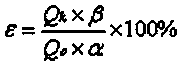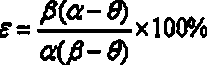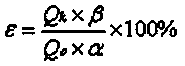Patents
Literature
166results about How to "High enrichment ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
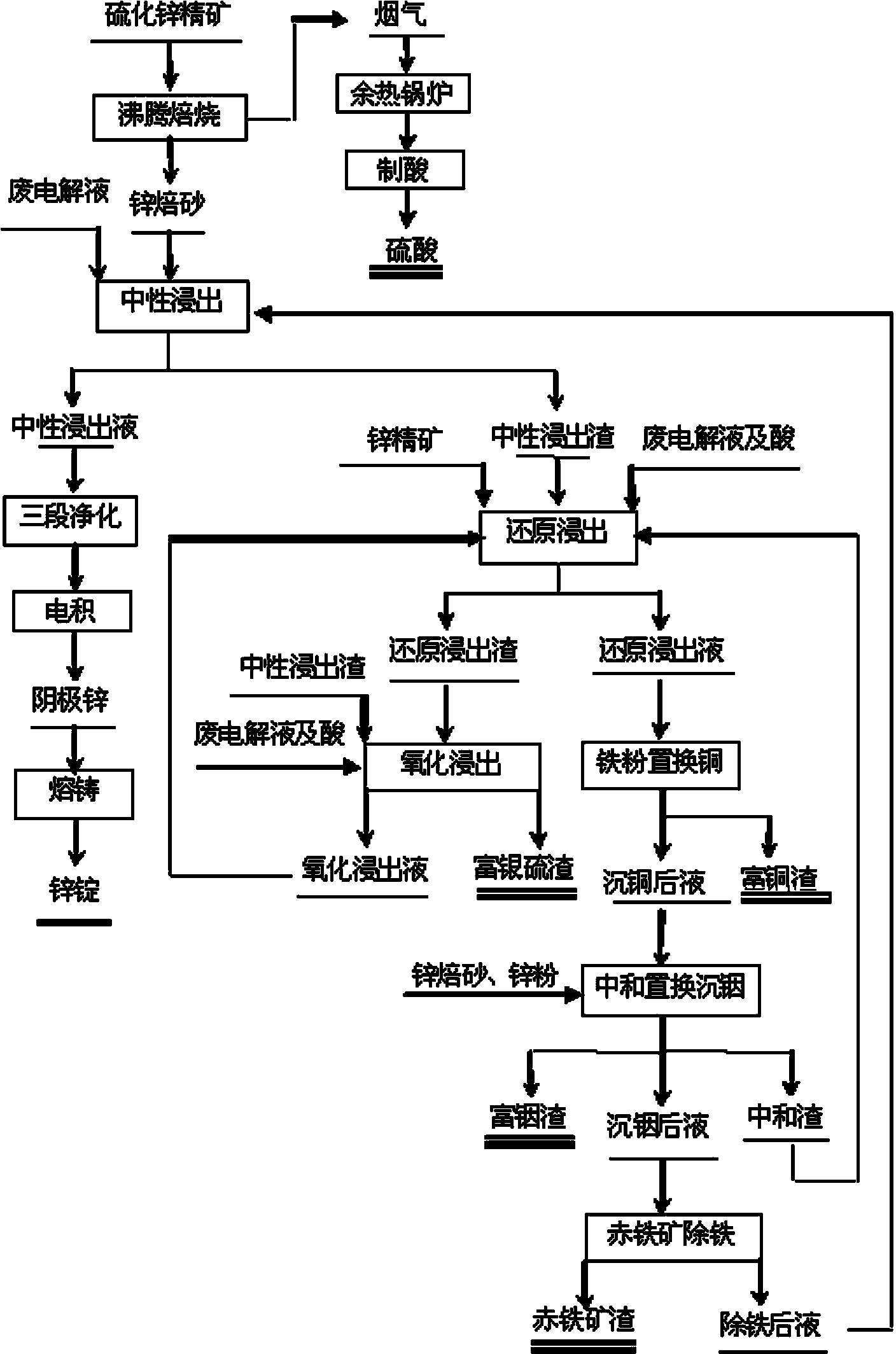
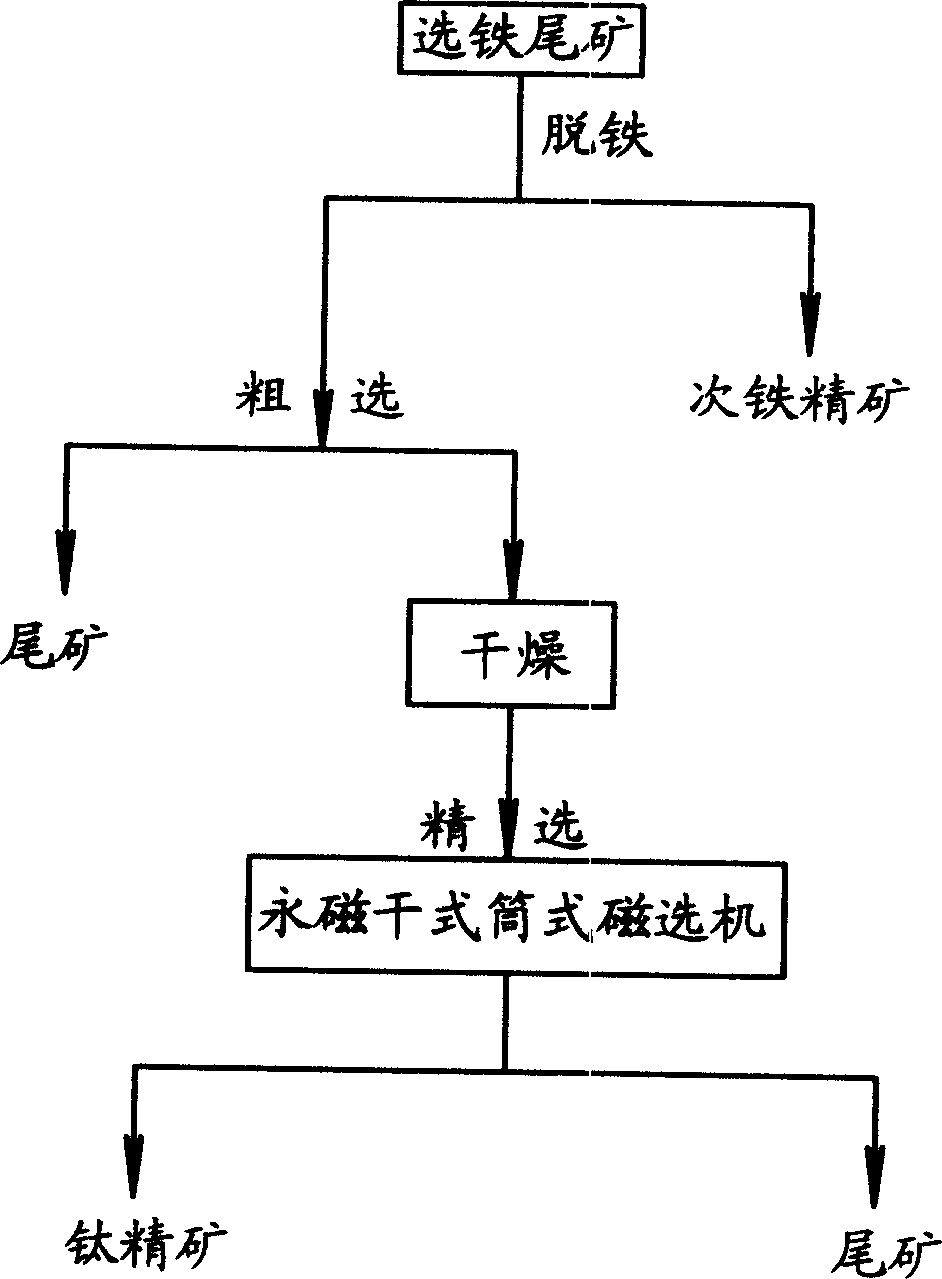
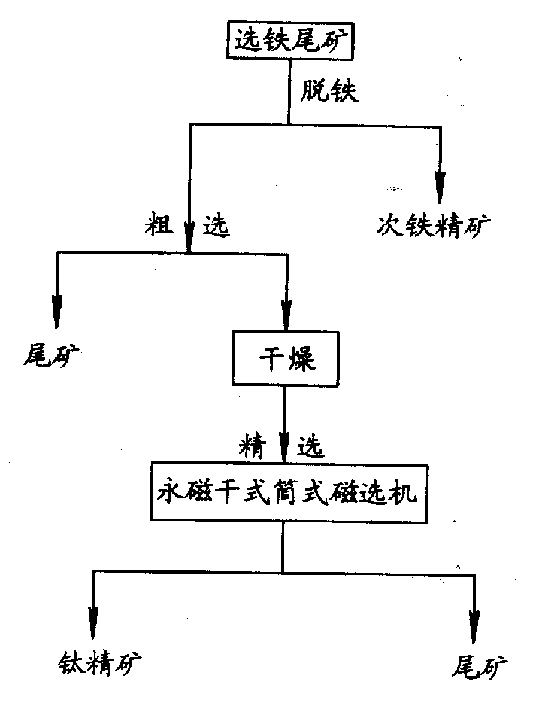
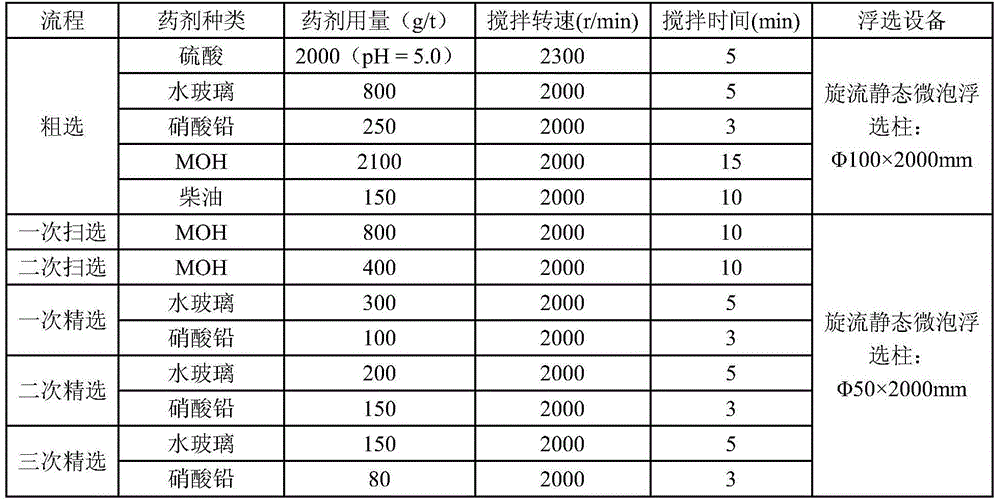
Method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
ActiveCN103409622AThe process is highly targetedHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrometallurgy
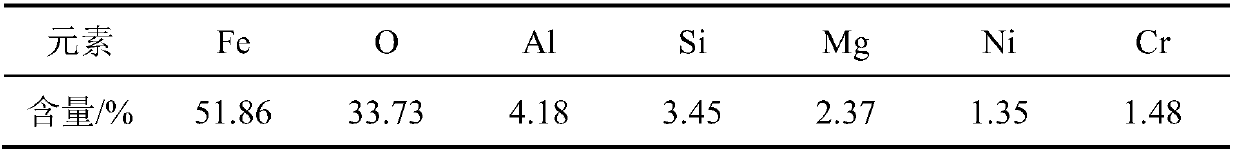
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises a step of subjecting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate to calcination in a fluidized bed combustion boiler to obtain zinc calcine; a step of subjecting the zinc calcine to neutral leaching to produce neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residue; a step of, after the neutral leaching residue and the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate are mixed, successively performing reduction leaching and oxidation leaching, and circulating oxidation leaching solution to the reduction leaching to produce reduction leaching solution and silver-rich sulfur residue; a step of replacing the reduction leaching solution by using iron powder to precipitate copper and to produce copper-rich slag and solution after copper precipitation; a step of subjecting the solution after copper precipitation to pre-neutralization by using the zinc calcine, and then replacing by using zinc powder to precipitate indium and to produce indium-rich slag and solution after indium precipitation; and a step of bubbling oxygen into the solution after indium precipitation, heating and removing iron to obtain iron removal solution and hematite slag. The hematite slag can be utilized as a raw material for ironmaking. The method has strong pertinence, short technological process and high metal recovery yield, and the method is clean, efficient, energy-saving and environmental friendly. Separation and comprehensive utilization of zinc, indium, copper and iron are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
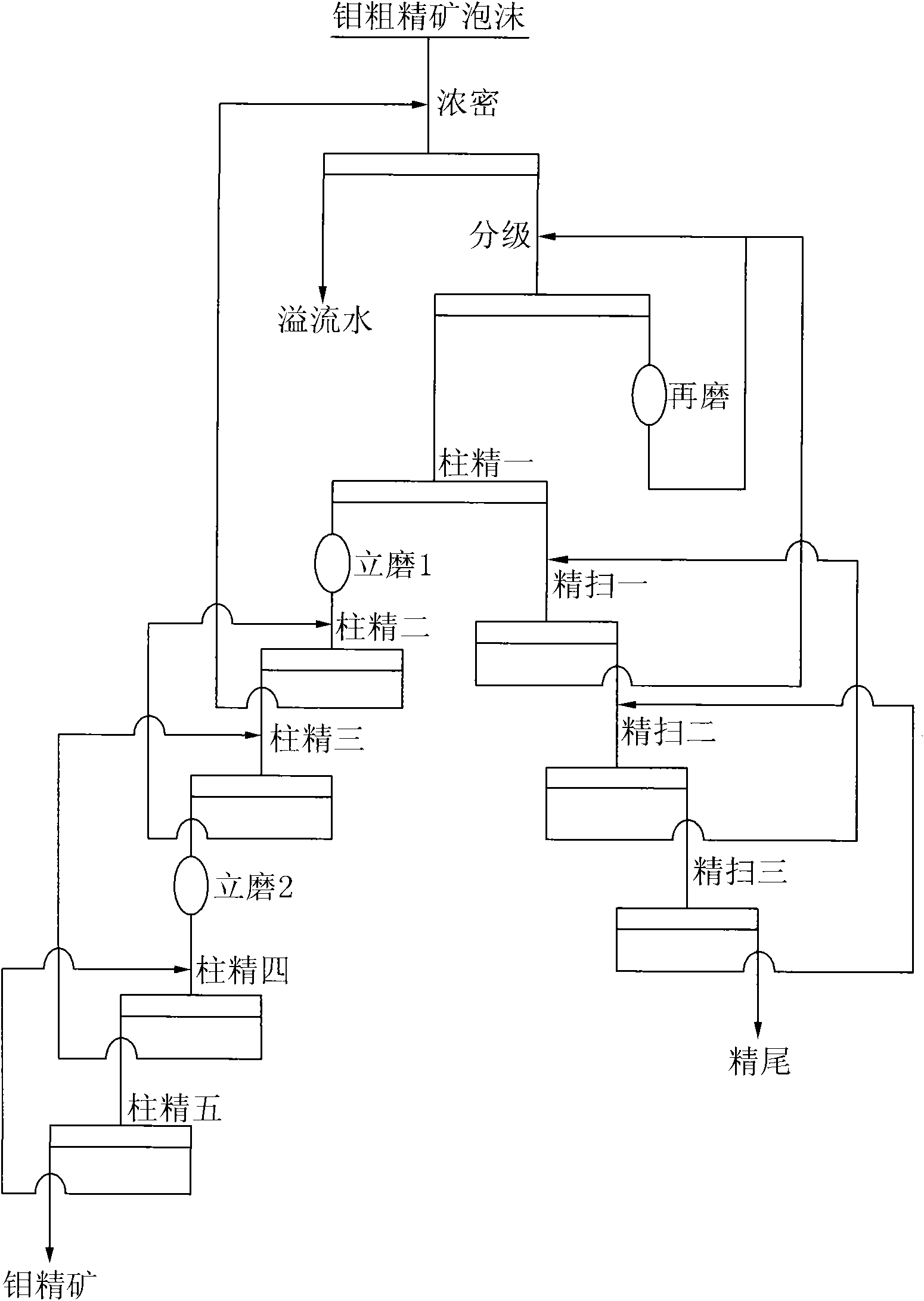
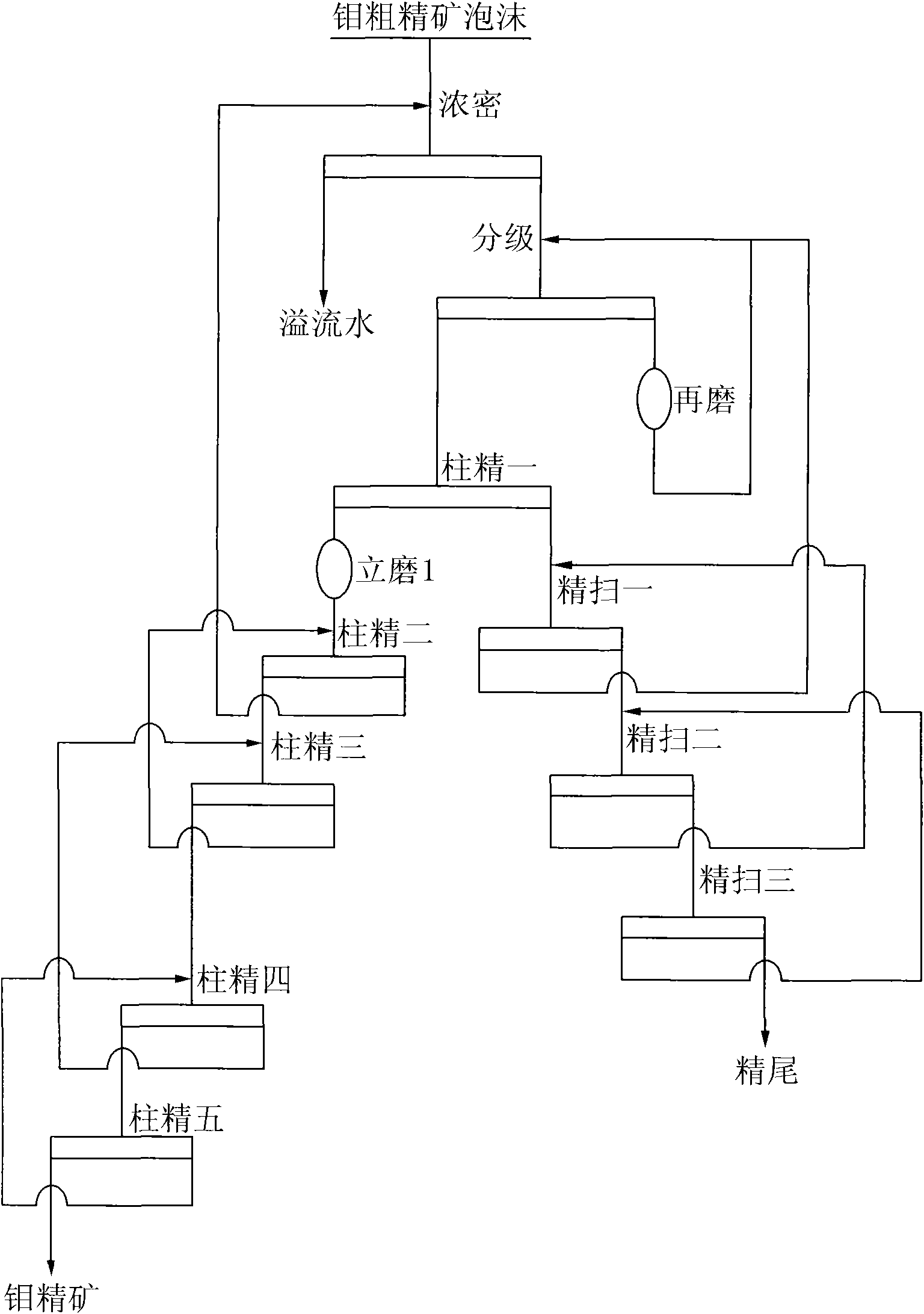
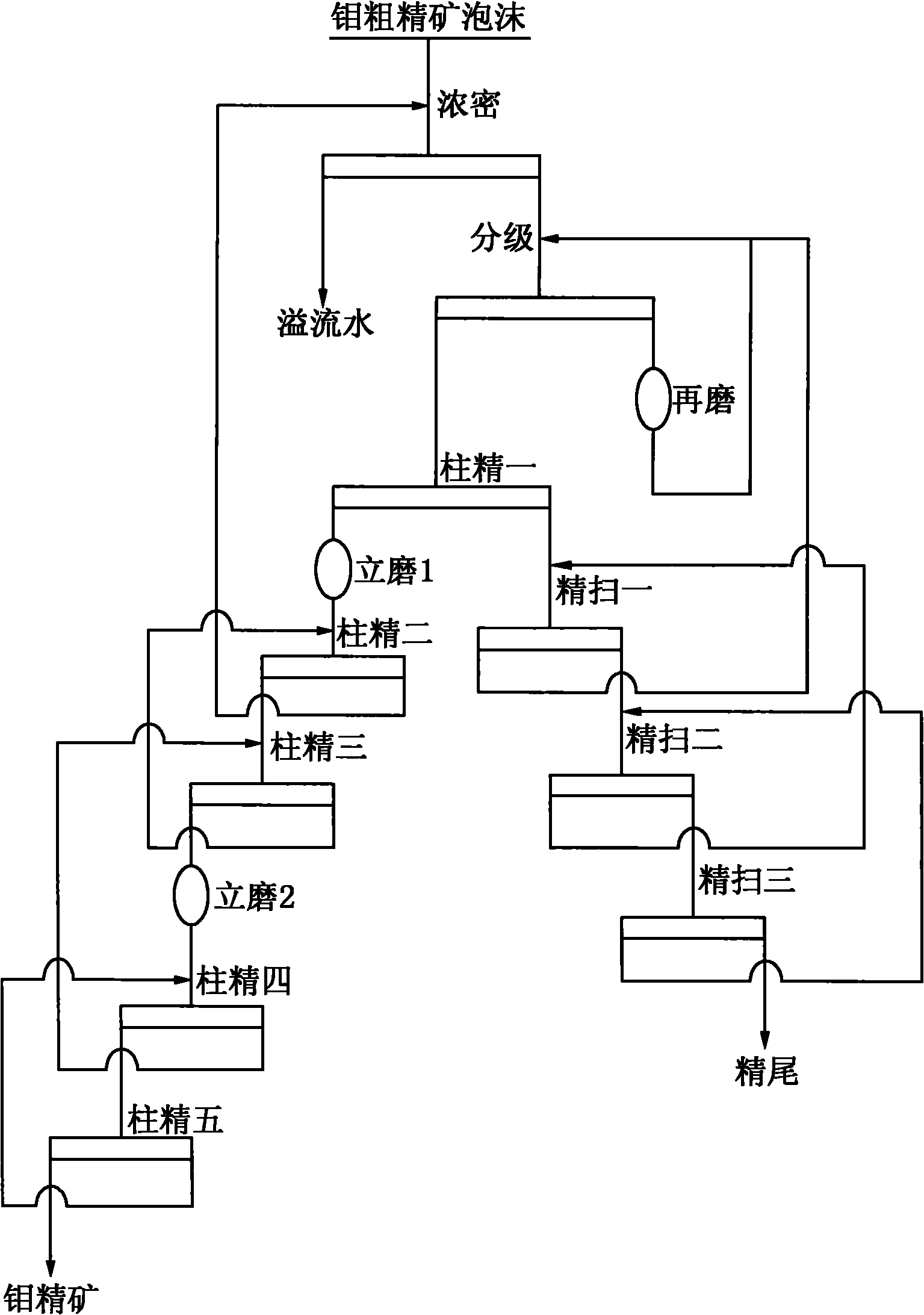
Production technology of high-grade molybdenum concentrate
ActiveCN101773871AReduce pollutionIncrease feed concentrationFlotationWet separationBall millReagent
The invention discloses a production technology of high-grade molybdenum concentrate, which comprises the following steps: rough molybdenum concentrate is obtained by roughing crude molybdenum ore, the rough molybdenum concentrate is concentrated and removed reagent through a thickener, underflow enters a hydraulic swirler to be graded previously, overflow after the grading enters a primary flotation column to be selected, the underflow after the grading enters a horizontal ball grinding mill to be reground, and after the regrinding, the ore discharge enters the hydraulic swirler to be regraded; selected concentrate from the primary flotation column is cleaned by a vertical ore mill to enter a secondary and a tertiary flotation columns to be selected, and the selected concentrate from thetertiary flotation column directly enters or enters a quartic or a quintic flotation columns to be selected after being cleaned by a second section of the vertical ore mill to obtain the high-grade molybdenum concentrate; the selected tailings from the primary flotation column is tertiary scavenged by a flotation machine, and the scavenged concentrate tailings from the tertiary scavenging enters the next procedure. The technology adopts the flotation columns and the flotation machine, so the flow is short, the agent system is simple, the adaptability of the crude ore is strong, and the molybdenum concentration ratio is high, the molybdenum concentrate has high grade, large yield and high recycling rate so as to provide excellent raw material to the following molybdenum chemical engineering and further processing.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
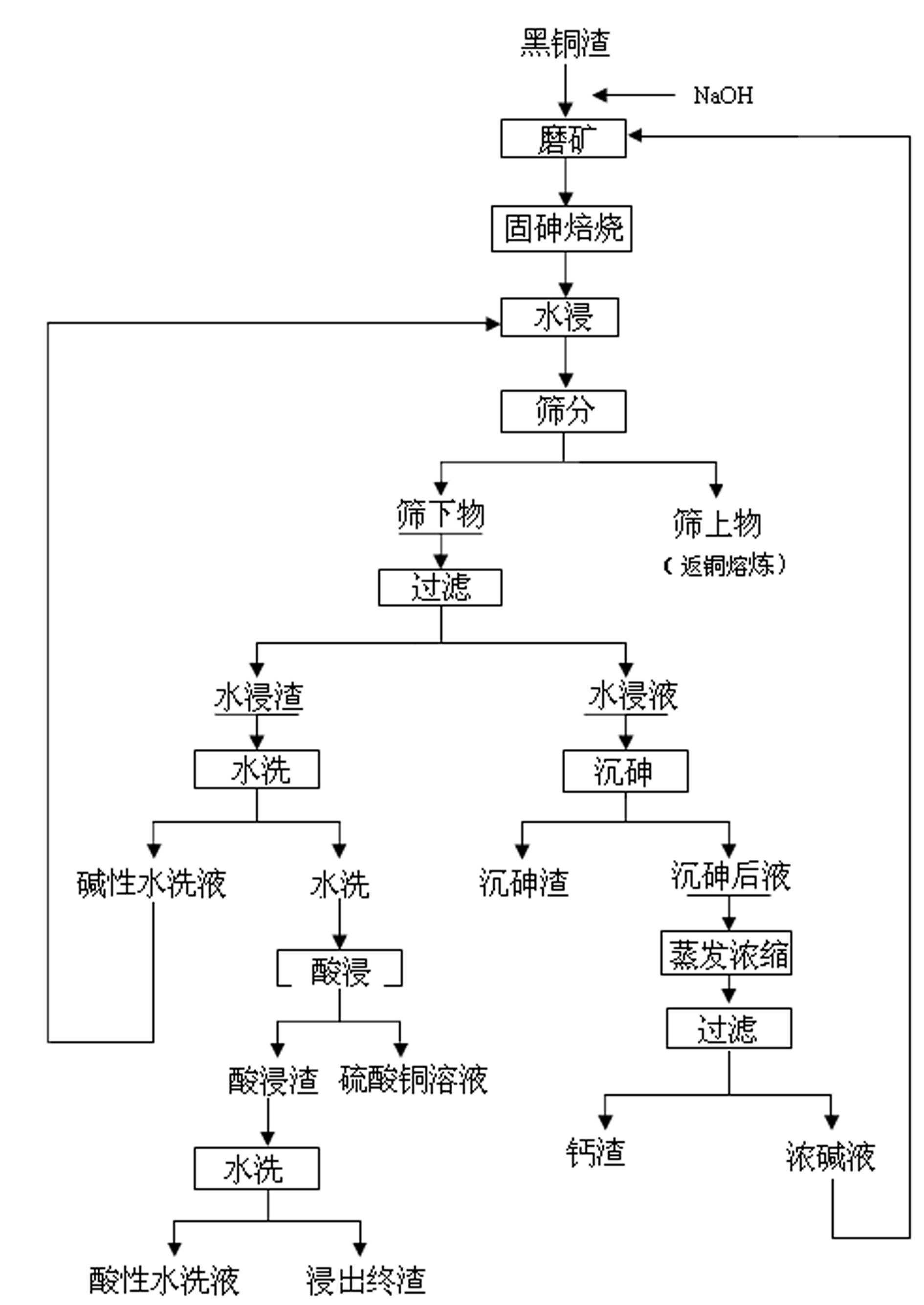
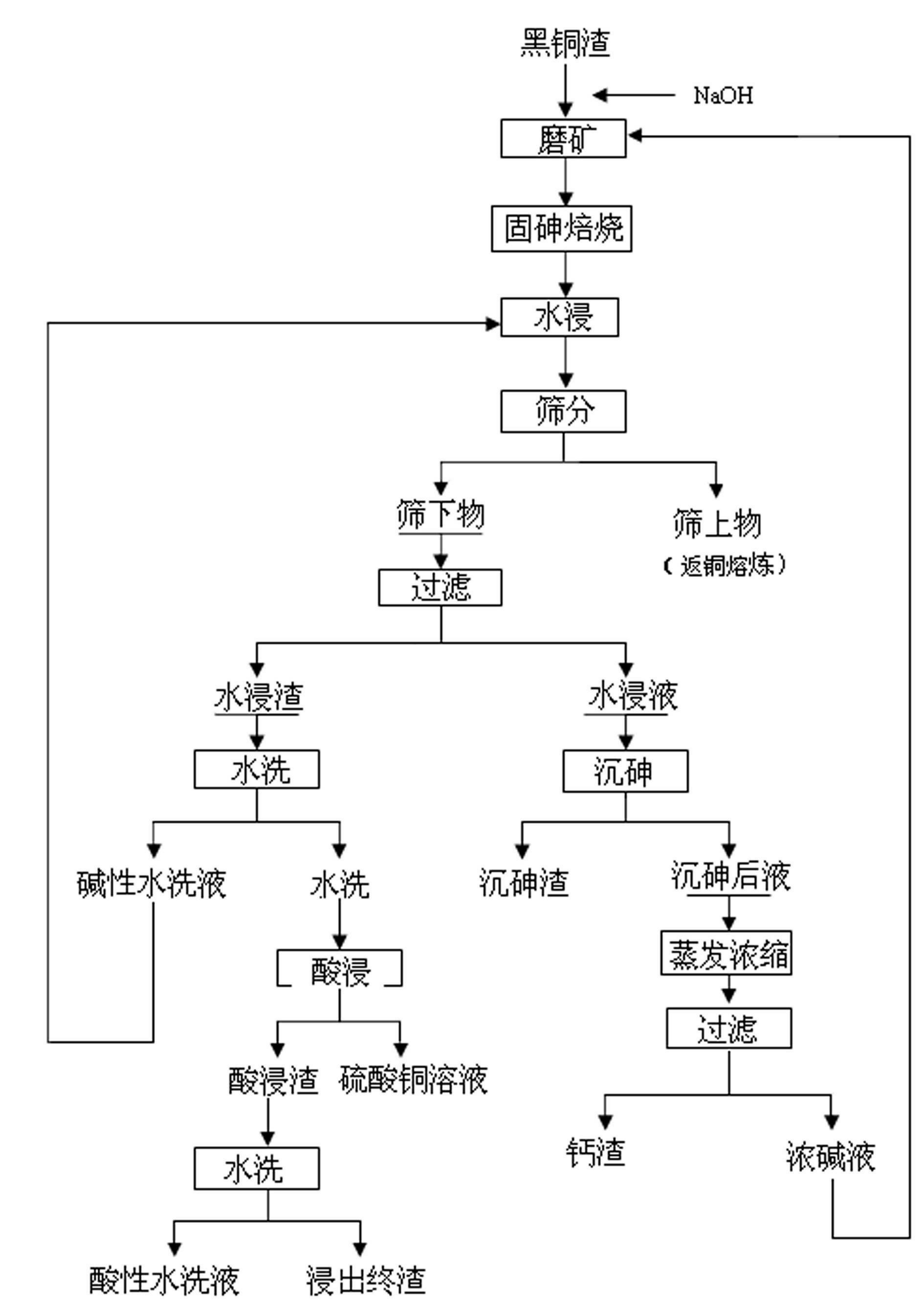
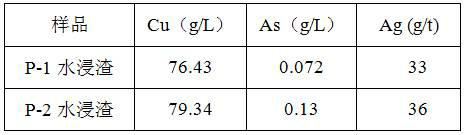
Method for treating arsenic-containing waste copper slag
InactiveCN102634672ASolve the open circuit problemHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementArsenateEnvironmental engineering
The invention provides a method for treating arsenic-containing waste copper slag. The method comprises the following steps of: adding alkali and arsenic fixation roasting on the arsenic-containing waste copper slag from a copper electrolysis purification procedure to convert the arsenic into low-toxicity, water-soluble and nonvolatile arsenate, leaching the roasting slag into water to remove the arsenic, recovering copper and enriching antimony bismuth silver by virtue of acid leaching, and embedding calcium arsenate sediment converted from the arsenic in the water leaching solution; and comprehensively recovering valued metals such as copper, silver, antimony and bismuth in the black copper slag. The method is a safe and effective wet smelting method for recovering the valued metals in the black copper slag, and the arsenic and the copper are leached separately; the recovery rate of the copper in the black copper slag reaches 99.6 percent, and the removal rate of the arsenic reaches over 98 percent; over 95 percent of antimony and over 98 percent of bismuth enter the slag, and over 98 percent of silver also enters the acid leaching slag by adding trace chlorine radicals during acid leaching, so that the antimony, the bismuth and the silver are comprehensively recovered; and the method has the advantages of low equipment investment, short flow, low running cost and safe and reliable operating environment.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
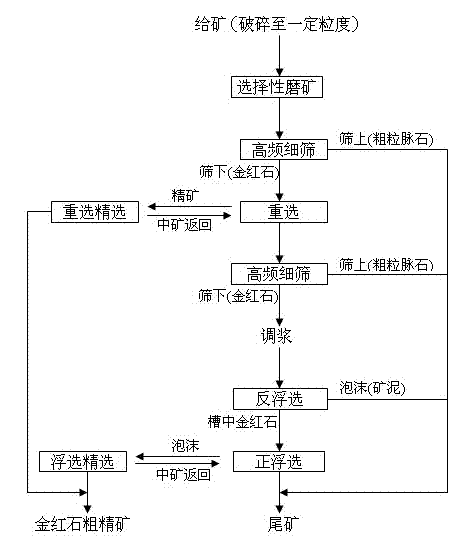
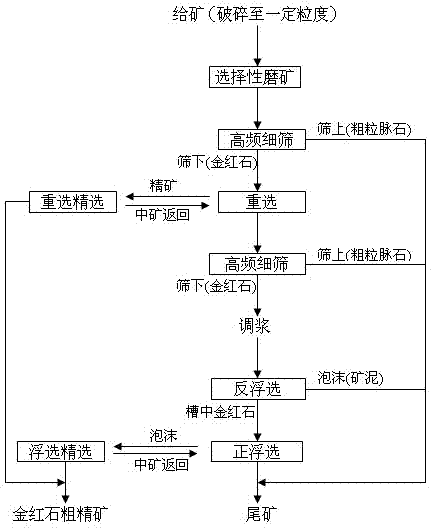
Rutile roughing technology consisting of selective ore grinding, coarse particle gravity separation and fine particle floatation
InactiveCN102500462AImprove the reselection indexEffectively discardWet separationHigh concentrationParticle composition
The invention discloses a rutile roughing technology for consisting of selective ore grinding, coarse particle gravity separation and fine particle floatation, belonging to the technical field of mineral processing engineering. According to the characteristics of complex mineral composition of rutile, containing of a large quantity of flaky rocky minerals in raw ore, small crystal size of rutile,non-uniform distribution, remarkable selective grinding phenomenon in an ore grinding process and the like, the technology comprises the following steps of: strengthening selective ore grinding by taking a steel forging as an ore grinding medium; pre-separating and discarding coarse particle tailings with a high-frequency fine sieve; narrowing the particle composition undersize minerals; recovering large-particle rutile by performing gravity separation, wherein rutile in gravity-separated tailings is distributed at a fine particle scale; sieving and discarding coarse-particle tailings; recovering small-particle rutile from minus sieve by suppressing rutile reverse flotation desliming and activating rutile positive floatation; and combining gravity-separated rough concentrate with floated rough concentrate, concentrating and purifying to obtain a high-quality rutile concentrate product. The technology has the characteristics of simple process, low ore dressing cost, high recovery rate,high concentration ratio, and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
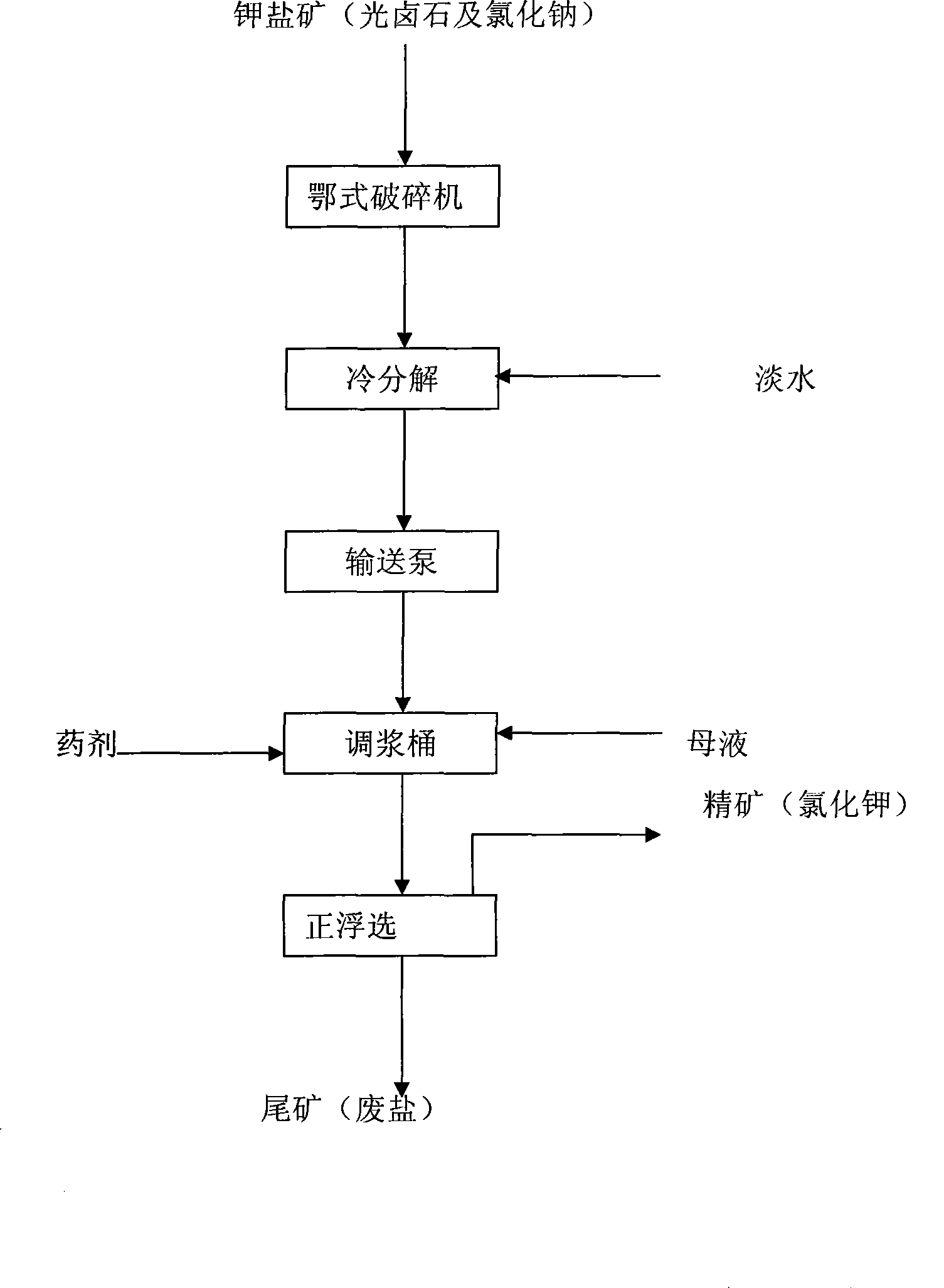
Method for flotation of potassium chloride from potassium salt mine
ActiveCN101474598ASimple equipment structureLarge amount of processingFlotationChemical industryAutomatic control
The invention relates to a method for the floatation of potassium chloride in a sylvite mine, and a method for producing the product of chemical industry, in particular to a novel floatation method for extracting the potassium chloride from the sylvite mine. The method of the invention mainly comprises the following steps: a. the sylvite mine is pulverized and graded, the particle size of the pulverized mine rages from 3 to 8mm, and the pulverized mine is processed by the operation of cooling decomposition by being added with sweet water; b. mine slurry obtained in the step a is led into a mineralization slot and is added with the saturated mother solution of potassium chloride, sodium chloride and magnesium chloride as well as a positive floating agent; and the mine slurry, the saturated mother solution and the positive floating agent are completely mixed to control the concentration of the mine slurry to be from 20 to 40 percent; c. the mine slurry obtained in the step b is led into a flotation separation device to obtain the potassium chloride by the positive floatation; and d. particles fallen to the bottom of a flotation column are milltailings, particles which are discharged from the flotation column and are caused to float to the top end of the flotation column are potassium chloride particles, and the particles are collected to be concentrated, filtered and dried. The method has the advantages of simple and stable process, easier automatic control, favorable flotation effect, low agent consumption and production cost, etc.
Owner:YUNNAN CHEM RES INST
Low-grade scheelite in molybdenum floatation tailings
InactiveCN101417267AHigh enrichment ratioReduce the number of operationsFlotationLower gradeLow graded
The invention discloses a recycling method of low grade white tungsten in molybdenum selection tailing, after molybdenum selection tailing is floated and desulfurized, white tungsten rougher flotation adopts one rougher flotation, one scavenging and one preconcentration to replace one rougher flotation, scavenging for three times and preconcentration for three times, and rough concentrate with about 1.2 percent of WO3 is obtained. The method reduces scavenging twice and preconcentration twice, the rougher flotation has high recovery rate which can achieve 75 percent, and is about 10 percent higher than the recovery rate of a flotation machine method; and the used device has high processing capacity and small occupied area, thus greatly reducing the operating personnel and labor intensity.
Owner:CINF ENG CO LTD
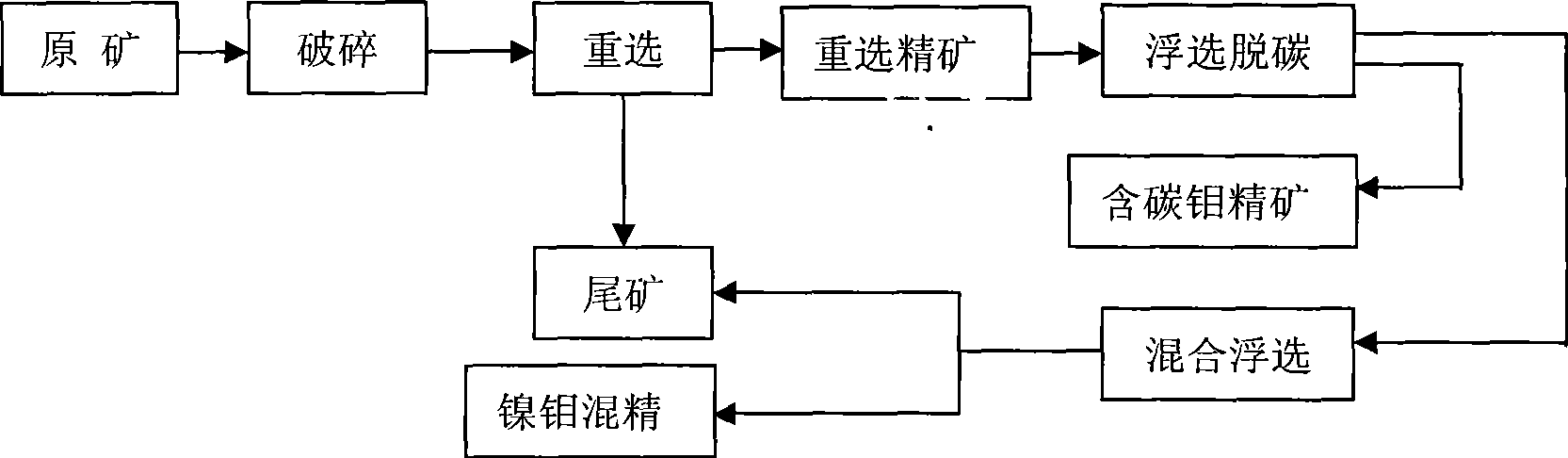
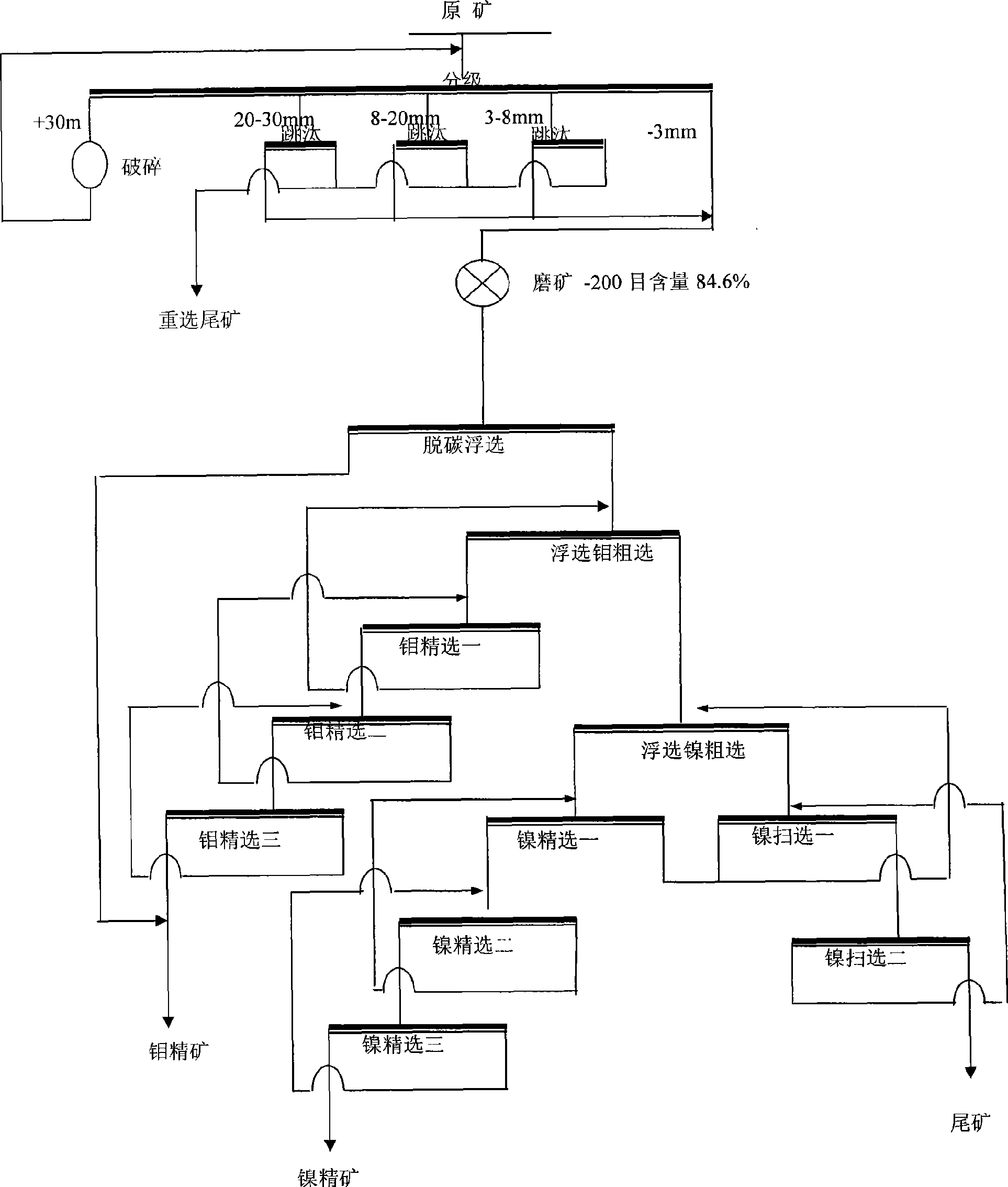
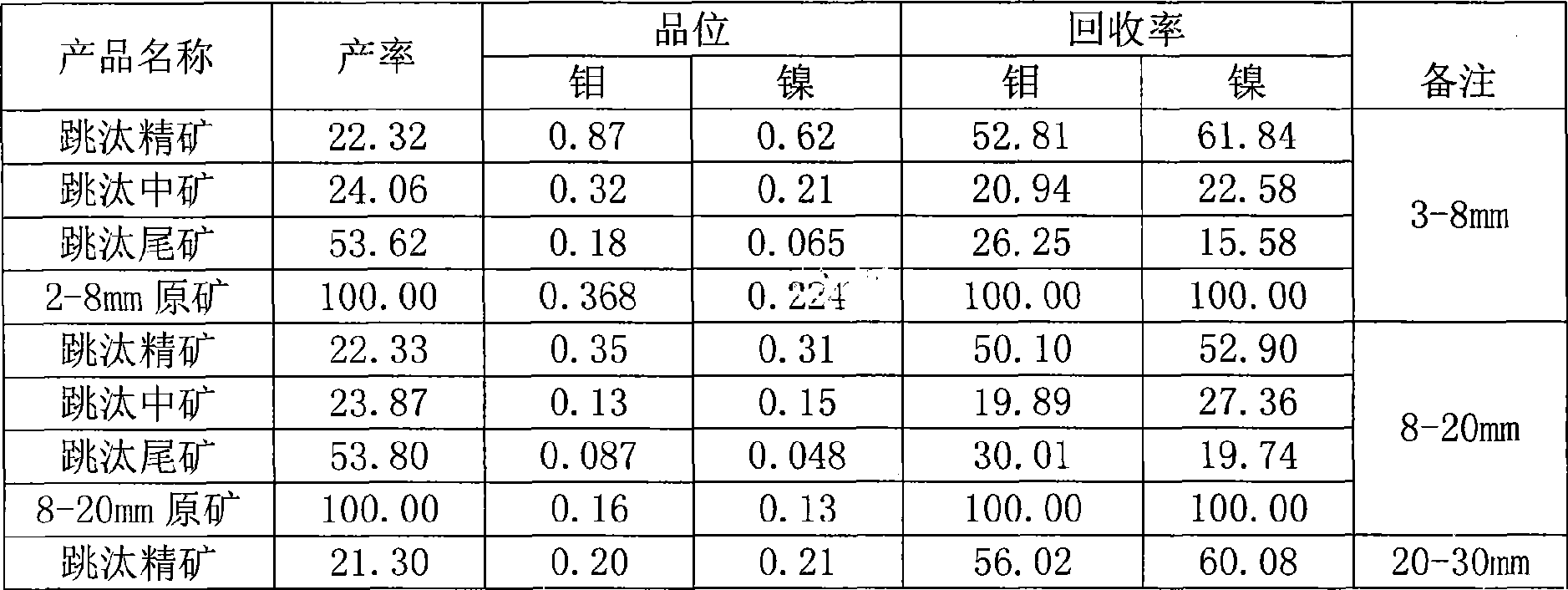
Mineral separation process of high-carbon molybdenum-nickel ore
The invention provides a beneficiation method for a high-carbon molybdenum nickel ore, which adopts floatation decarbonization so as to eliminate the influence of high-content carbon substances on subsequent nickel floatation. Furthermore, the beneficiation process adopts sieve classification with jigging and tail throwing so as to enhance the floatation and selected grade, then rough concentrates are selected again and treated by floatation after being ground, and the ore concentrates are selected again with tail throwing to enhance the floatation and selected grade without ore grinding. The invention can greatly reduce the floatation quantity, has good beneficiation index and provides a new way for developing a low-grade high-carbon molybdenum nickel ore.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Beneficiation method of sulphide ore
ActiveCN103736569AIncrease productivityIncrease production costFlotationGrain treatmentsMining engineeringSulfidation
A beneficiation method of sulphide ore relates to improvement of a beneficiation method of sulphide ore, and especially adopts a combined flotation method with a cylindrical grinder. The beneficiation process comprises the steps of performing first-stage screening of sulphide ore to obtain a first-stage coarse particle concentrate A1 and a first-stage tailing product A2; and the beneficiation process is characterized in that the first-stage tailing product A2 is subjected to a combined screening process by a cylindrical grinder. The method of the invention can effectively overcome the problem that sulphide ore with a small disseminated grain size and complex material composition cannot be recovered effectively with routine flotation methods in a flotation process, adopts a combined screening process of first-stage tailings by using a cylindrical grinder, and achieves satisfied metal recovery effect on ultrafine particle fractions in the ore by beneficiation with a cylindrical grinder.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Ore concentration technique for laterite nickel ore rich in nickel and/or cobalt
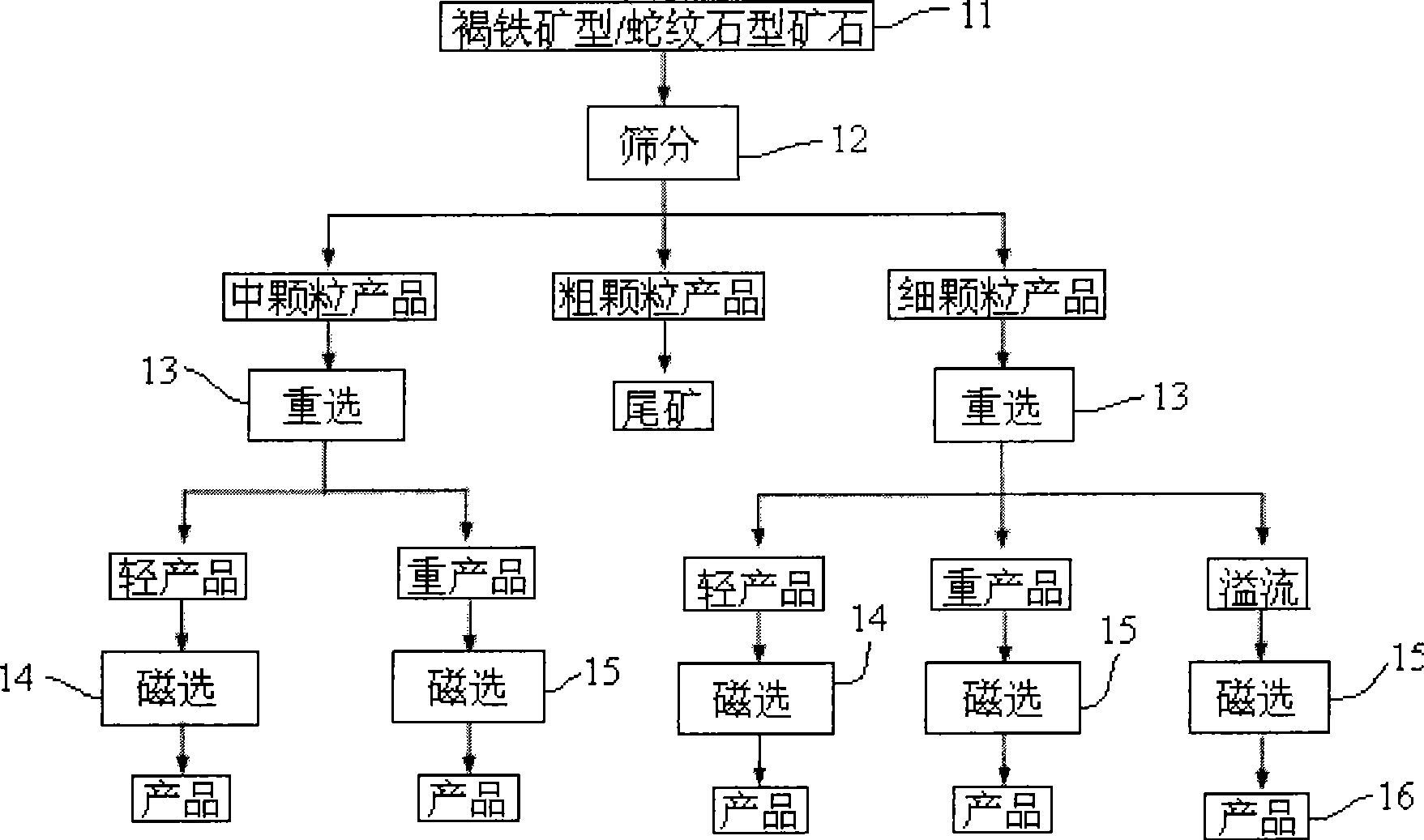
A mineral dressing technique used for enriching nickel and / or cobalt is characterized in that limonite type ore and serpentine type ore are separated for mineral dressing, and adopt a sieve to be processed by classification for at least once after being processed by ore washing; mineral dressing is carried out on the products with granulometric classes, and the target concentrated ore is obtainedby the techniques of reelection and magnetic classification. According to the invention, after the limonite type ore and the serpentine type ore are treated by sieve classification, coarse fraction materials directly enter subsequent hydrometallurgy operation, so that the handling capacity of the selected crude ore is reduced, and the sorting conditions are improved; materials with medium fraction and fine fraction adopt a combined process flow of reelection and magnetic classification for sorting to obtain the target concentrated ore, so that the mineral quantity entering the process flow ofhydrometallurgy is reduced. Mineral dressing is respectively carried out on the limonite type ore and the serpentine type ore in lateritic nickel, thus obtaining the concentrated ore having higher quality, recovery rate and concentration ratio.
Owner:JIANGXI RARE EARTH & RARE METALS TUNGSTEN GRP
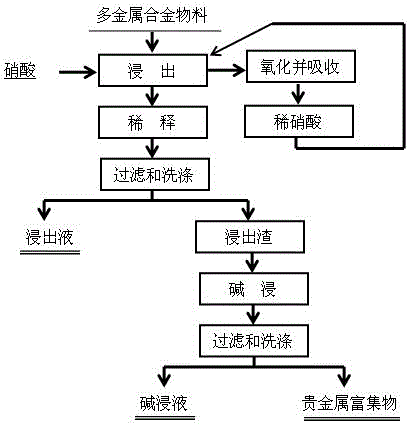
Method for enriching precious metal by dissolving multi-metal alloy material through nitric acid
ActiveCN105886769AEasy to operateMature production equipmentProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmentally friendlyBismuth
Owner:KUNMING BOREN PRECIOUS METALS
Method for separating and enriching valuable metals from copper anode mud
ActiveCN105112668AHigh removal rateHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementMaterials scienceAntimony
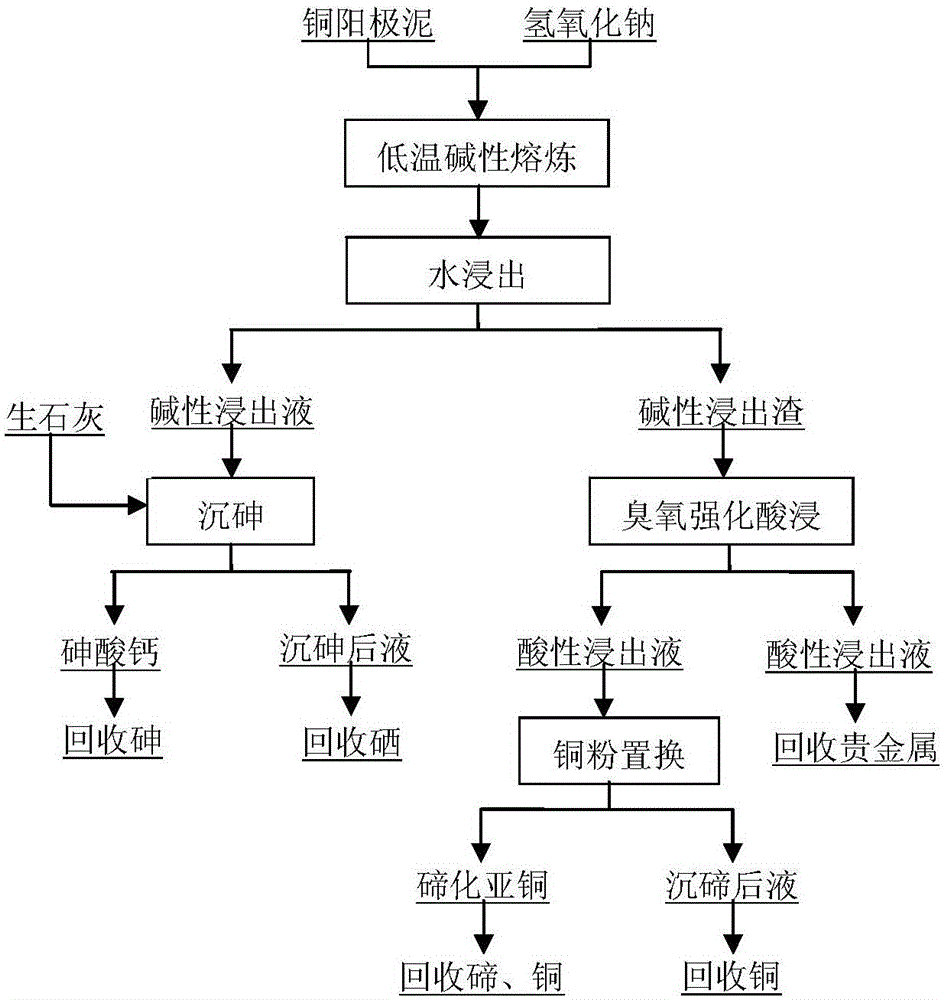
The invention discloses a method for separating and enriching valuable metals from copper anode mud. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the copper anode mud and a smelting agent are mixed evenly and are smelted at the temperature of 350-700 DEG C, and a smelting product is obtained; (2) the smelting product is crushed and immersed in water, alkaline leaching residues and alkaline leaching liquid are obtained, and selenium and arsenic are recycled from the alkaline leaching liquid; (3) acid and sodium chloride are added into the alkaline leaching residues, ozone is introduced in the alkaline leaching residues for ozone strengthening acid leaching, and acid leaching residues and acid leaching liquid are obtained; and copper and tellurium are recycled from the acid leaching liquid, and lead, stibium and precious metals are recycled from the acid leaching residues. According to the process, the method has the advantages that the selenium and arsenic removal rate is high; the moving directions of the valuable metals are more reasonable and concentrated; the enrichment ratio of the precious metals is high; the direct recovery rate of all elements is high; the comprehensive recovery benefits are good; the problem that tellurium and arsenic in the copper anode mud are dispersed seriously in a traditional process is solved; operation is safe; the labor intensity is low; the treatment time is short; and the operation environment is good.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
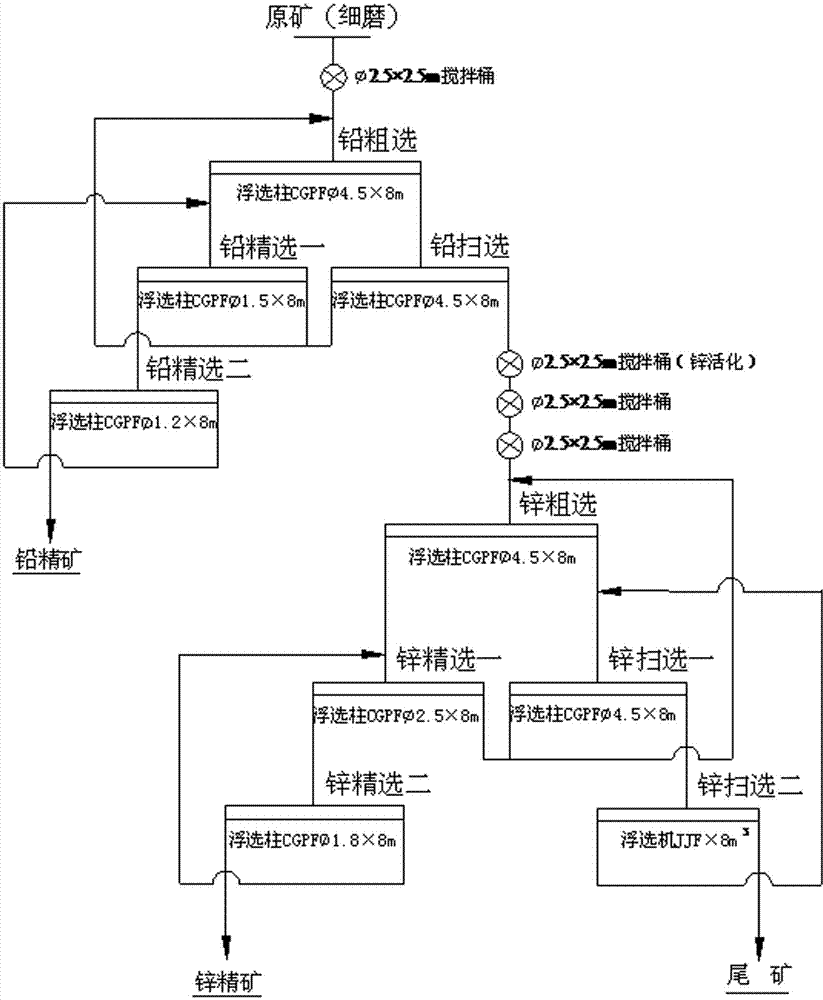
Technology for flotation of lead and zinc sulfide ores through inflatable floatation columns
ActiveCN103934117AImprove beneficiation efficiencyHigh enrichment ratioFlotationMineralogyMining engineering
The invention discloses a technology for floatation of lead and zinc sulfide ores through inflatable floatation columns. The floatation columns are fully utilized, and the method includes the steps of ore grinding, mixing of ore pulp and flotation reagents, rougher flotation operation, concentration operation, scavenging operation and the like. The method is based on the flotation column three-phase flow mechanics theory, through process mineralogy research and technological process research of low-grade, complex and refractory lead and zinc sulfide ores of mines and research and improvement on an inflatable flotation column device, the flotation columns are successfully applied to the flotation technology of low-grade, complex and refractory lead and zinc sulfide ores, and the technological process that the floatation columns are adopted in all the flotation operations of rougher flotation, concentration and scavenging of lead and zinc sulfide ores is achieved. The technology has the advantages that the automation degree is high, labor intensity of workers is low, ore flotation efficiency is high, the technological process is simple, production indexes are stable, maintenance is convenient, building investment and production cost are low, consumption of the reagents is saved by about 10%, electricity consumption is saved by about 20 %, and water consumption is saved by about 20 %.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHONGJIN LINGNAN MINING CO LTD
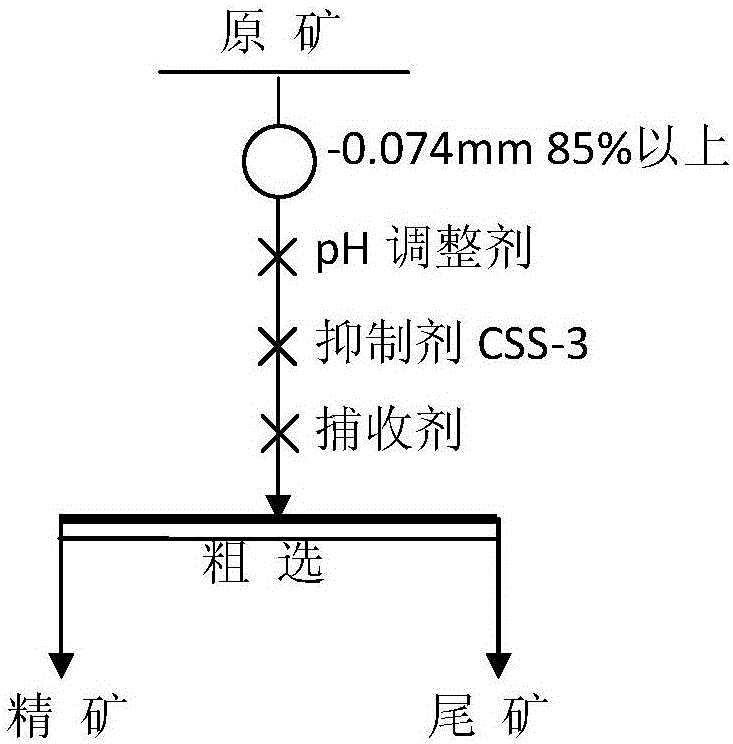
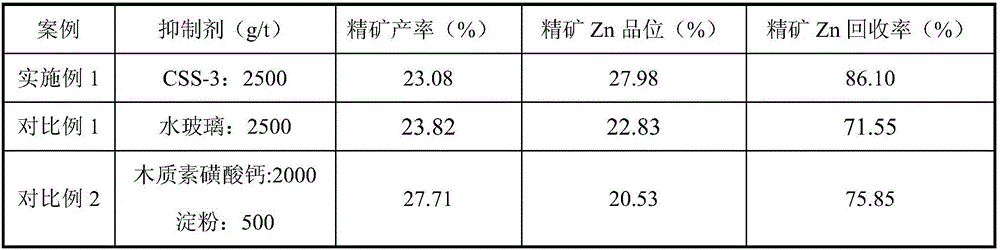
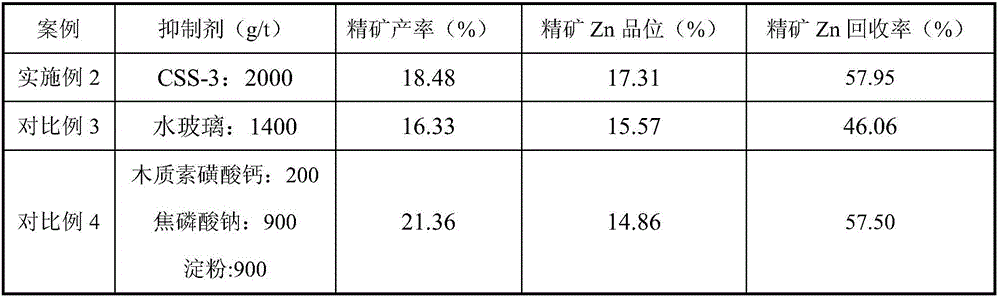
Lead-zinc oxide ore flotation inhibitor and application thereof
The invention relates to a lead-zinc oxide ore flotation inhibitor and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The designed inhibitor comprises the following components in parts by mass: 30-80 parts of lignosulfonate, 10-40 parts of assistant A, and 10-30 parts of soluble starch. The application scheme comprises the following steps: a raw ore is finely grinded to particles with a particle size not larger than 0.074 mm; after the particles are more than 85% of total mass of the raw ore, the size mixing is performed to obtain preselected slurry; after the pH value of the preselected slurry is adjusted to 8-11, the lead-zinc oxide ore flotation inhibitor is added for uniformly stirring; and then, a capturing agent is added to obtain a rough concentration of zinc oxide. The inhibitor is reasonable in component design, has dual attributes of dispersion and inhibition, has such advantages as high selectivity, high inhibition capacity, no poison and pollution and convenience for operation and management, and is convenient for large-scale industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for demagging from phosphate ore
ActiveCN101049584ATo removeAchieve the effect of removing magnesium impurities in phosphate rockFlotationSludgePhosphoric acid
A process for removing Mg from phosphorus ore in order to prepare phosphoric acid by wet method features use of static microbubble floatation column, and includes such steps as breaking the crude phosphorus ore, grinding, classifying, mineralizing by mixing the reverse floatation chemical with ore sludge, and floatating in said static microbubble floatation column while conditioning the ore sludge to obtain the bubble-phase tailings and low-Mg phosphorus ore concentrate from the column bottom.
Owner:YUNNAN CHEM RES INST
Flotation cell without transmission
ActiveCN101439315AImprove filtering effectIncrease the number ofFlotationPulp and paper industrySilicon
The invention discloses a flotation cell without transmission, which comprises a cell body and a pulp distributer; wherein, a feeding pipe arranged above the pulp distributer, and at least one venturi pipe is arranged under the pulp distributer; the venturi pipe is connected with a mineralized pipe which is connected with the pulp distributer, the bottom end of which is provided with at least onepiece of steel pipe, and a pulp ejector device is arranged at the bottom end of the steel pipe and is provided with a plurality of nozzles; the steel pipe is installed in the cell body, and a foam collecting groove is installed at the upper part of the cell body; the cell body is connected with a middling ore box by a pipeline; the flotation cell has high separation efficiency and low energy consumption, can meet the requirements of aluminum-silicon separation process of alumyte flotation desiliconization with different fractions, and has wide application scope.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Complex force field spiral chute for ore dressing
The present invention discloses a complex force field spiral chute for ore dressing, and fine particles can be effectively prevented from entering into a tailing zone. The spiral chute comprises a channel steel support, an ore-feeding device, magnetic poles, a pulsating pressure water tank, a spiral blade, an ore dividing bucket, an ore intercepting bucket and an ore receiving bucket. The permanent magnetic fixed magnetic poles are installed at an external portion of a spiral blade of an existing spiral chute, so that magnetic fine particles in magnetic mineral can be forced by an inward-radial magnetic retentive force to enter into a concentrate zone under the function of an applied magnetic field. The pulsating water tank is installed at the bottom of a spiral surface, ore particles are prevented from rubbing with the spiral surface, so that the ore particles can be well layered and separated conveniently, and equipment abrasion can be eliminated conveniently. Concentrate grades can be improved, concentration ratio can be increased, mineral recovery rates can be improved, an existing spiral ore dressing technology can be simplified, and equipment maintenance rates and equipment power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Large-particle vertical ring pulsation high-gradient magnetic separator
ActiveCN102614983AHigh enrichment ratioMeet the requirements of the sorting channelHigh gradient magnetic separatorsMagnetic mediaMagnetic separator
The invention discloses a large-particle vertical ring pulsation high-gradient magnetic separator. The large-particle vertical ring pulsation high-gradient magnetic separator comprises a machine frame, wherein magnetic yokes, excitation coils, a swivel, a concentrate bucket, a concentrate collecting tank and a tailing bucket are arranged on the machine frame; the swivel is provided with a magnetic medium pile; the tailing bucket is connected with a pulsation drive mechanism; the magnetic medium pile consists of thin stainless steel plates and medium rods inserted in the stainless steel plates; the high gradient of magnetic fields is ensured by selecting the diameters and the spatial arrangement ways of the medium rods under the condition that 2 to 5mm of material particles can smoothly pass; the outer side wall, the front side wall and the rear side wall of the concentrate bucket are arranged in a manner of inclining to a bottom discharge port, and a discharge pipe connected with the discharge port is arranged in a manner of inclining downwards; and the bottom wall of the concentrate collecting tank and the inclined side wall of the tailing bucket are horizontally provided with material baffle plates. Due to a series of improvement on the conventional magnetic separator, the vertical ring pulsation high-gradient magnetic separator can directly separate 2 to 5mm of large-particle materials and provides reliable technical guarantee for the exploitation and utilization of lean ore resources.
Owner:赣州金环磁选科技装备股份有限公司
Beneficiation method and apparatus for fine granule attractive mineral
ActiveCN101402064ATargetedImprove sorting efficiencyMagnetic separationWet separationMagnetic mineralsMaceral
The invention discloses a method and a device for mineral processing of micro-granular magnetic minerals. The method is as follows: the gradient and the rotating speed of a sorting and revolving cylinder are set according to the components of mineral materials; after being put into the sorting and revolving cylinder, the mineral materials are absorbed on the sorting and revolving cylinder and rotate along with the sorting and revolving cylinder; the mineral materials are washed by rinse water and non-magnetic minerals and weak magnetic minerals in the mineral materials are separated to move towards the lower end of the sorting and revolving cylinder to a mine tailing discharge hopper; and under the action of the relative movement of the sorting and revolving cylinder and a spiral magnetic system, the magnetic minerals are moved to the high end of the sorting and revolving cylinder spirally, and are discharged into a concentrate discharge hopper through a spiral mineral discharging plate after the magnetic minerals break away from a magnetic field. The device comprises a stander, a support, a rinsing device, a feeding hopper, a spiral magnetic system, a magnetic conducting outer cylinder, the sorting and revolving cylinder and a transmission device. The sorting and revolving cylinder is supported on the support through a carrier roller; one end of the sorting and revolving cylinder is provided with the mine tailing discharge hopper, while the other end is provided with the concentrate discharge hopper and the spiral mineral discharging plate; and the support is hinged with the stander at the mine tailing discharge end, and is supported on the stander at the concentrate discharge end through a gradient regulating device. The method has large handling capacity and high concentration ratio, and the device has strong handling ability and high coefficient of recovery.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Sulfur slag vacuum volatilizing process for enriching noble metal
InactiveCN1986850AReduced vacuum requirementsLow temperature requirementProcess efficiency improvementSlagSulfur
The present invention relates to sulfur slag vacuum volatilizing process for enriching noble metal, and belongs to the field of vacuum fire metallurgy process. Sulfur slag material is distilled in a vacuum smelting furnace at pressure of 10-30 Pa and temperature of 250-400 deg.c for 50-120 min to volatilize sulfur and the sulfur vapor is cooled to form liquid and exhausted from the vacuum smelting furnace, so as to obtain metal sulfide powder with enriched Cu, Ni, Os, Ag, Au, etc. The process is simple, and has high noble metal enriching ratio, no environmental pollution, low power consumption and low production cost.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Selective flocculation flotation method for extremely fine ilmenite
The invention discloses a selective flocculation flotation method for extremely fine ilmenite. The selective flocculation flotation method comprises the following steps of stirring the extremely fine ilmenite with a dispersing agent, an activating agent, collector and an auxiliary collector into slurry, and then, performing rougher flotation by adopting a flotation column to obtain rougher concentrate and rougher tailings; adding the collector to the obtained rougher tailings and stirring, and performing secondary scavenging by adopting the flotation column to obtain secondary scavenging concentrate and secondary scavenging tailings, wherein the secondary scavenging tailings are final tailings; adding the dispersing agent and the activating agent to the obtained rougher concentrate and stirring; performing triple concentration by adopting the flotation column to obtain triple concentration concentrate and triple concentration tailings, wherein the triple concentration concentrate is final concentrate. The current situation that the extremely fine ilmenite is directly thrown away as slurry can be solved by the selective flocculation flotation method disclosed by the invention; moreover, the selective flocculation flotation method is high in flotation efficiency and high in stability, and has good indexes.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
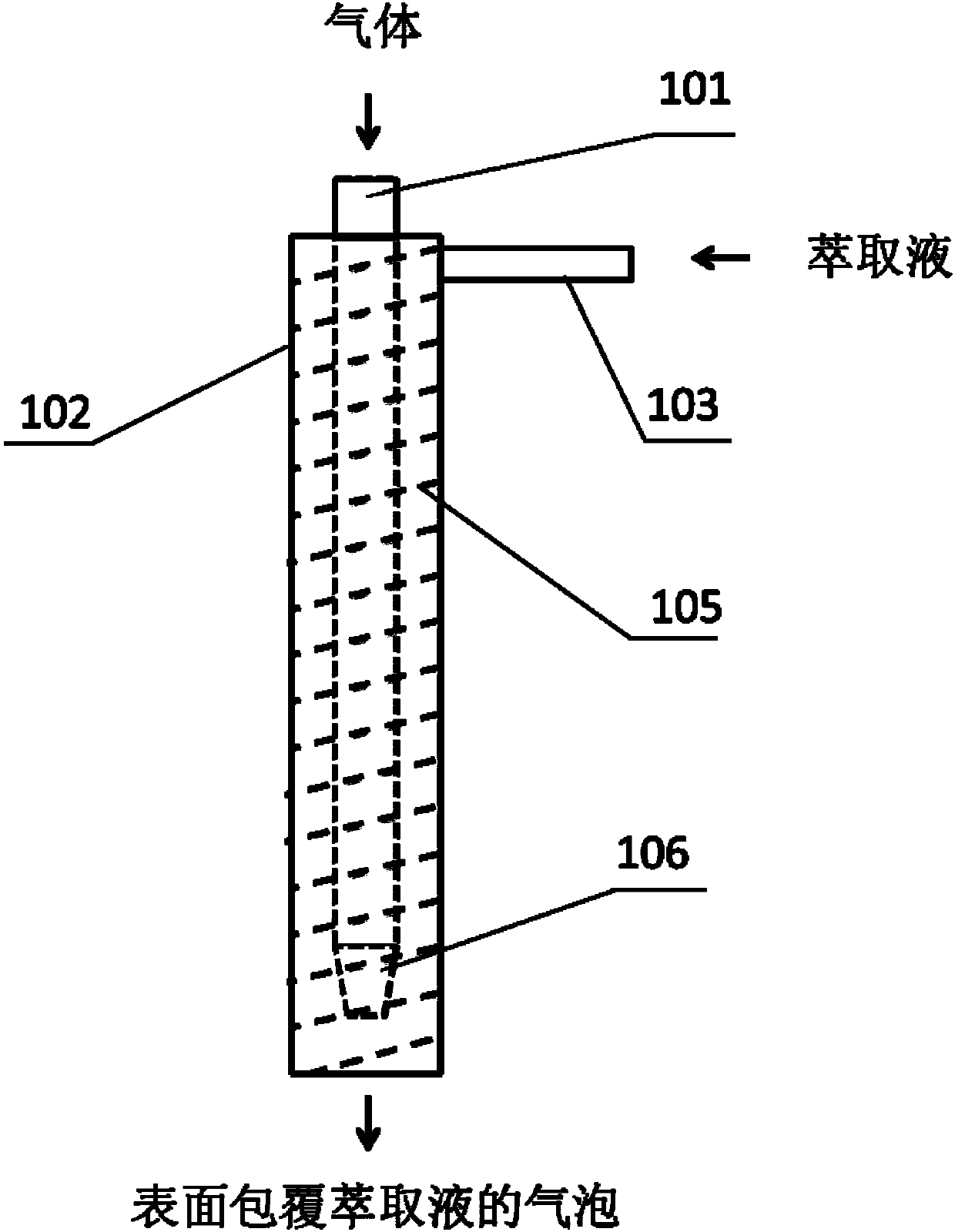
Rare earth element ion extraction method and obtained rare earth enrichment liquid
PendingCN107828961AHigh extraction rateDoes not affect extraction capacityProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementRare earth ions
The invention relates to a rare earth element ion extraction method. The rare earth element ion extraction method comprises the following steps that bubbles of which the surfaces are coated with extraction liquid are added into a water solution containing rare earth ions, the bubbles break after floating, and reversed-phase extraction is performed on an organic phase to obtain rare earth enrichment liquid. As the extraction liquid is dispersed on the surfaces of the bubbles with extremely small sizes and led into a rare earth ion solution, the rare earth solution and an organic extracting agent are in two-phase contact under the condition of an extremely large volume ratio, efficient extraction of low-concentration rare earth ions can be realized on the premise of not performing saponification pretreatment on the extraction liquid, and nitrogenous or concentrated salt wastewater cannot be produced; the original extracting agent can be recycled after reversed-phase extraction is performed on the organic phase; and the rare earth element ion extraction method has the advantages of saving energy, protecting the environment and being simple in process and economical in product.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
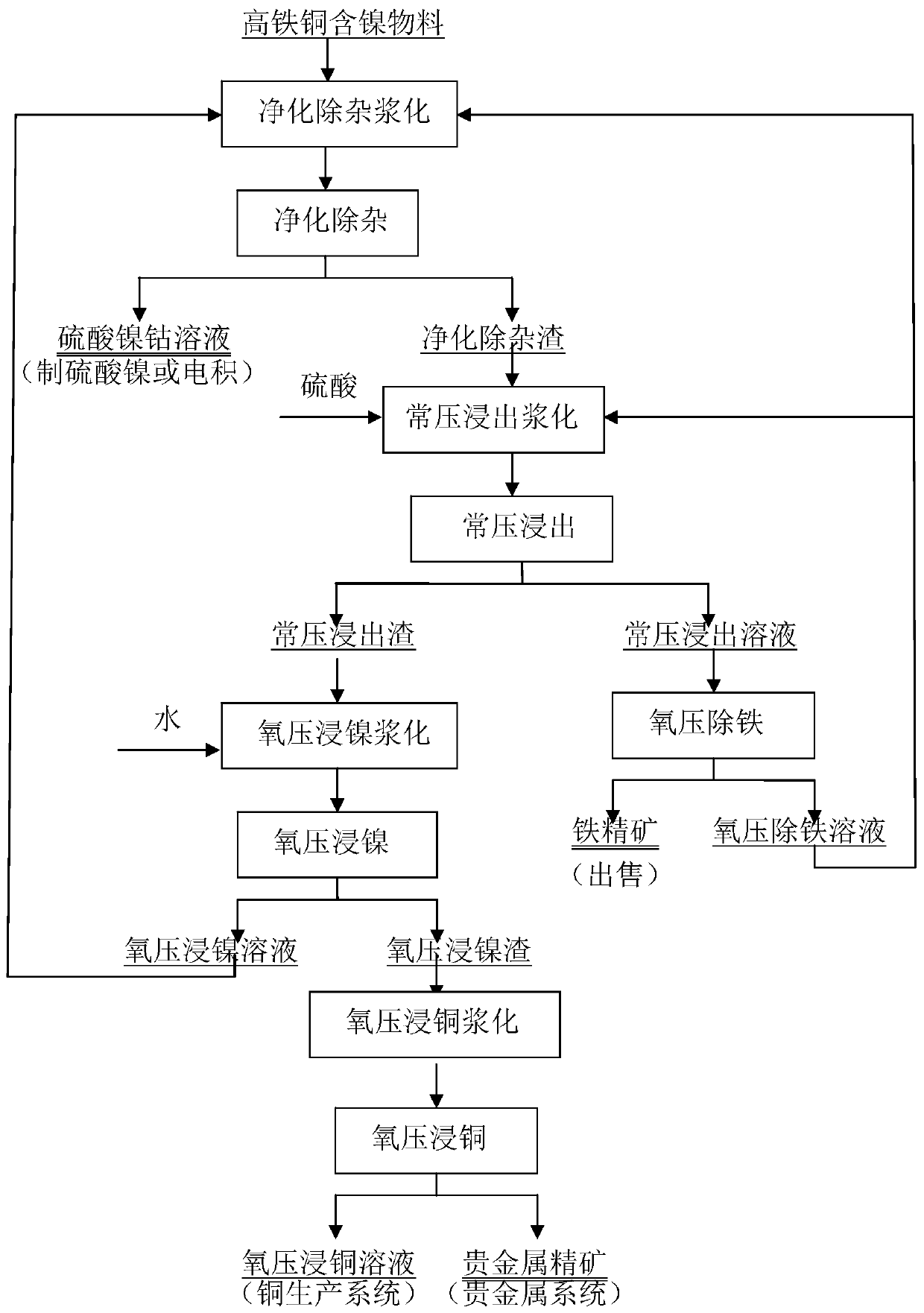
Selective oxygen pressure leaching method for the enrichment of precious metals from high-iron, high-copper and nickel-containing materials
ActiveCN110241310AImprove direct yieldHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementAlloyNickel sulfide
The invention belongs to the technical field of nonferrous metallurgy, and particularly relates to a selective oxygen pressure leaching method for the enrichment of precious metals from high-iron, high-copper and nickel-containing materials. The method comprises the following steps of purification and impurity removal, normal-pressure leaching, oxygen-pressure deironing, oxygen-pressure nickel immersion and oxygen-pressure copper immersion. The method is short in technological process and high in direct yield, and can be used for selectively leaching nickel, cobalt, copper and iron and respectively realizing open circuit; and the method is wide in raw material adaptability, suitable for treating various high-iron high-copper nickel-containing materials such as intermediate product low-nickel matte generated in the conventional nickel sulfide ore smelting process, primary alloys, fine grain alloys, cobalt-rich low-nickel matte and cobalt-rich matte, and is remarkable in benefit. The nickel sulfate cobalt sulfate solution obtained by adopting the method is high in the product quality, and the requirements of multi-variety production can be met at the same time; the noble metal can be totally enriched in the oxygen pressure leaching copper slag and can be used as a noble metal concentrate, the direct yield and the enrichment ratio are high, and iron is directly used in a product form; and copper is leached to obtain a copper sulfate solution, and crystallized copper sulfate or electrodeposition copper can be produced.
Owner:SHENZHEN KUNPENG METALLURGY ENG TECH LTD
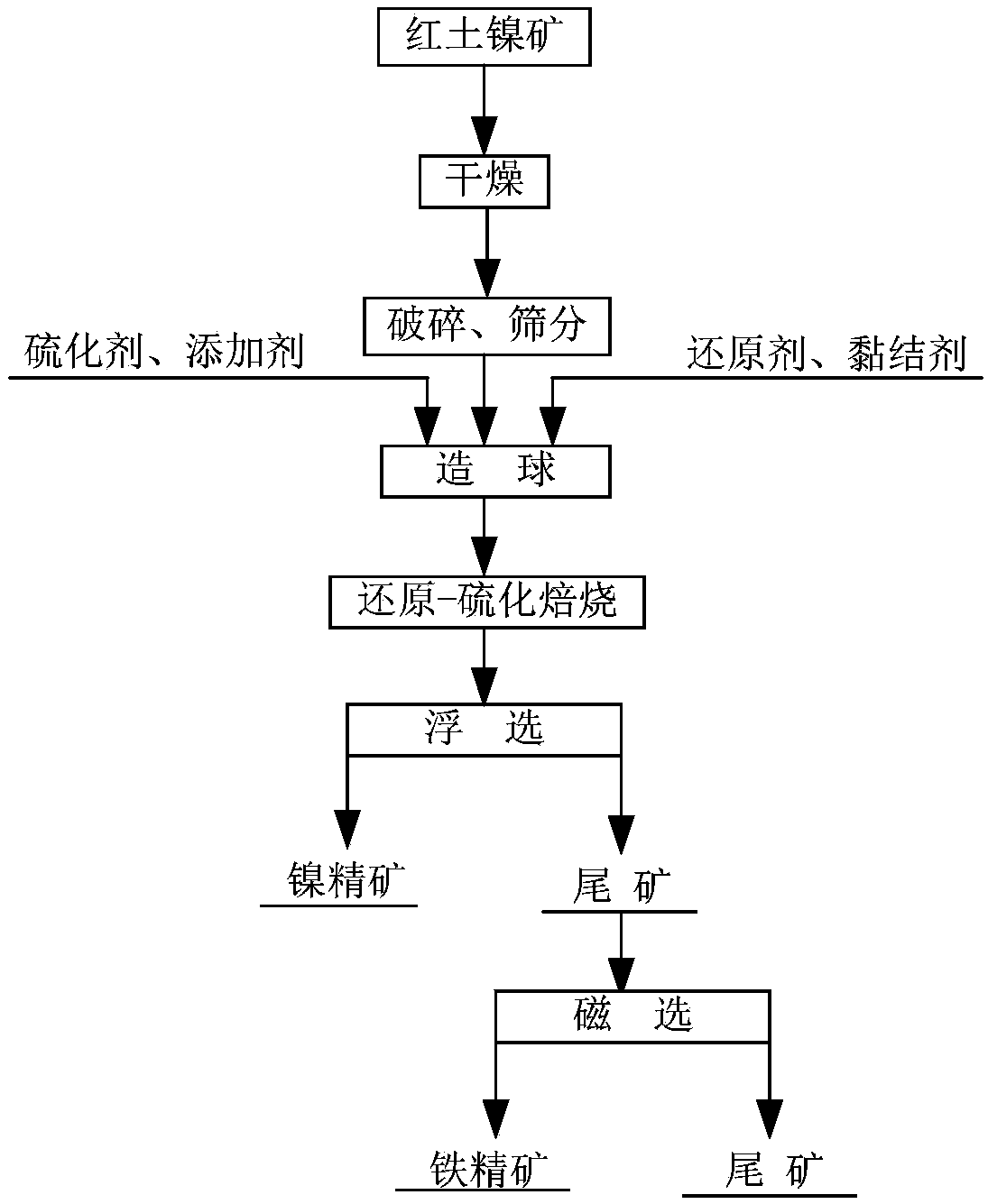
Method of selective sulfidation roasting for laterite nickel ore
ActiveCN109097562AEfficient separation and recoveryLow recovery rateRotary drum furnacesFlotationSulfidationLaterite
The invention discloses a method of selective sulfidation roasting for laterite nickel ore. According to the method of selective sulfidation roasting for the laterite nickel ore, the laterite nickel ore is mixed with raw materials including a carbonaceous reducing agent, a sulfurizing agent, an alkali metal salt additive and a binder for even mixing and pelletizing, the obtained pellets are roasted in the first stage at low temperature and roasted in the second stage at high temperature; and nickel products are recovered from roasted materials by a flotation method, and iron products are recovered from flotation tailings by a magnetic separation method. The method has a good recovery effect on nickel and iron, low energy consumption, low cost and simple process, and is beneficial to industrial large-scale production and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Printing and dyeing wastewater processing technique
InactiveCN101381178AReduce chromaReduce CODMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationEmission standardTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a printing-dyeing wastewater treatment process, which belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The treatment process uses a foam separation technique together with Fenton oxidation to treat printing-dyeing wastewater containing more than two dyes, and concretely comprises the following: a step of collecting and filtering the printing-dyeing wastewater containing more than two dyes; a step of detecting and pretreating, which is to detect the pigment composition, chemical oxygen consumption, color, pH value and suspended solid content of the dyes contained in the printing-dyeing wastewater and to regulate the pH value of the wastewater to between 6.0 and 8.0 by use of hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide; a step of separating foam and decolorizing, which is to add Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide as surfactant to the wastewater treated through the previous step and then to decolorize by use of a bubbling tower; and a step of carrying out Fenton oxidation to the wastewater obtained in the previous step. The COD of the treated wastewater meets the national emission standard. The process overcomes the disadvantage that the prior printing-dyeing wastewater treatment process is large in occupied area, causes secondary pollution, is low in color removal rate, great in treatment effect fluctuation, complex in process and high in cost, or can not achieve ideal effects.
Owner:天津市瑞德赛恩新材料开发有限公司
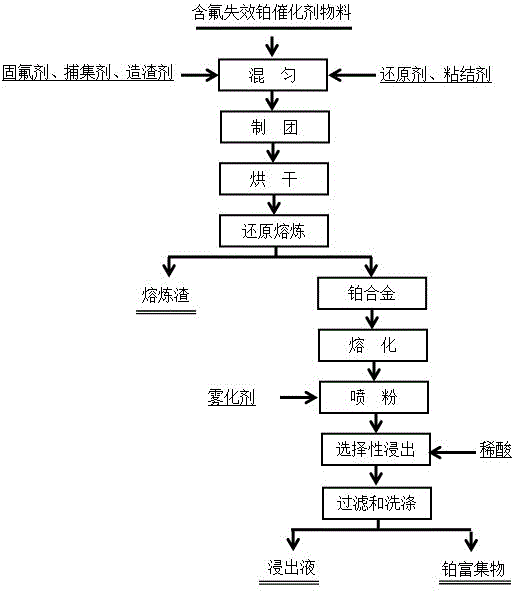
Method for enrichment of platinum in fluorine-containing spent platinum catalyst
ActiveCN104372173AEfficient separationSimple processProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnacePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for enrichment of platinum in a fluorine-containing spent platinum catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of mixing a fluorine-containing spent platinum catalyst, a fluoride retention agent, a platinum trapping agent, a slagging agent, a reducer and a binder to obtain a uniform mixture, carrying out granulation by a granulator to obtain granules with 5cm, carrying out drying, carrying out melting by an electric-arc furnace at a temperature of 1300-1400 for 1-2h to obtain platinum alloy and melting slag, adding fluorine into the melting slag in melting, melting the platinum alloy by an intermediate frequency furnace, carrying out atomization powder injection to obtain fine platinum alloy particles, carrying out selective leaching of iron in the platinum alloy particles, and carrying out filtration and washing to obtain platinum richment which is platinum concentrate. The platinum concentrate has platinum content greater than 30%, a platinum enrichment ratio 25-35 times the original ratio and a platinum yield greater than 99.0% and is a high-quality raw material for platinum purification. The method has simple processes, a high platinum yield, a high enrichment ratio, environmental friendliness, a low cost and a good industrialization prospect.
Owner:大城县荷丰有色金属有限公司
Mineral processing method of ilmenite
InactiveCN104437851AAvoid Oxygenation InterferenceImprove qualityFlotationMagnetic separationSulfurIlmenite
The invention aims to provide a mineral processing method of ilmenite, which improves the ilmenite recovery ratio when ensuring the ilmenite concentrate quality. The mineral processing method of the ilmenite comprises the following steps: crushing a raw material to powder materials of 200-300 meshes; adding a sulfur floating agent to the powder materials for sulfur floatation; concentrating by utilizing a thickener to obtain base flow ore pulp; removing iron from the base flow ore pulp; performing a first-section strong magnetic separation, and a second-section strong magnetic separation; scavenging tailings after being subjected to strong magnetic separation twice, recovering the ilmenite to perform the strong magnetic separation. The mineral processing method of the ilmenite has the beneficial effects that the sulfur floatation is firstly performed, sulfur in the ilmenite is enriched and floated, so as to avoid oxidation interference of the sulfur in the subsequence steps; sulfur-floated ilmenite crude ore pulp is concentrated by the thickener to obtain crude ore; more nonmagnetic gangues can be removed through strong magnetic separation twice, so that the ilmenite quality is improved; simultaneously, the tailings are scavenged, recycled and circulated, so that the recovery ratio of the ilmenite is improved; the whole process flow is simple, the operability is high, and the enrichment proportion is high.
Owner:TIANJIN KAITELONG WELDING MATERIAL
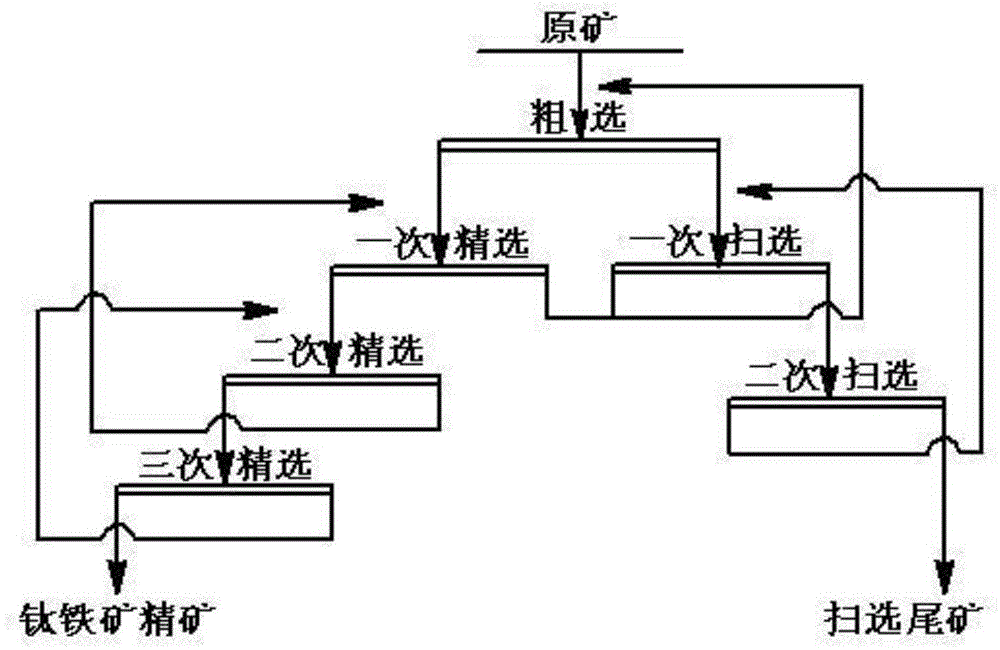
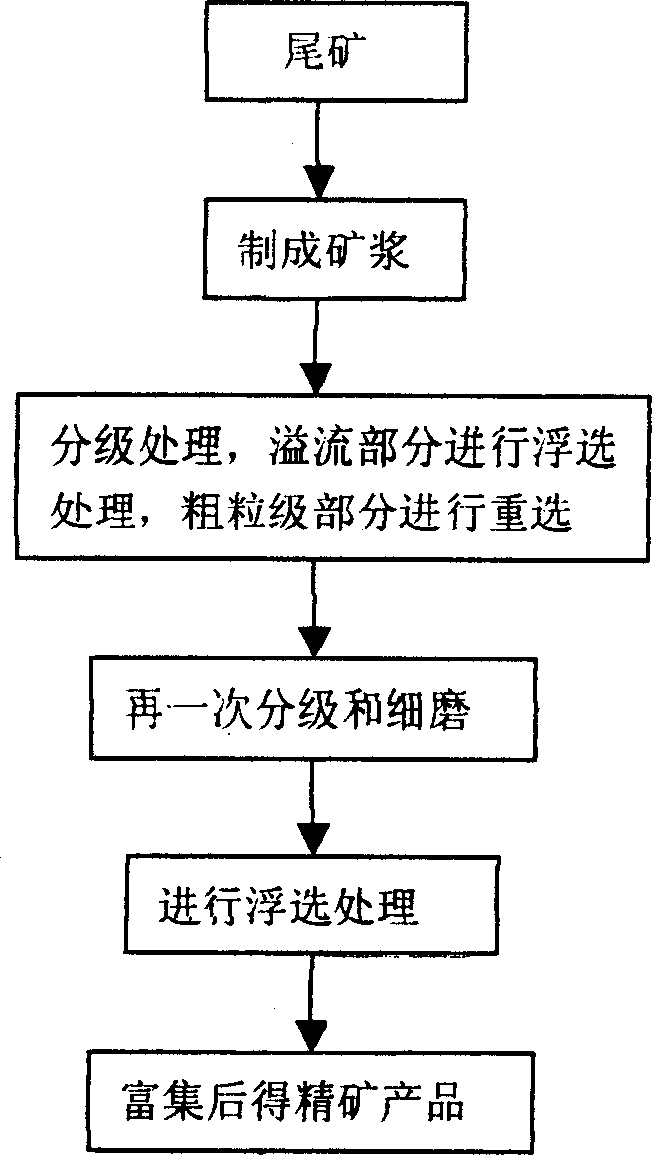
Re-dressing utilizing method for non-ferrous metal tailings
This invention relates to a recleaning using method of non-ferrous metal tailings, its feature is that the procedures of the method said are as following: a. obsolescence tailings are selected from tailings dam, then ore magma is agitated with water in conditioning pool. b. the magma is stage treated, then flotation treatment is done to overflow part, macrograin part is selected again. c. the ore foam and middlings got from reelecting after classification are done another calssificaiton and fine grinding. d. the overflow part from procedure c is flotation treated, then finished ore product is got after progressive enrichment. The waste water in tailings can be eliminated by using segregation processing, and damage of argillization matter and medicine pollution. Mineral grain120-300 items can be large treated in classification and reelection. Its accommodation limit is wide, then the monomer is liberated after again classification and fine grinding of the foam and middlings so the concentration ratio is heightened and high recovery is realized.
Owner:上海维莎宝矿产设备有限公司
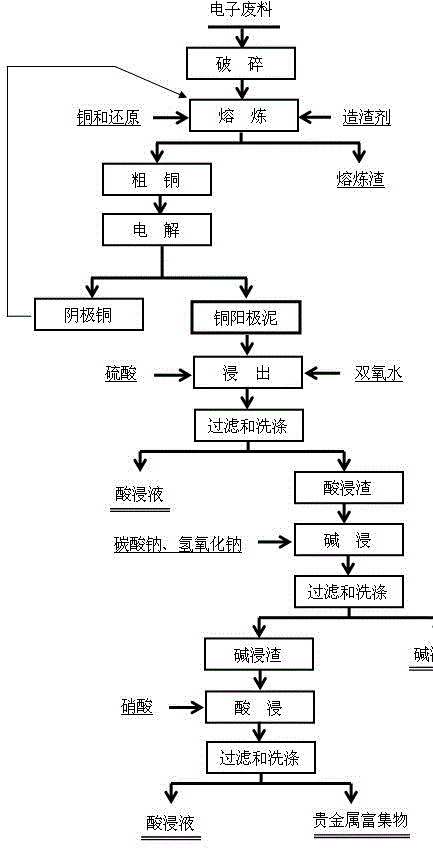
Method for efficiently enriching precious metal from electronic waste
InactiveCN105886768AIncrease capture rateHigh Blister Copper Containing CopperProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisElectric arc furnace
The invention discloses a method for efficiently enriching precious metal from electronic waste. Particularly, anode slime is obtained from the electronic waste which is subjected to copper smelting capture and then subjected to electrolysis. The method comprises the steps that the electronic waste is crushed, added with copper, a reducing agent and a slag former and placed in an electric arc furnace to be smelted, so that crude copper is obtained, and the precious metal is effectively captured; the crude copper is then subjected to electrolysis, the precious metal enters copper anode slime, and thus preliminary enrichment of the precious metal is achieved; the copper anode slime material is mixed with sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide and placed in a reaction kettle to be leached, so that acid leaching residue and acidic leaching liquid are obtained; the acid leaching residue is added with sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate and subjected to alkali leaching, so that alkali leaching residue and alkali leaching liquid are obtained; and the alkali leaching residue is added with nitric acid to be leached, and lead enters the solution, so that the enriched precious metal is obtained after filtering and washing are conducted. The enriched precious metal is obtained from the electronic waste. The method for efficiently enriching the precious metal from the electronic waste is easy to operate, environmentally friendly, low in production cost, easy to industrialize, high in precious metal yield and good in application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY COLLEGE
Method for increasing molybdenum ore recovery using fine-sweeping
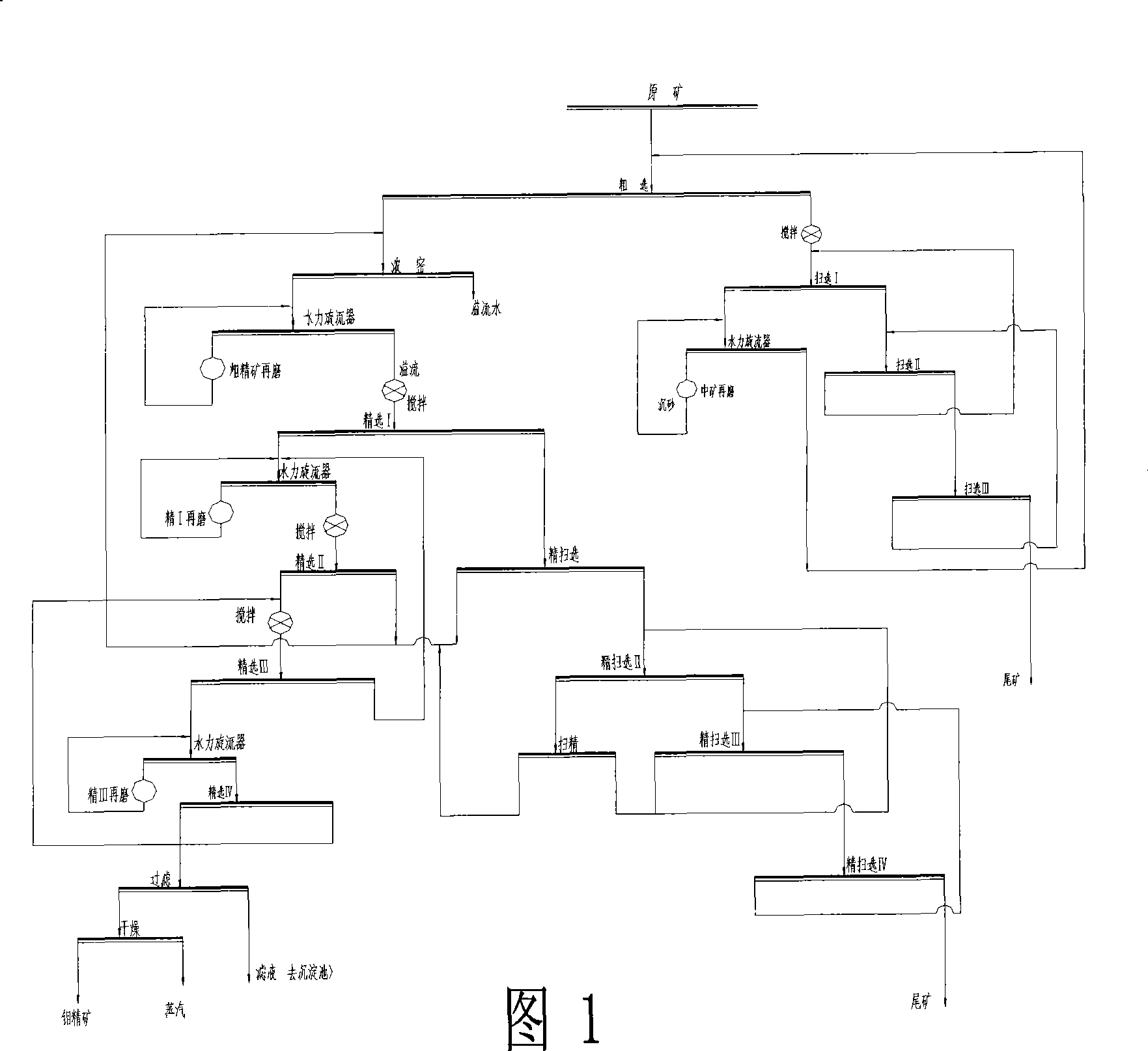
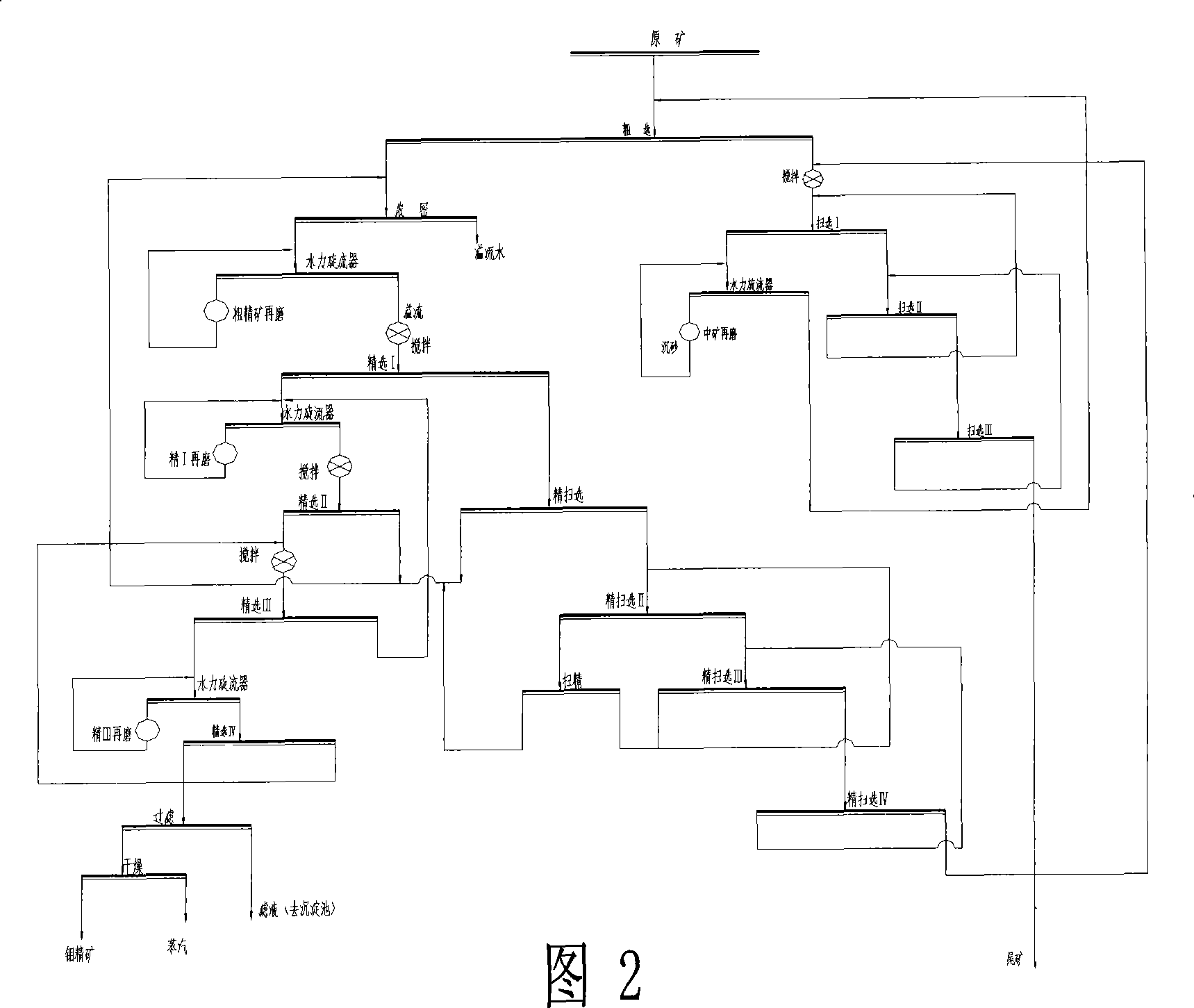
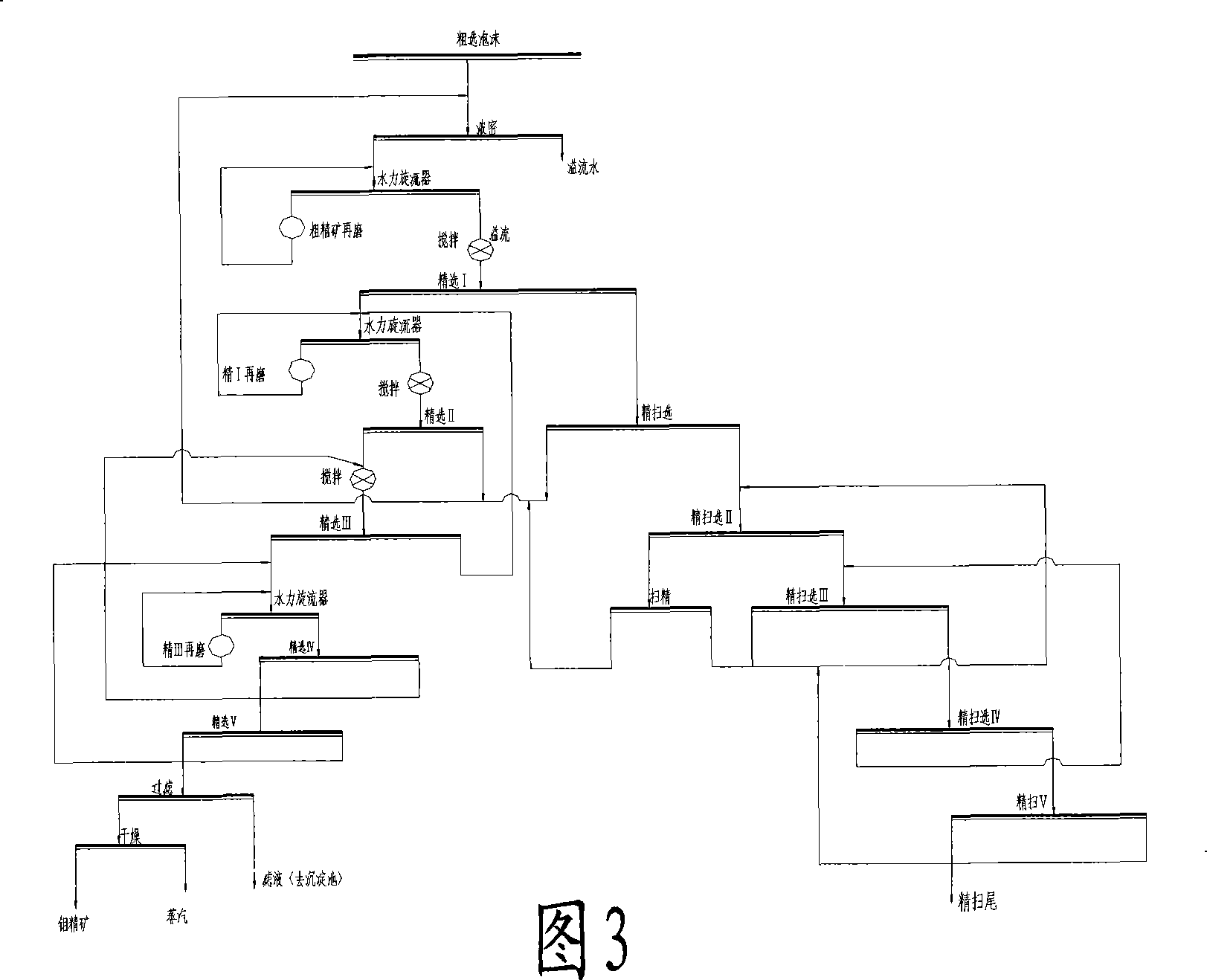
The invention discloses a method used for improving the recovery of the molybdenum processing by fine sweeping section; the method comprises five selection operations such as fine sweeping I, II, III, IV and V; wherein, fine sweeping I foam and fine sweeping foam are returned to a slurry pond 2 together; fine sweeping II gangue is classified by a hydrocyclone and the overflow thereof is used as fine I given ore; fine sweeping I gangue enters a fine sweeping II flotation machine; the fine sweeping II flotation machine foam enters fine sweeping; fine sweeping II gangue enters a fine sweeping III flotation machine and is classified; the fine sweeping III gangue is re-classified by fine sweeping IV and used as final fine sweeping gangue; the foam thereof is re-returned to the fine sweeping III flotation machine to be classified; after the selection operation of the fine sweeping IV, a floatation column is provided so as to lead the fine sweeping IV gangue to directly enter a newly increased flotation column (fine sweeping V) and to be classified; subsequently, the gangue is directly used as final fine sweeping gangue tail and the foam as well as the fine sweeping III foam and fine sweeping gangue is returned to the fine sweeping II flotation machine and re-classified. The method leads the original fine gangue to be re-classified, reduces the grade of the final gangue and improves the recovery at the same time, and increases the yield of molybdenum concentrates.
Owner:CHINA MOLYBDENUM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com