Method for efficiently enriching precious metal from electronic waste
A technology for electronic waste and precious metals, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of difficult extraction of precious metals, achieve high yield of precious metals, facilitate subsequent electrolysis, and high enrichment ratio of precious metals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
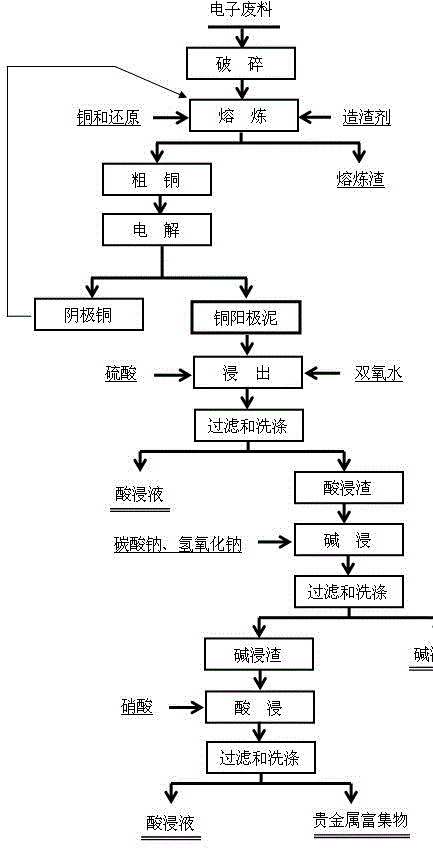
[0020] See attached figure 1 , conditions: electronic waste crushing, weight 5000 grams, electronic waste crushing, adding copper oxide concentrate is 40% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, the reducing agent is coke powder, the amount added is 3% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, slagging agent is added The amount is 30% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, mixed evenly, and placed in an electric arc furnace for smelting to obtain blister copper, and the precious metal is effectively captured; the blister copper is then electrolyzed, and the precious metal enters the copper anode slime, realizing the initial enrichment of the precious metal; Mix the copper anode slime material with sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. The amount of sulfuric acid is 50% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime, and the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 60% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime. It is placed in a reaction kettle for leaching. The reaction temperature i...
Embodiment 2
[0022] See attached figure 1, Conditions: electronic waste crushing, weight 5000 grams, electronic waste crushing, adding scrap copper is 20% of electronic waste weight ratio, reducing agent is anthracite, adding amount is 5% of electronic waste weight ratio, slagging agent adding amount is 40% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, mixed evenly, placed in an electric arc furnace for smelting to obtain blister copper, and the precious metals were effectively captured; the blister copper was then electrolyzed, and the precious metals entered the copper anode slime, realizing the initial enrichment of precious metals; The anode slime material is mixed with sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. The amount of sulfuric acid is 60% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime, and the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 40% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime. It is placed in a reaction kettle for leaching. The reaction temperature is 85 ° C, the time is 4 hours, liquid-solid ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] See attached figure 1 , Conditions: electronic waste crushing, weight 5000 grams, electronic waste crushing, adding electrolytic cathode copper is 20% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, the reducing agent is coke powder, the amount added is 2% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, and the amount of slagging agent It is 40% of the weight ratio of electronic waste, mixed evenly, and placed in an electric arc furnace for smelting to obtain blister copper, and the precious metal is effectively captured; the blister copper is then electrolyzed, and the precious metal enters the copper anode slime, realizing the initial enrichment of the precious metal; The copper anode slime material is mixed with sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. The amount of sulfuric acid is 60% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime, and the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 70% of the weight ratio of the copper anode slime. It is placed in a reaction kettle for leaching. The reaction temp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com