Patents
Literature
3594 results about "Cooling methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cooling method. [′kül·iŋ ‚meth·əd] (thermodynamics) A method of determining the specific heat of a liquid in which the times taken by the liquid and an equal volume of water in an identical vessel to cool through the same range of temperature are compared.
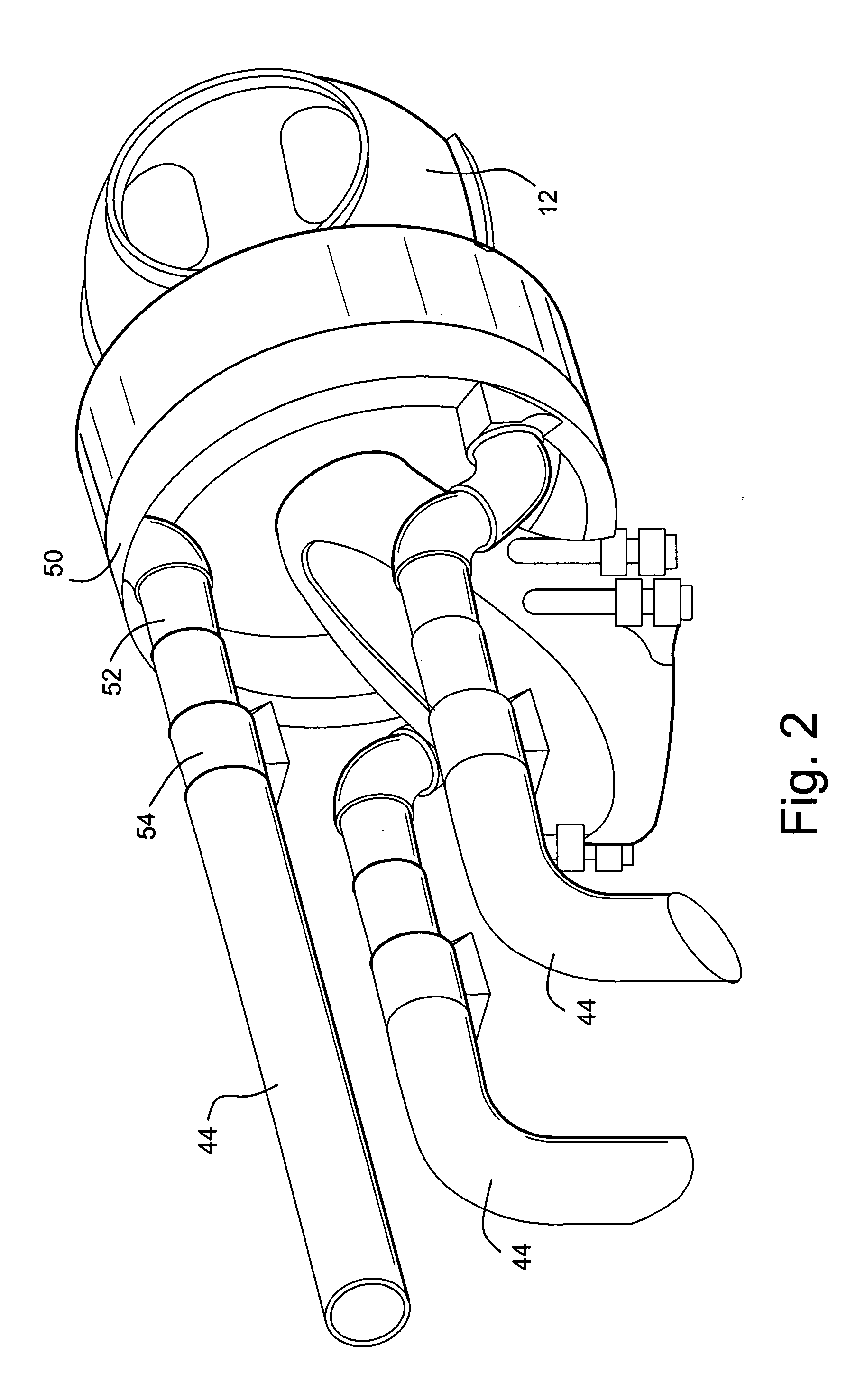
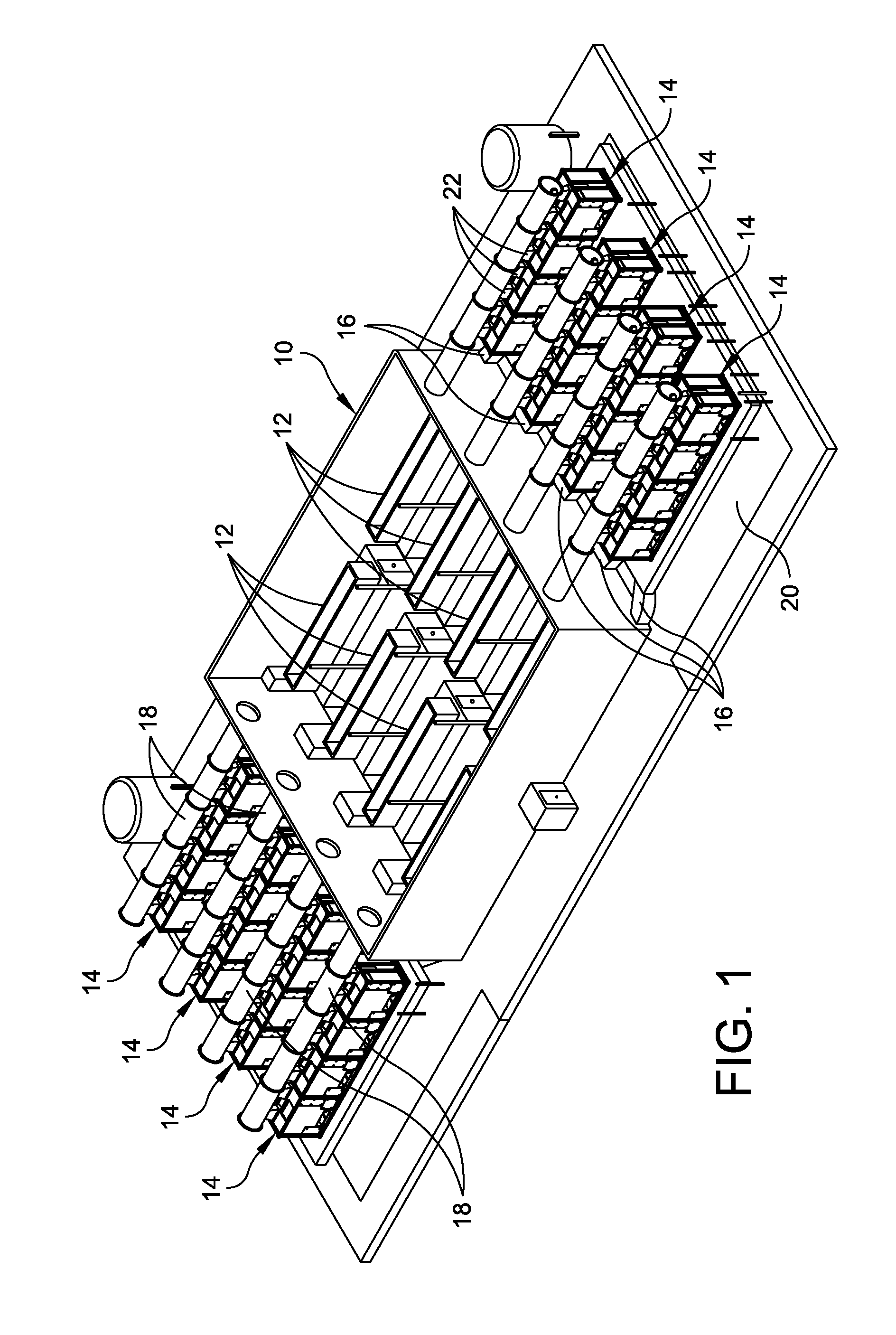
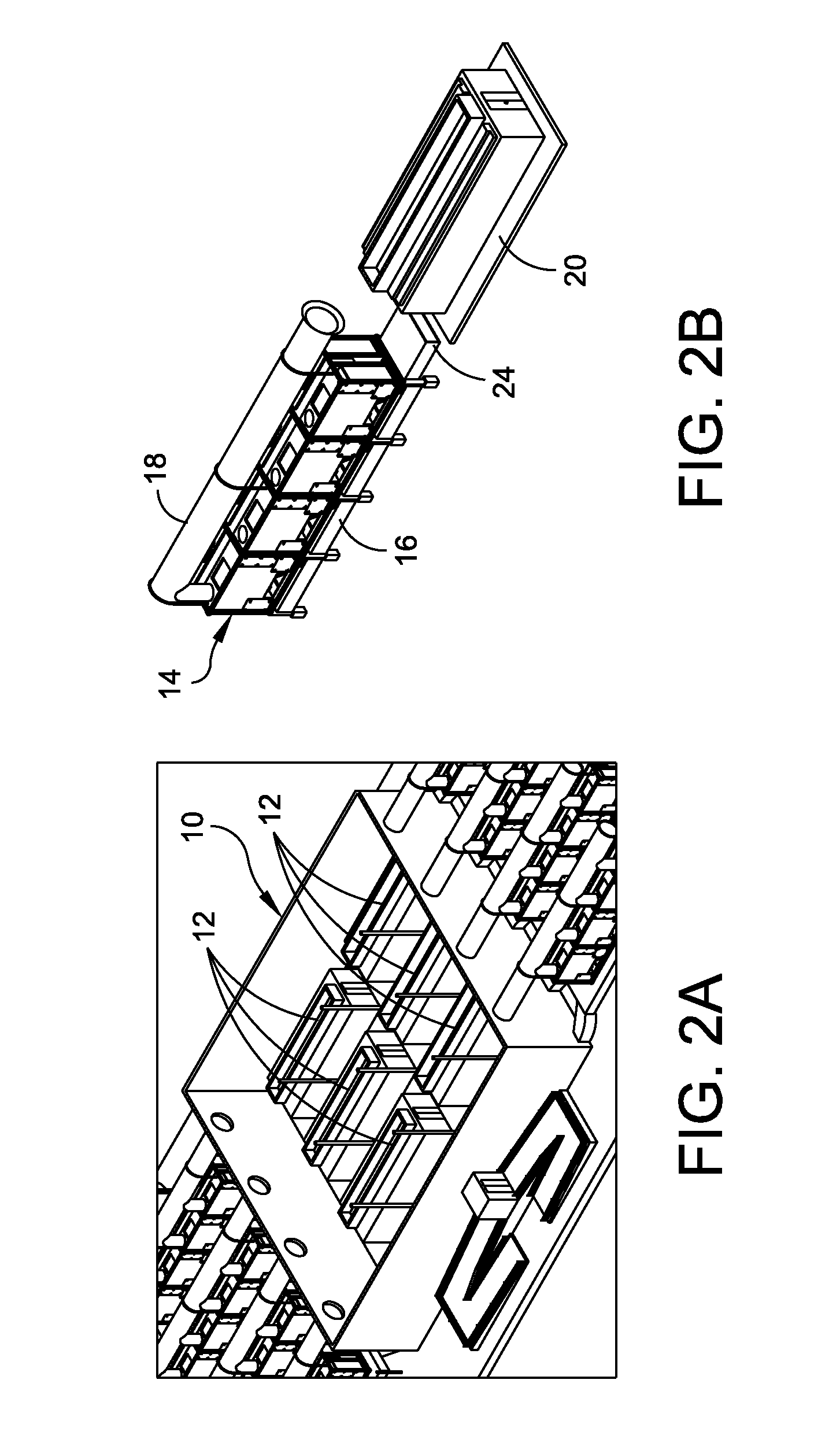
Thermal processing apparatus and cooling method
InactiveUS9099505B2Efficient solutionLow heat resistanceAfter-treatment apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess engineeringHeating furnace
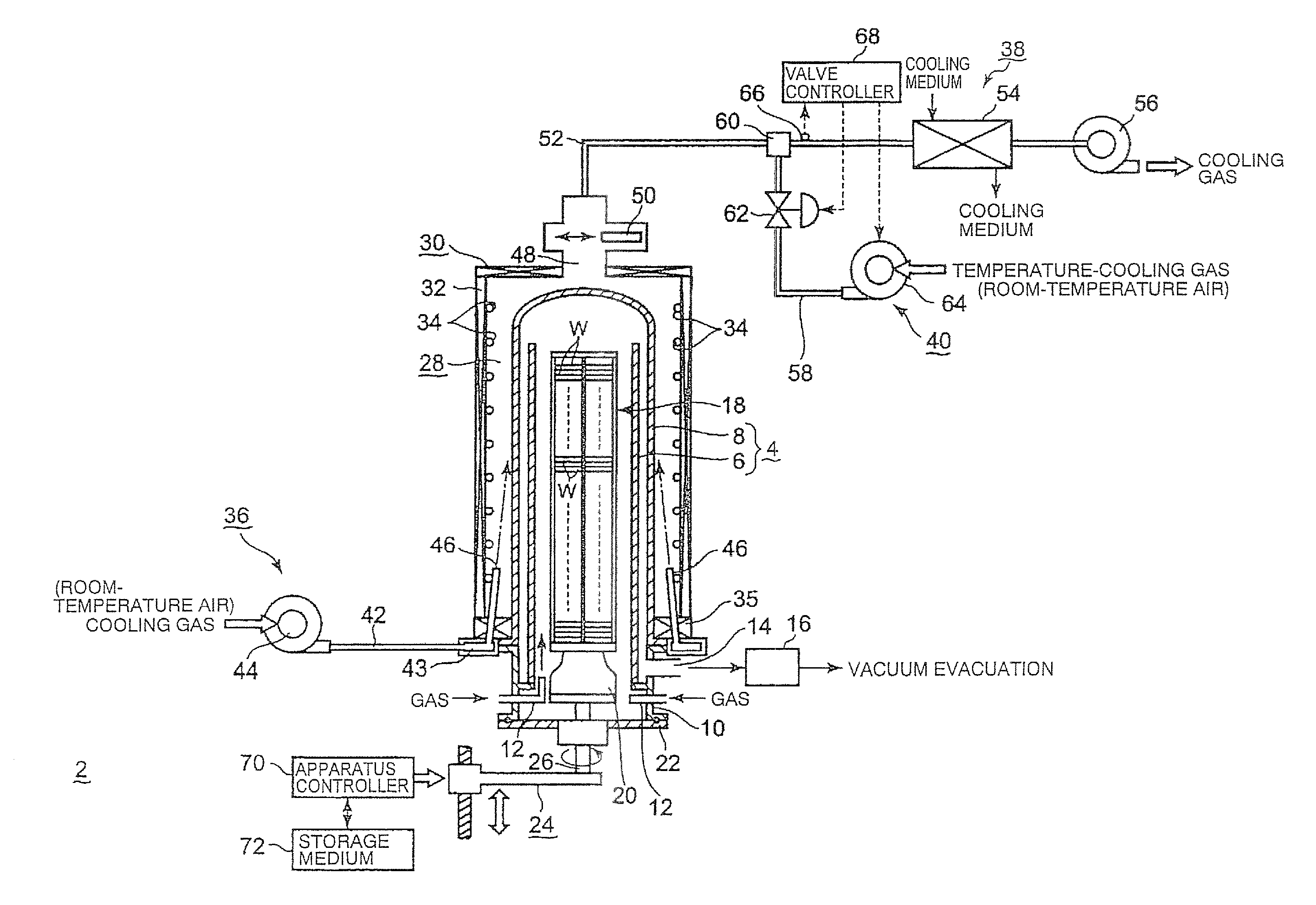
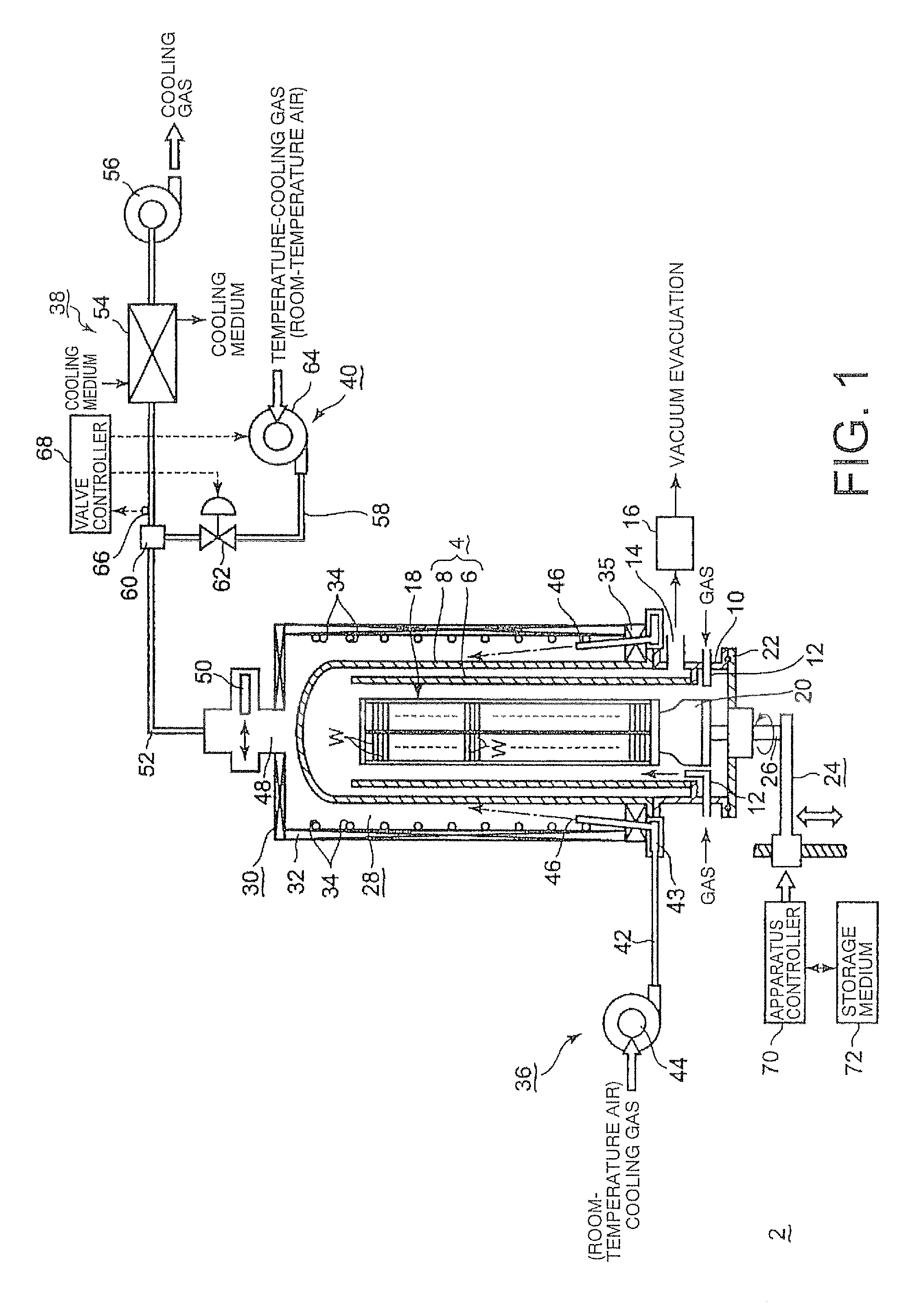
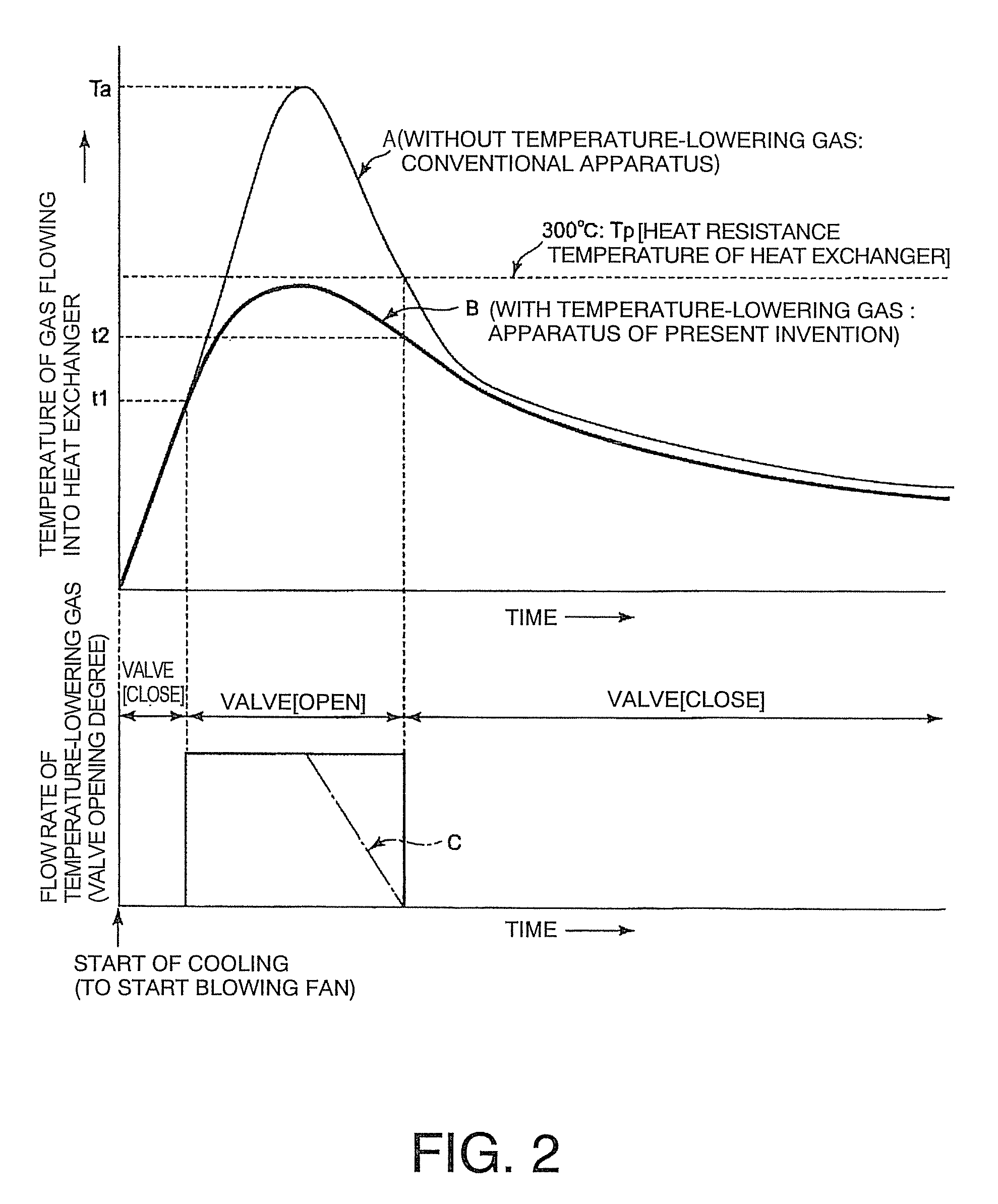
A thermal processing apparatus including: a cylindrical processing vessel; a support unit to be loaded into and unloaded from the vessel; and a heating furnace surrounding an outer periphery of the vessel, with a cooling space therebetween. The furnace is connected to a cooling-gas introduction unit, including a gas introduction passage to which a blowing fan is connected, for introducing a cooling gas into the cooling space during a temperature lowering operation after a thermal process. The furnace is connected to a cooling-gas discharge unit, including a heat exchanger, a suction fan, and a gas discharge passage, for discharging the cooling gas of a raised temperature from the cooling space. Connected to the gas discharge passage at a position upstream of the heat exchanger is a temperature-lowering gas introduction unit for introducing a temperature-lowering gas to the cooling gas of a raised temperature so as to lower its temperature.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Controlled cooling methods and apparatus for laser sintering part-cake
ActiveUS20060118532A1Effectively transferring heat awayEfficient heatingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallurgyLaser
The invention is a method for controllably cooling at least a portion of a part-cake from a laser sintering system to minimize cool down time, maximize throughput, and minimize thermal gradients within the part-cake. The method generally comprises forming one or more thermal transfer channels within the part-cake. The thermal transfer channels can include ducts and cooling fins in the part-cake surrounding the formed part. The method can further comprise removing unfused powder from the ducts and introducing cooling media into the ducts. The invention also includes a part-cake having thermal transfer channels formed therein and a laser sintering apparatus comprising a part-cake containing cylinder having permanent fittings therein for receiving terminal portions of thermal transfer channels formed in the part-cake.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and system for providing cooling of components in a data storage system
ActiveUS7751188B1Improve cooling effectConsume high powerDomestic cooling apparatusCompression machinesCold airElectronic systems
Owner:EMC CORP
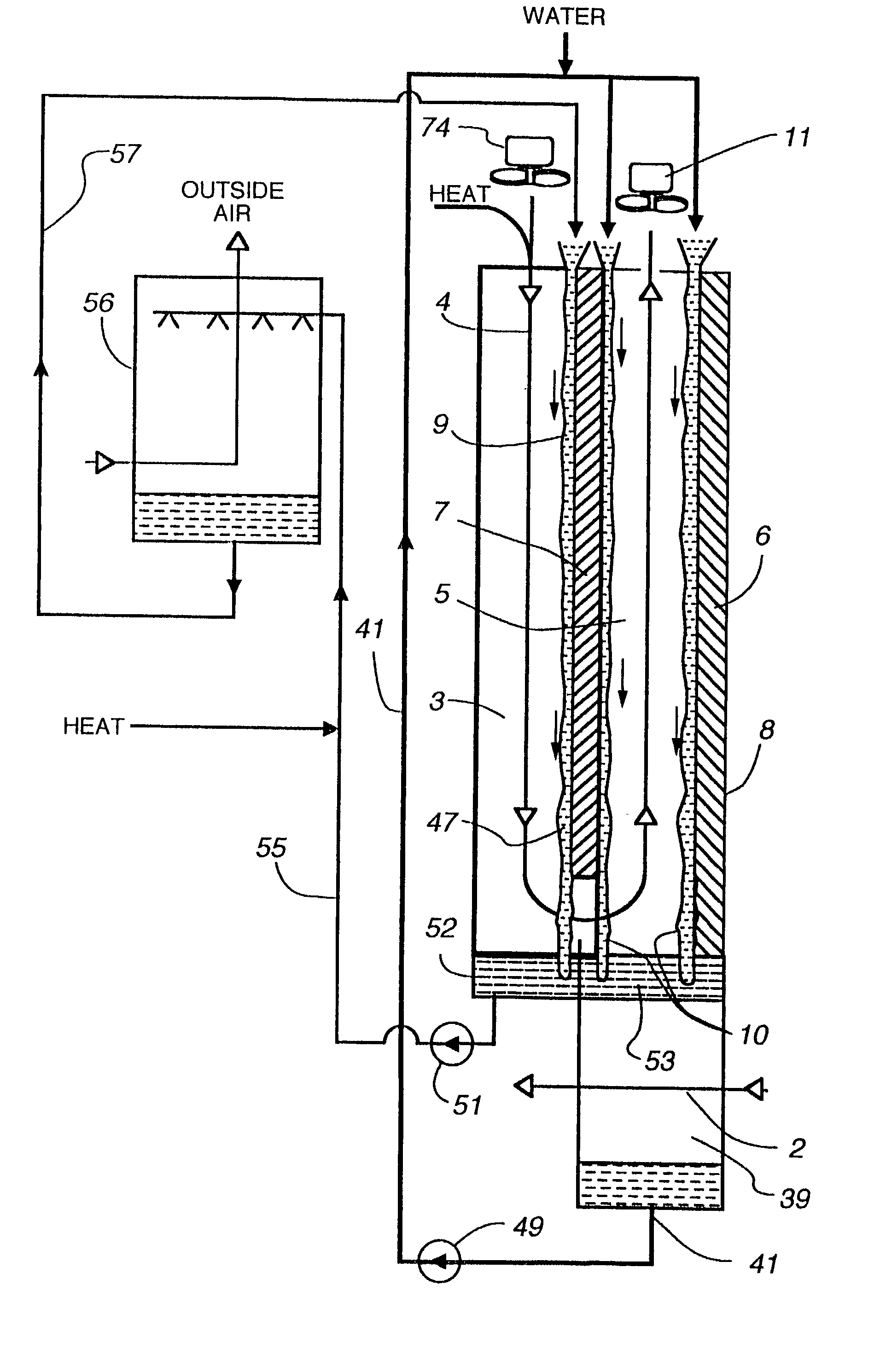
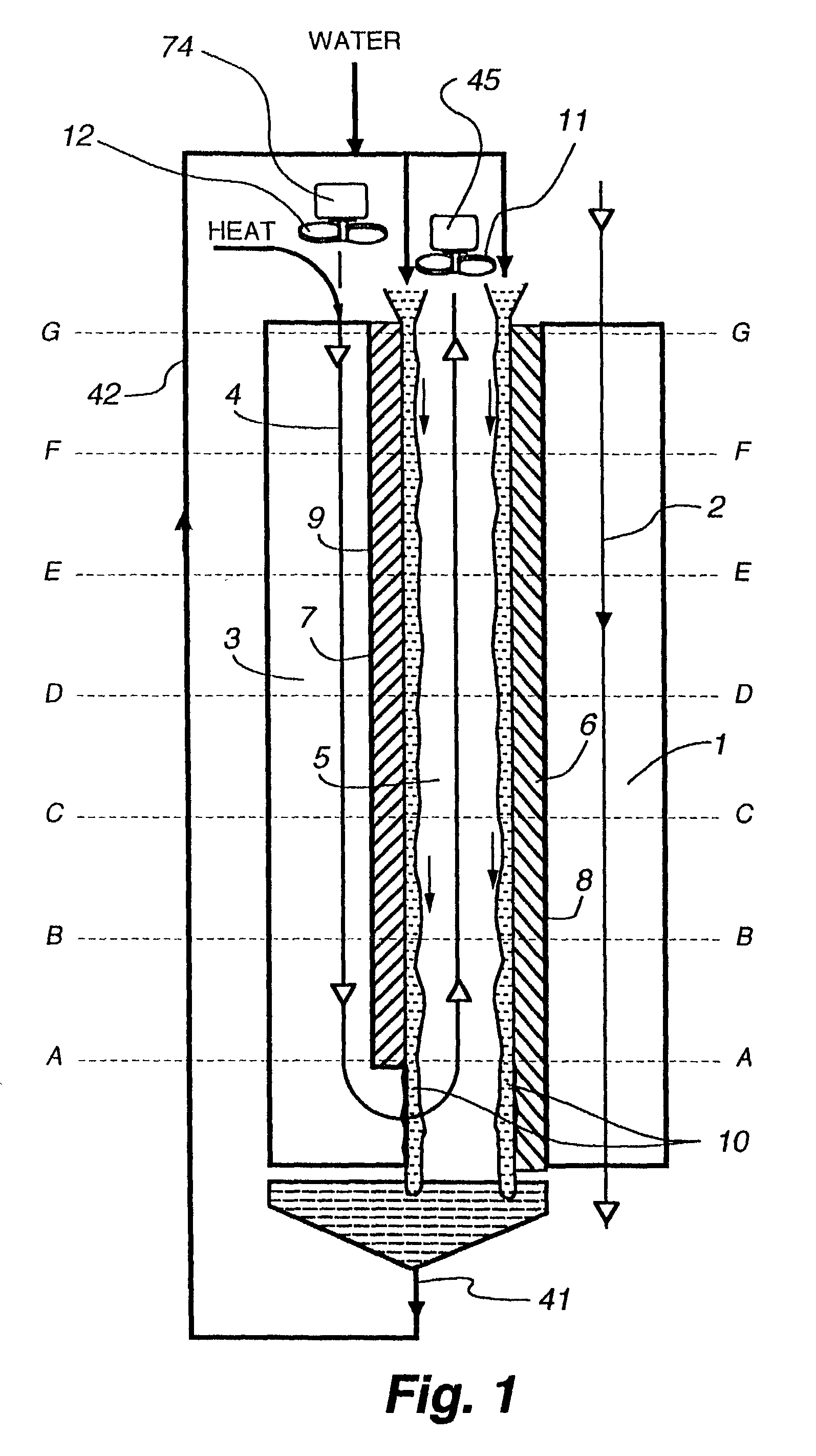
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
InactiveUS6497107B2Less energyHigh energy costFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesWorking fluidEvaporation
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
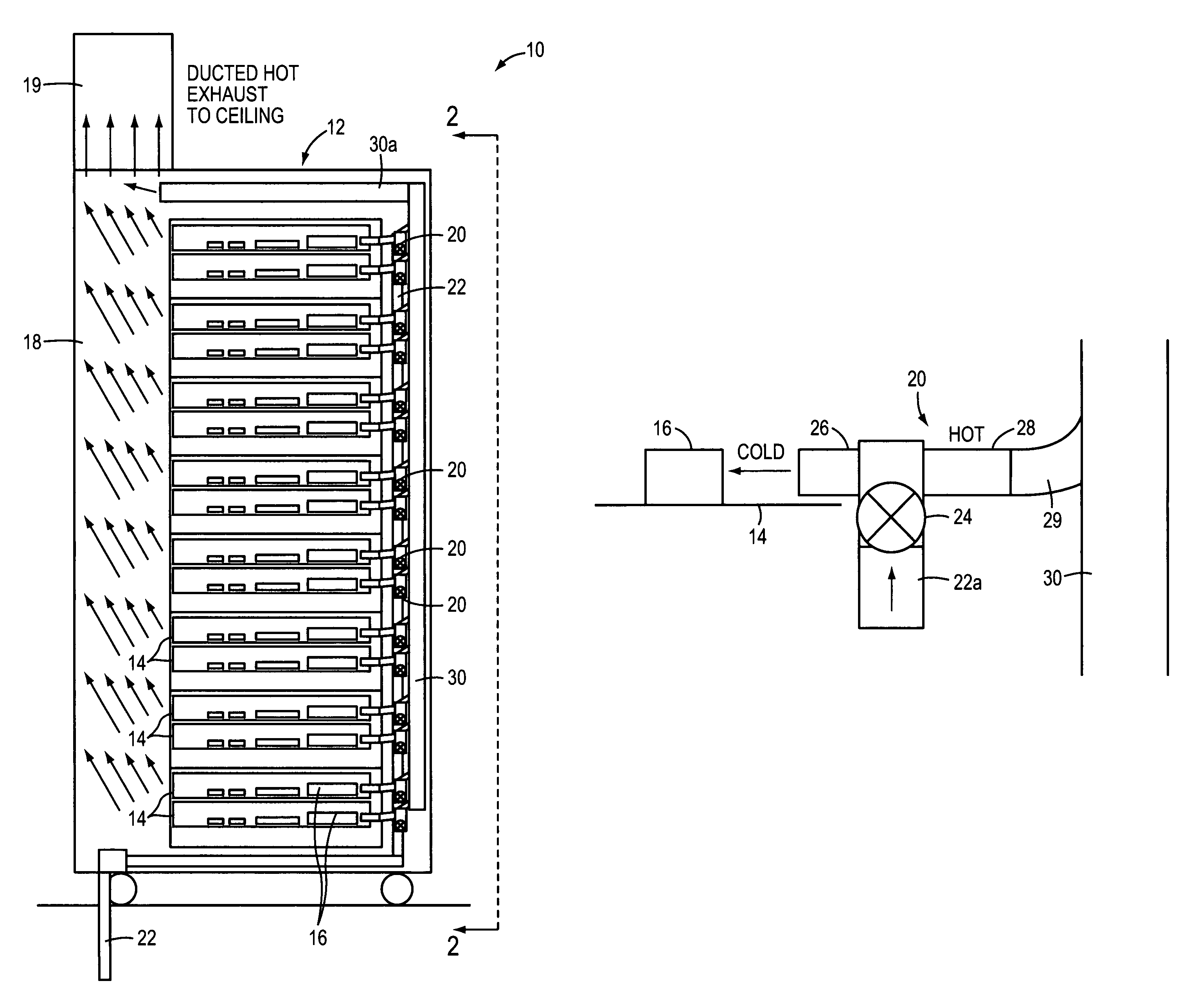
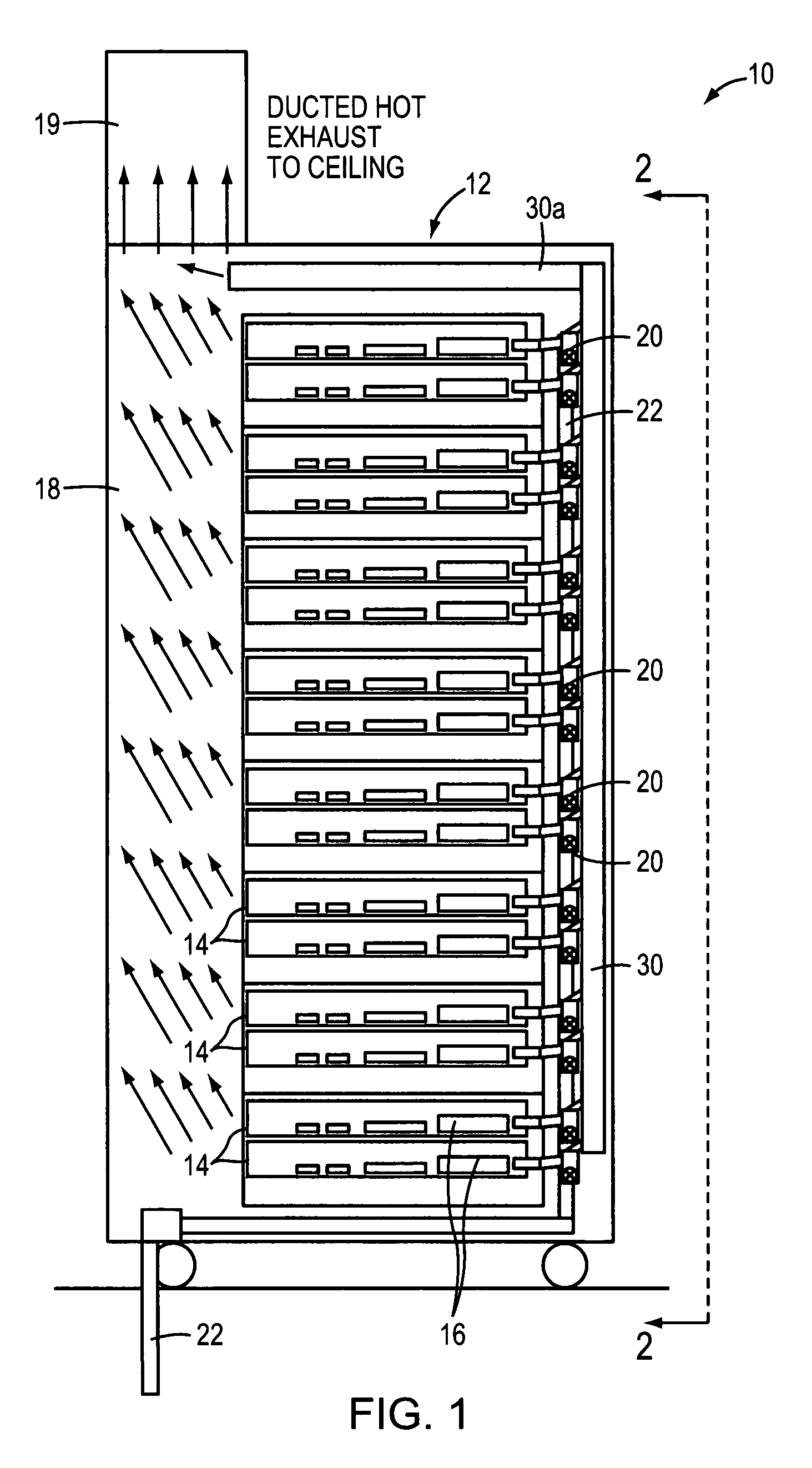
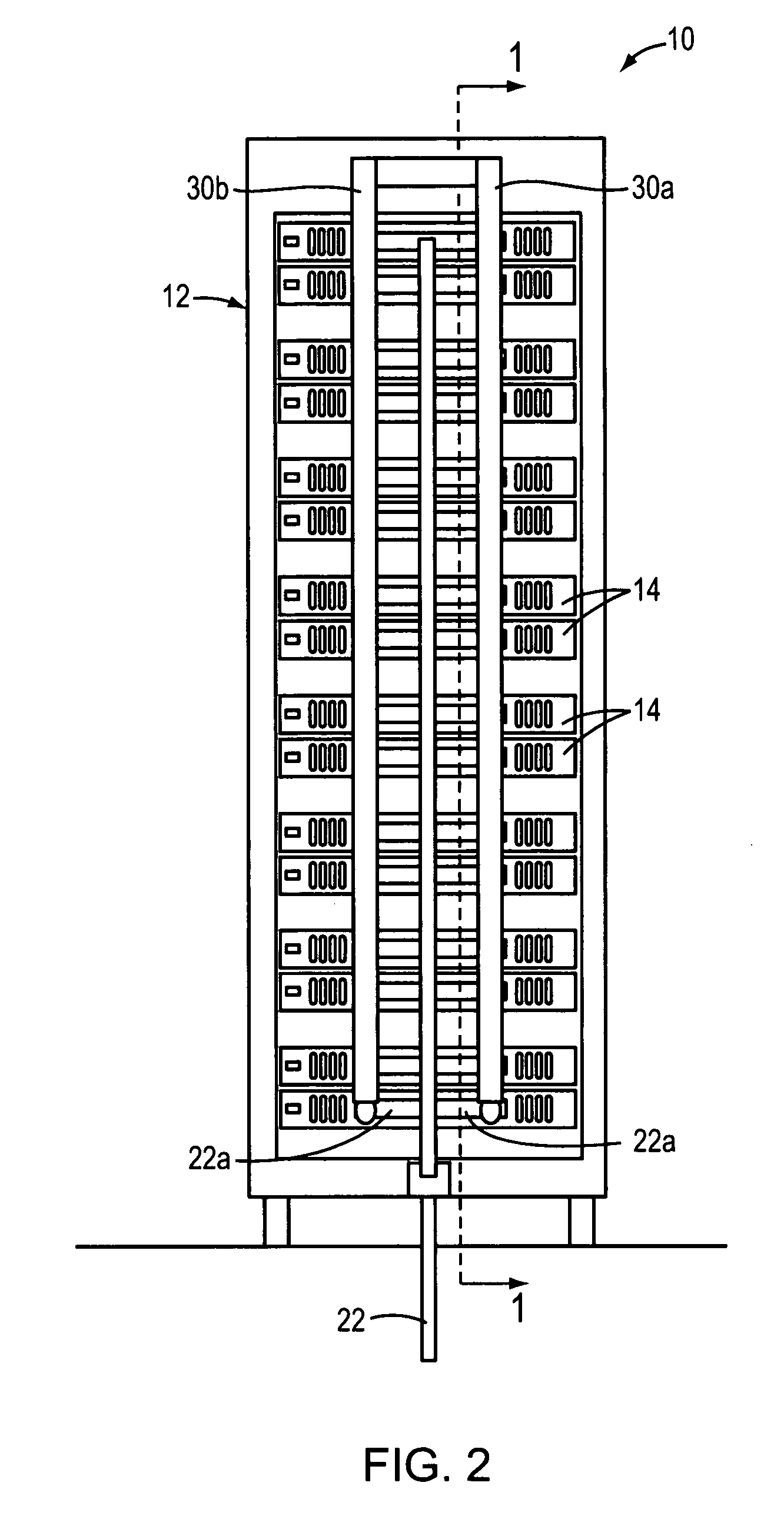
Method of facilitating cooling of electronics racks of a data center employing multiple cooling stations
InactiveUS7477514B2Improve cooling effectEasy accessDomestic cooling apparatusHeat exchange apparatusData centerElectronics
A cooling method are provided for cooling air exiting one or more electronics racks of a data center. The cooling system includes at least one cooling station separate and freestanding from at least one respective electronics rack of the data center, and configured for disposition of an air outlet side of electronics rack adjacent thereto for cooling egressing air from the electronics rack. The cooling station includes a frame structure separate and freestanding from the respective electronics rack, and an air-to-liquid heat exchange assembly supported by the frame structure. The heat exchange assembly includes an inlet and an outlet configured to respectively couple to coolant supply and coolant return lines for facilitating passage of coolant therethrough. The air-to-liquid heat exchange assembly is sized to cool egressing air from the air outlet side of the respective electronics rack before being expelled into the data center.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cooling apparatus for fired body, firing furnace, cooling method of ceramic fired body, and method for manufacturing honeycomb structure
InactiveUS20080136053A1Small distanceCharge manipulationHandling discharged materialAir atmosphereMetallurgy
A cooling apparatus for a fired body includes a transporting member for transporting a firing jig in which a ceramic fired body is housed; a plurality of blowers for cooling the ceramic fired body; and a suction mechanism for changing the atmosphere inside the firing jig from an inert gas atmosphere to an air atmosphere.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
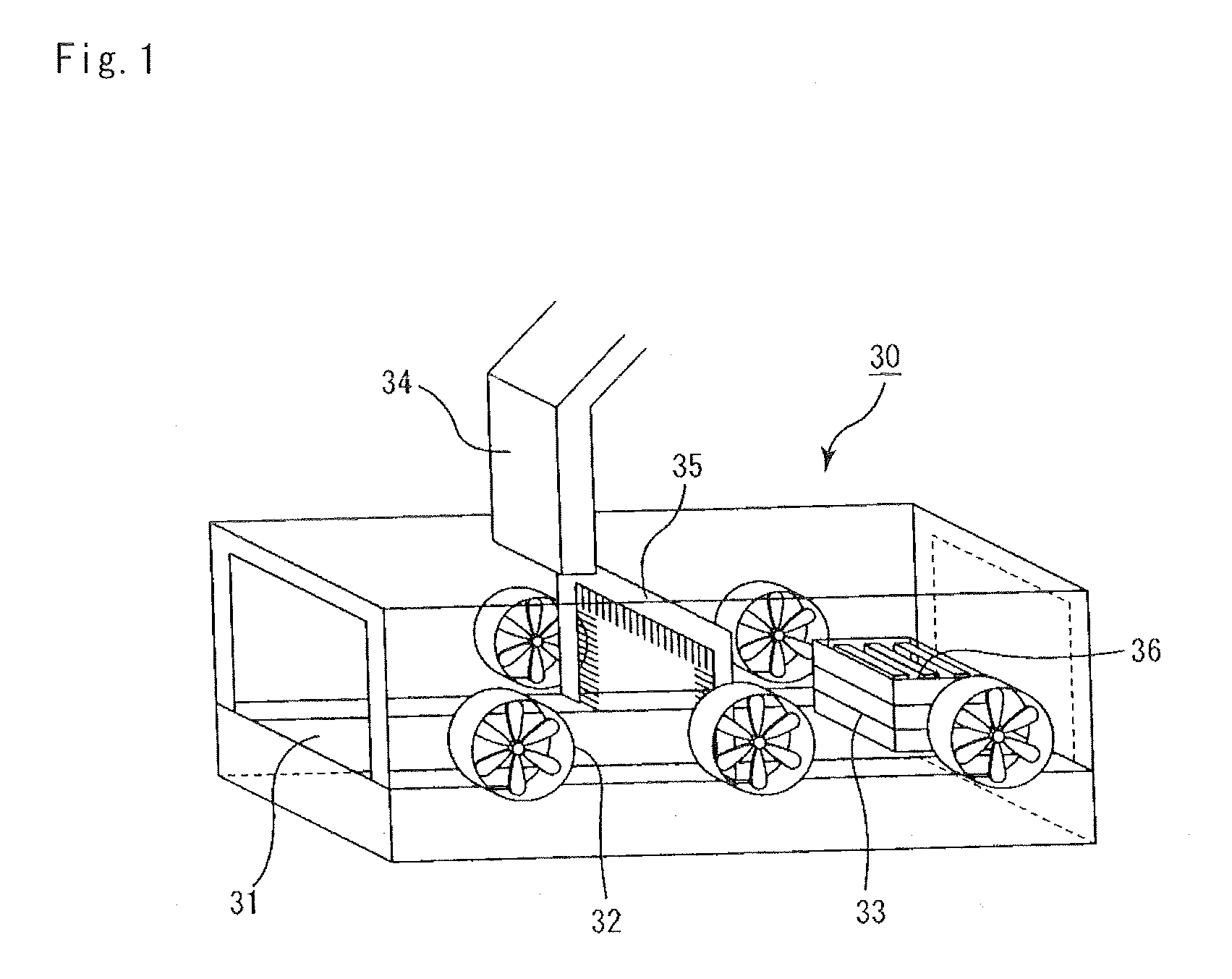
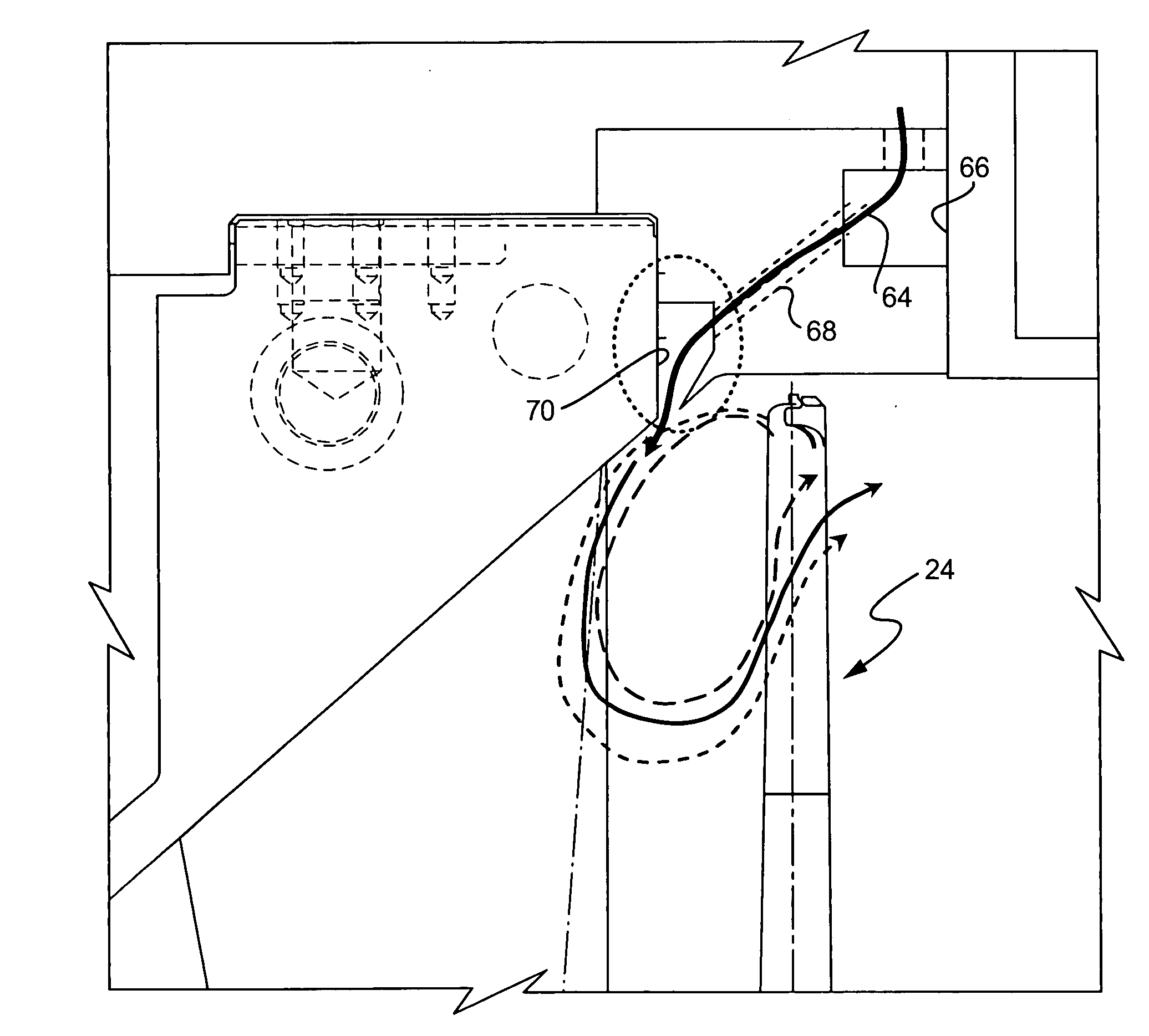
Wind turbine generators having wind assisted cooling systems and cooling methods
A wind generator includes: a nacelle; a hub rotatably carried by the nacelle and including at least a pair of wind turbine blades; and an electricity producing generator including a stator and a rotor carried by the nacelle. The rotor is connected to the hub and rotatable in response to wind acting on the blades to rotate the rotor relative to the stator to generate electricity. A cooling system is carried by the nacelle and includes at least one ambient air inlet port opening through a surface of the nacelle downstream of the hub and blades, and a duct for flowing air from the inlet port in a generally upstream direction toward the hub and in cooling relation to the stator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
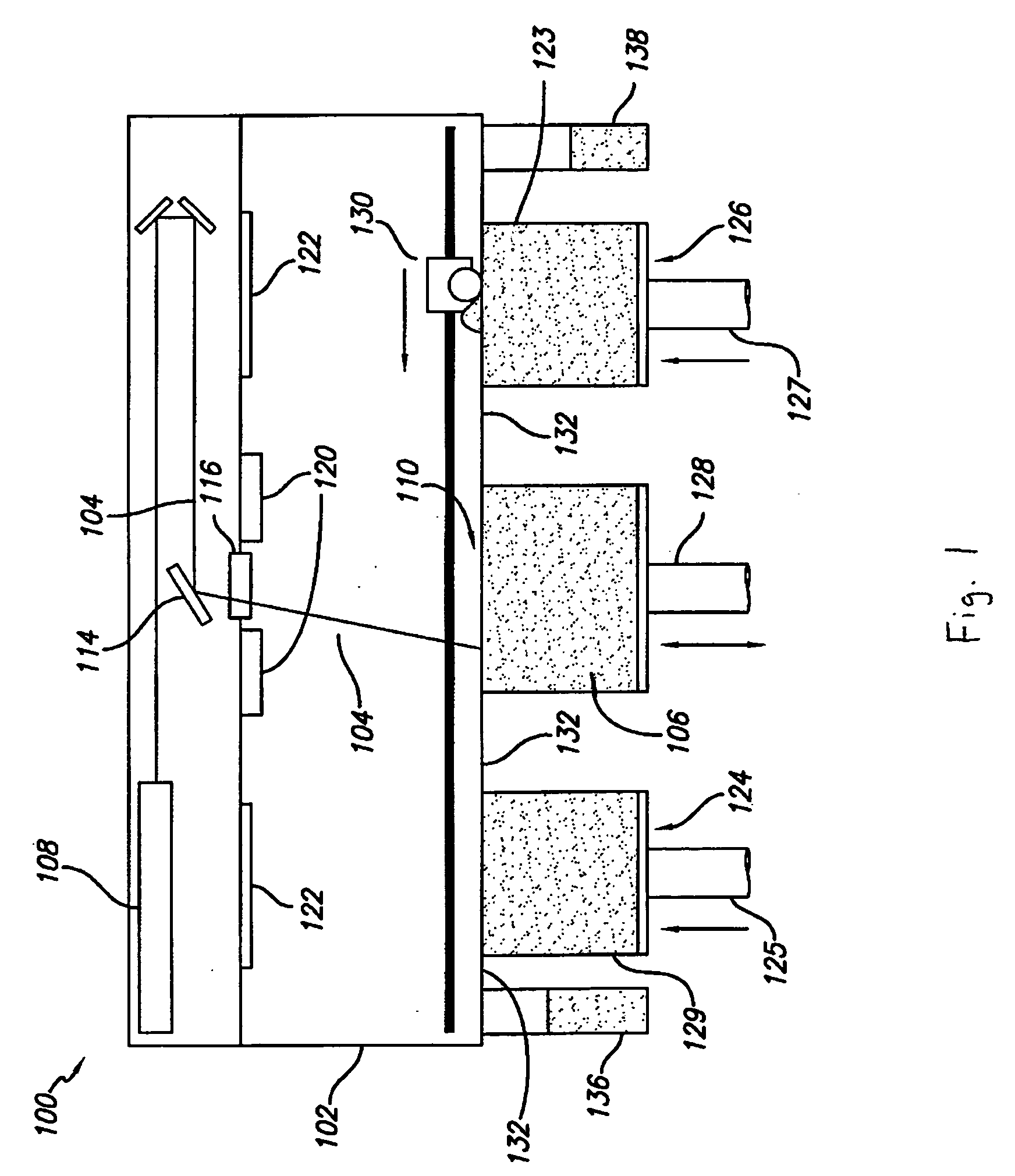
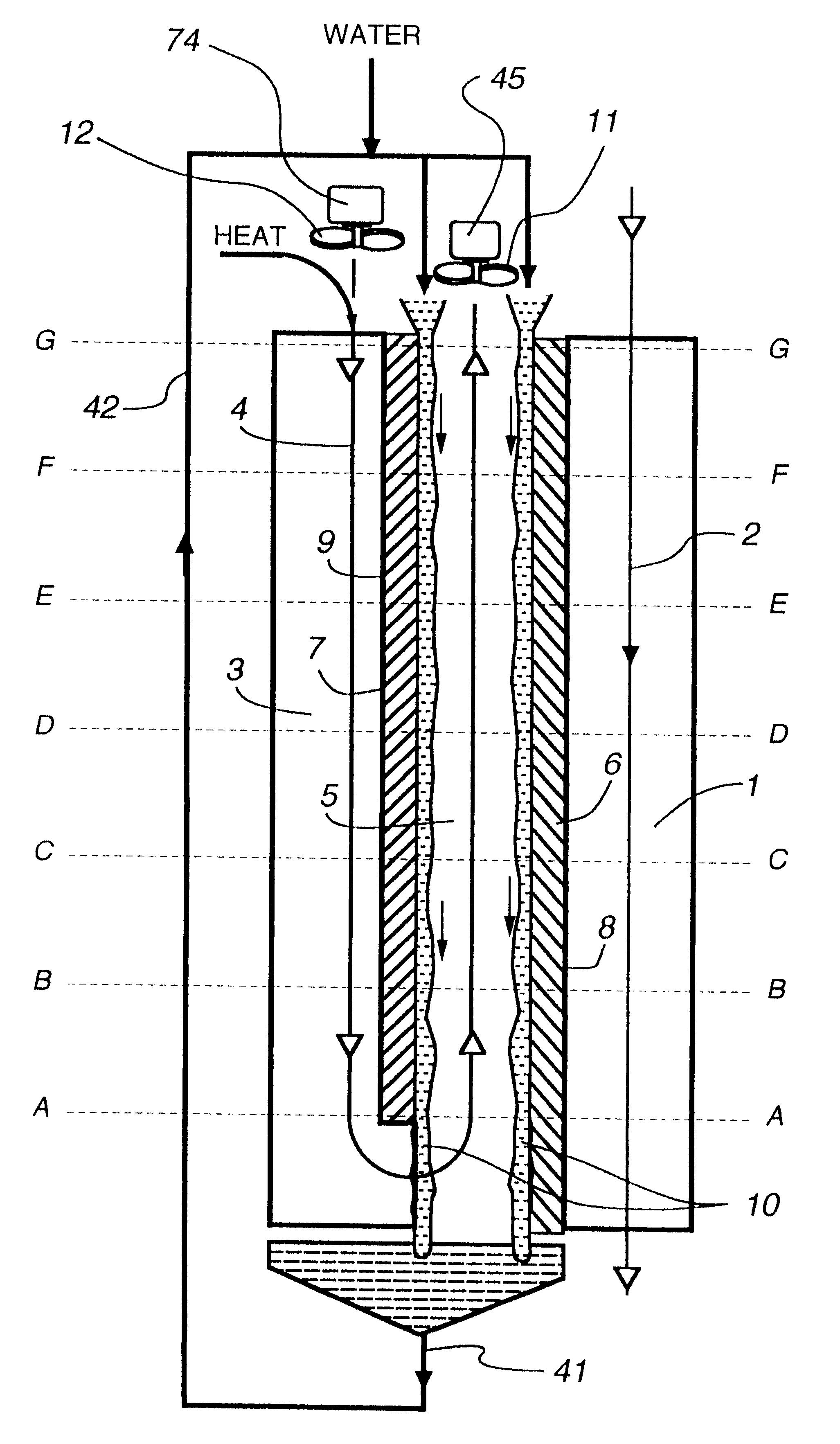
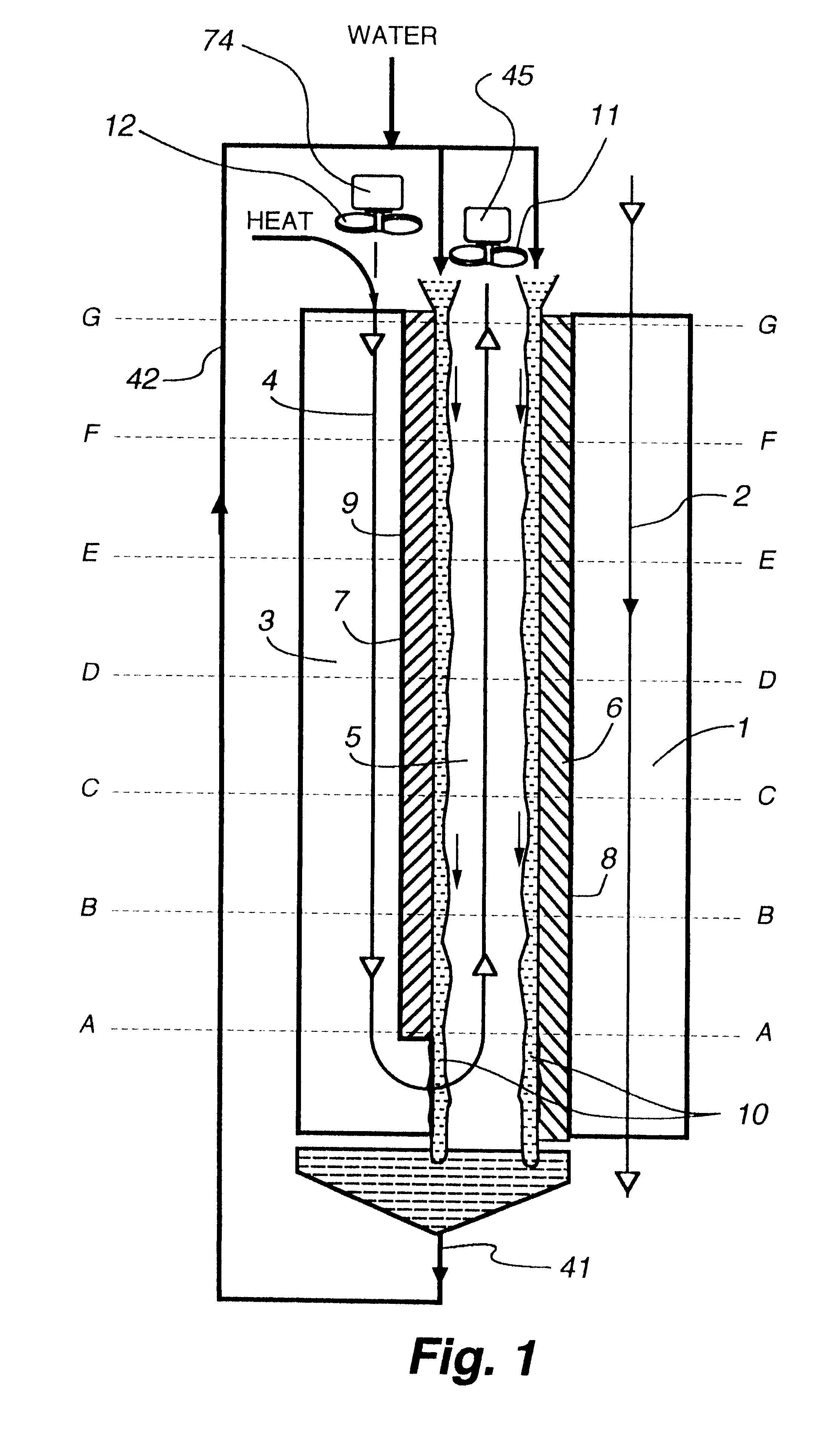
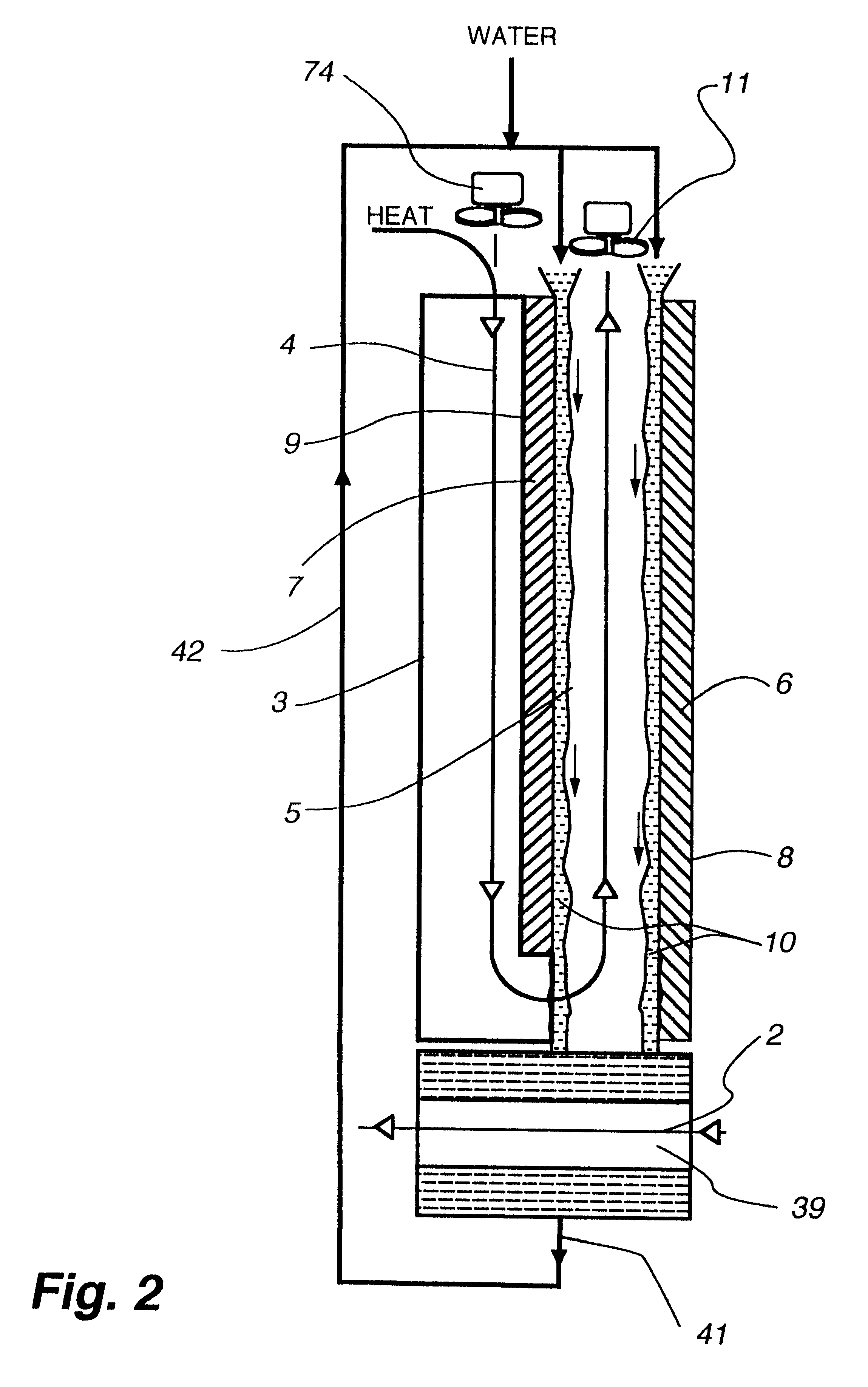
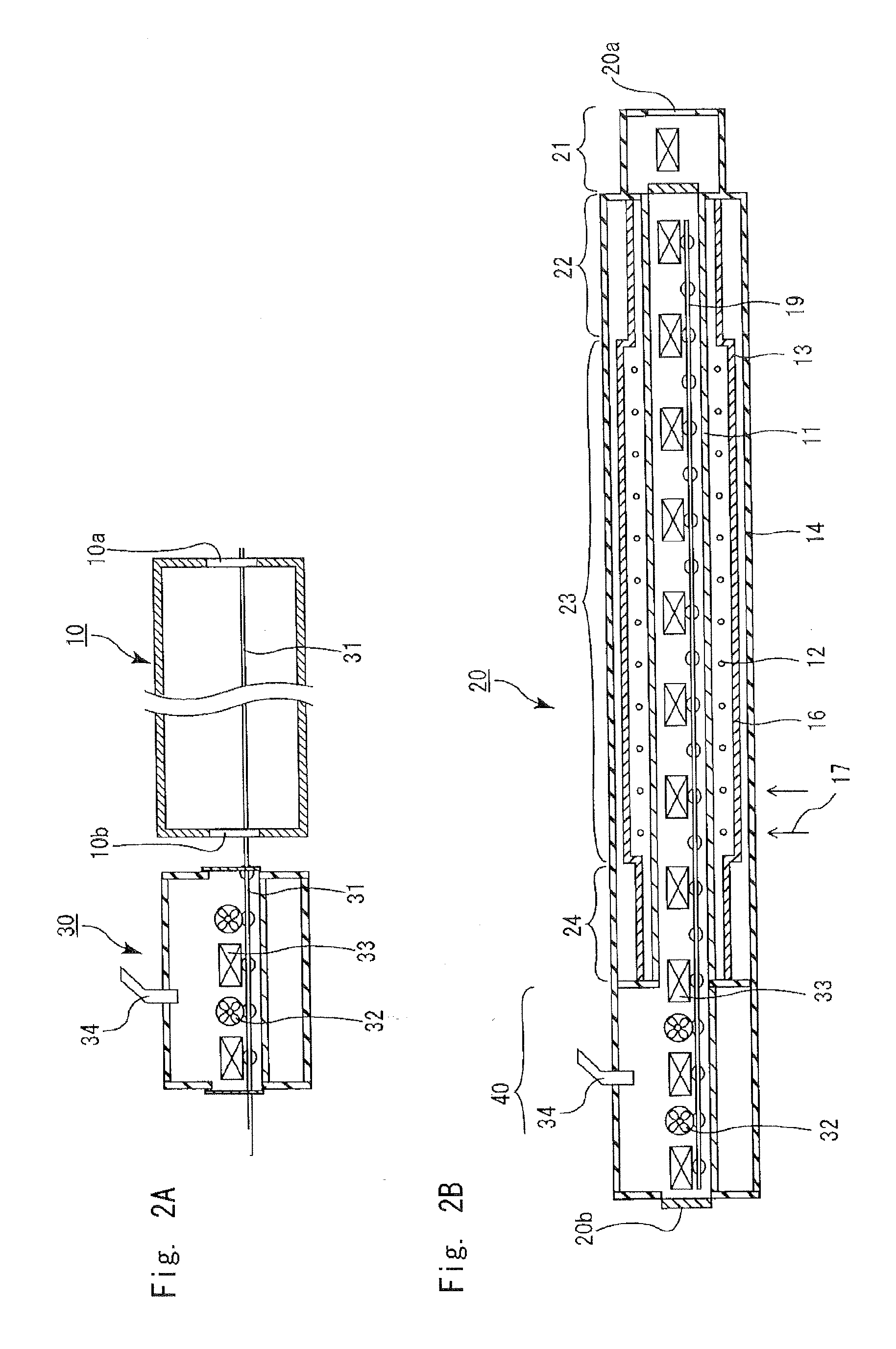
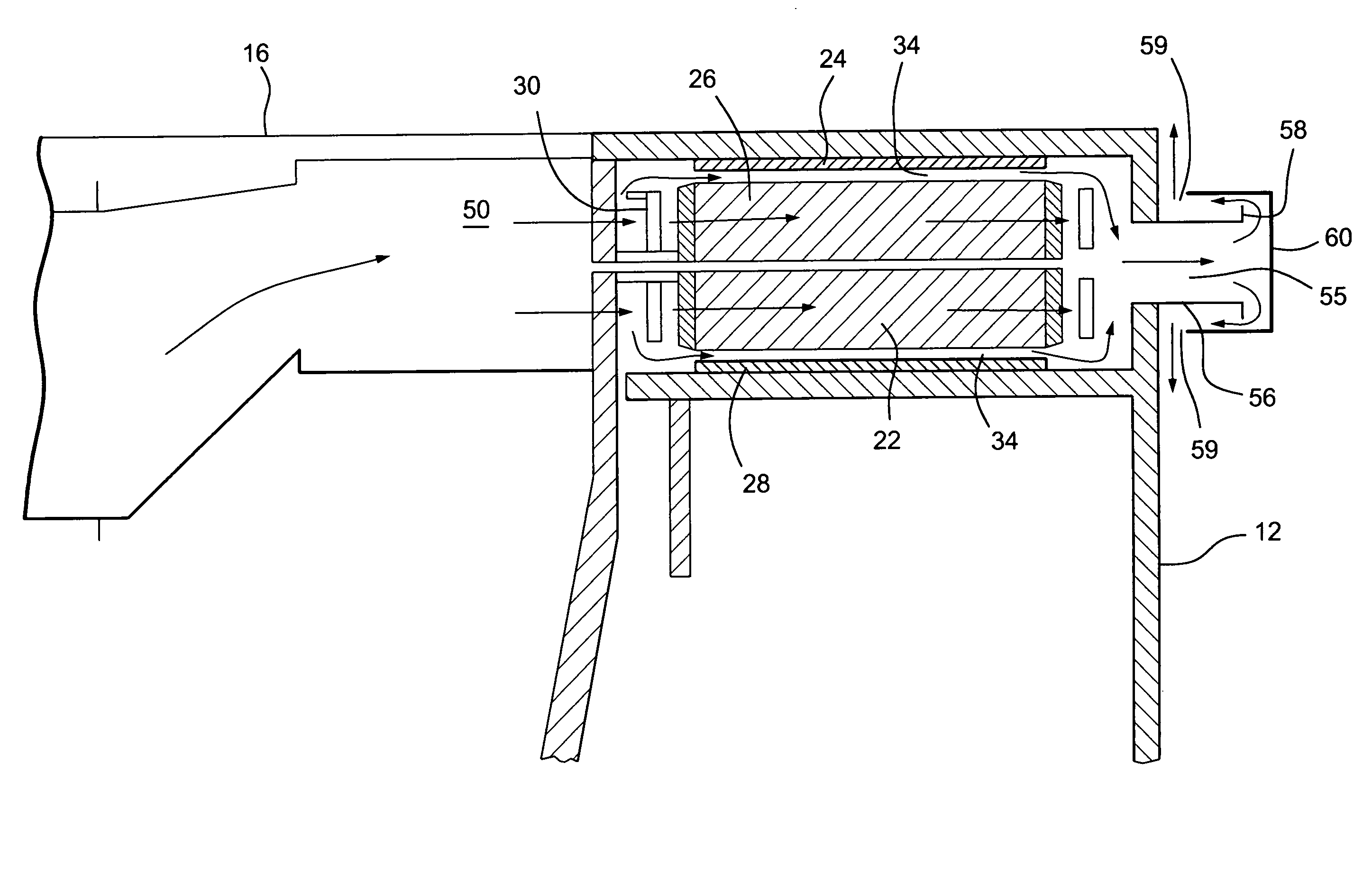
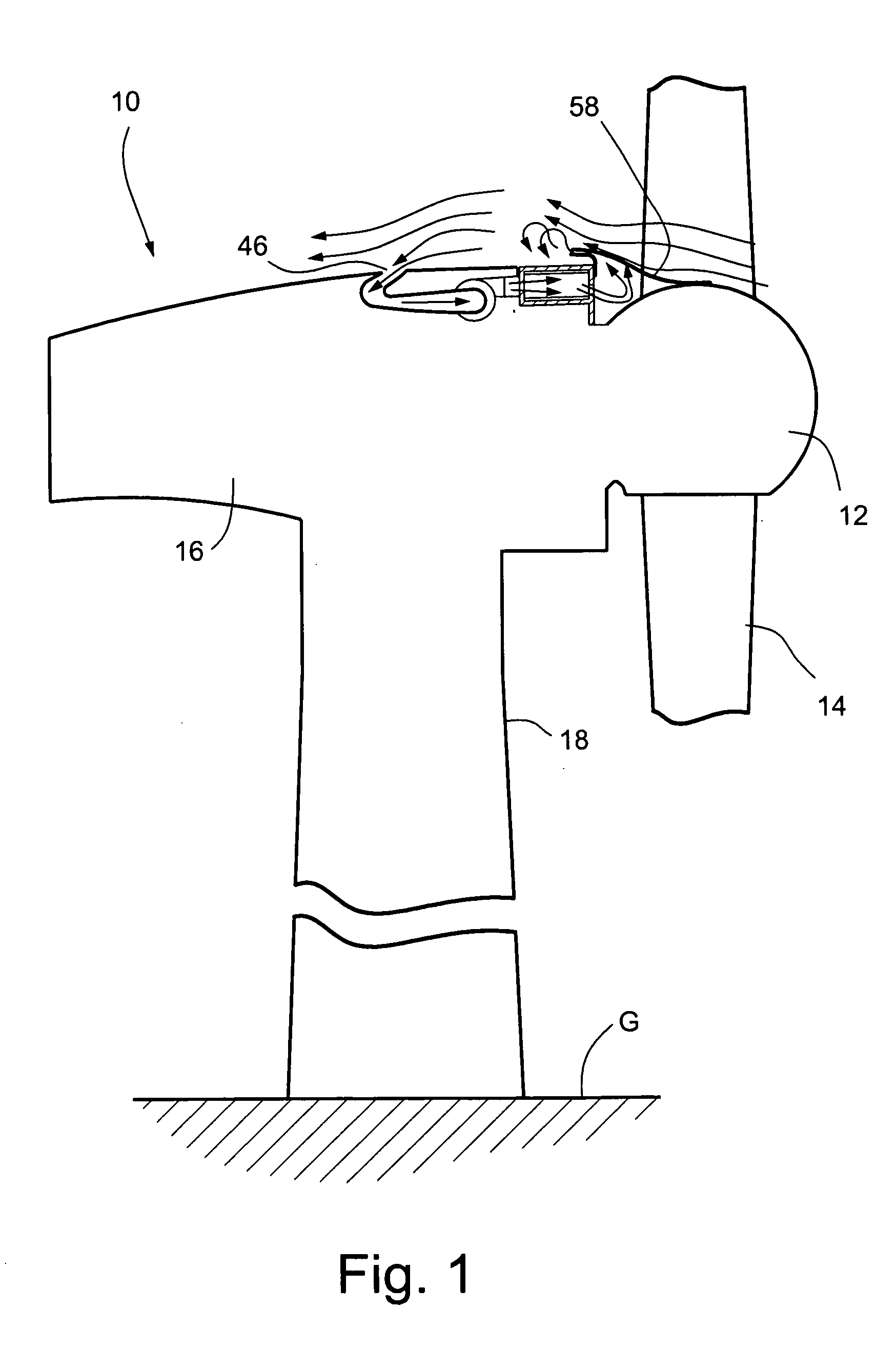
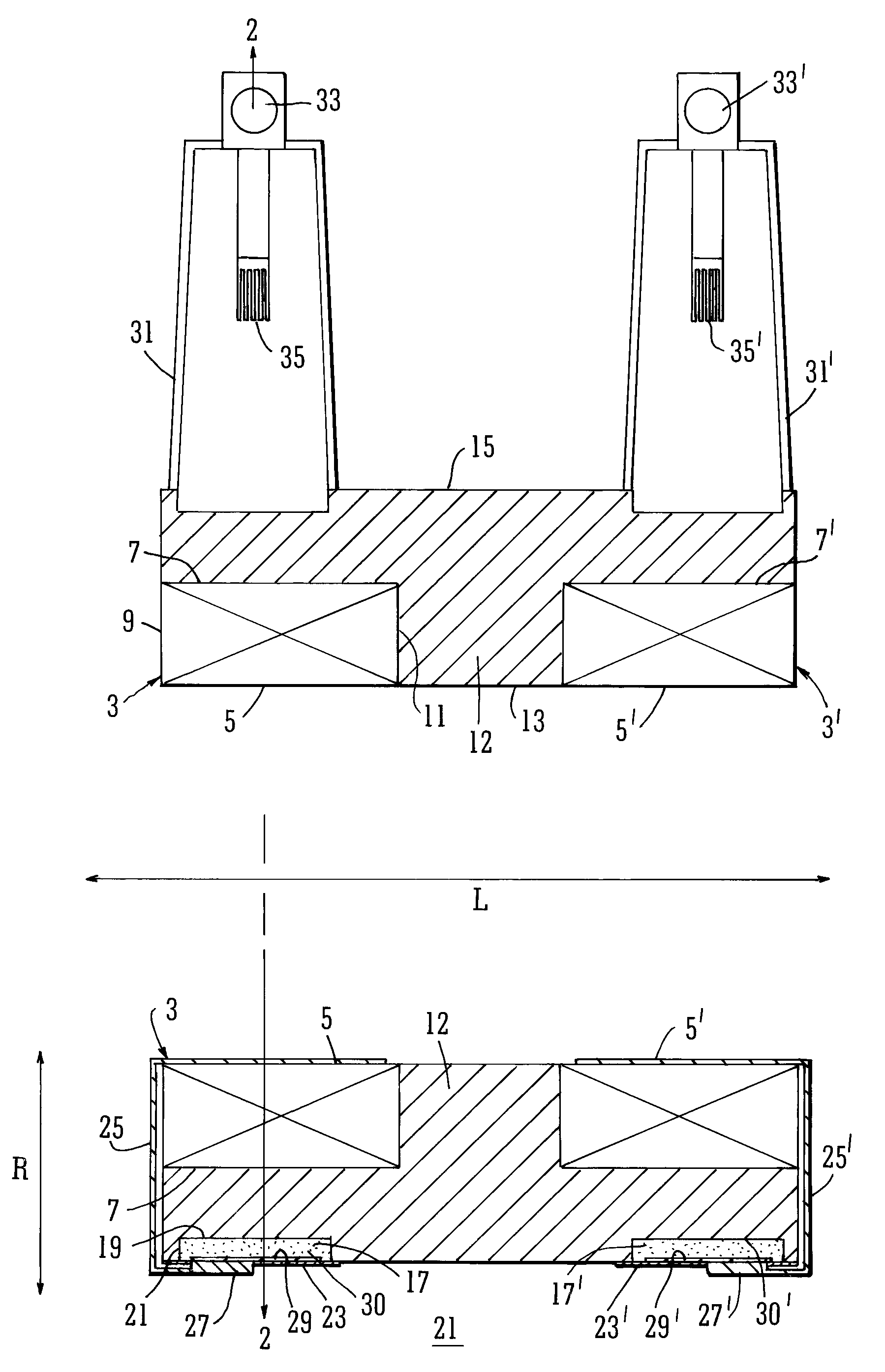
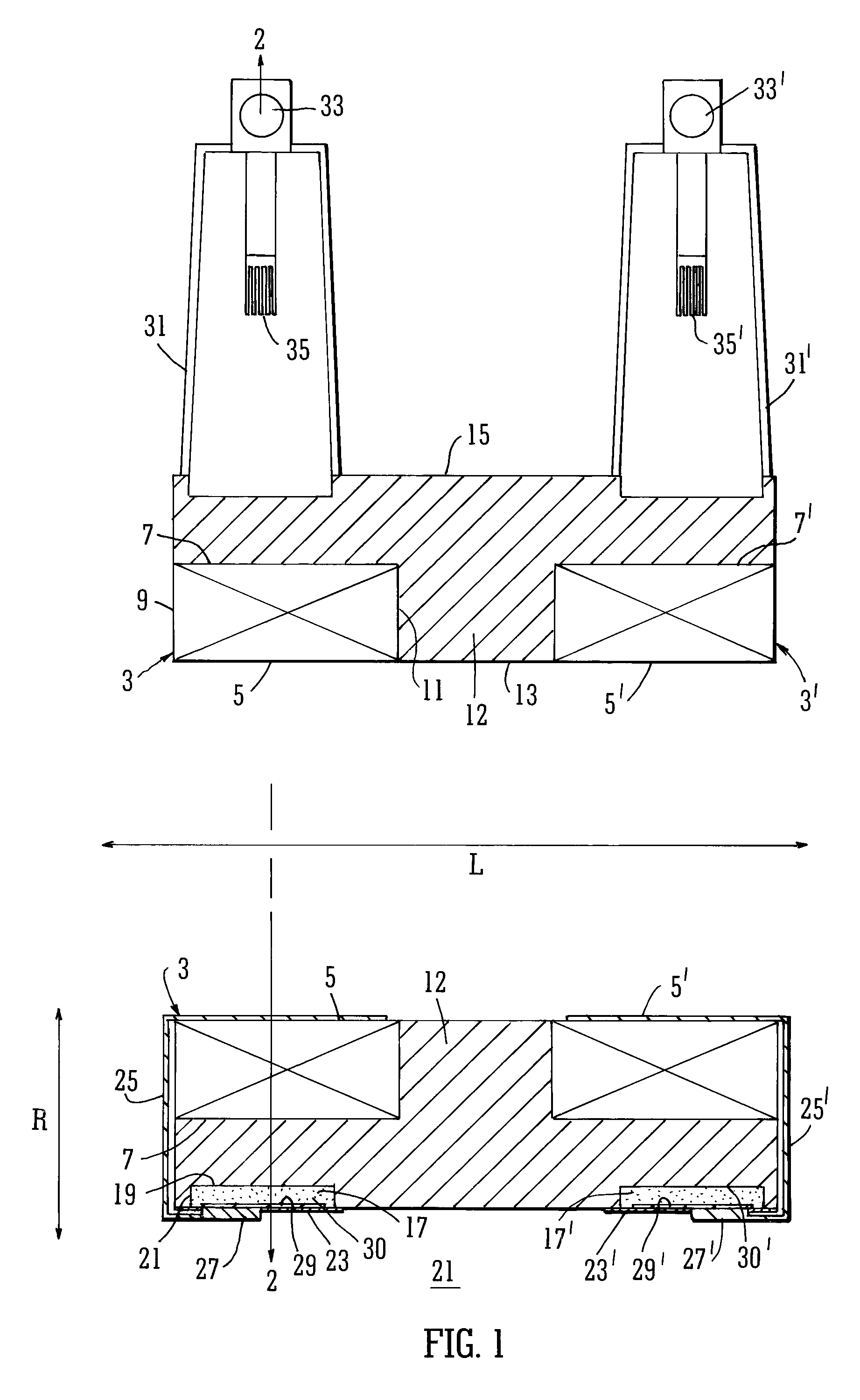
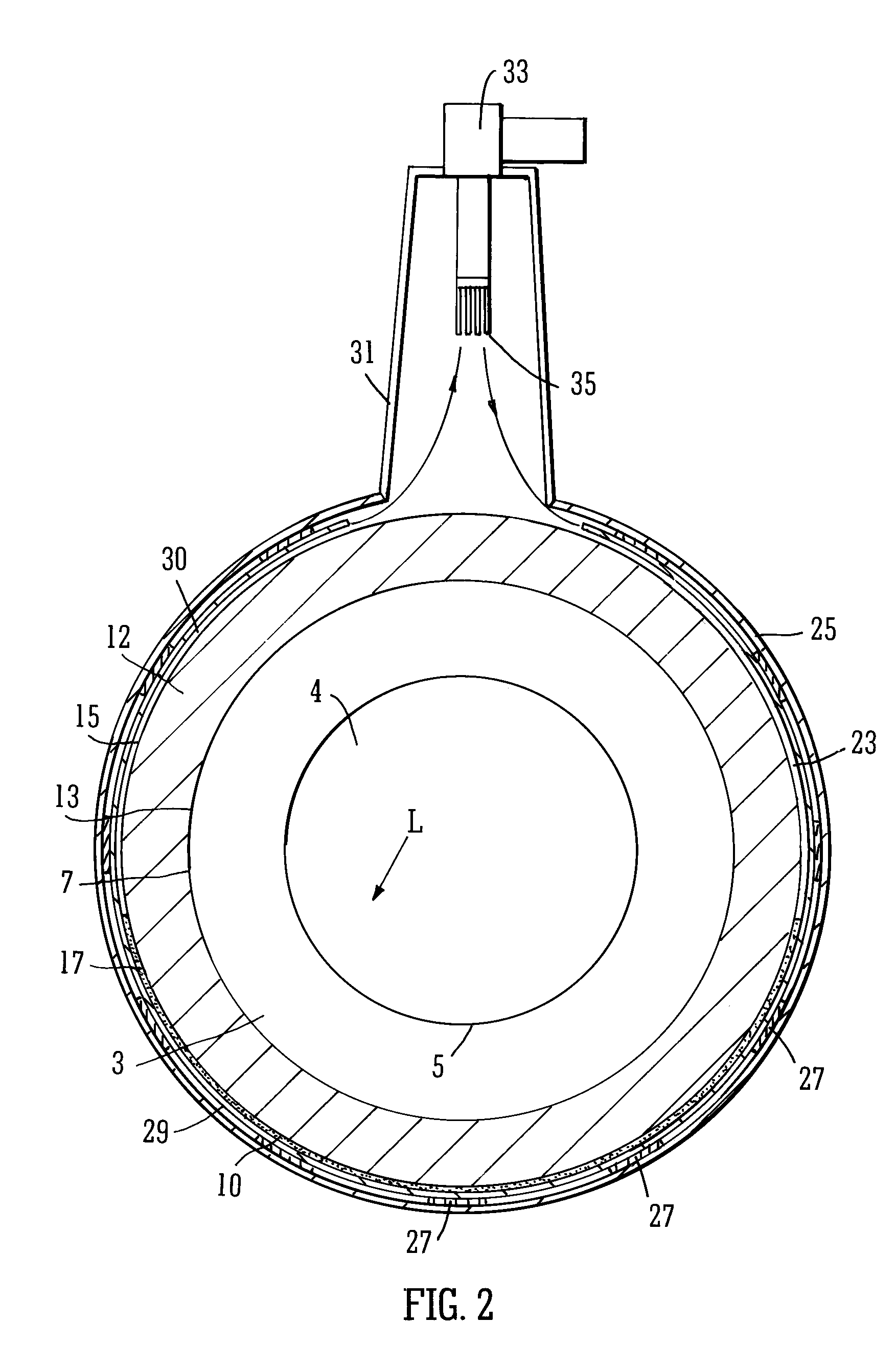
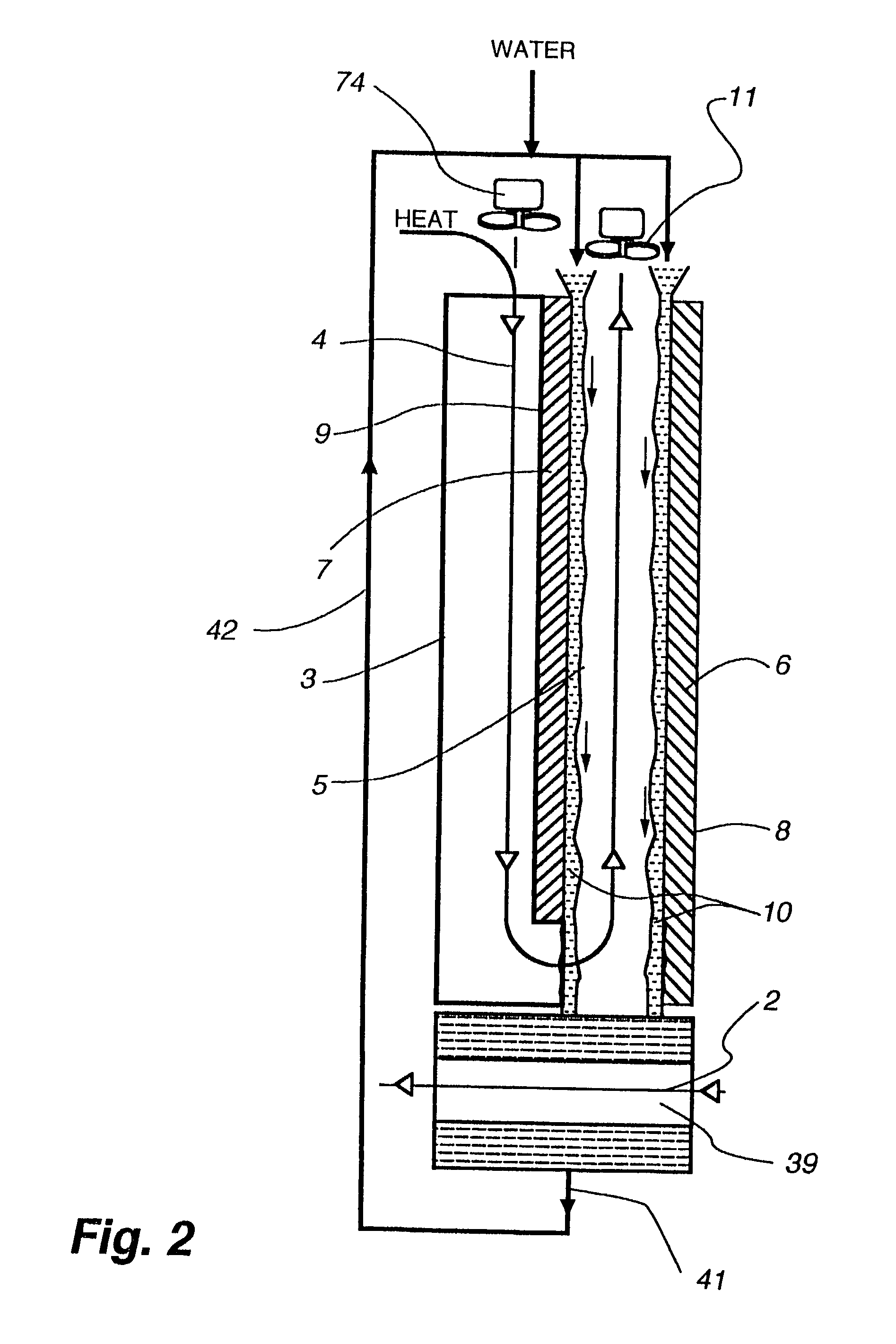
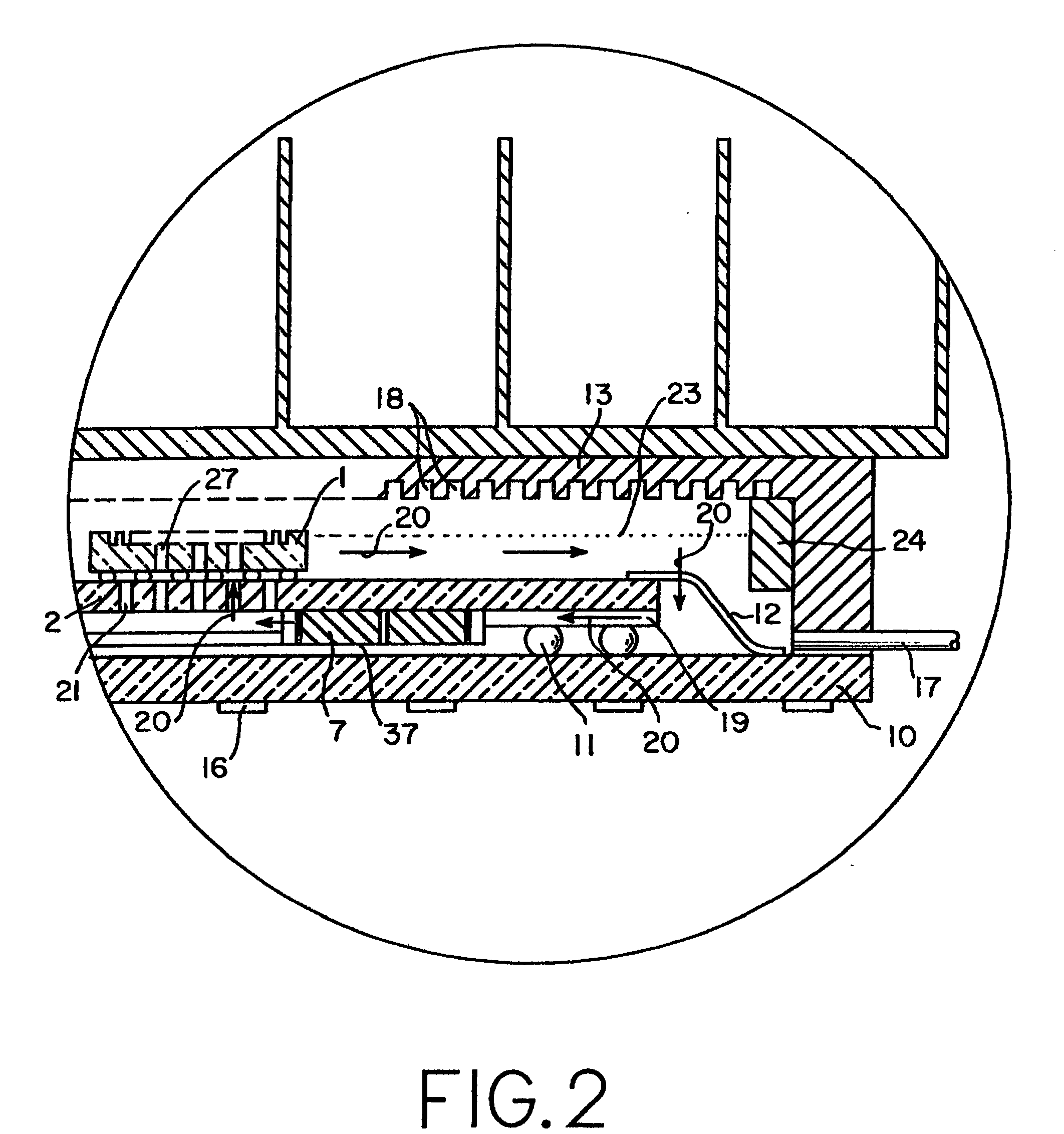
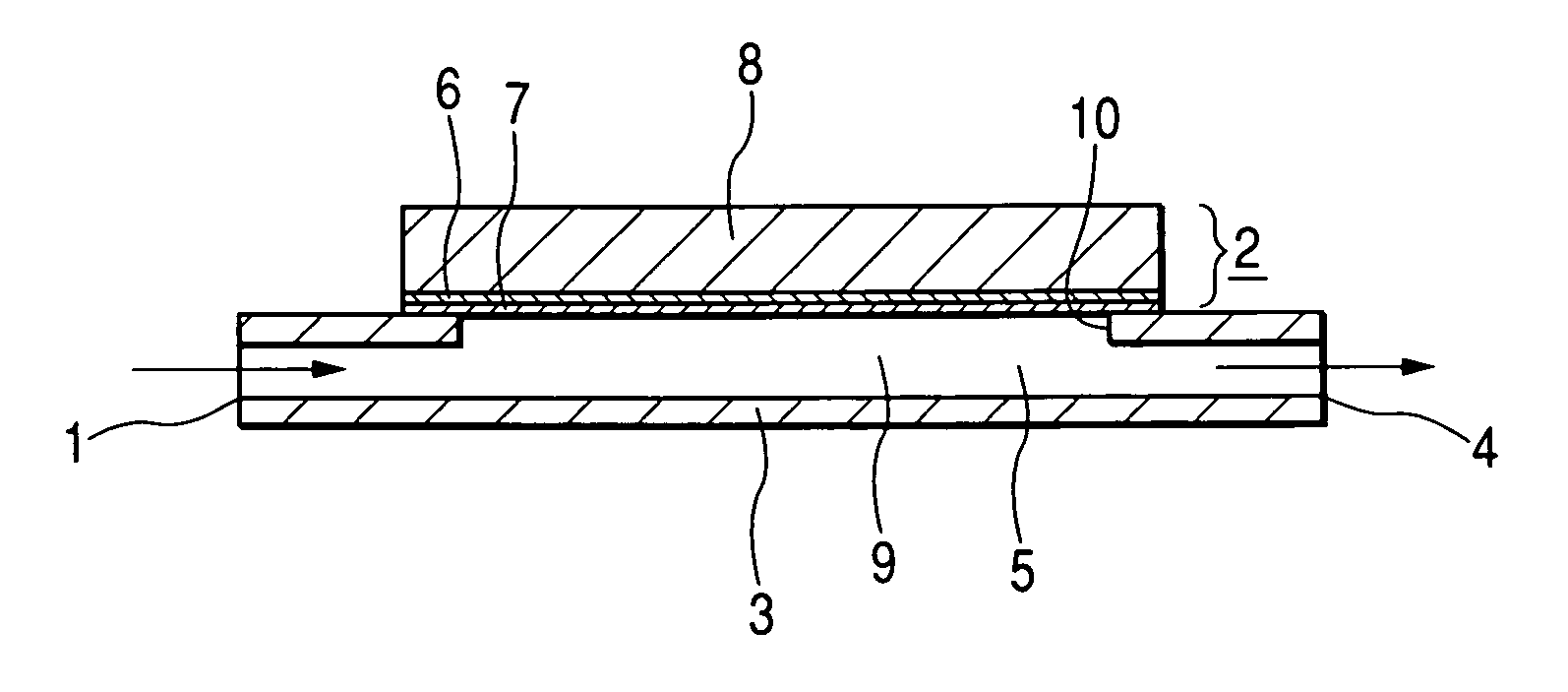
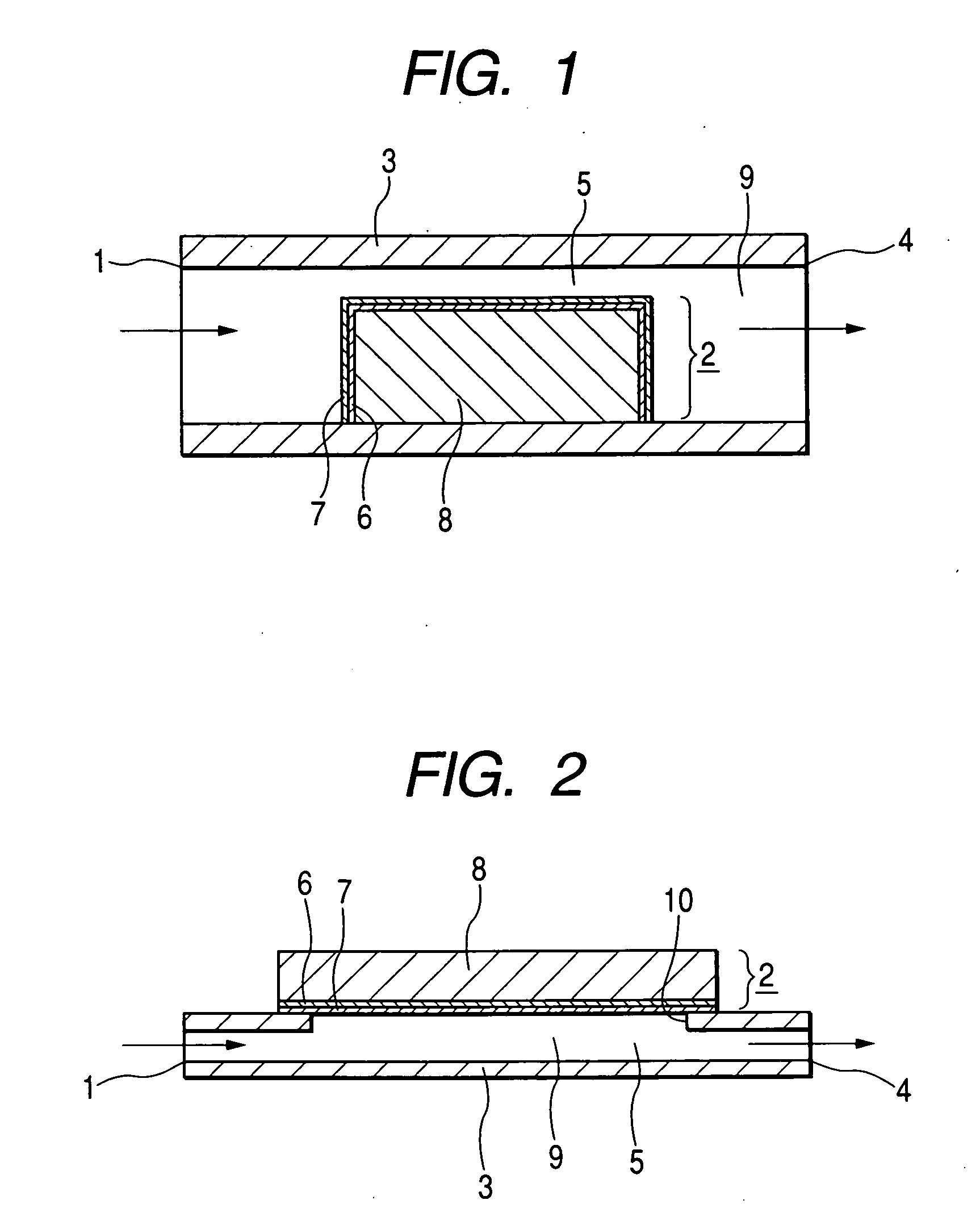
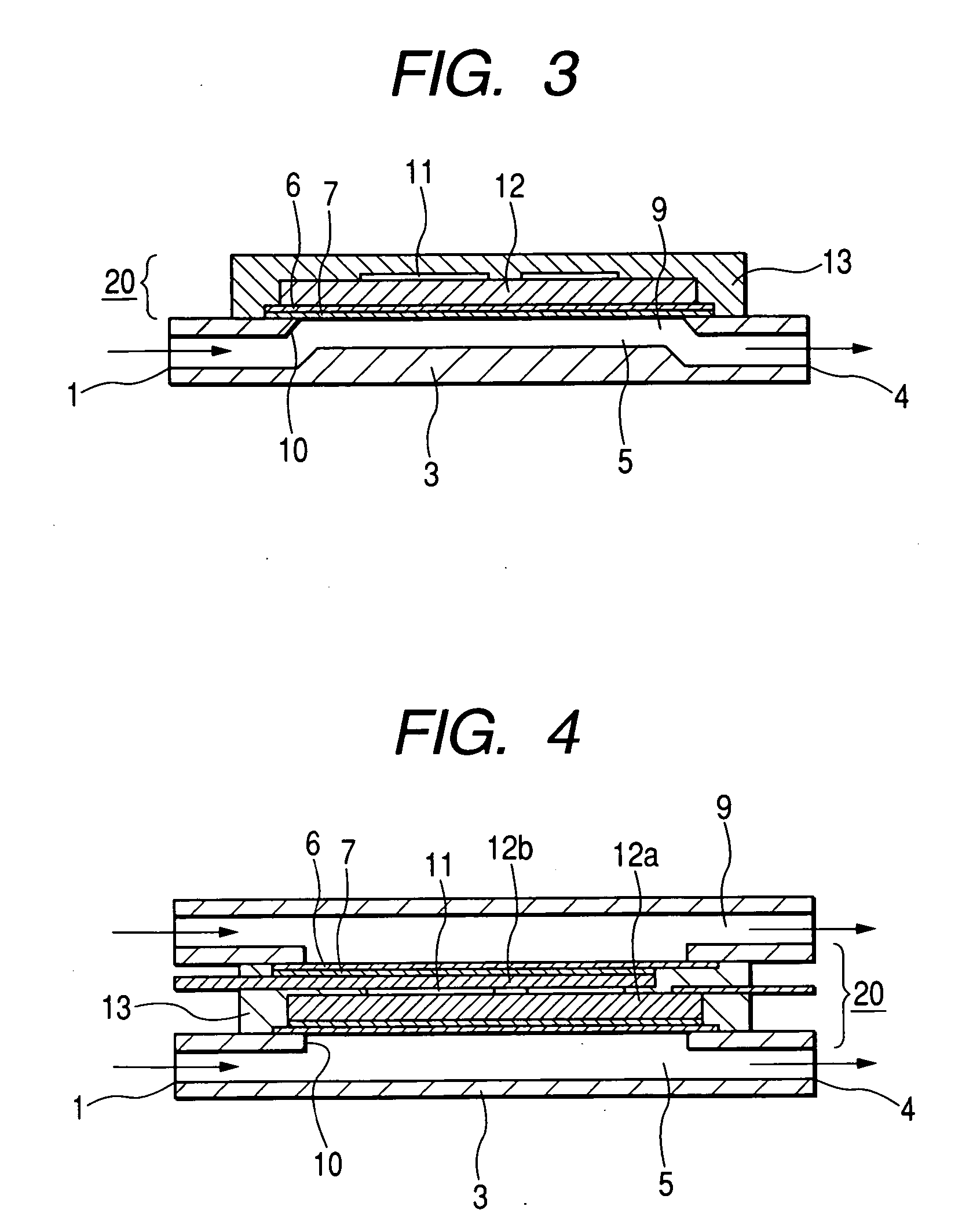
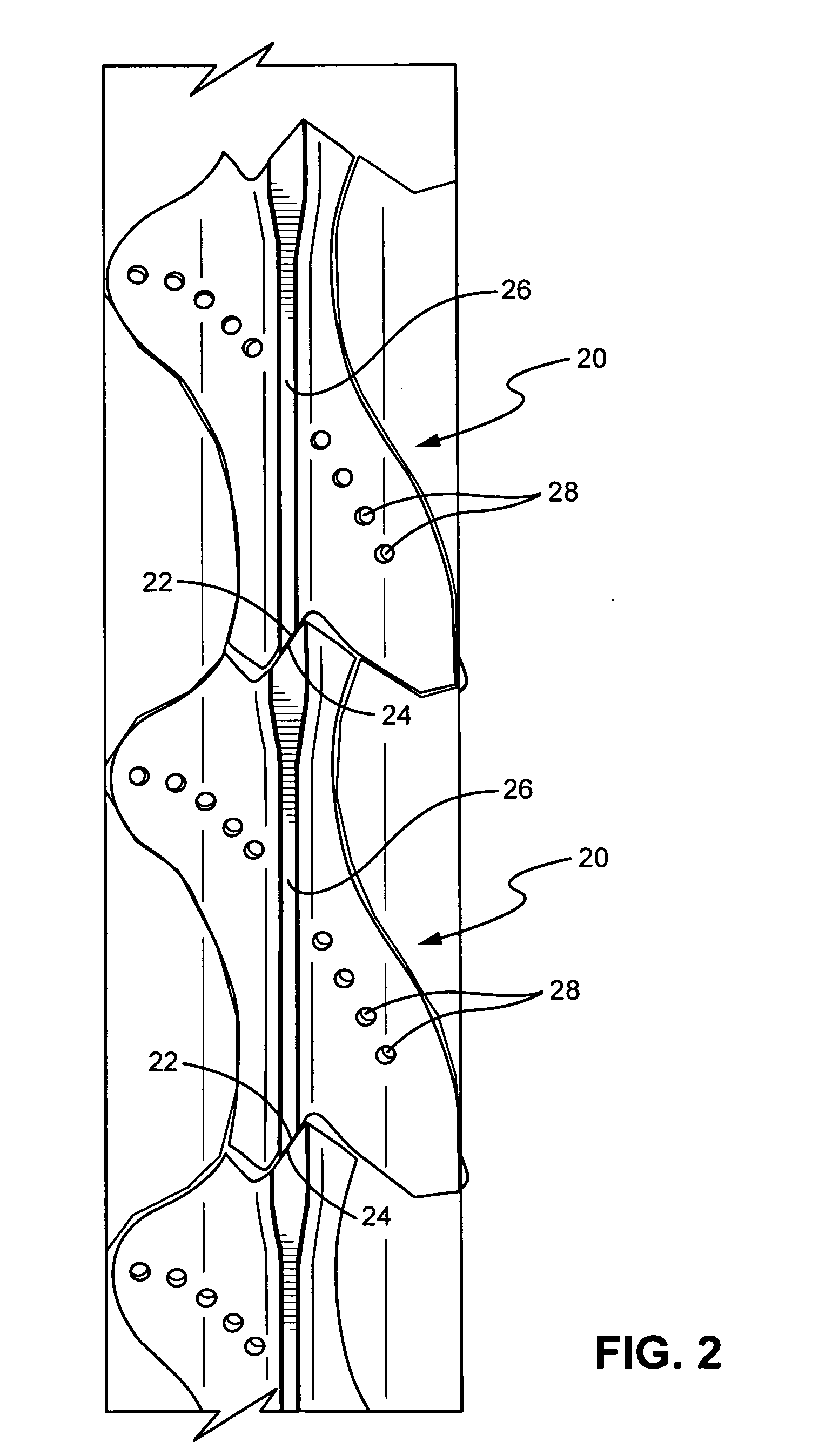
Cooling methods
InactiveUS20090038318A1Improve heat transfer performanceRemove heatTransformers/inductances coolingMagnetic measurementsSuperconducting CoilsEngineering
A superconducting system comprises a superconducting coil (3) mounted in a support (12). The coil is surrounded by a cryogen chamber (17) which is located radially outwardly from the coil (3) on the other side of the support (12). The cryogen chamber is in fluid communication with a cryogen recondensing unit (33) whereby vaporized cryogen may flow from the cryogen chamber (17) to the cryogen recondensing unit (33) to be recondensed in use before returning to the cryogen chamber. Thermally conductive means (25) is arranged to facilitate heat transfer from the superconducting coil (3) to the cryogen chamber (17) to vaporize cryogen contained therein in use and thereby remove heat from the coil. The thermally conductive means (25) is highly thermally conductive at cryogenic temperatures. In use, the highly thermally conductive means (25) facilitates transfer of heat from the coil (3) to the interior of the cryogen chamber (17) to vaporize cryogen located therein. A thermal conduction path is therefore used to transfer heat from the coil to the cryogen in the cryogen chamber. Cryogen vaporized in the cryogen chamber then flows to the cryogen recondensing unit (33) to be recondensed before returning to the chamber, while the vaporized cryogen acts as the heat transfer medium over the longer distance between the cryogen chamber and the recondensing unit.
Owner:TESLA ENG
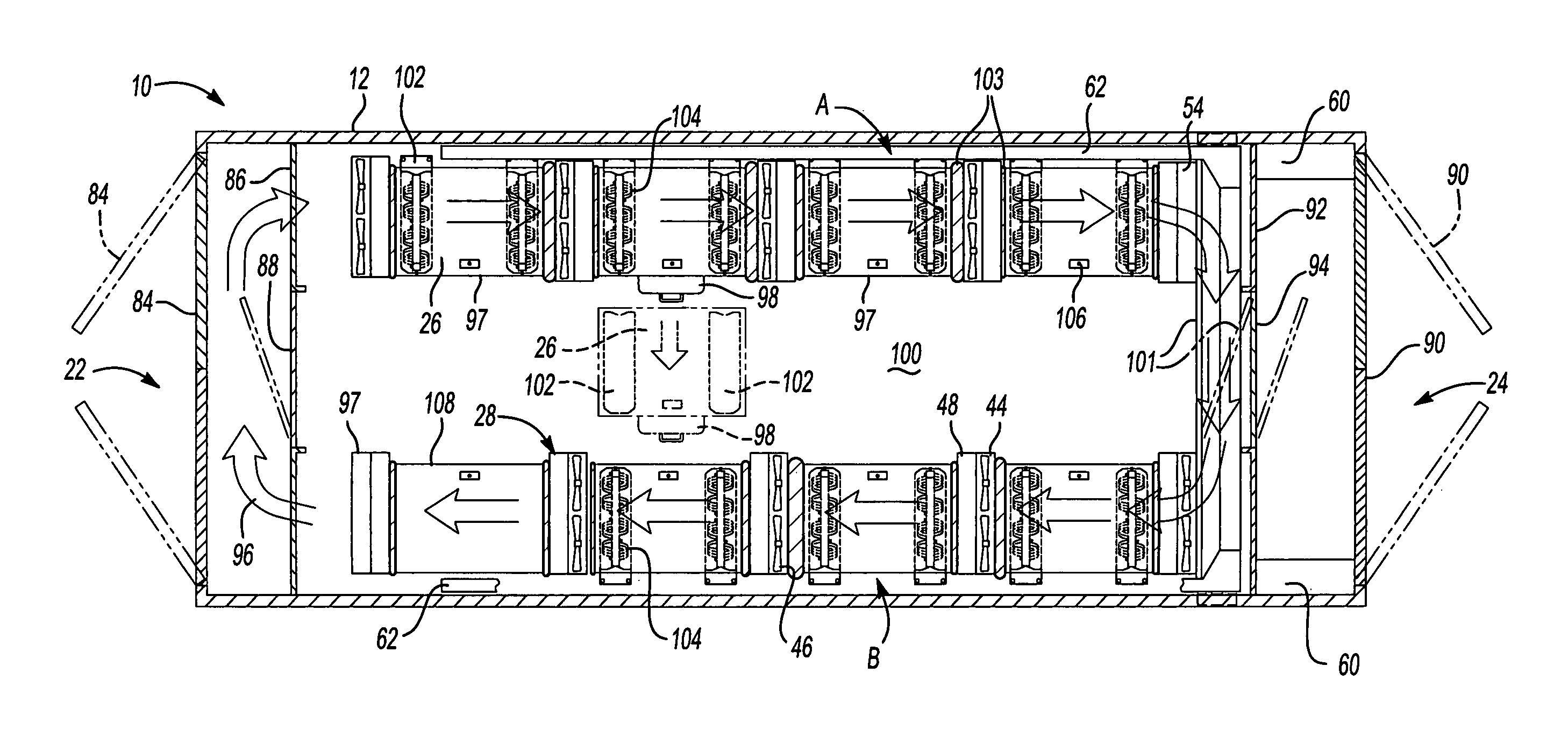
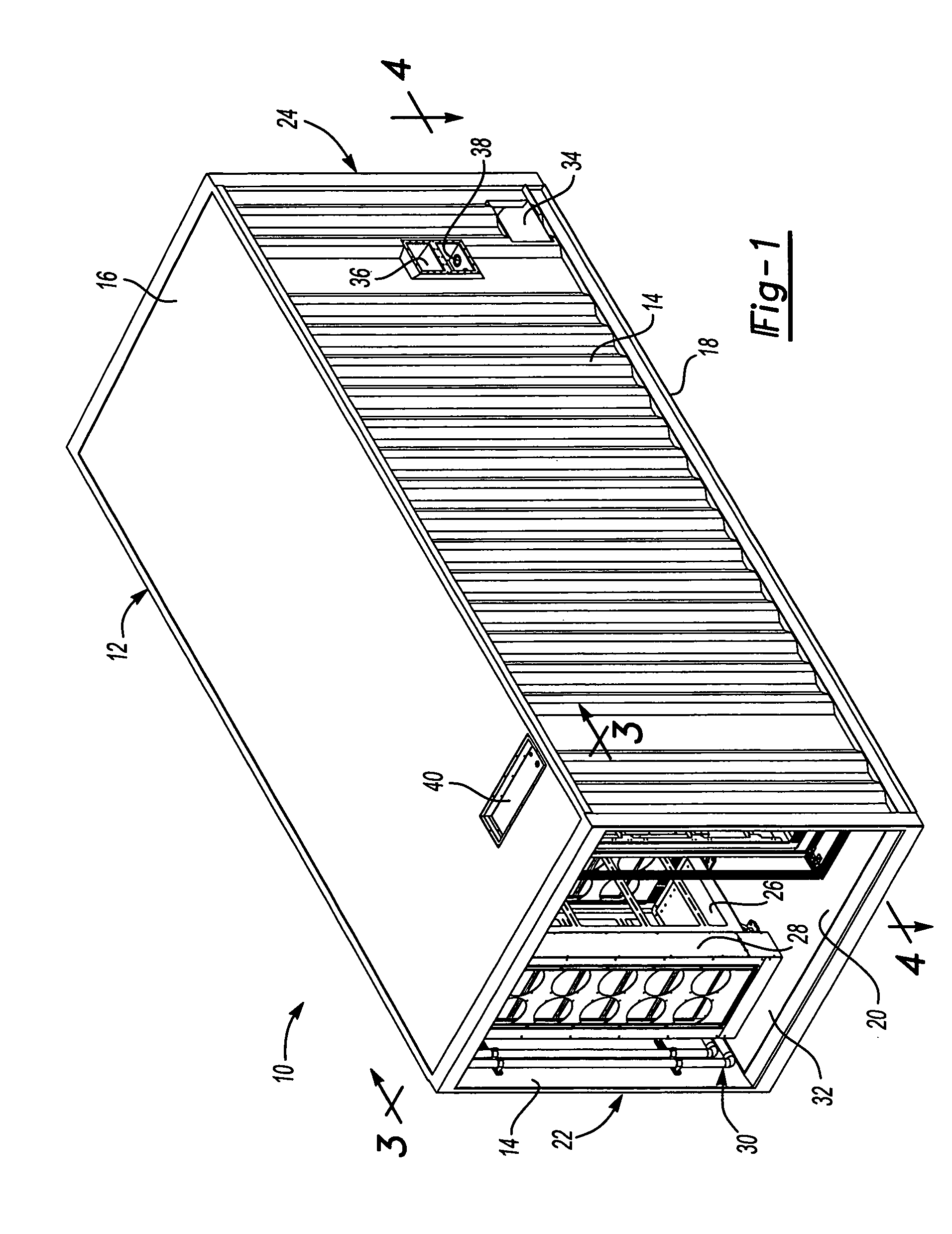
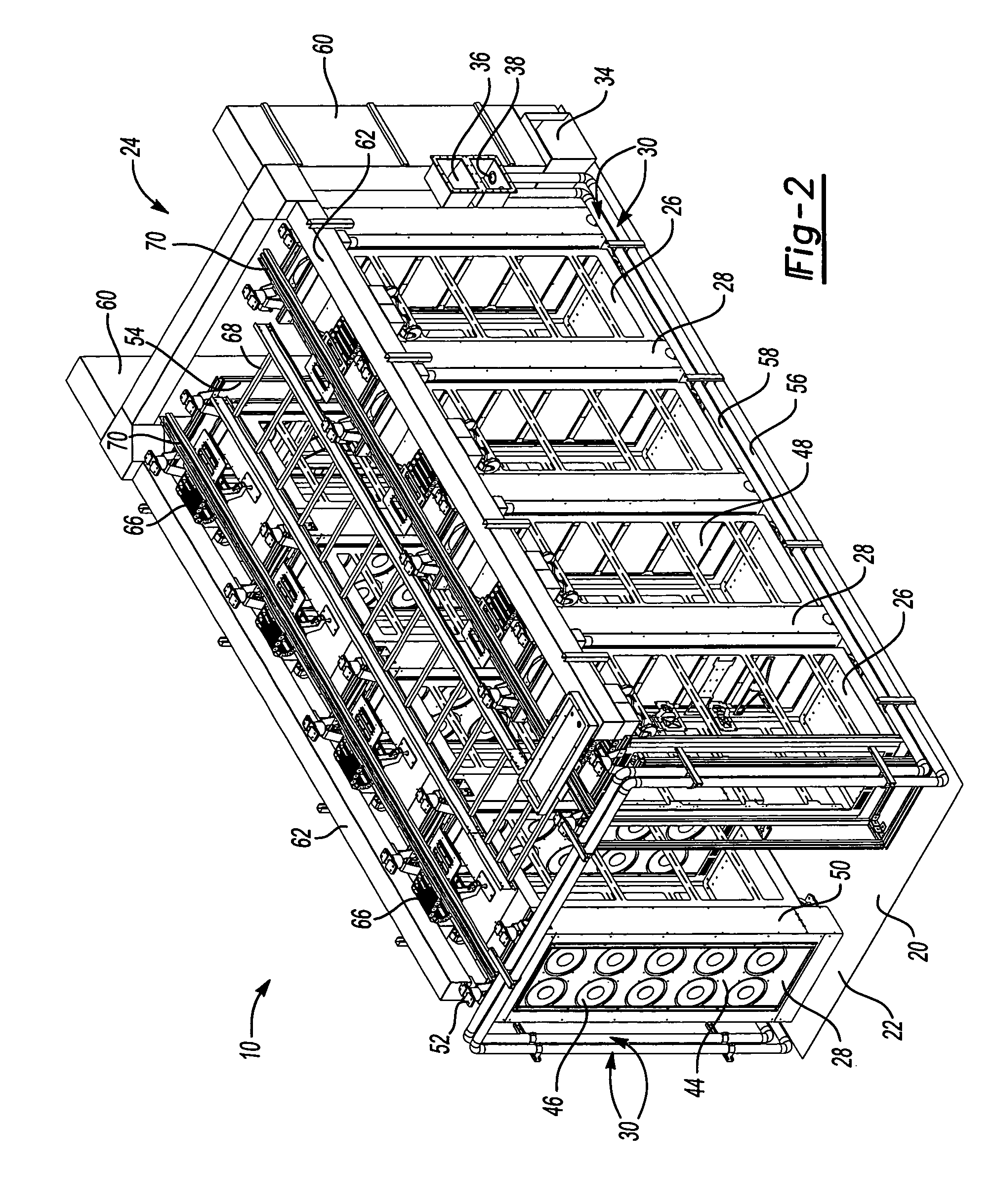
Cooling method for a data center in a shipping container
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Module cooling method and plenum adaptor
InactiveUS20120287575A1Effective matingMore efficientWave amplification devicesClamping/extracting meansComputer moduleVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for cooling modules in a radio system is disclosed. The apparatus comprises an adaptor module with side walls and integrated heat exchanging elements. The adaptor module adapts the air flow from a chassis in the radio system such that the exiting ducting on the chassis efficiently mate with the air conduits in the modules. The adaptor allows the use of new high power density modules in the existing chassis without changing the module design. The use of adaptor module in chassis provides efficient cooling and use less volume in the chassis.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Controlled cooling methods and apparatus for laser sintering part-cake
ActiveUS7521652B2Efficient heatingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallurgyHeat sink
The invention is a method for controllably cooling at least a portion of a part-cake from a laser sintering system to minimize cool down time, maximize throughput, and minimize thermal gradients within the part-cake. The method generally comprises forming one or more thermal transfer channels within the part-cake. The thermal transfer channels can include ducts and cooling fins in the part-cake surrounding the formed part. The method can further comprise removing unfused powder from the ducts and introducing cooling media into the ducts. The invention also includes a part-cake having thermal transfer channels formed therein and a laser sintering apparatus comprising a part-cake containing cylinder having permanent fittings therein for receiving terminal portions of thermal transfer channels formed in the part-cake.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Low-carbon steels of superior mechanical and corrosion properties and process of making thereof
InactiveUS6273968B1Simple structureAccelerated corrosionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCrystal twinningCarbide
Alloy steels that combine high strength and toughness with high corrosion resistance are achieved by a dislocated lath microstructure, in which dislocated martensite laths that are substantially free of twinning alternate with thin films of retained austenite, with an absence of autotempered carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides in both the dislocated martensite laths and the retained austenite films. This microstructure is achieved by selecting an alloy composition whose martensite start temperature is 350° C. or greater, and by selecting a cooling regime from the austenite phase through the martensite transition region that avoids regions in which autotempering occurs.
Owner:CMC STEEL FABTORS
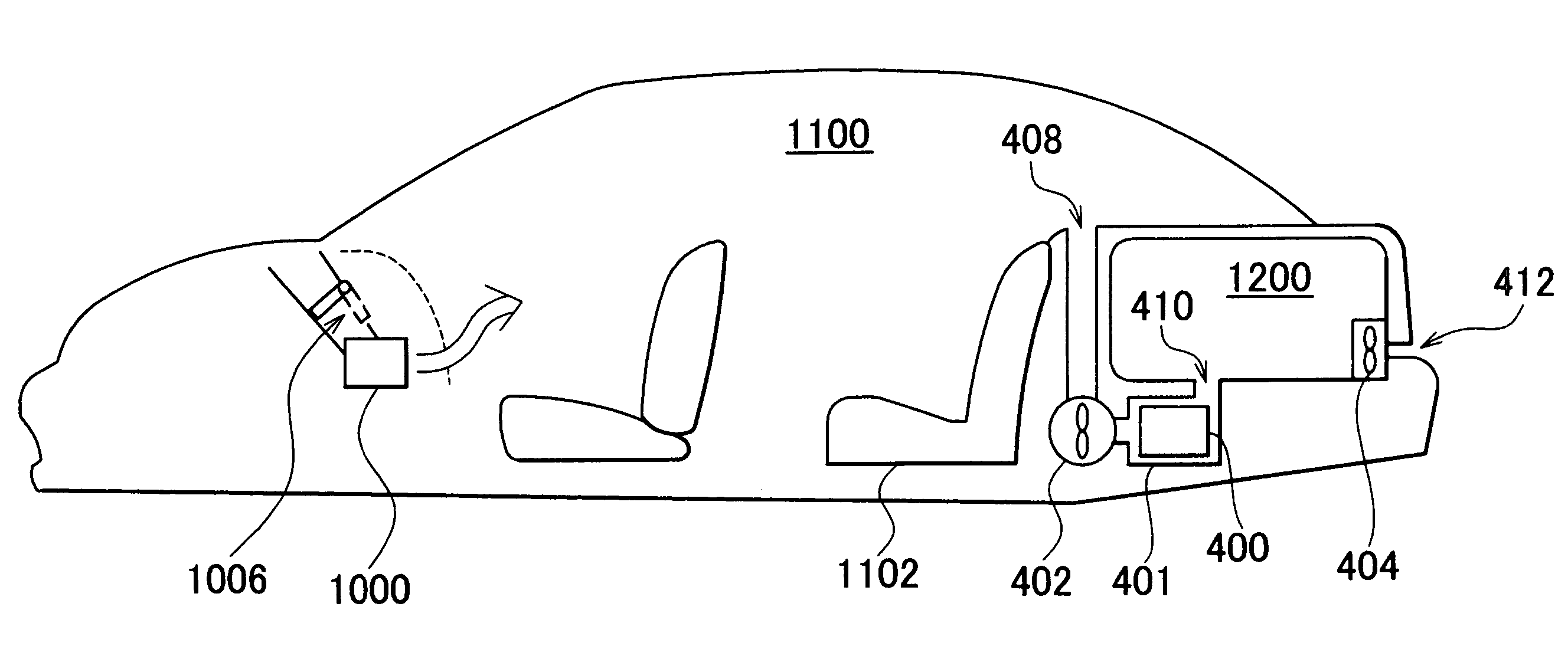
Cooling system for power storage mechanism, cooling method of the same, and vehicle
InactiveUS20050138941A1Avoid influenceReduce stepsHybrid vehiclesCell temperature controlBattery packHeat transfer
A battery pack is communicated with a luggage compartment via an outlet such that cooling air that has been heat transferred with a battery is released into the luggage compartment. A ventilation hole is formed in a rear portion of the luggage compartment. An inlet is opened toward the outside of the vehicle. An exhaust fan that discharges the cooling air at the temperature increased through heat transfer with the battery in the battery pack is provided to the front of the ventilation hole.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Container air handling unit and cooling method
A modular cooling system configured to treat IT air generated by a data center includes a frame and a plurality of cooling sub-system modules supported by the frame. The plurality of cooling sub-system modules are configured to operate in parallel to achieve total cooling effect or a lesser cooling effect with some level of redundancy within the data center. Each cooling sub-system module includes a housing configured to support cooling equipment, an air-to-air heat exchanger supported by the housing to cool IT air generated by the data center, the air-to-air heat exchanger having at least one tube configured to direct IT from one end of the air-to-air heat exchanger to an opposite end of the air-to-air heat exchanger and configured so that outdoor air circulates around the at least one tube, and a mechanical cooling system supported by the housing. The mechanical cooling system is configured to receive IT air treated by the air-to-air heat exchanger and to provide further cooling to the treated IT air. Other embodiments of the cooling system and methods of cooling are further disclosed.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
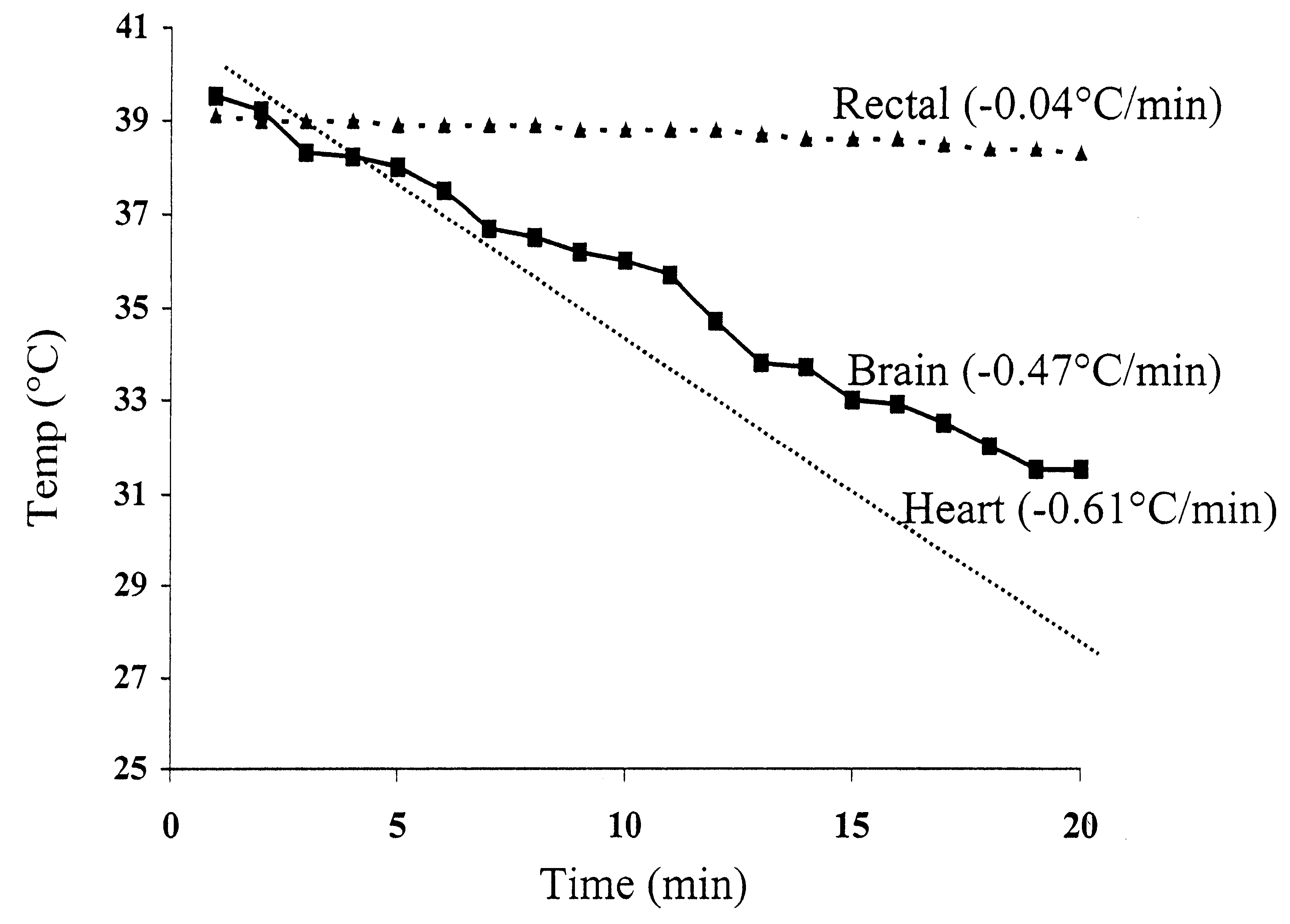
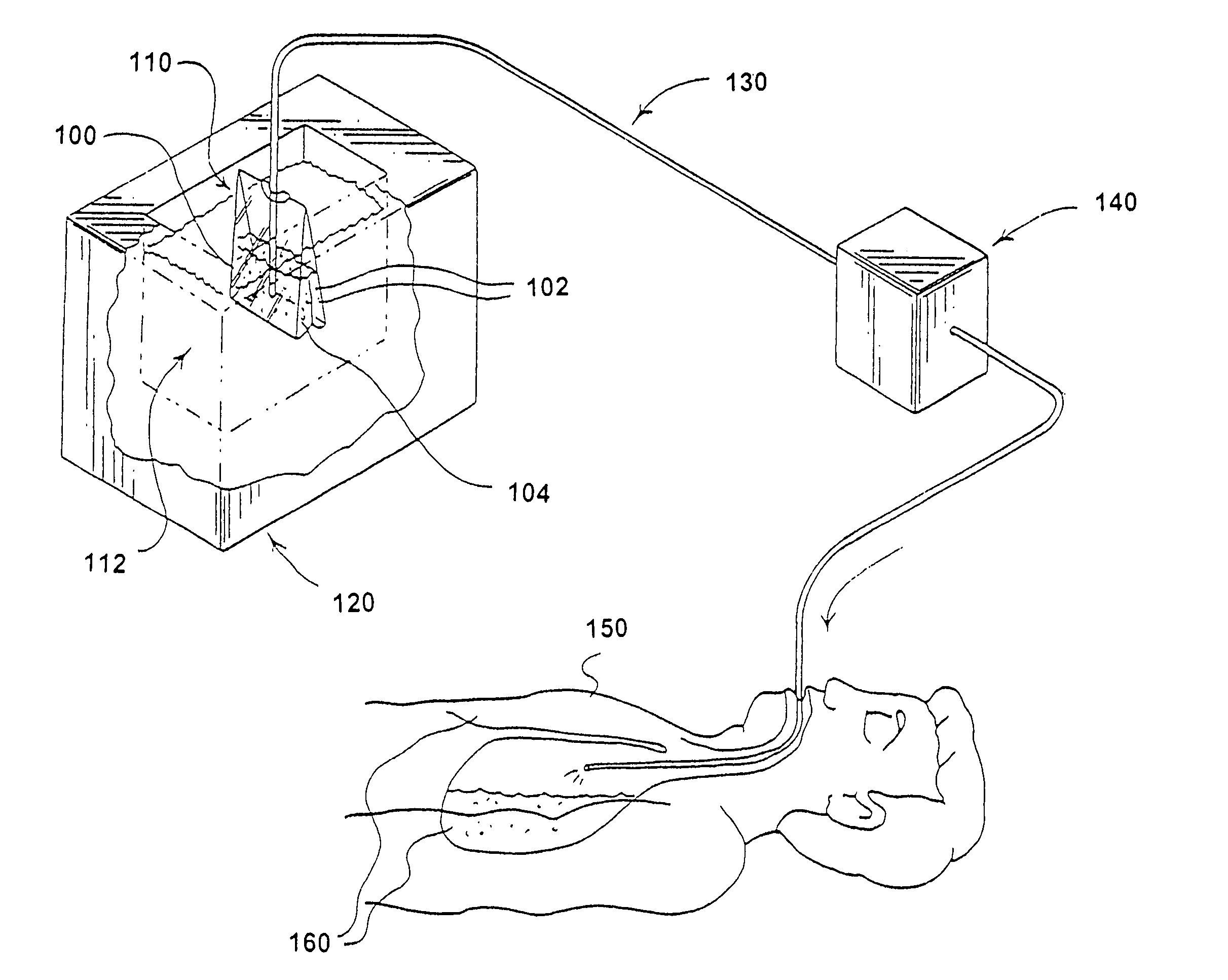
Method for inducing hypothermia
InactiveUS6962601B2Simple methodImprove the protective effectOther chemical processesLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesSlurry
Systems for phase-change particulate slurry cooling equipment and methods to induce hypothermia in a patient through internal and external cooling are provided. Subcutaneous, intravascular, intraperitoneal, gastrointestinal, and lung methods of cooling are carried out using saline ice slurries or other phase-change slurries compatible with human tissue. Perfluorocarbon slurries or other slurry types compatible with human tissue are used for pulmonary cooling. And traditional external cooling methods are improved by utilizing phase-change slurry materials in cooling caps and torso blankets.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Method for inducing hypothermia
InactiveUS20050203598A1Improve the protective effectPromote resultsLighting and heating apparatusIce productionParticulatesSlurry
Systems for phase-change particulate slurry cooling equipment and methods to induce hypothermia in a patient through internal and external cooling are provided. Subcutaneous, intravascular, intraperitoneal, gastrointestinal, and lung methods of cooling are carried out using saline ice slurries or other phase-change slurries compatible with human tissue. Perfluorocarbon slurries or other slurry types compatible with human tissue are used for pulmonary cooling. And traditional external cooling methods are improved by utilizing phase-change slurry materials in cooling caps and torso blankets.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Method and apparatus for vacuum diode heat pump
InactiveUS6089311AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringKinetic energy
A new use for thermionic vacuum diode technology is disclosed wherein a vacuum diode is constructed using very low work function electrodes. A negative potential bias is applied to the cathode relative to the anode, and electrons are emitted. In the process of emission the electrons carry off kinetic energy, carrying heat away from the cathode and dissipating it at an opposing anode. The resulting heat pump is more efficient than conventional cooling methods, as well as being substantially scalable over a wide range of applications. Fabrication using conventional microelectronic fabrication techniques is possible.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
InactiveUS20030014983A1Economic securityFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesDesiccantHeat transmission
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:MAISOTSENKO VALERIY +3
Method and apparatus for data center air conditioning
Modular data center containers with modular components suitable for use with rack or shelf mount computing systems currently use cooling methods that do not include economizers due to size constraints of structural steel support infrastructure associated with modular data centers and removable economizers to facilitate portability of modular data centers. The modules allows introduction of outside air to the cooling cycle with the unique elements embodied within airside economizer components. The modules in conjunction with the data center represents a new and useful process to allow the economizer elements to bring outside air into the modular data center cooling cycle.
Owner:LARSEN ARTHUR E
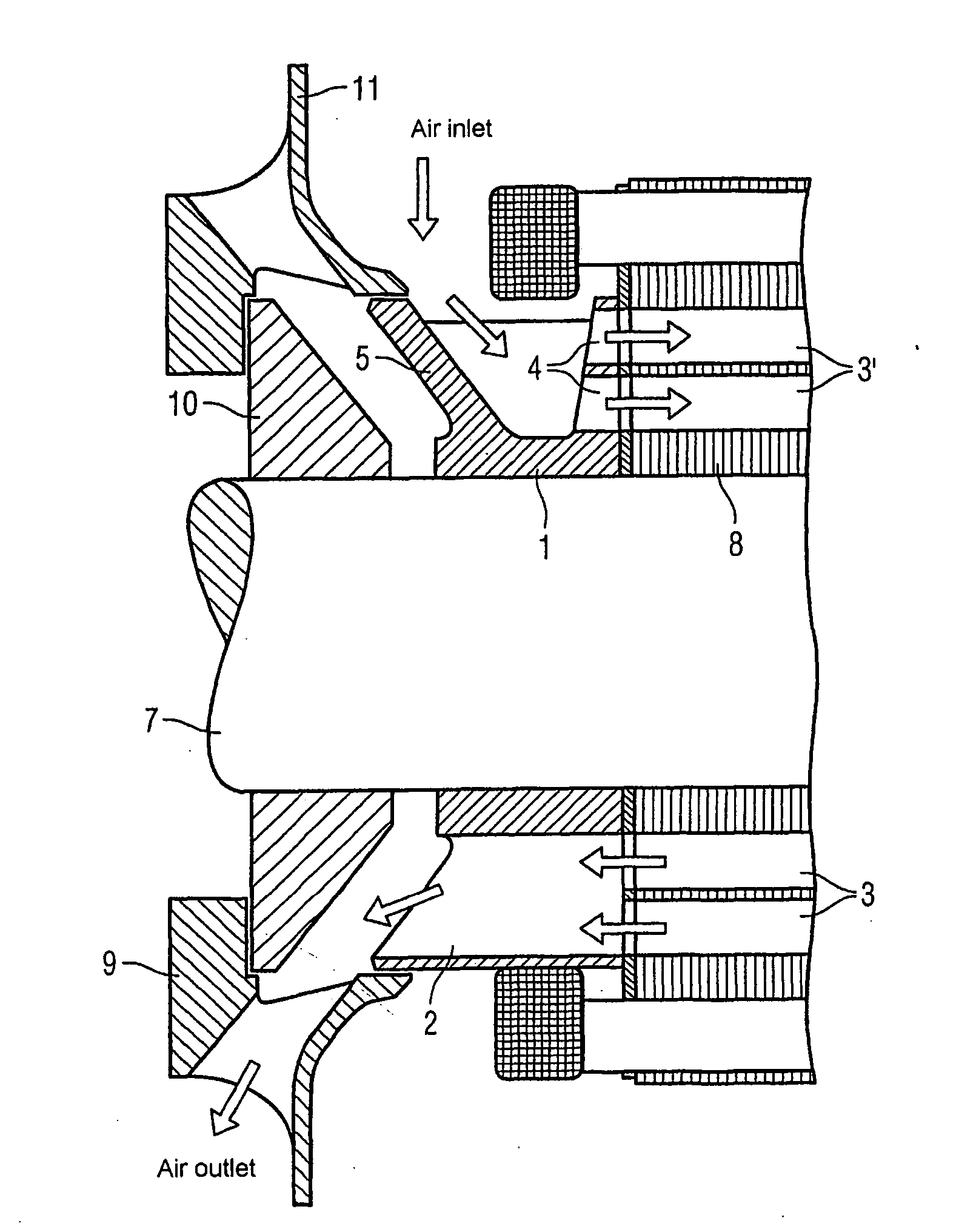
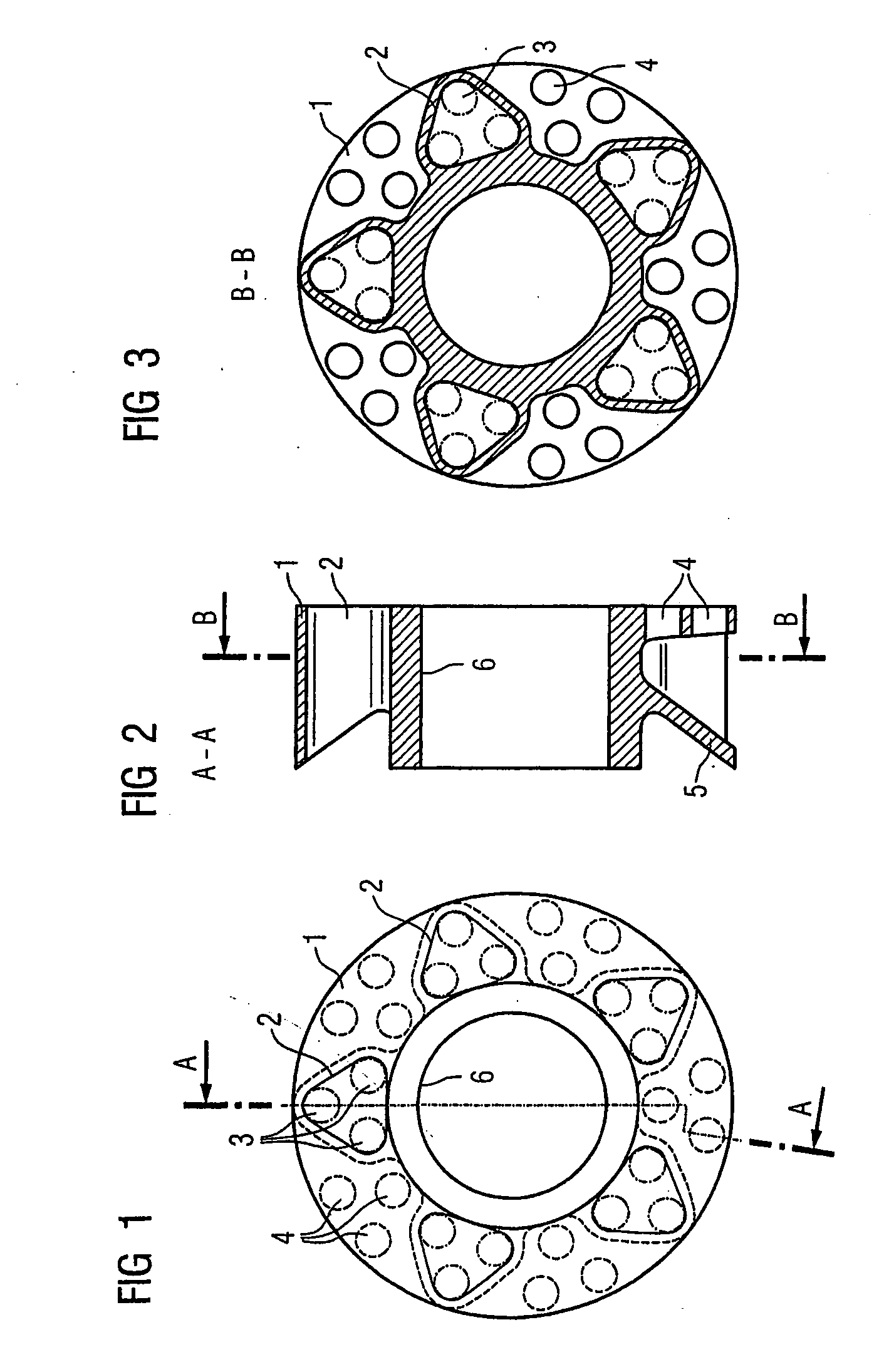
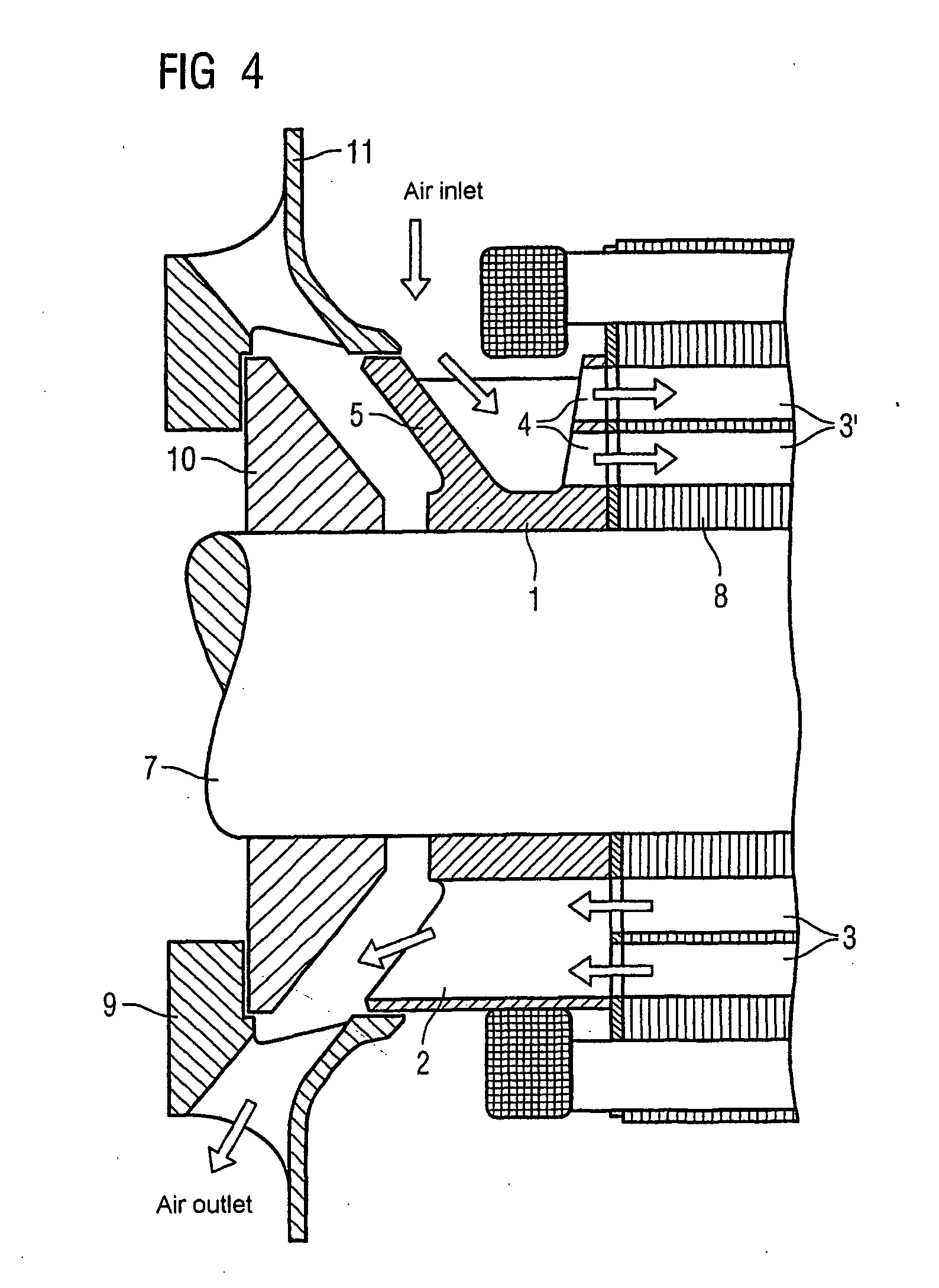
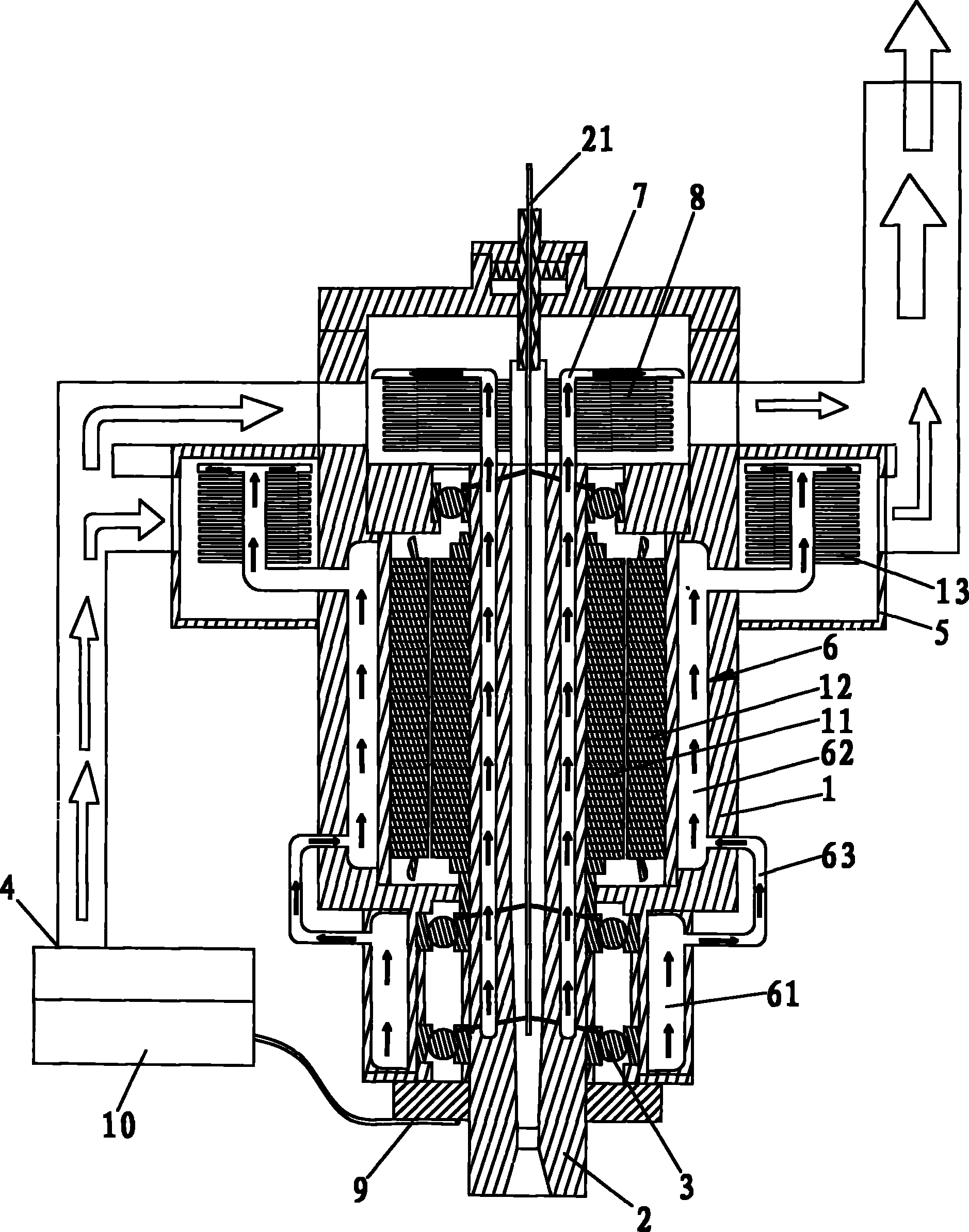
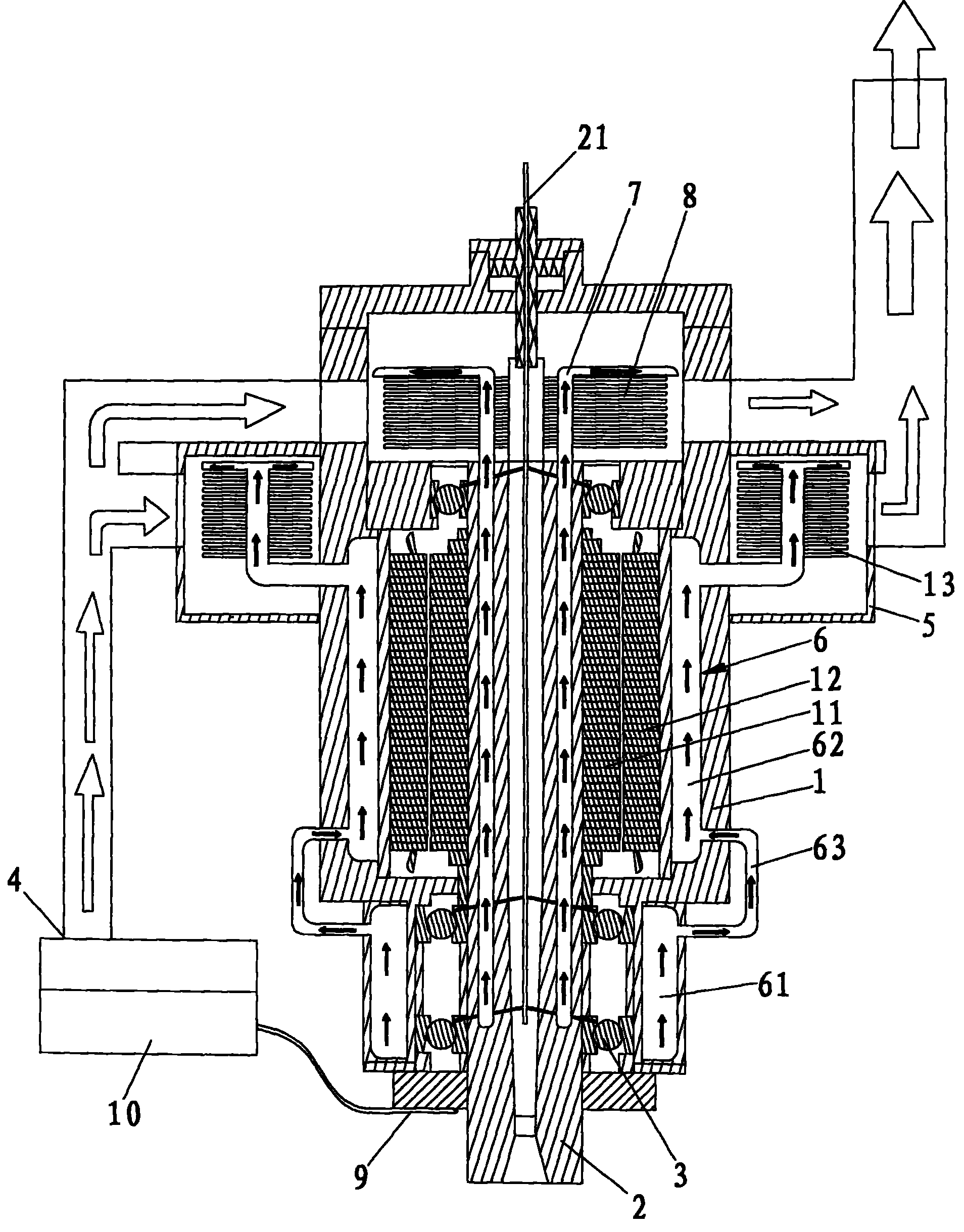
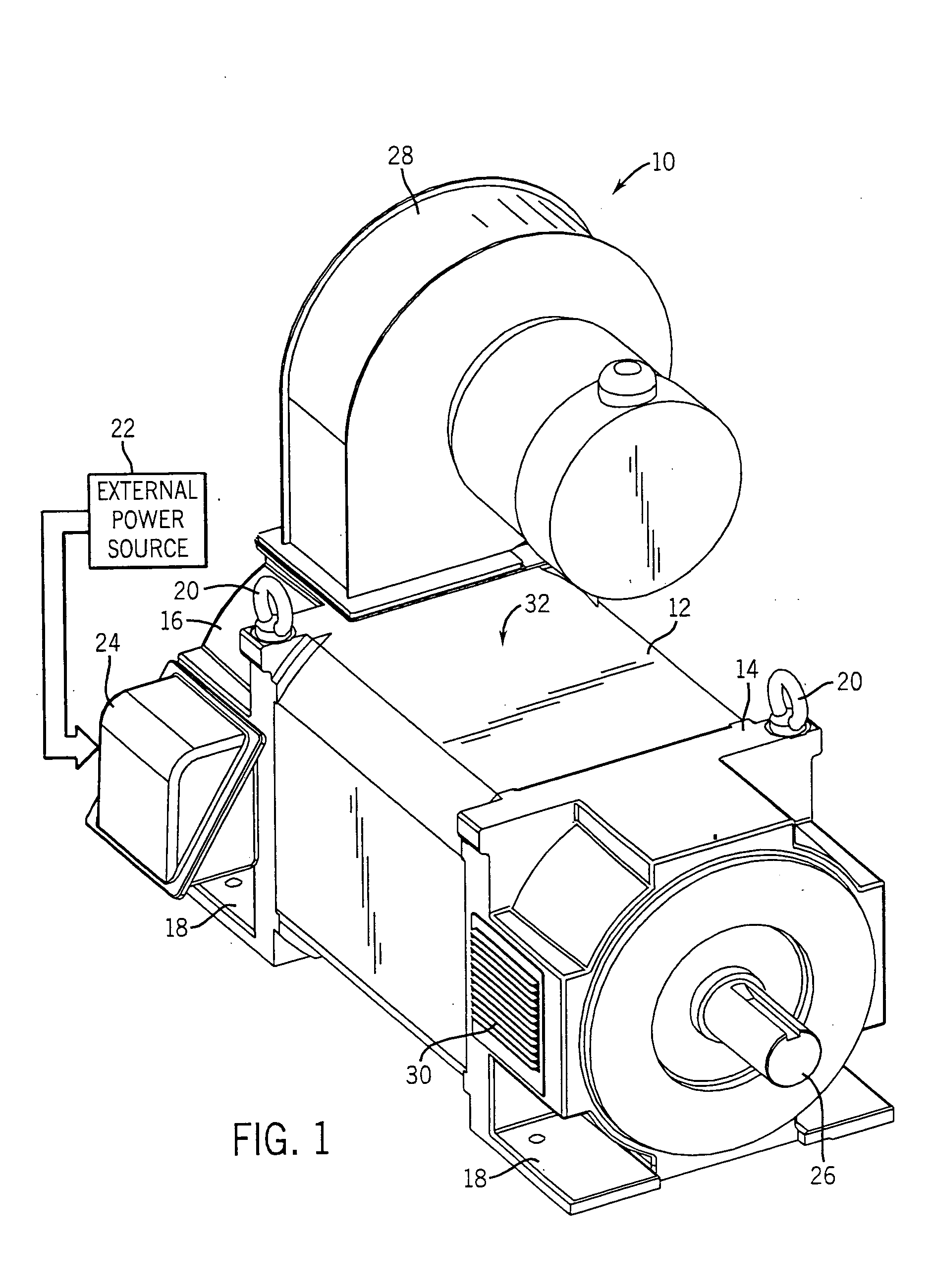
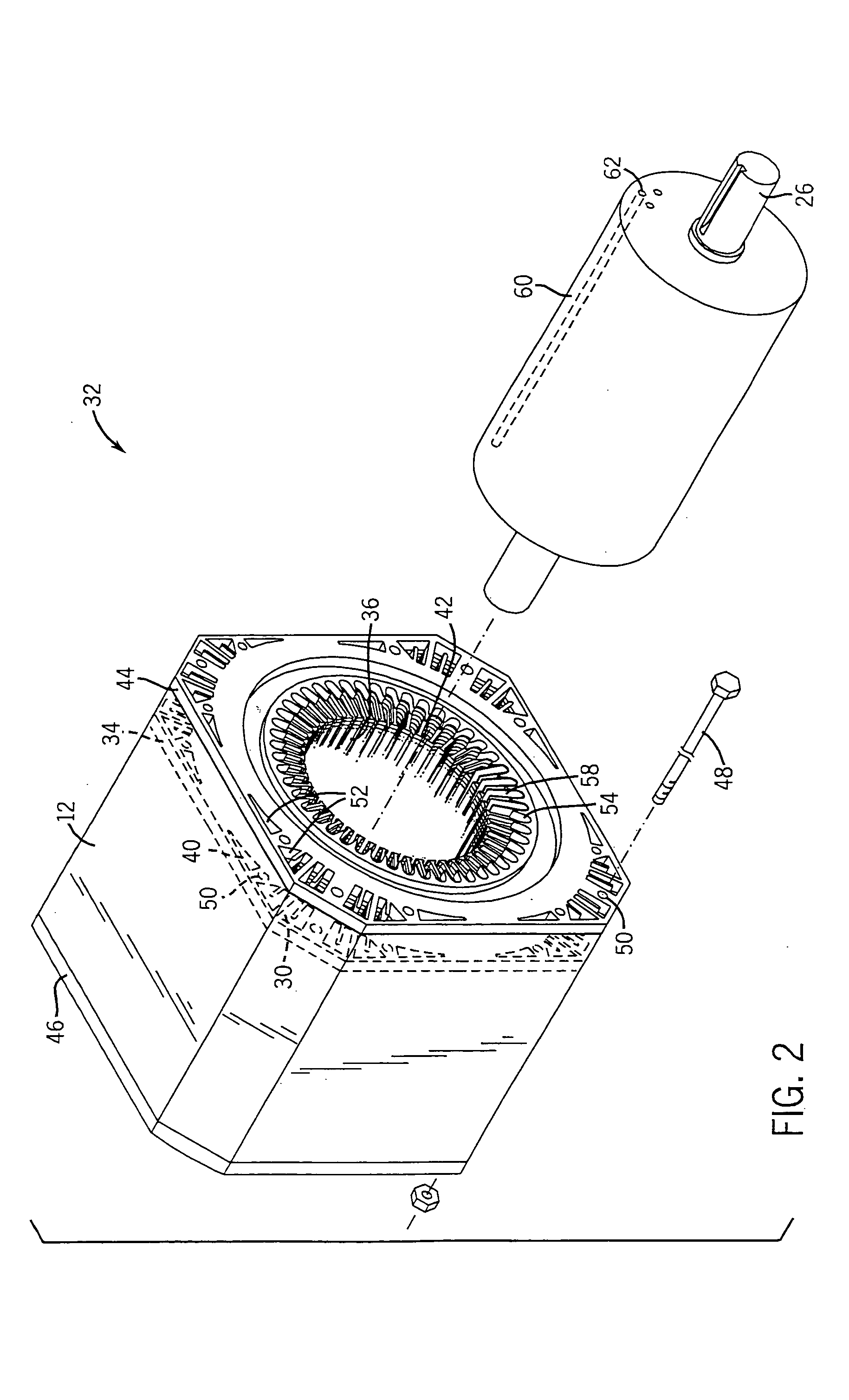
Electric machine with rotor cooling and corresponding cooling method
ActiveUS20070024130A1Cost-effective wayIncrease coolant flowMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineEngineering
The aim of the invention is to optimize cooling of a rotor using simple means. A rotor is provided, comprising rotor pressure rings (1) such that at least one of the two rotor pressure rings (1) is configured in order to enable targeted guiding of the coolant through the axial bores (3, 3′) in the rotor. In a special embodiment, the rotor pressure ring (1) can be formed in such a manner that it produces, in several bores (3′) in the rotor sheet stack (8), a flow of coolant in a first direction and in other bores (3), a flow of coolant in the other direction. An even, opposite flow cooling can be exclusively obtained by the contour of the rotor pressure ring (1).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
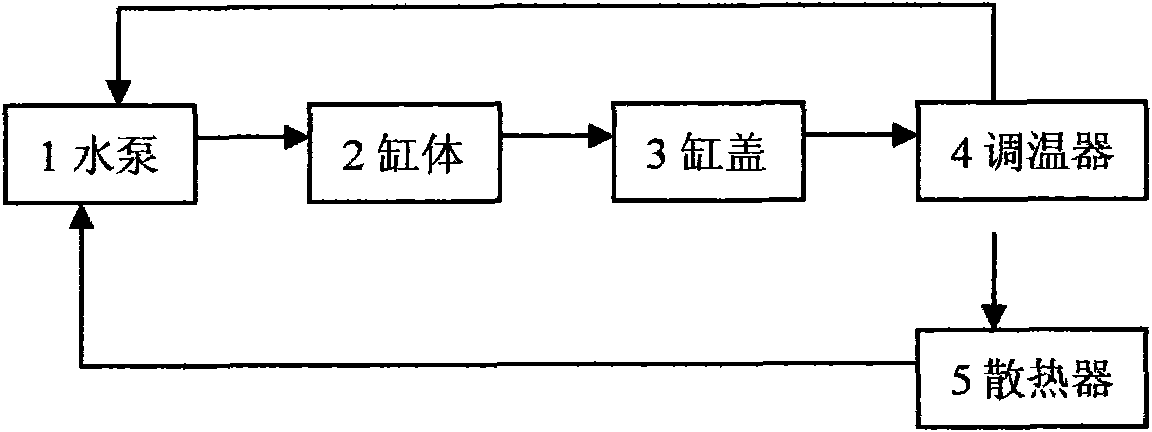
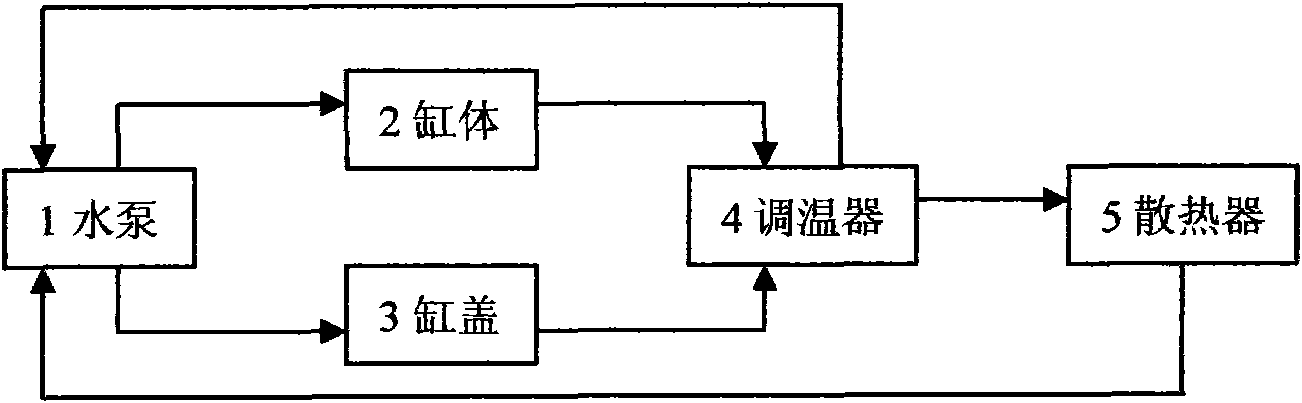
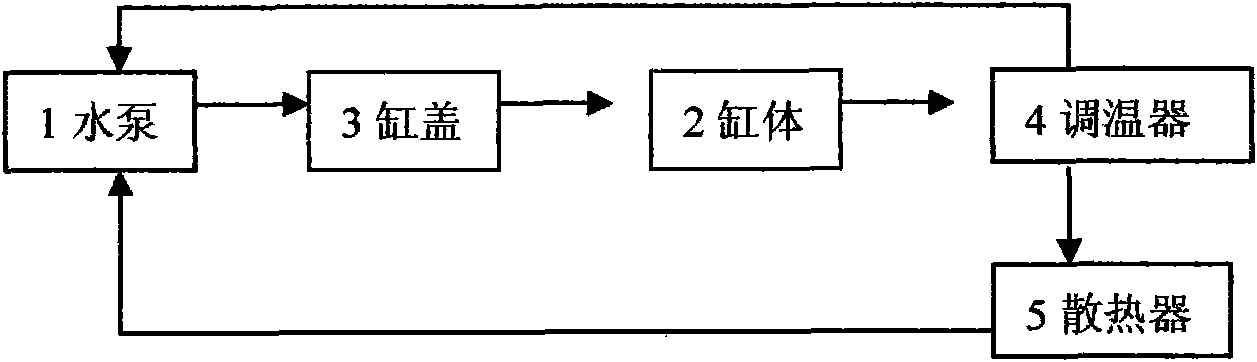
Engine cooling system and cooling method
InactiveCN101655027AReduce the temperatureReduce formationLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlFuel efficiencyEngineering
The invention discloses an engine cooling system and a cooling method. The cooling system comprises a water pump, a double-valve temperature regulator, a machine oil cooler, a water jacket of a cylinder body, a water jacket of a cylinder cover, a water tank radiator and an EGR cooler. The cooling system adopts a water passage circulation as follows: when the engine is started, the water pump begins to work; cooling liquid firstly flows into the machine oil cooler and enters in the water jacket of the cylinder cover to cool the key area of the cylinder cover, and then enters in the water jacket of the cylinder body from a gasket circulating hole of the cylinder cover to cool the cylinder body and the EGR cooler. The cooling liquid in the cooling system firstly cools the cylinder cover to reduce the temperature of the cylinder cover by 10 DEG C to 15 DEG C, enhance aeration efficiency, enlarge air inlet quantity, promote complete combustion, reduce the formation of discharge objects andenhance output efficiency; After cooling the cylinder cover, the cooling liquid enters in the cylinder body for cooling the cylinder body; the higher temperature of the cylinder body can reduce friction, improve fuel efficiency, enhance the output efficiency and reduce peak value pressure and temperature in the cylinder.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
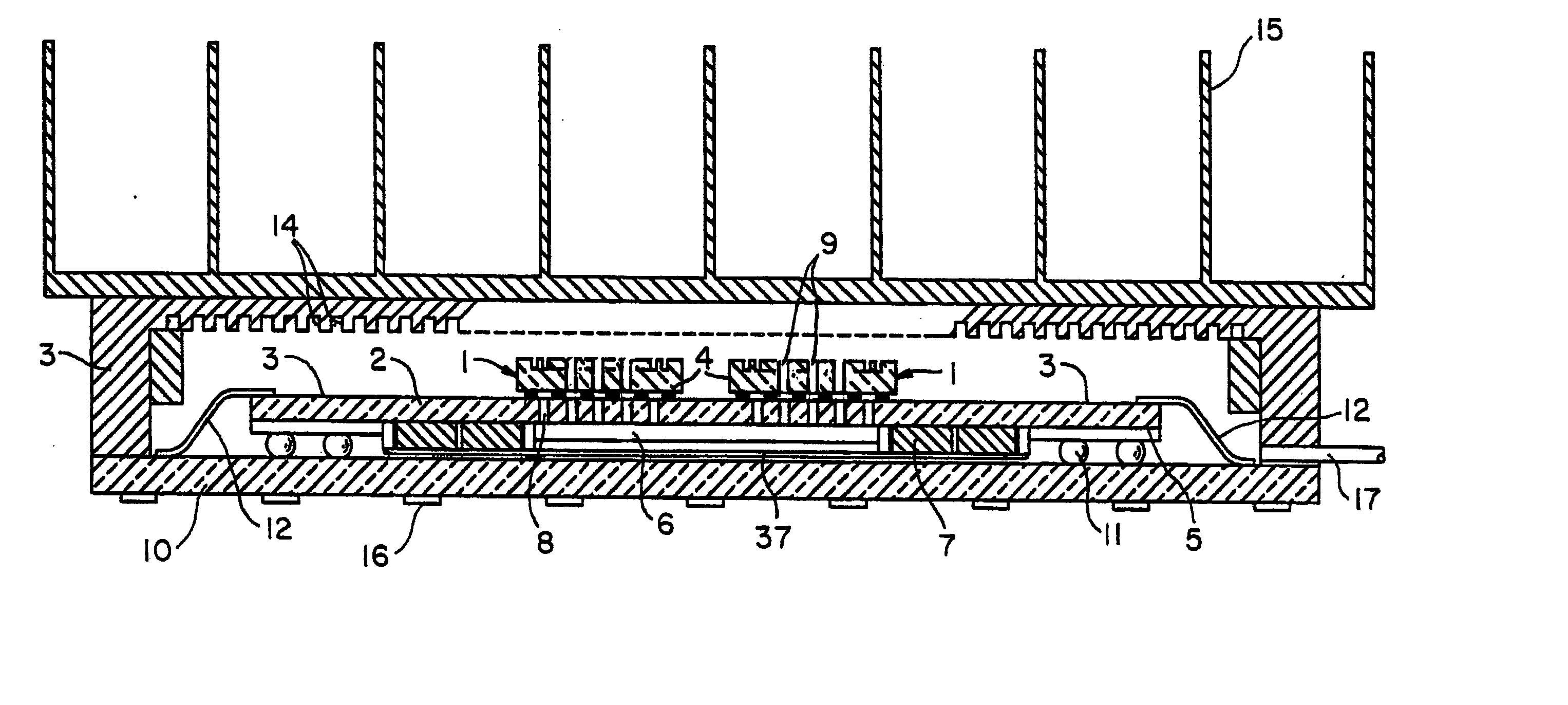
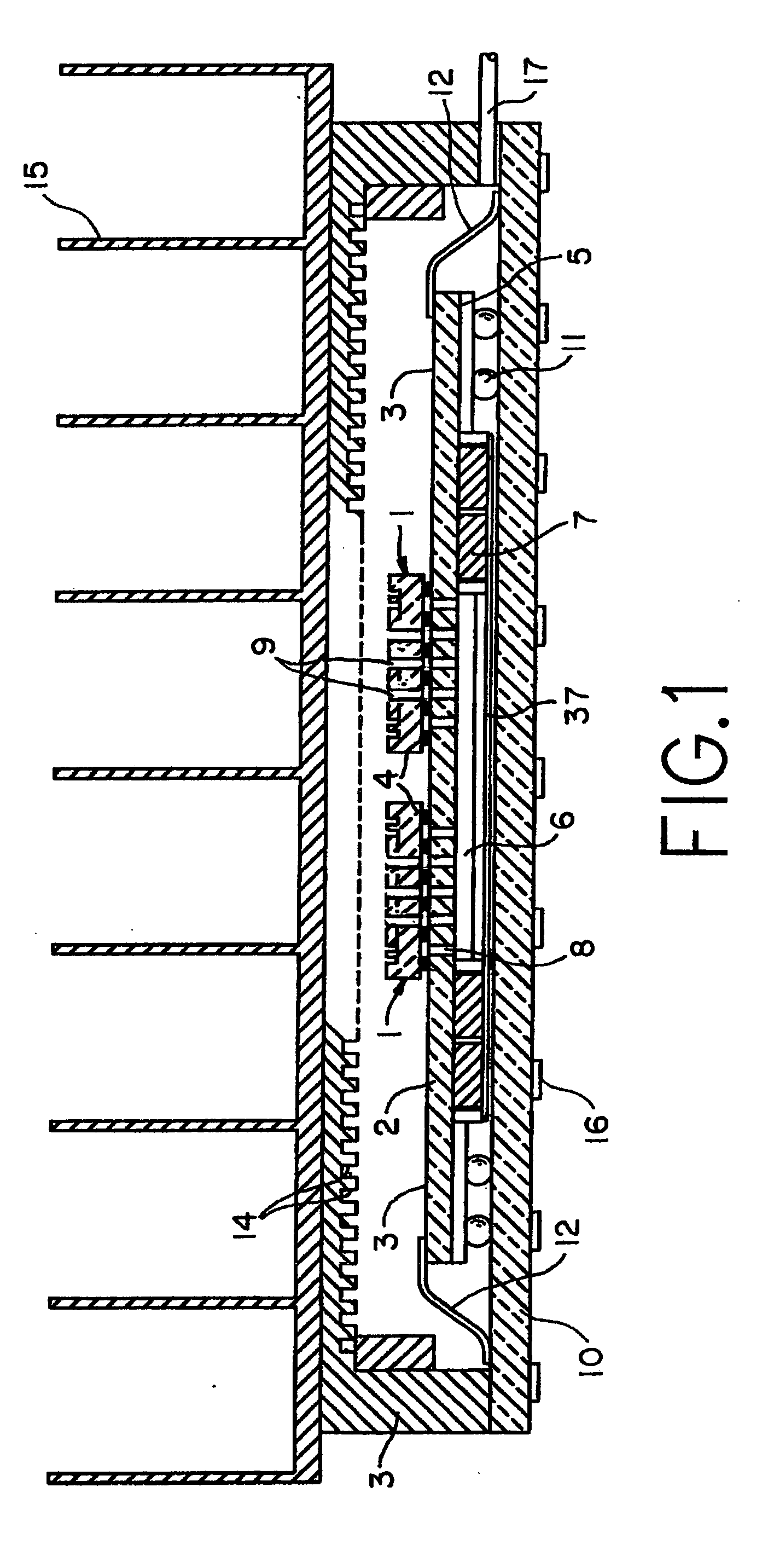
Chip packaging module with active cooling mechanisms
InactiveUS20050168947A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSubstation/switching arrangement cooling/ventilationActive coolingCoolant flow
The invention is directed to structure and methods of improving the cooling capacity of chip packaging modules. The chip packaging module has a substrate with thin-film wiring on one side and grooves or channels etched on one or both sides where coolant pumps are embedded. The coolant pumps are used to enhance the liquid flowing inside the module. The coolant flows through the chips within the vias in the chips or around the chips when the chips do not have vias. Both cooling modes, single or two-phase modes can be adopted in the module.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-speed precise electric spindle cooling system
InactiveCN102120266AGuaranteed temperature stabilityControl temperature riseCooling/ventillation arrangementSupports/enclosures/casingsElectricityThermal energy
The invention relates to the technical field of an electric spindle, in particular to a high-speed precise electric spindle cooling system which comprises an electric spindle shell cooling part, an electric spindle core cooling part and a bearing spindle core lubricating / cooling part, wherein when the electric spindle works, the temperature rise change can be controlled within + / -1 DEG C. The concrete scheme is as follows: a ring sleeve type heat pipe cooling mode is arranged at the electric spindle shell part, and the heat of the shell is taken away quickly by increasing the cooling contact surface; the spindle core cooling part is provided with symmetrical bar-type heat pipes which are uniformly distributed on the spindle core, and the spindle core is cooled by use of the high-speed conductivity and homoiothermy of the heat pipes; and a spindle core liquid lubricating / cooling mode is adopted at the bearing lubricating / cooling part, and makes full use of the high rotation speed of the high-speed electric spindle to generate centrifugal force so that the lubricating / cooling liquid is uniformly distributed on the bearing roller. The temperature stability of the electric spindle can be ensured, the processing precision error caused by thermal expansion of the electric spindle is minimized, and the service life of the spindle and the spindle bearing can be prolonged at the same time.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
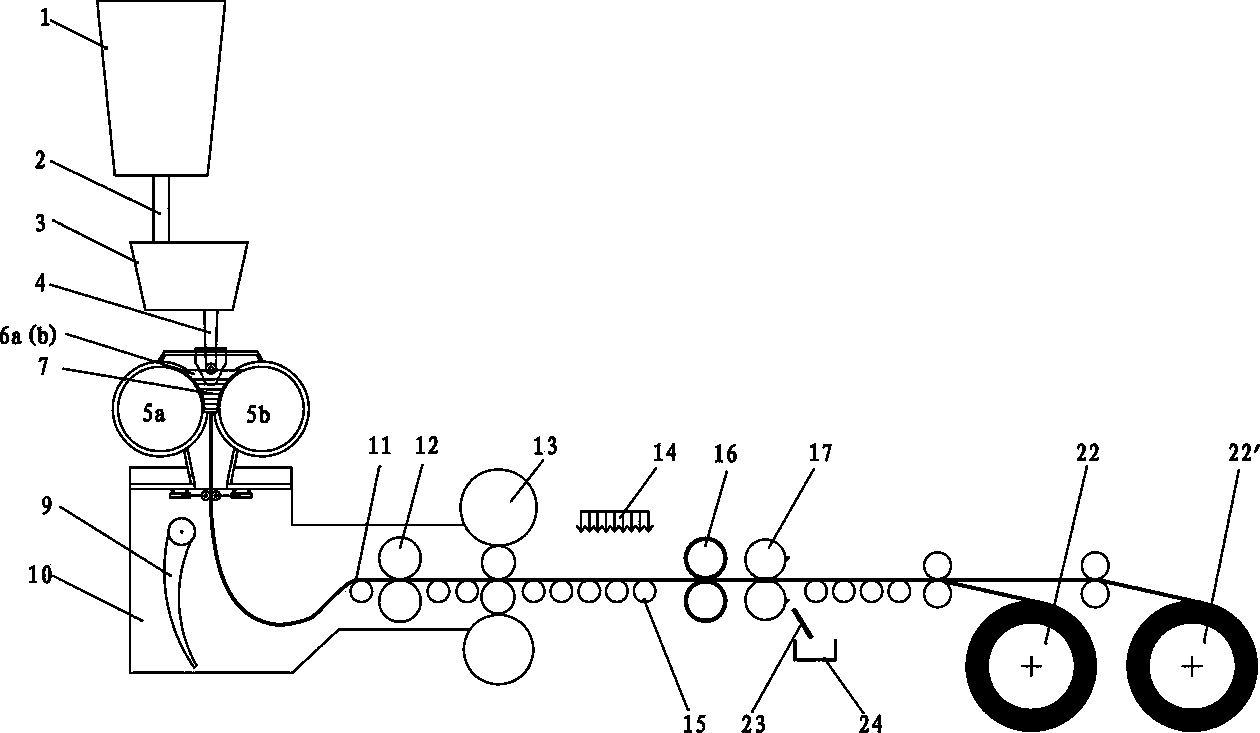
Method for producing high-strength thin strip steel in short process
ActiveCN103658178ACost-effectiveShorten the lengthWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsRare-earth elementMicroscopic scale
The invention relates to a method for producing high-strength thin strip steel in a short process. Twin roll strip casting is adopted for producing an atmospheric-corrosion-resistant steel casting belt containing a rare earth element Re, hot rolling, cooling and anti-oxidation intensive cooling scale removing are performed on the steel casting belt, and then the steel casting belt is reeled up after being straightened, wherein in the hot rolling process of the strip steel, rolling reduction is not smaller than 20%, and finishing rolling temperature is 850-1000 DEG C; then, a staged cooling mode of atomization cooling plus anti-oxidation intensive cooling ( spraying dry ice) is adopted, and intensive cooling is carried out on the high-temperature strip steel, wherein the cooling rate in the atomization cooling process is 50-100 DEG C / s, and the cooling rate in the anti-oxidation intensive cooling process is 100-200 DEG C / s. In this way, through the combined type staged cooling, the uniform steel of a bainite microscopic structure can be obtained, and the bainite structure can remarkably improve the toughness of the steel. The method is especially applicable to atmospheric-corrosion-resistant high-strength thin strip steel with the surface roughness Ra smaller than 2 microns, the thickness of typical strip steel is 0.8-1.6mm, and the strip steel can be supplied in a hot mode instead of a cool mode.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
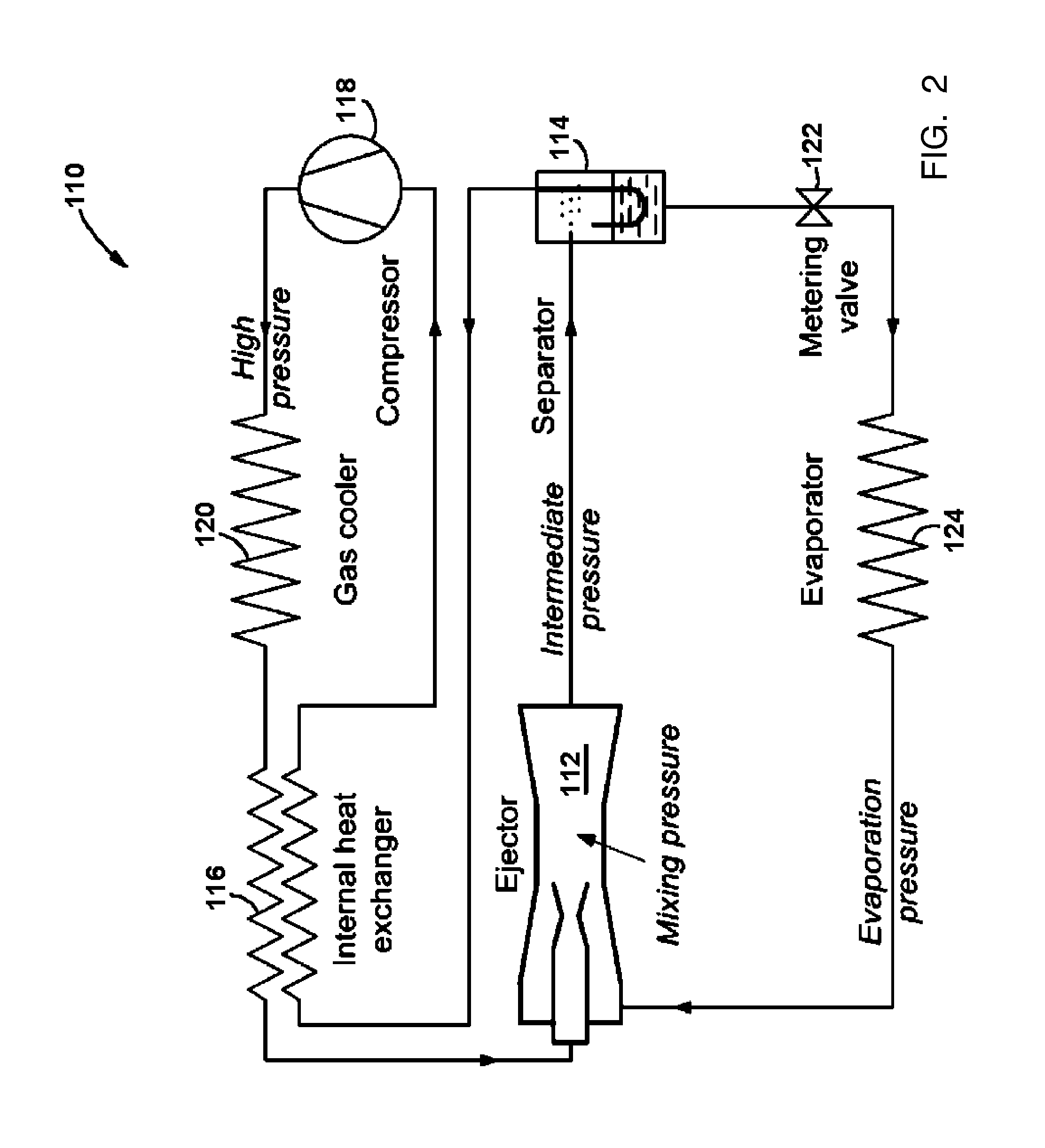
High efficiency r744 refrigeration system and cycle
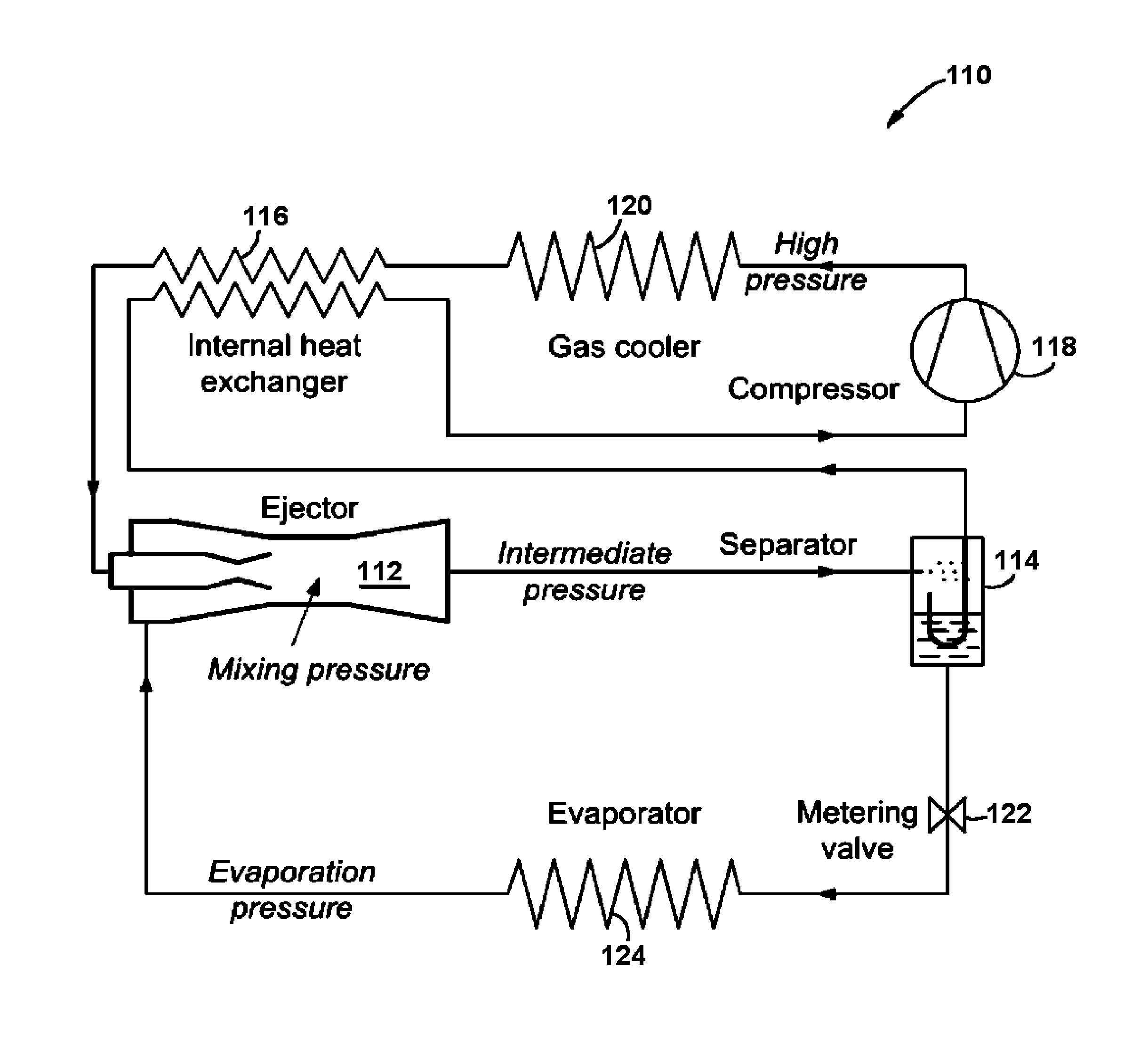
InactiveUS20100313582A1Reduce compressionImprove cycle efficiencyCompression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementEngineeringHigh pressure
A high efficiency R744 air conditioning and refrigeration system and cycle comprises a vapor compressor and two independent ejectors operatively connected to high and low-pressure sides of the compressor, respectively. The two ejectors reduce the overall pressure ratio of the mechanical vapor compressor resulting in dramatically increased thermodynamic cycle efficiency. As one example of its potential applications for residential, commercial or industrial uses, a 150 ton capacity of a water-cooled chiller designed in accordance with the present invention is predicted to provide the power consumption as low as 0.47 kW / ton, when operated in accordance with the cooling methods of the present invention, which corresponds to 7.47 of Coefficient of Performance (COP).
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
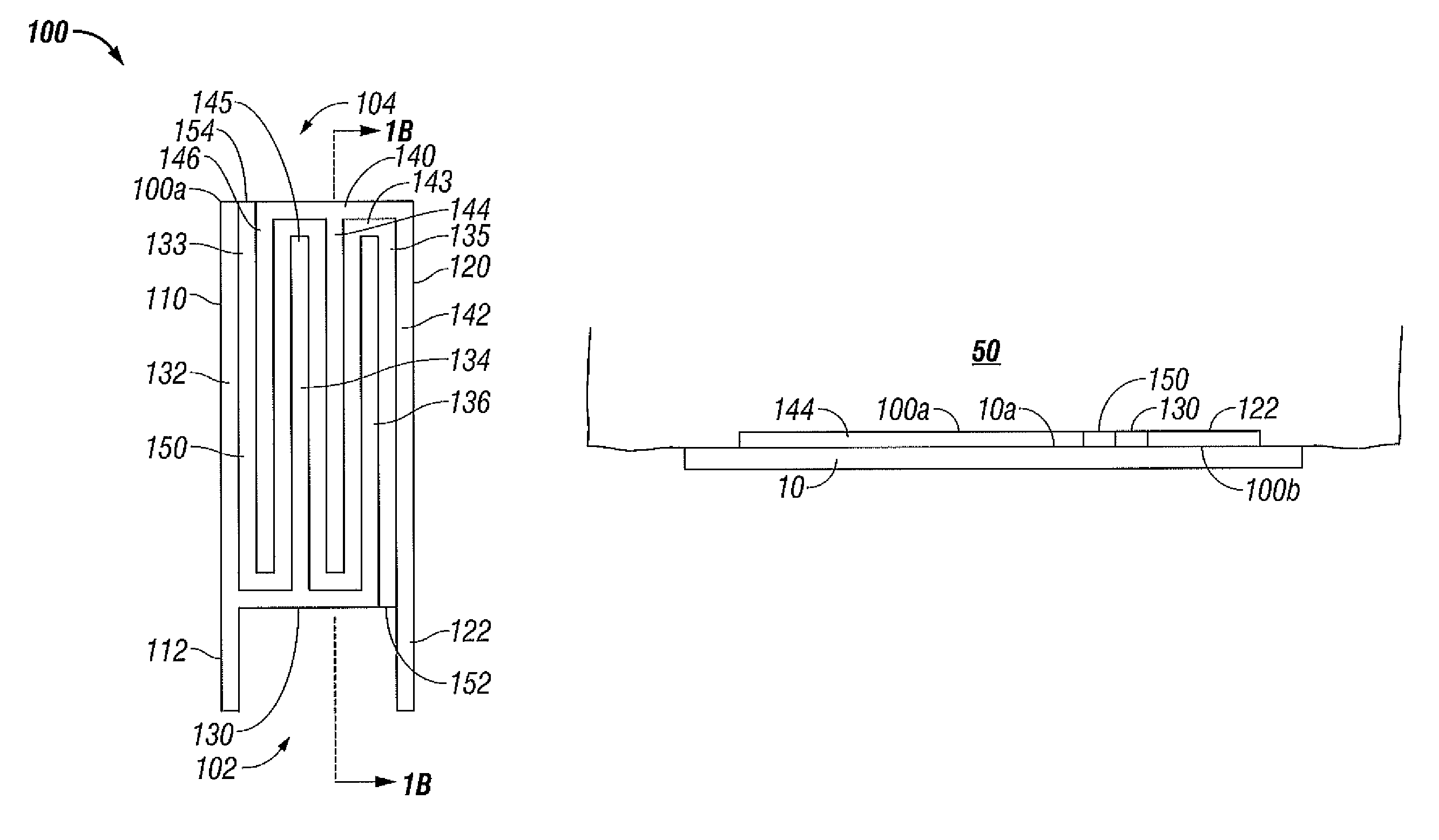
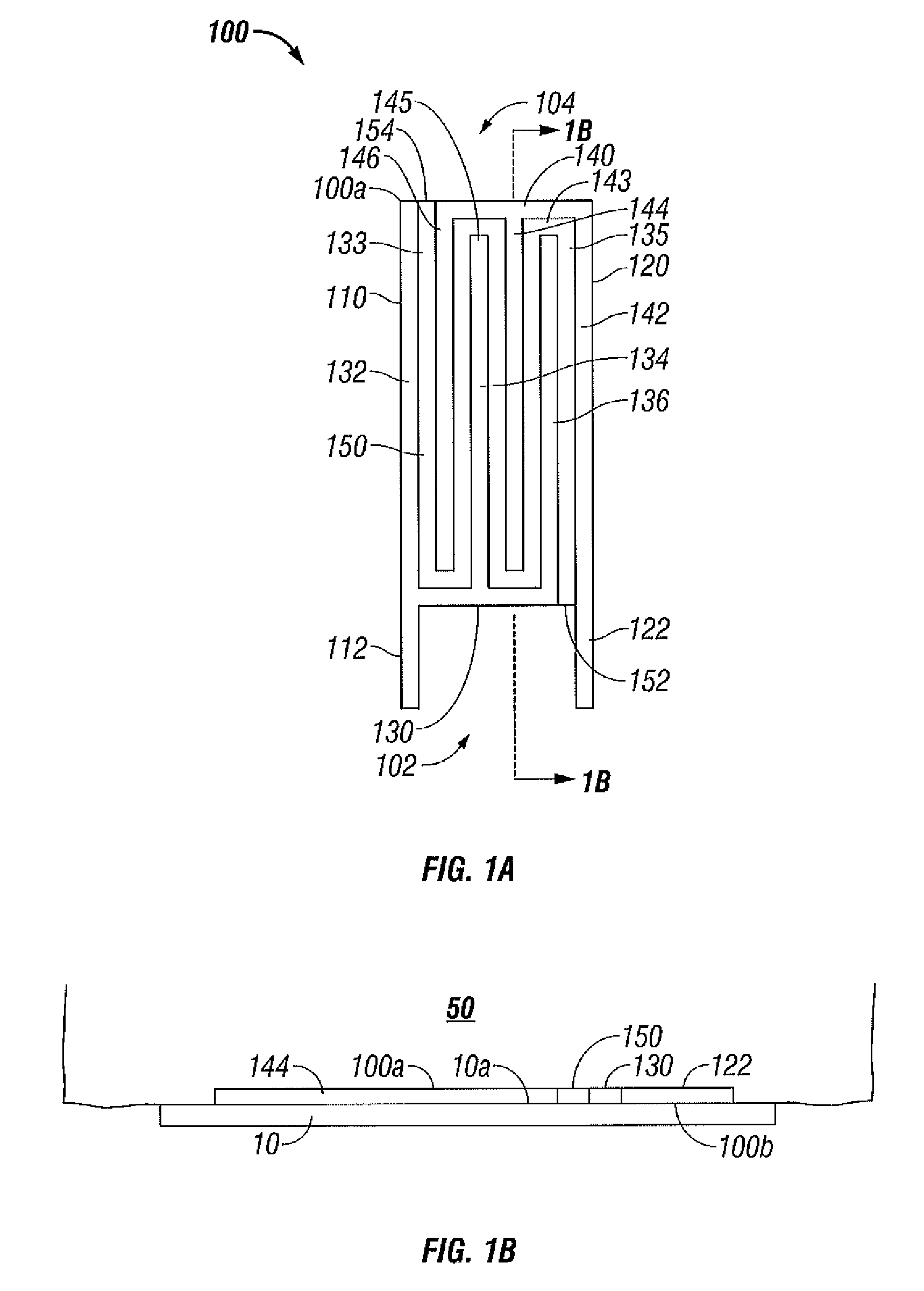
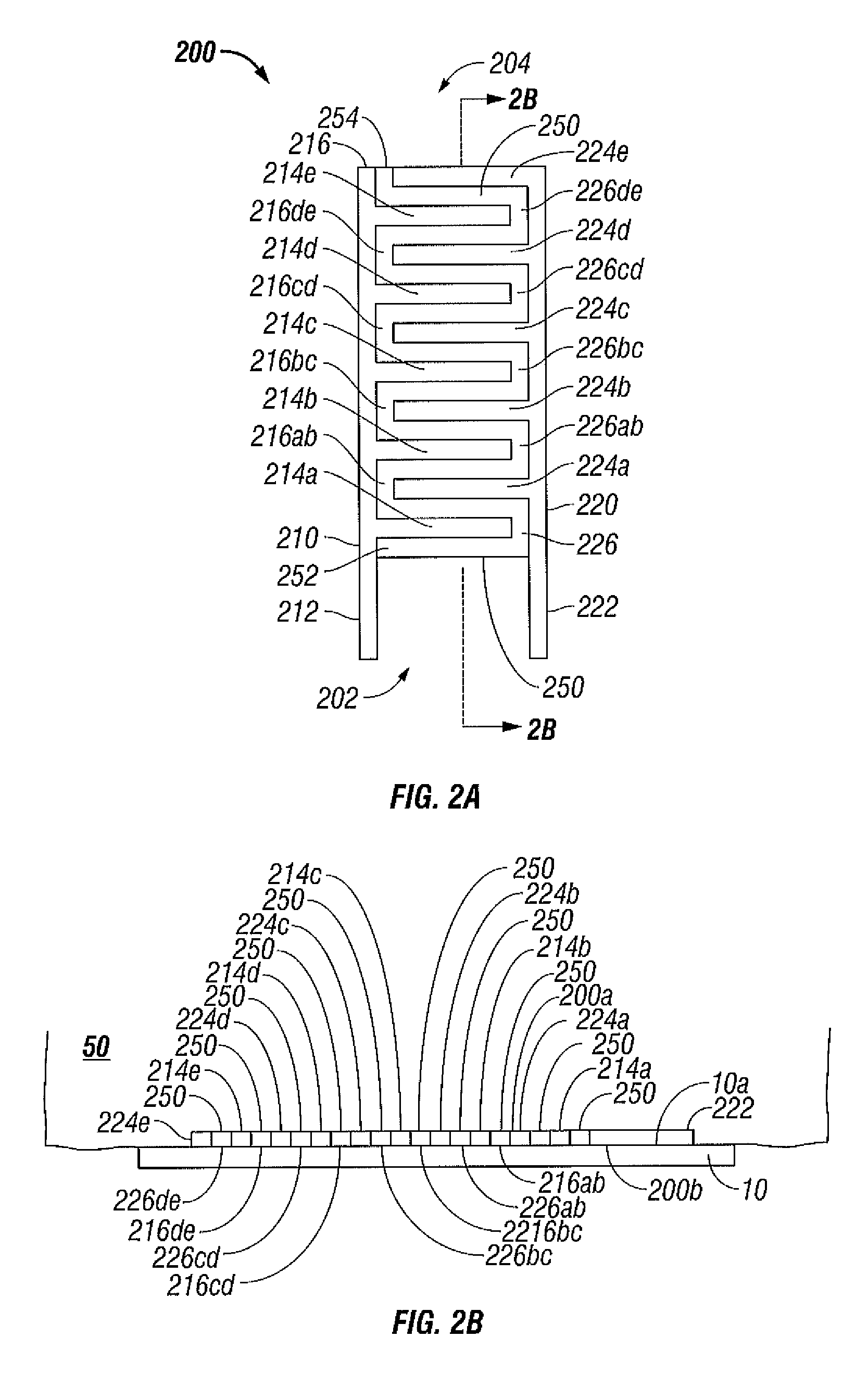
Surface ablation process with electrode cooling methods
ActiveUS8192427B2Improve treatmentReduction in tissue build-upSurgical instruments for heatingBiomedical engineeringCooling medium
A bipolar electrode assembly includes a substrate having proximal and distal ends and supports first electrode and second electrodes. The first and second electrodes are disposed in an interwoven configuration across the surface of the substrate from the proximal to distal ends. A cooling medium is disposed interposed between the first and second electrodes from the proximal to distal ends. The first and second electrodes each include a plurality of finger-like prongs which either extend lengthwise or transversely or the first and second electrodes extend spiral inwardly along the surface of the substrate. The prongs of the first electrode intermesh with the prongs of the second electrode. Each prong is separated by the cooling medium. First and second electrodes may be disposed in a lengthwise alternating configuration across the surface of the substrate with a cooling medium disposed in vertical registration thereunder.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
System design and cooling method for LP steam turbines using last stage hybrid bucket
InactiveUS20070292265A1Expands the hybrid blade conceptSimple designPump componentsBlade accessoriesSystems designCombined use
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cooling structure, heatsink and cooling method of heat generator
ActiveUS20070062674A1Good heat dissipationLess pressure lossSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal foilEngineering
A cooling structure includes a heat dissipation structure 20 having a heat generator 8 and a heatsink 7 that is adhered through an insulating adhesive layer 6 to at least a surface of the heat generator 8 that faces a cooling fluid 9 and made of a metal foil having the flexibility; and a fluid flow path 5 that is disposed outside of the heat dissipation structure 20 so that the cooling fluid 9 flowing inside thereof and the heatsink 7 may directly come into contact. Furthermore, on a surface of the heatsink that directly comes into contact with the cooling fluid 9, a fine recess 15 is disposed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Impingement cooled bucket shroud, turbine rotor incorporating the same, and cooling method
ActiveUS20080170946A1Reduce metal temperatureEffectively cool the blade tip shroudPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringCooling methods
A localized directional impingement cooling is used to reduce the metal temperatures on highly stressed regions of the tip shroud.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
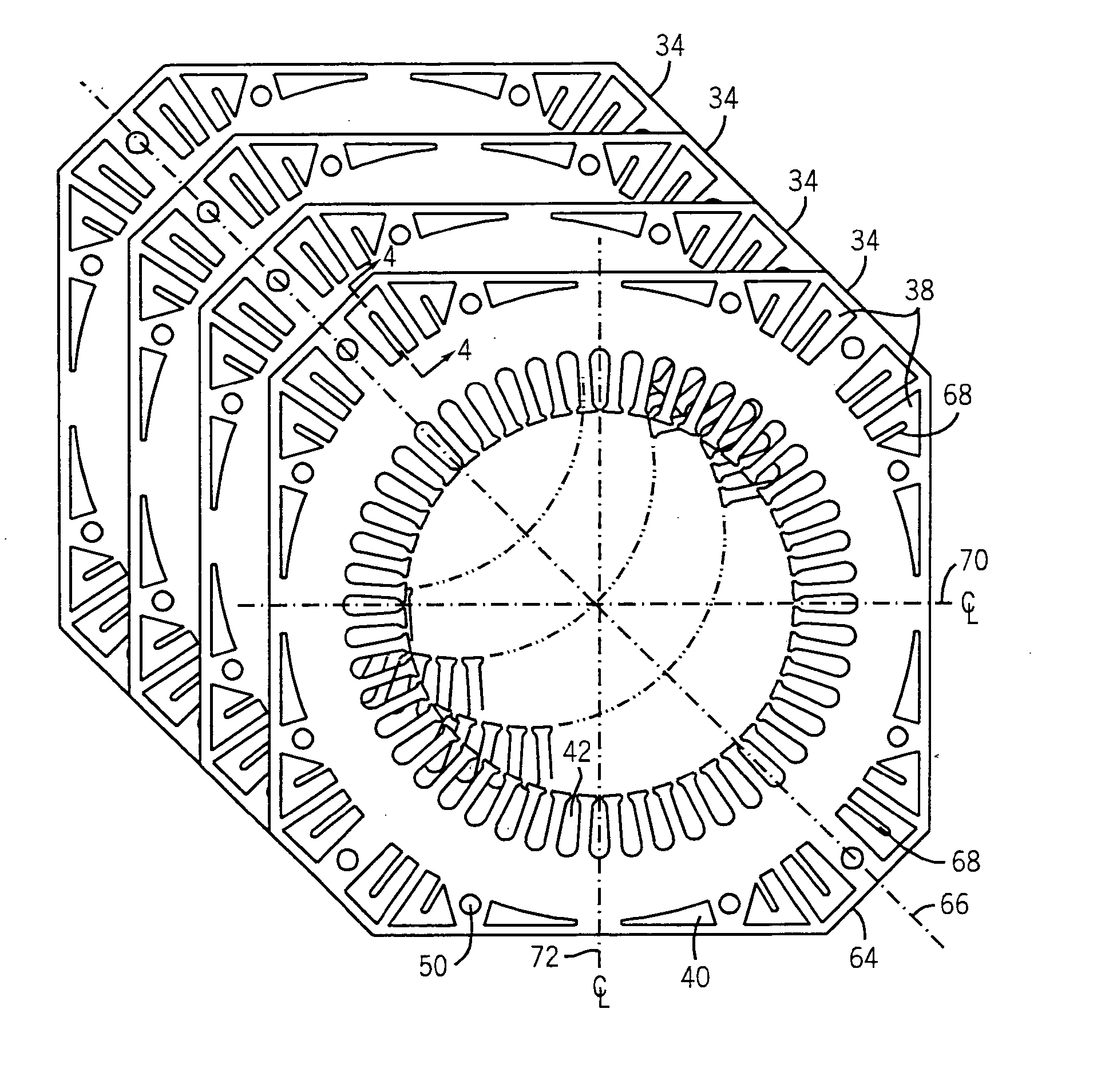
Stator cooling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050067905A1Improve cooling effectImproved convection coolingMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringForced-air
According to one embodiment of the present technique, forced air (i.e., air flow) is routed through a motor stator having corners and center ducts. Advantageously, by routing the air flow through ducts in accordance with the present technique, air flow is more evenly distributed throughout the motor, thereby reducing hotspots. By way of example, the motor stator my include fins that affect air flow and provide heat dissipation surfaces to the motor.
Owner:RELIANCE ELECTRIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com