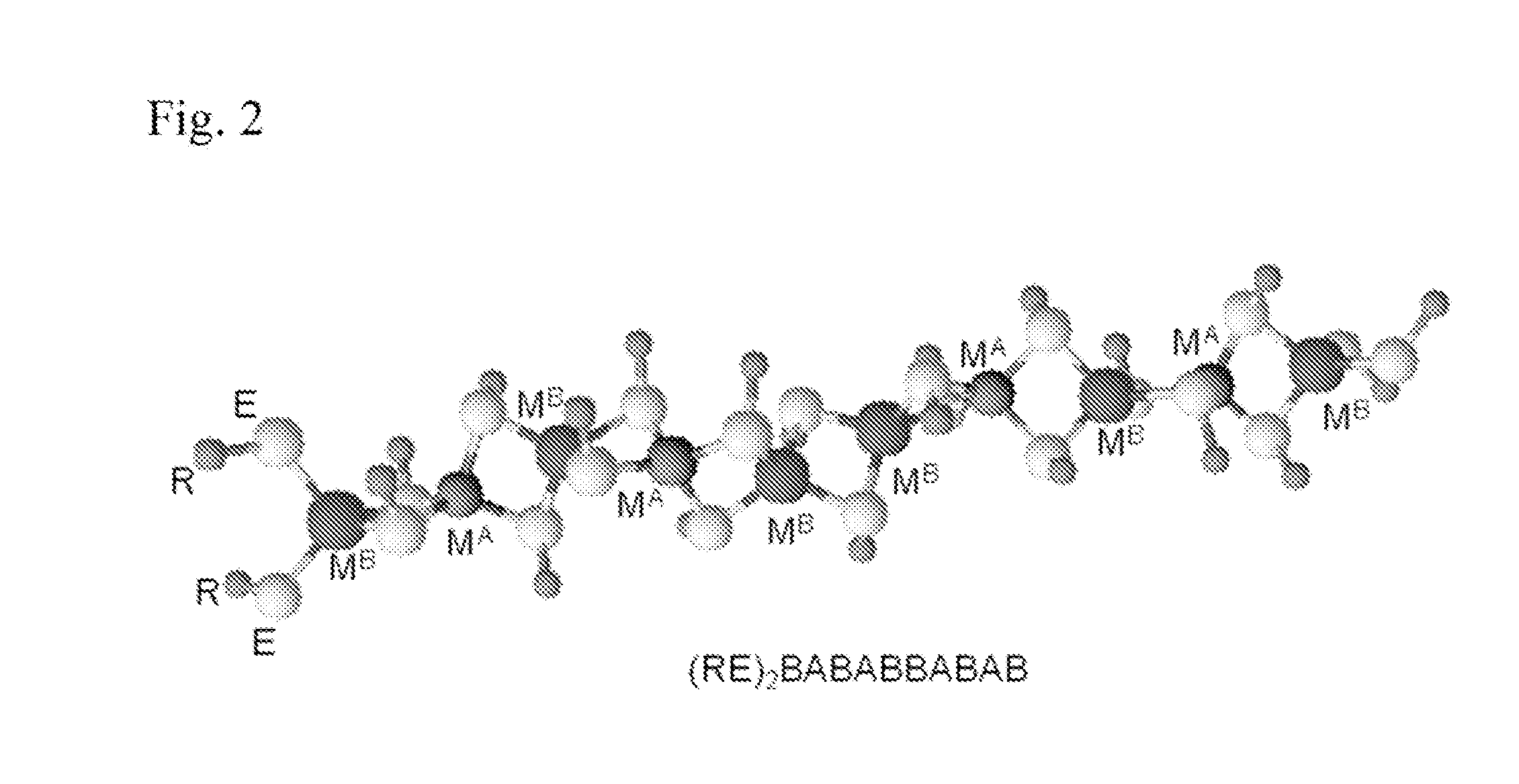
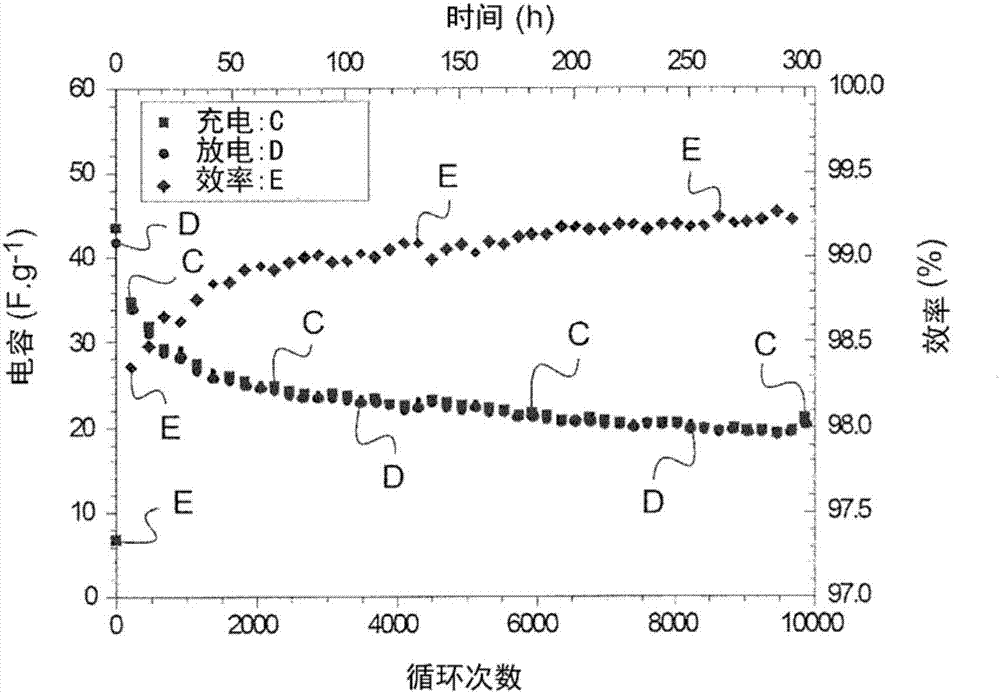
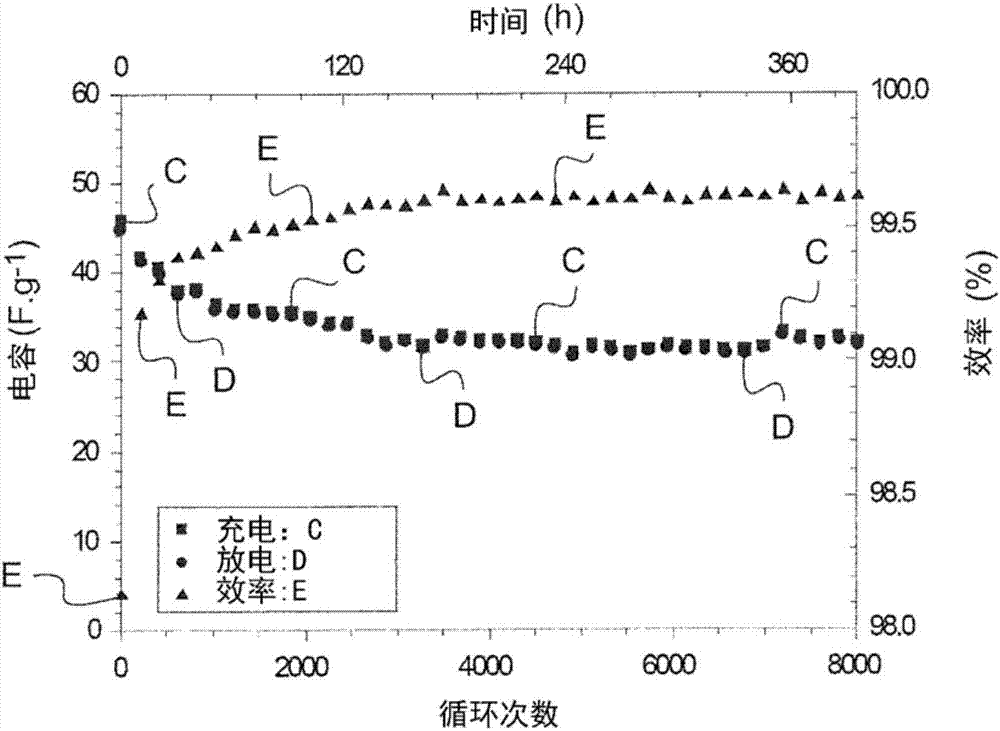
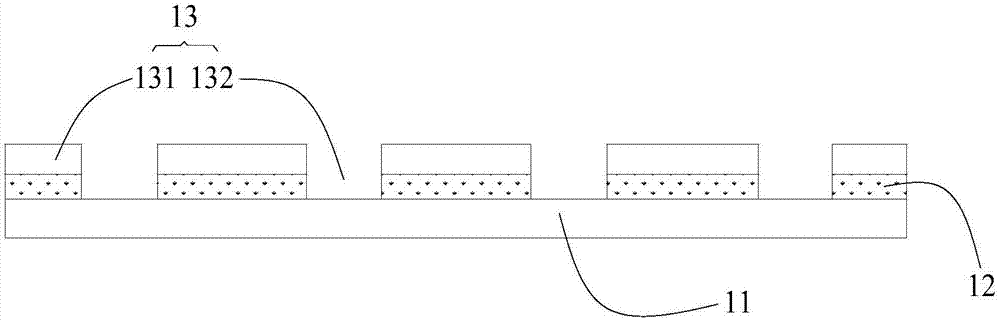
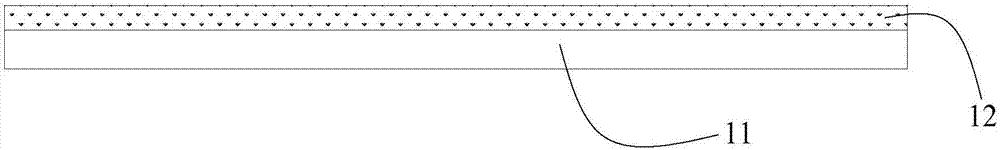
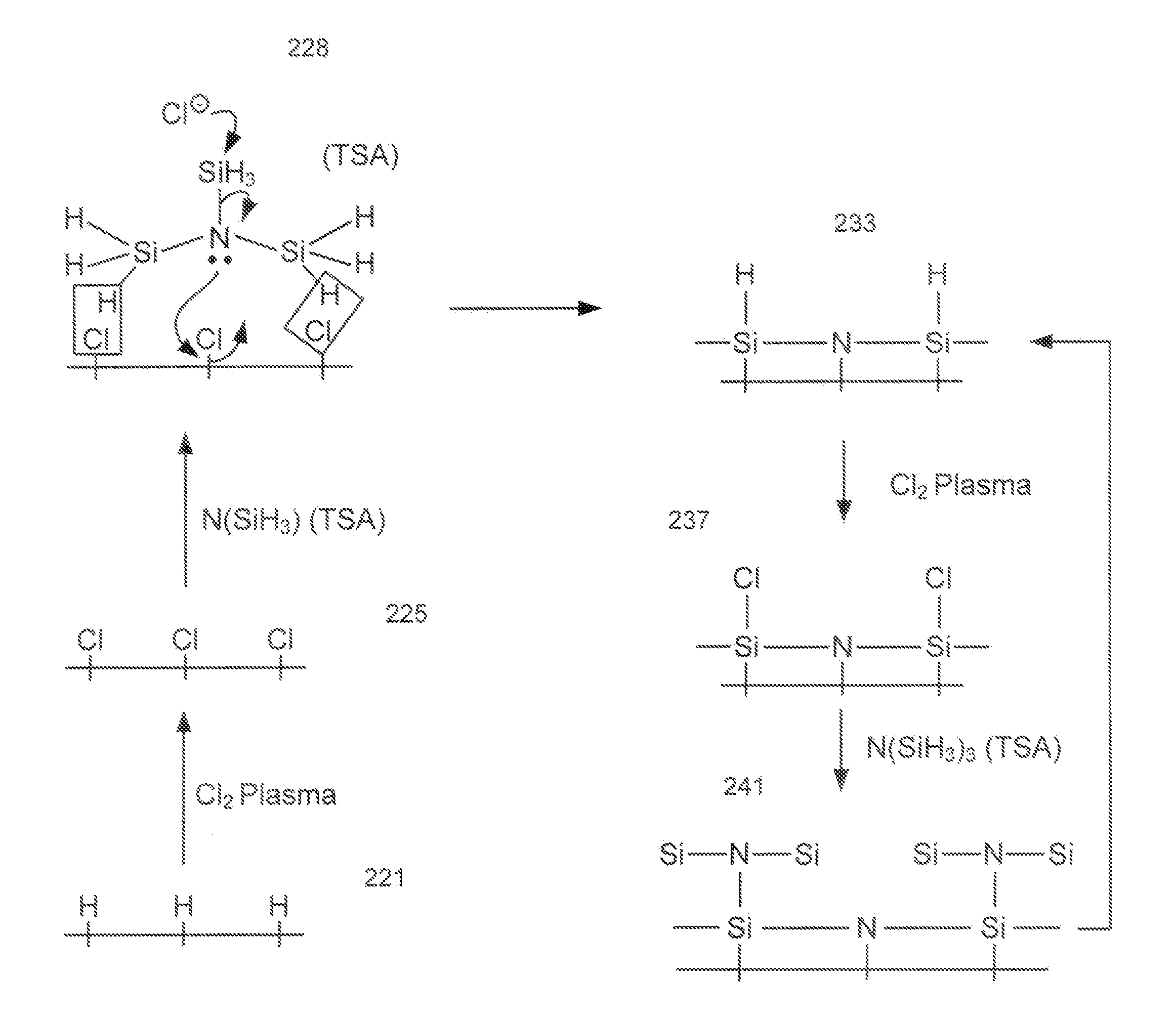Patents
Literature
70 results about "Molecular precursor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
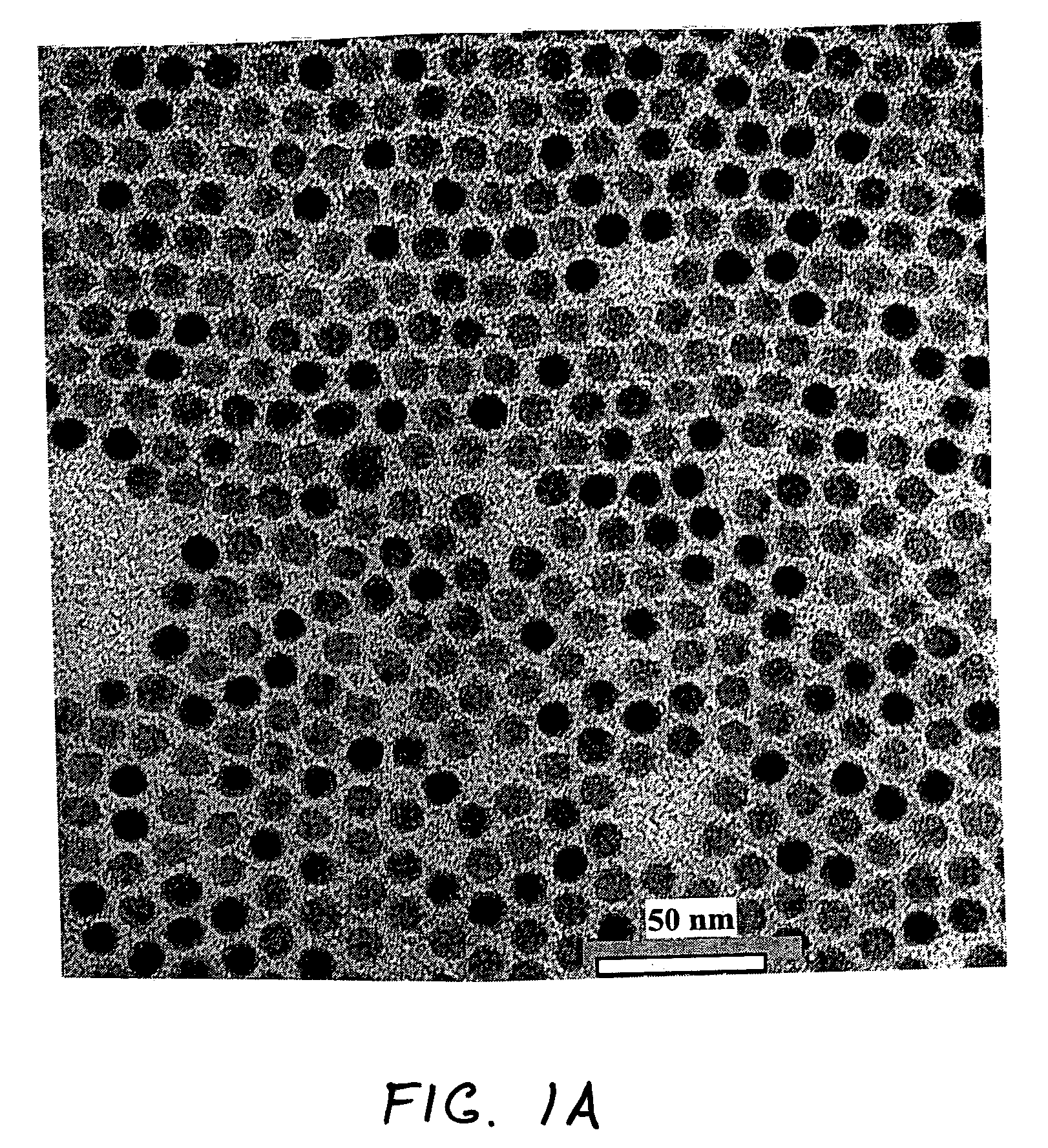
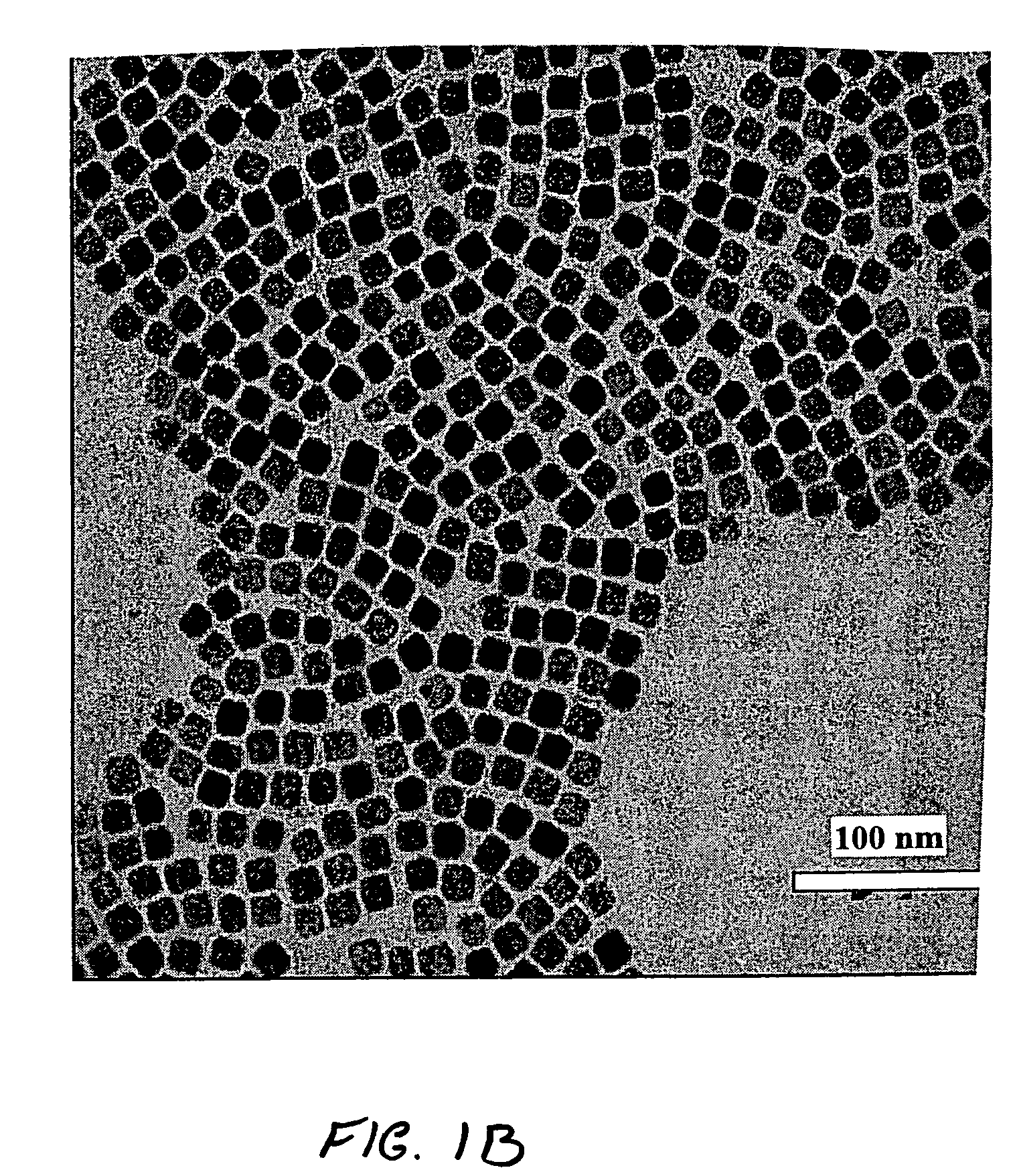
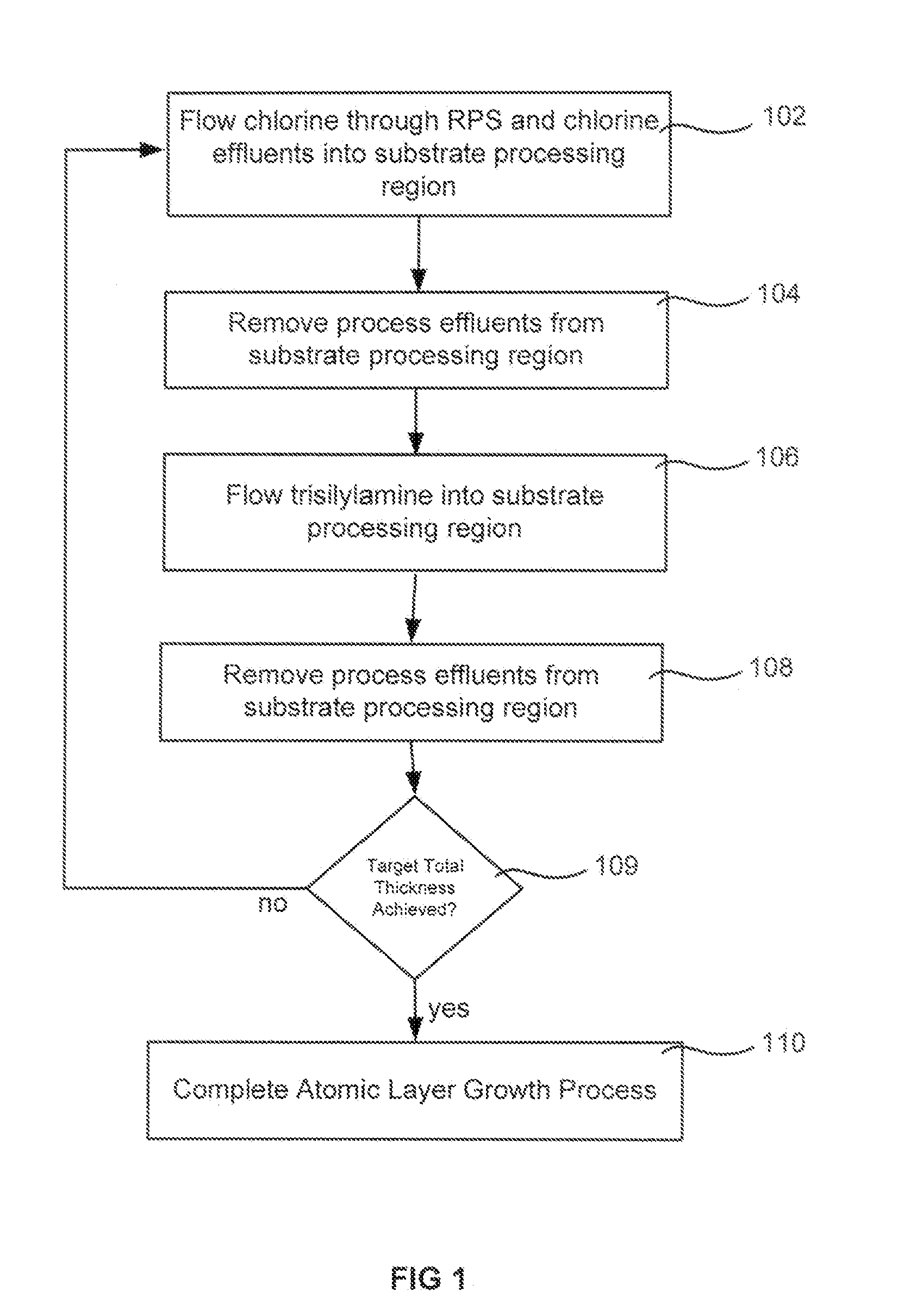
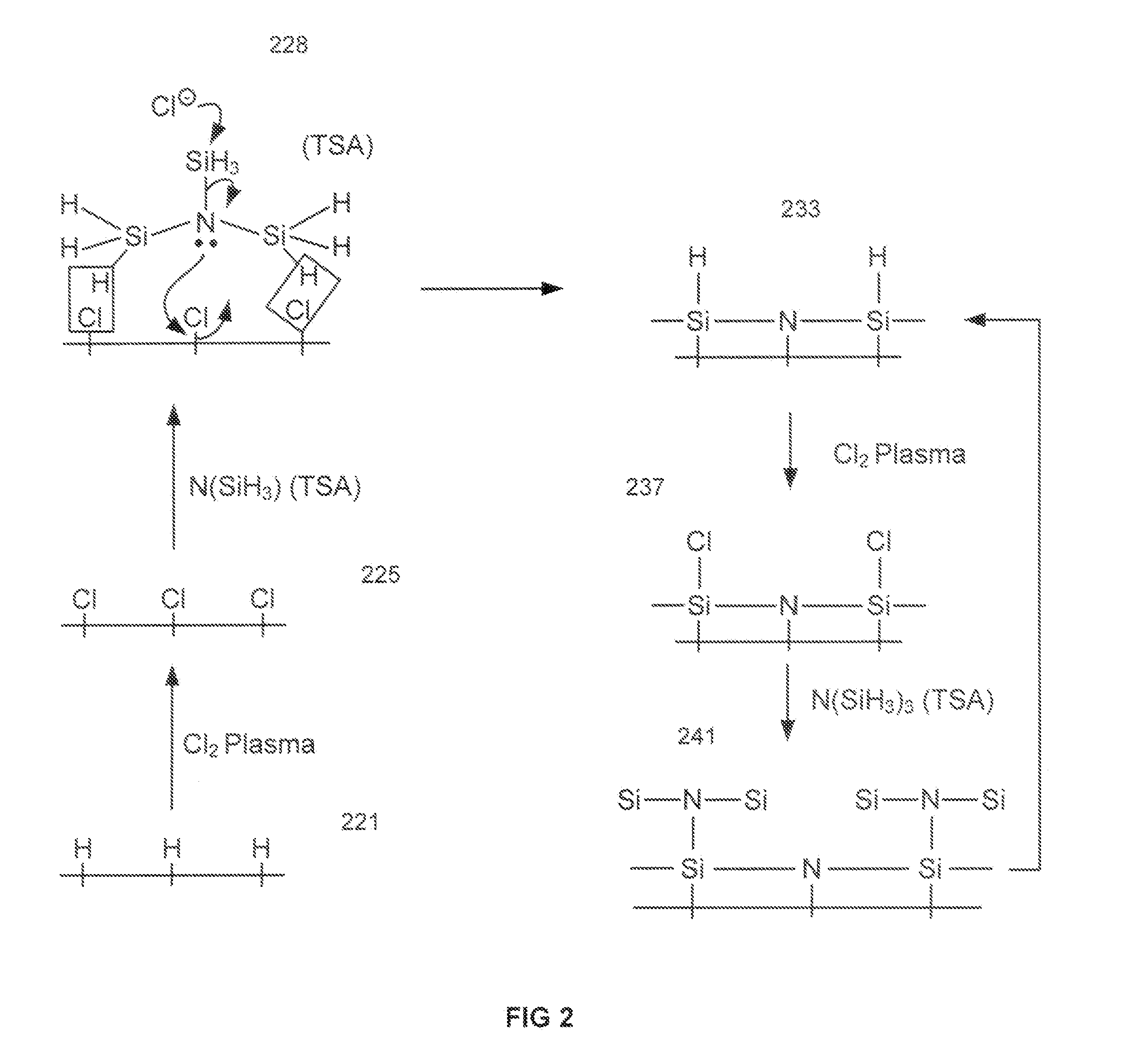
Atomic layer deposition of silicon nitride using dual-source precursor and interleaved plasma
InactiveUS20120213940A1Reduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesSelf limitingSilicon nitride
Atomic layer deposition using a precursor having both nitrogen and silicon components is described. The deposition precursor contains molecules which supply both nitrogen and silicon to a growing film of silicon nitride. Silicon-nitrogen bonds may be present in the precursor molecule, but hydrogen and / or halogens may also be present. The growth substrate may be terminated in a variety of ways and exposure to the deposition precursor displaces species from the outer layer of the growth substrate, replacing them with an atomic-scale silicon-and-nitrogen-containing layer. The silicon-and-nitrogen-containing layer grows until one complete layer is produced and then stops (self-limiting growth kinetics). Subsequent exposure to a plasma excited gas modifies the chemical termination of the surface so the growth step may be repeated. The presence of both silicon and nitrogen in the deposition precursor molecule increases the deposition per cycle thereby reducing the number of precursor exposures to grow a film of the same thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
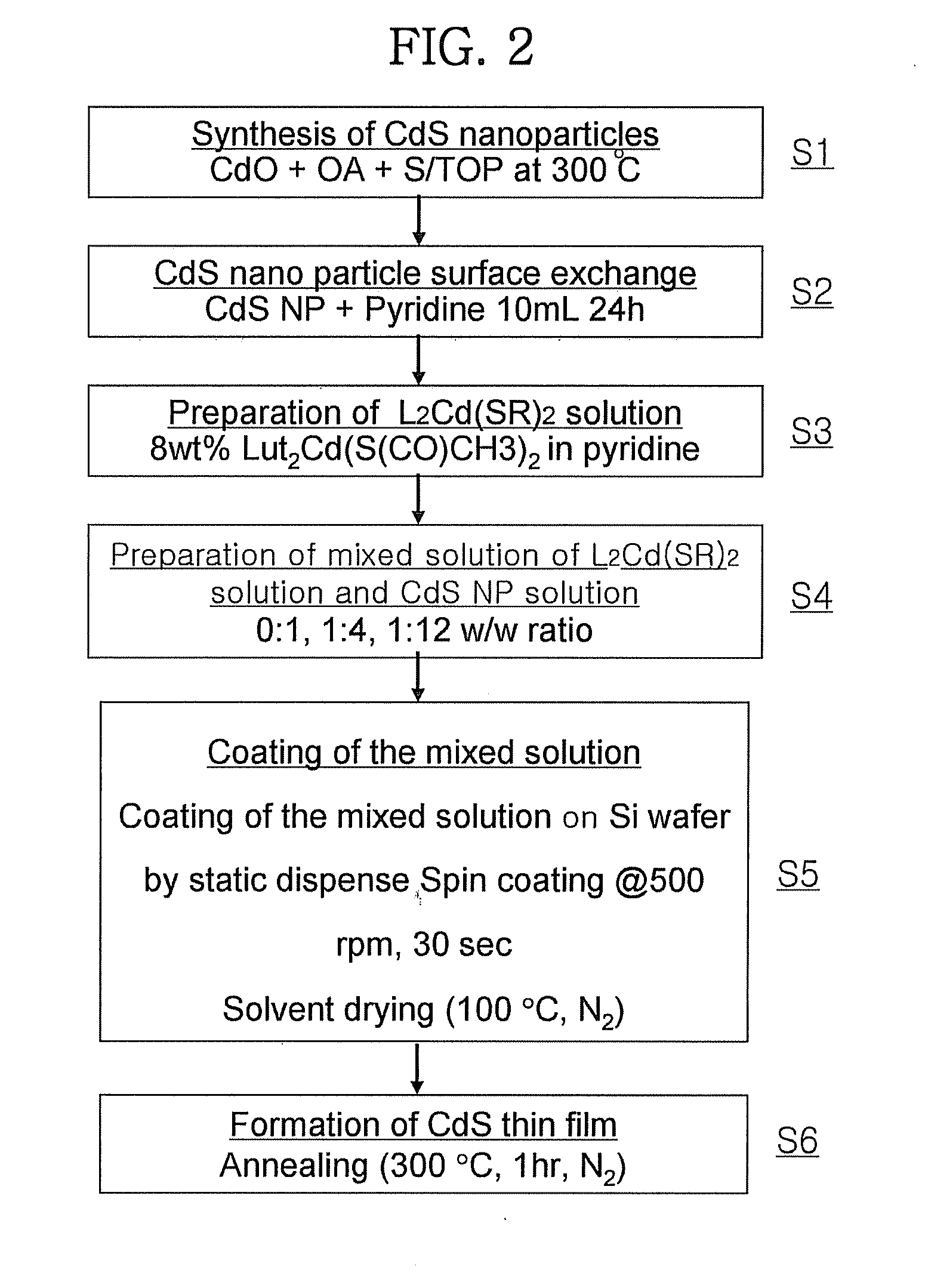
Method for the preparation of IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060110313A1Controlled in sizeControl shapeMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsOrganic solventQuantum dot
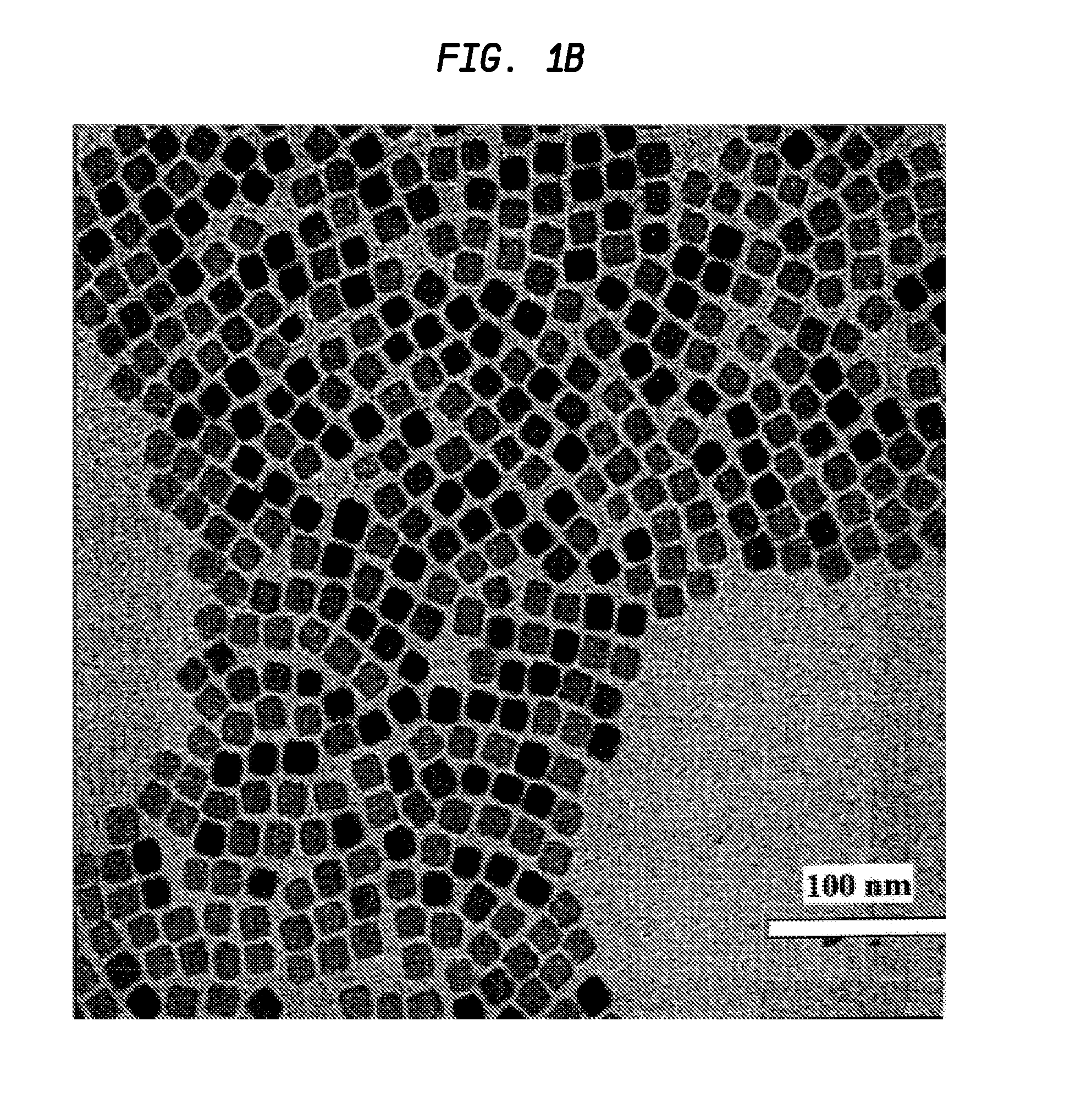
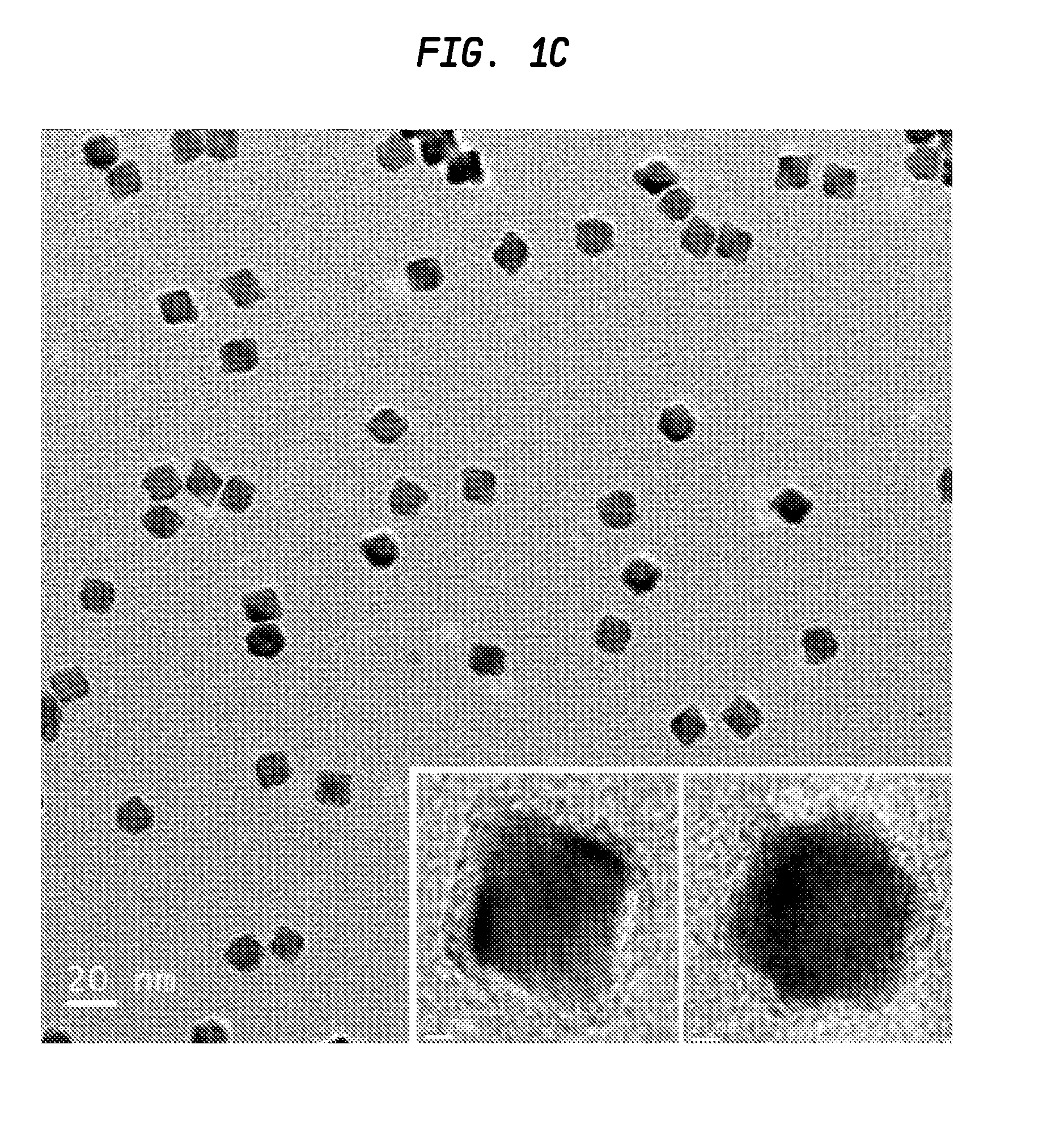
A high temperature (on the order of about 90° C. or above) non-aqueous synthetic procedure for the preparation of substantially monodisperse IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles (quantum dots) is provided. The procedure includes first introducing a first precursor selected from the group consisting of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element and a molecular precursor of a Group VI element into a reaction vessel that comprises at least an organic solvent to form a mixture. Next, the mixture is heated to a temperature of about 90° C. or above and thereafter a second precursor which is different from the first precursor and is selected from the group consisting of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element and a molecular precursor of a Group VI element is added into the heated mixture. The reaction mixture is then mixed to initiate nucleation of IV-VI nanocrystals and the temperature of the reaction mixture is controlled to provide substantially monodispersed IV-VI nanoparticles having a diameter of about 20 nm or less.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC +1
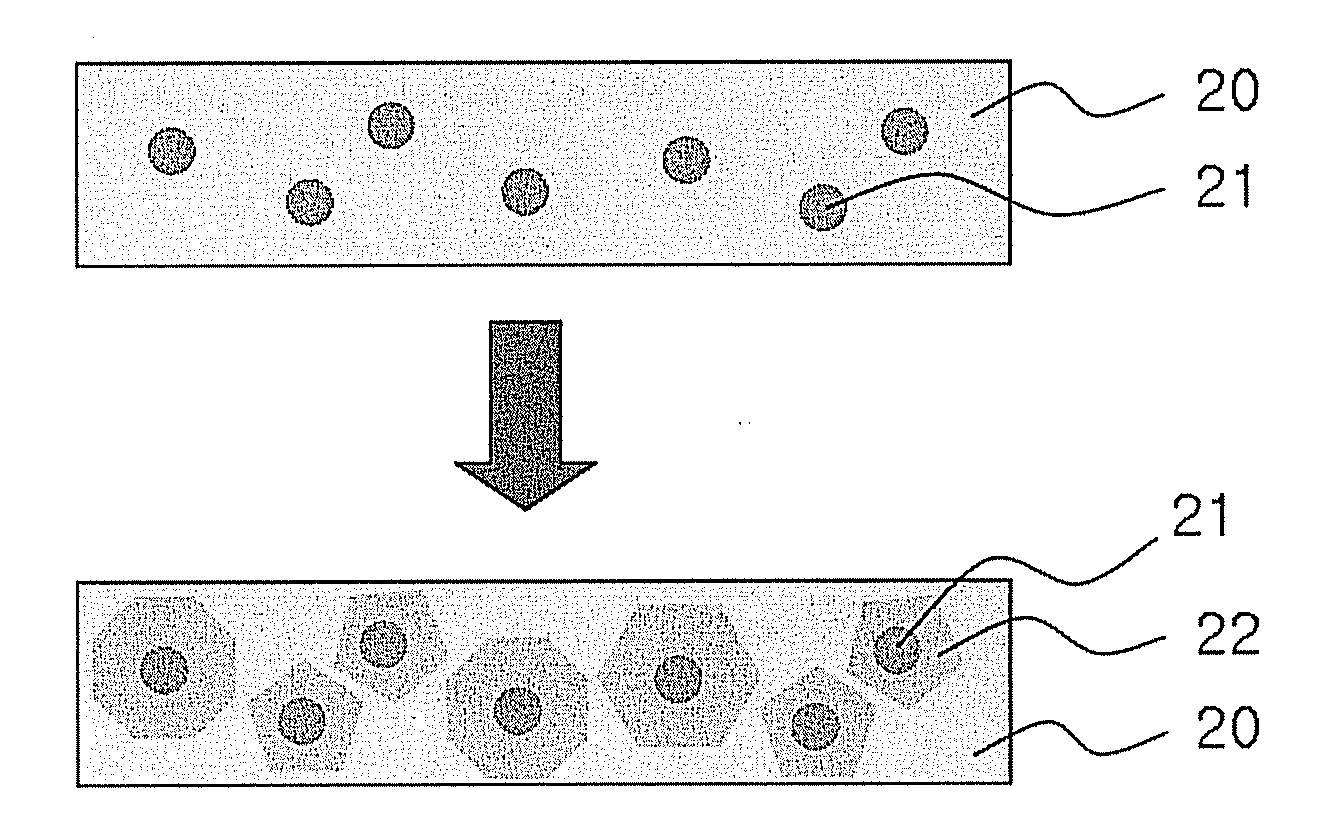
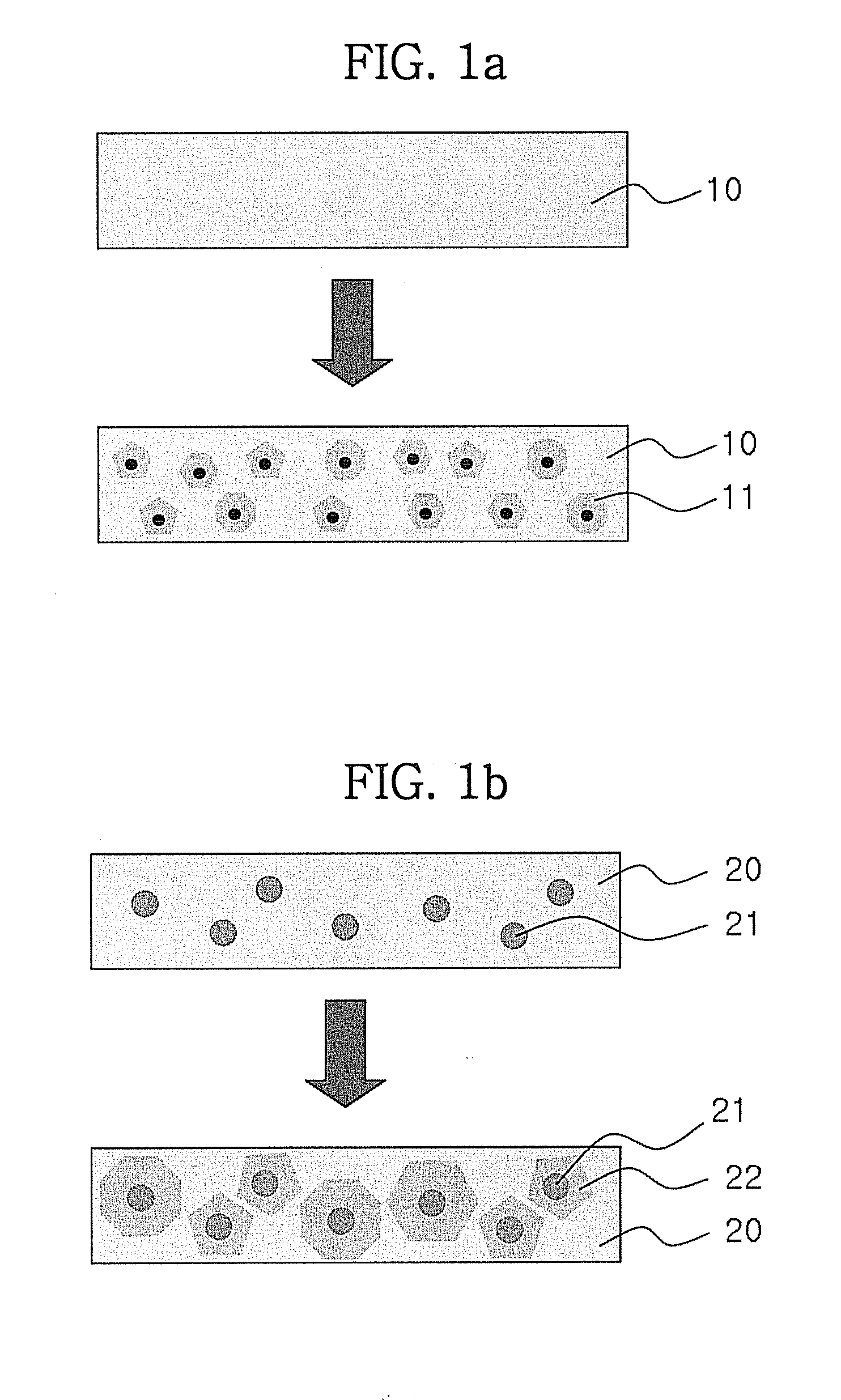
Thin film containing nanocrystal particles and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070298160A1High crystallinityReduce grain boundariesMaterial nanotechnologyWater-repelling agents additionMolecular precursorCrystallinity
Disclosed herein is a thin film prepared using a mixture of nanocrystal particles and a molecular precursor. The nanocrystal is used in the thin film as a nucleus for crystal growth to minimize grain boundaries of the thin film and the molecular precursor is used to form the same crystal structure as the nanocrystal particles, thereby improving the crystallinity of the thin film. The thin film can be used effectively in a variety of electronic devices, including thin film transistors, electroluminescence devices, memory devices, and solar cells.Further disclosed is a method for preparing the thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
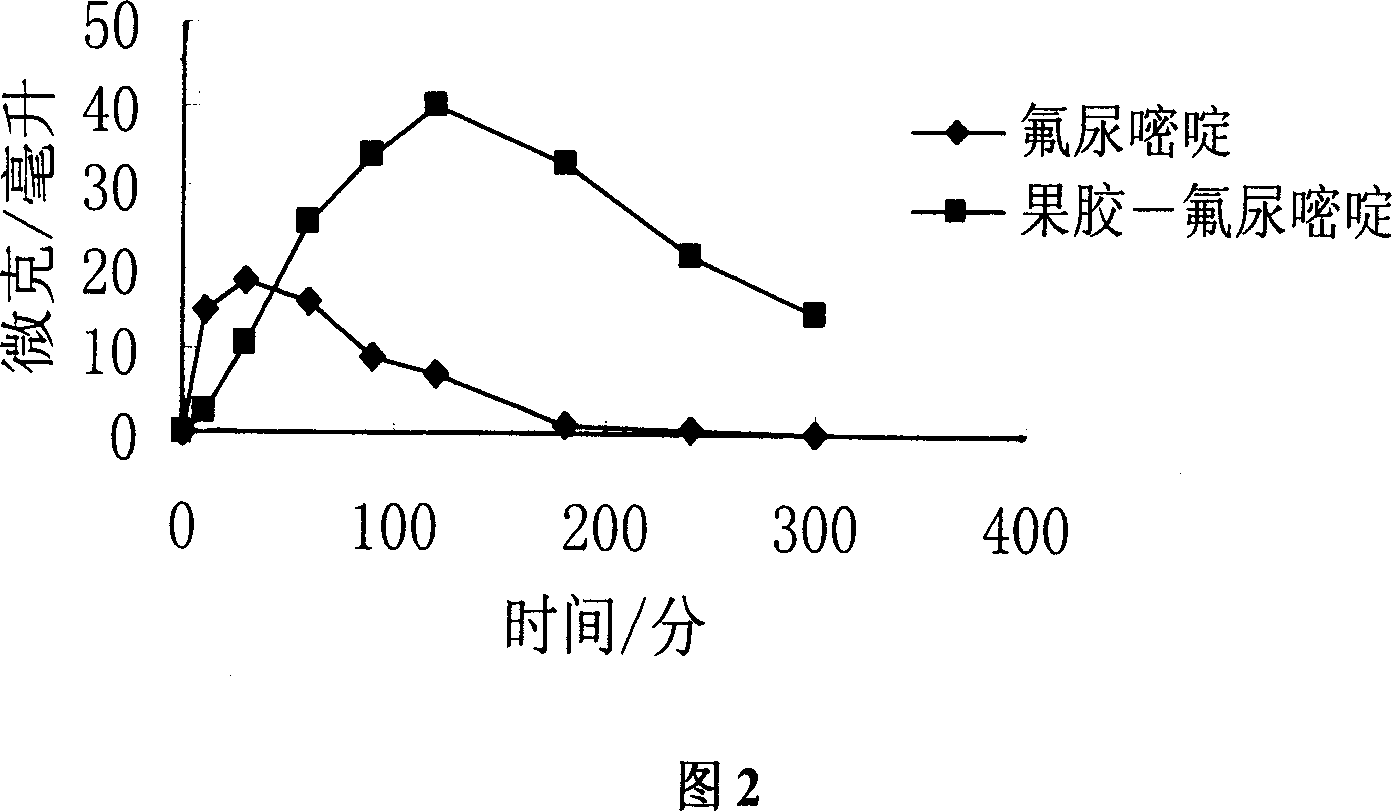
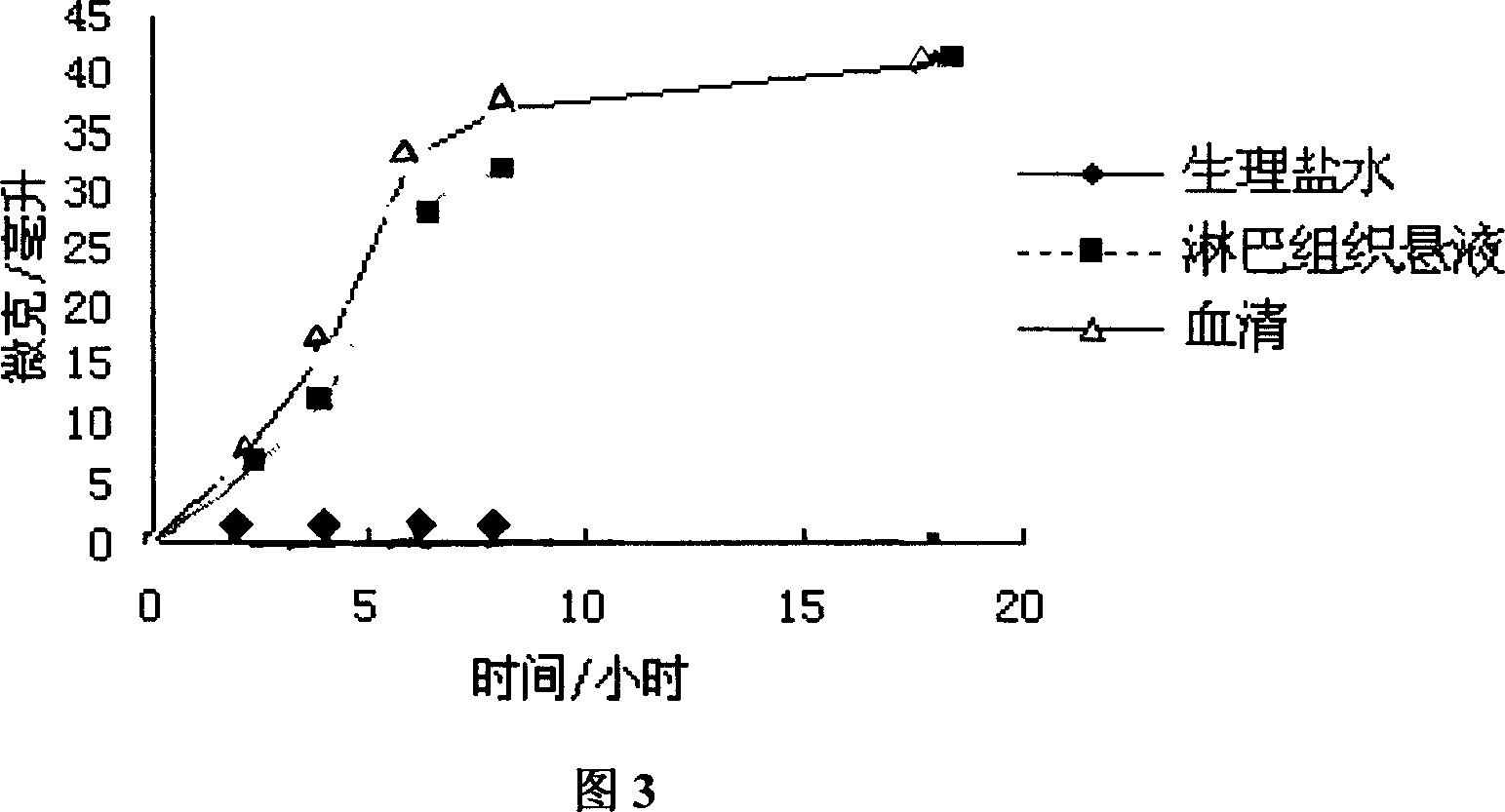
High molecular anticarcinogenic prodrug, its preparing method and use
ActiveCN101045163ALymphatic targetingTargetedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMolecular precursorDrainage lymph nodes
An anticancer high-molecular precursor medicine C-Spacer-P, where P is high- molecular pectin, C is an anticancer medicine containing amino radical or hydroxy radical, and Spacer is the spacing radical, is prepared by bonding the amino or hydroxy of an anticancer medicine with the hydroxy, carboxy, or hydroxymethyl of high- molecular pectin via spacing radical. It is an injection suitable for the solid cancer, and cancerous ascites or hydrothorax.
Owner:SICHUAN YINGRUI PHARMA TECH CO
Molecular precursors for optoelectronics
InactiveUS20110146532A1Improve machinabilityReduce the temperatureTin organic compoundsInksMolecular precursorSolar cell
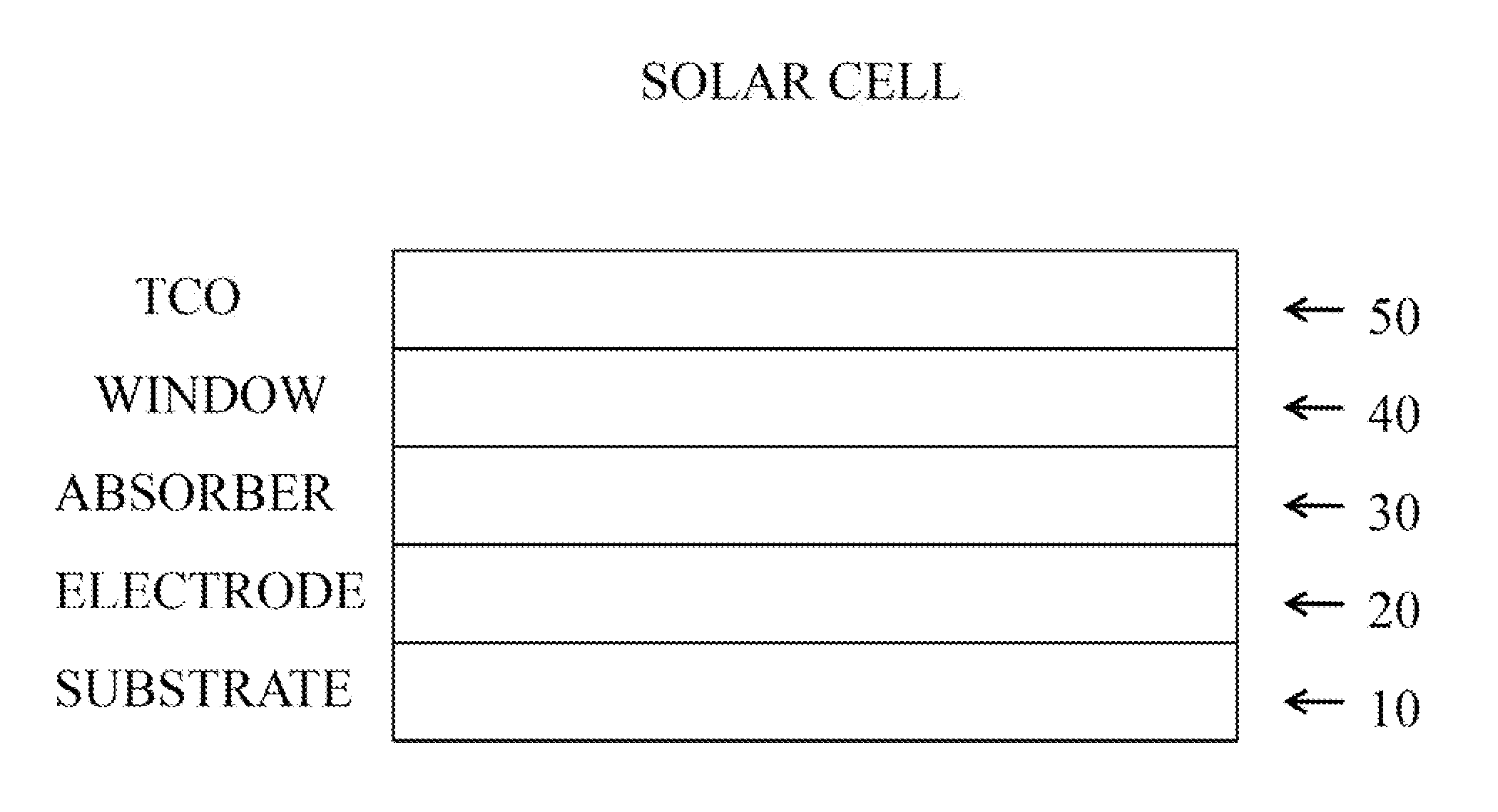
This invention relates to compounds and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices. This invention provides a range of compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Processes for polymeric precursors for caigas aluminum-containing photovoltaics
InactiveUS20110031453A1Easy to controlEasy to processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesFinal product manufactureMolecular precursorConductive materials
This invention relates to processes for compounds, polymeric compounds, and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices including thin film and band gap materials. This invention provides a range of compounds, polymeric compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, transparent conductive materials, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to polymeric precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers including CAIGAS.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Formation of carbon and semiconductor nanomaterials using molecular assemblies
ActiveUS20070264764A1Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMetal oxide nanoparticlesGas phase
The invention is directed to a method of forming carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials. The method comprises providing a substrate and attaching a molecular precursor to the substrate. The molecular precursor includes a surface binding group for attachment to the substrate and a binding group for attachment of metal-containing species. The metal-containing species is selected from a metal cation, metal compound, or metal or metal-oxide nanoparticle to form a metallized molecular precursor. The metallized molecular precursor is then subjected to a heat treatment to provide a catalytic site from which the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials form. The heating of the metallized molecular precursor is conducted under conditions suitable for chemical vapor deposition of the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for the preparation of IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles
InactiveUS7208133B2Uniform shapeImprove attributesMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsOrganic solventMolecular precursor
A high temperature non-aqueous synthetic procedure for the preparation of substantially monodisperse IV-VI semiconductor nanoparticles is provided. The procedure includes introducing a first precursor selected from the group consisting of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element and a molecular precursor of a Group VI element into a reaction vessel that comprises at least an organic solvent to form a mixture. Next, the mixture is heated and thereafter a second precursor of a molecular precursor of a Group IV element or a molecular precursor of a Group VI element that is different from the first is added. The reaction mixture is then mixed to initiate nucleation of IV-VI nanocrystals and the temperature of the reaction mixture is controlled to provide nanoparticles having a diameter of about 20 nm or less.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC +1
Polymeric precursors for caigas aluminum-containing photovoltaics
InactiveUS20110030582A1Easy to processLow-temperature processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesFinal product manufactureMolecular precursorConductive materials
This invention relates to compounds, polymeric compounds, and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices including thin film and band gap materials. This invention provides a range of compounds, polymeric compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, transparent conductive materials, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to polymeric precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers including CAIGAS.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Formation of carbon and semiconductor nanomaterials using molecular assemblies
ActiveUS7544546B2Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMetal oxide nanoparticlesGas phase
The invention is directed to a method of forming carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials. The method comprises providing a substrate and attaching a molecular precursor to the substrate. The molecular precursor includes a surface binding group for attachment to the substrate and a binding group for attachment of metal-containing species. The metal-containing species is selected from a metal cation, metal compound, or metal or metal-oxide nanoparticle to form a metallized molecular precursor. The metallized molecular precursor is then subjected to a heat treatment to provide a catalytic site from which the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials form. The heating of the metallized molecular precursor is conducted under conditions suitable for chemical vapor deposition of the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Polymeric precursors for CAIGAS aluminum-containing photovoltaics
InactiveUS8158033B2Easy to controlEasy to processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesFinal product manufactureMolecular precursorConductive materials
This invention relates to compounds, polymeric compounds, and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices including thin film and band gap materials. This invention provides a range of compounds, polymeric compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, transparent conductive materials, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to polymeric precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers including CAIGAS.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Molecular precursor methods and articles for optoelectronics
InactiveUS20110146764A1Easy to processLow-temperature processAnodisationCellsMolecular precursorSolar cell
This invention relates to compounds and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices. This invention provides a range of compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds, precursor materials and methods for preparing photovoltaic layers.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
"one pot" synthesis of 2d, 1d, and 0d NANO crystals of tungsten and molybdenum chalcogenides (ws2, mos2) functionalized with long chain amine and/or carboxylic acid and/or thiol
InactiveUS20130281335A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCarboxylic acidMolecular precursor
The present invention describes a new synthetic strategy that permits to produce 2D 1D, e OD hybrid organic-inorganic nanocrystals of tungsten / molybdenum chalcogenides. The innovative chemical approach is based on the thermal decomposition of a molecular precursor containing both metal and sulphur, in a mixture of long chain amines and / or fatty acids and / or long chain thiols. By the control of reaction conditions is possible to address the synthesis can be driven towards the formation of nanosystems with different morphologies such as sheets, particles, rods, tubes.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PARMA
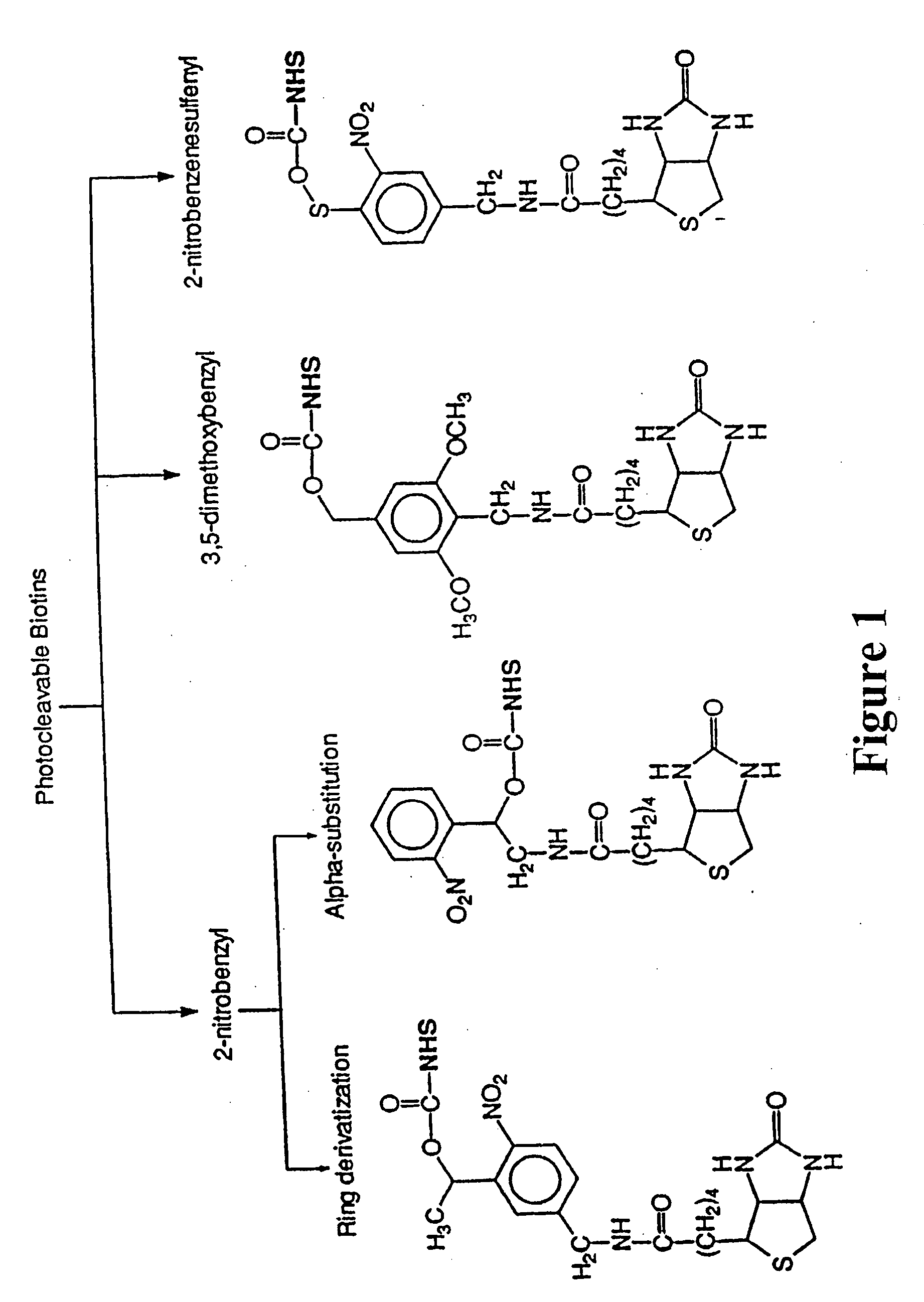
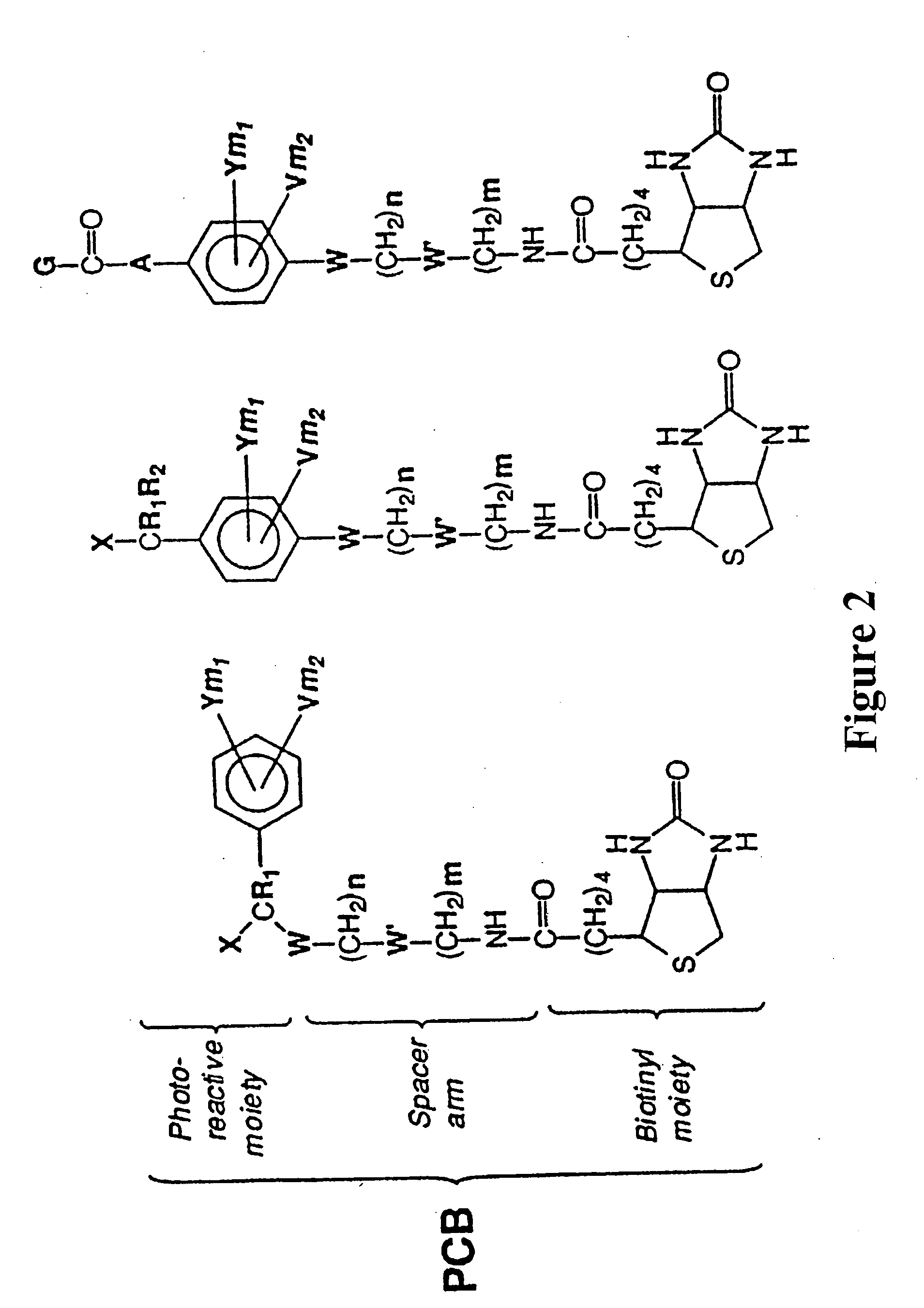
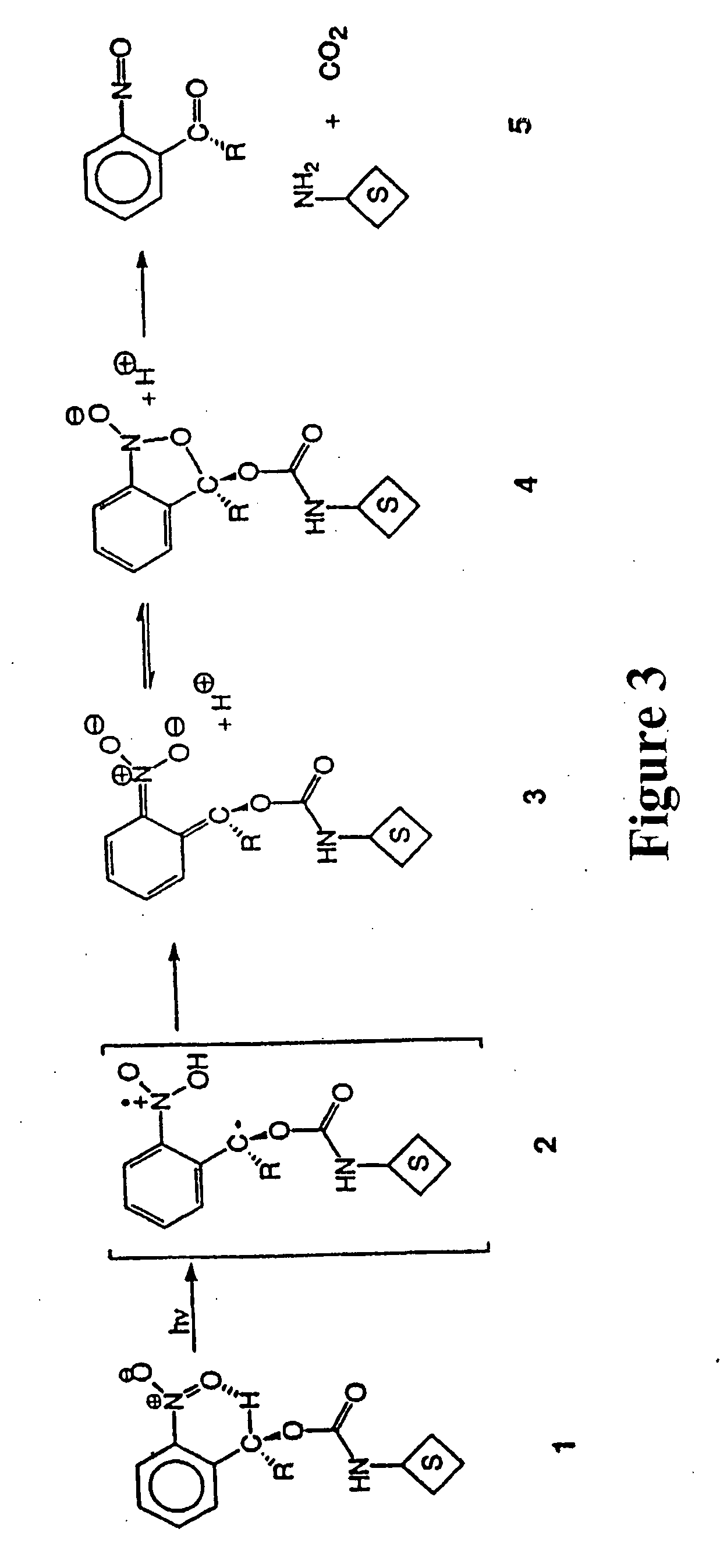
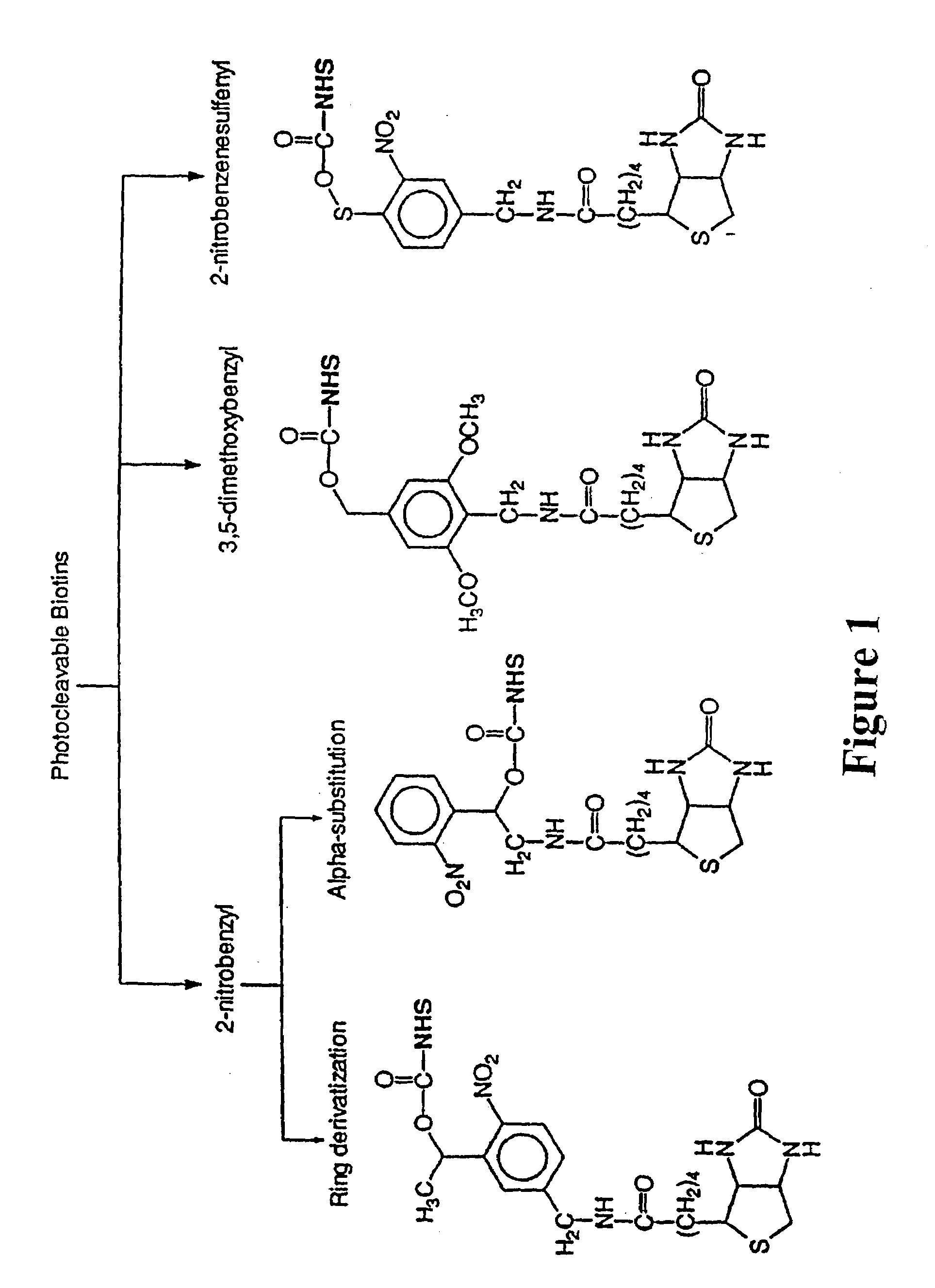
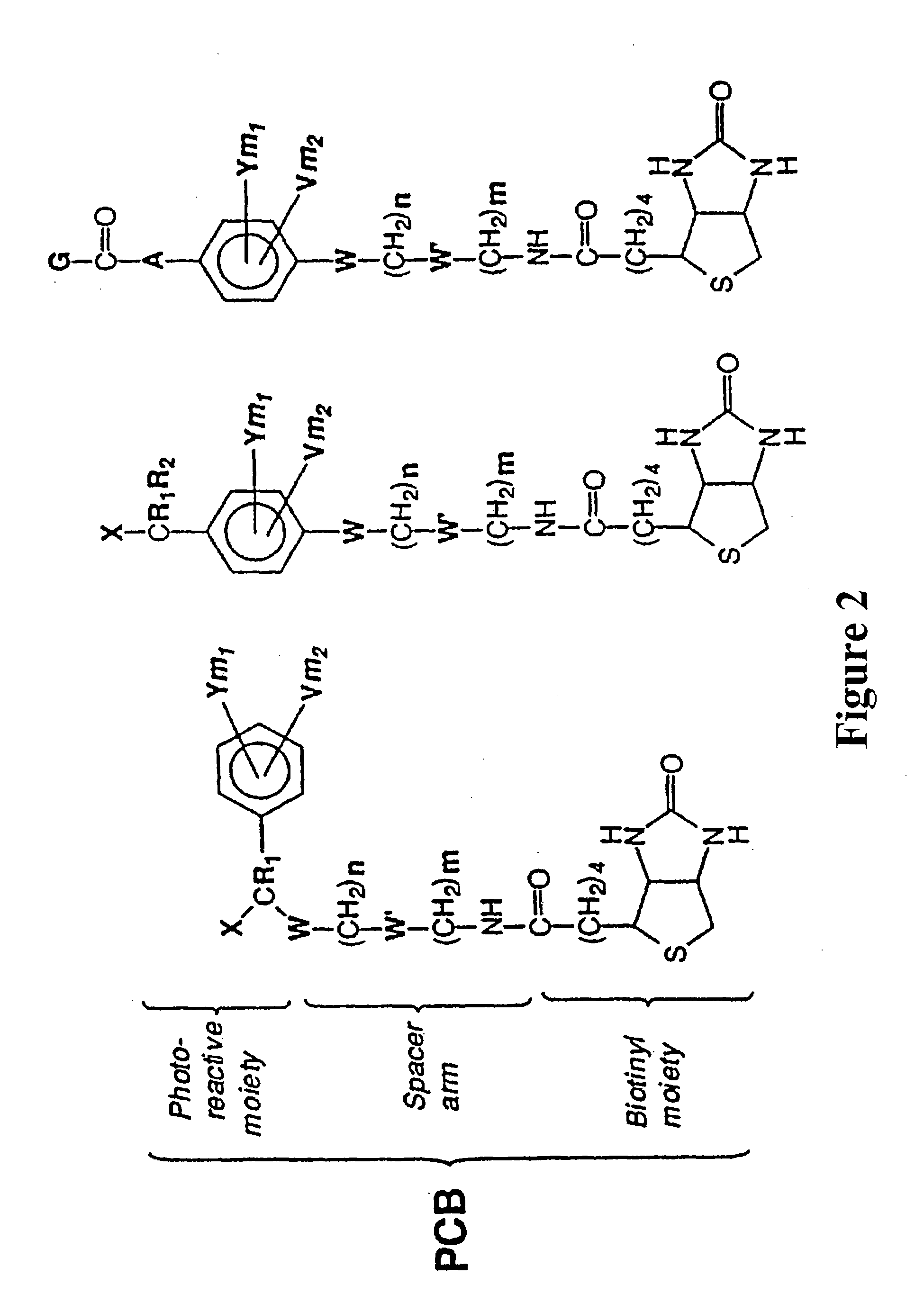
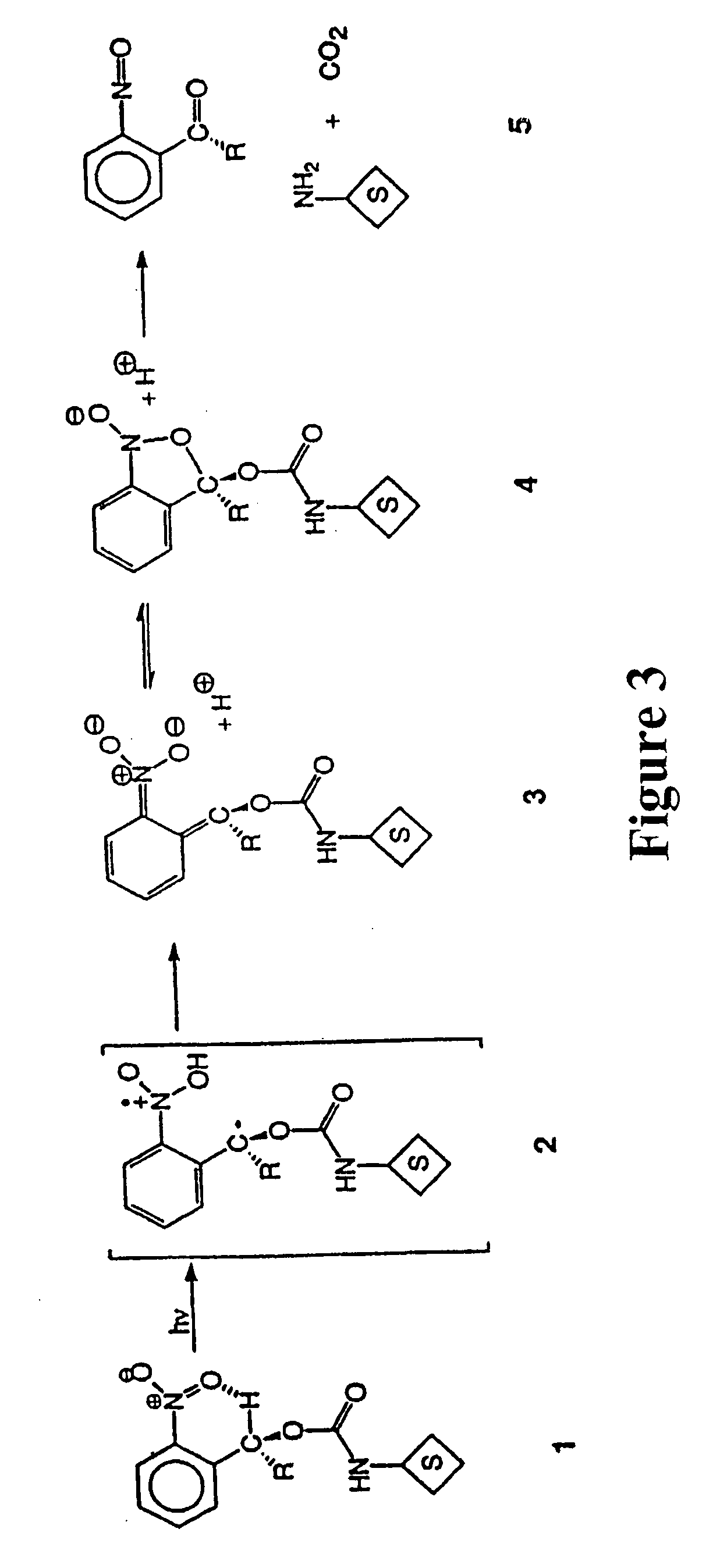
Photocleavable isotope-coded affinity tags
InactiveUS20050085630A1Remove any variabilityEasy to analyzePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesHeterologousMammal
This invention relates to agents and conjugates that can be used to detect and isolate target components from complex mixtures such as proteins and protein fragments from biological samples from in vivo and in vitro sources. Agents comprise a detectable group bound to a photoreactive group. Conjugates comprise agents coupled to substrates by covalent bounds which can be selectively cleaved with the administration of electromagnetic radiation. Targets substances labeled with detectable molecules can be easily identified and separated from a heterologous mixture of substances. Exposure of the conjugate to radiation releases the target in a functional form and completely unaltered. Using photocleavable molecular precursors as the conjugates, label can be incorporated into macromolecules, the nascent macromolecules isolated and the label completely removed. The invention also relates to targets isolated with these conjugates which may be useful as pharmaceutical agents or compositions that can be administered to humans and other mammals.
Owner:AMBERGEN
Photocleavable isotope-coded affinity tags
InactiveUS7145019B2Easy to detectFacilitates quantitative determinationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsHeterologousMammal
This invention relates to agents and conjugates that can be used to detect and isolate target components from complex mixtures such as proteins and protein fragments from biological samples from in vivo and in vitro sources. Agents comprise a detectable group bound to a photoreactive group. Conjugates comprise agents coupled to substrates by covalent bounds which can be selectively cleaved with the administration of electromagnetic radiation. Targets substances labeled with detectable molecules can be easily identified and separated from a heterologous mixture of substances. Exposure of the conjugate to radiation releases the target in a functional form and completely unaltered. Using photocleavable molecular precursors as the conjugates, label can be incorporated into macromolecules, the nascent macromolecules isolated and the label completely removed. The invention also relates to targets isolated with these conjugates which may be useful as pharmaceutical agents or compositions that can be administered to humans and other mammals.
Owner:AMBERGEN INC
Method for constructing single-site electrocatalyst by metal phthalocyanine molecular precursor and application
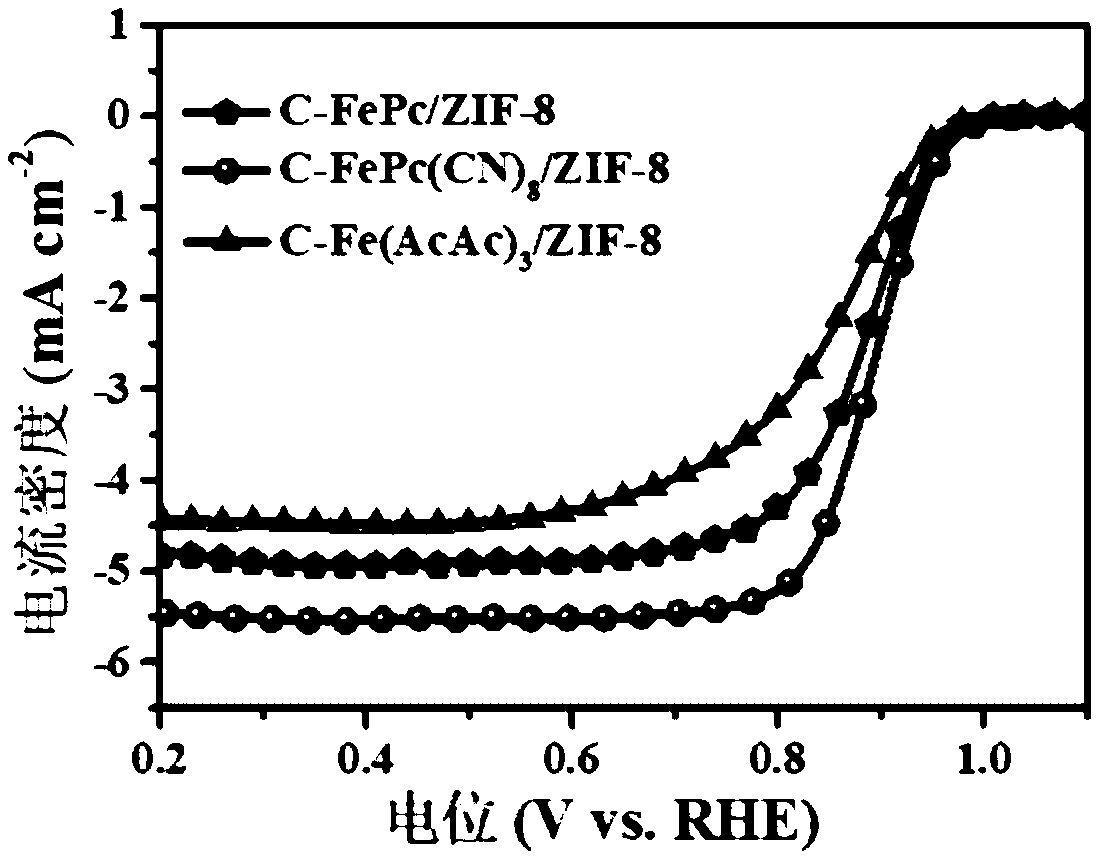
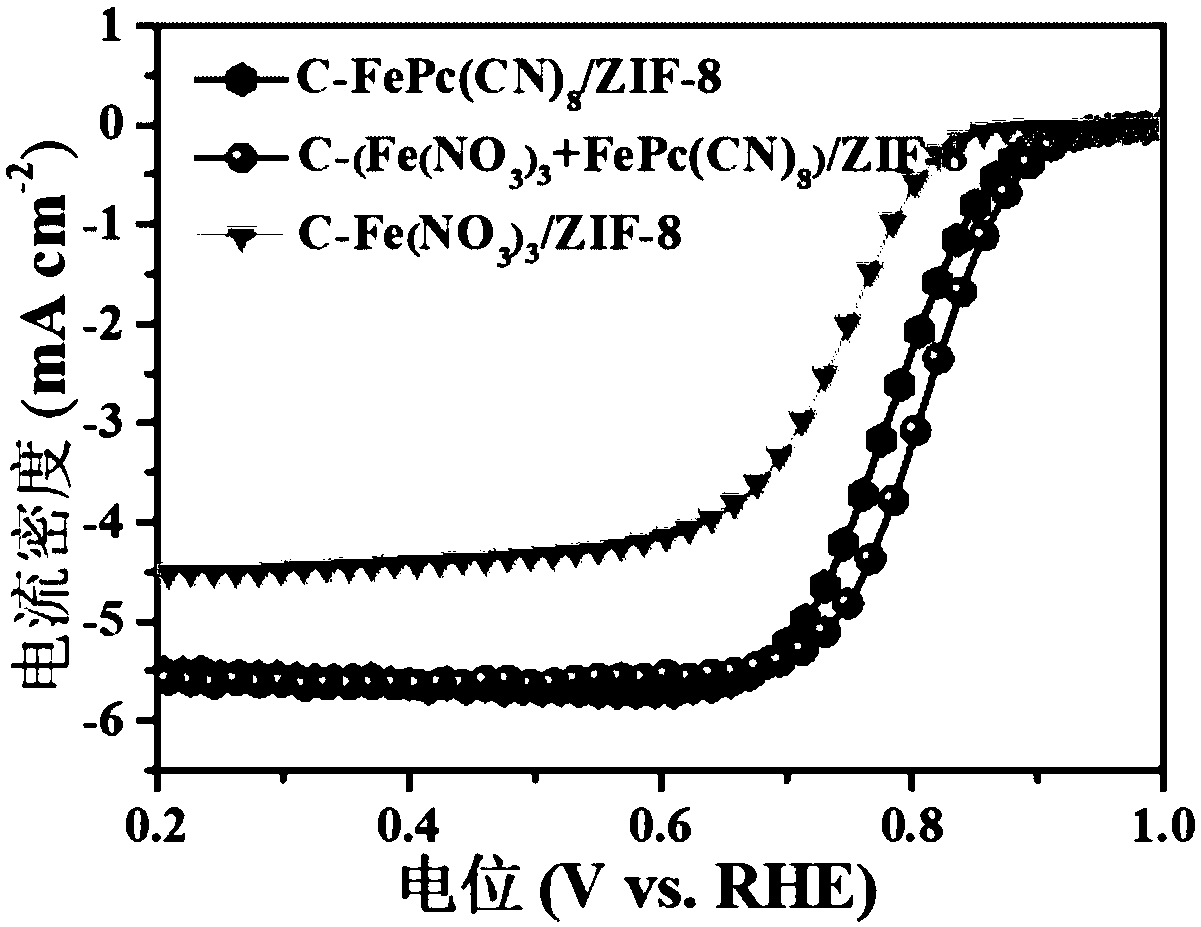
ActiveCN109659569AExcellent electrocatalytic oxygen reduction performanceIncrease loadCell electrodesMolecular precursorPhthalocyanine
The invention provides a method for constructing a single-site electrocatalyst by a metal phthalocyanine molecular precursor and application. The method comprises subjecting a zeolitic imidazolate framework structure material and metal phthalocyanine molecules to coordination reaction; and subjecting a coordination reaction product to pyrolysis to obtain the electrocatalyst. The zeolitic imidazolate framework structural material includes a metal site to be coordinated and an imidazole nitrogen site to be coordinated. The method subjects the zeolitic imidazolate framework structural material (ZIFs) with high specific surface area and the metal phthalocyanine molecules with high stability to coordination reaction, significantly increases the number of active sites of the catalyst, and can avoid the aggregation of metal atoms. The prepared electrocatalyst has the advantages of high metal load capacity per site, good stability, and high catalytic activity.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Methods and articles for caigas aluminum-containing photovoltaics
InactiveUS20110030798A1Easy to processLow-temperature processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesLiquid surface applicatorsMolecular precursorConductive materials
This invention relates to methods and articles using compounds, polymeric compounds, and compositions used to prepare semiconductor and optoelectronic materials and devices including thin film and band gap materials. This invention provides a range of compounds, polymeric compounds, compositions, materials and methods directed ultimately toward photovoltaic applications, transparent conductive materials, as well as devices and systems for energy conversion, including solar cells. In particular, this invention relates to polymeric precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers. In particular, this invention relates to molecular precursor compounds and precursor materials for preparing photovoltaic layers including CAIGAS.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Organic pore-borne material generated by self-assembly of organic and organic, and preparation method
InactiveCN1696180AImprove thermal stabilityLarge specific surface areaActive agentMolecular materials
A process for preparing organic meso-porous material by organic-organic self-assembly features that the surfactant or organic high-molecular material is used as the structure guider, and the high-molecular precursor and said structure guider take part in organic-organic self-assembly. Said meso-porous material has ordered mesoporous arteries with different structures, high pore volume and high specific surface area.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
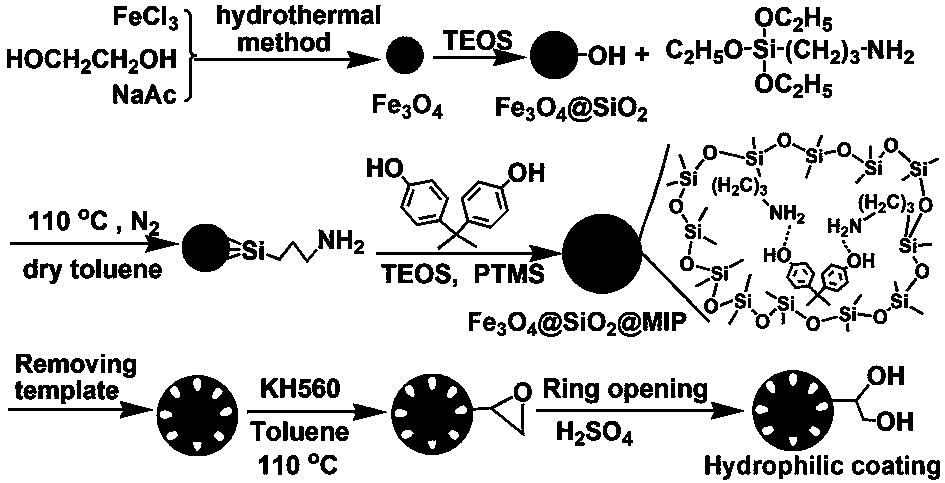
Preparation method of molecularly-imprinted magnetic silica microsphere with hydrophilic external surface
The invention relates to a preparation method of a molecularly-imprinted magnetic silica microsphere with a hydrophilic external surface. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A, preparing a magnetic silica microsphere by taking Fe3O4 as magnetic particles, ethyl alcohol and distilled water as reaction solvents and TEOS (Tetraethyl Orthosilicate) as a molecular precursor; B, with anhydrous methylbenzene as a solvent, and reacting the magnetic silica microsphere with KH-550 to obtain an amination magnetic silica microsphere; C, with bisphenol A as a template molecule, TEOS and PTMS (Phenyltrimethoxysilane) as cross-linking agents and HCl as a catalyst, reacting with the amination magnetic silica microsphere, and eluting the template molecule to obtain a bisphenol A imprinted magnetic silica microsphere; and D, reacting the bisphenol A imprinted magnetic silica microsphere with KH-560, and performing hydrolysis to obtain the molecularly-imprinted magnetic silica microsphere with the hydrophilic external surface. The method has the advantages of simplicity in preparation, strong selectivity, excellent enrichment and high separation efficiency, is capable of effectively excluding biomacromolecules and reducing impurities of treated samples and can be widely used in separation and extraction of pretreatment of the samples.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Process For Producing a Coating Based on an Oxide Ceramic that Conforms to the Geometry of a Substrate Having Features in Relief
InactiveUS20080292790A1Sure easyPretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingOxide ceramicSufficient time
The invention relates to a process for producing layers made of oxide ceramic that conform to substrates having features in relief comprising:a step of depositing on said substrate a layer of a sol-gel solution that is a precursor of said ceramic;a heat treatment step of said layer with a view to converting it to the ceramic;said steps being optionally repeated one or more times, characterized in that the sol-gel solution that is a precursor of said ceramic is prepared by a process successively comprising the following steps:a) preparing a first solution by bringing the molecular precursor or precursors of the metals intended to be incorporated into the composition of the ceramic into contact with a medium comprising a diol solvent and optionally an aliphatic monoalcohol;b) leaving the solution obtained in a) to stand for a sufficient time needed to obtain a solution that has a substantially constant viscosity;c) diluting the solution obtained in b) to a predetermined amount with a dial solvent optionally identical to that from step a) or a solvent that is miscible with the dial solvent used in step a).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
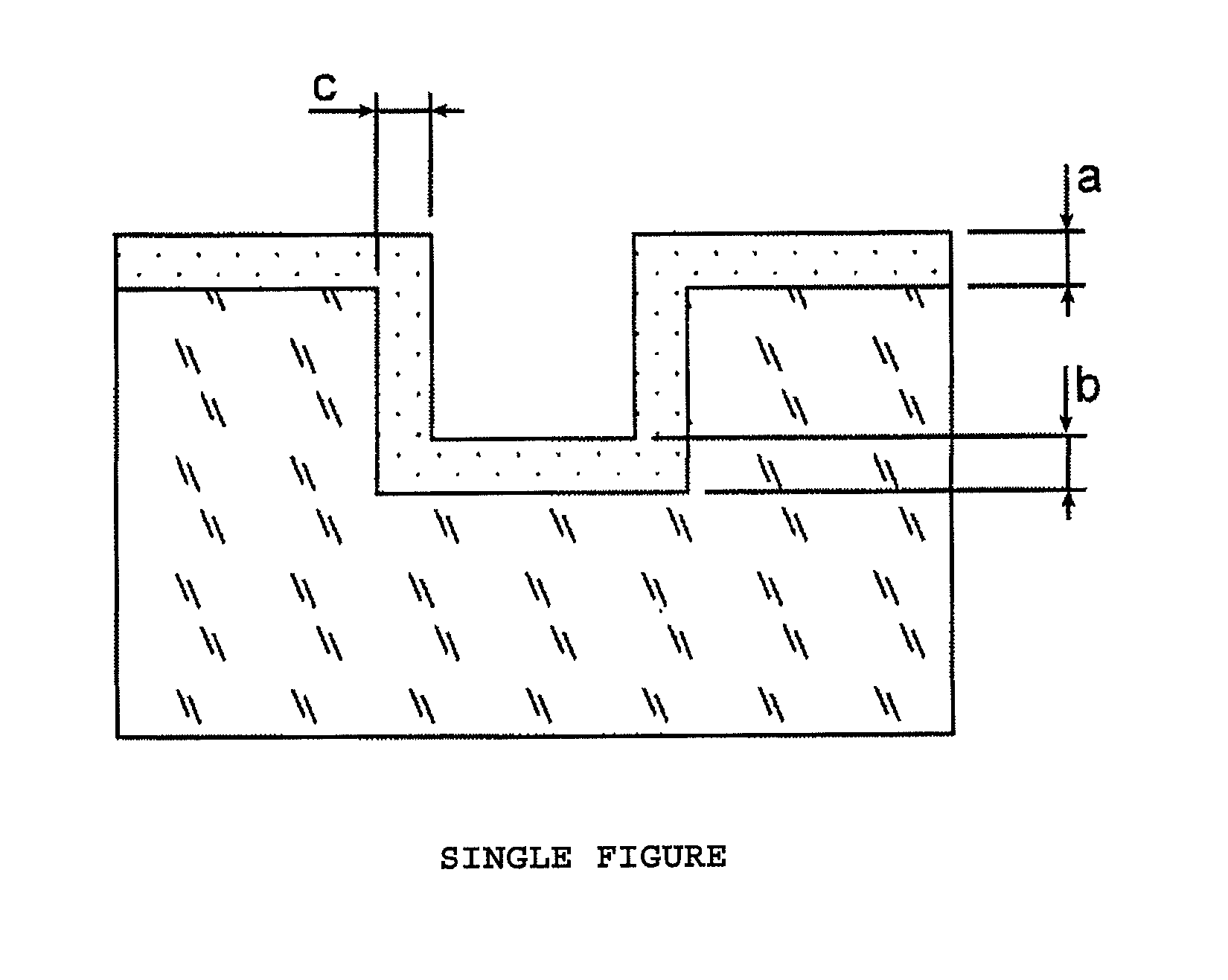
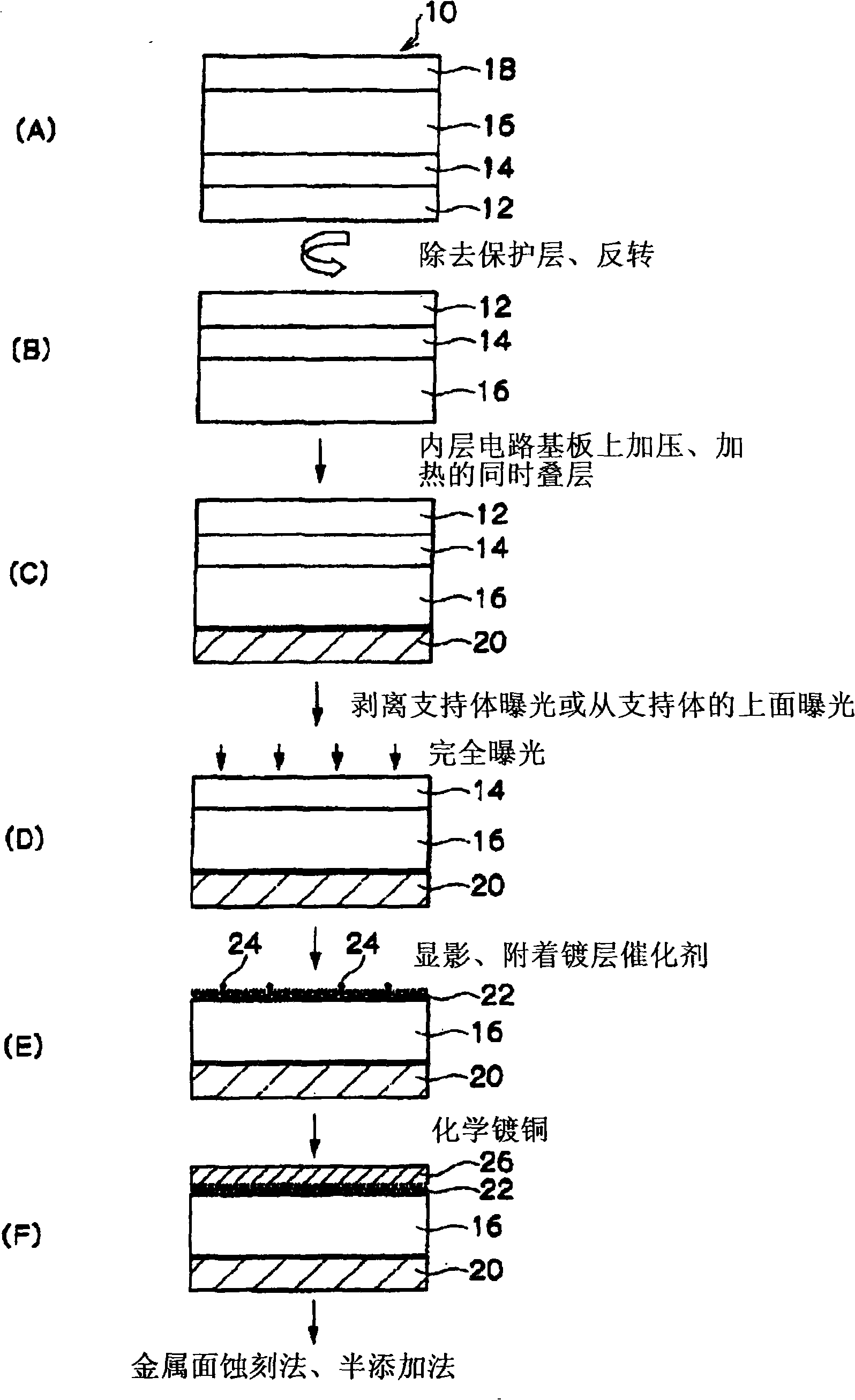
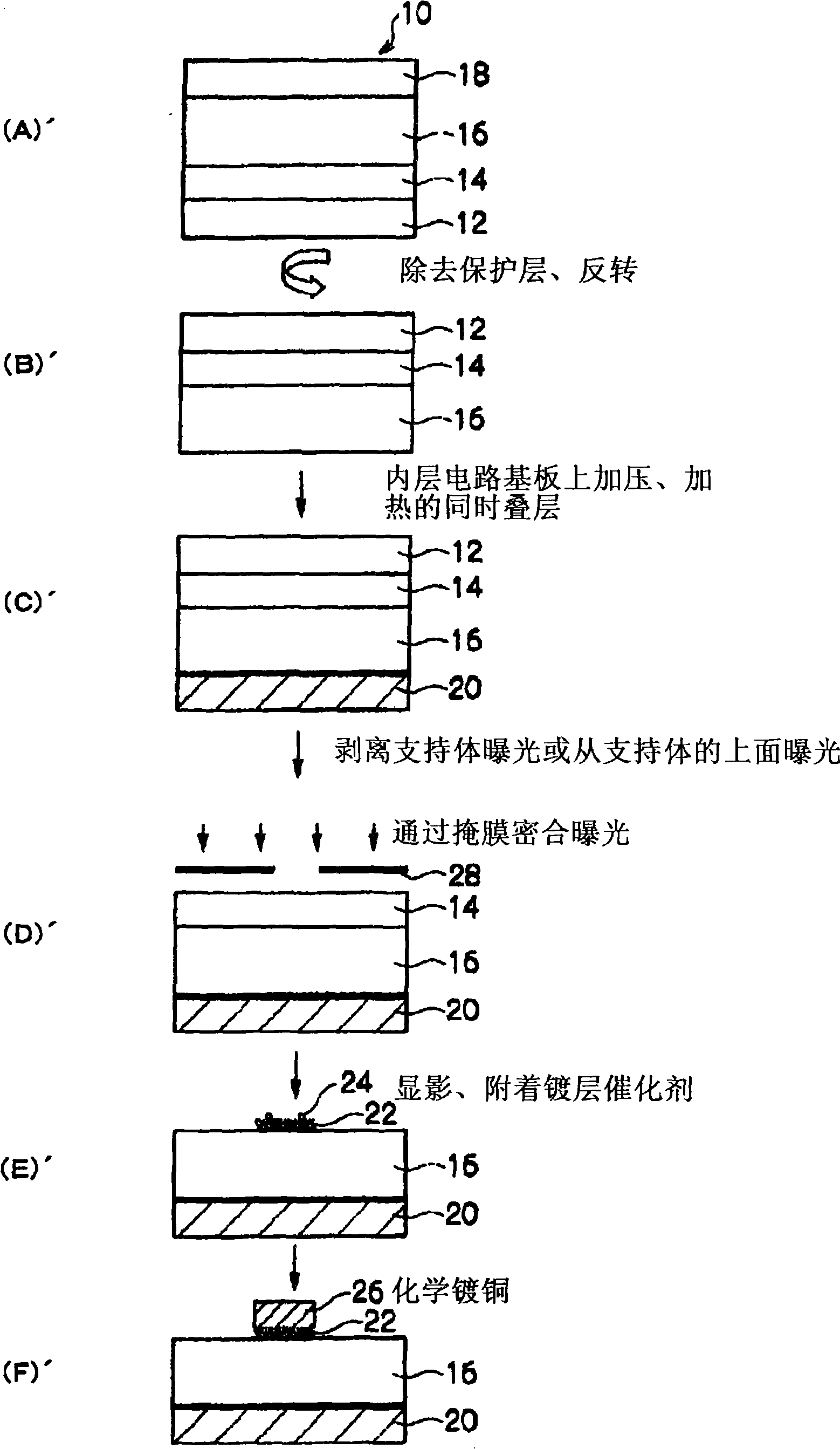
Laminate for printed wiring board, printed wiring board using same, method for manufacturing printed wiring board, electrical component, electronic component, and electrical device
InactiveCN101300134AExcellent adhesionWell formedSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsPolymer scienceEngineering
Disclosed is a laminate characterized by having, on a supporting body, an insulating resin composition layer which is capable of producing a reactive active species when provided with energy and a reactive polymer precursor layer containing a compound which is capable of forming a polymer compound by reacting with the insulating resin composition layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
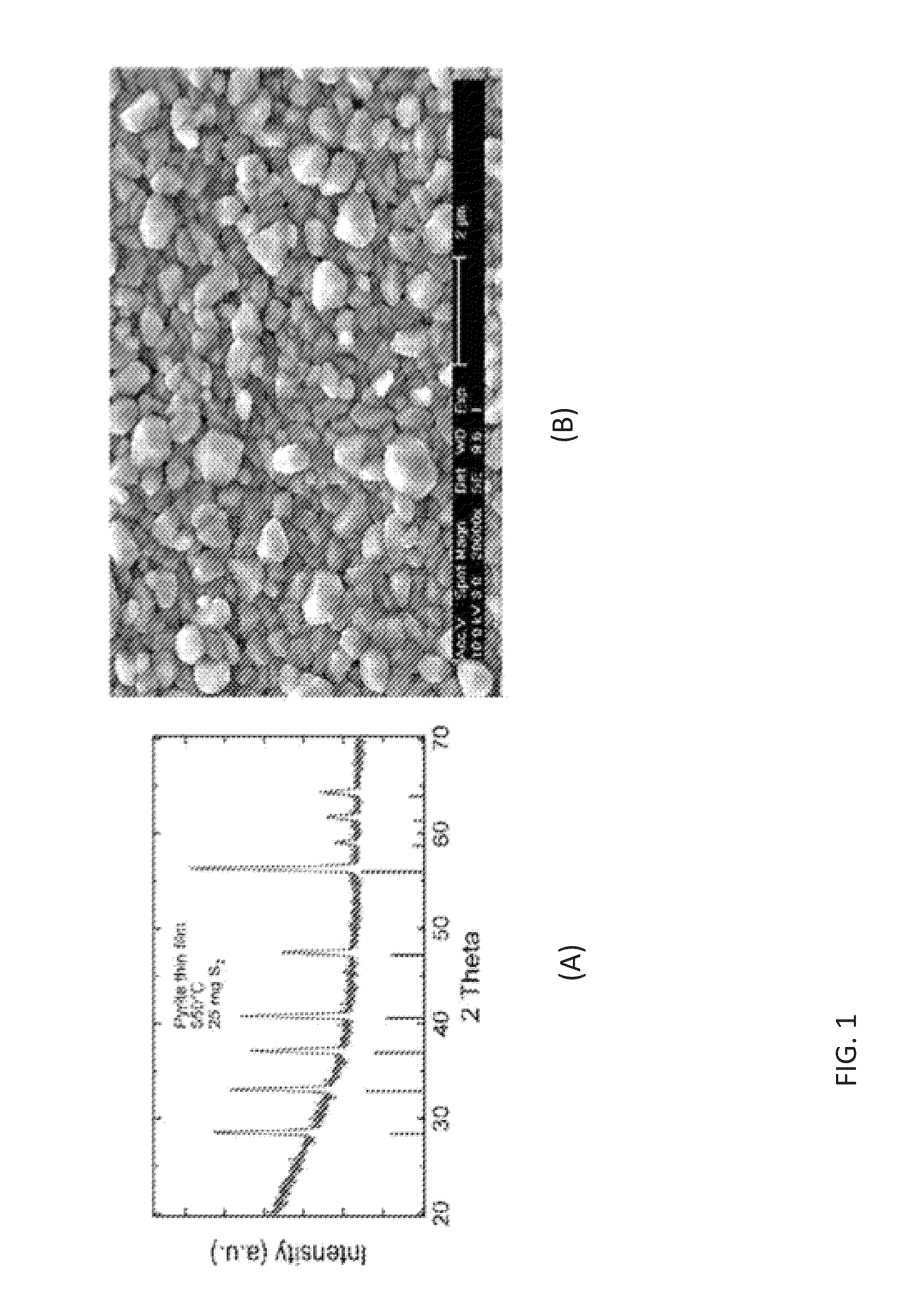
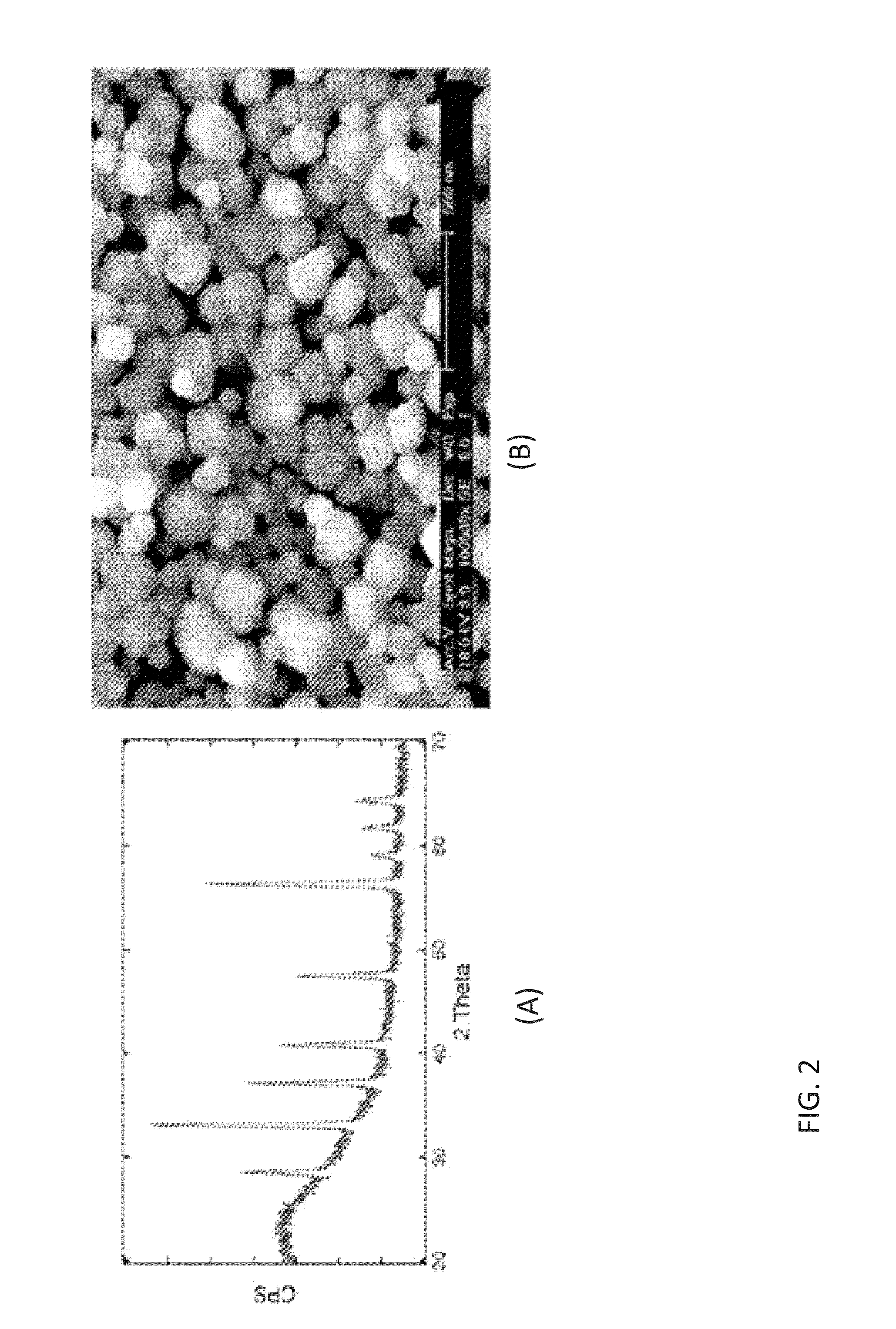
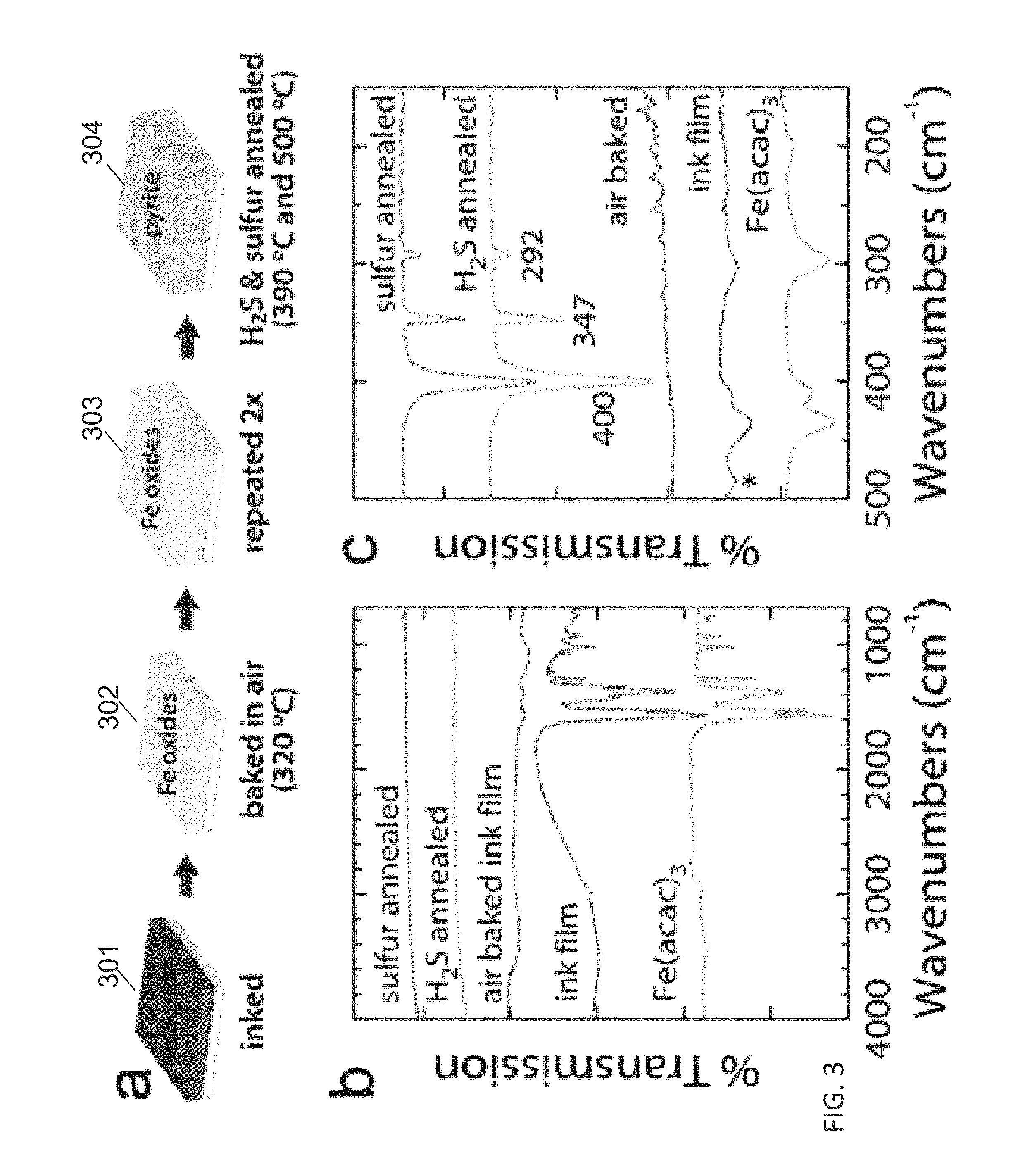
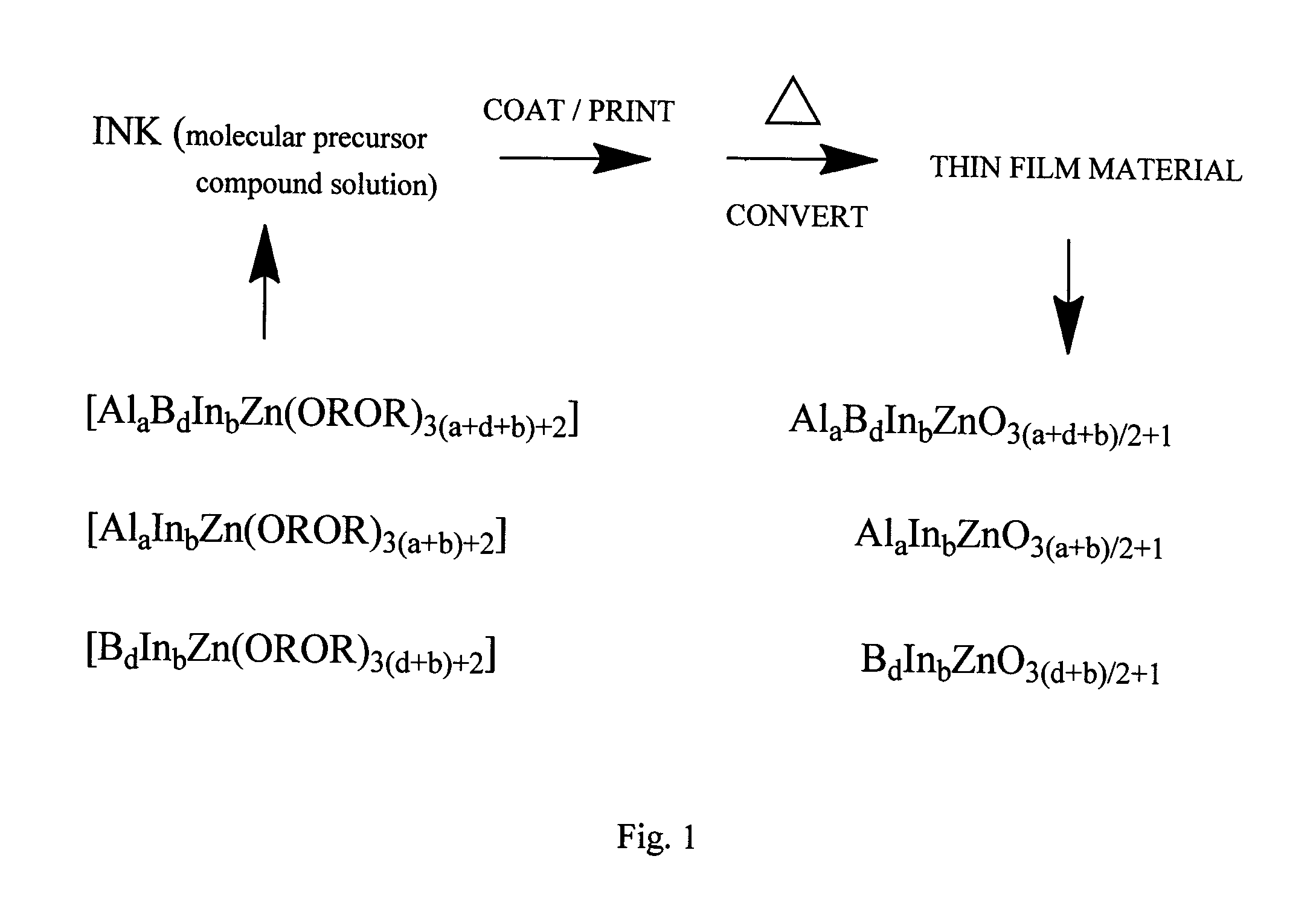
Iron pyrite thin films from molecular inks
Systems and methods are provided for fabricating pyrite thin films from molecular inks. A process is provided that comprises dissolving simple iron-bearing and sulfur-bearing molecules in an appropriate solvent and then depositing the solution onto an appropriate substrate using one of several methods (roll-to-roll coating, spraying, spin coating, etc.), resulting in a solid film consisting of the molecules. These molecular precursor films are then heated to 200-600° C. in the presence of sulfur-bearing gases (e.g., S2, H2S) to convert the molecular films into films of crystalline iron pyrite (FeS2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Thin film containing nanocrystal particles and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS8501595B2High crystallinityReduce grain boundariesMaterial nanotechnologyWater-repelling agents additionMolecular precursorSolar cell
Disclosed herein is a thin film prepared using a mixture of nanocrystal particles and a molecular precursor. The nanocrystal is used in the thin film as a nucleus for crystal growth to minimize grain boundaries of the thin film and the molecular precursor is used to form the same crystal structure as the nanocrystal particles, thereby improving the crystallinity of the thin film. The thin film can be used effectively in a variety of electronic devices, including thin film transistors, electroluminescence devices, memory devices, and solar cells. Further disclosed is a method for preparing the thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of Preparing Stable Oxide Ceramic Precursor Sol-Gel Solutions Based on Lead, Titanium, Zirconium and Lanthanide(s) and Method of Preparing Said Ceramic
InactiveUS20080175985A1High dielectric constantImprove dielectric performance characteristicOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide ceramicLanthanide
The invention relates to a method of preparing a stable sol-gel solution as precursor of an oxide ceramic based on lead, titanium, zirconium and one or more lanthanides, comprising, in succession, the following steps:a) a sol-gel solution is prepared by bringing a lead-containing molecular precursor, a titanium-containing molecular precursor, a zirconium-containing molecular precursor and a lanthanide-metal-containing molecular precursor into contact with a medium comprising a diol solvent and optionally an aliphatic monoalcohol;b) the solution obtained in step a) is left to stand for a sufficient time needed to obtain a solution having an approximately constant viscosity; andc) the solution obtained in step b) is diluted to a predetermined amount with a diol solvent identical to that of step a) or a solvent miscible with this solvent.Application to the preparation of an oxide ceramic material comprising lead, a lanthanide metal, titanium and zirconium.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Graphite-phase carbon and nitrogen compound powder, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102218339ARealize large-scale manufacturingLow costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEnergy based wastewater treatmentMolecular precursorRaw material
The invention relates to graphite-phase carbon and nitrogen compound powder, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The powder uses an aromatic multimember heterocyclic ring composed of carbon and nitrogen elements as a repeat unit, and has a layered graphite phase structure. The preparation method of the powder comprises the following steps of: slowly heating an organic small-molecule compound containing carbon and nitrogen elements and other precursors to 450-600 DEG C, reacting at the temperature to form a yellow solid, washing the solid with an acidic solution and drying to obtain a target product. According to the invention, the product is acquired by carrying out a solid phase reaction under normal pressure and using inexpensive and easily available raw materials containing carbon and nitrogen elements as a single molecular precursor, the process is simple, the reaction atmosphere does not need to be adjusted and controlled, the equipment investment is low, the large-scale production can be realized, and the obtained product has multiple optional practical forms and can be widely applied in the industries of air purification, such as sewage treatment, self-cleaning coating, environmental purification including hydrogen preparation through utilizing water photolysis and CO2 photocatalytic reduction and the like, solar energy conversion and utilization, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Ionogel forming an autosupported electrolyte film, electrochemical device incorporating same and fabrication process for ionogel
The invention relates to an ionogel that may be used for making a self-supporting film forming a solid electrolyte of an electrochemical device, to such a device incorporating this ionogel and to a process for manufacturing this ionogel. the invention generally appplies to all energy storage devices such as supercapactiors or storage batteries (e.g. lithium-ion) An ionogel according to the invention comprises: a polymeric confinement matrix which comprises at least one polyactic acid, and at least one ionic liquid confined in this matrix. According to the invention, this matrix also comprises a polycondensate of at lest one sol-gel molecular precursor bearing hydrolysable group(s).
Owner:HUTCHINSON SA +2
High-molecular mask plate and manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN107574408AIncrease pixel densitySame sizeVacuum evaporation coatingPhotomechanical apparatusMagnetite NanoparticlesLaser scanning
The invention discloses a high-molecular mask plate. The high-molecular mask plate comprises a bearing substrate, a sacrificial layer and a mask, and the sacrificial layer and the mask are sequentially arranged on the bearing substrate in an overlapped mode. The mask comprises a high-molecular membrane layer and a plurality of holes which are formed in the high-molecular membrane layer and penetrate through the high-molecular membrane layer, and magnetic nano-particles are doped in the high-molecular membrane layer. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the high-molecular mask plate. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that S1, the sacrificial layer is manufactured on the bearing substrate; S2, the sacrificial layer is coated with a high-molecular precursor doped with the magnetic nano-particles, curing is conducted for membrane forming, and a raw high-molecular membrane is formed; S3, ablation is conducted on the area, unshielded by a photomask mask plate,of the raw high-molecular membrane through the photomask mask plate in a laser scanning mode so as to form holes and the mask, and a high-molecular mask plate precursor is obtained; and S4, after thehigh-molecular mask plate precursor is cleaned and dried, the acting force between the bearing substrate and the mask is weakened, and the high-molecular mask plate is obtained. The invention furtherdiscloses application of the high-molecular mask plate to OLED manufacturing.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
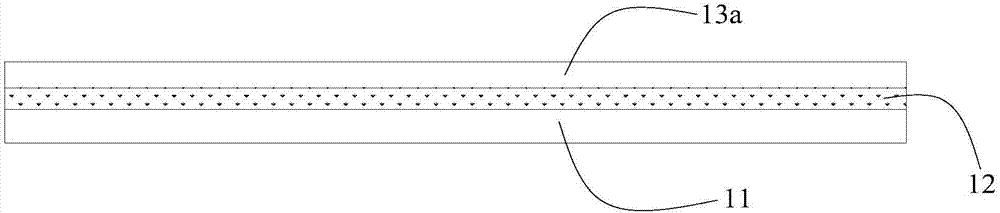
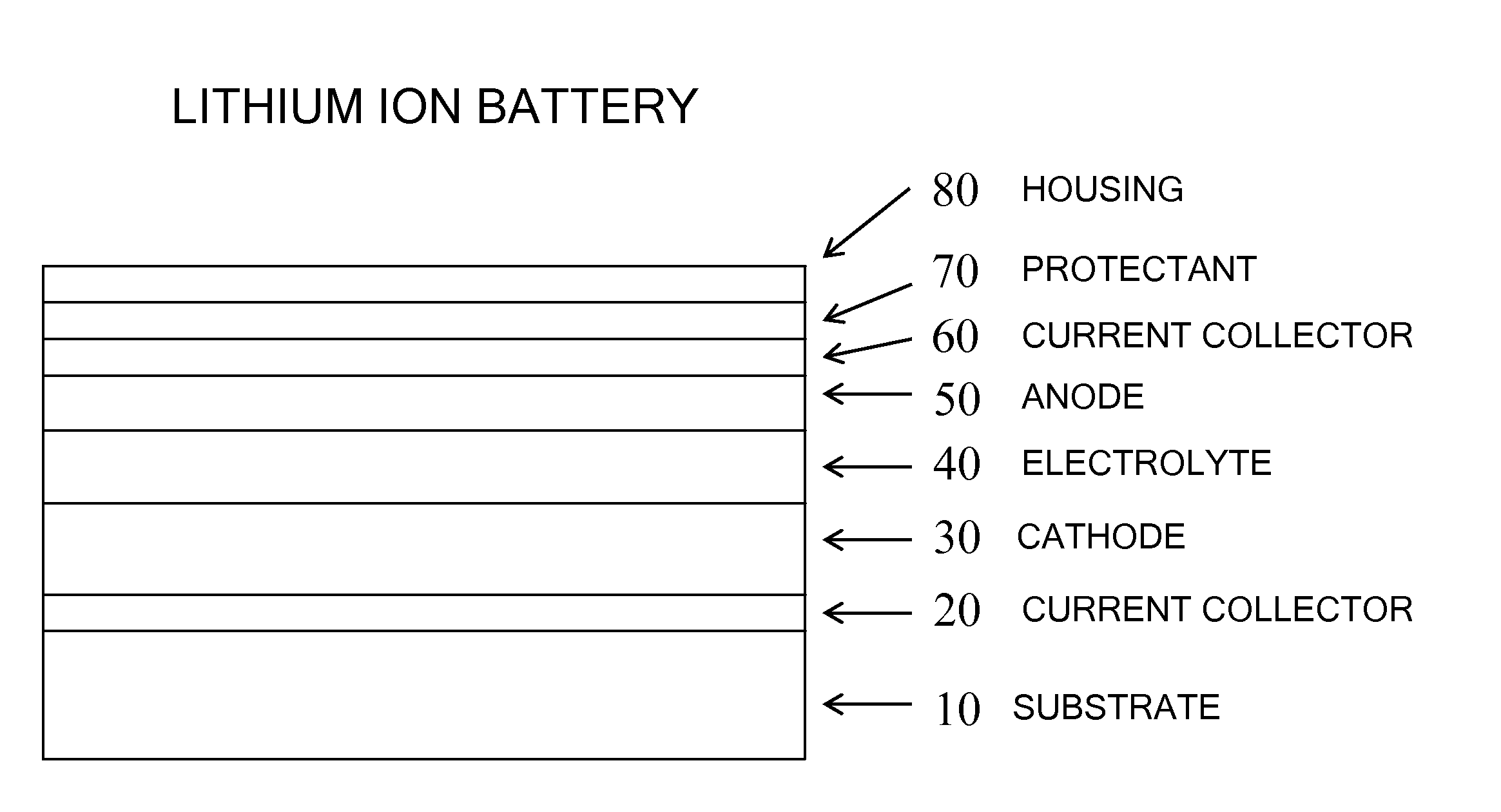
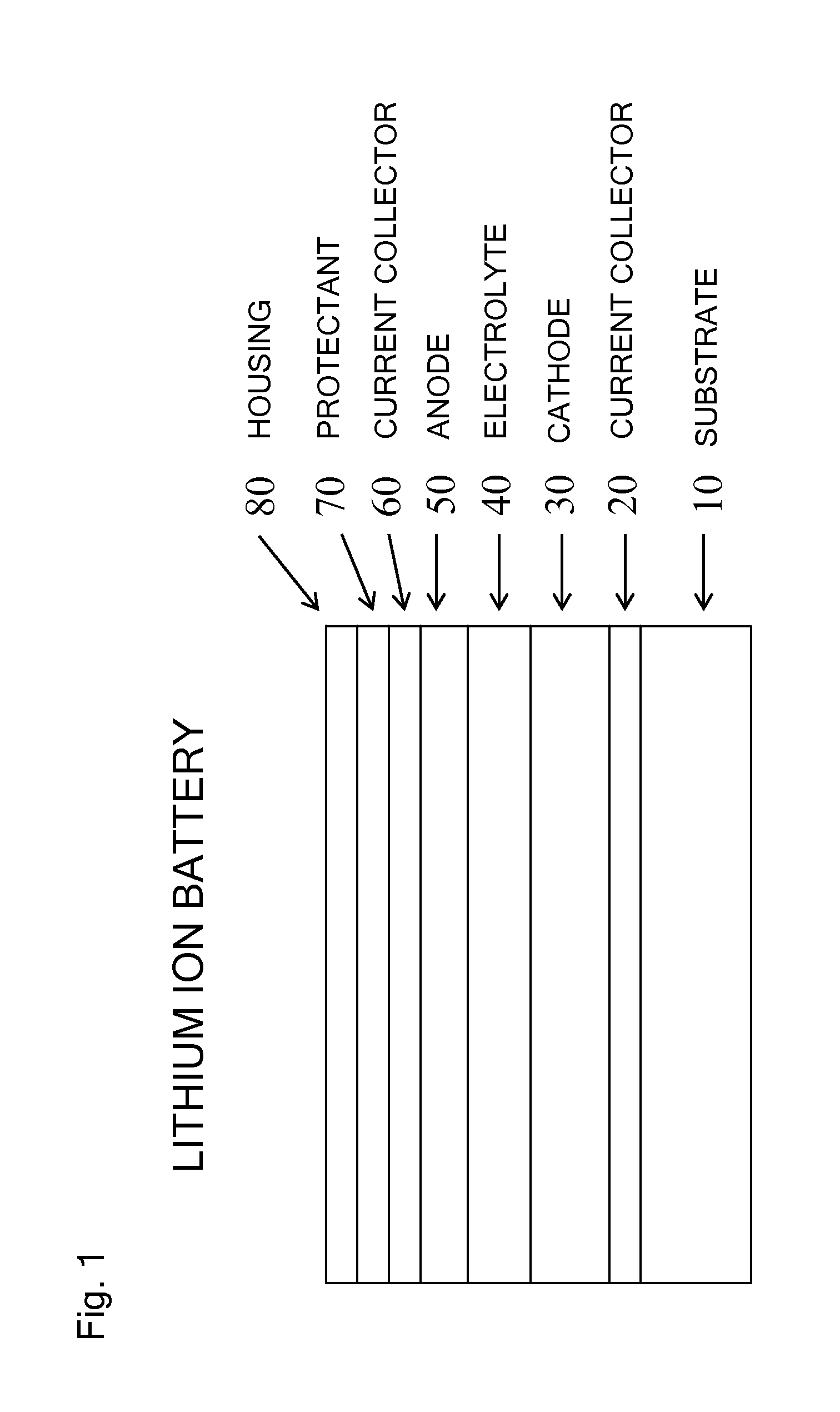
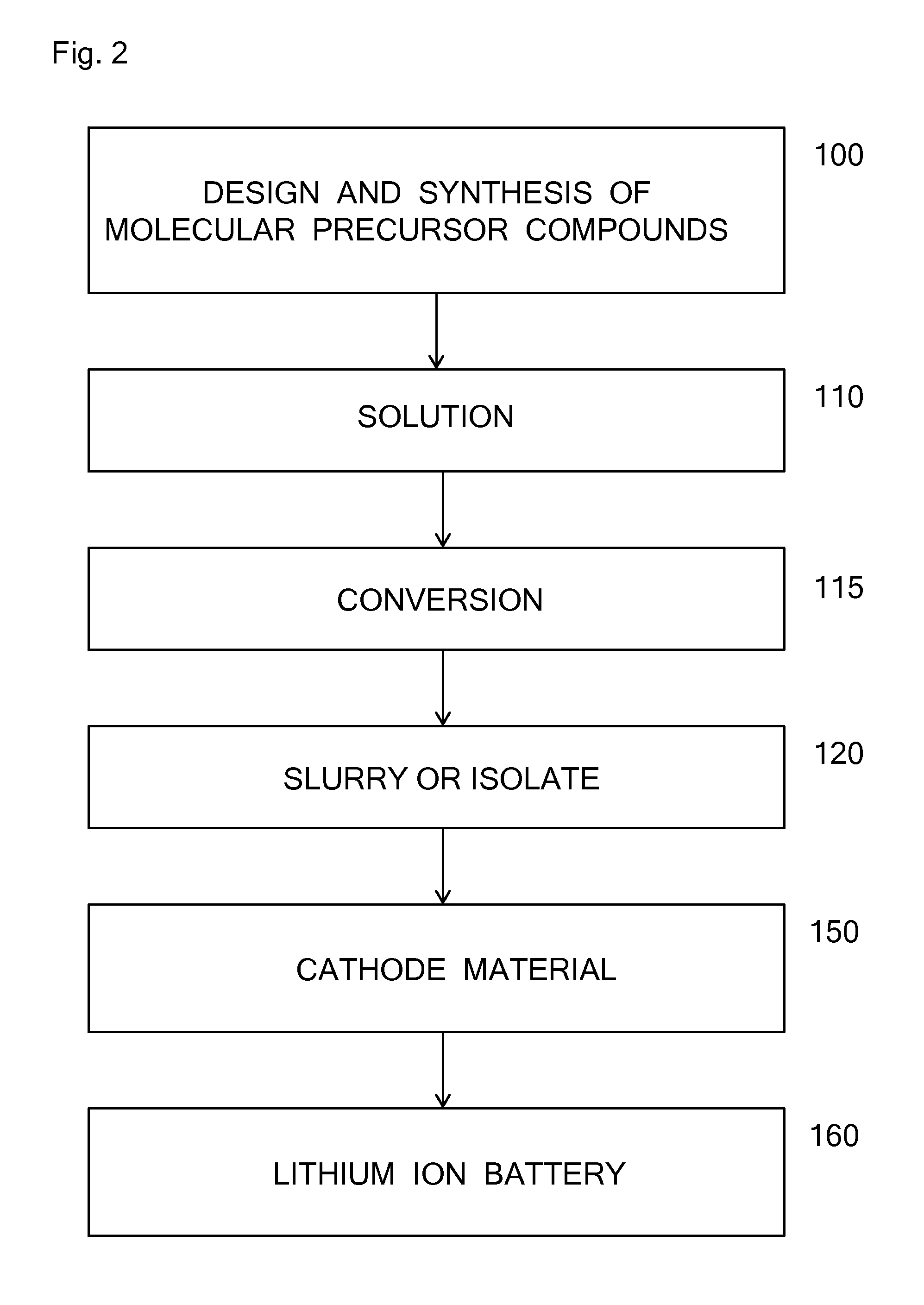
Molecular precursors for lithium-iron-containing cathode materials
InactiveUS20140011086A1PhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesLithium iron phosphateMolecular precursor
Lithium-iron molecular precursor compounds, compositions and processes for making a cathode for lithium ion batteries. The molecular precursor compounds are soluble and provide processes to make stoichiometric cathode materials with solution-based processes. The cathode material can be, for example, a lithium iron oxide, a lithium iron phosphate, or a lithium iron silicate. Cathodes can be made as bulk material in a solid form or in solution, or in various forms including thin films.
Owner:TRANSTRON SOLUTIONS LLC
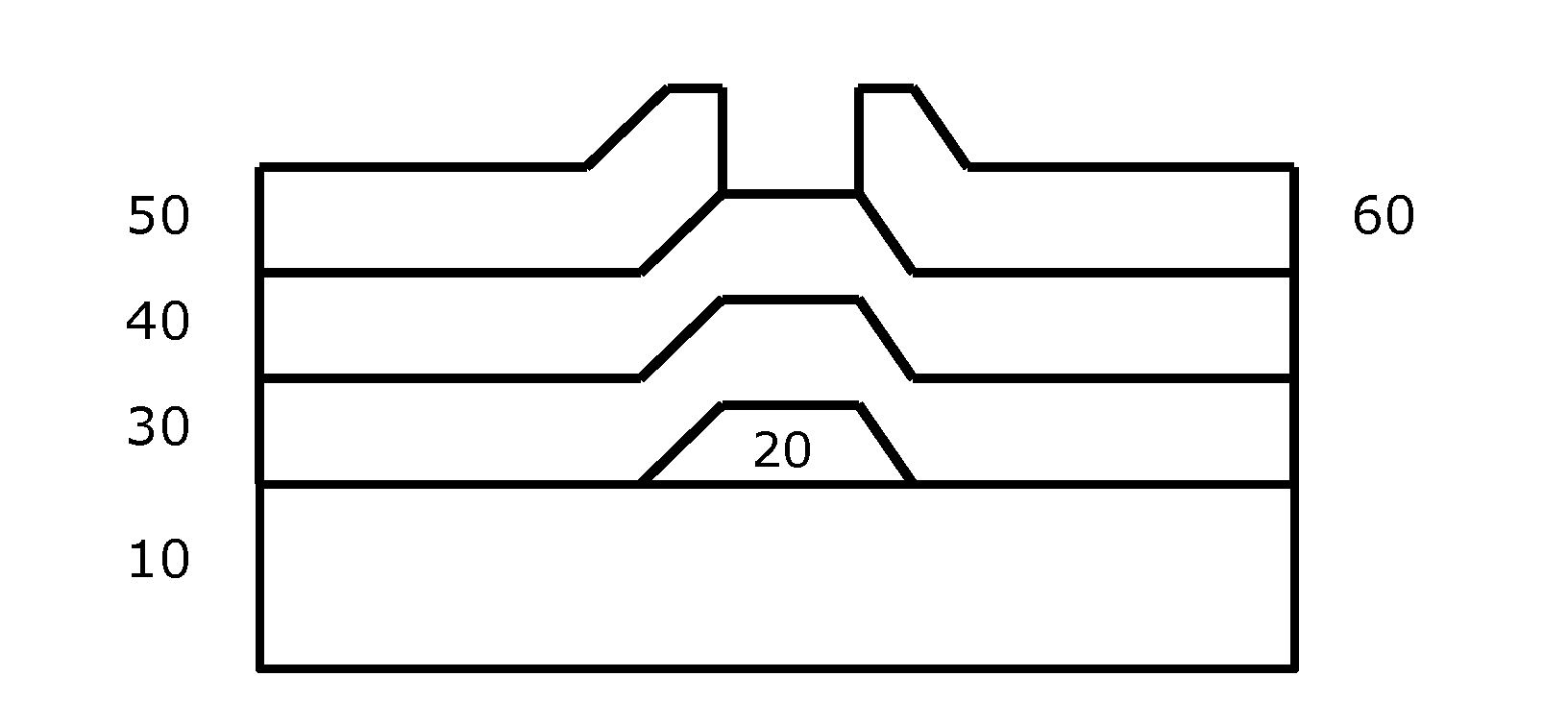
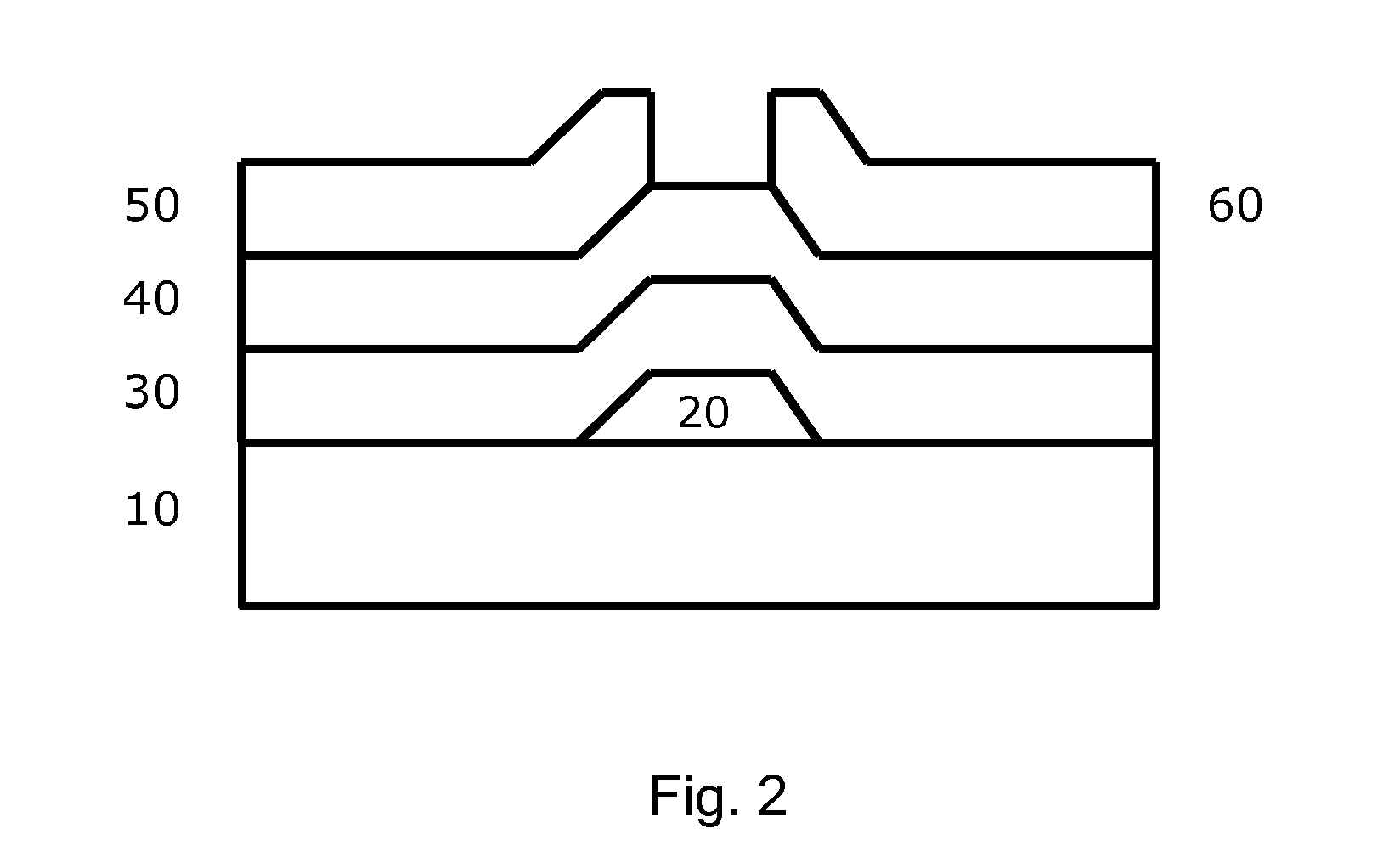
Molecular precursor compounds for abizo zinc-group 13 mixed oxide materials
InactiveUS20150221772A1Increase speedHigh yieldTransistorGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesMixed oxideCompound (substance)
Molecular precursor compounds, processes and compositions for making Zn-Group 13 mixed oxide materials including ABIZO, AIZO and BIZO, by providing inks comprising a molecular precursor compound having the empirical formula AlaInbBdZn(OROR)3(a+b+d)+2, and printing or depositing an ink in a film on a substrate. The printed or deposited film can be treated to convert the molecular precursor compounds to a material.
Owner:PRECURSOR ENERGETICS
Graphene-laminated composite doping method
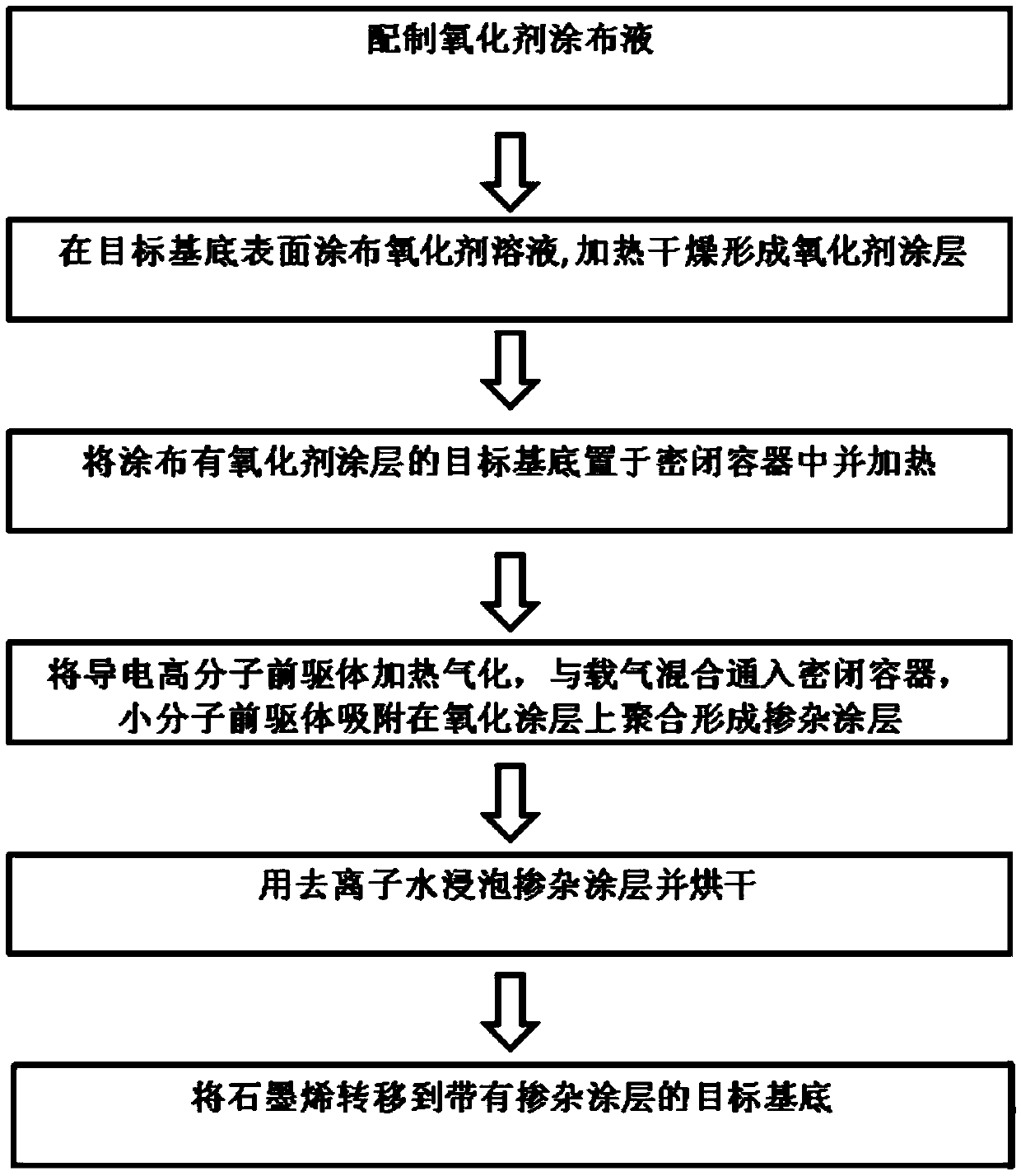
InactiveCN105504326ASuitable for large area productionStable doping effectCoatingsConductive polymerMolecular precursor
The invention provides a graphene-laminated composite doping method, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an oxidant coating liquid; (2) coating the surface of a target substrate with an oxidant solution, and heating and drying to form an oxidant coating; (3) putting the target substrate coated with the oxidant into an airtight container, and heating to a certain temperature; (4) heating and gasifying a conductive polymer precursor, mixing with a carrier gas to introduce into the airtight container, and adsorbing a small molecular precursor to an oxidative coating to form a doping coating through polymerization; (5) soaking the doping coating with deionized water and drying the doping coating; and (6) transferring graphene into the target substrate with the doping coating, and furthermore, repeating the steps (2) to (5) on the graphene to form a second doping coating. A layer of doping coating with uniform and controllable thickness is formed on the surface of the target substrate in situ; the doping effect is uniform; in addition, the doping coating is stable, and is located between the graphene and the target substrate after being transferred; and the doping effect is stable and lasting.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com