Flotation separation method for molybdenite and galena
A separation method and technology for galena, applied in flotation, solid separation and other directions, can solve the problems of low recovery rate of molybdenum, viscous pulp, difficult separation of molybdenite and galena, etc. The effect of industrialization and high practical value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
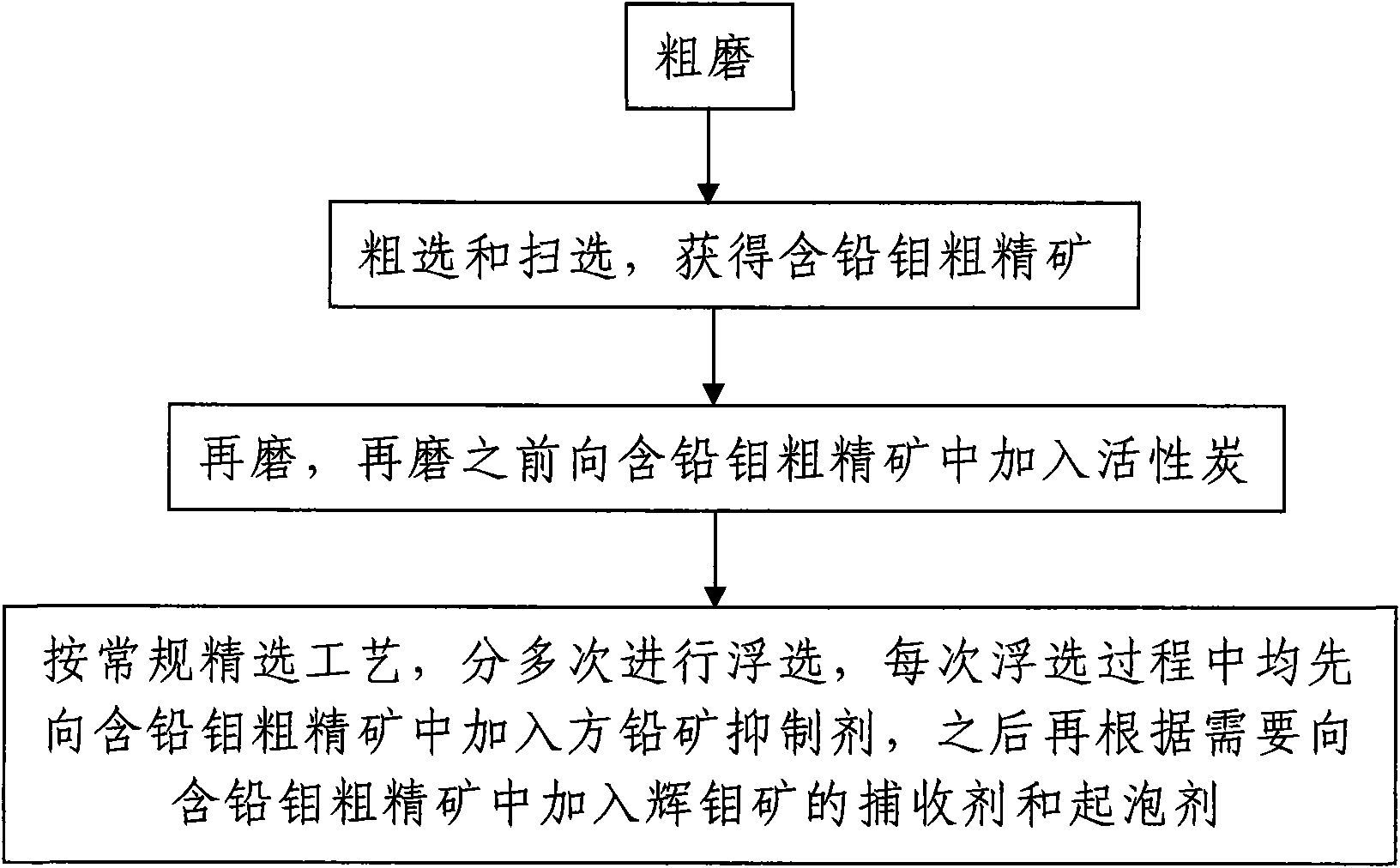
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, the flotation separation method of molybdenite and galena according to the present invention includes the following steps:
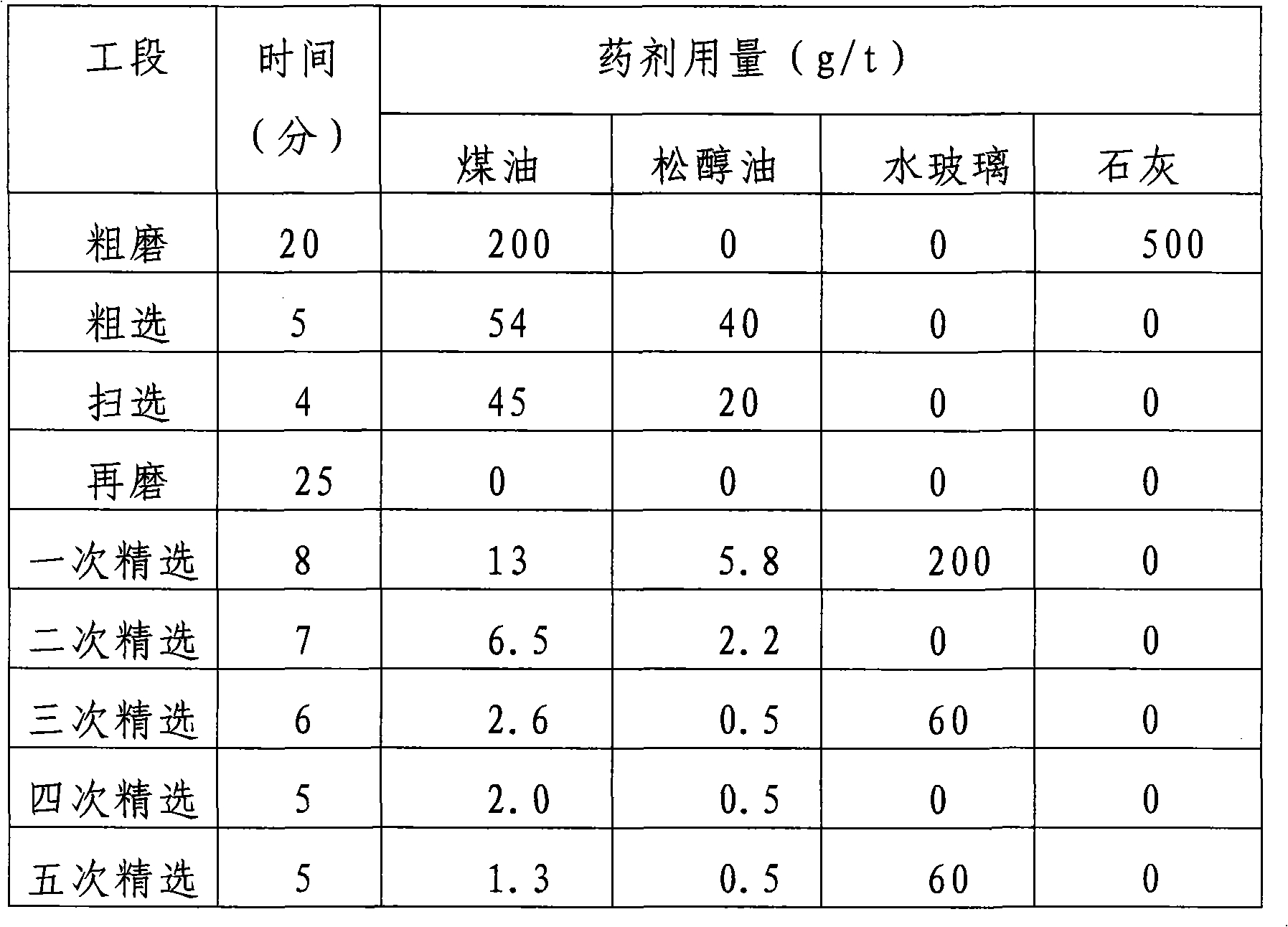
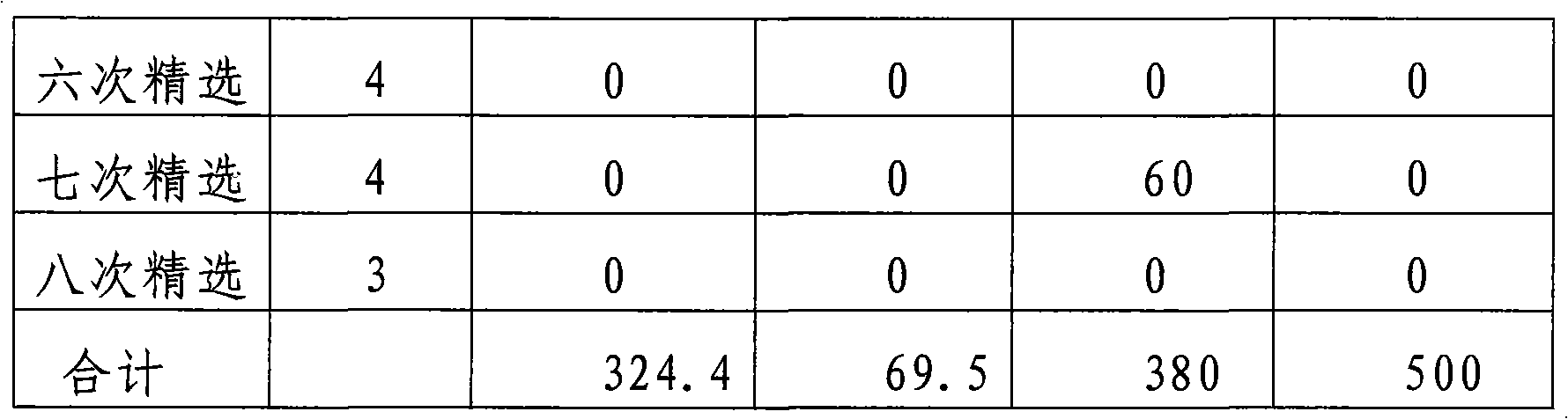
[0029] Step 1. Coarse grinding: According to the conventional flotation separation and coarse grinding process, the molybdenum ore, ie the raw ore, is coarsely ground by a ball mill, and the grinding fineness is -200 mesh, accounting for 65-70%. Before coarse grinding, conventional molybdenum flotation agents and pH regulators are added to the raw ore as needed. The raw ore is molybdenum ore containing lead>0.1wt%.
[0030] In this embodiment, the raw ore is a molybdenum ore containing 0.082% by weight of molybdenum and 0.2% by weight of lead, and has a mass of 25 kg. The conventional molybdenum flotation agent added is a collector, specifically kerosene; the pH regulator is lime. Before coarse grinding, kerosene and lime were added to the ore, and the amounts of the two were 200 g / ton of ore (200g of kerosene per ton of o...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In this embodiment, the difference from embodiment 1 is: before the regrind described in step 3, to the lead-containing molybdenum crude concentrate, activated carbon with a particle size of 200±50 mesh is added and the amount of activated carbon added is 100 ~200 g / ton of raw ore, the specific amount of activated carbon added is 150 g / ton of raw ore and the total amount of phosphorus knox added in the multiple beneficiation process is 800 g / ton of raw ore. In this embodiment, the remaining separation steps are the same as in embodiment 1.
[0044] In addition, for the convenience of comparison, a set of flotation separation process is used to flotate the raw ore, that is, no activated carbon is added in step 3 and galena inhibitor-phosphonox is not added in step 4, and the rest of the steps are all implemented Example 1 is the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com