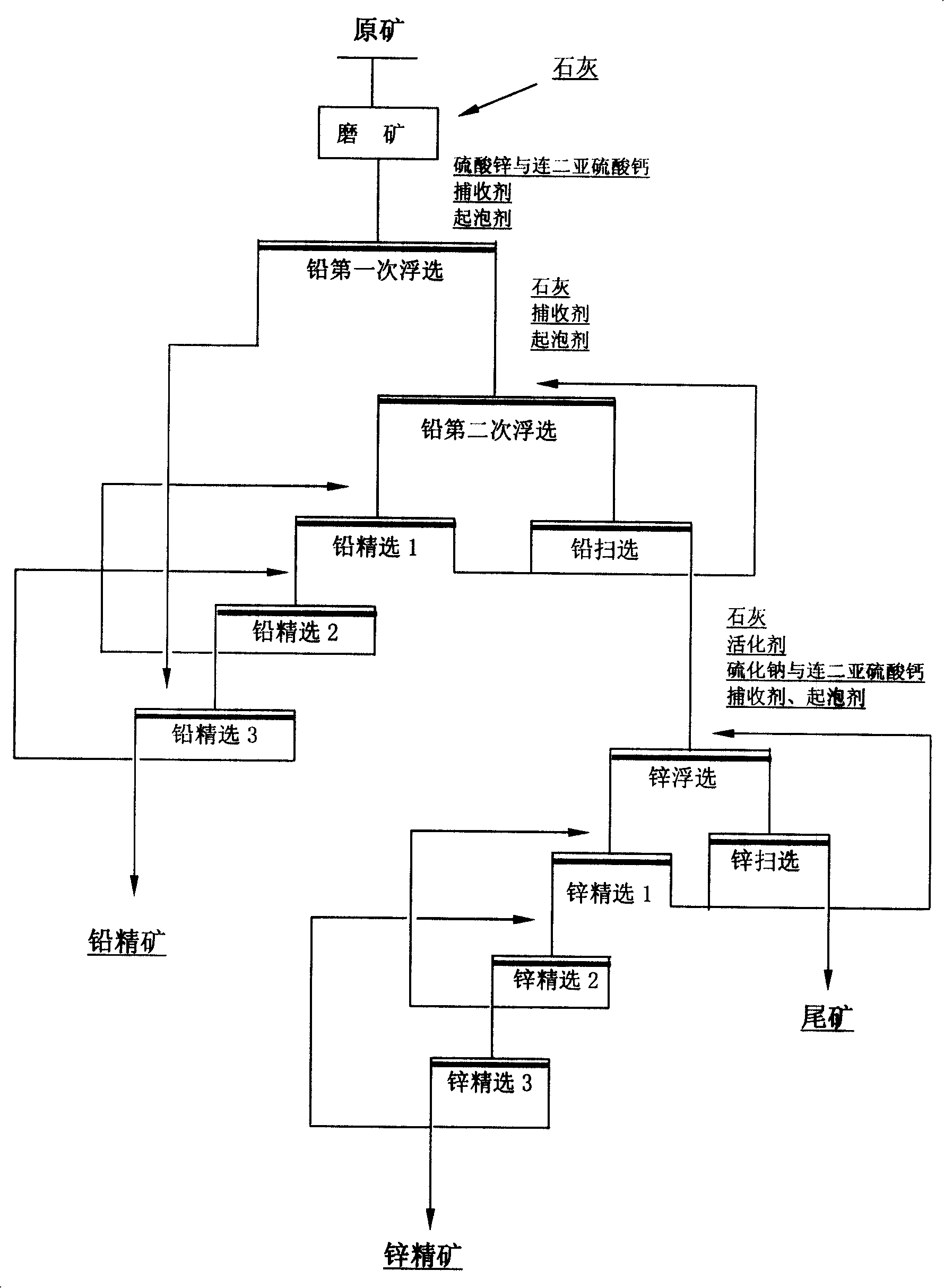
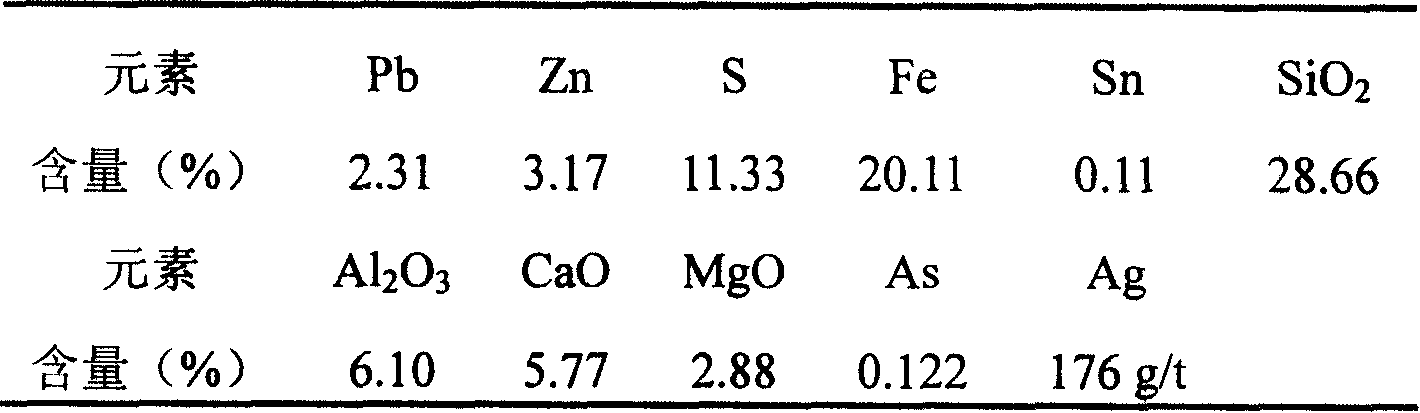
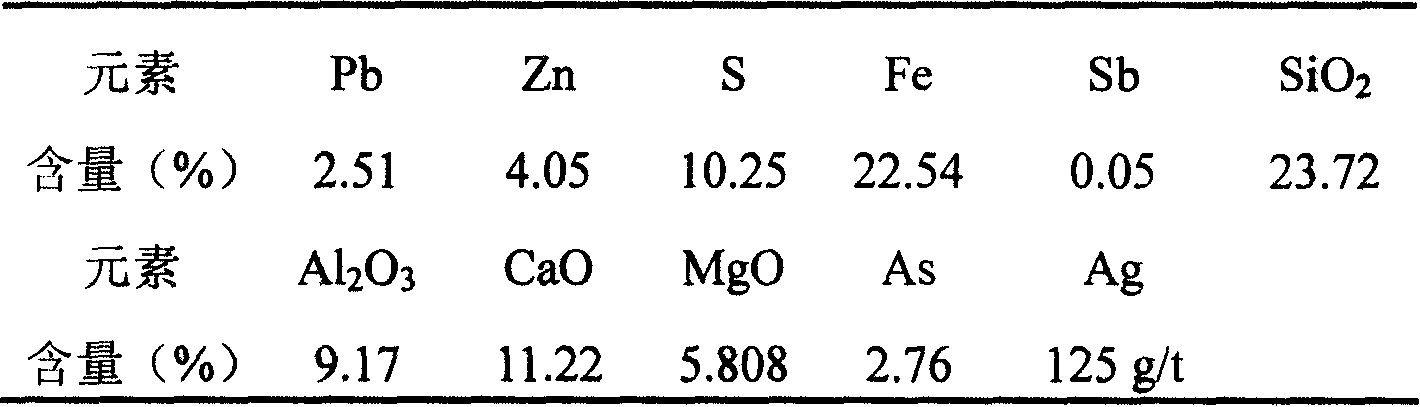
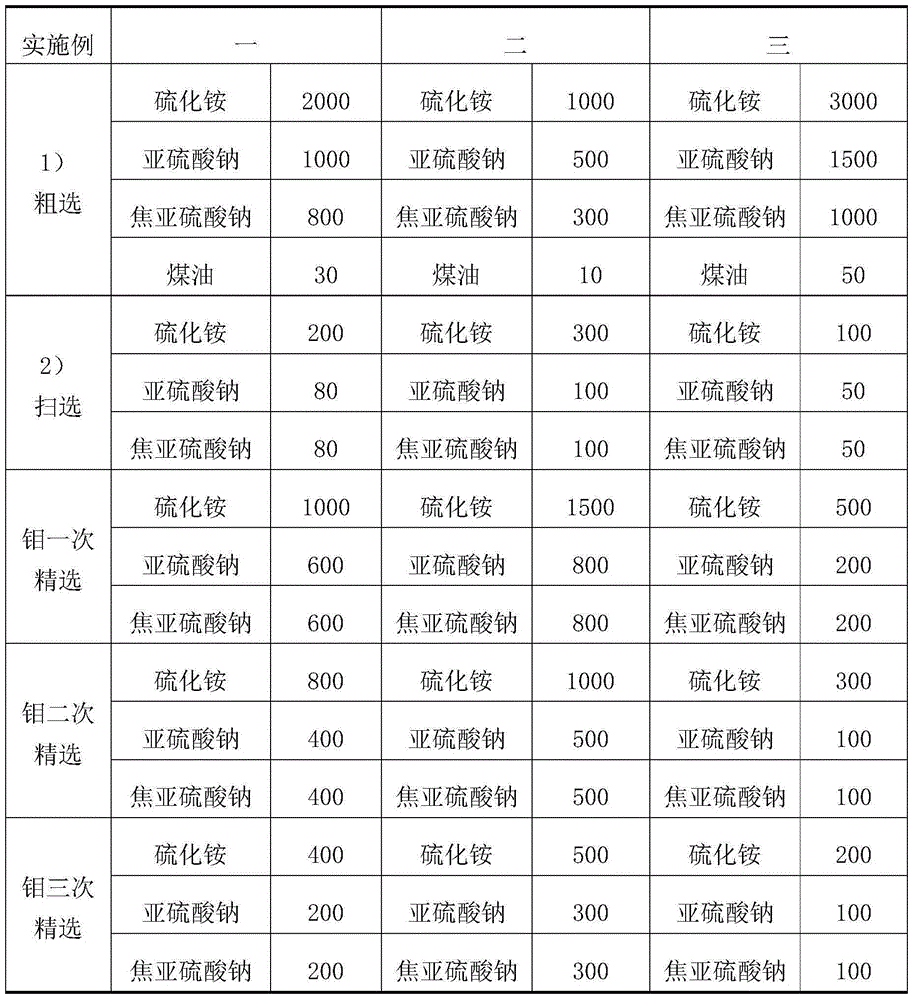
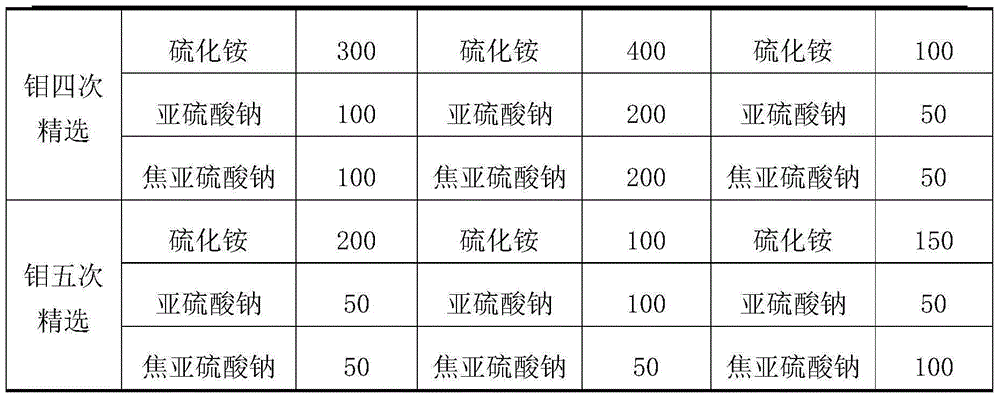
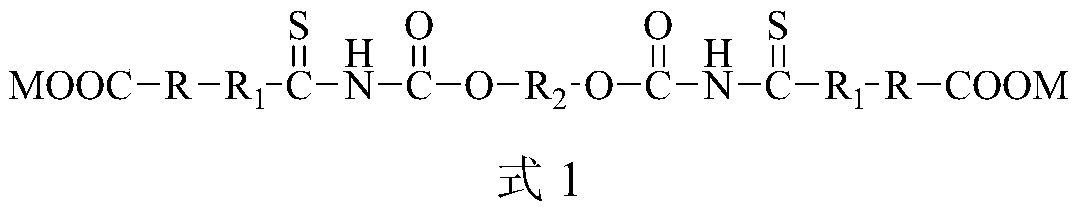
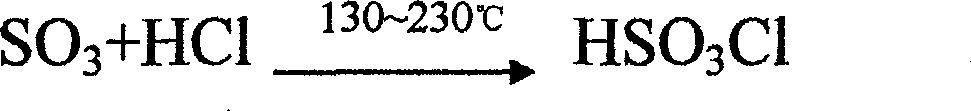
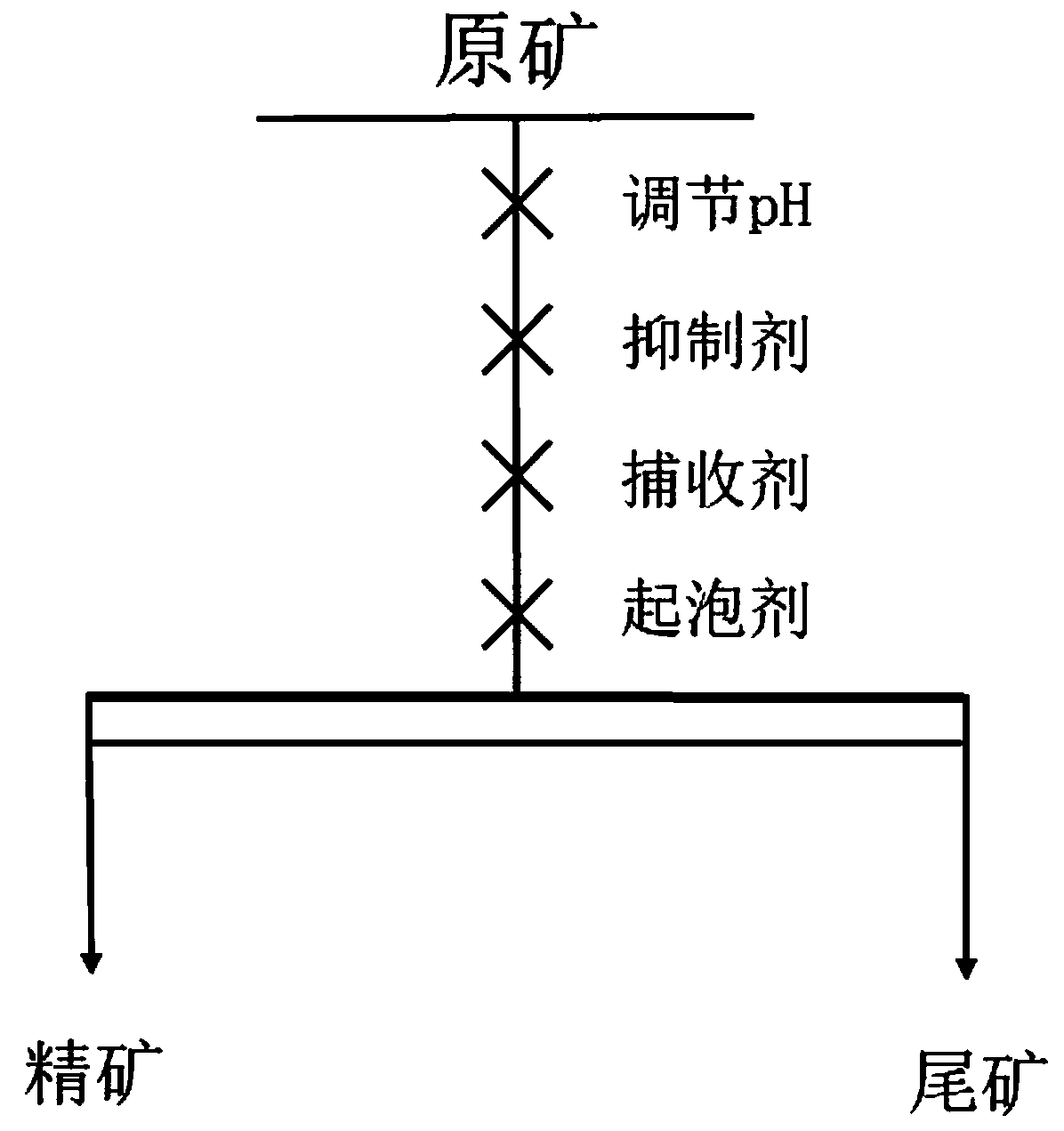
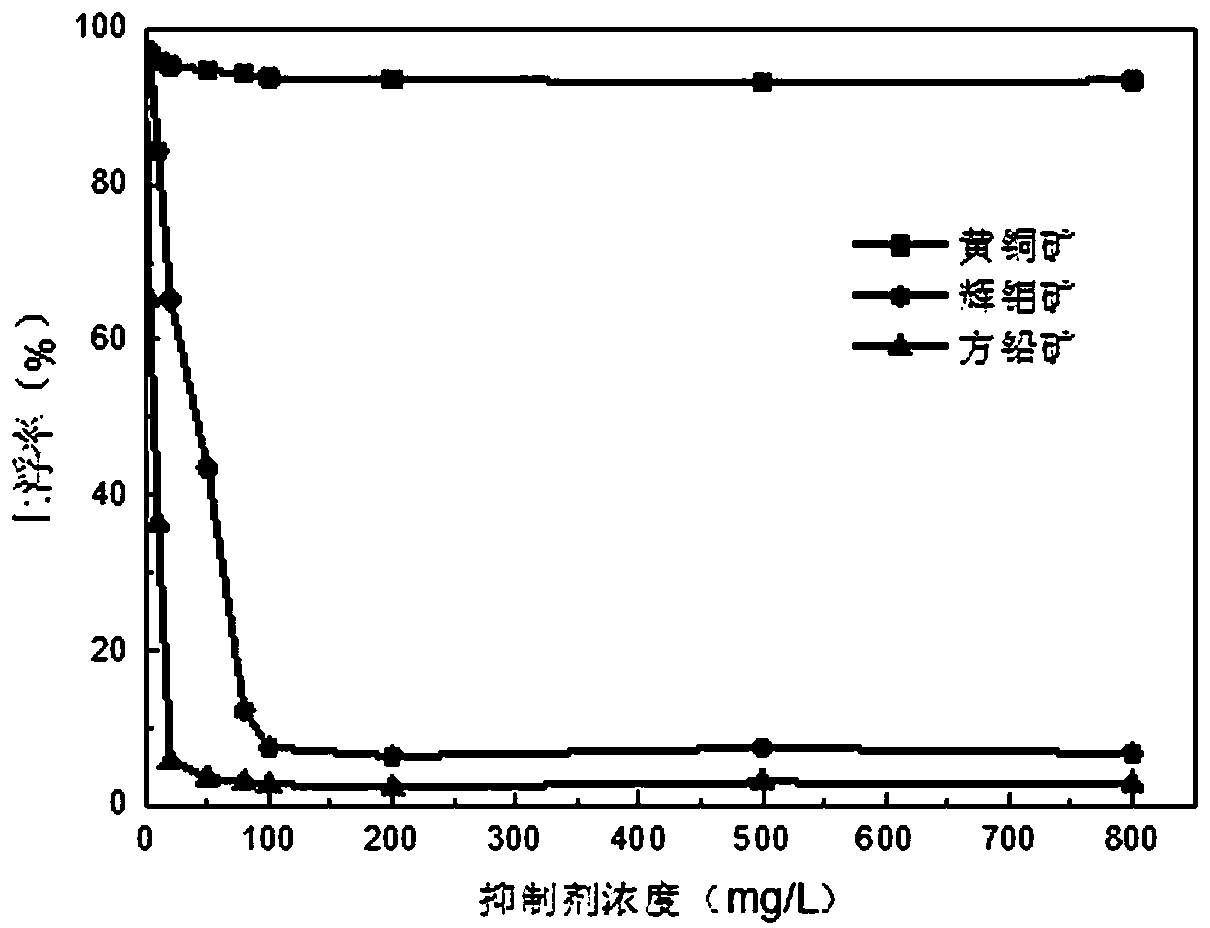
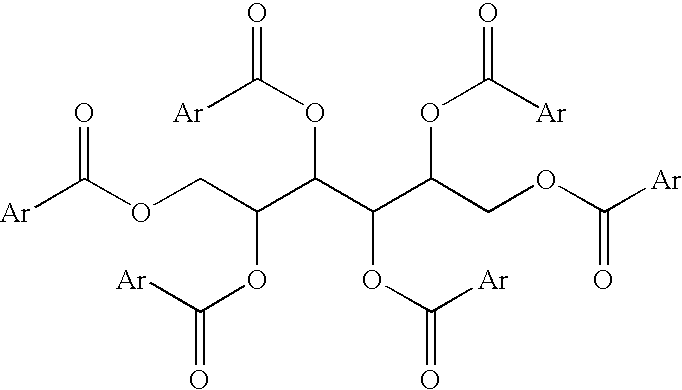
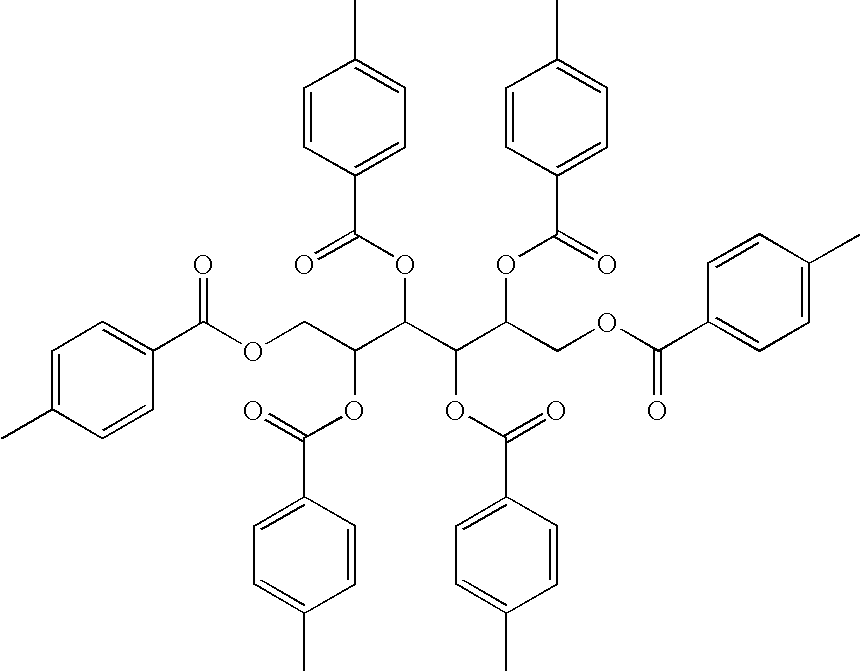
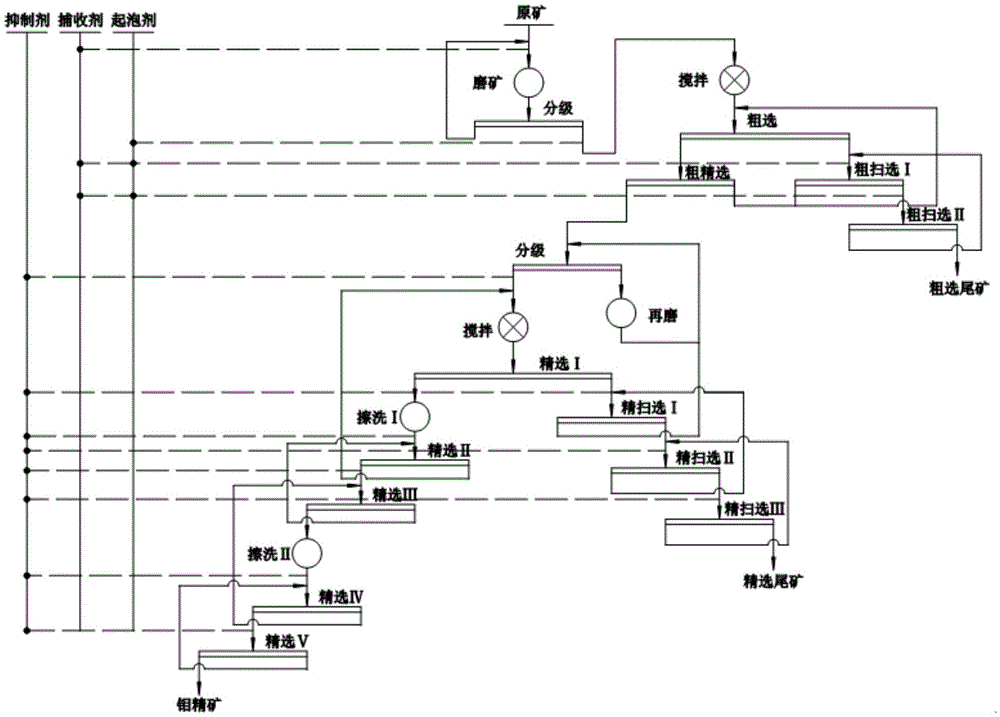
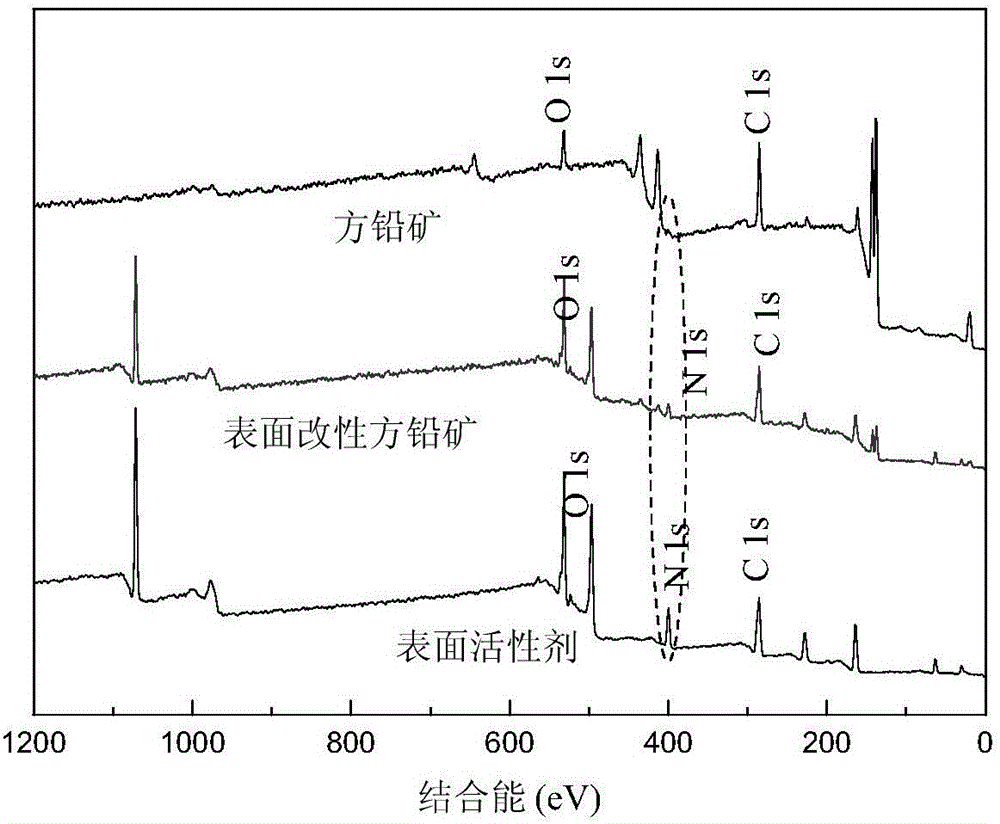
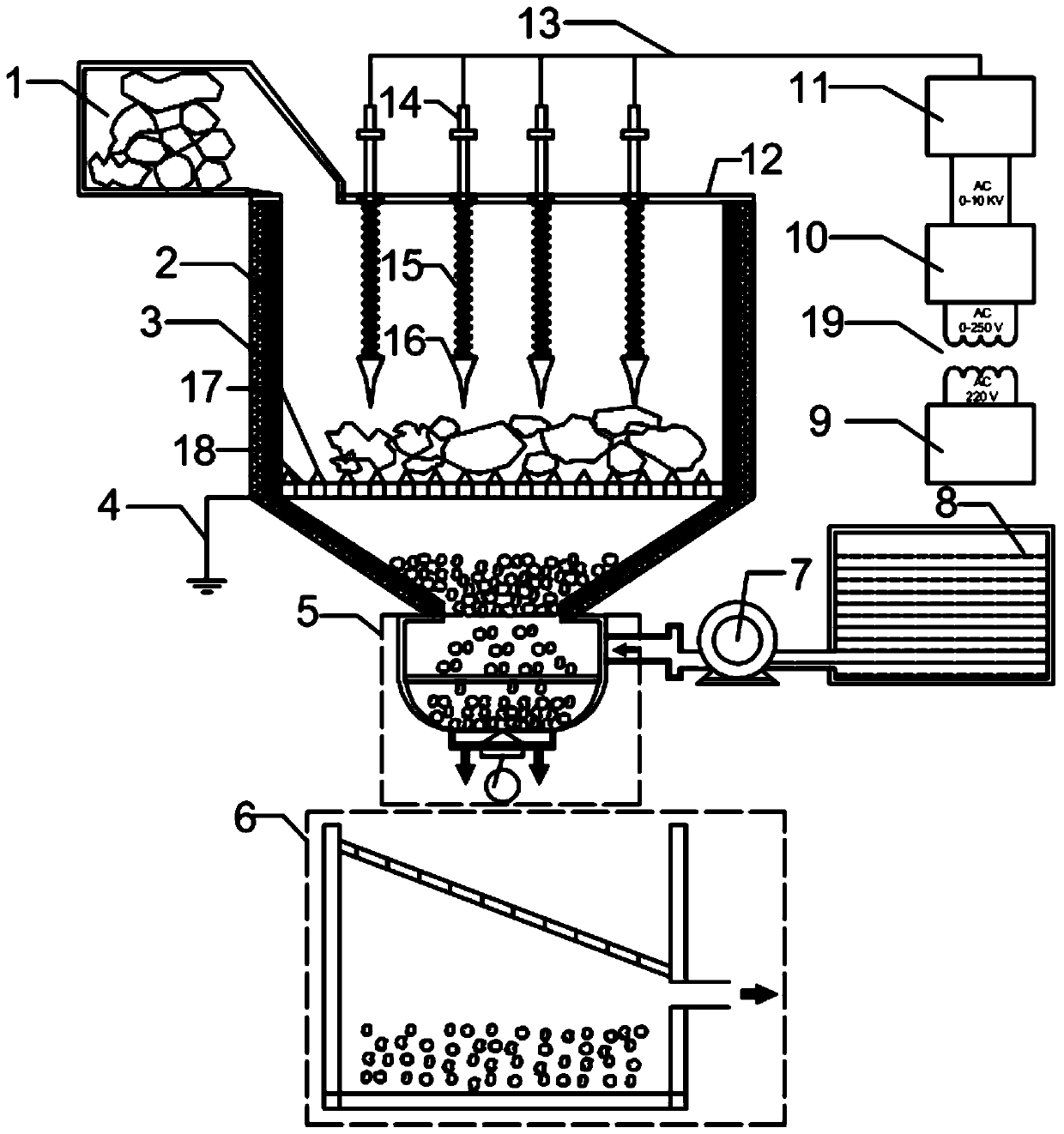
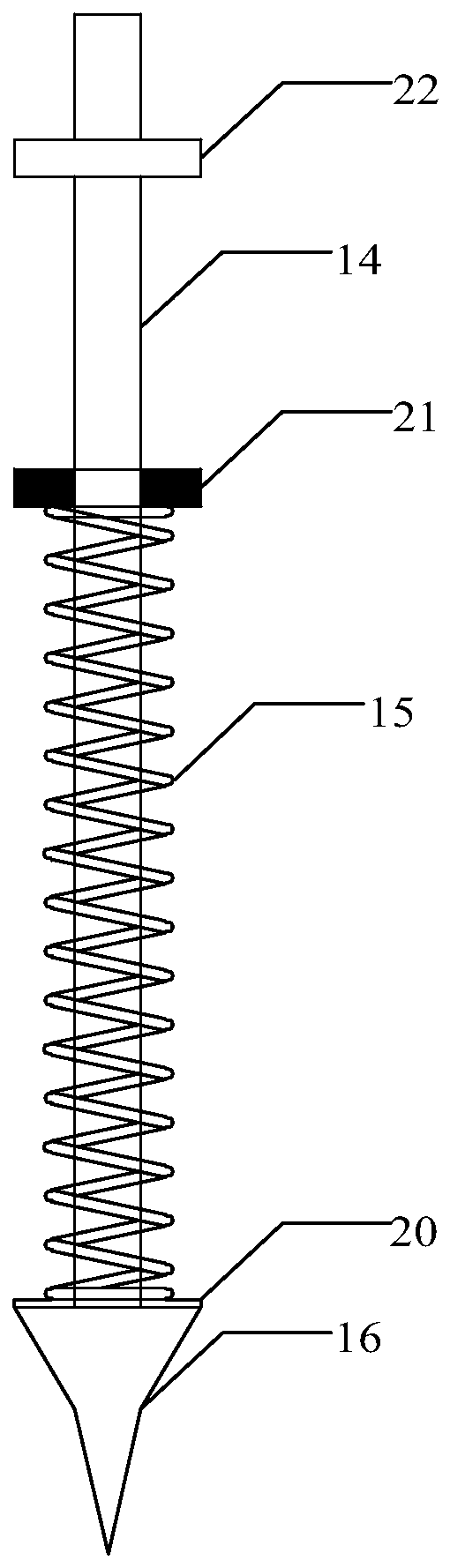
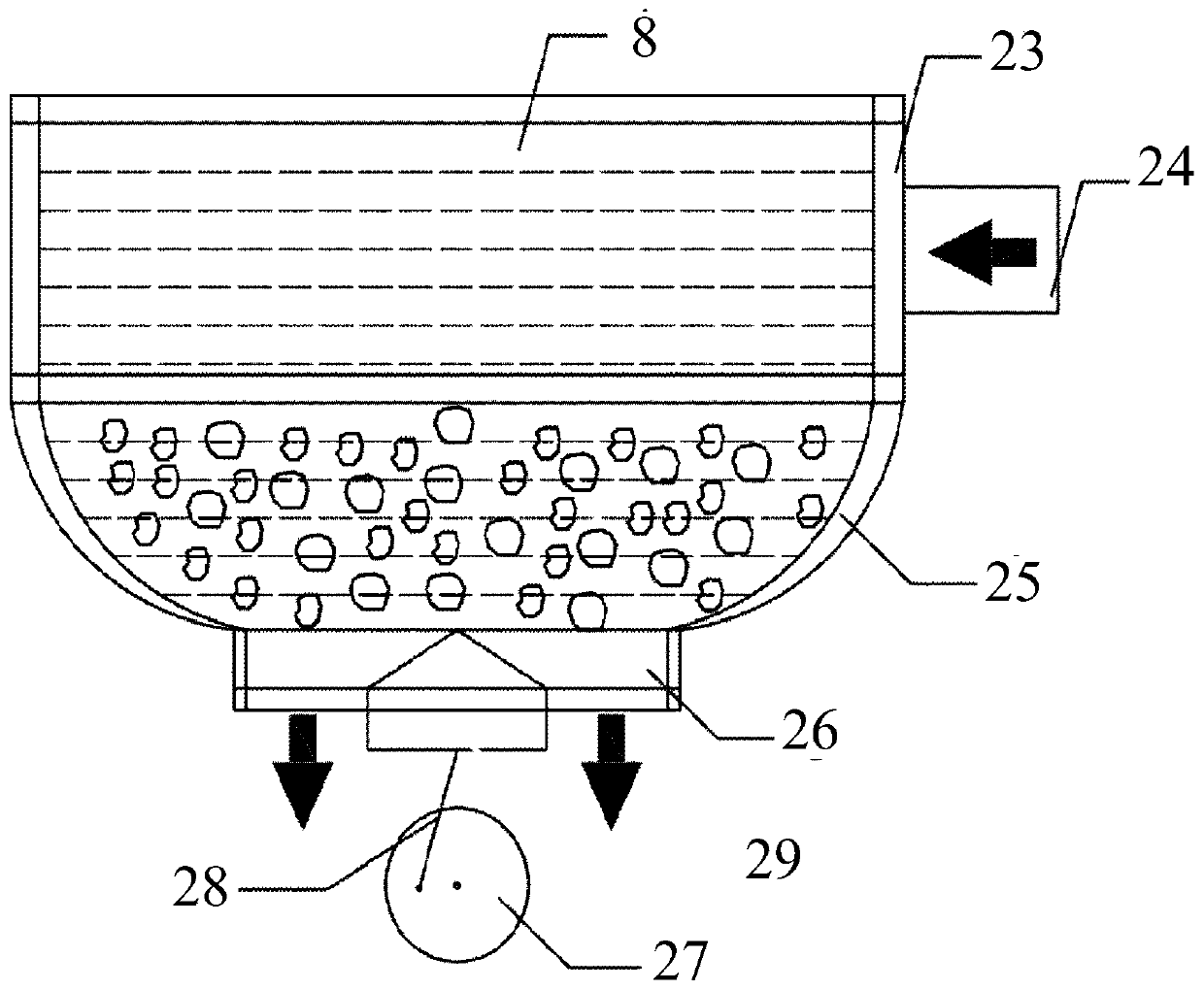
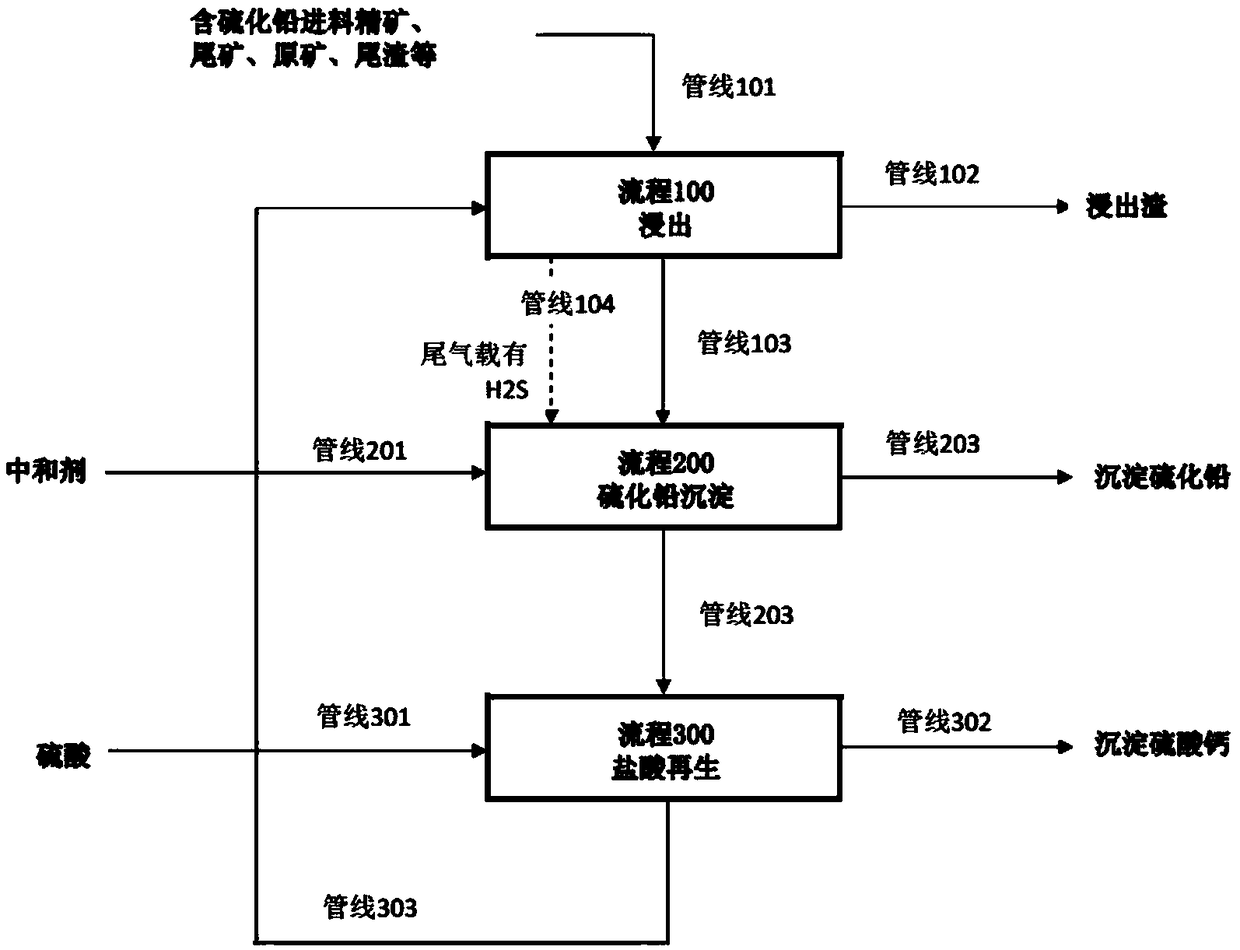
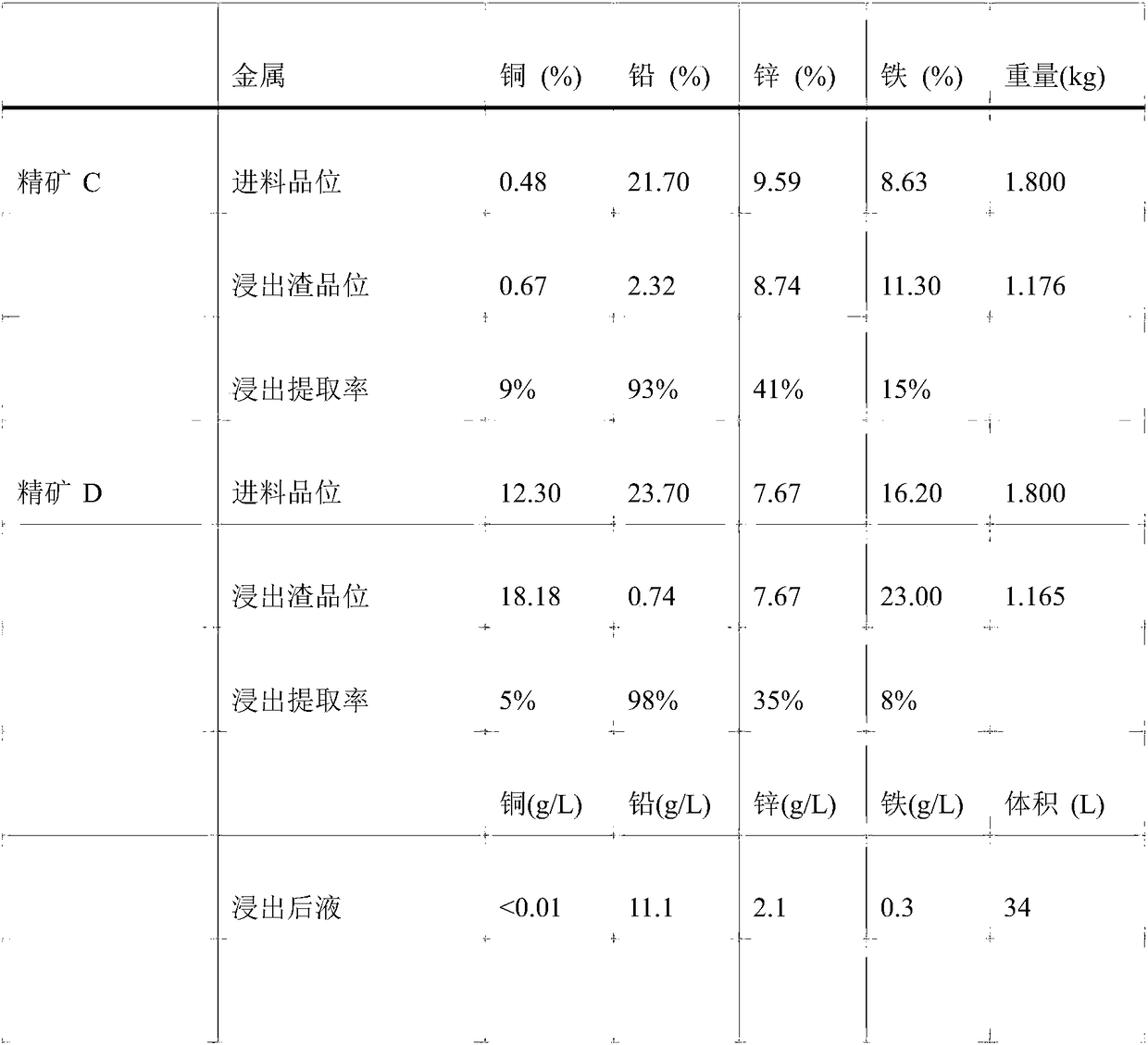
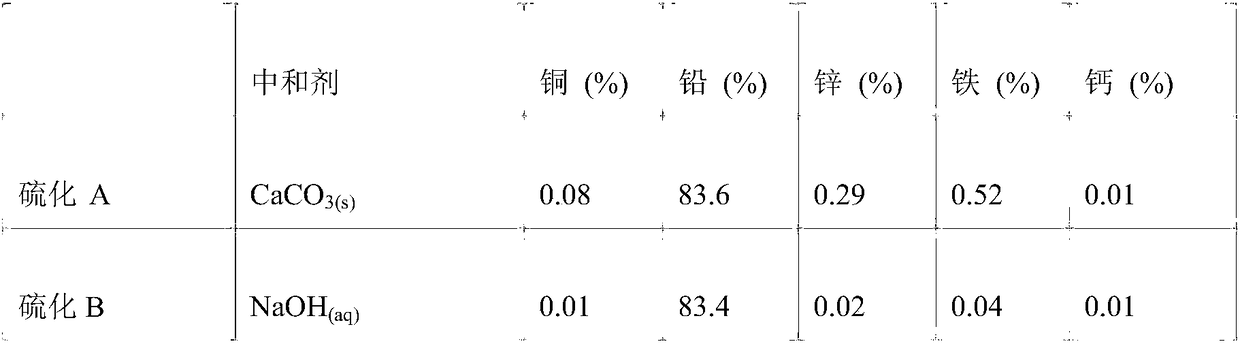
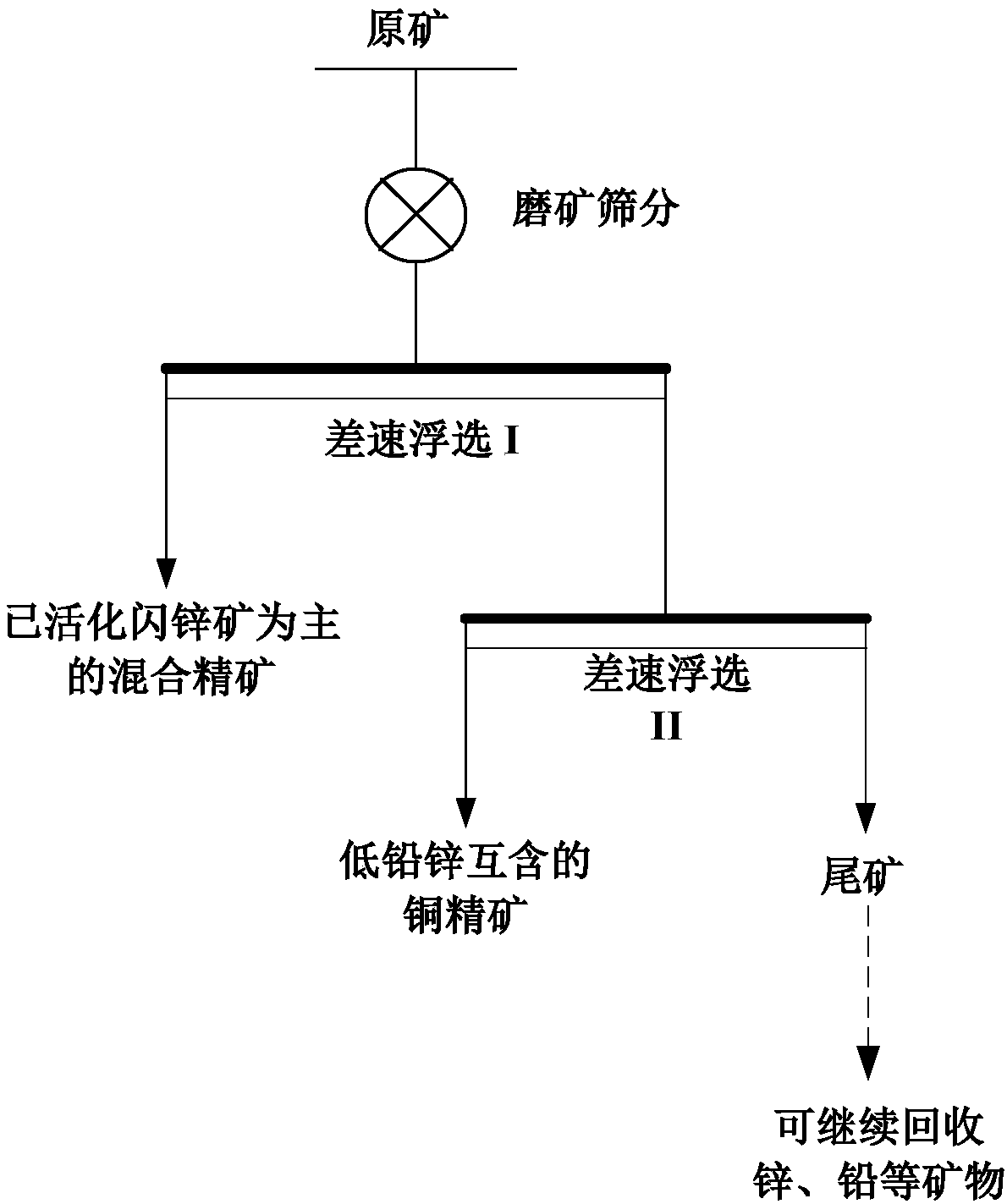
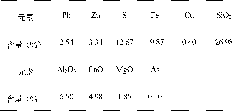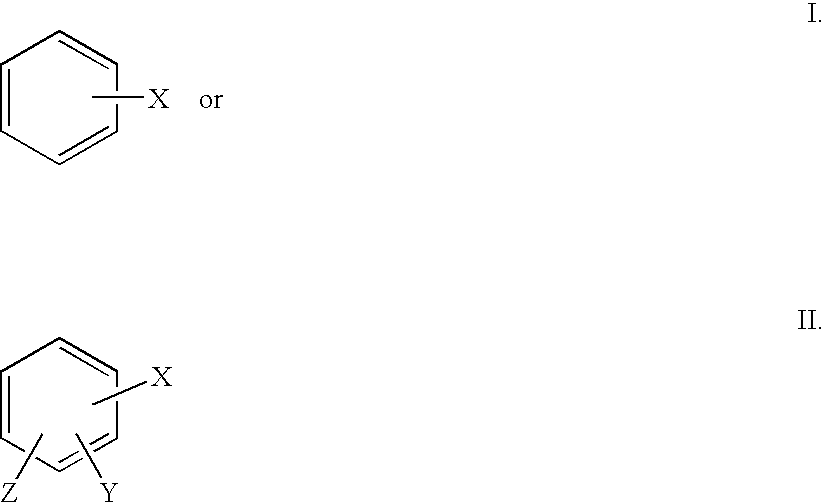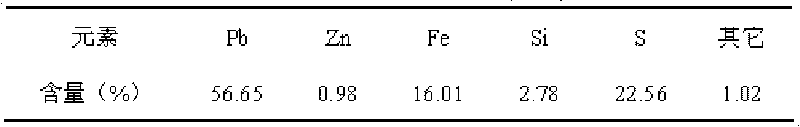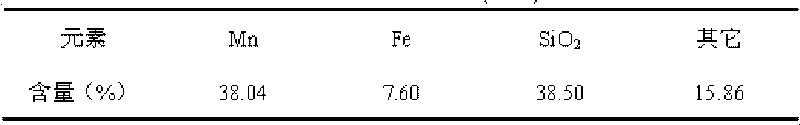Patents
Literature
119 results about "Galena" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver. Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite.
Complex plumbum, zinc, silver vulcanizing ore containing newboldite and pyrrhotite floatation method
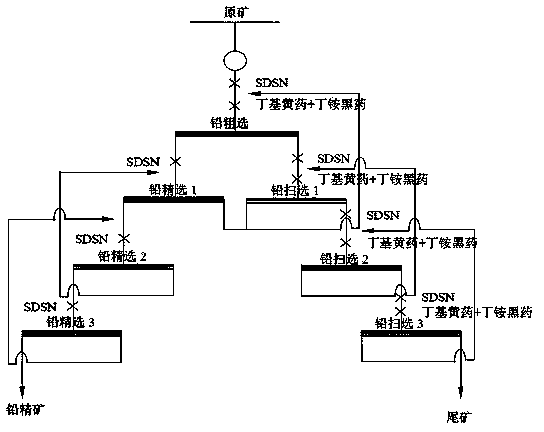
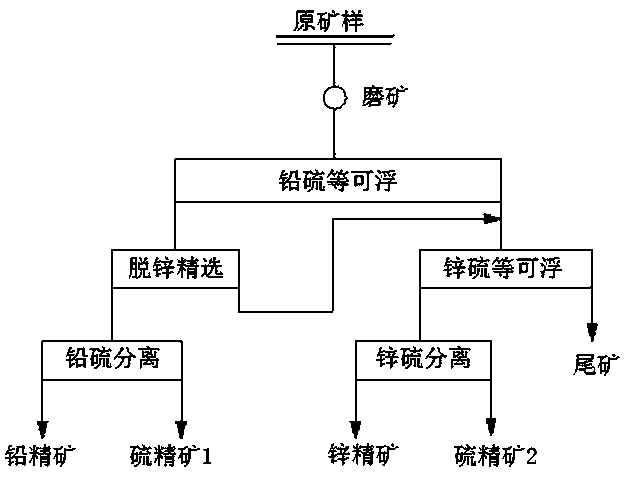
The invention discloses a lead and zinc flotation method to ferreous blende and pyrrhotite typed complex lead zinc silver sulphide ore, mainly comprising lead ore branch flotation which controls the electrochemical conditions of the flotation and the zinc and sulfur flotation separation which controls the electrochemical conditions of the flotation. The invention has the advantages of implementing the lead-zinc sulfur separation by adopting twice branch flotation, carrying out fast flotation to the lead ore by using a novel composite catching agent to the galena and silver ore with easy floating coarse grains under the conditions of higher ore pulp potential and low pH; the normal flotation of the lead ore with difficultly floated fine grains is carried out under the conditions of lower ore pulp potential and high pH. The pH of the ore pulp is adjusted to more than 12 by lime for the gangue after the lead is floated; the iron blende is activated by bluestone; the iron blende is recovered by the catching agent with the same type of the lead sulfide floatation, thus leading the property of the lead flotation waste water to be basically consistent with that of the zinc flotation waste water and being beneficial for the circular application of floatation waste water.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flotation method of brass ore-containing complex lead-zinc sulphide ore
The invention discloses a flotation method of a brass ore-containing complex lead-zinc sulphide ore, which comprises the steps of: adjusting the pH value to be 10-11 in the process of ore grinding; adding ore pulp electric potential regulating agent-sodium pyrosulfite to adjust the electric potential of the ore pulp to be at 220-260mV (relative to hydrogen standard potential); adding zinc sulfate, ethoxy-dithioformicacid ethyl formate and ethyl thio carbamate grinding ore; performing one roughing, one scavenging and two selecting to enrich copper-lead mineral by means of mixing and floating and to form into copper-lead mixed concentrate; performing reagent desorption to the copper-lead mixed concentrate by adding active carbon; adding potassium peroxydisulfate and carboxymethyl starch to restrain lead-containing mineral in the copper-lead mixed concentrate such as galena and the like; performing one roughing, one scavenging and three selecting to obtain copper concentrate; adjusting the pH value of tailings after recovering copper mineral by floating the copper-lead mixed concentrate to be 9.0; adding sodium pyrosulfite, ethyl thio carbamate and butyl ether alcohol; and performing one roughing, one scavenging and two selecting to obtain lead concentrate. The method guarantees the grade of the copper and the lead concentrate, and reduces the environmental pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
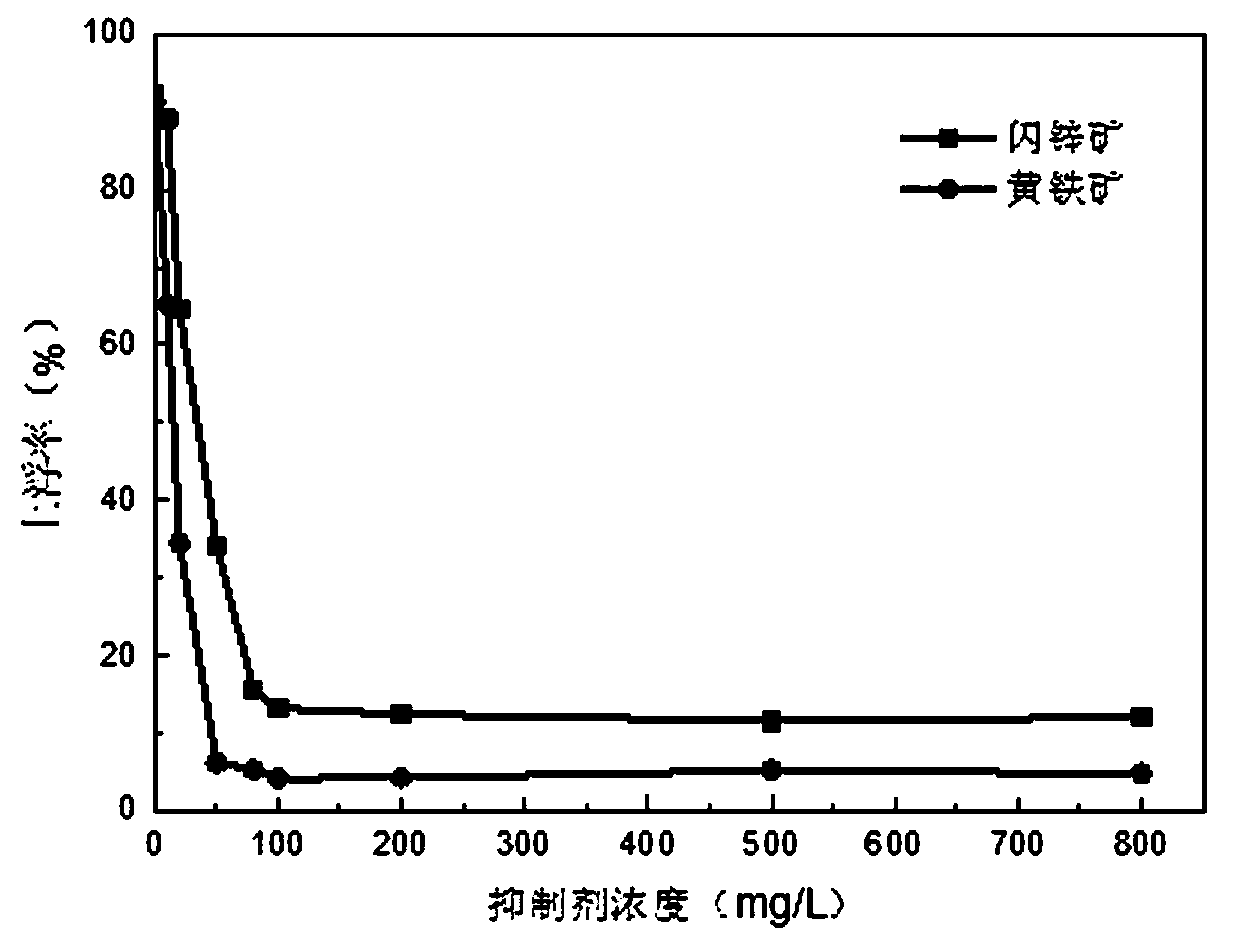
Flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite
InactiveCN103909020AEfficient separationPlay a synergistic roleFlotationEcological environmentSeparation technology
The invention discloses a flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The method includes adopting raw ores of sulfide lead-zinc mine as raw material, and adding SDSN (dimethyl dithiocarbamate : 2-(methylthio)ethylamine = 1-3:1)to serve as inhibitor of the pyrite and the sphalerite so as to perform lead and zinc sulphur flotation separation after the raw ores are grinded. Compared with an existing lead and zinc sulphur separation technology, the composite inhibitor SDSN has the advantages that selectivities of the pyrite and the sphalerite are high, inhibiting capability is high, usage is fewer, and adding is facilitated. The the pyrite and the sphalerite can be inhibited well, efficient separation of the galena and the zinc sulphur is implemented, the problems that according to the traditional lime or cyanide method, the recovery rate of associated gold, silver and other precious metals in the lead-zinc sulfide mine is low and ecological environment is seriously damaged are overcome, and an efficient and environment-friendly flotation separation method is provided for complex sulfide lead-zinc mine separation.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Method for floatation and recovery of lead zinc mixed concentrate from gold mine cyaniding slag tails
InactiveCN1865461AHigh recovery rateNo emissionsFlotationProcess efficiency improvementChlorinated limeSlag
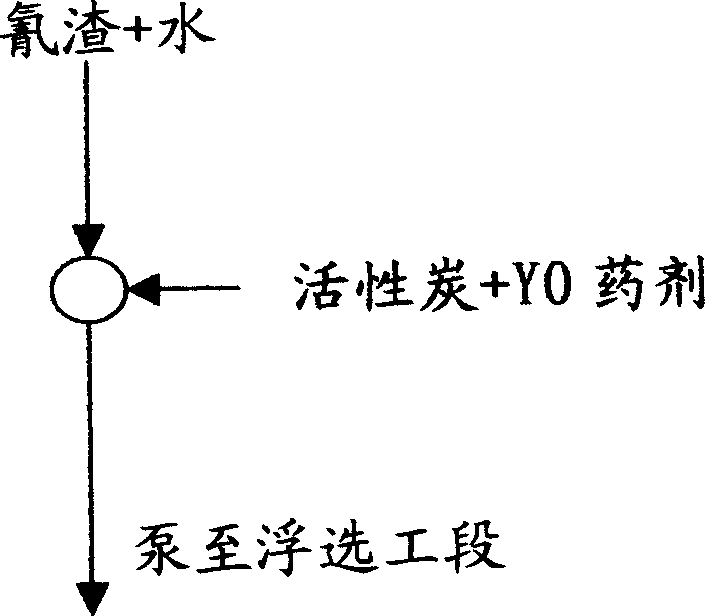
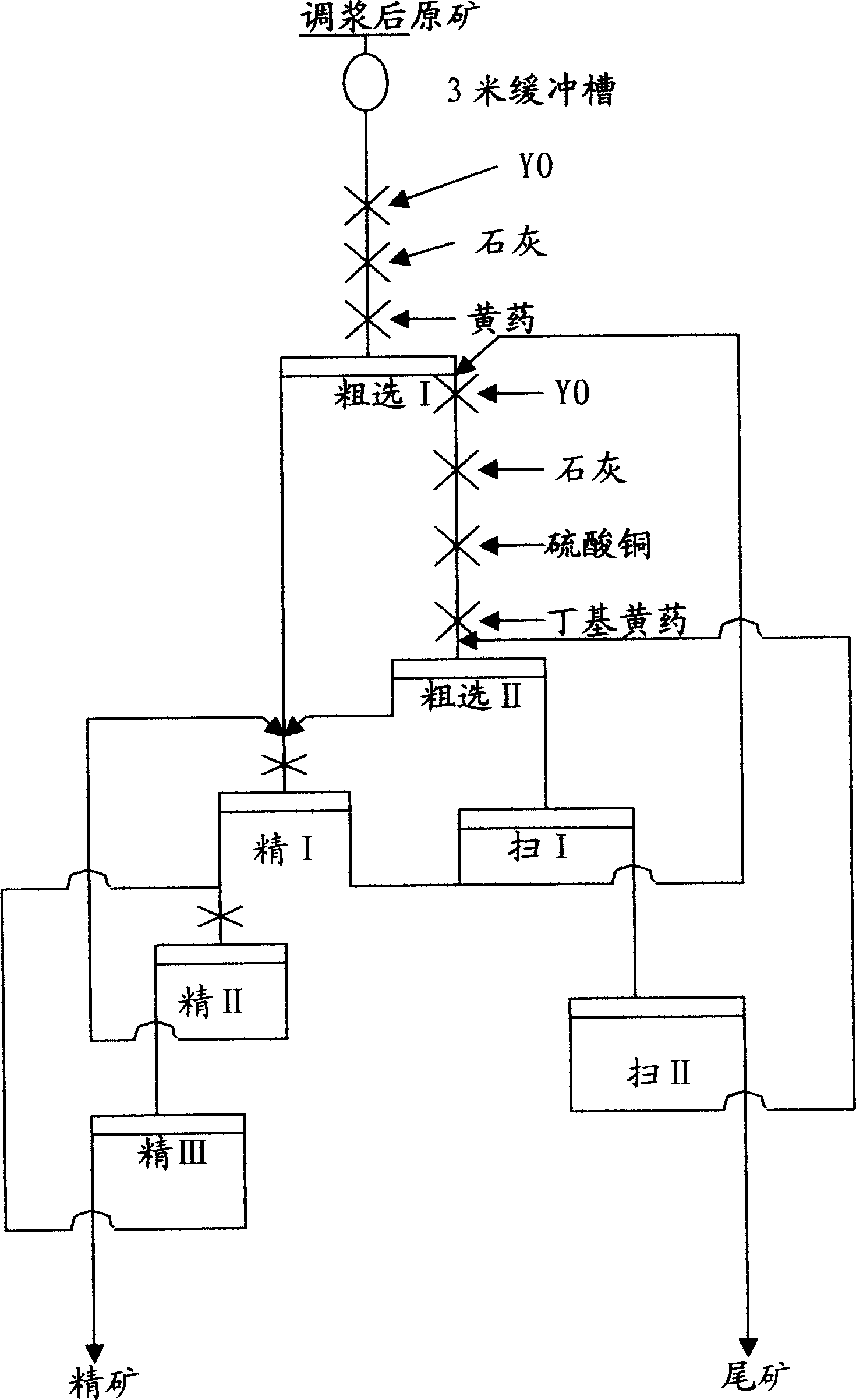
The invention discloses a lead-zinc floating recycling method from gold ore cyanation tailings, which comprises the following steps: (1) predisposing: adding water in the cyanation tailings; stirring to form ore paste; adding active carbon, Y0 agent, FeSO4+ammonium persulphate in the ore paste; (2) asynchronous mixing-selecting: sending the predisposed ore paste to the floater group I to proceed first roughing separation; adding Y0 agent, limestone, butyl airpotato yam to float galena; sending the tailings in the first roughing separation to floater group II; adding Y0 agent, limestone, cupric sulfate, butyl airpotato yam to float zincblende; (3) recycling and purifying tailing water: adding chlorinated lime in the tailing water to decompose CN- less than 0.5 mg per L; recycling the tailing water.
Owner:青岛黄金铅锌开发有限公司
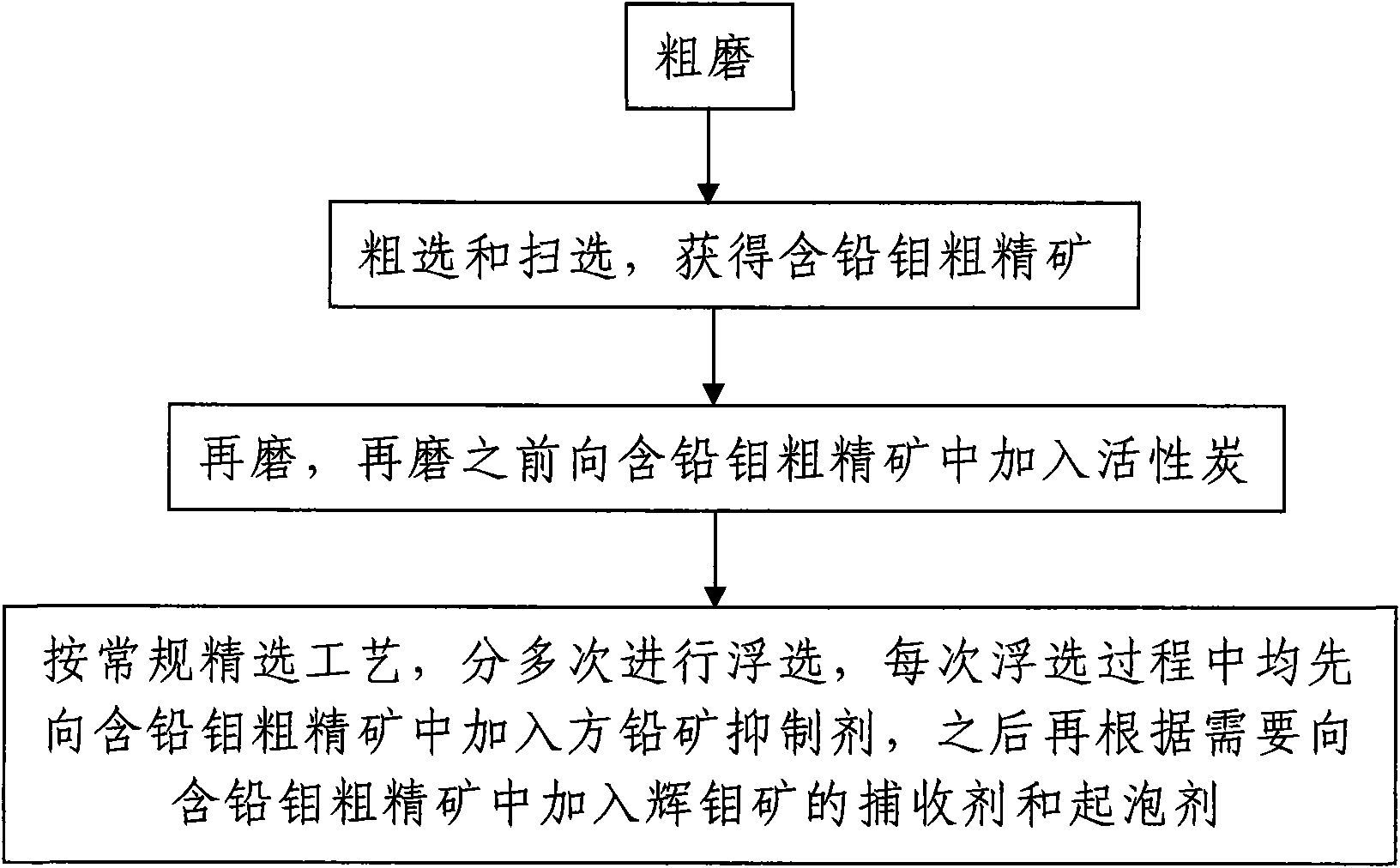
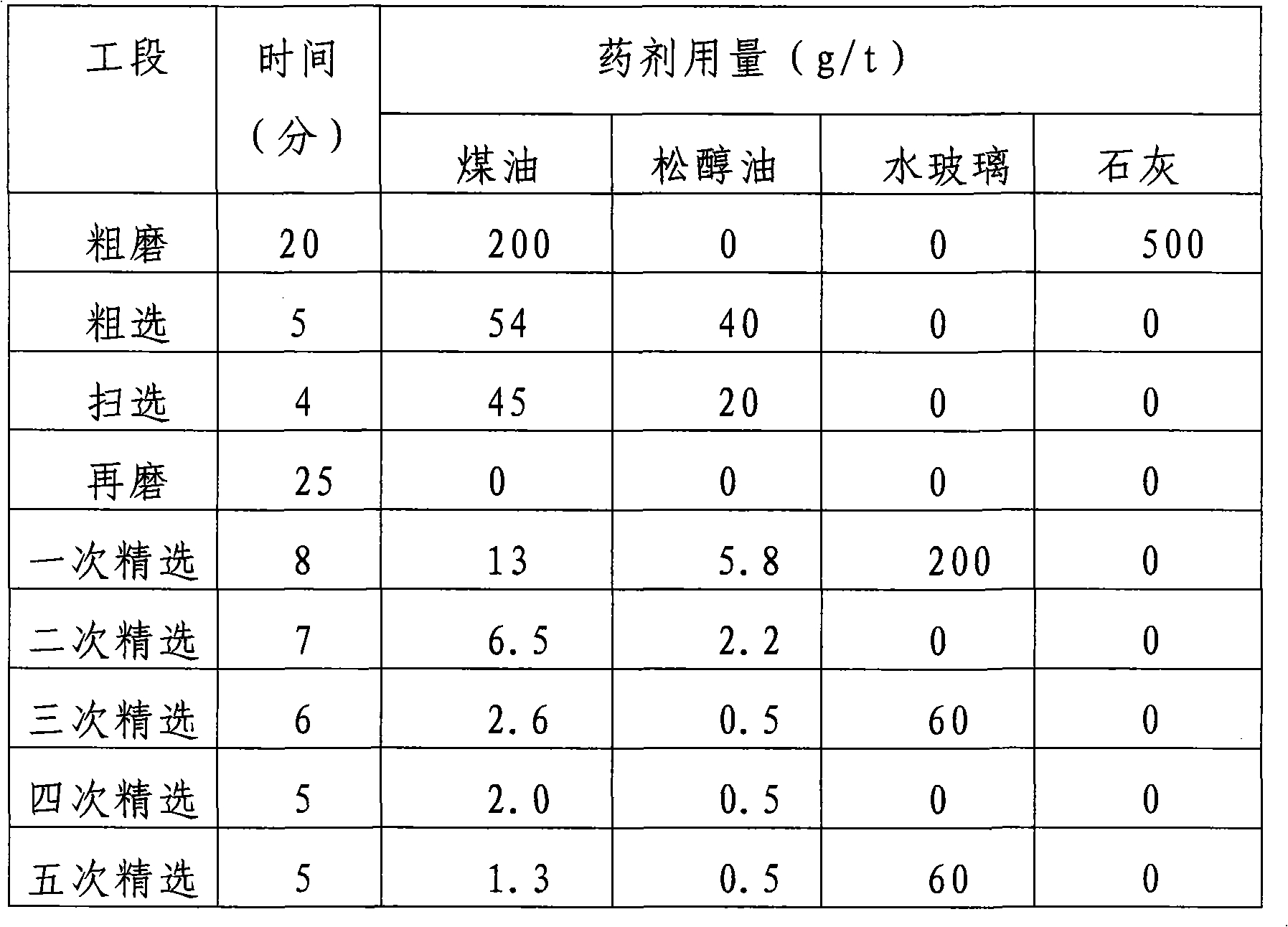
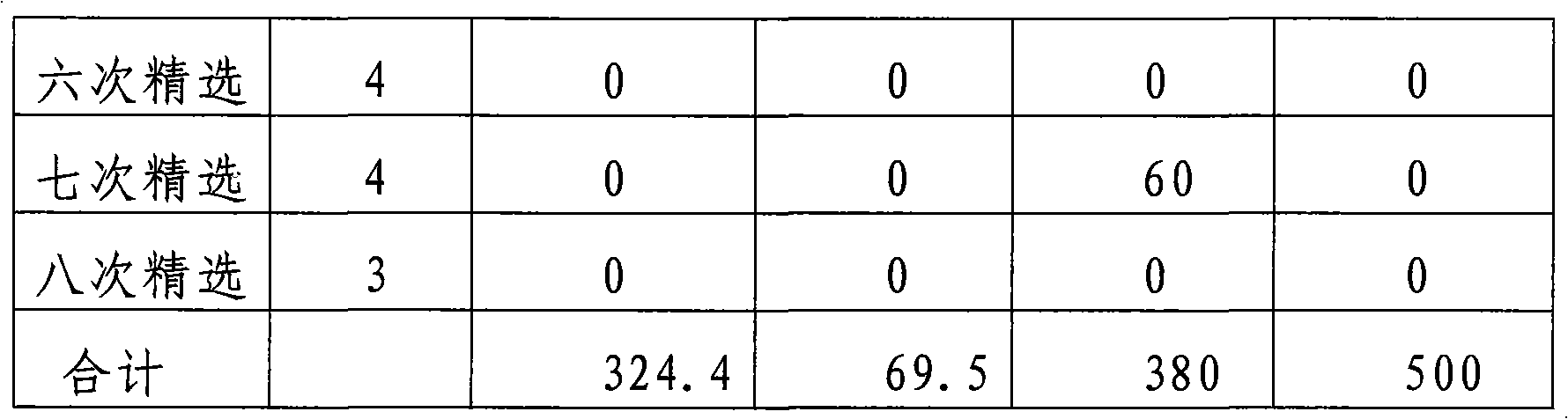
Flotation separation method for molybdenite and galena
The invention discloses a flotation separation method for molybdenite and galena, which comprises the following steps of: 1, rough grinding; 2, rough selection and scavenging for obtaining lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate; 3, regrinding after a certain amount of active carbon is added into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate; and 4, multiple selection: selecting the reground lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate for multiple times according to the conventional selection process, adding a galena inhibitor into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate at each time of selection, and then adding a molybdenite collecting agent and a foaming agent into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate as required. The method has the advantages of simple separation process, reasonable design, good separation effect and capabilities of reducing the lead content to be as minimum as possible in an ore dressing process of molybdenum, effectively improving the reclamation rate of the molybdenum and thoroughly reducing the pollution of the lead to the environment at the same time of reducing the molybdenum concentrate smelting production cost and simplifying the production process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Preparation method and application of non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor. The preparation method for the flotation and separation inhibitor comprises the step of enabling phosphorus pentasulfide and alkaline compounds to react with water-soluble macromolecules, and thus the flotation and separation inhibitor can be obtained. According to the preparation method for the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor, operation is easy, the process conditions are mild, the raw material cost is low, and the industrial production requirements are met; and moreover, the prepared product directly serves as the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral inhibitor applied to flotation and separation of molybdenum sulfide minerals and non-molybdenum sulfide minerals, the molybdenum sulfide minerals and the non-molybdenum sulfide minerals can be effectively separated, the grade of molybdenum concentrates is improved, and the flotation and separation inhibitor is particularly suitable for flotation and separation of molybdenite, copper sulfide ore, galena, pyrite, jamesonite, arsenopyrite, bismuth sulfide ore and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
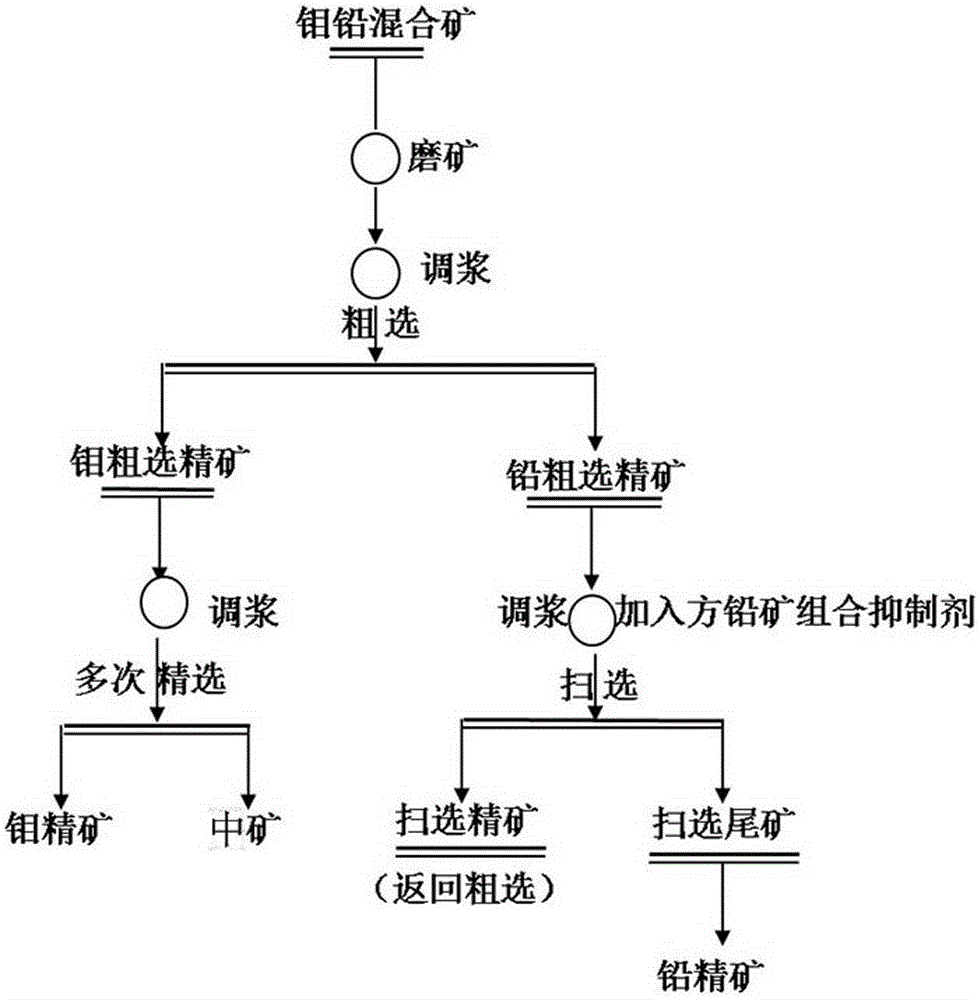
Separation mineral processing method for molybdenite and galena
The invention provides a separation mineral processing method for molybdenite and galena. The method is characterized in that molybdenum lead mixed ore, that is, raw ore is ground to be in the certain fineness, and the concentration and the PH of the slurry are adjusted; a galena combined inhibitor is added to restrain the galena, and a molybdenite collecting agent is added to achieve separation of the molybdenite and the galena; and the galena combined inhibitor is composed of ammonium sulfide, sodium sulfite and sodium pyrosulfite. A medicine agent used in the method is environment-friendly, and finally-obtained molybdenum concentrates and lead concentrates are high in grade. The mineral processing method is simple in technology, management and operation on site are easy, and the higher economic and technical indexes can be obtained through the technology.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105801458ASpecial molecular structureHas surfactant propertiesOrganic chemistryFlotationChloroformateNickel sulfide
The invention provides an ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or an ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular structure of the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative contains a large quantity of thioamide or thiourea or thioacid amide ether or other lipophilic groups and carboxyl hydrophilic groups. The preparation method includes the steps that bis-chloro-carbonic ester and thiocyanate are subjected to a substitution reaction, an intermediate product containing bis-acyl bis-isothiocyanate is generated, the intermediate and an alcohol compound or an amine compound or a phenol compound are subjected to an addition reaction, and then the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative is obtained. The preparation method is simple, the prepared product directly serves as a non-molybdenum sulphide ore inhibitor, and floatation separation of molybdenum sulfide ore and the non-molybdenum sulphide ore can be effectively achieved. The preparation method is especially suitable for separation of molybdenite and copper sulphide ore, galena, sphalerite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, jamesonite concentrate, nickel sulfide ore, bismuth sulfide ore and the like, and the grade of molybdenum concentrate is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for dismutation electrolytic production of hydrogen, copper, lead, zinc, acid and alkali-chloride by elemental sulfur
InactiveCN101368278AIncrease capacityReduce power consumptionPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsDecompositionGalena
The invention relates to a method for preparing H, Cu, Pb, Zn, acid and chlor-alkali through the disproportionation and electrolyzing of S; the catalyzing, disproportionation and electrolyzing of the element S at a normal temperature to prepare H is circulated; sulfurous acid is electrolyzed to prepare H; the NaHSO4, Na2SO4 and the H2SO4 converted by decomposition water, the hydrochloric acid, HCl and SO3 manufactured by the pyrolyzing of solid NaCl as well as concentrated H2SO4, Na2SO4 are disproportionated and reduced with the molten salt element S to generate SO2 and NaS; membrane electrolysis is carried out on Na2S to prepare H2, NaOH and regenerate S; the NaOH is concentrated by a fuel battery; alkali is disproportionated and catalyzed by the element S to decompose sulphide ores like a galena, a sphalerite, a copper pyrites, an iron pyrites, and the like. The sulphide ore is decomposed by the alkali; an infusion membrane is electrolyzed to prepare H2, regenerate NaOH and recover S; the anode membranes of CuCl and Na2S are electrolyzed in the same bath by an anode membrane to prepare Cu powder and regenerate S; the cathode membranes are electrolyzed to prepare Cu2O and H2; CuCl is electrolyzed with wasted copper in the same bath and the wasted copper is regenerated.
Owner:贾建立
Non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor and application thereof
ActiveCN110918263AEnhanced inhibitory effectEfficient flotation separationFlotationSulfide mineralsGalena
The invention relates to the technical field of non-ferrous metal beneficiation, in particular to a non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor and application thereof. The non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor isprepared from the following components in parts by mass: 1-3 parts of xanthan gum, 1-2 parts of pectin and 1-2 parts of arabic gum. The non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor is simple in preparation, lowin cost and green and environment-friendly and has a quite high inhibition effect on molybdenite, galena, sphalerite, pyrite and other sulphide ores in the copper bulk concentrate. With application ofthe inhibitor, efficient flotation separation of chalcopyrite and other sulfide minerals can be achieved.
Owner:SDIC XINJIANG LUOBUPO POTASH CO LTD
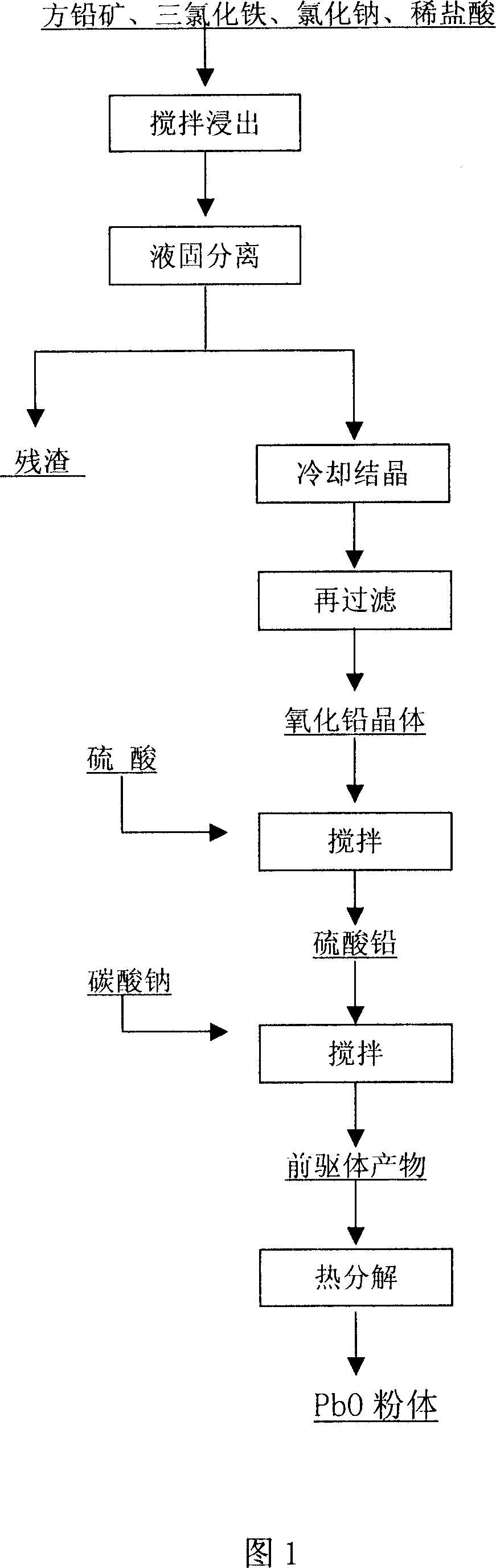
Method of directly producing ultra-fine lead oxide powder from galena concentrate
InactiveCN1920065AExpand sourceReduce contentLead monoxideProcess efficiency improvementLead carbonateLead oxide
The invention relates the method for producing super fine lead oxide powder from blue lead finished ore. The method comprises the following steps: using blue lead finished ore as raw material, leaching, crystallizing, getting PbCl2 crystal, adding sulfuric acid into PbCl2 crystal to get PbSO4 powder, carrying out chemical precipitation method for PbSO4 powder, getting the mixture of PbCO3 and 2PbCO3.Pb(OH)2, carrying out thermal decomposition, and getting the ultra-fine and high-purity beta-PbO. The method has the advantages of reducing the cost, extending the origin of raw materials, and reducing the impurity. The product has high activity, and the particle mean size of the products is 4.0-5.0 mum.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Application of aminotriazolethione compound serving as metal sulfide mineral surface modification agent
ActiveCN107029893ASpecial molecular structureSuppression of floatingFlotationBismuth sulfideChemical compound
The invention discloses application of an aminotriazolethione compound serving as a metal sulfide mineral surface modification agent. The aminotriazolethione compound comprises a hydrophilic modification perssad and an aminotriazolethione perssad at the same time. The aminotriazolethione compound mainly serves as the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral surface modification agent for flotation separation of the molybdenum sulfide mineral and the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral, the hydrophilia of the surfaces of the sulfide minerals with the natural hydrophobicity can be enhanced, especially, the hydrophilia of the surfaces of copper pyrites, chalcocite, galena, blende, brasses, the bismuth sulfide mineral and other non-molybdenum sulfide minerals can be effectively improved, and efficient flotation separation of the molybdenum sulfide mineral and the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for separating lead and antimony of jamesonite
InactiveCN102628108AAvoid the impact of incomplete separationNo need to consumeProcess efficiency improvementAlloyStibnite
The invention provides a method for separating lead and antimony of jamesonite. The method comprises the following steps: controlling proper heating temperature and condensing temperature according to the special molecular organization of the jamesonite (Pb4FeSb6S14); and respectively volatilizing and condensing galena (PbS) and stibnite (Sb2S3) by means of a special vacuum environment so as to effectively separate the lead and the antimony from each other. According to the invention, the galena and the stibnite can be directly obtained by directly treating the jamesonite; the jamesonite is treated by using an economic and environment friendly vacuum technology and no reagent needs to be consumed; and the method for separating the lead and the antimony of the jamesonite, provided by the invention, has the advantages of low production cost, no pollution to the environment, no requirement on raw material component content, and wide adaptability; and because no alloy is generated, the product can be directly used for smelting lead-antimony metals.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
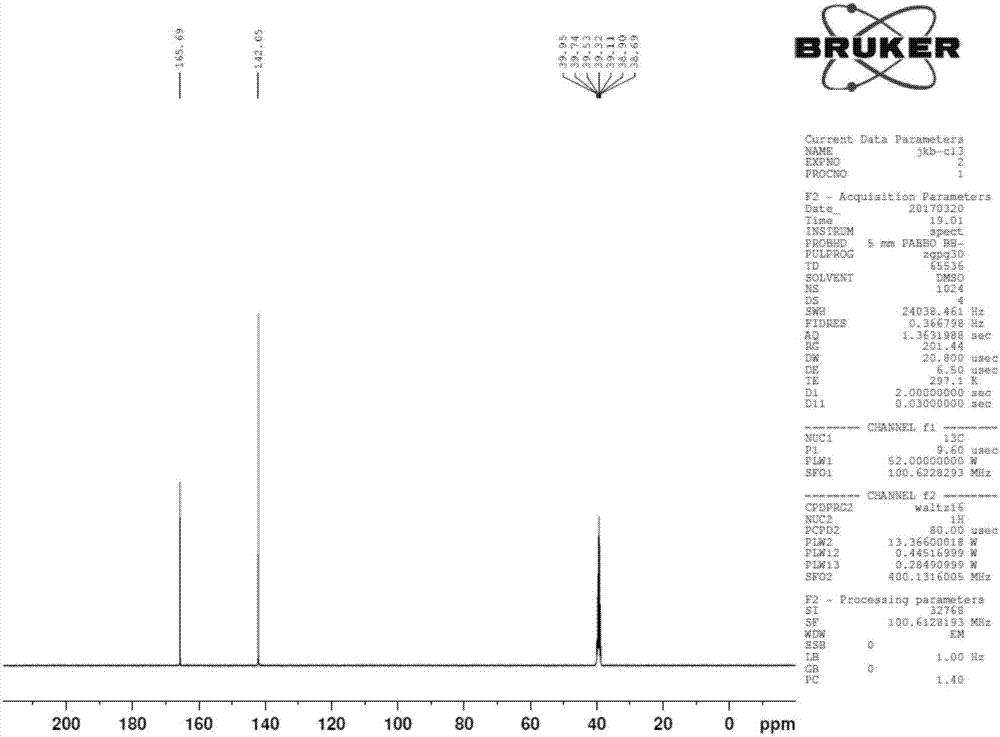
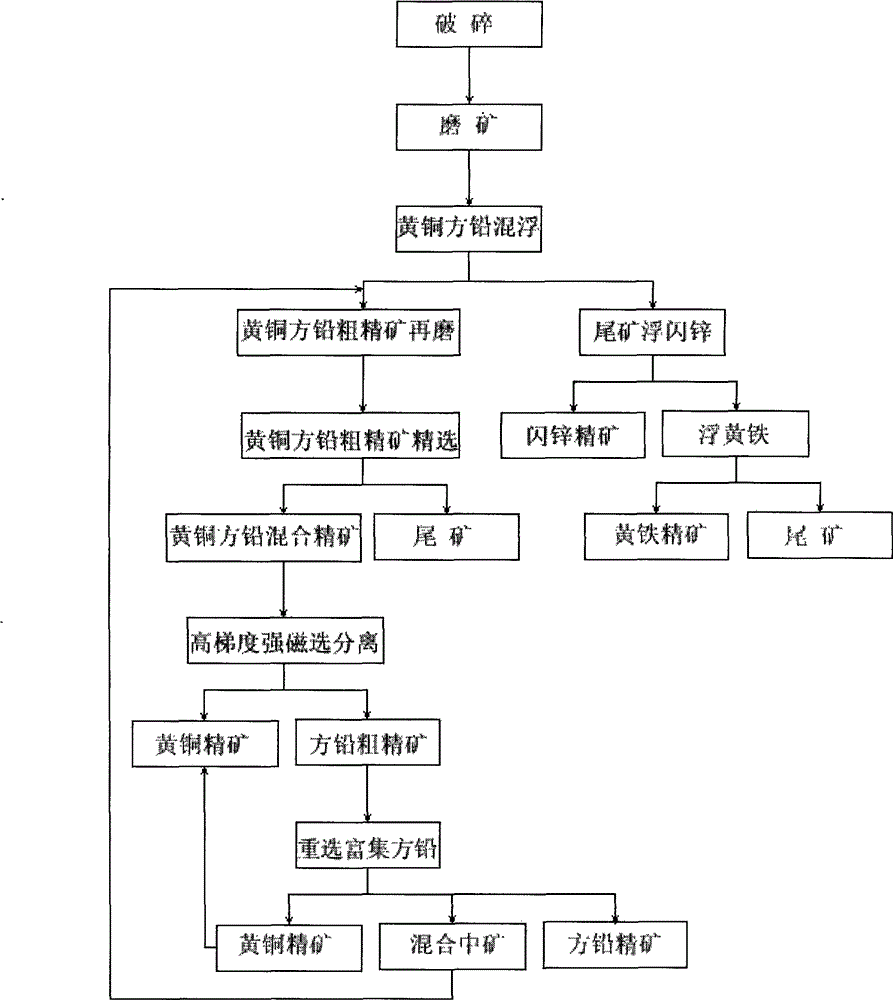
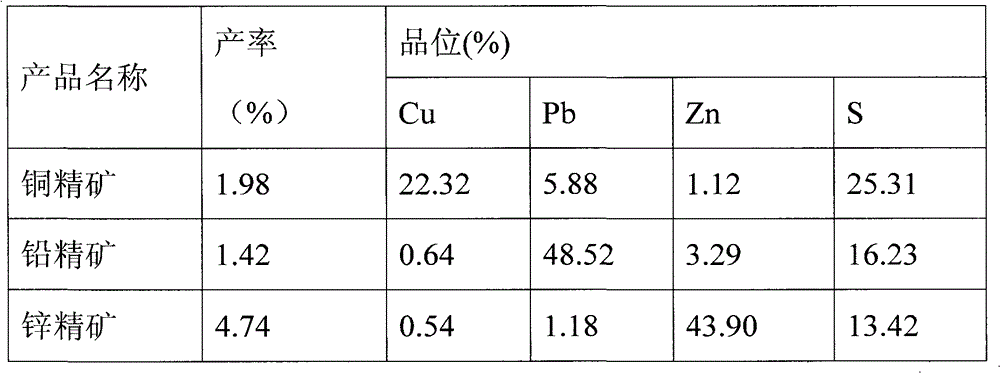
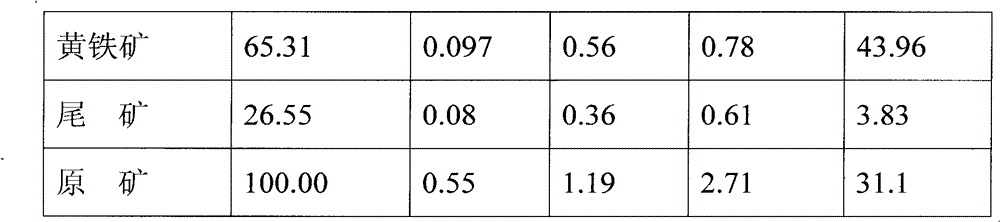
Mineral processing technology combined with high-gradient high-intensity magnetic separation, re-grinding, re-separation and flotation
The invention provides a mineral processing technology combined with high-gradient high-intensity magnetic separation, re-grinding, re-separation and flotation, wherein after crude brass, galena, blende and pyrite are crushed and grinded as raw materials, the brass and the galena are mixed for the routine flotation for enrichment of brass and galena; after rough concentrate is re-grinded, the flotation of a concentrate is performed, in order that the quality of the mixed brass and galena is improved; next, the high-gradient high-intensity magnetic separation is carried out to separate the brass from the galena, so that the qualified brass concentrate is obtained; tailings are re-separated in order that the galena, the brass and other impurities are separated; in this way, a galena concentrate is obtained; ores which are being re-separated return to a technology for re-grinding the rough concentrate of the brass and the galena to enter a circulation system; the post-mixed tailings of the brass and the galena undergo the router flotation of the blende and the pyrite, so that a qualified blende concentrate and a qualified pyrite concentrate are obtained; and as such, separation of the brass, the galena, the blende and the pyrite which are complicated and are difficultly separated is realized. The technology has the advantage that the defects that the brass and the galena are low in quality and are mixed with each other during the separation of the brass and the galena are prevented.
Owner:北京华夏建龙矿业科技有限公司
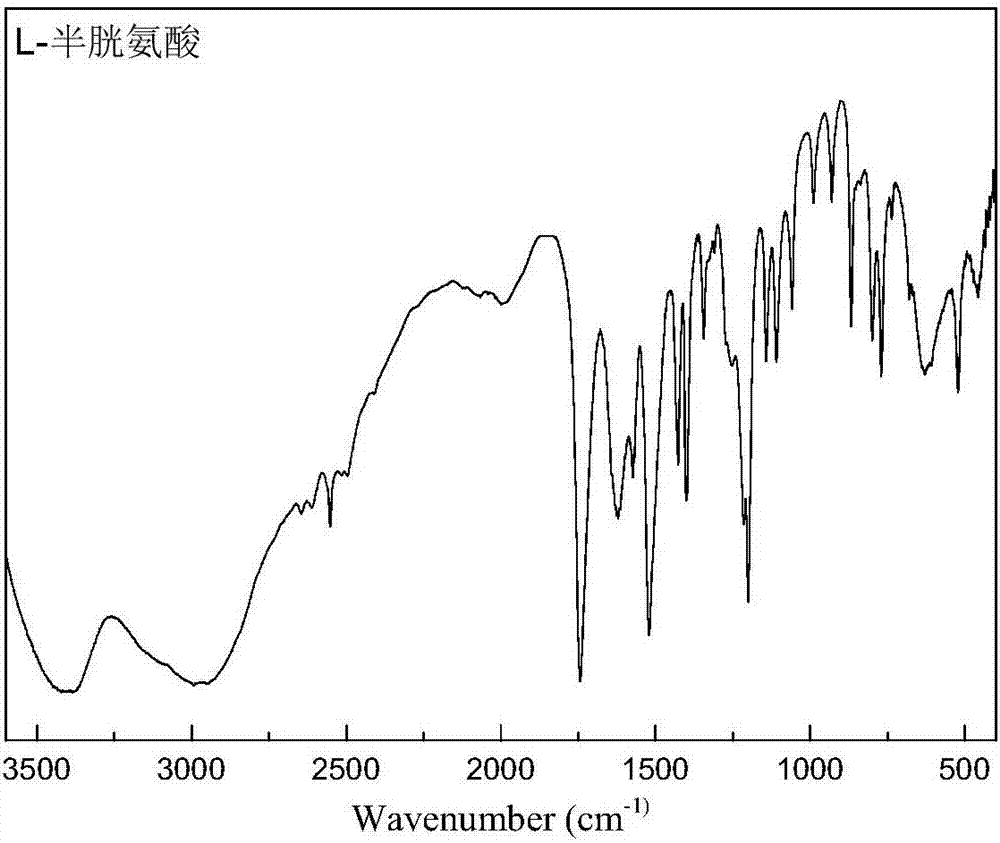
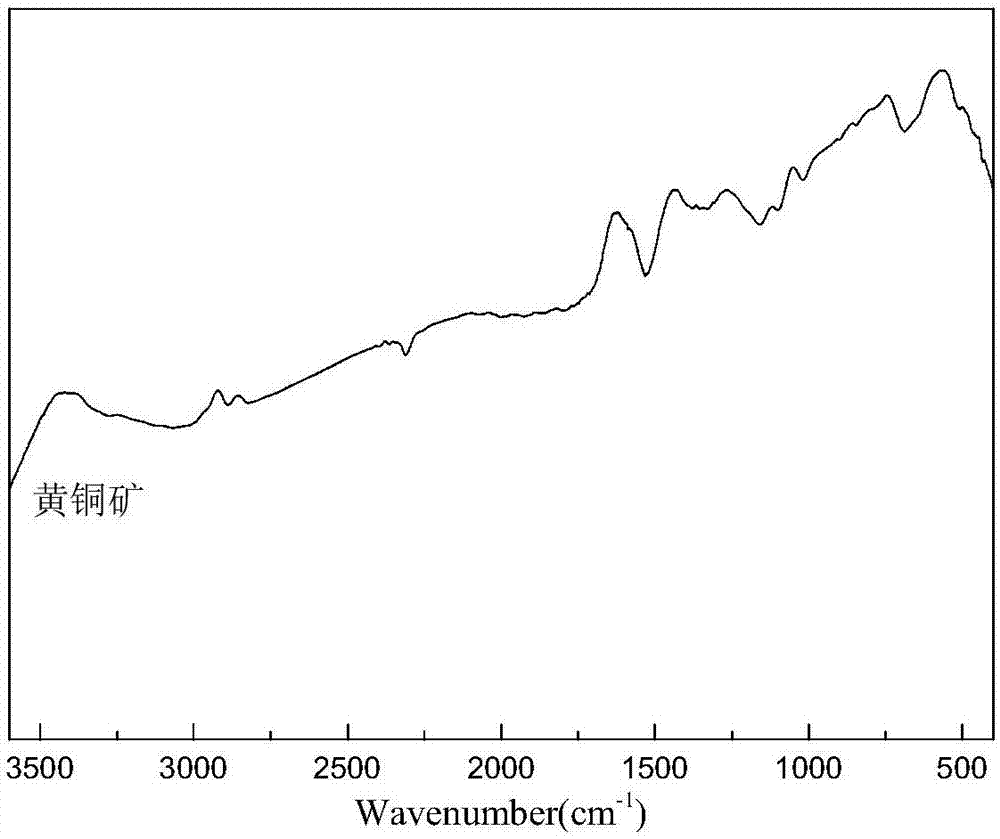
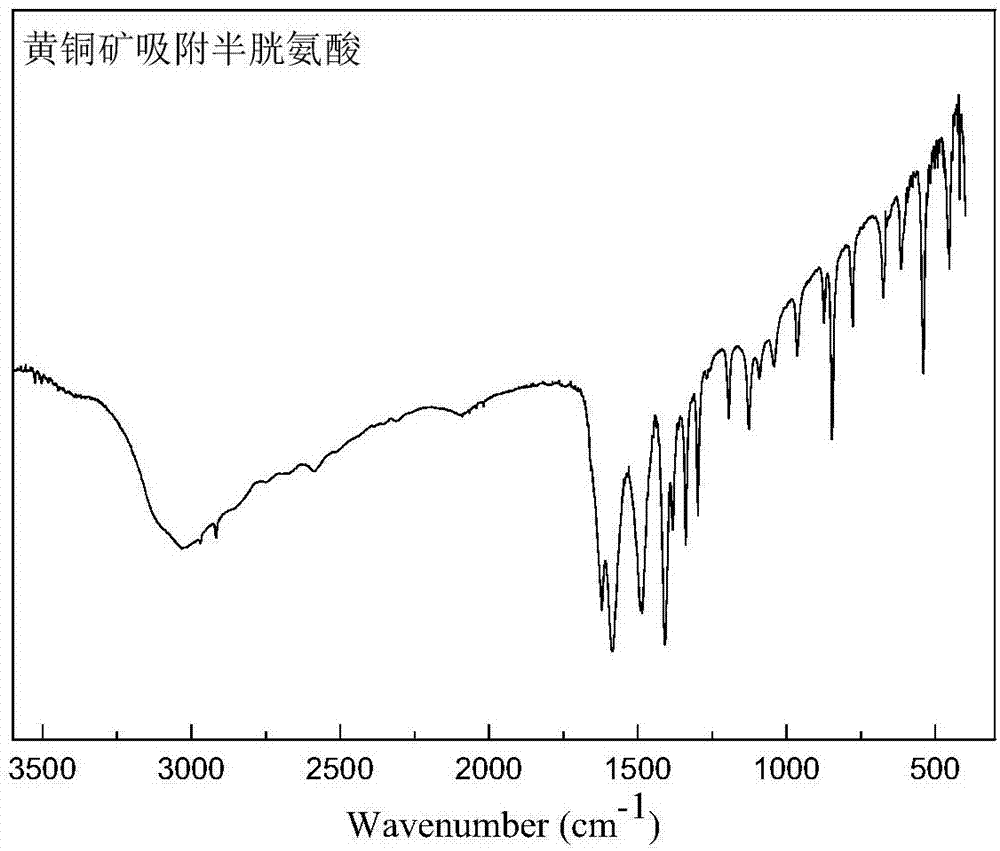
Application of L-cysteine and L-cysteine salt in metal sulfide mineral flotation separation
InactiveCN107138286AImprove surface hydrophilicityEfficient flotation separationFlotationBismuth sulfideCysteine thiolate
The invention discloses application of L-cysteine and L-cysteine salt in metal sulfide mineral flotation separation. L-cysteine and / or L-cysteine salt are / is used as non-molybdenum sulphide mineral inhibitors to be applied to flotation separation of sulphur molybdenum and non-molybdenum sulfide mineral; and the molecular structure of L-cysteine simultaneously contains three kinds of functional groups comprising sulfydryl, amidogen and carboxyl, wherein sulfydryl and amidogen are solid-philic groups and can be combined with metal ions to generate stable pentacyclic chelate, and carboxyl is a hydrophilic group mainly. The L-cysteine is mainly used as a non-molybdenum sulfide mineral surface modification activator, can enhance the hydrophilia of the surface of the sulfide mineral with the natural hydrophobicity, particularly can effectively enhance the hydrophilia of the surface of the non-molybdenum sulphide mineral such as copper pyrites, chalcocite, galena, blende, iron pyrite and bismuth sulfide ore, restrains upward flotation of the non-molybdenum sulphide mineral, and achieves efficient flotation separation of the sulphur molybdenum and the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral.
Owner:刘秀云
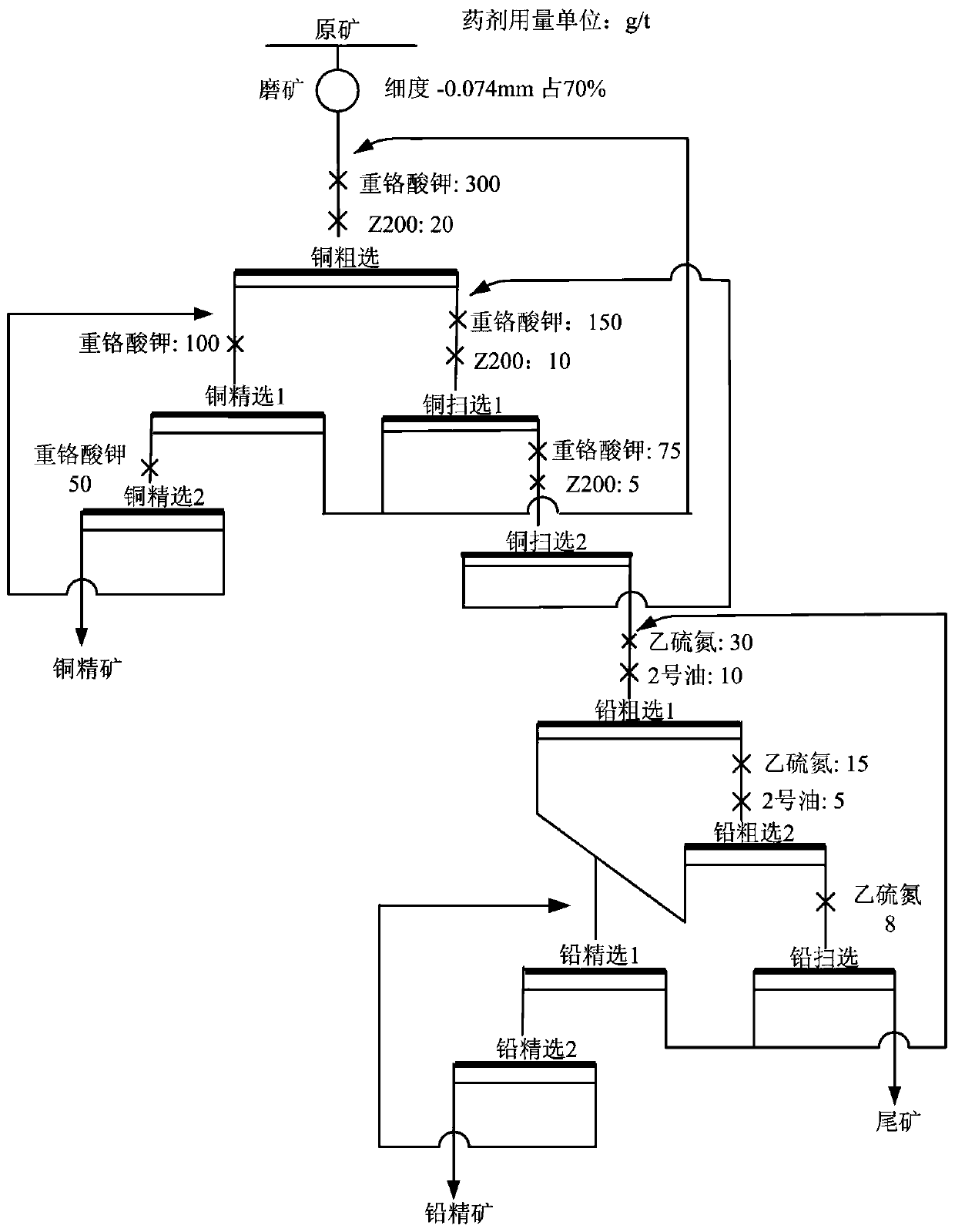
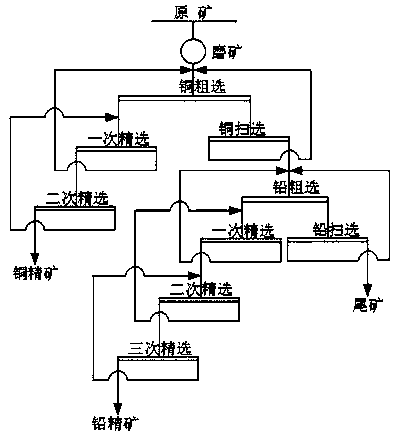
Differential flotation method for copper lead sulfide minerals
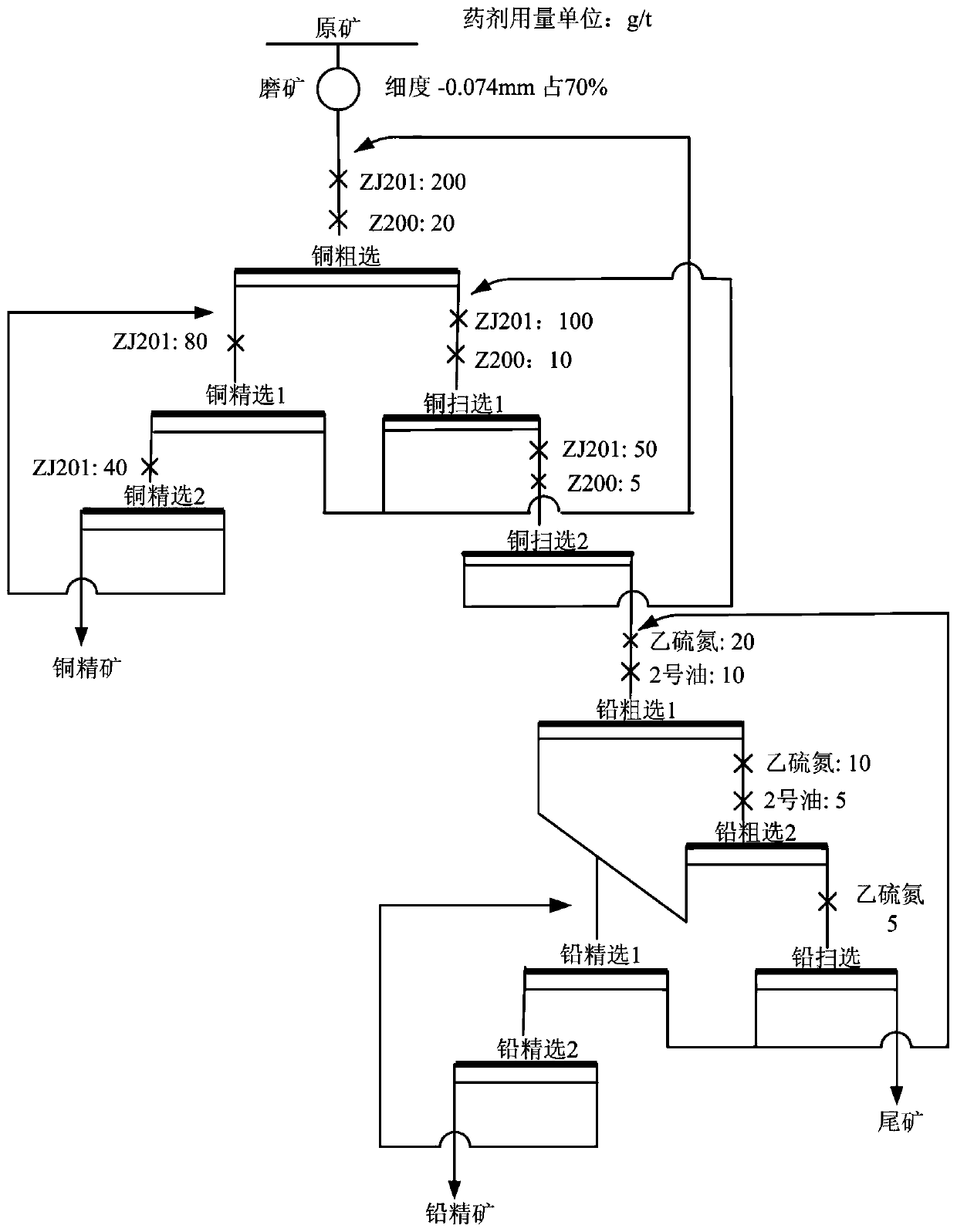
The invention relates to a differential flotation method for copper lead sulfide minerals. The differential flotation method comprises the following conventional procedures: grinding raw ore; carryingout roughing on copper, and then separating the copper having undergone roughing into two copper paths; subjecting copper in one of the copper paths to secondary copper concentration so as to obtaina copper concentrate, and other in the other of the copper paths to secondary copper scavenging and secondary lead roughing; further dividing a material obtained after secondary copper scavenging andsecondary lead roughing into two branches; and subjecting one branch of the material to lead concentration so as to obtain a lead concentrate and subjecting the other branch of the material to secondary lead scavenging so as to obtain tailings. The differential flotation method is characterized by further comprising a step of preparation of a galena inhibitor ZJ2001. The ZJ201 is used for inhibiting lead sulfide ore at first, and then ethyl thio carbamate is used for flotation of the lead sulfide ore; and the lead sulfide ore suppressed by ZJ2001 can be floated without any activation in advance. The self-made galena inhibitor ZJ2001 is capable of efficiently separating various minerals in the copper lead sulfide minerals, substantially improves the recovery rate and quality of the copper concentrate and the lead concentrate, and has the advantages of no toxicity, environment friendliness, low usage amount, low cost, safety in addition, convenience in usage, promotion and application value in the flotation separation of copper lead sulfide minerals, etc. The method of the invention is applicable to the field of mineral processing.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP +1
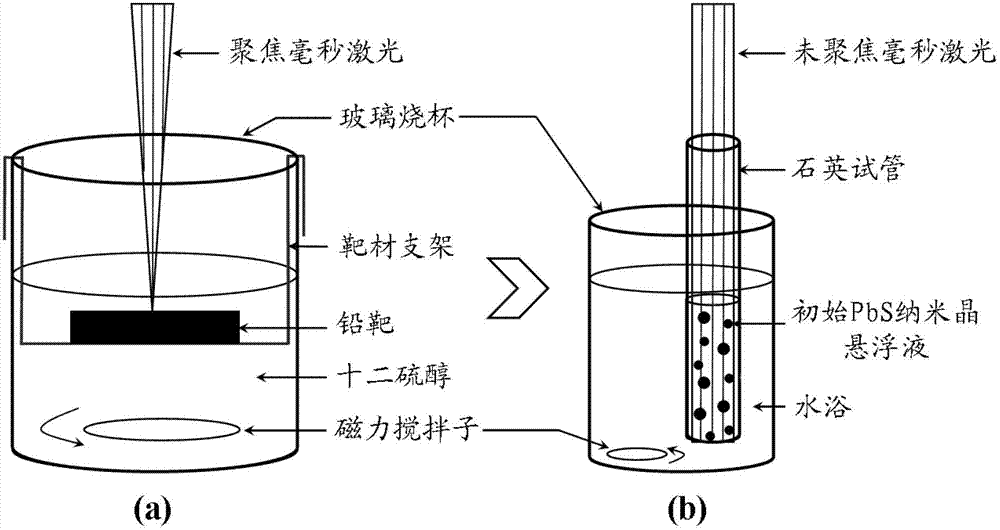
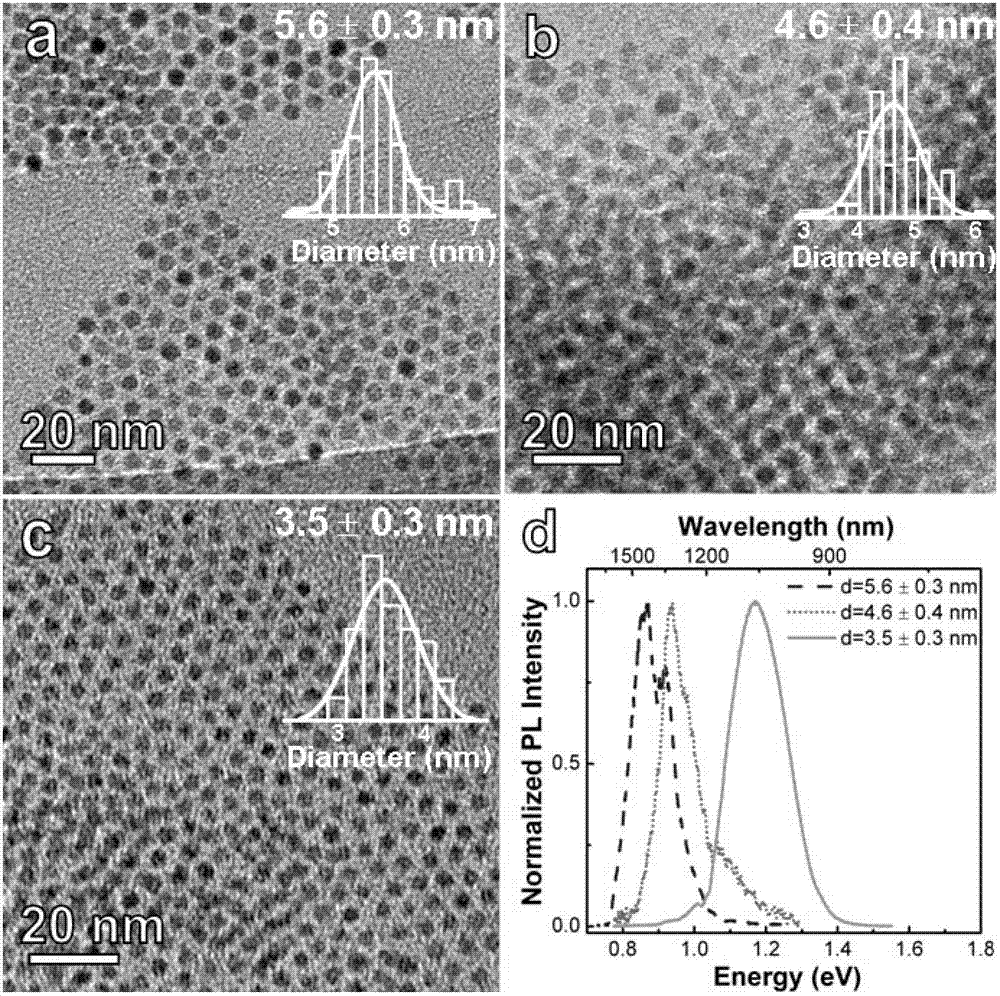
Method for synthesizing monodisperse colloid lead sulphide quantum dots with laser
InactiveCN102826596AAchieving controllable synthesisGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyLead sulfidesWater bathsReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing monodisperse colloid lead sulphide quantum dots with laser; a block-shaped metal lead target serves as a raw material and is arranged in dodecyl mercaptan, and millisecond pulse laser is used for ablating the lead target; a product which is ablated by the laser is purified, dried, weighed and re-scattered in the dodecyl mercaptan, and initial galena nanocrystalline suspension with the concentration being 4.3mM is prepared; 90 percent of the dodecyl mercaptan is added into the initial galena nanocrystalline suspension with the volume percentage being 10 percent, and initial galena nanocrystalline suspension with the concentration being 0.43mM is obtained and heated in water bath; and millisecond pulse laser which is not focused is used for radiating the suspension for 20 minutes, and the high-purity monodisperse colloid lead sulphide quantum dots with good dispersion and crystallinity are obtained. According to the method for synthesizing monodisperse colloid lead sulphide quantum dots with laser, the process is simple and convenient, the control is easy, no by-products and impurities are produced, raw materials are simple and low-toxin, the reaction temperature is low, and the method is an environment-friendly green synthesis process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Methods of reducing sag in non-aqueous fluids
InactiveUS20050164891A1Reduce saggingHigh viscosityFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic EsterEmulsion
Methods of reducing sag include combining a cystol ester compound with a non-aqueous fluid and particles to reduce sag in the resulting fluid composition without significantly increasing the viscosity of the fluid composition. The fluid composition comprises the non-aqueous fluid, the particles, and the cystol ester compound. Suitable cystol ester compounds include cystol ester and derivatives of cystol ester having mono-, di-, or tri-substituted aromatic compounds as substituents. The non-aqueous fluid -may comprise an invert emulsion, diesel oil, mineral oil, an olefin, an organic ester, a synthetic fluid, or combinations thereof. Further, the fluid composition may be used as a wellbore servicing fluid such as a drilling fluid. The particles may comprise a weighting agent, e.g., barite, galena, hematite, dolomite, calcite, or combinations thereof. The fluid composition may also include organophilic clay.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Process for separating molybdenum from lead in high-lead molybdenum ore
InactiveCN105597945AEnhanced inhibitory effectControl flotation speedFlotationGalenaMaterials science
The invention discloses a process for separating molybdenum from lead in high-lead molybdenum ore. The process comprises the following step: performing primary classification on crude ore after primary grinding. The process further comprises the following steps: firstly, feeding overflow of primary classification into a flotation machine or a flotation column for roughing so as to obtain rougher foams and rougher tailings, and adding a phosphorus-Nokes inhibitor into roughing; secondly, feeding the rougher tailings into the flotation machine for primary rough scavenging; thirdly, feeding the tailings after primary scavenging into the flotation machine for secondary rough scavenging; fourthly, performing rough concentration on the rougher foams so as to obtain rough concentrate, feeding the rough concentrate into a hydrocyclone for secondary classification, regrinding the bottom flow after secondary classification, and feeding back to the hydrocyclone for reclassification; fifthly, concentrating the overflow after secondary classification. As the phosphorus-Nokes is added into the roughing operation to pre-inhibit galena, a remarkable galena inhibition effect can be achieved, technical indexes such as the rough concentrate molybdenum recycling rate and the yield are equivalent to those of an original process, and no adverse effect can be caused to concentration.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for separating lead concentrate from ore
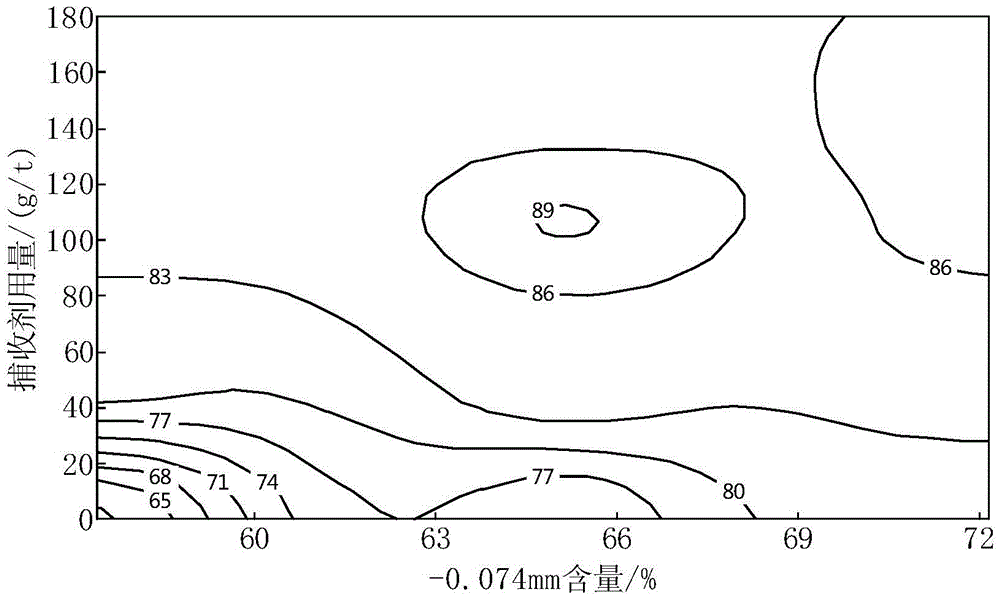
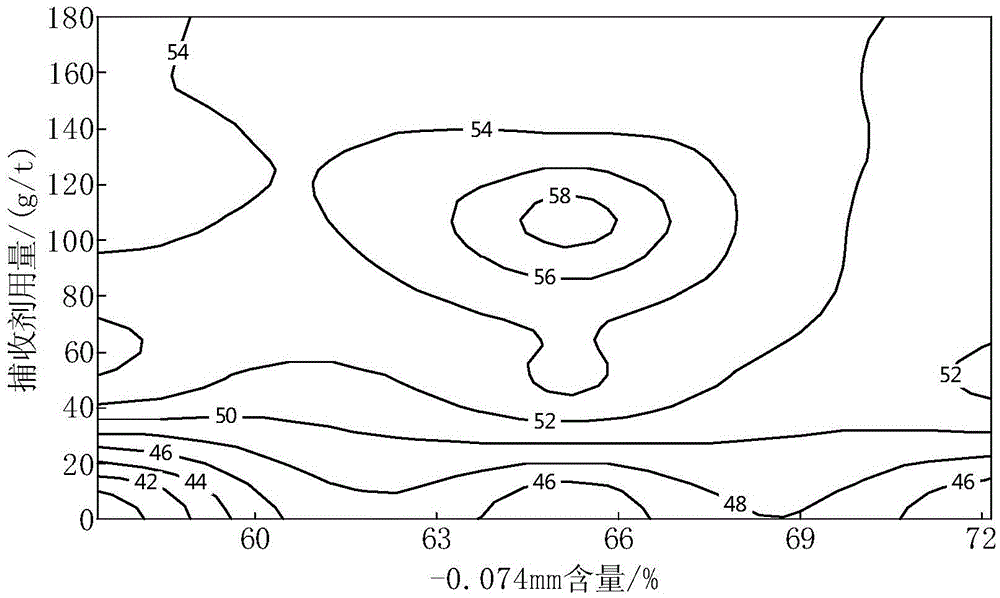
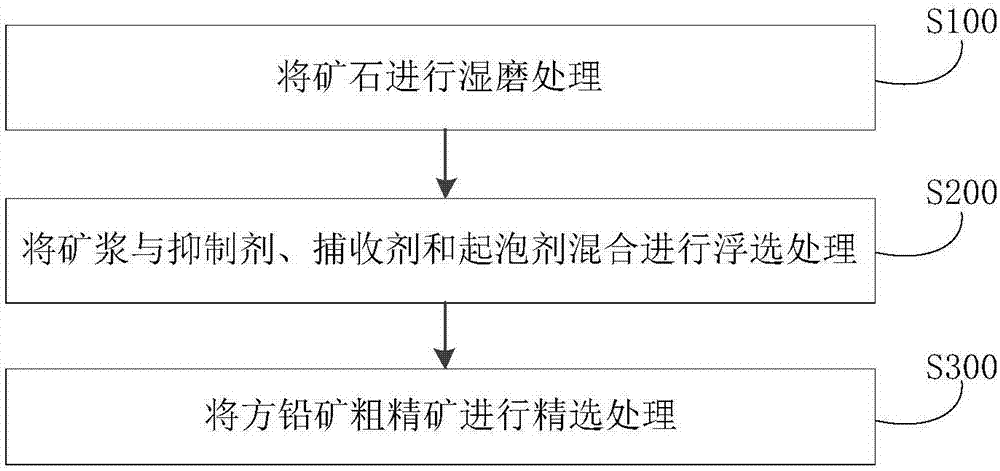
The invention discloses a method for separating lead concentrate from ore. The ore comprises galena, pyrite and marmatite. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out wet grinding treatment on the ore to obtain ore pulp; 2 mixing the ore pulp with an inhibitor, a collecting agent and a foaming agent to carry out flotation treatment so as to obtain rough concentrate and tailings of galena; and 3, carrying out selection treatment on the rough concentrate of galena to obtain lead concentrate. With adoption of the method, the grade of the lead concentrate can be increased by 68% or above, the cost is low, the environmental protection is realized and the economic benefit is remarkable.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Flotation separation method of refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore and sphalerite inhibitor of refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore
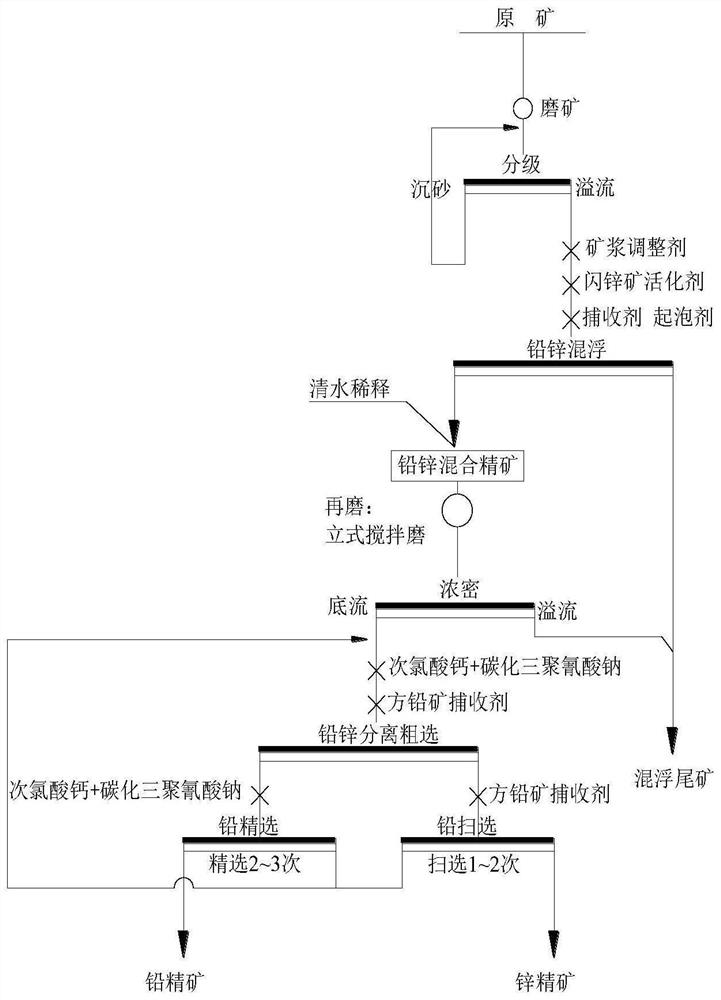
The invention discloses a flotation separation method of refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore and a sphalerite inhibitor of the refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore, the sphalerite inhibitor is a composition of calcium hypochlorite and carbonized sodium cyanurate, the mass ratio of calcium hypochlorite to carbonized sodium cyanurate is 1: (2 to 4), and the inhibitor composition can have a strong inhibition effect on sphalerite. The invention further provides a flotation separation method of the refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore, the refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore is subjected to ore grinding and grading treatment and size mixing, a sphalerite activating agent, a flotation collecting agent and a foaming agent are added, then inflation flotation is conducted, lead-zinc bulk concentrate dense underflow is obtained through regrinding and thickening, and the sphalerite inhibitor and a galena collecting agent are added for flotation separation; and the separated lead rough concentrate is subjected to sphalerite inhibition and repeated concentration to obtain lead concentrate, the galena collecting agent is added into the separated lead rough concentrate for repeated lead scavenging to obtain zinc concentrate, and therefore the refractory lead-zinc sulfide ore is economically and efficiently separated and enriched, and the method has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHONGJIN LINGNAN MINING CO LTD +1
Low-sulfur type copper-lead-zinc polymetallic ore sequential preferential flotation separation method
The invention discloses a low-sulfur type copper-lead-zinc polymetallic ore sequential preferential flotation separation method. According to the technical scheme, flotation of copper is carried out before flotation of lead. In the preferential flotation of copper, a combined inhibitor T-9 is used, and effective separation of valuable element copper in ore from lead and zinc is realized under the condition of pH 6-7. In the preferential flotation of lead, an inhibitor F-8 is used, and floating of zinc mineral is effectively inhibited. The T-9 reduces floatation activity of lead and zinc minerals and effectively increases floatability difference between copper and lead and zinc minerals, and the composition is nontoxic and harmless and is green and pollution-free. The inhibitor F-8 has a good inhibiting effect on sphalerite, has high activity to galena and silver mineral, has a certain collecting effect on galena, and is good for reducing mutual Inclusion of lead and zinc in the product. By the method, the target minerals copper, lead and zinc are effectively separated, thus achieving the purpose of comprehensive recovery and utilization of mineral resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Hydrazine derivative, preparation method of hydrazine derivative and application of hydrazine derivative as sulphide ore surfactant
ActiveCN106748938ASpecial molecular structureHas surfactant propertiesOrganic chemistryFlotationTroiliteHydrazine compound
The invention provides a hydrazine derivative, and a preparation method and application of the hydrazine derivative. .The hydrazine derivative structurally contains sulphide ore surface solid-tropy groups of hydrazine, dithioacid and the like, and hydrophilic groups of carboxyl, sulfonic group, hydroxyl, amidogenand the like. According to the preparation method, the hydrazine and carbon disulfide take a reaction under the alkaline condition to obtain 1-diazanyl-dithio formate; the 1-diazanyl-dithio formate takes a reaction with one-molecule or two-molecule halogenated carboxylate to obtain the hydrazine derivative; the hydrazine derivative is used as the sulphide ore modified surfactant. The hydrophilicity of the sulphide ore with the natural hydrophobicity can be enhanced; particularly, the hydrophilicity of non-molybdenum sulphide ore such as chalcopyrite, chalcocite, galena, blende, troilite and bismuth sulphide ore can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-voltage electric pulse pretreatment method for strengthening galena crushing and sorting
ActiveCN110215984AImprove sorting indexPromote productionGrain treatmentsPretreatment methodEngineering
The invention relates to a high-voltage pulse pretreatment method for strengthening galena crushing and sorting. The method adopts a high-voltage pulse device, and is carried out according to the following steps that (1) a water pump is started to enable water to continuously enter a pulsating insulating barrel and be discharged from a water outlet of a product collector; (2) galena ore is transferred to a pulse insulating barrel through a ore feeding bin, and stacked on a screen with the top in contact with a high voltage electrode; (3) a power supply is turned on, discharging occurs betweenthe high-voltage electrode and a high-voltage negative electrode, so that the galena ore is crushed; (4) a pulsating conical body moves up and down periodically through the rotation of an eccentric wheel, and the small particle part of the galena ore on the screen gradually moves downwards; and (5) the crushed galena ore enters the product collector. By means of the method, the useful mineral content of a crushed product can be increased, the monomer dissociation degree of the crushed product can be improved, the reduction of the energy consumption of subsequent processing procedures is facilitated, and the enterprise cost is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Composite inhibitor for galena and application method thereof
The invention discloses a composite inhibitor for galena and an application method thereof. The composite inhibitor comprises the following raw materials of, in percentage by weight, 10-14% of ferricsulfate, 18-22% of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether, 13-17% of glycerol, 20-26% of carboxymethyl cellulose, and 26-32% of sodium silicate; the ferric sulfate, the fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether, the glycerol, the carboxymethyl cellulose, and the sodium silicate are separately prepared into a solution with the mass percent concentration of 10% under the normal temperature status, then all the solutions are mixed, and uniformly stirring is carried out to obtain an emulsion so as to obtain the composite inhibitor for later use; and the composite inhibitor is added in the rough flotation process of the galena, the next step is carried out after stirring, and the composite inhibitor is added in the copper scavenging process, the use amount of the composite inhibitor is half of the use amount of the rough flotation, and the next step is carried out after stirring. The composite inhibitor is added in the copper-lead separation process, so that the qualities of copper concentrate and lead concentrate can be remarkably improved, and the flotation recovery rate of copper-lead minerals is improved. The composite inhibitor and the application method thereof has the advantages of beingenvironment-friendly, high in sorting efficiency, low in reagent cost, simple and convenient and the like, and is suitable for beneficiation of complex copper-lead sulfide ores.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods of reducing sag in non-aqueous fluids
Methods of reducing sag include combining a cystol ester compound with a non-aqueous fluid and particles to reduce sag in the resulting fluid composition without significantly increasing the viscosity of the fluid composition. The fluid composition CONTAINS the non-aqueous fluid, the particles, and the cystol ester compound. Suitable cystol ester compounds include cystol ester and derivatives of cystol ester having mono-, di-, or tri-substituted aromatic compounds as substituents. The non-aqueous fluid may CONTAINS an invert emulsion, diesel oil, mineral oil, an olefin, an organic ester, a synthetic fluid, or combinations thereof. Further, the fluid composition may be used as a wellbore servicing fluid such as a drilling fluid. The particles may CONTAINS a weighting agent, e.g., barite, galena, hematite, dolomite, calcite, or combinations thereof. The fluid composition may also include organophilic clay.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Method of selectively leaching lead sulphide from lead sulphide bearing material
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for lead glance and other lead-containing sulfide materials and minerals, including ores, concentrates, tailings and other similar materials or wastes. These materials may be flotation products, filter cakes, ores, tailings, and the like. The process can be used to selectively separate lead components from other metal materials such as zinc, copper, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, and the like.
Owner:MINICAP HLDG PTY LTD
Partial zinc blende activated complex copper-lead-zinc sulfide ore differential flotation separation method
The invention discloses a partial zinc blende activated complex copper-lead-zinc sulfide ore differential flotation separation method. The method comprises the steps that by adding a flotation rate regulator and a pH regulator, the flotation rate of copper pyrites and non-activated zinc blende is lowered, the activated zinc blende flotation rate is increased, and bulk concentrate adopting the activated zinc blende as the main component is obtained through differential flotation; on the basis of the flotation rate regulator and the pH regulator, the flotation rate difference between the copperpyrites and the non-activated zinc blende is increased, high-grade copper concentrate is obtained through flotation separation preferentially, and zinc blende and a small amount of galena can continueto be recycled in nonfloat. The method achieves mineral individuation and differential flotation separation, high-grade copper concentrate can be obtained, meanwhile, the comprehensive recycling rateof copper zinc in sample ore is increased, the flow technology is easy to implement, the economic benefits are remarkable, and comprehensive recycling of hard-dressing complex copper-lead-zinc sulfide ore resources is effectively achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing lead sulfate and mangano-manganic oxide materials from galena and pyrolusite
InactiveCN101712488AExpand sourceReduce generationManganese oxides/hydroxidesLead sulfatesPyrolusiteGalena
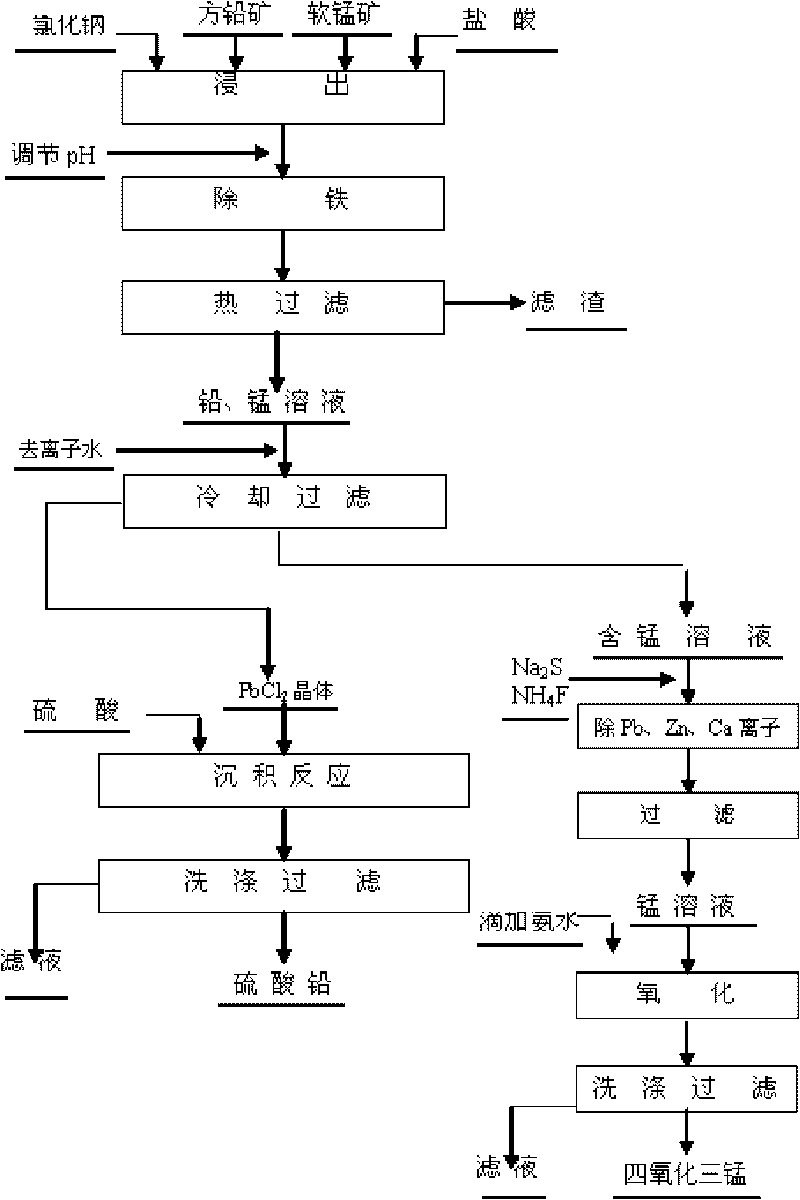
The invention discloses a method for preparing lead sulfate and mangano-manganic oxide materials from galena and pyrolusite. The method comprises the following steps of: using pyrolusite and ore concentrates of galena as materials, leaching lead and manganese by the oxidizability of the pyrolusite, purifying the lixivium, simultaneously cooling and diluting to obtain high-purity PbCl2 crystals, and adding sulfuric acid to the PbCl2 crystals to prepare PbSO4 powder; and for the manganese-contained solution with lead ions isolated, removing the lead, zinc and calcium ions to prepare the mangano-manganic oxide material. By using the selective natural ore concentrates of galena and pyrolusite to directly prepare the material, the invention uses the complementarity of the qualities of the galena and the pyrolusite to directly and simultaneously obtain electroactive materials for producing lead-acid accumulators, the lead sulfate and mangano-manganic oxide materials, thereby greatly reducing the production cost, enlarging the material source and having the characteristics of low cost and short process.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flotation separation technology for high-sulfur and low-grade lead-zinc ore
The invention discloses a flotation separation technology for a high-sulfur low-grade lead-zinc ore. The technology is provided against the characteristics of low galena and sphalerite content and extremely high pyrite content of the high-sulfur and low-grade lead-zinc ore and serious unbalance of the proportions of the lead-zinc mineral content and the pyrite mineral content in the ore. The principle flow of floatability of sulfur and the like is adopted in the lead-zinc-sulfur flotation separation process flow design to make a part of pyrite with good floatability preferentially float upwards together with galena, lead-sulfur separation is carried out, a part of pyrite with poor floatability and sphalerite in tailings are subjected to flotation, and then zinc-sulfur separation is carriedout. The technology avoids strong pressure and strong tension of a large amount of pyrite, reduces the use amounts of medicaments and also reduces the loss of lead-zinc ore in pyrite. Compared with atraditional lead-zinc-sulfur full-priority flotation process, a lead-sulfur mixed separation-lead-sulfur separation-tailing zinc separation process, a priority lead separation-tailing zinc-sulfur mixed separation-zinc-sulfur separation process or other derived processes, the technology of the invention has the advantages of good index, stable process, low medicament consumption and the like.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com