Hydrothermal stabilized curing treatment method of arsenic sulfide residue water
A solidification treatment, arsenic sulfide technology, applied in the field of environmental protection, can solve the problem of undiscovered arsenic sulfide slag artificial synthetic minerals, etc., to achieve the effect of a wide range of pretreatment agents, simple and convenient operation, and low treatment cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
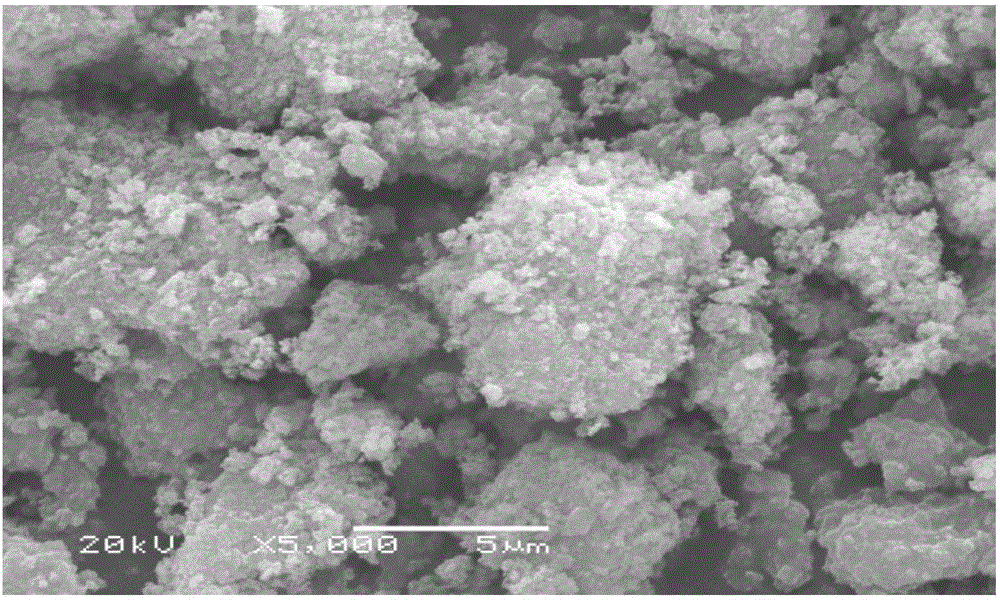
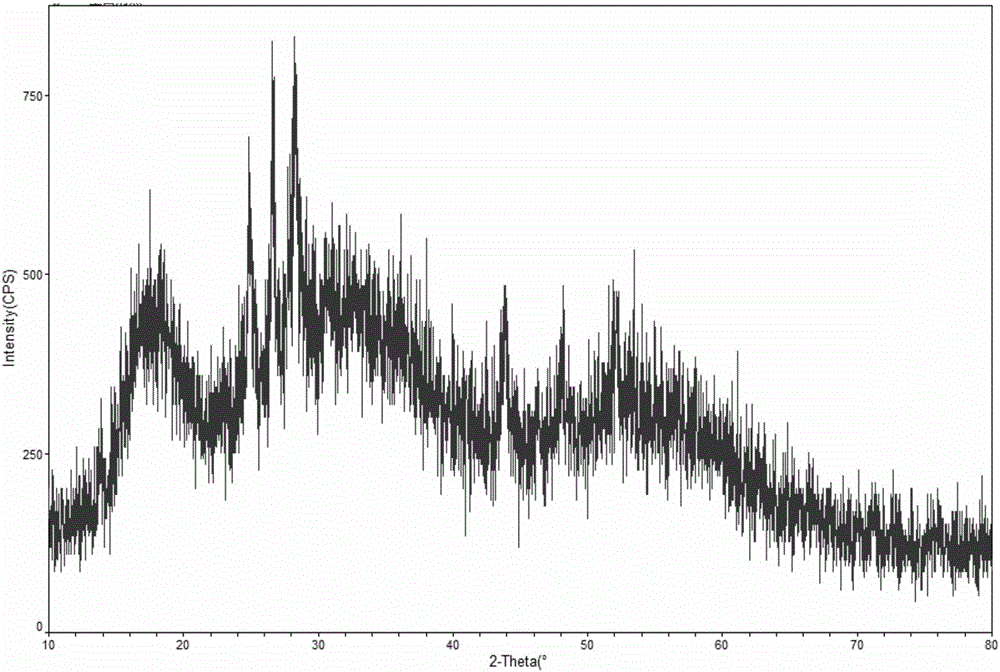
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The arsenic sulfide slag from a copper smelter produced by sulfuric acid hydrogen sulfide treatment in a copper smelter has a moisture content of 70%, and the mass analysis of all elements shows that it mainly contains 25.7% of arsenic, 30.5% of sulfur, 0.71% of Cu, 0.17% of iron, and 0.12% of antimony %, lead 0.005%, cadmium 0.006%. Take 100g of its slag, add 600mL of water, the pH is 1.2, add 0.5g of ferrous sulfide, 0.1g of sodium thiosulfate, redox potential Eh=-0.31v. After stirring evenly, put the pretreated sample into a 1L high-temperature and high-pressure reactor with a filling rate of 70%. Turn on the stirring paddle, set the stirring rate to 1200 rpm, and adjust the heating rate to 1K / min. When the temperature reaches 180°C, keep it warm After 3 hours, the pressure was 0.45 MPa, and then cooling water was passed into the ring cooling pipe for cooling (the cooling rate was 50K / min) to lower the temperature to obtain the amorphous solid of arsenic sulfide. Th...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Take arsenic sulfide slag from a lead-zinc smelter produced by sulfuric acid sodium sulfide sulfidation treatment. The slag has been stockpiled in the enterprise for many years. 0.07%, zinc 0.13%, lead 0.012%, cadmium 0.001%. Take 200g of its slag, add 400g of water, the pH is 2.6, add 1g of ferrous sulfide, the redox potential Eh=-0.21v. After stirring evenly, put it into a 1L (filling rate of 60%) high-temperature and high-pressure reactor, turn on the stirring paddle, set the stirring rate to 100 rpm, adjust the heating rate to 5K / min, and keep it warm for 2 hours when the temperature reaches 200°C. After the temperature, the pressure is 0.52 MPa, and then the air is naturally cooled (cooling rate 2K / min). According to the experimental results, the arsenic sulfide amorphous solidified block obtained has arsenic leaching toxicity of 0.62 mg / L and block compressive strength of 11.6 MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0047] The difference from Example 1 is that arsenic sulfide slag produced from high-arsenic electrolytic waste liquid of another lead-zinc smelter is selected, and the mass content of the slag is 4.15% cadmium, 0.81% zinc, and 24% arsenic. The arsenic leaching toxicity obtained after the experimental treatment was 1.2mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com