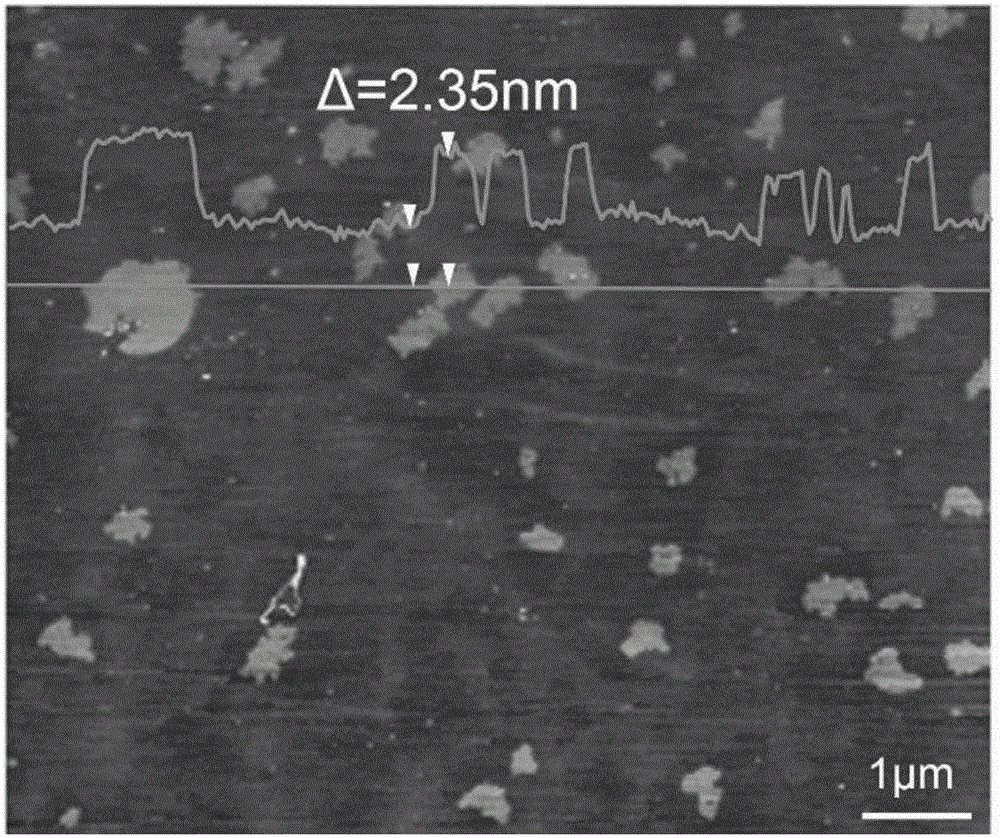
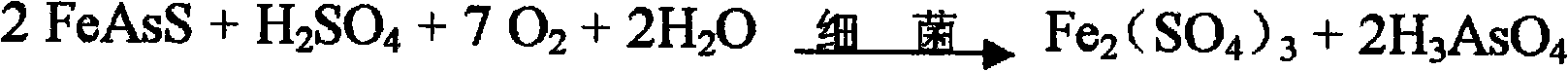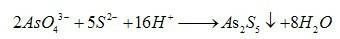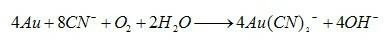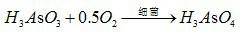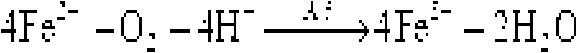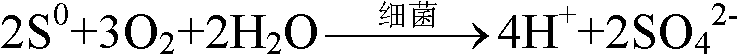Patents
Literature
51 results about "Bacterial oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
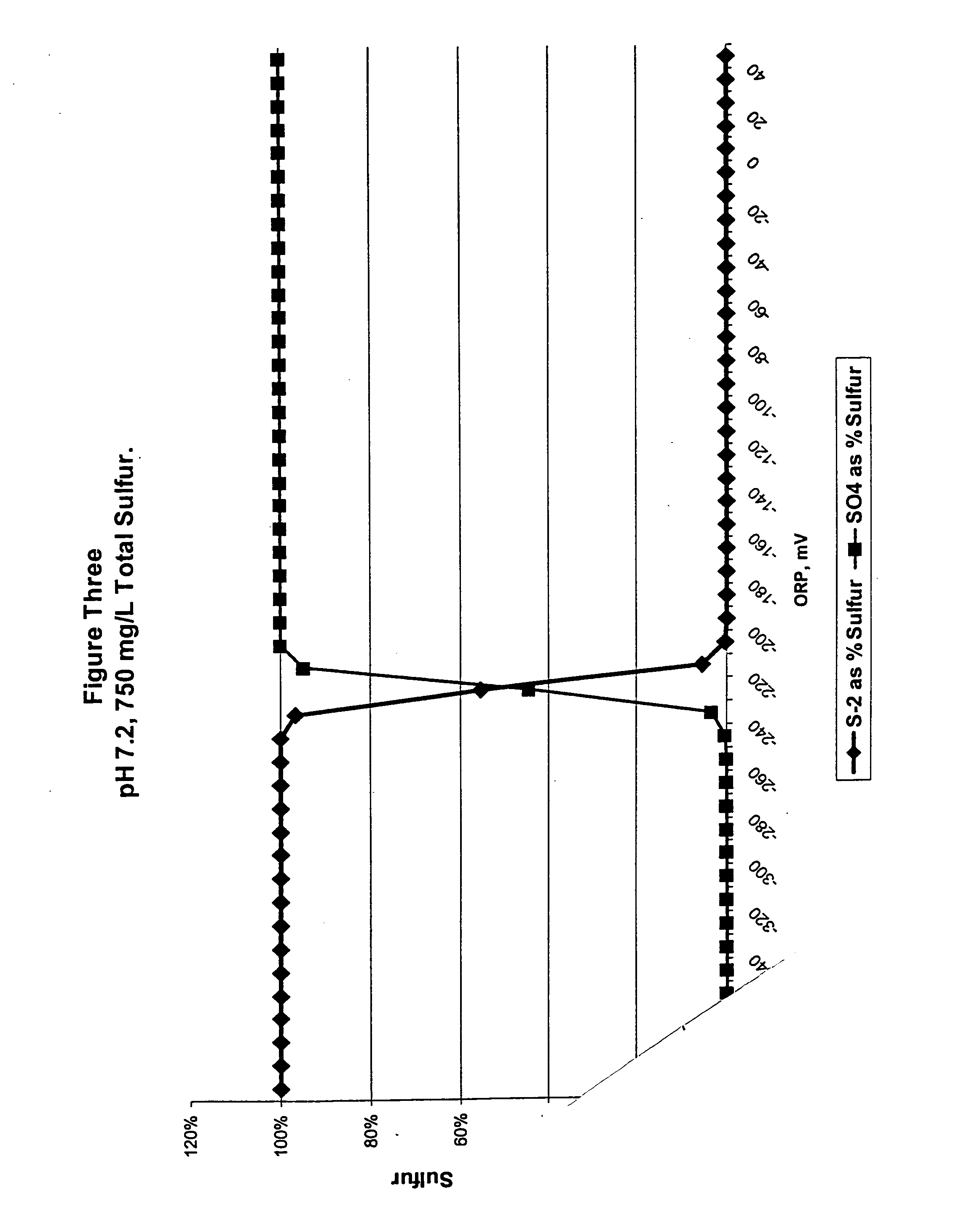
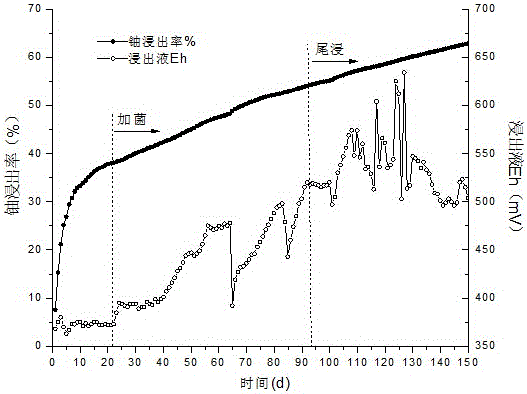
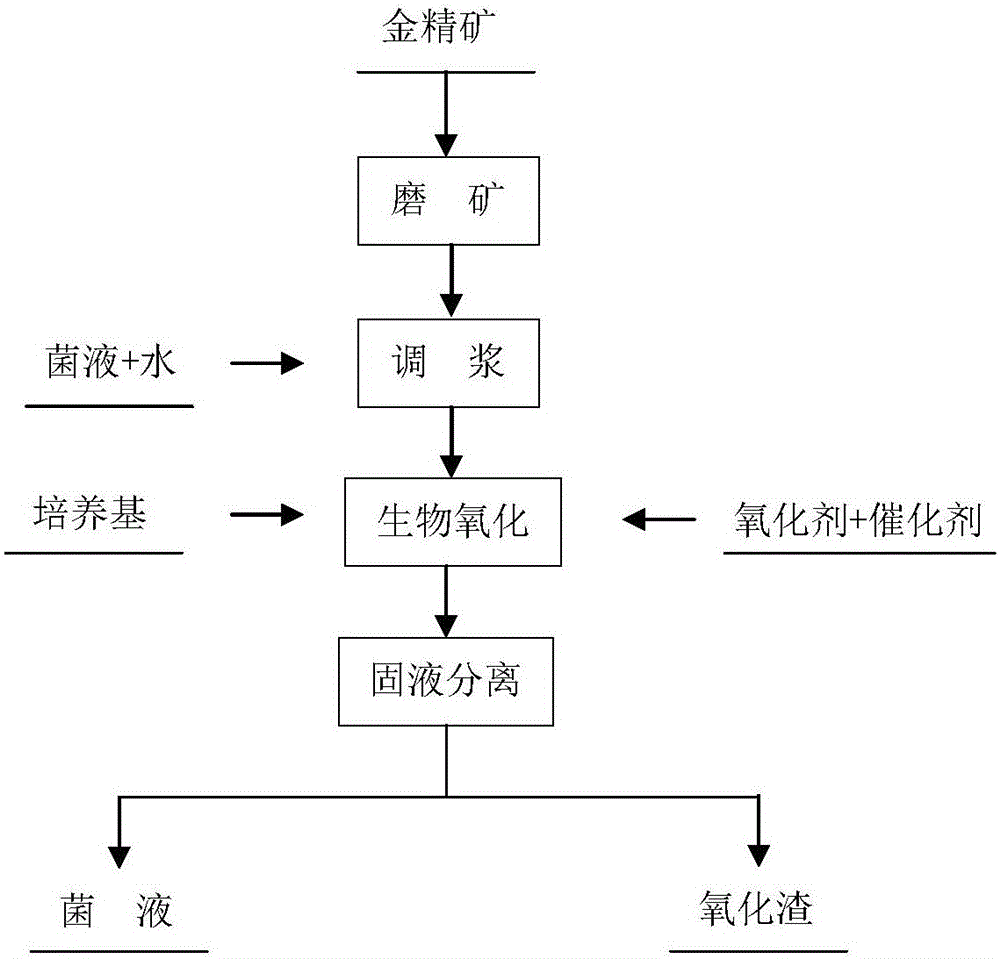
Bacteria biooxidation is an oxidation process caused by microbes where the valuable metal remains (but becomes enriched) in the solid phase.In this process, the metal remains in the solid phase and the liquid can be discarded. Bacterial oxidation is a biohydrometallurgical process developed for pre-cyanidation treatment of refractory gold ores or concentrates. The bacterial culture is a mixed culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans. The bacterial oxidation process comprises contacting refractory sulfide ROM ore or concentrate with a strain of the bacterial culture for a suitable treatment period under an optimum operating environment. The bacteria oxidise the sulfide minerals, thus liberating the occluded gold for subsequent recovery via cyanidation.
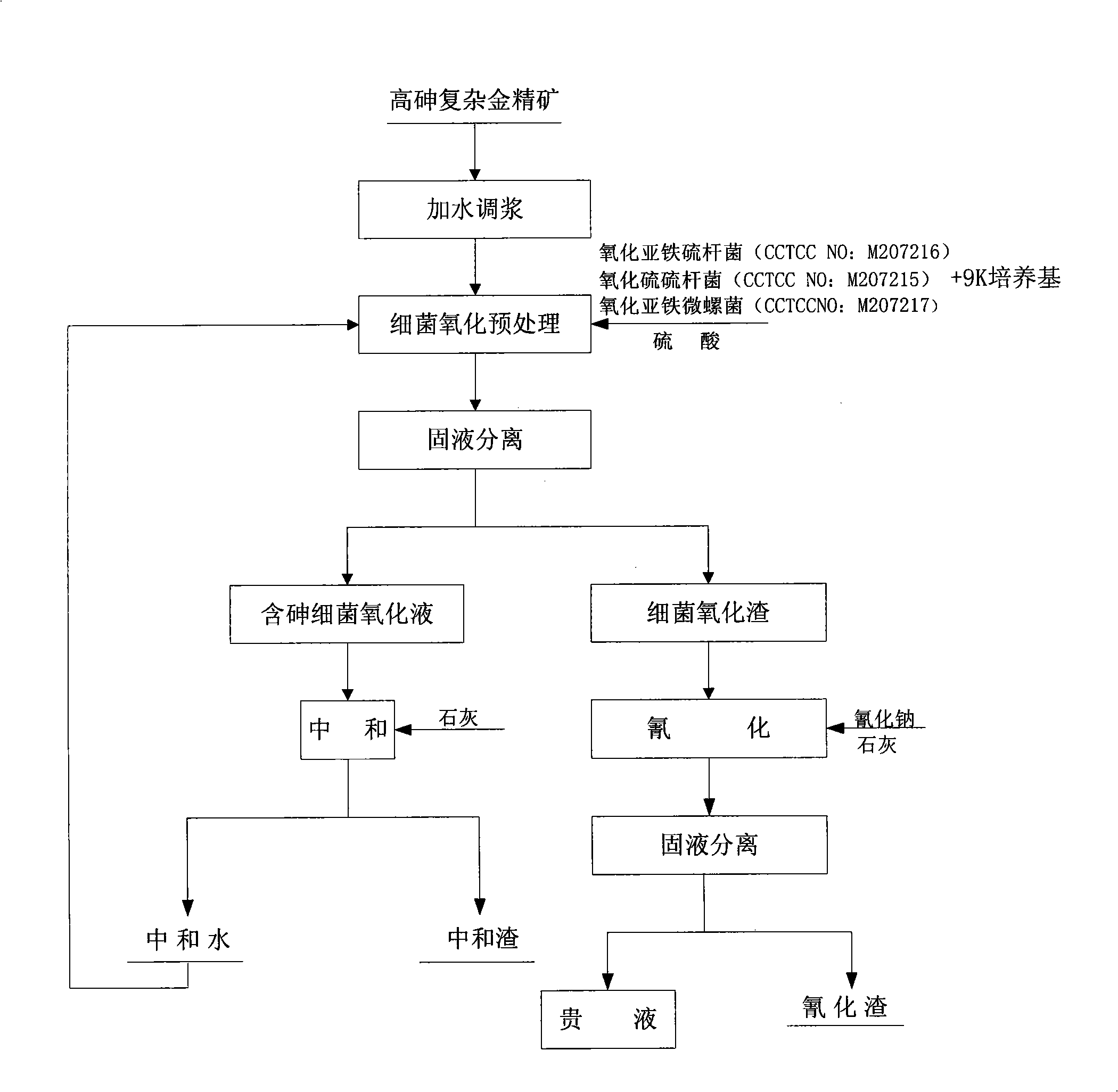
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
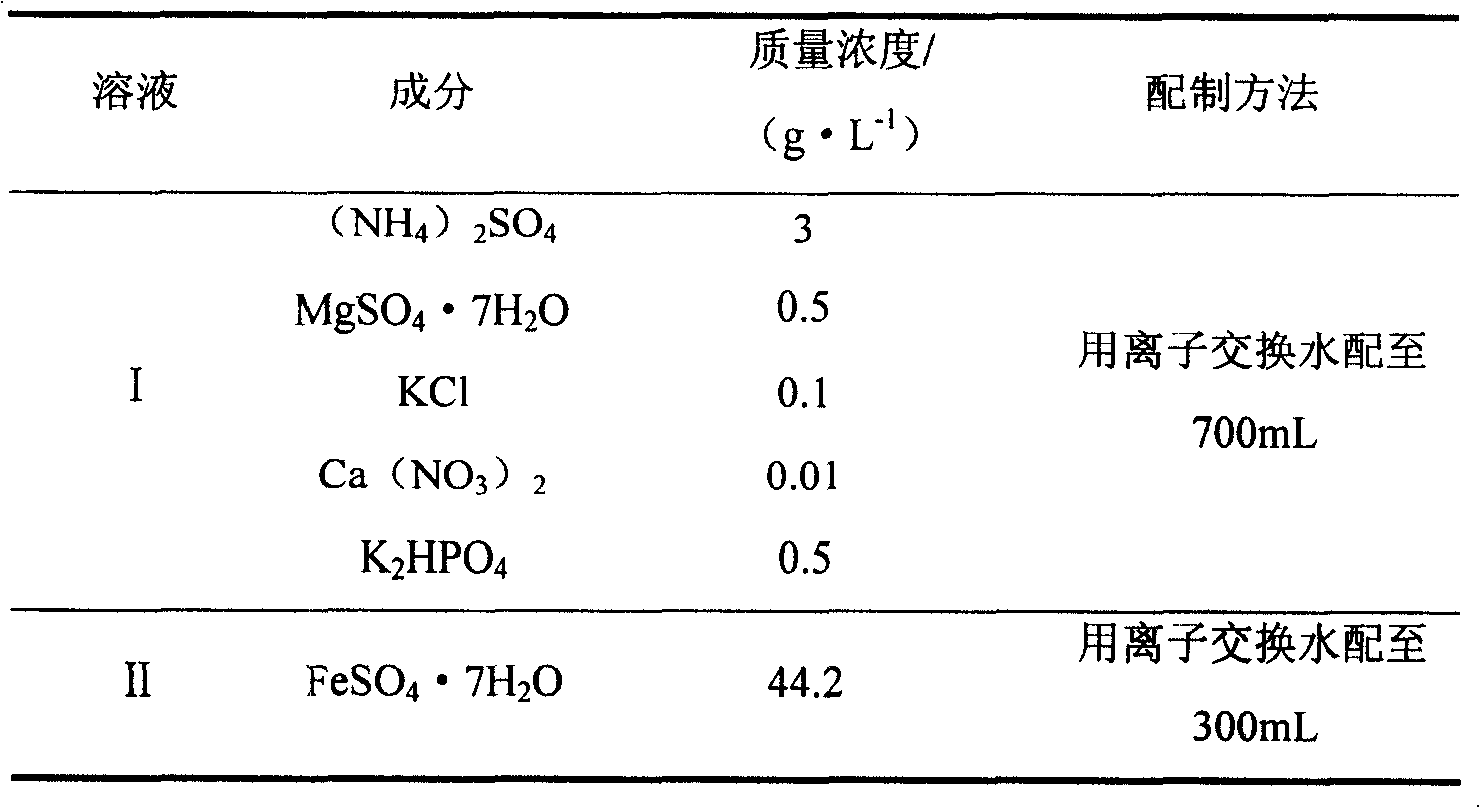
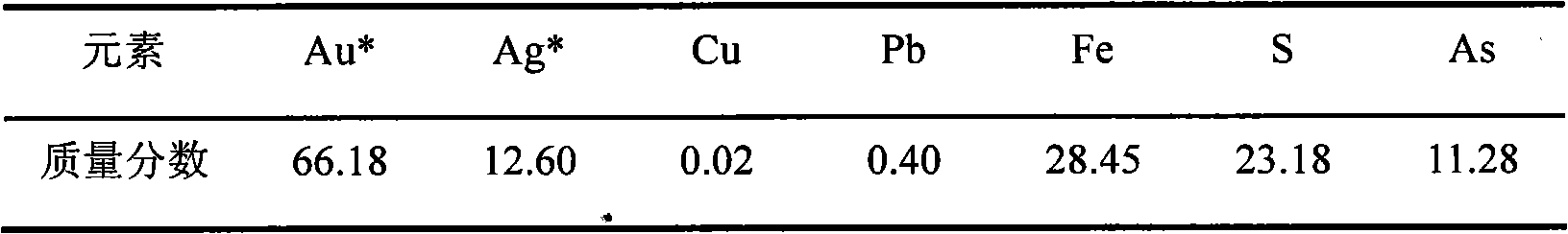
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
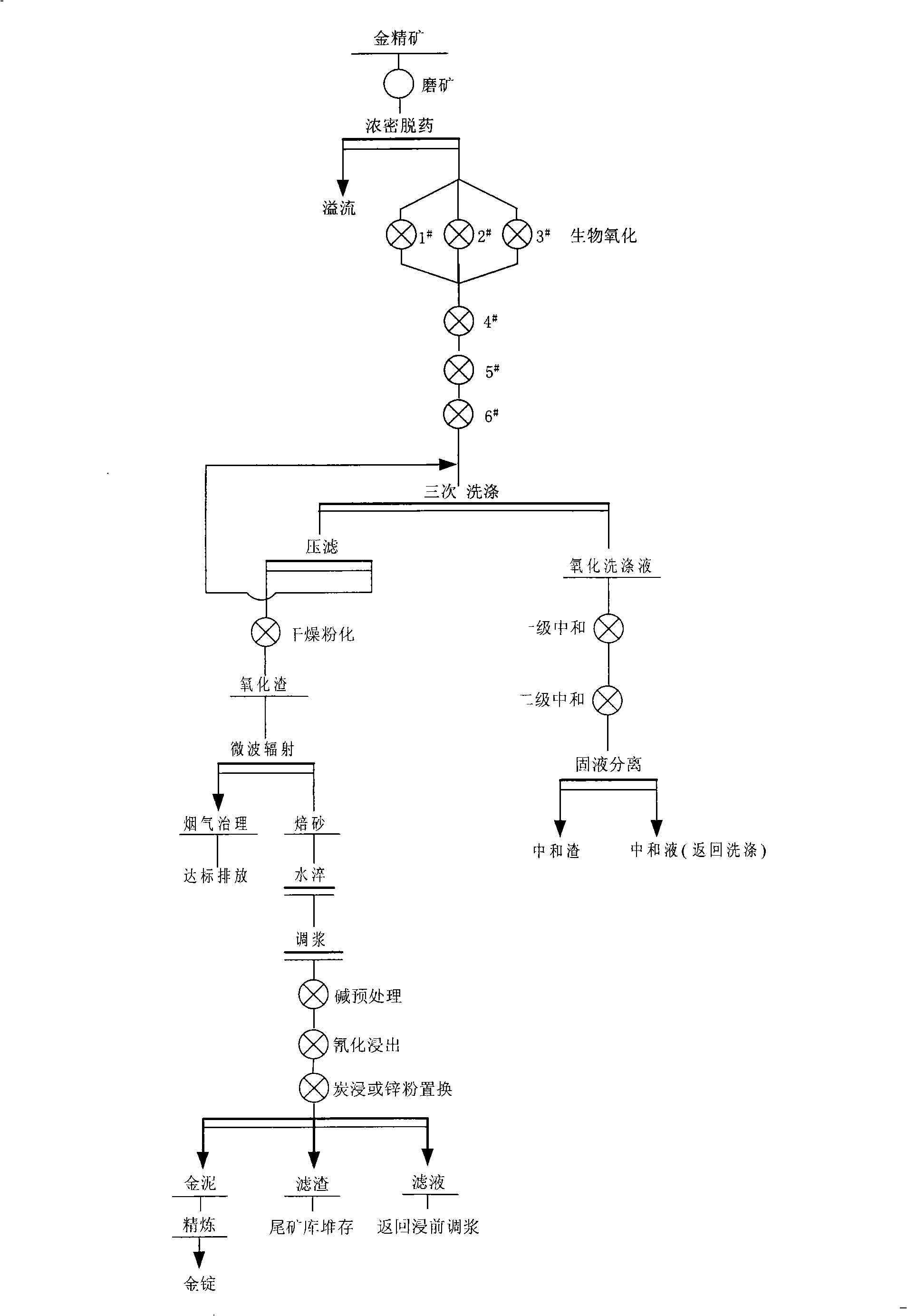
Gold extraction process with low pollution and high recovery for refractory gold concentrate
ActiveCN101285126AReduce pollutionAvoid secondary packagingProcess efficiency improvementSlagSulfide minerals
The invention relates to a process for extracting gold of refractory gold concentrates with low pollution and high recovery rate, belonging to the metallurgical process class. The process proposal which combines organically the bacterial oxidation technology with the microwave irradiation technology comprises the following steps of: oxidizing and decomposing sulfide minerals by means of the bacterial oxidation technology first; exposing and dissociating sufficiently the gold; oxidizing a large part of sulfur and arsenic to enter a liquid-phase; carrying out the neutralization treatment to the oxidizing liquid and returning to use; roasting oxidizing slag with microwave at the low temperature; and removing organic carbon in ore. The process solves completely the problem of absorbing the gold in the subsequent cyaniding gold extraction work. The process has high recovery rate of the gold and less environment pollution, is easy to automatically control and saves energy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST +1
Efficient biological desulfurization method for coal
InactiveCN103937576AEffectively retain active ingredientsEasy to operateSolid fuelsThiobacillus ferrooxidansThiobacillus
The invention discloses an efficient biological desulfurization method for coal, which is characterized in that coal is crushed through a crusher until the particle size is below 150 meshes; and three bacteria, namely Thiobacillus thioxidans, Thiobacillus caldus and Pseudomonas stutzeri, are adopted. The desulfurization process comprises the following sequential steps: removing organic sulfur in the coal through the Pseudomonas stutzeri; after the primary desulfurization is finished, preparing the Thiobacillus thioxidans and the Thiobacillus caldus into a desulfurization solution according to a certain total bacterial count ratio, and removing inorganic sulfur of the coal; and washing the desulfurized coal with water, filtering, and drying. The total sulfur removal ratio of the desulfurized coal is up to 57.8%; and the method is simple to operate, mild in treatment conditions and low in cost, and effectively retains effective components in the coal, thus being a desulfurization technology having very wide market prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
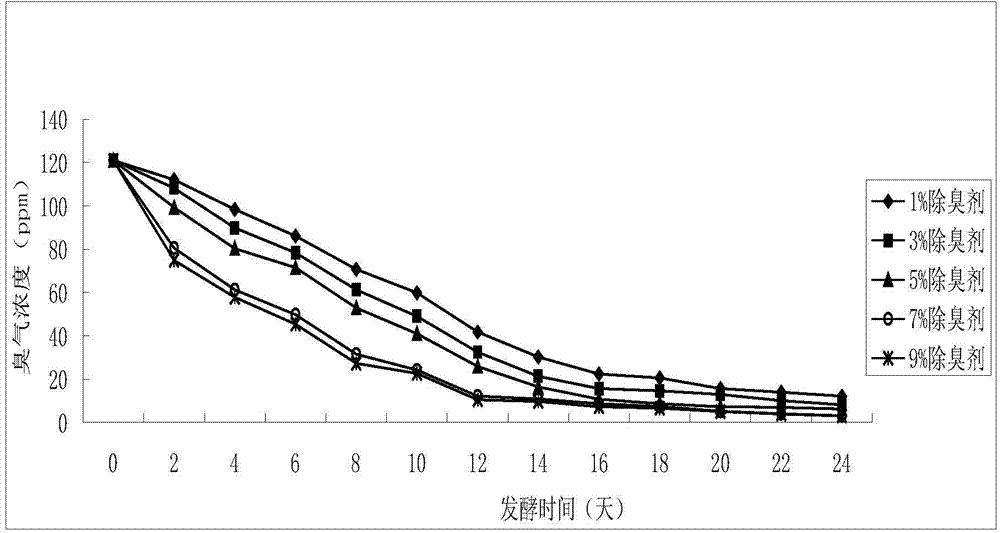
Biological deodorant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104258440AImprove adsorption capacityImprove working environmentBio-organic fraction processingDeodrantsBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a biological deodorant. The biological deodorant is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 20%-30% of a complex microbial agent, 40%-50% of organic acid and 30%-40% of calcium superphosphate, wherein the complex microbial agent comprises saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus subtilis, germany lactic acid bacteria, nitrobacteria, thiobacillus thiooxidans, acetobacter oxydans and an adsorption material; and the organic acid is selected from one or more of oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, polybasic carboxylic acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, amino acid, sulfoacid and sulfinic acid. According to the biological deodorant, the original foul gas in garbage can be quickly and effectively adsorbed, removed and covered, the work environment of a worker in a composting plant is improved, composting and stabilizing of organic garbage are accelerated, and novel foul gases such as ammonia and hydrogen sulfide generated and released in the composting process are prevented from being reduced.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY +1
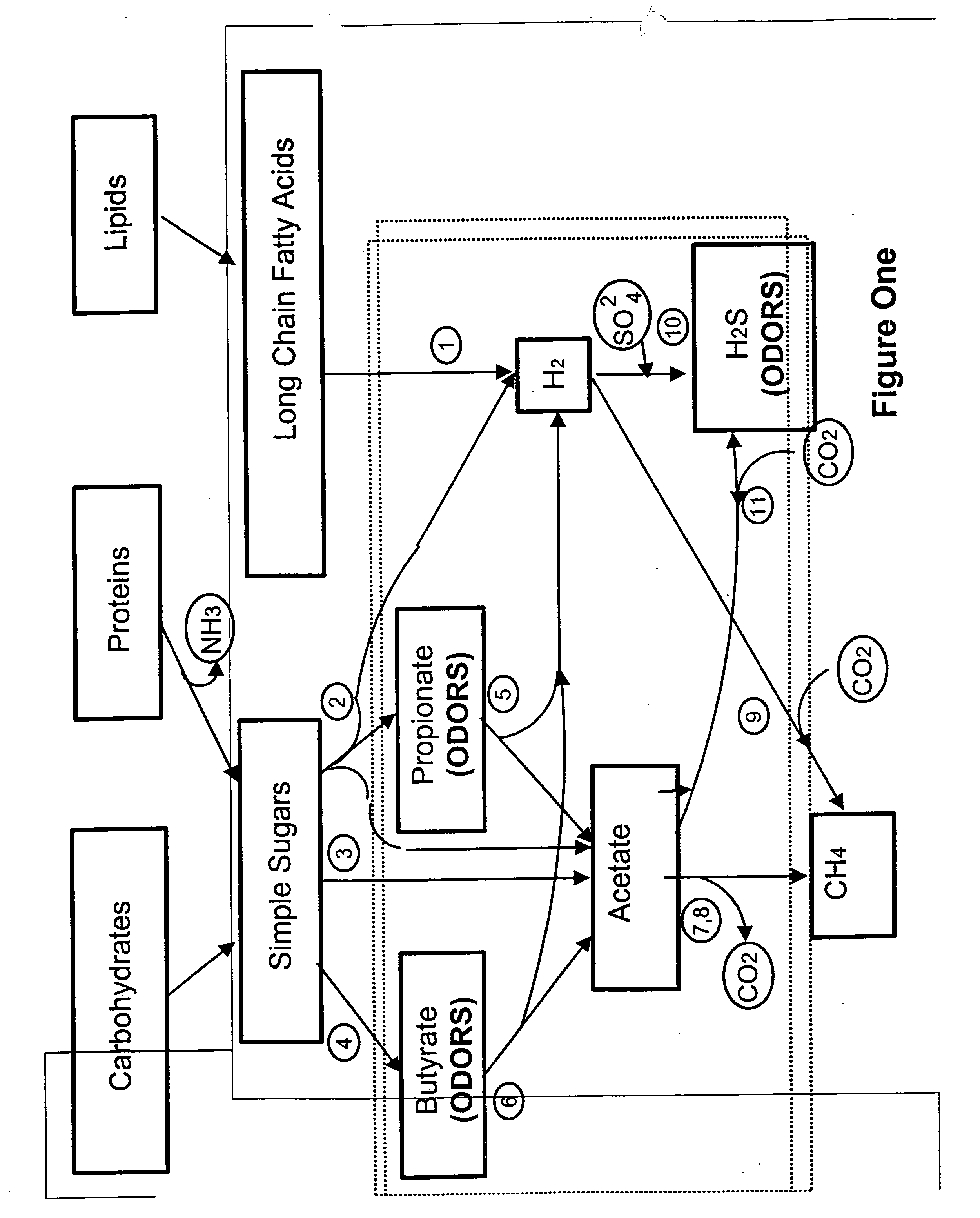
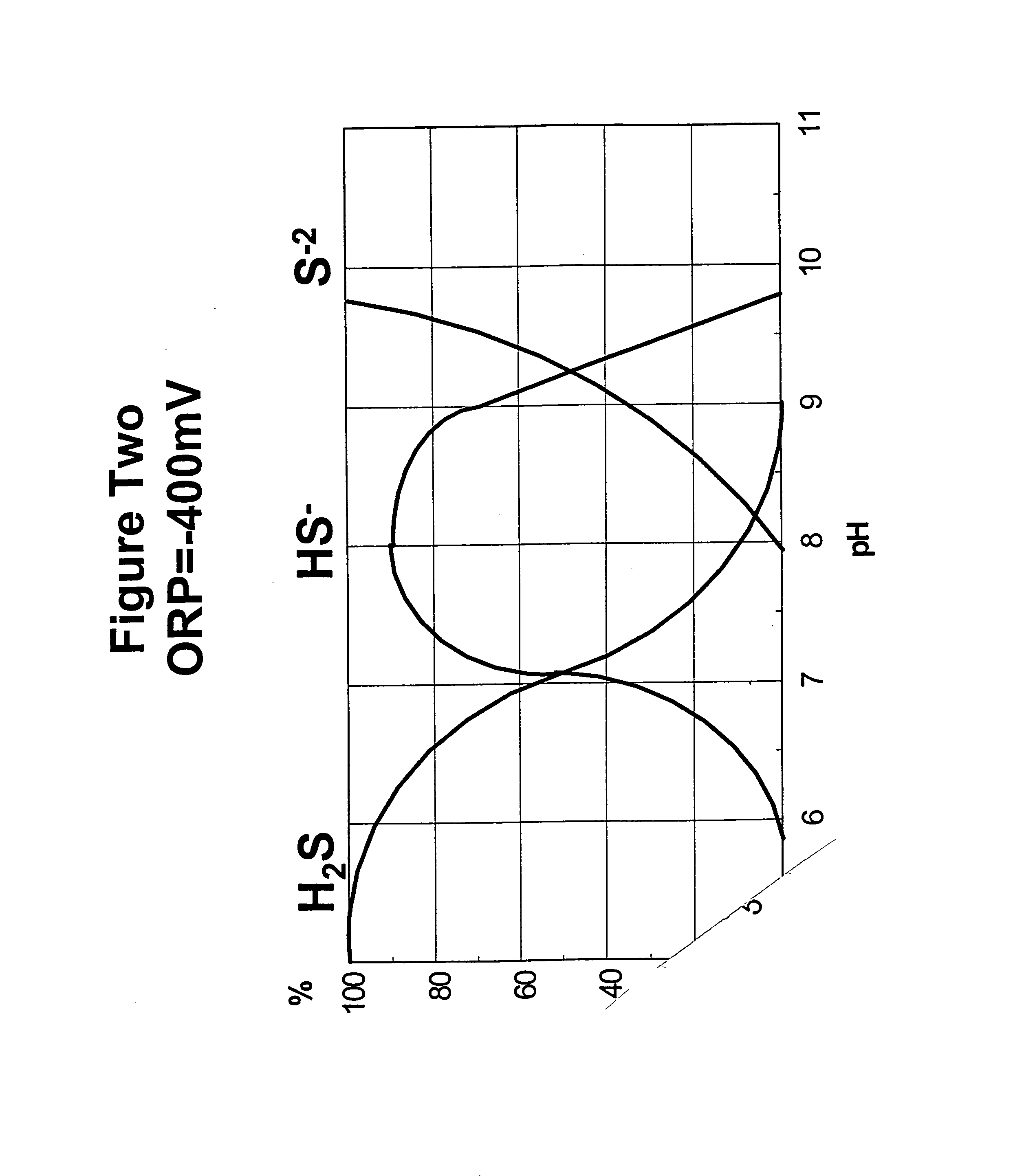
Odor control
InactiveUS20040180424A1Reduce and eliminate odorMinimizing expenseWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaSynechococcusOxygen
Disclosed herein is a method for treating odors in wastewater treatment bodies. The pH of the body is preferably established above about 6 and most preferably above about 7, usually by adding a base to the body. The oxidation reduction potential of the body is established at about -300 mV or higher and more preferably about -200 mV or higher, usually by adding an oxidizing agent such as oxygen or nitrates. After these conditions are established, sulfur oxidizing bacteria are added to the body. These preferably include Paracoccus denitrificans (formerly called Thiosphaera pantotropha) ATTC number 35,512. The sulfur oxidizing bacterial population should be established at levels of at least about 1x10<4 >cfu / mL and more preferably at levels of 1x10<5 >to 1x10<6 >cfu / mL or higher. The increased ORP and pH levels make sulfate reduction thermodynamically unfavorable. Additionally, the presence of an alternative electron acceptor such as oxygen or nitrate allows the sulfur oxidizing bacteria to oxidize organic acids.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Arsenic-resistant bacteria and method for performing oxidation treatment on high-arsenic gold concentrate by using same
InactiveCN101993835AReduce consumptionEfficient recyclingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIron sulphurOxidative treatment
The invention relates to a method for treating high-arsenic gold concentrate, which belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. Arsenic-resistant bacteria of the invention are arsenic-resistant thiobacillus ferrooxidant (CCTCCCNO: M2010072) which are obtained by breeding and domesticating thiobacillus ferrooxidant-containing high-arsenic gold concentrate acid mine pit water. The method for treating the high-arsenic gold concentrate by using the arsenic-resistant bacteria comprises the steps of expanding and culturing the bacteria, performing paste mixing on the high-arsenic gold concentrate, performing bacterial oxidation treatment, acidizing to remove arsenic, cyaniding to extract gold, recovering the arsenic and the like. Compared with the conventional method for pretreating high-arsenic gold ore, the method for treating the high-arsenic gold concentrate has the advantages of efficiently recovering noble metal gold, recycling the side product, namely arsenic, solving the environmental problem of high arsenic content of sewage and waste residues subjected to the bacterial oxidation process treatment, reducing the consumption of a cyaniding medicament, increasing the gold-extracting ratio of the high-arsenic gold concentrate and contributing to the environmental protection and the sustainable development of the huge-reserve high-arsenic gold concentrate in China.
Owner:威远川奇生工科技有限责任公司 +1
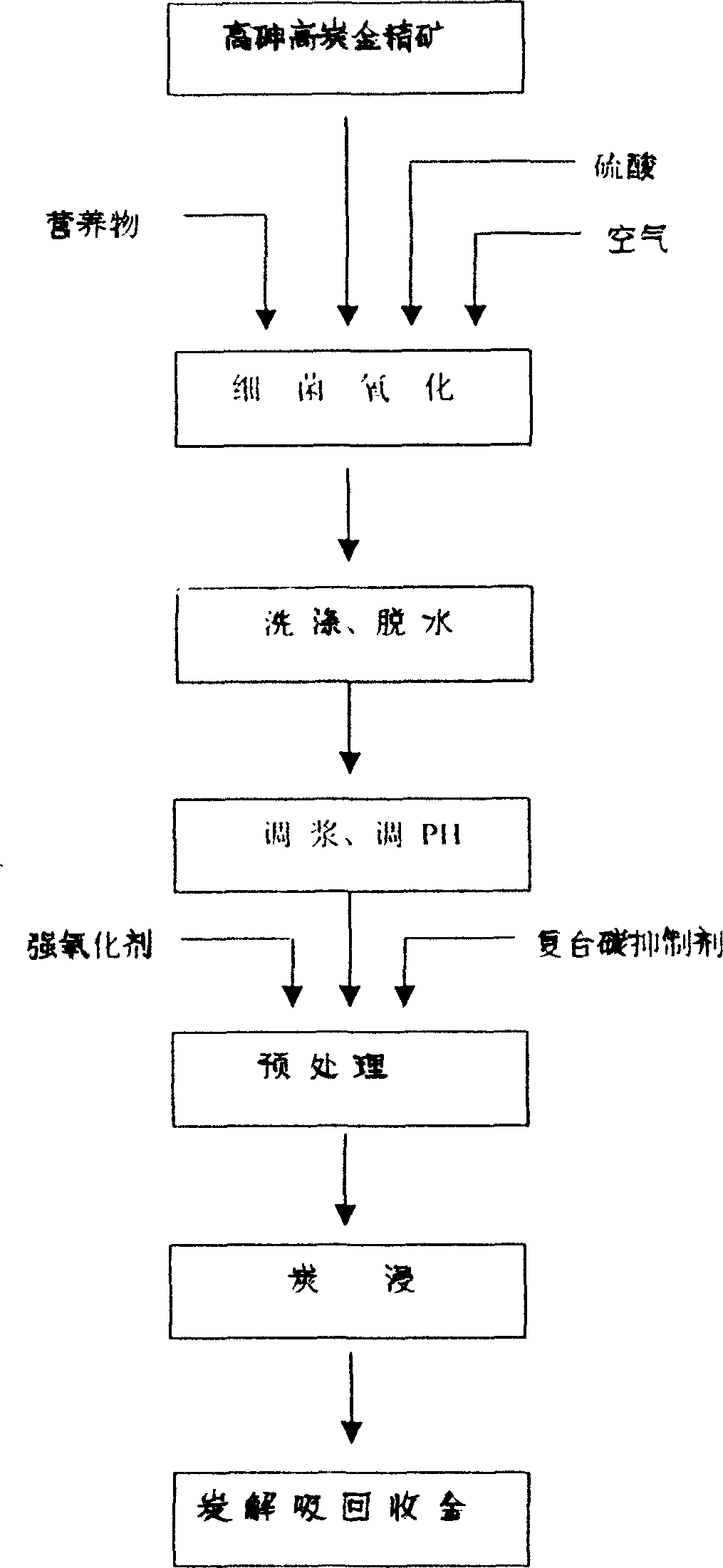
Process for treating high arsenic high carbon gold mine
InactiveCN1683570AHigh recovery rateReduced ability to adsorb gold cyanide complexesProcess efficiency improvementHigh carbonSlurry
The process of treating high arsenic and high carbon gold ore includes the first bacteria oxidation, in which bacteria propagate with sulfur and iron in ore as food under condition suitable for microbe to grow, so as to dissociate the gold coating mineral and expose gold; and the subsequent reinforced carbon soaking and cyaniding after adding additive into the mineral slurry to destroy organic carbon compound and inorganic carbon compound in mineral and inhibit covering. The present invention has active carbon using life, greatly raised gold recovering rate and other advantages, and can treating gold ore with As content as high as 8 % and carbon content as high as 10 % to reach gold leaching rate up to 90 %.
Owner:莱州泰源冶金技术有限公司
Application of additive in enhancing oxidization of arsenical gold mineral by bacteria
ActiveCN102634661AOxygenPromote oxidationProcess efficiency improvementBiological oxidationGold deposit
The invention provides an application method of an additive in enhancing oxidization of arsenical gold mineral by bacteria. The additive is ammonium persulfate, and the dosage is 20-50% of total amount of the arsenical gold mineral. Two adding modes are adopted, the first adding mode is adding to a leaching system together with bacteria liquid, and the second adding mode is adding to the leachingsystem after bacterial leaching for a certain period of time. When the first adding mode is adopted, the additive mainly contains oxidized arsenical pyrite, the dosage of the additive is increased to50% from 0%, and the oxidation rate of the arsenical pyrite is increased to 95% from 8.7%. When the second adding mode is adopted, the additive mainly contains As(III) in oxidizing solution, the dosage of the additive is increased to 50% from 0%, and the oxidation rate of As(III) is increased to 91.12% from 4.9%. Reproduction and activity of the bacteria are not affected after the additive is added; the oxidation of the arsenical pyrite or As(III) can be obviously enhanced in an oxidization process; the problem of toxicity of a biological oxidation product can be solved, and the application method becomes an important measure for increasing the speed of oxidizing the arsenical gold mineral by the bacteria.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for reinforcing bacterial preoxidation of arsenic-containing gold ore
The invention provides a method for reinforcing bacterial preoxidation of an arsenic-containing gold ore. Two additives (separately silver nitrate and ferric sulfate or ferric nitrate) are added. When being in use, a chloride-free 9K solution is prepared with the concentration of Ag(I) and Fe(III) reaching 0.005-0.05 g / L and 1-10 g / L respectively; then the arsenic-containing gold ore is added to the solution; and finally, a certain amount of a bacterium liquid is inoculated to the system for bacterial preoxidation. Under the synergistic effects of Ag(I) and Fe(III), the bacterial oxidation rate of the arsenic-containing gold ore can reach higher than 90%; and oxidation time is greatly shortened. On one hand, the synergistic reinforcement of Ag(I) and Fe(III) accelerates the dissolution of the arsenopyrite; on the other hand, toxicity of As (III) in the system toward to the bacteria is lowered, so that the bacterial oxidation of the arsenic-containing gold ore is reinforced; and important theoretical and technical guidance for increasing efficiency bacterial preoxidation-cyanide gold leaching process of the gold ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Bacterial oxidation pretreatment and cyanidation gold extraction method of arsenopyrite and realgar type refractory gold ores
The invention relates to a bacterial oxidation pretreatment and cyanidation gold extraction method of arsenopyrite and realgar type refractory gold ores, comprising the following steps of: inoculating a mixed bacterial solution containing CCTCC NO: M209074 and CCTCC NO: M207215 to a 9K culture medium for culturing; adding ore powder to a bacterial culture solution; carrying out bacterial oxidation pretreatment at the temperature of 44-60 DEG C, wherein pH is 0.8-2.5; charging air and stirring for 4-8 days, wherein the aeration rate is 0.1-0.3m3 / h and the stirring rate is 600-1400 turns / min; adding water to bacterial oxidation slag and blending into a slag slurry; regulating the pH value of the slag slurry to 9.0-12; then adding sodium cyanide, wherein the pH value in the cyanidation process is 9.0-12, and the cyanidation time is 24-48 hours. The leaching rate of gold is greatly increased and can reach by more than 94 percent after cyanidation leaching is carried out on the bacterial oxidation treated bacterial oxidation slag, and the economic benefit is extremely remarkable.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Biological-chemical dipolar reactor leaching process
ActiveCN101298640ANot affect growthImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementChemical reactionChemical reactor
The invention discloses a mineral leaching technique of a double-stage biological and chemical reactor, which separates the traditional biological mineral leaching process into a biological reacting process with bacteria growth and Fe2+ oxidation as well as a chemical reacting process with bacteria product oxidation and mineral leaching, and suitable conditions of the two processes are respectively controlled, thus improving efficiency of bacteria oxidation and mineral leaching. Compared with currently popular biological mineral leaching methods, the mineral leaching technique of the double-stage biological and chemical reactor greatly improves production efficiency.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Biological gold extraction method of difficult separation concentrate and special equipment
InactiveCN1410563AHigh recovery rateImprove arsenic toleranceProcess efficiency improvementOre concentrateBacterial oxidation
A biological process for extracting gold from the metallurgical ore concentrate difficult to separate includes such steps as grinding the said ore concentrate, preparing slurry, oxidizing with mesophilic bacteria mixture at 35-45 deg.C by 4 stages for 2-6 days, washing, neutralizing and cyanating the oxidized dregs to extract gold. Its advantages are high recovery rate of gold, low loss, and reduced environmental pollution.
Owner:山东天承生物金业有限公司
Biological gold extraction process of antimony-bearing complex refractory gold ore and microorganism used in same
The invention provides a biological gold extraction process of antimony-bearing complex refractory gold ore and a microorganism used in the process. The process comprises the following steps: inoculating bacteria with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2014120 in a 9K culture medium for culture; adding antimony-bearing complex refractory gold ore into the bacterial culture solution, performing bacterial oxidation pretreatment at 25-55 DEG C and at a pH of 0.6-2.2 while injecting air with an injection rate of 0.1-0.4 m3 / h and stirring at a stirring speed of 600-1000 rmp, performing oxidation for 4-8 days; after bacterial oxidation, performing solid-liquid separation, adding water into bacterial oxidation residues to obtain residue slurry with a pH value being adjusted to 9-11, and adding sodium cyanide for cyaniding at a pH value of 10-11 for 24-48 hours. The process of the invention makes full use of antimony-bearing complex refractory gold ore resources, has a gold leaching rate of up to more than 90%, saves the cost, improves the profit, and is green and environment-friendly.
Owner:招金矿业股份有限公司技术中心
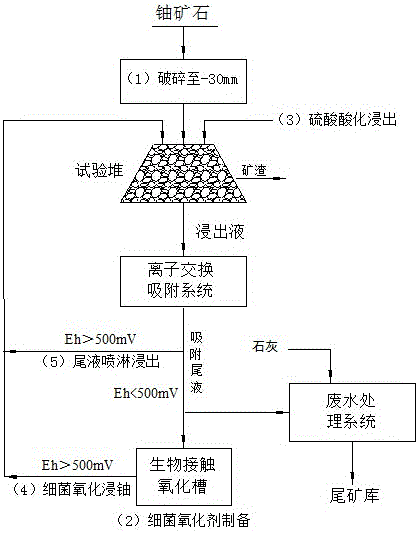
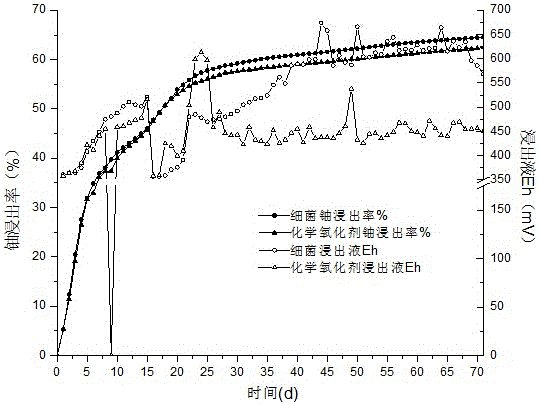
Carbonate-siliceous-pelitic-type uranium ore bacterium uranium leaching method
The invention discloses a carbonate-siliceous-pelitic-type uranium ore bacterium uranium leaching method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing carbonate-siliceous-pelitic-type uranium ore, of which the organic carbon content is greater than or equal to 12.57%, the sulfur content is greater than or equal to 1.18% and the iron content is greater than or equal to 4.19%, until the particle size is less than 30mm; (2) enriching acid mine water and uranium ore collected in the target carbonate-siliceous-pelitic-type uranium ore region to obtain active mixed bacteria, wherein the mixed bacteria can enable the ferrous oxidation rate to be 0.22+ / -0.02 g / (L.H) in an environment with the pH value of 1.7-2; (3) adding the crushed ore into a testing column, and carrying out sulfuric acid acidifying uranium leaching; (4) spraying the prepared bacterial oxidizer into the acidification-preleached ore to carry out bacterial oxidation uranium leaching; and (5) circularly spraying the adsorption raffinate onto the uranium ore subjected to bacterial oxidation leaching, and carrying out raffinate oxidation uranium leaching. The method has the characteristics of low energy consumption, high uranium recovery rate, environment friendliness and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Terephthalic acid producing proteobacteria
InactiveUS6461840B1More cost-effectivelyHarmful wasteBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesBacterial strain
This invention relates to a biocatalytic process to produce terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid from p-xylene and m-xylene, respectively. Terephthalic acid has been prepared by oxidizing p-xylene with bacteria belonging to the genus Burkholderia. Conversion of p-xylene into terephthalic acid is accomplished by a single bacterial strain that produces all of the requisite enzymes. In addition, this invention relates to the preparation of isophthalic acid from a mixture of m- and p-xylene.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for preparing iron oxide red through bacterial oxidation
InactiveCN104313056AShorten the production cycleReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationSulfateThiobacillus
The invention relates to a method for preparing iron oxide red through bacterial oxidation, belonging to the technical field of biochemical industry. The method comprises the steps of oxidizing ferrous sulfate by eosino-ferrous oxide thiobacillus to obtain ferric ion, adjusting the pH value of the solution to over 4.0, so as to precipitate all iron ions, finally, calcining at 400-800DEG C to obtain the product iron oxide red. The method has a short production process and a simple technology, does not prepare seed crystal, has low production cost, has no pollution to the environment, is very easy for industrial production, and provides an environmental-friendly efficient process route for production of iron oxide red.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
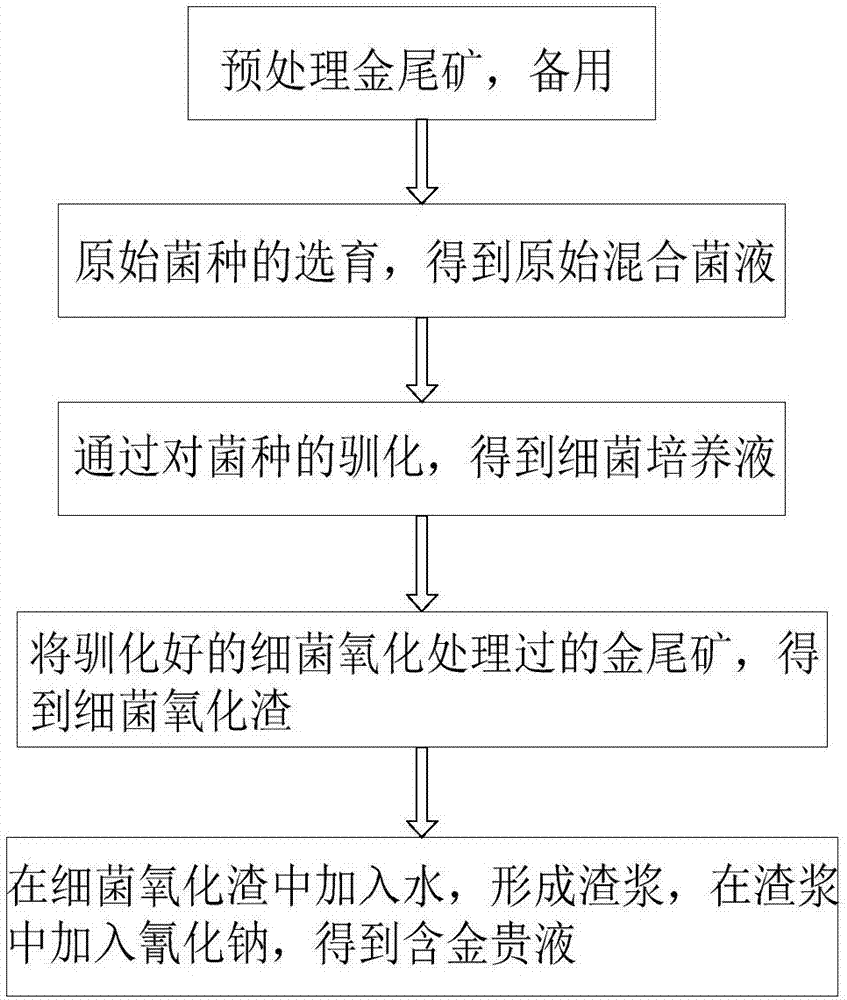
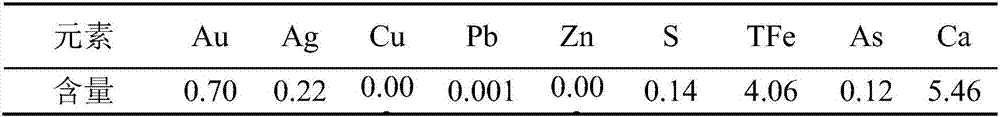
Method for conducting bacterial oxidation treatment on gold tailings and recycling gold in gold tailings through cyaniding
InactiveCN107012325AImprove leaching rateEfficient ore leaching bacteriaProcess efficiency improvementPre treatmentSodium cyanide
The invention belongs to the technical application field of gold tailings resource comprehensive utilization, and particularly relates to a method for conducting bacterial oxidation treatment on gold tailings and recycling gold in the gold tailings through cyaniding. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the gold tailings are subjected to pretreatment including washing and acid soaking; 2, breading of original bacteria is conducted; 3, the original bacteria are acclimatized; 4, oxidation treatment is conducted on the gold tailings through the acclimatized bacteria; and 5, cyaniding gold extraction is conducted by adding sodium cyanide, and golden liquid is obtained. According to the method, the gold tailings are subjected to washing, acid soaking and bacterial oxidation treatment, and then subjected to cyanide leaching, the gold leaching rate is substantially increased and reaches 85% or above; and in addition, operation is easy, the cost is low, the environmentally friendly effect is achieved, the economical benefits are remarkable, the valence gold in the gold tailings can be effectively recycled, and an economical and environment-friendly win-win situation is created.
Owner:西北有色地质矿业集团有限公司 +1
Oxidation pretreatment method for strengthening arsenic containing gold concentrates through cooperation of oxidizing agent and catalyst
InactiveCN105907961AImprove oxidation capacityIncreased redox potentialProcess efficiency improvementPretreatment methodCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to an oxidation pretreatment method for strengthening arsenic containing gold concentrates through cooperation of an oxidizing agent and a catalyst, and belongs to the field of pretreatment of gold ore hard to treat. In the biological oxidation process, the proper quantity of the catalyst and the proper quantity of the oxidizing agent are put into biological oxidation ore pulp of a certain concentration, the redox potential of an ore pulp solution can be improved, and metal sulfide in the ore pulp is promoted to be oxidized and dissolved. Along with dissolution of minerals, a large number of Fe2+ and As3+ ions can be generated in the solution, the proper quantity of the catalyst and the proper quantity of the oxidizing agent are added and oxidized with germs to form composite catalytic oxidation Fe2+ ions, the Fe2+ ions are oxidized to generate Fe3+ ions, the As3+ ions are further oxidized through the Fe3+ ions, and therefore the concentration of the As3+ ions in the ore pulp solution is reduced, the inhibition effect of arsenic ions on the germ activity is reduced, and the oxidization effect of the arsenic containing gold concentrates is improved; and after the catalyst and the oxidizing agent are added, the oxidization removal rate of arsenic, iron and sulfur in the biological oxidation process can be remarkably increased.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
Comprehensive utilization method for acid waste liquid containing arsenic
InactiveCN101269890AReduce occupancyTake advantage ofArsenites/arsenatesMultistage water/sewage treatmentArsenateFlue gas
The invention relates to a comprehensive utilization method of arsenious acid waste liquid, which utilizes waste liquid produced during the technical gold production in the treatment of the arsenious aurine mine by a bacterial oxidation technology as the raw material, and has the procedures that the waste liquid is reduced by reducing agent and the pH value range of the waste liquid is more than 2.5 and less than 7 through being adjusted by adding water, so as to realize the separation of FeAsO4, the FeAsO4 filter residue and the FeAsO4 filter liquid are obtained after being filtered. The FeAsO4 filter liquid is concentrated, crystallized, separated, and dried to obtain the green copperas product. The FeAsO4 filter residue is panned, dried, dehydrated, and crushed to obtain the ferric arsenate product. The ferric arsenate product is roasted for 1-2 h, the roasting temperature is 700-1200 DEG C, the flue gas generated by the roasting is cooled and collected to obtain the arsenic trioxide product, and the roasting residue is collected to obtain the ferric oxide product. The process of the invention is simple, and the comprehensive utilization of the waste liquid is realized by less investment, so the effects of energy conservation and carbon emission reduction as well as source scientific utilization are achieved.
Owner:林建忠
Sludge film composite autotrophic nitrogen removal technology and reactor based on light induction
ActiveCN113979539AAutotrophic denitrification achievedAchieve elutriationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsActivated sludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention provides a sludge film compound type autotrophic nitrogen removal process based on light induction, and belongs to the technical field of biological sewage treatment. The process is characterized in that ecological niche differentiation of functional bacteria is promoted through a method of adding a biofilm carrier and controlling process parameters, anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria mainly survive in a biofilm, and nitrifying bacteria including aerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria, nitrite oxidizing bacteria and the like mainly survive in activated sludge, so that efficient interception of anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria is realized; further, growth of nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the activated sludge is selectively inhibited through an ultraviolet light induced bacterial oxidative stress method, so that elutriation of the nitrite oxidizing bacteria is achieved; and finally, the nitrosation-anaerobic ammonia oxidation process is completed through cooperation of the aerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria and the anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria in the system, so that autotrophic nitrogen removal of the municipal sewage is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Application of ferric phosphate for reinforcement of bacterial leaching out of nickel sulphide ores
ActiveCN104531992AShorten the leaching cycleImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionPhosphate
The invention provides an application method of ferric phosphate for reinforcement of bacterial leaching of nickel sulphide ores, wherein the dosage of ferric phosphate is 0.2-0.6g / L; under the action of ferric phosphate, the leaching rate of the bacterial leaching out of the nickel sulphide ores is greatly increased and is more than 95%, and moreover, the oxidation time is greatly shortened; phosphoric acid in ferric phosphate provides the nutritive phosphorus needed by bacteria and reinforces the activity and ore leaching function of the bacteria, and moreover, Fe(III) released from ferric phosphate due to bacterial oxidation and Fe(II) in solution form a high redox couple, thus promoting the oxidative decomposition of the nickel sulphide ores, and Fe(II) and S generated by the decomposition enables the energy of bacterial growth and reproduction to further reinforce the leaching of the nickel sulphide ores, thus promoting the speed of the bacterial leaching out of the nickel sulphide ores, and providing important theoretical and technical guidance for the reinforcement of the bacterial leaching of the nickel sulphide ores.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
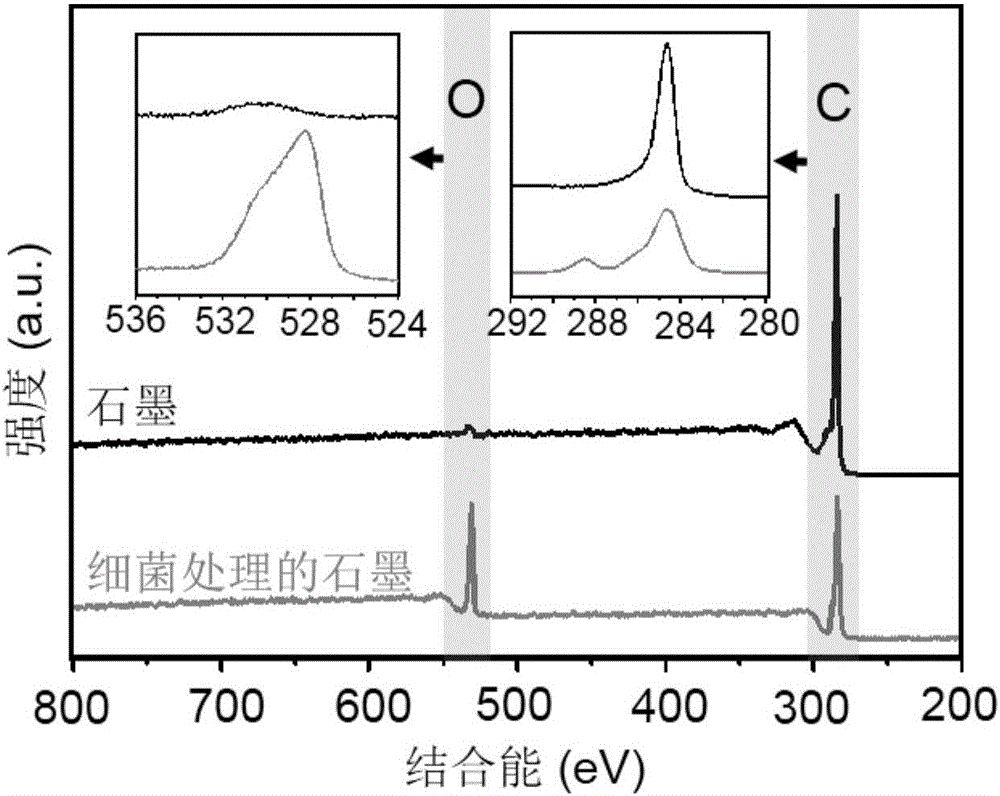
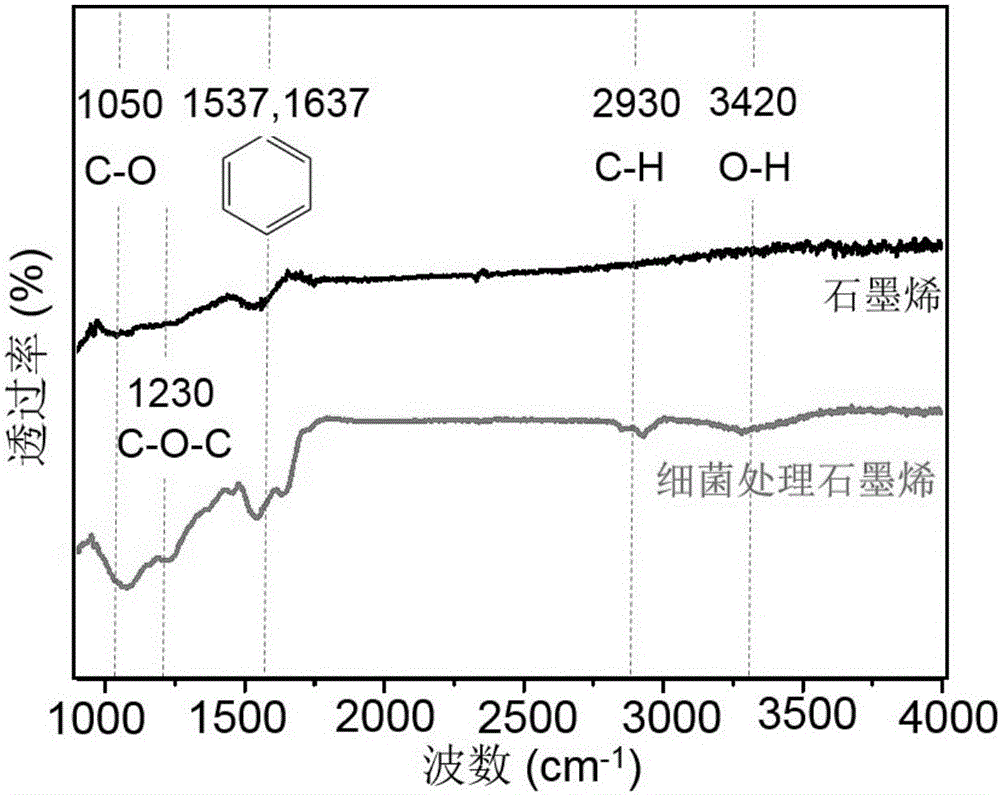
Method for oxidizing and degrading graphite material through naphthalene degrading bacteria
The invention discloses a method for oxidizing and degrading a graphite material through naphthalene degrading bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of environmental biology. The method includes the steps that the naphthalene degrading bacteria are inoculated in an inorganic salt culture medium containing naphthalene; the bacteria and the graphite material are mixed to be co-cultured after the bacteria multiply; the graphite material acting on the bacteria is taken out 3 days to 14 days later; and a product of the graphite material oxidized by the bacteria is obtained after purifying and drying are conducted. According to the method, the graphite material is oxidized and degraded through the naphthalene degrading bacteria, and the method is gentle and controllable, has high environment compatibility, can be used for oxidizing graphite or graphene to prepare oxidized graphite, and can be used for degrading carbon nanometer materials in the environment as well.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
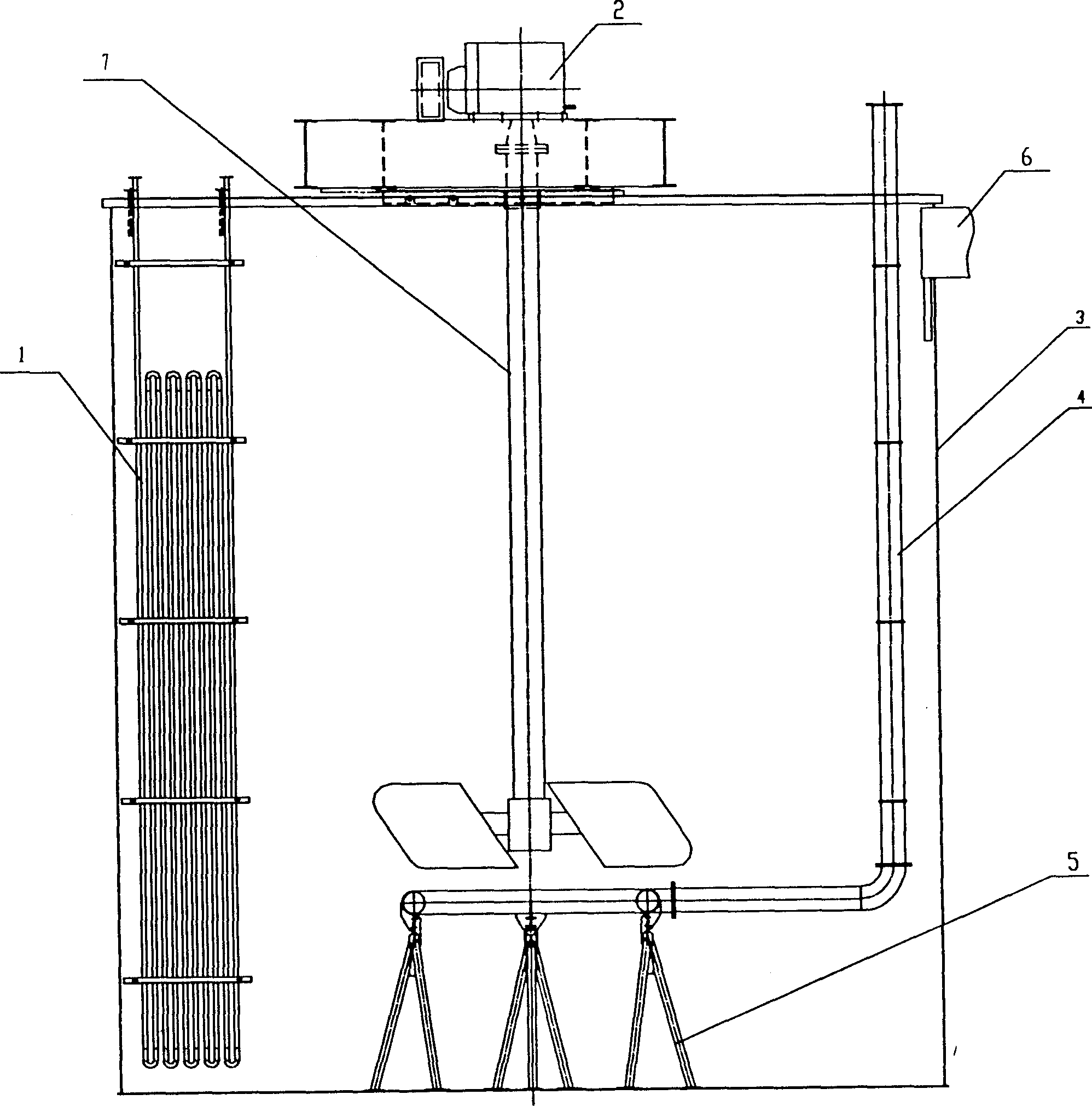
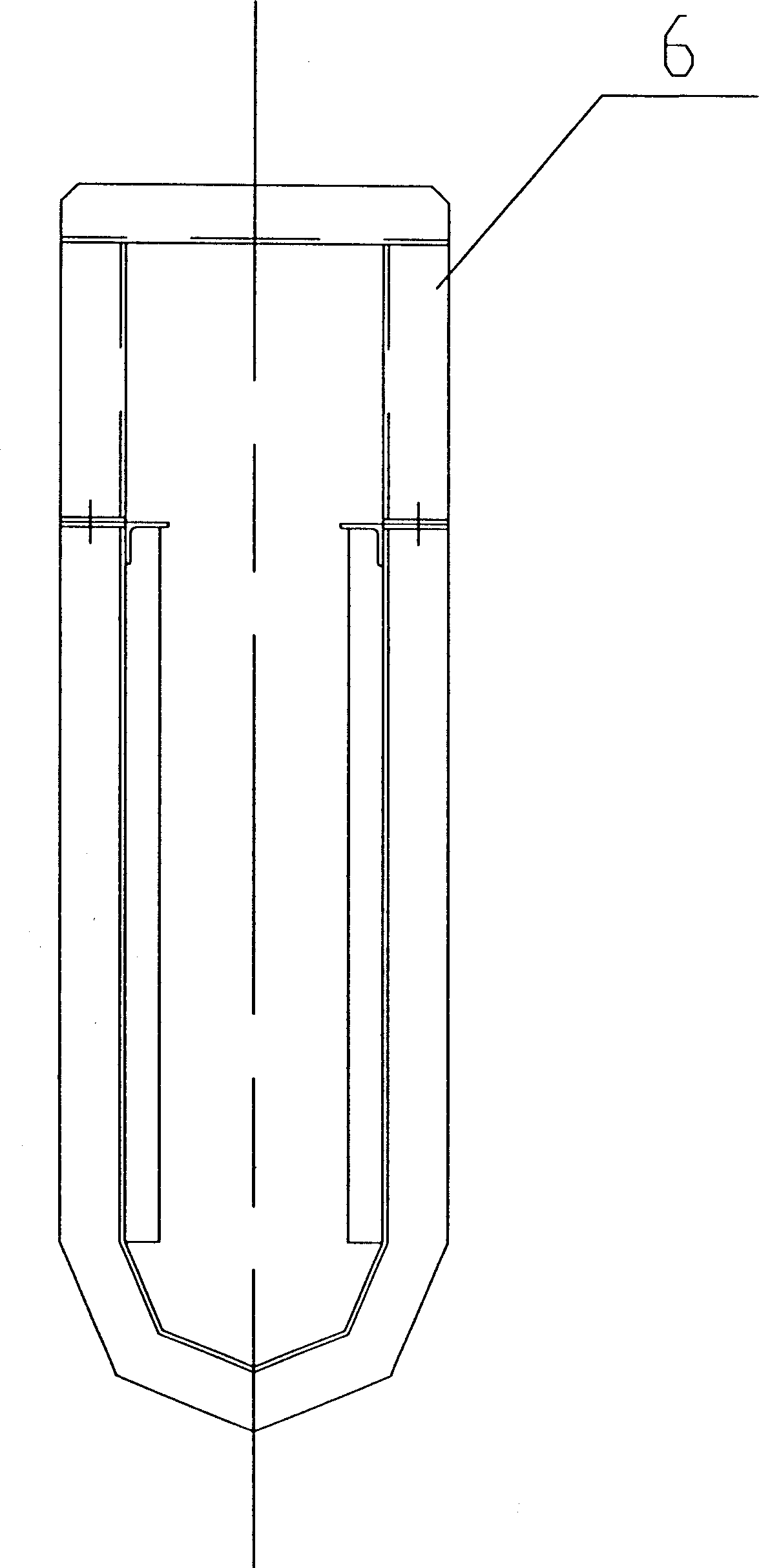
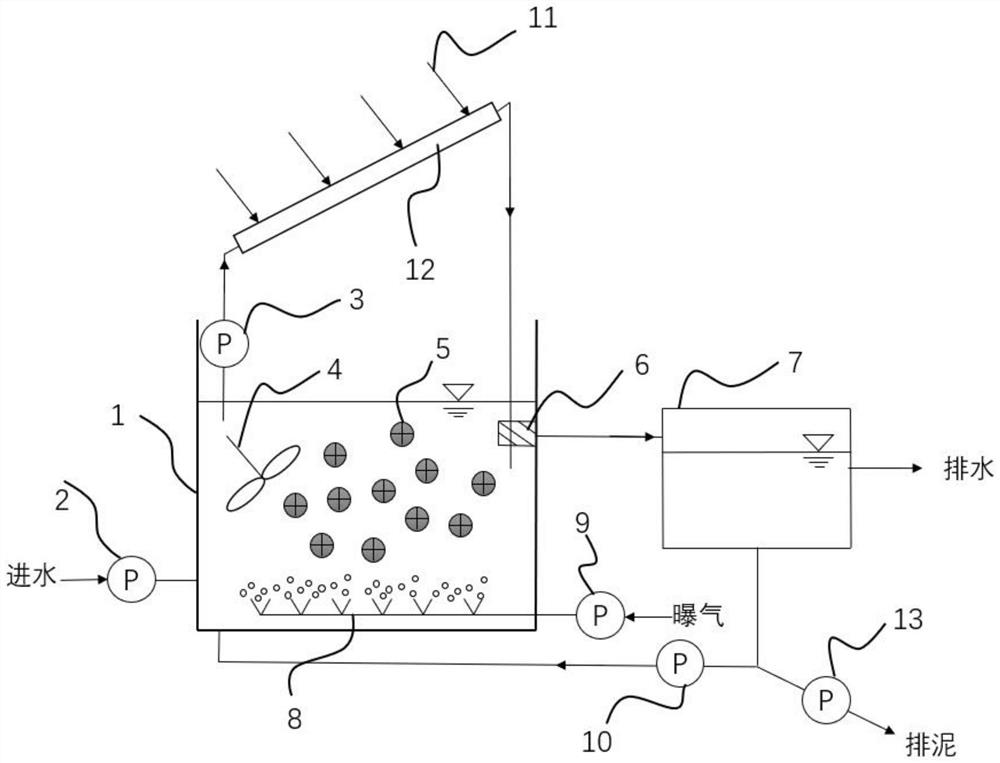
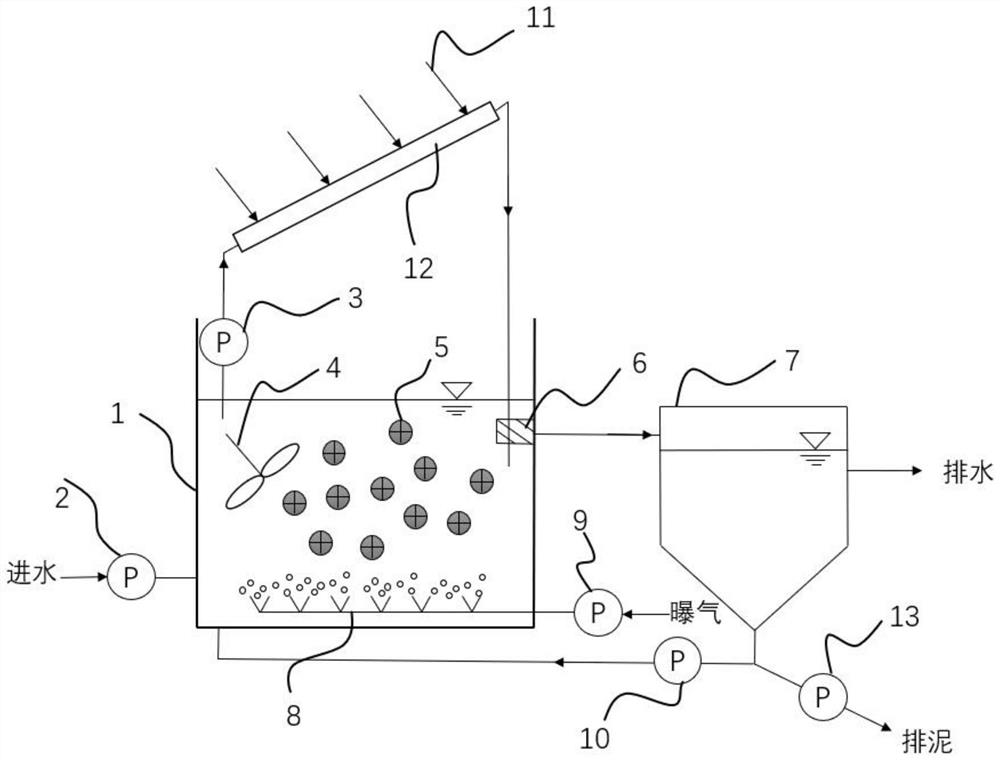
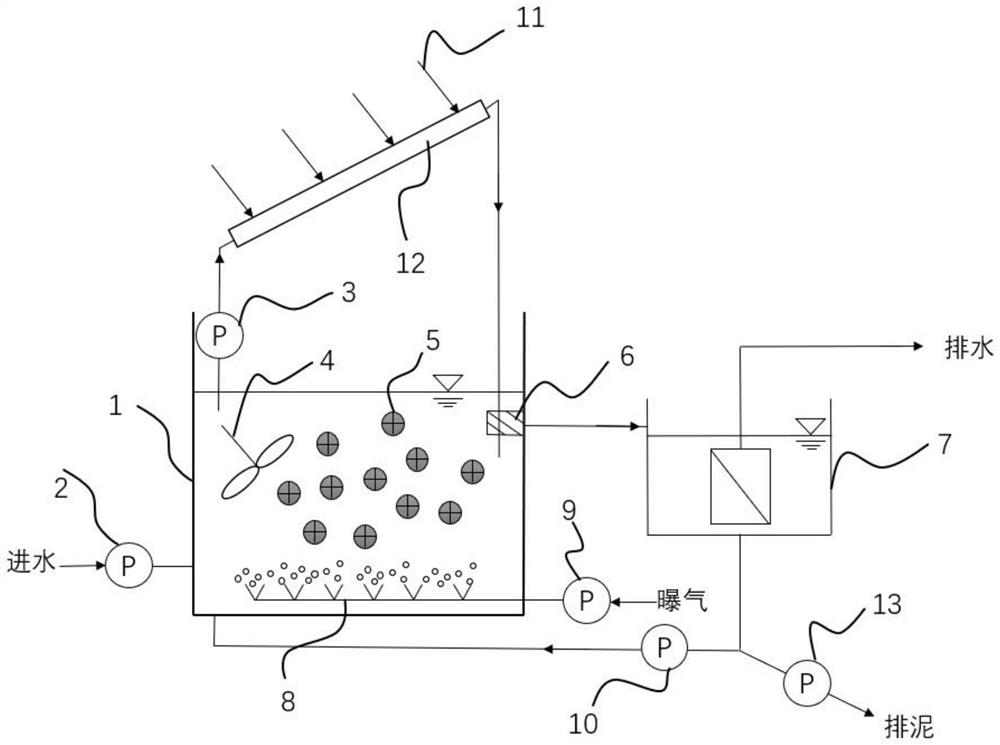
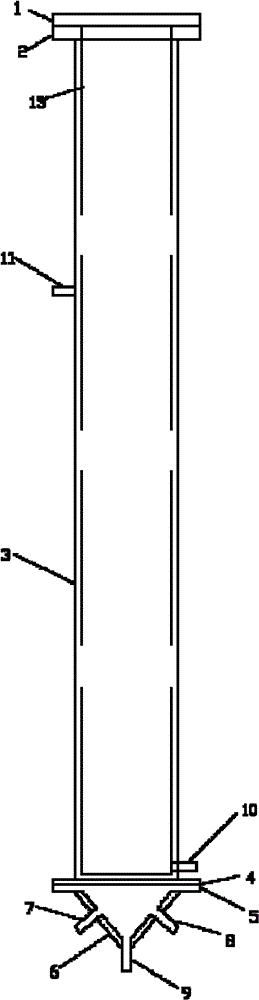
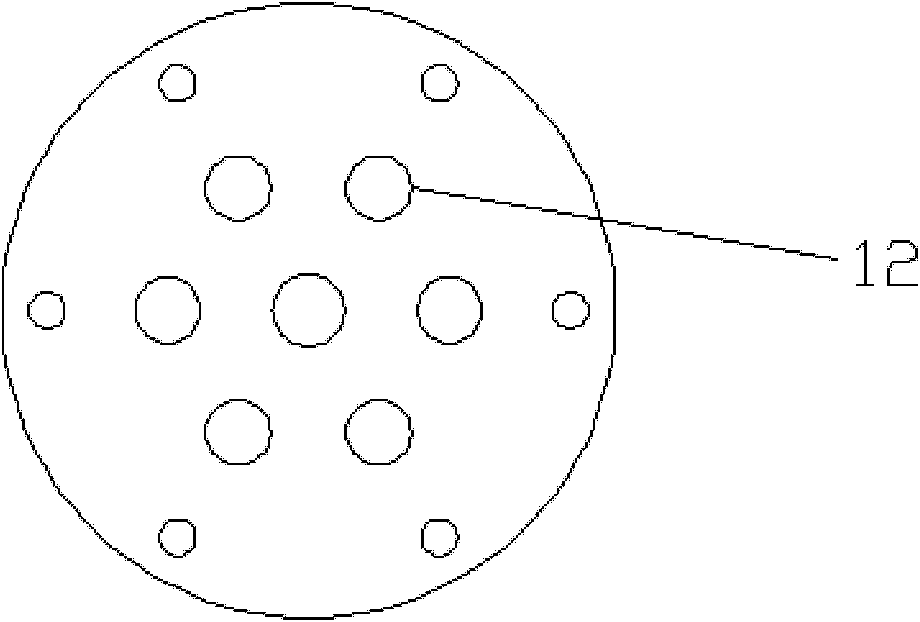
Vertical cell immobilized reactor for producing ferric irons by biological oxidation
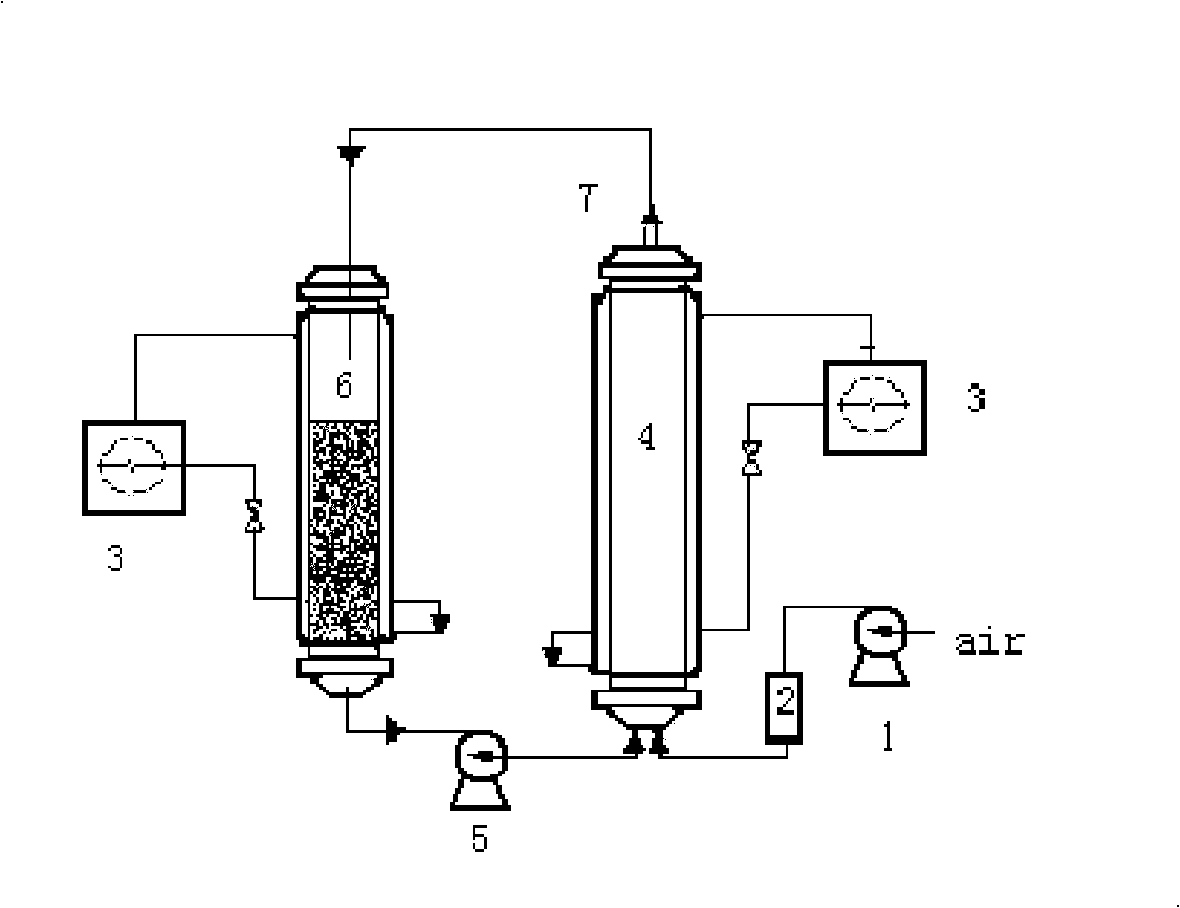
The invention discloses a vertical cell immobilized reactor for producing ferric irons by biological oxidation. The immobilized reactor is mainly composed of a round top cover (1), an upper flange (2), a reactor cylinder (3), a gas distributor (4), a lower flange (5), an inverted cone pedestal (6), a feeding inlet (7), a waste liquid-discharging port (8), an air vent (9), a sampling outlet (10), a discharging port (11) and an air hole board (12). The immobilized reactor is a cell immobilized reactor for producing the ferric irons which employs moderate thermophilic Siberian influenza bacteria as immobilized bacteria and polyurethane foam as a vector. The immobilized reactor solves the problem of low reaction rate and toxicity by toxic ions in a solution during a process of oxidizing Fe2+ into Fe3+ by bacterial oxidation in a biology process during a preoxidation treatment process of minerals during a gold production process, and can increase the oxidation rate of Fe2+ by the bacteria. The vertical cell immobilized reactor has the advantages of few bacterial contaminations, uniform and sufficient air supply, capacity for continuous operation, high oxidation rate, etc.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antifreezing method of sulfide ore bioleaching ore heap
InactiveCN102251109AIncrease concentrationReduce heat lossProcess efficiency improvementThermal energyPregnant leach solution
The invention relates to sulfide ore bioleaching ore heap technology, and particularly discloses an antifreezing method of a sulfide ore bioleaching ore heap, which improves the bacterial concentration of a biological leachate, and realizes the artificial control of the heat output from an ore heap by adding a bacterial oxidation heat releasing substance into ore; a heat-insulating material and abreathable heat-absorbing material are coated on the surface of the ore heap so as to reduce heat dissipation of the ore heap and absorb solar heat energy; finally, through auxiliary heating pipes and the flow control of the ore heap leachate, the effect of the leachate on the temperature of the ore heap is reduced; after the control of each link, the temperature change of the ore heap can be changed artificially according to the ambient temperature of the external surface, and the effect of external ambient temperature on the bioleaching process is reduced or prevented. The application of the technology allows the application of the heap bioleaching technology in alpine region, and increases the heap bioleaching efficiency under winter or low-temperature conditions.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Application of anthraquinone-2-sodium sulfonate in cyaniding and leaching high-grade gold in oxidized ore
InactiveCN102008977AReduce consumptionImprove leaching rateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsProcess efficiency improvementSulfonateAnthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid
The invention relates to application of anthraquinone-2-sodium sulfonate in cyaniding and leaching high-grade gold in oxidized ore, in particular to application of anthraquinone-2-sodium sulfonate as a catalyst for oxidizing and slowly releasing H2O2 in the cyaniding and leaching reaction of gold. The invention can be realized on the traditional equipment and has the advantages of low cost of used anthraquinone-2-sodium sulfonate, convenient preparation and wide raw material source, and a product of leaching reaction does not influence the following treatment operation. As far as ore property is concerned, the anthraquinone-2-sodium sulfonate is used for catalyzing and leaching gold and has higher competitiveness on treating high-grade gold oxidized ore obtained after carrying out preoxidation treatment (oxidation roasting, pressure heating oxidation and bacterial oxidation) on floating gold concentrate ore of coated type vulcanized gold ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Stone coal vanadium extraction production process
PendingCN111455163AEliminate the effects ofEfficient use ofWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsVanadateCalcination
The invention belongs to the field of the stone coal vanadium ore vanadium extraction and smelting technology and particularly relates to a stone coal vanadium extraction production process. The stonecoal vanadium extraction production process comprises the steps of 1, conducting carbon flotation on high-carbon stone coal; 2, conducting high-carbon concentrate fluidized-bed roasting; 3, conducting bacterial oxidation on fluidized-bed calcine, smoke dust, low-carbon stone coal and carbon flotation tailings; 4, diffusing and dialyzing an ionic membrane; 5, immersing vanadium in sulfuric acid; 6, conducting resin adsorption; 7, conducting loaded vanadate resin desorption; 8, precipitating vanadium through ammonium chloride; 9, conducting microwave irradiation on wastewater to remove ammonianitrogen; and 10, conducting calcination. The stone coal vanadium extraction production process is simplified, high in automation degree, high in production capacity and vanadium leaching efficiency and small in environmental pollution.
Owner:新疆星塔矿业有限公司
Sulfur and arsenic containing difficult-to-treat gold mine gold extraction method
InactiveCN106148693AShorten the leaching cycleImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementBiological oxidationGranularity
The invention provides a sulfur and arsenic containing difficult-to-treat gold mine gold extraction method. According to the method, firstly, solid active carbon is added for enhancing bacterial oxidation pretreatment; then, after the ore pulp concentration and the pH are regulated, active carbon adsorption is performed for leaching gold. At the biological oxidation stage, the dosage of the solid active carbon is 6g / L to 10g / L; the granularity range is 1mm to 5mm; under the effect of the solid active carbon, the oxidation time of sulfur and arsenic containing difficult-to-treat gold mine biological leaching is greatly shortened; the leaching rate is greatly improved; after the pre-oxidation is completed, the ore pulp concentration and the pH are regulated, and the gold leaching is directly performed; gold and arsenic are recovered through analysis after the gold leaching. The method provides important theoretical and technical guidance for sulfur and arsenic containing difficult-to-treat gold mine biological pre-oxidation and gold leaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for bacteria leaching uranium from carbon-silicon mudstone-type uranium ore
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring antioxidant activity of materials
InactiveCN105483203AMethod results are accurateLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAntioxidant capacity
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for pretreating arsenic-containing gold ore by collaborative enhancement of bacterial oxidation
ActiveCN108998667AIncrease contentIncrease oxidation potentialProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansIron(II) oxide
The invention discloses a method for pretreating an arsenic-containing gold ore by collaborative enhancement of bacterial oxidation. The method comprises the following steps of: adding fine-ground arsenic-containing gold ore into a culture medium; subsequently filling thiobacillus ferrooxidans and adding Cu2+ ions and sodium oxalate; regulating the pH of ore pulp until the ore pulp is acidic; andcarrying out biological oxidation pretreatment on the arsenic-containing gold ore. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Cu2+ ions and the sodium oxalate are added into the ore pulpof the arsenic-containing gold ore; by collaborative action of the Cu2+ ions and the sodium oxalate, generation of inactive materials in a biological oxidation process is fundamentally and greatly reduced; the biological oxidation period is shortened by more than two days; the leaching rate of arsenic is increased by more than 10%; and the method is low in cost, high in efficiency and simple and easy to operate, and solves the technical problems that an existing method for pretreating the arsenic-containing gold ore by utilizing a biological oxidation method is low in oxidation speed and longin oxidation period.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com