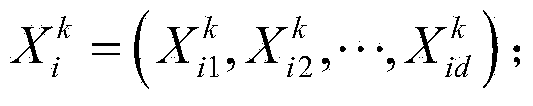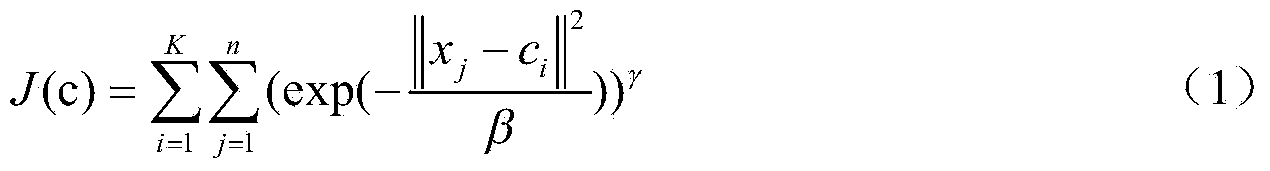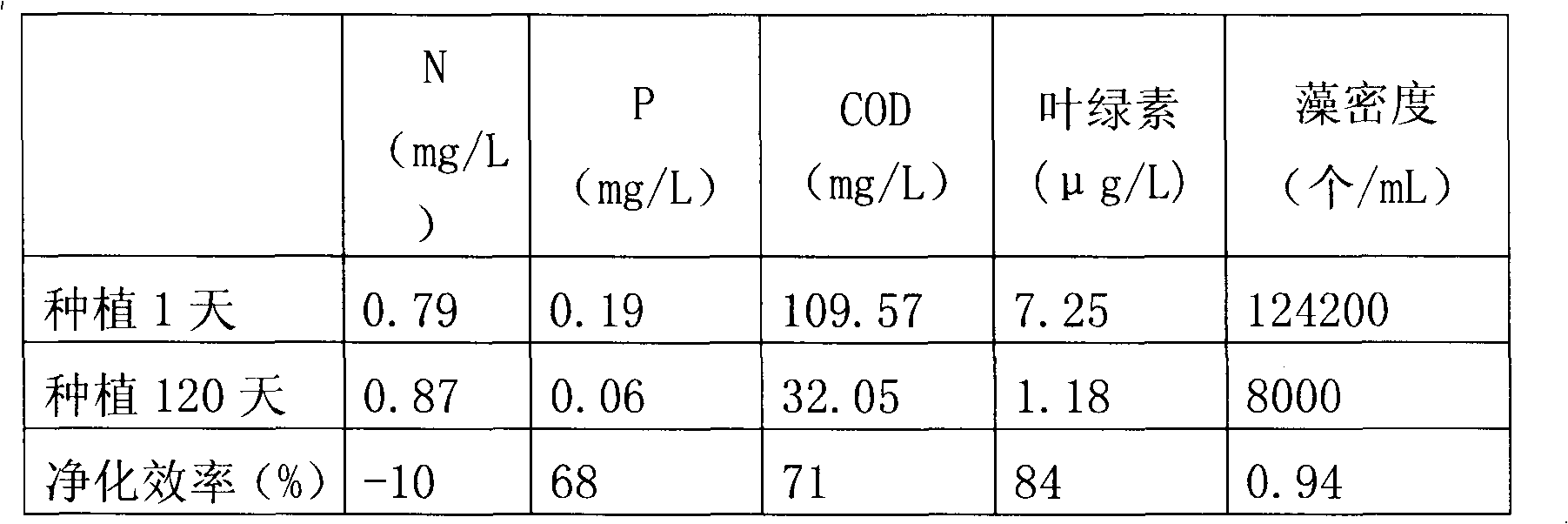Patents
Literature
248 results about "Ecological niche" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In ecology, a niche (CanE, UK: /ˈniːʃ/ or US: /ˈnɪtʃ/) is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".
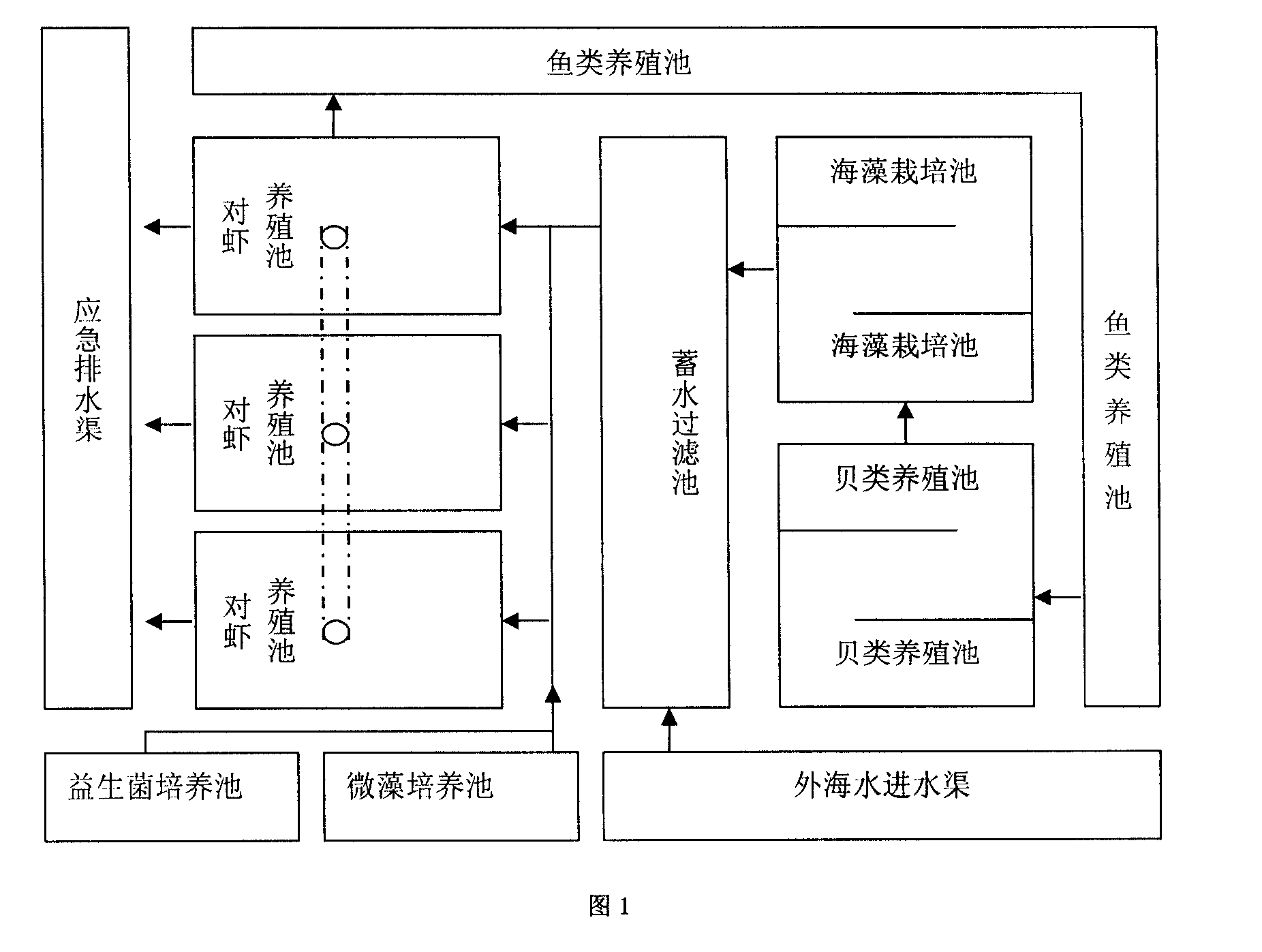
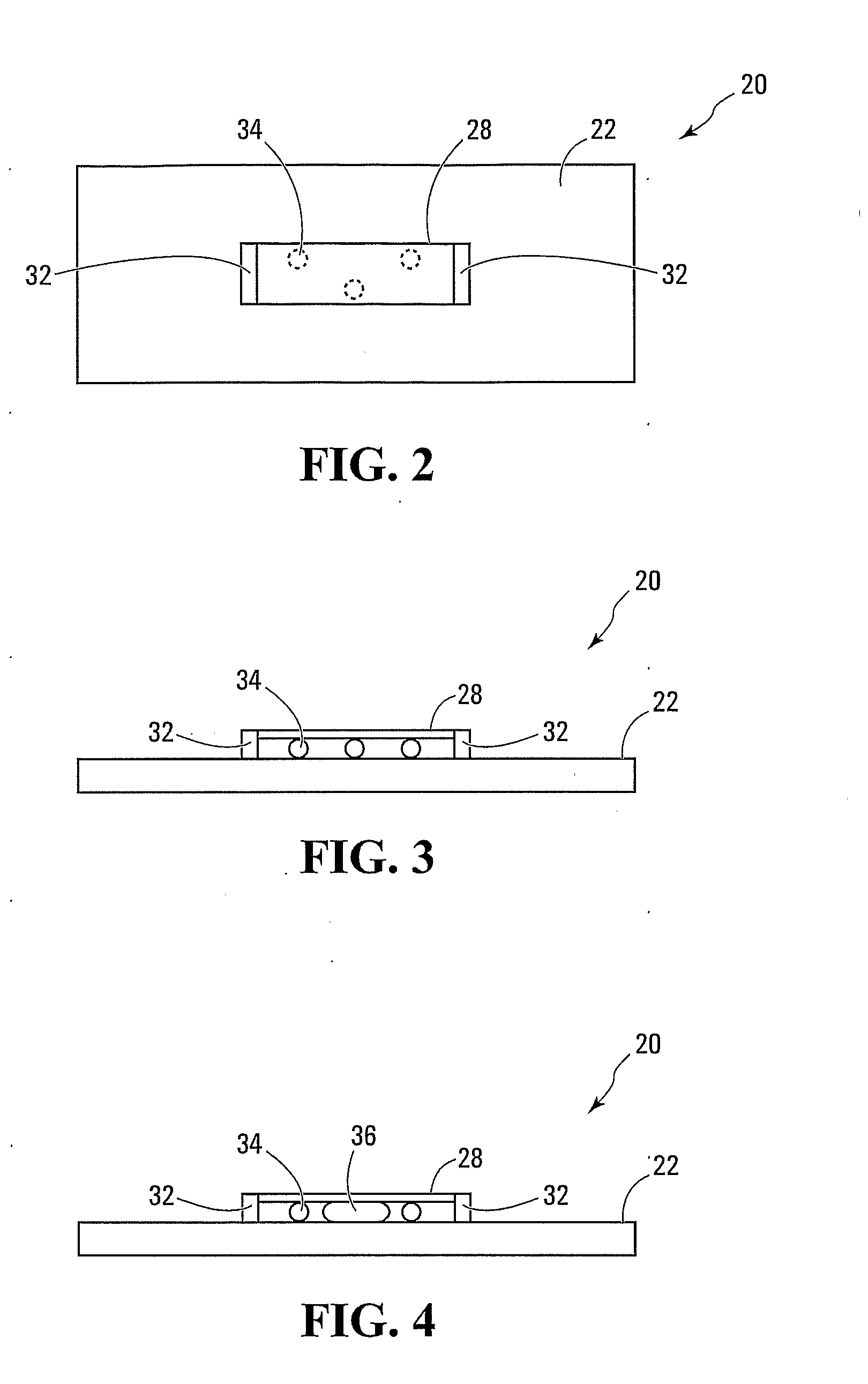
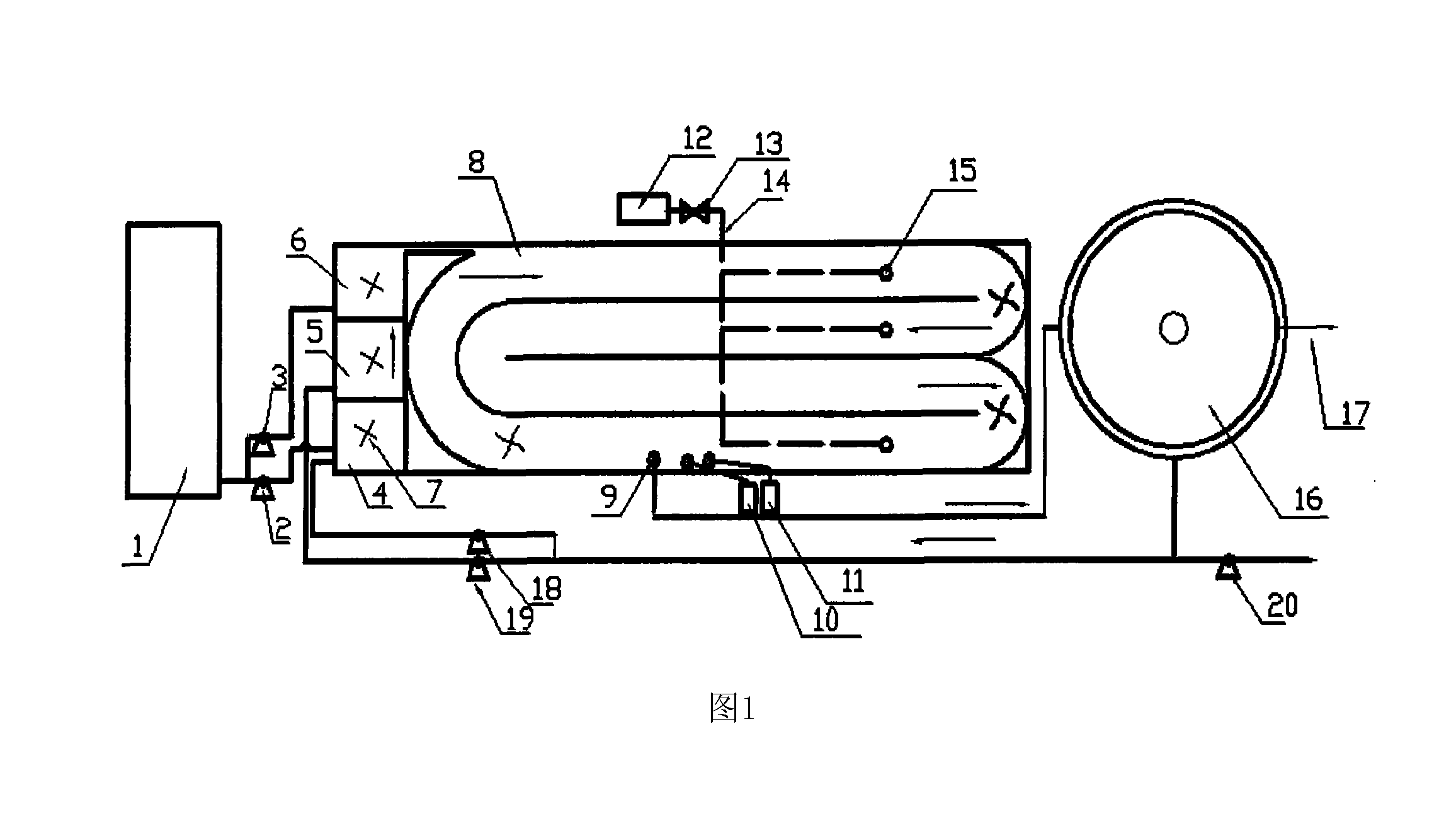
Shrimp-fish-shellfish-algae multiple cultivation and water quality biological regulate and control system thereof
InactiveCN101248766AAvoid direct competitionReduce mutual harmClimate change adaptationMultistage water/sewage treatmentMacrocystis pyriferaWater quality
The invention provides a shrimp-fish-shellfish-alga multi-unit culture and aquatic organism regulation system thereof. A shrimp culture zone, a fish culture zone, a shellfish culture zone, a large scale alga cultivation zone, a probiotics and microalga culture zone, a water processing zone and an emergency drainage system are arranged in a closed water circulation culture system, wherein the culture water circulates in different culture and water processing units. As the water circulates in different culture units and is utilized in multiple levels by various aquatic organisms of different trophic level and ecological niche, the system gives the various aquatic organisms full play to the positive bait resource complementarity, prevents the aquatic organisms from directly competing on living space and dissolved oxygen and reduces the mutual damage caused by organic remains and metabolic waste, achieves the 'self-modification' and 'biomanipulation' of the culture environment, enables the environment itself to recover from the pollution in culture process, and decontaminates the seawater culture environment.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
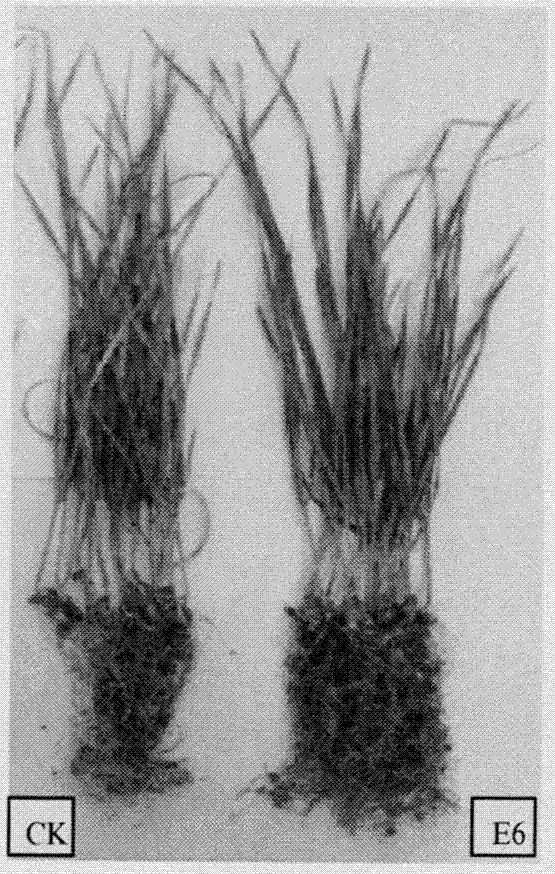
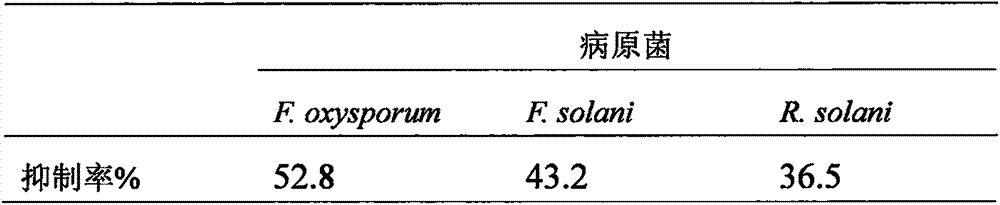
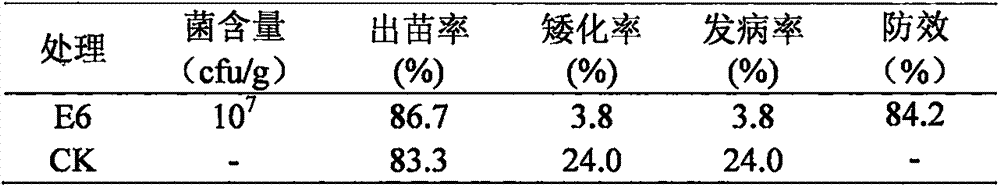
Anti-disease, growth promotion and drought-resistant functional plant endogenous bacillus velezensis and application thereof
The invention relates to plant endogenous bacillus velezensis which is capable of preventing and treating plant diseases and insects and has functions of growth promotion and drought resistance, and application thereof. The preservation number of the Bacillus velezensis E6 provided by the invention in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No. 9665. The strain is separated from a plant root, is rapid to grow, can be rapidly and greatly colonized at plant roots and has ecological niche advantages; the strain E6 not only has an efficient prevention and treatment function on plant soil-borne fungal diseases and is capable of promoting growth of plant root systems and improving drought resistance of plants, but also is capable of damaging formation of pathogenic bacterium bacterial biofilms, is free of drug resistance of bacteria, has relatively good advantages when being compared with other fungicides, is simple in nutrition requirement and low in productioncost, and has good application prospects.
Owner:河北伊诺生化有限公司
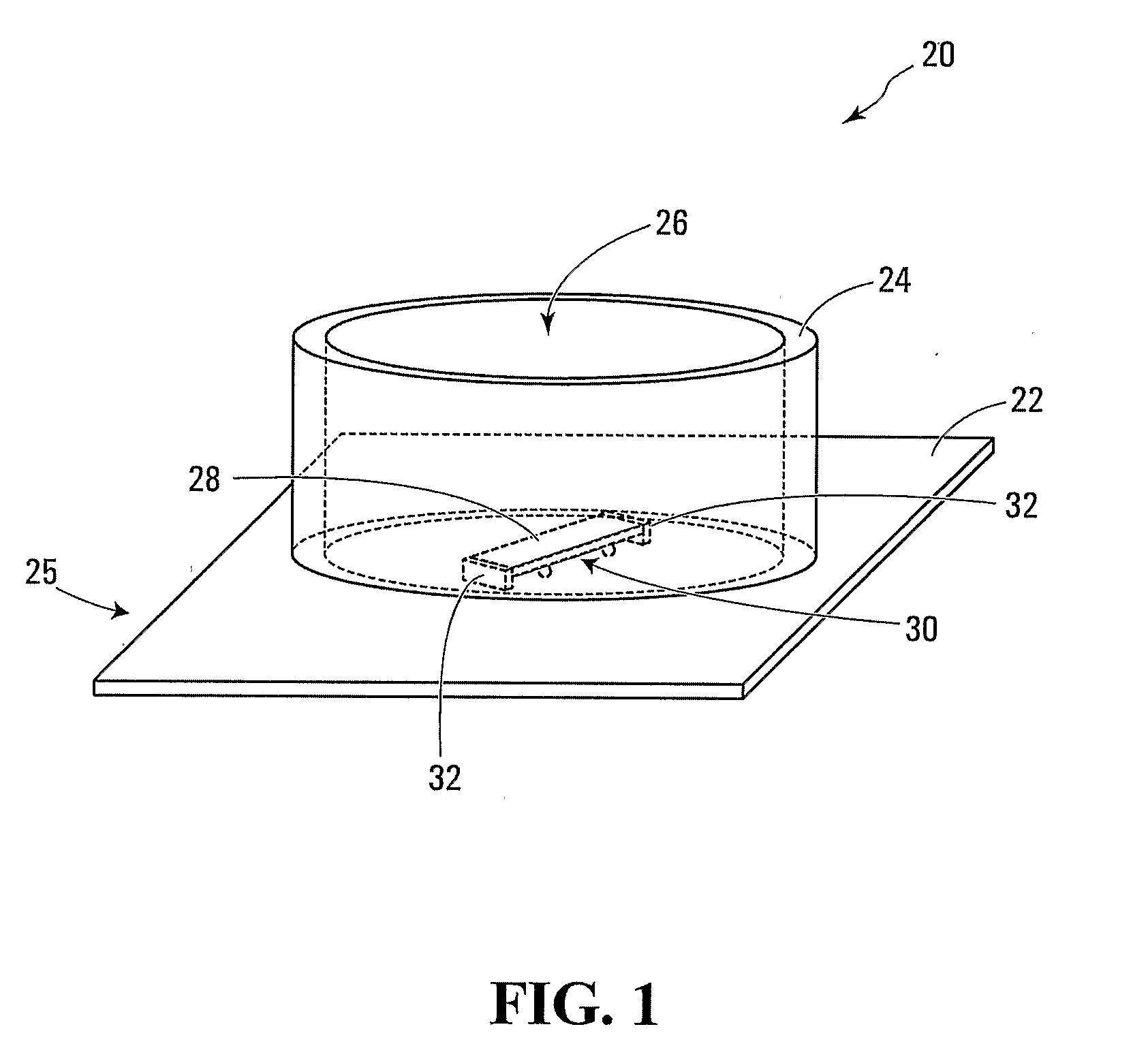
Cultured cell and method and apparatus for cell culture
InactiveUS20070161106A1Improve image qualityEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCultured cellFluorescent imaging
One or more cells can be cultured when confined in space by barriers. The distance between barriers can be comparable to the size of a cell to be cultured. The space between barriers can also be sufficiently small to allow control of cell properties or monitoring of the cell(s) cultured therein. The cell(s) may be confined completely or may be mobile between two opposing barrier surfaces. The gap between two opposing barriers may be sufficiently narrow to allow only a monolayer of cells to be cultured. A barrier can be transparent. The surfaces of the barriers may have one or more pre-selected characteristics that mimic the characteristics of a biological niche of the cells(s). The number of cells in a cell culture may be limited to permit control of properties of individual cells. The cultured cell(s) may be monitored, such as imaged, over a long period of time, using standard bright field or fluorescent imaging techniques.
Owner:WATERLOO UNIV OF
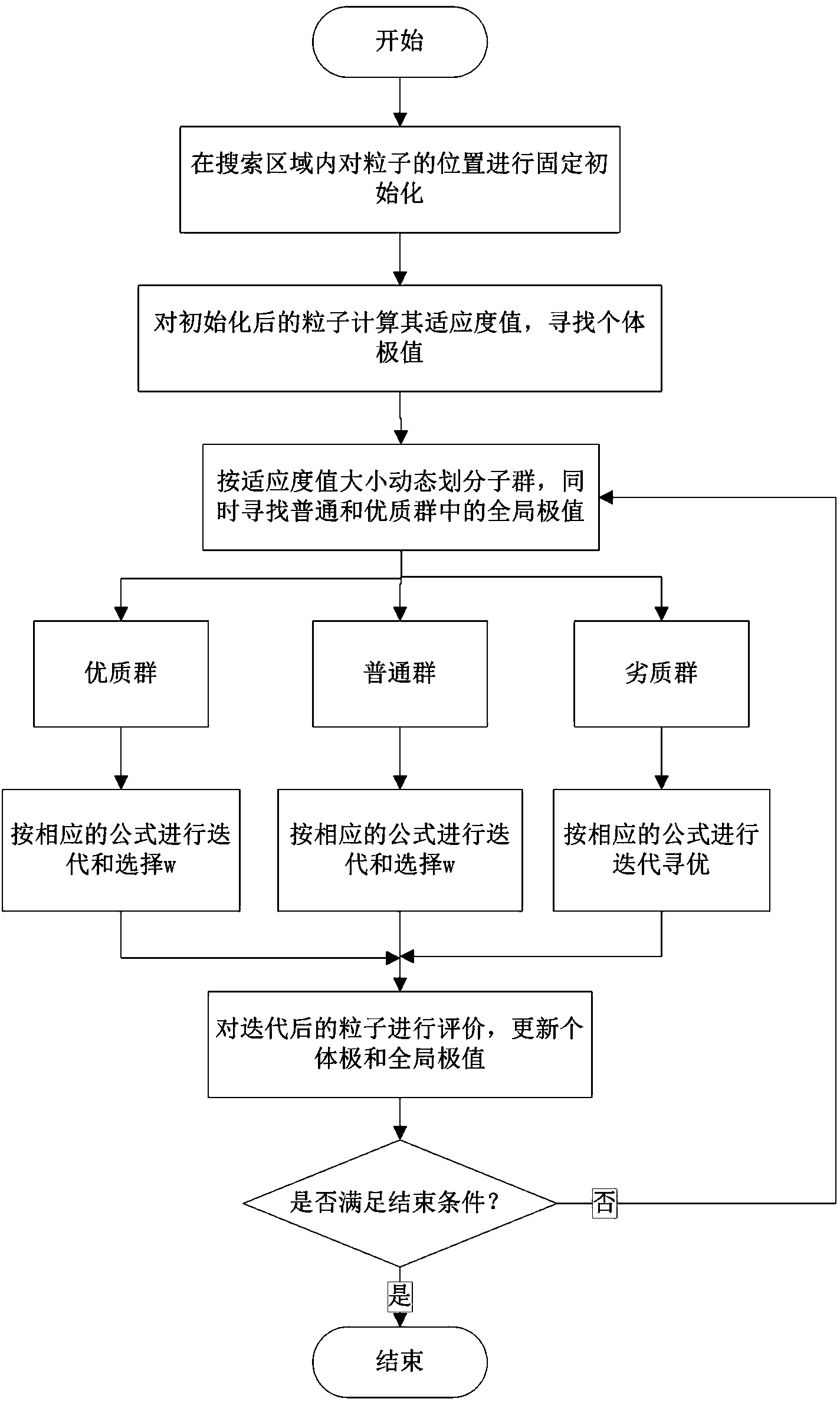
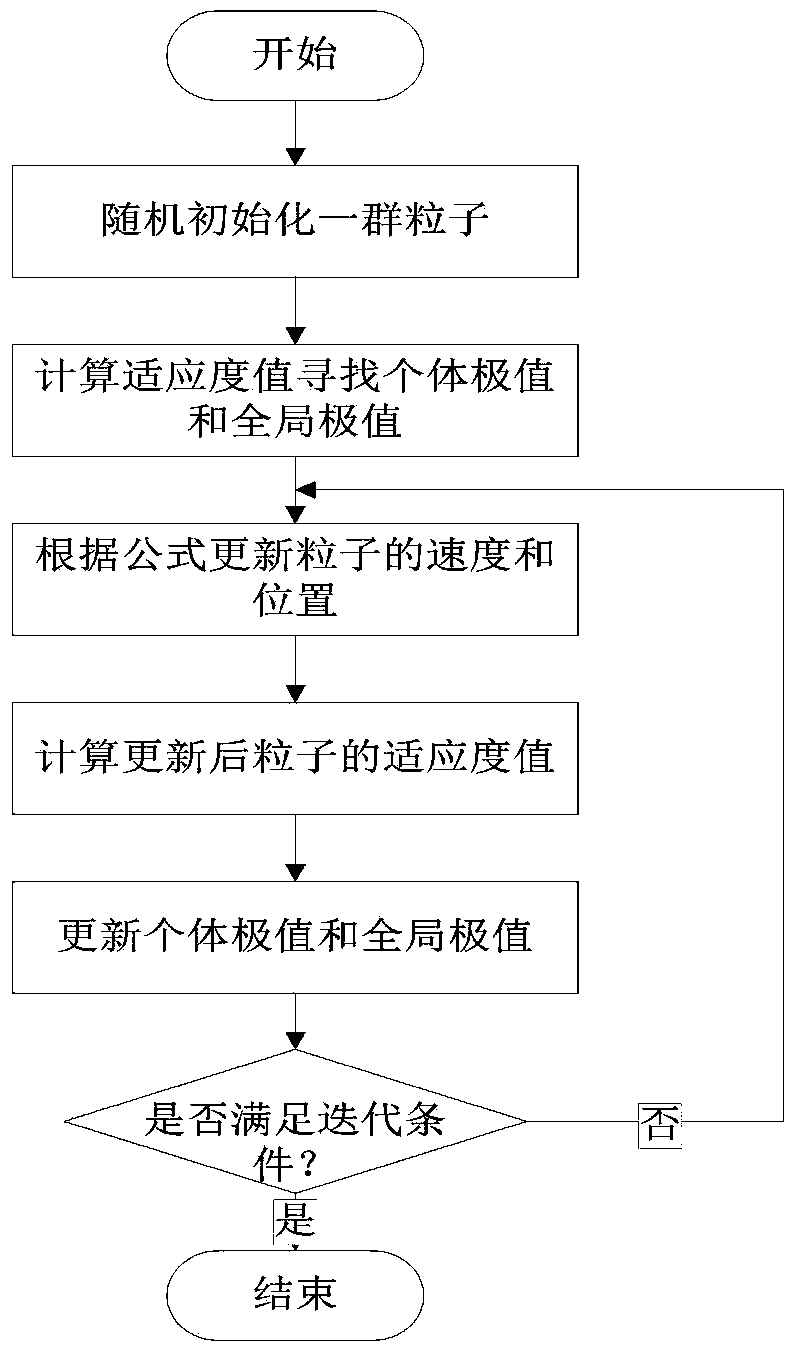
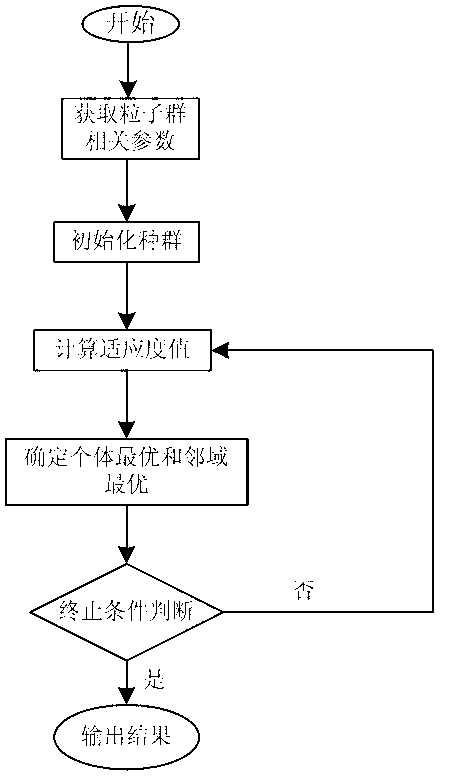
Cascade reservoir optimal operation method based on adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm
InactiveCN103942612ADiversity guaranteedAvoid falling intoForecastingBiological modelsLocal optimumFunction problem
The invention discloses a cascade reservoir optimal operation method based on the adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm. According to the method, aiming at the defect of the particle swarm method in cascade reservoir optimal operation, fixed initialization improvement is conducted firstly on particle random initialization to enable the algorithm to have the possibility of approaching the optimal value at the beginning, large-scale dead zones do not exist, convergence speed is increased, and the stability of the algorithm is improved; then according to the group cooperation idea and the cluster ecological niche idea, an initialized group is dynamically divided into three subgroups, optimization and parameter selection are conducted on each subgroup in an adaptive mode according to the difference of particles, and in this way, the particle diversity is improved, the information exchange model is changed, and local optimum of the algorithm is avoided. According to the improved algorithm, the function problems of nonlinearity and multiple local minima can be well solved, and an effective and feasible solution is provided for cascade reservoir optimal operation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Planting method for interplanting Chinese angelica in orchard
ActiveCN103250610AImprove survival rateImprove qualityCultivating equipmentsHorticultureMedicinal herbsEcological environment
The invention relates to a planting method for interplanting Chinese angelica in an orchard and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine materials and agricultural planting. The planting method for interplanting the Chinese angelica in the orchard comprises the steps that the Chinese angelica is interplanted in the orchard of peaches, pears, plums, apples and cherries, and field management can be carried out according to corresponding cultivation technologies. According to the planting method, spatial ecological niche complementary advantages of the Chinese angelica and fruit trees are fully utilized, a utilization rate of the orchard fields can be increased, a survival rate of seedlings of the Chinese angelica is increased, quality of the Chinese angelica medical materials is improved, incomes of farmers are increased, ecological environment of the orchard is improved, damage of weeds and diseases and pests is reduced, less pesticides are used, growth of the fruit trees is promoted, orchard management cost is lowered, and the planting method has good economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Ecological compound planting method of Paris polyphylla
InactiveCN101926257ASolve the problem of raw materialsRealize three-dimensional ecological compound plantingHorticultureBudBoronia pinnata
The invention relates to an ecological compound planting method of Paris polyphylla, belonging to the technical field of plant cultivation. The invention utilizes that principle of the stratification of different plants and ecological niche space complementation, adopts the compound planting mode of spruce or Alnus nepalensis+ apple+ Paris polyphylla to improve the survival rate of Paris polyphylla and lower planting cost. The specific steps are as follows: after artificially planting spruce forests or Alnus nepalensis forests for two years, planting Amomum tsao-ko; after planting for one year, developing the ecological compound planting of the Paris polyphylla by the natural shade and water retention effect formed by an artificial forest and apples; reasonable management of a seedling stage and modes, such as reasonable fertilization, weeding, topping, bud picking and the like are utilized to realize the ecological compound planting of the Paris polyphylla. The invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, high benefit, small risk, land and labor saving, environment protection, easy popularization and high economic benefit, sets a good basis for artificial scale planting of the Paris polyphylla, has favourable economic benefit, social benefit and ecological benefit.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and compositions for growth hydrocarbons in botryococcus sp.
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
Lake mandarin fish scale culturing method
InactiveCN101720682AEstimated productivityEstimating Production PotentialClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSustainable productionDistribution characteristic
The invention discloses a lake mandarin fish scale culturing method, comprising feeding efficiency, defecation rate, excretion rate, standard metabolism, SDA, activity metabolism and fish physical ability value and growth sub-model. The growing conditions and the bait consumption rate of the piscivorous fish after stocking can be predicted by the model; water body is taken as the research site, the time and space distribution characteristics, the biomass, the structure of the main population, the population growth trends of the growth period, the bait base and tropic niche width and competition overlapping of the advantageous small-sized fish in the shallow water reeds lakes are systematically researched, thus establishing the quantitatively acquiring method of the small-sized fish in theshallow water reeds lakes, completing the productivity analysis and measurement of the advantageous population of the small-sized fish in the shallow water reeds lakes, and estimating the sustainableproduction capacity of the lake bait fish.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Planting and breeding integrated ecological breeding method for large fishpond
InactiveCN103181343APlay the role of purifying water qualityGood effectClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFecesMelicertus
The invention discloses a planting and breeding integrated ecological breeding method for a large fishpond. Famous and special breeding varieties such as common carps, golden carps, grass carps, chubs, penaeus vannawei, loaches, soft-shelled turtles, river crabs and the like are put in a suitable place to breed in a breeding pond; and the stocking ratio of herbivorous fishes to forage fishes to demersal residual feed animals by weight percentage is (35-40%) to (50-55%) to (10-15%). Proper biological varieties are selected according to biological requirements of ecological niches and cooperate to build an eco-friendly environment, forage grasses are planted for feeding the herbivorous fishes, the feces of the herbivorous fishes and a water body can produce primary biological baits, the primary biological baits are supplied to shrimps and secondary nutritional fishes, and organic detritus produced by the water body sinks to the bottom of water and is ingested by the demersal loaches, crabs and the like. At the same time, lotus roots and cane shoots are planted in the breeding water body and nutritive salt in the water body is removed for purifying the water, so that a novel high-efficiency energy-saving planting and breeding integrated ecological breeding mode is formed.
Owner:TIANJIN KAIRUN FRESH WATER BREEDING CO LTD
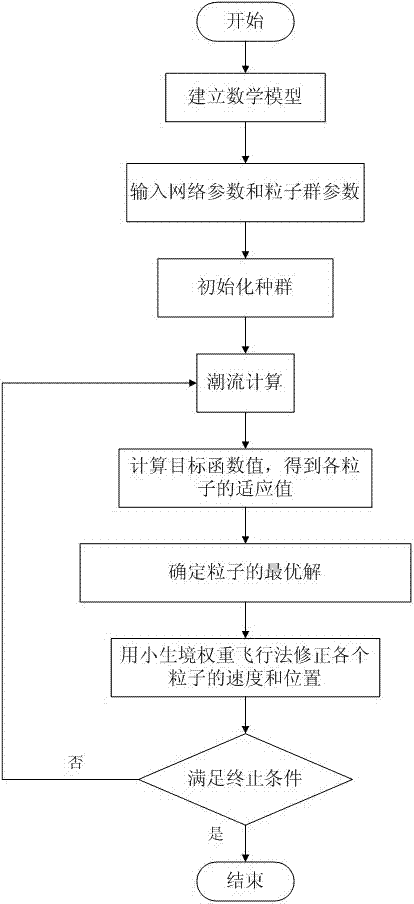
Power distribution network reactive power optimization method based on ecological niche particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN102856918AStrong global solution abilityReduce computational complexityBiological modelsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationMathematical modelOriginal data
The invention discloses a power distribution network reactive power optimization method based on an ecological niche particle swarm algorithm. The method comprises the steps of S1, building a reactive power optimization mathematical model of a power distribution network, inputting original data, and acquiring relevant parameters; S2, acquiring system node information and branch information, acquiring the number of control variables and the value range of the control variables, and acquiring parameters such as a group size of a particle swarm; S3, initializing the population and setting parameters; S4, conducting load flow calculation and obtaining the fitness value and the current individual optimum solution of particles; S5, setting parameters in a particle swarm iterative formula and adjusting; S6, subjecting each of particles in the updated particle swarm to load flow calculation, calculating the comprehensive cost of each of the particles in the swarm, and updating the historical individual extreme value pBesti and the historical neighbourhood optimum value pBestn,I; S7, determining whether a requirement of an end condition is met, and if the requirement of the end condition is met, carrying S8, otherwise, returning the S4; and 8), stopping iteration, outputting the optimum solution and achieving reactive power configuration.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
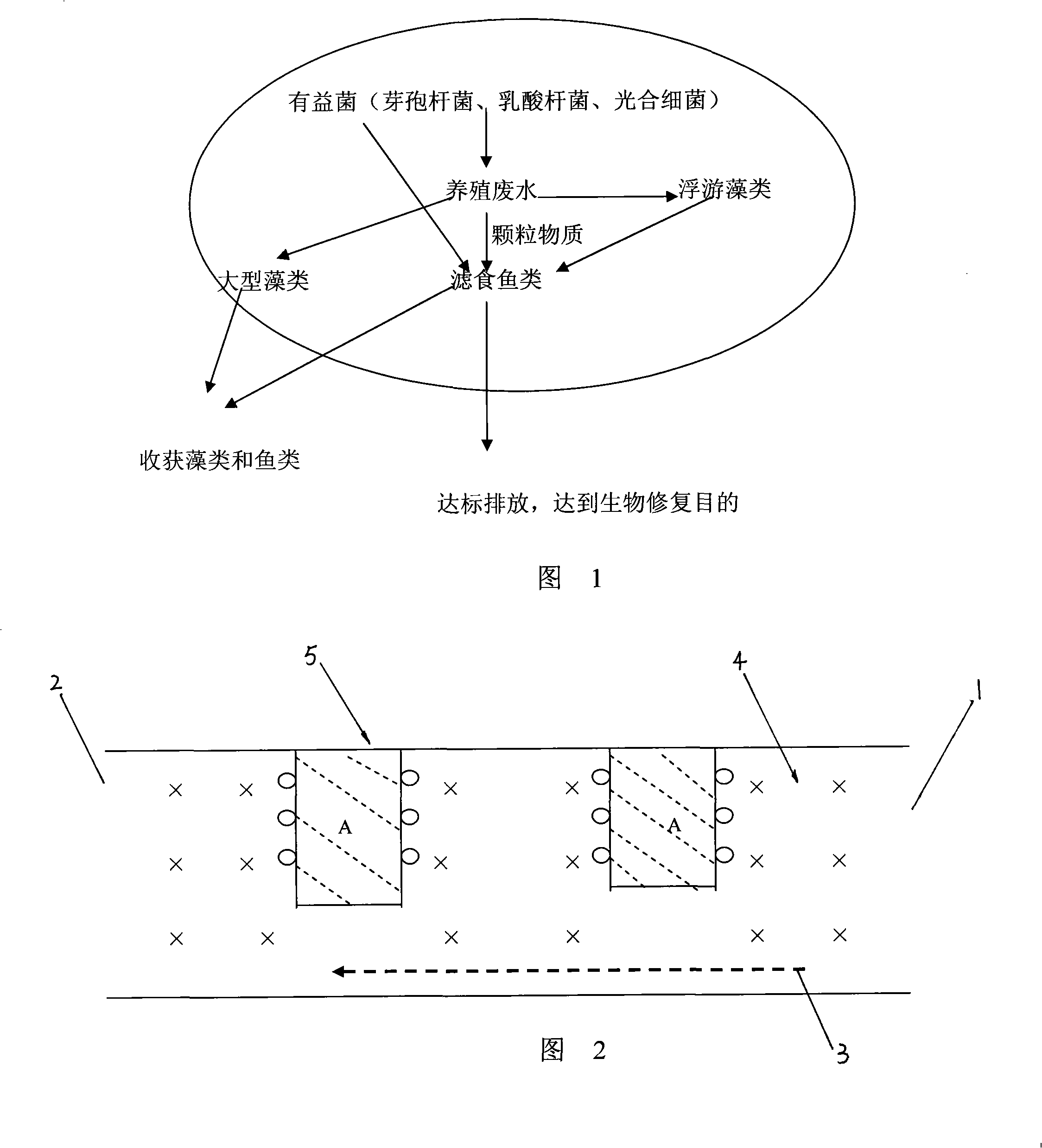
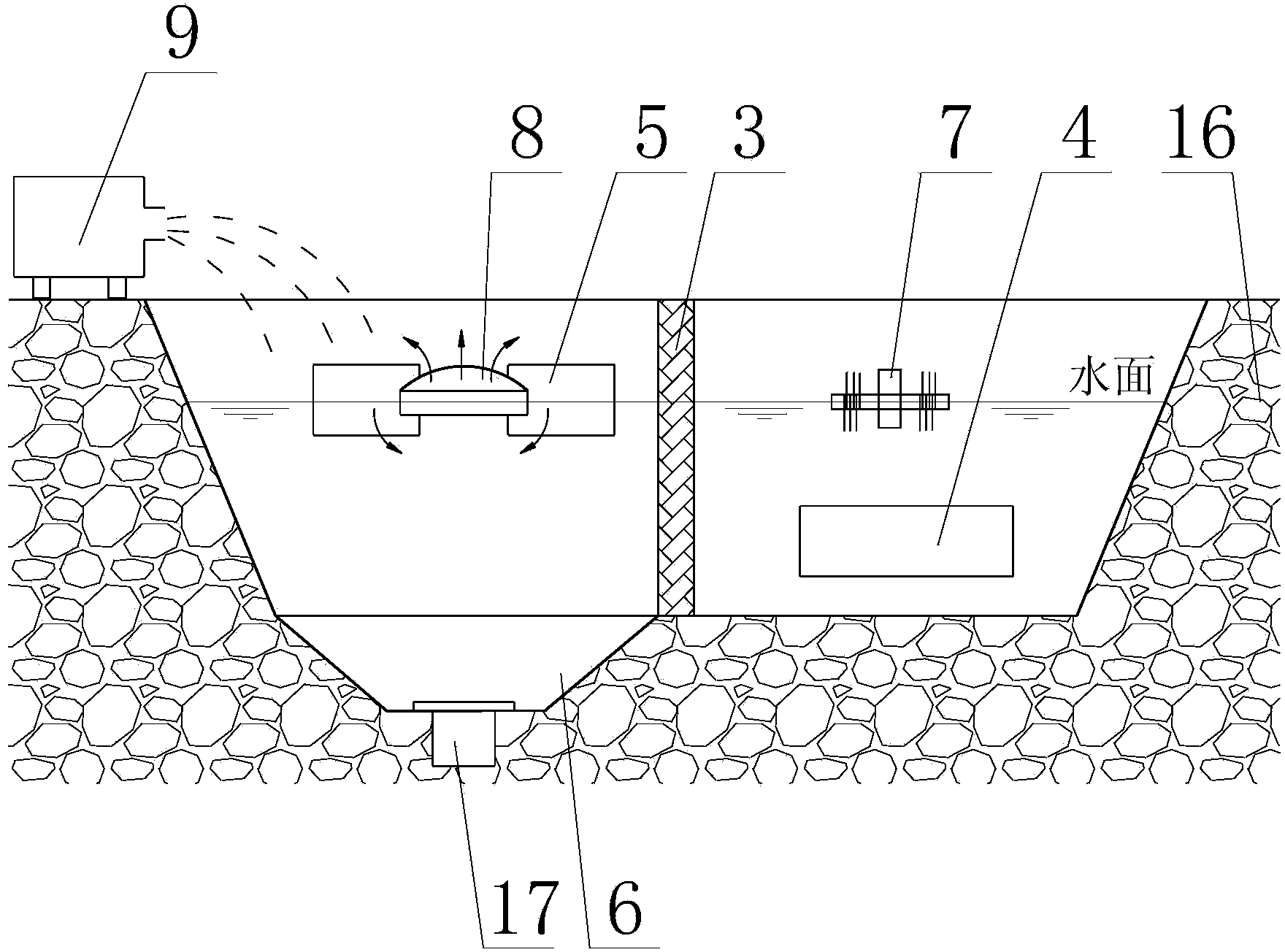
Sea water culture environment multiple state position biological restoring method
InactiveCN101264980AAchieve sustainable developmentReduce pollutionBiological water/sewage treatmentMarine aquacultureMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention discloses a multi-ecological niche bioremediation method of seawater aquiculture environment, which comprises the steps of draining aquiculture wastewater into an aquiculture trench, adding beneficial bacteria to remove nitrogen and phosphorous and convert organic matters on the first stage, culturing filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed to form a multi-ecological niche biosphere coexisting microalgae, filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed in the second stage, and allowing bioremediation of seawater aquiculture environment by utilizing different ecological niches of beneficial bacteria, microalgae, filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed through synergic action of organisms. The inventive method can clean aquiculture wastewater to meet discharge standards, remediate aquiculture environment, and obtain fishes and large-scale seaweed, thereby bringing environmental, economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Processes and systems for predicting biological species invasions
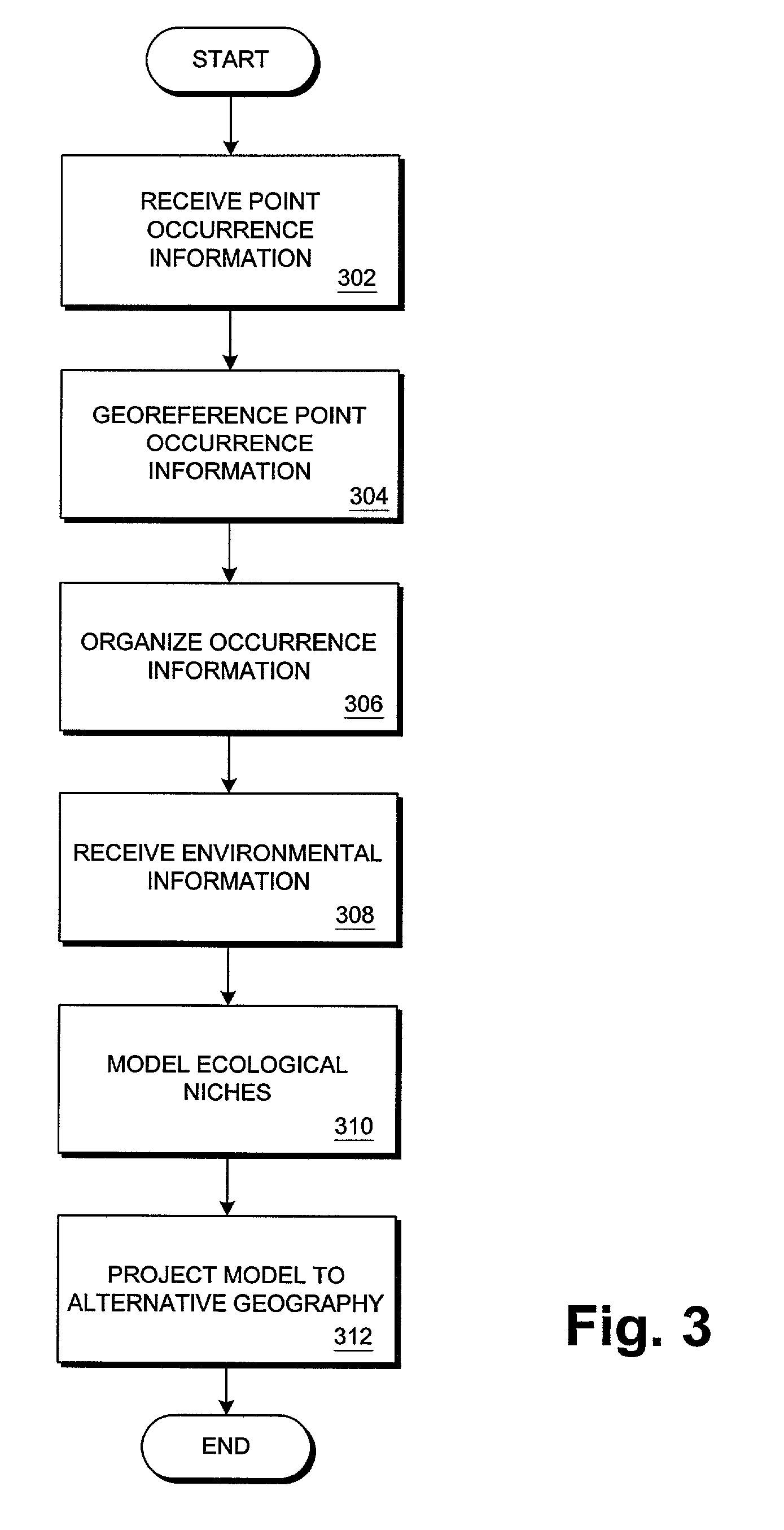
InactiveUS20030023416A1Difficult to predictEpidemiological alert systemsAnalogue computers for chemical processesEnvironment of AlbaniaBiological species
Methods and systems are disclosed for predicting species invasions. Native species occurrence information and native environmental information are received. At least one ecological niche model is formulated based on the native species occurrence information and the native environmental information. Target environmental information corresponding to an alternative geography is received. The ecological niche model is projected onto the alternative geography to predict characteristics of an invasion of the species.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF THE
Reactive power optimization method of power distribution network
InactiveCN102856917AAvoid oscillationHigh speedReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationMathematical modelOriginal data
The invention discloses a reactive power optimization method of a power distribution network. The method comprises the steps of 1), building a mathematical model of a fan; 2), initializing the node voltage; 3), building a reactive power planning mathematical model and converting into a multi-objective optimization problem; 4), inputting original data; 5), forming an initial particle swarm and initializing the speeds and the positions of particles; 6), performing load flow calculation and obtaining adaptive values and a current optimum value of the particles; 7), correcting the speeds and the positions of the particles by using an ecological niche weight flight time method; 8), calculating the adaptability of the whole population, obtaining the adaptability value and updating the current optimum solution pBestid; 9), adjusting a control variable of a border crossing point of an individual particle and modifying a border crossing state variable; and 10), determining whether a requirement of an end condition is met, if the requirement of the end condition is met, outputting the result, otherwise, returning to the 6).
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
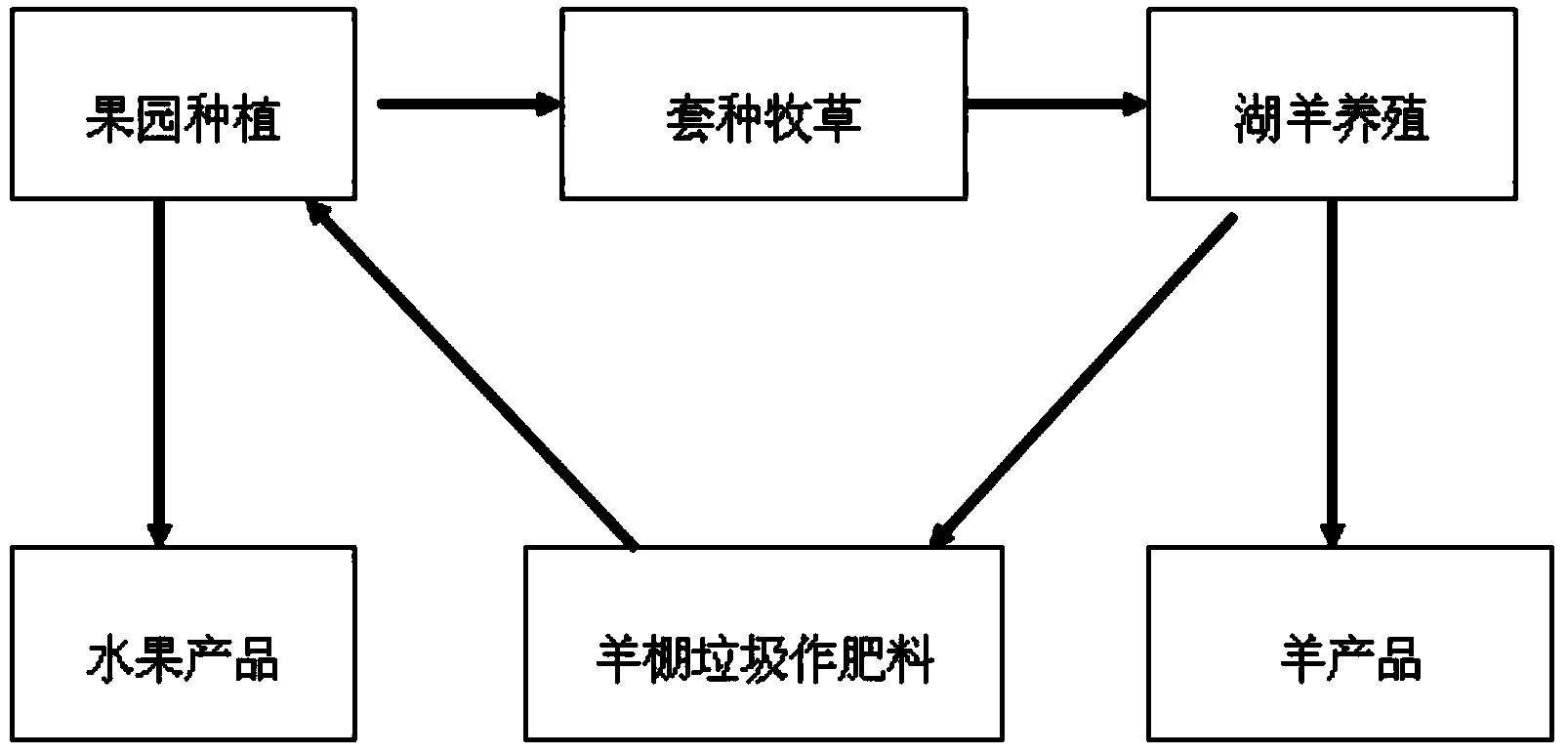
Planting method for growing grass and breeding sheep cyclically in hillside orchard
The invention discloses a planting method for growing grass and breeding sheep cyclically in a hillside orchard. According to the method, naturally-growing crab grass and interplanted pasture in the orchard are used as substrate fodder for breeding the sheep, and sheep shed rubbish produced in sheep breeding is used as organic fertilizer for fruit trees after being subjected to harmless treatment. The method includes the specific steps that by using pasture-ryegrass which is interplanted in gaps of the orchard, 2-3 sheep are bred in each mu of orchard in a captive mode, and the ryegrass and the crab grass which are harvested in each mu of orchard are provided for the 2-3 sheep as the fodder; the sheep shed rubbish is subjected to harmless treatment after being collected and serves as the organic fertilizer which can be applied to the orchard. According to the method, in common hillside orchards in the Yangtze River delta region, by building sites for breeding sheep around the orchards and growing fine pasture in gaps between fruit trees to breed the sheep, the cyclic development mode of growing the grass and breeding the sheep in the orchards is realized, the technology of quantifiably allocating the different ecological niches of the fruit trees, the sheep and the pasture is achieved, and economic benefits, ecological benefits and social benefits are achieved at the same time.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for ecologically culturing high-quality red testis river crabs
ActiveCN101584304AImprove water qualityQuality improvementClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentWater quality
The invention discloses a method for ecologically culturing high-quality red testis river crabs, which fully utilizes natural conditions and resources of ponds, natural waters, rivers, reservoirs, lakes and wetlands, starts from biological, ecological and environmental mechanisms, follows the characteristics of respective econiches occupied by various organisms in biology, is based on biological characteristics of river crabs such as life habit, feeding habit, growth and development and the like, reasonably applies ecological balance breeding technology and nutrient balance technology, builds the best ecological environment of the culture of the river crabs, and meets the nutritional need of the growth and development of the river crabs to raise the high-quality 'red testis' river crabs. The ecological culture method comprises the following steps of: culture pond pretreatment, aquatic plant cultivation, shellfish transplantation, freshwater shrimp stocking, crab seedling stocking, siniperca chuatsi delivery, water quality control, bait feeding, and disease control. The method for culturing the river crabs can produce the high-quality and high-grade 'red testis' river crabs, can greatly improve the economic benefit of crab farmers, and can greatly improve the sustainable development of crab culture industry and the ecological benefit, the economic benefit and the social benefit of crab culture.
Owner:潘洪强 +1
Ecological planting method for himalayan teasel roots
InactiveCN102487691AHarm reductionReduce usageAgriculture gas emission reductionPlant protectionPEAREcological environment
The invention relates to an ecological planting method for himalayan teasel roots and belongs to the technical field of Chinese medicinal crop and agriculture planting. The ecological planting method for the himalayan teasel roots provided by the invention comprises the following steps: inter-planting the himalayan teasel roots in an economic forest of walnuts, Chinese chestnuts, pears, peaches and cherries, and performing field management according to a corresponding planting technology. According to the ecological planting method, the advantage of complementation of the himalayan teasel roots and the space ecological niche of the economic forest is fully utilized, the harm caused by weeds and insect pests is reduced, the usage of pesticides is reduced, the quality of the himalayan teasel roots and the use ratio of land are increased, the income is increased, the ecological environment of the economic forest is improved, the growth and development of economic trees are boosted, the soil erosion in the forest land is reduced, and the economic and ecological benefits are excellent.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
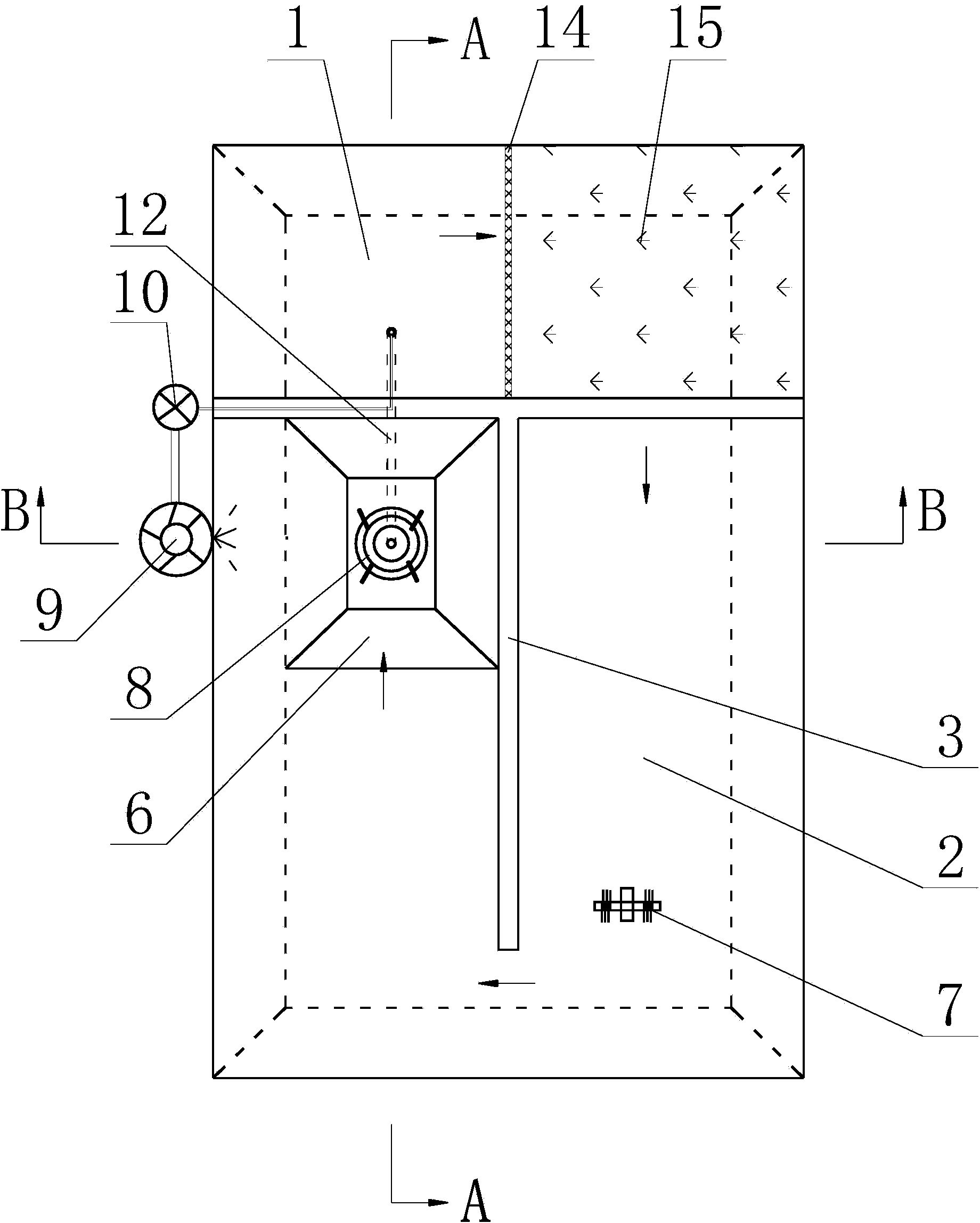
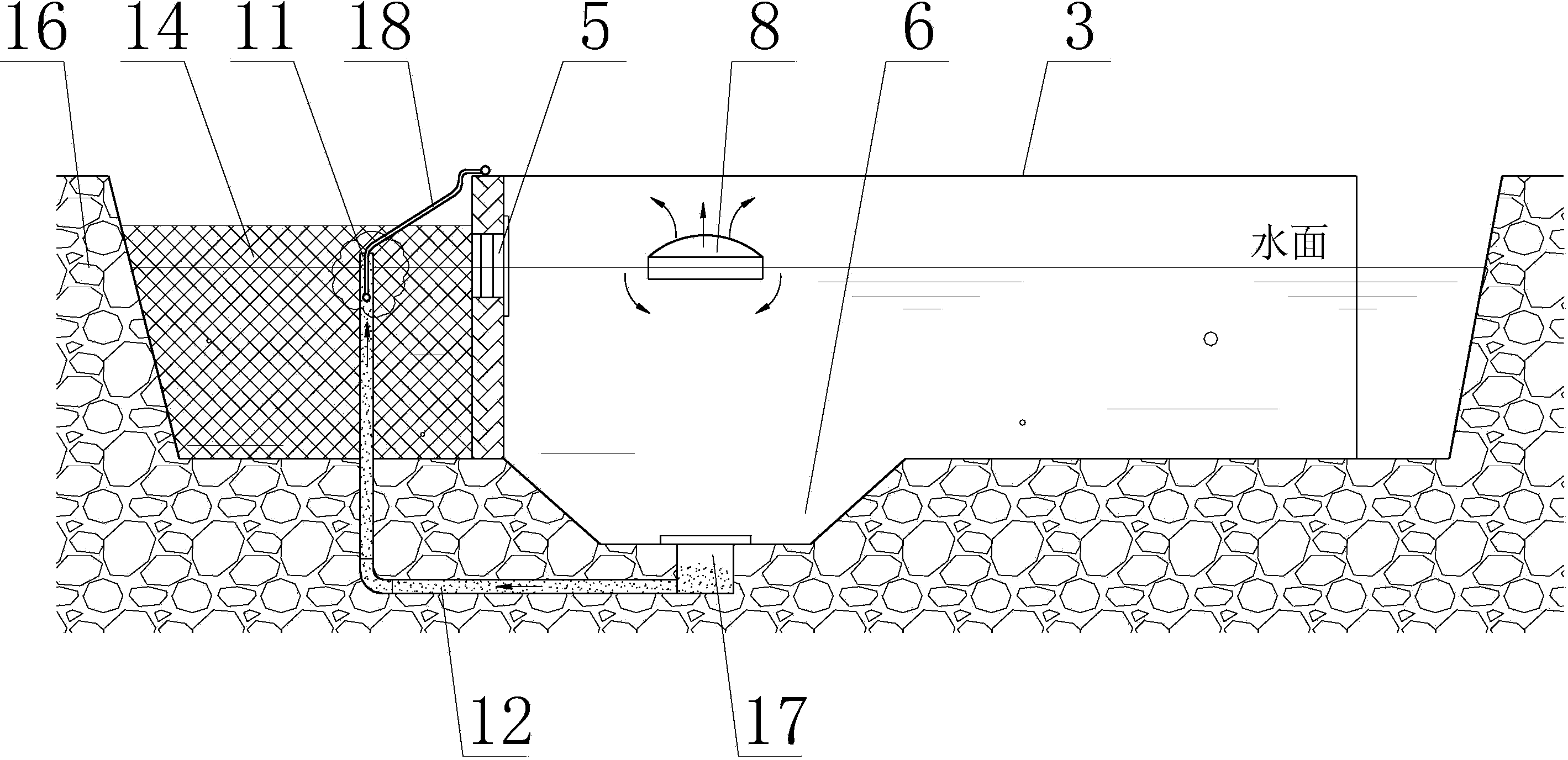
Pond differential niche ecological water treatment facility
InactiveCN103461263AImprove the ecological effect of farmingReduce farming pollutionPisciculture and aquariaFecesWater flow
A pond differential niche ecological water treatment facility is characterized in that a T-shaped water partition wall is arranged in a long strip-shaped aquiculture pond along the length direction to divide the cultivation pond into an eating fish aquiculture zone and a filter feeding fish aquiculture zone; the two zones are communicated by a fishing gate, a water inlet gate, a sewage colleting pipe and an aeration pipe; a conical sewage collecting pit is arranged at the pond bottom of one end, close to the fishing gate, of the eating fish aquiculture zone as an eating and defecting zone for fishes. Fishes of different niches in the pond are cultured in a separating mode, feces and residual baits of the eating fishes are concentrated and input to the filter feeding fish aquiculture zone by pneumatic water flows, and are re-eaten, purified, disintegrated or adsorbed by algae in the filter feeding fish aquiculture zone, thus ensuring the good water quality of the eating fish aquiculture zone, facilitating the growth of eating fishes, culturing the filter feeding fishes with the feces and residual baits of the eating fishes, improving the ecological effect of the pond aquiculture and reducing culture pollution.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Anaerobic-anoxic oxidation pitch technique denitrification dephosphorization device and method
ActiveCN101186390AStable biological phosphorus removalEase competitionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesDenitrifying bacteriaSludge bulking
The invention relates to an anaerobic-anoxic oxidation ditch technique denitrification dephosphorization device and a method thereof, and pertains to the technical field of sewage treatment. Directed against the problem that the present oxidation ditch technique has unsatisfactory biological dephosphorization effect, the invention improves the traditional oxidation ditches so as to strengthen the dephosphorization capacity. Based on the traditional oxidation ditch treatment devices, an anaerobic tank and an anoxic tank A and an anoxic tank B are additionally provided, and a novel oxidation ditch technique that has the capability of denitrification and dephosphorization is developed. Characteristics and differences of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, denitrifying bacteria and denitrification phosphorus removal bacteria are fully utilized so as to lead microorganisms of three kinds to occupy different ecological niches in three different selectors in one system, thereby realizing different functions respectively. By distributing reflux sludge and feeding water in a reasonable way, the invention relieves conflict between the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and the denitrifying bacteria, and the competitive edge of the denitrifying bacteria is enhanced during competition, thus realizing high efficiency of denitrification and dephosphorization. The invention has the advantages of high dephosphorization efficiency, relatively stable operation, sludge bulking resistance, etc.
Owner:中山公用水务投资有限公司
Method for establishing grazing artificial pasture on black soil beach
The invention discloses a method for establishing a grazing artificial pasture on a black soil beach, which includes: firstly using locally introduced and domesticated local grass-seeds; and secondly, according to biological characteristics of forage grass and the principle of species niche in communities, mixing Qinghai Festuca sinensis, Qinghai Poa crymophila and Qinghai Poa pratensis according to a certain seeding proportion, mixing Elymus nutans or Elymus sibiricus Qingmu No.1, Qinghai Poa pratensis, Qinghai Poa crymophila and Puccinellia tenuiflora according to a certain seeding proportion, and mixing Elymus nutans or Elymus sibiricus Qingmu No.1, Qinghai Festuca sinensis, Qinghai Poa pratensis, Qinghai Poa crymophila and Puccinellia tenuiflora according to a certain seeding proportion, so that utilization rate of environmental sources (water, heat and light) is increased, and pasture service life is prolonged. The grass-seed combination and establishment technique is extensional, and with development of research and production practice, the combination and establishment technique is still expansible.
Owner:QINGHAI ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE
Stereoscopic ecologic-cultivation method of Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome
InactiveCN103210758ASolve the shade problemLow construction costCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsSocial benefitsLower risk
The invention discloses a stereoscopic ecologic-cultivation method of Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome, wherein broad-leaf economic forest is firstly and manually planted in a region in which the Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome is to be planted, and is used for shading the Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome naturally by utilizing the layering situation of different plants and an ecological niche space complementary principle, so that the shading problem of the Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome is effectively solved, the construction cost of a sun shelter is saved, the planting cost is reduced, products of the economic forest can be obtained at the same time, the land revenue is largely improved, and the plant risk is reduced. The stereoscopic ecologic-cultivation method of the Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome, which is disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, easiness in popularization, land saving, environment-friendliness, high yield, low risk and the like, provides a new optimization scheme for the manual scale plant of the Yunnan manyleaf paris rhizome, and has excellent economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:师宗县同达农业科技开发有限责任公司
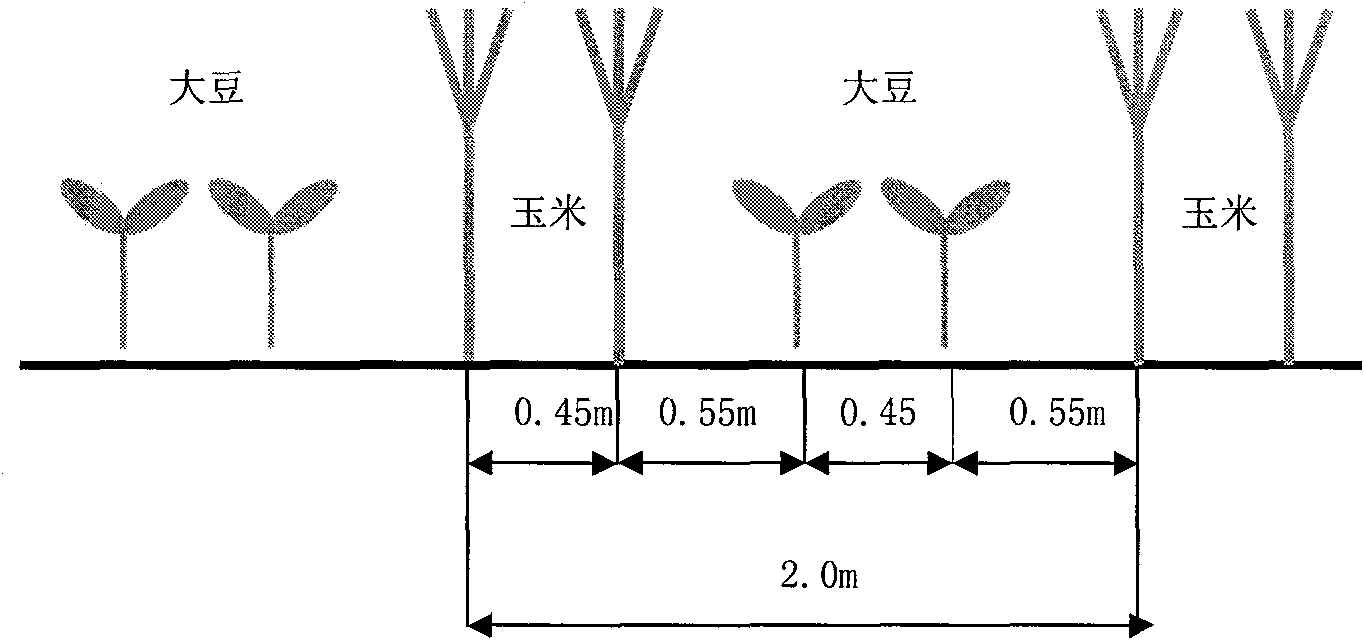
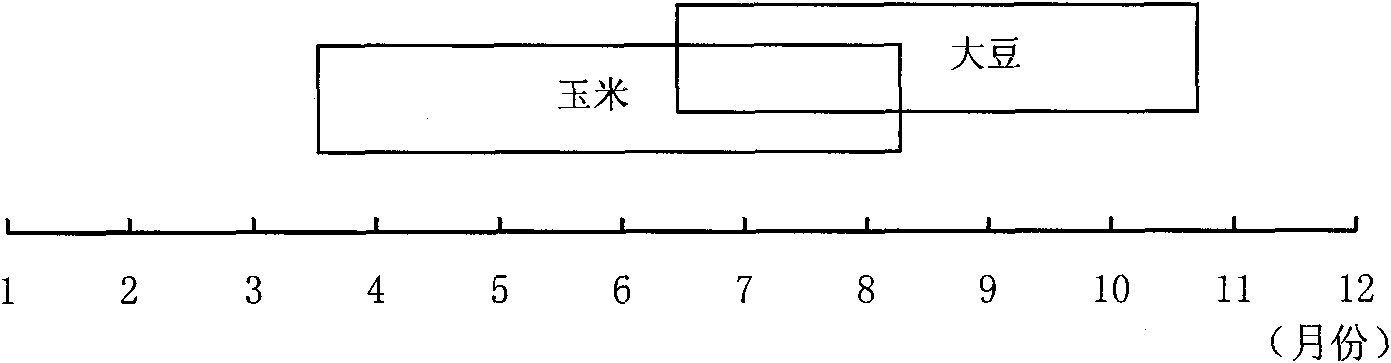
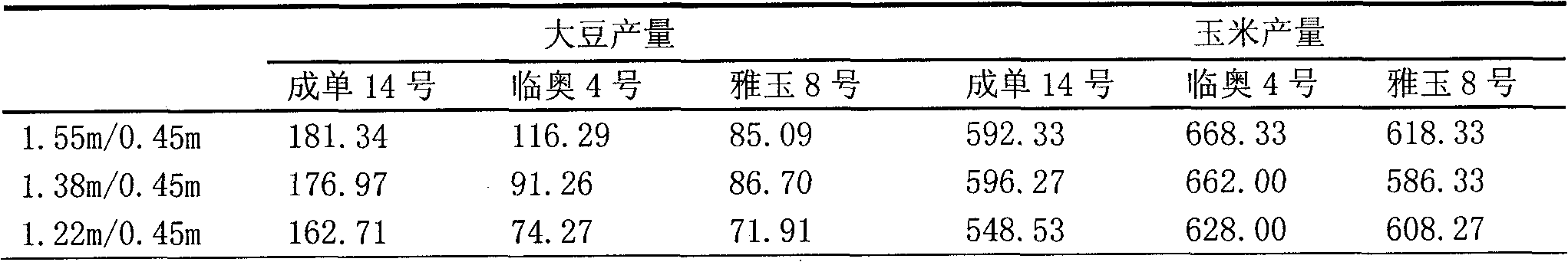
Method for cultivating soybeans and maize by utilizing spatiotemporal dislocation
InactiveCN102067774ARealize complementary use of time and spaceImprove yield per unit areaHorticultureCrop cultivationDislocation
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop cultivation, and in particular relates to a method for cultivating soybeans and maize in the southern area by utilizing spatiotemporal dislocation on resources. The method comprises the following steps that: the maize selects compact type and middle short stalk early-middle maturity spring maize variety, and the soybeans select shade-tolerant lodging-resistant middle late maturity summer soybean variety; the maize is early sown at proper time, the soybeans are sown in time before or after rain of middle-late growing stage (May 25 to June 15) of the maize; the soybeans and the maize are planted by adopting wide-narrow rows, wherein the wide rows of the maize are 1.55m, while the narrow rows of the maize are 0.45m; when the soybeans are sown, 2 rows of soybeans are sown between the wide rows of the maize, and the distance between soybean rows is 0.45m, and the distance between the maize row and the soybean row is 0.55m; 2 plants of the maize are planted in each hole in two rows alternately, while 3 plants of the soybeans are dibbled in each hole in two rows alternately; nitrogenous fertilizer is applied to the soybeans according to the growing trend of field plants; and prevention and control to maize insects during symbiotic growing period of the maize and the soybeans are improved. The method sufficiently utilizes the advantage of niche complementarity of space and time of the soybeans and the maize in southern area on light, heat, water and earth resources to achieve the aims of improving the land utilization efficiency, improving peasant income, and realizing resource sustainable utilization.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Submerging bed-floating bed coupled water purifying device
InactiveCN104743673AAvoid restrictionsDeep ecological nicheBiological treatment apparatusWater qualityPolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses a submerging bed-floating bed coupled water purifying device. The submerging bed-floating bed coupled water purifying device comprises a submerging bed and a floating bed which are made of UPVC (hard polyvinyl chloride) tubes, wherein the submerging bed comprises upper and lower rectangular frames which are the same in shape; a plurality of perpendicular connecting tubes are arranged between the two rectangular frames; a plurality of horizontal connecting tubes are arranged in the lower rectangular frame; the frames are internally communicated; a floating block capable of being spliced is embedded into the lower rectangular frame, and a planting pot in which submerged plants are planted is arranged on the floating block; a floating block capable of being spliced is also embedded into the floating bed, a planting pot in which emergent aquatic plants are plants is arranged on the floating block, and artificial seaweeds are suspended between adjacent floating blocks of the floating bed; the submerging bed is placed on the center of the inner outline of the floating bed; a connecting rope is arranged between the submerging bed and the floating bed. According to the submerging bed-floating bed coupled water purifying device disclosed by the invention, positions, in water, of submerged plants are regulated by internally watering and pumping the submerging bed, so that the positions of the submerged plants are changed along with ecological niches of water level, transparency and the like, and a natural water environment is simulated to a greatest extent. The water plant planting amount is large, the varieties are rich, the survival rate is high, and the restoration of water body ecological community is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
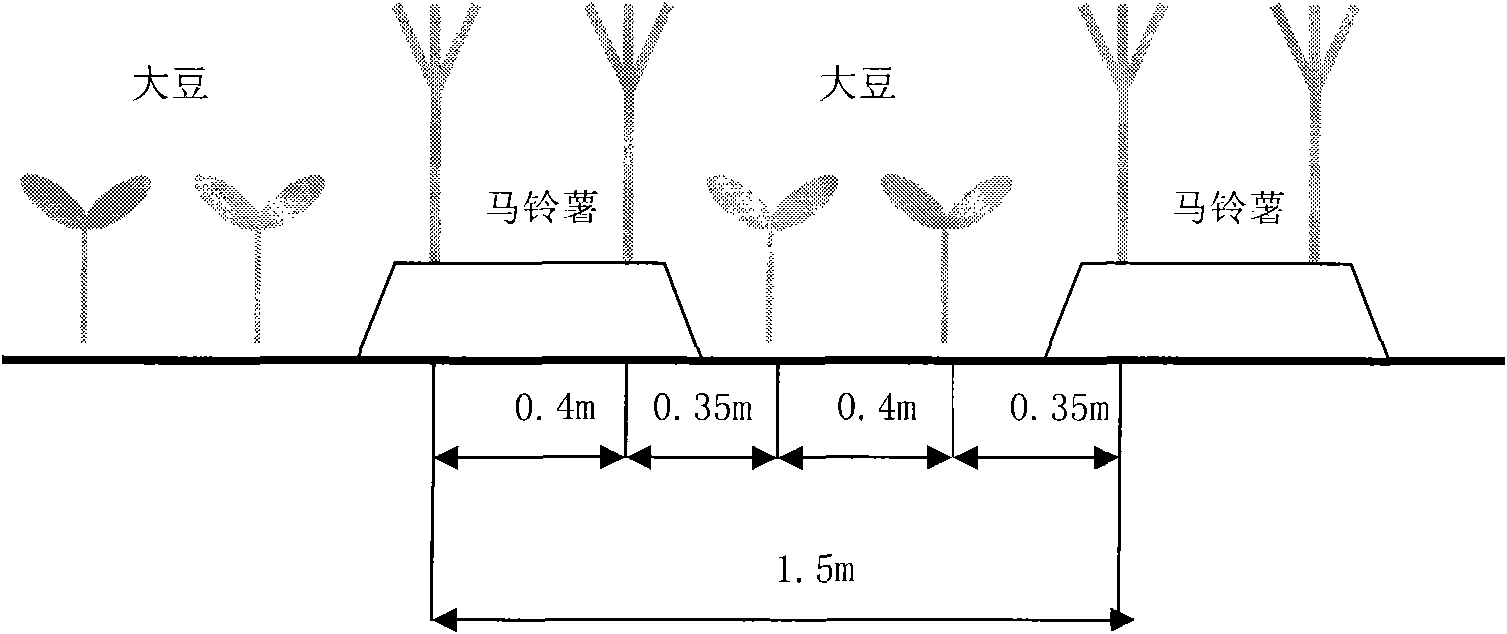
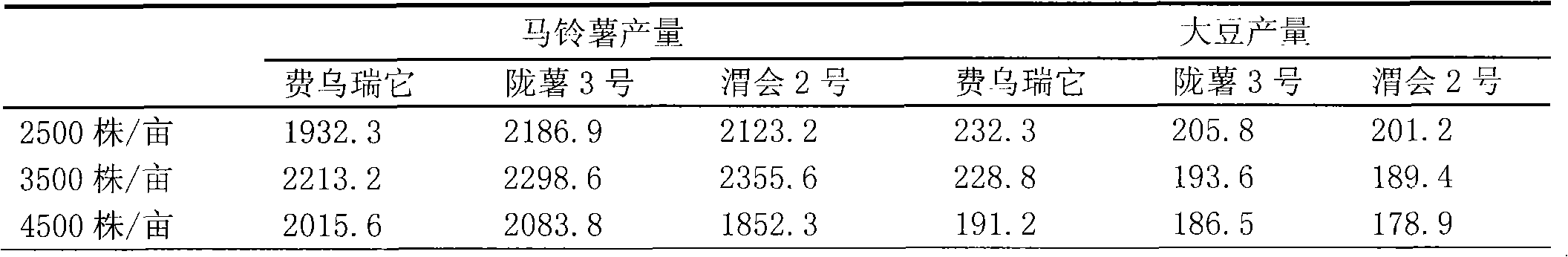
Novel compensation cultivation method for interplanting potato with soybean
InactiveCN102067775ARoot systemStrong shade toleranceFertilising methodsHorticulture methodsAgroecology in Latin AmericaInterspecies interaction
The invention relates to a compensation cultivation method for interplanting potato with soybean in the northwest of China, belonging to crop cultivation in the technical field of crop cultivation. According to the interspecies interaction principle of the agricultural ecology, in the method, the complementary utilization of nutrients and luminous energy in the same habitat is realized by the difference of the ecological niche of the potato and the soybean, and the purposes on improving resource utilization efficiency and soil production rate and increasing the income of farmers are achieved. The method comprises the following specific steps: selecting early-maturing spring potato species with vertical plant, few branches and shorter plants; and selecting drought-enduring and lodging-resistance late-maturing summer soybean species; early sowing the potato in due time according to temperature rebound condition; sowing the soybean in time before or after Grain Rain in the medium growth period of the potato; planting the potato and the soybean in narrow and wide rows, wherein the wide row of the potato is 110cm, and the narrow row on the ridge is 40cm; when the soybean is sown, planting two rows of soybean in the wide row of the potato, wherein the line space of the soybean is 40cm, and the line space between the potato and the soybean is 35cm; planting the potato in a double-row, single-plant and staggered-hole mode; and carrying out bunch planting on the soybean in a double-row, three-plant and staggered-hole mode.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Ecological method for controlling excessive proliferation of periphytic filamentous algae through submerged plant patch mosaic pattern
ActiveCN105830711ASolve the problem of low survival rate and single underwater ecological nicheReasonable designClimate change adaptationSustainable biological treatmentEutrophicationLower grade
The invention discloses an ecological method for controlling excessive proliferation of periphytic filamentous algae through a submerged plant patch mosaic pattern. The ecological method comprises steps as follows: 1), water environment features including water depth, water flow, transparency, sediments, nutritive salts, plankton and the filamentous algae of a to-be-restored area are surveyed; 2), purse seining is performed by the aid of nylon ropes, a purse seine is dropped to be contacted with the sediments, and if a number of herbivorous fishes exist in the submerged plant patch mosaic pattern restoration area, the herbivorous fishes are expelled manually; 3), submerged plant species are selected according to the restoration area water environment obtained through the survey; 4), the submerged plant patch mosaic pattern is designed according to underwater ecological niche, growth and propagation features and water level of submerged plants; 5), submerged planting is performed in a clustering manner according to the designed submerged plant patch mosaic pattern; 6), the growth vigor of the submerged plants is monitored regularly. With the adoption of the ecological method, the problems of low survival rate and single underwater ecological niche of the submerged plants are solved, and the cover degree of the restored submerged plants is up to 70%; abnormal proliferation of the low-grade periphytic filamentous algae in a lake with eutrophication is effectively controlled, and the growth rate of the periphytic filamentous algae is reduced by 35% averagely.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Tea planting method
ActiveCN103749119AImprove soil fertilityMoisture increase effectHorticultureInsect pestPlant disease
The invention discloses a tea planting method. The tea planting method comprises the steps of planting tea trees on planting ridges of a tea garden in single rows, controlling row spacing between the tea trees to be 1.2-1.5m, controlling plate spacing between the same row of tea trees to be 0.8-1.0m and planting 800-1000 tea tree seedlings in each unit of area; and planting camphor trees on the periphery of the tea garden and the roads in the tea garden and planting ryegrass between the rows of the tea trees. According to the tea planting method, the camphor trees and the Mexico's perennial ryegrass are interplanted; the growth environment of each tea tree is effectively guaranteed between the tea trees through spacing between the camphor trees and the Mexico's perennial ryegrass; the risk of plant diseases and insect pests during planting the tea trees in large areas; even if single tea tree suffers from plant diseases and insect pests, the plant diseases and insect pests are not easy to infect and convenient to control; sustainable development of the tea garden and forming of a tea garden benign ecological system are facilitated, so that the tea trees are in ecological niches.
Owner:黄山市洪通农业科技有限公司
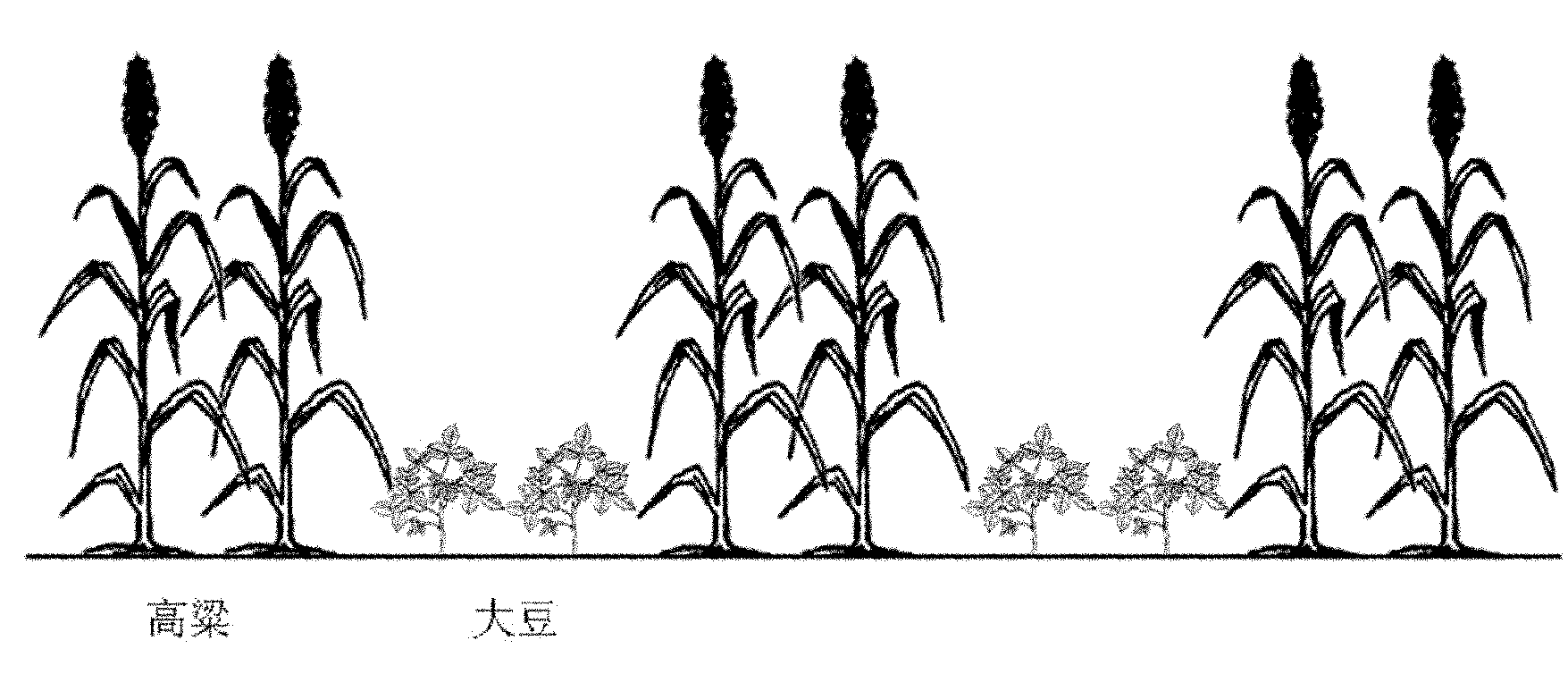
Three-dimensional cultivation method of interplanting soybeans and sorghums
InactiveCN102172159APromote production and incomeImprove light energy utilization efficiencyHorticultureResource utilizationLight energy
The invention discloses a three-dimensional cultivation method of interplanting soybeans and sorghums. The sorghums are planted prior to the soybeans; a strip-shaped open box with box face width of 120-135 cm is adopted; the sorghums are planted in wide and narrow lines; distances between the wide lines are 80-100 cm while distances between the narrow lines are 35-40 cm; 1 to 2 lines of soybeans are planted in the wide lines of the sorghums; distances between the soybeans and the sorghums are 35-50 cm; and distances between the soybeans in soybean zones are 30 cm. In the cultivation method disclosed by the invention, complementary spatial niche advantages of long-stalk crops sorghums and short-stalk crops soybeans are sufficiently utilized and a high and low scattered canopy architecture is formed in the field so that ventilation and light transmission in the field are enhanced and the light energy utilization efficiency is improved; and spaces between the wide lines of the sorghums and idle growing seasons after the sorghums are harvested are sufficiently utilized so that the land-use efficiency and the resource utilization rate are improved and both the production and the income are increased.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for predicting camellia oleifera suitable area
InactiveCN106845699AAccurate predictionHigh reference valueForecastingCamellia oleiferaComputer science
The invention discloses a method for predicting a camellia oleifera suitable area. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: obtaining camellia oleifera distribution point data; S2: obtaining the environmental data of the distribution point; S3: selecting a maximum entropy model to construct an ecological niche model, and dividing a suitable level for the potential distribution area of the camellia oleifera according to a distribution probability value for ecological niche model prediction; and S4: carrying out the reliability analysis of a prediction result. By use of the method, existing camellia oleifera distribution data and environment data can be utilized, the maximum entropy model is adopted to construct the ecological niche model, the camellia oleifera suitable area is predicted, a prediction result is accurate so as to be favorable for knowing a camellia oleifera distribution rule, and the method has a high reference value for guiding camellia oleifera production and searching wild camellia oleifera resources.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
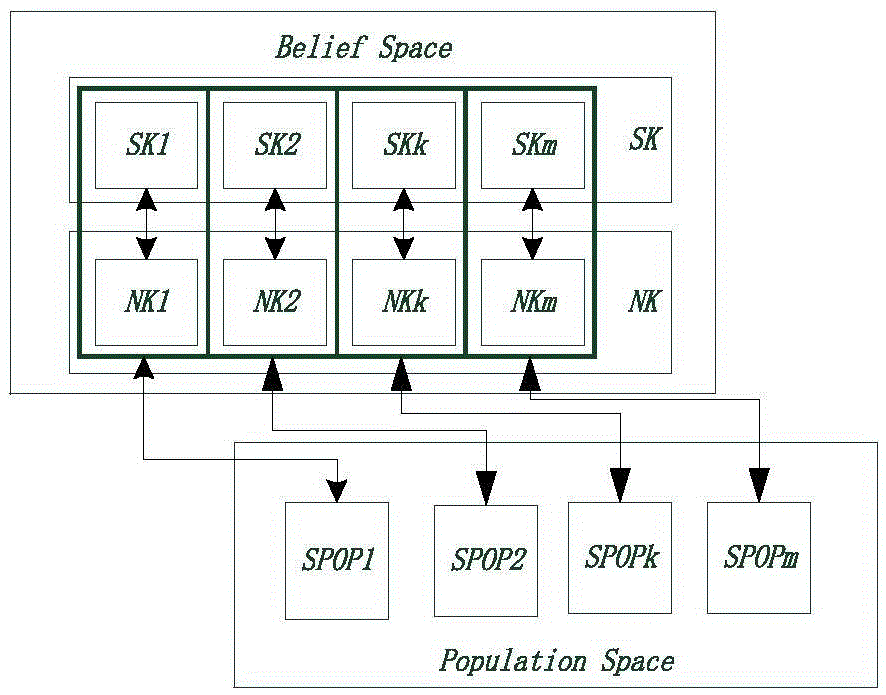
Clustering method based on ecological niche genetic algorithm with diverse radius technology
InactiveCN104239434AImprove clustering effectImprove stabilityGenetic modelsRelational databasesAlgorithmGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a clustering method based on an ecological niche genetic algorithm with a diverse radius technology. The clustering method based on the ecological niche genetic algorithm with the diverse radius technology comprises the following steps that (1) chromosome coding and population are initialized; (2) the individual fitness is calculated; (3) the position, content and number of the ecological niches in the population are identified by adopting a dynamic identification method; (4) the radius information of each ecological niche is adjusted by executing the diverse radius mechanism; (5) the new individual fitness is recalculated by applying a fitness sharing function; (6) selection, intersection and mutation operations are executed; (7) an elite strategy is executed to replace the worst individual in the population; (8) if a termination condition is met, the operation is terminated, otherwise the step (5) is executed. The clustering method based on the ecological niche genetic algorithm with the diverse radius technology has the advantages that the clustering effect is good, and the stability is good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for testing categorical data set
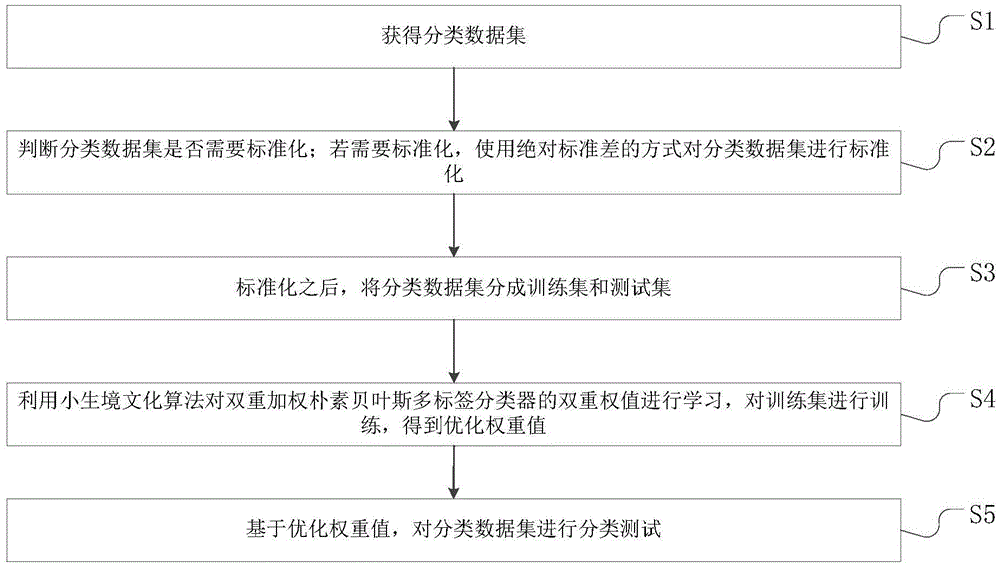
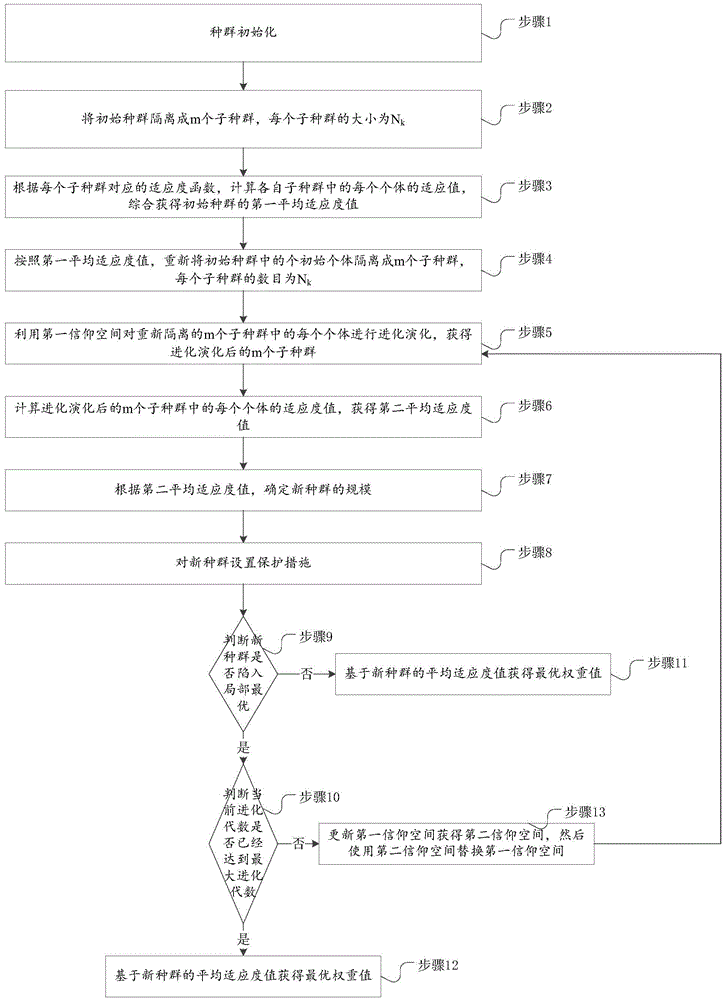
InactiveCN105095494AAccelerated trainingImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsData setMulti-label classification
The invention discloses a method for testing a categorical data set. The method includes the steps that after the categorical data set is obtained, if the categorical data set needs to be processed in a standardization mode, the categorical data set is standardized in an absolute standard deviation mode; the categorical data set is divided into a training set and a test set, an ecological niche cultural algorithm is used for learning to obtain dual weight values of a dual weighted naive Bayes multi-label classifier, and then the training set is trained to obtain optimized weight values; the optimized weight values are substituted into the test set for prediction. A data training process is added on the basis of a traditional naive Bayes multi-label algorithm, and then the categorical data set is predicted. As traditional data classification is improved through a particle swarm optimization algorithm, the improved algorithm can improve the classification accuracy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Aquatic plant compositing technology used for reclaimed water and landscape waterbody eco-remediation
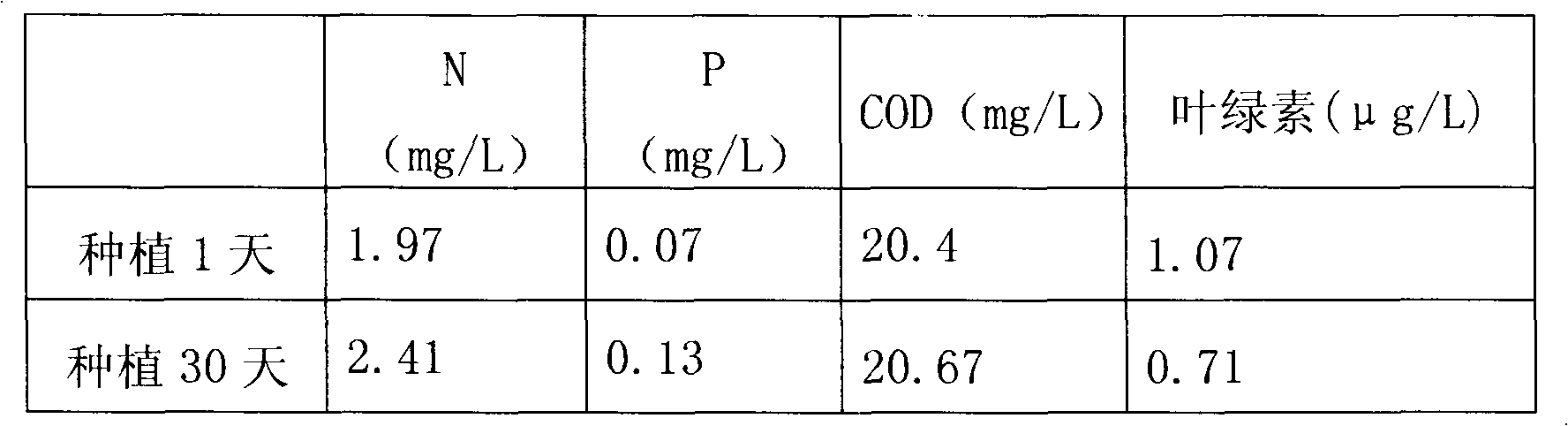
ActiveCN101880088ANo secondary pollutionRealize three-dimensional distributionSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationWater source
The invention discloses aquatic plant compositing technology used for reclaimed water and landscape waterbody eco-remediation. In the method, native aquatic pioneer plants for inhibiting algae and reducing nutrients in the water environment suitable for reclaimed water serving as a supplementing source are optimized and subjected to compositing and optimized allocation, so the constructed aquatic plant growth environment supplement the water environment each other. By analyzing water quality characteristics of the reclaimed water and the water environment and basic conditions such as waterbody area, shape, depth, temperature change and base, native submerged plants, floating plants and emergent aquatic plants are selected according to plant characteristics, ecological niche cross and ornamentation, and are allocated and composited; the planting areas of the plants and the planting types of the plants are controlled; and the plants ecologically purify the water environment taking the reclaimed water as the supplementing source deeply and inhibit pioneer algae causing eutrophication so as to achieve the effects of reducing the content of nutrients such as N and P in the water environment, and delaying and preventing the burst of the eutrophication in the water environment.
Owner:国家城市给水排水工程技术研究中心 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com