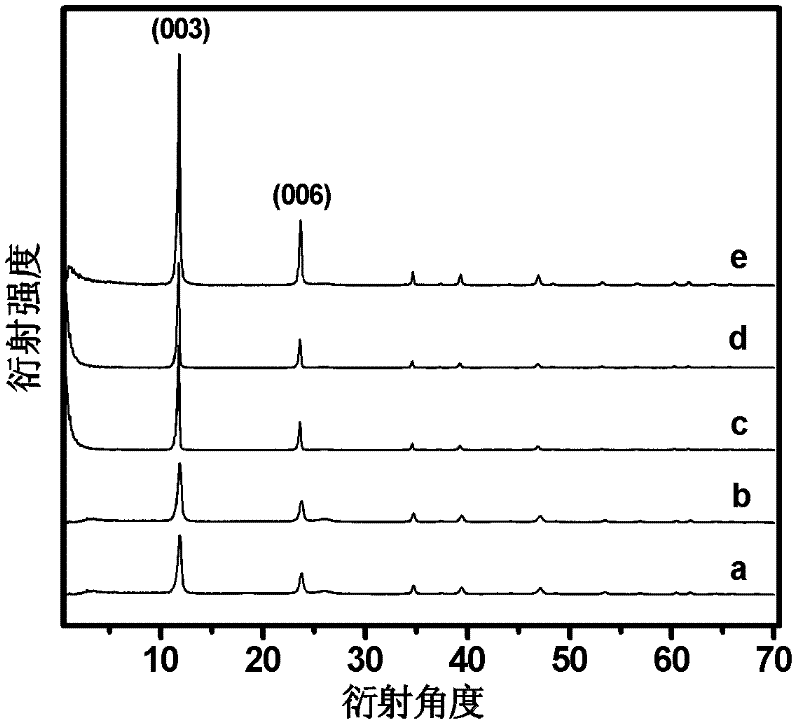
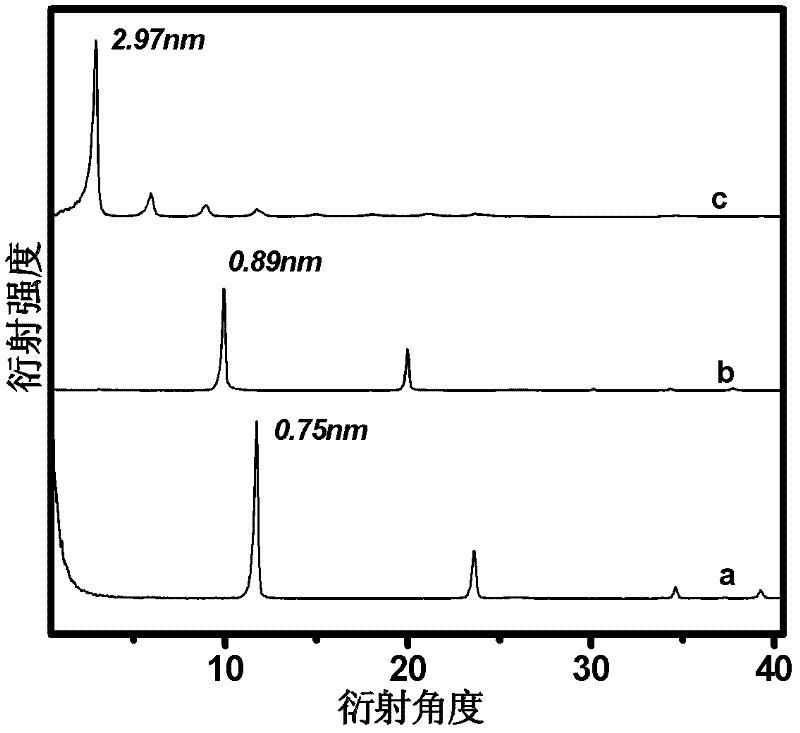
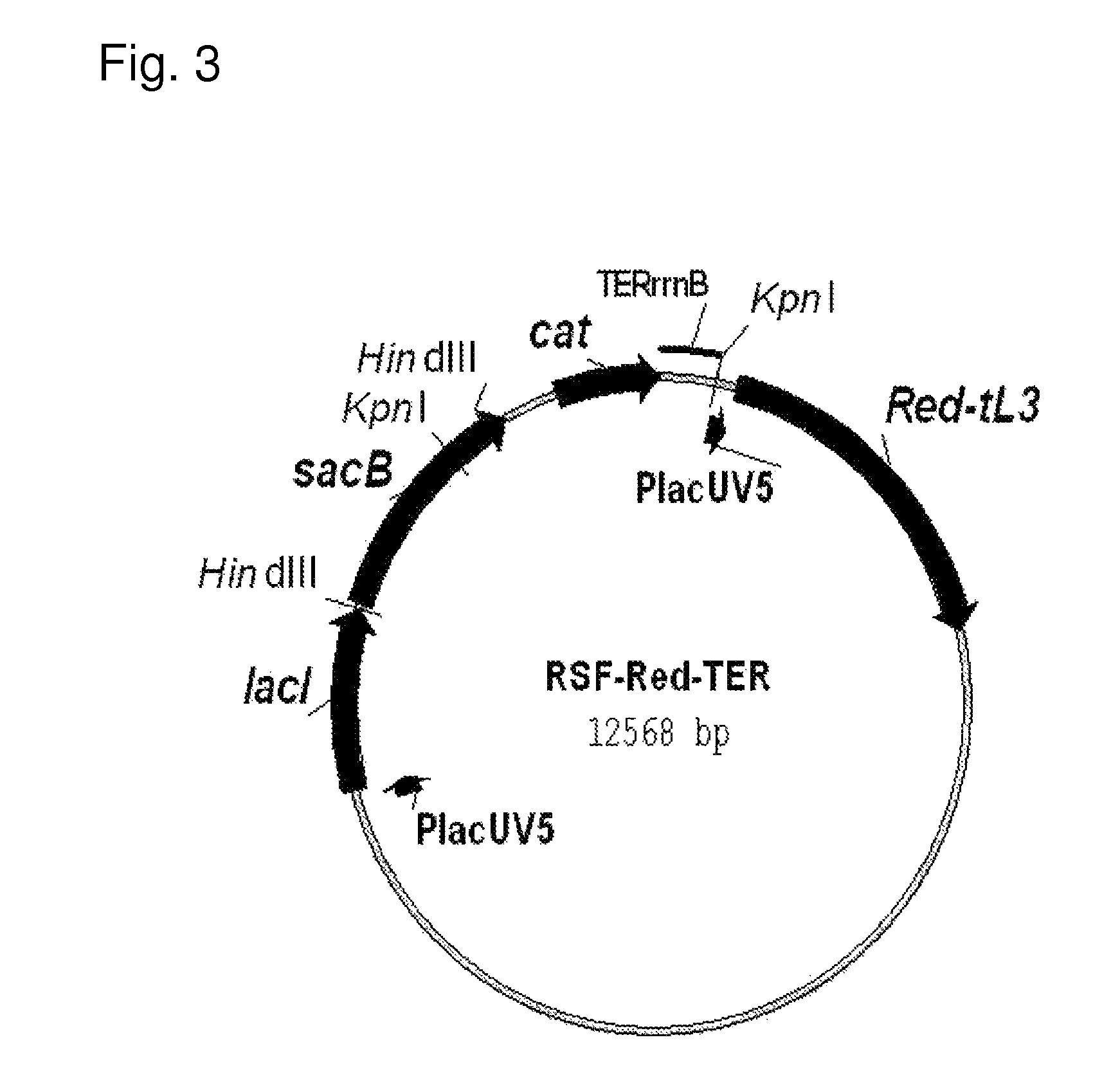
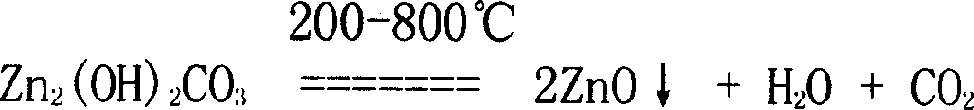Patents
Literature
547 results about "Carbonate Ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
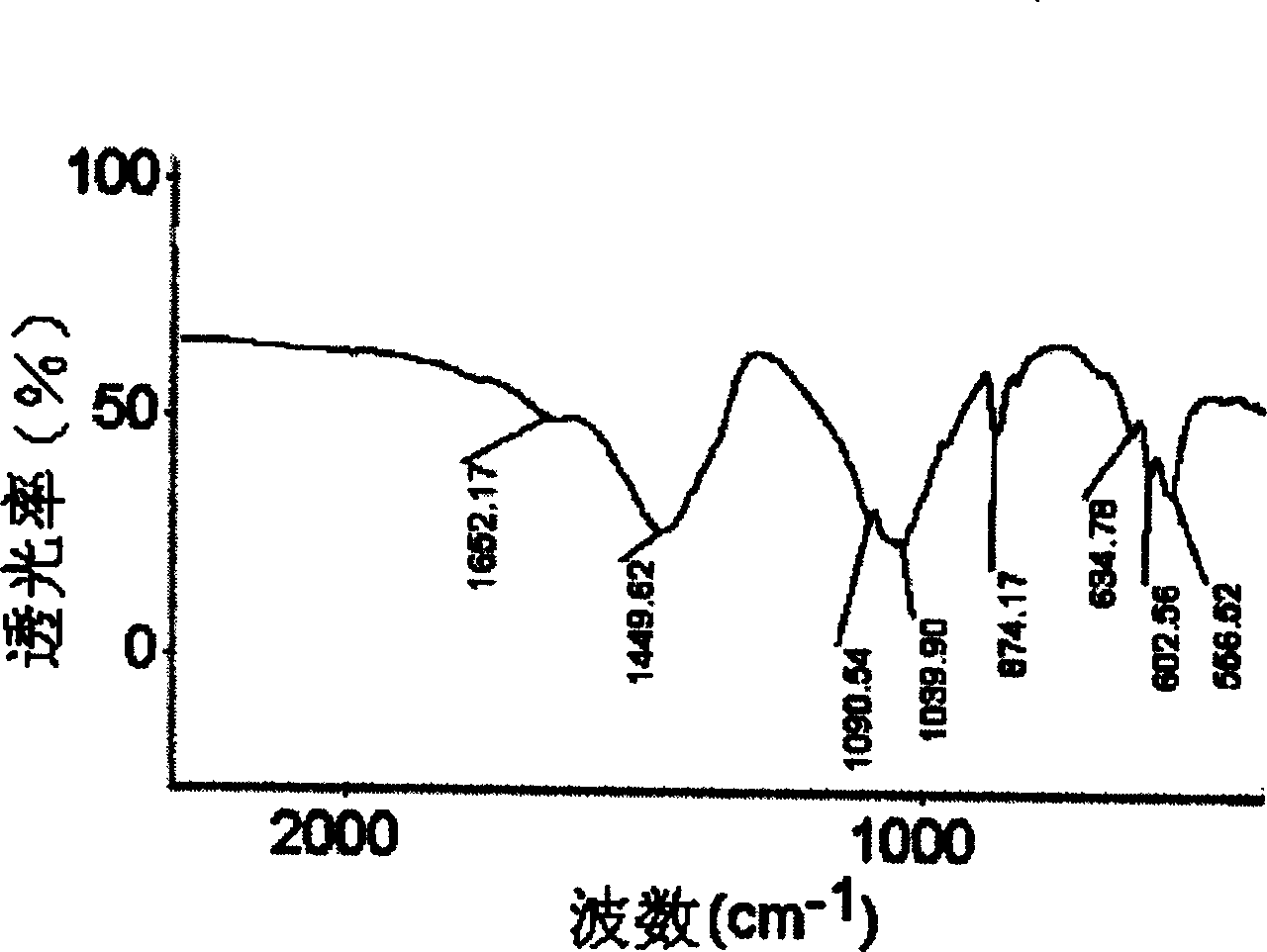
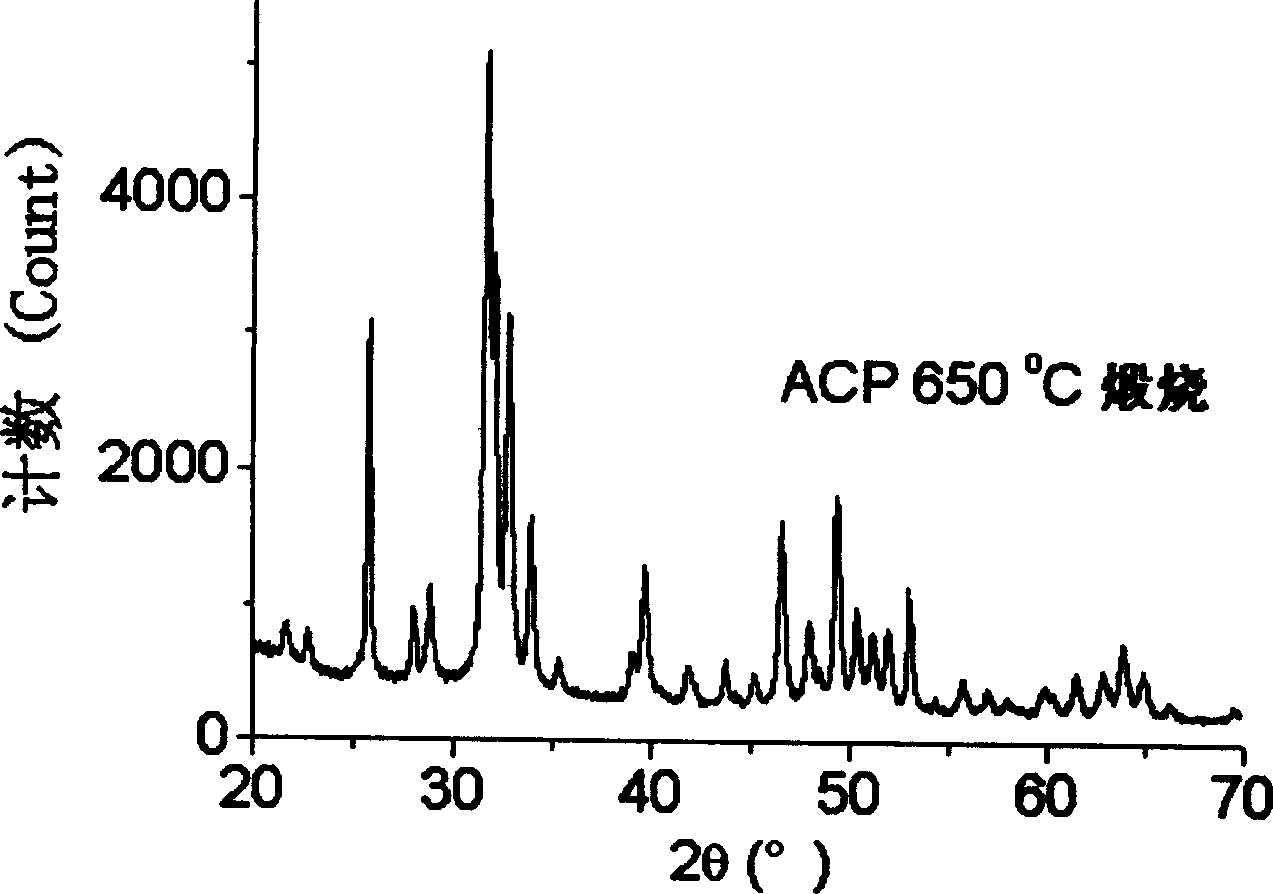
A polyatomic ion with formula of CO3-.
Stable solution of zinc ions and bicarbonate and/or carbonate ions
InactiveUS6015547APrevention and counteractingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideZinc ionBicarbonate Ion
A storage stable aqueous solution or aqueous gel of zinc ions in the presence of bicarbonate ions is disclosed. The solution comprises: (a) a source of zinc ion, (b) a source of a stabilizing anion which can stabilize soluble zinc and bicarbonate and / or carbonate in solution; (c) a source of bicarbonate ion; and (d) a solvent therefor. The solvent comprises a major proportion of water. The zinc salt is present in an amount suitable for the intended purpose; the stabilizing anion in an amount B of at least 1.2 equivalents per equivalent of zinc ion; and the bicarbonate ion cannot exceed certain levels which are related to the level of the stabilizing anion.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
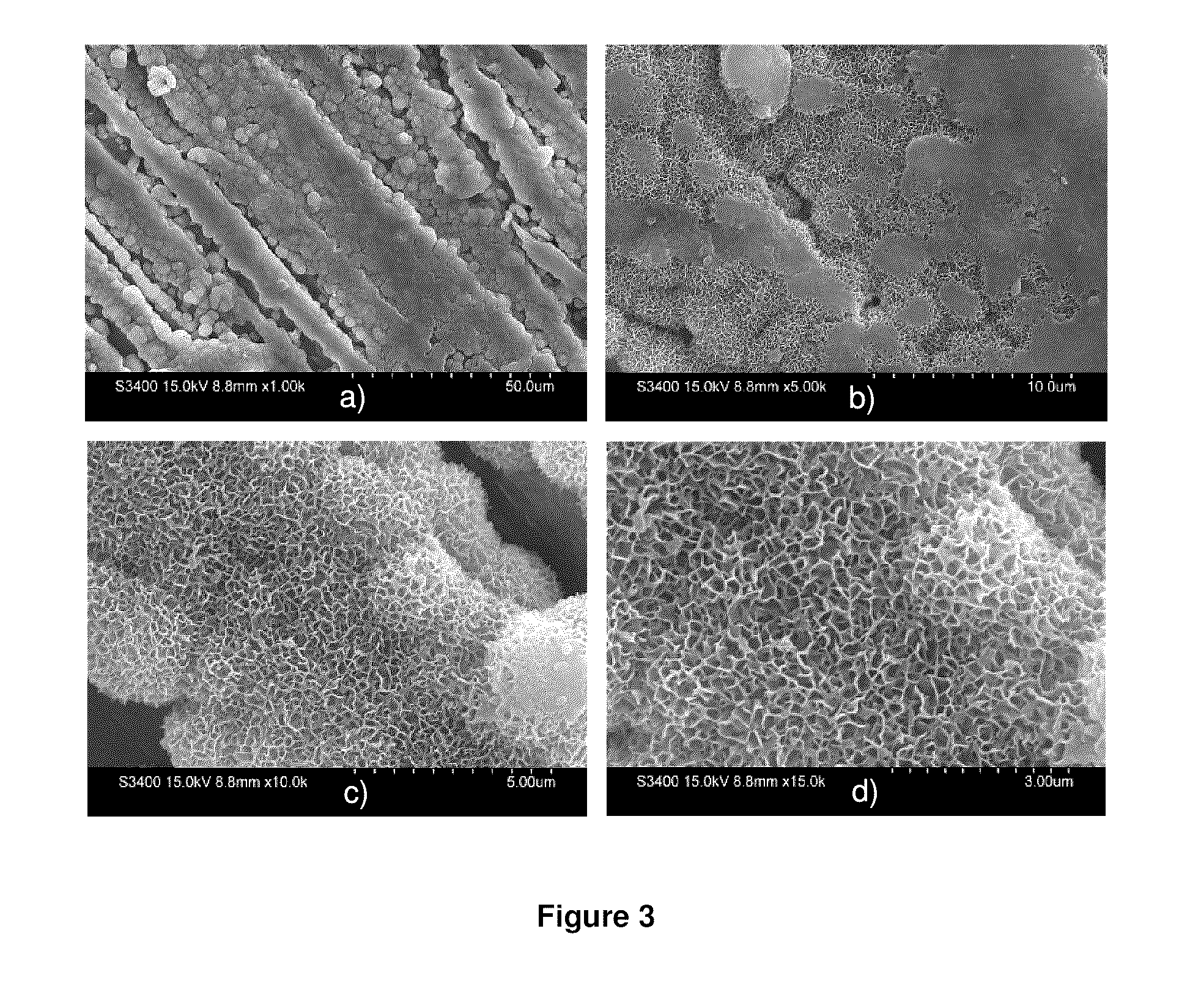
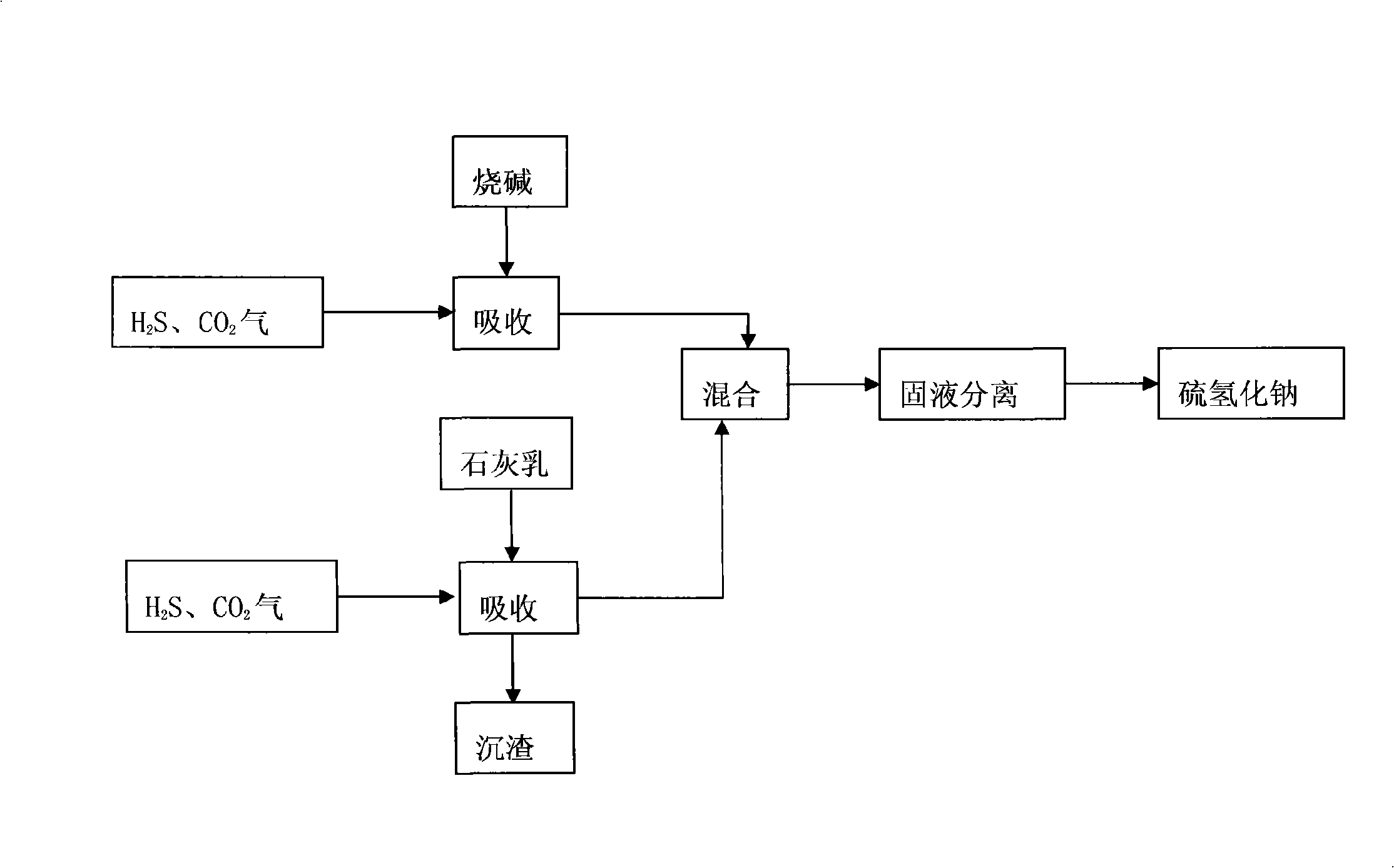
Method for preparing sodium hydrosulfide
InactiveCN101337661AQuality improvementIncrease profitSulfur compoundsHydrogenCALCIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION
The invention discloses a method for preparing sodium hydrosulfide. The production process is as follows: introducing a mixed gas containing sulfureted hydrogen H2S with the content larger than 10 percent and carbon dioxide CO2 with the content not larger than 90 percent into lime cream of about 12 percent of concentration, under the condition of a certain temperature and pressure and under agitation; stopping reaction when CaS is less than or equal to 0.5 percent; separating sediments out to obtain a sulfur calcium hydroxide solution; introducing a mixed gas of sulfureted hydrogen and carbon dioxide into a caustic soda solution with concentration larger than 30 percent under the condition of a certain temperature and pressure and under agitation; stopping reaction when Na2S is less than or equal to 0.5 percent to obtain a sodium hydrosulfide solution containing carbonate ions; and adding slightly not enough sodium hydrosulfide solution under agitation according to the amount of the carbonate ions in the sodium hydrosulfide solution, and separating sediments out to obtain sodium hydrosulfide with low carbonate ions.
Owner:褚亚华
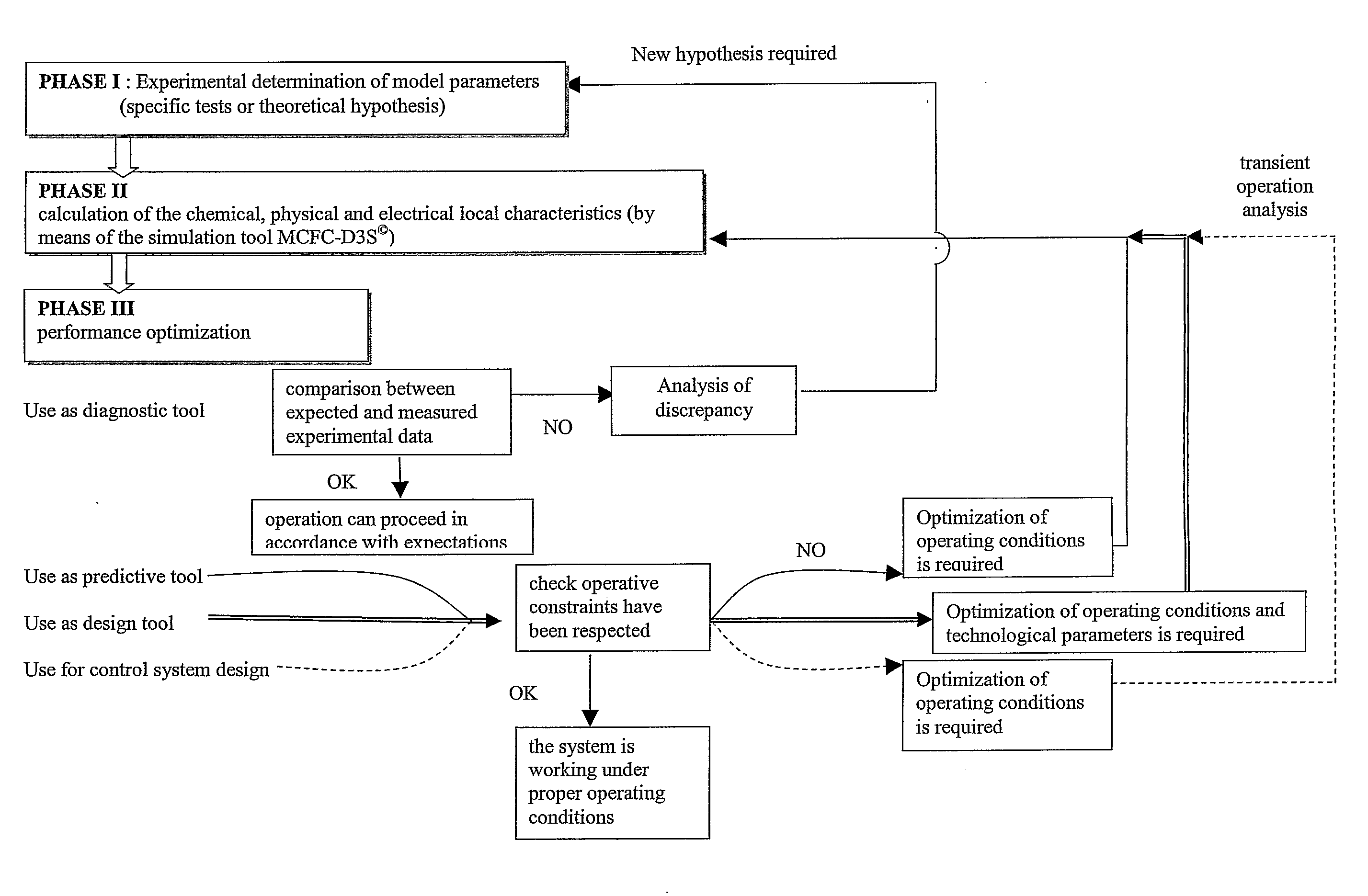
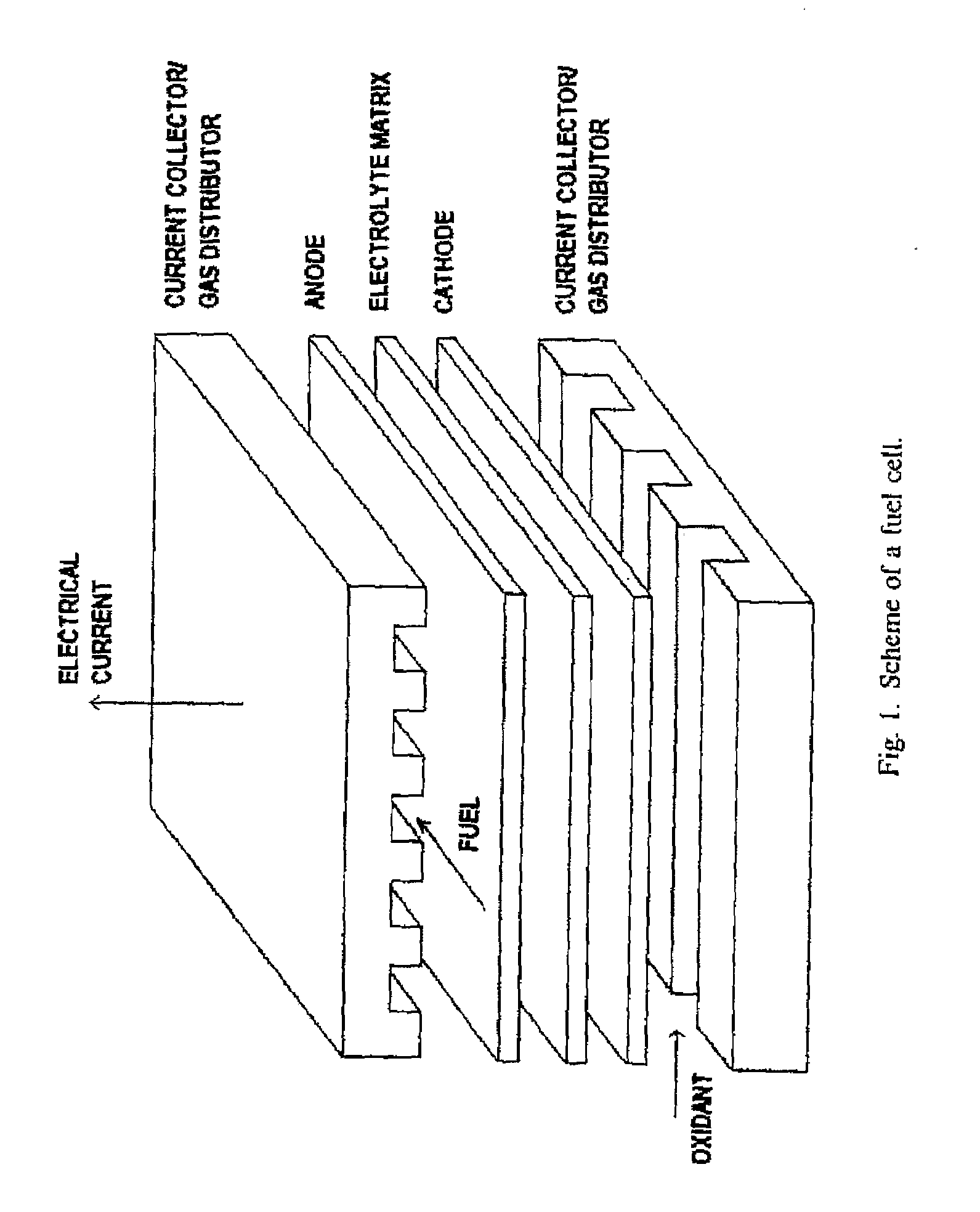
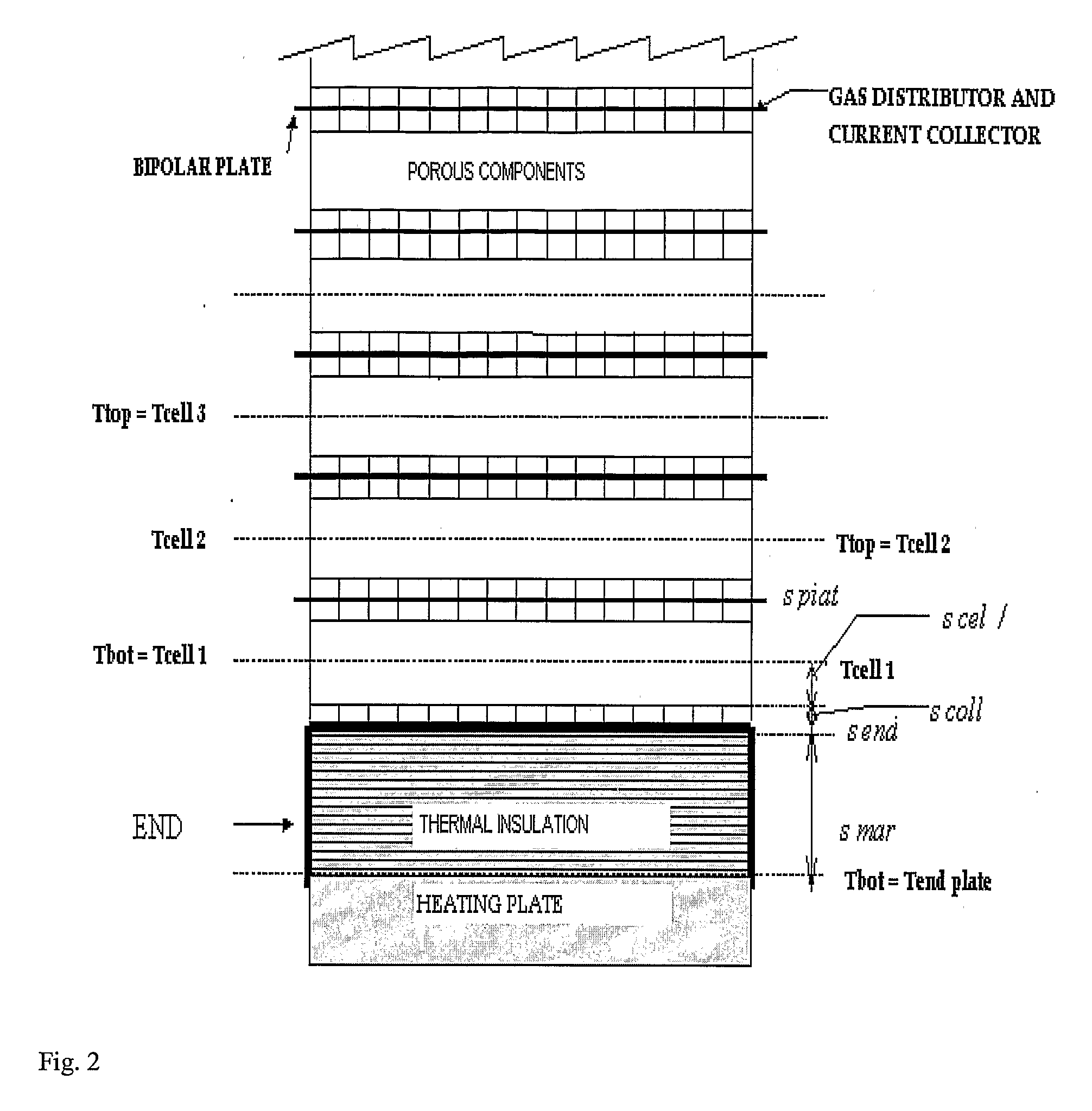
Method and System of Operating Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells
A molten carbonate fuel cell stack and a method of operating a molten carbonate fuel cell stack, which fuel cell comprises a porous anode, a carbonate-comprising matrix and a porous cathode, wherein the anode section is supplied with a hydrogenous gas and the cathode section is supplied with a gaseous mixture comprising oxygen and carbon dioxide, the fuel cell is operated at a temperature in a range of about 823-973 K, with the carbonate of the carbonate-comprising matrix being in a fluid state, oxygen and carbon dioxide are reacted at the cathode, yielding carbonate ions which move from the cathode to the anode generating an electric voltage between the anode and the cathode and an electrical current circulating in the external circuit and water that has been formed is led away from the fuel cell together with carbon dioxide, comprising sampling the temperature of inlet of the reactants, sampling the temperature of outlet of reactants, sampling the current density and voltage sampling the flow rate and gas composition of the inlet and outlet gases analyzing the sampled temperature, current density, voltage flow rates and gas composition, and regulating the inlet flow rate such as the pressure drop between inlet and outlet is below 20 mbar and the temperature in each element of a cell of the stack is below 973K.
Owner:PARODI FILIPPO +2
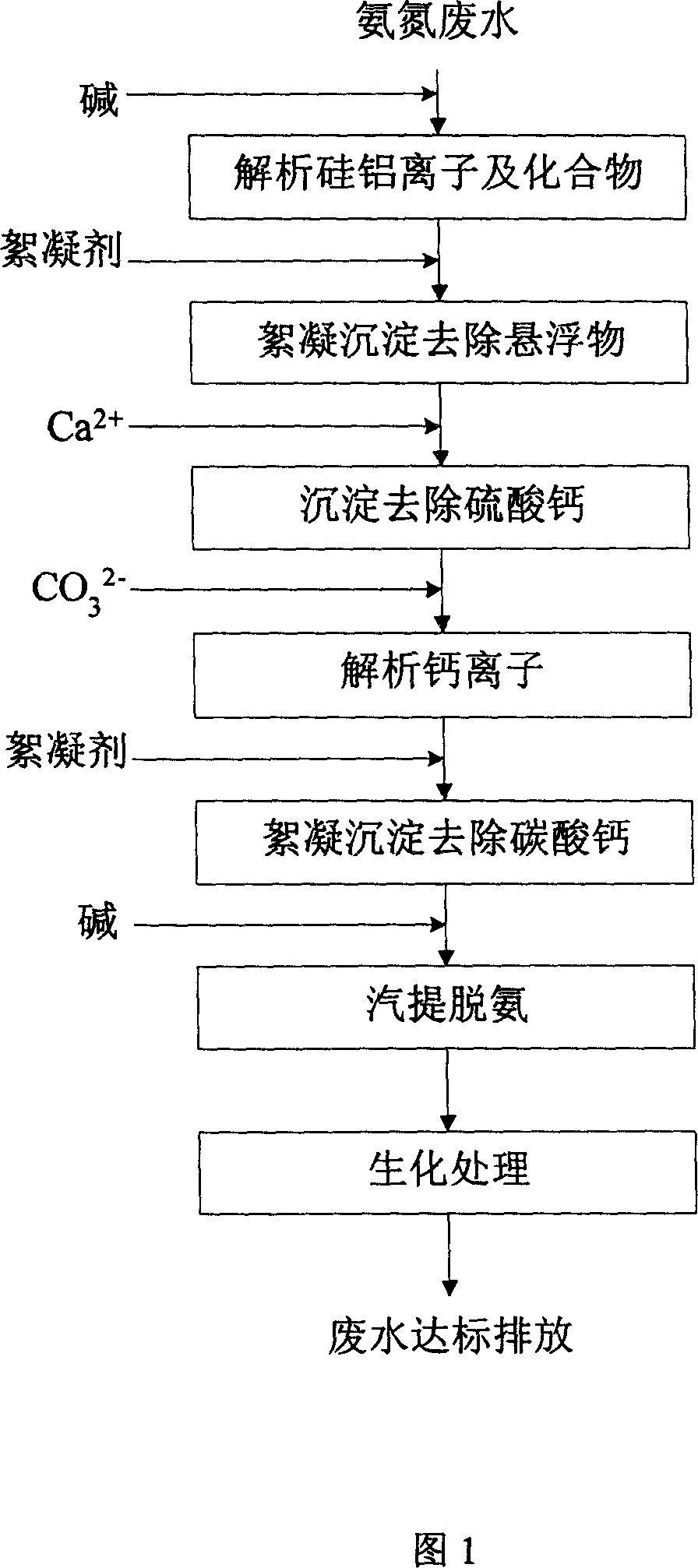
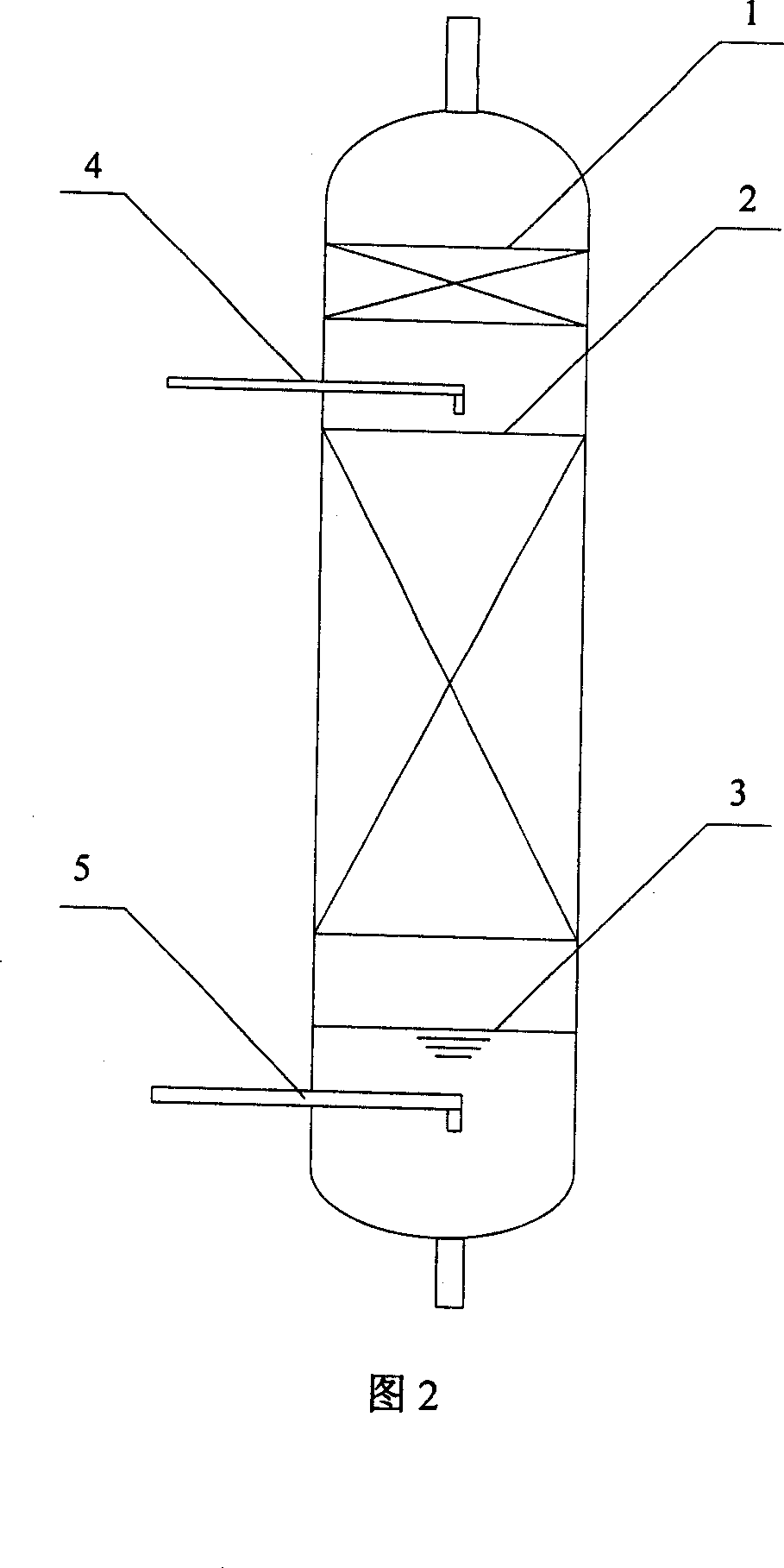
Method for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater
ActiveCN1958471APrevent scalingAvoid problems such as tower blockageTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationTherapeutic effect
This invention relates to a method for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater, especially high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater produced during manufacture of oil-refinery catalyst. The method comprises: (1) adjusting the pH value of the wastewater, and solid-liquid separating to remove suspended matters and dissolved Si2+, Al3+ and their compounds; (2) adding Ca2+ to form CaSO4 precipitate, and solid-liquid separating to reduce acidic matters in the wastewater; (3) adding CO32- to form CaCO3 precipitate, and solid-liquid separating to remove Ca2+ in the wastewater; (4) steam-stripping for deamination, and performing biochemical treatment so that wastewater reaches state discharge standards. The method can solve the problems of low effect on removing suspended matters and dissolved Si2+, Al3+ and their compounds, scaling and column blockage during steam-stripping process, and the need for a large amount of alkali added, and can improve wastewater treatment effect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of rapid hair dyeing
The present invention relates to a method of hair colouring and bleaching compositions providing a composition comprising i) at least one source of peroxymonocarbonate ions, ii) at least one alkalizing agent, preferably a source of ammonium ions, and iii) at least one radical scavenger, wherein said composition has a pH of up to 9.5, and applying the composition to the hair and retaining on the hair for a period of less than 20 minutes, which provide a high level of lift and lightening and the required dye deposition and grey coverage whilst reducing the concentration of peroxide, the ammonia odour and reducing the hair fibre damage.
Owner:WELLA OPERATIONS US LLC
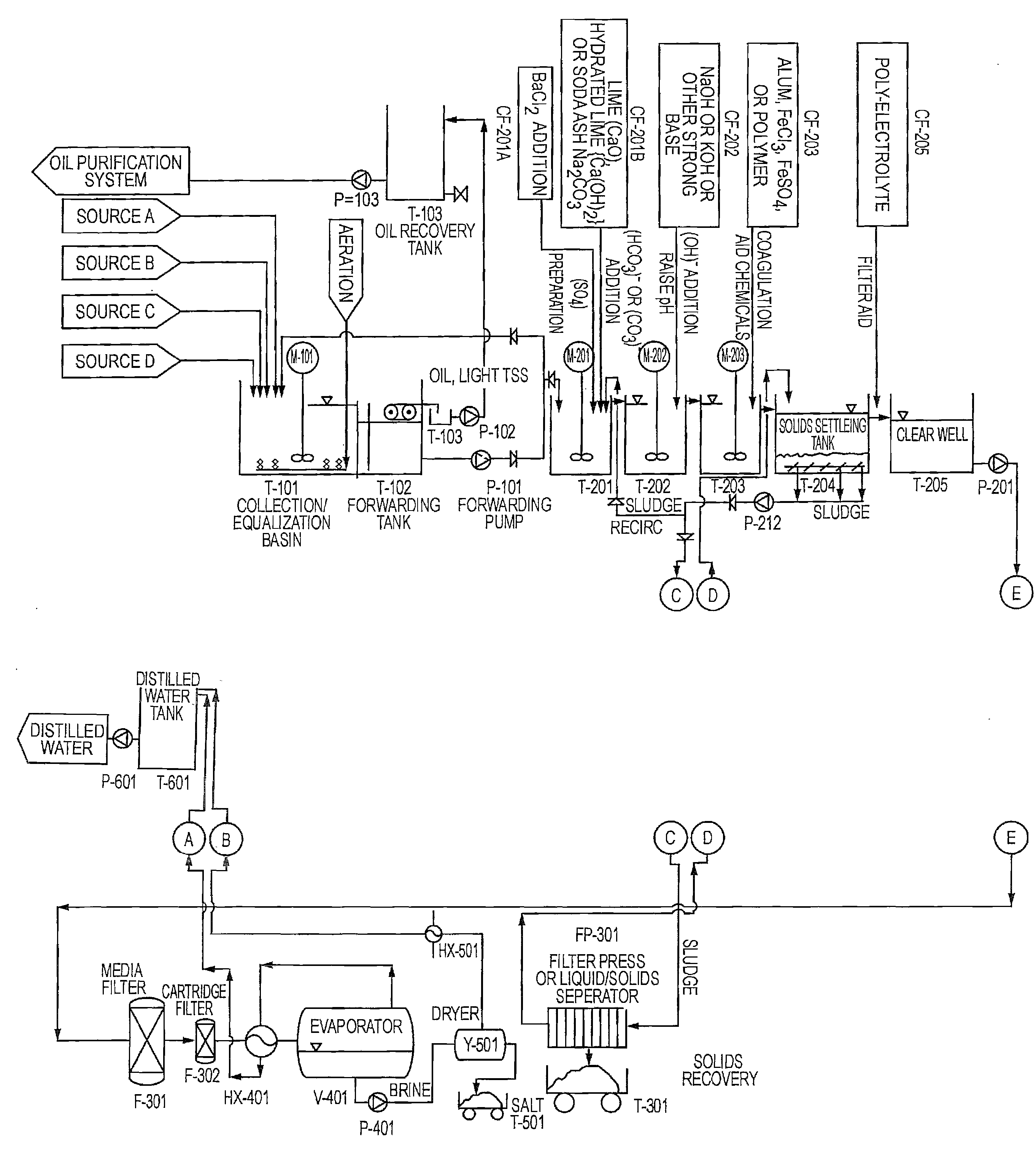
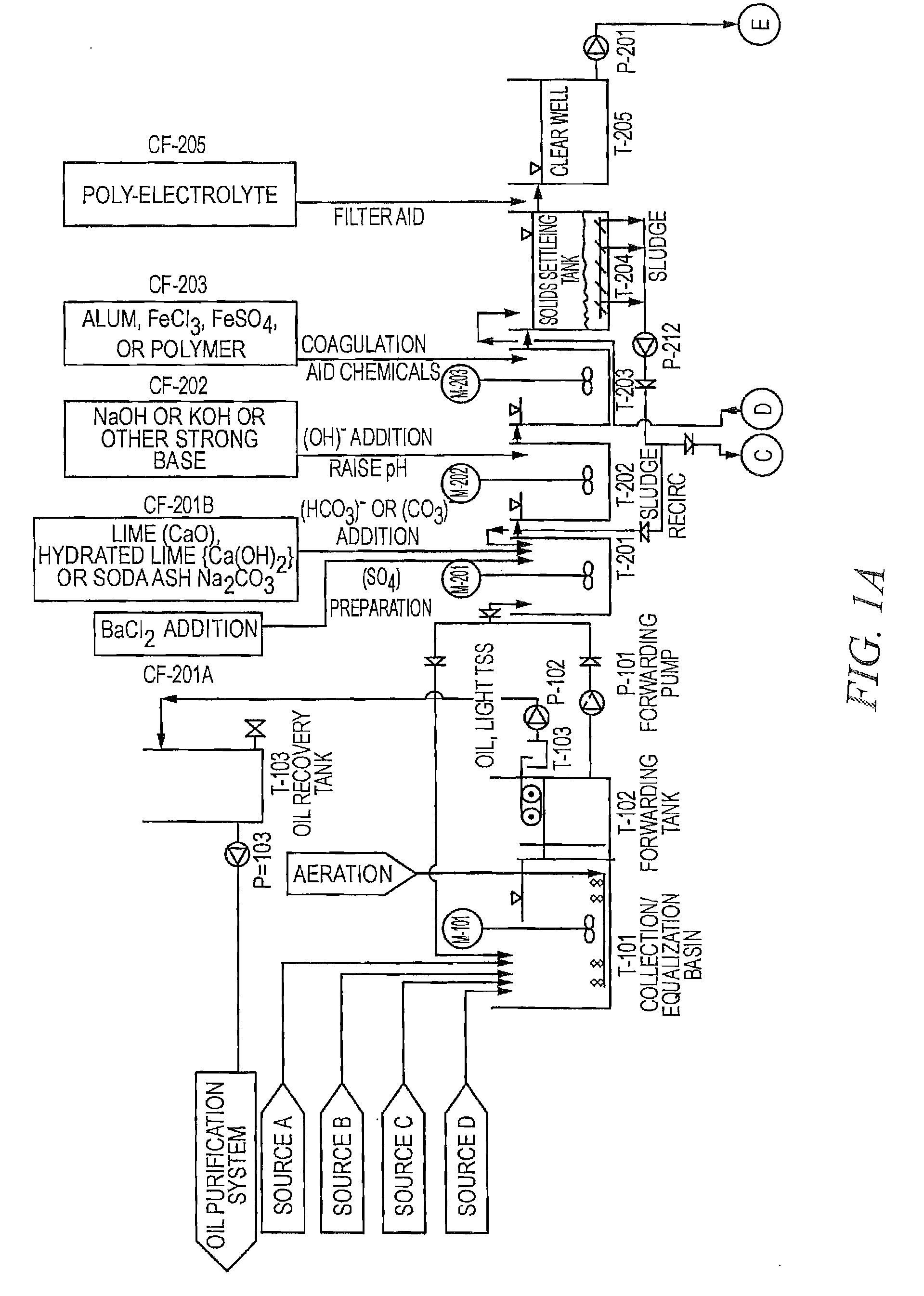
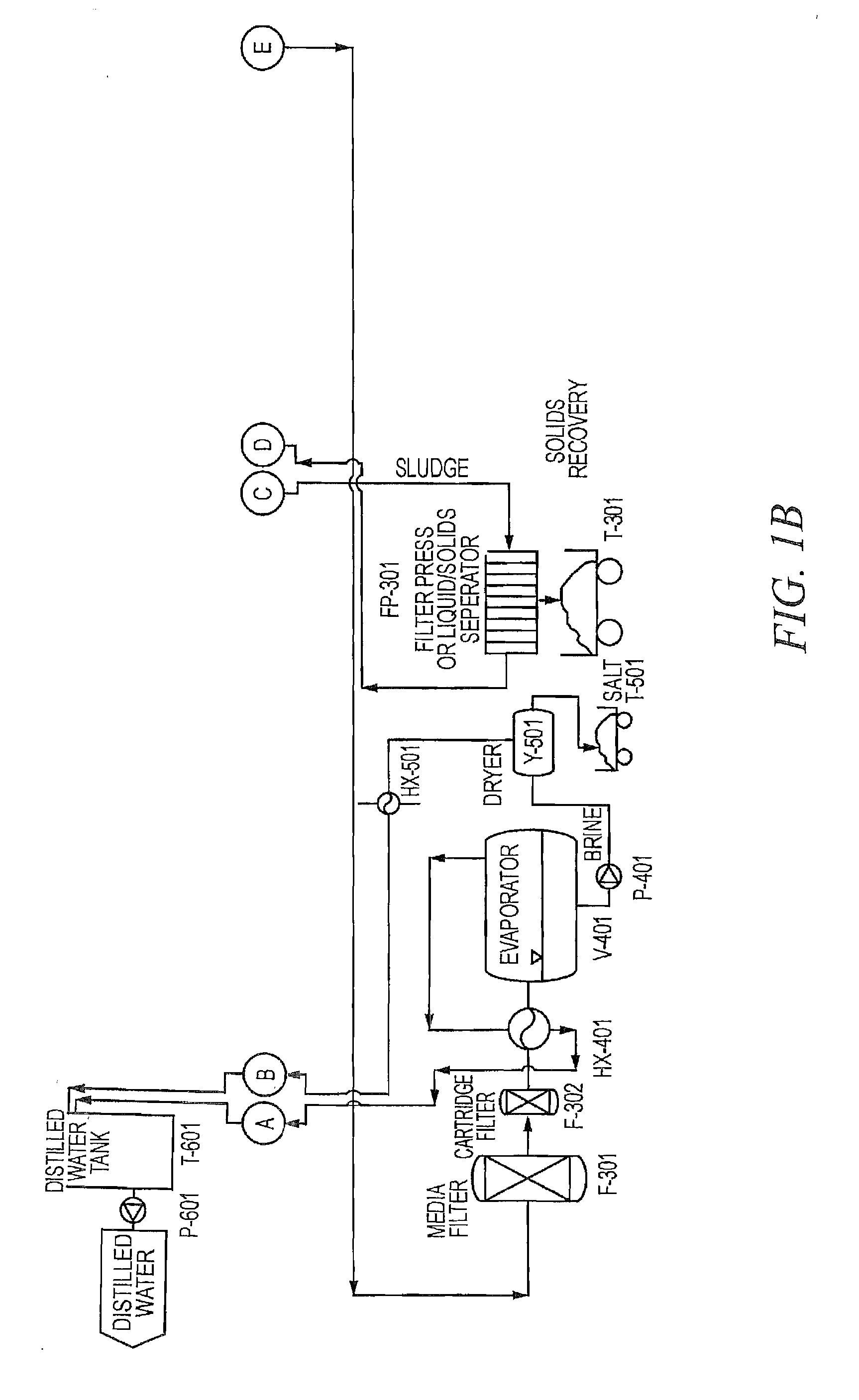
High Efficiency Water-Softening Process
ActiveUS20120145643A1Reduce pollutant contentSludge treatmentUltrafiltrationPolyelectrolyteWater softening
A high-efficiency water softening process is disclosed. The softening-process is particularly effective for the treatment of water process streams containing a broad array of contaminants, such as Ca, Mg, Ba, Sr, iron, aluminum, manganese, copper, zinc, silica, TOC, oil, and grease. The softening-process includes steps of: (a) adding carbonate ions and hydroxide ions to said water process stream until the process stream pH is raised to between at or about 10.5 and at or about 14.0; (b) optionally adding a coagulation aid so as to facilitate the creation of separated solids comprising a substantial portion of the contaminants; (c) optionally adding a polyelectrolyte so as to facilitate the creation of separated solids comprising a substantial portion of the contaminants; and (d) phase-separating the separated solids so as to remove the contaminants and produce a highly purified water process stream.
Owner:PANDYA KEN V
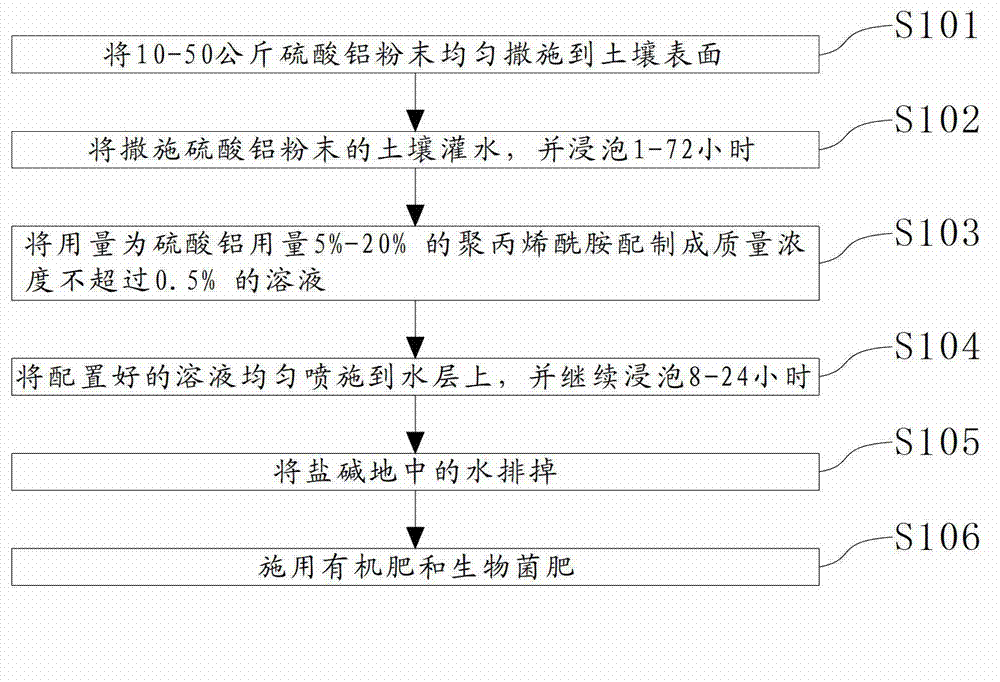
Improvement method for saline-alkali soil
ActiveCN103109615AImprove propertiesImprove permeabilitySoil-working methodsAlkali soilPolyacrylamide
The invention relates to the agricultural field, in particular to an improvement method for saline-alkali soil. The improvement method for the saline-alkali soil comprises the following steps: sprinkling 10 to 50 kilograms of aluminum sulfate powders on the surface of the saline-alkali soil evenly; irrigating the soil with the aluminum sulfate powders and soaking the soil with the aluminum sulfate powders for 1 hour to 72 hours; compounding polyacrylamide with a dosage which is 5% to 20% of the dosage of the aluminum sulfate powders into a solution, wherein the mass concentration of the solution is no more than 0.5%; evenly spraying the compounded solution onto the water layer, and continuing to soak the soil with the aluminum sulfate powders for 8 hours to 24 hours; draining the water in the saline-alkali soil; and applying organic fertilizer and biological bacterial fertilizer to the saline-alkali soil. The improvement method for the saline-alkali soil can improve the sodium ions, the carbonate ions and the bicarbonate radical ions in the soil, so that the potential of hydrogen (pH) value of the solution of the soil can be reduced. The aluminum sulfate is increased, so that the soluble salts released by the soil particles are also increased, so that the salt materials in the soil can be reduced remarkably. Due to the fact that the macromolecule polyacrylamide is added, the soil can congeal into bigger particles like pea grains, so that permeability and water and fertilizer preserving capability of the soil can be improved.
Owner:黑龙江省汉通生物工程有限公司
Polymer thickened hair colouring and bleaching compositions
InactiveUS20060117493A1Improve hair damage profileCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsHair dyesScavenger
The present invention relates to hair colouring and hair bleaching compositions comprising a source of carbonate ions, at least one oxidizing agent and a specified polymer thickner wherein said composition is free of a source of radical scavengers. The compositions surprisingly provide improved hair colourant and bleaching compositions which deliver improved lift, lightening and colour delivery whilst minimizing damage which are easy to manufacture and have long shelf life stability.
Owner:NOXELL CORP
In situ precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by indigenous microorganisms to improve mechanical properties of a geomaterial
A method for increasing the concentration of calcium carbonate in a geomaterial that contains indigenous microorganisms capable of hydrolyzing urea to ammonia, which method includes enriching the geomaterial with a source of nutrients, adding urea to the geomaterial which is hydrolyzed to ammonia and which raises the pH of the geomaterial, and adding a source of calcium ions to the geomaterial. Carbonate ions obtained by the hydrolysis of the urea combine with calcium ions to form calcium carbonate.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IDAHO
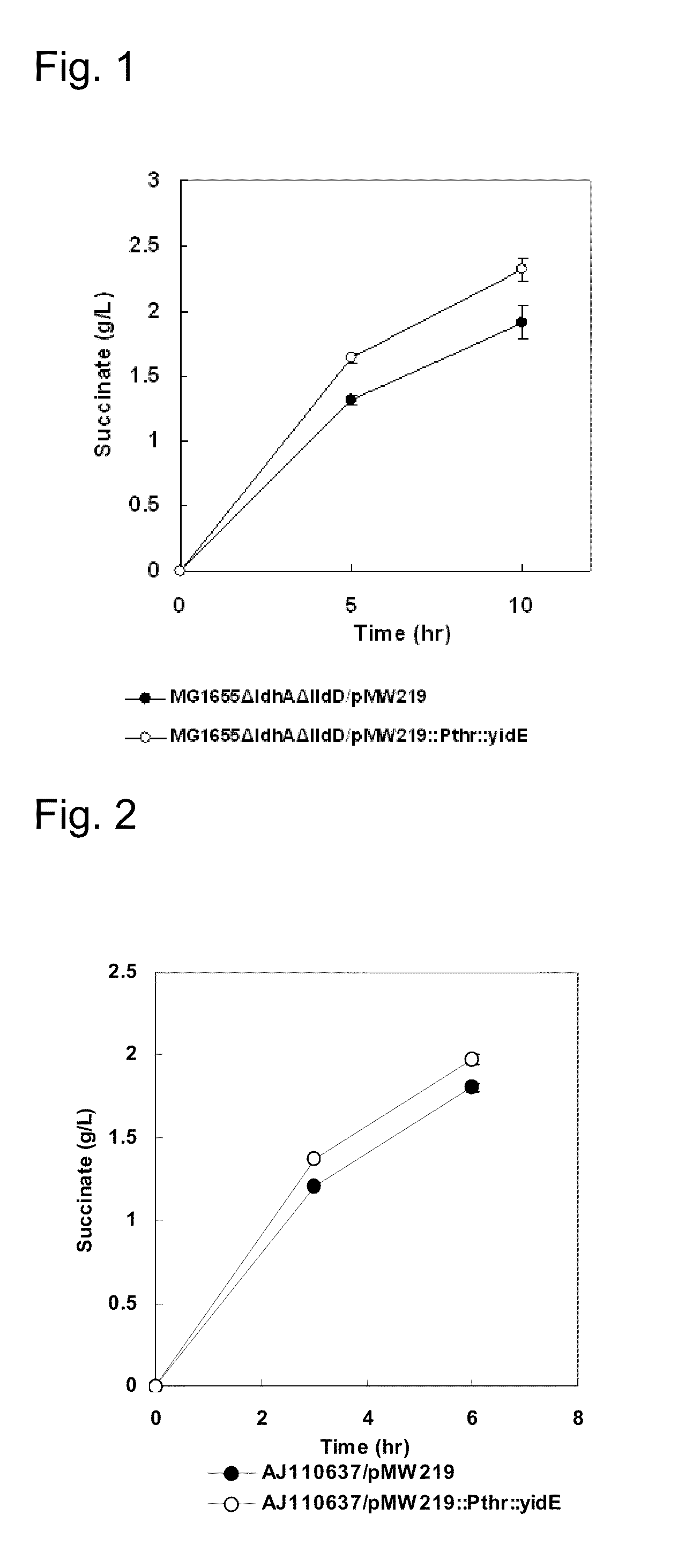
Process for producing succinic acid
ActiveUS20060205048A1Improve productivityProducing succinicBacteriaSugar derivativesPyruvate carboxylaseLactate dehydrogenase
Succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance fumarate reductase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. More preferably, succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance activities of fumarate reductase and pyruvate carboxylase and decrease lactate dehydrogenase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. Succinic acid is obtained by collecting the produced succinic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Preparation method for anion-exchangeable, layered double hydroxides
InactiveUS20100279848A1Overcome defectsSimple methodProductsGas treatmentIon exchangeDivalent metal ions
The invention has for its object to provide a preparation method for preparing an anion-exchangeable LDH by decarbonation of a carbonate ion type LDH, which makes sure de carbonation is implemented with safety in a continuous manner while crystal shape, crystal structure and crystallinity are kept intact.The invention provides a preparation method for preparing an anion-exchangeable, layered double hydroxide wherein a carbonate ion type layered double hydroxide (LDH) having a composition represented by a general formula: QxR(OH)z(CO32−)0.5-y / 2(X−)y.nH2O where x is indicative of a numeral range of 1.8≦x≦4.2; z is indicative of 2(x+1); y is indicative of a minimum value of at least 0 that increases to less than 1 when anions (X−) remain or a part of anions is introduced; Q is a divalent metal ion; R is a trivalent metal ion; and n is 2±2 is used as a starting material, and y in said general formula increases to a maximum of 1 by substitution of a minus monovalent anion (X−1) at a carbonate ion site thereby implementing substitution, characterized in that the starting material is dispersed in an aqueous solution mixed with a salt containing minus monovalent anions (X−) in an amount enough for substitution at the carbonate ion site while said aqueous solution is kept at a pH (hydrogen ion exponent) of greater than 4 to less than 7.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Method for separating methionine from mixed solution of methionine salt and carbonate by using bipolar membrane electrodialysis
The invention discloses a method for separating methionine from a mixed solution of methionine salt and carbonate by using bipolar membrane electrodialysis. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of arranging a bipolar membrane electrodialysis system, and separating methionine from a mixed solution of methionine salt and carbonate by using a bipolar membrane electrodialysis process, wherein a bipolar membrane is capable of simultaneously generating hydroxyl ions and hydrogen ions through hydrolytic dissociation, the hydrogen ions are capable of neutralizing methionine ions and carbanions in the mixed solution of methionine salt and carbonate to generate methionine, and the generated hydroxyl ions are capable of combining with positive ions to obtain inorganic base. According to the method, a large quantity of acid and alkaline are not required to be additionally introduced in the bipolar membrane electrodialysis process, the environment friendliness is achieved, the process cost is lowered, no inorganic salt waste residue is generated in the process, the recovery efficiency of methionine is high, and the purity is high, thus the generated wastewater is more easily treated.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method by utilizing double markers to acquire share of inorganic carbon source utilized by plants
ActiveCN102511362AFew stepsSimple calculationCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationSodium bicarbonateCulture fluid
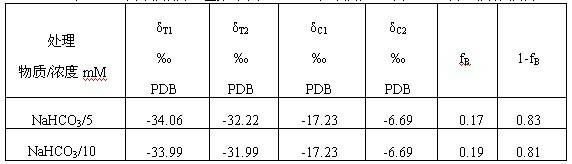
The invention discloses a method by utilizing double markers to acquire share of inorganic carbon source utilized by plants, which comprises the following steps that: A. sodium bicarbonate produced by different manufacturers is determined, two types of sodium bicarbonate with delta 13C difference being more than eight thousandths are used as an isotopic marker 1 and an isotopic marker 2 to be respectively added into nutrient fluid to culture plants; delta 13C value of bicarbonate ion in nutrient fluid of the isotopic marker 1 is delta C1, and delta 13C value of bicarbonate ion in nutrient fluid of the isotopic marker 2 is delta C2; and B. after more than four leaves appear, the values of delta 13C consisting of stable carbon isotopes of plant leaves to be observed correspondently culturedby the nutrient fluid of the two types of isotopic markers are respectively determined as delta T1 and delta T2; and C. delta C1, delta C2, delta T1 and delta T2 are brought into equation fB= to calculate the share fB of the carbonate ions utilized by the plants. Due to the adoption of the method, the share of the inorganic carbon source utilized by the plants can be rapidly acquired, the steps are fewer, simplicity in calculation can be realized, and data is reliable.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Saponification of organic extractant
ActiveCN1817403AEliminate pollutionReduce manufacturing costLiquid solutions solvent extractionProcess efficiency improvementIon exchangeRare earth
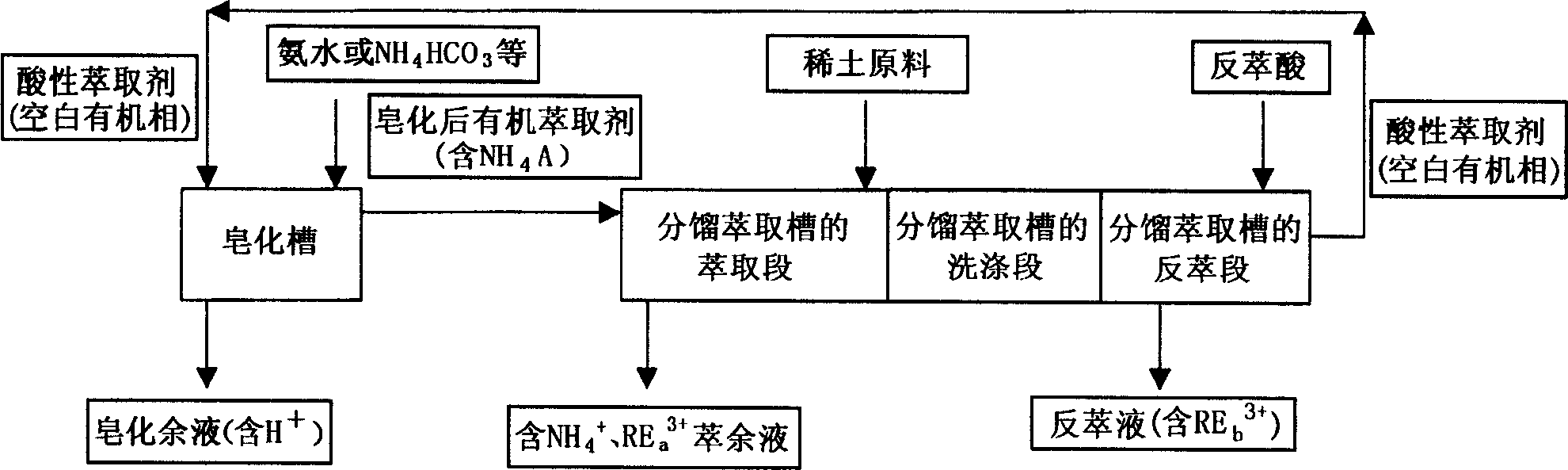
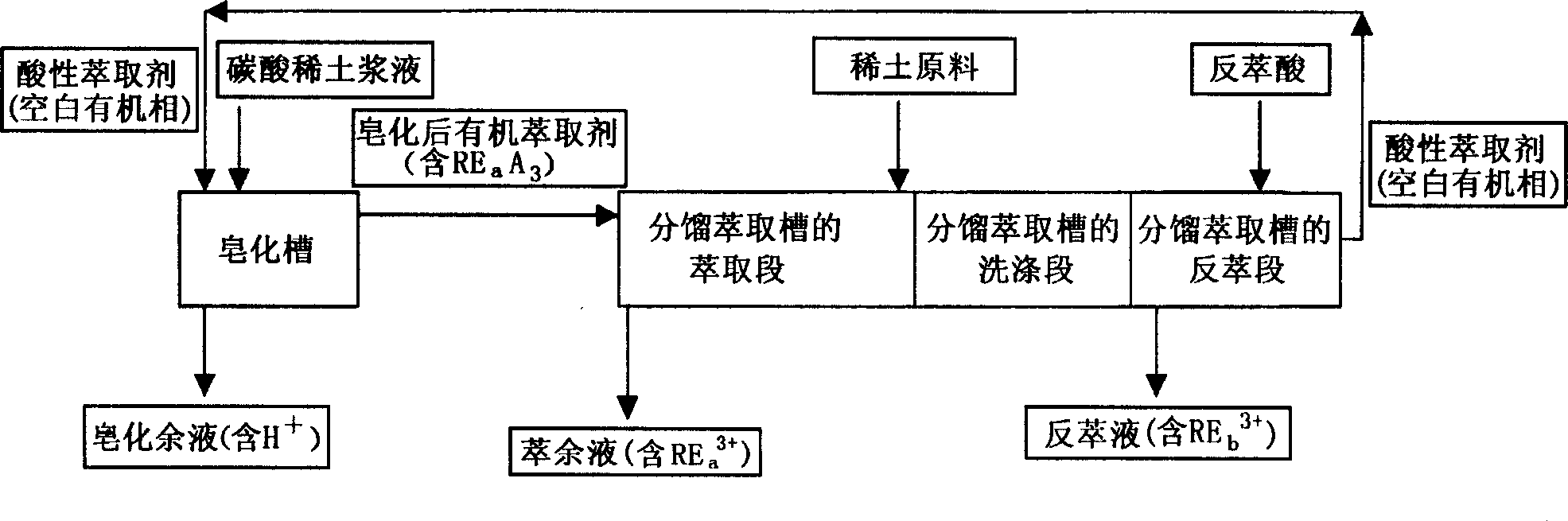
A process for saponifying the organic extractant used for separating RE includes such steps as mixing the extractant with RE carbonate in RE solution or acidic solution, ion exchange reaction between RE ions and H ions of extractant, binding H ions with radical of carbonic acid to generate CO2 and H2O for gradually dissolving RE, extracting RE ions into organic phase, and reusing the residual liquid after supplementing RE solution or acid solution. Its advantages are no environmental pollution and low cost.
Owner:CHINALCO GUANGXI NONFERROUS RARE EARTH DEV CO LTD
Porous materials coated with calcium phosphate and methods of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20120270031A1Increase rate of changeLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCalcium biphosphateCalcium phosphate coating
The present invention relates to a method of coating a porous material such as a medical implant with a layer of calcium phosphate, wherein the material is submersed in an aqueous solution of calcium, phosphate and carbonate ions, and the pH of the solution is gradually increased. A calcium phosphate coating is formed on an internal surface of the porous material by agitating the solution during coating formation.
Owner:TISSUE REGENERATION THERAPEUTICS
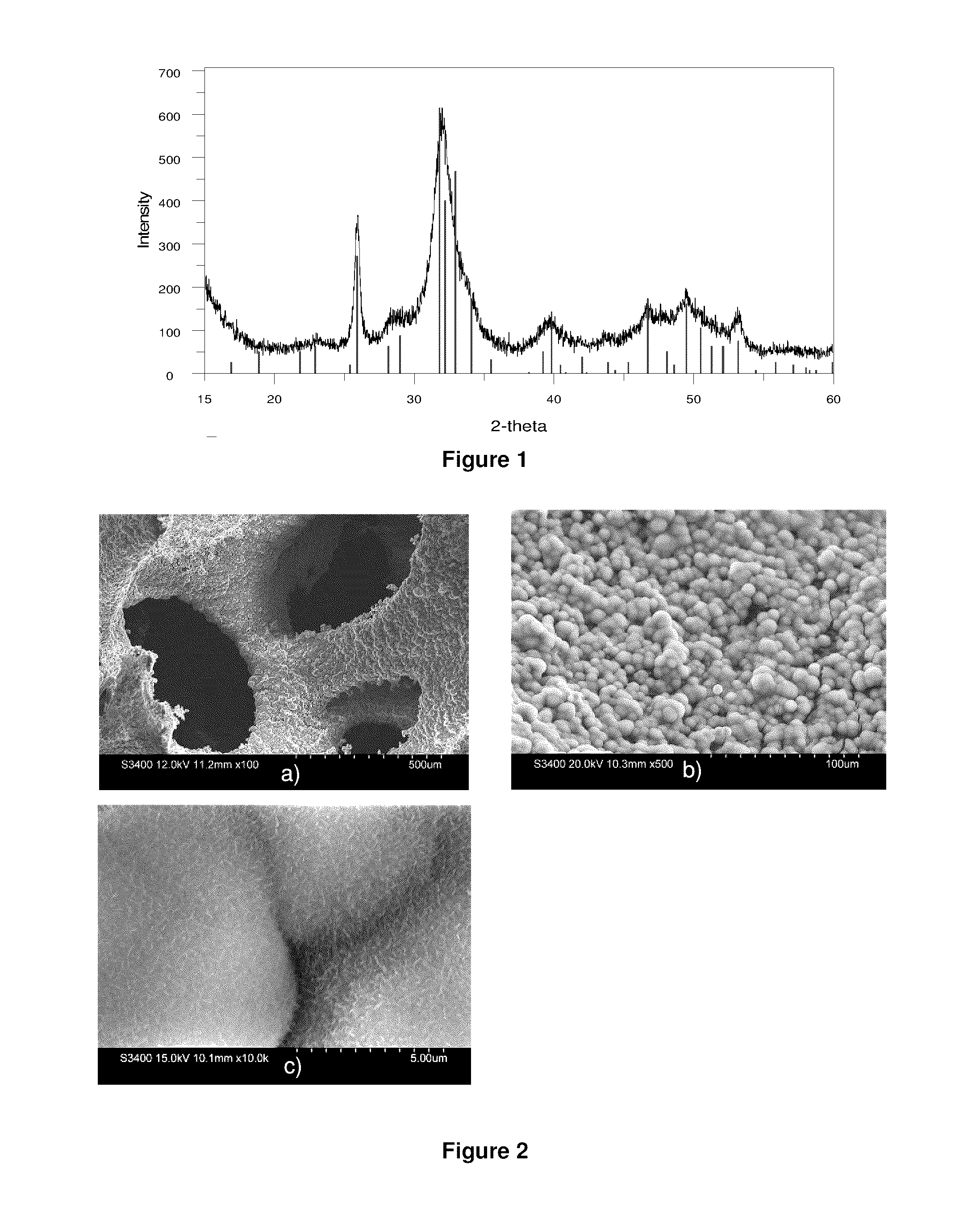
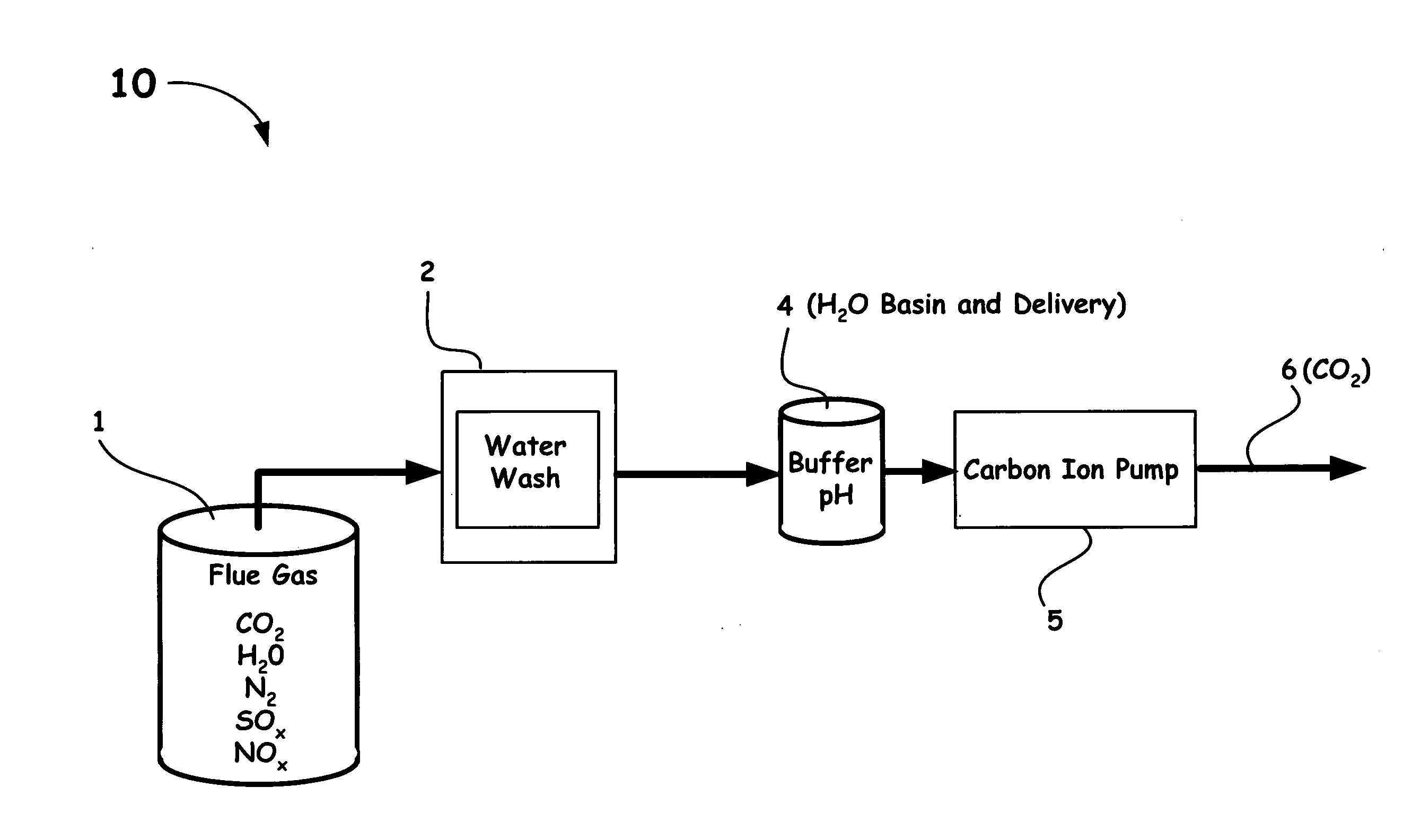
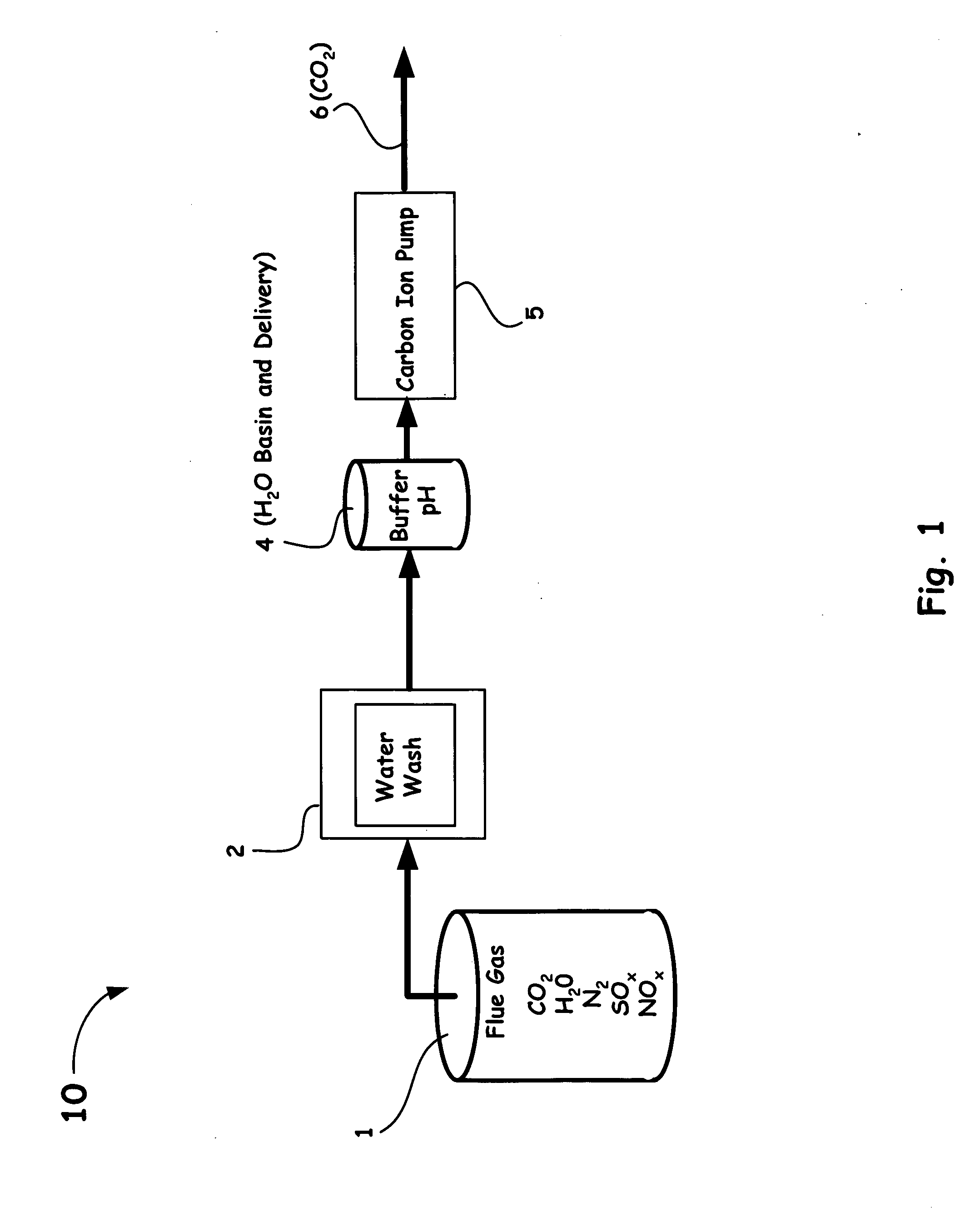
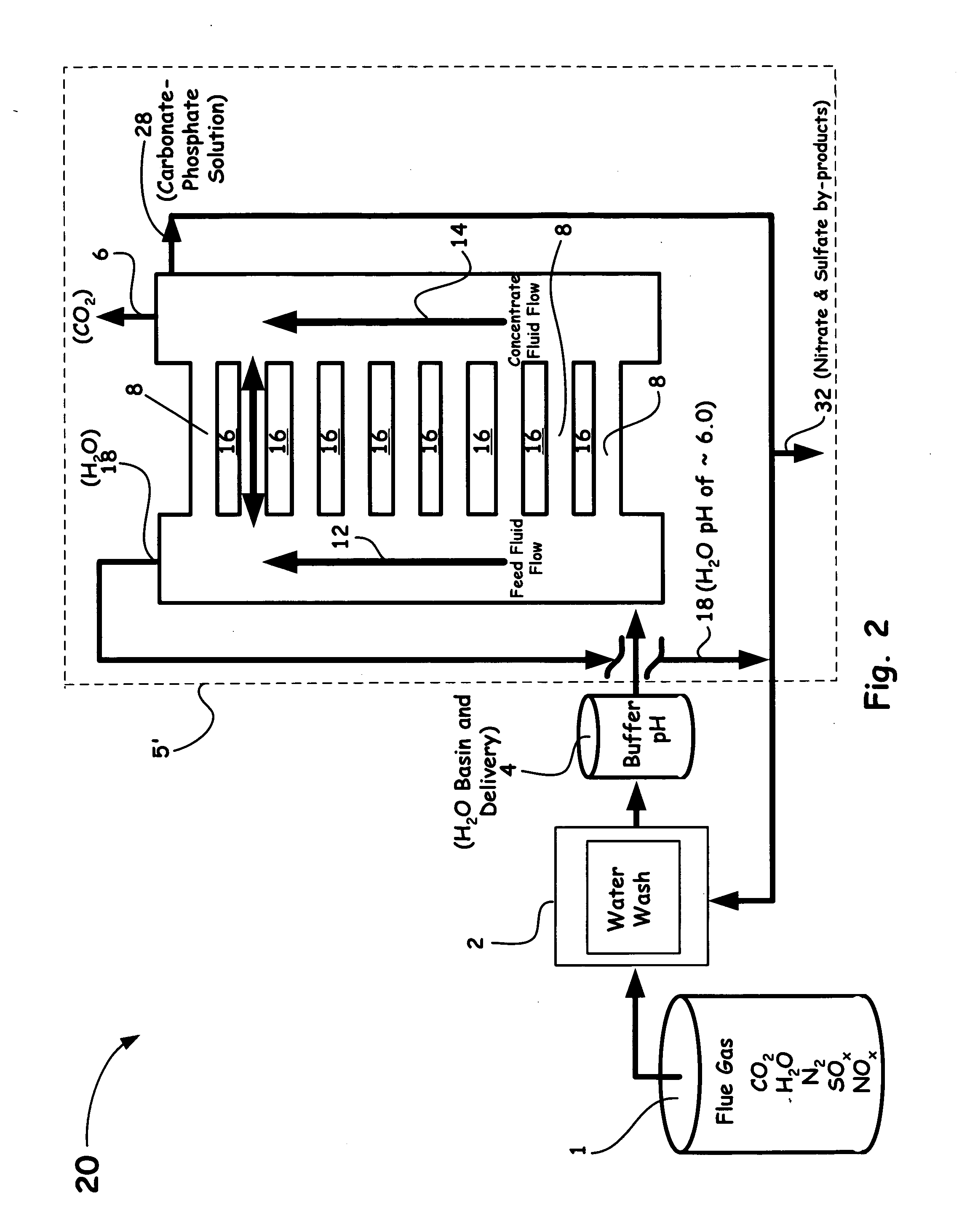
Carbon ion pump for removal of carbon dioxide from combustion gas and other gas mixtures
InactiveUS20070169625A1Improve concentrationIncrease vapor pressureLiquid separation by electricityCarbon compoundsCarbon ionReverse osmosis
A novel method and system of separating carbon dioxide from flue gas is introduced. Instead of relying on large temperature or pressure changes to remove carbon dioxide from a solvent used to absorb it from flue gas, the ion pump method, as disclosed herein, dramatically increases the concentration of dissolved carbonate ion in solution. This increases the overlying vapor pressure of carbon dioxide gas, permitting carbon dioxide to be removed from the downstream side of the ion pump as a pure gas. The ion pumping may be obtained from reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, thermal desalination methods, or an ion pump system having an oscillating flow in synchronization with an induced electric field.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Coating of particles comprising a pharmaceutically active ingredient with a carbonate salt or phosphate salt
InactiveUS20130115301A1Simple coating processInhibition of dissolutionOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPhosphate ionPharmaceutical industry
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical industry and relates to a process for coating a particle comprising a pharmaceutically active ingredient (API) comprising the steps of providing a composition comprising carbonate ions, phosphate ions, or a mixture thereof, providing a particle comprising an API, and precipitating a carbonate salt, a phosphate salt or a mixture thereof onto said particles.The present invention is also directed to a particle comprising an API, wherein the particle is coated with a coating comprising a carbonate salt, phosphate salt, or mixture thereof, and to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said particles.Moreover, the present invention is also directed to the use of said particles for preparing a medicament,
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108373175AIncrease profitOvercoming the problem of large differences in sedimentation velocityHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesCobalt(II,III) oxideCobalt salt
The invention discloses a preparation method of aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide, comprising the steps of (1) mixing aluminum salt solution and a complexing agent to obtain a mixed liquid; (2) adding cobalt salt solution, a precipitating agent solution containing carbonate ions and the mixed liquid of step (1) into a reaction device in concurrent manner, and co-precipitating to obtain aluminum-doped cobalt carbonate; (3) calcining the aluminum-doped cobalt carbonate of step (2) to obtain the aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide. The three solutions are fed in concurrent manner, so that the problem is solved that the process of preparing aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide by liquid co-precipitating experiences great differences between precipitating speeds of various elements; the prepared aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide has uniform distribution of elements, and the doping quantity of aluminum in the aluminum-doped cobalt(II,III) oxide can be significantly increased to 0.3-0.6%.
Owner:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Method for preparing active silver electrode
InactiveCN101235515ALarge specific surface areaImprove electrocatalytic activityElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesOxidation statePhenol
The invention provides a method for preparing an active silver electrode, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out anode oxidation reaction to the silver electrode to form a silver oxidation state layer on the surface of the silver electrode in water solution with anion,, secondly, changing polarity of the silver electrode, and carrying out cathode oxidation reaction to cathode of the silver electrode to obtain the active silver electrode, wherein anion is compounded by one, or two, or more than two following ions, namely, (1) perchlorate ion, (2) hypochlorous acid ion, (3) hydroxide ion, (4) nitrate ion, (5) sulfate ion, (6) carbonate ion, (7) halide ion, (8) organic acid ion and (9) phenol hydroxyl root ion, the active silver electrode which is obtained according to the method of the invention is not only provided with a more specific surface, but also provided with higher electro-catalysis activity, longer electro-catalysis performance and less power loss, and the obtained active silver electrode can be used to electrolyze 3,4,5,6-tetrachloropicolinic acid and to compound 3,6-dichloropicolinic, which not only has lower energy consumption, but also has higher production efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing peeled layered material/ carbon nano tube complex in aqueous solution
InactiveCN102502519AAvoid destructionGood dispersionOxide/hydroxide preparationNickel oxides/hydroxidesCarbon nanotubeIon exchange
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
In situ precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by indigenous microorganisms to improve mechanical properties of a geomaterial
A method for increasing the concentration of calcium carbonate in a geomaterial that contains indigenous microorganisms capable of hydrolyzing urea to ammonia, which method includes enriching the geomaterial with a source of nutrients, adding urea to the geomaterial which is hydrolyzed to ammonia and which raises the pH of the geomaterial, and adding a source of calcium ions to the geomaterial. Carbonate ions obtained by the hydrolysis of the urea combine with calcium ions to form calcium carbonate.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IDAHO
Method for producing an organic acid
An organic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium which has an ability to produce an organic acid and has been modified so that expression of yidE gene is enhanced, or a product obtained by processing the bacterium, to act on an organic raw material in a reaction mixture containing carbonate ions, bicarbonate ions, or carbon dioxide gas to produce the organic acid, and collecting the organic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Conductive membrane for carbon dioxide separation
Disclosed are a conductive membrane able to selectively separate carbon dioxide from a gas mixture containing carbon dioxide, a manufacturing method thereof, and a method of separating carbon dioxide using the membrane. The conductive membrane for carbon dioxide separation includes molten carbonate, acting as a carbonate-ion conductor, and oxide, acting as an electronic conductor, and has infinite selectivity for carbon dioxide at high temperatures of 500° C. or more.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP +1
Uniformly coordinating precipitation method for preparing nano zinc oxide
InactiveCN1616354AReduce concentrationEvenly distributedOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideZinc oxides/hydroxidesZno nanoparticlesSulfide
The present invention relates to uniformly coordinating precipitation process of preparing nanometer zinc oxide. The technological scheme includes the reaction between zinc oxide or zinc salt material and ammonia and carbonate as coordinating agent to produce water soluble coordinating compound tetraammonium-zinc carbonate solution; adding sulfide solution to eliminate heavy metal ion inside the coordinating compound solution; adding surfactant, water for dilution or heating decomposing the coordinating compound solution to separate zinc ion and to react with carbonate radical ion to produce fine basic zinc carbonate precipitate; washing the precipitate with ethanol, methanol or acetone, filtering, stoving at 40-80 deg.c and heating at 200-800 deg.c to decompose into nanometer zinc oxide. The production process is simple and has low cost.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for preparing silicon-carbon composite material by molten salt electrolysis
ActiveCN109950494AImprove structural stabilityGood flexibilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesStructural stability
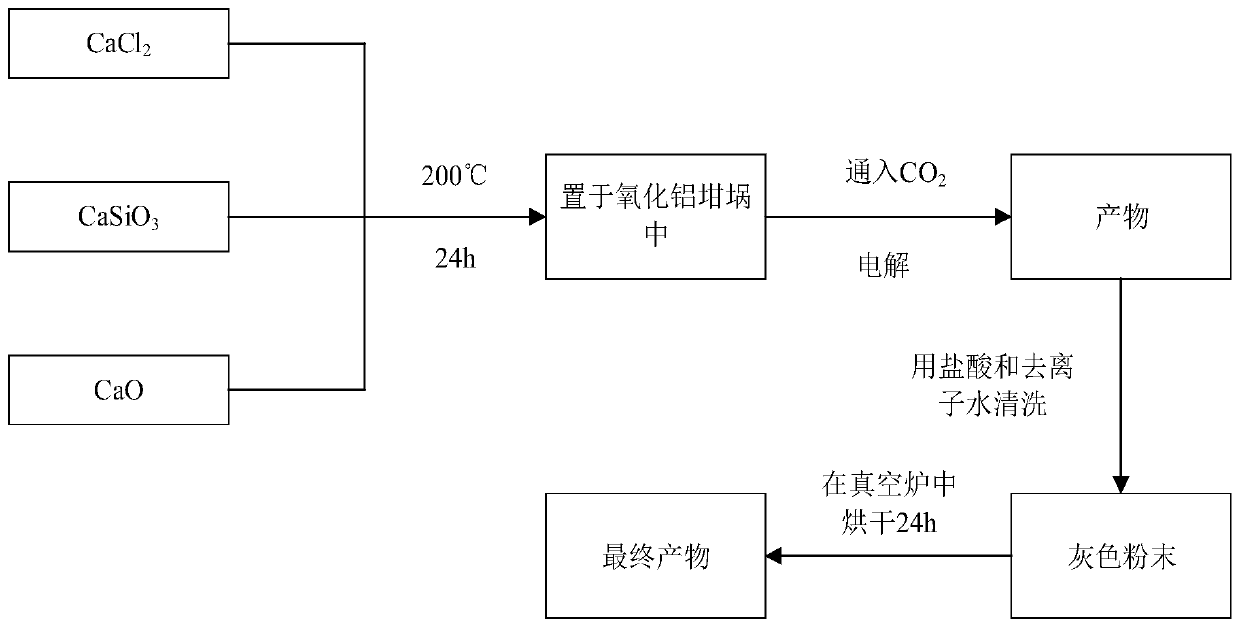
The invention discloses a method for preparing a silicon-carbon composite material through molten salt electrolysis. The method comprises the following steps: introducing CO2 gas in a CaCl2-CaSiO3-CaOmolten salt electrolysis process; dissolving CaSiO3 in molten salt to obtain silicate ions, and reducing the silicate ions at the cathode of an electrolytic tank to obtain a nano silicon material; capturing CO2 by utilizing oxygen ions in CaCl2-based molten salt, immobilizing the CO2 into carbonate ions, enabling the carbonate ions to reach a cathode through diffusion in the molten salt, and reducing the carbonate ions into a nano-carbon material on the cathode, thereby obtaining the silicon-carbon composite material on the cathode. The prepared silicon-carbon composite material utilizes thegood structural stability, flexibility and lubricity of the carbon material, so the silicon carbon composite material has the advantages of high specific capacity of silicon storage, high conductivityof a carbon material and the like, thereby solving the problems that the volume of silicon can be changed slightly in the silicon embedding process of lithium ions and the silicon is expanded and pulverized when lithium is embedded into silicon. Moreover, the obtained silicon carbon composite material has the advantages of high specific capacity of silicon storage, high conductivity of the carbonmaterial and the like and achieves the purpose of complementary advantages.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Sustained-release composition process for producing the same and preparation thereof
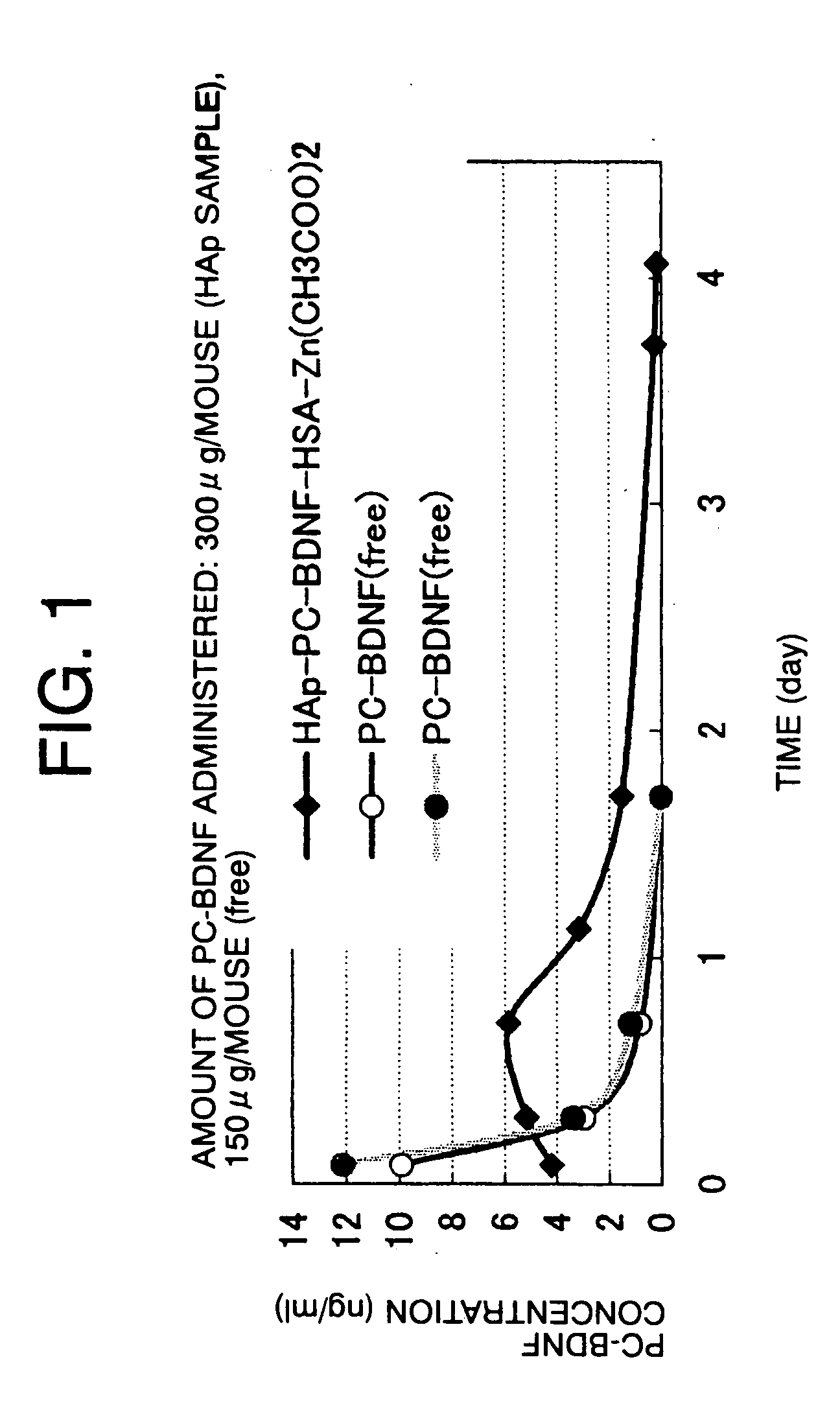
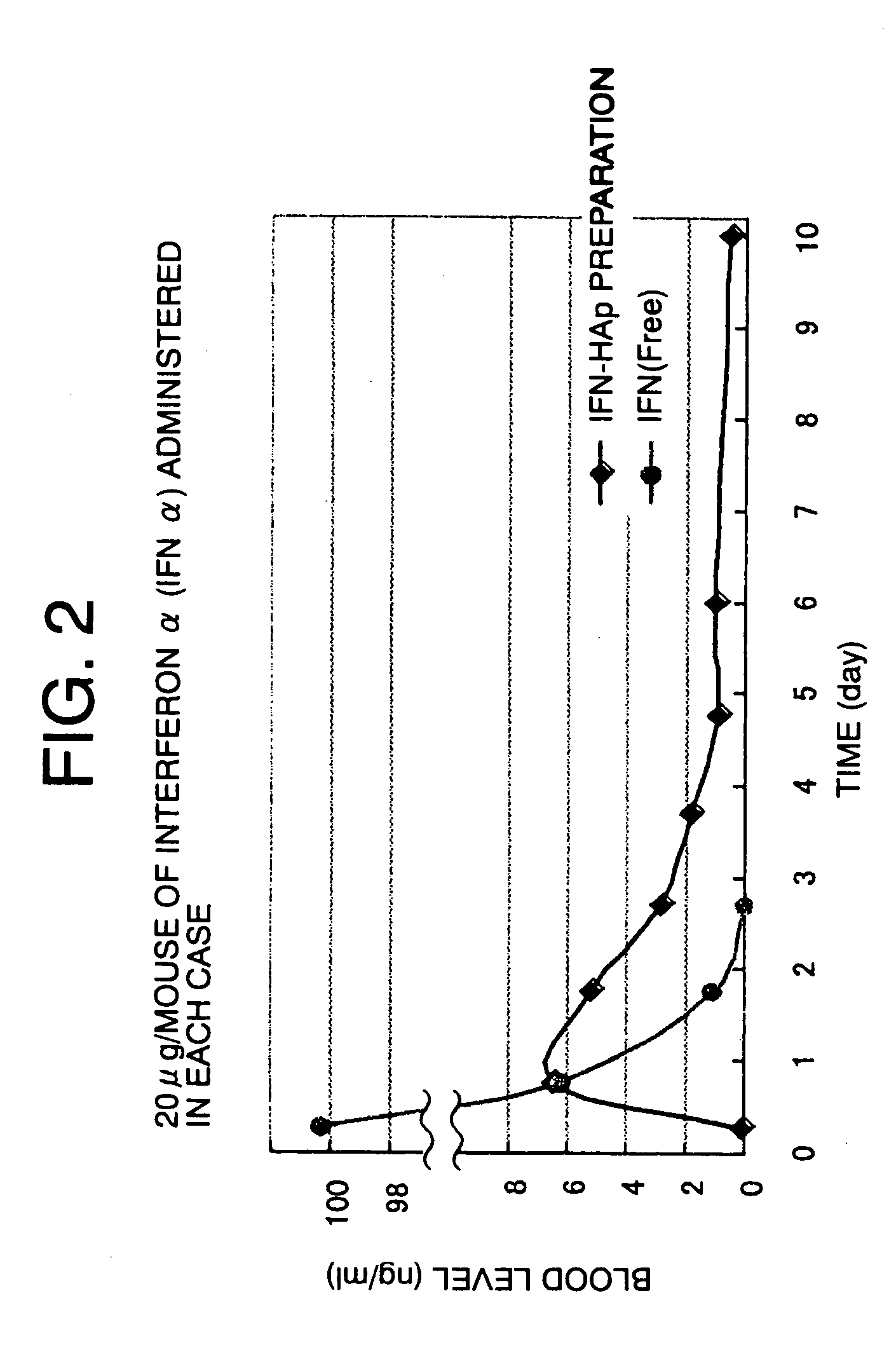
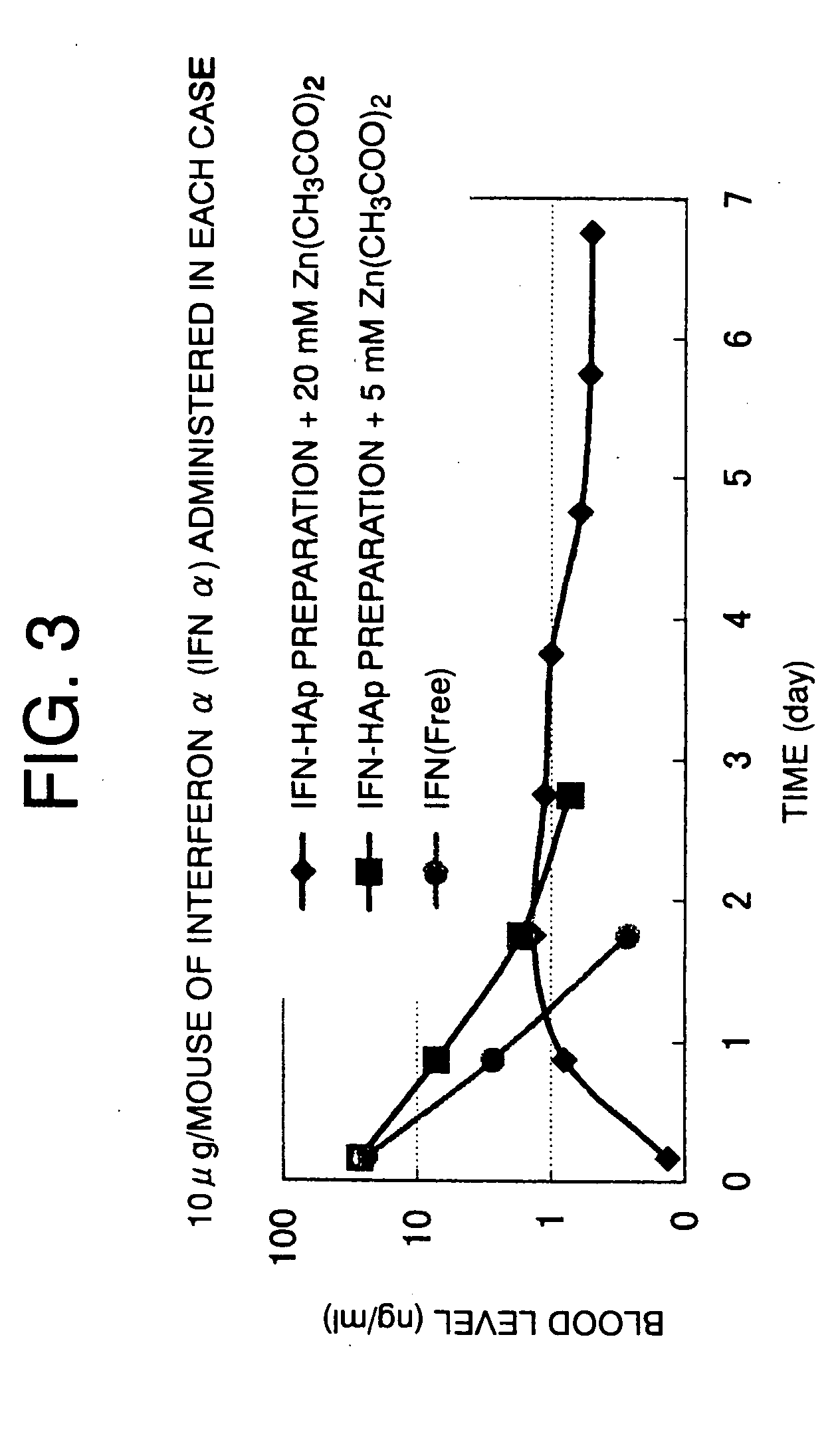
The present invention provides a sustained-release composition by which a sustained-release effect can be obtained for a long time when injecting microparticles of the composition in an amount that can be subcutaneously or intramuscularly injected to a human with ease and without pain. The composition comprises porous hydroxyapatite microparticles having pores embolized by filling the pores in the microparticles with a biologically active drug, a human serum protein, and a mucopolysaccharide, and adding a divalent metal ion. Alternatively, the composition comprises porous hydroxyapatite microparticles having pores embolized in the outer layer by filling the pores in the microparticles with a biologically active drug, a human serum protein, and a water-soluble calcium salt one after another or at one time, and then adding sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, or an aqueous carbonate ion solution.
Owner:LTT BIO PHARMA
Thickened hair colourant and bleaching compositions
InactiveUS20060117498A1Improve hair damage profileCosmetic preparationsHair removalFree radicals scavengerDermatology
The present invention relates to hair colouring and hair bleaching compositions comprising a source of carbonate ions, at least one oxidizing agent and a specified gel network thickener system wherein said composition is free of a source of radical scavengers. The compositions surprisingly provide improved hair colourant and bleaching compositions which deliver improved lift, lightening and colour delivery whilst minimizing damage which are easy to manufacture and have long shelf life stability.
Owner:NOXELL CORP
Saline-alkali soil improver as well as preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN103937507ALower pHKeep Fertilizer NutrientsOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsAlkali soilGypsum
The invention discloses a saline-alkali soil improver as well as a preparation method and a use method thereof. The saline-alkali soil improver is prepared by irradiating, modifying and grafting materials such as attapulgite, decomposed coal and sodium polyacrylate. According to the saline-alkali soil improver, carbonate ions in deep soil are cured through ardealite, the pH value of the soil is reduced and the soil can be loosened under the acidic action of the decomposed coal, and the effect of protecting the soil nutrient is achieved by virtue of the attapulgite.
Owner:高程华
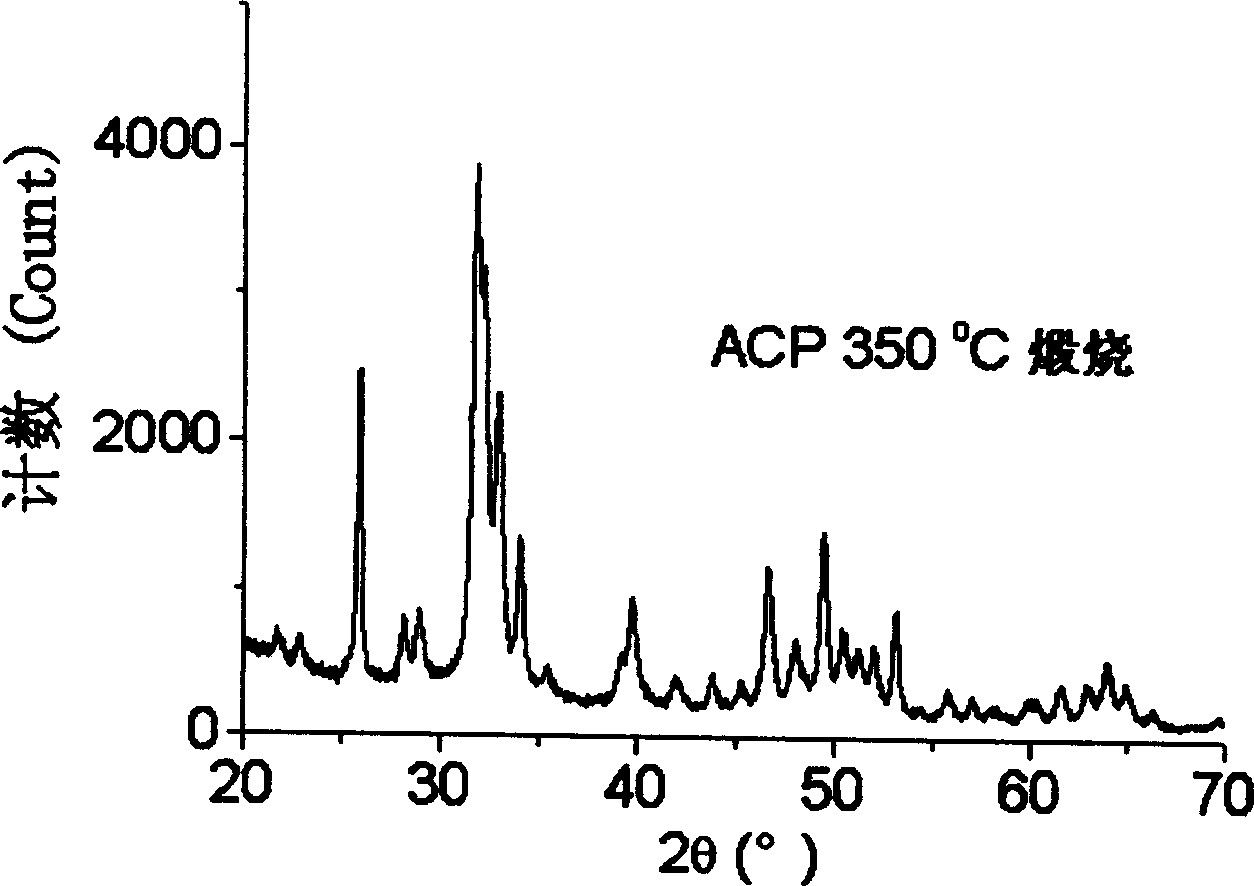
Carbonic acid type high activity partially crystallized calcium phosphate and its prepn
ActiveCN1772602AHigh reactivityImprove solubilityPhosphorus compoundsProsthesisTri calcium phosphateHigh activity
The present invention is carbonic acid type high activity partially crystallized calcium phosphate and its preparation. The material has the nonstoichiometric crystallization state between the crystal and amorphous substance and contains carbonate radical, Mg, Sr and Zn essential for human body bone tissue. It is prepared with water soluble phosphate and calcium salt as material and through adding carbonate, Sr salt and / or Mg salt and / or Zn salt, reaction in water solution, separating, drying and calcining reaction product to obtain carbonic acid type high activity partially crystallized calcium phosphate powder. The powder has high bioactivity, reaction activity and biodegradability, and may be used widely in replacing and repairing hard tissue.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Metal electrolytic ceramic coating method, electrolytic solution for metal electrolytic ceramic coating, and metal material
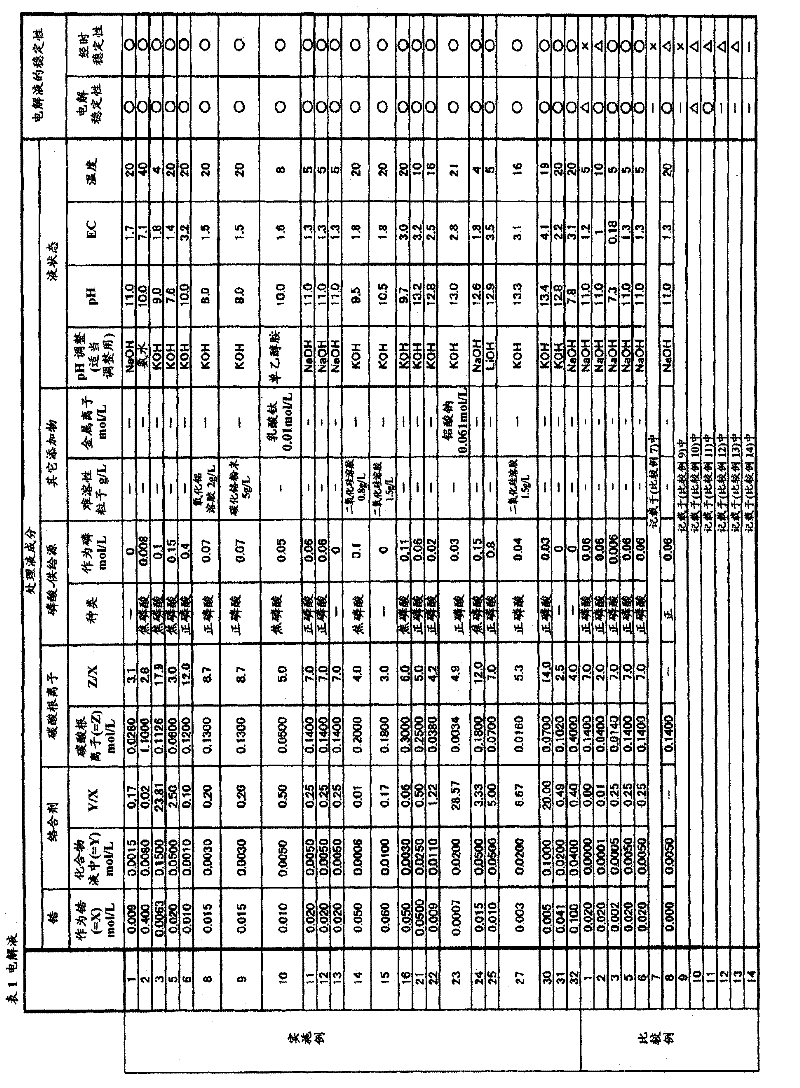
The electrolysis solution for electrolytic ceramic coating includes water, a water-soluble zirconium compound, a complexing agent, carbonate ion, and at least one member selected from the group consisting of an alkali metal ion, ammonium ion and an organic alkali. Te zirconium compound is included at a concentration (X) in terms of zirconium of 0.0001 to 1 mol / L, the complexing agent is included at a concentration (Y) of 0.0001 to 0.3 mol / L, the carbonate ion is included at a concentration (Z) of 0.0002 to 4 mol / L, a ratio of the concentration (Y) of the complexing agent to the concentration (X) in terms of zirconium (Y / X) is at least 0.01, a ratio of the concentration (Z) of the carbonate ion to the concentration (X) in terms of zirconium (Z / X) is at least 2.5, and the electrolysis solution has an electrical conductivity of 0.2 to 20 S / m.
Owner:NIHON PARKERIZING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com