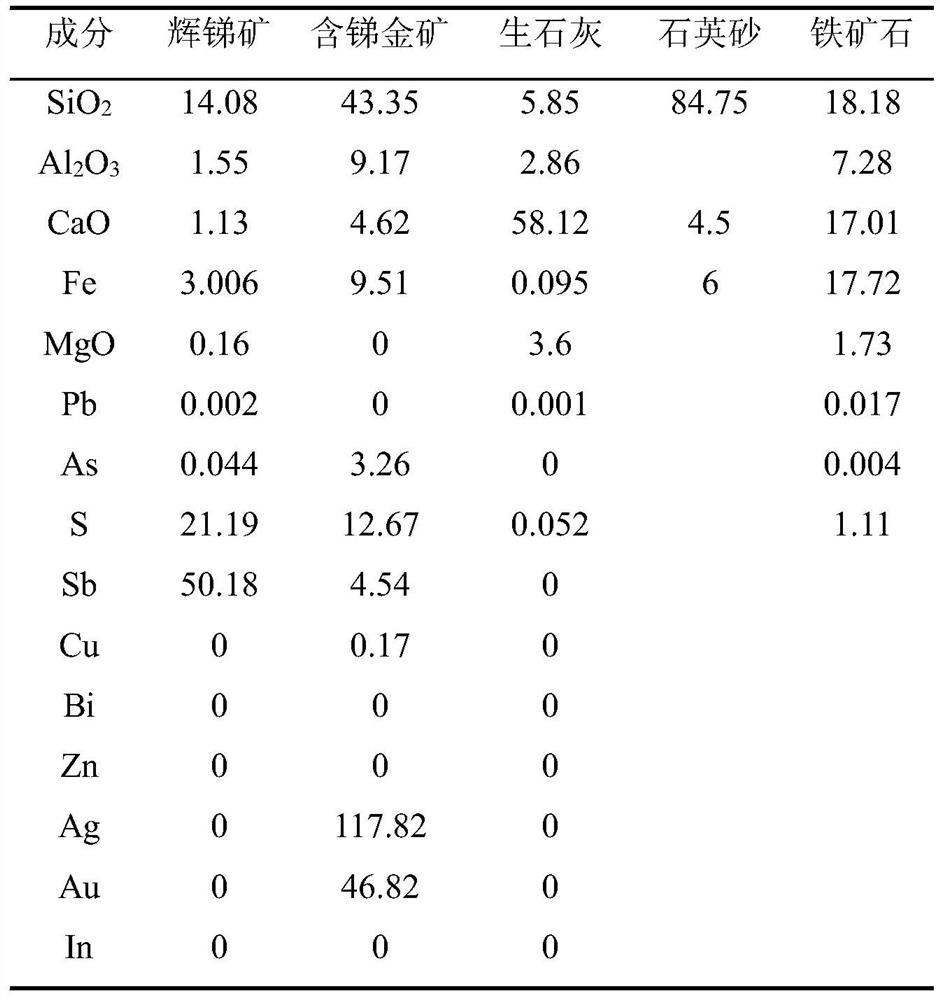
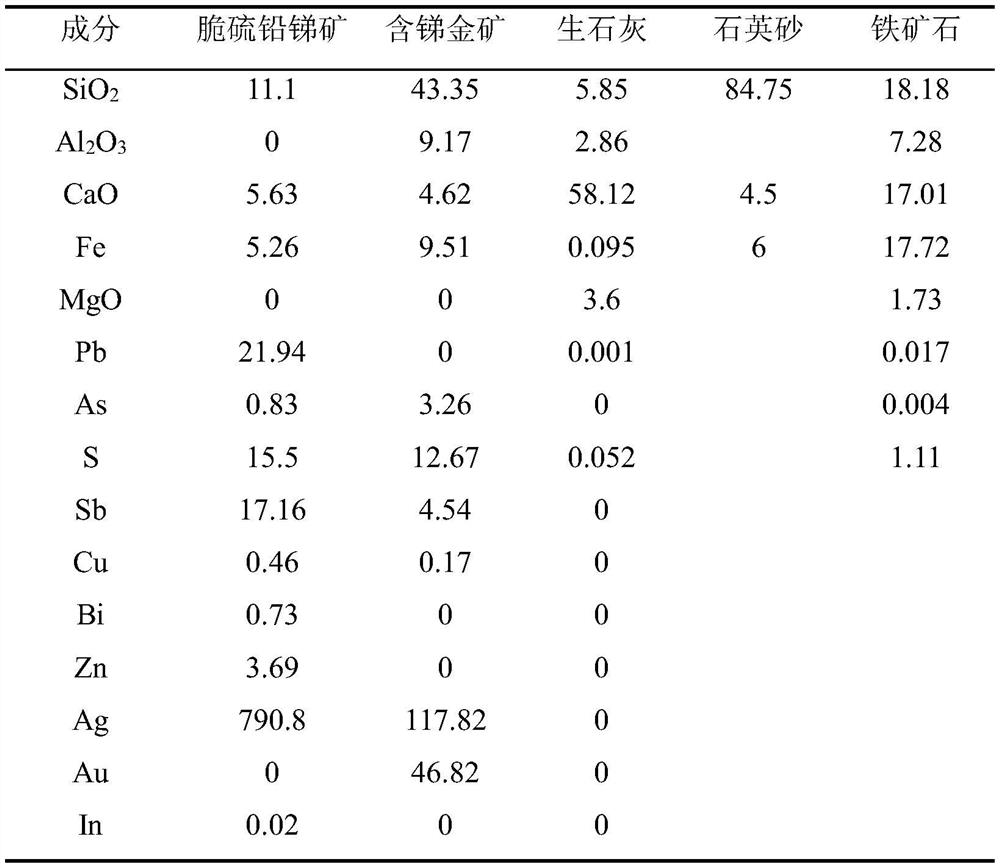
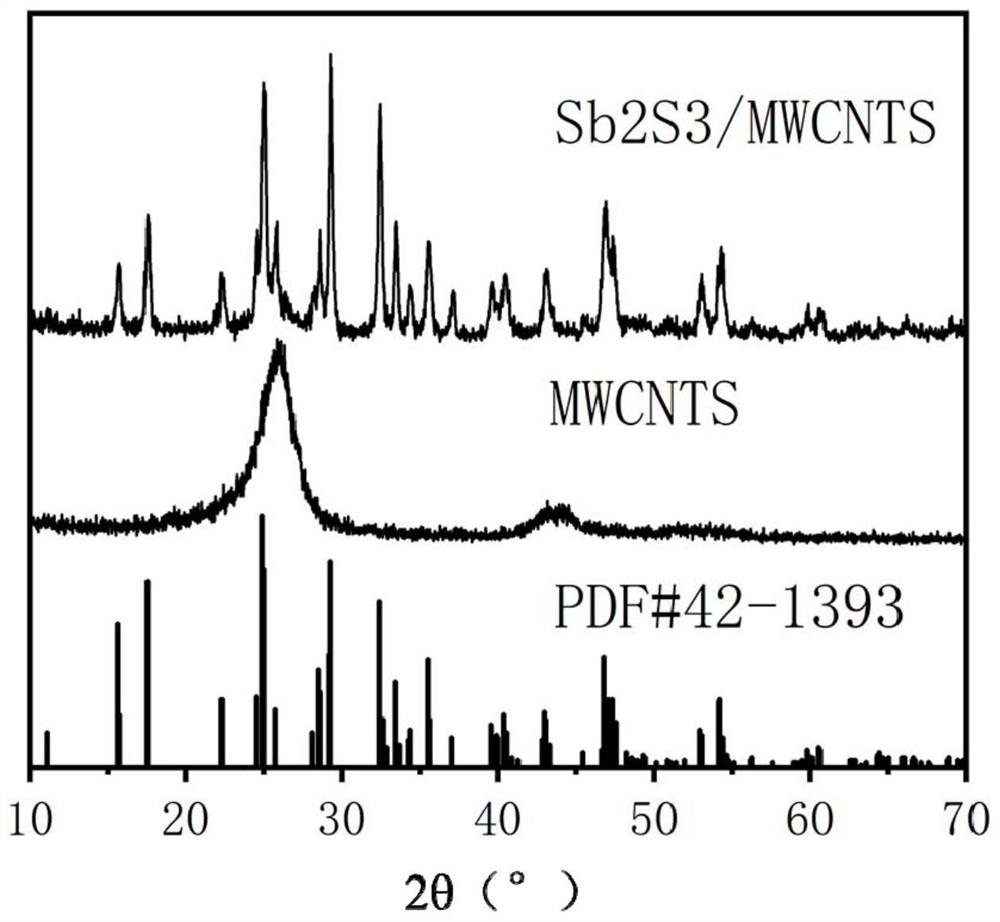
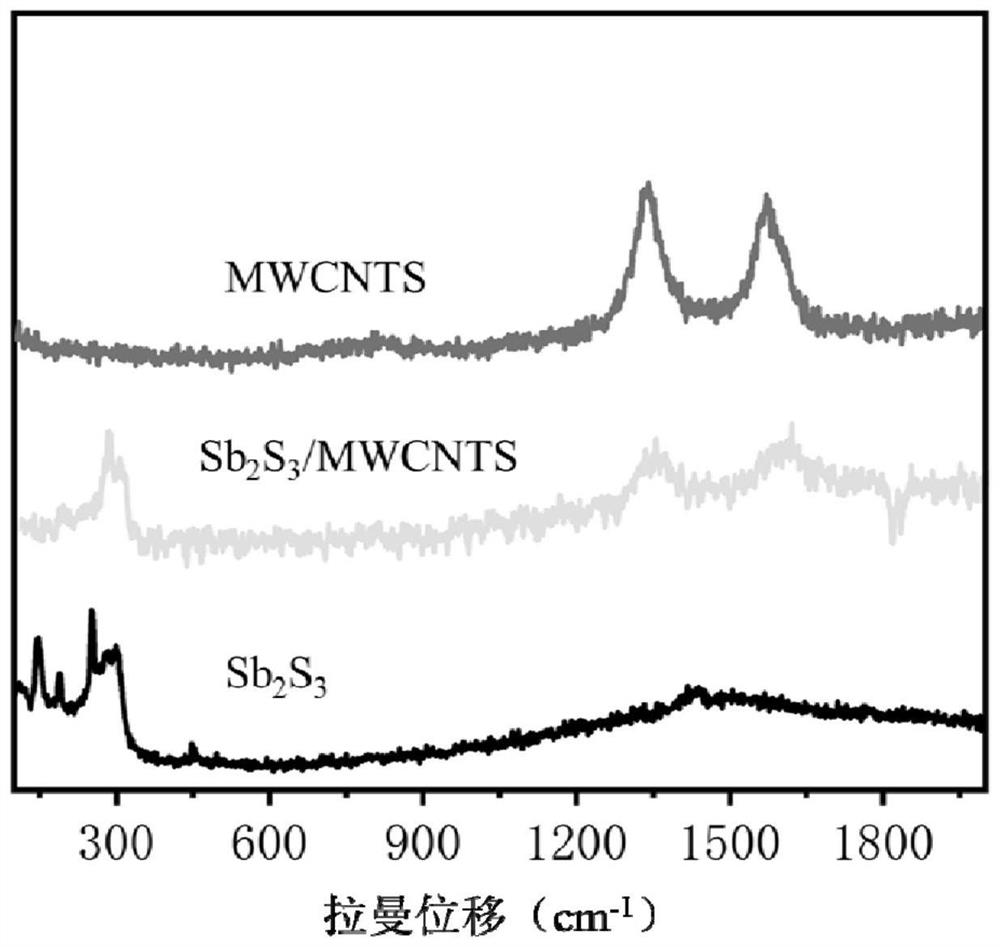
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Stibnite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
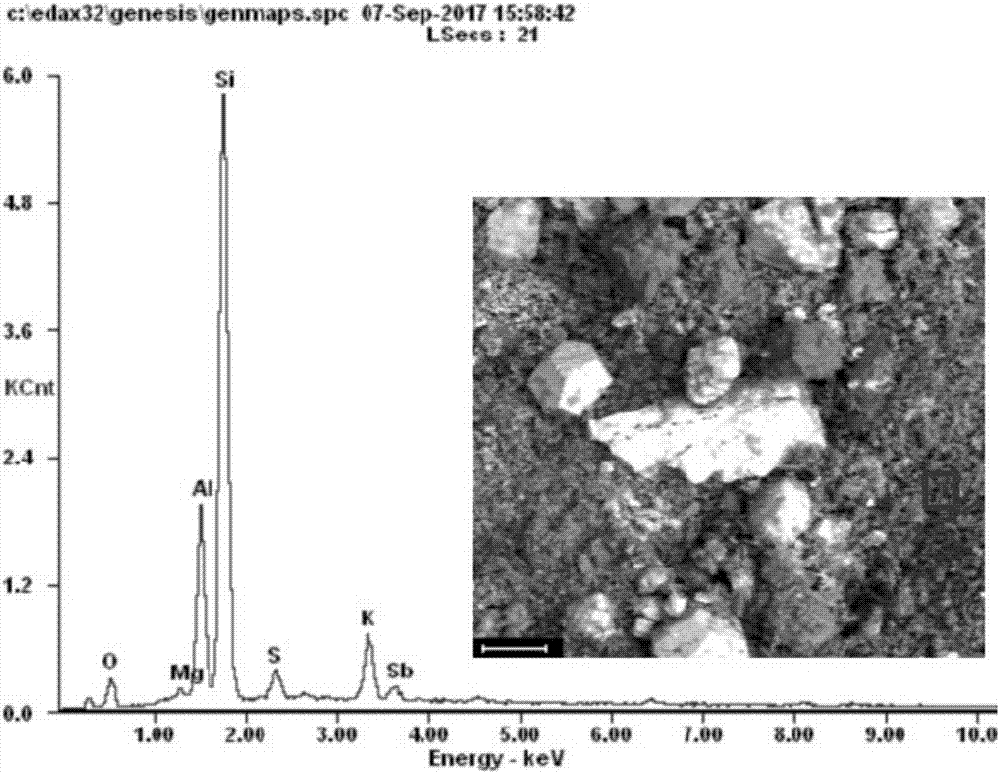
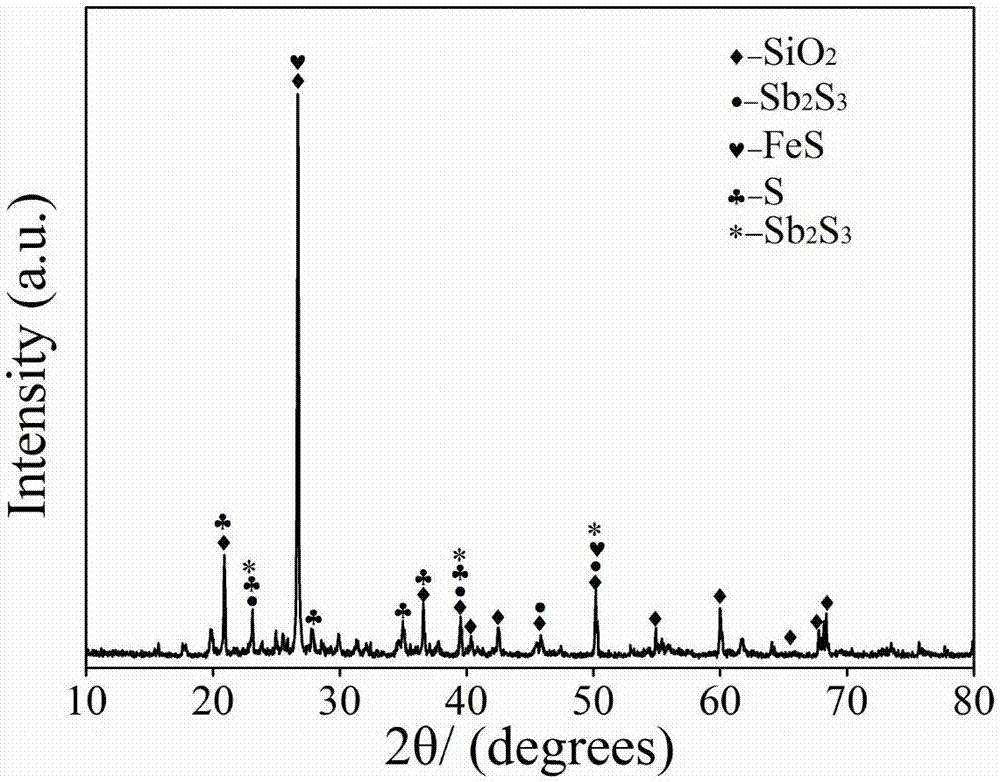
Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb₂S₃. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is from the Greek στίβι stibi through the Latin stibium as the old name for the mineral and the element antimony.
Method for preparing lithium ion battery antimony sulfide nanorod negative electrode
ActiveCN110474049ABroaden the industrial value of the application fieldLow costMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesArgon atmospherePorous carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing a lithium ion battery antimony sulfide nanorod negative electrode. The method includes the following steps: weighing a preset mass of antimony sulfide and porous carbon, adding the antimony sulfide and porous carbon to a ball milling tank, adding ball milling beads according to a preset mass ratio, ball milling the antimony sulfide and the porous carbon to obtain a mixture of the antimony sulfide and the porous carbon; melting and annealing the obtained mixture in an argon atmosphere to reorganize the antimony sulfide, cooling the product to obtain an antimony sulfide nanorod negative electrode material partially or completely coated with porous carbon. The method can directly use natural stibnite as an electrode active material, and melt-combines the natural stibnite with a porous carbon material to prepare the porous carbon-coated stibnite nanorod negative electrode. Using the method to prepare the negative electrode material has advantages of low cost, short process, simple control, no waste water, waste gas or waste residue, excellent performance, and is suitable for large-scale industrialization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
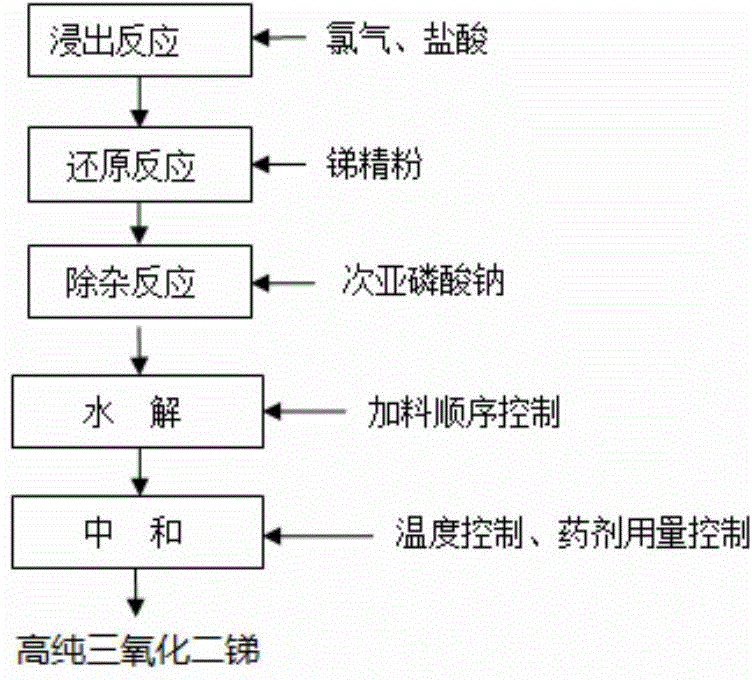
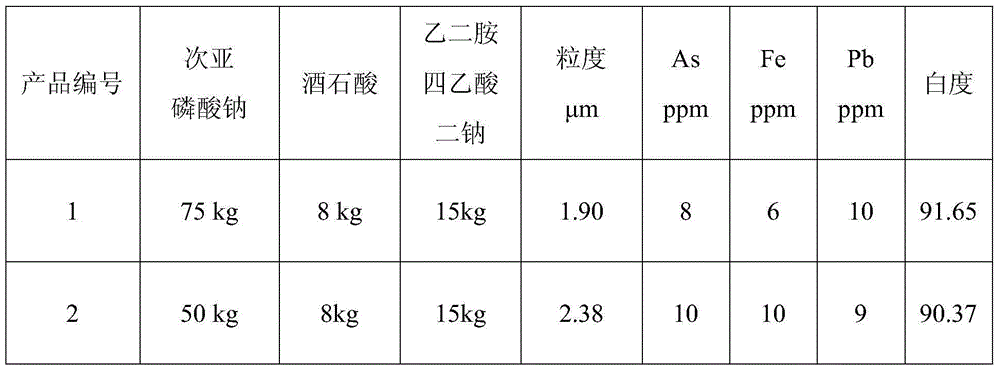
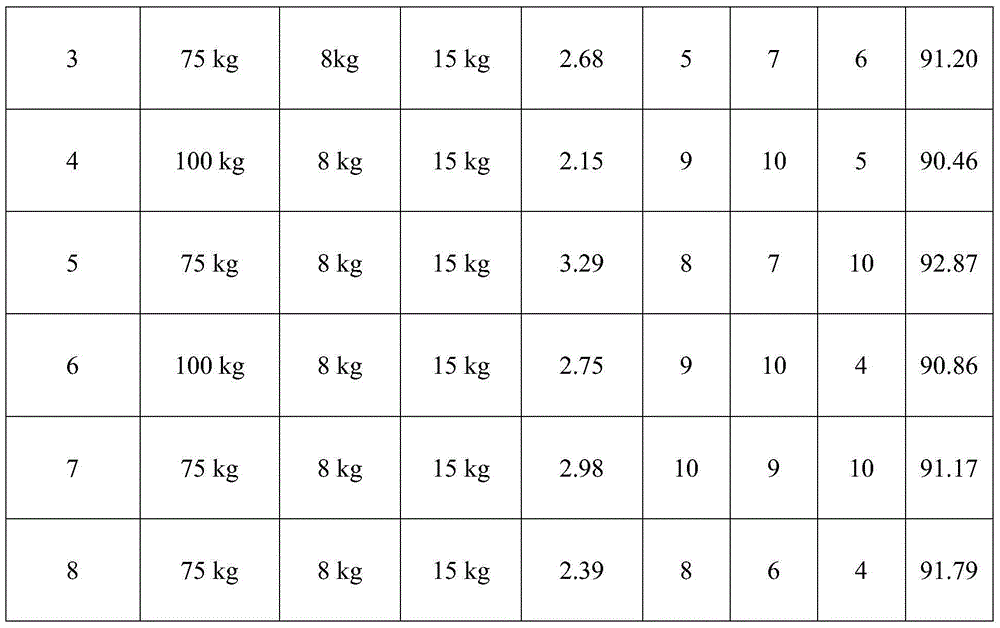
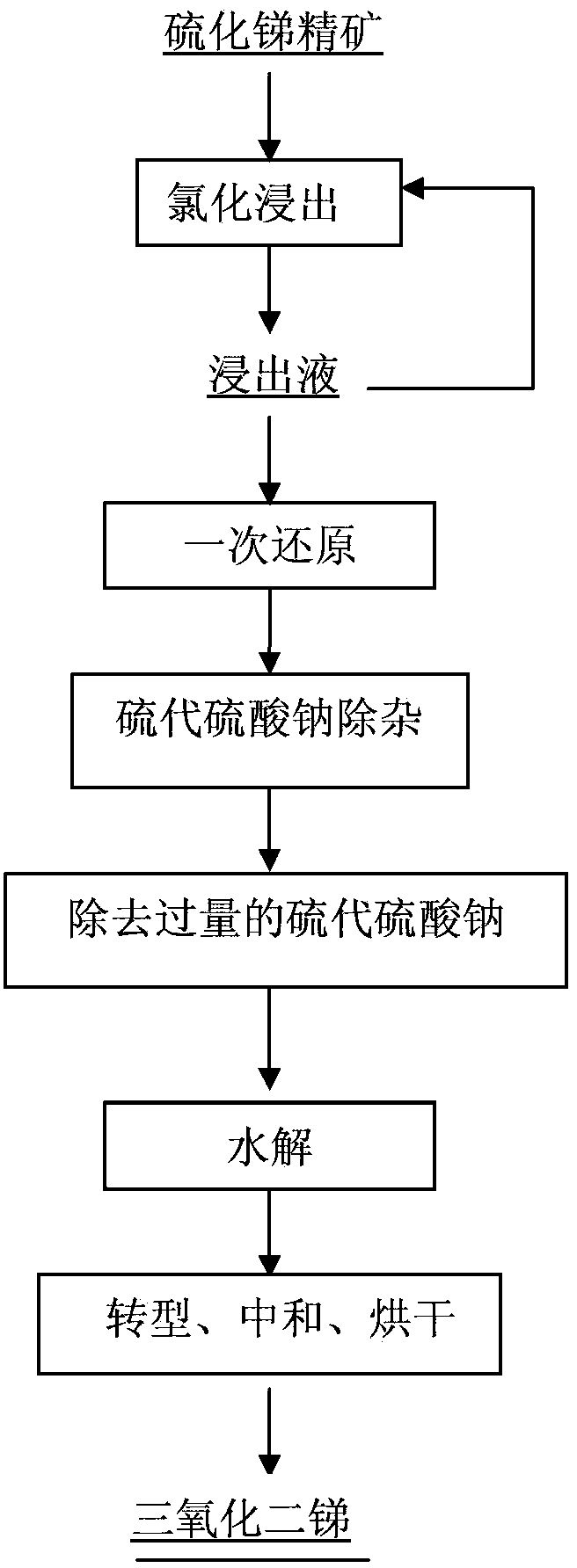
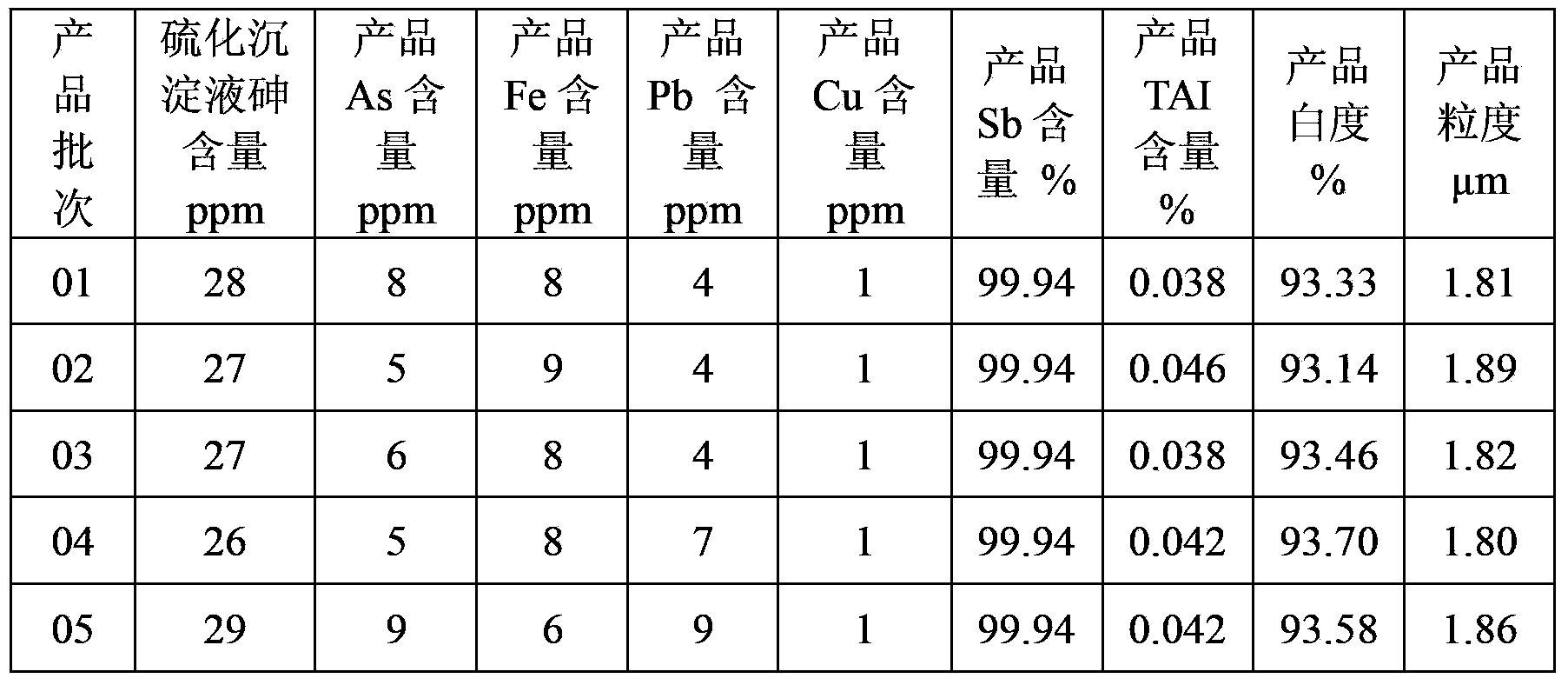
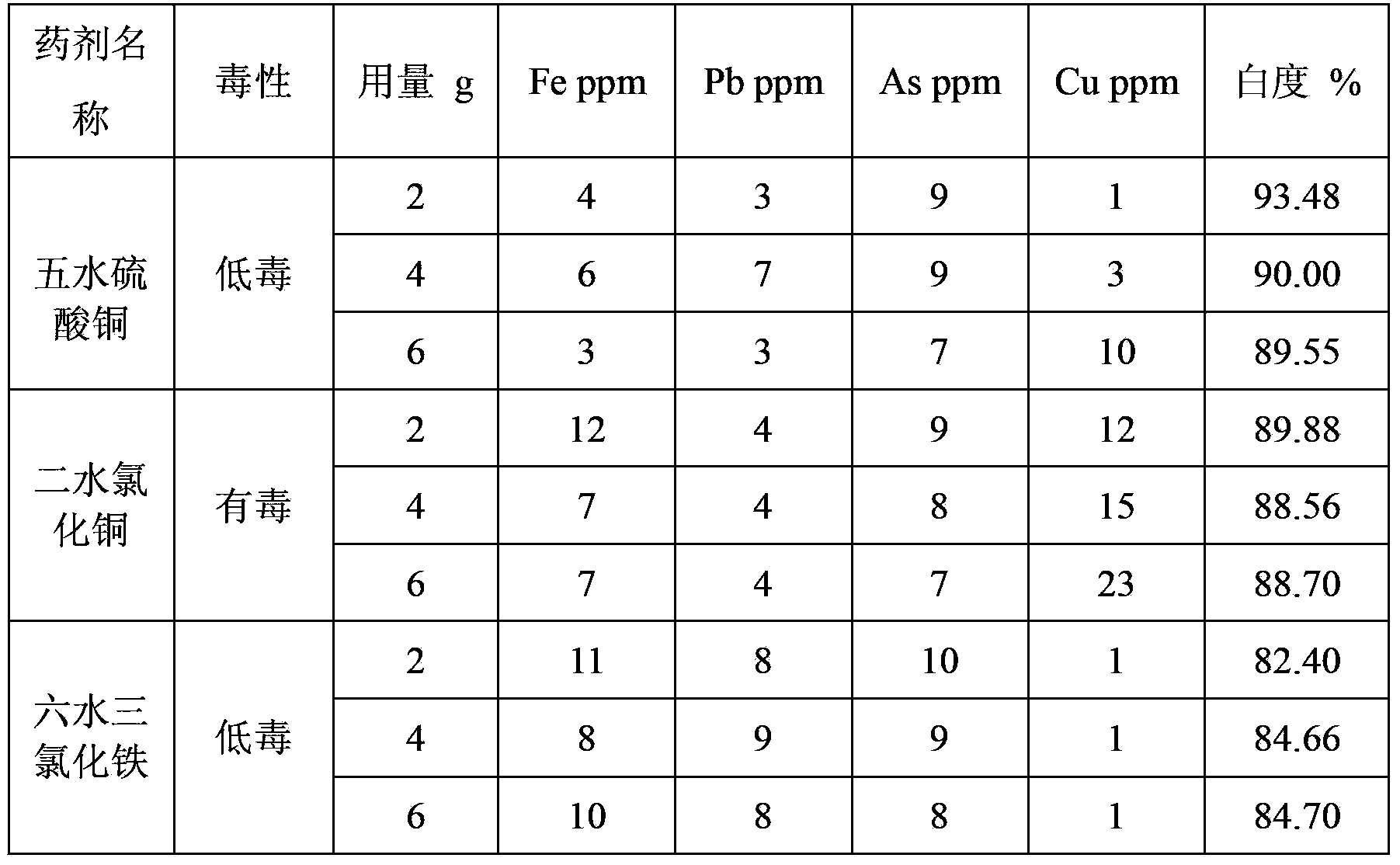
Technique for producing high-purity antimonous oxide by processing stibnite concentrate through wet method
InactiveCN104944469AHigh purityUniform particle sizeAntimony compoundsEthylene diamineAcid concentration
The invention discloses a technique for producing high-purity antimonous oxide by processing stibnite concentrate through the wet method. According to the technique, the stibnite concentrate is chloridized, a leaching agent is reduced by means of fine stibium powder, reduction liquid is selectively reduced through sodium hypophosphite under the proper temperature and proper acid concentration conditions so that arsenic is removed, iron in a solution subjected to arsenic removal is removed through hydrolysis, and lead in the solution subjected to arsenic removal is removed through ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid; meanwhile, growth of crystals is controlled by adding dihydroxysuccinic acid and controlling the neutral reaction condition, and in this way, a high-purity antimonous oxide product containing main impurities such as lead, arsenic and iron all being within 10 ppm and the average particle sizes being 2-3 microns can be produced. According to the technique, the stibium loss is small, operation is easy, production cost is low, and industrial production requirements are met.
Owner:HUNAN CHENZHOU MINING CO LTD
Method for separating lead and antimony of jamesonite
InactiveCN102628108AAvoid the impact of incomplete separationNo need to consumeProcess efficiency improvementAlloyStibnite
The invention provides a method for separating lead and antimony of jamesonite. The method comprises the following steps: controlling proper heating temperature and condensing temperature according to the special molecular organization of the jamesonite (Pb4FeSb6S14); and respectively volatilizing and condensing galena (PbS) and stibnite (Sb2S3) by means of a special vacuum environment so as to effectively separate the lead and the antimony from each other. According to the invention, the galena and the stibnite can be directly obtained by directly treating the jamesonite; the jamesonite is treated by using an economic and environment friendly vacuum technology and no reagent needs to be consumed; and the method for separating the lead and the antimony of the jamesonite, provided by the invention, has the advantages of low production cost, no pollution to the environment, no requirement on raw material component content, and wide adaptability; and because no alloy is generated, the product can be directly used for smelting lead-antimony metals.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing carbon fiber/antimony sulfide composite negative electrode of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN110492074AImprove conductivityReduce usageCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon fibersHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a carbon fiber / antimony sulfide composite negative electrode of a lithium ion battery. Natural stibnite can be directly used as an electrode active substance, and carbon fiber is used as a conductive matrix. The novel negative electrode material in which the carbon fiber matrix is coated with the nanoscale antimony sulfide is synthesized through melting. The structure effectively releases the stress change in the antimony sulfide crystal grains in the lithium embedding process; meanwhile, the transmission path of Li<> and electrons in the materialis shortened, the carbon fiber matrix provides an excellent conductive network for the composite material, and because the natural stibnite can be used as a direct raw material of an electrode activesubstance, a high-energy-consumption and high-pollution metallurgy purification process is removed; the nano composite material is prepared by adopting a solid-phase mixed melting method, and a wastetreatment process is removed.
Owner:湖南恩捷前沿新材料科技有限公司
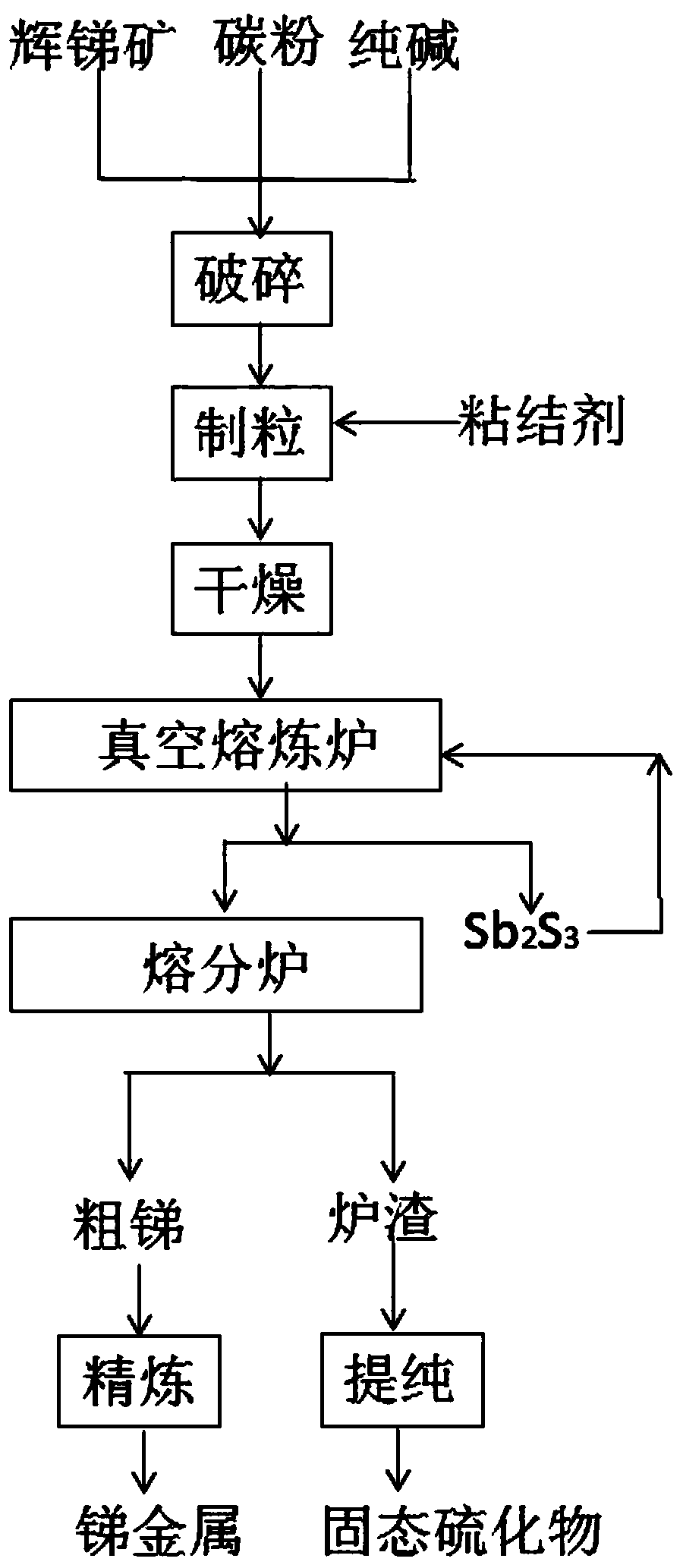
Smelting processing method adopting oxygen-enriched molten pool for stibnite
The invention discloses a smelting processing method adopting oxygen-enriched molten pool for stibnite. The method comprises the steps that oxygen-enriched air is blown into the oxygen-enriched moltenpool, then stibnite materials, aluminum oxide waste red mud, lime and a reducing agent are mixed and then fed into an oxygen-enriched smelting tank for oxygen-enriched reduction smelting, the antimony oxide with 86% of the antimony is obtained, and the temperature in the molten pool is controlled to be 990-1360 DEG C in the smelting process; the antimony oxide and the waste residue are recoveredand separated; and flue gas containing SO2 discharged from the top of the oxygen-enriched molten pool is collected, and the flue gas is recycled through waste heat, the flue gas is carried out purifying and dust removing, and sent into a sulfuric acid workshop for acid production, and the collected smoke dust and the waste residue are subjected to granulation and then returned to the oxygen-enriched smelting pool for the oxygen-enriched reduction. The method has the advantages that the adaptability of raw materials is high, the energy consumption is low, the direct yield of the antimony metaland the recovery rate are high, the treatment process is short, the process is stable, the production efficiency is high, the labor intensity is low, the production is clean and environment-friendly,environmental pollution and stacking management of the red mud are reduced, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:广西生富锑业科技股份有限公司
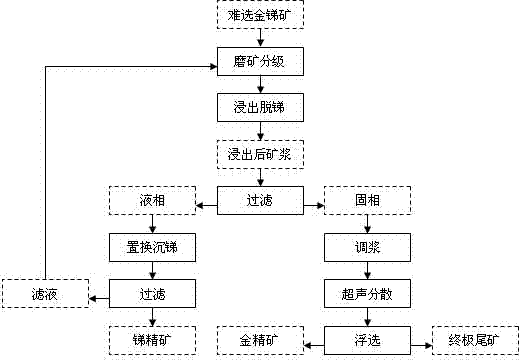
Method for gold separation by means of removing antimony
InactiveCN103203281AEliminate negative effectsSimplified process conditionsWet separationSulfidationSulfide minerals
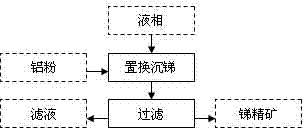
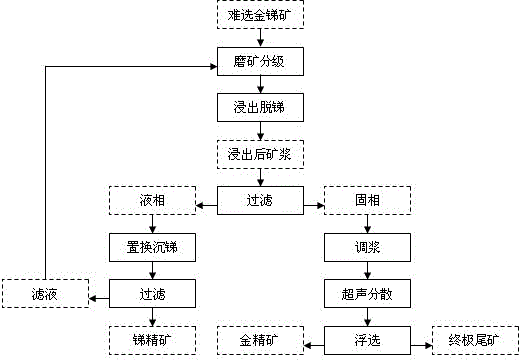
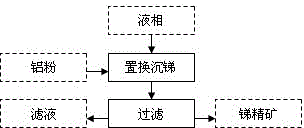
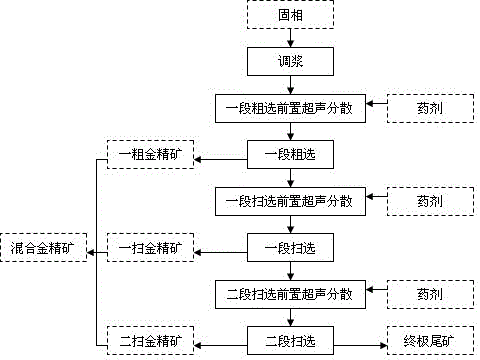
A method for gold separation by means of removing antimony is used for treating refractory gold and antimony ores by a leaching antimony removing process, so that the antimony in an ion state is turned into a liquid phase, and the gold in a crystalline state remains in a solid phase. The refractory gold and antimony ores at least comprise elementary gold and gold-carrying minerals; the elementary gold includes visible gold and invisible gold; the gold-carrying minerals at least include gold-carrying oxygenic salt minerals and gold-carrying sulfide minerals; the oxygenic salt minerals at least include carbonate minerals and silicate minerals; and the sulfide minerals at least include antimony glance and (or) iron pyrite and (or) arsenic pyrite. An antimony removing gold separation dressing and smelting technology for implementing the method for gold separation by means of removing the antimony is characterized by comprising 1), treating the refractory gold and antimony ores by the leaching antimony removing process so that the antimony in the ion state is turned into the liquid phase and the gold in the crystalline state remains in the solid phase; 2), performing solid and liquid separation for ore pulp obtained after leaching, and generating a liquid phase and a solid phase; 3), treating the liquid phase by a displacement antimony settling process so that the antimony is turned into a crystalline state from the ion state; and 4), treating the solid phase by a floatation process so that the elementary gold and the gold-carrying sulfite minerals are separated from gangues.
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
Chlorine dioxide preoxidation method of sulfur-contained gold ores
ActiveCN108103310AImprove leaching rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementChlorine dioxideGalena
The invention belongs to the technical field of gold ore mineral processing, and in particular, relates to a chlorine dioxide preoxidation method of sulfur-contained gold ores. Chlorine dioxide is used as an oxidizing agent for redox reaction with such sulfides as stibnite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, galena, blende and chalcopyrite in refractory gold ores, so that gold surrounded by the sulfides is released, the contact probability of gold with gold leaching medicament is increased, the gold recovery rate in subsequent leaching flow is increased, and the consumption of the gold leaching medicamentis reduced. The used oxidizing agent-chlorine dioxide is safe and nontoxic, and has higher environmental protection advantage. Chlorine dioxide is prepared by direct reaction of binary solid medicament in pulp, is prepared when being needed, is not needed to store, and is high in conversion efficiency. The method is performed under the conditions of low temperature, normal pressure and no need ofcontrolling acidity; reaction conditions are mild; and requirements on a reaction container are low. In conclusion, the method is a new method for metal sulfide ore wet oxidation pretreatment with environmental protection, high efficiency and prominent economical benefit.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Application of trichloroisocyanuric acid as novel beneficiation inhibitor
The invention advances an application of trichloroisocyanuric acid acting as a new ore-dressing inhibitor at 200-400g / t with respect to weight, trichloroisocyanuric acid is mainly used to sterilize and bleach, and it is for the first time that it acts as an inhibitor of arsenical pyrite and sulfurous iron ore, as a new ore-dressing inhibitor, it plays a remarkable role in separating white antimony from arsenical pyrite and from sulfurous iron ore, showing a stronger inhibition of arsenical pyrite and sulfurous iron ore but has no bad influence on the white antimony, good-selectivity, an effective inhibitor of arsenical pyrite and sulfurous iron ore.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
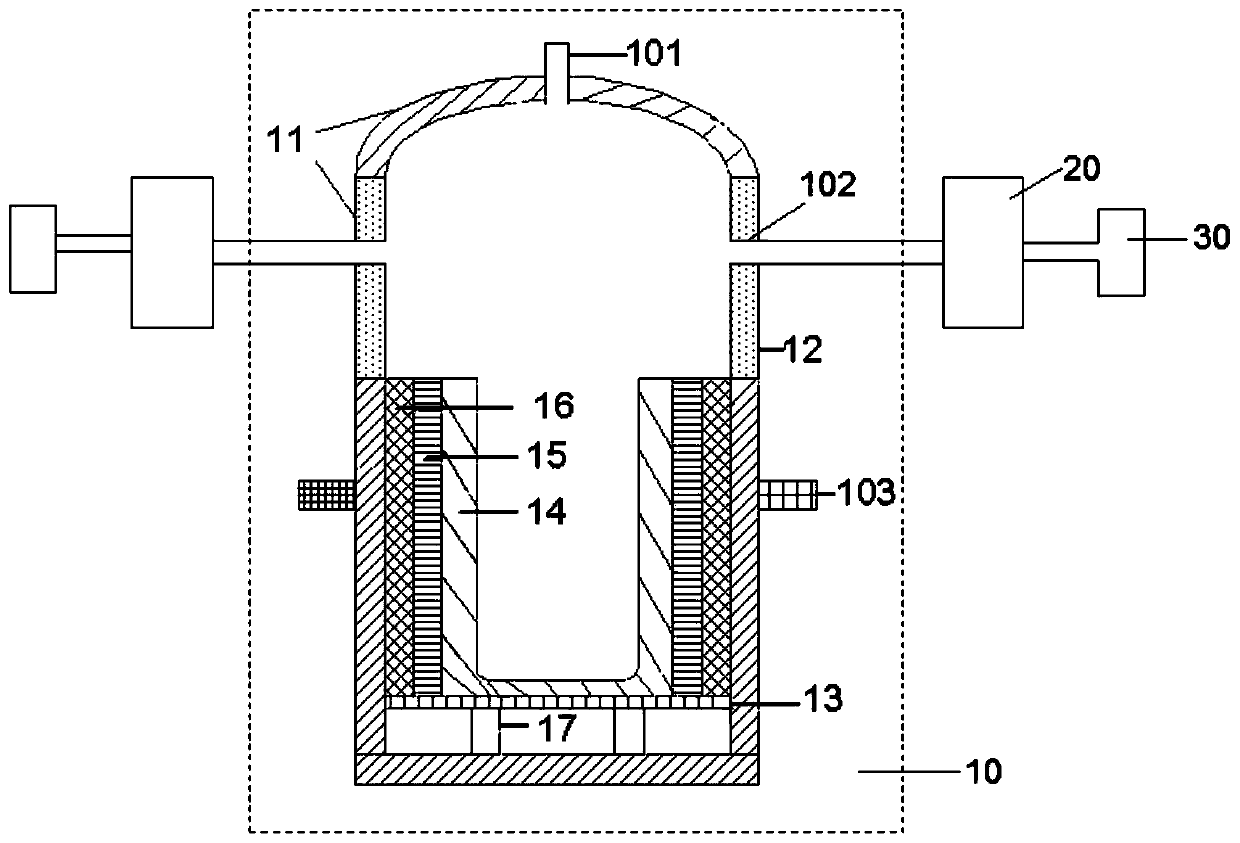
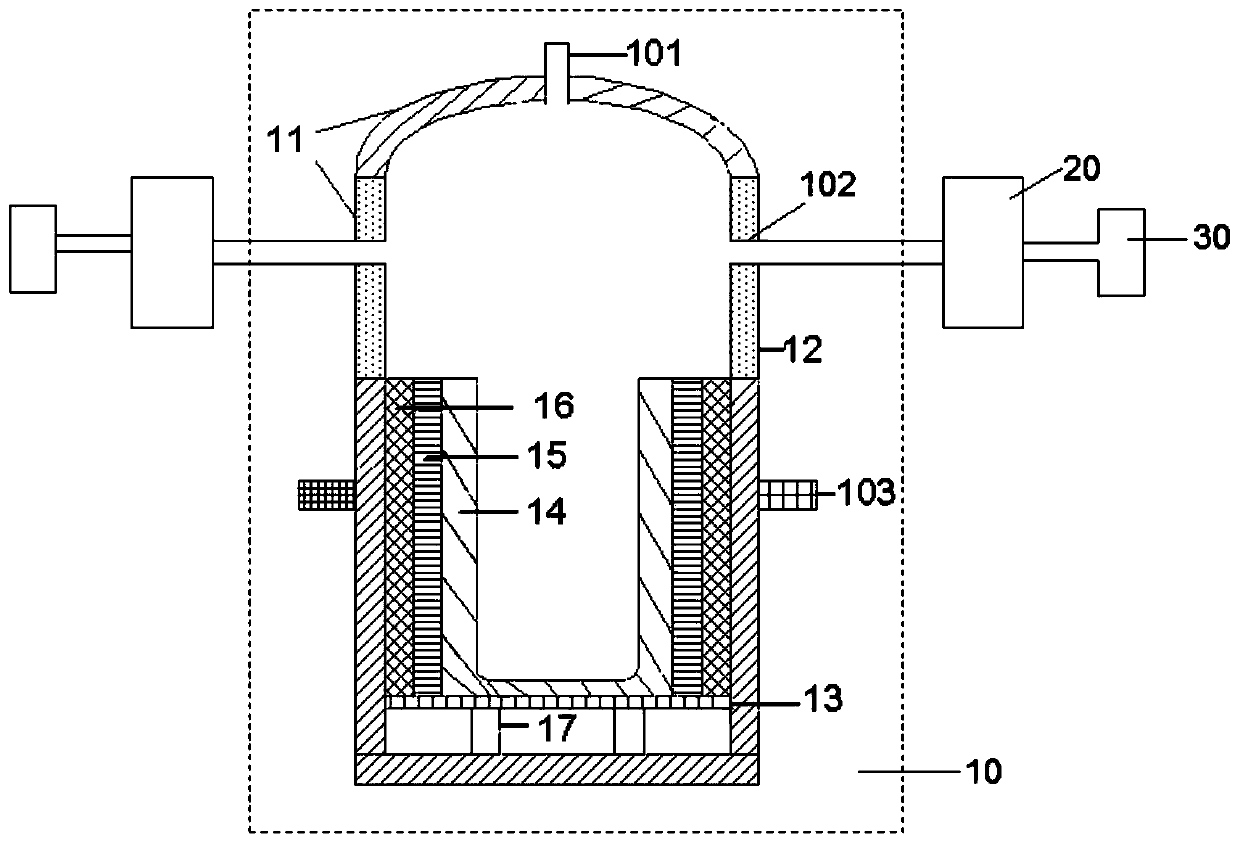
Antimony concentrate vacuum smelting device
PendingCN111156820AIncrease generation speedHigh recovery rateRemovable covers for furnacesCharge treatment typeTemperature controlProcess engineering
The invention provides an antimony concentrate vacuum smelting device. The antimony concentrate vacuum smelting device comprises a shell, a program temperature control device and a pressure control device, wherein a smelting cavity, a charging port and a pressure control port are arranged in the shell, and the charging port and the pressure control port communicate with the smelting cavity; the charging port is used for adding stibnite, reducing fuel and an alkaline additive; the program temperature control device is used for controlling the temperature in the smelting cavity in stages; and the pressure control device communicates with the pressure control port and is used for controlling the vacuum degree in the smelting cavity. By adopting the vacuum smelting device to extract metallic antimony from the stibnite, the recovery rate of the metallic antimony is greatly improved, the process flow is simplified, and the recovery cost is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
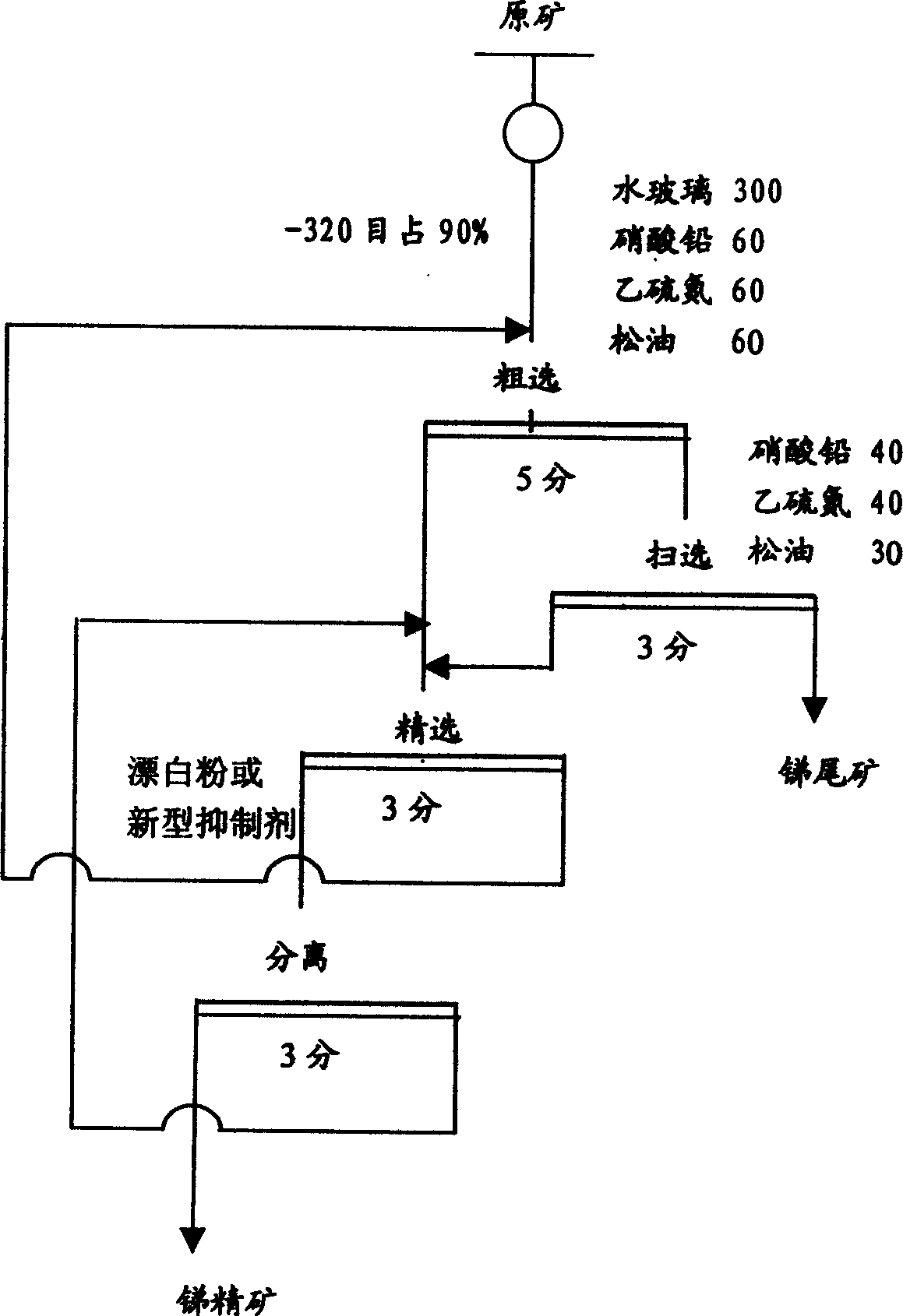
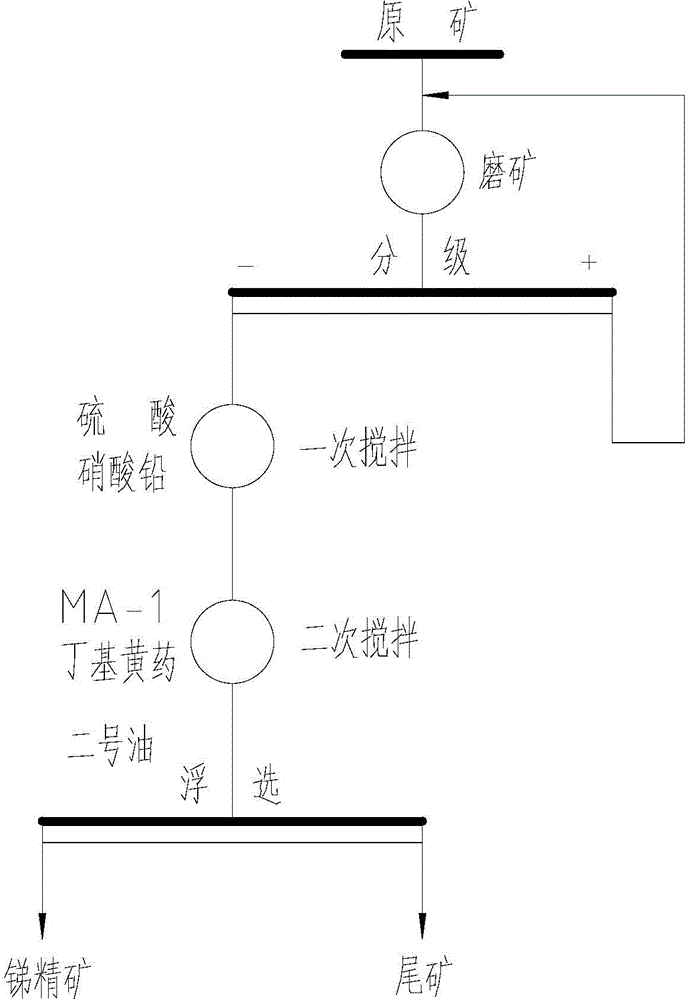
Stibnite flotation technology
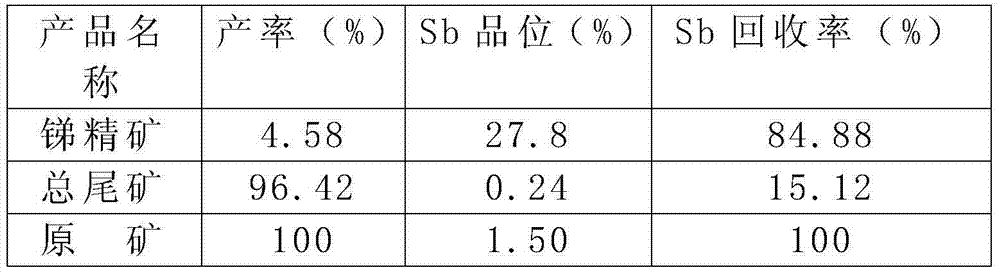
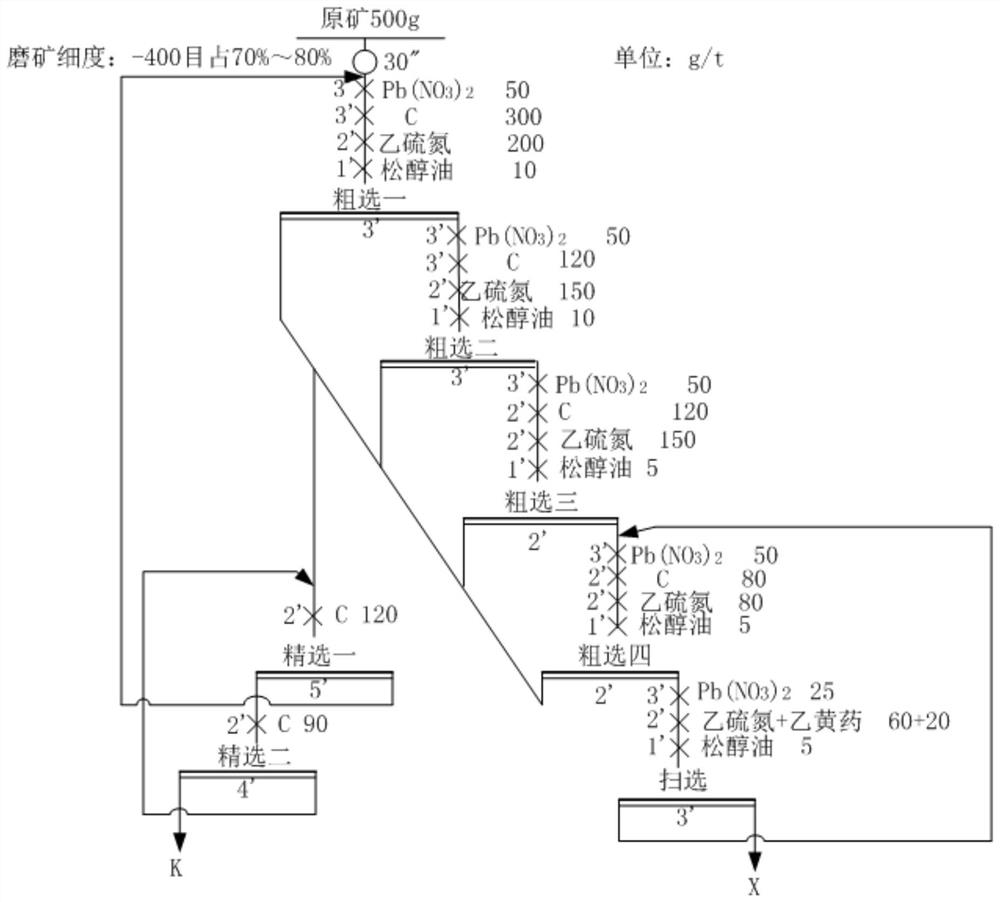
The invention discloses a stibnite flotation technology. The stibnite flotation technology comprises the steps of dispersing stibnite raw ores into water through ball milling to obtain pulp; adjusting the pH of the pump to be faintly acid, then adding a composite collecting agent consisting of MA-1 and butyl xanthate to perform flotation collection so as to obtain stibnite. In the process, the selective collecting capacity of antimony in the stibnite is greatly improved by utilizing the composite collecting agent, and the antimony recovery rate is improved. In addition, by means of the process, the using amount of lead nitrate can be decreased, the lead content in floated antimony concentrate can be reduced, and the follow-up floated antimony concentrate smelting cost can be reduced.
Owner:HUNAN ANHUA ZHAZIXI MINING
Corrosion-resistant cement clinker warehouse top conveyor
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistant cement clinker warehouse top conveyor. A processing method for steel in the corrosion-resistant cement clinker warehouse top conveyor comprises the steps that (1) high-manganese steel, zinc oxide, chromic oxide, nickel sulfate, graphite, asbestos, chalcocite, stibnite and cassiterite are molten at the temperature of 1390-1450 DEG C so as to obtain molten mixture; and (2) silicon carbide, magnesium borate whiskers, graphene and the molten mixture are reheated at the temperature of 1550-1620 DEG C, and then water quenching is conducted at the temperature of 1240-1310 DEG C so as to obtain the steel in the corrosion-resistant cement clinker warehouse top conveyor. The corrosion-resistant cement clinker warehouse top conveyor has excellent mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
Owner:WUHU ADER CONVEYOR MACHINERY
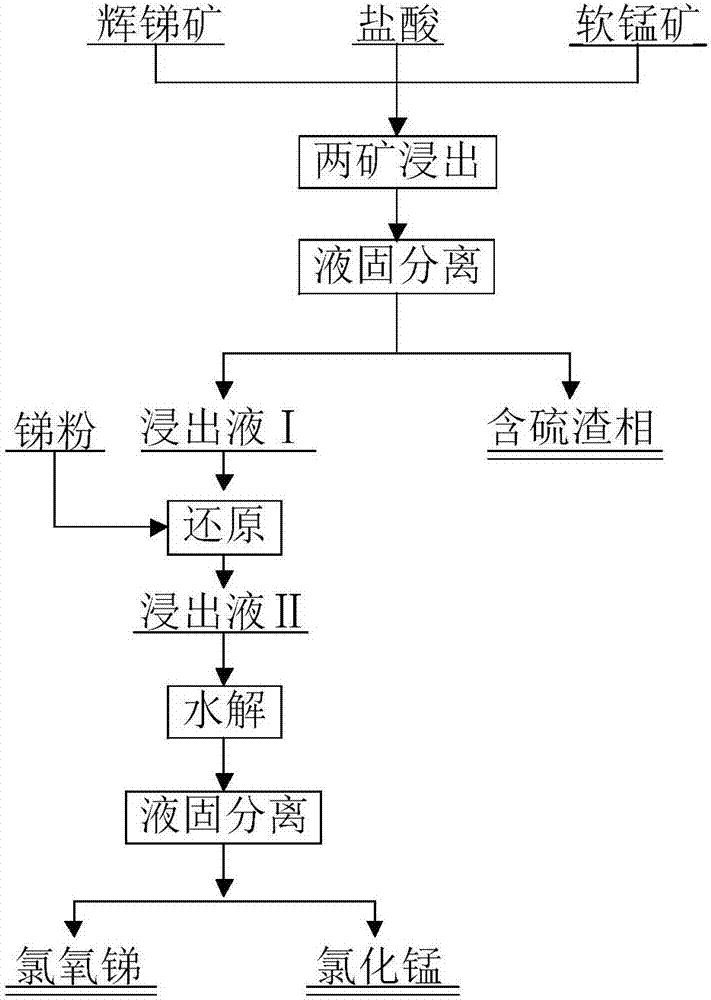
Method used for leaching antimony and manganese simultaneously from stibnite and pyrolusite
The invention discloses a method used for leaching antimony and manganese simultaneously from stibnite and pyrolusite. The method comprises the steps that (1) the stibnite and pyrolusite are disposedin hydrochloric acid solutions to be leached simultaneously, and then liquid-solid separation is conducted on leached ore pulp to obtain leaching liquid I containing antimony manganese salt solutionsand sulfur-containing leaching residue; (2) antimony powder is added to the leaching liquid I for restoring to obtain leaching liquid II with antimony butter and manganese chloride as priority; and (3) the leaching liquid II is hydrolyzed, and antimony oxychloride hydrolysis residue and manganese chloride solutions can be obtained after liquid-solid separation. A wet process is adopted to leach the antimony and the manganese simultaneously from the stibnite and the pyrolusite, and poor production environment, serious sulfur dioxide pollution and other problems in the pyrometallurgy process areeffectively avoided. The method is suitable for low-grade stibnite and low-grade pyrolusite to improve the utilization rate of increasingly depleted antimony ore and manganese ore resources and reduce environmental pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing steel additives through waste rare earth materials
InactiveCN105316562ANo secondary pollutionIncrease resourcesProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceRare earth
The invention discloses a method for preparing steel additives through waste rare earth materials. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that S1, silicon iron, lime, fluorite, graphite, iron and the waste non-alloy rare earth materials are added into an electric-arc furnace, stibnite and / or bismuthinite are added into the electric-arc furnace, and the electric-arc furnace is electrified for smelting; S2, residues inside the furnace are poured out, one or more of ferrotitanium, ferroboron and waste alloy rare earth materials are added into the electric-arc furnace, nitrogen is introduced, and stirring is conducted; and S3, cooling is conducted, and the finished steel additives are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method for preparing the steel additives through the waste rare earth materials has the advantages that environmental friendliness is achieved, energy is saved, the steel additives can be produced by directly recycling the waste rare earth materials, and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:LUFENG DONGXUAN IND CO LTD
Preparation method of auxiliary collecting agent for improving recovery rate of associated gold in antimonite
A preparation method of an auxiliary collecting agent for improving the recovery rate of associated gold in antimonite comprises the following steps: first mixing oxalic acid, hydrochloric acid and water at a mass ratio of (1-1):(1-2):(2-3) to obtain a solution 1; then adding ammonium phosphate into the solution 1 at a mass ratio of (1-2):(2-5), and performing stirring at 70-75 DEG C to dissolve the ammonium phosphate to obtain a solution 2; and next, adding ammonium sulfolipid into the solution 2 at a mass ratio of (1-2):(1-3), conducting reaction for 2-4 h at 2-2.5Mpa to obtain a liquid agent, namely the auxiliary collecting agent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
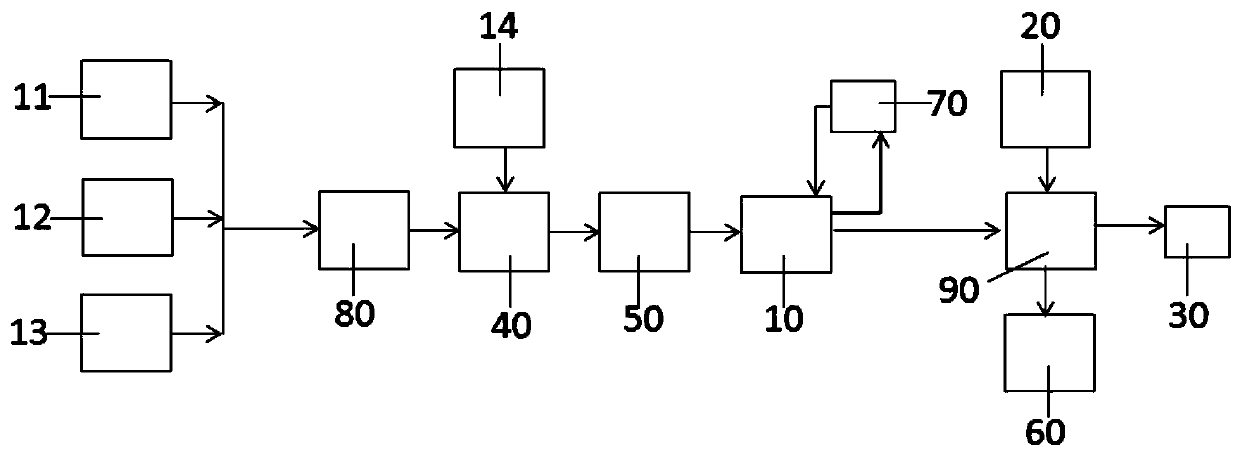
Smelting system and method of stibnite
ActiveCN111074081AIncrease generation speedLow recovery rateIncreasing energy efficiencySlagPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a smelting system and method of stibnite. The melting system comprises a vacuum smelting device, a smelting furnace, a pressure control device and a refining device, the vacuumsmelting device and the smelting furnace are correspondingly selected from an electric heating device or an electromagnetic induction heating device, the pressure of the vacuum smelting device is 1-100 Pa, and a feeding opening and an antimony-containing product outlet are formed in the vacuum smelting device; and the smelting furnace pressure is atmospheric pressure, an antimony-containing product inlet, a crude antimony outlet and a slag discharging opening are formed in the smelting furnace, the antimony-containing product inlet communicates with the antimony-containing product outlet, thetemperature in the smelting furnace is higher than that in the vacuum smelting device, the pressure control device is used for controlling the vacuum degree in the vacuum smelting device and the smelting furnace, a crude antimony inlet and a metal antimony outlet are formed in the refining device, and the crude antimony inlet communicates with the crude antimony outlet. According to the smelting system of the stibnite, by adopting the above vacuum alkaline smelting system, the recovery rate of the metal antimony can not only be greatly improved, the technological process is simplified, the recovery cost is reduced, the environmental pollution and waste of sulfur elements can be further reduced, and the environmental protection property is improved.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for preparing antimony sesquioxide by stibnite concentrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing antimony sesquioxide by stibnite concentrate. The method comprises the steps as follows: adding a solution subjected to a chlorination leaching reaction and a primary reduction reaction with sodium thiosulfate for removing arsenic, depositing for at least 24 hours to enable the arsenic content in a liquid phase to be lower than 30 ppm, filtering, adding filter liquor with copper sulfate pentahydrate for removing excess sodium thiosulfate, and hydrolyzing, neutralizing and drying filter liquor after reactions to prepare the high-purity antimony sesquioxide with the iron, lead and arsenic content of less than 10 ppm, the copper content of 1 ppm and the whiteness of more than 93%. According to the method for preparing antimony sesquioxide by stibnite concentrate, the whiteness stability of antimony sesquioxide can be improved and the production process can be simplified.
Owner:HUNAN CHENZHOU MINING CO LTD
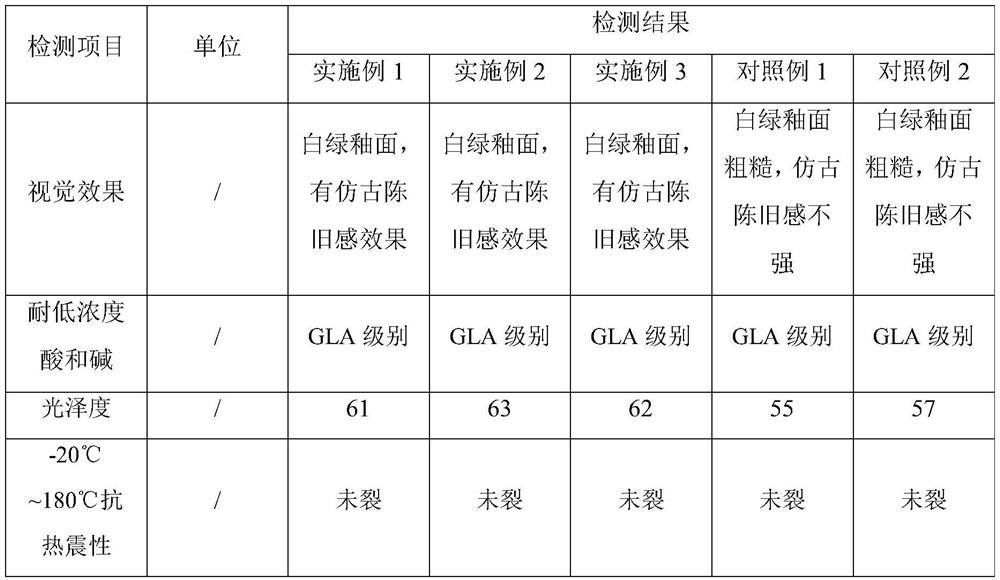
Antique white-green glaze and preparation method thereof, and preparation method of antique white-green glaze ceramic product
PendingCN113233764AMolding stabilitySmall particle sizeCeramic materials productionCeramicwareGlazeKaolin clay
The invention discloses an antique white-green glaze and a preparation method thereof, and a preparation method of an antique white-green glaze ceramic product, and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The antique white-green glaze is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by mass: 70-80 parts of kaolin, 6-8 parts of feldspar, 5-7 parts of quartz, 2-5 parts of zinc oxide, 3-6 parts of calcium carbonate, 13-20 parts of stibnite, 7-8 parts of wollastonite, 6-9 parts of chalk soil, 11-17 parts of diabase, 1-3 parts of iron oxide and 5-11 parts of medical stone. The prepared antique white-green glaze ceramic product is high in glaze stability, high in strength and old-fashioned.
Owner:DEHUA HENGHAN ARTS
Method for preparing stibnite inhibitor
The invention provides a method for preparing a stibnite inhibitor. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing zinc sulfate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide and water in a mass ratio of (1-2):(1-2.5):(1-3):(1-4) to obtain a solution 1; (2) adding starch into the solution 1 in a mass ratio of (0.5-0.6):(3-7), stirring until the starch is dissolved to obtain a solution 2; (3) adding sodium sulfite and tanning extract into the solution 2 in a mass ratio of (1-2):(0.1-0.2):(2-5), controlling the temperature of the solution 2 to be 70-75 DEG C, stirring to react, and keeping for 3.5-4 hours to obtain a solution 3; and (4) sucking and filtering the solution 3 to obtain paste, and drying the paste at 60-55 DEG C to obtain the stibnite inhibitor. The inhibitor prepared by adopting the method can be used for inhibiting stibnite, and enables flotation separation of gold-containing pyrite and stibnite to obtain gold concentrate and antimony concentrate.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
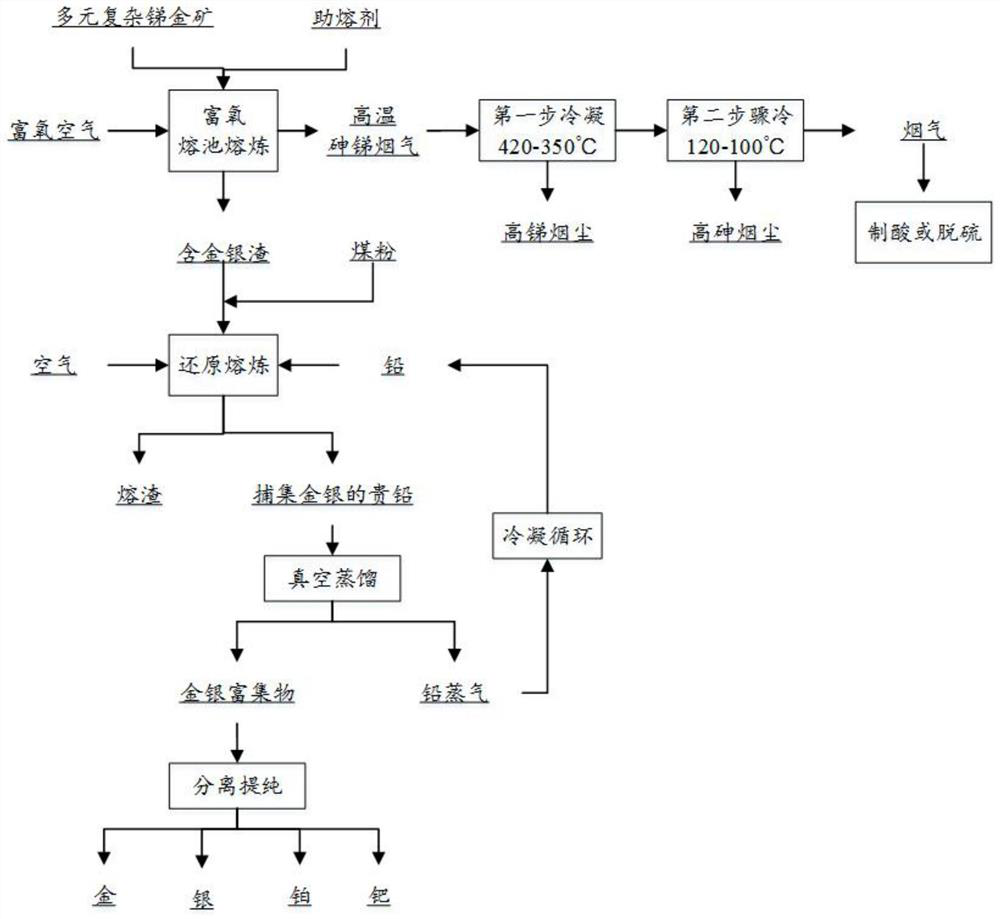
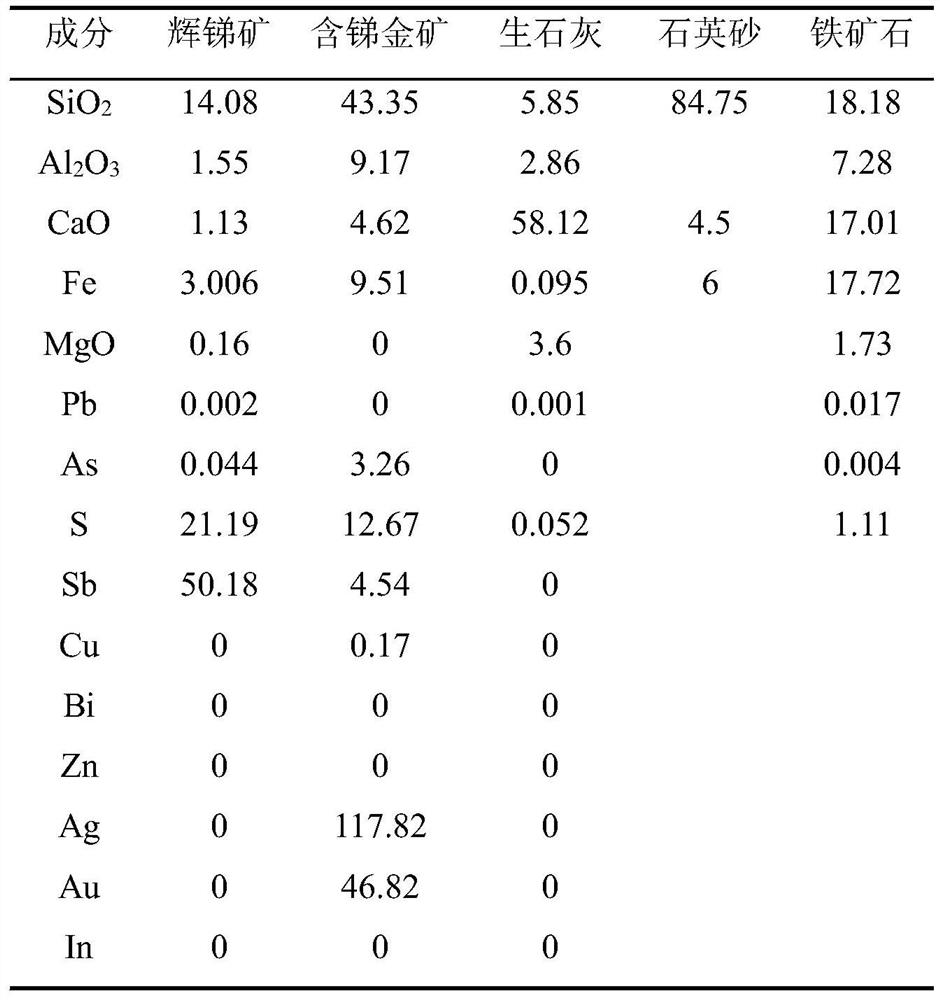
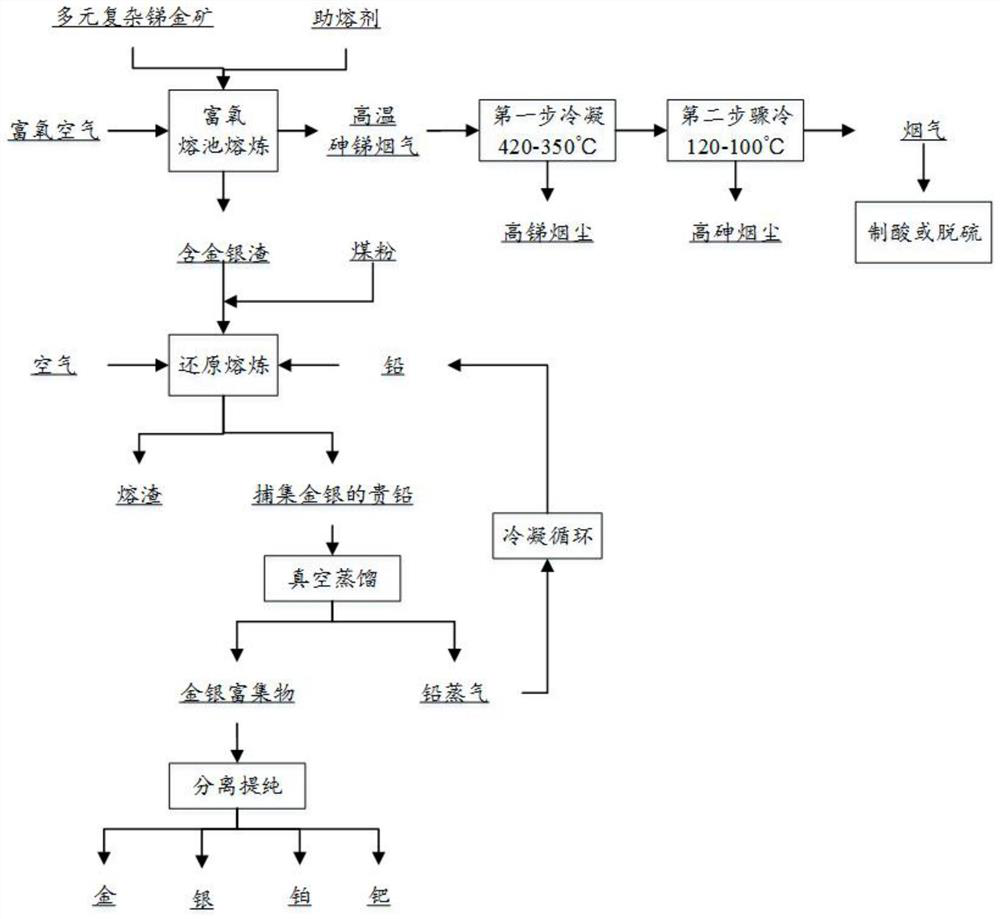
Antimony-gold complex resource collaborative smelting method
The invention discloses an antimony-gold complex resource collaborative smelting method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing at least one of stibnite and jamesonite with antimony-containing gold ore, grinding and drying to obtain pretreated ore charge; (2) mixing the pretreated ore charge with a fluxing agent, feeding the mixture into a smelting furnace, and introducing oxygen-enriched air for heating and smelting to obtain high-temperature arsenic-antimony flue gas and precious metal furnace slag; (3) performing step-by-step condensation treatment on the high-temperature arsenic-antimony flue gas to obtain antimony flue dust and arsenic flue dust respectively; (4) adding the precious metal furnace slag and metal lead into the smelting furnace, blowing in air for reduction smelting, and capturing precious metals through the lead to obtain precious lead into which the precious metals are captured and tailings; and (5) carrying out vacuum distillation treatment on the precious lead into which the precious metals are captured to obtain a precious metal phase and lead steam, and condensing the lead steam to obtain lead powder. According to the antimony-gold complex resource collaborative smelting method, cooperative smelting of the precious metals and antimony is achieved, antimony and the precious metals can be recovered respectively, and the recovery rate of antimony and the precious metals of gold and silver is high.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
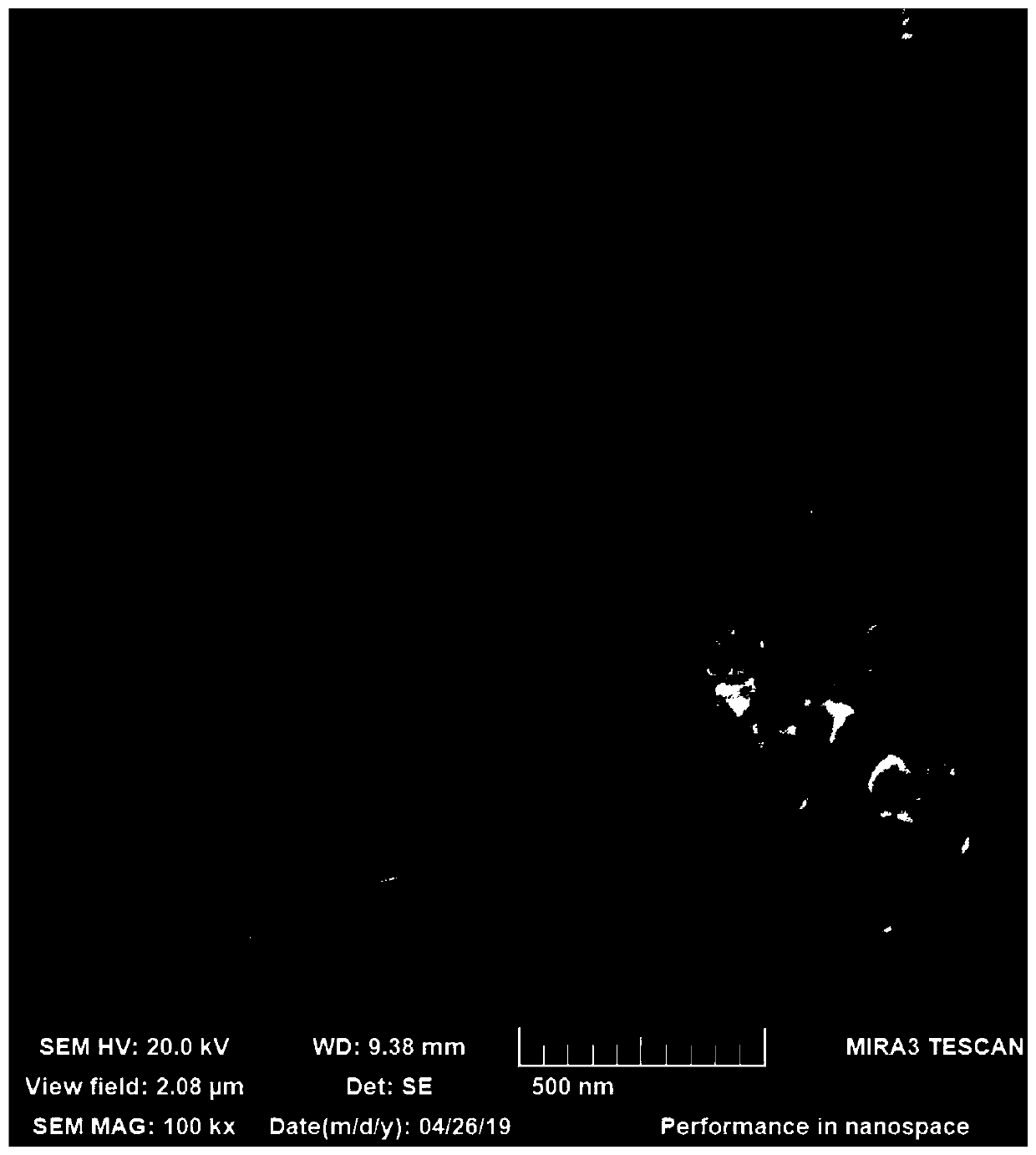
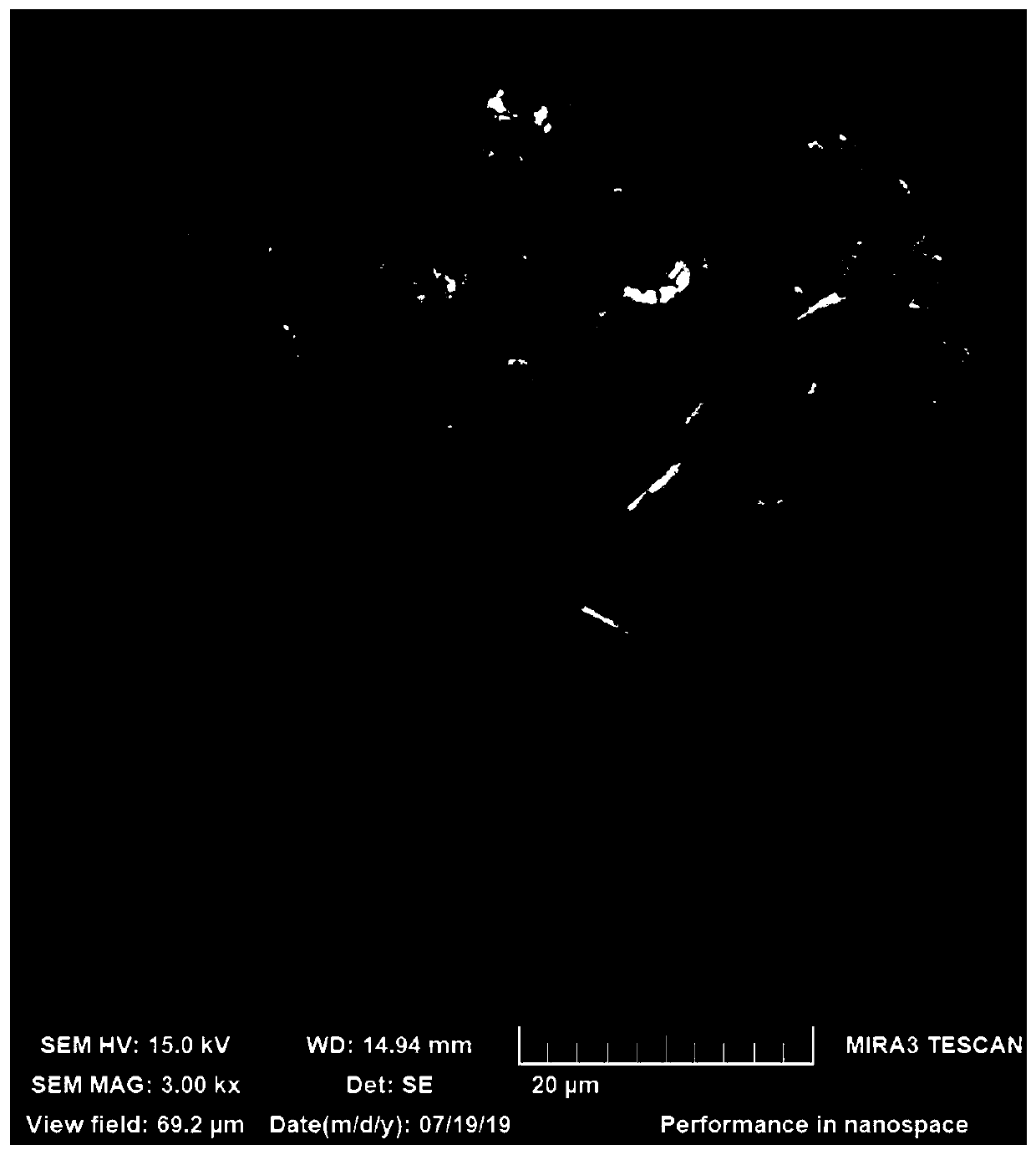
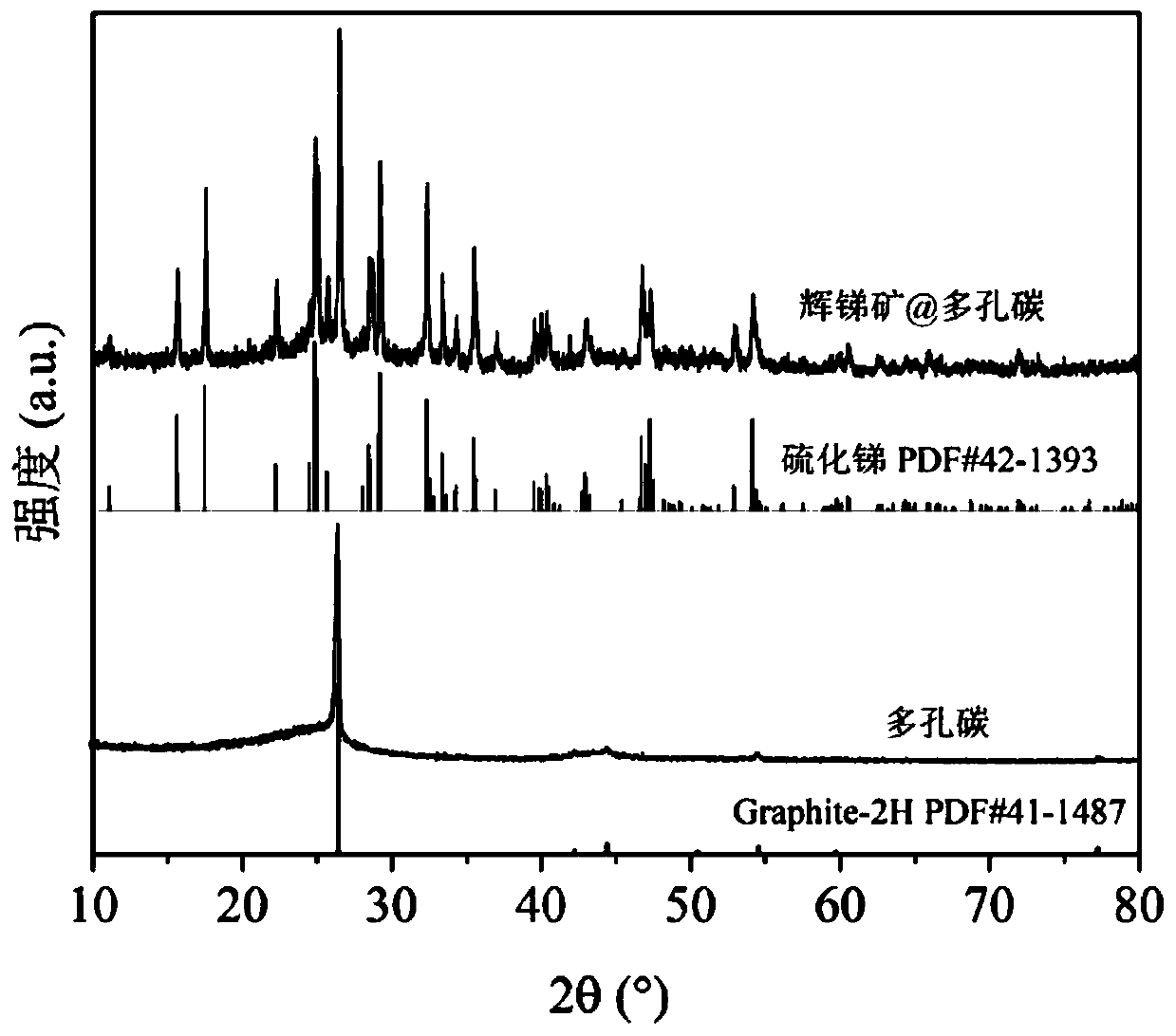
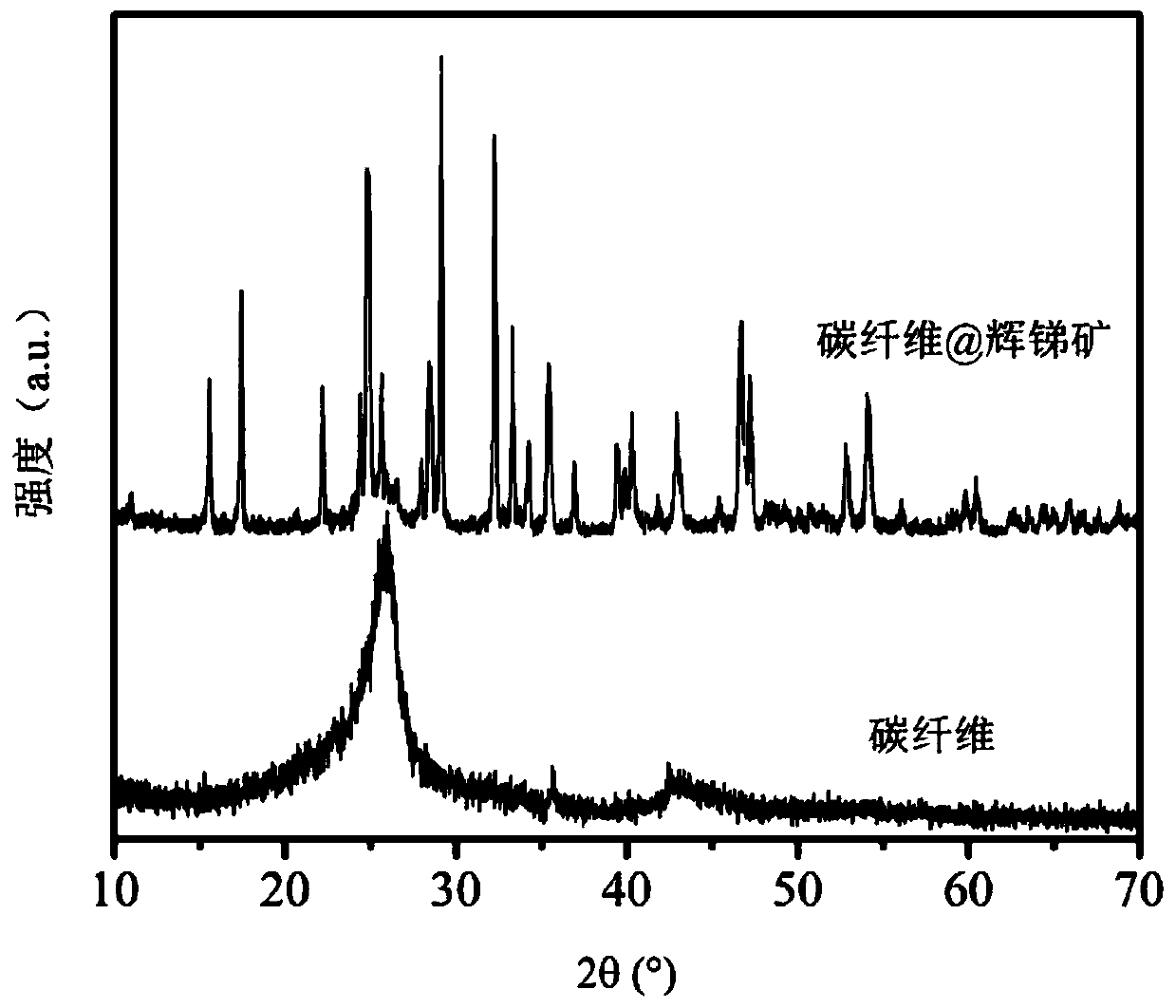
Antimony sulfide-based composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112072107AImprove conductivitySolve conductivity problemsSecondary cellsNegative electrodesSodium-ion batteryStibnite
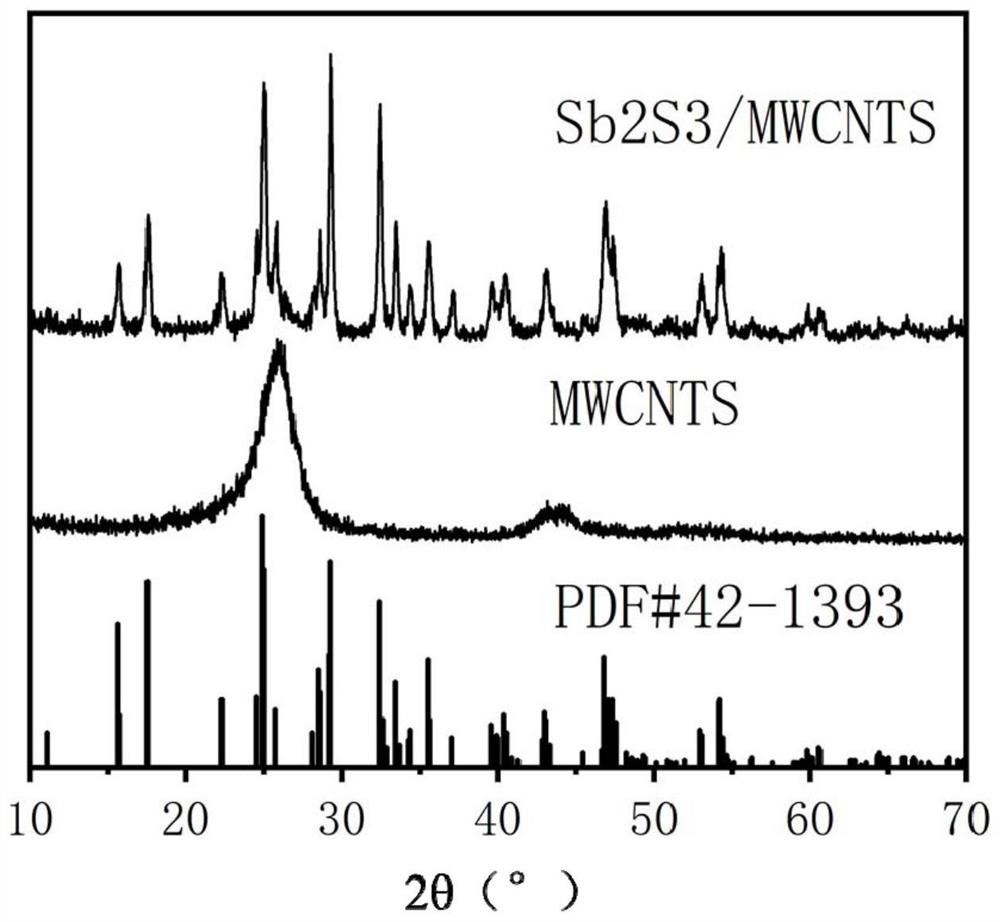
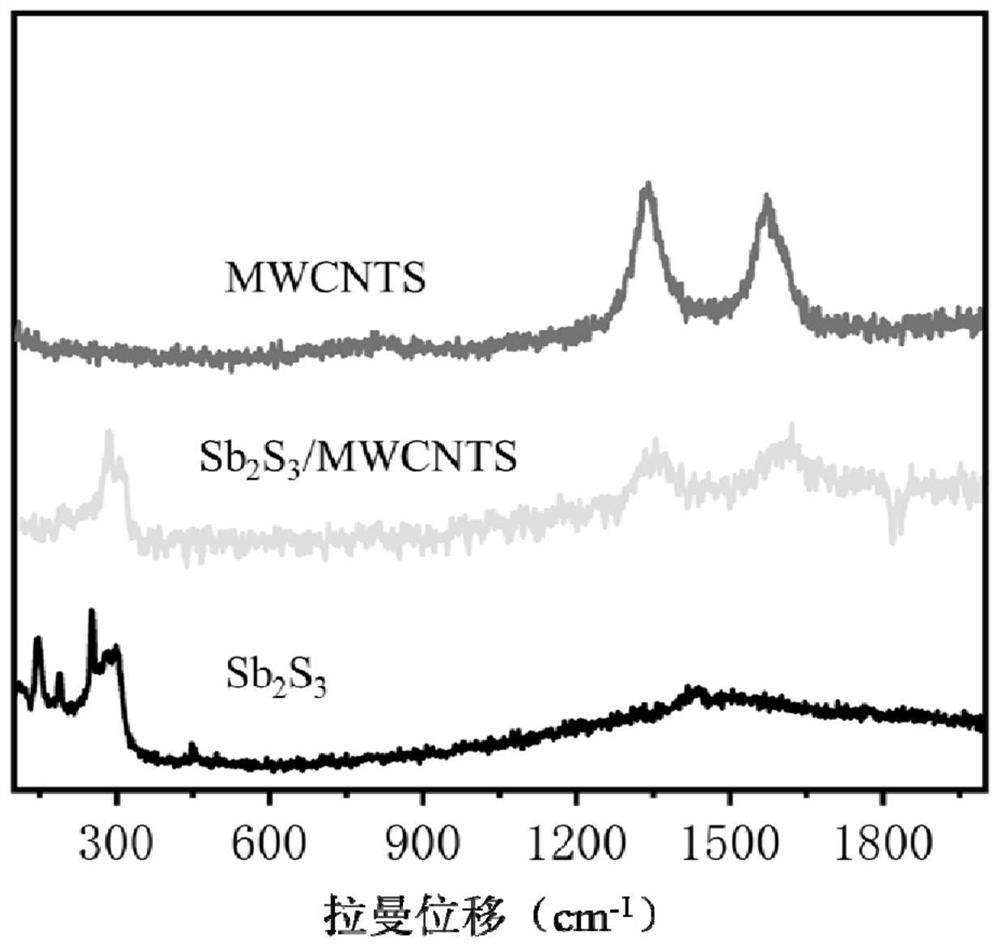
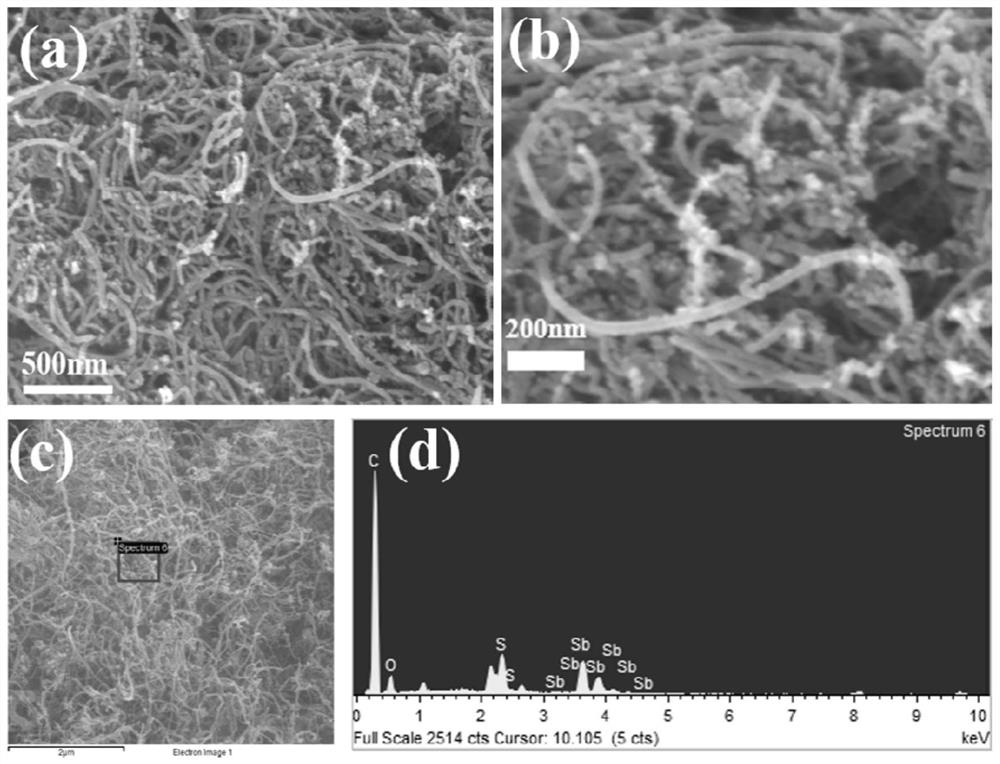
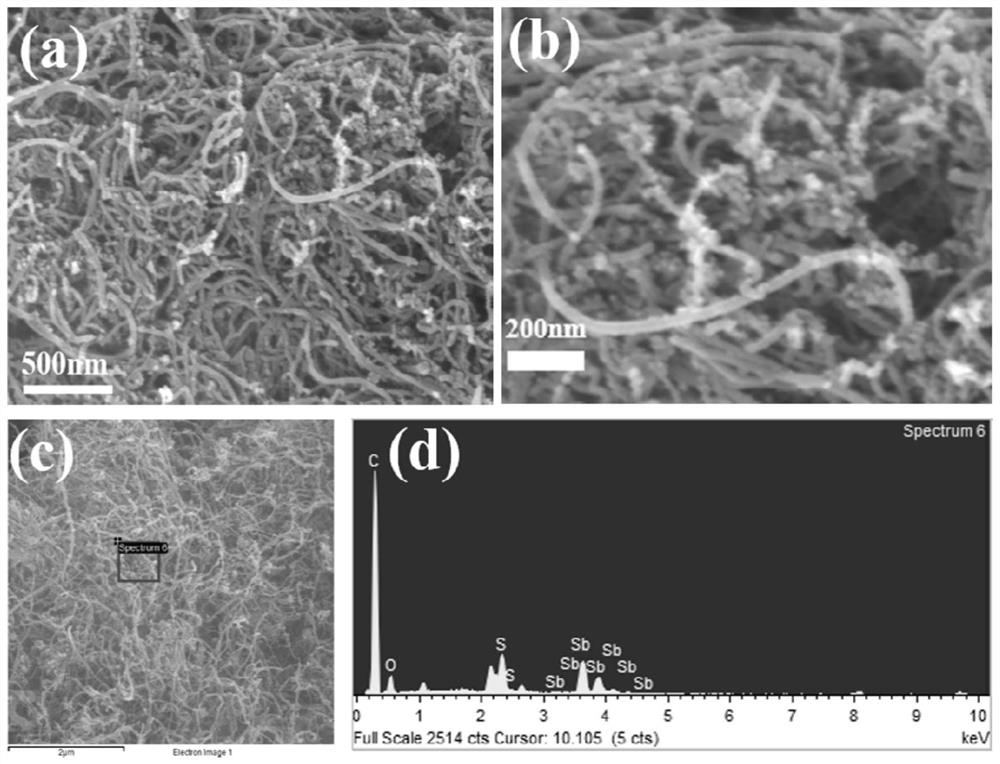
The invention discloses an antimony sulfide-based composite material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The antimony sulfide-based composite material is prepared from natural stibniteand a carbon material, and specifically, a solution obtained by dissolving the natural stibnite is mixed with a suspension containing the carbon material, and hydrothermal treatment and calcination treatment are performed to obtain the antimony sulfide-based composite material. The antimony sulfide-based composite material provided by the invention takes natural stibnite as a raw material, avoidsthe problems of environmental pollution and high cost in the process of preparing high-purity antimony sulfide, is simple and efficient in technological process, greatly reduces the preparation cost,is stable and reliable, is wide in application range, and has a wide application prospect as a lithium ion or sodium ion battery negative electrode material.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
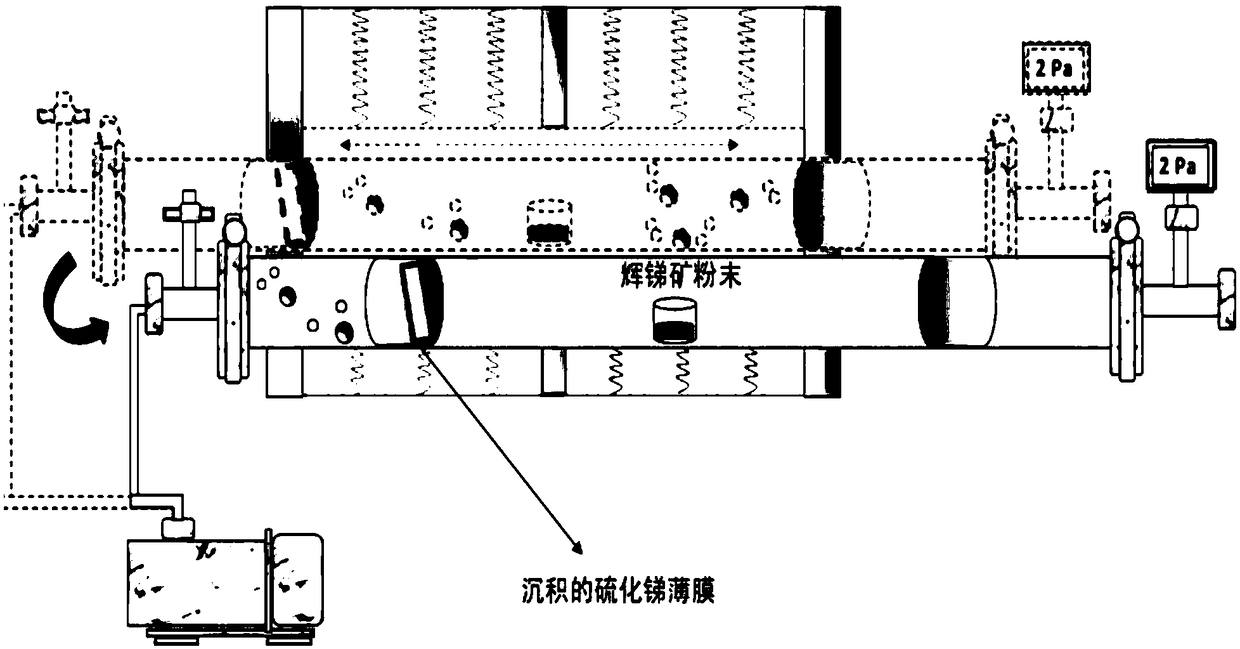
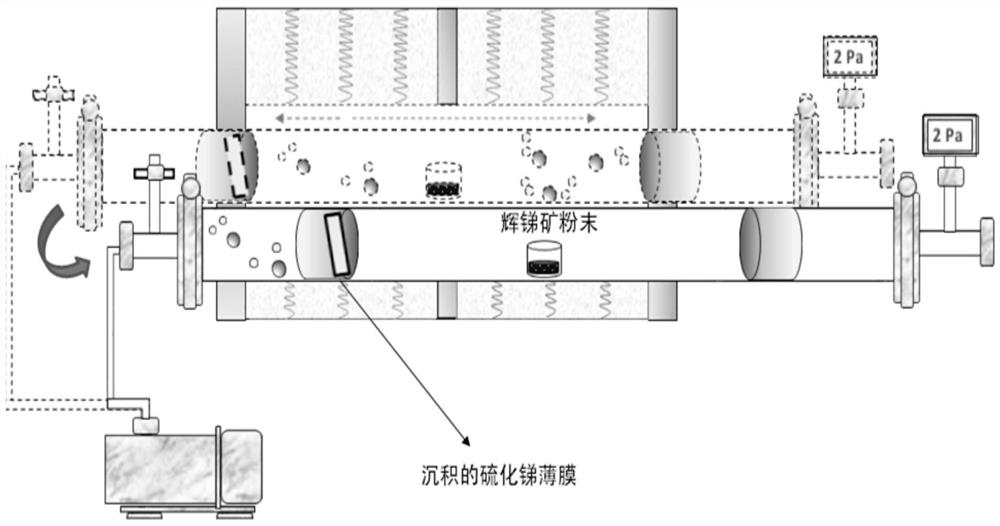
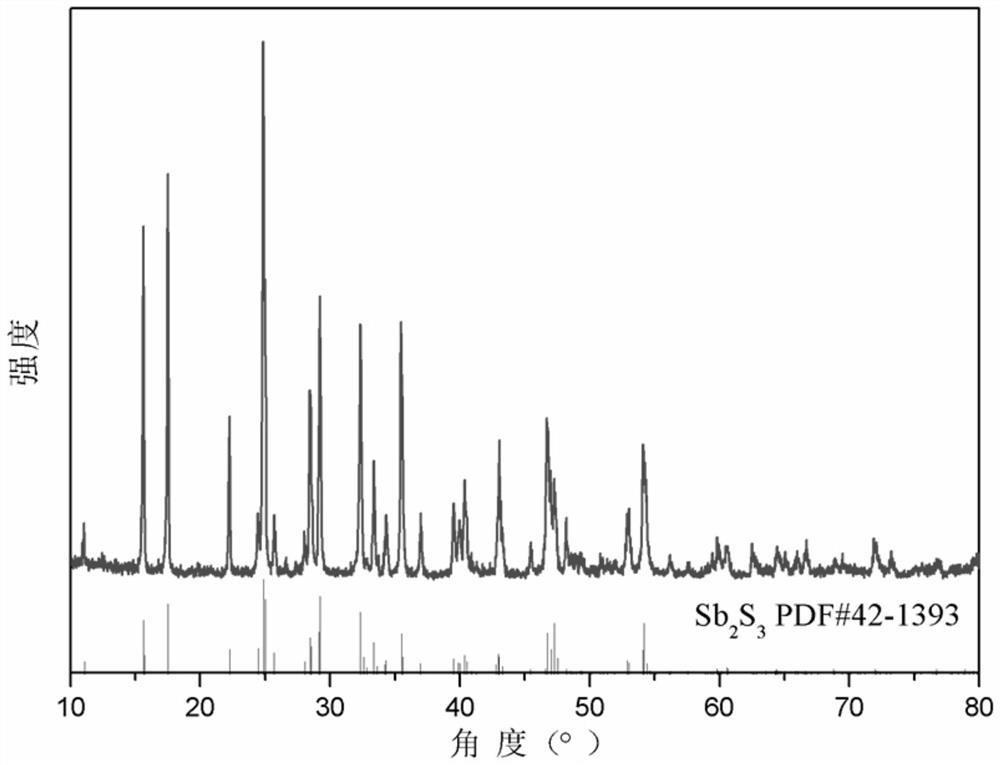
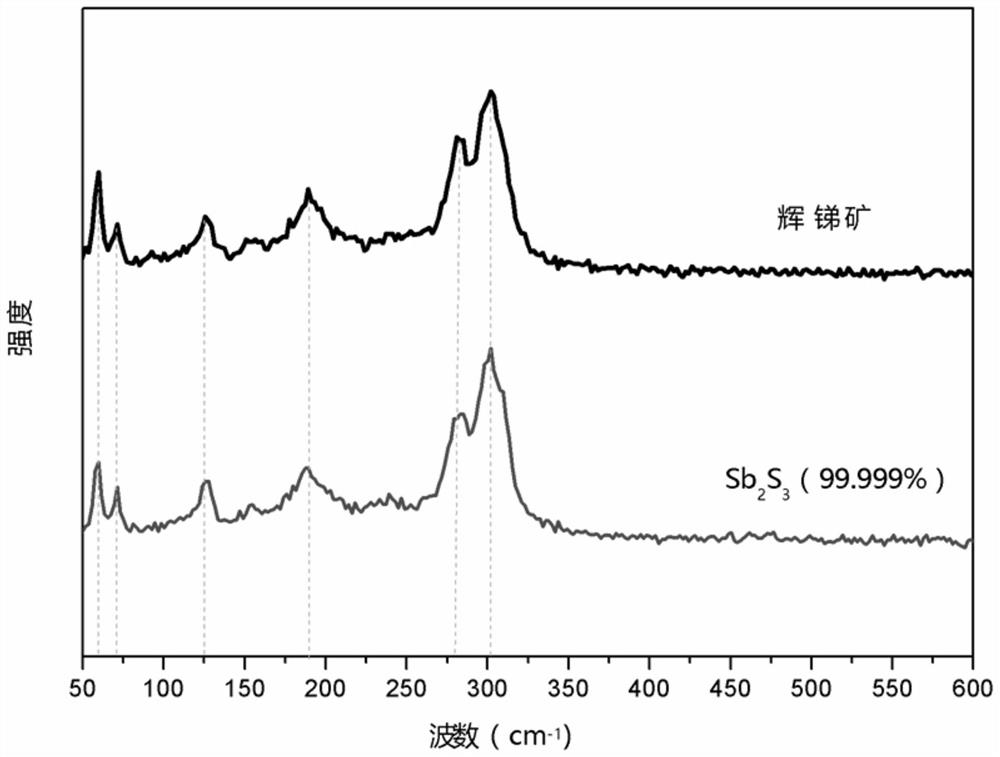
Preparation method for antimony sulfide film
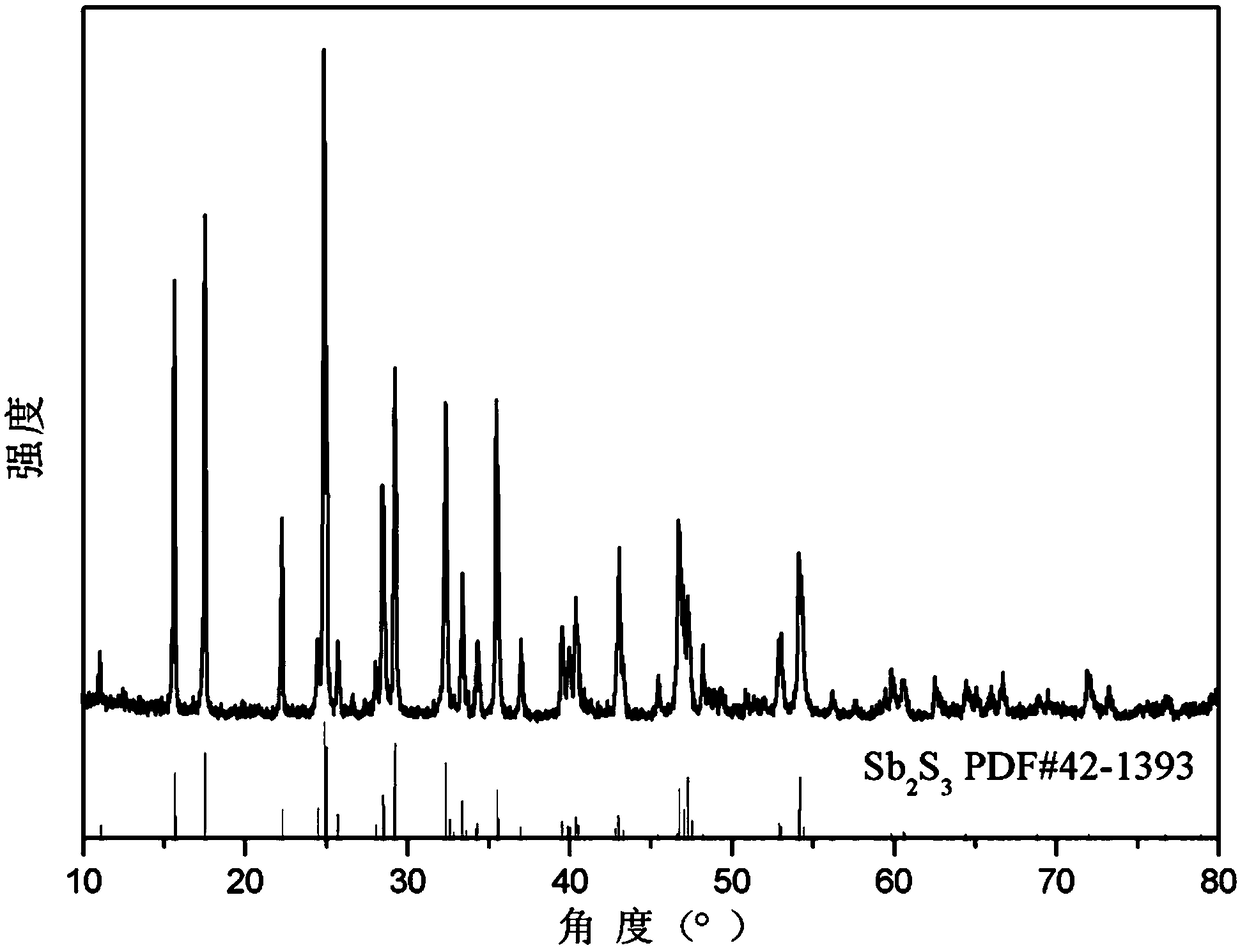
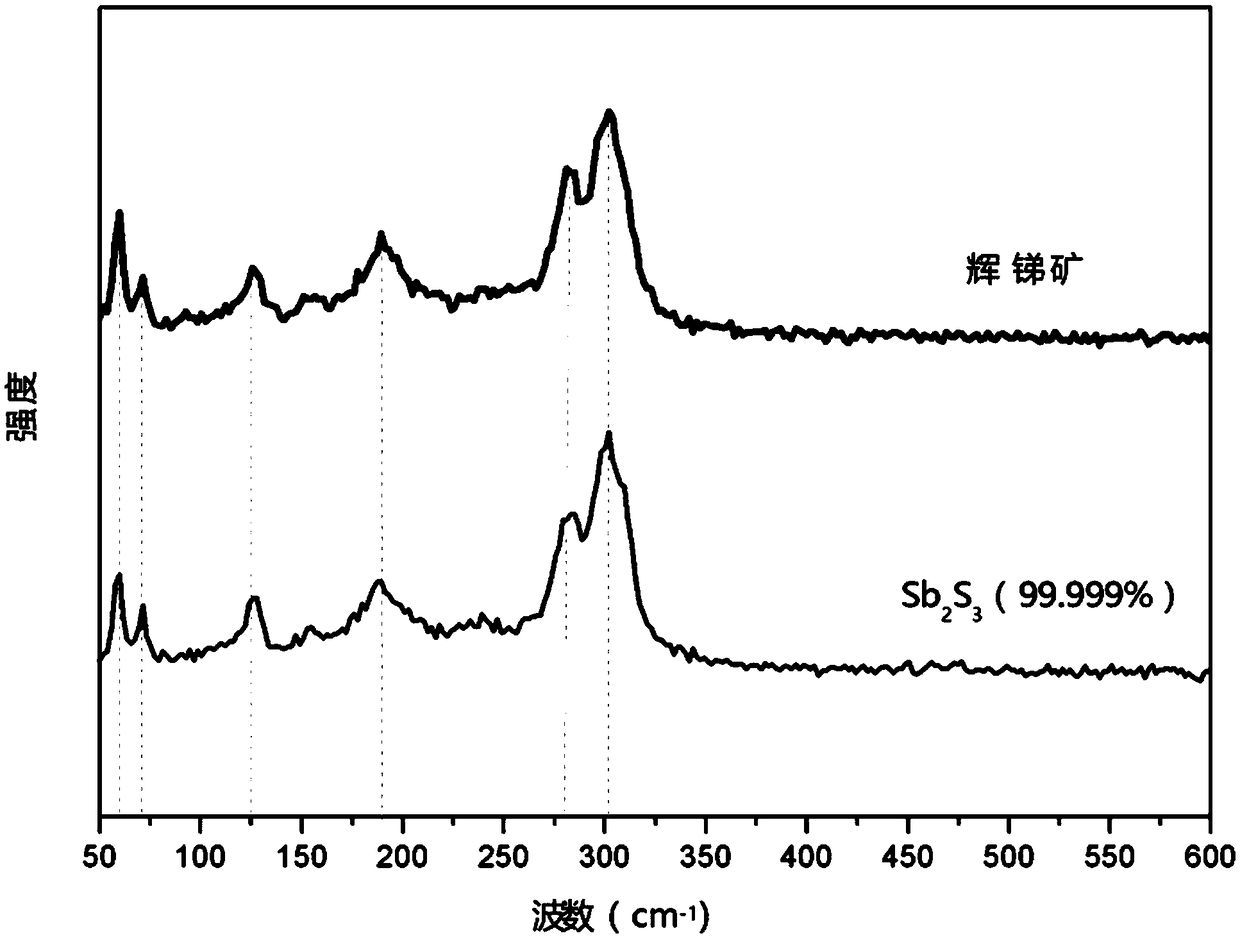
ActiveCN109504939ASolve the problem of impuritiesSolve the problem of low sulfurVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingStibniteImpurity
The invention discloses a preparation method for an antimony sulfide film. Raw materials for preparing the antimony sulfide film are stibnite which is simply screened. According to the preparation method, melting point differences of antimony sulfide in the stibnite from other impurities are used, tubular annealing furnace coating and annealing one-step treatment is used in cooperation, and the film which can be on a par with a film made of a raw material being high-purity antimony sulfide (with the purity higher than or equal to 99.999%) is prepared. In the process of preparing the antimony sulfide film, the preparation method can avoid the environmental pollution problem generated in the process of preparing the high-purity antimony sulfide raw material, can solve the problems of impurities and insufficient sulfur in the process of preparing the antimony sulfide film through the stibnite, is simple and efficient in technological process, greatly reduces the preparation cost, is stable, reliable, wide in application range and suitable for most substrates requiring coating with antimony sulfide, and is an energy-saving, high-efficiency, green and environment-friendly method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Sulfuration roasting flotation process for low-grade antimony oxide ore
InactiveCN103480496ASolve the problem of low recycling rateImprove Sb gradeFlotationMass ratioCalcite
The invention discloses a sulfuration roasting flotation process for low-grade antimony oxide ore. According to oxidation antimony ore (antimony ore is cervantitepseudomorph after stibnite and stibnite, gangue minerals are mainly quartz and calcite) containing 0.5%-2% Sb (stibium, by mass ratio), the ore is filtered and dried after 65%-85% ore (by mass ratio) is grinded to be minus 0.074mm (millimeter) in fineness, 1%-3% elemental sulfur powder (by mass ratio) is mixed up in fine ore and goes through reducing roasting under the temperature of 300-450 DEG C for 30-45 minutes, roasted products cool naturally, and then combination collecting agent of amyl xanthate and ammonium dibutyldithiophosphate is added and stibium is recovered according to sulfuration antimony ore flotation process. By the aid of the sulfuration roasting flotation process, the problem of low recovery and use rate of oxidation antimony ore resources is solved, compared with conventional antimony oxide reelection and flotation processes, grade and recovery rate of stibium in the fine ore can be greatly improved, and a good application prospect is provided for middle-and-low grade complex antimony oxide ore resources difficult in flotation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flotation inhibitor for separating fine stibnite from pyrite and application of flotation inhibitor
ActiveCN112237996AEnhanced inhibitory effectReduce inhibitionFlotationCelluloseCarboxymethyl cellulose
The invention discloses a flotation inhibitor for separating fine stibnite from pyrite and application of the flotation inhibitor, and the flotation inhibitor is composed of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, polyaspartic acid, sodium silicate and sodium sulfite in a mass ratio of (1.2-2.4): (0.4-0.6): (1-2): (1-2). The flotation inhibitor can be applied to separation flotation of fine-grained stibnite and pyrite, has an obvious inhibition effect on pyrite, has a weak stibnite inhibition effect, can achieve a good separation effect, can treat fine-grained stibnite with the raw ore stibium grade of 30-35%, and can obtain stibium concentrate with the stibium recovery rate of more than 85% and the stibium grade of more than 45%. In a conventional stibnite pyrite separation flotation inhibitor, cyanide with the good effect has toxicity, the cost is high, environmental pollution is large, and the inhibitor C is environmentally friendly and low in price. The inhibitor disclosed by the inventionis a combination of conventional industrial medicaments, is simple to prepare and is easy for industrial implementation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for producing free-cutting steel using stibnite
ActiveCN106011692BRealize comprehensive utilizationReduce enrichment segregationMineral SourcesMetallic materials
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy from ore raw materials
ActiveCN113061689AImprove organizationImprove mechanical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingFurnace temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing a silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy from ore raw materials, and relates to the technical field of multi-component alloy preparation. The method comprises the following steps of S1, cleaning silica, lime, barium ore, bauxite, semi-coke, fluorite, stibnite, bismuthine and lead-zinc slag, and crushing; S2, mixing the crushed silica, lime, barium ore, bauxite, semi-coke, stibnite and bismuthine in proportion, adding the mixture into a preheated submerged arc furnace for smelting in multiple times, and feeding once every 25 to 40 minutes; S3, adding the fluorite into the furnace 20 to 30 minutes before the smelted alloy is discharged out of the furnace; and when the furnace temperature is higher than 1780 DEG C, adding the lead-zinc slag to lower the furnace temperature, and obtaining the silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy after normal circulating smelting is conducted for 2.5 to 4 h. The silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy prepared by the method provided by the invention has excellent mechanical properties, high hardness and good wear resistance; and the silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy is good in deoxidizing capacity and desulfurizing capacity, can be used as a deoxidizing agent and a desulfurizing agent for a steelmaking process, and is beneficial to effectively improving the quality of steel.
Owner:SHIZUSN KETONG METALLURGY IND & TRADE
Method for preparing silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy with ore raw material
ActiveCN113061689BImprove organizationImprove mechanical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingFurnace temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloys from ore raw materials, and relates to the technical field of multi-element alloy preparation, including: S1: silica, lime, barium ore, bauxite, semi-coke, fluorite, stibnite, stibnite The bismuth ore and lead-zinc slag are cleaned and crushed; S2: Mix the crushed silica, lime, barium ore, bauxite, semi-coke, stibnite, and bismuthite in proportion, and add the mixture to the pre- Smelting in a hot submerged arc furnace, feeding once every 25 to 40 minutes; S3: adding fluorite to the furnace 20 to 30 minutes before the smelted alloy is released; when the furnace temperature is higher than 1780°C, add lead and zinc slag to reduce the furnace temperature, The silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy can be obtained after 2.5-4 hours of normal circulation smelting. The silicon-calcium-barium-aluminum alloy prepared by the invention has excellent mechanical properties, high hardness, and good wear resistance; good deoxidation and desulfurization capabilities, and can be used as a deoxidizer and desulfurizer for steelmaking processes, effectively improving the quality of steel .
Owner:SHIZUSN KETONG METALLURGY IND & TRADE
A kind of preparation method of antimony sulfide film
ActiveCN109504939BSolve the problem of impuritiesSolve pollutionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing an antimony sulfide thin film, wherein the raw material for preparing the antimony sulfide thin film is antimony mineral which has been simply screened. The present invention utilizes the difference in melting point between antimony sulfide and other impurities in antimony minerals, and combines the one-step treatment of coating and annealing in a tubular annealing furnace to prepare a film with properties comparable to those prepared by using high-purity antimony sulfide (≥99.999%) as a raw material. film. In the process of preparing antimony sulfide film, the present invention can not only avoid the environmental pollution problem produced in the process of preparing high-purity antimony sulfide raw material, but also solve the problem of impurities and less sulfur in the preparation of antimony sulfide film from stibnite, and the process The process is simple and efficient, greatly reduces the preparation cost, is stable and reliable, and has a wide range of applications. It is suitable for most substrates that need to be coated with antimony sulfide. It is an energy-saving, efficient, green and environmentally friendly method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
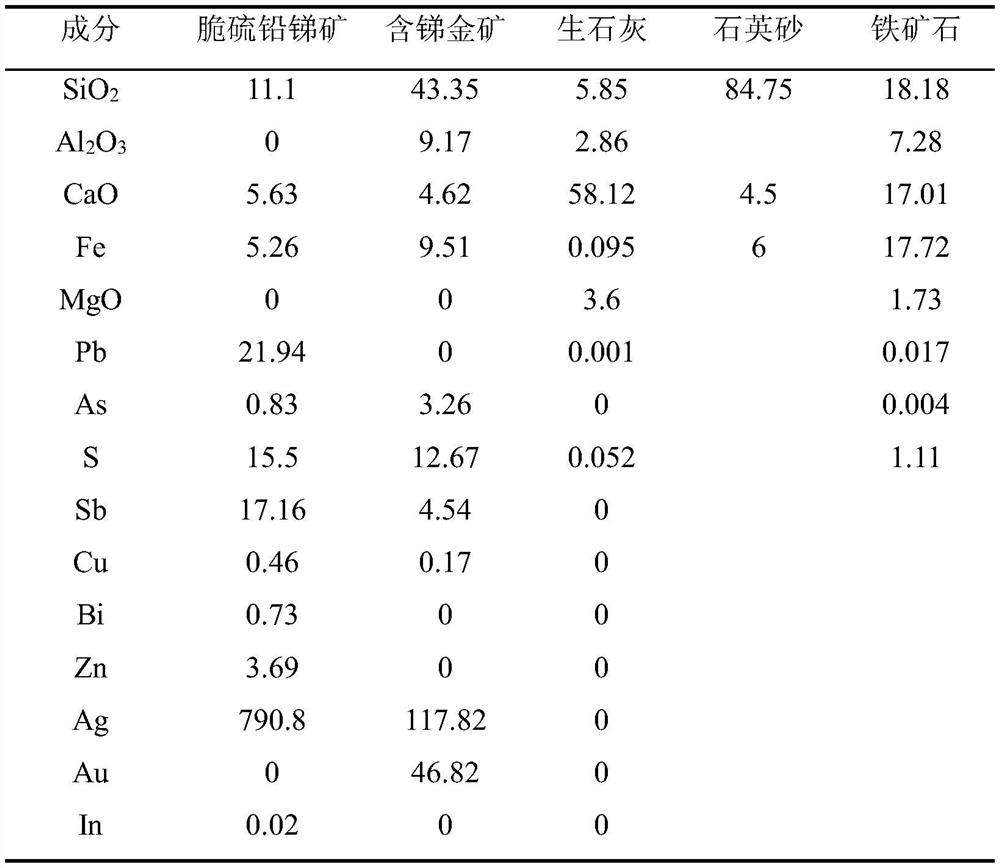
A kind of antimony gold complex resource collaborative smelting method
A method for synergistic smelting of complex resources of antimony and gold, comprising the following steps: (1) mixing at least one of stibnite, brittle sulphur lead-antimony and antimony-containing gold ore, grinding and drying to obtain pretreated mineral material; (2) ) Mixing the pretreated ore and flux into the smelting furnace, feeding oxygen-enriched air for heating and smelting, to obtain high-temperature arsenic-antimony flue gas and precious metal slag; (3) adopting step-by-step condensation treatment of high-temperature arsenic-antimony flue gas to obtain antimony respectively , arsenic soot; (4) adding precious metal slag and metal lead into the smelting furnace, blowing air for reduction smelting, trapping precious metal by lead to obtain precious lead and tailings for capturing precious metal; (5) adding precious metal trapping Precious lead is subjected to vacuum distillation to obtain precious metal phase and lead vapor, and lead vapor is condensed to obtain lead powder. The invention realizes the synergistic smelting of precious metal and antimony, and can recover antimony and precious metal respectively, and the recovery rate of antimony and precious metal gold and silver is high.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of antimony sulfide-based composite material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112072107BImprove conductivityLithium intercalation path shortenedNegative electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses an antimony sulfide-based composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. The antimony sulfide-based composite material is prepared from natural stibnite and carbon materials. The suspension of the carbon material is mixed and then subjected to hydrothermal treatment and calcination to obtain the antimony sulfide-based composite material. The antimony sulfide-based composite material provided by the invention uses natural stibnite as raw material, avoids the problem of environmental pollution and high cost in the process of preparing high-purity antimony sulfide, and has a simple and efficient technological process, greatly reduces the preparation cost, and is stable and reliable. , the obtained antimony sulfide-based composite material has a wide range of applications, and has broad application prospects as a negative electrode material for lithium ion or sodium ion batteries.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for gold separation by means of removing antimony
InactiveCN103203281BEliminate negative effectsSimplified process conditionsWet separationSulfidationSulfide minerals
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com