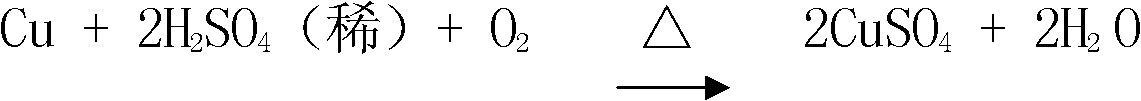Patents
Literature
386results about "Copper sulfates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
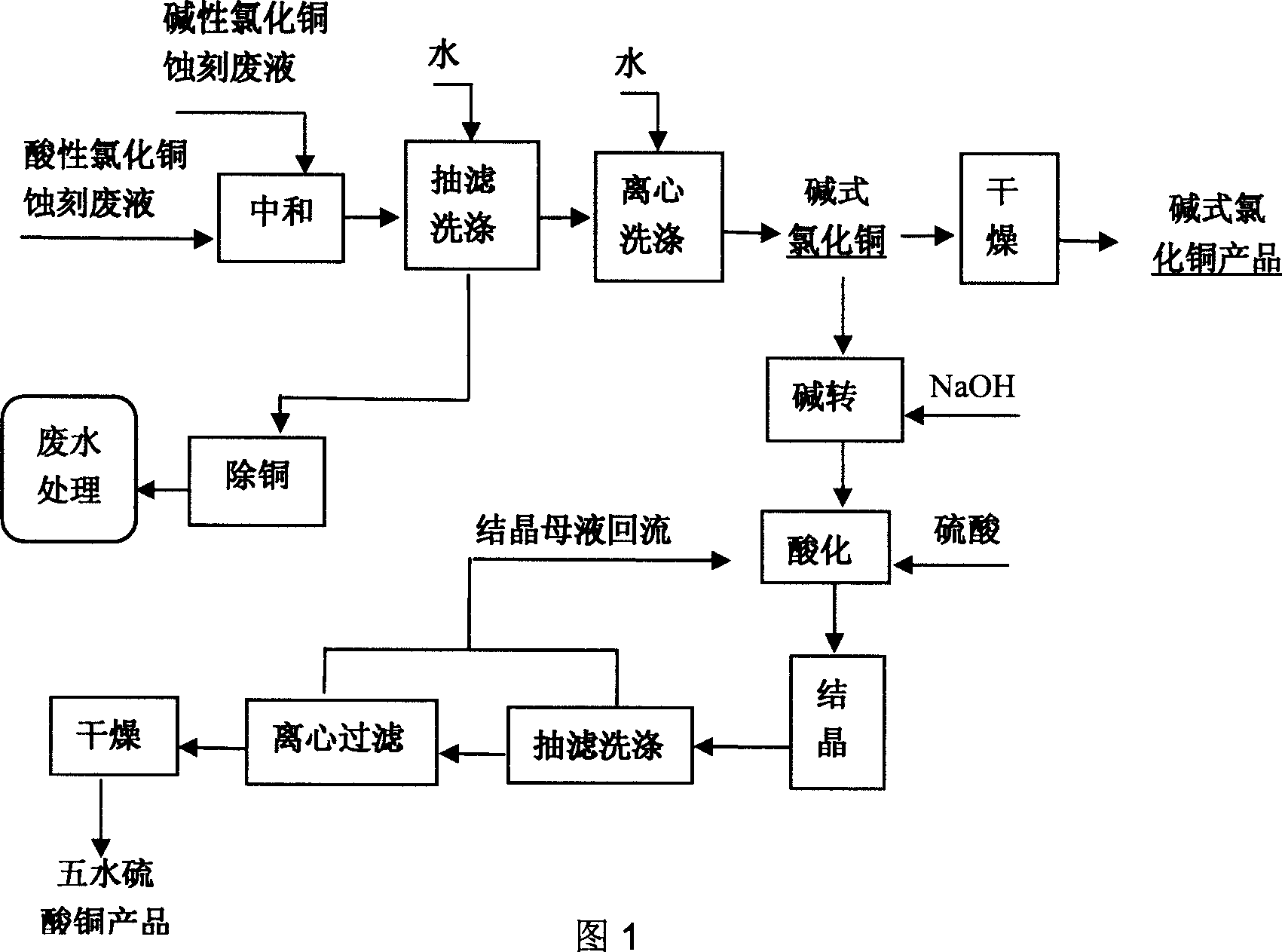
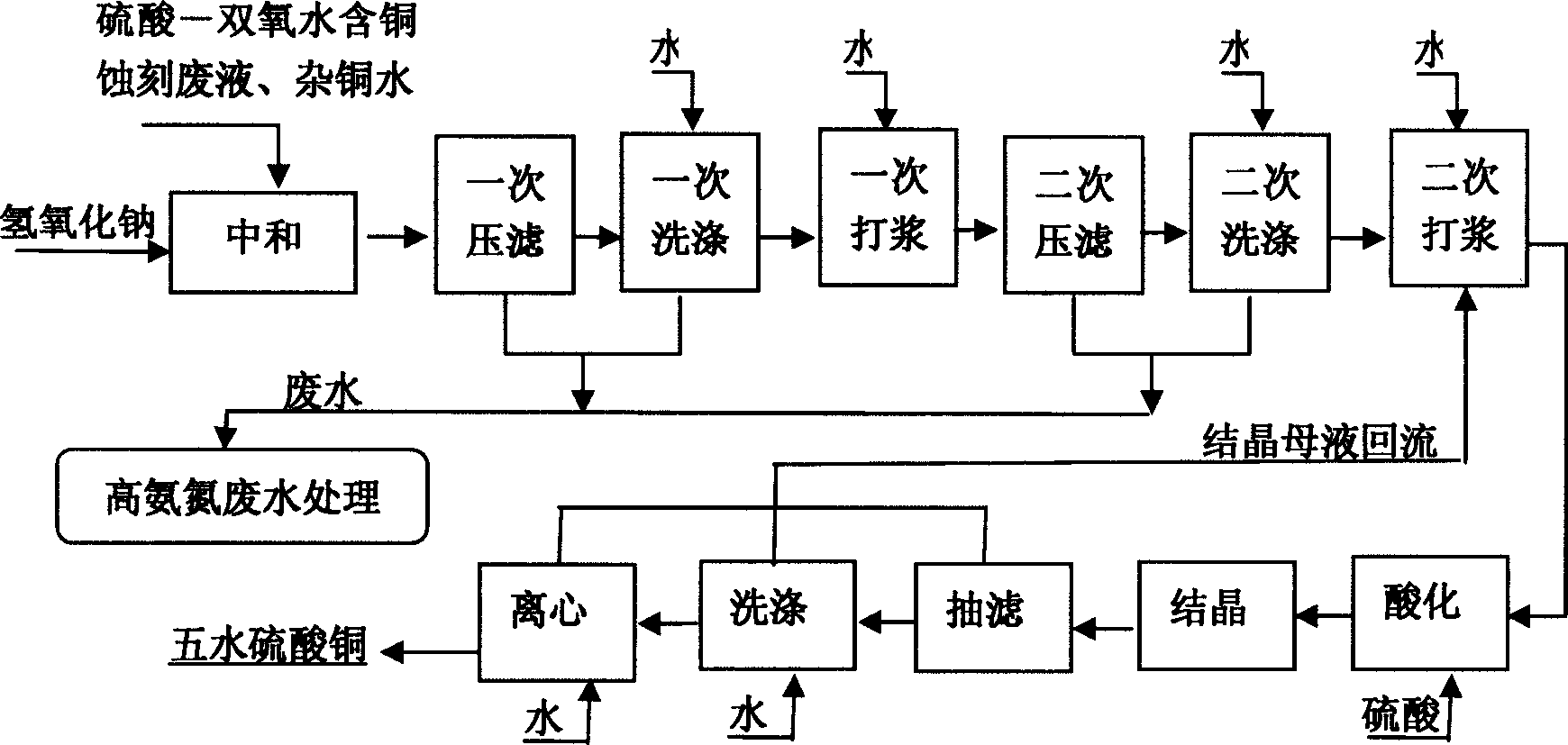
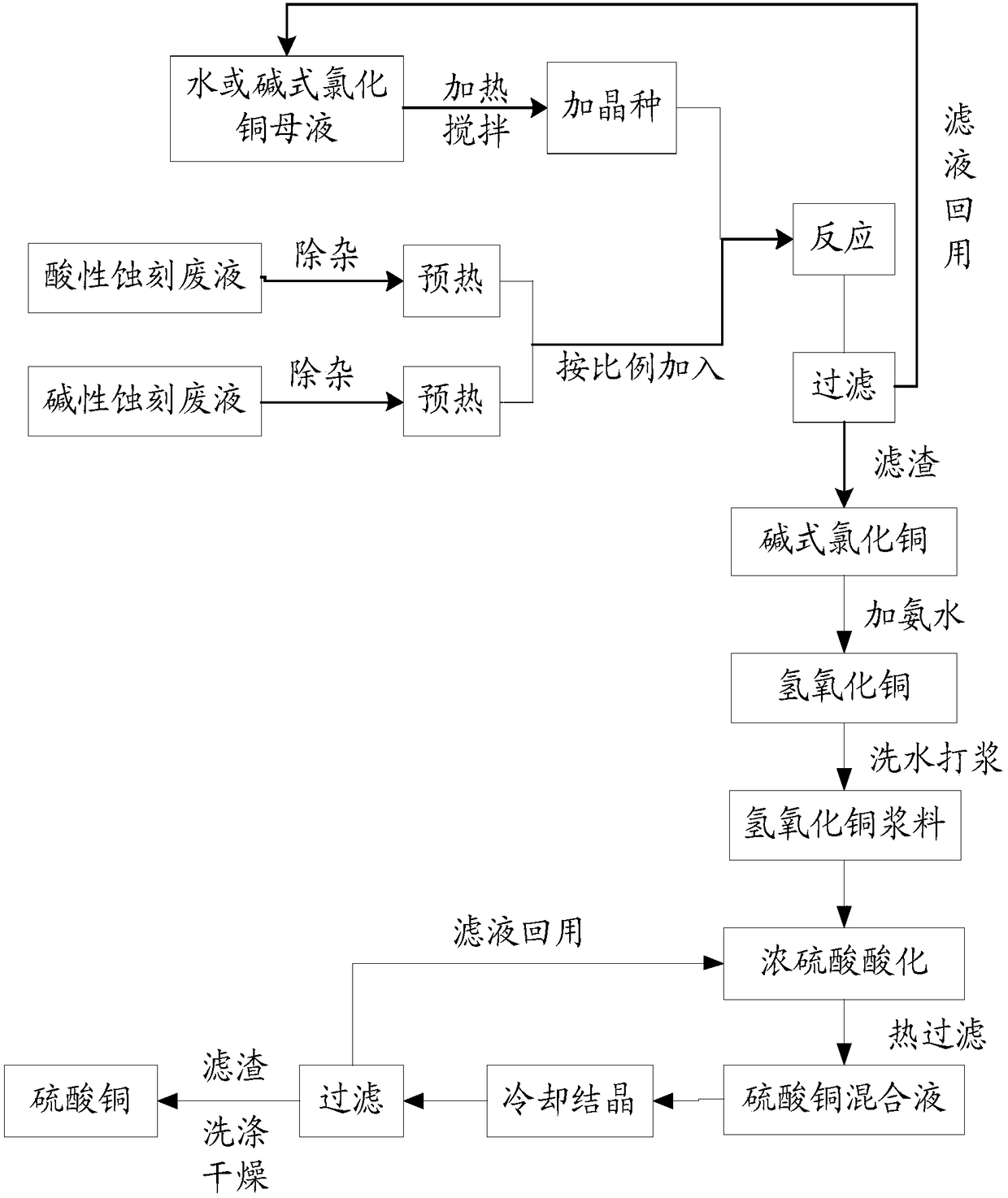
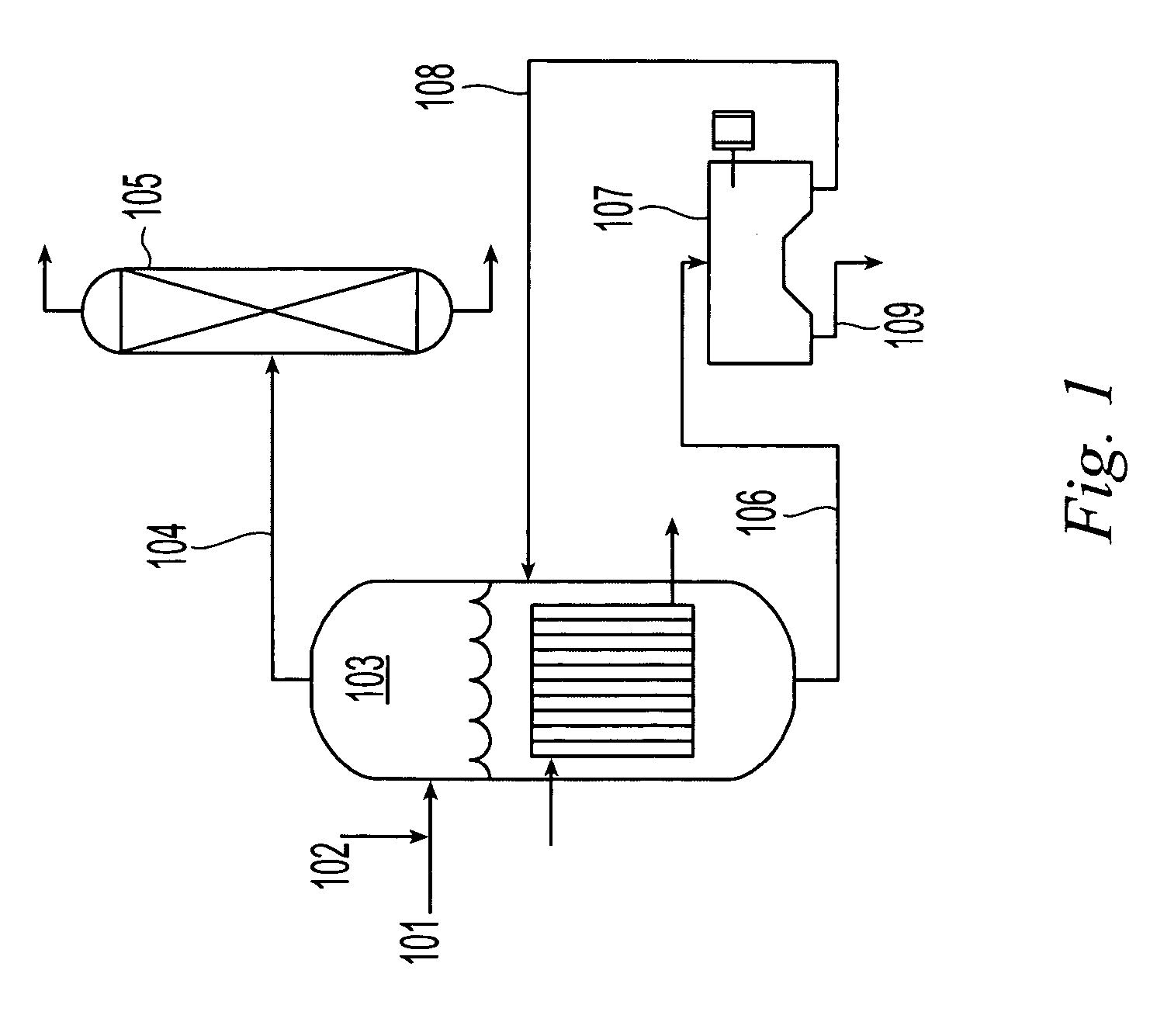
Method for producing basic copper chloride, cupric sulfate pentahydrate from copper-containing etching waste liquid
ActiveCN101391800AEfficient removalImprove product qualityCopper chloridesMultistage water/sewage treatmentCopper chlorideSulfate
The invention relates to a method for producing copper chloride hydroxide and blue vitriod by using cupriferous etching wastewater; the method comprises the following steps: acidic copper chloride etching wastewater and alkaline copper chloride etching wastewater are neutralized and crystallized to get acidic copper chloride crystal under the condition of strictly controlling filling liquid and the Ph range of a reaction kettle, and then pumped and filtrated, and centrifugated; part of the obtained alkaline copper chloride crystal is dried to obtain finished products while the other is added with NaOH solution for alkali conversion to obtain copper oxide, and then is acidulated by sulphuric acid, crystallized, washed, centrifugated, and dried to obtain blue vitriod products. The method for producing blue vitriod by directly using sulphuric acid-oxyful etching wastewater includes the following steps: sulphuric acid-oxyful etching wastewater and composition brass wasterwater in a PCB manufacture are blended together and added with NaOH to form cupric hydroxide precipitation which filtrated, washed, and then acidulated by sulphuric acid to obtain copper sulphate solution; after the copper sulphate solution is cooled, crystallized, centrifugated and dried, and the blue vitriod is obtained.
Owner:HUIZHOU DONGJIANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
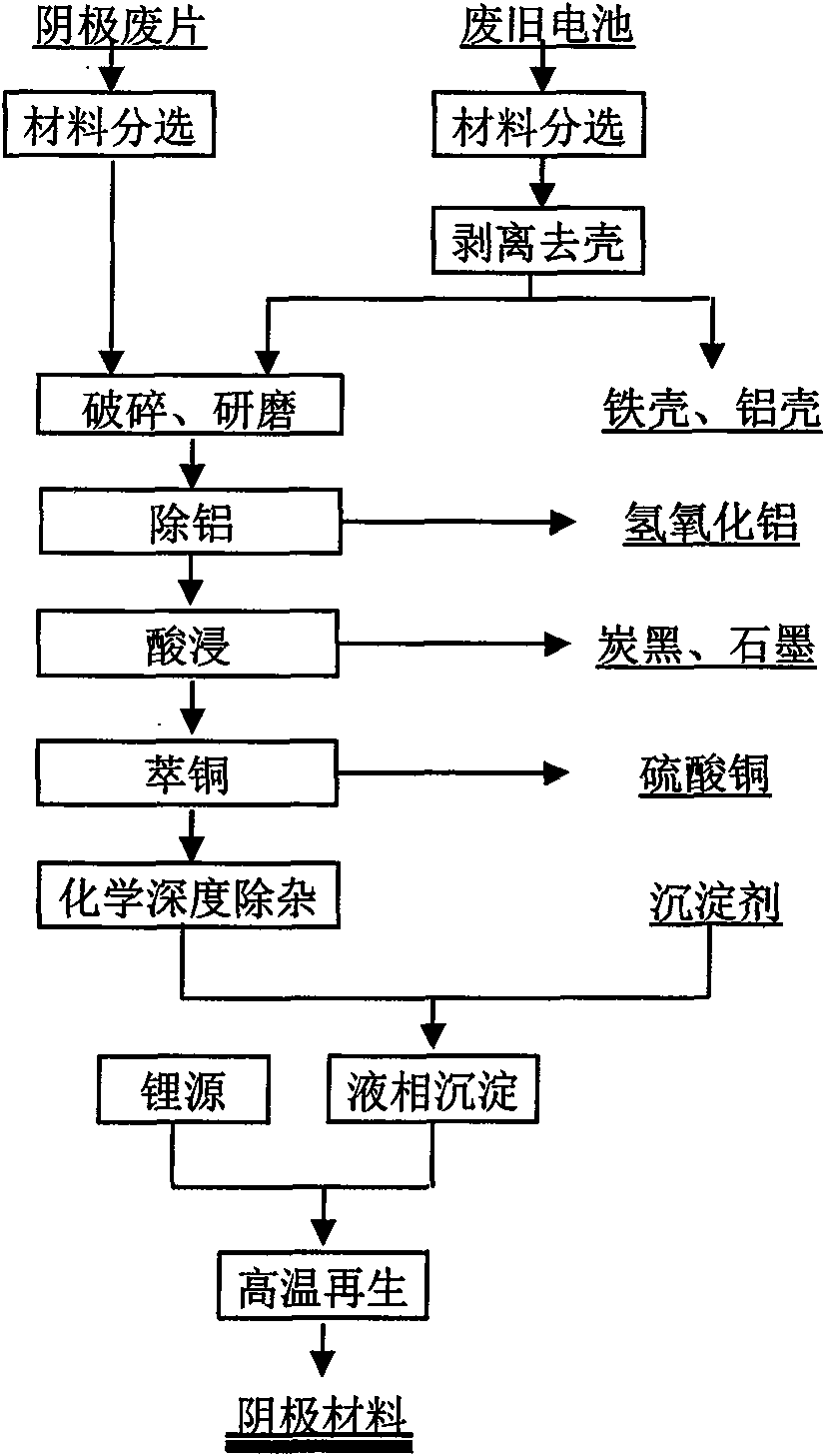
Method for recovering and recycling waste lithium ion battery cathode material
InactiveCN101555030AAchieve recyclingAchieve regenerationCobalt compoundsNickel compoundsEngineeringLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a method for recovering and recycling waste lithium ion battery cathode material, belonging to the fields of lithium ion battery material preparation and recycling use of waste resources. The method has the technical proposal with the key points as follows: the recovered waste batteries are sorted, cathode waste material (after being sorted) which is stripped to remove the shell and generated in the production process of the lithium ion battery is directly crushed and ground, and then processed by the procedures such as aluminum removing, acid dipping, copper extracting, chemical purification and the like under different conditions, so that byproduct materials such as aluminum hydroxide, carbon black, graphite, copper sulphate and the like are generated; reaction products are added with precipitator with certain concentration for liquid-phase precipitation and then added with lithium source, so that cathode material can be generated in the high temperature environment. The technical proposal successfully realizes the valuable constituent recovery and cathode material regeneration of the waste lithium ion battery cathode material.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
Method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge
The invention relates to a method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge, belonging to the technical field of chemical engineering and metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: acid leaching, vulcanizing for separation and enrichment, hot-pressure leaching, extracting for separation, hot-press oxidizing chromium, purifying chromium solution, extracting ferric chloride and the like. The method has obvious advantages of strong adaptability to different kinds of plating sludge, high utilization of metal resources, high value-added content of product,less process waste residue, thorough deintoxication and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
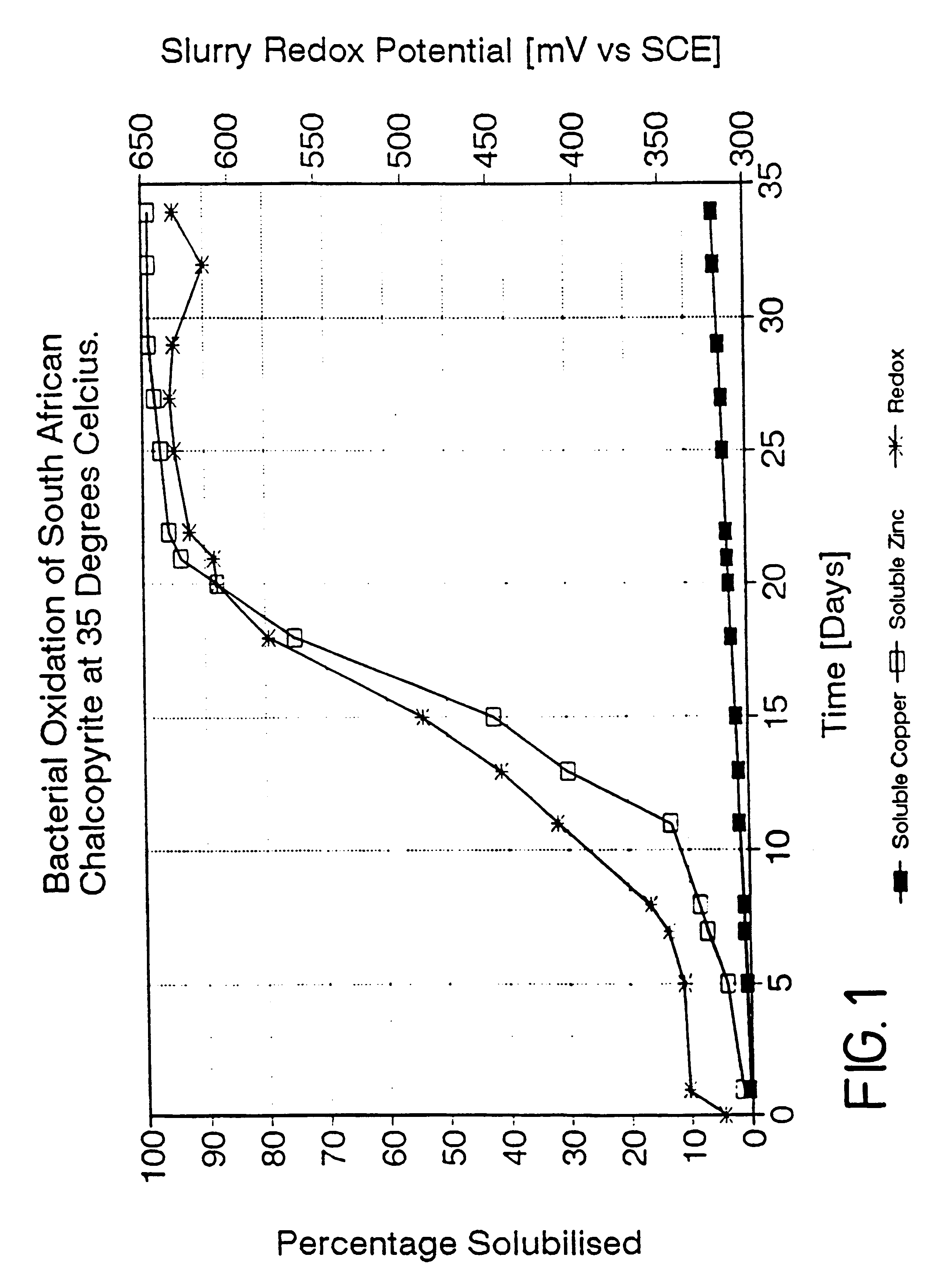
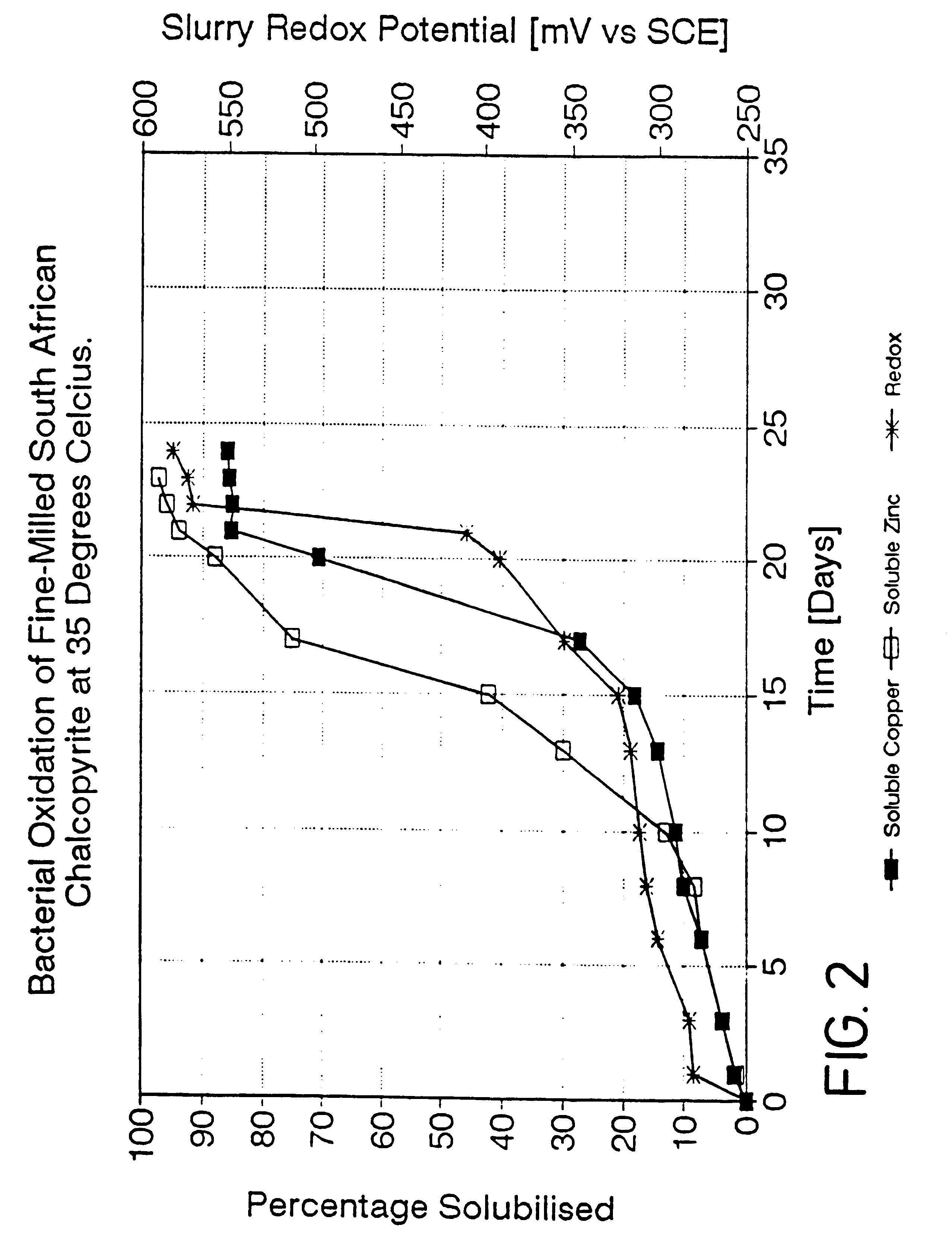
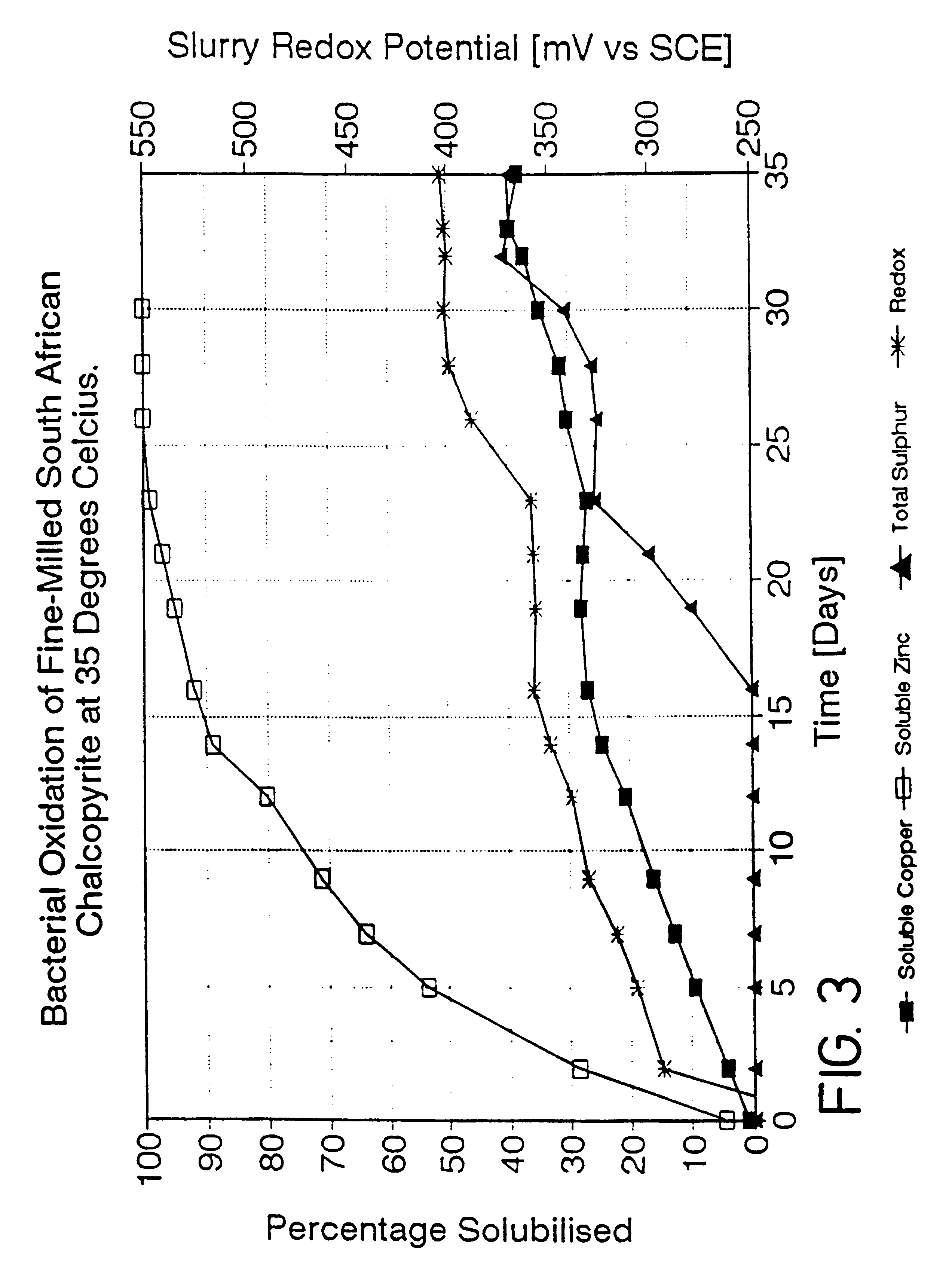
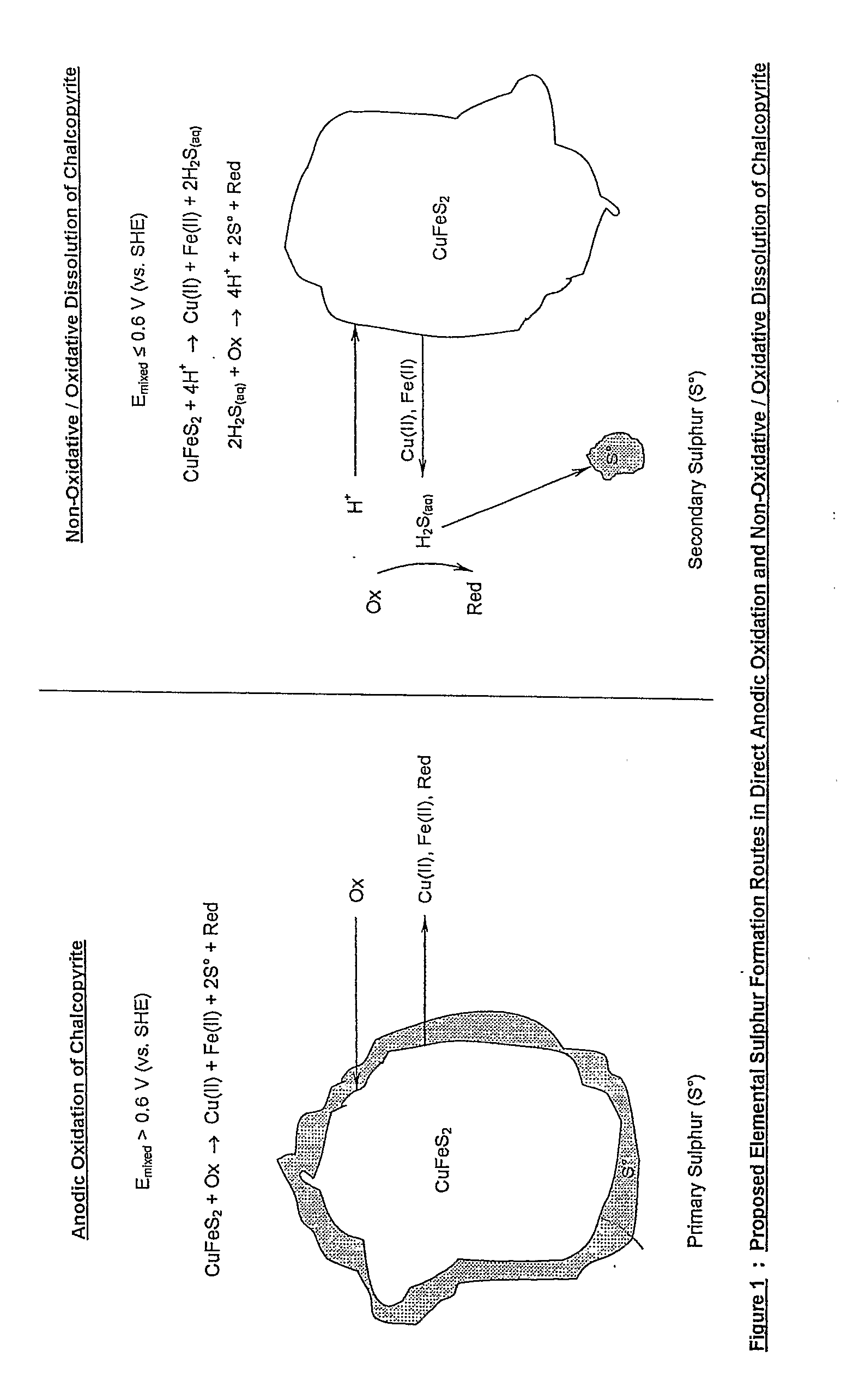
Process for the rapid leaching of chalcopyrite in the absence of catalysts
InactiveUS6277341B1Increase surface areaImprove misalignmentSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
Owner:MINTEK
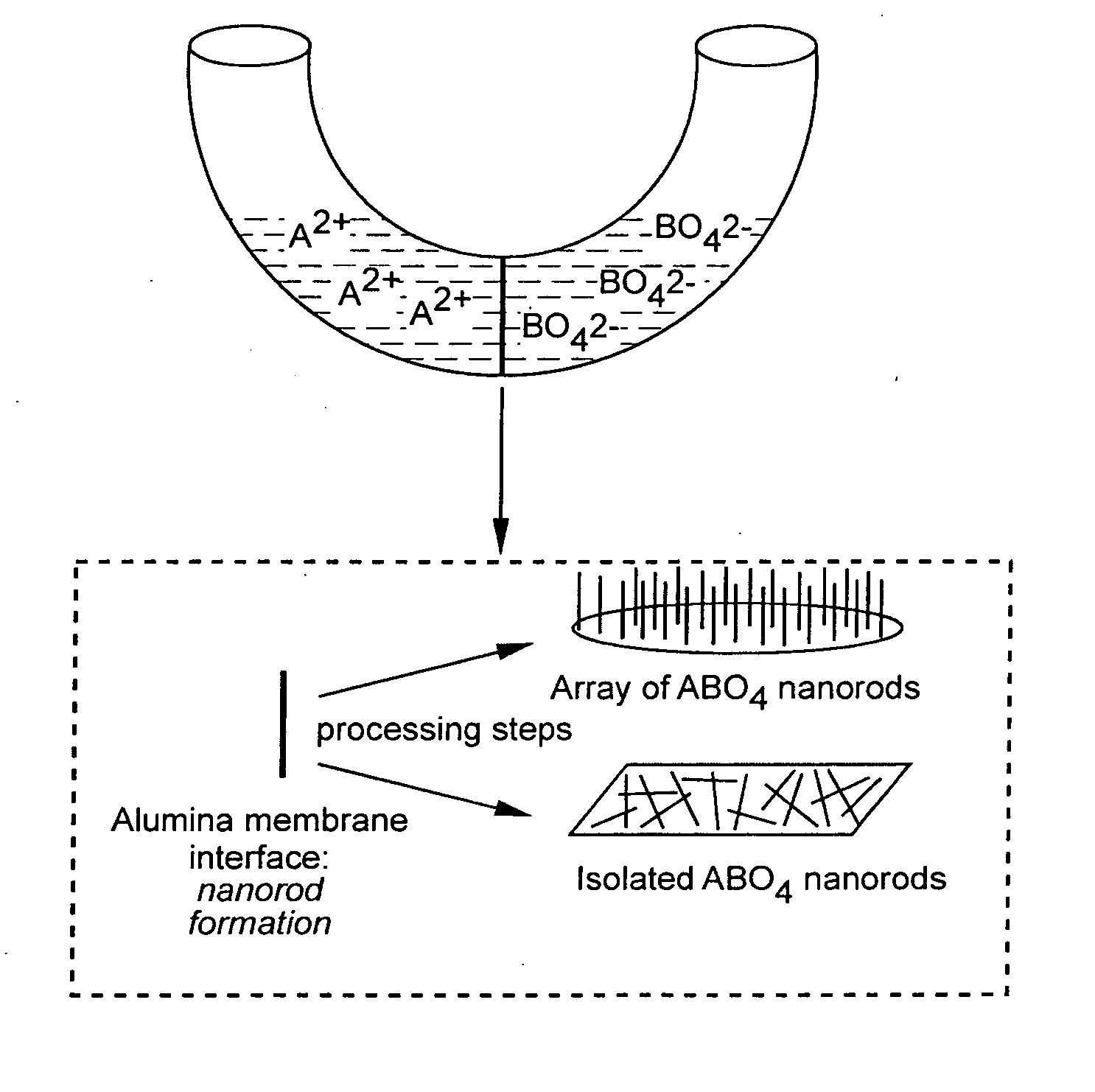
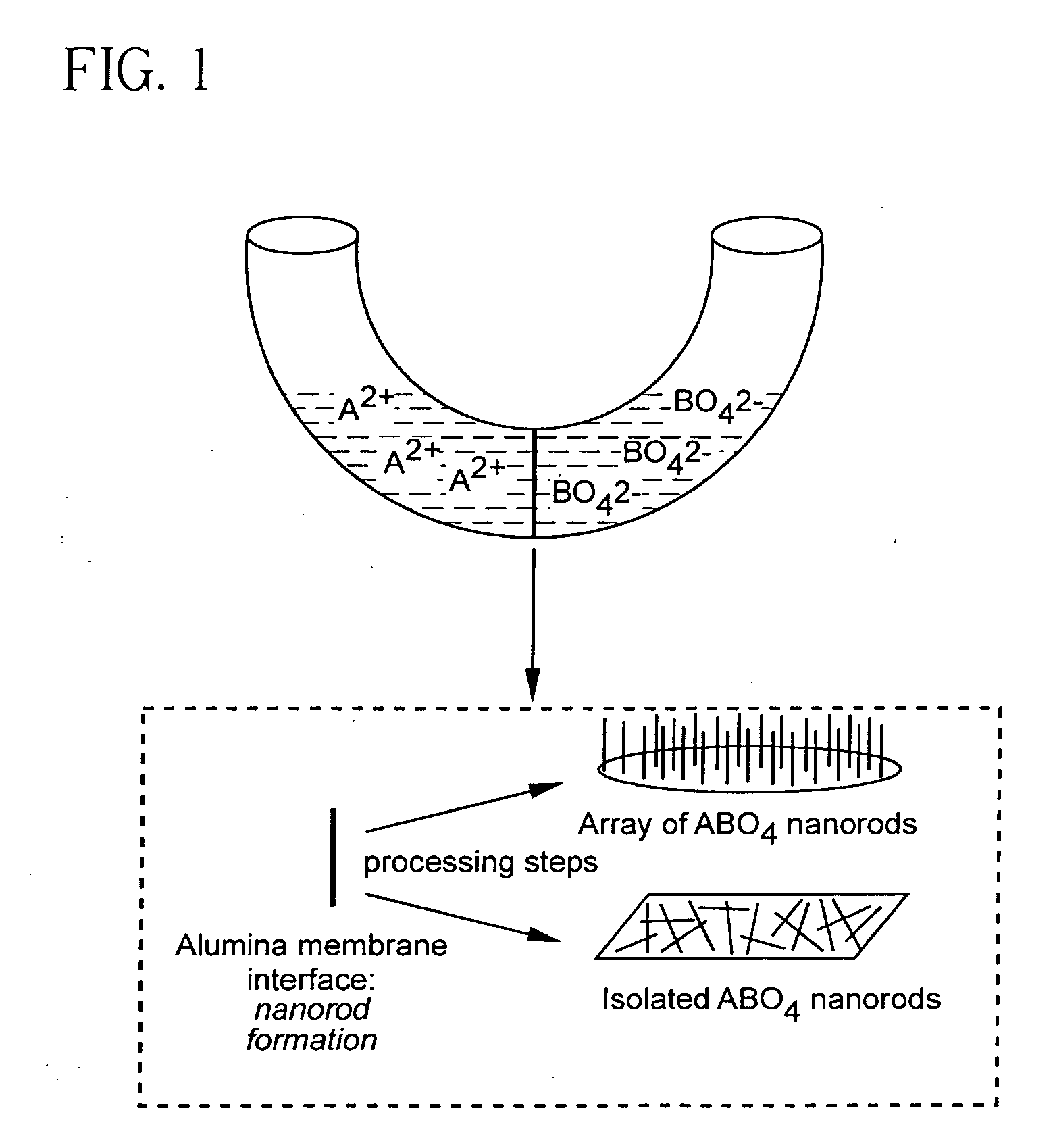
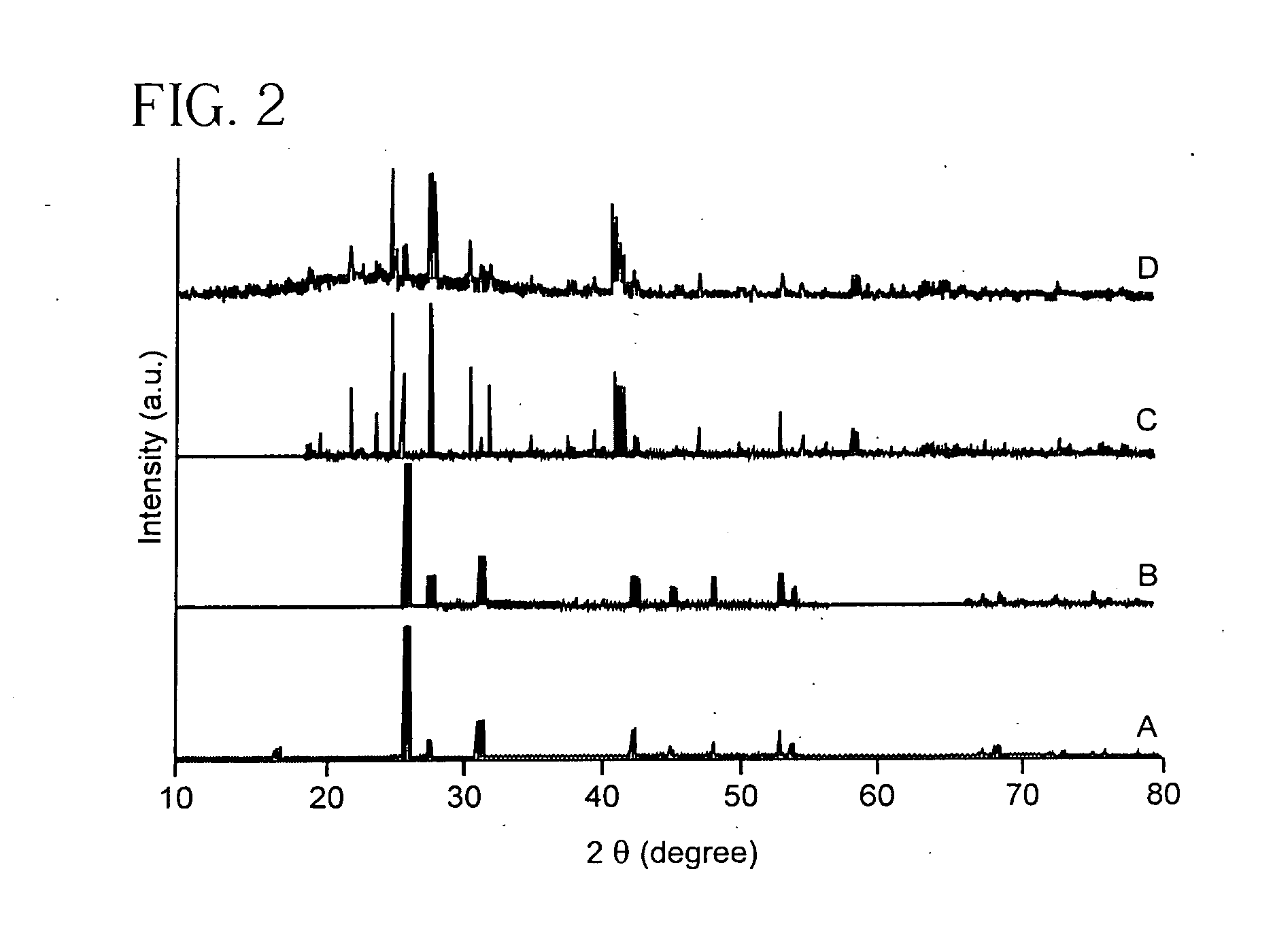
Metal oxide and metal fluoride nanostructures and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070113779A1Easy to controlOvercomes shortcomingMercury oxidesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSingle crystalNanostructure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
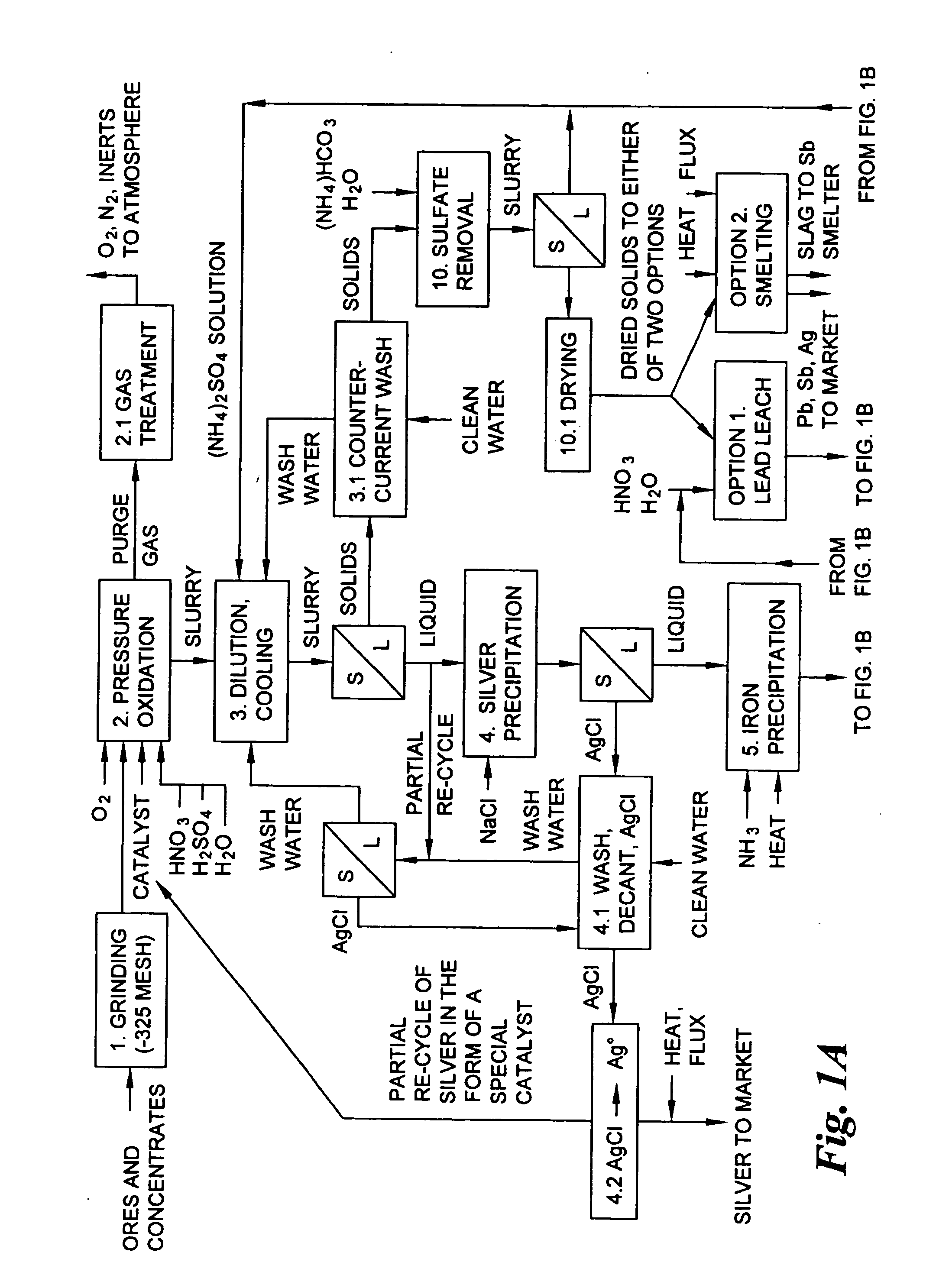
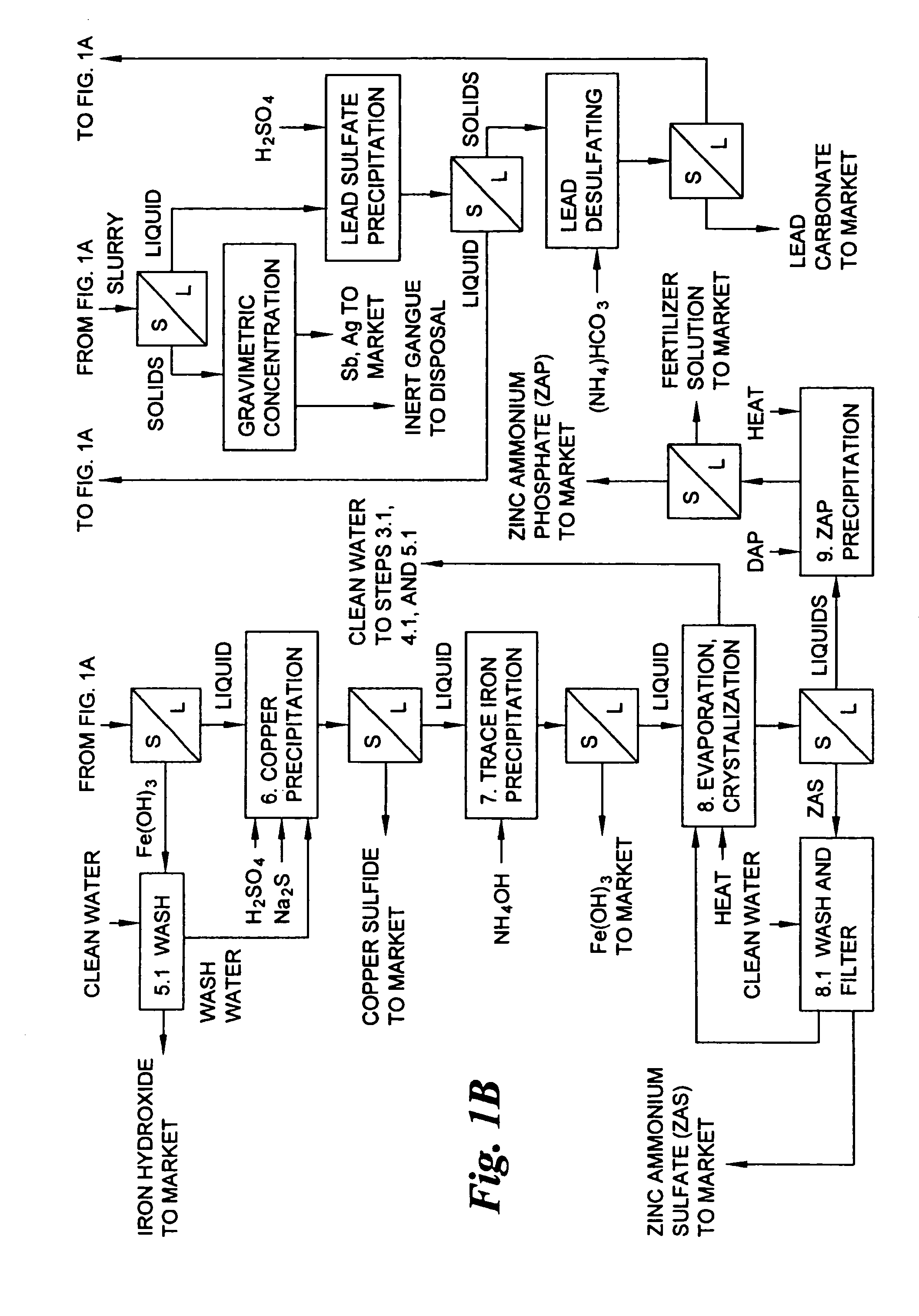
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
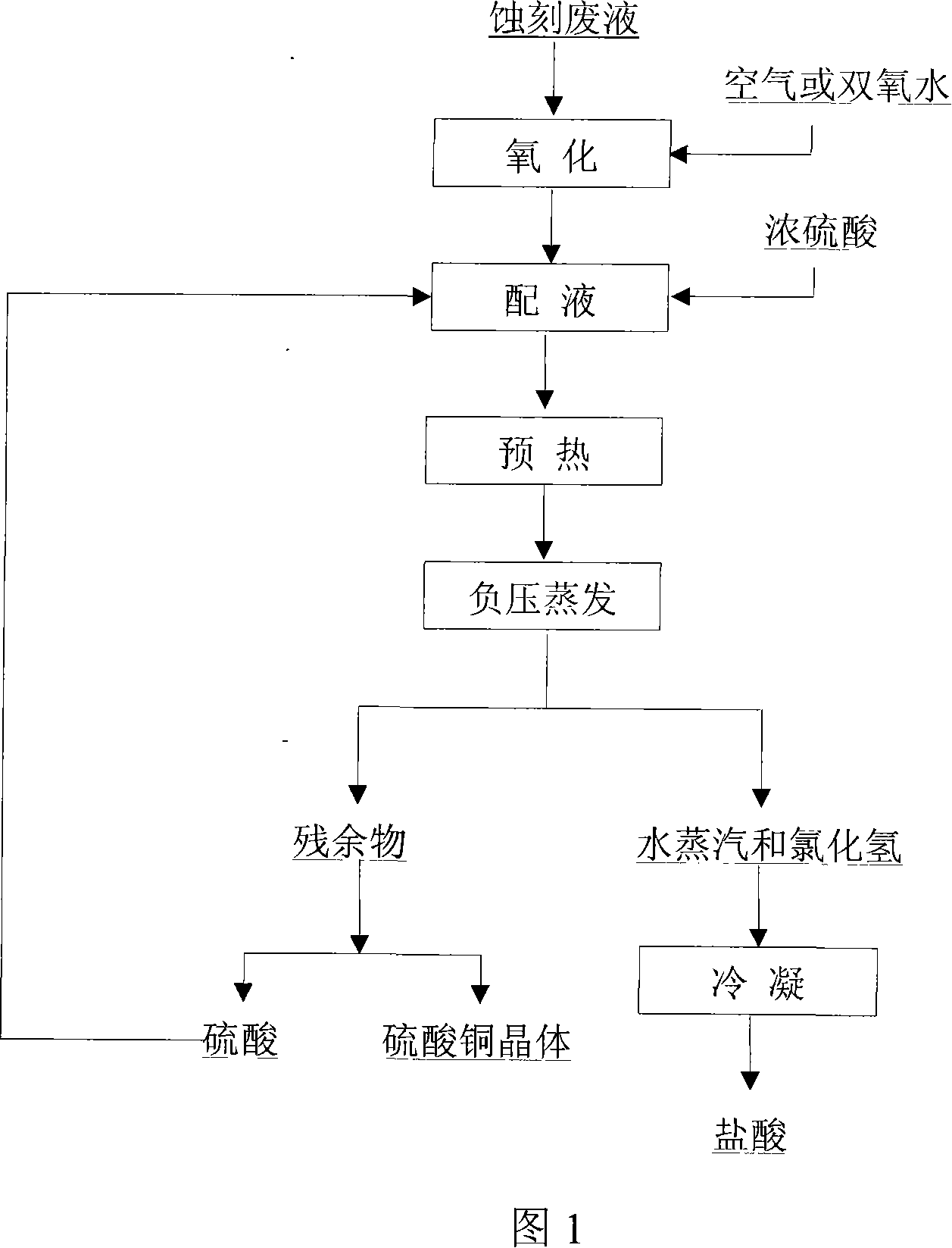
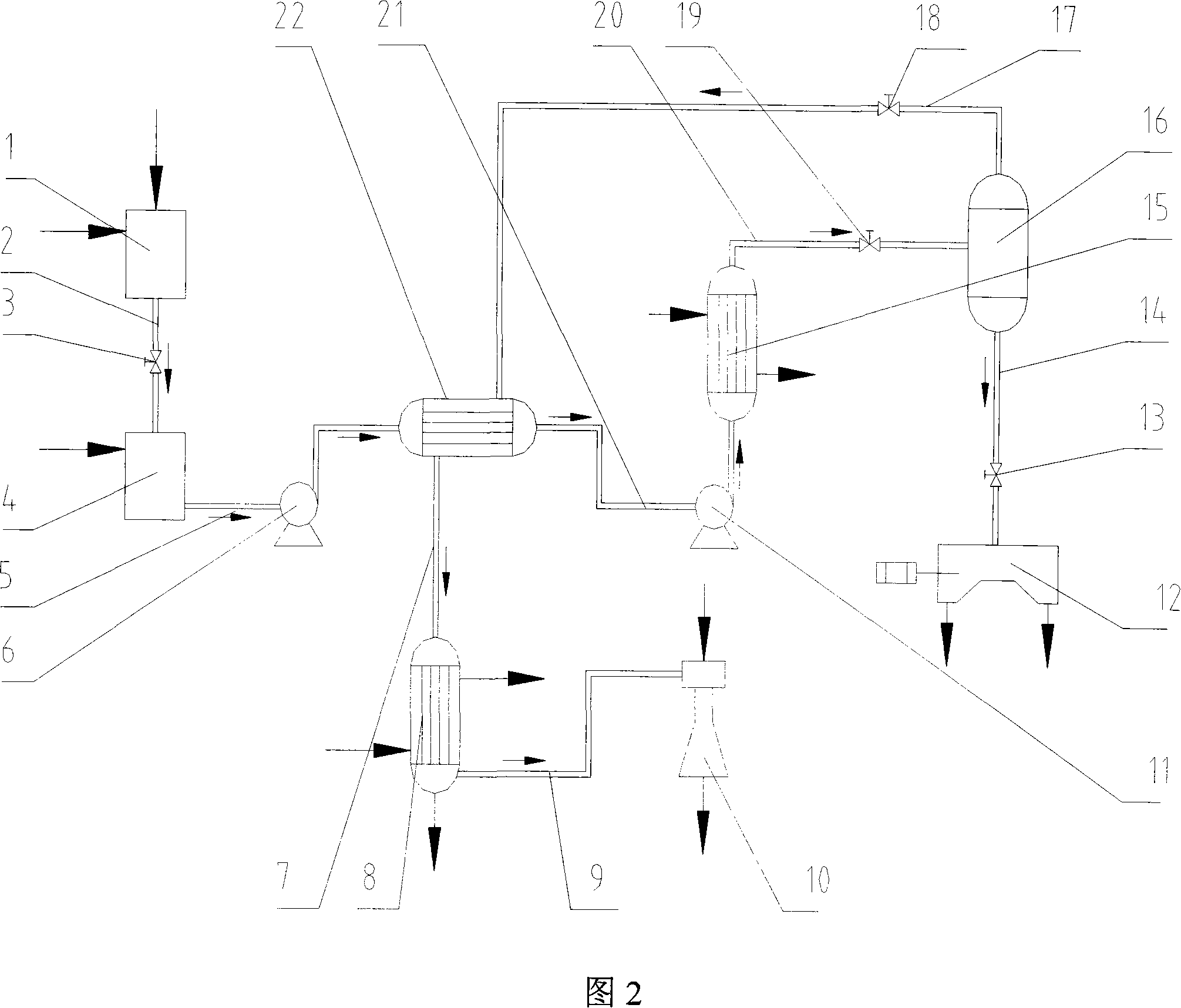
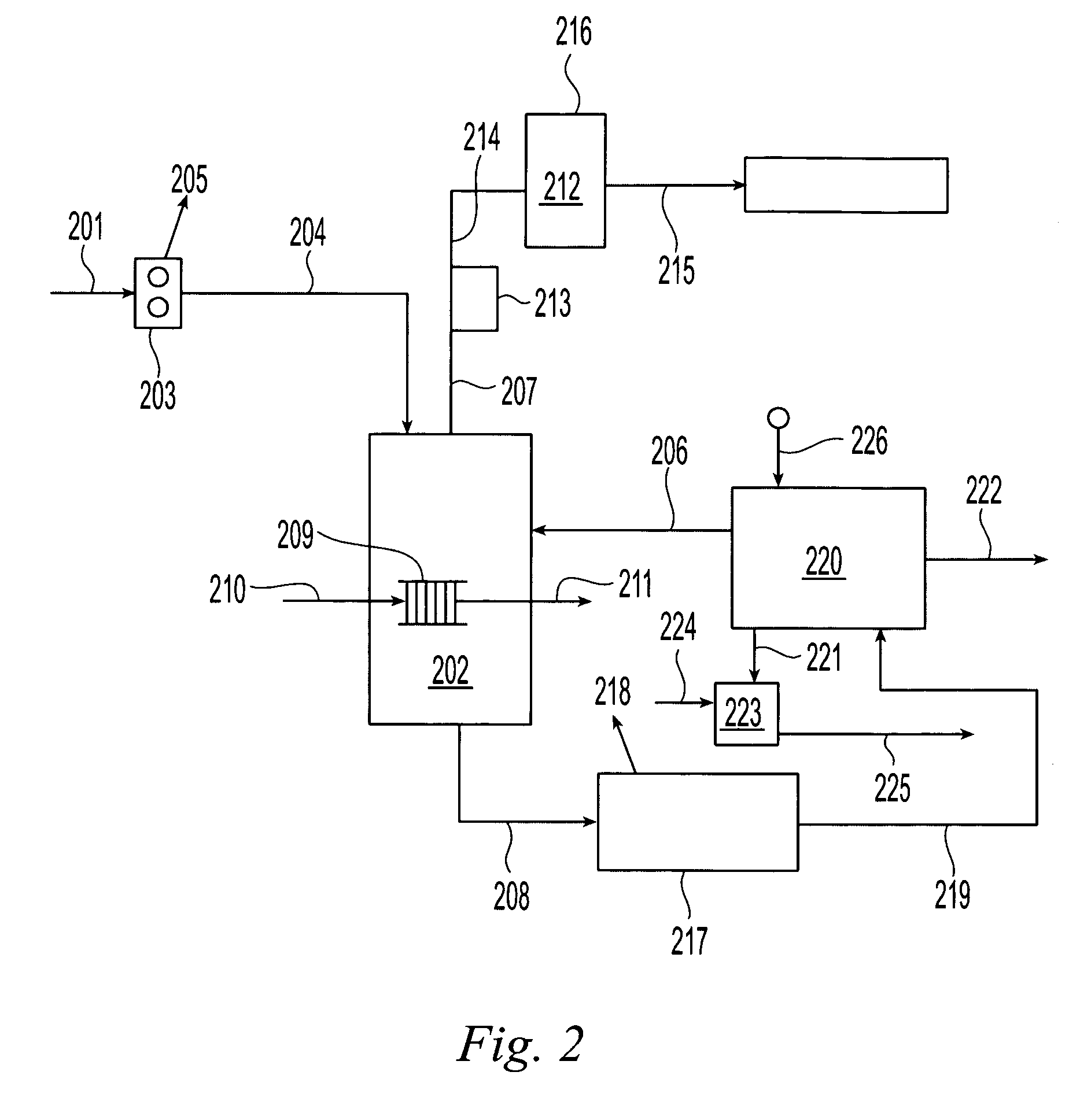
Method and system for reclaiming valuable resource in acidic etching waste liquid
InactiveCN101215062AImprove liquidityReduce cooling energy consumptionChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteWater vapor
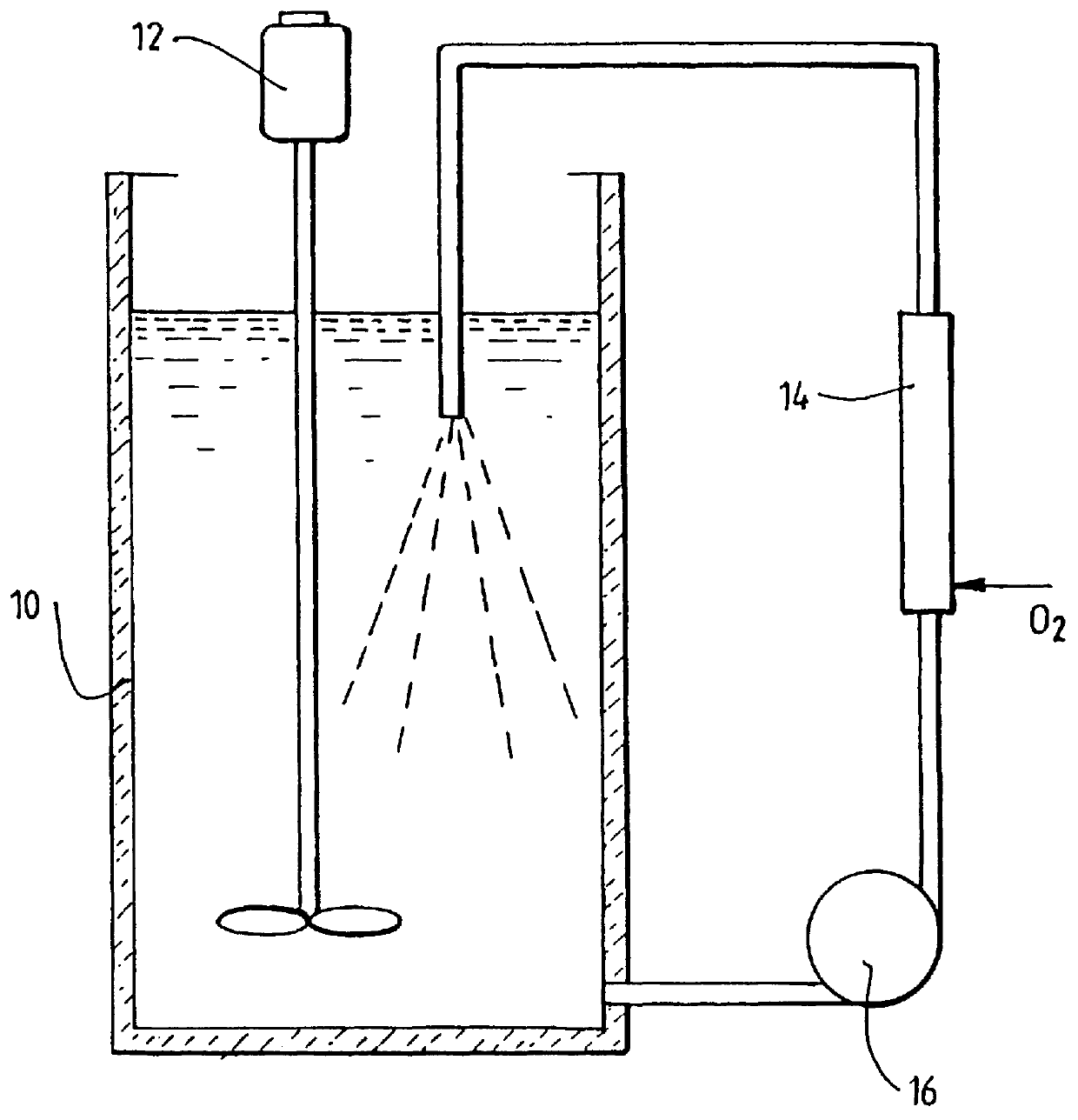
Provided are system of value resource in acidic corrosion waste fluid and a recycling method. The recycling method of the invention includes the following steps that adding oxidation agent and concentrated sulfuric acid into the corrosion waste fluid, pre-heating and heating the corrosion waste fluid, evaporating out water vapor and hydrogen chloride under negative pressure and recycling hydrochloric acid, the residue separates hydric sulphate from blue copperas crystal via centrifugal filtration and recycle hydric sulphate, washing blue copperas crystal by blue copperas crystal solution and absolute ethyl alcohol and recycling blue copperas. The recycling system comprises an oxidation ditch, a dosage bunker, a pre-heater, a heat booster, an evaporation tank, a filter, a cooler, a spraying and absorbing device and the like. The recycling method of the invention increases the recovery rate of metal copper and hydrogen chloride, with both recovery rates more than 99%. The method can employ scheme of batch operation or continuous recycling, which is adapted for industry utilization.
Owner:郝屿
Production of silver sulfate grains using organo-sulfate or organo-sulfonate additives
ActiveUS7261867B1Uniform morphologyUniform sizePigmenting treatmentCosmetic preparationsOrganic sulfonic acidSulfonate
An aqueous precipitation process for the preparation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, comprising reacting an aqueous soluble silver salt and an aqueous soluble source of inorganic sulfate ion in an agitated precipitation reactor vessel and precipitating particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, wherein the reaction and precipitation are performed in the presence of an aqueous soluble organo-sulfate or organo-sulfonate additive compound, the amount of additive being a minor molar percentage, relative to the molar amount of silver sulfate precipitated, and effective to result in precipitation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate having a mean grain size of less than 50 micrometers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
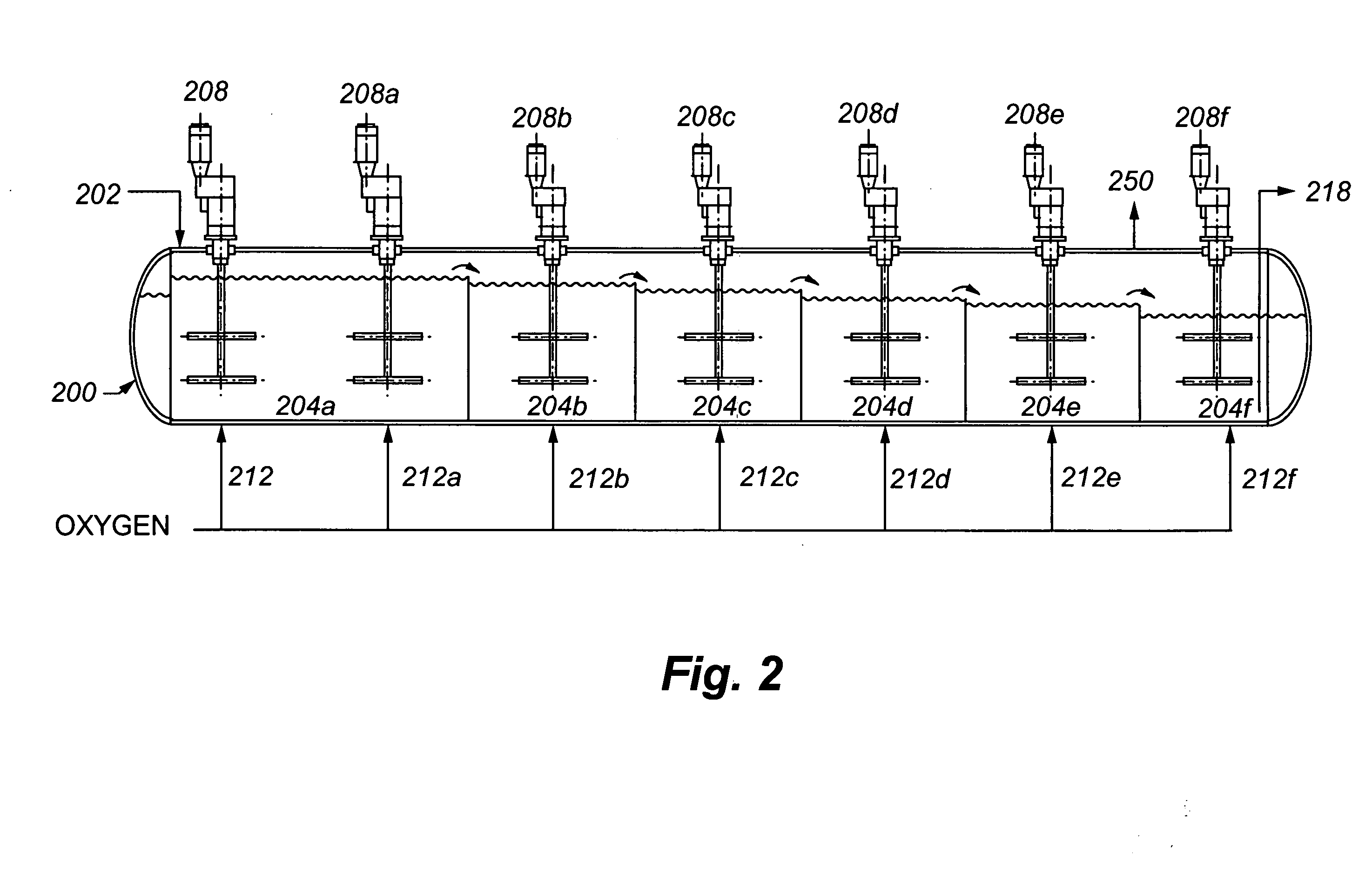
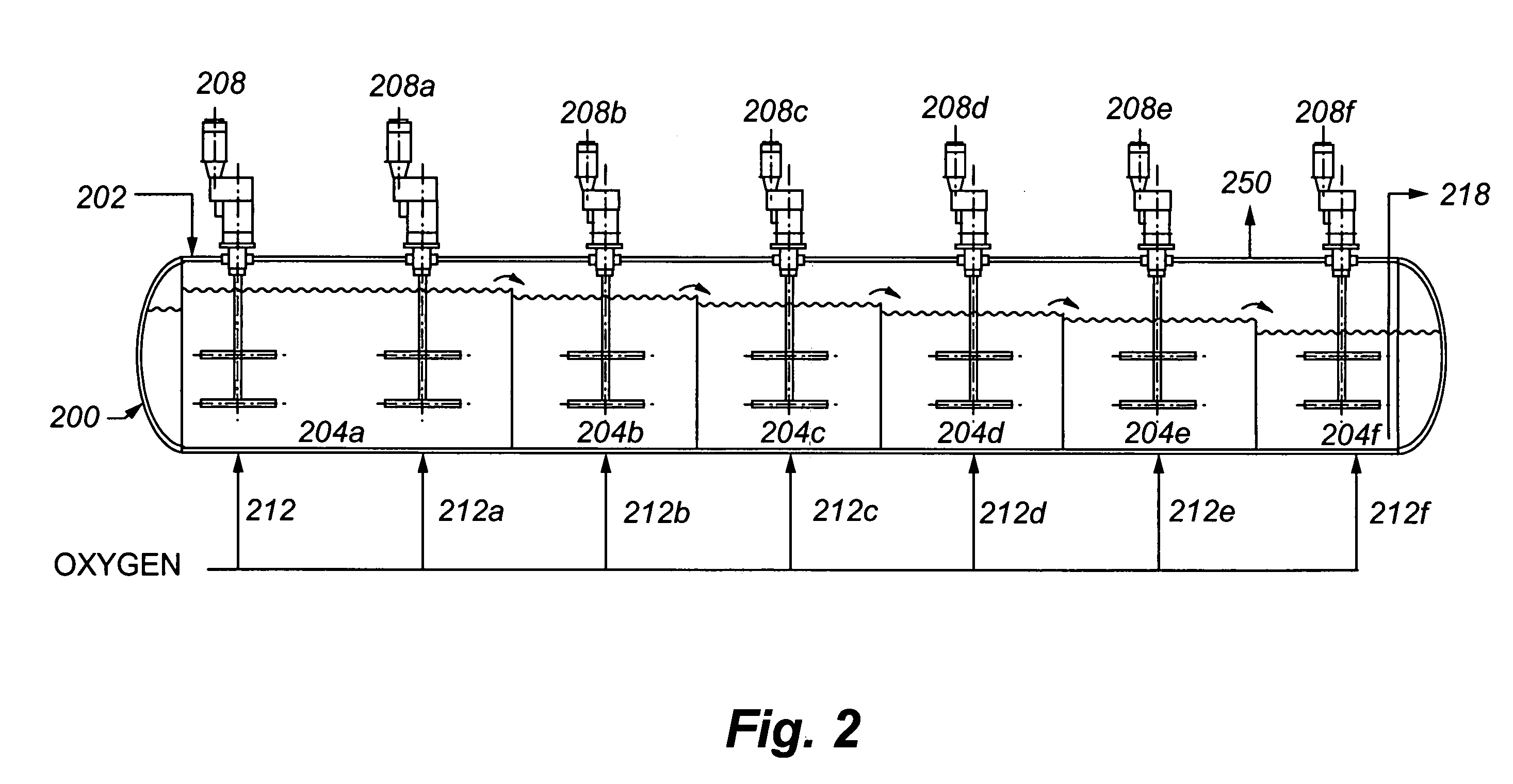
Autoclave with underflow dividers
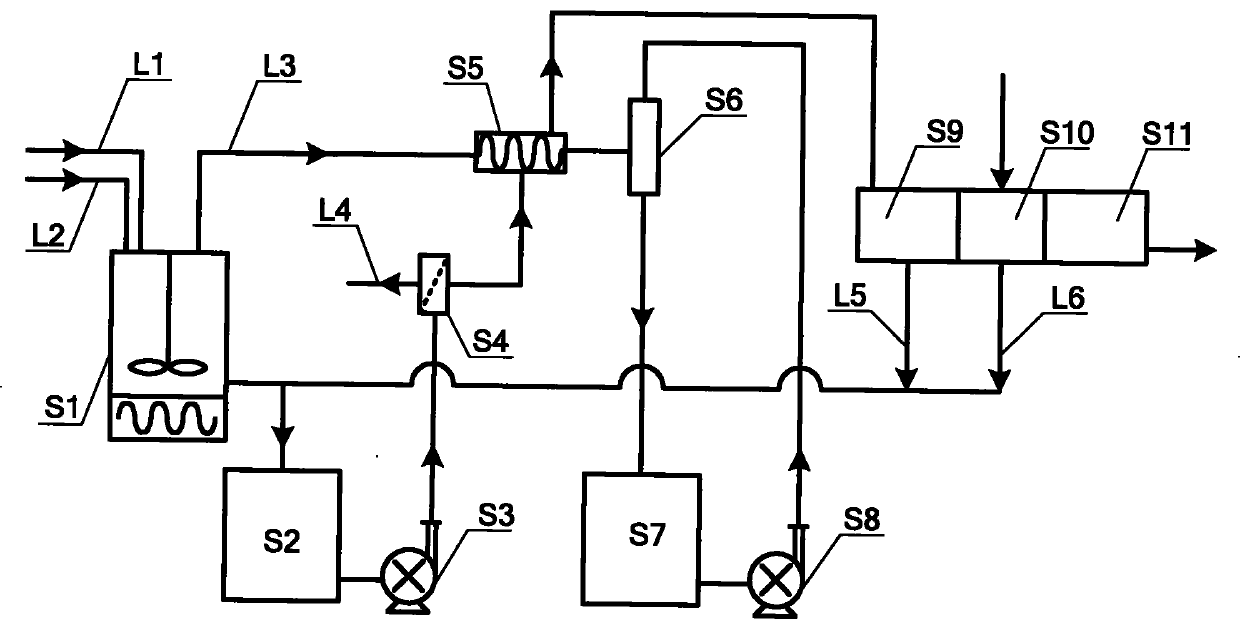
InactiveUS20070217285A1Lower Level RequirementsEasy constructionSolvent extractionRotary stirring mixersEngineeringAutoclave
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
Chloride assisted hydrometallurgical extraction of metal
A process for the extraction of a metal from an ore or concentrate comprises subjecting the ore or concentrate to pressure oxidation in the presence of oxygen and an acidic solution containing halogen ions and a source of bisulphate or sulphate ions, such as H2SO4. The metals which can be extracted by the process comprises copper as well as non-cuprous metals such as zinc, nickel and cobalt. During pressure oxidation the metal may be precipitated as an insoluble basic salt, such as basic copper sulphate, or substantially completely solubilized and precipitated later as the basic metal salt.
Owner:CESL LIMITED
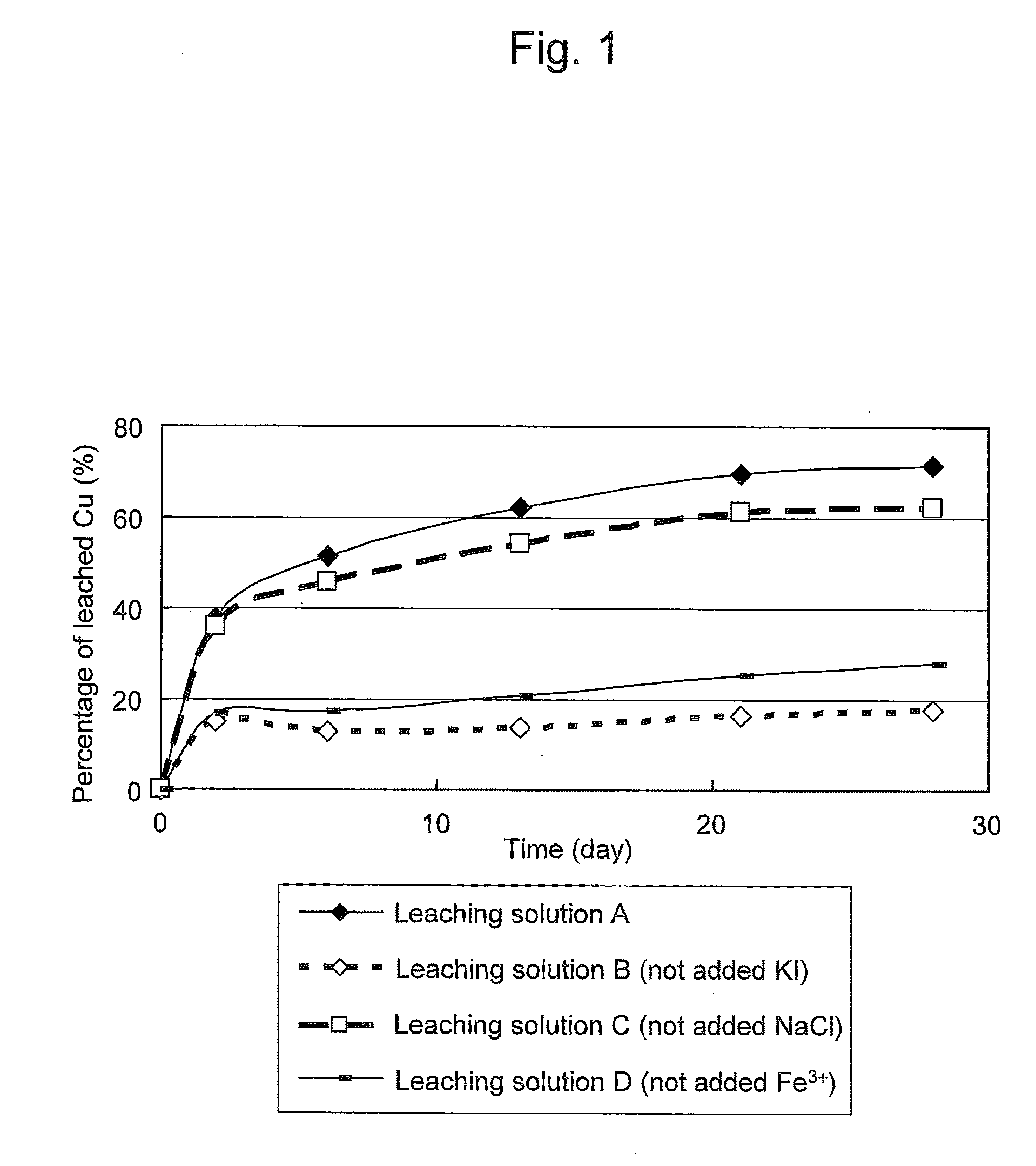
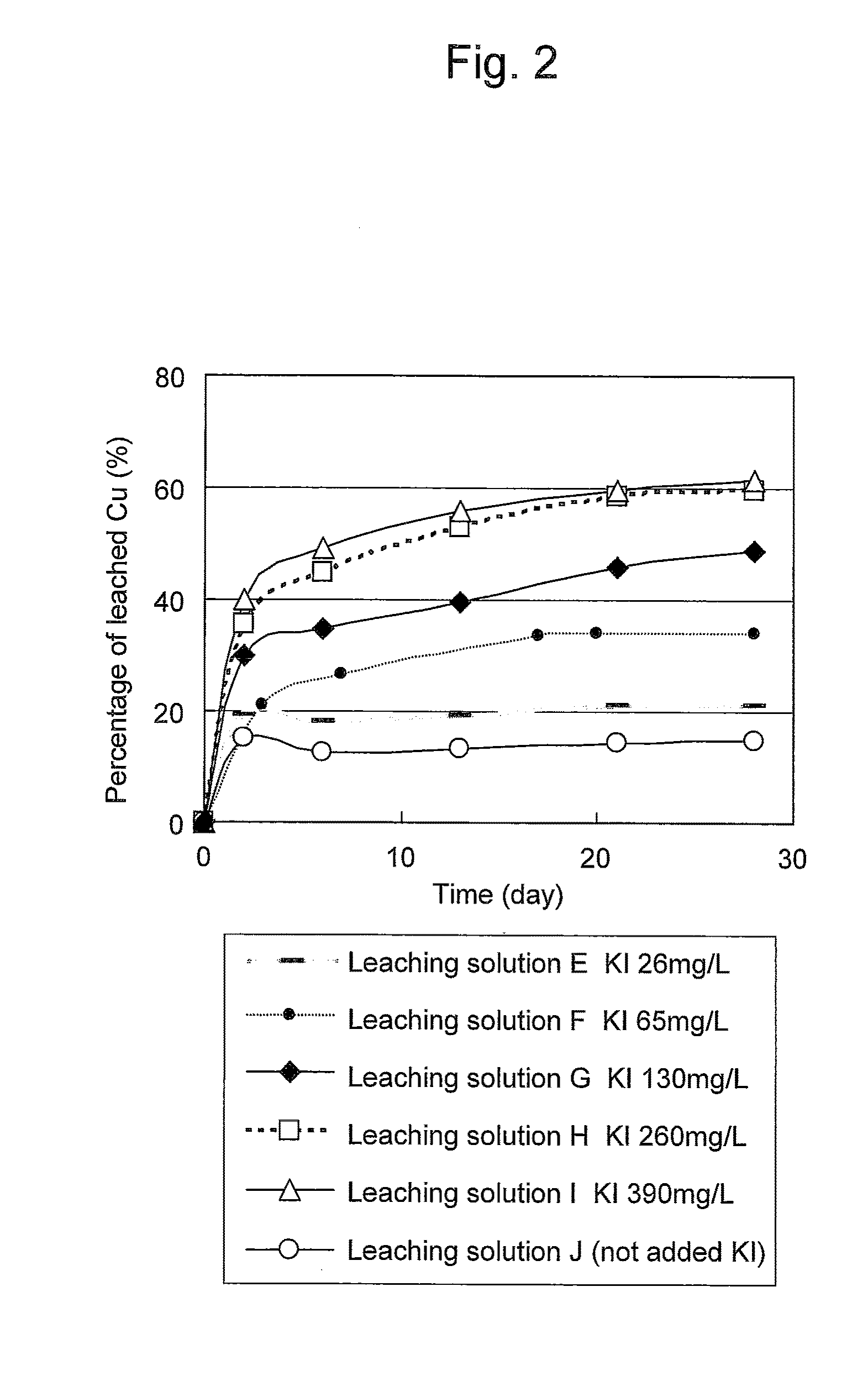
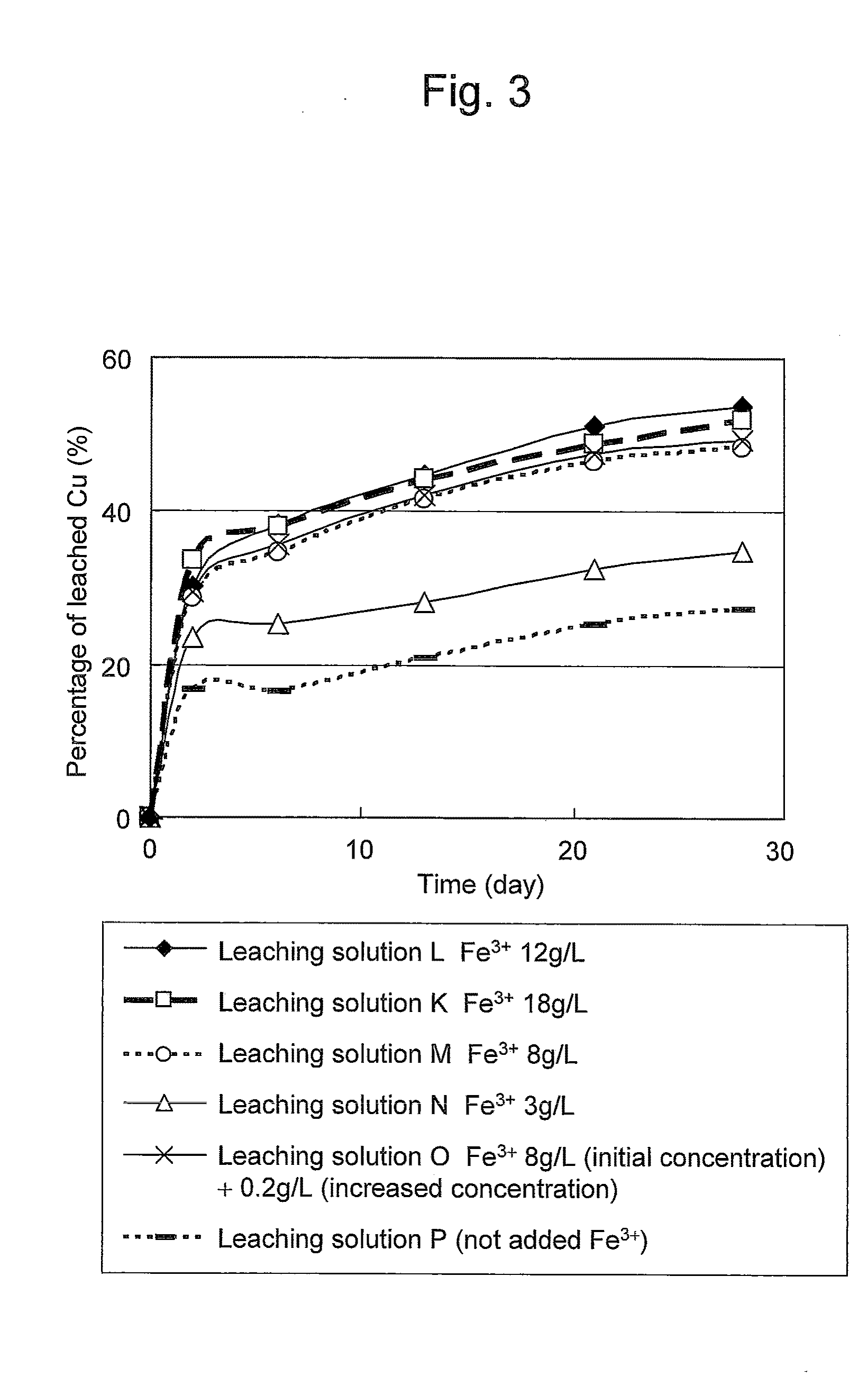
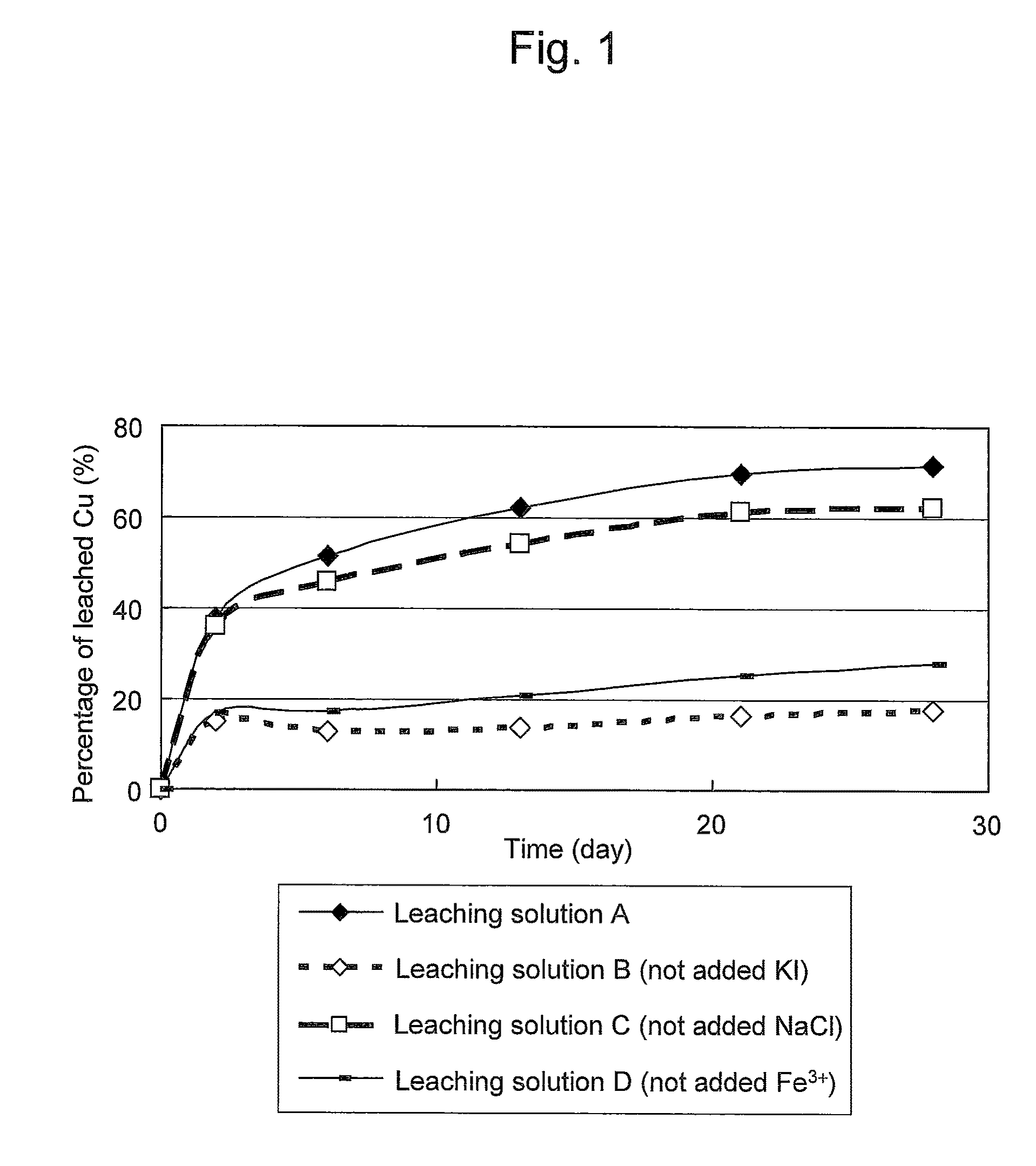
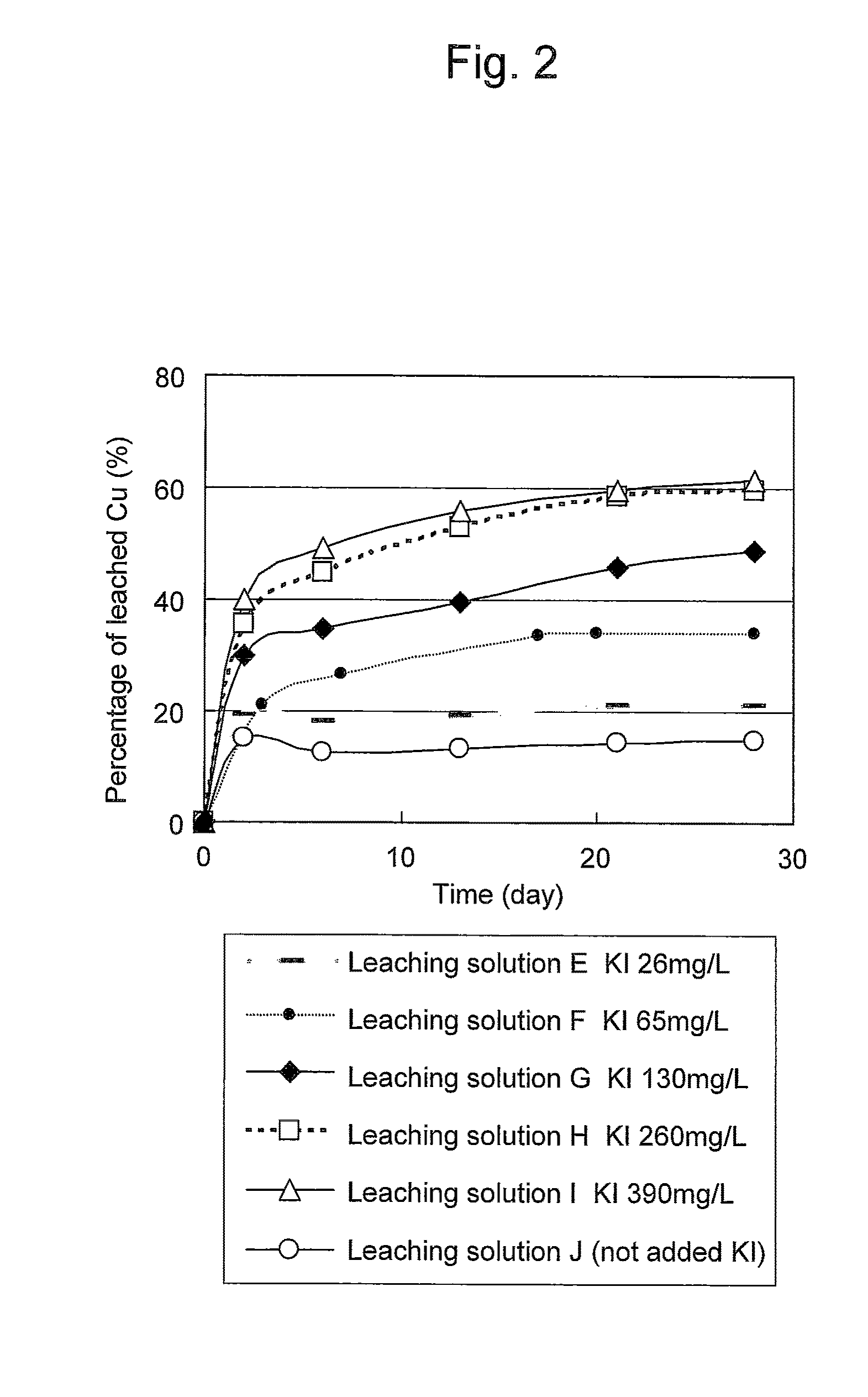
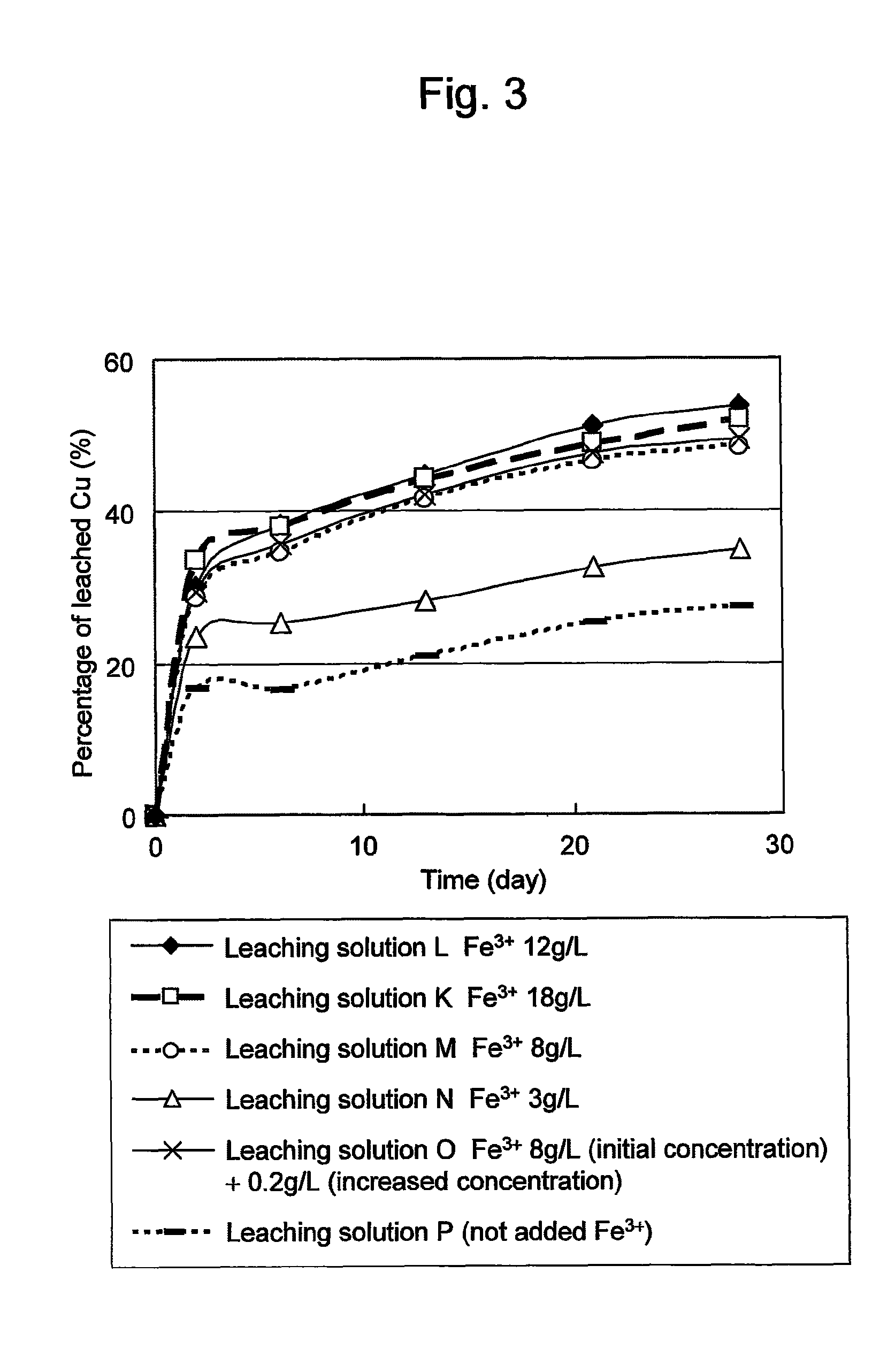
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS20100018349A1Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Technique for extracting copper ions from industrial wastewater
ActiveCN104355474AHigh extraction rateGood removal effectWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeIon exchangeIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a technique for extracting copper ions from industrial wastewater, which comprises the following steps: 1) respectively pretreating an acidic coppery etching waste liquid and an alkaline coppery etching waste liquid; 2) neutralization and precipitation: carrying out neutralization reaction on the acidic coppery etching waste liquid and alkaline coppery etching waste liquid in a neutralizing tank, and precipitating to obtain a basic copper chloride precipitate and a filtrate; 3) adding the basic copper chloride precipitate into a reaction tank, and adding sulfuric acid to obtain a copper sulfate crystal; 4) sending the filtrate into an ion exchange resin tower to adsorb the rest unrecovered copper ions, thereby obtaining ammonia nitrogen wastewater; and 5) carrying out evaporative concentration on the ammonia nitrogen wastewater by a vapor recompression technique, crystallizing the concentrate to produce an ammonium chloride product, treating the condensation water by an ion-exchange process, and discharging after reaching the standard. The technique can greatly enhance the extraction rate of copper ions, solves the problem of environmental pollution caused by heavy metal ions, and can produce other products from the waste liquid to implement cyclic utilization, thereby saving the resources and protecting the environment.
Owner:清远市中宇环保实业有限公司
Method for concentration of gold in copper sulfide minerals
ActiveUS20100242681A1Efficient separationEffective recoveryPhotography auxillary processesGold compoundsEnrichment methodsHydrometallurgy
Disclosed herein is a method for concentrating gold contained in a leach residue obtained in a copper hydrometallurgical process for recovering copper from a copper sulfide mineral to efficiently separate and recover gold from the leach residue. According to the method, a gold-bearing copper sulfide mineral is subjected to pressure leaching with sulfuric acid at a temperature higher than 102° C. and 112° C. or lower to obtain a leach residue, and the leach residue is subjected to flotation to separate it into a float fraction and a sink fraction. The float fraction obtained by flotation is desulfurized by heating at a temperature of 250 to 800° C. under an inert atmosphere to obtain a desulfurized product. The desulfurized product is subjected to oxidative roasting by heating at a temperature of 600 to 800° C. under an atmosphere of flowing oxygen or air to obtain an oxidatively-roasted product. The oxidatively-roasted product is dissolved in a sulfuric acid solution to obtain a copper solution, and a gold-bearing residue is separated and recovered from the copper solution.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
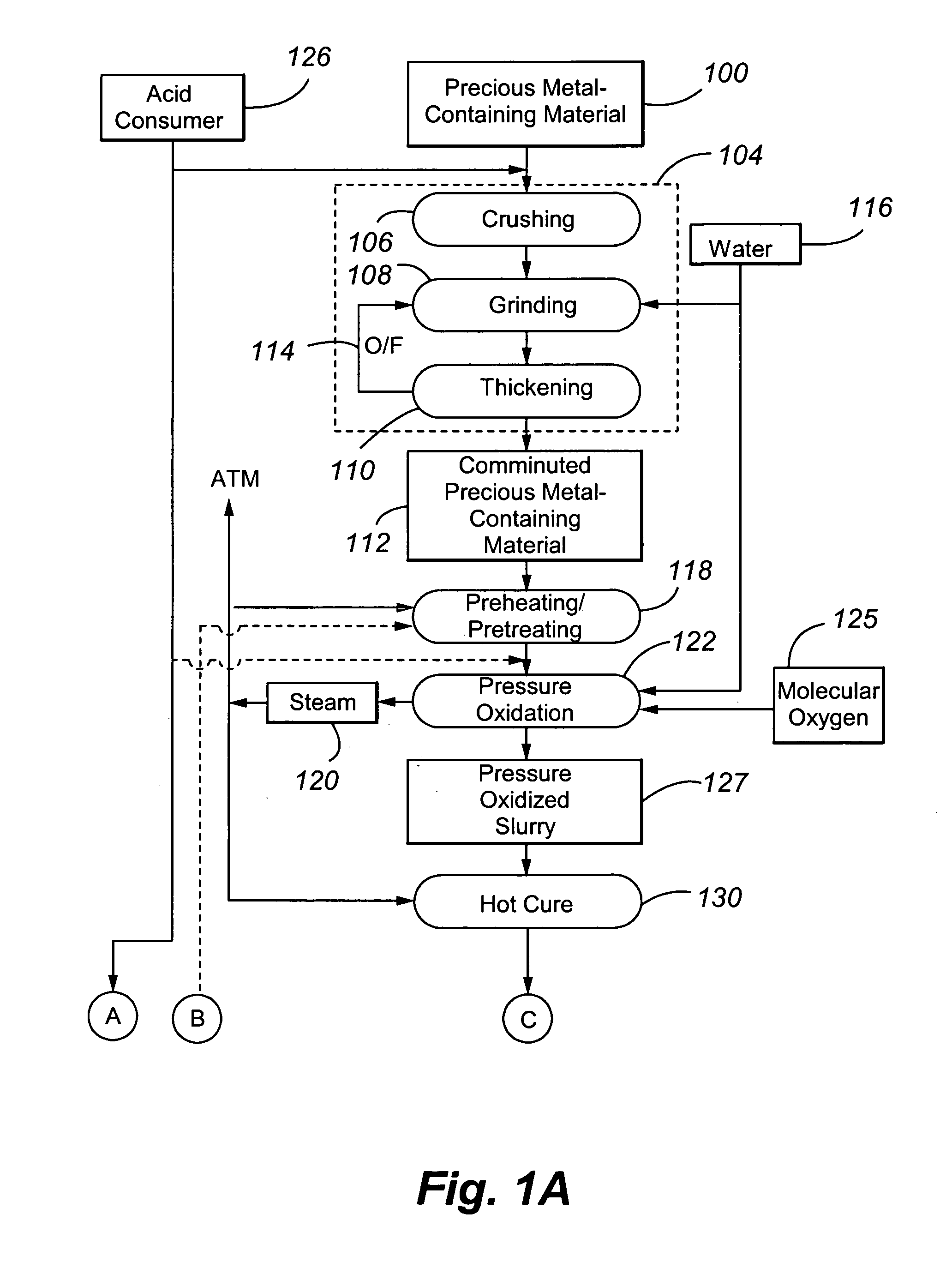
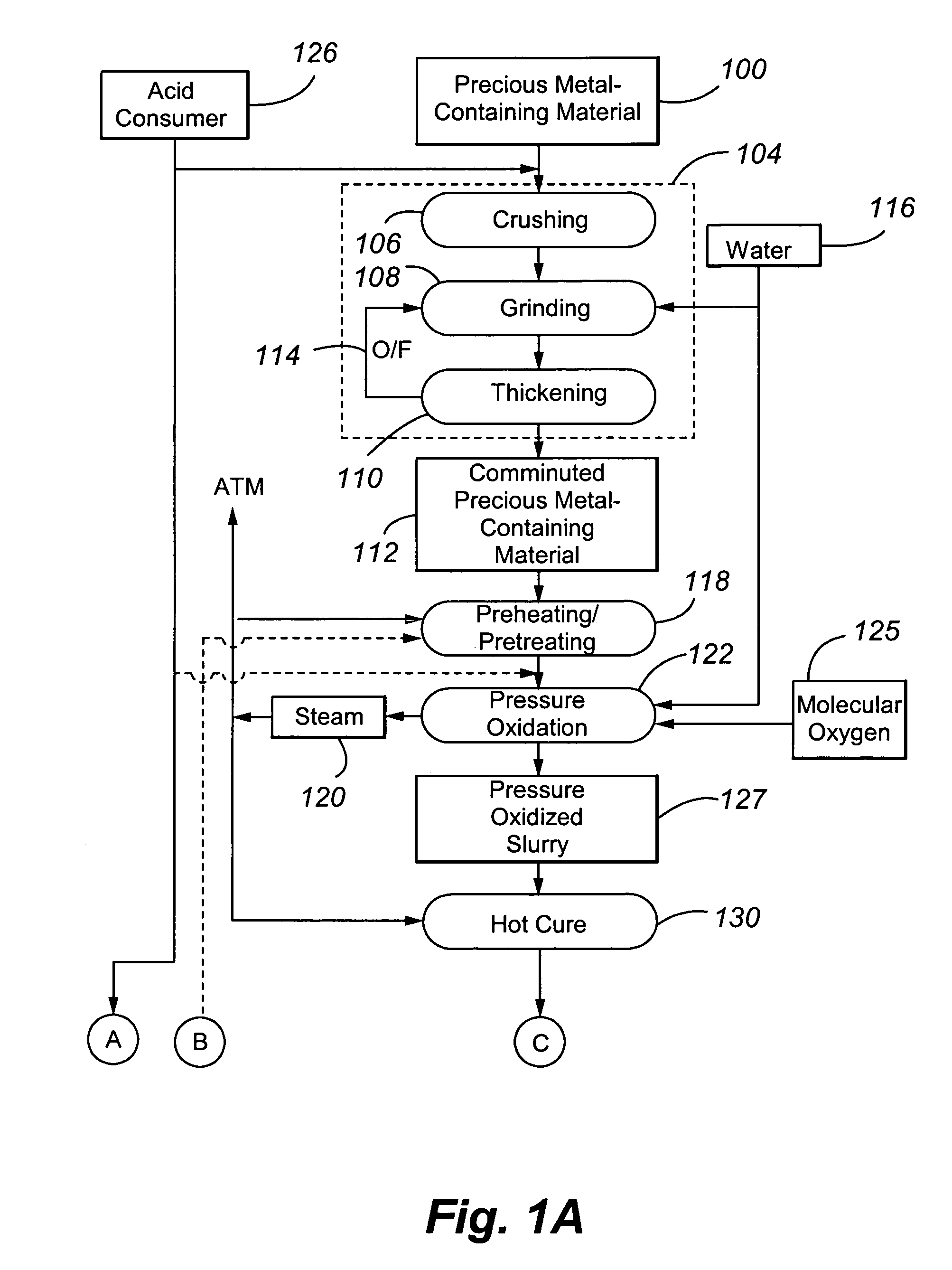
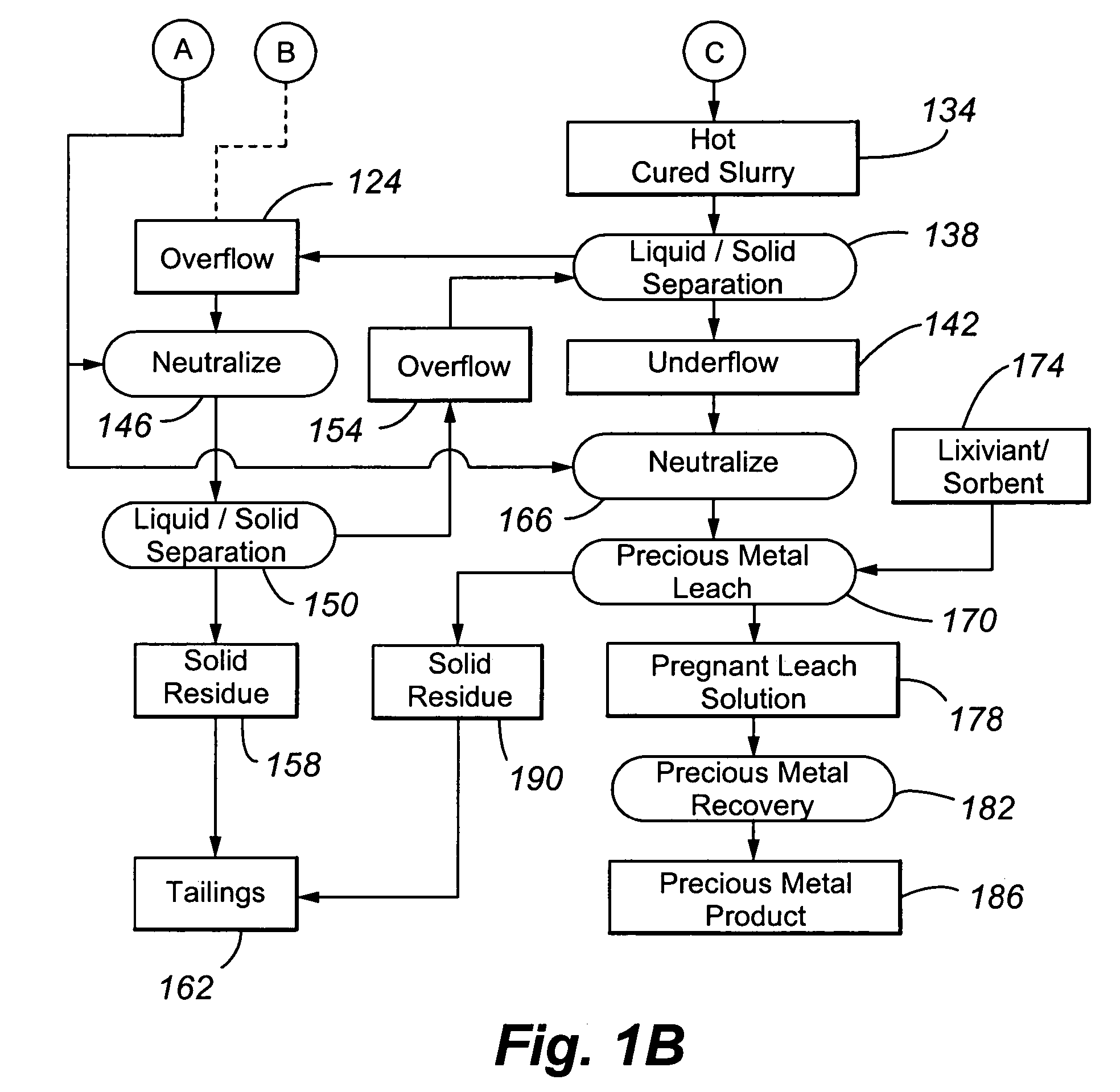
Reduction of lime consumption when treating refractory gold ores or concentrates
ActiveUS20060133974A1Improve the level ofReduce operating costsSolvent extractionGold compoundsSlurryGold ore
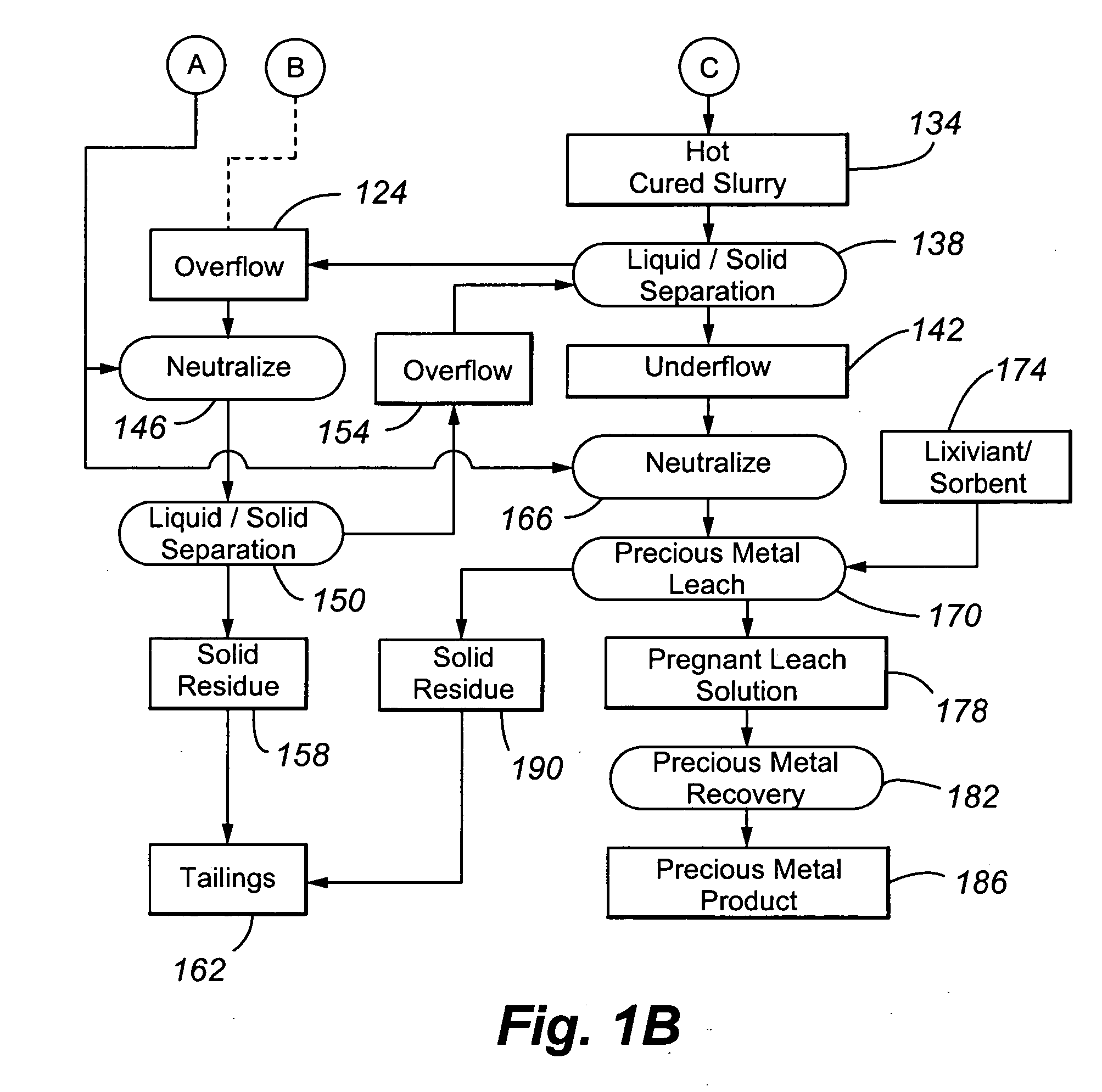
The present invention is directed to a precious metal recovery process in which basic ferric sulphates and / or jarosites are controlled by a number of mechanisms, including control of the oxidation reaction conditions in the first autoclave compartment, hot curing of the autoclave discharge slurry, and / or contacting of the autoclave feed slurry with the hot cured discharge liquid.
Owner:PLACER DOME TECHN SERVICES
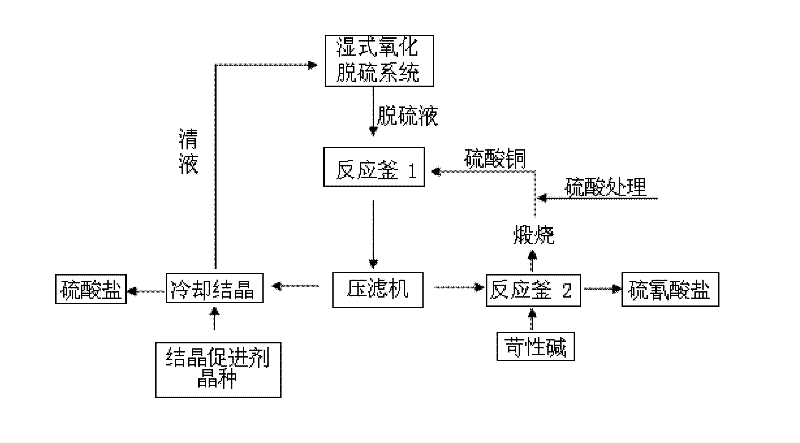
Method for recovering secondary salts from desulfurization liquid and recycling desulfurization liquid
ActiveCN102225816AAchieve recyclingHigh crystallinityThiocyanic acidMultistage water/sewage treatmentSulfatePollutant emissions
The present invention relates to a method for recovering secondary salts from a desulfurization liquid and recycling the desulfurization liquid, which comprises the following steps of: adding CuSO4 to the desulfurization liquid discharged from a wet oxidative desulfurization system for treatment, filtering to obtain CuSCN precipitates and a sulfate solution; adding the CuSCN precipitates to caustic alkali for treatment to recover thiocyanate; and cooling and crystallizing the sulfate solution to recover sulfates and returning the clear liquid to the desulfurization system. The method provided by the present invention simplifies the treatment process of desulfurization liquid wastewater, reduces pollutant emission, recovers the secondary salts from the desulfurization liquid and realizes the recycling of the desulfurization liquid, has a simple process, is environmentally-friendly, realizes the recycling of resources and has a good application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING BAIAONA HI TECH
Circuit board acid-base etching waste liquid recycling treatment technology
InactiveCN108862365AImprove protectionEasy to operateCopper sulfidesCopper sulfatesEconomic benefitsCopper oxide
The invention discloses a circuit board acid-base etching waste liquid recycling treatment technology. Acidic etching waste liquid and alkaline etching waste liquid are neutralized to generate copperoxychloride, copper oxychloride reacts with an alkaline solution to generate copper oxide, copper oxide reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to generate copper sulfate, and filtrate and washing water in the reactions are collected. The circuit board acid-base etching waste liquid recycling treatment technology makes copper ions precipitate to generate different copper-containing products througha plurality of steps, operation is easy, the cost is low, etching waste liquid ca be treated on a large scale, meanwhile, the treated filtrate is sufficiently utilized to prepare etching liquid again, the economic benefit is enhanced, emission is reduced, and environmental protection is facilitated.
Owner:广东省博罗县湘澧精细化工有限公司
Reduction of lime consumption when treating refractory gold ores or concentrates
The present invention is directed to a precious metal recovery process in which basic ferric sulphates and / or jarosites are controlled by a number of mechanisms, including control of the oxidation reaction conditions in the first autoclave compartment, hot curing of the autoclave discharge slurry, and / or contacting of the autoclave feed slurry with the hot cured discharge liquid.
Owner:PLACER DOME TECHN SERVICES
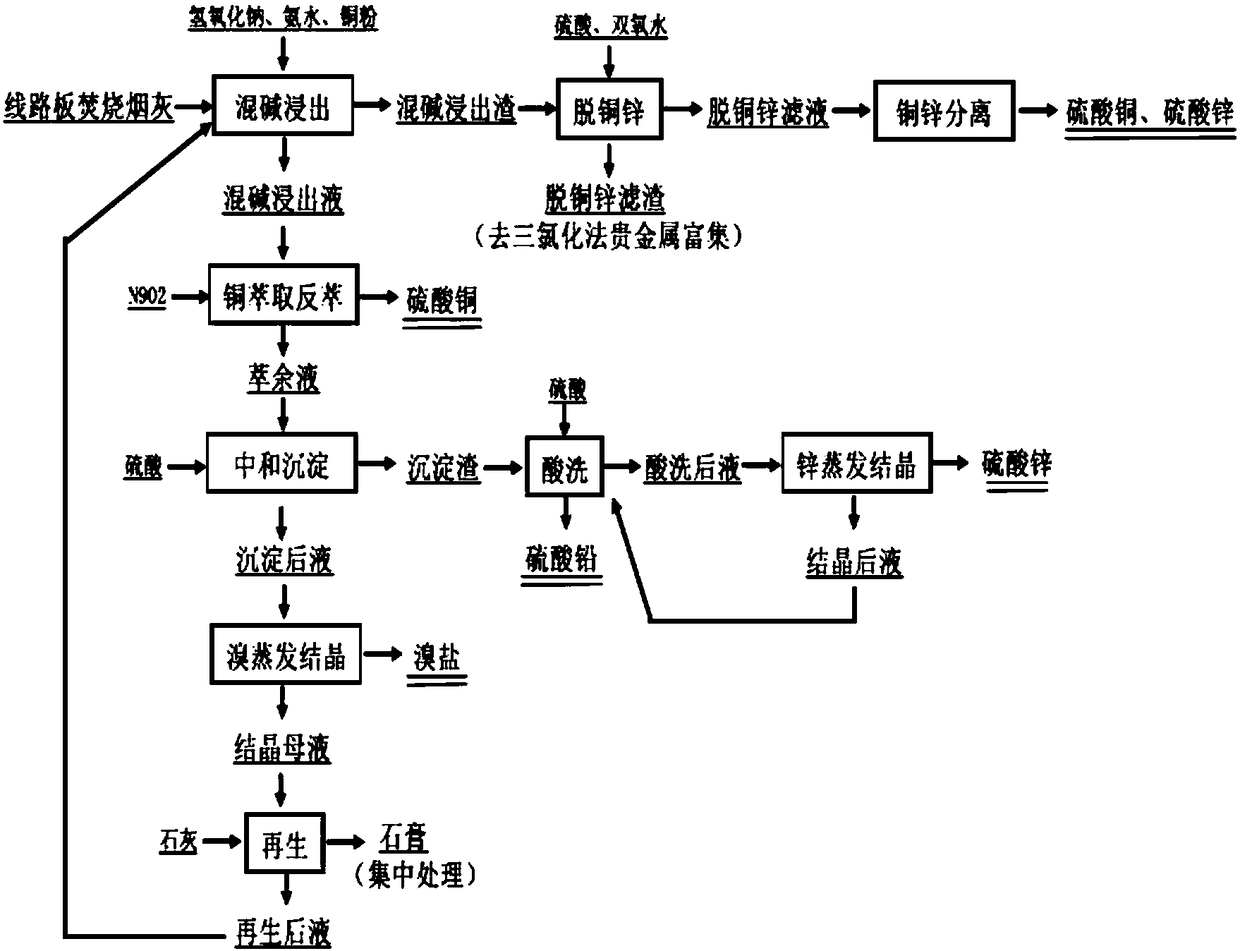
Method for pretreating incineration ash of circuit board and recovering bromine
ActiveCN108118157AEasy to recycleNo emissionsZinc sulatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesRecovery methodBromine
The invention discloses a method for pretreating incineration ash of a circuit board and recovering bromine, belongs to the field of comprehensive recovery of ash whole-wet valuable metal and particularly relates to a method for recovering valuable metal, enriching precious metal and recovering bromine salt in the pretreatment process of incineration ash of the circuit board. The method mainly comprises the steps: extracting mixed alkali; recovering copper by copper extraction and back extraction; carrying out neutralization and precipitation to separate lead and zinc; evaporating and crystallizing bromine; regenerating mixed alkali extracting liquor; removing zinc by acid pickling; evaporating and crystallizing zinc; carrying out zinc and copper removal on mixed alkali extracting residuesand the like. Compared with a traditional ash comprehensive process, the technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages that recovery of valuable metals such as copper, zinc and lead and enrichment of precious metal such as silver in the pretreatment process of the ash is realized to the maximum extent; meanwhile, the bromine salt is separated and recovered; the method has the characteristics of high recovery added value, no tail liquid drainage and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
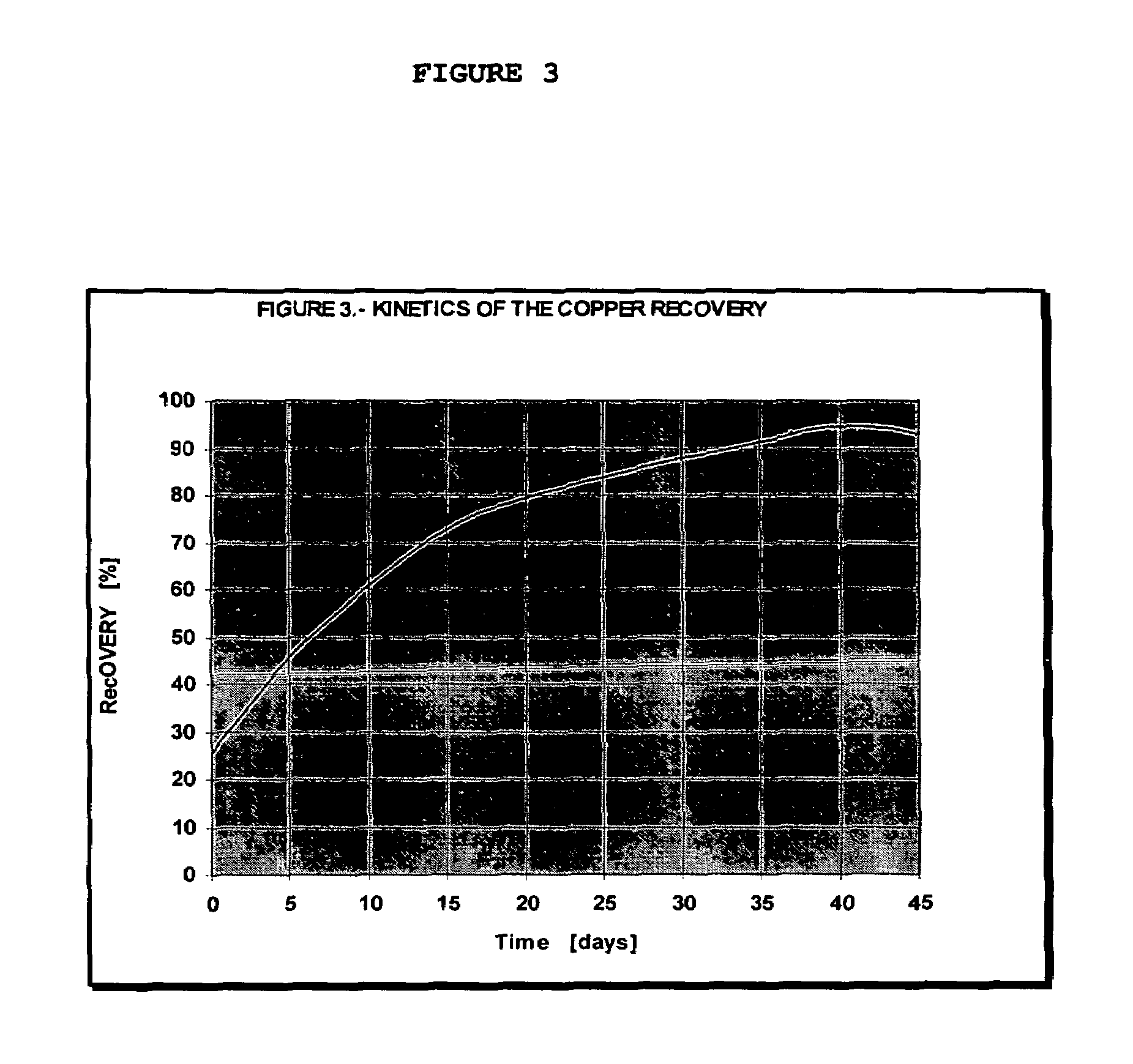
Process method for producing copper sulfate by using copper scale at normal temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN102140581ALow equipment requirementsMinistry of Investment in IndustrializationProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfatesGranularityRoom temperature
The invention discloses a process method for producing copper sulfate by using copper scale at normal temperature and normal pressure, belonging to the technical field of comprehensive recycling of ferrous metal smelting. In the method, under the conditions of normal temperature (to 25DEG C) and normal pressure (to 1.01*10<5>pa, after the ore grinding granularity reaches between -120 and -200 meshes, the copper scale containing 20-60 percent of copper (other components including 1-15 percent of Zn, 5-15 percent of Pb and 1-8 percent of Cd) is mixed with a sulfuric acid solution containing 120-180g.L<-1> of acid and the mixed solution is added in a mechanical stirring groove; and air containing 0.05-0.5m<3>min<-1>.kg<-1> of copper scale is introduced into the groove and sufficient oxidizing atmosphere in the groove is kept. The oxidizing reaction of copper and dilute sulfuric acid is promoted by using the heat released by a neutralization reaction of copper oxide and sulfuric acid and is fully carried out for 18-24h, and then the copper can be better leached to the solution, wherein the leaching rate reaches over 94 percent.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
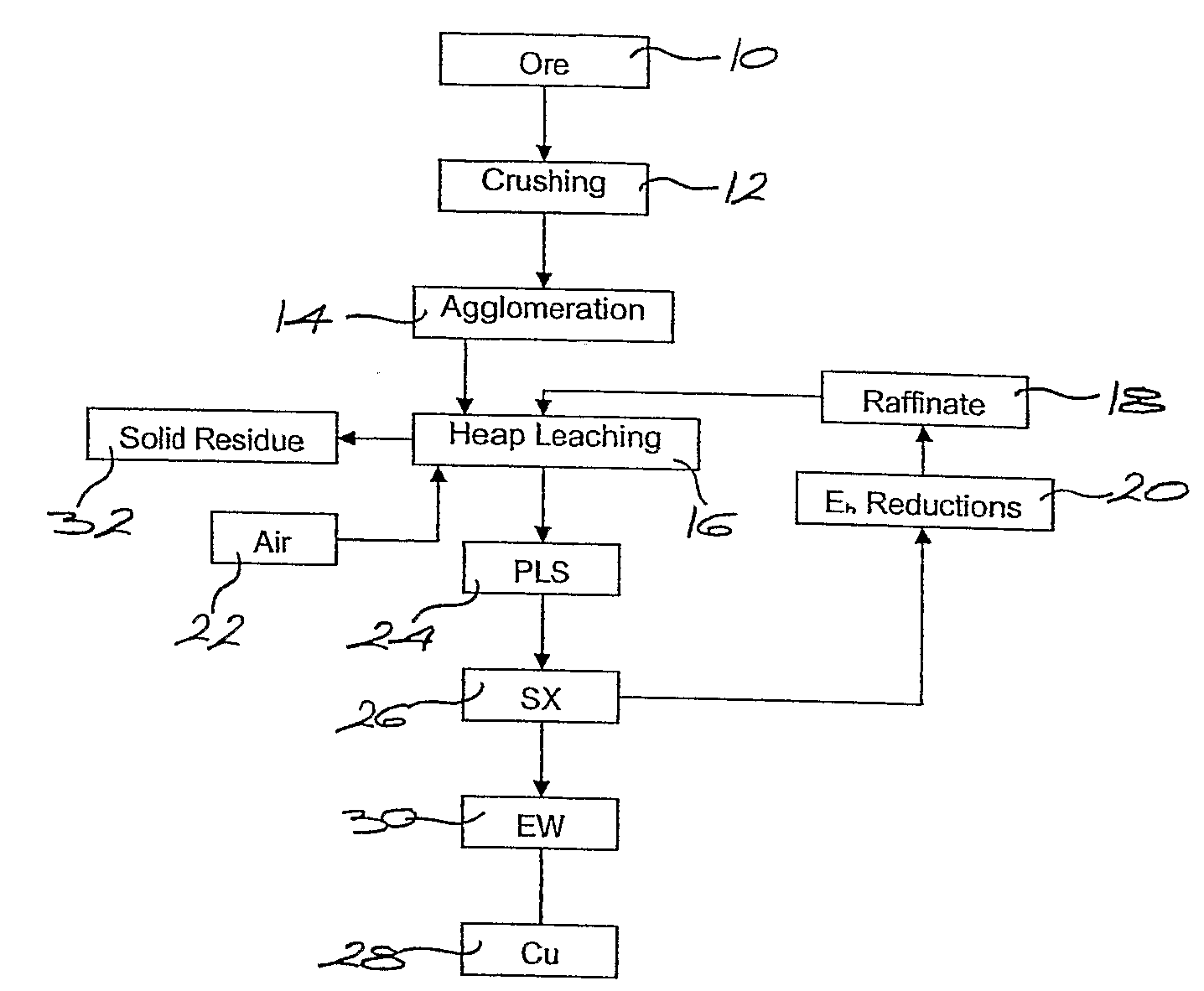
Leaching of mineral ores
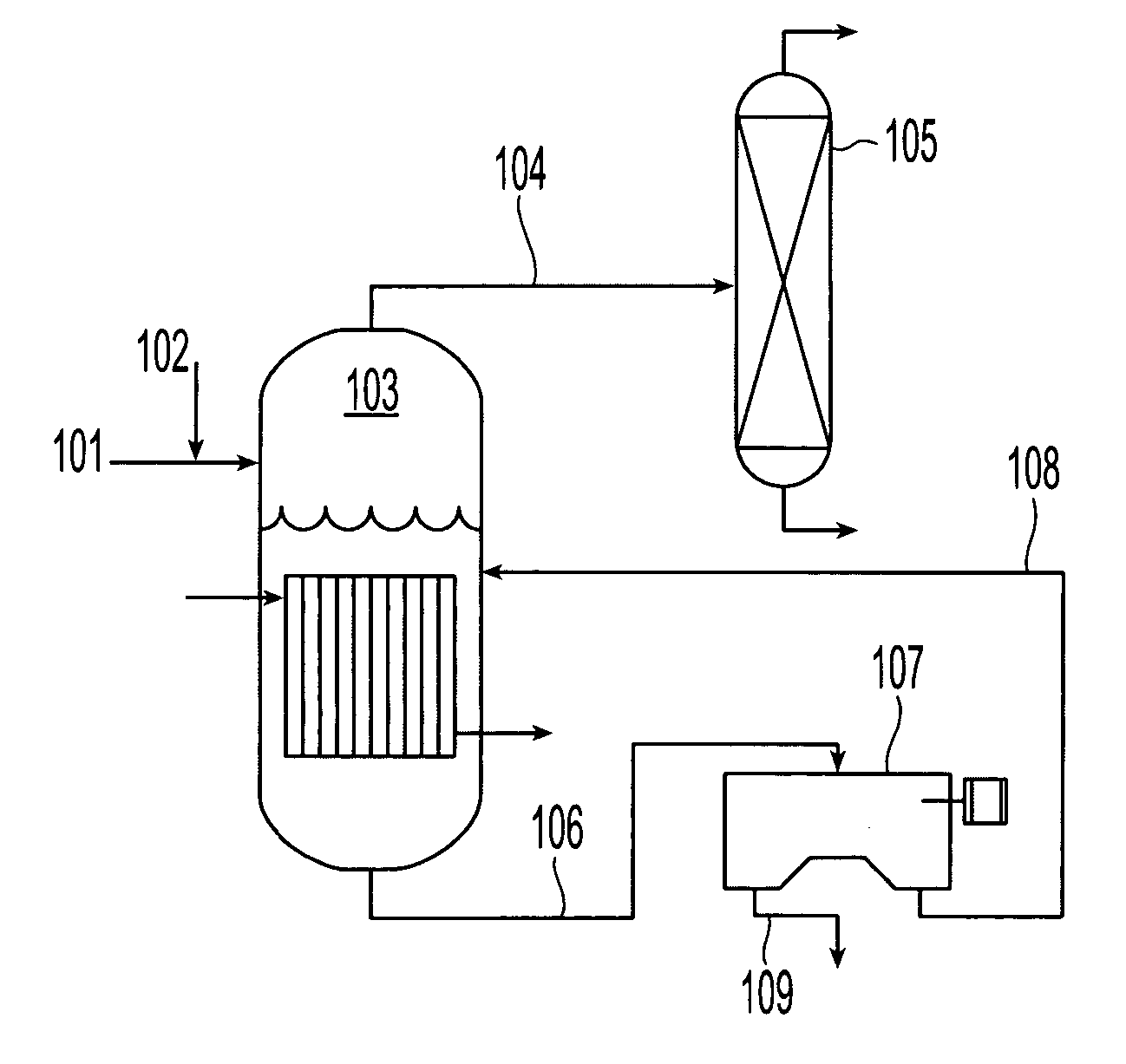
A process for oxidation of ferrous ions in solution, and more particularly a process for improved base metal and / or uranium leaching from ores, concentrates or tailings using ferric ion as an oxidizing agent. A reaction vessel (10) holds a ferrous ion-containing solution, for example, a copper sulphide leach slurry or concentrate. An agitator (12) may be provided to promote leaching of the base metal into solution. Some of the ferrous ion-containing solution is drawn off from the reaction vessel (10) and pumped through an in-line mixer (14) via a feed pump (16). Oxygen is injected into the reactor (14) to facilitate oxidation of the ferrous sulphate to form ferric sulphate. The ferric ion-containing solution is then recirculated back to the reaction vessel (10) where the ferric ions are reused in the dissolution of copper sulphide into soluble copper sulphate. The two processes of ferrous oxidation and metal leaching can be conducted either simultaneously or sequentially to effect recovery of copper, other base metals or uranium from ores, concentrates or tailings.
Owner:ATOMAER
Comprehensive treatment method of acidic etching waste liquid
InactiveCN101792220AImprove resource recoveryGuaranteed emission standardsChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideWaste water treatment from metallurgical processLiquid wasteDistillation
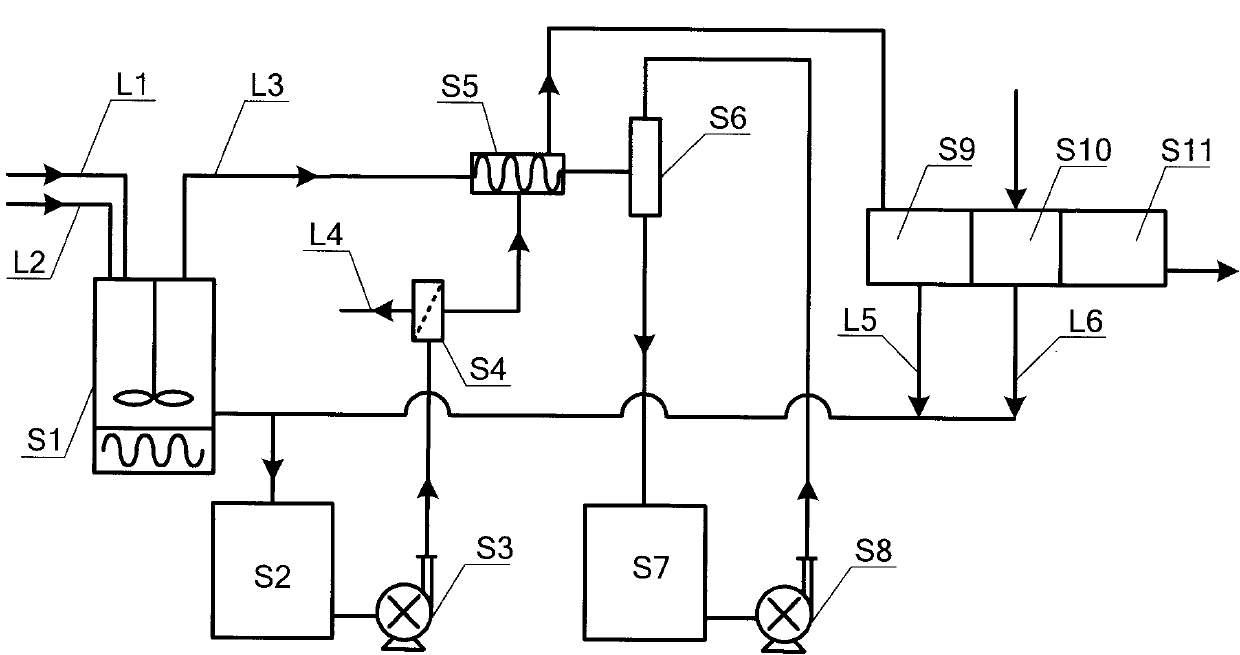
The invention relates to a comprehensive treatment method of acidic etching waste water. Tail water treated by the existing treatment method can not conform to the standard. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adding oxydol to an acidic etching waste liquid to be treated for breaking and regeneration; then adding 98% concentrated sulfuric acid, distilling by heating, and absorbing the distilled steam with clean water to obtain dilute hydrochloric acid; dissolving residues after the distillation in a solution to generate a mother solution, throwing nano filter membranes and reverse osmosis membranes for concentration and separation, cooling and crystallizing the condensed mother solution, rinsing with water, and drying to obtain a copper sulfate crystal product. The method comprehensively uses the resources of the acidic etching waste liquid, produces the industrial dilute hydrochloric acid and copper sulfate products, ensures that the discharged waste water conform to the standard, improves the resource recovery rate of copper, and also raises the distillation speed.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
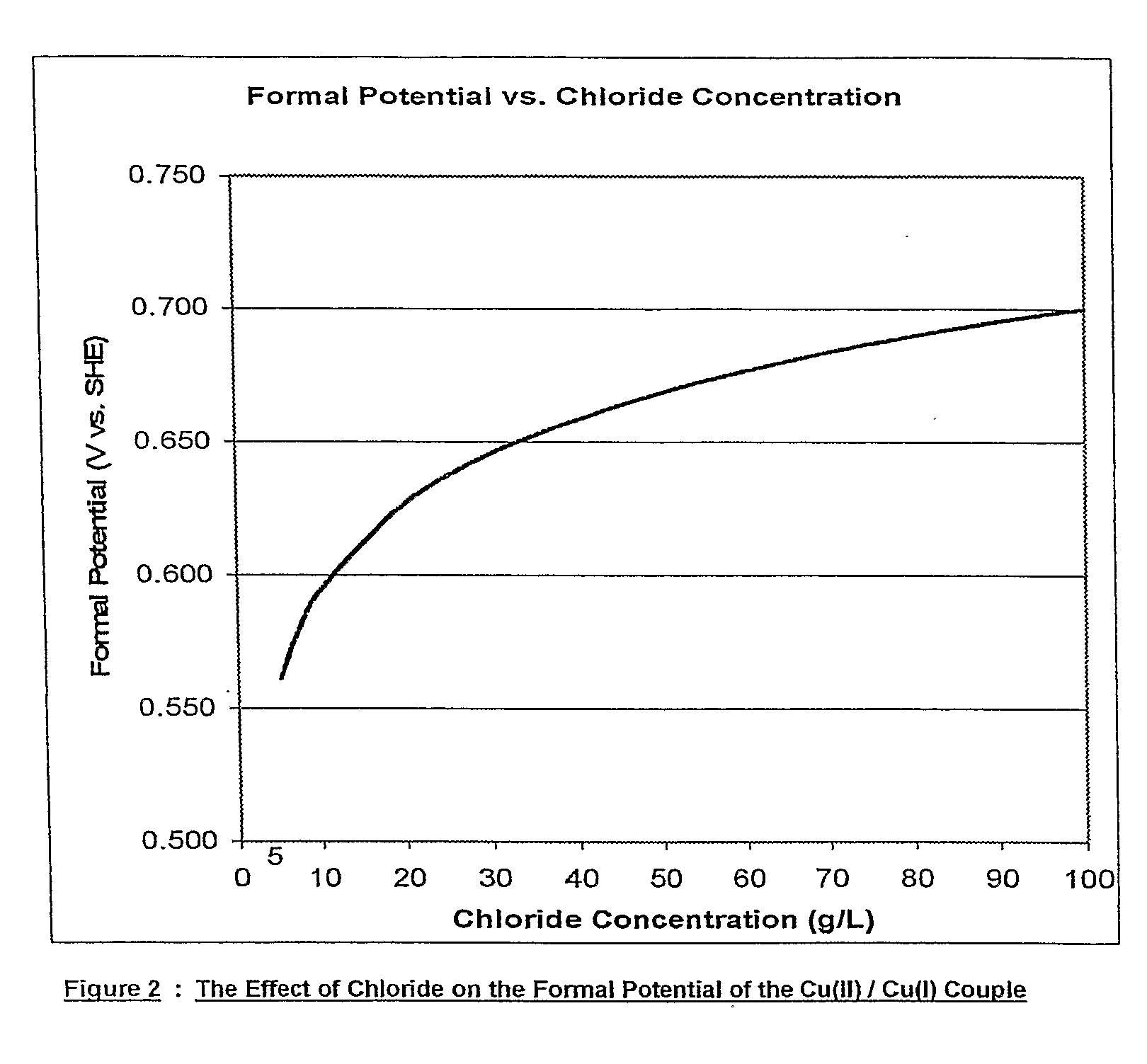
Chloride Heap Leaching
ActiveUS20090173188A1Lower potentialRaise the potentialSolvent extractionGold compoundsSulfateChloride
A heap leaching method to recover copper from a primary copper sulphide mineral wherein the mineral is leached in an acidic chloride / sulphate solution in the presence of oxygen with the surface potential of the mineral below 600 mV (vs. SHE) to cause dissolution of the copper sulphide.
Owner:CONSOL NOMINEES
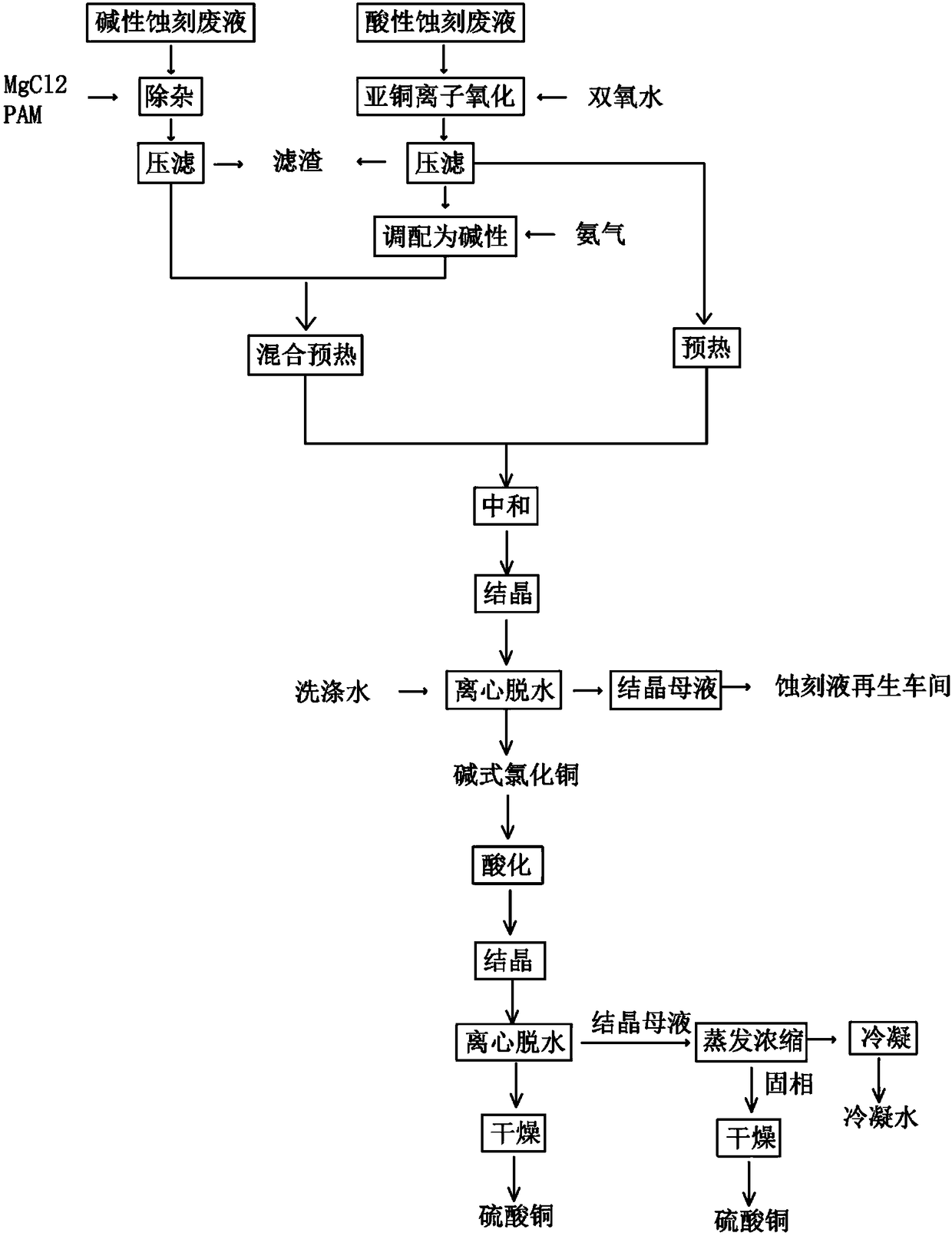
Production method of copper sulfate
ActiveCN108341424AReduce temperature gapResponse control is appropriateCopper sulfatesAcid etchingFiltration
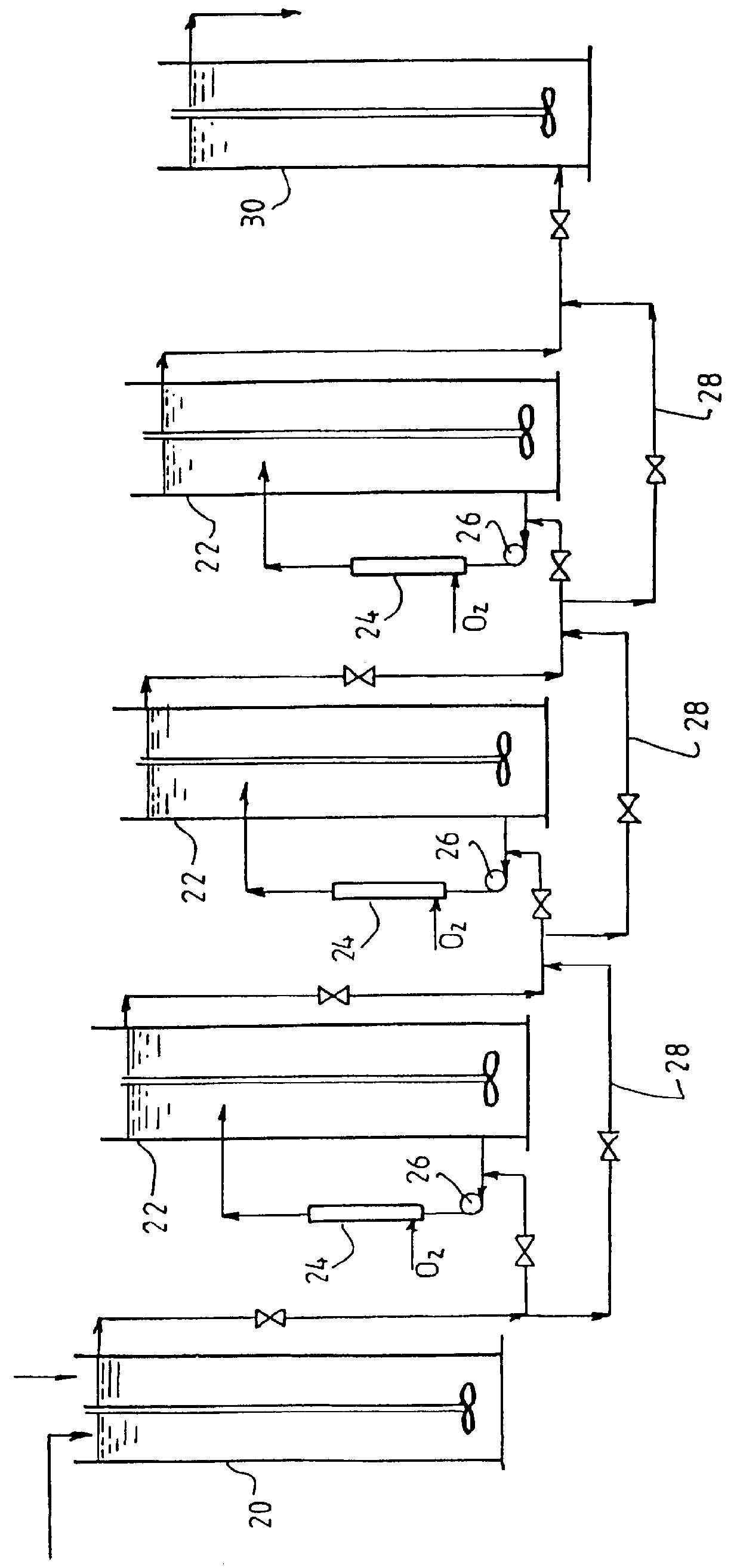
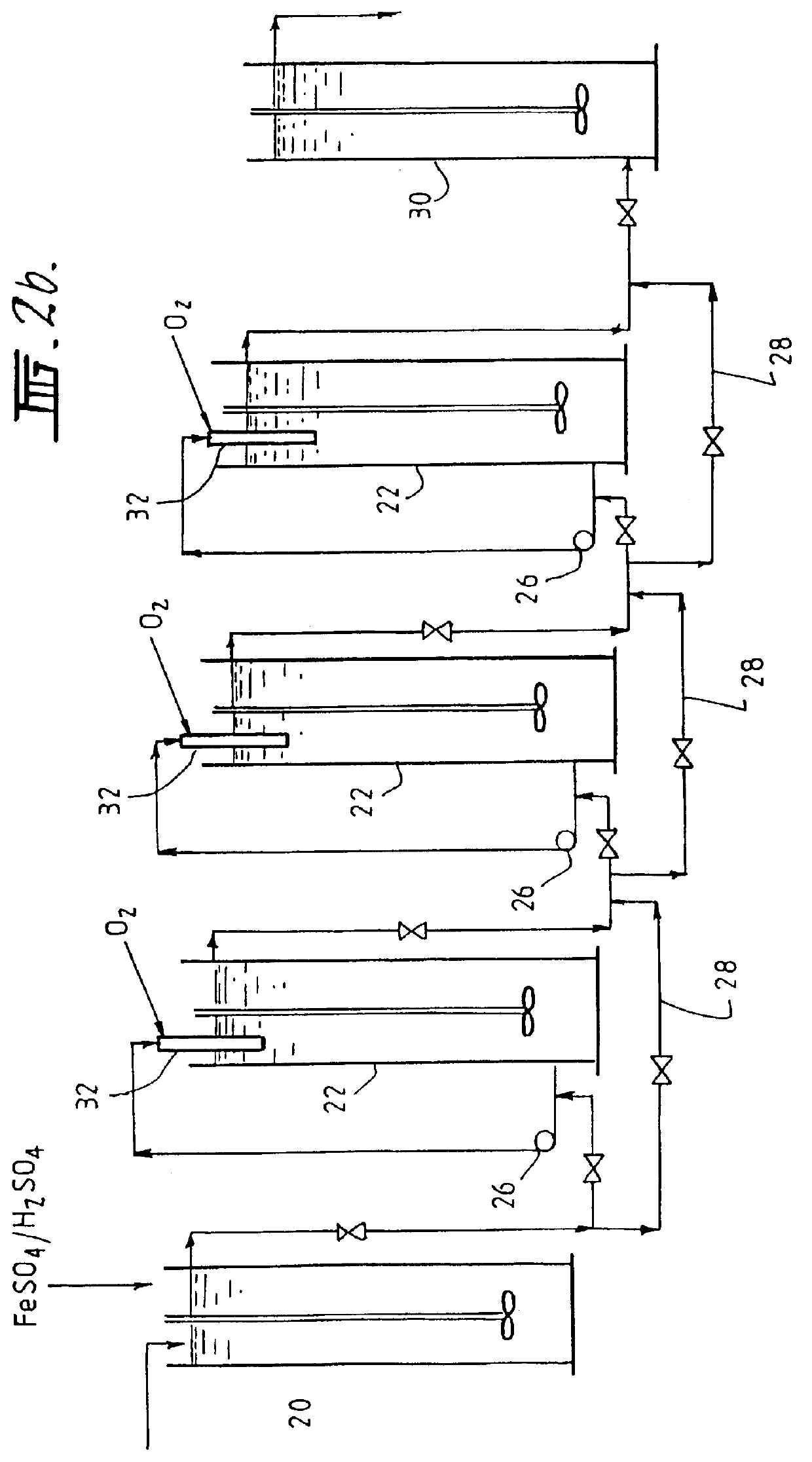
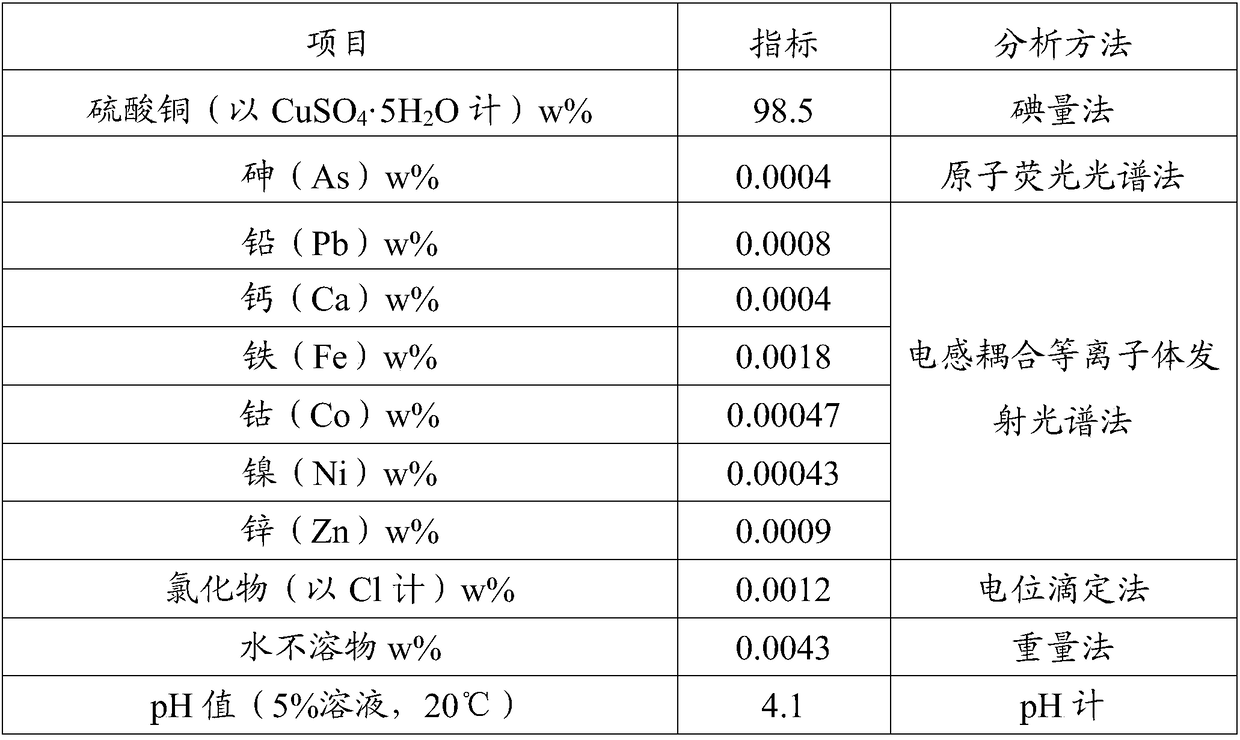
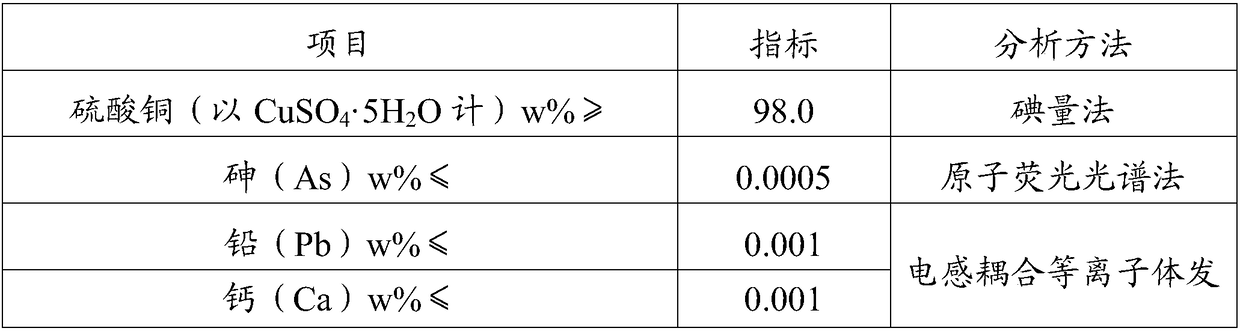
The invention discloses a production method of copper sulfate. The production method comprises the following steps: adding an oxidizing agent into an acid etching waste solution to oxidize cuprous ions and ferrous ions in the acid etching waste solution; then regulating a pH value to reach 1.7 to 1.9 and carrying out stirring and reaction; then adding activated carbon again; performing settlementlayering and taking supernatant liquid to perform filtration to obtain an impurity-removed acid etching waste solution; adding soluble magnesium salt into an alkali etching waste solution and carryingout stirring and reaction; then performing settlement layering and taking supernatant liquid to obtain an impurity-removed alkali etching waste solution; performing mixed reaction on the impurity-removed acid etching waste solution and the impurity-removed alkali etching waste solution to obtain basic copper chloride; converting basic copper chloride ammonia into copper hydroxide; then performingfiltration on copper hydroxide, washing and purifying copper hydroxide and pulping copper hydroxide; then adding sulfuric acid to be acidified until pH is 0.5 to 1.0; then performing heat filtration,cooling crystallization, solid-liquid separation and drying treatment to obtain copper sulfate. Copper sulfate produced by the method can reach electroplating grade standard; moreover, a recovery ratio of copper in the etching waste solutions is high.
Owner:东莞市恒建环保科技有限公司
Regeneration of cupric etchants and recovery of copper sulfate
InactiveUS7175819B2Easy to useLower requirementBiocideChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationDistillationCopper chloride
Spent, acidic solutions comprising cupric chloride and hyrdrochloric acid from the copper etching process are regenerated by a process in which the acid is subjected to distillation with sulfuric acid. In one embodiment, the process comprises (a) providing a spent etchant comprising at least about 10% by weight chloride and at least about 5% dissolved copper; (b) adding at least about 2 moles of sulfuric acid per mole of dissolved copper to the spent etching solution, thereby converting copper chloride into hydrochloric acid and precipitated copper sulfate; (c) distilling the mixture from step (b) to vaporize at least a portion of the hydrochloric acid; (d) condensing at least a portion of the vaporized hydrochloric acid; (e) separating at least a portion of the precipitated copper sulfate from the residual liquid, wherein said residual liquid comprises sulfuric acid; and (f) reusing at least a portion of the residual liquid as a sulfuric acid source in step (b).
Owner:PHIBRO TECH
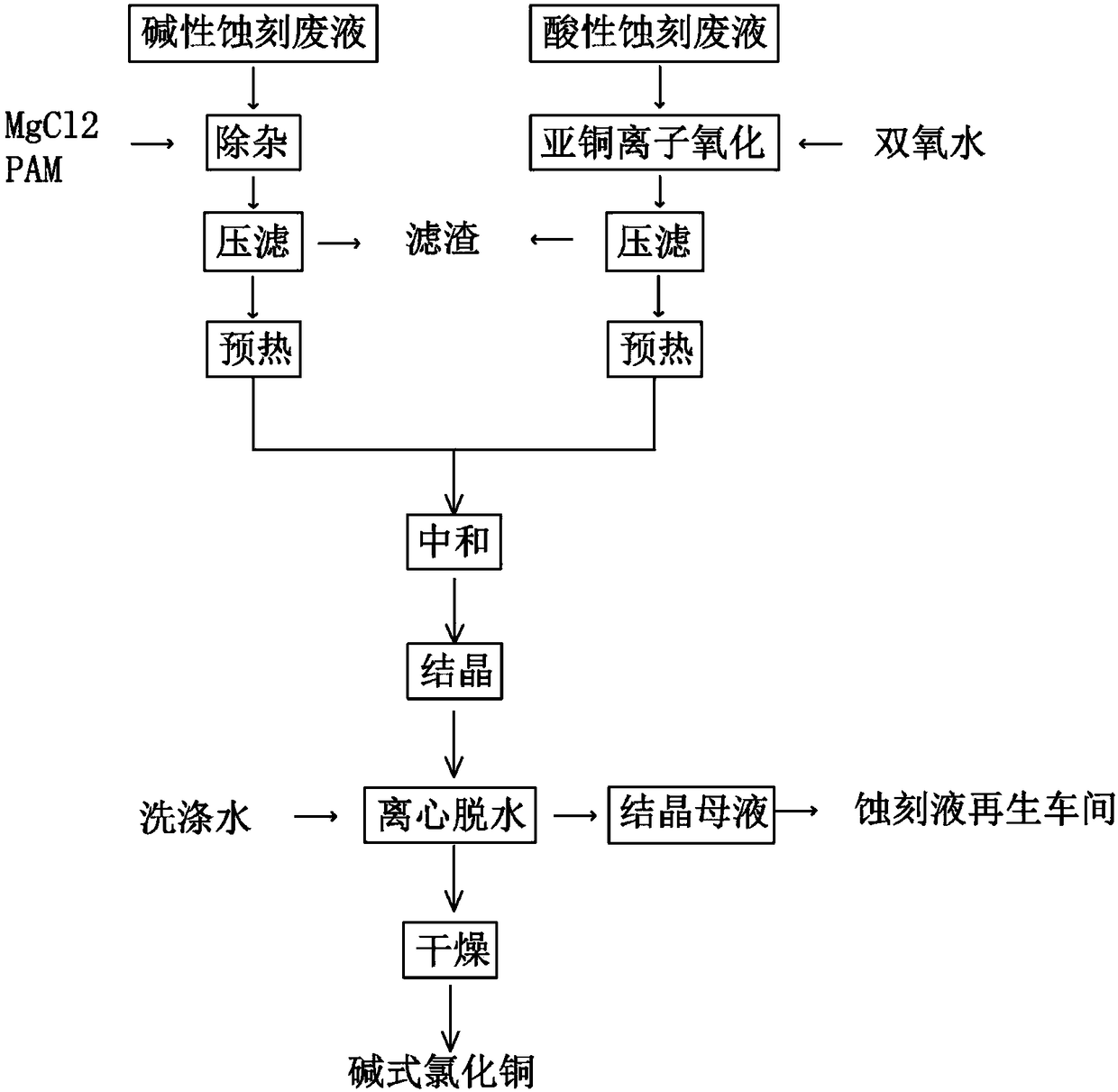
Comprehensive recycling process of copper-containing etching waste solution
InactiveCN108249472AHigh recovery rateEfficient removalCopper chloridesCopper sulfatesCopper chlorideChloride
The invention discloses a recycling process of a copper-containing etching waste solution. The recycling process comprises the following steps: removing mechanical particles and arsenic in an alkalinewaste solution by virtue of magnesium chloride, PAM and a press filtering machine, removing the mechanical particles and oil contaminants in an acid waste solution by virtue of a press filtering machine, neutralizing the acid waste solution and alkaline waste solution to obtain alkaline copper chloride, or acidifying by using sulfuric acid to obtain copper sulfate; and when the alkaline waste solution is insufficient, introducing ammonia gas into the acid waste solution with the mechanical particles and the oil contaminants removed by virtue of the press filtering machine, adjusting the solution to be alkaline, and then performing the neutralization reaction to obtain alkaline copper chloride or copper sulfate. The comprehensive recycling process is simple, low cost, capable of massivelytreating the etching waste solution, and capable of recycling the copper and realizing the safety up-to-standard treatment of the etching waste solution.
Owner:韶关鹏瑞环保科技有限公司
Autoclave with underflow dividers
InactiveUS8061888B2More volumePrevent overflowSolvent extractionTransportation and packagingEngineeringAutoclave
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
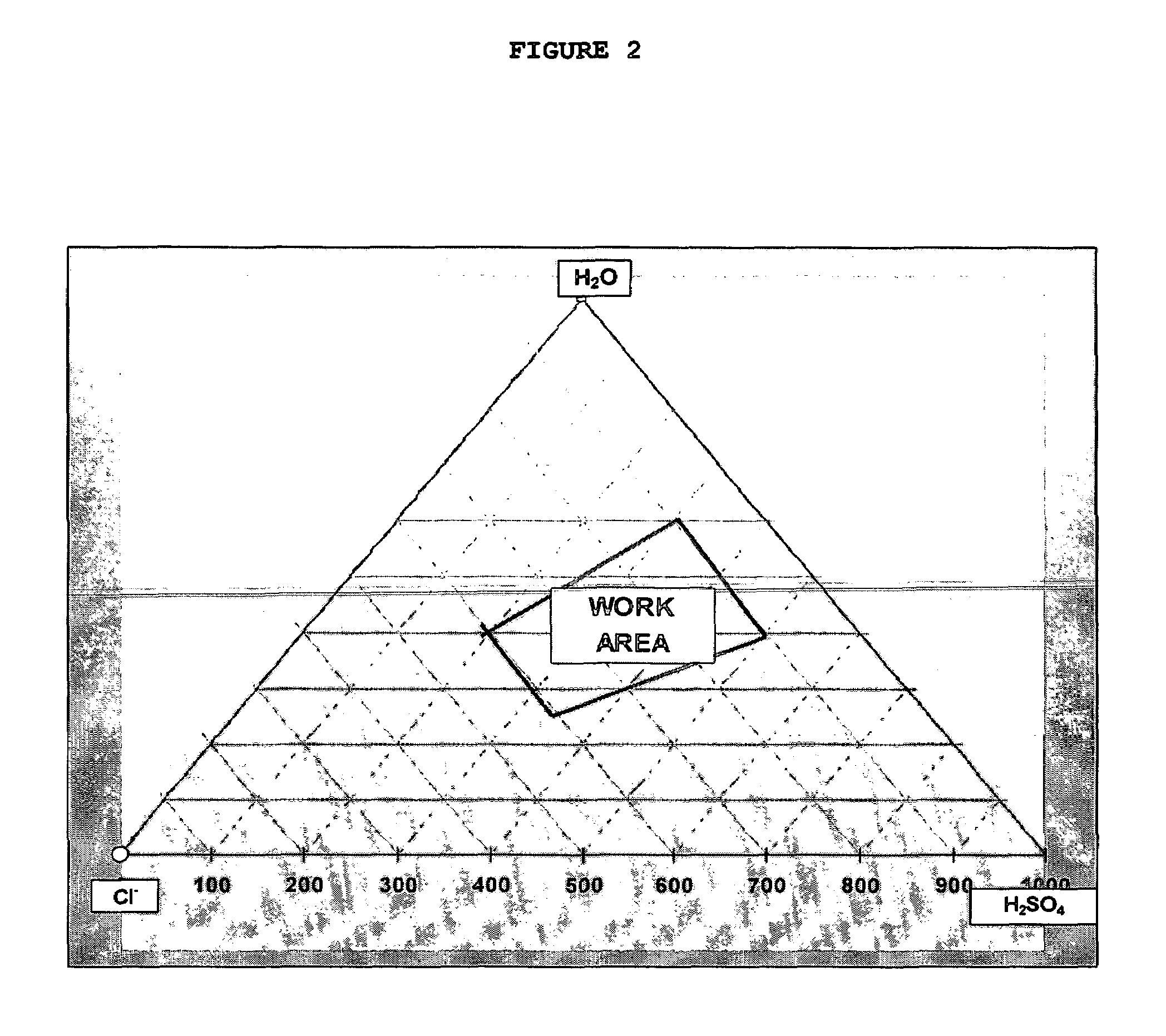
Procedure to leach copper concentrates, under pressure and at ambient temperature, by forming a reactive gel in a sulfate-chloride medium
ActiveUS7491372B2Reduce investmentKeep for a long timeSolvent extractionGold compoundsHigh concentrationChemical process
A chemical process to leach copper concentrates in the presence of a concentrated solution of sulfates and chlorides. The process includes forming a high reactivity chemical paste containing a high concentration of ions in the liquid phase of the paste which react with copper ores and forms a series of soluble salts. The salts are extracted by a simple wash. Mixing equipment for handling high viscosity liquids is used. The total mixing time is about 5 minutes, after which the paste is poured into a rectangular mold, of several hundred meters per side, and is left to settle and breathe. During settling, water and sulfuric acid are added at intervals to replace that consumed by the reactions taking place during the aeration, until the reactions have virtually end. This treatment results in a dry, very resistant mass, containing the copper extracted in form of chlorine salts, and sulfate.
Owner:MINERA MICHILLA
Production method of high-purity copper sulphate
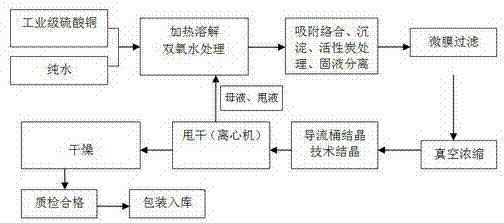
InactiveCN102826584ASimple and fast operationImprove product qualityCopper sulfatesFiltrationTechnical grade
The invention discloses a production method of high-purity copper sulphate. The production method of high-purity copper sulphate comprises the following steps of: dissolving industrial grade copper sulphate into ultrapure water, heating to the temperature of 40-70 DEG C, dropwise adding sulphuric acid to regulate pH to be 1.0-2.0, stirring and dissolving, and then adding hydrogen peroxide; mixing polymeric ferric sulphate with basic copper carbonate in a mass ratio of 1: (2.5-4.5) to prepare a precipitation complexing agent, adding the precipitation complexing agent the weight of which is 0.5-2.5wt% of weight of the solution into the insulated solution, then adding activated carbon the weight of which is 0.5-2.5wt% of the weight of the solution, stirring for 3-7 hours, cooling to room temperature, and standing overnight; and carrying out rough filtration on the solution, then filtering with a microporous membrane with the size of 0.2mu m, and concentrating and crystallizing filtrate to obtain high-purity copper sulphate.
Owner:XILONG SCI CO LTD
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS8163063B2Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
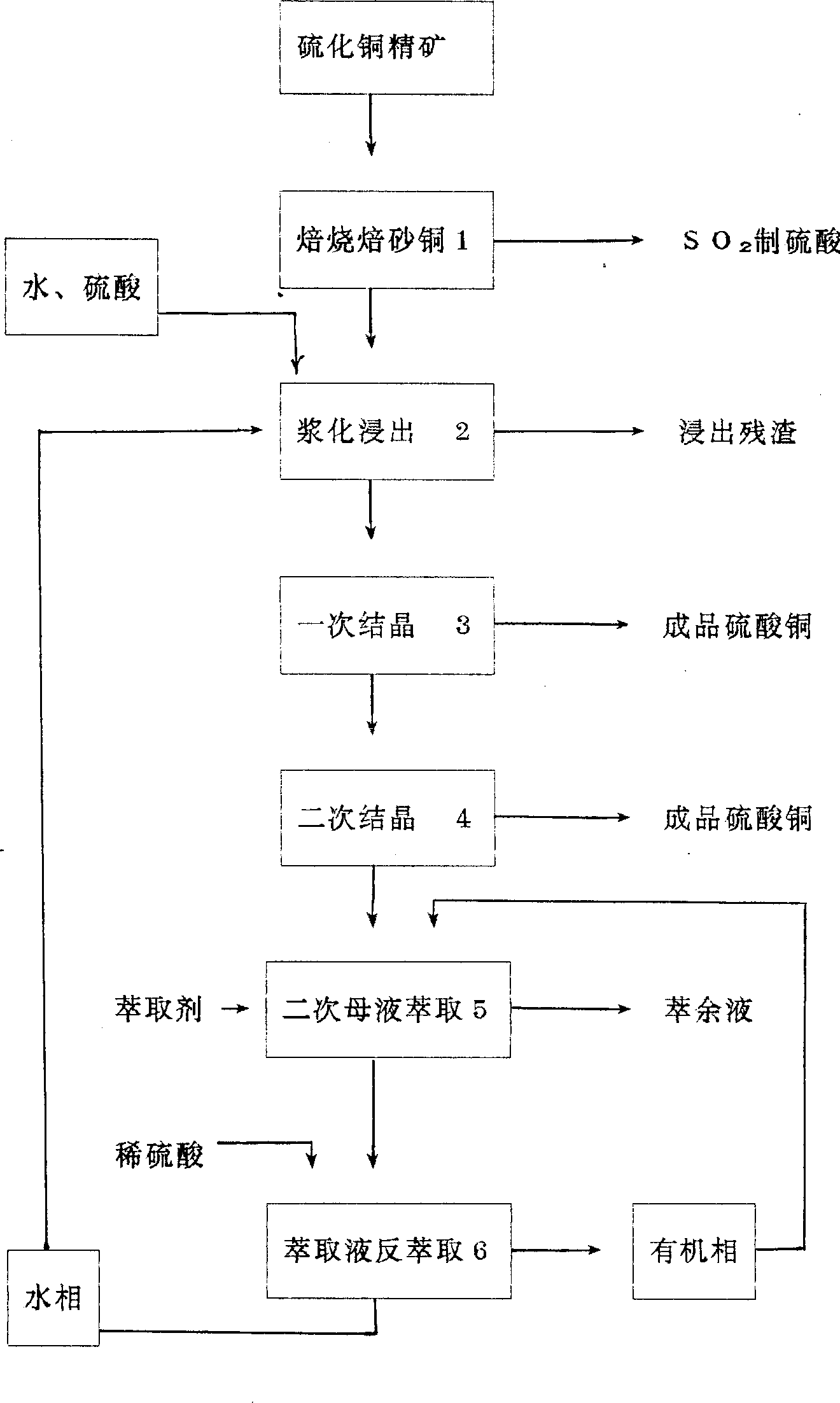
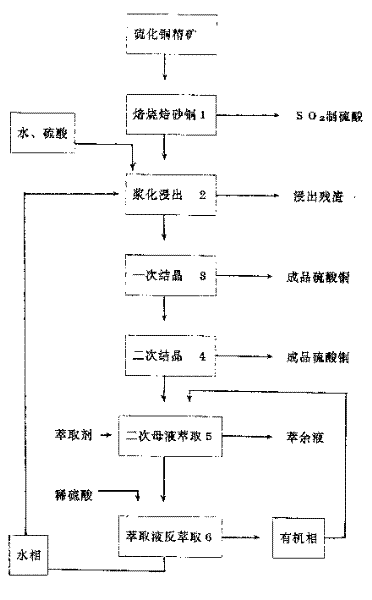
Production process of copper sulfate from copper sulfide ore
InactiveCN1370742AIncrease production capacityContact mix evenlyProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfatesCopper sulfateCopper ore
The present invention relates to a process of producing copper sulfate from copper sulfide ore. In one Lurgi boiling bed roaster, copper sulfide ore powder is roasted at 660-710 deg.c into roasted sand copper with acid dissolving rate of 98 % and water dissolving rate of 60-70 % and the exhausted SO2 is used directly in preparing acid. Roasted sand copper is made to mix with dilute copper sulfatesolution returned from extraction step and sulfuric acid is added to regulate liquid-to-solid ratio of 1-2 and ultimate H2SO4 concentration lower than 20 g / L. The copper leaching rate is greater than98%. The crystallized secondary mother liquid is extracted and purified to recover copper sulfate. The extracting liquid is back extracted with dilute sulfuric acid, the back extracting liquid is returned to leaching step and the organic phase containing extractant is returned to secondary mother liquid.
Owner:XINTAI COPPER IND LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com