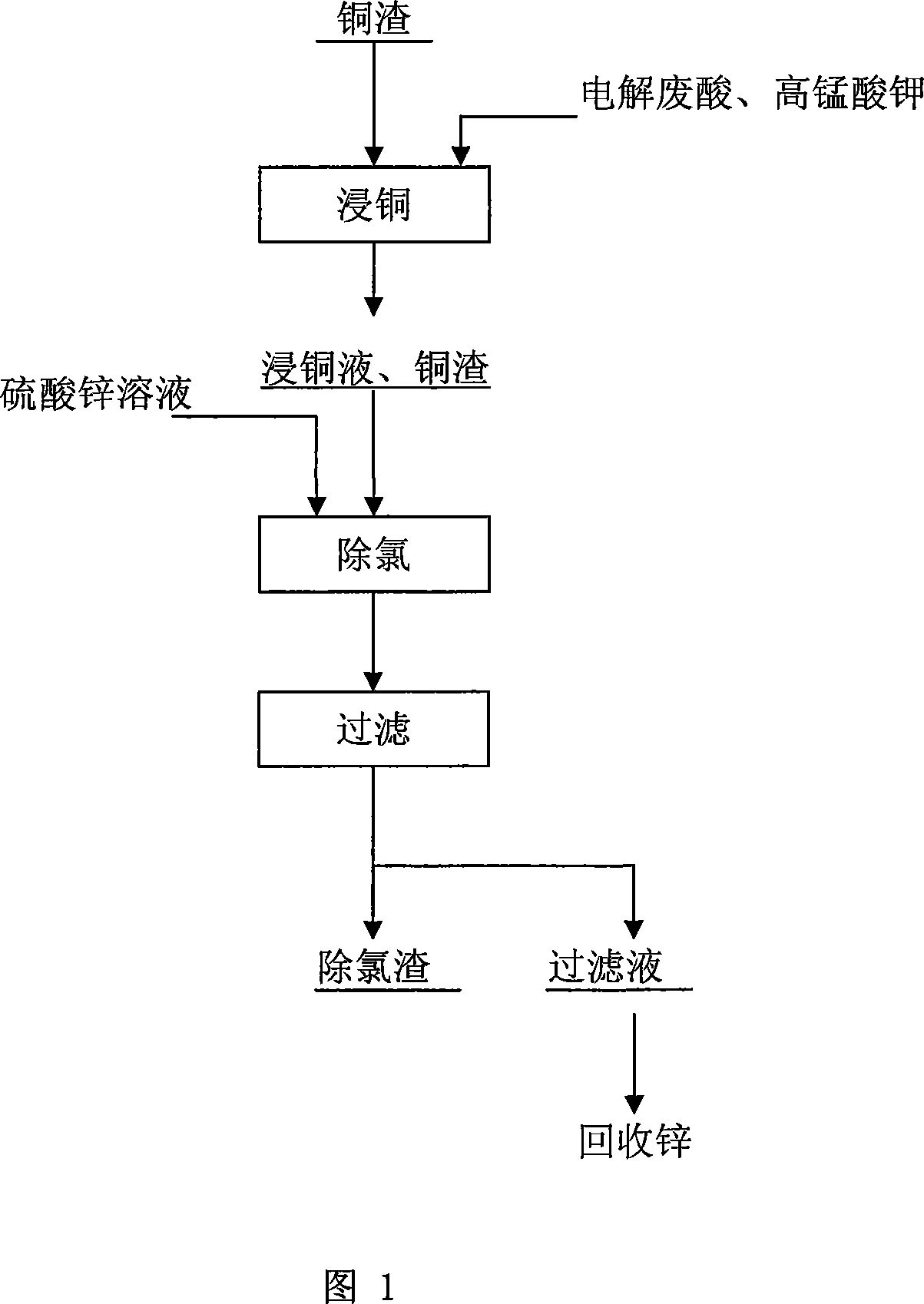
Method for removing chlorine from zinc sulfate solution
A zinc sulfate solution and removal technology, applied in directions such as zinc sulfate, can solve the problems of high production cost, high production cost, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing waste residue, reducing consumption and simplifying operation procedures.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution: Cl 1.1g / l, Zn 140g / l, Cu 0.3g / l, Fe 0.02g / l, Cd 0.8g / l, the production process conditions are shown in Table 1:
[0037] Table 1: Process conditions for removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
(kg)
pulped water
Product (m 3 )
Weight (kg)
Electrolytic waste acid
Volume (m / 3 )
copper immersion time
(h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Liquid volume (m 3 )
Dechlorination time
(h)
800
5
20
3
2
40
1
[0039] The results of leaching copper slag and zinc sulfate solution to remove chlorine:
[0040] Copper slag leachate contains Cu 2+ 5.8g / l, acid 110g / l, chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution after chlorine removal: Cl 0.22g / l, Zn 132g / l, Cu 2.1g / l, Fe 0.02g / l, Cd 1.42g / l. Chemical composition of chlorine residue: Cl 3.2%, Cu 34.2%.
Embodiment 2
[0042] The chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution: Cl 1.36g / l, Zn 130g / l, Cu 0.2g / l, Fe 0.025g / l, Cd 0.7g / l, the production process conditions are shown in Table 2:
[0043] Table 2: Process conditions for removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
[0044] Copper slag weight
(kg)
pulped water
Product (m 3 )
Weight (kg)
Electrolytic spent acid
Volume (m 3 )
copper immersion time
(h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Volume (m 3 )
Dechlorination time
(h)
1100
5
25
4
3
40
1.5
[0045]The results of leaching copper slag and zinc sulfate solution to remove chlorine:
[0046] Copper slag leachate contains Cu 2+ 14g / l, acid 130g / l, chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution after chlorine removal: Cl 0.28g / l, Zn 120g / l, Cu 1.5g / l, Fe 0.02g / l, Cd 1.6g / l. Chemical composition of chlorine residue: Cl 5.42%, Cu 34.07%.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution: Cl 1.5g / l, Zn 130g / l, Cu 0.8g / l, Fe 0.2g / l, Cd 1.2g / l. The production process conditions are shown in Table 3:
[0049] Table 3: Process conditions for removing chlorine in zinc sulfate solution
[0050] Copper slag weight
(kg)
pulped water
Product (m 3 )
Weight (kg)
Electrolytic spent acid
Volume (m 3 )
copper immersion time
(h)
Zinc sulfate solution
Volume (m 3 )
Dechlorination time
(h)
600
5
20
2
1.5
40
1.5
[0051] The results of leaching copper slag and zinc sulfate solution to remove chlorine:
[0052] Copper slag leachate contains Cu 2+ 7.2g / l, acid 90g / l, chemical composition of zinc sulfate solution after chlorine removal: Cl 0.24g / l, Zn 124g / l, Cu 3.1g / l, Fe 0.23g / l, Cd 1.56g / l. Chemical composition of chlorine residue: Cl 3.2%, Cu 34.2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com