Saponification of organic extractant
An organic extractant and saponification technology, applied in the field of saponification of organic phase, can solve the problems of ammonium consumption, high recovery cost, difficult recovery, etc., and achieve the effects of eliminating pollution, reducing production cost and saving three waste treatment costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
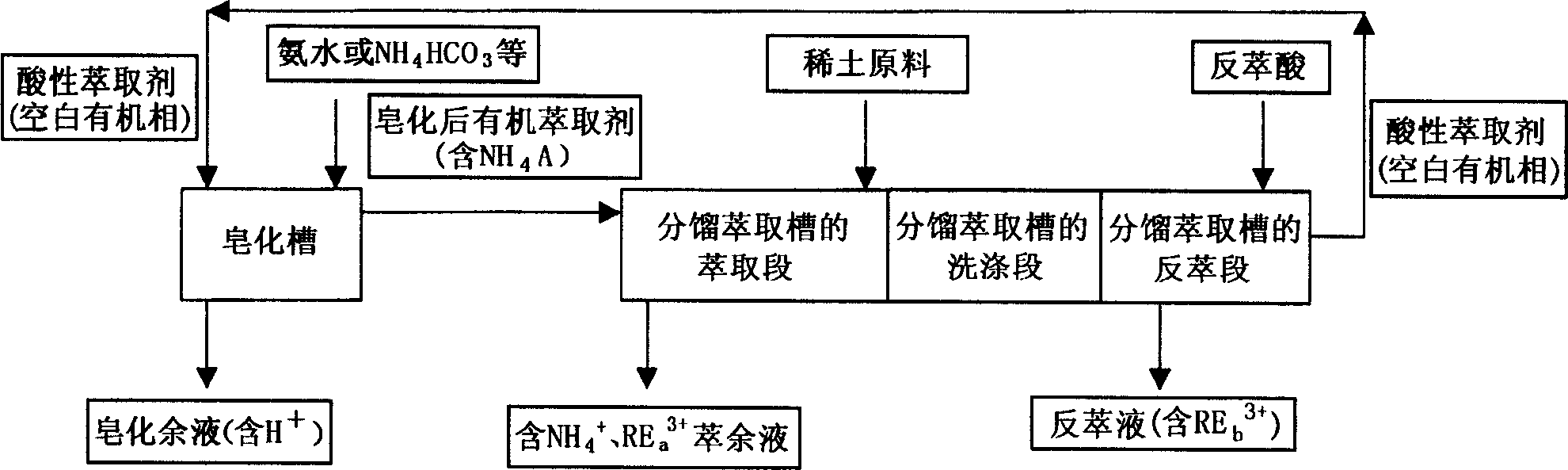
[0035] 1.4mol / l P204 (kerosene dilution) flows into the first stage mixing chamber of saponification tank with the speed of 5 liters / min; , the acidity is PH4 rare earth solution (5 liters / min) pulping, also with the speed of 5 liters / min the first-stage mixing chamber of the saponification tank is continuously introduced to mix with the organic extractant; level clarification.
[0036]The organic extractant after saponification contains rare earth La-NdREO 27.0g / l, and the saponification rate is 34.6%. It directly flows into the first stage of the cerium grouping extraction section.
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1.5mol / l P507 (sulfonated kerosene dilution) flows into the first-stage mixing chamber of the saponification tank at a speed of 10 liters / min; the rare earth carbonate (REO 43%, 450 g / min) containing La-Gd is used to contain REO 13.5g / l, the rare earth solution (10 liters / min) with an acidity of PH3 is slurried, and is also continuously introduced into the first-stage mixing chamber of the saponification tank at a speed of 10 liters / min to mix with the organic extractant; adopt 3-stage mixing and clarification tank co-flow Extraction saponification, 2-stage clarification.
[0039] The organic extractant after saponification contains rare earth La-GdREO 29.3g / l, the saponification rate is 34.7%, and directly flows into the first stage of the Gd-Tb grouping extraction section.
Embodiment 3
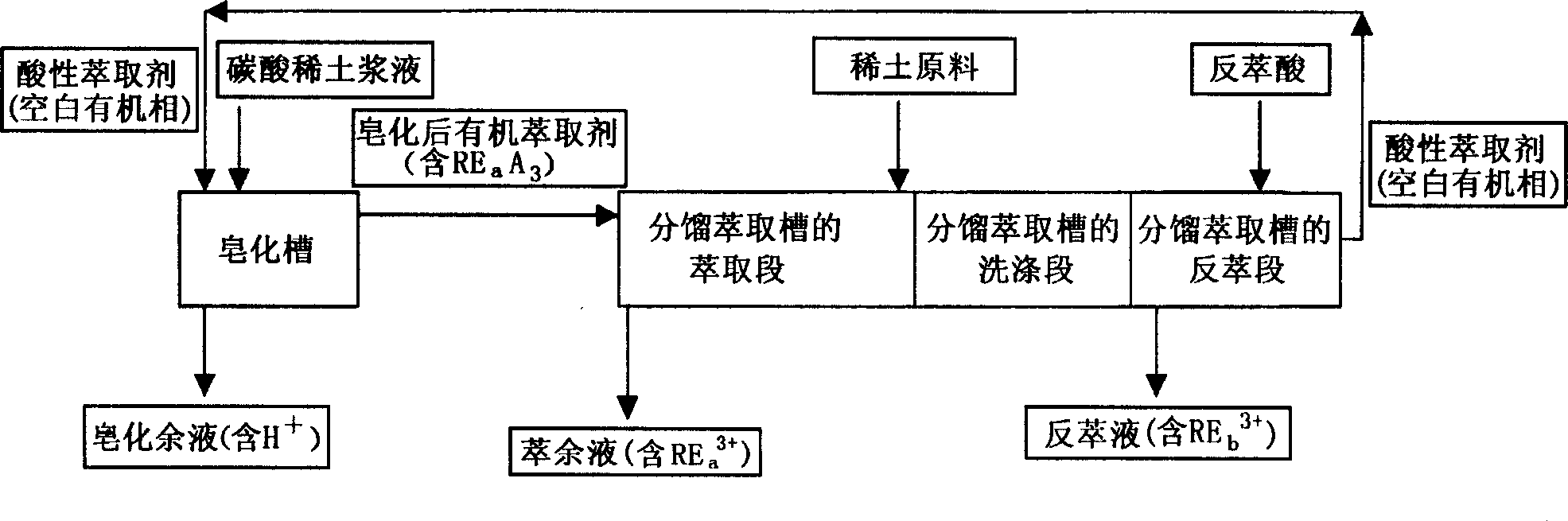
[0041] The rare earth carbonate (REO 42% 343 g / min) obtained by ammonium bicarbonate precipitation in the ion-adsorption type rare earth ore water immersion solution is mixed with 0.3N hydrochloric acid solution (5 liters / min), and then continuously introduced into the mixing chamber of the saponification tank; 1.5mol / l P507 (kerosene dilution) blank organic phase also flows into the mixing chamber of the saponification tank at a speed of 5 liters / min to mix and react with the rare earth carbonate slurry; adopt 4-stage mixing and settling tank for co-flow extraction saponification, and 2-stage clarification.
[0042] The saponified organic extractant contains REO 28.7g / l, saponification rate is 34.0%, and directly flows into the first stage of the gadolinium-terbium grouping extraction section.
[0043] The acidity of the saponification residual liquid is 0.3N, and the concentration of REO is 0.11g / l, and it is directly returned to be used for rare earth carbonate pulping.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com