Clean metallurgical method for low-temperature molten salt of antimony
A low-temperature molten salt and clean technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, can solve the problems of complicated operation, pollute the ecological environment, high production cost, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing antimony smelting temperature, promoting energy saving and emission reduction, and promoting technological progress.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
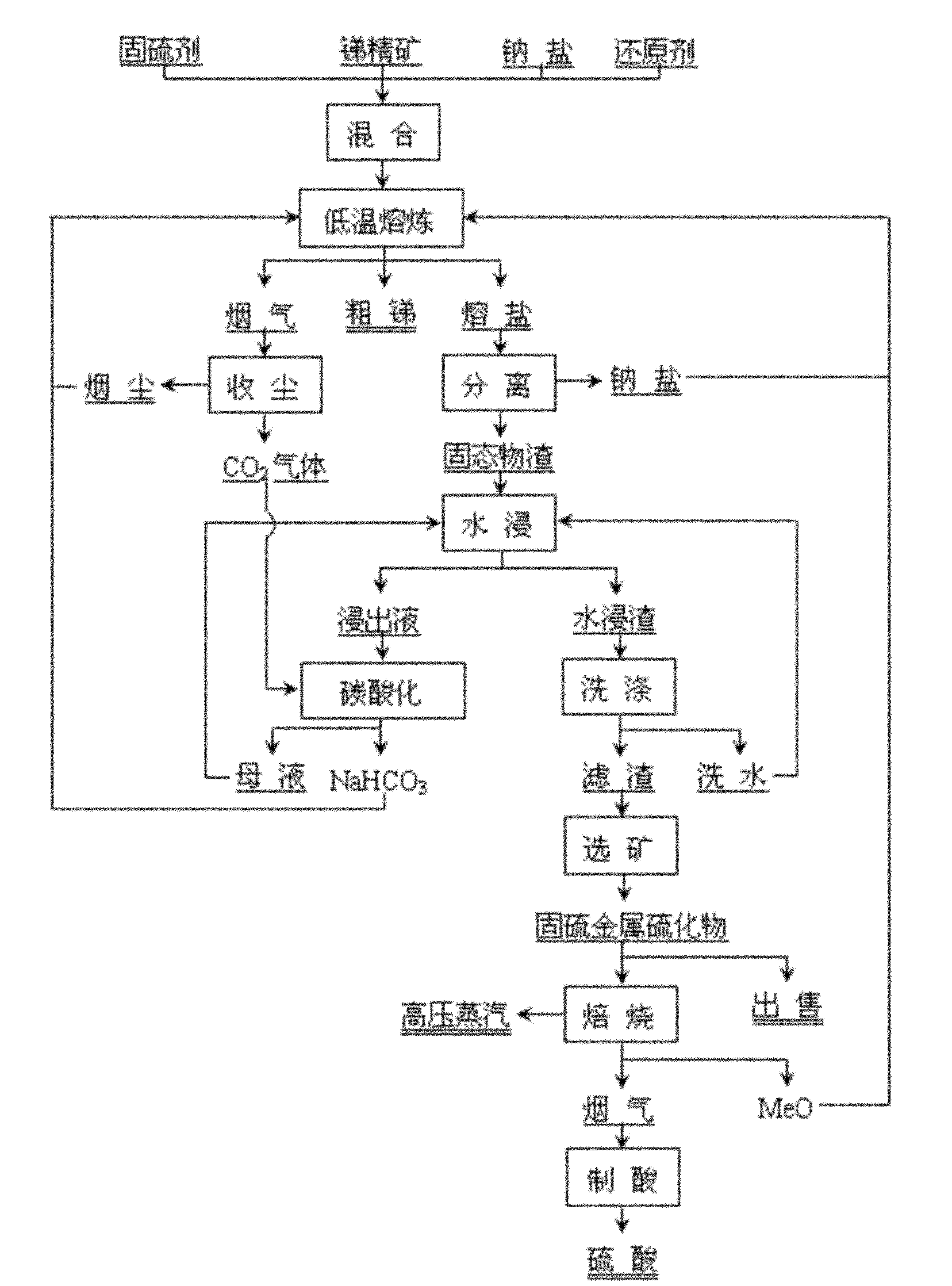
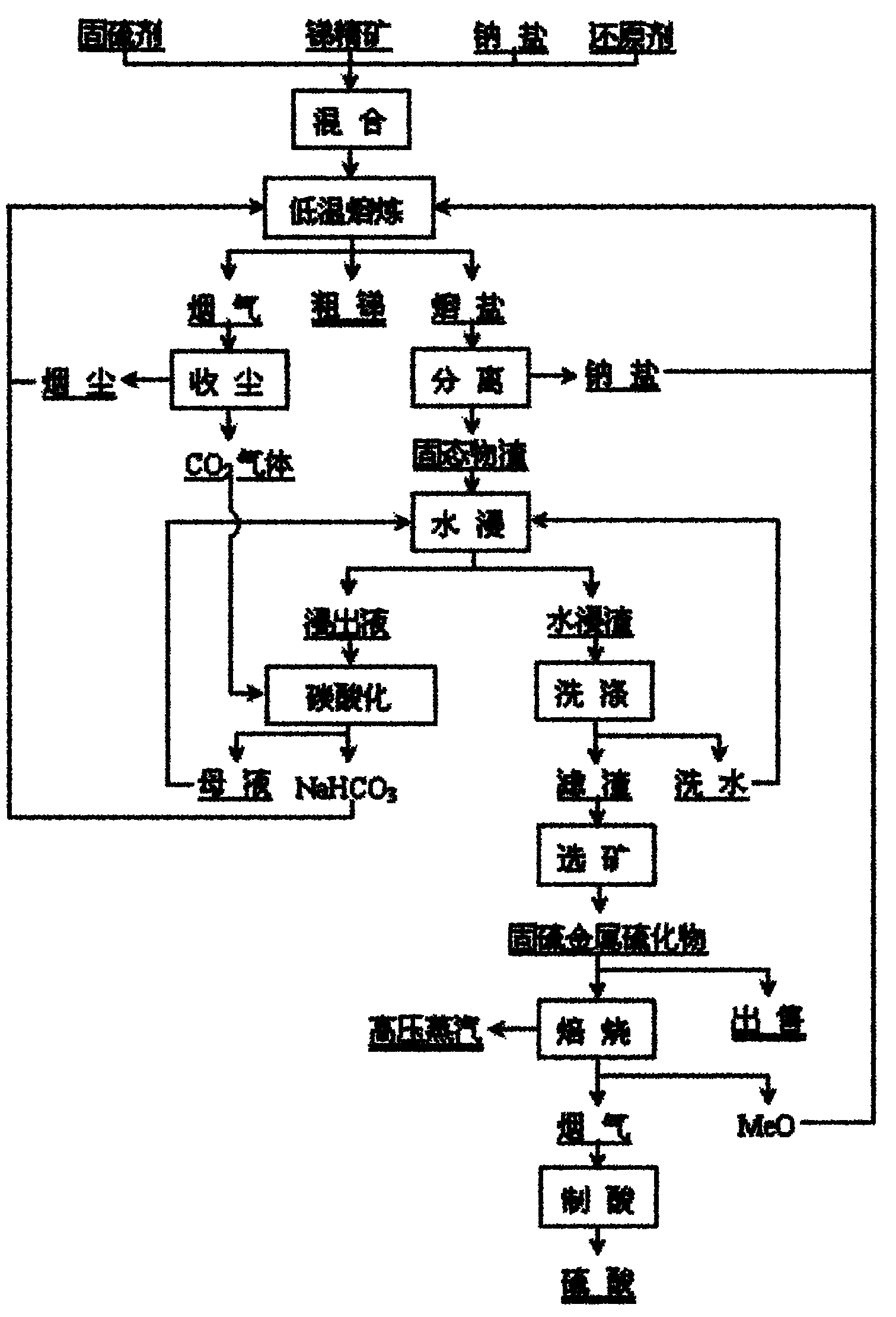
[0029] see figure 1 , the chemical composition of antimony sulfide concentrate is (%): Sb 63.91, Fe 0.94, S 24.91, Cu 0.43, Pb 0.43, Cd 0.0038, As 0.10, SiO 2 5.28 Al 2 o 3 2.38, CaO 1.21, MgO 1.95, the chemical composition of pulverized coal is (%): C 82.33, S 3.01, SiO 2 6.66, CaO 0.83, Al 2 o 3 4.81. Weigh 100g of antimony sulfide concentrate, 9.48g of pulverized coal, 297.02g of industrial grade sodium carbonate and 64.4g of zinc suboxide containing Zn 78.33% and mix evenly. After the mixture is loaded into a graphite crucible, 74.26g of industrial grade sodium carbonate. Push the graphite crucible into a resistance furnace, melt at 900°C for 2 hours, and produce 63.6g of crude antimony containing 99.02% of Sb, and the direct yield of antimony reaches 98.54%; stand at 900°C to clarify and separate the inert molten salt and solid After 1 hour, slowly pour the upper part of the clarified molten salt to obtain 301.5 g of molten sodium carbonate and 155.93 g of soli...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The chemical composition of the antimony sulfide concentrate is the same as in Example 1, and coke powder (containing 82% of C and 10% of ash) is used as a reducing agent. Weigh 100g of antimony sulfide concentrate, 8g of coke and 68.19g of copper oxide calcined sand containing Cu 49.03% and mix evenly. After the mixture is loaded into a graphite crucible, add 301.5g of molten sodium carbonate returned in Example 1, and then cover Example 1. 1 returns NaHCO 392.1g and 22g of technical grade sodium carbonate. Push the graphite crucible into a resistance furnace, melt at 870°C for 3 hours, and produce 64.25g of crude antimony containing 98.78% of Sb, and the direct yield of antimony reaches 99.31%; stand at 800°C to clarify and separate the inert molten salt and solid After 5 hours, slowly pour the upper part of the clarified molten salt to obtain 296.5 g of molten sodium carbonate and 175.43 g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium carbonate. The latter is ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Using brittle pyrostibite as raw material, its chemical composition is (%): Sb 26.36, Pb 31.33, Zn 3.92, Fe 8.69, Cu 0.12, S 22.10, As 0.58, SiO 2 1.56, CaO 1.44, Al 2 o 3 0.34, coal powder is a reducing agent, and its chemical composition is the same as that of Example 1, and zinc oxide calcine is a sulfur-fixing agent, and its chemical composition is (%): Zn 52.87, Cu 3.58, Pb 0.35, Sb 0.68. Weigh 100g brittle styrofoam concentrate, 80.63g zinc oxide calcine, 10g coal powder, 306g industrial grade sodium bicarbonate and 25.66g industrial grade sodium hydroxide, mix them evenly and put them into a graphite crucible, and then place them in a resistance furnace Melted at 820°C for 4 hours, the output of antimony-lead alloy 56.87g, containing Sb46.58%, Pb 51.42%, the direct yield of antimony and lead were 98.45% and 92.50% respectively; Salt and solid matter, slowly pour the upper part to clarify the molten salt after 3 hours, and obtain 286.25 g of molten sodium carb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com