Patents
Literature
332results about How to "Improve direct yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
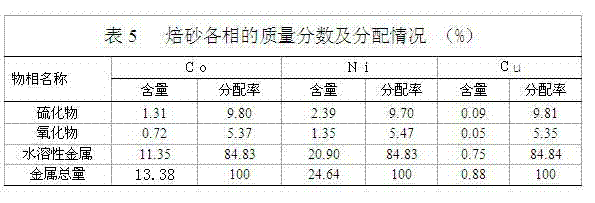
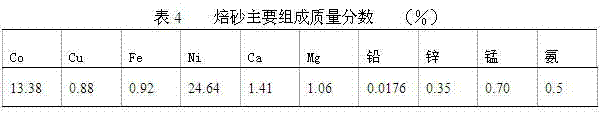
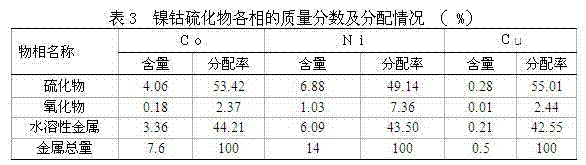
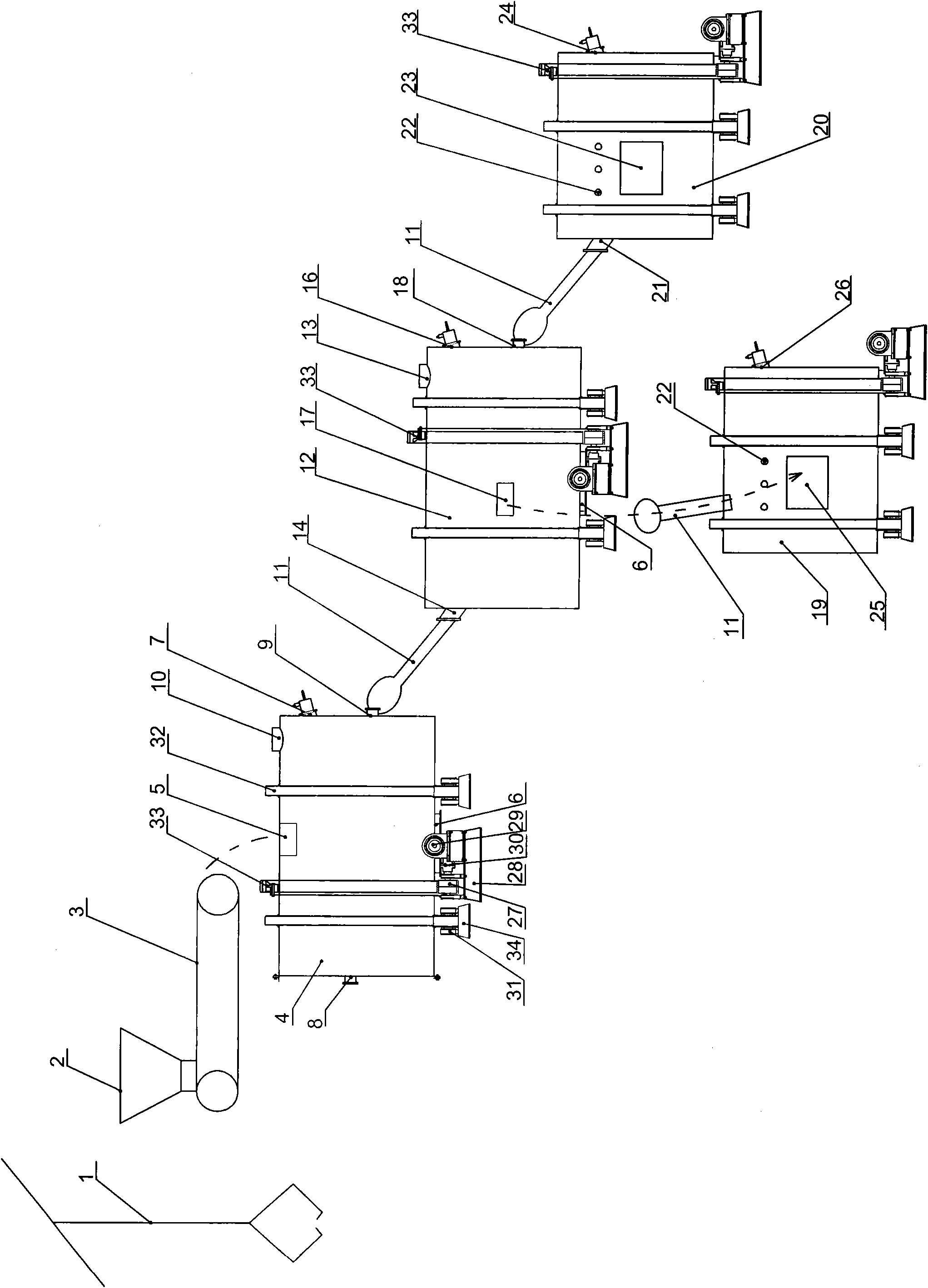
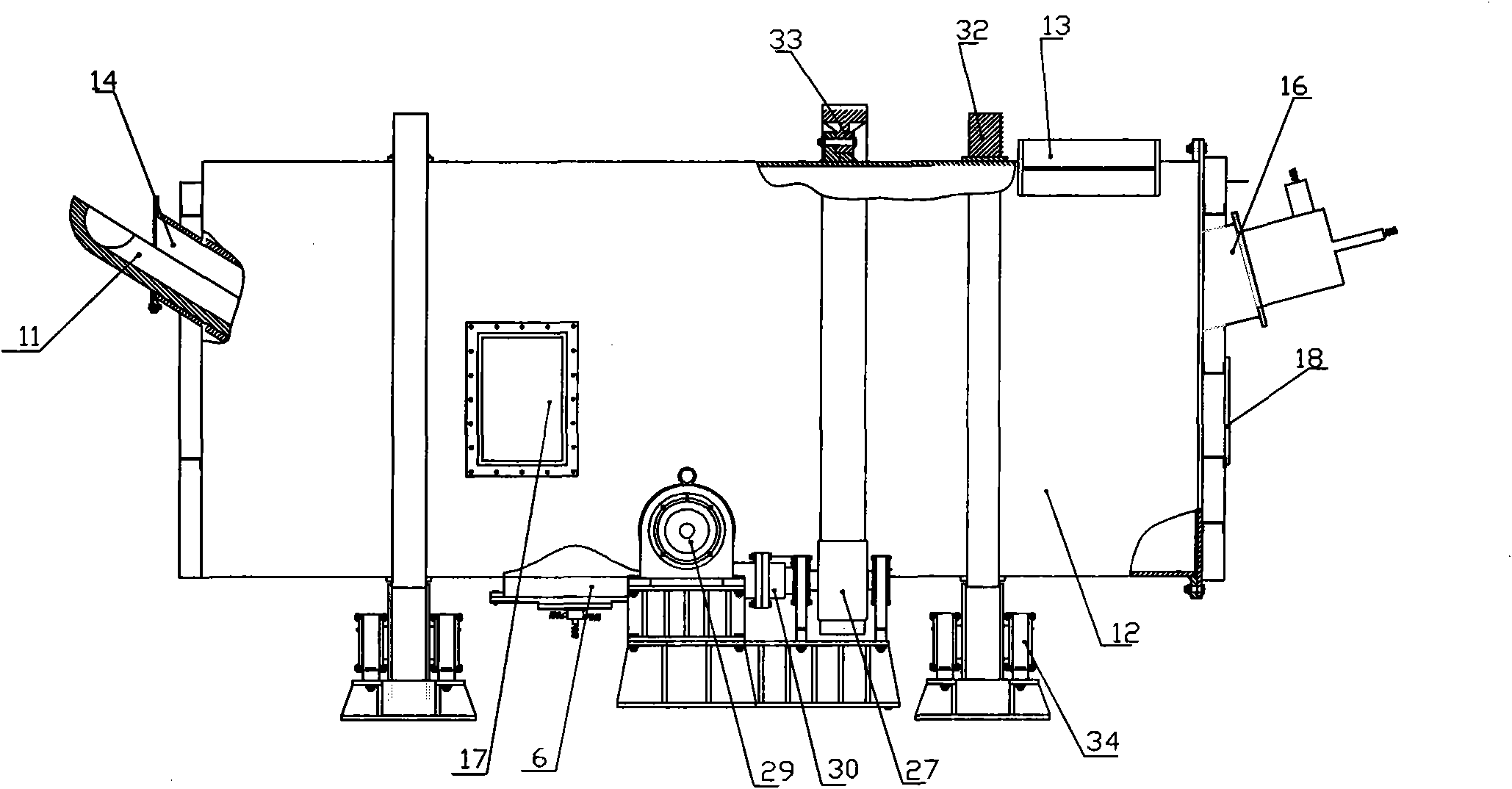
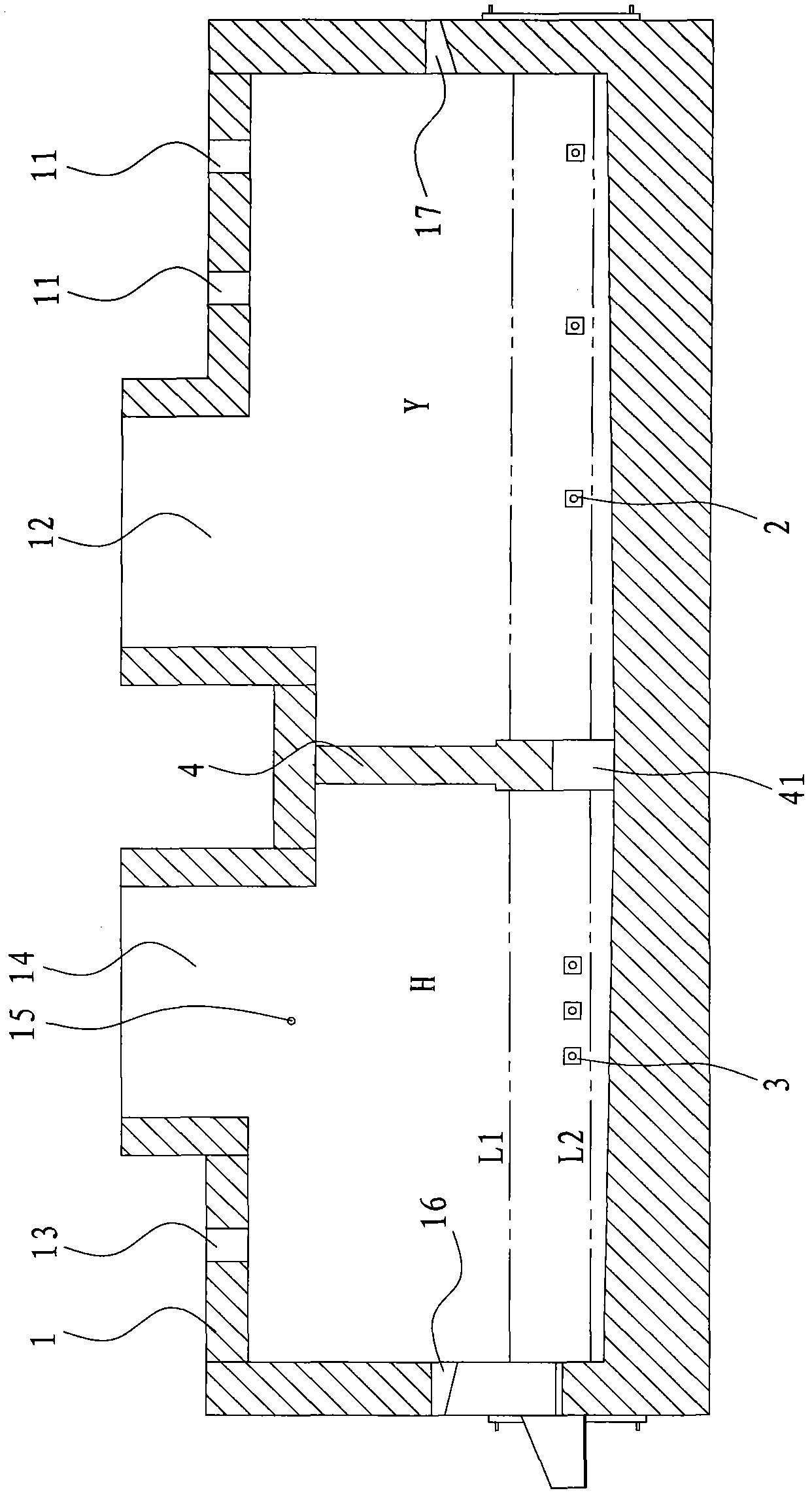
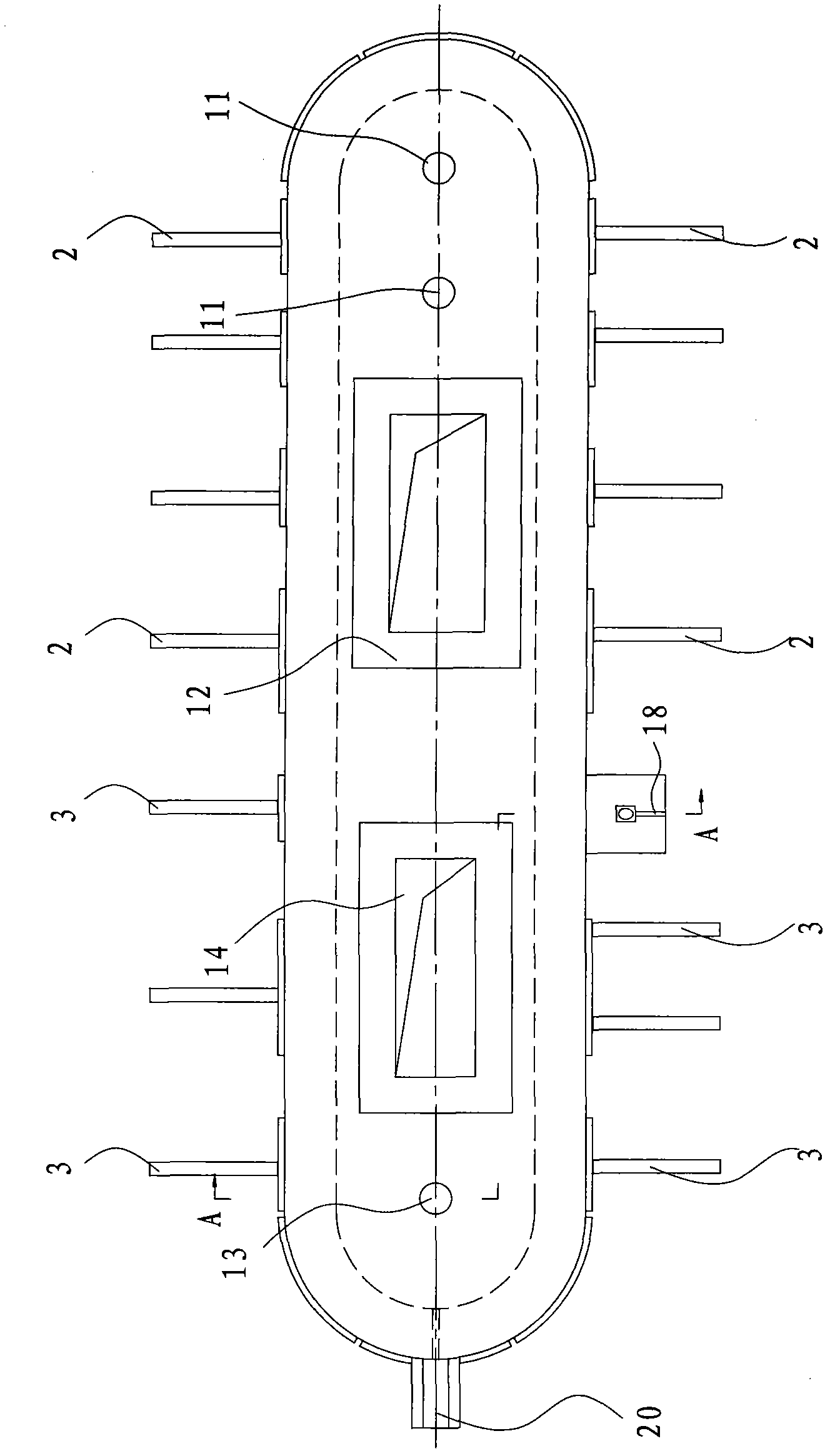
Treatment method of nickel-cobalt material
The invention provides a treatment method of a cobalt-containing material, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal smelting. In the treatment method, through six steps such as peroxidation roasting, sulfuric acid leaching, N902 extraction of copper, chemical iron calcium magnesium removal, P204 extraction and impurity removal, P507 extraction and separation of nickel-cobalt, nickel,cobalt and copper in the nickel-cobalt material are extracted in high recovery, and impurities such as iron, zinc, manganese, calcium, magnesium and the like in the nickel-cobalt material are removed, thereby achieving nickel-cobalt-copper separation and resource comprehensive utilization. According to the treatment method provided by the invention, the process is simple and production cost is relatively low; the adaptability of the method on raw materials is strong and can be used for treating the nickel-cobalt material with complicated components and high copper-zinc-magnesium contents.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
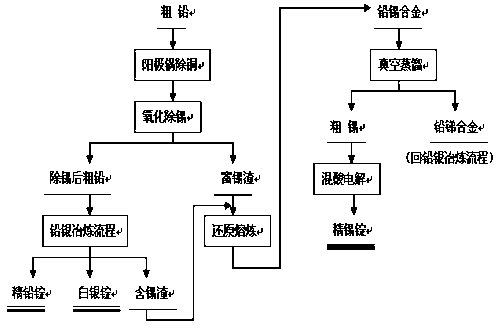
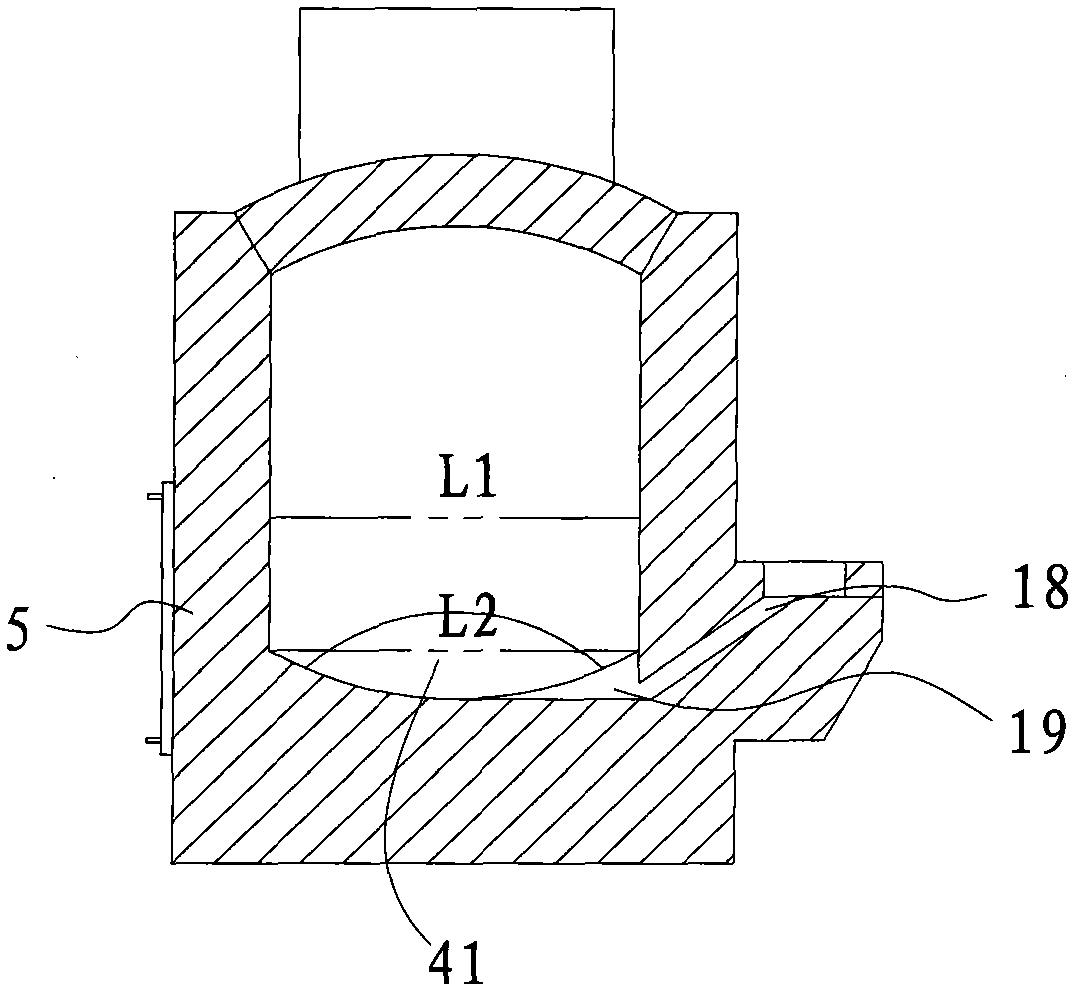
Method for recycling tin from lead bullion
InactiveCN104141152AImprove efficiencyImprove production costsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisLead smelting
The invention discloses a method for recycling tin from lead bullion, and belongs to the technical field of pyrogenic process and wet process combined metallurgy. The method comprises the steps that after liguation decoppering processing is carried out on the lead bullion, caustic soda, caustic soda and salt are added into the lead bullion according to the content of the tin in the lead bullion to gather and remove the tin in the lead bullion, and tin-rich slag is obtained; sodium carbonate and reduction coal are added into the tin-rich slag and all tin-containing slag produced by a lead smelting system, and the tin-rich slag and the tin-containing slag generate terne metal through reduction smelting; the terne metal is processed through vacuum distillation to obtain crude tin; highly purified precipitated tin is obtained from the crude tin through electrolytic refining of mixed acid with silicofluoric acid-sulfuric acid as an electrolytic medium, and the precipitated tin is processed through simple smelting to obtain a tin ingot product meeting the national standard. The method sets the precedent for producing tin ingot products through comprehensive utilization of tin resources obtained from lead through smelting, has the advantages of being concise in technology, high in tin product yield, low in processing cost and the like, particularly separates tin alloys through introduction of vacuum distillation, and has the significant advantages in the aspects such as energy conservation and environment protection.
Owner:蒙自矿冶有限责任公司
Preparation of high dispersed superfine spherical silver powder for conductive silver slurry
A preparation method of high-dispersion ultra-fine spherical silver powder used for conductive silver paste relates to a preparation method of ultra-fine spherical silver powder, in particular to the preparation method of the high-dispersion ultra-fine spherical silver powder for the conductive silver paste in the electronic industry. The preparation method is characterized in that silver ammonia solution is dropped in a reduction system which consists of a reducing agent of formaldehyde, a dispersant of polyvinyl alcohol PVA and sodium hydroxide solution, thus obtaining high-dispersion ultra-fine silver powder slurry, and the high-dispersion ultra-fine spherical silver powder with the particle size range of 0.3 to 1.0Mum can be obtained by solid-liquid separation and drying. The method of the invention has simple and feasible process flow, low production cost, less equipment investment, stable and reliable process conditions, small particle size of the product silver powder, narrow distribution range, high yield and easy realization of industrial mass production.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
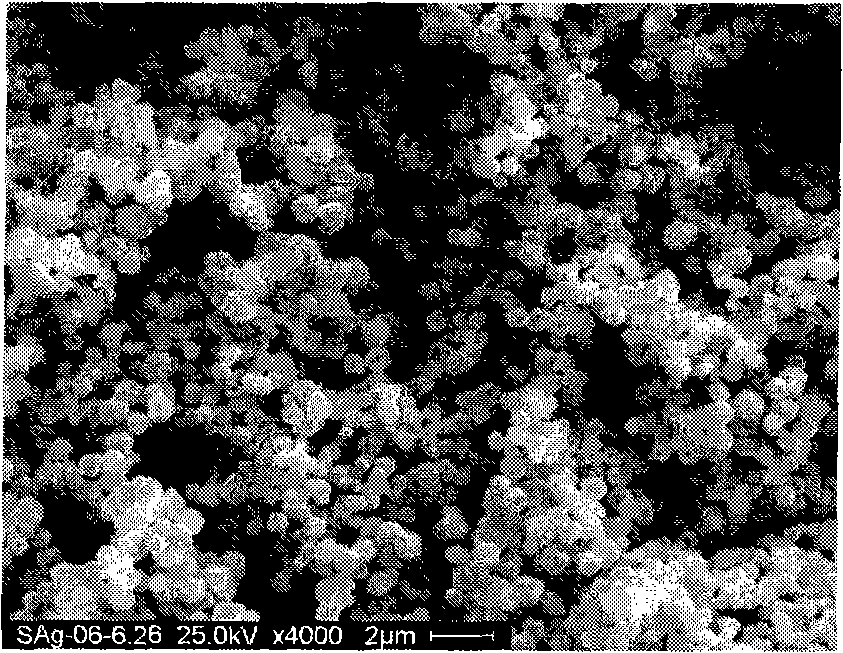
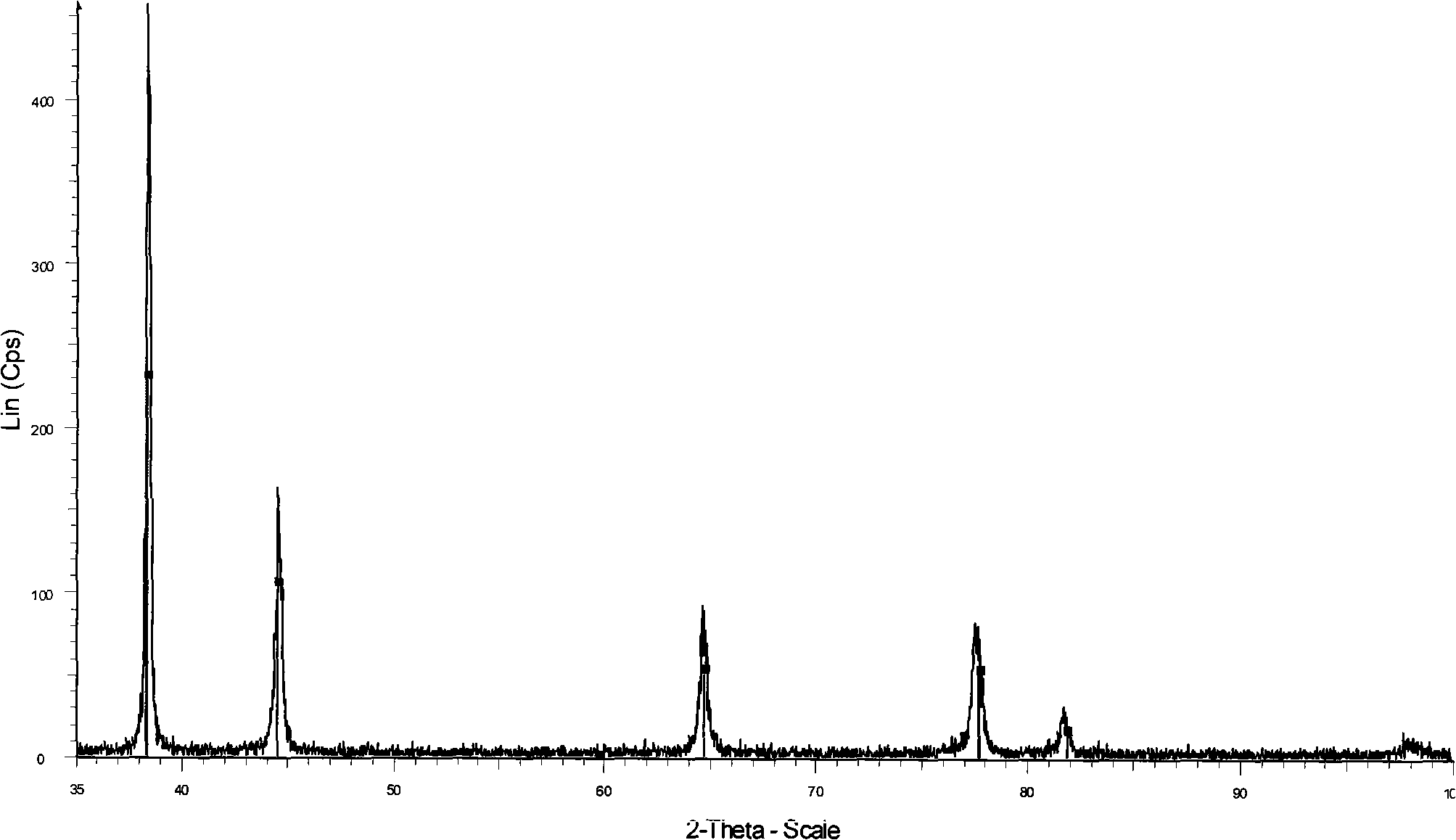
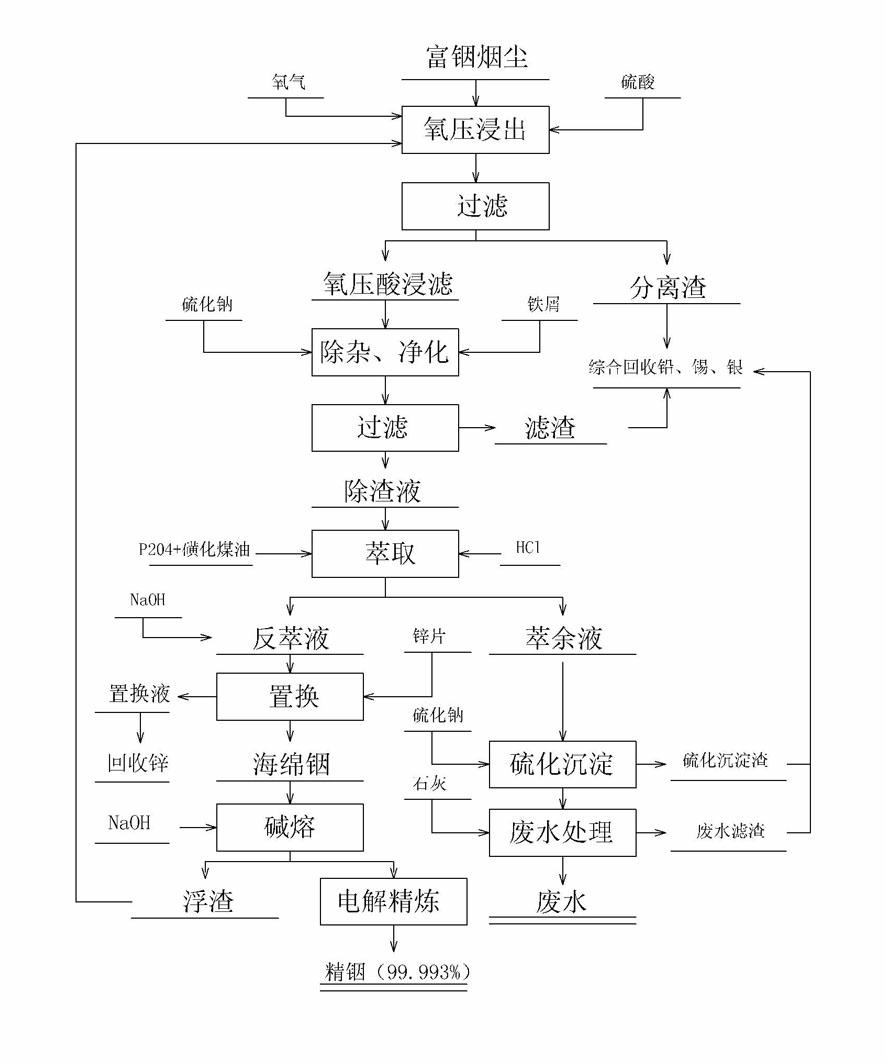
Method for extracting indium from indium-rich smoke dust by using oxygen pressure technology
The invention provides a method for extracting indium from indium-rich smoke dust by using an oxygen pressure technology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: carrying out leaching indium extraction of the difficult-to-handle indium-rich smoke dust of a Pb-Sn reverberatory furnace by adopting a wet-process metallurgical oxygen pressure acid leaching technology, and highly enriching and recycling valuable metals in the raw material; and purifying to remove impurities of leachate, and carrying out extraction, replacement and electrolytic refining, thereby obtaining greater than 99.995% of electrical indium products. The technology method has the advantages that the indium leaching rate of the indium-rich smoke dust of the Pb-Sb reverberatory furnace and the enrichment rate of the valuable metals can be obviously increased, and the comprehensive recycling effect can be achieved, thereby waster water of indium smelting can be discharged up to the standard after being processed with low cost, the environmental pollution in the indium extraction process is eliminated. In the process, the leaching rate of the indium is more than 97%, leaching residues containless than 0.01% of indium, the enrichment rate of plumbum, tin, bismuth and zinc is more than 98%, the quality of refined indium products is more than 99.995%, and plumbum enriching slag containing greater than 60% of Pd is obtained. The technical scheme can independently form a system, can also be used for improving and perfecting old technologies and has higher popularization and application value.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Method for preparing stannous oxide
InactiveCN101665266ASimple production processImprove direct yieldTin oxidesChemical industrySodium carbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing an inorganic tin compound, in particular to a method for preparing stannous oxide, belonging to the technical field of chemical industries. The method comprises the following technical steps: (1) slowly adding a sodium carbonate solution into a stannous chloride solution by stirring and carrying out neutralization reaction till the pH value is 6 to 7; (2) conversion reaction: immediately heating a neutralization reaction product, adding a sodium hydroxide solution into the materials, maintaining a boiling state and converting till a white sediment is converted into a black blue sediment; (3) washing the converted product by water to remove Cl<->, washing till the concentration of the Cl<-> is smaller than 0.2 percent, and adding antioxidant;after filtering the product, heating and drying in vacuum to obtain a stannous oxide product. The method has simple operation, easy control of process parameter and low cost; the purity of the prepared stannous oxide is more than 99 percent, the Cl<-> is smaller than and equal to 0.02 percent, and the product is dissolved into 30 percent of methanesulfonic acid to obtain a clear solution.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN
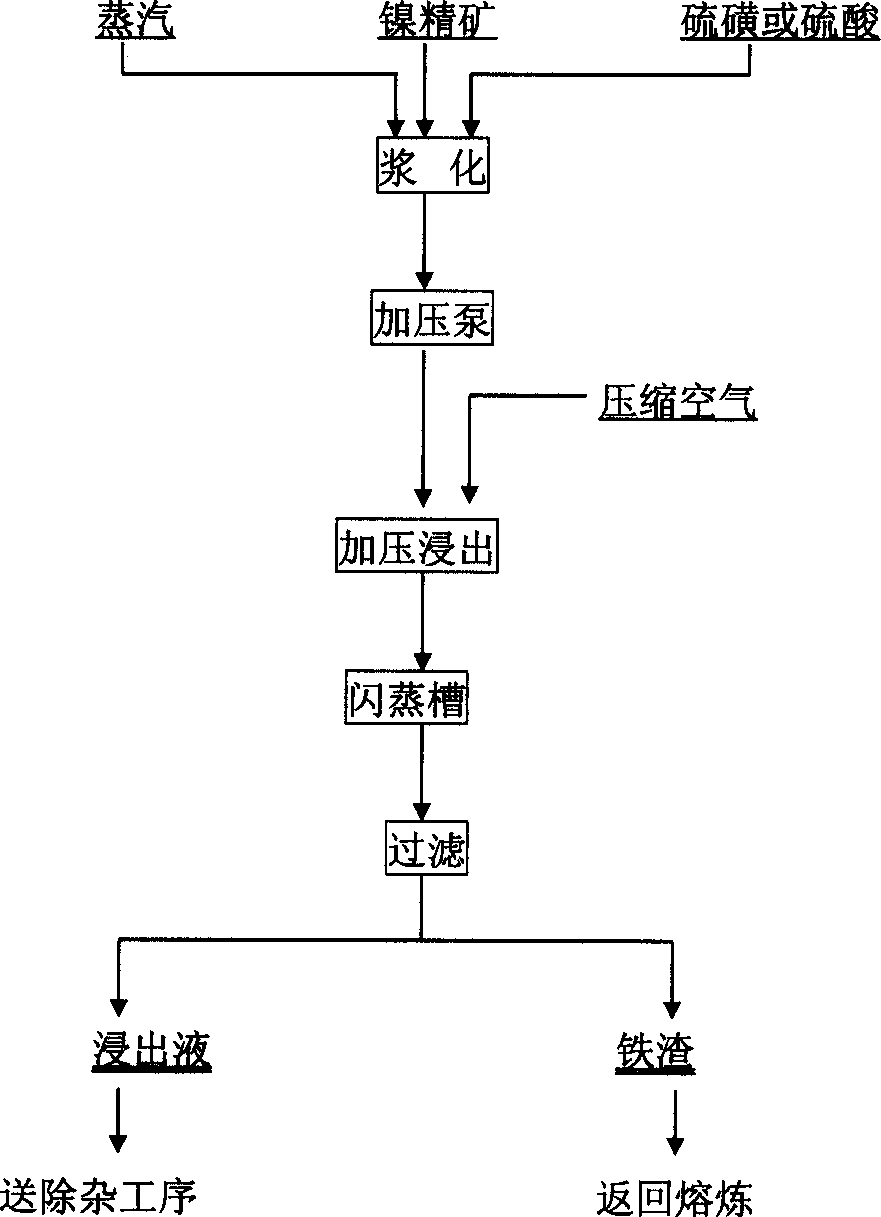
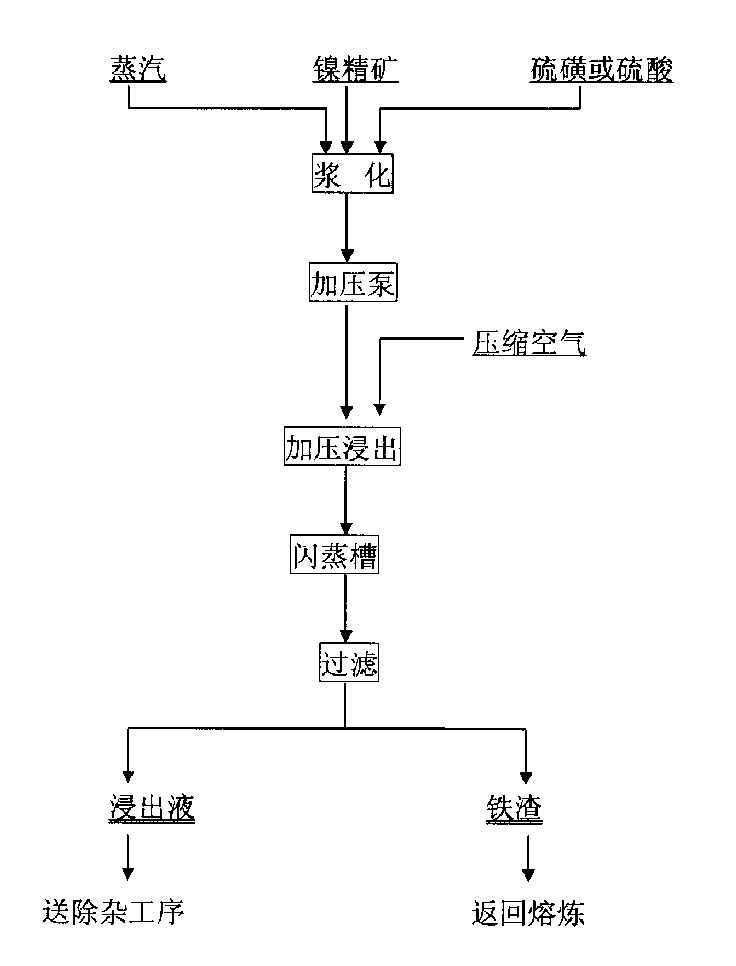
Process for extracting nickel from nickel sulfide material with low copper content
The nickel extracting process of the present invention relates to the one-stage pressurized leaching extraction of nickel from nickel concentrate with low copper content or high sulfur nickel concentrate separated through milling and floating procedure. The process features that under oxygenation and adding sulfur or sulfuric acid, and in 100-180 deg.c and oxygen pressure 50-300 KPa, nickel concentrate is one-step pressurized leached to complete the Ni, Co and Cu leaching process with Fe being fixed in slag. Nickel sulfate solution after liquid-solid separation may be used in production pure nickel sulfate or electrolyte while recovering Co, Cu and other valuable metals. The process is simple and high in production efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
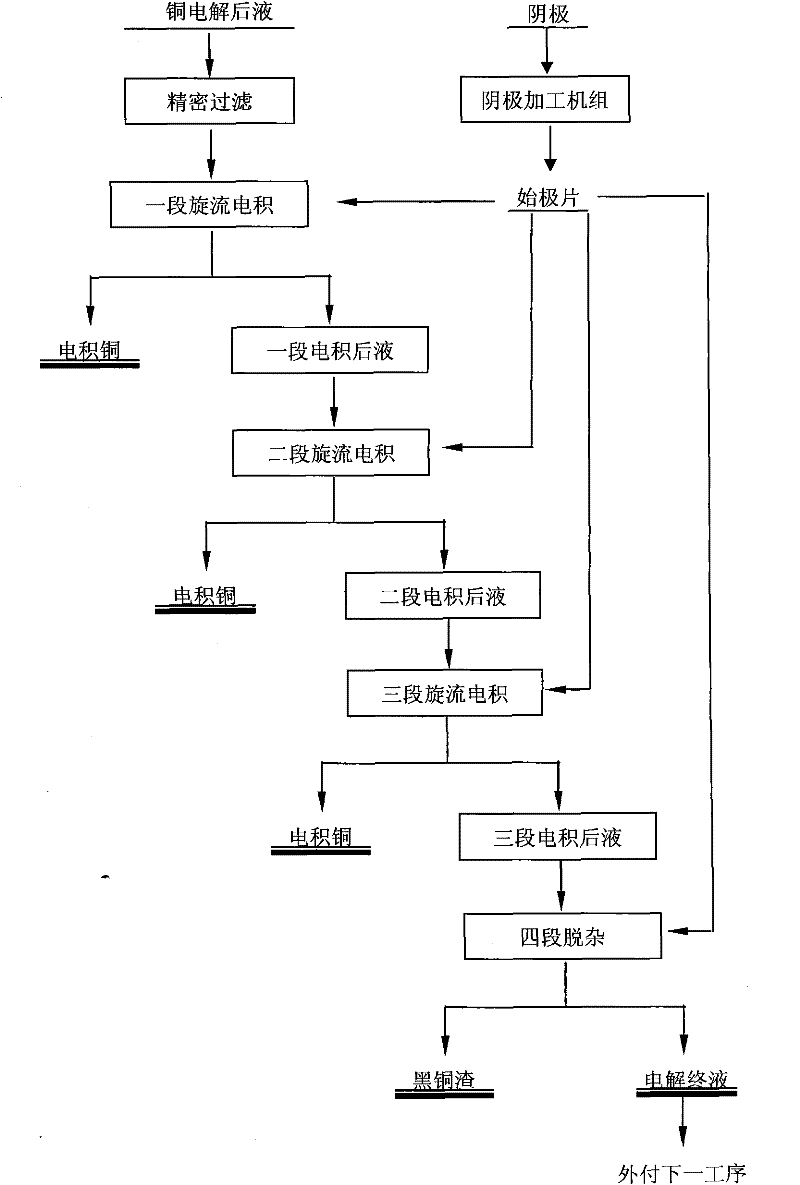
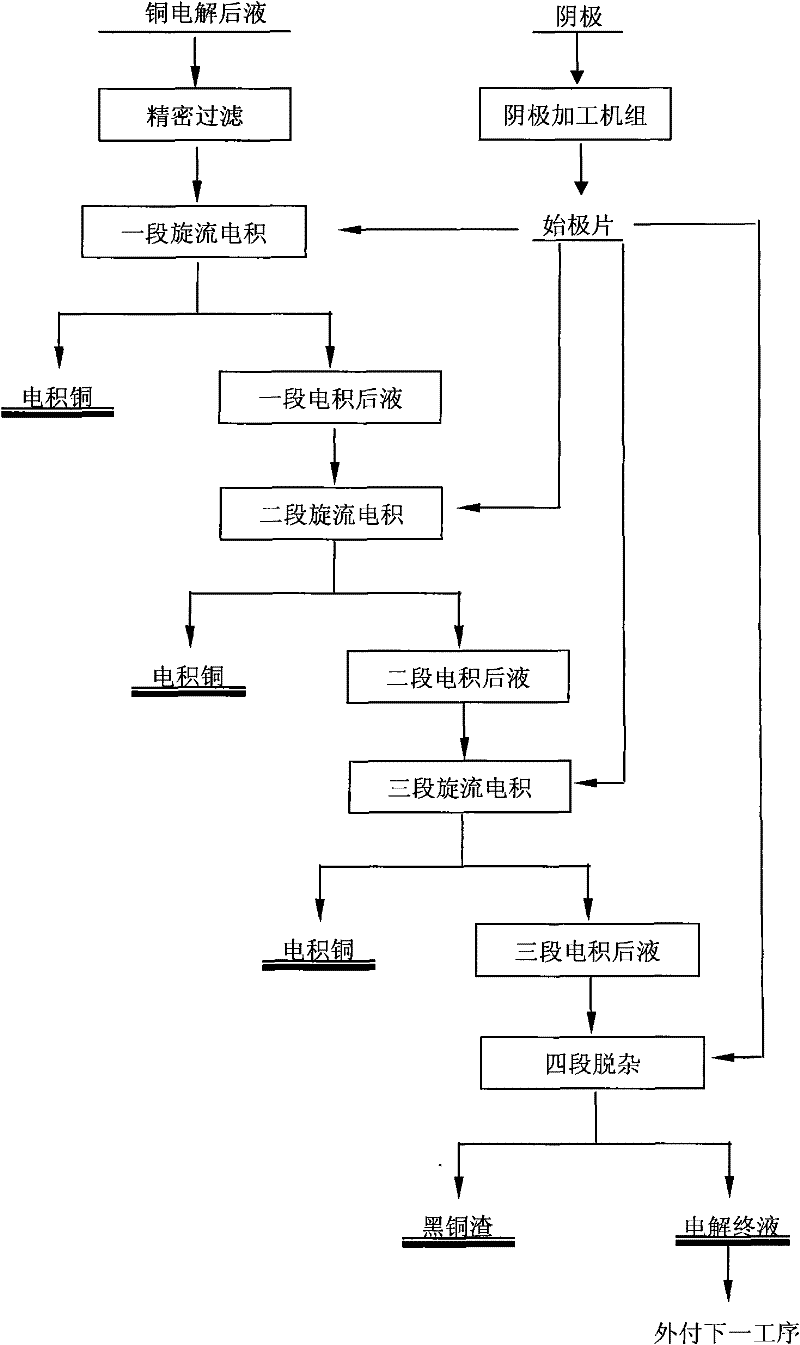
Technology for treating and purifying copper electrolyte by vortex electrolysis
InactiveCN102453931AIncrease current densityImprove current efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisBismuth
A technology for treating and purifying copper electrolyte by vortex electrolysis relates to the technical field of copper electrolyte purification. The treatment process comprises the steps of: 1. carrying out secondary filter on copper electrolyte to be purified and treated; 2. sending into a vortex electrolysis system to produce standard cathode copper; 3. after three segments of vortex electrolysis, sending the solution with a copper content of 2-4g / L to a vortex electrolysis powder impurity removal stage; 4. removing impurities of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in a powder vortex electrolytic tank; and 5. forming a small amount of black copper ash with a low copper content in a filter cake after press filtration and sending a filtrate into a next operation. The technology of the invention can substitute a traditional induction copper and impurity removal method for purifying and treating copper electrolysis waste liquid, so as to provide an electrolysis technical scheme, which is efficient and reliable, and has simple process flow, simple operation and low cost, for purifying copper electrolysis waste liquid.
Owner:浙江科菲科技股份有限公司
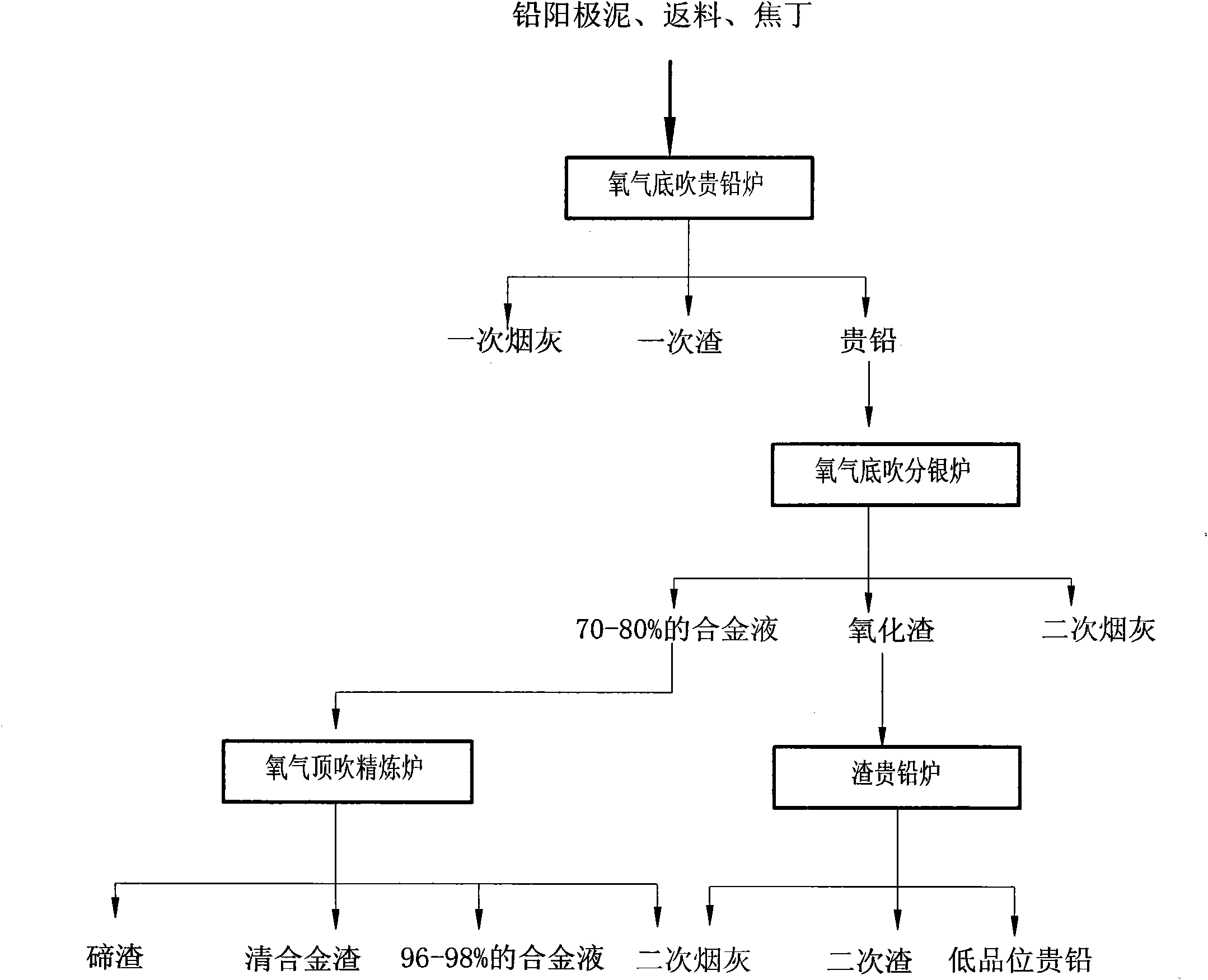
Method and device for continuously treating lead anode slime
ActiveCN101892388AEnables continuous processingShort processing cycleProcess efficiency improvementMelting tankSmelting process
The invention relates to a method and device for continuously treating lead anode slime by bath smelting. The method comprises the following steps: proportionally adding lead anode slime, recycled materials and nut coke as charging materials into an oxygen bottom blowing bullion lead furnace for smelting to generate bullion lead of which the bullion grade is 25-50%, primary slag and primary soot; adding the bullion lead into an oxygen bottom blowing silver-smelting furnace to react to generate oxidizing slag, secondary soot and alloy liquid of which the bullion grade reaches 70-80%; introducing the alloy liquid into an oxygen top blowing refining furnace to react to generate tellurium slag, clear alloy slag, secondary soot and alloy liquid of which the bullion grade reaches 96-98%; and discharging the oxidizing slag, then enabling the oxidizing slag to enter a slag bullion lead furnace, and adding the nut coke to react to generate low-grade bullion lead, secondary slag and secondary soot, wherein the low-grade bullion lead is returned for proportioning. The invention realizes the continuous treatment of the anode slime, strengthens the smelting process, improves the direct recovery rate of the bullion, lowers the production cost, reduces the environmental pollution, and shortens the treatment period of the anode slime.
Owner:JIYUAN YUGUANG NONFERROUS METALLURGY DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD
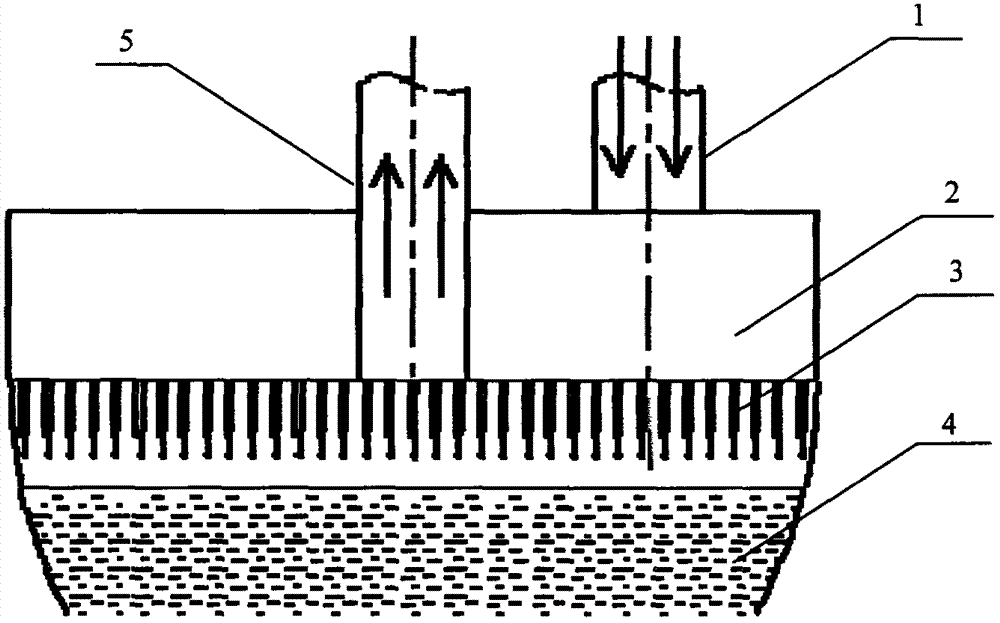
Continuous lead-smelting device and continuous lead-smelting process
ActiveCN102011014AStable lead contentTake advantage ofLighting and heating apparatusLead smeltingFlue gas
The invention discloses a continuous lead-smelting device which comprises a reaction furnace, a side-blown spraying gun for an oxidation zone and a side-blown spraying gun for a reduction zone, wherein, the reaction furnace is internally equipped with a partition wall for dividing a furnace chamber of the reaction furnace into the oxidation zone and the reduction zone, the lower part of the furnace chamber forms a molten pool, the bottom of the partition wall is equipped with a communicating channel for communicating the oxidation zone with the reduction zone, the roof of the oxidation zone is respectively equipped with a feed inlet for the oxidation zone and a flue gas outlet for the oxidation zone respectively, the roof of the reduction zone is equipped with a reductant feed inlet and a flue gas outlet for the reduction zone, and the furnace wall of the furnace chamber is equipped with a siphon lead discharge port and a slag discharge port; the side-blown spraying gun for the oxidation zone is connected with the side wall of the oxidation zone of the reaction furnace so as to laterally blow oxygen into the molten pool of the oxidation zone; and the side-blown spraying gun for the reduction zone is connected with the side wall of the reduction zone of the reaction furnace so as to laterally blow fuel and oxygen into the reduction zone. The continuous lead-smelting device disclosed by the invention has the advantages that oxidation and reduction are realized in single reaction furnace, lead content in slag is low, stability and tightness are good, environmental protection property is high, heat content of the slag is fully utilized and energy consumption is lowered. The invention further provides a continuous lead-smelting process.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
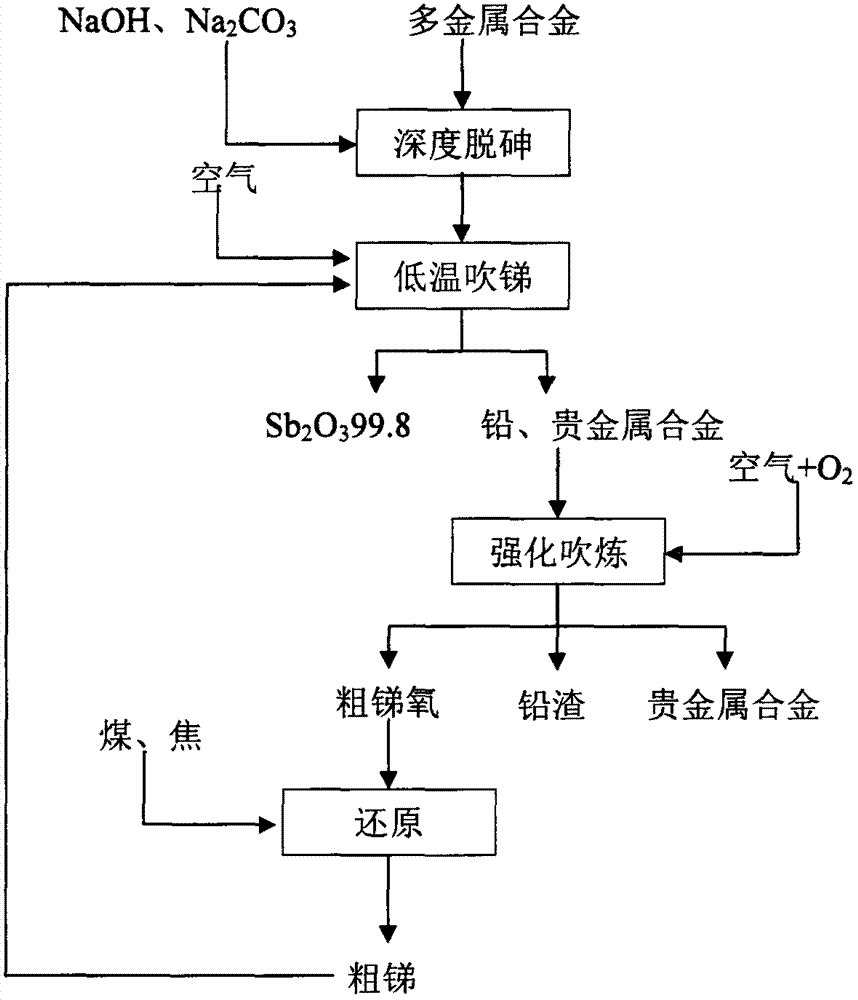
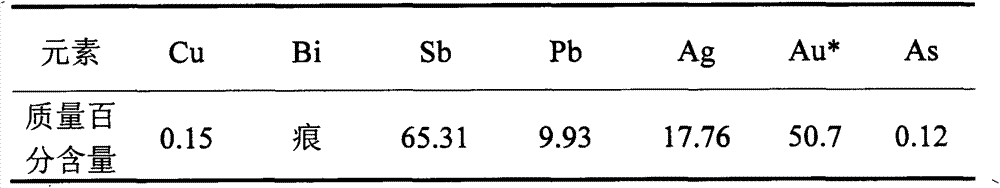
Treatment method for polymetallic alloy formed by arsenic-lead-antimony and noble metal
InactiveCN103194605AReduce the temperatureReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementLead oxideAlloy
The invention discloses a treatment method for a polymetallic alloy formed by arsenic-lead-antimony and noble metal. In order that the polymetallic alloy formed by arsenic-lead-antimony and noble metal is directly prepared to meet the international standard Sb20399.8, the noble metal is enriched in the noble metal alloy. The treatment method comprises the following steps of: carrying out alkalification and deep dearsenification treatment on the polymetallic alloy formed by arsenic-lead-antimony and noble metal; then converting antimony white at low temperature in a special converting furnace; and finally blasting and highly oxidizing lead slagging to obtain the noble metal alloy. According to the treatment method, the antimony directly satisfies the output requirement of antimony white; the energy consumption is low, and the direct yield rate of the noble metal is improved to more than 98%; and the converting and slagging time of residual alloy after removal of arsenic and antimony is shortened within 30 hours, which is reduced by more than 50% compared with the conventional process.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for preparing high pure gold and enriching silver, platinum and palladium from silver anode mud
ActiveCN106119554AHigh removal rateHigh gold contentProcess efficiency improvementSlagMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for preparing high pure gold and enriching silver, platinum and palladium from silver anode mud. The process of separating silver with nitric acid, recycling silver, platinum and palladium with silver-enriched liquid, decomposing silver separating slag with aqua regia and preparing high pure gold with a one-time unsaturation reduction method is adopted and comprises the steps: leaching the silver anode mud with nitric acid to obtain separated silver, adding sodium chloride into the silver separating liquid to deposit the silver to obtain silver chloride sediment and silver depositing liquid, adding iron powder into the silver chloride sediment for replacement, returning the crude silver back to a Kaldo furnace for melting, and adding sodium hydrogen sulfite into the silver depositing liquid to reduce, deposit and recycle platinum and palladium; performing gold separating on the silver separating slag with aqua regia to obtain gold separating liquid and gold separating slag, performing the iron powder replacement step on the gold separating slag, adding the sodium hydrogen sulfite into the gold separating liquid to perform unsaturation reduction to obtain gold powder and gold depositing liquid, washing, drying and ingotting the gold powder to obtain a product gold ingot, and adding the sodium hydrogen sulfite into the gold depositing liquid to reduce and recycle the platinum and palladium for the second time to obtain the crude gold powder, and returning back to the previous steps. The method solves the problems of long leaching flow, high agent cost, complex operation, more devices and low recycle rate of the silver anode mud.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
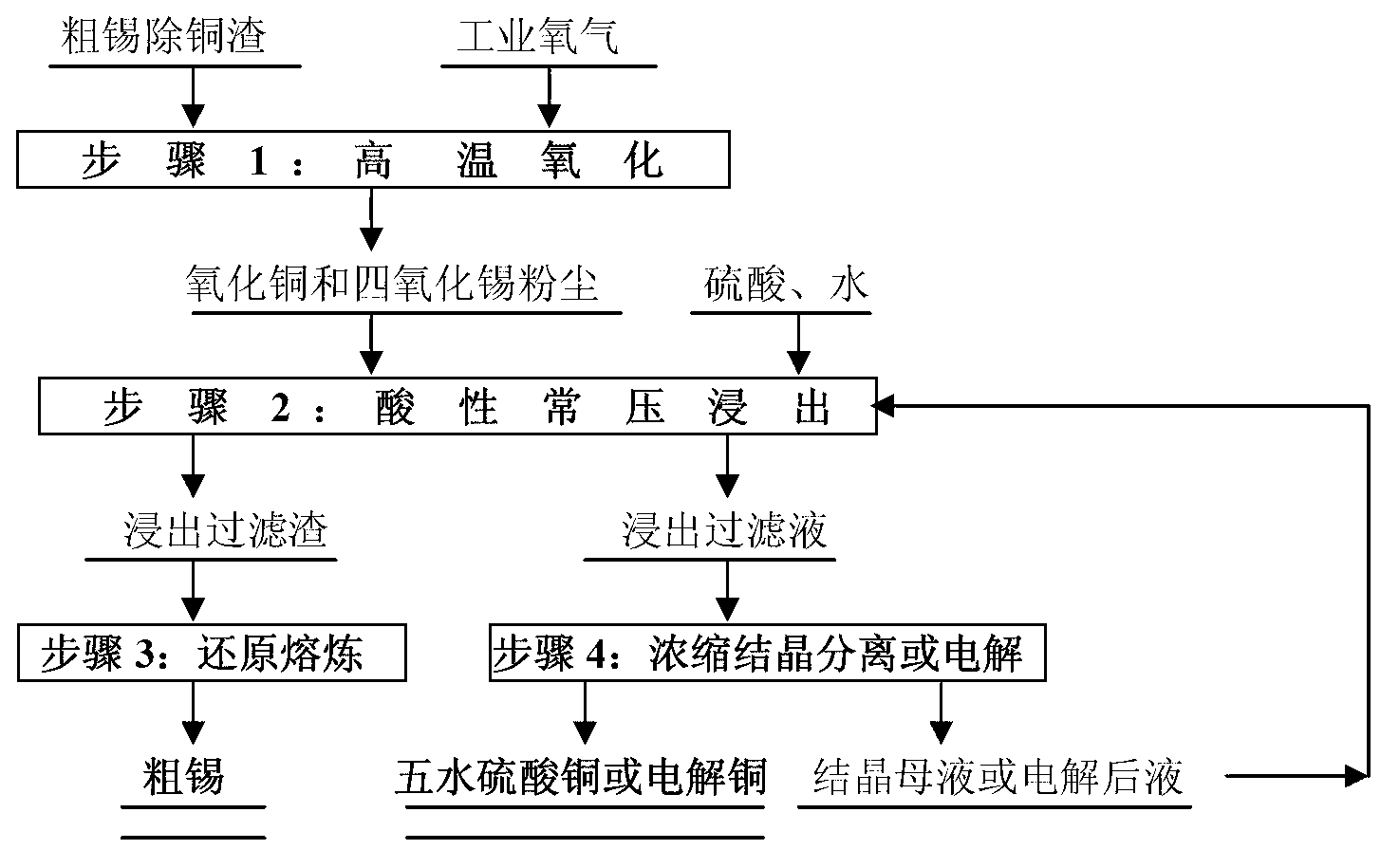
Treatment method of coarse tin decoppered slag
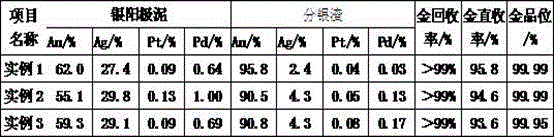
InactiveCN102851514AImprove direct yieldSafe separationProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention relates to a treatment method of coarse tin decoppered slag, which comprises the following steps: jetting industrial oxygen with the purity of 93-98.5% to the surface or inside of the coarse tin decoppered slag at the temperature of 850-1250 DEG C until the coarse tin decoppered slag is completely oxidized into copper oxide and tin tetroxide dust; leaching the copper oxide and tin tetroxide dust for 2-3 hours under atmospheric pressure and temperature under the condition of the initial acid of 70-120 g / L to obtain leached filtered slag, and carrying out reduction smelting to produce coarse tin; concentrating the leached filtrate to crystallize, and separating to produce chalcanthite product, or carrying out electrolysis to produce electrolytic copper; and returning the crystallization mother solution or electrolysis solution to the leaching process for solution preparation. The invention can separate tin and copper in the crude tin decoppered slag in a safe and efficient way, and does not generate waste water, waste gas or waste residue.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Zinc-aluminum-rare earth middle alloy and its use in hot galvanizing alloy production
The invention relates to a process for producing a hot dip galvanizing alloy and an interalloy thereof. The technical proposal comprises that the interalloy of zinc, aluminum and rare earth consists of the following components in mass percentage: 3 to 5 percent of Al, 6 to 10 percent of RE, and the balance being Zn. The method of producing the hot dip galvanizing alloy comprises the following steps: mixing the zinc, the aluminum and the rare earth according to the following weight ratio: 3 to 5 percent of the Al, 6 to 10 percent of the RE, and the balance being the Zn; melting the materials in an interalloy smelting furnace with smelting temperature of between 500 and 650 DEG C; stirring the materials evenly and casting the materials into the interalloy of the zinc, the aluminum and the rare earth; adding the solid zinc required for the production of the hot dip galvanizing alloy into the smelting furnace made from the hot dip galvanizing alloy to be melted into zinc liquid; adding a slag former to the zinc liquid, stirring the mixture and forming slag at a temperature of between 470 and 480 DEG C; removing the slag in the furnace; adding the alloy of the zinc, the aluminum and the rare earth required according to the mixture ratio of the produced hot dip galvanizing alloy to the zinc liquid; and stirring the mixture to obtain the hot dip galvanizing alloy. The process reduces the temperature for alloy smelting, shortens the smelting and stirring time, prolongs the service life of a core-type induction furnace and is advantageous to uniform the components of the hot dip galvanizing alloy, and has the advantages of low equipment cost and simple and convenient maintenance.
Owner:湖南株冶火炬新材料有限公司
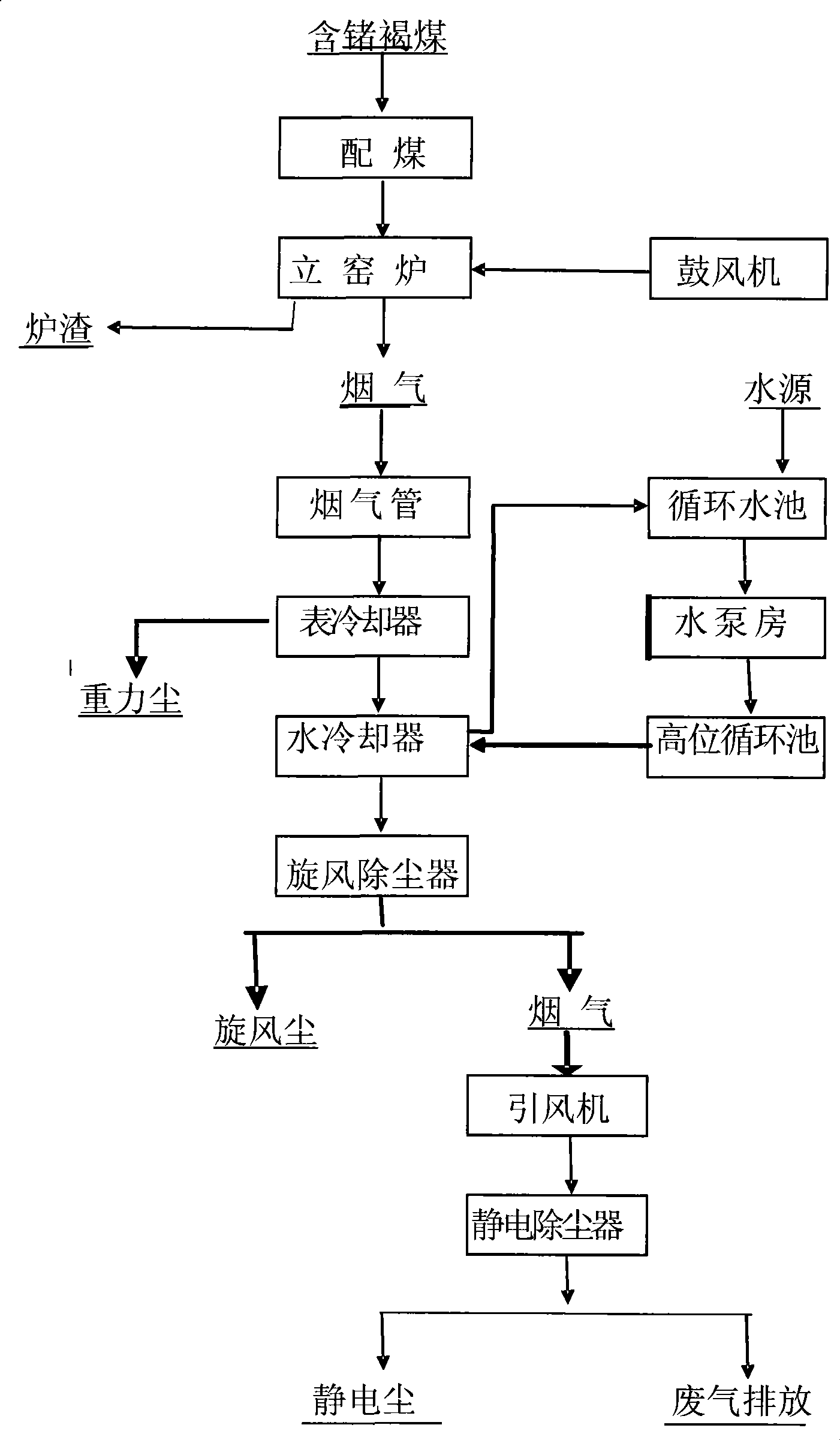
Method for extracting germanium from lignite by pyrogenic process
InactiveCN101413063AImprove direct yieldHigh germanium gradeGermanium monoxideElectrostatic precipitator
The invention provides a method for extracting germanium from lignite through a pyrogenic process. The method is characterized in that germanium-containing lignite volatilizes germanium in a pyrogenic-process smelting procedure of a vertical kiln; a control condition of volatilizing germanium is that the temperature is between 1,150 and 1,250 DEG C; in a suitable reducing atmosphere, the germanium existing as germanium dioxide generates germanium monoxide after reduction reaction through carbon particles and carbon monoxide; a suitable oxidizing atmosphere ensures that the germanium monoxide follows dust particles volatilized simultaneously to meet excessive oxygen in a flue gas tube and then is oxidized to be the germanium dioxide; the temperature of the germanium dioxide is lowered through a cooler; the generated germanium dioxide is changed into a solid state and is attached to the surfaces of the dust particles; the germanium-enriched dust particles pass an electrostatic dust catcher and then are attached to the electrostatic dust catcher; and germanium-enriched electrostatic dust is collected so as to obtain germanium concentrate. The method is advanced in technology, economical, practical and low in cost for extracting germanium. Compared with a chain-boiler germanium extracting process and other germanium extracting methods, the method has the advantages that the method is high in germanium volatilizing efficiency, the direct recovery rate of the electrostatic dust, the germanium-containing grade of the electrostatic dust and the post wet treatment yield of the output electrostatic dust, and is convenient for subsequent processing, and the like.
Owner:JIUJIANG BAIDUN VANADIUM TECH TRADING
Technique for extracting germanium from germanium-containing material by pressure leaching
ActiveCN101205572AImprove direct yieldSimple processProcess efficiency improvementHigh polymerGermanium
The present invention relates to a germanium-containing material leaching method and a germanium extracting technique. The method comprises the following steps of adding germanium-containing materials, zinc electro deposited waste liquid, oxygen with the purity of 70-90 percent or oxygen-enriched air into a pressure reactor, controlling leaching temperature and pressure, directly leaching the germanium in the germanium-containing materials, obtaining germanium-containing solution, adding neutralizing agent into the germanium-containing solution to precipitate germanium, controlling temperature and the final pH value, forming high polymer molecules of germanium and iron for coprecipitation, obtaining first-stage enriched slag of germanium, using electro deposited waste liquid containing zinc sulfate to leach the obtained the first-stage enriched slag of germanium, controlling leaching time and temperature to effectively dissolve germanium out, obtaining germanium-enriched leaching solution, having the obtained germanium-enriched leaching solution extracted and reextracted, and obtaining germanium-containing enriched products through enriching once again. The pressurized leaching treatment of germanium-containing materials is a novel smelting method with high efficiency, low consumption and low pollution.
Owner:云南驰宏国际锗业有限公司
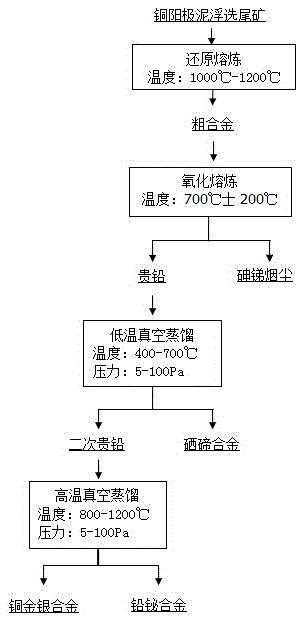
Method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings
InactiveCN105483384ASettle the lossHigh removal rateSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSootAntimony
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings and belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy. The method comprises: firstly, performing retailoring on the copper anode mud flotation tailings to obtain a reduction product, and then performing oxidative blowing on the reduction product to obtain rich lead and arsenic and antimony containing soot; first-stage low-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary low-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 400-700 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining secondary rich lead and a selenium-tellurium alloy; and second-stage high-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary high-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained secondary rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 800-1200 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining a lead-bismuth and a copper-gold-silver alloy. The method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings is safe and controllable in whole process flow, simple and convenient to operate, simple in equipment needed, free from three-waste emissions, and environment-friendly.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Copper scum smelting process
InactiveCN101994013AHigh recovery rateSolve the big environmental pollutionProcess efficiency improvementReverberatory furnaceAntimony oxide
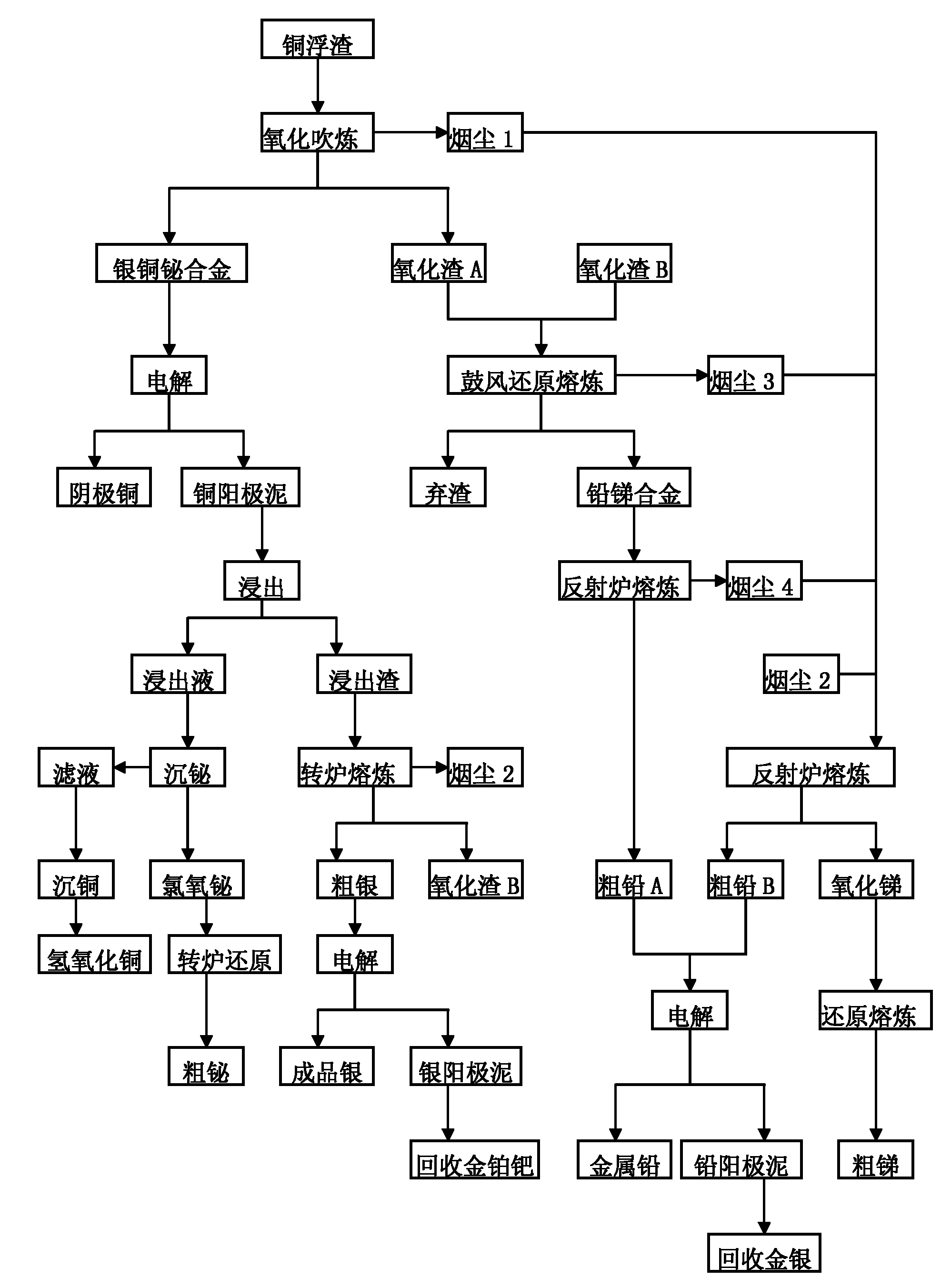
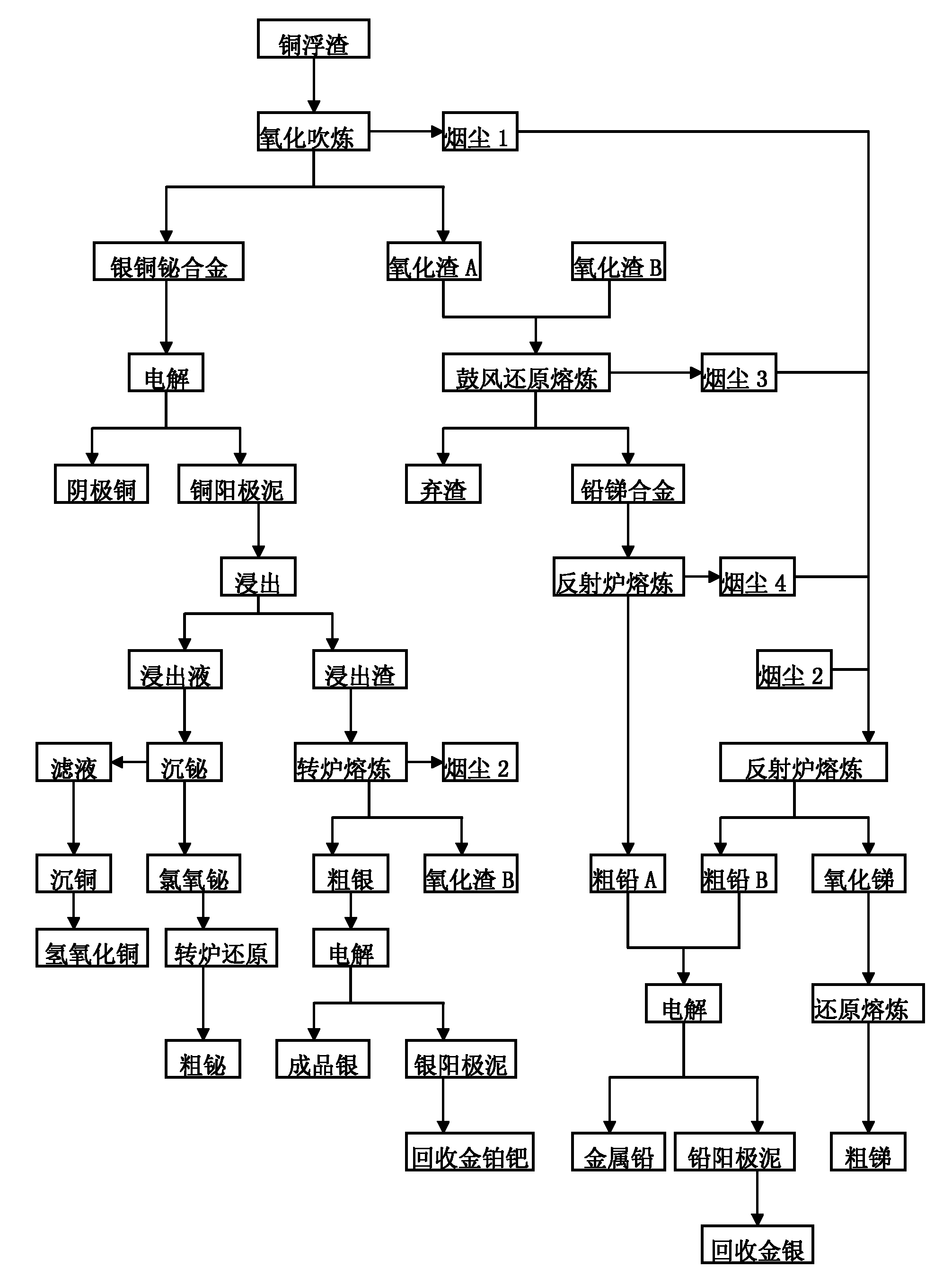
The invention discloses a copper scum smelting process comprising the following steps of: carrying out oxidation converting on copper scum to produce silver-copper-bismuth alloy, smoke 1 and oxidizing slag A; electrolyzing the silver-copper-bismuth alloy to produce cathode copper and copper anode mud, leaching the copper anode mud, precipitating bismuth in a leaching agent to obtain bismuth oxychloride, carrying out reduction smelting on the bismuth oxychloride to produce crude bismuth, then precipitating copper to obtain copper hydroxide, and smelting leached slag in a rotary furnace to produce crude silver, smoke 2 and oxidizing slag B; electrolyzing the crude silver to produce finished-product silver and silver anode mud, and recovering gold, platinum and palladium from the silver anode mud; carrying out reduction smelting on the oxidizing slag A and the oxidizing slag B in a blast furnace to obtain lead-antimony alloy, smoke 3 and waste slag, and smelting the lead-antimony alloy in a reverberatory furnace to obtain crude lead A and smoke 4; smelting the smoke 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the reverberatory furnace to produce crude lead B and antimony oxide, and carrying out reduction smelting on the antimony oxide to produce crude antimony; and electrolyzing the crude lead A and the crude lead B to produce lead and lead anode mud, and recovering the gold and silver from the lead anode mud. In the method, the gold silver yield reaches at least 99 percent, the yield of copper, bismuth, lead and antimony reaches at least 98 percent, and the recovery rate of all metals is greatly improved.
Owner:SIHUI CITY HONGMING PRECIOUS METALS +1
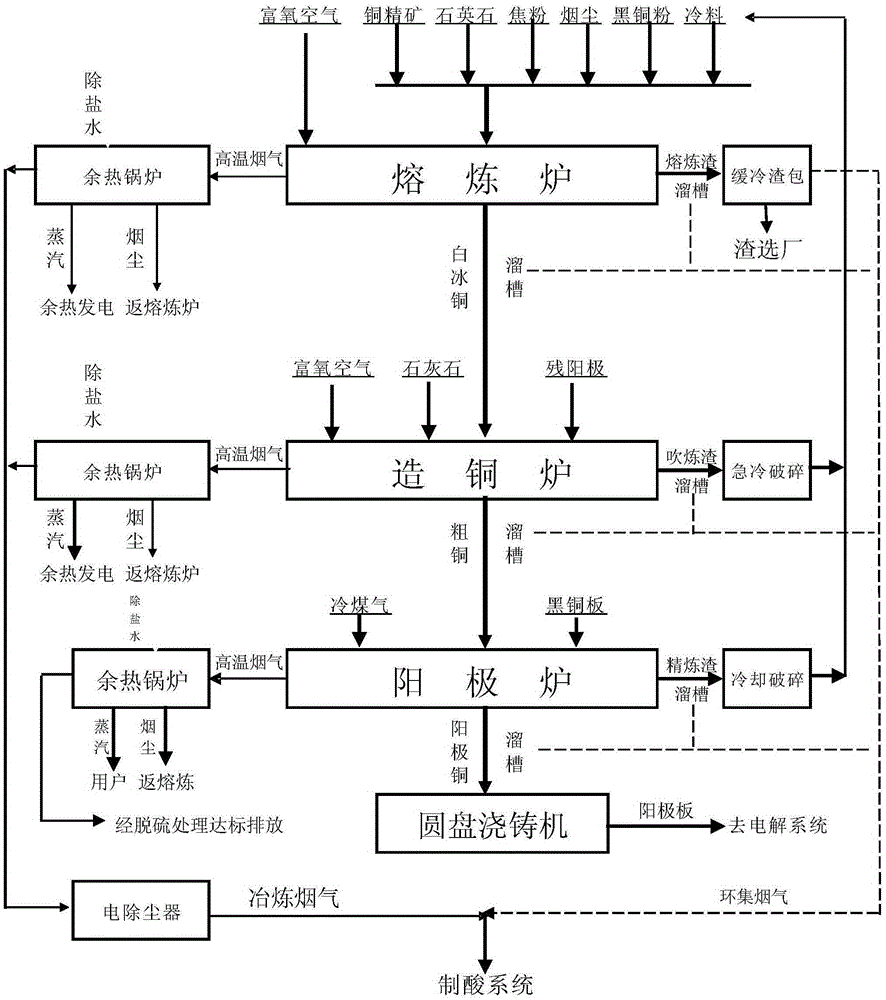
Three continuous furnace technology for continuous production of anode copper with copper concentrate
InactiveCN105238938AReduce metallurgical equipment and plant investmentAvoid sensible heat lossRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesSlagContinuous operation
The invention provides a three continuous furnace technology for continuous production of anode copper with copper concentrate. The technology is particularly characterized in that a smelting furnace, a copper making furnace and an anode furnace are in tandem arrangement successively, and kilns are connected by chutes. The technology comprises the steps that the copper concentrate and flux enter the smelting furnace and react with oxygen-enriched air to generate white matte, smelting slag and high-temperature smoke; the smelting slag overflows continuously; a slow cooling slag ladle is put through the chutes for floatation and depletion; the white matte continuously flows into the copper making furnace via siphon through the chute and reacts with the flux and the oxygen-enriched air to generate raw copper, copper converting slag and high-temperature smoke; the raw copper continuously or intermittently flows into the anode furnace via siphon through the chute; the anode furnace alternately operates and produces the anode copper via oxygenation and reduction; and the converting slag is regularly discharged, chilled, broken and returned to the smelting furnace. The technology achieves continuous operation of smelting production of the raw copper with the copper concentrate.
Owner:CHIFENG JINFENG METALLURGICAL TECH DEV
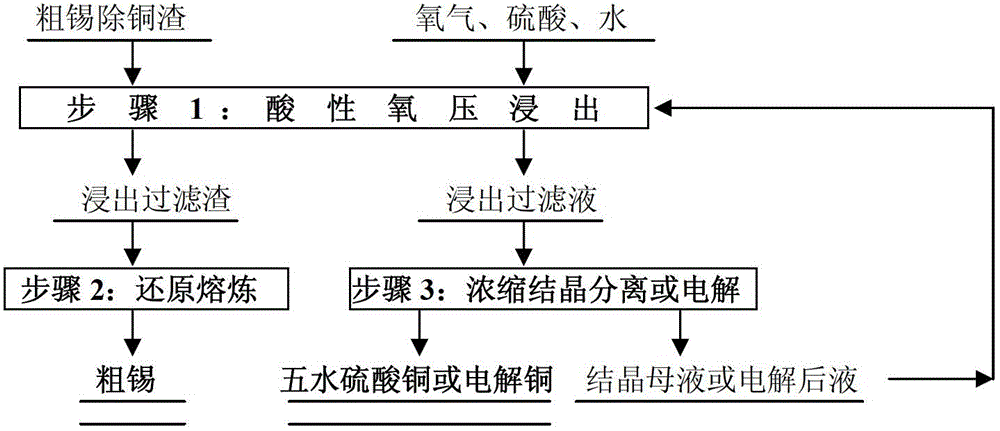
Direct acidity oxygen pressure leaching treatment method of crude tin copper removal residues
InactiveCN102876903AImprove direct yieldEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisLiquid state
Disclosed is a direct acidity oxygen pressure leaching treatment method of crude tin copper removal residues. The method includes that the crude tin copper removal residues containing 55-75% of tin and 8-18% of copper produced when liquid-state crude tin is added to sulphur to remove copper are leached for 4-6 hours and filtered to obtain a filtrate and residues with final acid of 46-118g / L under the conditions that the temperature is 120-150 DEG C, oxygen partial pressure is 0.15-0.25MPa and the initial acid is 100-250g / L, the residues are subjected to reduction smelting to produce crude tin, the filtrate is subjected to concentration, cooling and crystallization to produce a copper sulfate pentahydrate product or subjected to electrolysis to produce electrolytic copper, and a crystallization mother liquor or an electrolyzed solution is returned to a leaching process for dispensing liquids. By means of the direct acidity oxygen pressure leaching treatment method of the crude tin copper removal residues, tin and copper in the crude tin copper removal residues can be rapidly and efficiently separated, and waste water, waste gases and waste residues are not generated.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Method for separating and enriching valuable metals from copper anode mud
ActiveCN105112668AHigh removal rateHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementMaterials scienceAntimony
The invention discloses a method for separating and enriching valuable metals from copper anode mud. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the copper anode mud and a smelting agent are mixed evenly and are smelted at the temperature of 350-700 DEG C, and a smelting product is obtained; (2) the smelting product is crushed and immersed in water, alkaline leaching residues and alkaline leaching liquid are obtained, and selenium and arsenic are recycled from the alkaline leaching liquid; (3) acid and sodium chloride are added into the alkaline leaching residues, ozone is introduced in the alkaline leaching residues for ozone strengthening acid leaching, and acid leaching residues and acid leaching liquid are obtained; and copper and tellurium are recycled from the acid leaching liquid, and lead, stibium and precious metals are recycled from the acid leaching residues. According to the process, the method has the advantages that the selenium and arsenic removal rate is high; the moving directions of the valuable metals are more reasonable and concentrated; the enrichment ratio of the precious metals is high; the direct recovery rate of all elements is high; the comprehensive recovery benefits are good; the problem that tellurium and arsenic in the copper anode mud are dispersed seriously in a traditional process is solved; operation is safe; the labor intensity is low; the treatment time is short; and the operation environment is good.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing molybdenum nickel alloy by directly reducing and smelting molybdenum nickel ore
The invention relates to a method for preparing molybdenum nickel alloy by directly reducing and smelting molybdenum nickel ore. The method comprises the following steps: grinding the molybdenum nickel ore into molybdenum nickel ore powder with the average particle size of less than or equal to 0.18 mm; adding a slag forming agent and a reducing agent with the average particle size of less than or equal to 0.18 mm into the molybdenum nickel ore powder to obtain furnace charge; mixing the furnace charge uniformly and pelletizing to obtain pellet; heating the pellet to 1,600 to 1,800 DEG C; smelting; and collecting liquid alloy, slag, smoke dust and furnace gas respectively, wherein the liquid alloy is crude molybdenum nickel alloy; the direct yield of the molybdenum and the nickel is 96 percent and 94 percent respectively; the molybdenum content of the smoke dust is less than 0.2 percent and the nickel content of the smoke dust is less than 0.2 percent; and the SO2 concentration of thefurnace gas is less than or equal to 400 mg / m<3>. The process method is simple and reasonable, and convenient to operate; the molybdenum nickel ore is not subjected to oxidizing roasting de-sulfuration; and the crude molybdenum nickel alloy is prepared by directly reducing and smelting the molybdenum nickel ore and by using the carbon of the molybdenum nickel ore as a reducing agent, so that indirect smelting is changed into direct smelting. The prepared molybdenum nickel alloy is low in sulfur content and phosphorus content, environment friendly and low in production cost; and the method is suitable for extraction of the molybdenum nickel ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +2
Secondary lead smelting method
The invention discloses a secondary lead smelting method which comprises the following steps: crushing scrap lead storage batteries, pre-desulfurizing, and separating to obtain lead plaster; and drying the lead plaster in a drying kiln, smelting in a lead plaster smelting furnace, treating the generated flue gas to obtain waste gas, and meanwhile, returning the waste gas into the drying kiln as a drying heat source. The hot waste gas obtained by waste heat recovery of the lead plaster smelting furnace and lead grid smelting furnace is used as the heat source for drying the lead plaster, thereby being beneficial to the smelting reaction of the lead plaster, enhancing the production efficiency and lowering the energy consumption; smoke dust obtained by treating the high-temperature flue gas generated in the lead plaster smelting furnace and lead grid smelting furnace is returned into the lead plaster smelting furnace to implement utilization of waste, and meanwhile, smelting slag generated by lead grid smelting and refining slag generated by refining also return to the lead plaster smelting furnace for treatment; and the complete treatment system has the advantages of high direct yield, low comprehensive energy consumption and low pollution, and implements optimized configuration of effective resources.
Owner:扬州市华翔有色金属有限公司
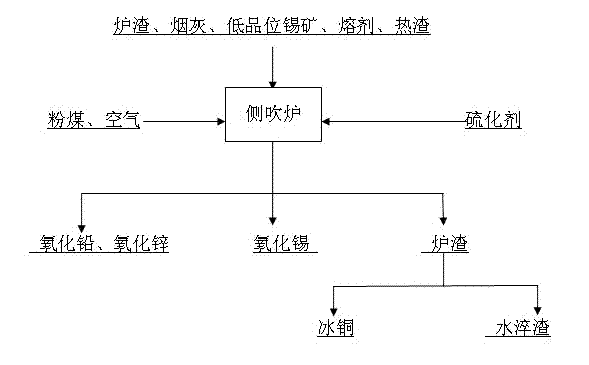
Process for recovering copper and zinc and tin and lead by utilizing side blown converter at the bottom
The invention discloses a process for recovering copper, zinc, tin and lead by utilizing a side blown converter at the bottom. The process is characterized in that materials dosed and mixed from slag, ash, low-grade tin ore and flux are selected for use, the water content of the dosed and mixed materials is <= 3%, the dosed and mixed materials are stand-by, hot slag of a reduction furnace is added into a side blown converter, the dosed and mixed materials are added to the side blown converter, mixed with the hot slag of the reduction furnace for reduction smelting, the tin content of the hot slag of the reduction furnace and the dosed and mixed materials which are added into the side blown converter is more than 3%, and the silicic acid degree of the slag is 1-1.2. In the first stage, the lead and the tin are volatilized in the reduction smelting mode, and lead oxide and tin oxide are obtained through dust collection. In the second stage, vulcanizing agents are added, tin sulfide is volatilized, and tin oxide is obtained after dust collection. In the third stage the slag and the copper settles and are separated to obtain copper matte and waste slag, the slag is quenched through water, and the copper matte is cast into ingots. The process for recovering the copper, the zinc, the tin and the lead by utilizing the side blown converter at the bottom is strong in adaptability, capable of separating out valuable metal such as the copper, the lead, the zinc and the tin through one-step smelting, high in direct recovery rate, and low in valuable metal containing rate of the slag.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
Method for preparing Ho-Fe alloy through molten salt electrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing Ho-Fe alloy through molten salt electrolysis, wherein a graphite crucible serves as an electrolyzer, a graphite flake serves as an anode, a pure iron rod serves as a cathode, a ferric crucible serves as a metal receiver, and holmium oxide serves as a raw material; and holmium fluoride and lithium fluoride serve as a binary system electrolyte and then are electrolyzed in a certain condition. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) drying the electrolyzer through an arching machine or a heating element oven; (2) switching on the power of the arching machine to 45kW, and continuously adding an electrolyte into the furnace continuously; (3) after the electrolyte is melted to a part which is 10cm far away from the upper edge of the electrolyzer, placing an iron crucible in the center of a furnace bottom, placing the pure iron rod above the iron crucible, and feeding a direct current to start electrolysis; (4) adding a small quantity of holmium oxide repeatedly or continuously and evenly adding holmium oxide during the electrolytic process, and intermittently adjusting the pure iron rod once intermittently; and (5) after the electrolysis is carried out for a period of time, taking out the iron crucible, pouring to obtain an ingot, and demoulding to obtain the Ho-Fe alloy after the cooling. The Ho-Fe alloy obtained by the invention is low in energy consumption, high in capacity and small in deviation, so that the Ho-Fe alloy is convenient for mass production.
Owner:JIANGSU JINSHI RARE EARTH CO LTD
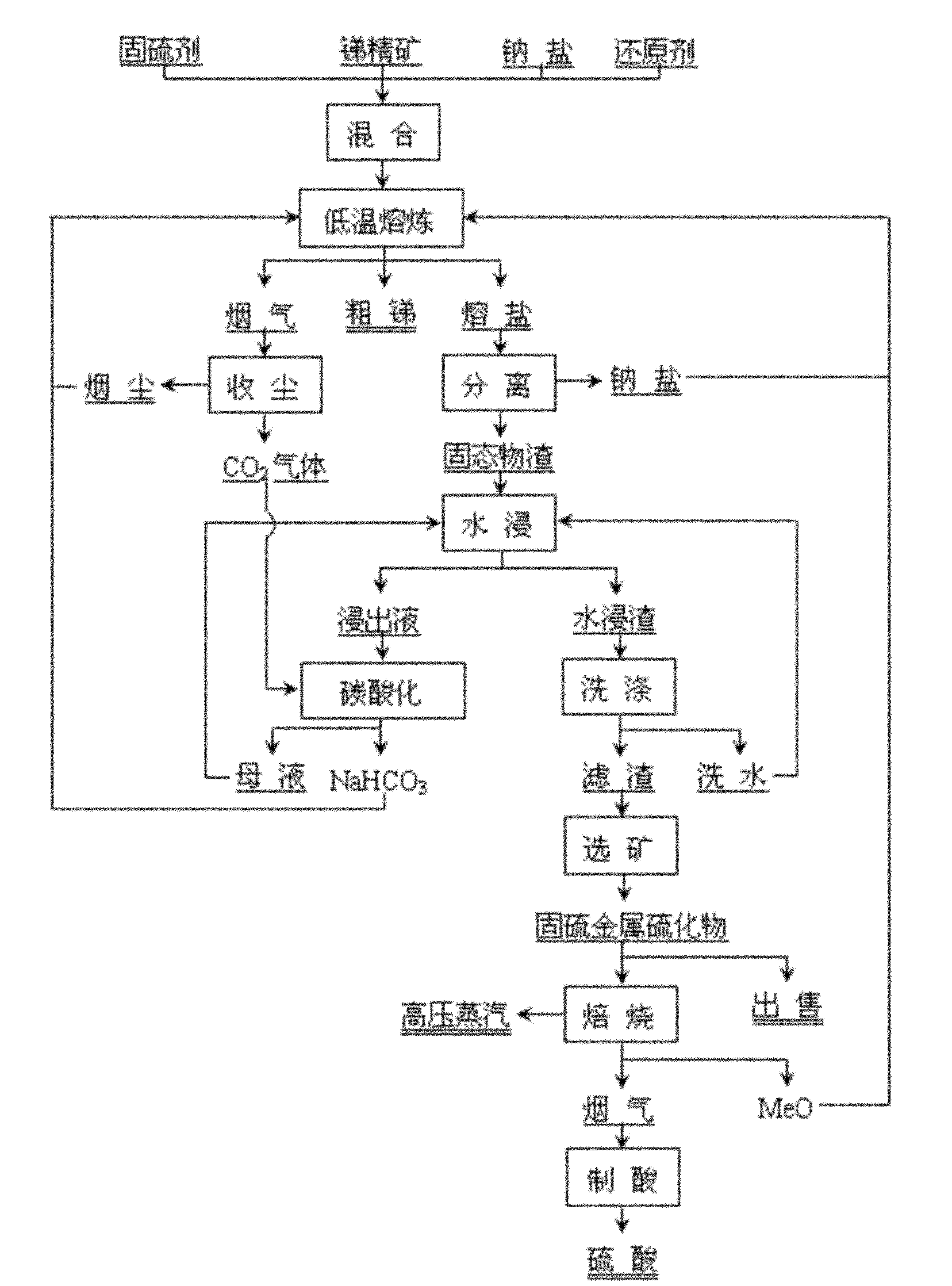
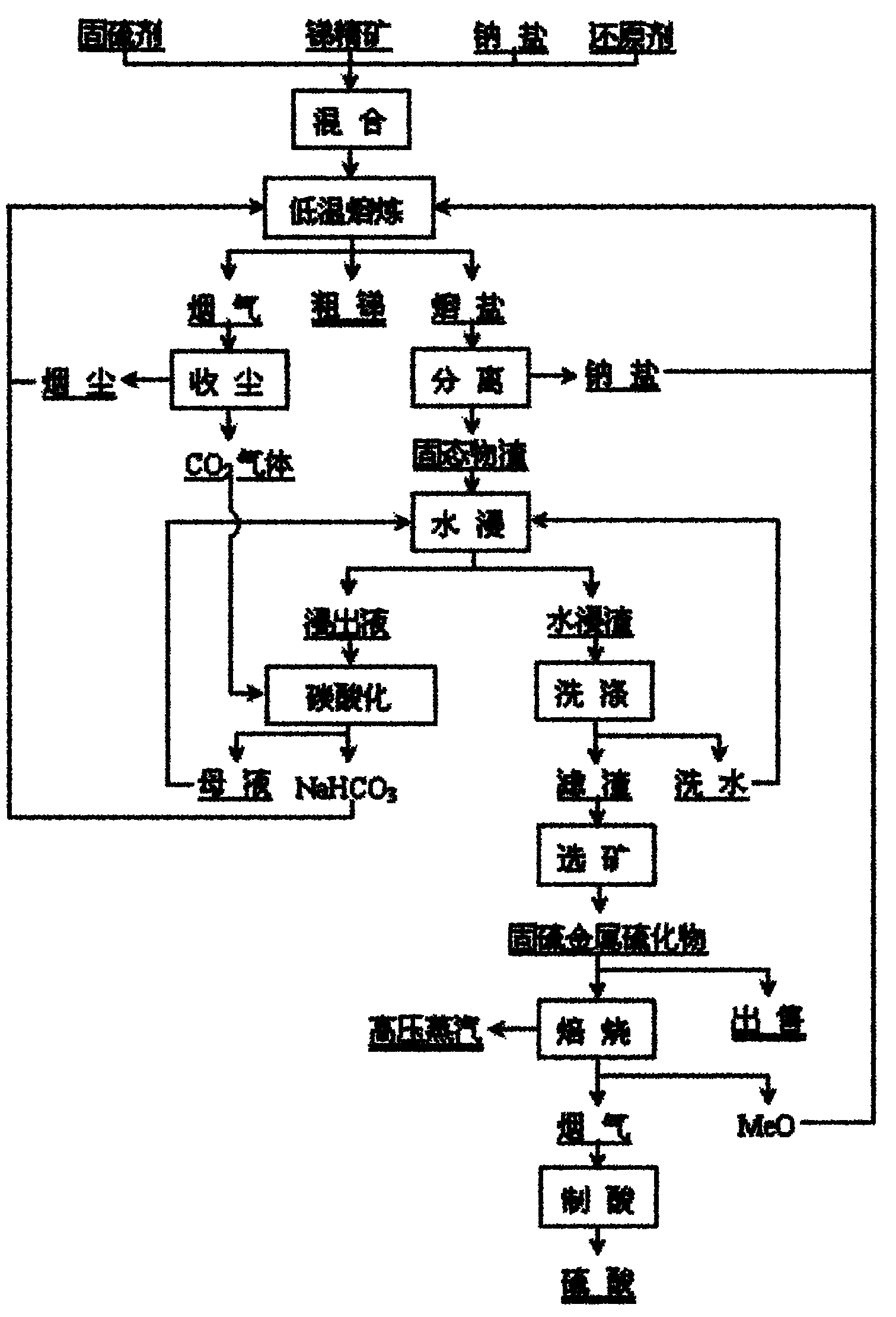
Clean metallurgical method for low-temperature molten salt of antimony
InactiveCN101914693ALower the smelting temperatureImprove direct yieldProcess efficiency improvementSlagSulfide
The invention discloses a clean metallurgical method for low-temperature molten salt of antimony, and belongs to the metallurgical field of non-ferrous metals. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: performing reductive sulfur-fixing melting on antimony concentrate and oxide of metal with higher sulfur affinity compared with the antimony in low-temperature inert molten salt to generate liquid metal antimony and sulfur-fixed metal sulfide, and forming molten salt slag by using the sulfur-fixed metal sulfide and non-reacted substances as solid substances; and separating most inert molten salt from the solid substances and then thermally returning the most inert molten salt to the melting process, regenerating NaHCO3 for recycling by using the molten salt slag through a 'water leaching-carbonated precipitation' process, reclaiming the sulfur-fixed metal sulfide concentrate for selling from the leached residue by ore dressing, or performing roasting desulfuration on the leached residue for heat energy utilization and smoke acid making, and returning oxide roasting sand serving as a sulfur-fixing agent to the melting process. The method greatly reduces the antimony melting temperature, produces the crude antimony at one step, realizes reclamation of sulfur and energy utilization of sulfide, thoroughly eliminates environmental pollution of low-concentration SO2 smoke at the same time of simplifying the flow, reducing the cost and greatly improving the direct yield of the antimony, and has the advantages of low carbon, cleanness and high efficiency.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
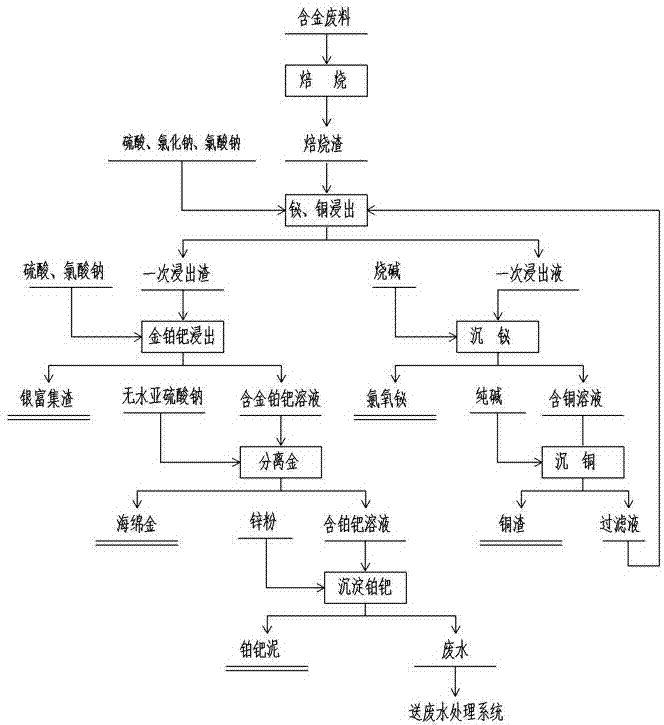
Process for comprehensively recovering rare and precious metals including gold, silver, platinum and palladium from gold-bearing wastes
ActiveCN104762479AReduce pollutionSolve technical problems that are difficult to leachingProcess efficiency improvementSulfite saltPollution
The invention relates to a process for comprehensively recovering rare and precious metals including gold, silver, platinum and palladium from gold-bearing wastes. The process comprises the steps of leaching copper, bismuth and the like in the gold-bearing wastes by using sulfuric acid, industrial salt and sodium chlorate after roasting the gold-bearing wastes in a rotary kiln, and then, respectively recovering copper and bismuth in a primary leachate by using caustic soda and calcined soda; leaching primary leaching residues by using hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid or sodium chloride to obtain secondary leaching residues and a solution containing gold, platinum and palladium; enriching silver in the secondary leaching residues; adding calcined soda into the solution containing gold, platinum and palladium to regulate the pH value of the solution, then, adding anhydrous sodium sulfite into the solution, and filtering after settling to obtain sponge gold and a solution containing platinum and palladium; adding zinc powder into the solution containing platinum and palladium, then, settling and filtering to obtain platinum and palladium mud and wastewater; and carrying out conventional extraction on platinum and palladium to obtain platinum powder and palladium powder. By using the process, the problems of serious environment pollution, low direct recovery rate, low-speed capital turnover, low labor productivity and the like in the traditional process can be solved.
Owner:郴州雄风环保科技有限公司
Method for separating indium and tin from In-Sn alloy by vacuum distillation
InactiveCN101660056AAchieve recyclingImprove direct yieldProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSmelting process
The invention relates to a method for separating indium and tin from In-Sn alloy by vacuum distillation. The method comprises the following steps: adding In-Sn alloy material which includes 40-99% ofIn and 1-60% of Sn into a vacuum furnace, controlling vacuum degree, temperature and distillation time in the furnace, and leading metal indium and tin to separate. The treated objects can be In-Sn alloy, In-Sn slag and the like generated during the non-ferrous smelting process. By vacuum distillation, the content of tin in metal indium is less than 0.5%, the content of indium in metal tin is lessthan 0.5%, and the total recovery efficiency of metal is more than 99%. During the process, any reagent does not need to be added, the technology is simple, the metal recovery efficiency is high, andthe electricity consumption is less than 10KW.h / kg.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Zinc-aluminum binary intermediate alloy and uses in hot galvanizing alloy production
The invention relates to a production process of a hot galvanizing alloy and a master alloy thereof, which has the technical proposal that, the components and the weight ratio of a zinc-aluminum binary master alloy are that 16-24 percent is aluminum and the rest is zinc. A method for producing the hot galvanizing alloy by the zinc-aluminum binary master alloy comprises the steps: mixing the zinc and the aluminum by the weight ratio, adding the mixture to a master alloy smelting furnace with the melting temperature of 560-680 DEG C to be molten, uniformly stirring, ingoting to a zinc-aluminum binary master alloy pig, adding the solid zinc required by hot galvanizing alloy production to a hot galvanizing alloy smelting furnace to be molten into zinc liquid, adding the zinc-aluminum binary master alloy required by the produced hot galvanizing alloy to the zinc liquid, and stirring for 20-40min at the melting temperature of 480-520 DEG C to prepare the hot galvanizing alloy. The invention which is applicable to the hot galvanizing alloy production by a cored induction furnace has the advantages of reducing the temperature of the melting alloy, shortening the melting and stirring time, prolonging the service life of the cored induction furnace and ensuring uniform hot galvanizing alloying components.
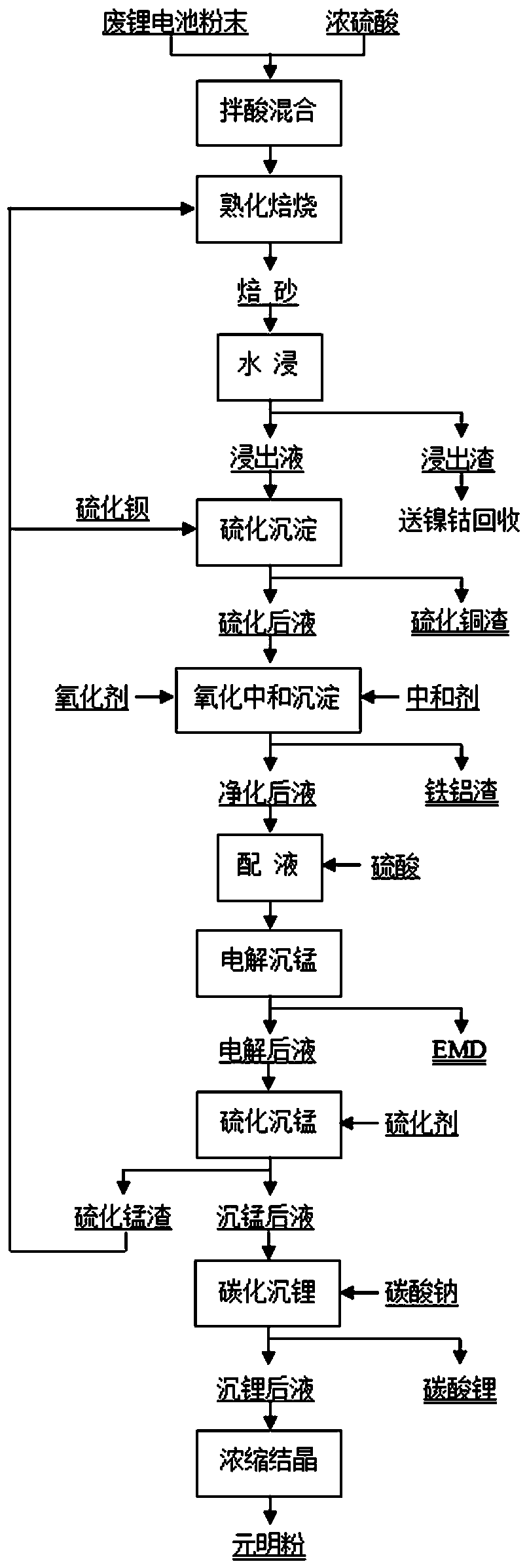
Manganese dioxide recovery method by waste lithium ion battery powder selective lithium-extracting and electrolytic separation
ActiveCN111254294AEfficient separationGood qualityElectrolysis componentsWaste accumulators reclaimingManganese oxideLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a manganese dioxide recovery method by waste lithium ion battery powder selective lithium-extracting and electrolytic separation. The method comprises the steps that a certainamount of waste lithium ion battery powder is weighed, concentrated sulfuric acid is added, and the mixture is fully stirred and mixed; the acid-stirred-and-mixed battery powder is placed in an electric furnace for being roasted at a certain temperature for a predetermined time; the roasted battery powder is mechanically stirred and leached with pure water at a predetermined temperature; slurry issubjected to liquid-solid separation, filter residue is fed to a wet method nickel-cobalt-manganese recovery system, and impurities of a lithium-containing leaching solution are removed by using sulfide precipitation and oxidation neutralization precipitation step by step; a lithium-containing purification solution electrolyzes to produce manganese dioxide powder at a predetermined current density, acidity and temperature; and after residual manganese ions of the lithium-containing solution after electrolytic manganese precipitation are removed, and a saturated sodium carbonate solution is added for carbonization lithium precipitation to produce lithium carbonate powder. The method creates good conditions for the subsequent recovery of nickel and cobalt by sulfuric acid leaching, and canrealize the efficient separation of lithium and manganese in lithium-rich liquid through electrodeposition, and comprehensively recover a electrolytic manganese dioxide product.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
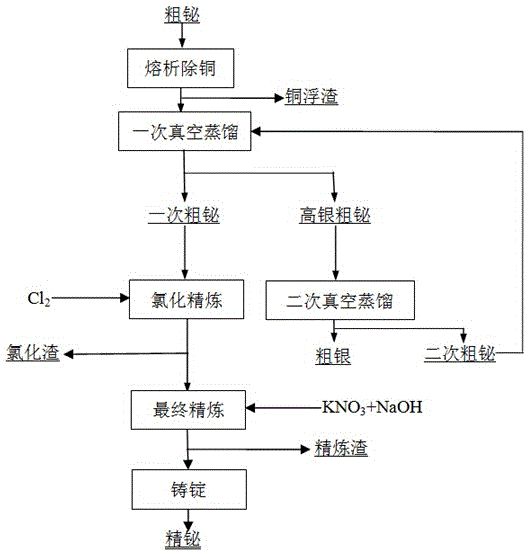
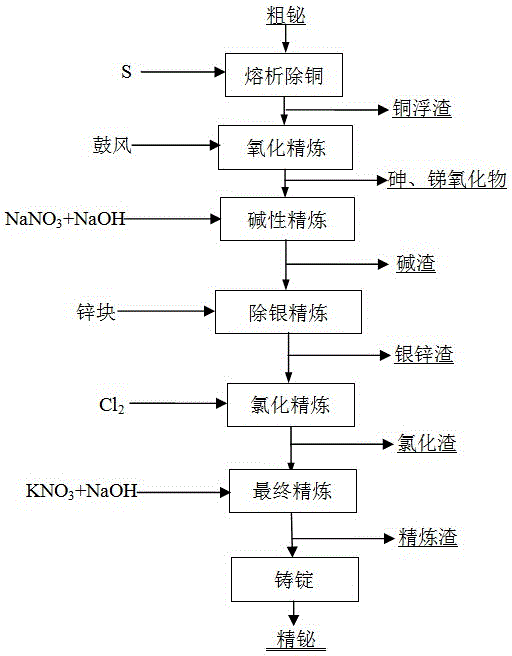
Fire-refining method of crude bismuth
The invention relates to a fire-refining method of crude bismuth, and belongs to the technical field of fire metallurgy. The fire-refining method comprises the following steps: liquating a crude-bismuth melt so as to remove copper; performing vacuum distillation again on the liquated crude-bismuth melt so as to remove impurities, such as lead and silver; performing chlorination refining; and finally performing refining so as to obtain refined bismuth. According to the fire-refining method disclosed by the invention, a vacuum distillation technique is adopted for replacing a procedure that zinc is added in a refining kettle so as to remove silver, and partial lead, antimony, tellurium and arsenic are removed, so that the labor strength of workers is reduced; through secondary vacuum distillation, crude silver with a high silver content can be directly collected in a vacuum furnace, and generated secondary crude bismuth can be recycled, so that the cost is greatly reduced; a subsequent zinc removing procedure is also omitted, and the amount of chlorine gas for subsequent chlorination refining is greatly reduced, so that harm to environment is reduced to a great extent, and the direct recovery rate of bismuth is increased; the whole technological process is safe and controllable, the operation is convenient, adopted equipment is simple, the universality of raw materials is high, the direct recovery rate of bismuth is high, and the slag yield is low.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com