Method for separating Co (cobalt) and Li (lithium) from LiCoO2 (lithium cobalt oxide) of waste lithium batteries to prepare cobaltous phosphate
A technology for waste lithium batteries and lithium cobalt oxide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, solid waste removal, phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve problems such as low recovery efficiency, secondary pollution, and complicated recovery process, and achieve separation and recovery High efficiency, small liquid-solid ratio, and solve the effect of complex recovery process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
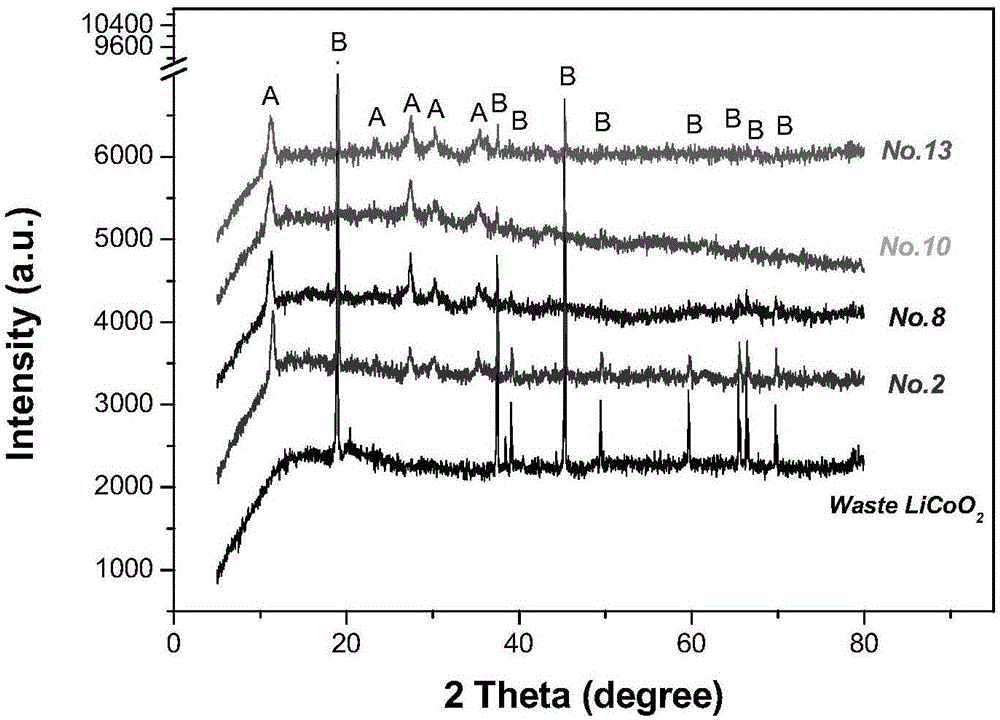
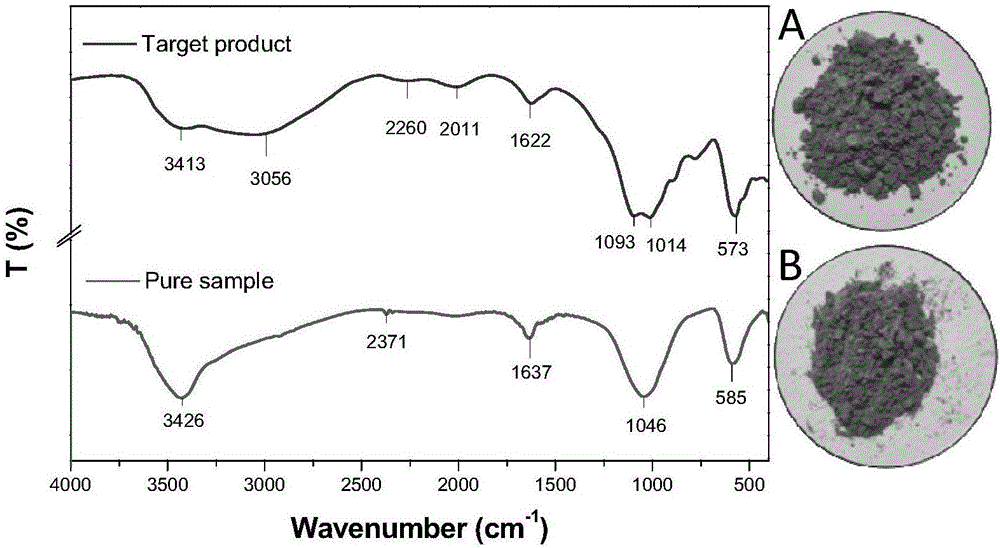
[0028] (1) Take about 5kg of typical waste lithium batteries (the positive electrode active material is LiCoO 2 ) for disassembly and pretreatment, and the metal case, separator, current collector pole piece (Al foil and Cu foil), positive and negative active material powder mixture and other components can be obtained respectively. Then the obtained 2.17kg positive and negative electrode active material powder (the main component is LiCoO 2 and C) calcined in a muffle furnace at 700 °C for 2 h, fully ground in a ball mill and passed through a 200-mesh sieve to obtain 1.38 kg of fine-grained waste LiCoO 2 powder.
[0029] (2) Then each time accurately weigh the LiCoO of the fine particles obtained above 2 About 5 grams of powder were placed in a 250mL three-necked flask; corresponding orthogonal experiments were designed (L16(4 5 ), a total of 16 experiments: No.1~No.16), under the experimental conditions of controlling the reaction temperature at 40~80℃, the stirring rate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com