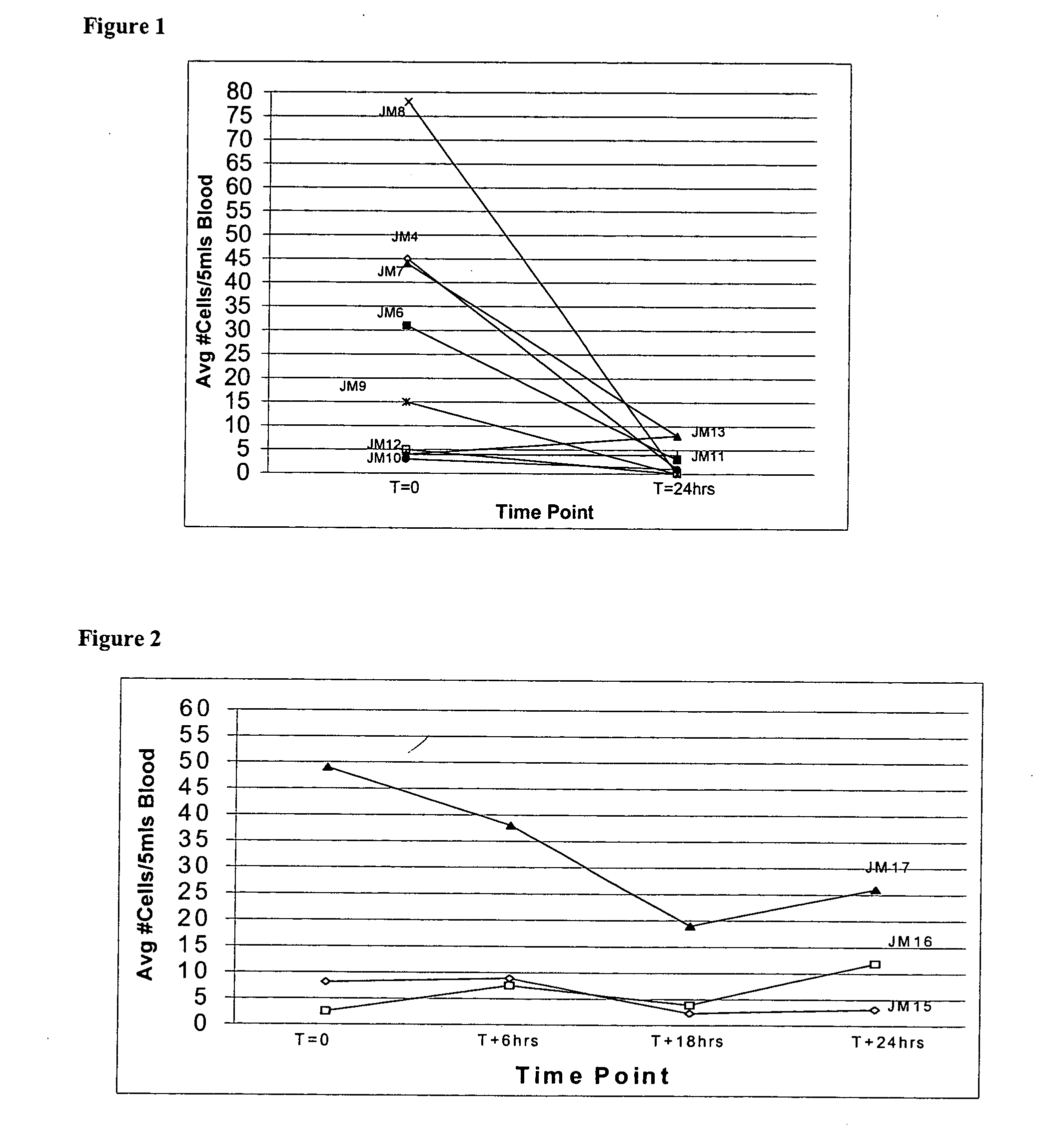
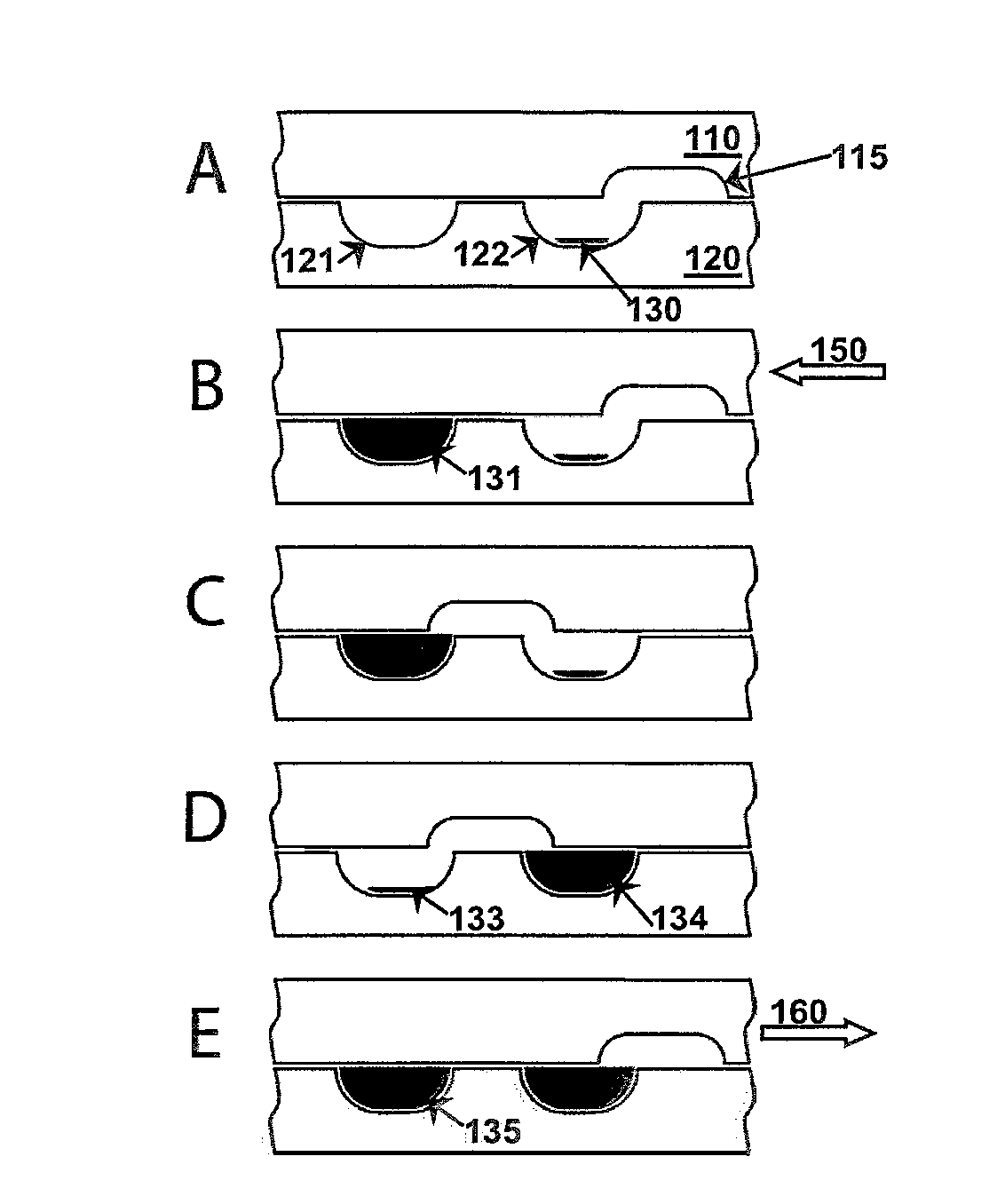
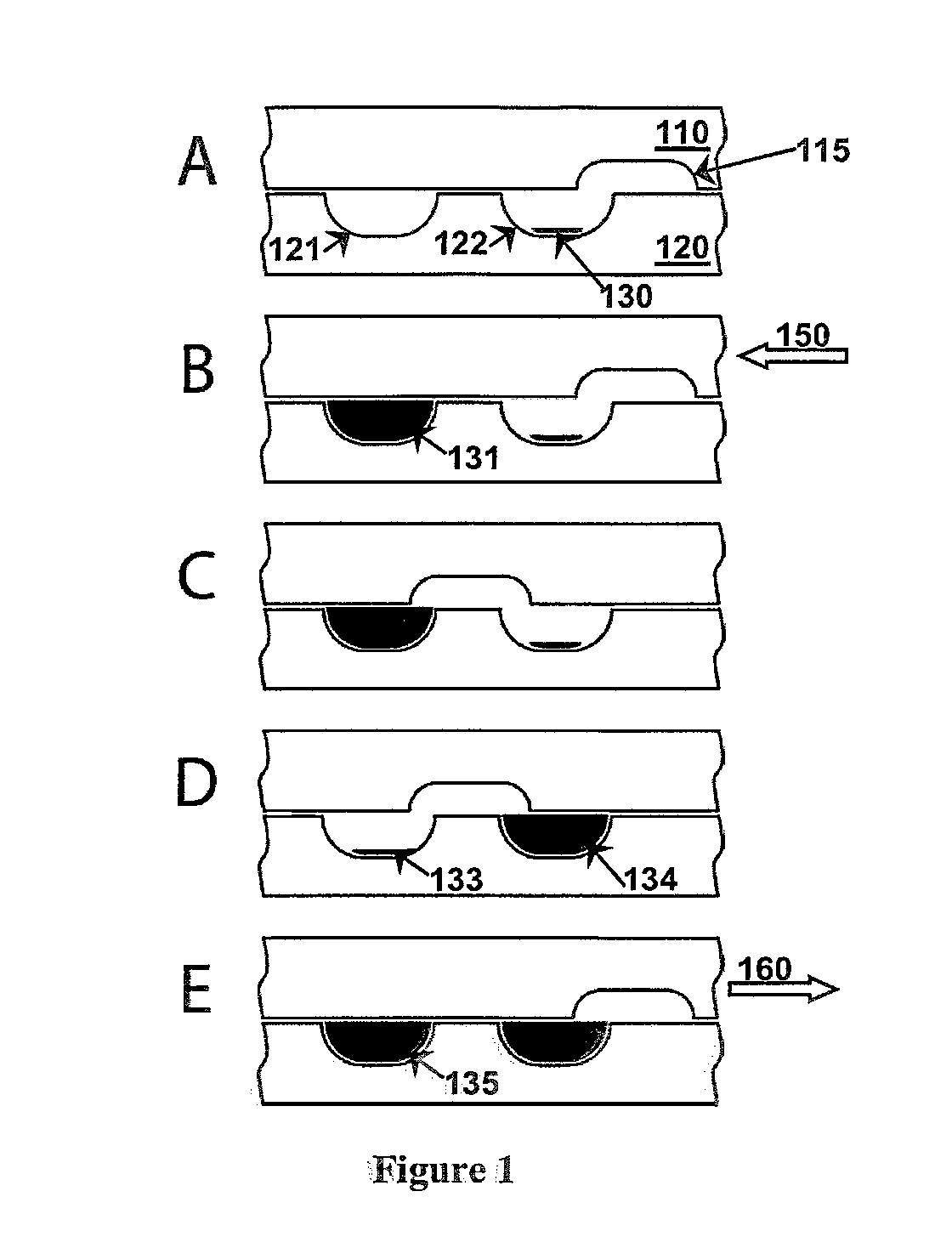
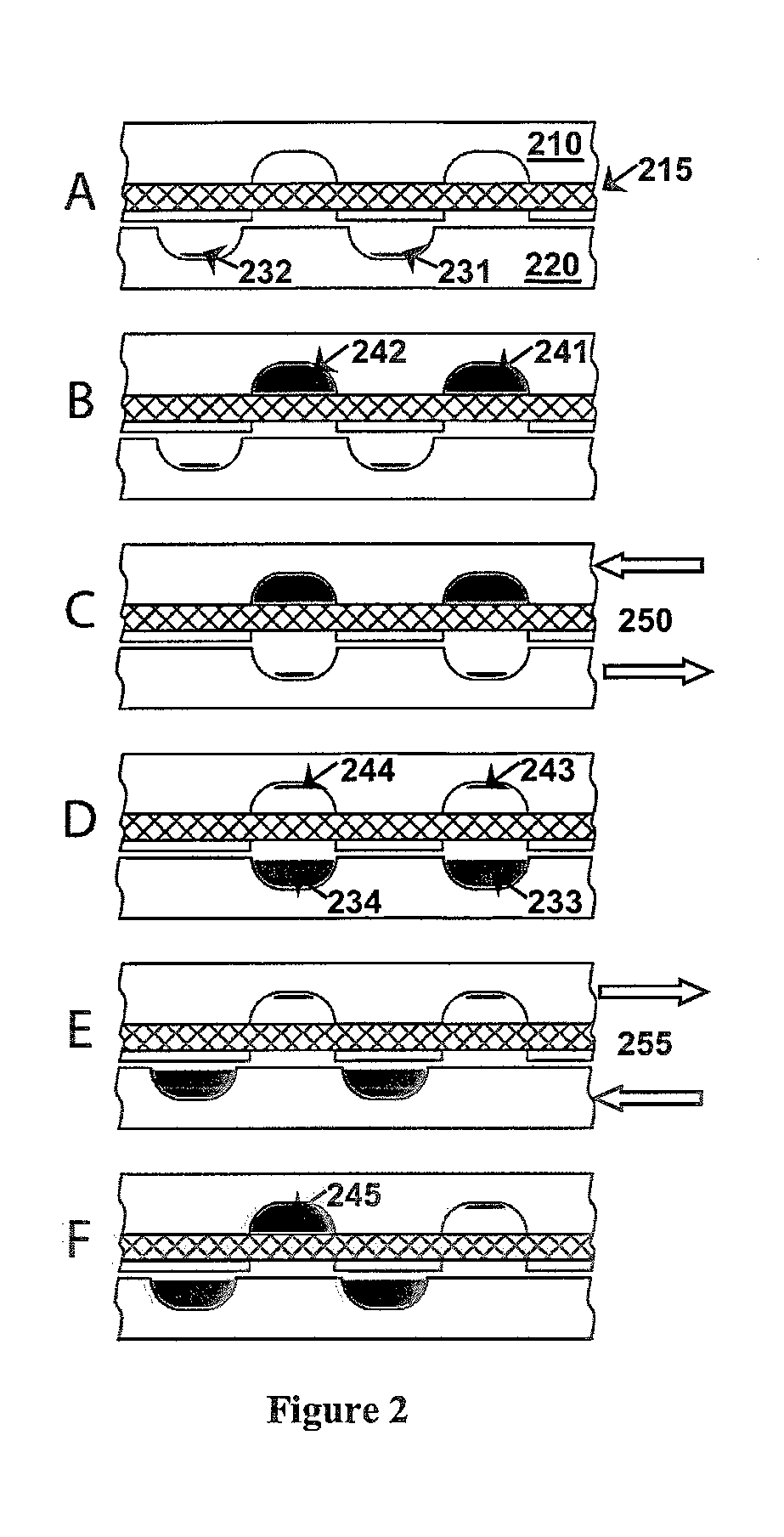
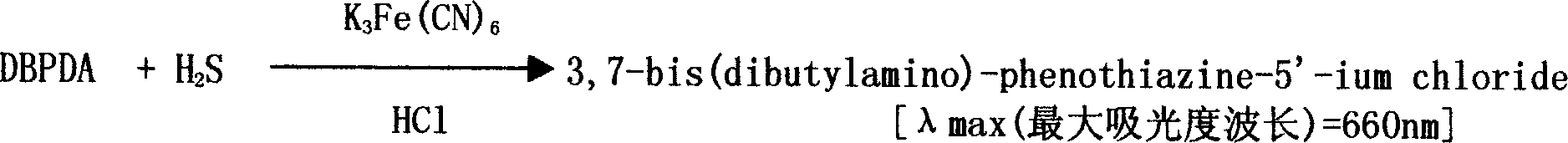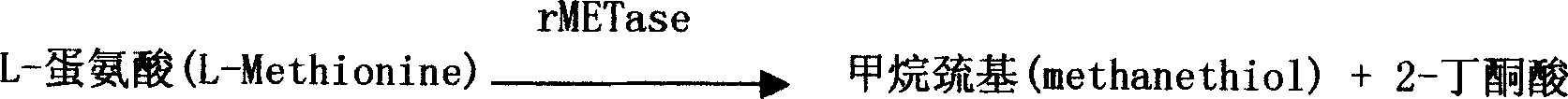Patents
Literature
283 results about "Biospecimen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A substance or portion of material originally obtained from an entity for use in testing, examination, or study. EXAMPLE(S): Blood obtained by a specimen collection activity performed on a study subject. A few grains of cattle feed obtained from a feed sack. A randomly selected pill from a blister pack. A serum specimen that resulted from Centrifugation procedure performed on a blood specimen. A DNA specimen extraction from a saliva specimen. A Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) block that resulted from a paraffin embedding procedure performed on a formalin fixed tissue specimen. A pooled blood sample that resulted from a mixing procedure performed on several blood samples taken from individual animals. OTHER NAME(S): Biologic specimen; Product specimen.
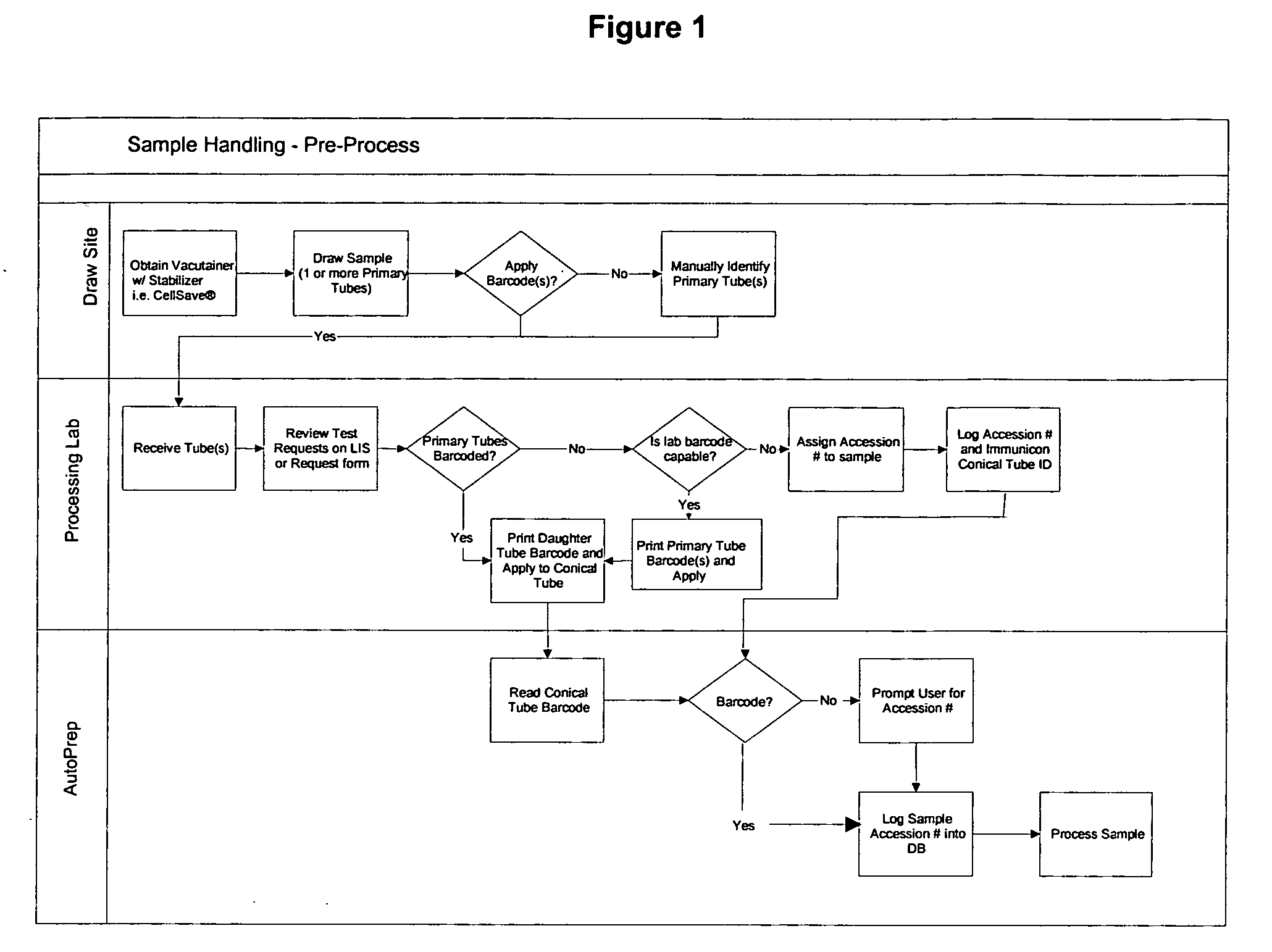
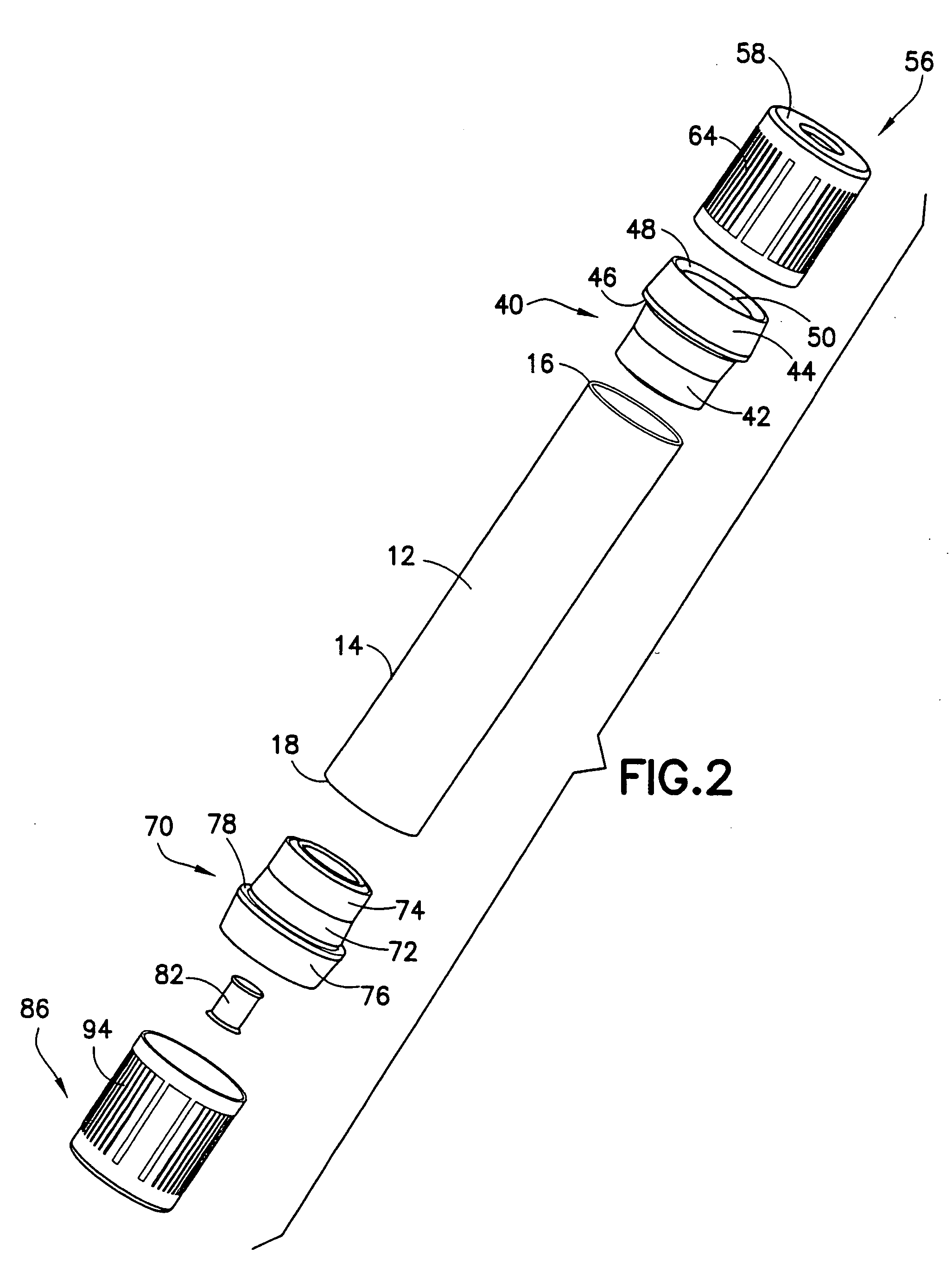
Method and device for withdrawing biological samples
InactiveUS6659338B1Eliminate disadvantagesExtensive automationWithdrawing sample devicesSurgeryWork cycleBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a method and device for withdrawing biological samples. The device has a receptacle which can receive one or several covers for sample containers, another receptacle which can receive one or several sample containers, and a mechanism. Said mechanism joins the covers and containers together during a working cycle in which the biological sample is withdrawn either through the cover or the sample container to a test capsule.
Owner:CAISLEY INT
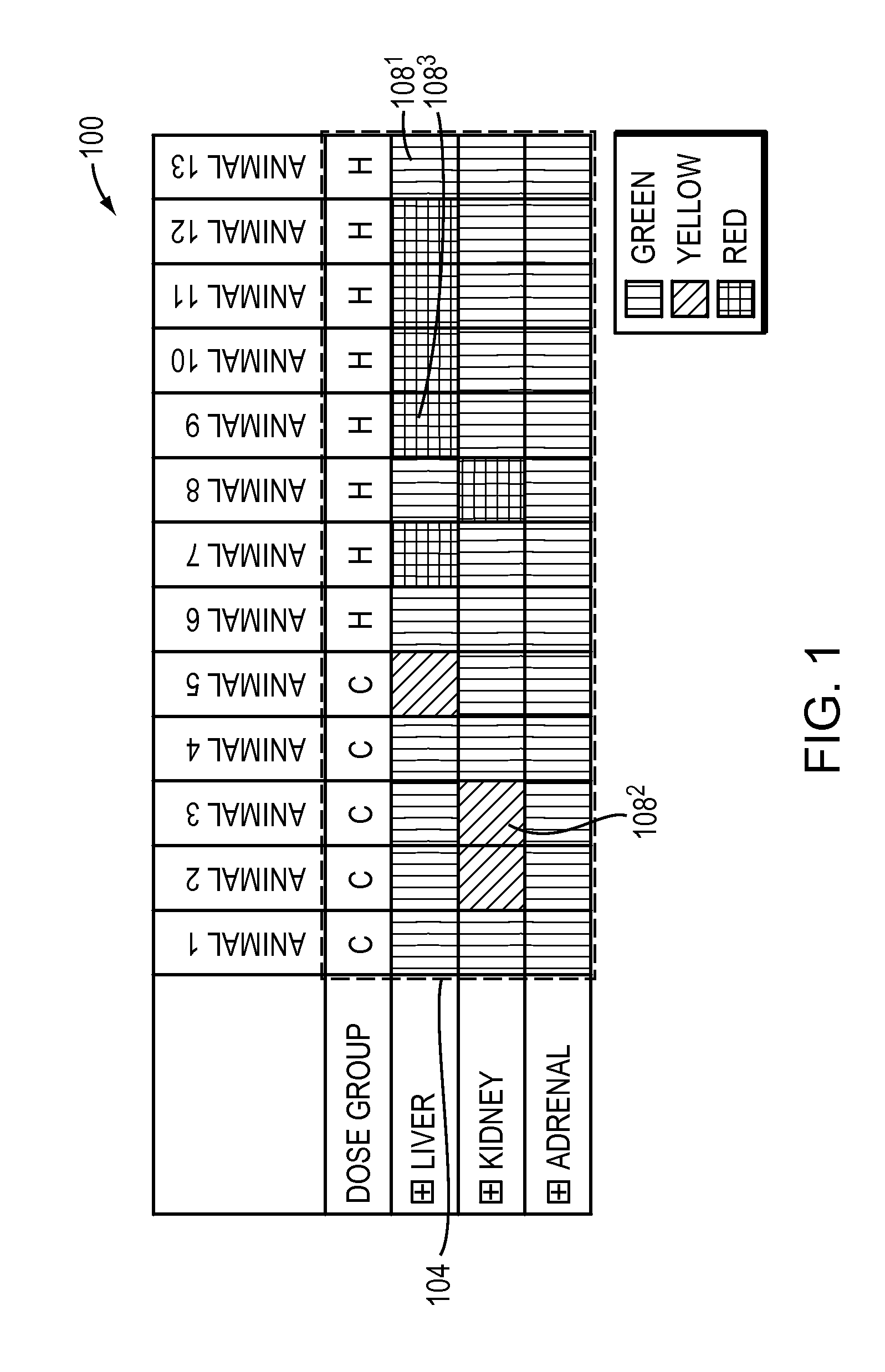
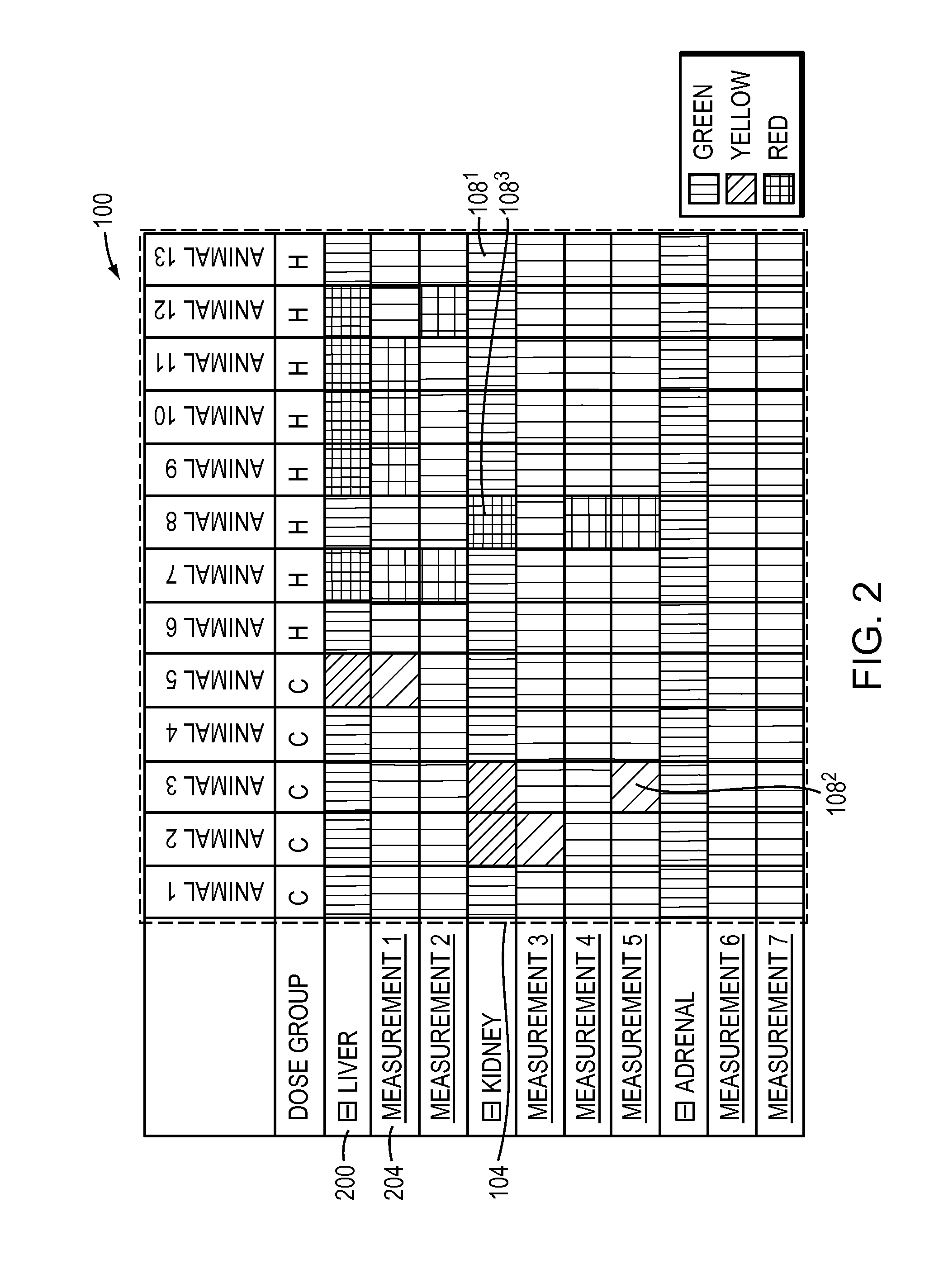
Methods and Apparatus for Interactive Display of Images and Measurements
InactiveUS20120019559A1Medical data miningDrawing from basic elementsInteractive displaysHuman–computer interaction
Owner:CHARLES RIVER LAB INC
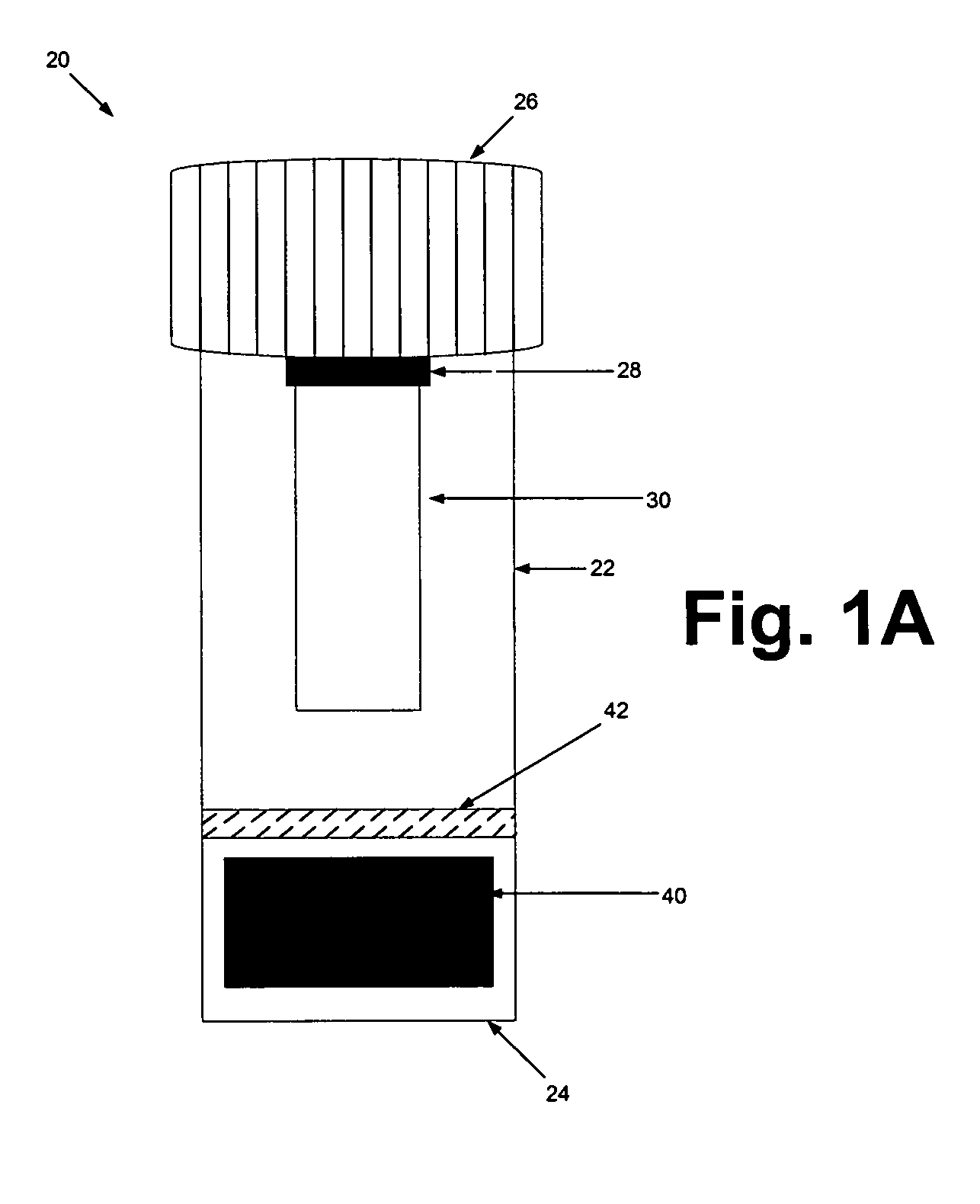
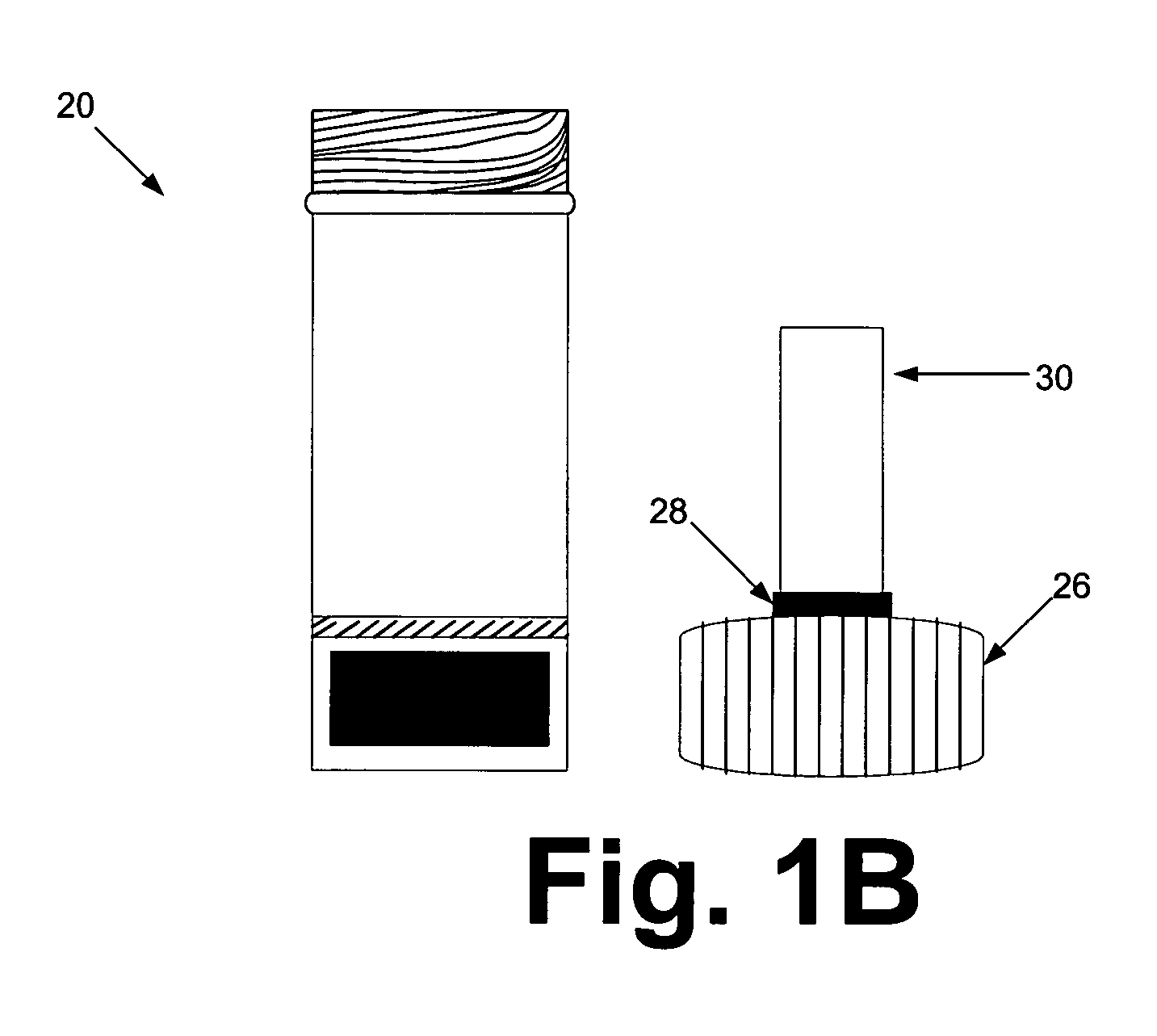
Devices and methods for collection, storage and transportation of biological specimens
InactiveUS20050227269A1Safe and convenient and simple deviceLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides devices and methods for collecting, storing or transporting liquid suspension of biological specimens containing analytes of interest in a dry state. The dried biological specimens containing analytes of interest are reconstituted and released for subsequent analysis by compressing the matrix in the device. Also provided are kits for collecting, storing, transporting and recovering biological specimens containing analytes of interest.
Owner:VIVEBIO
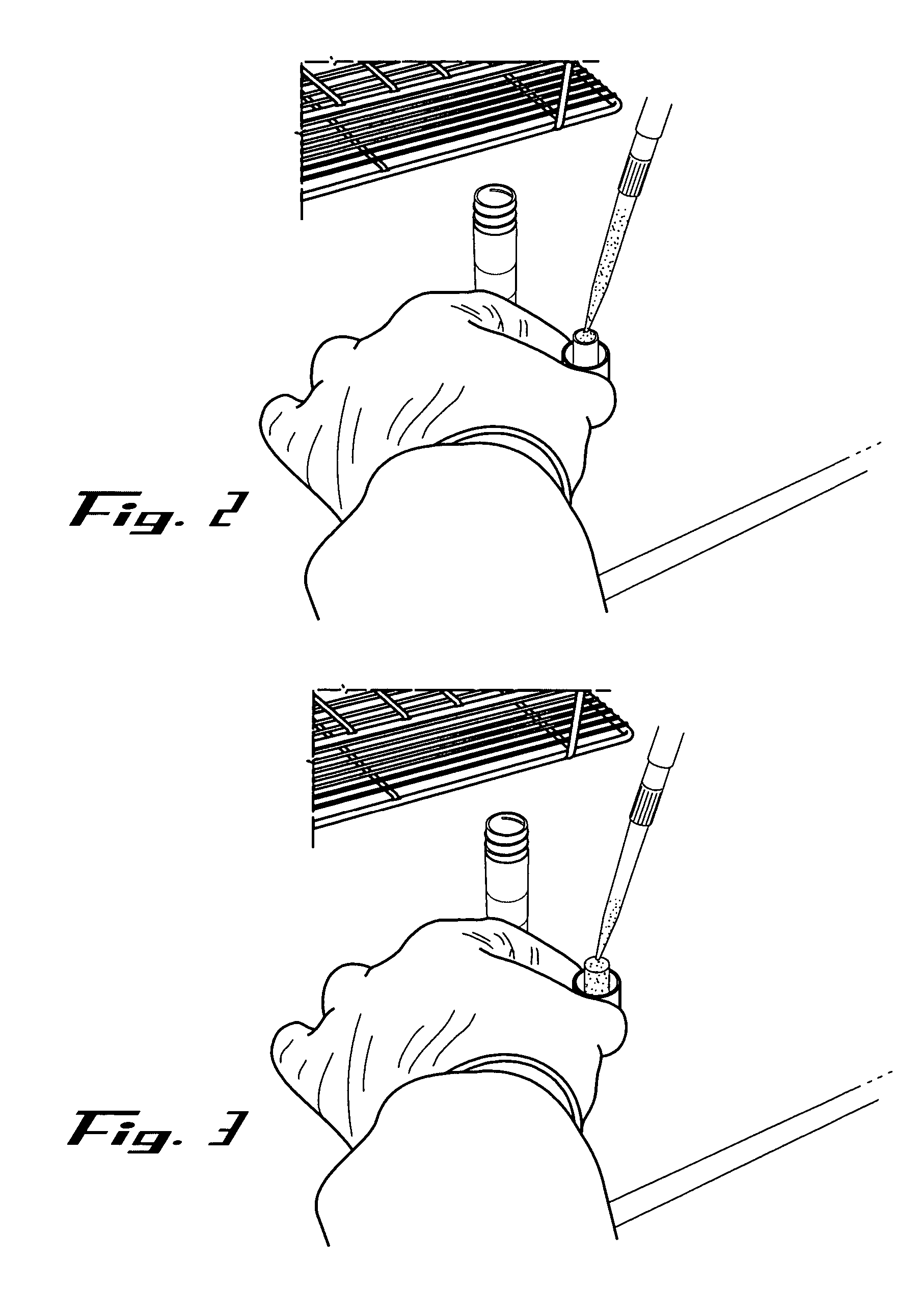
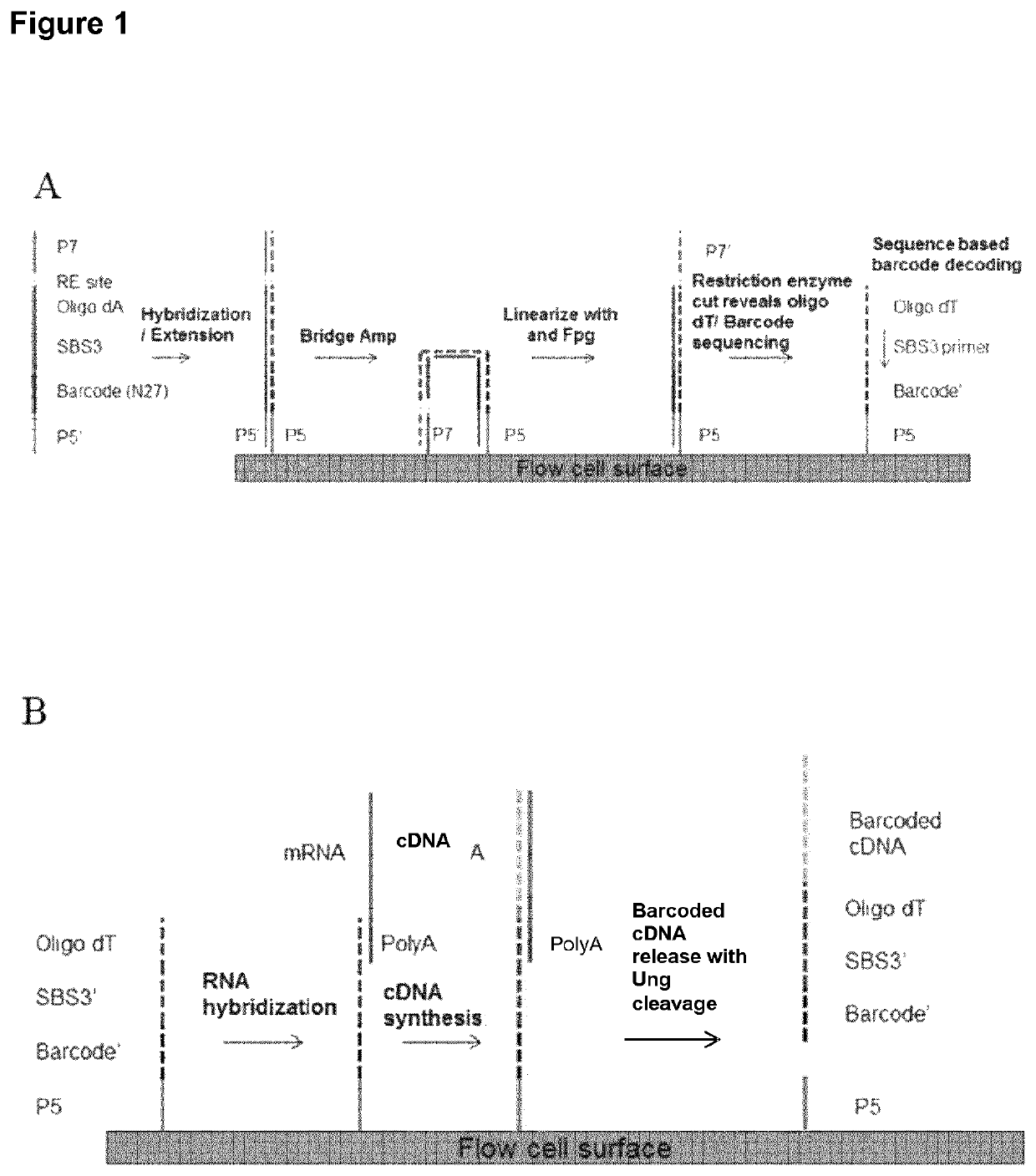
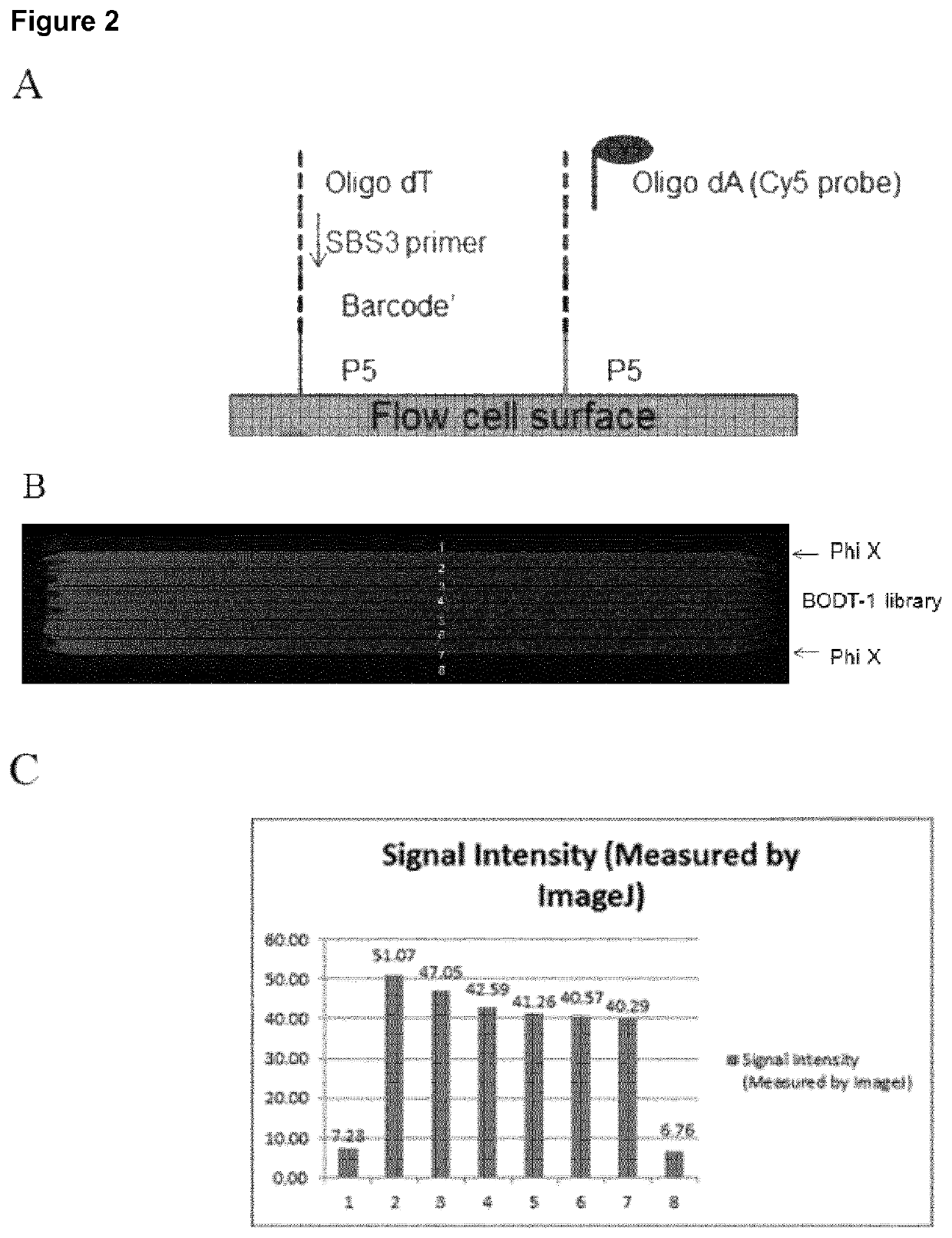
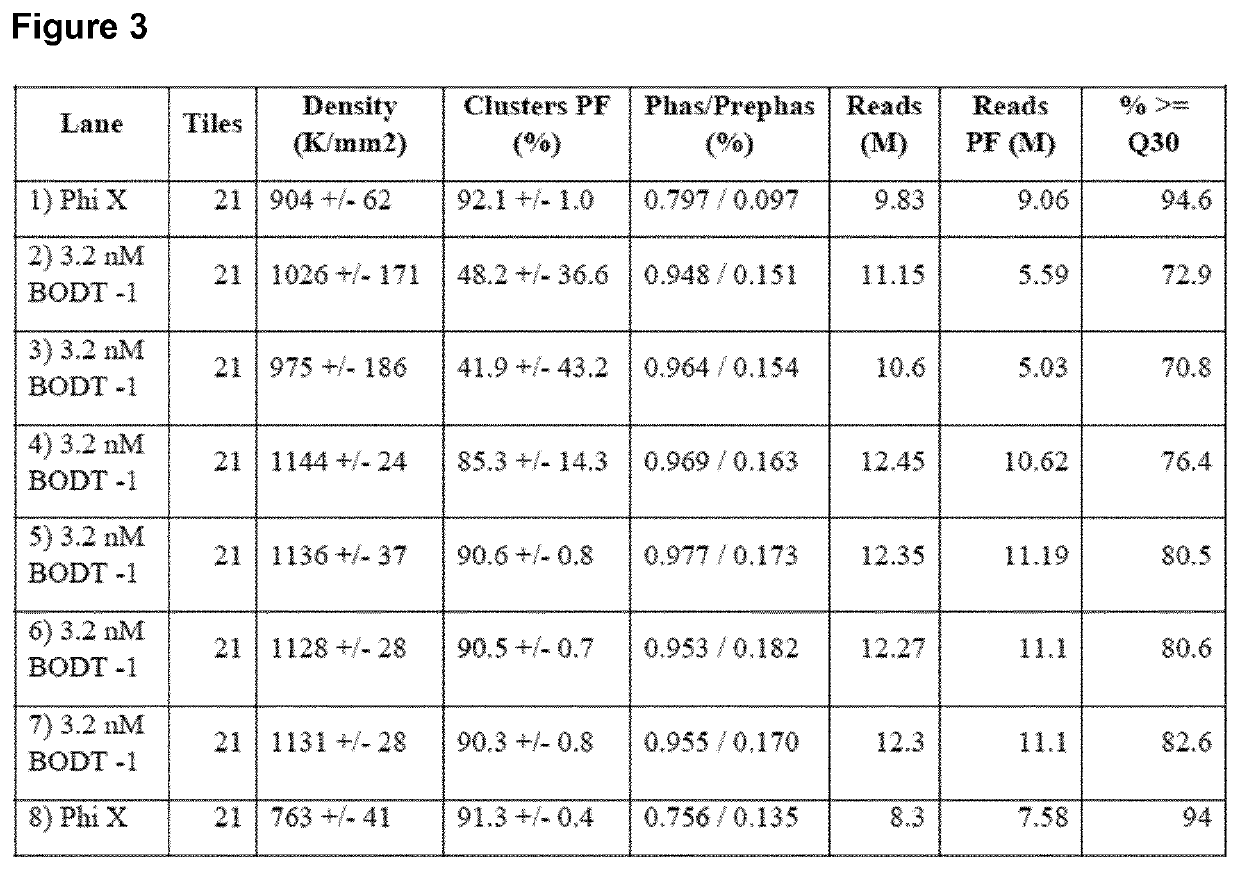
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
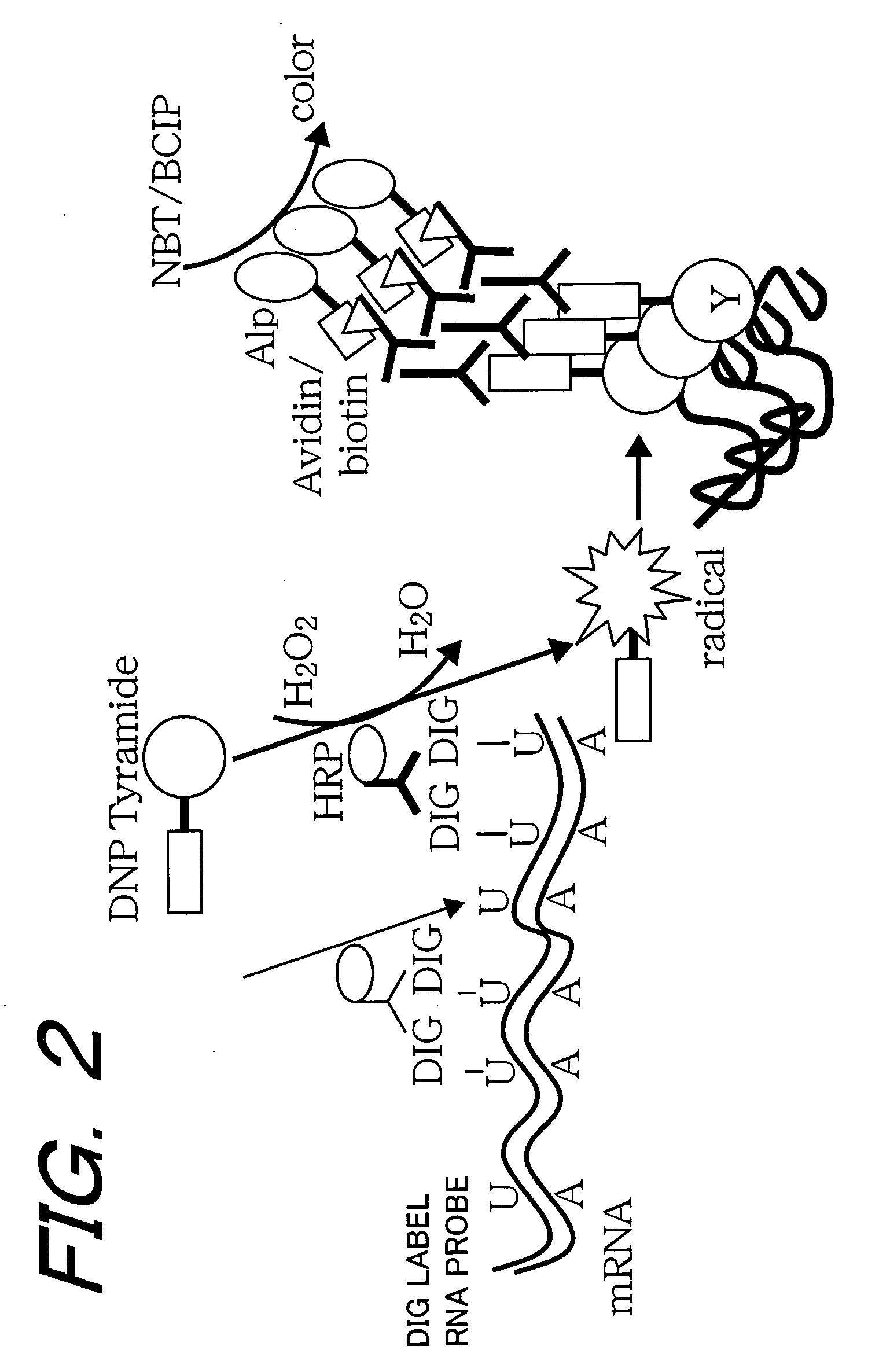
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:X GENOMICS SWEDEN AB +1
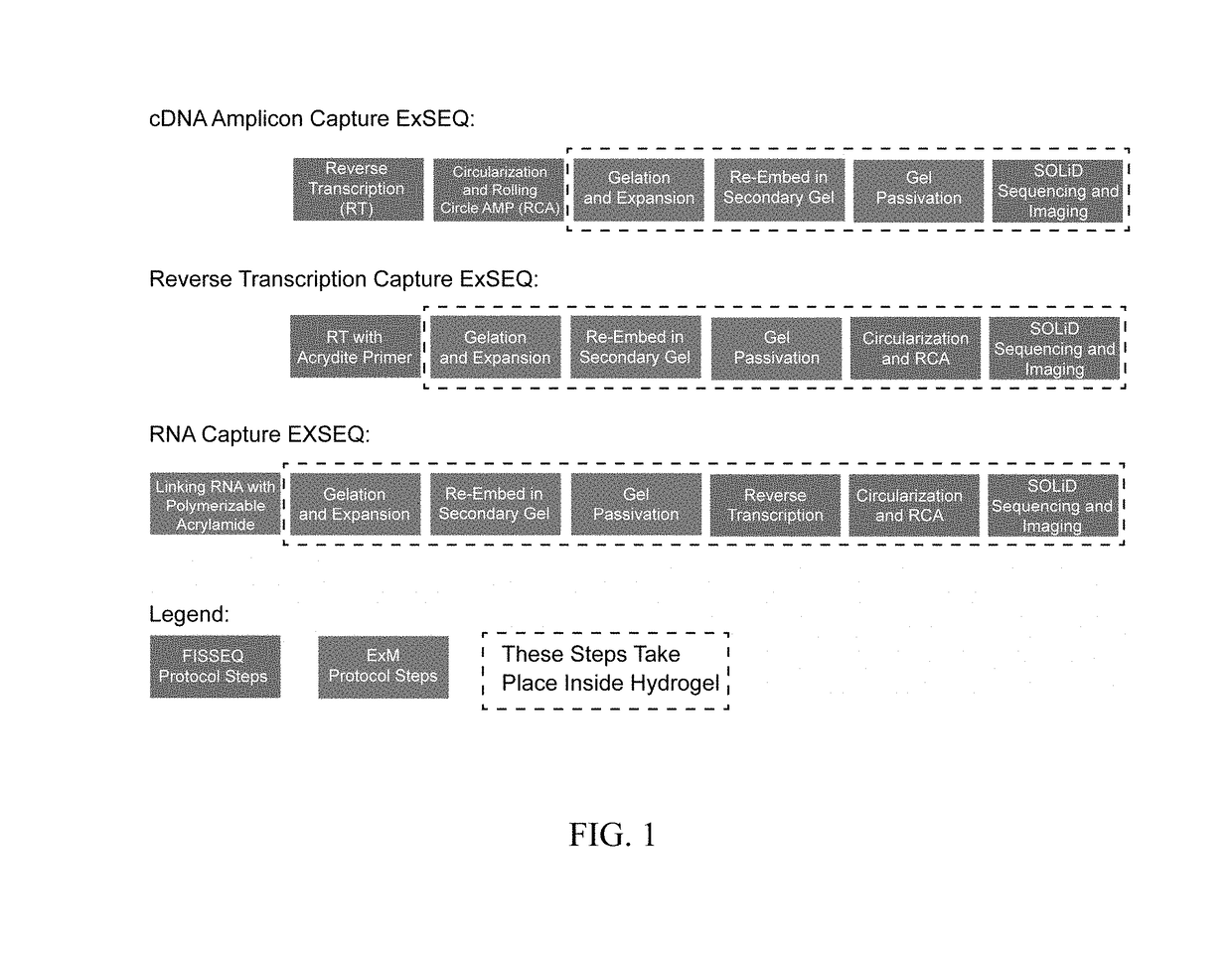
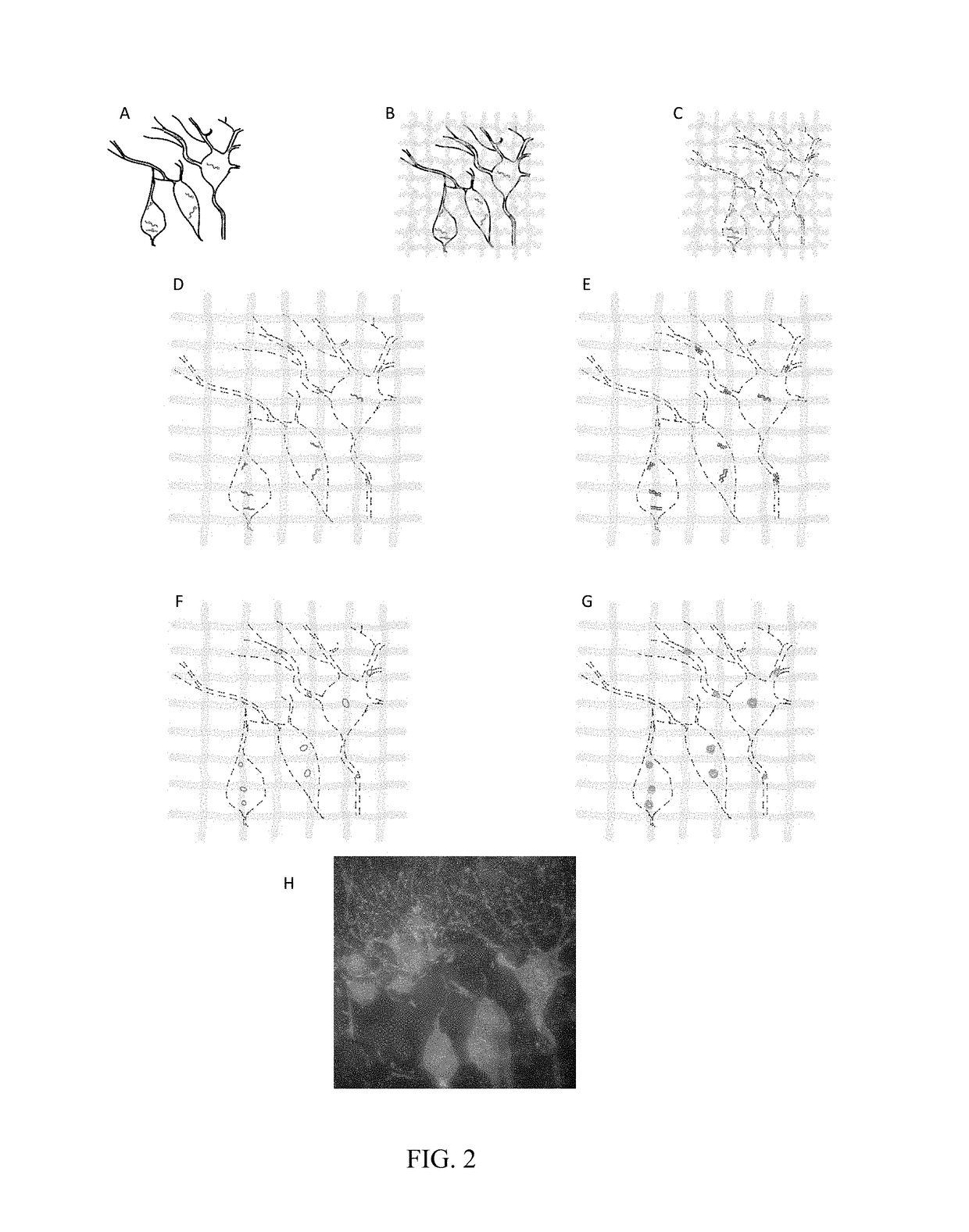
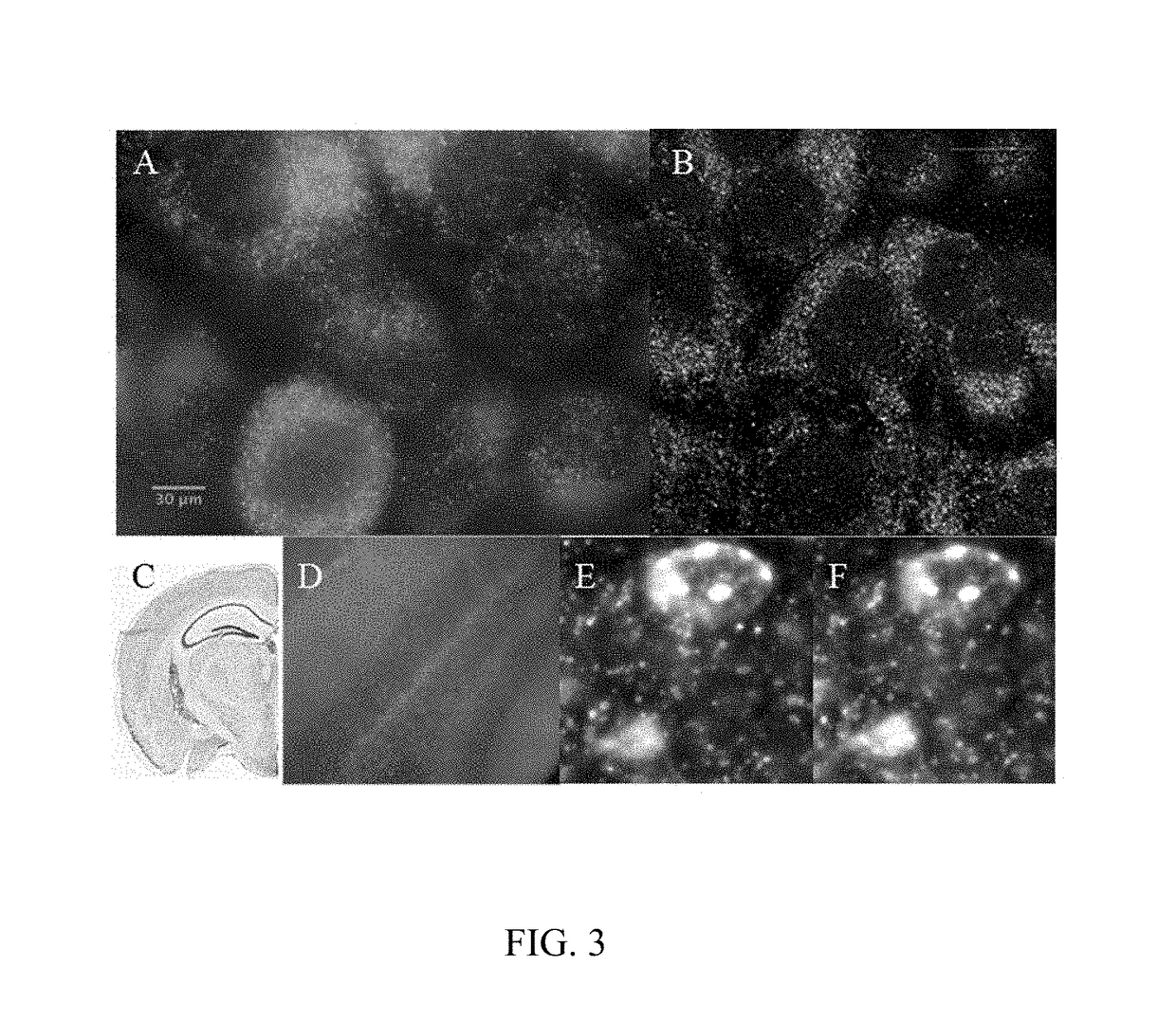
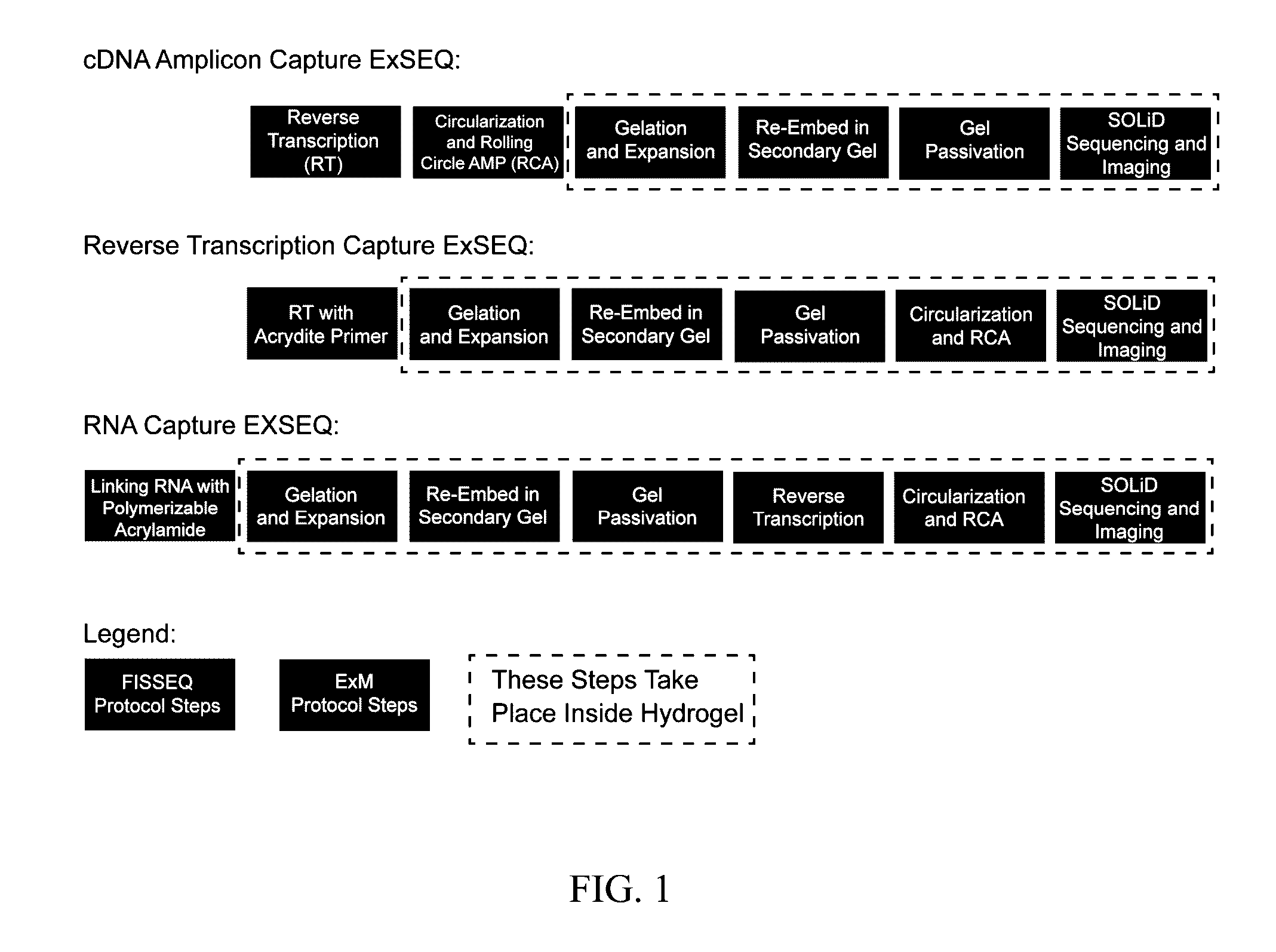
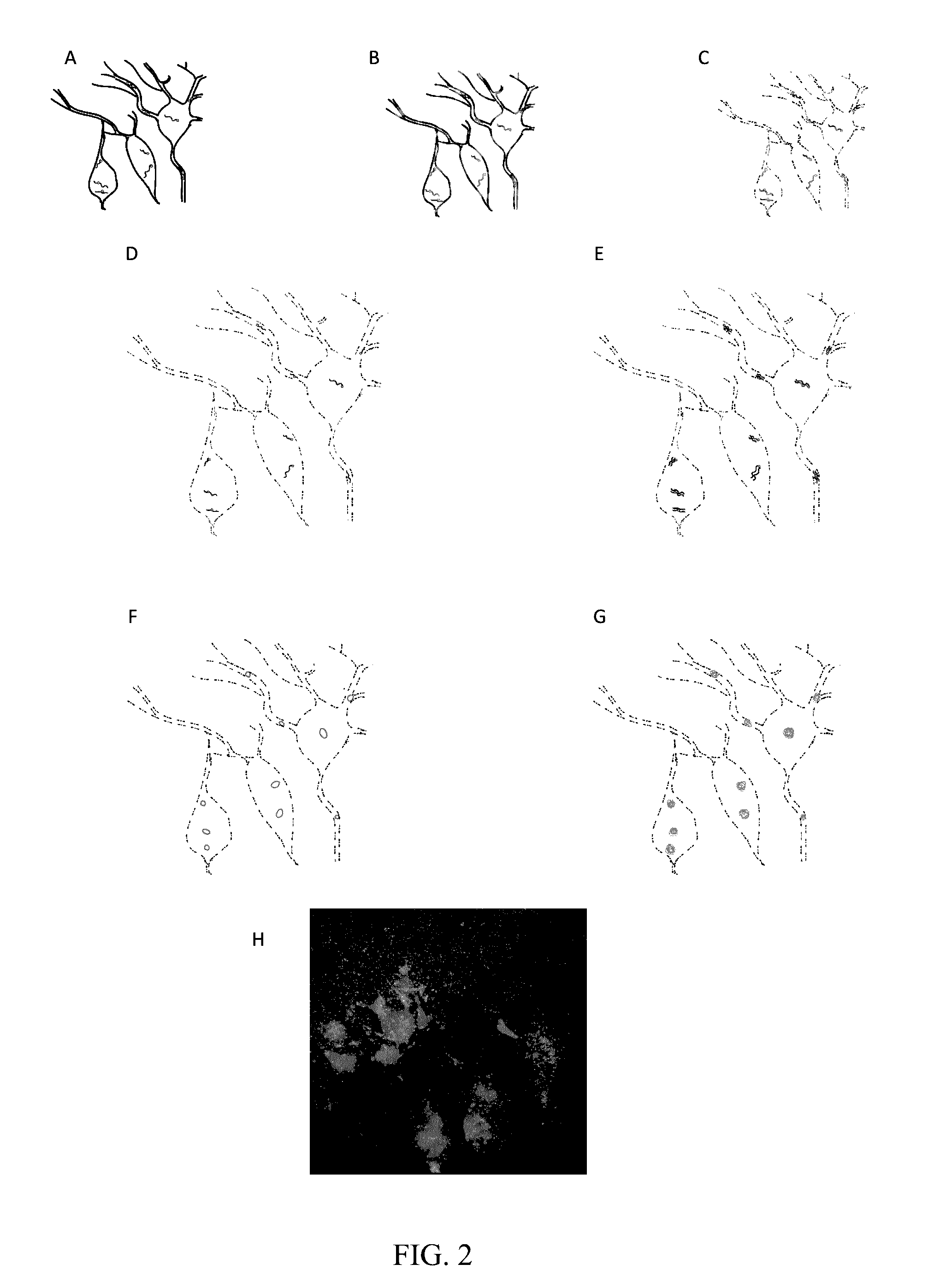
In situ nucleic acid sequencing of expanded biological samples
ActiveUS10059990B2Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory apparatusFluorescent in situ sequencingNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides in situ nucleic acid sequencing to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ sequencing of nucleic acids as well as new methods for fluorescent in situ sequencing (FISSEQ) in a new process referred to herein as “expansion sequencing” (ExSEQ).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
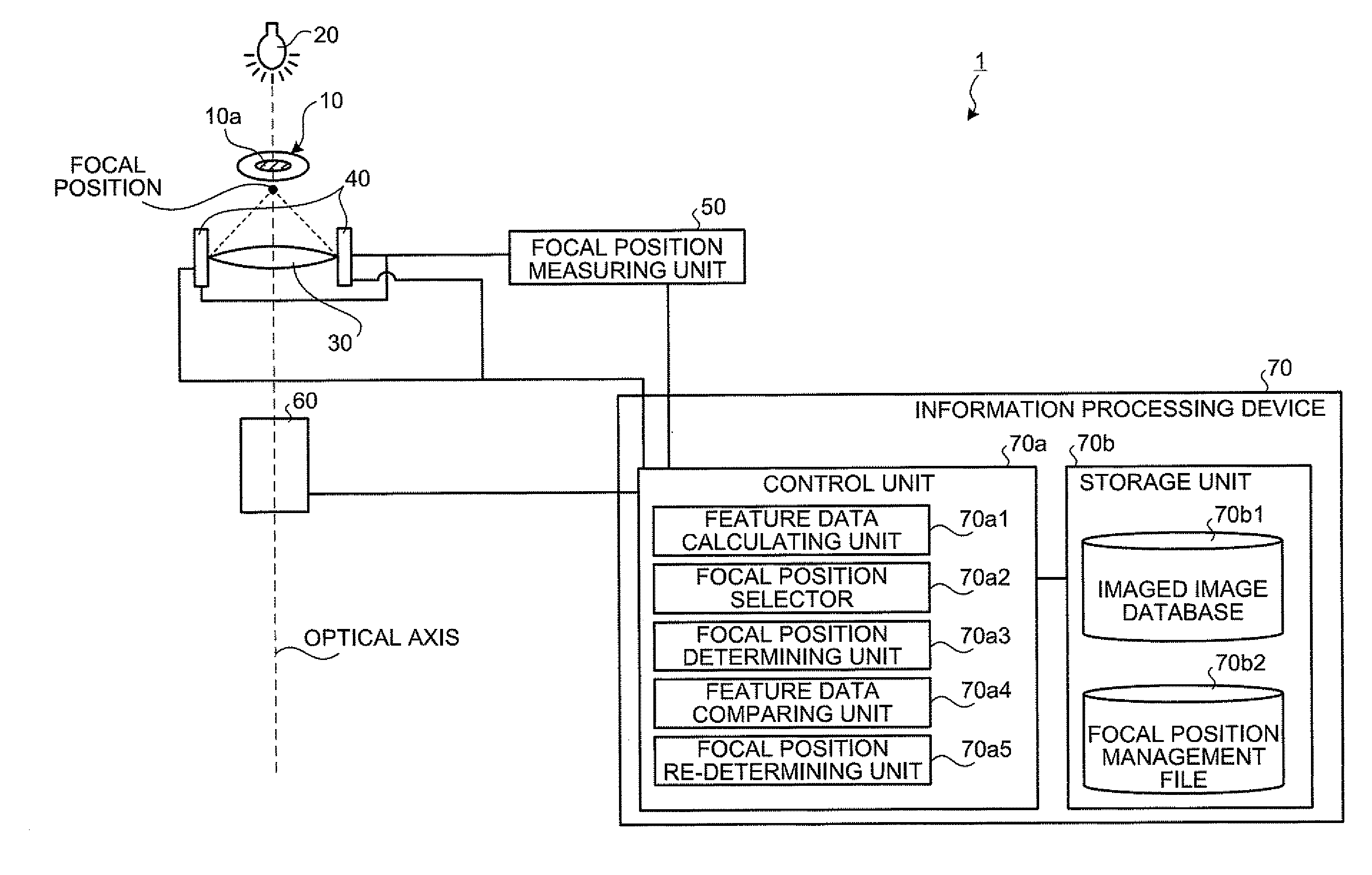
Biological specimen imaging method and biological specimen imaging apparatus
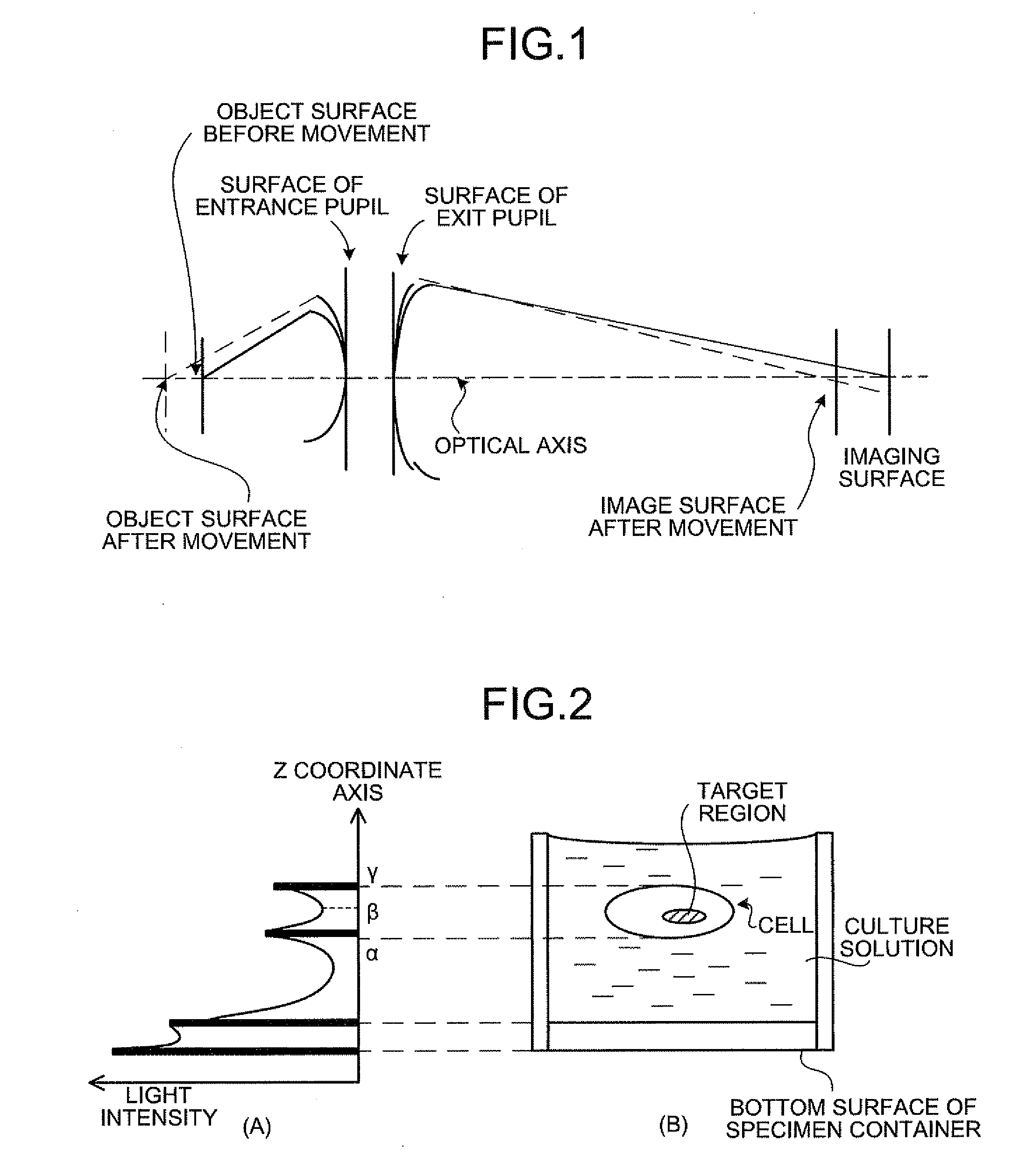
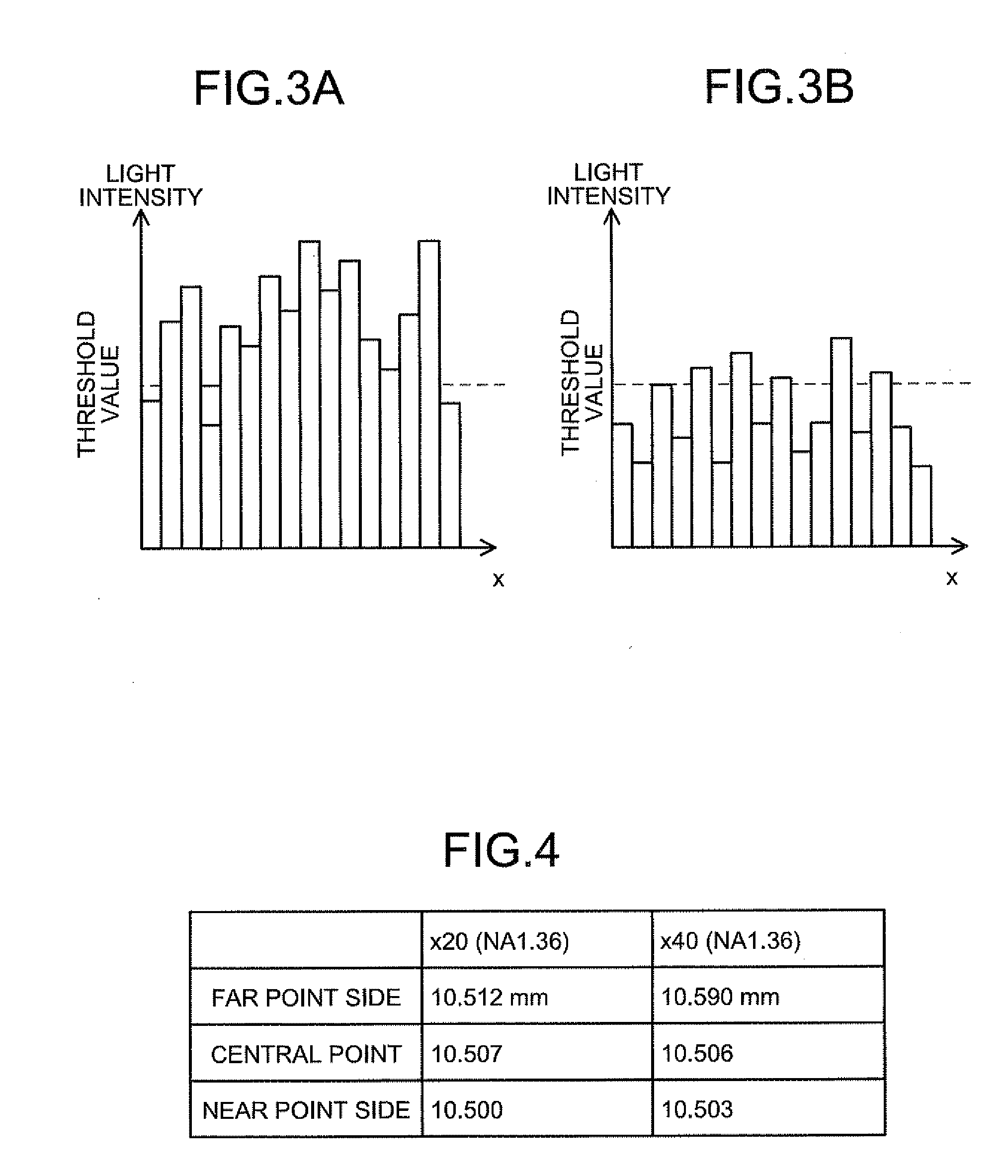
InactiveUS20090086314A1Improve spatial resolutionShort exposure timeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFocal positionField of view
In a biological specimen imaging method, a biological specimen which is stored in a storing section of a substrate having plural storing sections and emitting a feeble light is imaged through an objective lens. The biological specimen imaging method includes moving any one of the substrate and the objective lens or both until the desired storing section falls within the field of view of the objective lens, measuring any one of a focal position at a near point and the focal position at a far point of the objective lens or both, determining the focal position of the objective lens focused on an observed target region in the biological specimen stored in the desired storing section based on the measured focal position, and adjusting the focal position of the objective lens to the determined focal position so as to image the biological specimen through the objective lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and kit for investigating humotype semi-cystinol by enzyme biochemical reaction
InactiveCN1693879AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical reactionFluorescence
The invention is an enzyme biologic and chemical reaction measure method to mensurate homotype cysteine in a biologic sample. Cysteine can lose its ammonia and be changed into alpha-4-ketone acid, ammonia and sulfureted hydrogen by L-ovi-ammonia acid and Y-dispeling enzyme. Sulfureted hydrogen and fluorescence cpd.DMPD2HCL can create blue product-sub-armour blue whose degree of absorbing light is 670nm, in the situation of Fe3+ and acid. Thus, people can mensurate the chroma of homotype cysteine in a biologic sample by knowing this degree. This method can measure the chroma of homotype cysteine(3-1000 uMs). The invention also involves a reagent box used for implementing the method mentioned above. The box uses liquid double reagents, and needs less quantity of samples(25 microlitre or serum or plasm);In addition, the respond time is short, and the operation is easy. Thus, this method is suitable for a great deal of examinations. The reagent box costs less than other types.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YAKE SCI & TECH +1
Fluidic devices and systems for sample preparation or autonomous analysis
ActiveUS20130309679A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusBiospecimenAnalytical chemistry
The present invention relates to fluidic devices for preparing, processing, storing, preserving, and / or analyzing samples. In particular, the devices and related systems and methods allow for preparing and / or analyzing samples (e.g., biospecimen samples) by using one or more of capture regions and / or automated analysis.
Owner:TALIS BIOMEDICAL CORP +1
Bio electron microscope and observation method of specimen
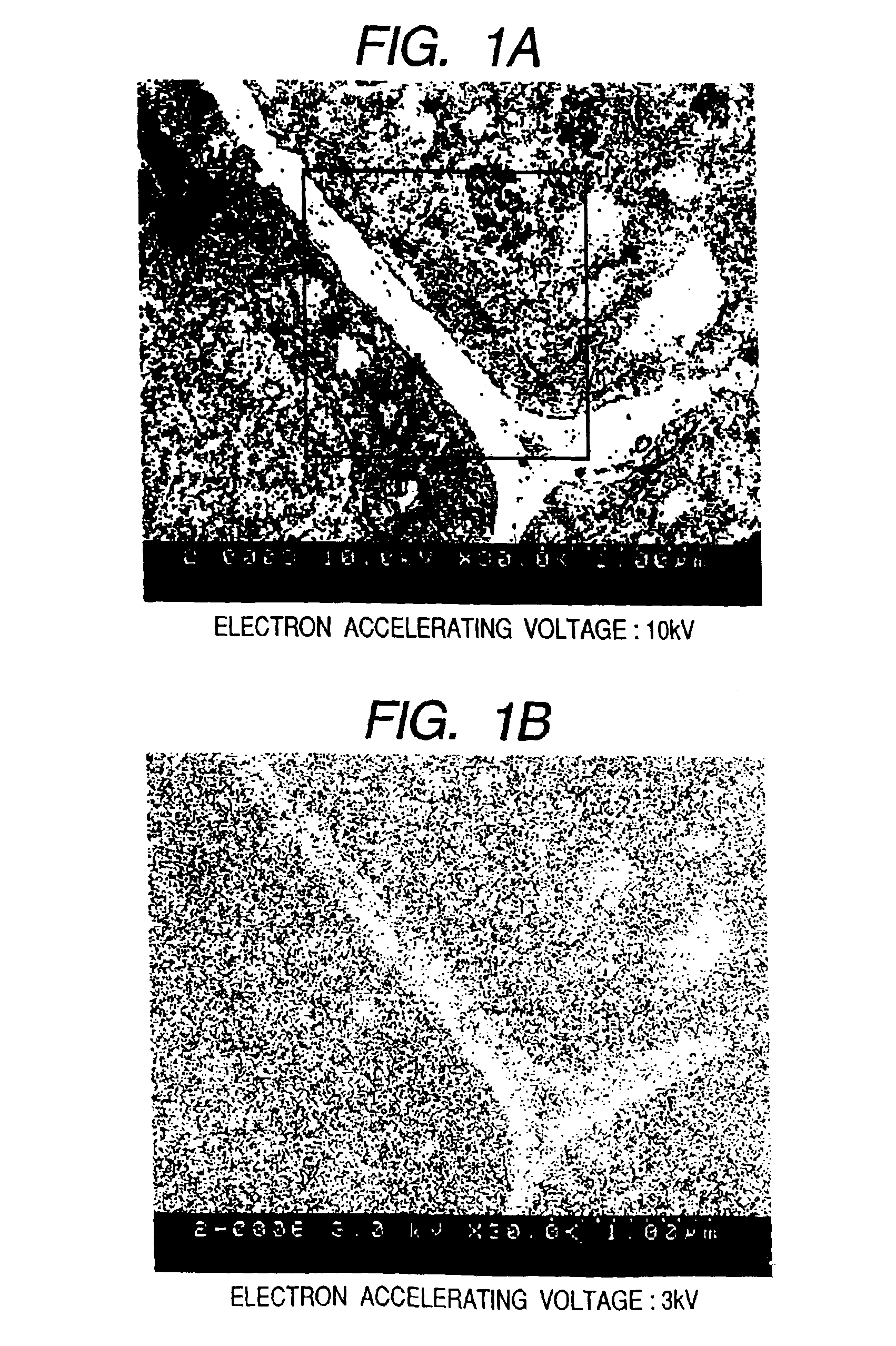
InactiveUS6875984B2Reduce harmHigh-accuracy image analysisEnergy spectrometersPreparing sample for investigationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
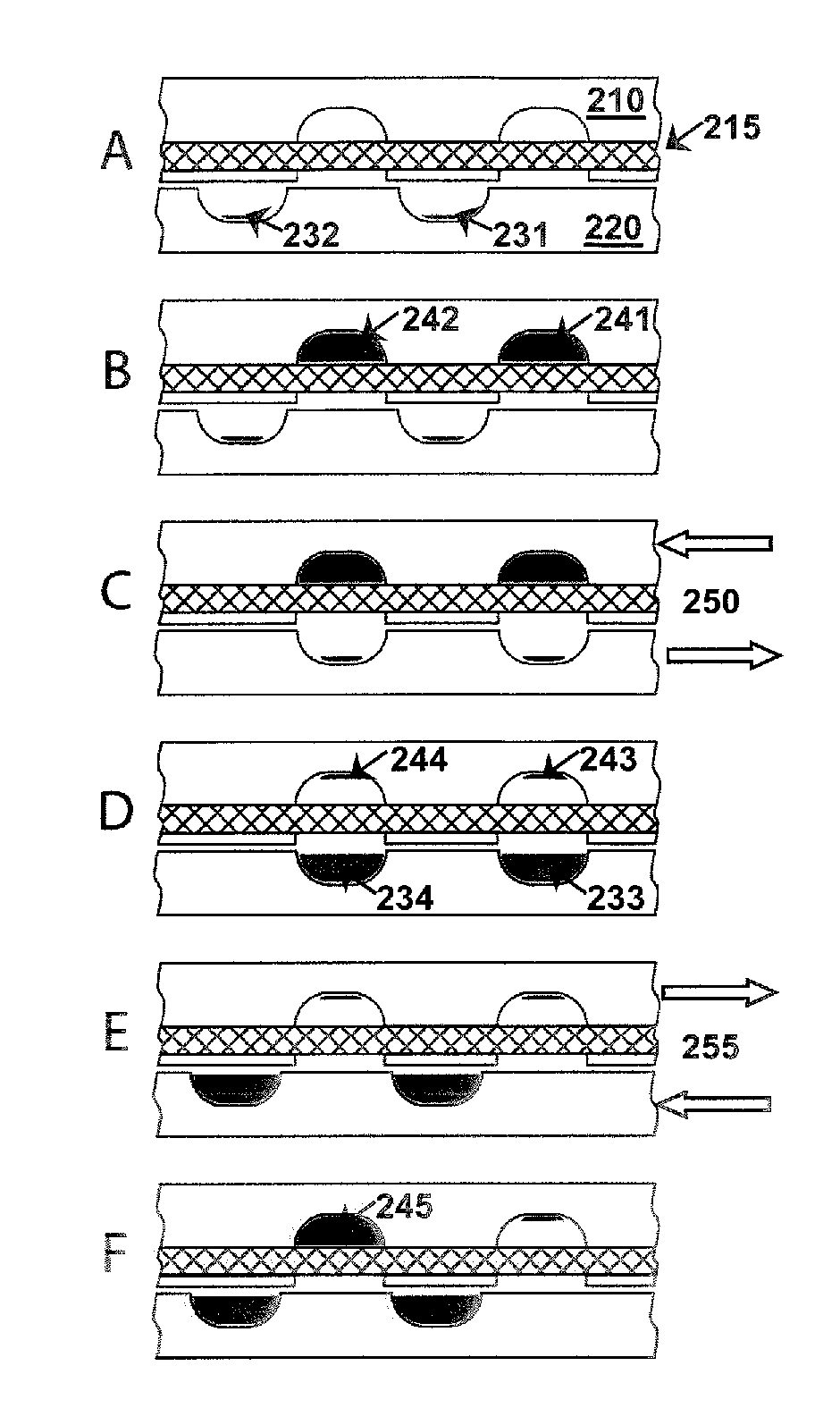
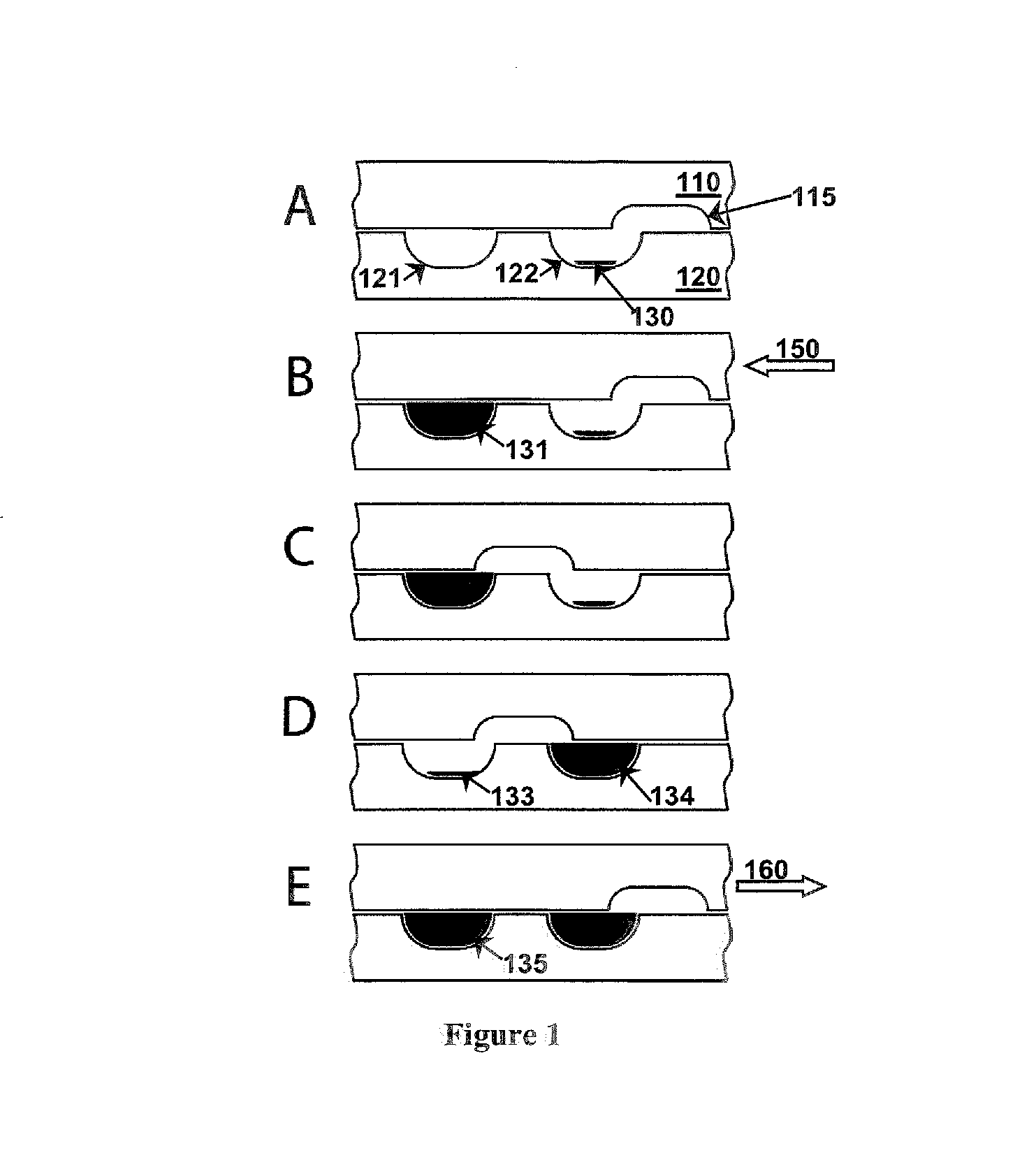
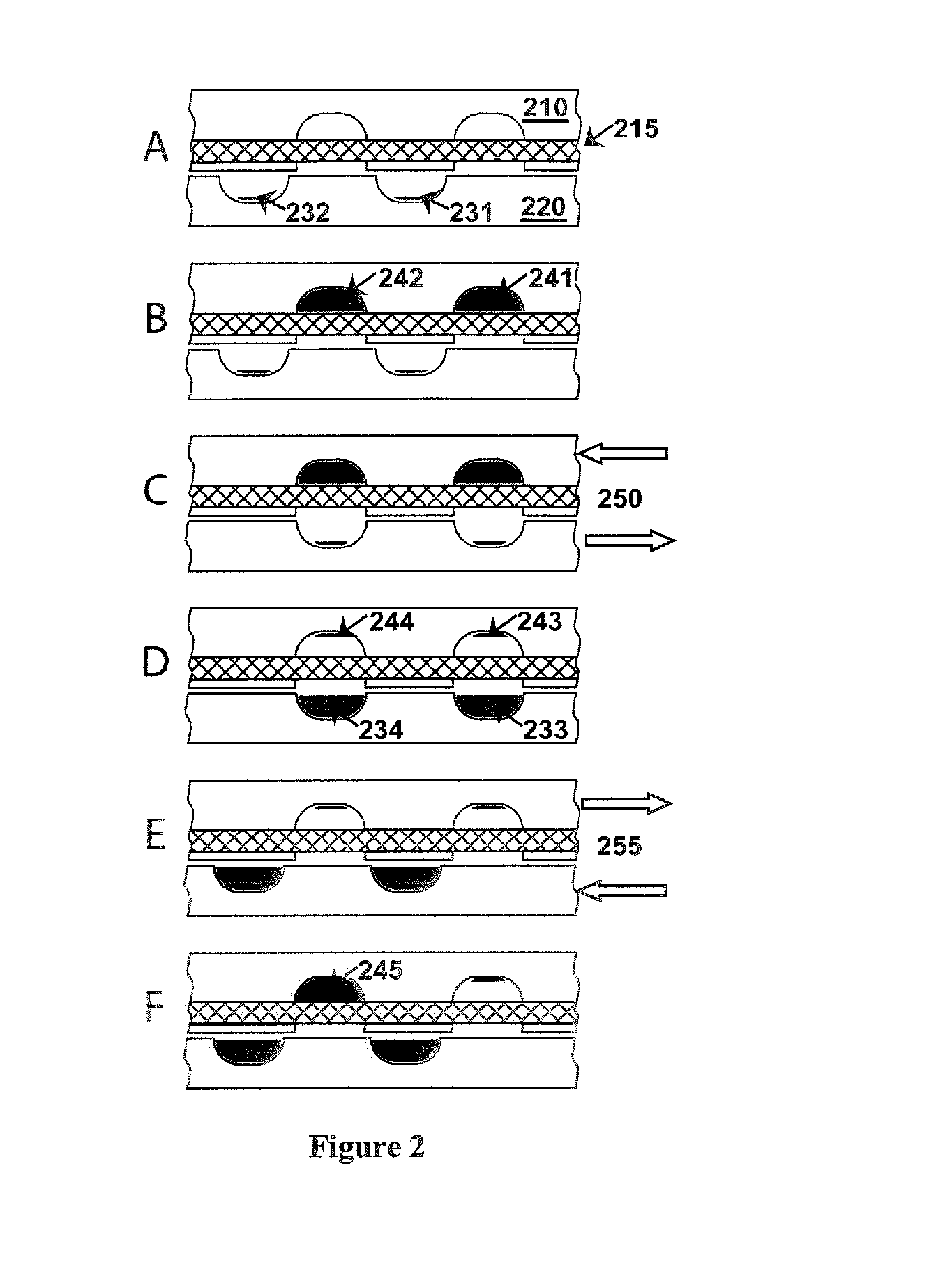
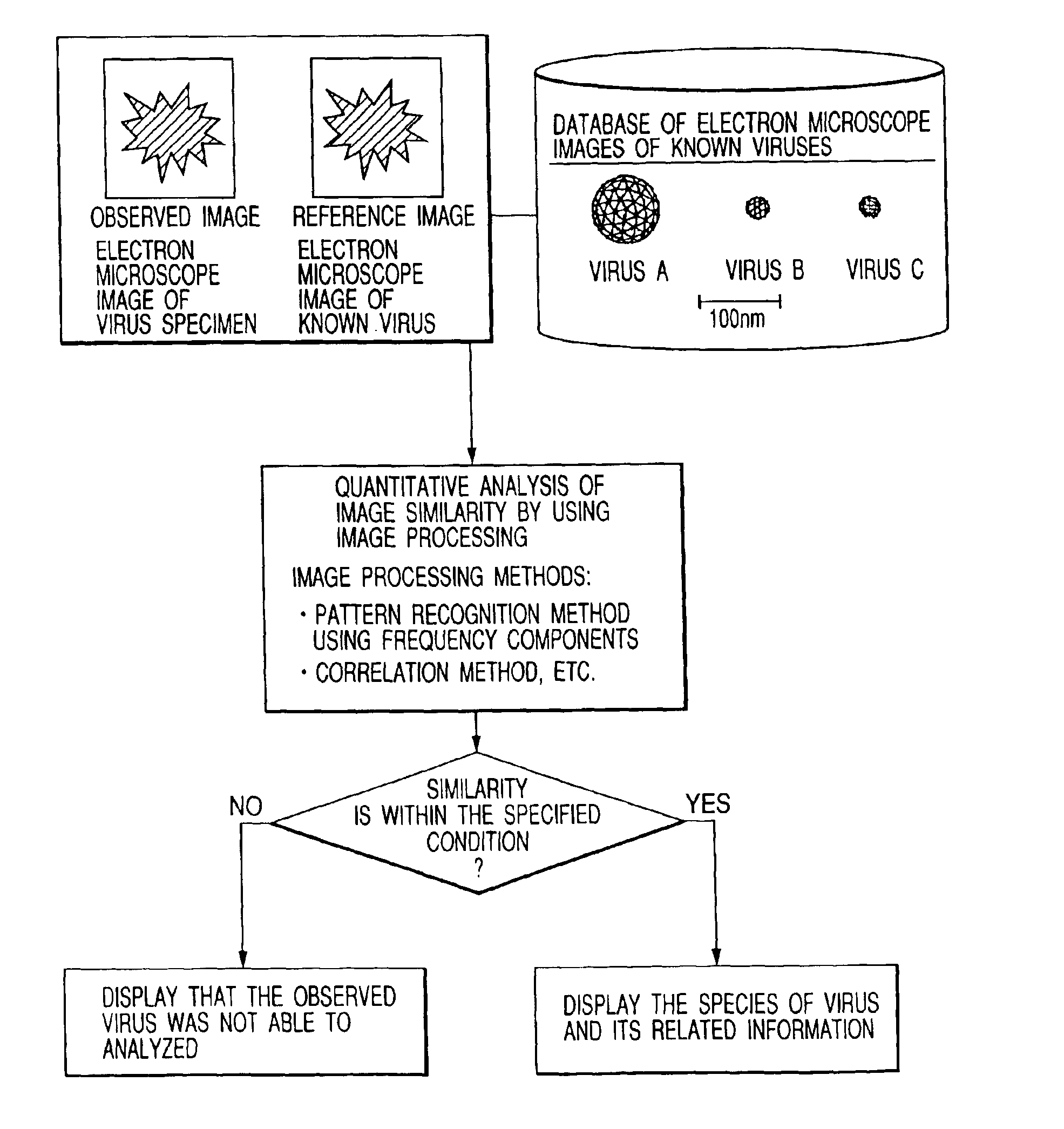
A bio electron microscope and an observation method which can observe a bio specimen by low damage and high contrast to perform high-accuracy image analysis, and conduct high-throughput specimen preparation. 1) A specimen is observed at an accelerating voltage 1.2 to 4.2 times a critical electron accelerating voltage possible to transmit a specimen obtained under predetermined conditions. 2) An electron energy filter of small and simplified construction is provided between the specimen and an electron detector for imaging by the electron beam in a specified energy region of the electron beams transmitting the specimen. 3) Similarity between an observed image such as virus or protein in the specimen and a reference image such as known virus or protein is subjected to quantitative analysis by image processing. 4) A preparation protocol of the bio specimen is made into a chip using an MEMS technique, which is then mounted on a specimen stage part of an electron microscope to conduct specimen introduction, preparation and transfer onto a specimen holder.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
Methods and systems for analyzing images of specimens processed by a programmable quantitative assay
ActiveUS20120163681A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionTissue sampleBioinformatics
Disclosed are methods and systems for analyzing images of specimens processed by a programmable quantitative assay or more specifically a robust programmable quantitative dot assay, PDQA, that enable specimens to be imaged and assessed across a wide variety of conditions and applications. Specific embodiments directed to immunohistochemical applications provide more quantitative methods of imaging and assessing biological samples including tissue samples.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Stabilization of cells and biological specimens for analysis
InactiveUS20050181353A1Improve stabilityMaintain qualityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthIn vivo
Compositions and methods for stabilizing rare cells in blood specimens, preserving the quality of blood specimens, and also serving as cell fixatives are disclosed which minimize losses of target cells (for example, circulating tumor cells) and formation of debris and aggregates from target cells, non-target cells and plasma components, thereby allowing more accurate analysis and classification of circulating tumor cells (CTC) and, ultimately, of tumor burdens in cancer patients. Stabilization of specimens is particularly desirable in protocols requiring rare cell enrichment from blood specimens drawn from cancer patients. Exposure of such specimens to potentially stressful conditions encountered, for example, in normal processing, mixing, shaking, delays due to transporting the blood, has been observed to not only diminish the number of CTC but also to generate debris and aggregates in the blood specimens that were found to interfere with accurate enumeration of target cells, if present. Stabilizers are necessary to discriminate between in vivo CTC disintegration and in vitro sample degredation.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Fluidic devices for biospecimen preservation
ActiveUS20130280725A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusDesiccantComputer science
The present invention relates to fluidic devices for preparing, processing, storing, preserving, and / or analyzing samples. In particular, the devices and related systems and methods allow for preservation or storage of samples (e.g., biospecimen samples) by using one or more of a bridge, a membrane, and / or a desiccant.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
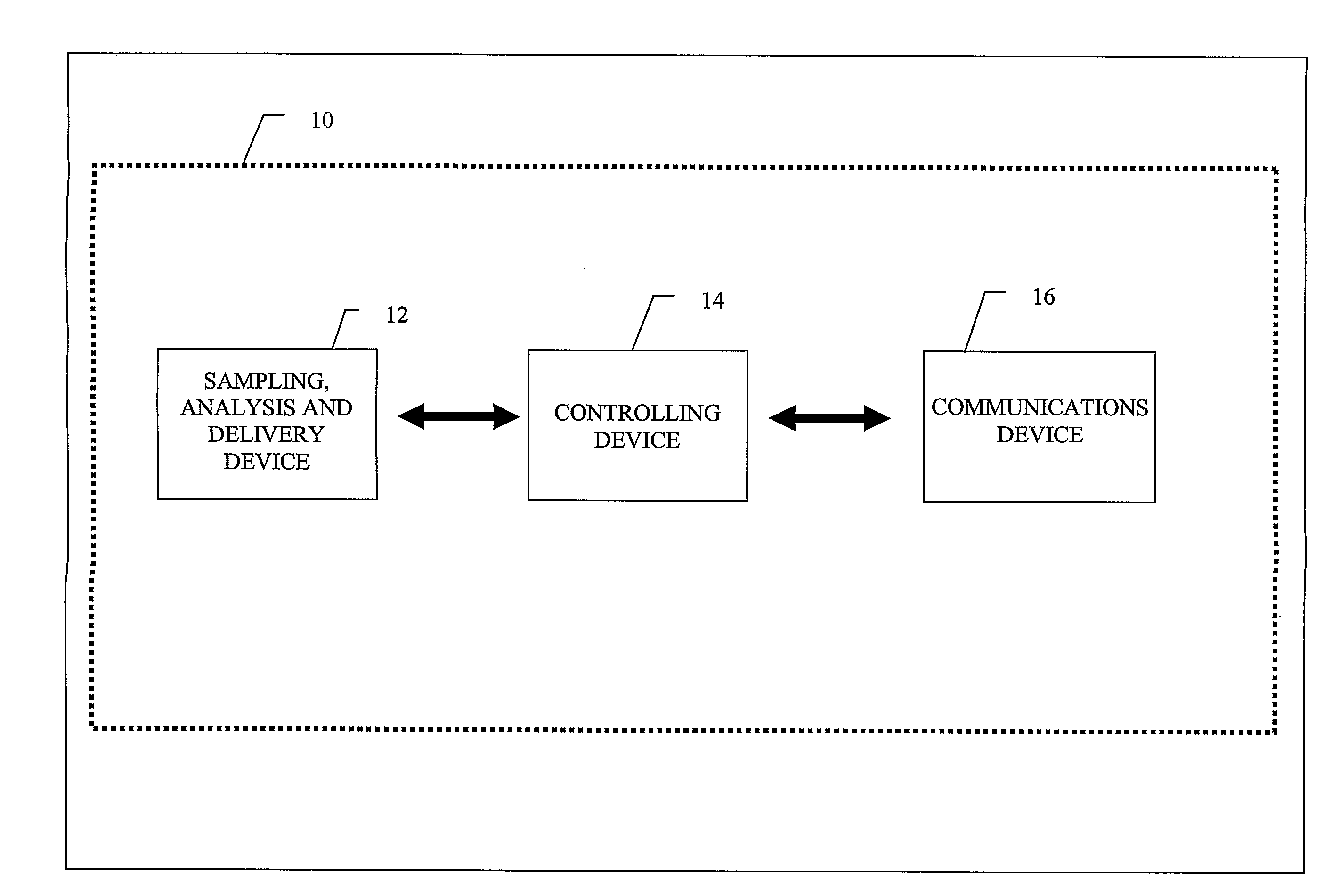
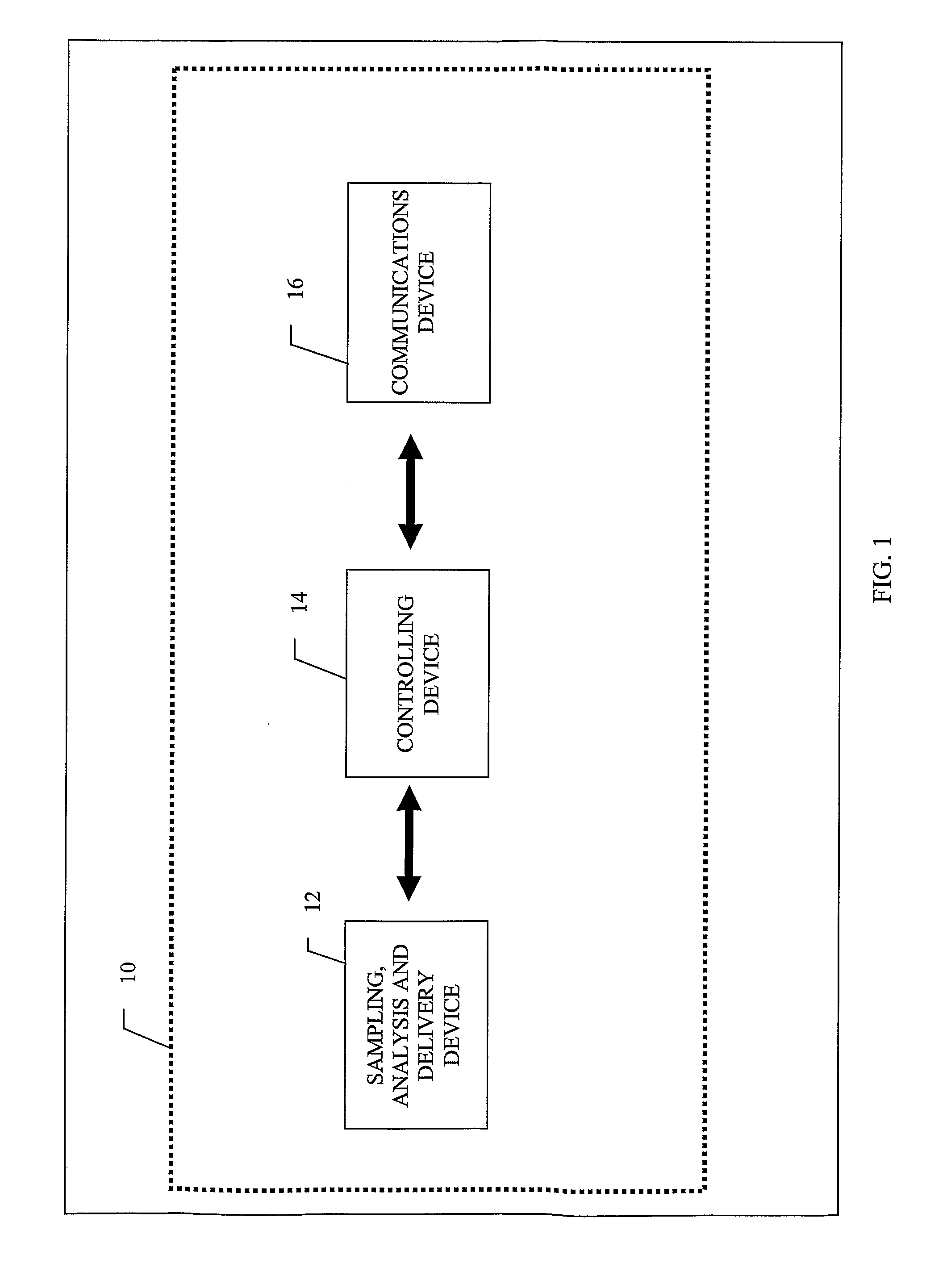
Flexible Apparatus and Method for Monitoring and Delivery
The present invention generally relates to a system and method that co-locates in a small flexible, configurable system and multi-level substrate sampling, rapid analysis, bio-sample storage and delivery functions to be performed on living tissues or matter obtained from living organisms. The types of the sampling may include chemical, biochemical, biological, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical sampling. In general, the analysis performed at the point of sampling measures the sample taken and records its value. The bio-sample storage function encapsulates a small sample of analyte and preserves it for subsequent examination or analysis, either on the organism by the system or at a remote location by an independent analysis system. Once stored, the sample can provide a record of a biological state at the precise time of sampling. The delivery at the point of sampling can include chemical, biochemical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic and optical stimuli.
Owner:FISH & RICHARDSON P C
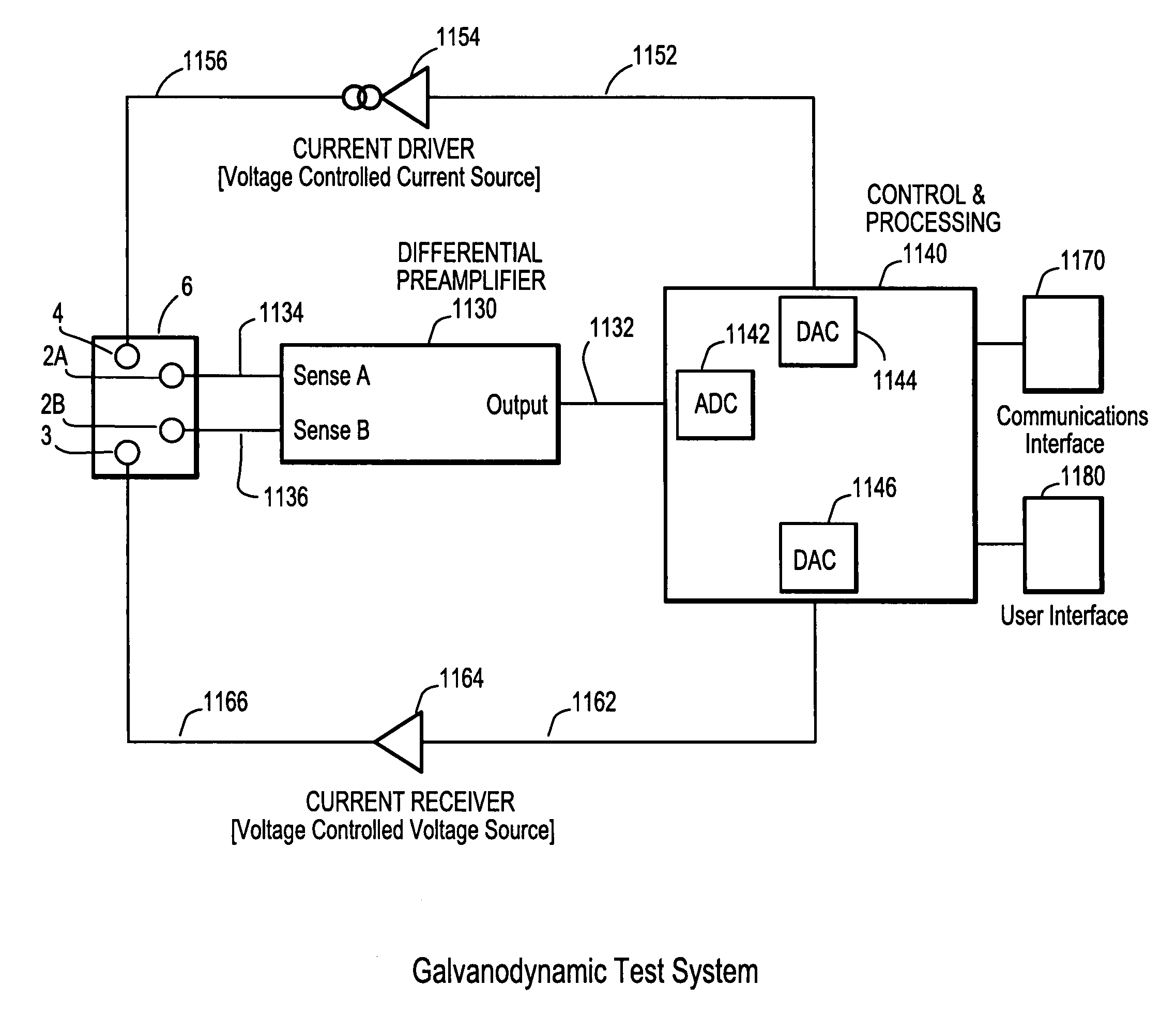
Method of analyzing the time-varying electrical response of a stimulated target substance
InactiveUS6990422B2Hysteresis effectBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringCurrent mode
A time varying electrical excitation(s) is applied to a system containing biologic and / or non-biologic elements, whereupon the time-varying electrochemical or electrical response is detected and analyzed. For biologic specimens, the presence, activity, concentration or relative quantity, and certain inherent characteristics of certain target substances (hereinafter referred to as “target analytes”) within, or comprising, the specimen of interest may be determined by measuring either the current response induced by a voltage-mode excitation, or the voltage response induced by a current-mode excitation. Labeling or marker techniques may be employed, whereby electrochemically active auxiliary molecules are attached to the substance to be analyzed, in order to facilitate or enhance the electrochemical or electrical response. The method may also be employed to test non-biologic systems comprising an electrochemical cell or a battery of cells, wherein complex pulse type excitation signals are applied to the cell and the resultant time varying polarization voltage information is extracted and analyzed to determine at least one characteristic of the cell(s) condition or state.
Owner:BIOURJA ENERGY SYST LLC
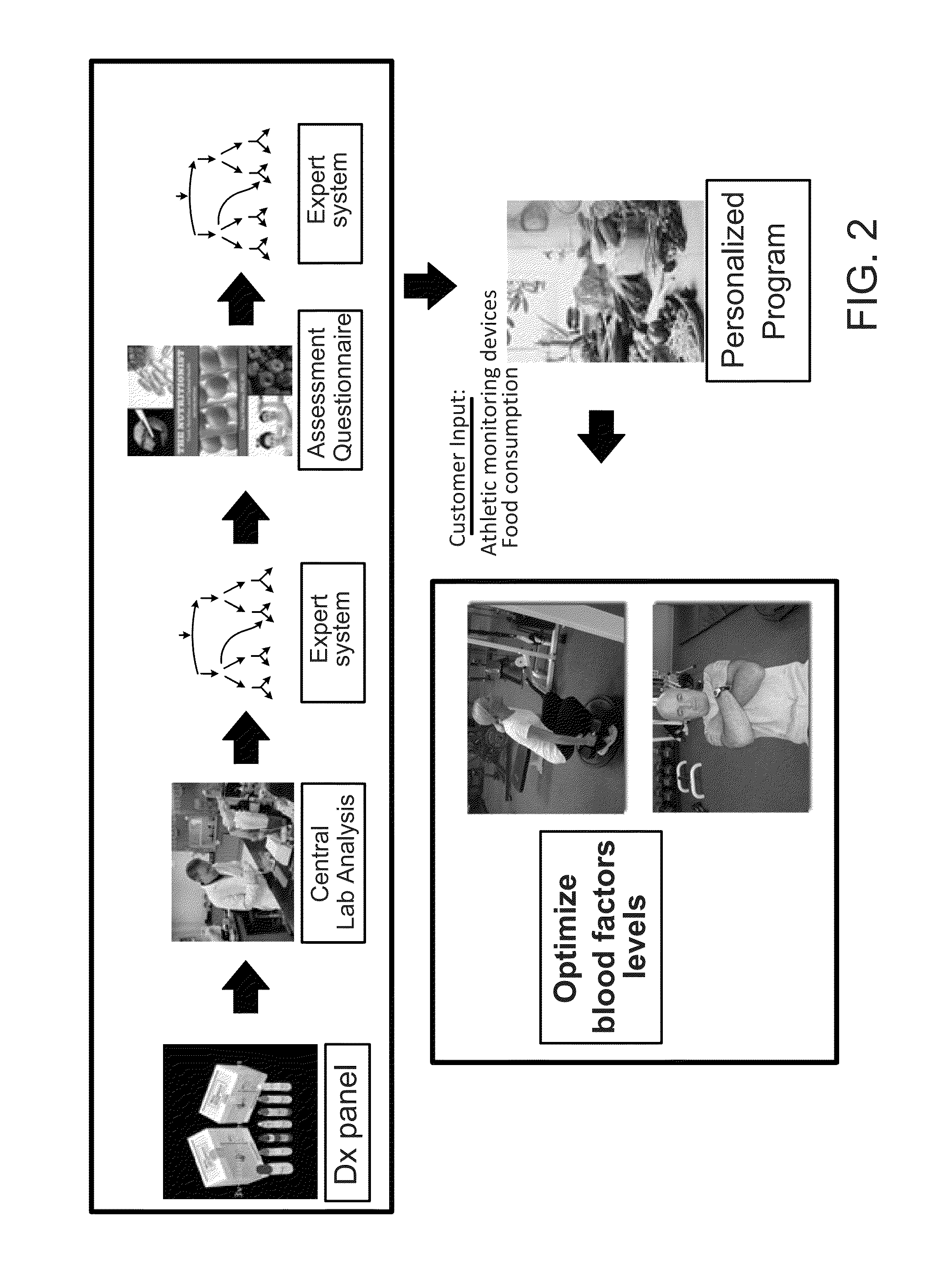
Methods and systems for generation of personalized health plans
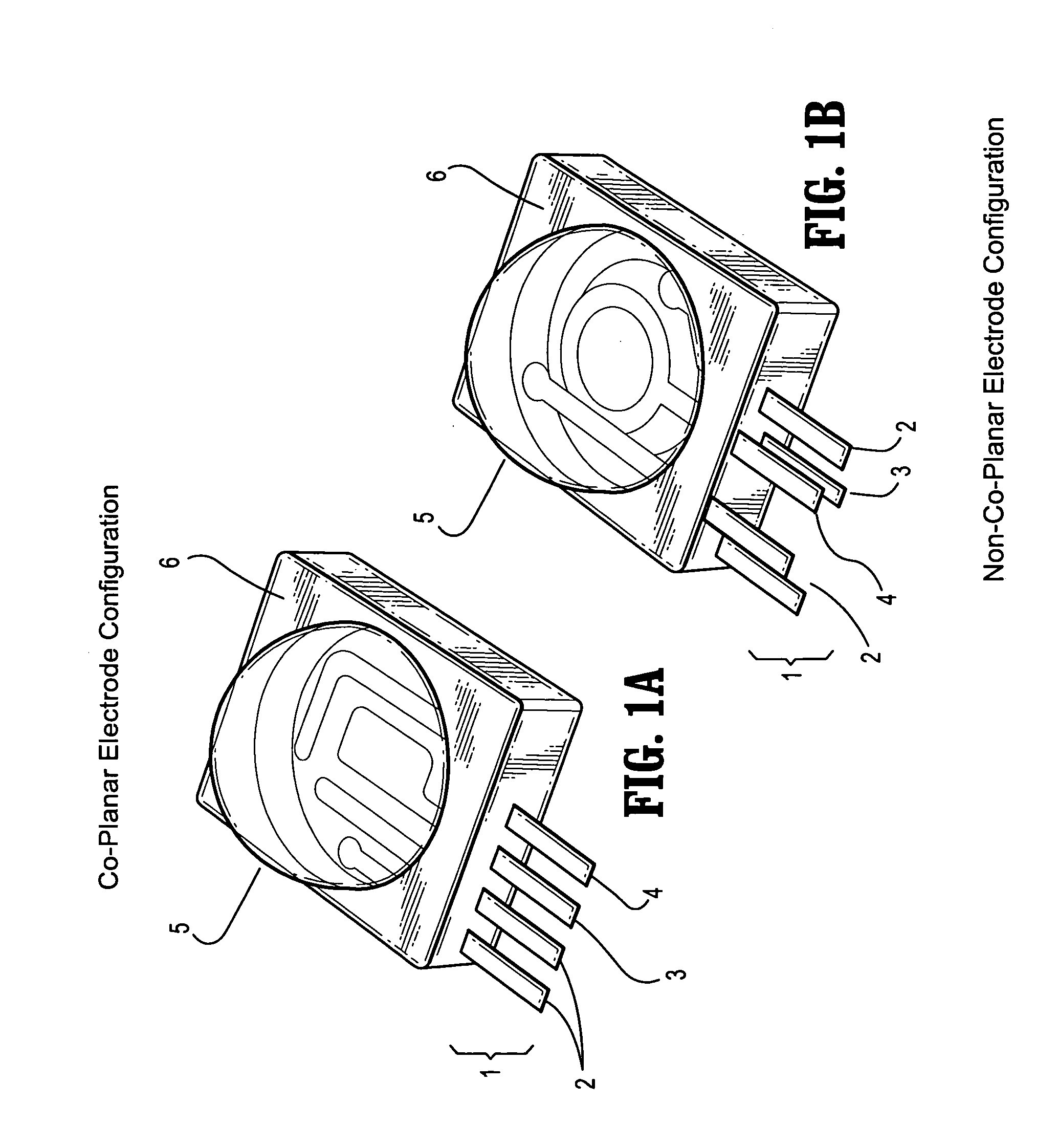
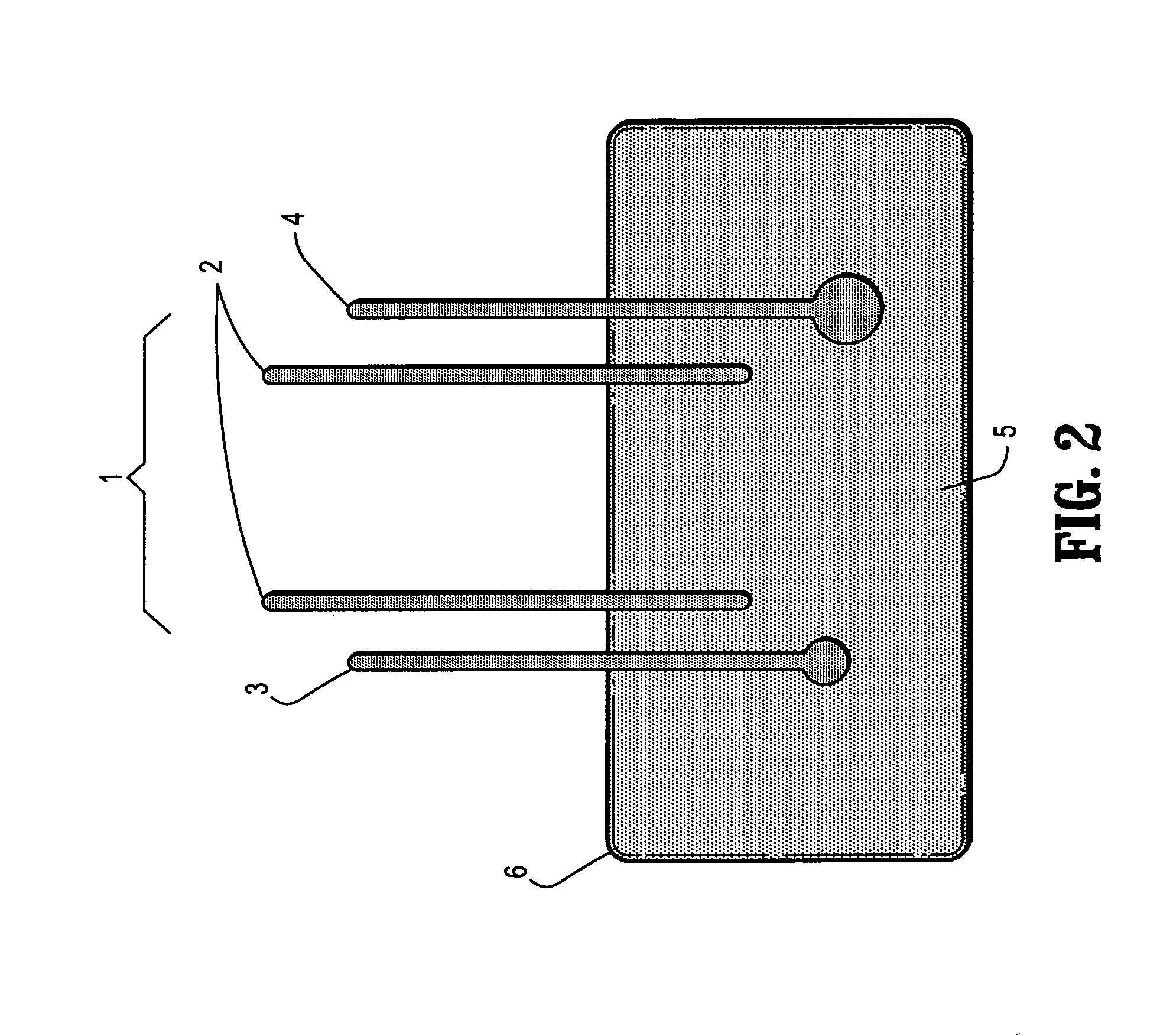
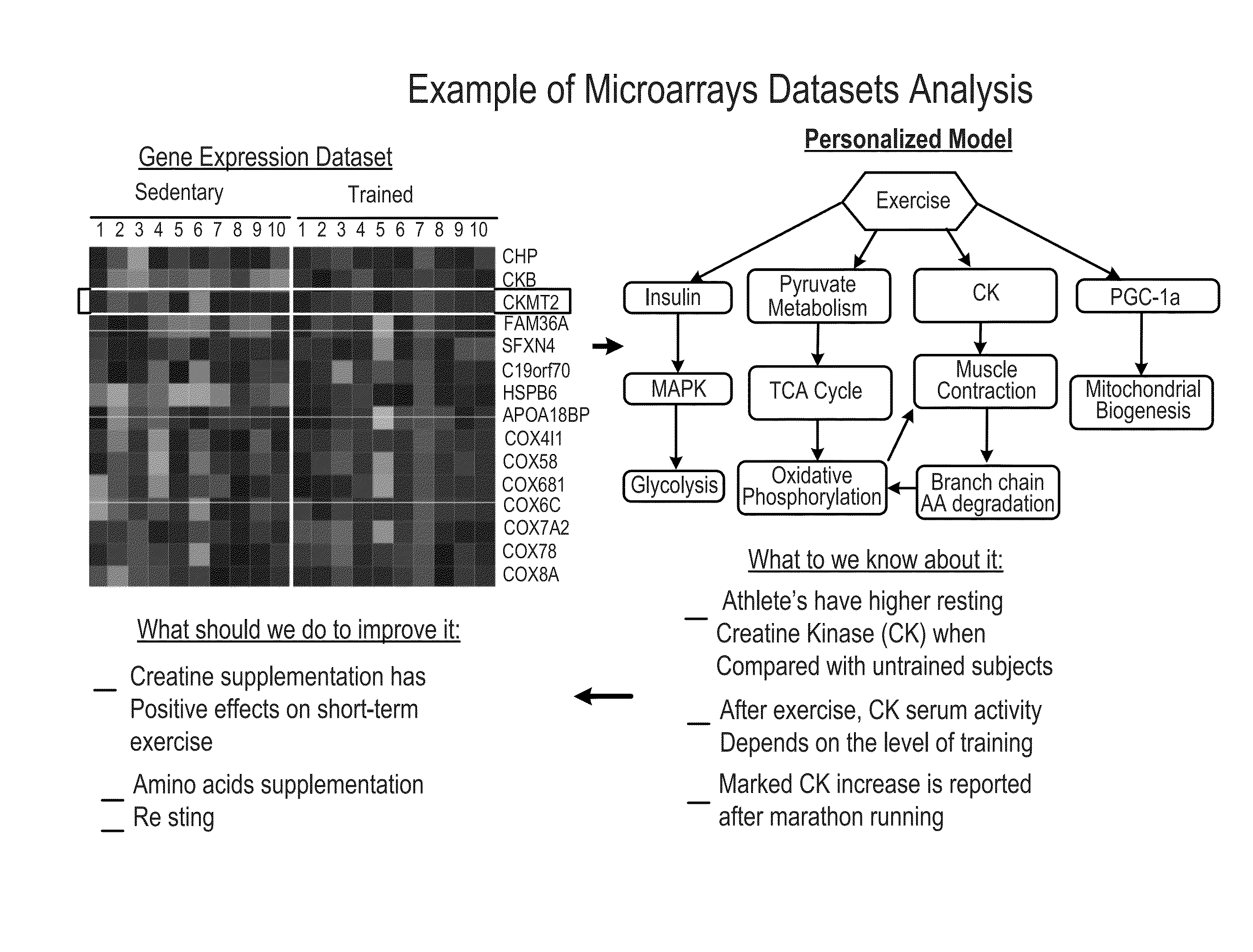
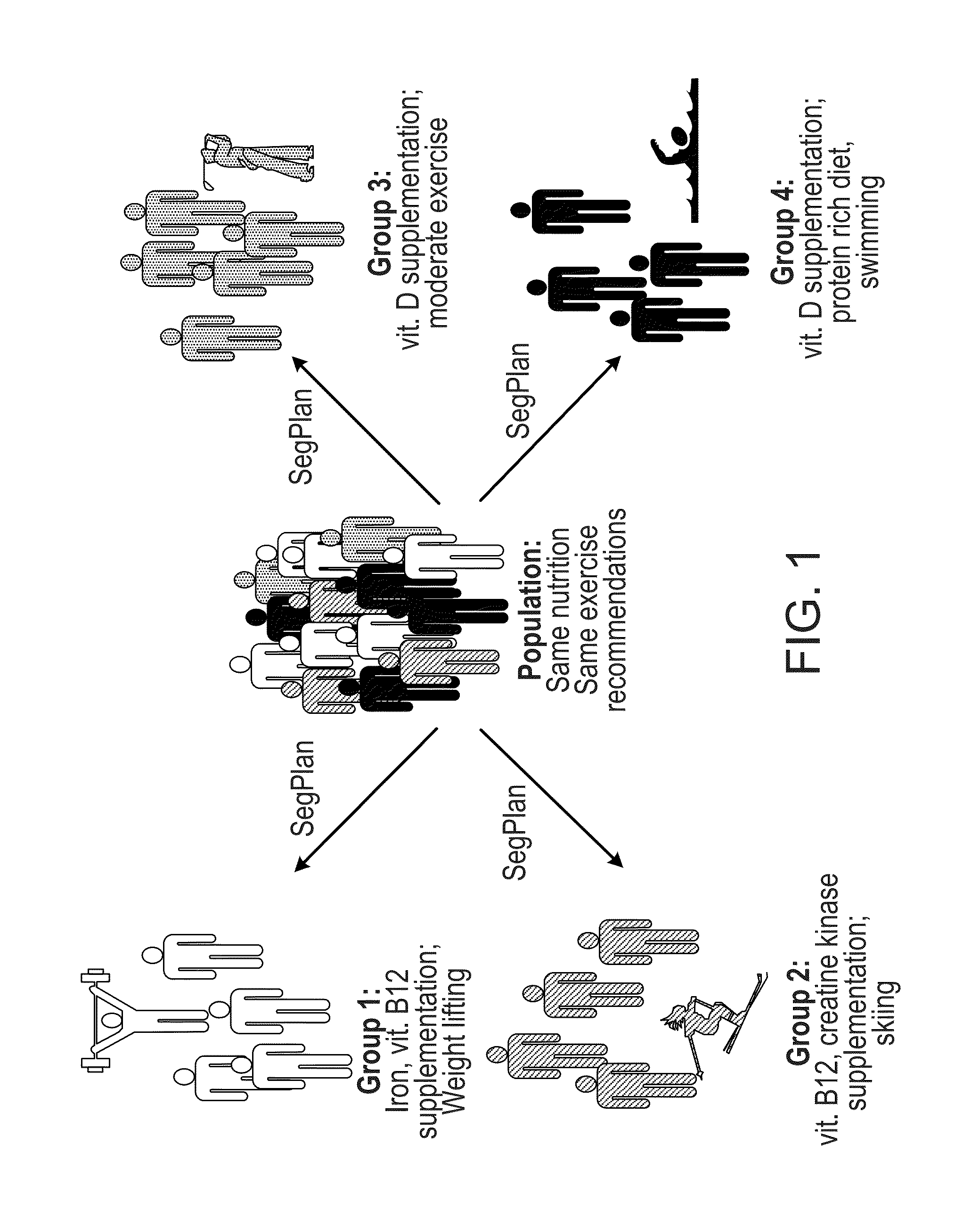
ActiveUS8762167B2Easy to derivePhysical therapies and activitiesBiostatisticsDiagnostic testNutrition
Personalized, health and performance programs are generated for individuals based on various biomarkers and performance and lifestyle assessments. In one embodiment, a diagnostic test of blood or other biological specimen(s) is used to determine key biological marker levels. Information and assessments of the user's physical performance, life style and health and wellness goals is also collected and provided to an expert system that matches the biomarker levels and assessments to a knowledgebase of scientific knowledge about biomarker levels and health and fitness outcomes. Personal recommendations and advice on nutrition and exercise is then generated, which may be used to help individuals reach their diet, fitness, and wellness goals and improve their physical and mental performance and well being in measurable ways.
Owner:SEGTERRA
Immobilizing and processing specimens on matrix materials for the identification of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6103192AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological unitOrganism
The invention is a method and device for collecting and processing a biological specimen for the analyses of nucleic acids. A device comprises a matrix to which cells and viruses adhere and a handle to manipulate the matrix. The devices are used to collect, dry, transport, store and process small amounts of blood or other tissue. The matrix of the device is transferred to a reaction tube and amplifying reagents added to it. Nucleic acid sequences and relative quantities are detected and analyzed from the same specimen. The relative amounts of amplified nucleic acid from one or more particular RNA sequences are compared to one another and to the amount of amplified nucleic acid from DNA sequences serving as an internal control for the number of biological units per specimen. The relative amounts of amplified viral sequences from suspected viruses in the biological specimen and from recombinant viral particles serving as a viral quantitation standard enable estimation of viral burden in a given quantity of specimen.
Owner:GENETEC
Operator independent programmable sample preparation and analysis system
ActiveUS20070212698A1Minimal operator interactionImprove processing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRegimenHandling system
The present invention provides a protocol and apparatus for enriching circulating tumor cells and other rare cells from blood, including debris and other components, from samples with high precision and at high throughput rates. This invention discloses an improved processing system from previously described semi-automated sample processing. The system further reduces operator intervention and hands-on time from prior systems. While this system has general utility in processing diverse materials, the system is configured for sample processing of biological specimens to provide an enriched fraction suitable for detection, enumeration and identification of target cells by appropriate analytical methodologies. The presence and quantities of such target cells in a sample specimen can utilized for screening and detection in disease such as cancer, assessing early stage pre-metastatic cancer, monitoring for disease remission in response to therapy and selection of more effective dose regimens or alternative therapies in case of relapse.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
In situ nucleic acid sequencing of expanded biological samples
ActiveUS20160304952A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory apparatusFluorescent in situ sequencingNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides in situ nucleic acid sequencing to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ sequencing of nucleic acids as well as new methods for fluorescent in situ sequencing (FISSEQ) in a new process referred to herein as “expansion sequencing” (ExSEQ).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
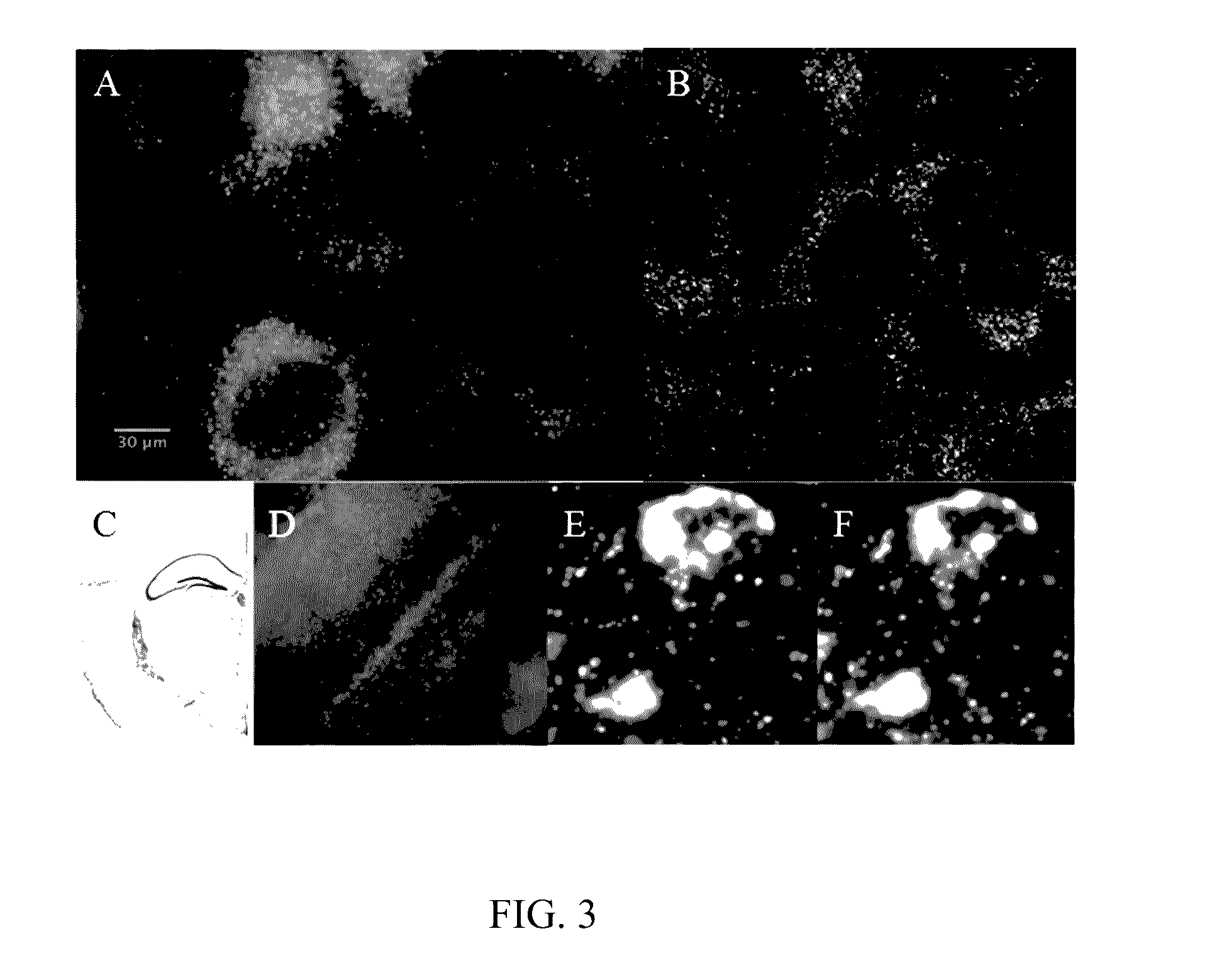
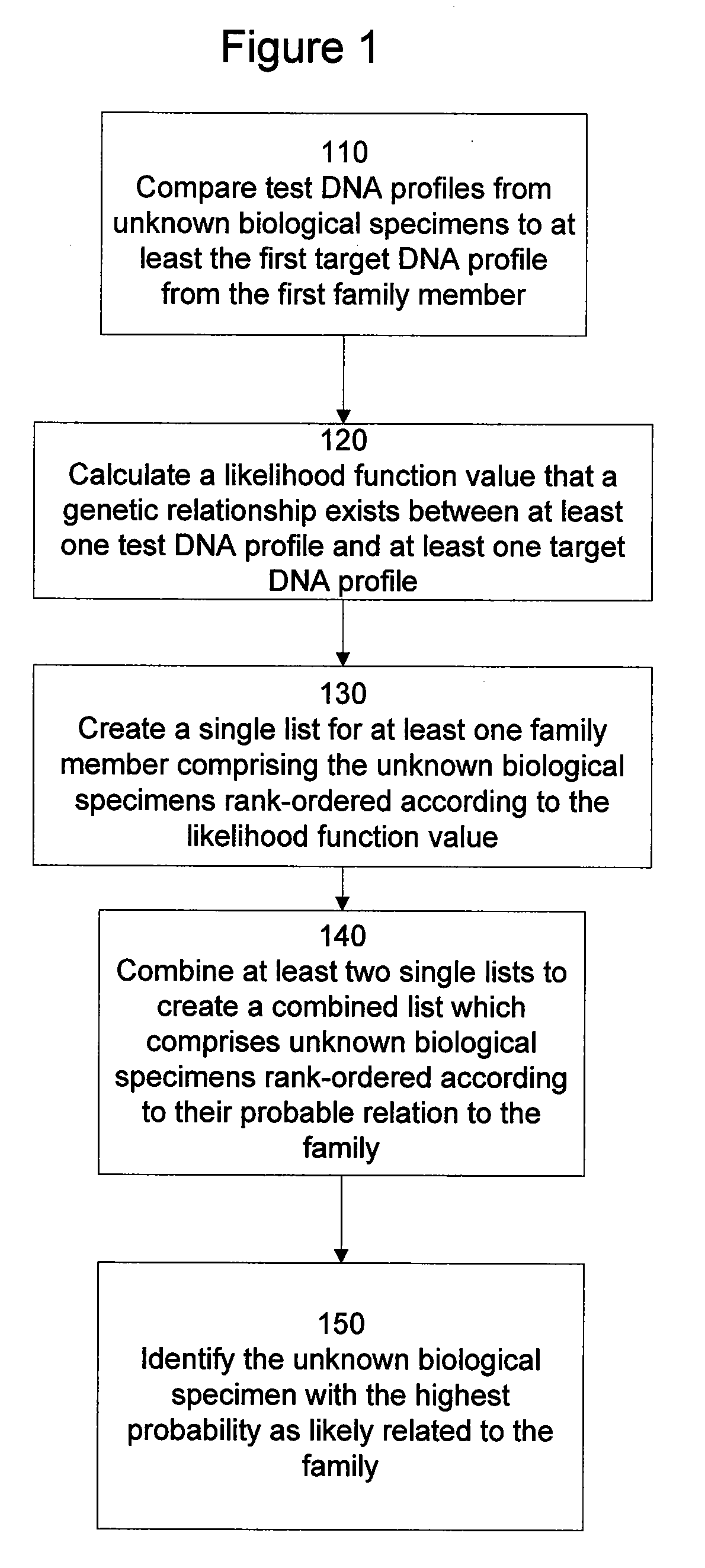
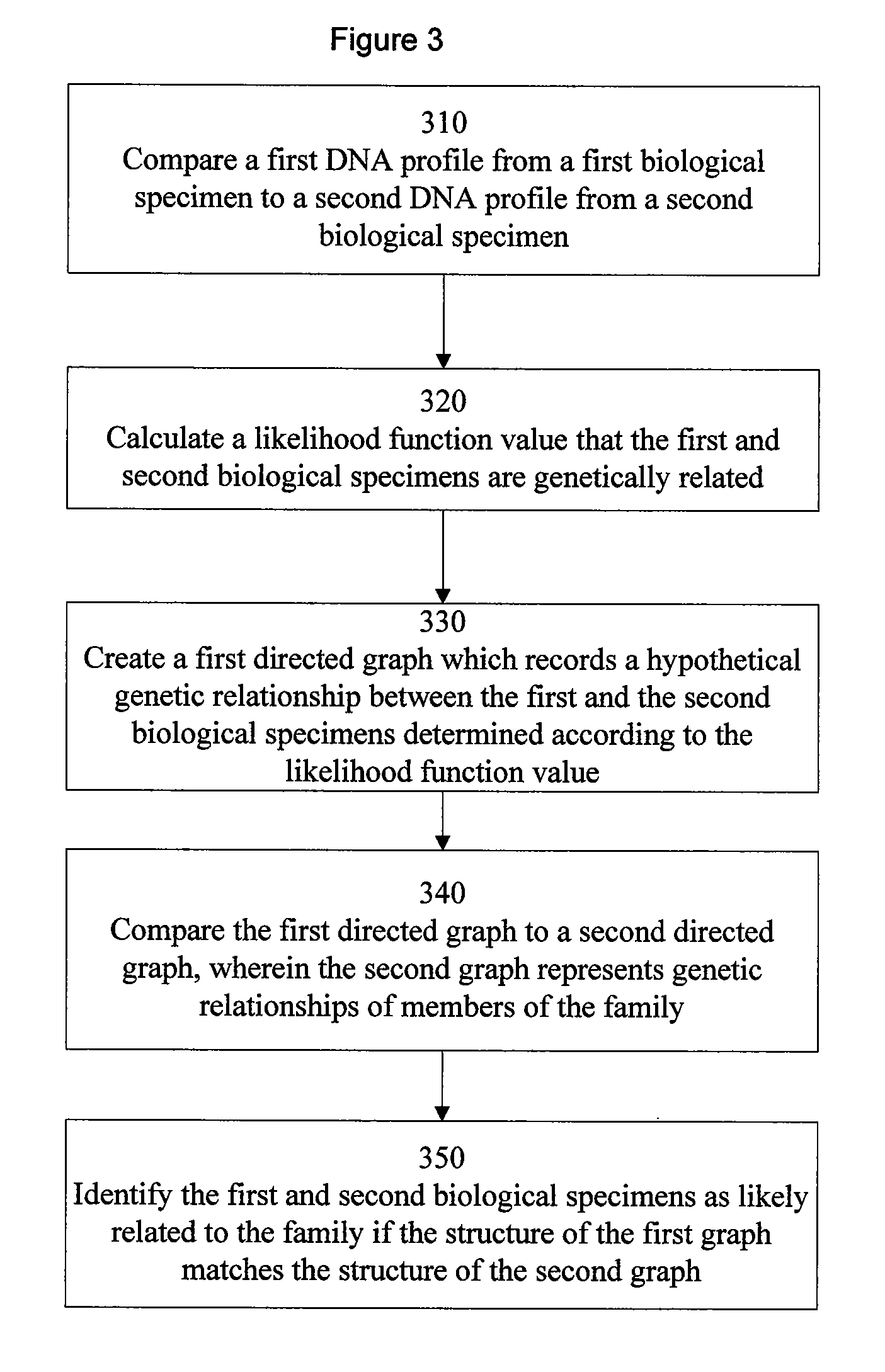
Methods of associating an unknown biological specimen with a family
The present invention provides at least three methods of predicting whether an unknown biological specimen originates from a member of a particular family. These methods compare DNA profiles from unknown biological specimens to DNA profiles of more than one family member, which significantly increases the methods' identification ability. In particular, the invention describes combining at least a ranked first family member list and a ranked second family member list to create a combined ranked list and identifying the unknown biological specimen as one contained among a list of specimens having the highest combined rankings representing the candidates that are most likely related to the family. A second method encompasses comparing test DNA profiles from unknown biological specimens to a family pedigree comprising target DNA profiles obtained from multiple biological specimens of family members. This method also embodies using a modified Elston Stewart algorithm to determine a pedigree likelihood ratio to rank and identify the test profile of the unknown biological specimen most likely to be the missing person sought after by the corresponding family represented by the family pedigree. A third method encompasses construction of a database or directed graph of discovered or known relationships between biological specimens and comparison to a graph representing a family pedigree to identify portions of the database or directed graph that correspond to portions of the family pedigree, in order to rank or identify one or more unknown biological specimens as most likely related to one or more family pedigrees.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus to minimize diagnostic and other errors due to transposition of biological specimens among subjects
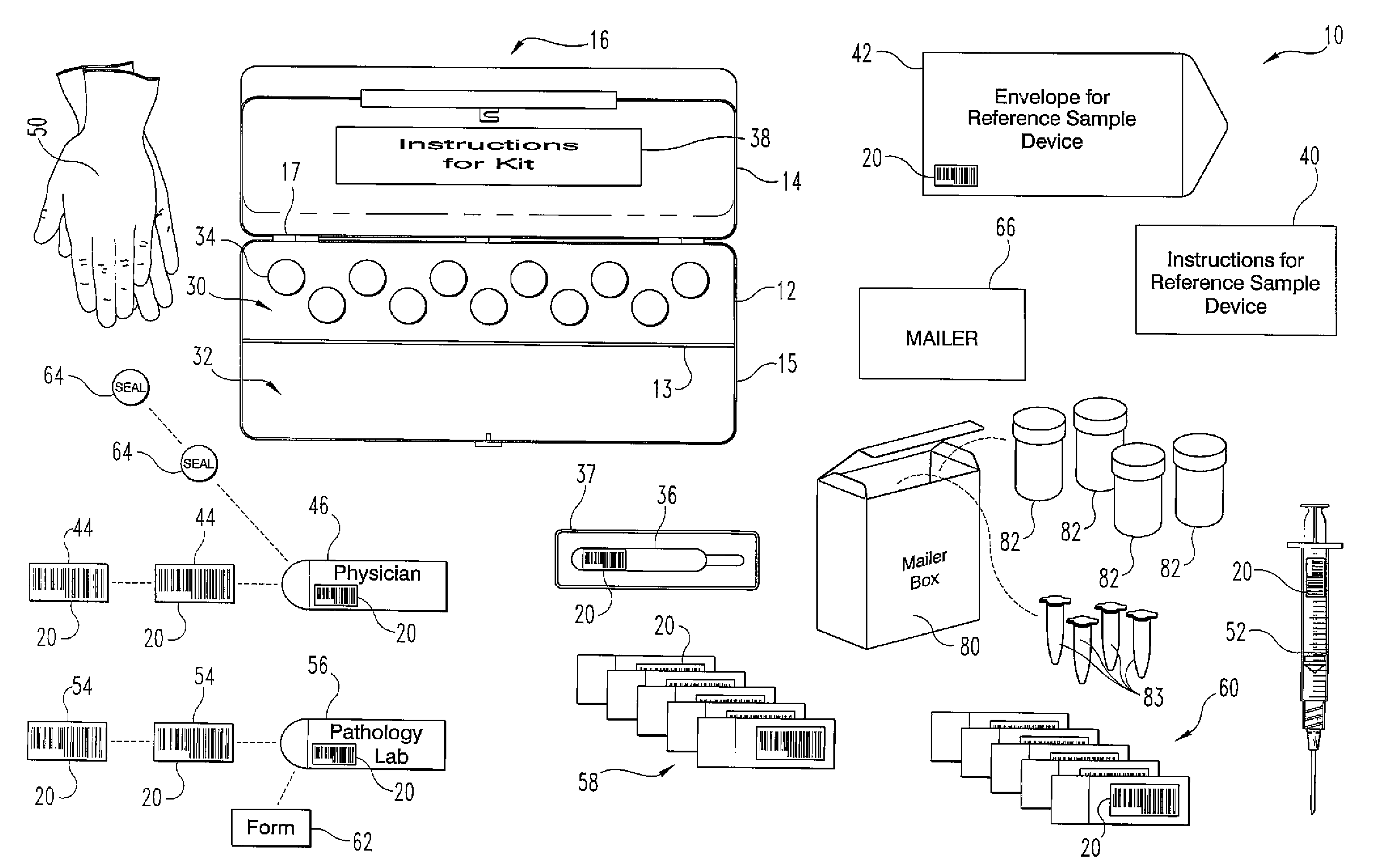
InactiveUS20090291449A1Burette/pipette supportsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyReference sample
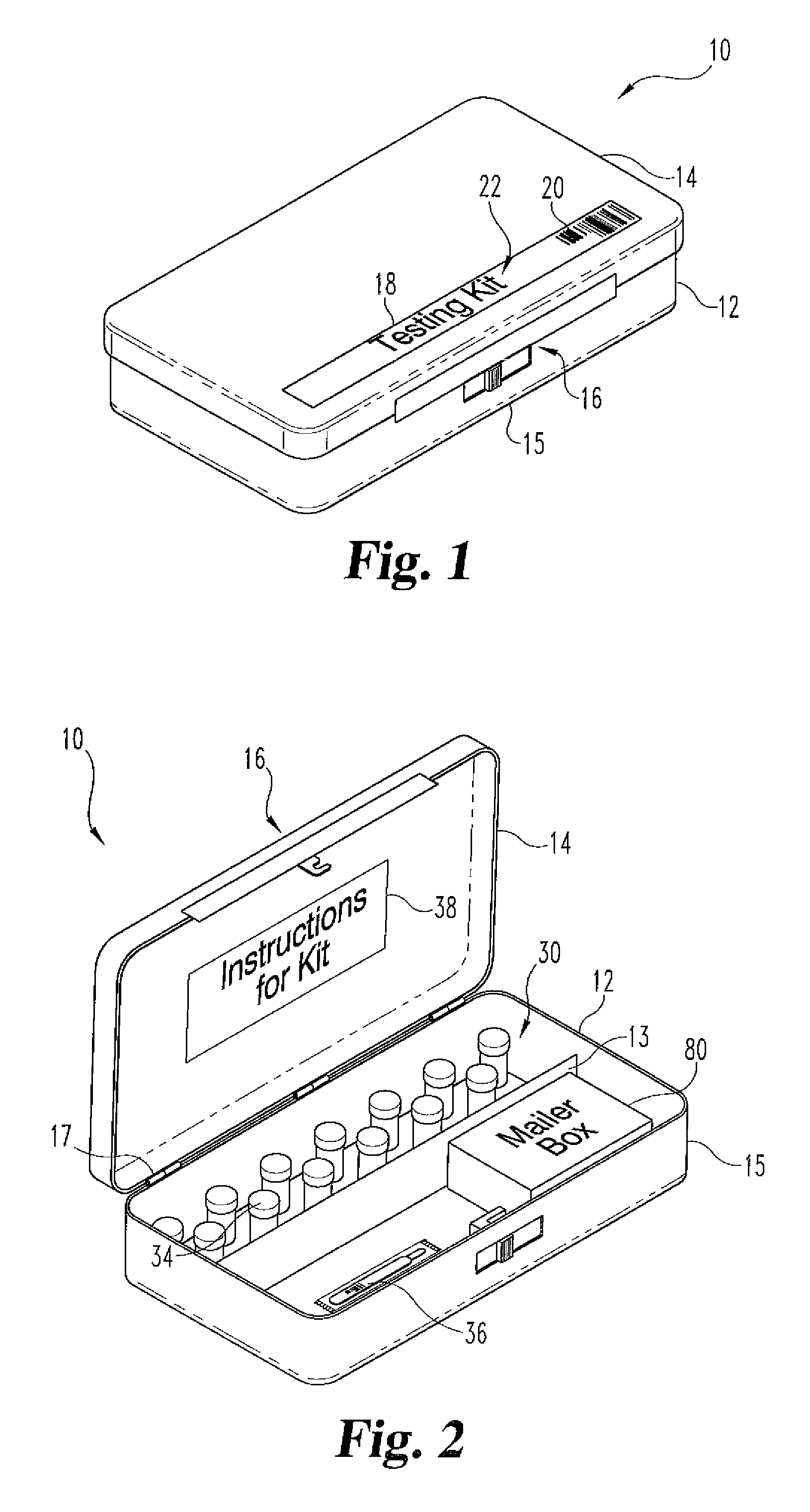
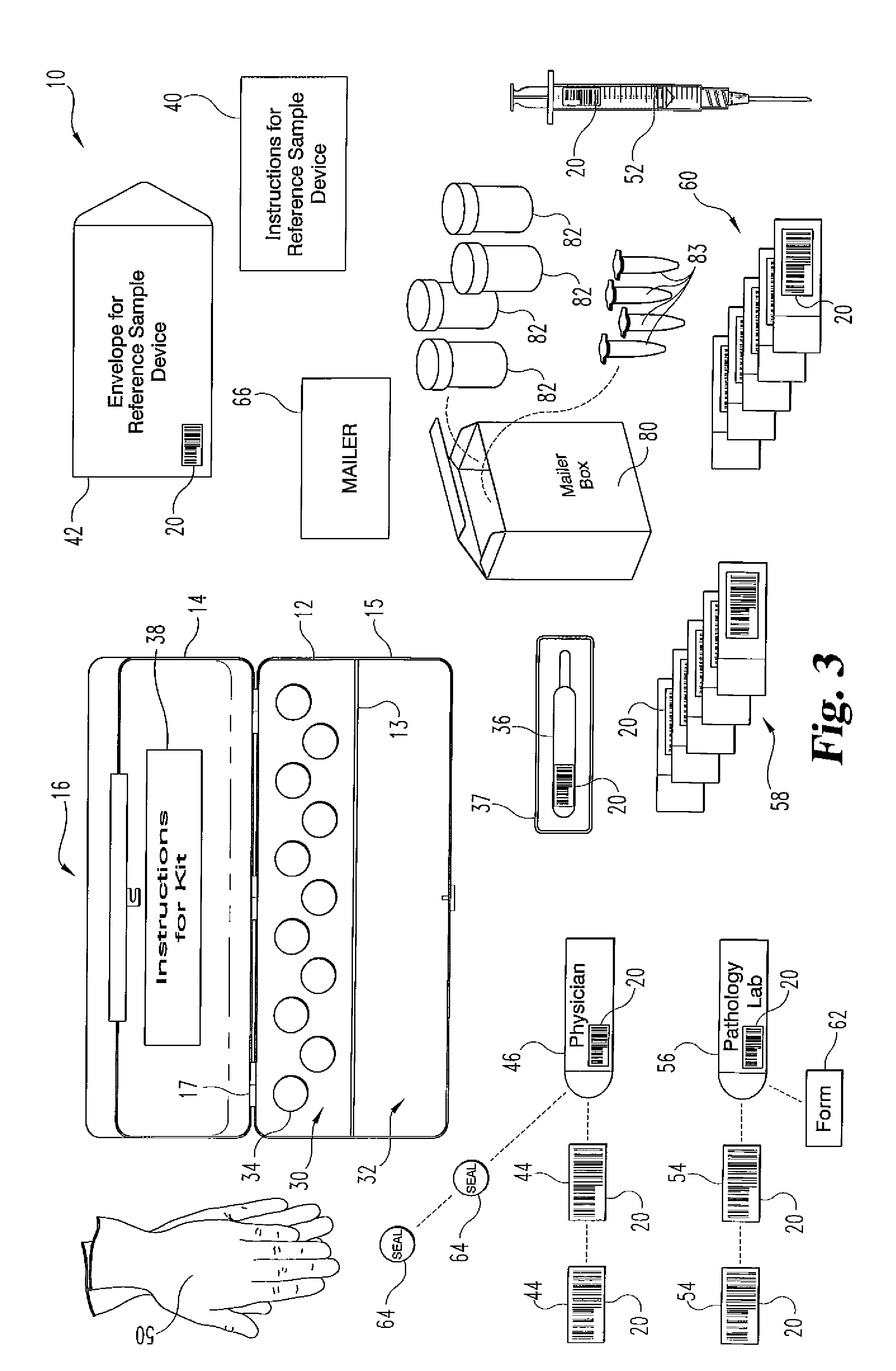
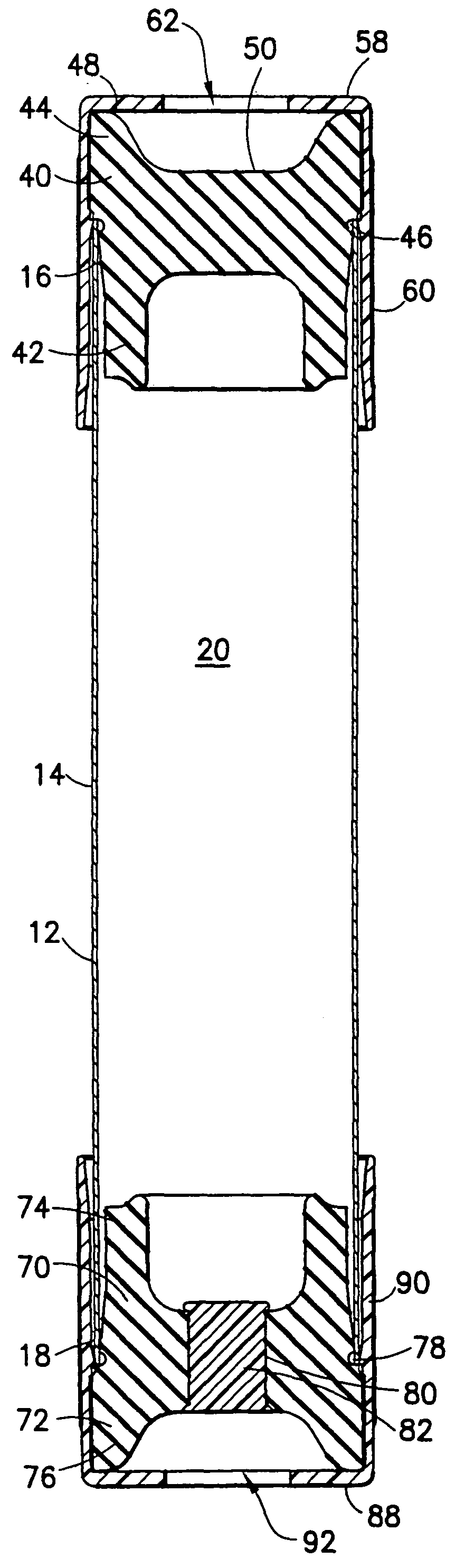
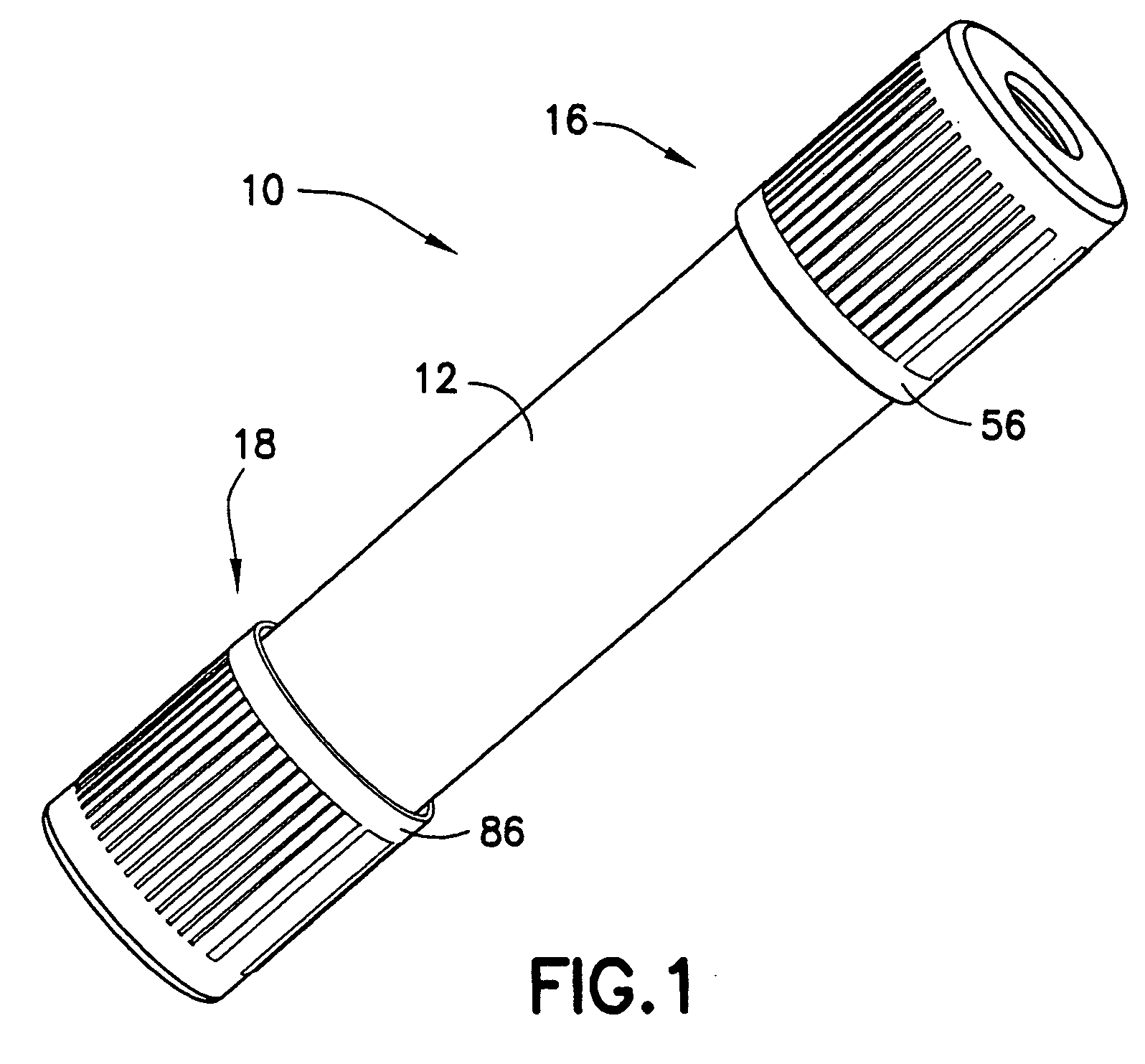
A method and apparatus for minimizing diagnostic errors due to transposition of biological specimens among subjects provides for independent biometric confirmation that a given specimen is from a given donor. In certain embodiments, a biological specimen confirmation kit comprises a portable and openable case housing components of the kit, at least one biological specimen container adapted to receive a biological testing specimen from a donor, and at least one reference sample device adapted to receive a biological reference specimen from the same donor, such that the testing and reference specimens can later be compared for donor match verification by a reference verification entity.
Owner:STRAND DIAGNOSTICS
Non-evacuated blood collection tube
InactiveUS20050065454A1Avoid displacementLaboratory glasswaresCatheterEvacuated blood collection tubeEngineering
A specimen collection container for collecting a biological sample such as blood which includes a non-evacuated collection tube. The tube includes a vent which is adapted for displacement of air from within the interior chamber of the collection tube to the external environment during collection of a blood sample therein. Desirably, the vent is air permeable and liquid impermeable, and seals upon contact with a liquid sample so as to become air impermeable.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
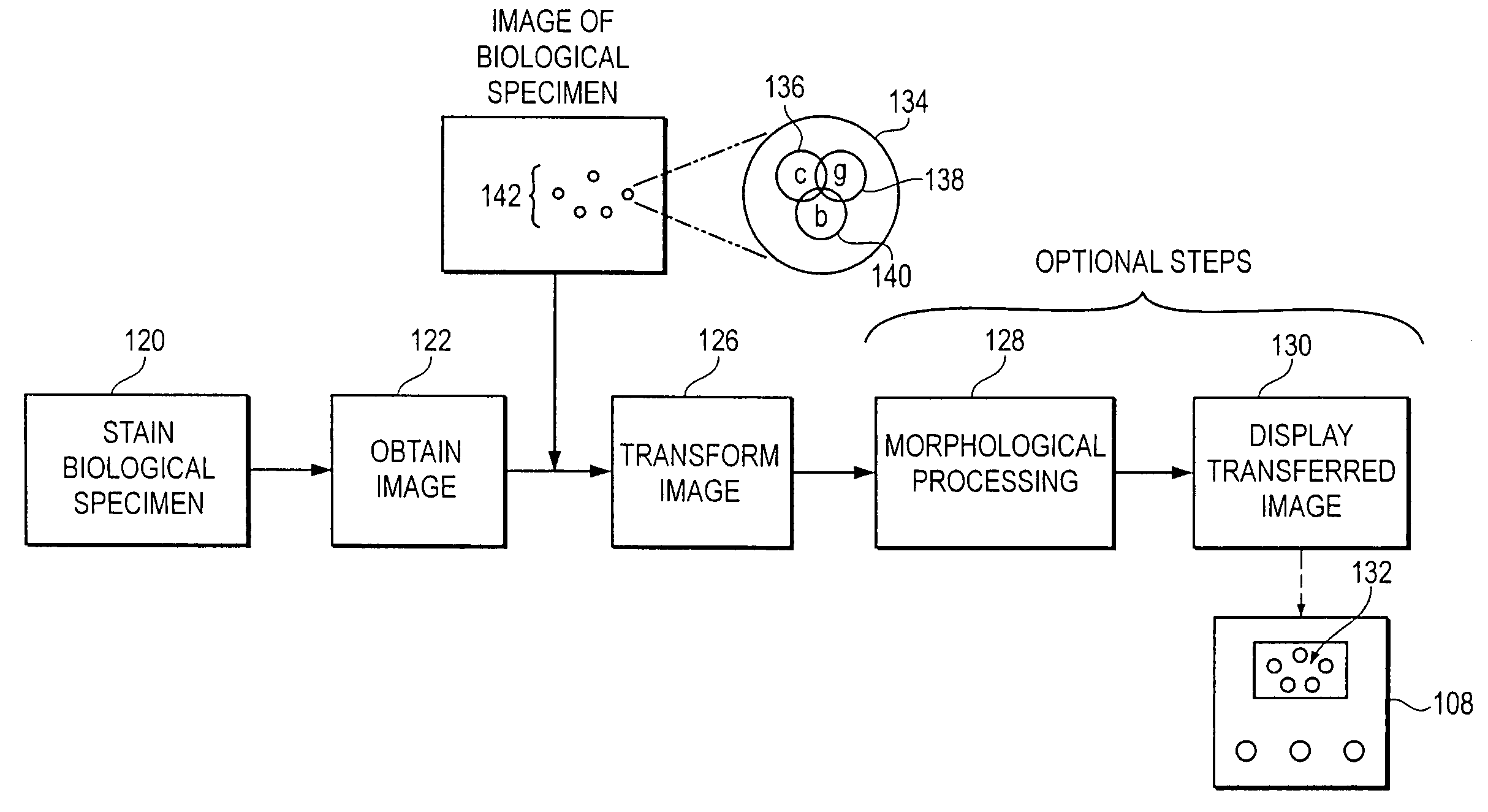
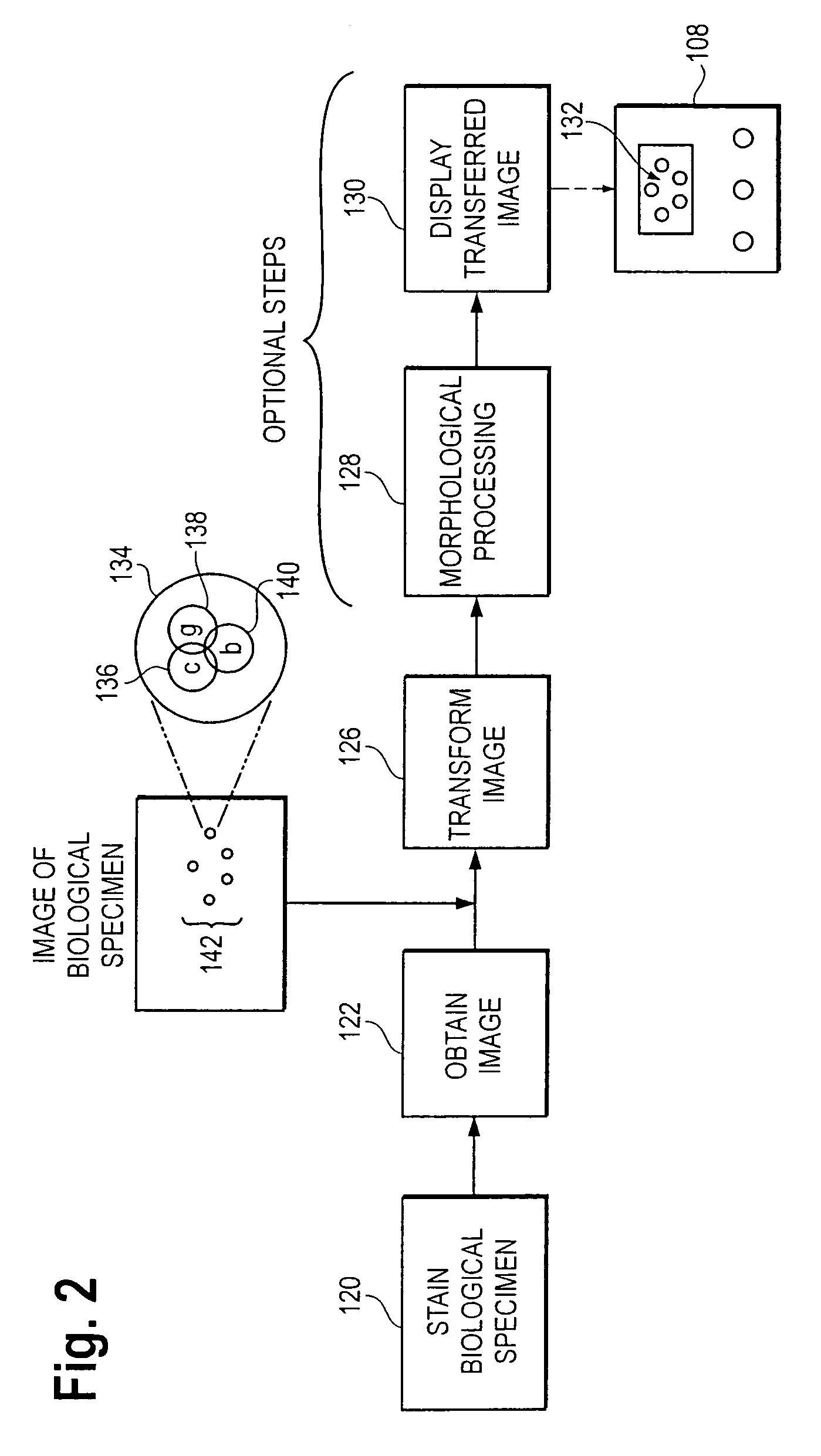
Color space transformations for use in identifying objects of interest in biological specimens
InactiveUS7200252B2Readily observe and identifyHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor transformation
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Diagnostic test device and method of using same
InactiveUS6991898B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiagnostic testTest room
A self contained diagnostic test device is provided for use in the collection and detection of a biological specimen or the like. The device comprises a tubular swab and reagent dispensing cap component for receiving specimens. The reagent dispensing cap component includes barrel, reagent chamber, and results window subcomponents, and delivers one or more selected reagents to a specimen testing chamber for contacting the collected specimen, upon the rotation of the reagent chamber component.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Biological sample observation system and biological sample observation method
InactiveUS20060023299A1Reduce harmRelieve effectBiochemistry apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansTime changesBiochemistry
A biological sample observation system wherein the fluorescence intensity of living cells and the like can be measured accurately in real time, and damage to the living cells can be reduced, and a biological sample observation method using the system are provided. A biological sample observation system for observing change with time in a biological sample being cultured, comprises: a culturing space where an inside environment is maintained at a predetermined level, and the biological sample is cultured under the environment; a buffering space which is formed outside of the culturing space to relieve the effect on the culturing space from the outside of the space, and which is substantially separated from the outside; and a detector which observes the biological sample inside the culturing space through at least a part of the buffering space.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
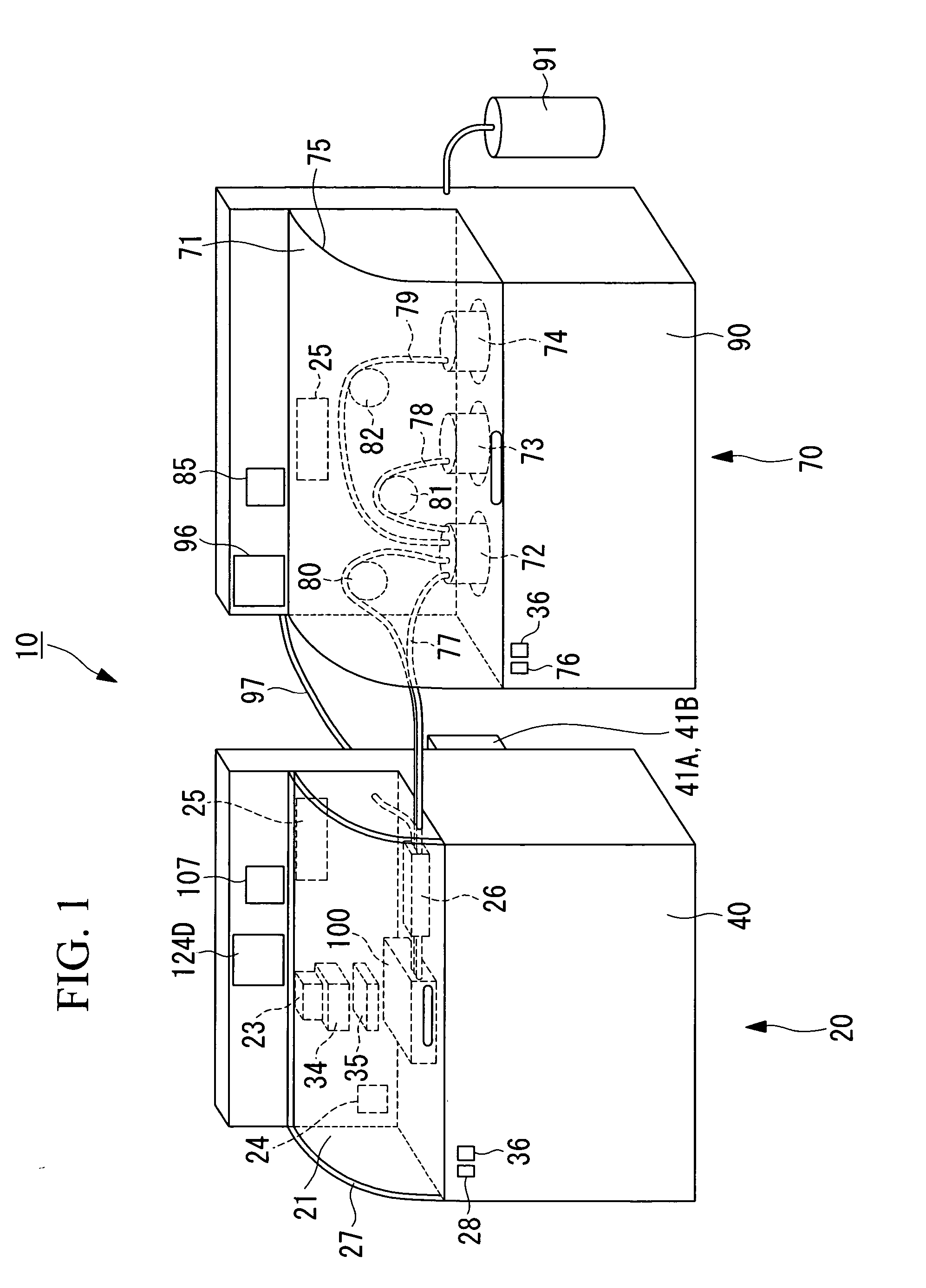
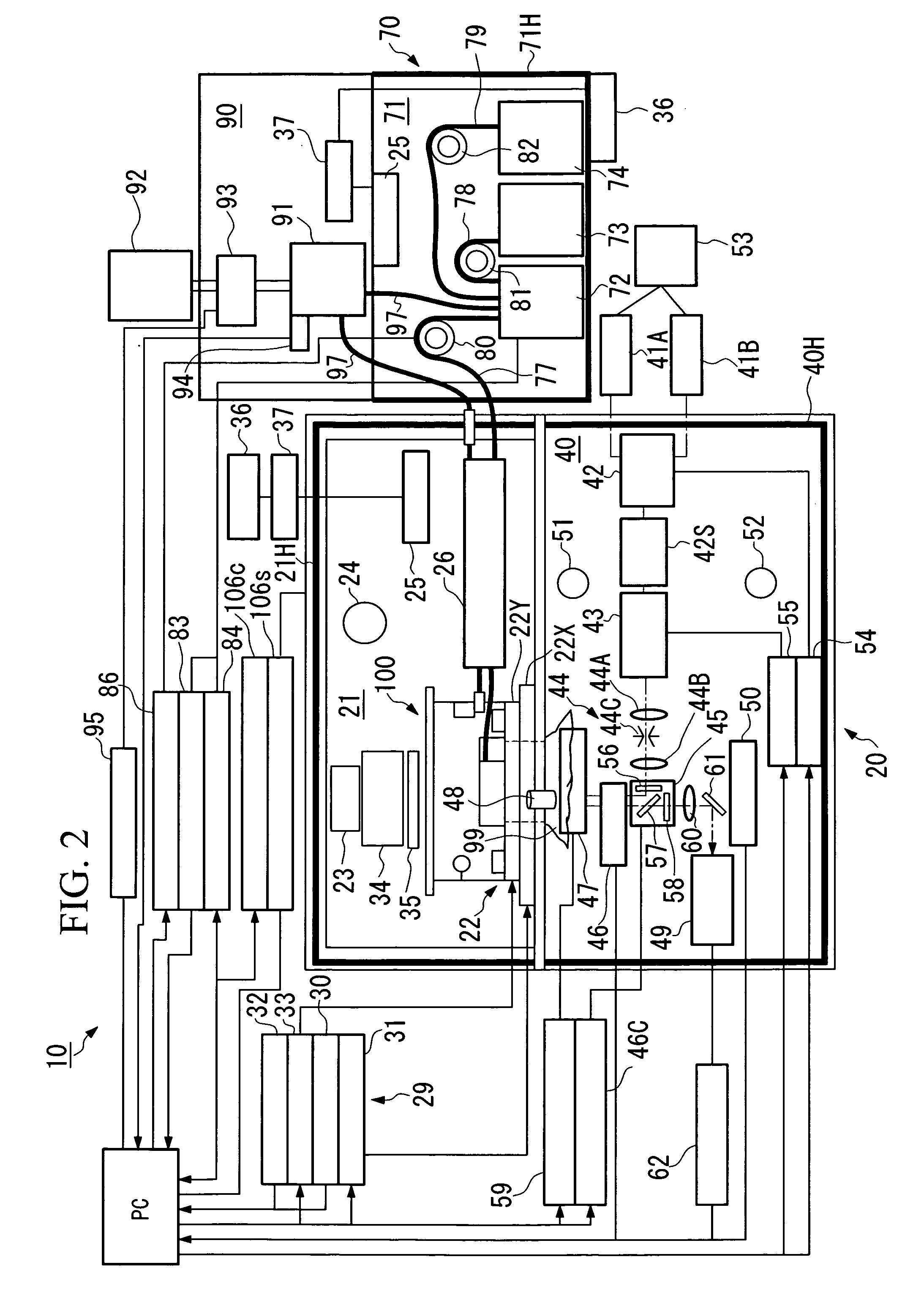
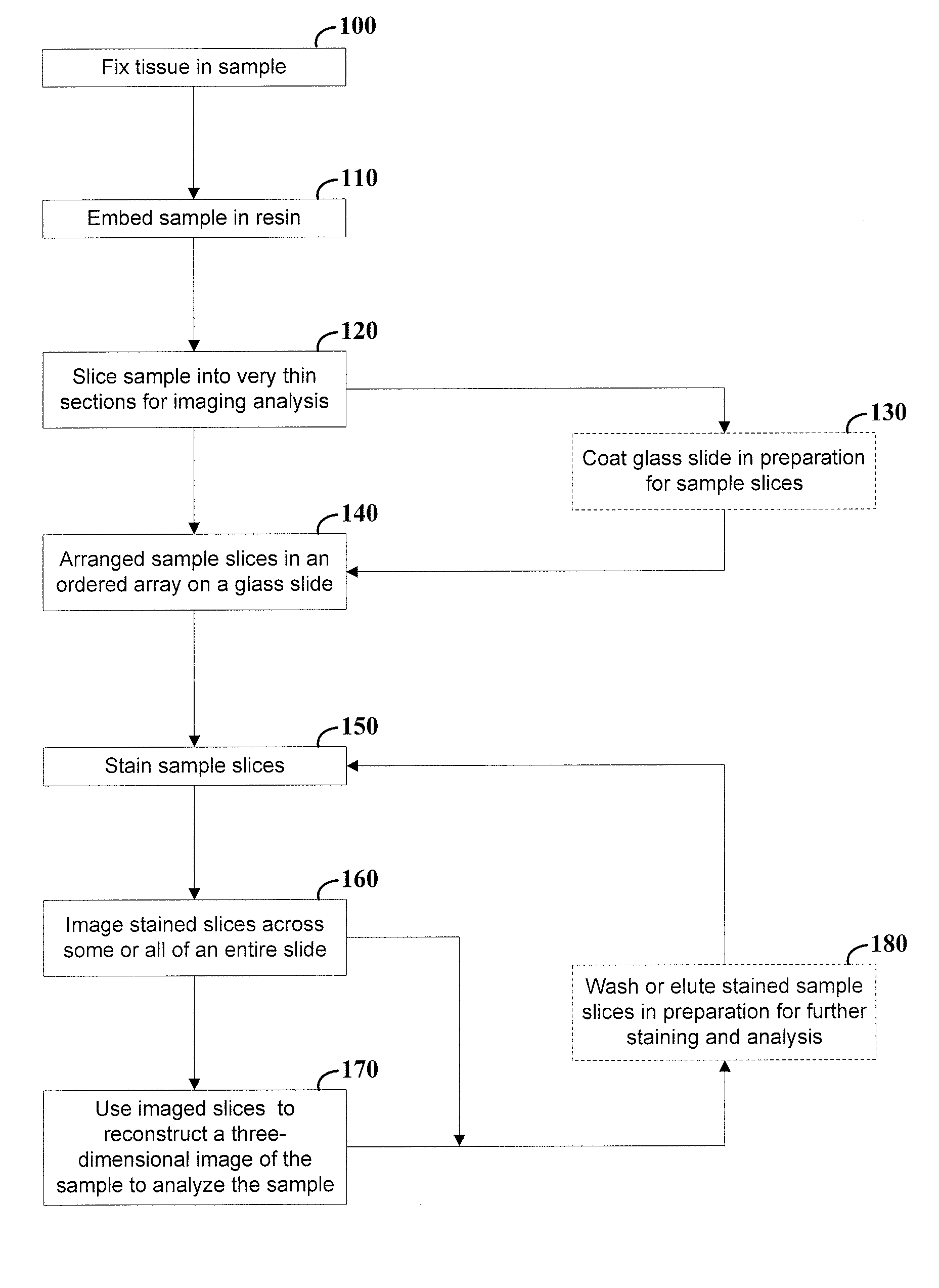
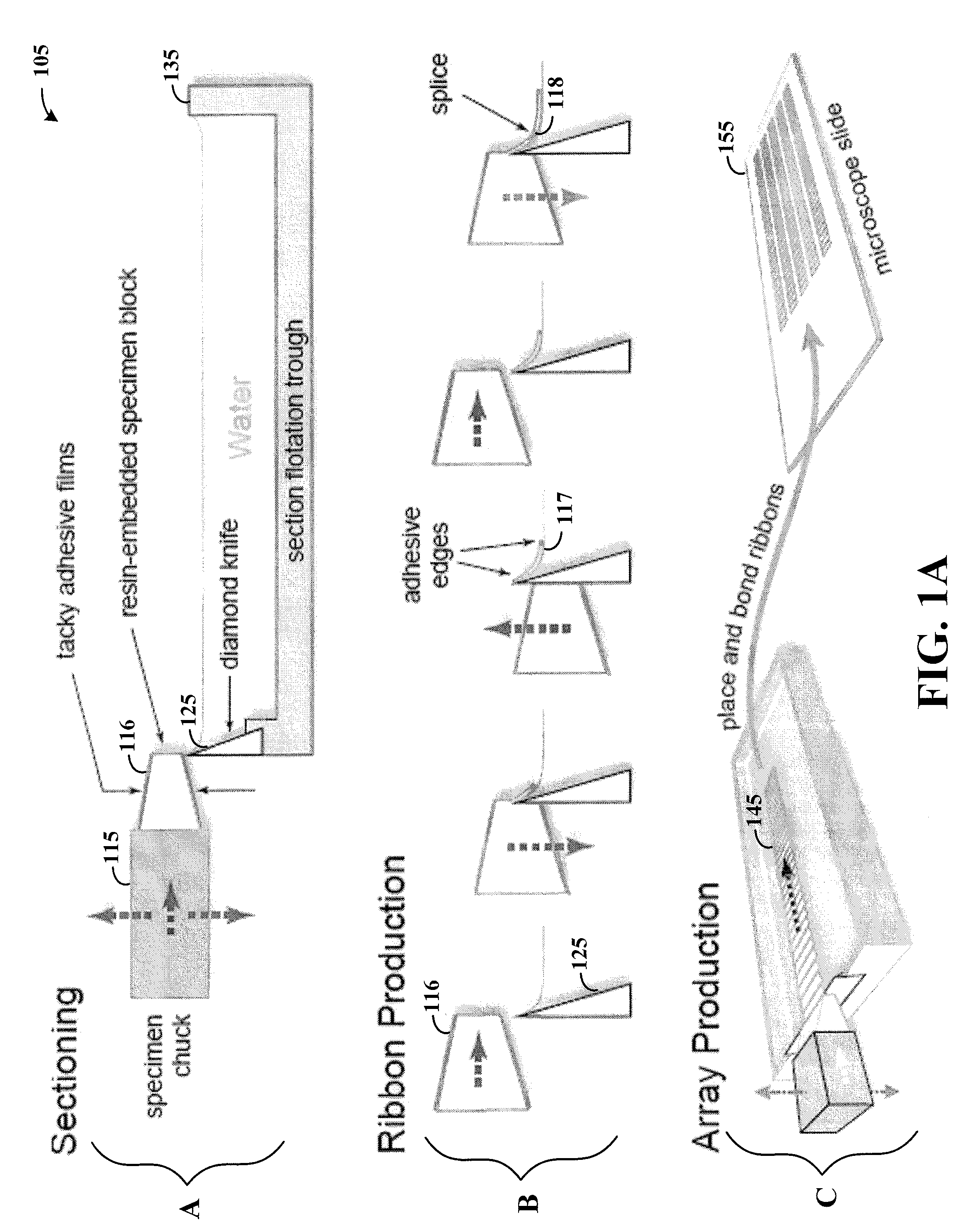
Arrangement and imaging of biological samples
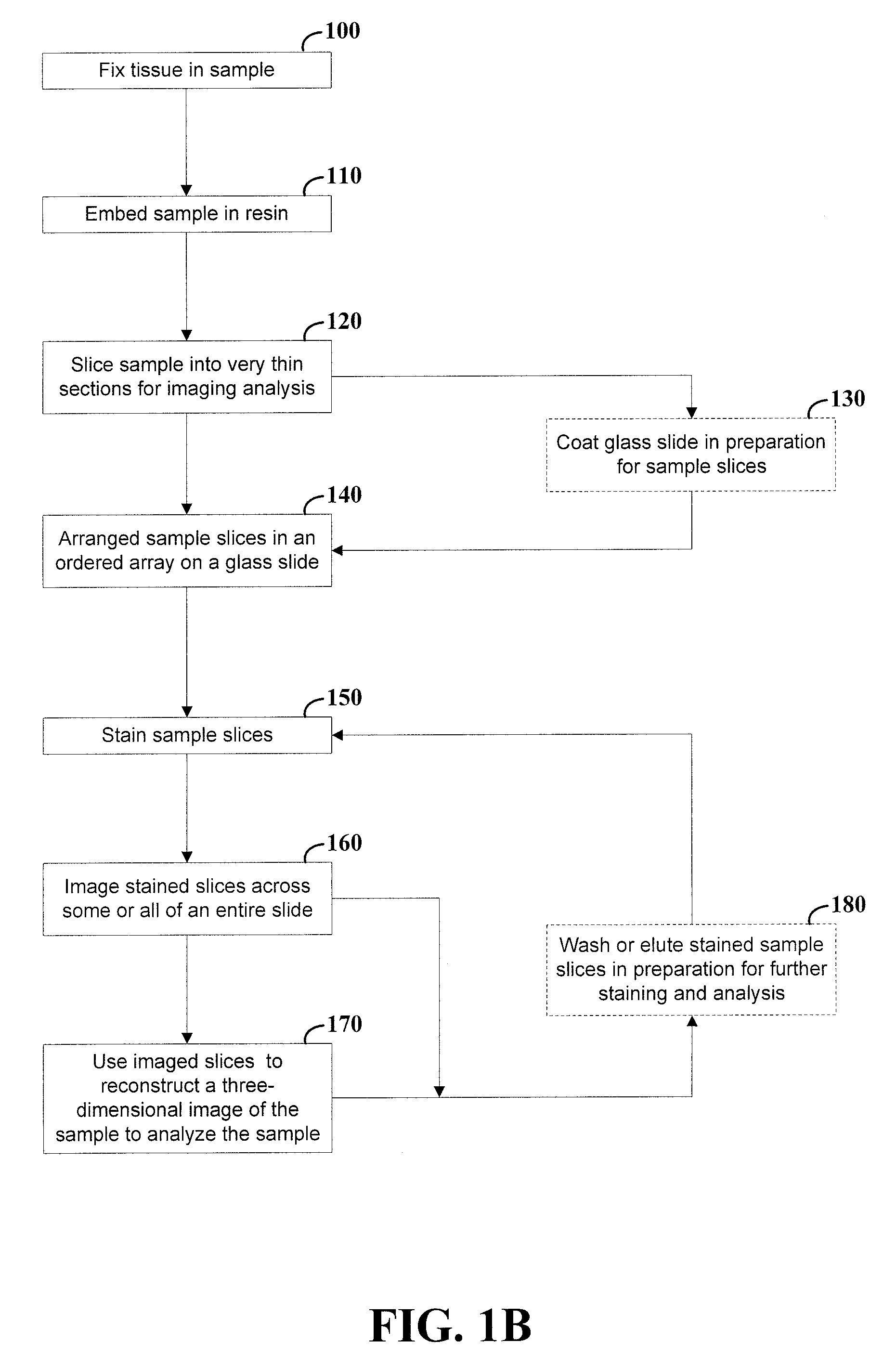
InactiveUS20080152207A1Reduces total image processing timeImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationMicroscope slideMultiple treatments
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of a specimen is facilitated. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, a series of very thin slices from a specimen are serially and robustly arranged on an imaging device such as a microscope slide. The slices are imaged and the images are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional image having high resolution at depths into the specimen. The serial arrangement of the slices facilitates the proper ordering of images for reconstruction. Further, the robust nature of the slice arrangement facilitates treatment of the slices and, in some applications, multiple treatments with corresponding imaging sequences for each treatment. Various embodiments are directed to methods and arrangements for three-dimensional characterization of biological specimen and to data that is accessible and / or executable by a computer for linking different images together in order to characterize such biological specimen in three dimensions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
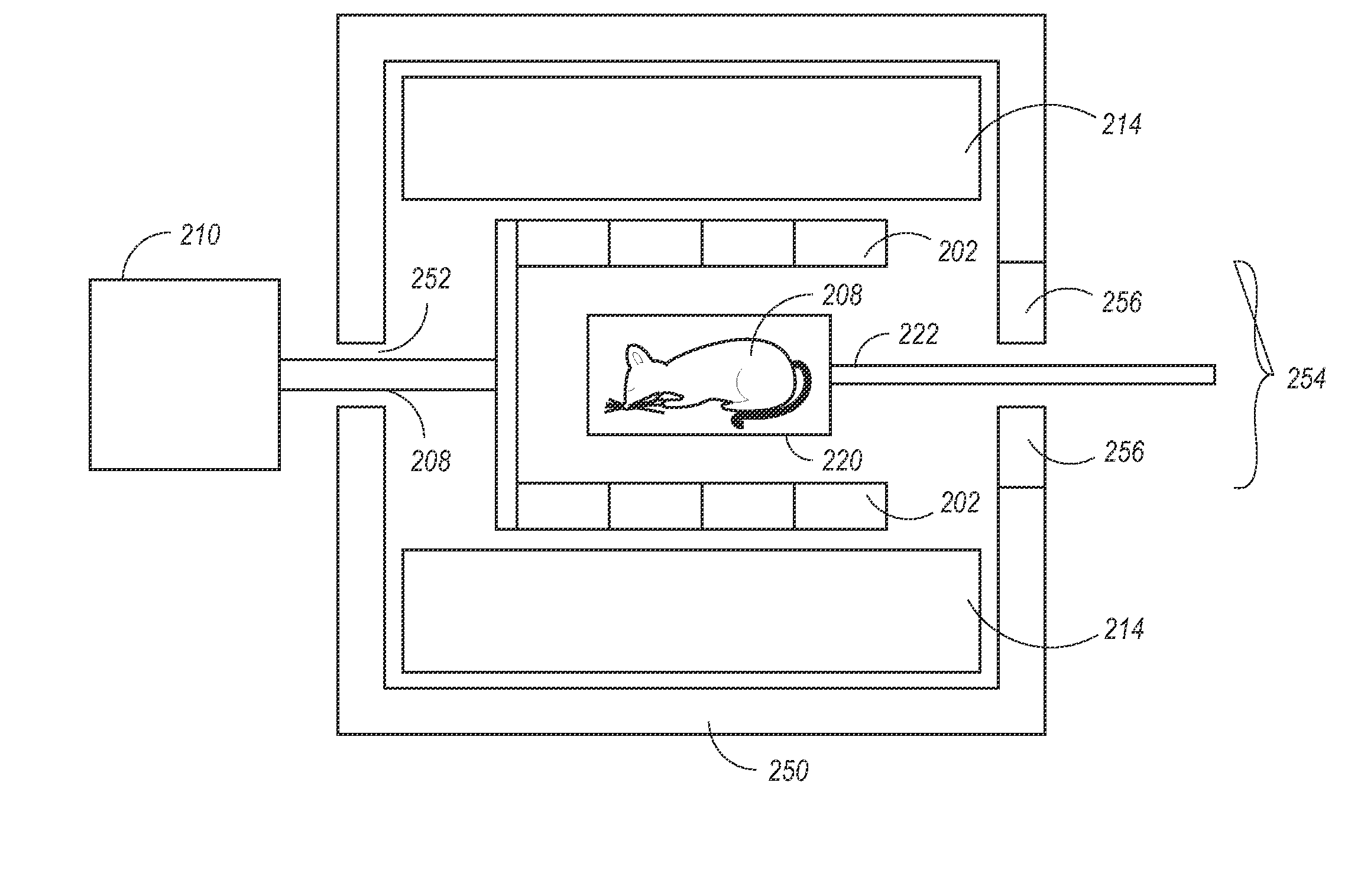
Miniaturized imaging devices, systems and methods
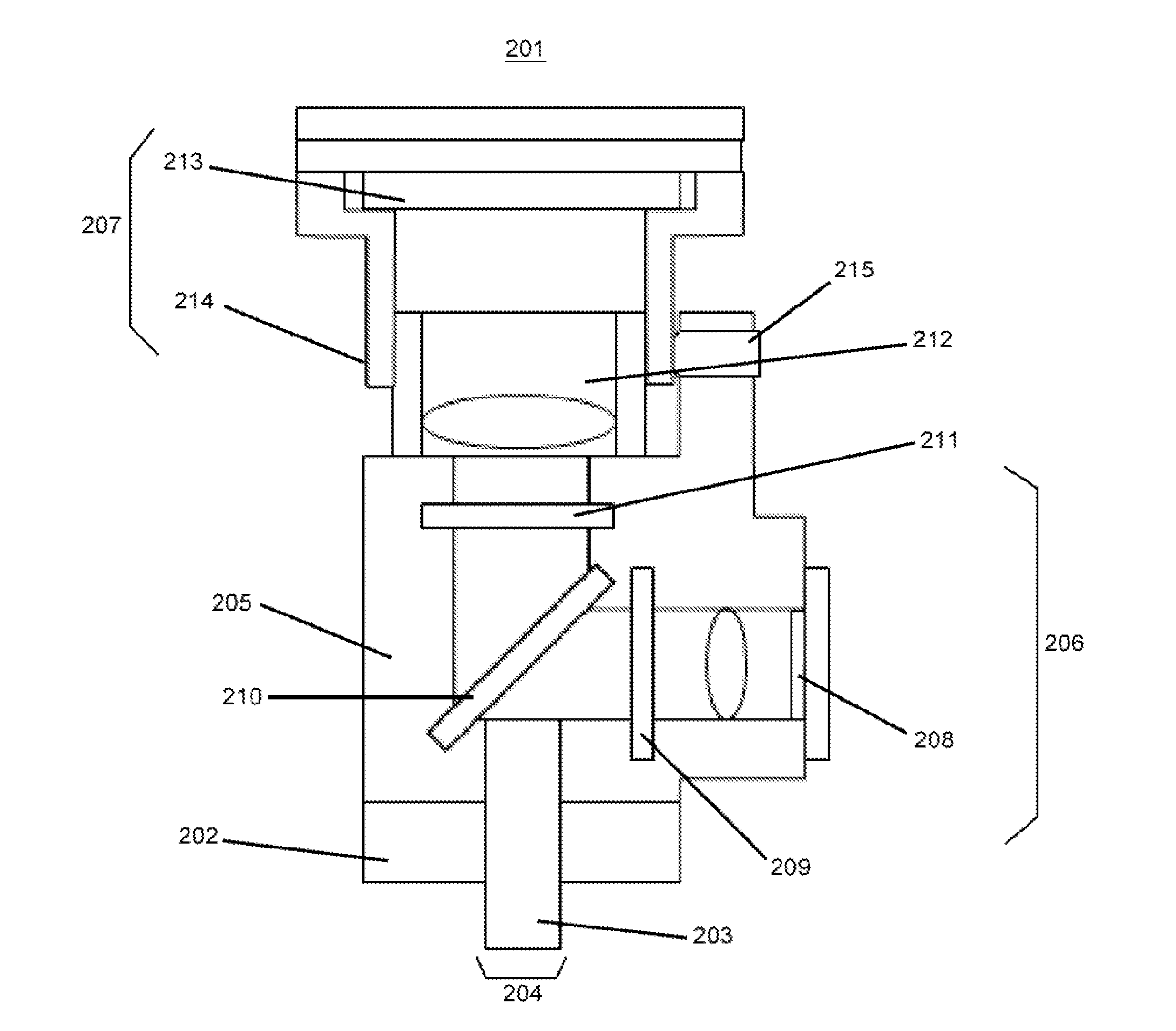
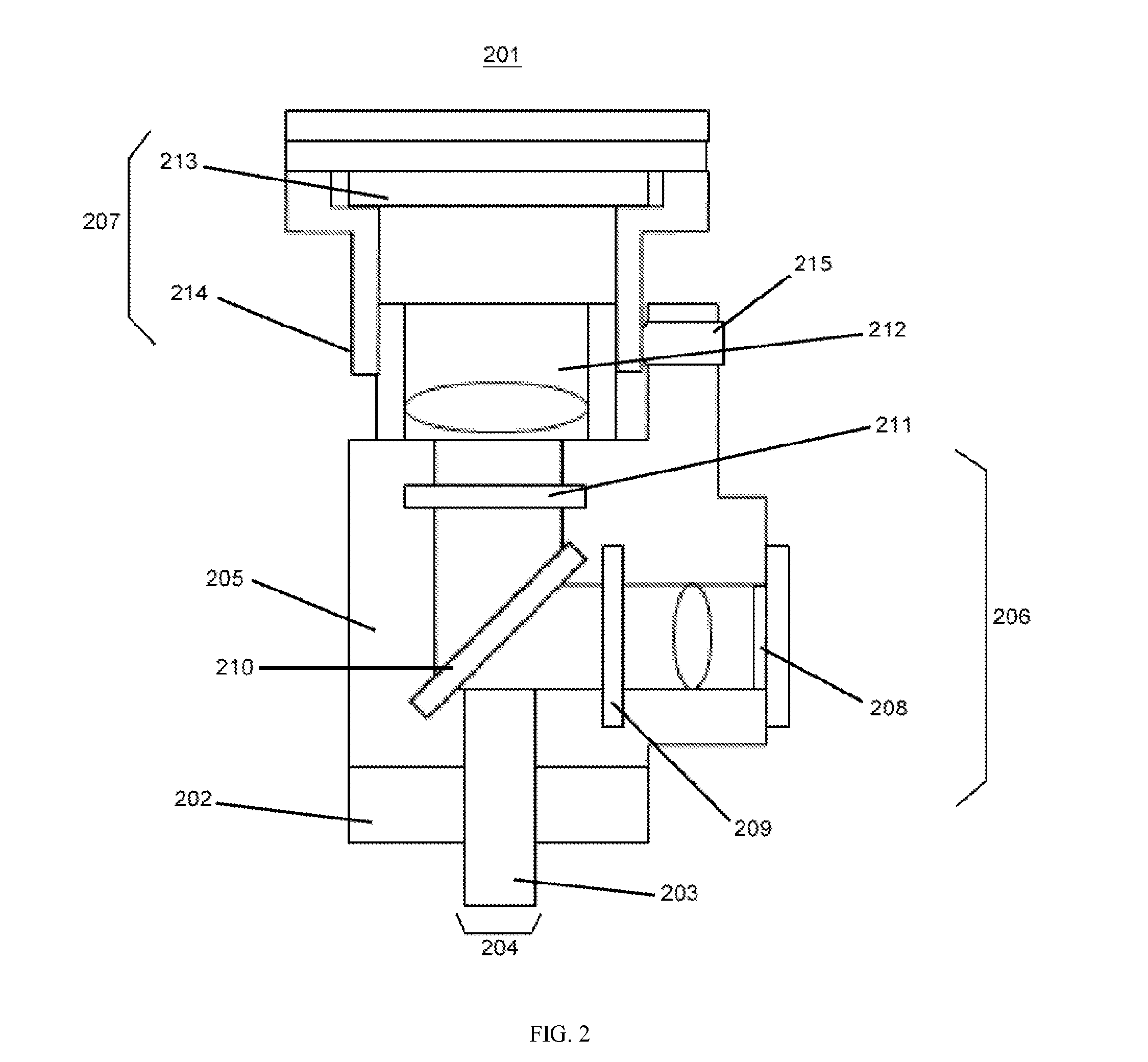
InactiveUS20150309295A1Easy to assemblePrevent movementDianostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsFluorescenceMiniaturization
The invention provides miniaturized devices, systems and methods for imaging of biological specimens. The devices and system provide accurate alignment and modular mounting of imaging components internally and in relation to the target subject. In some embodiments, the invention provides devices, systems and methods for in vivo fluorescent brain imaging in freely-behaving rodents.
Owner:INSCOPIX
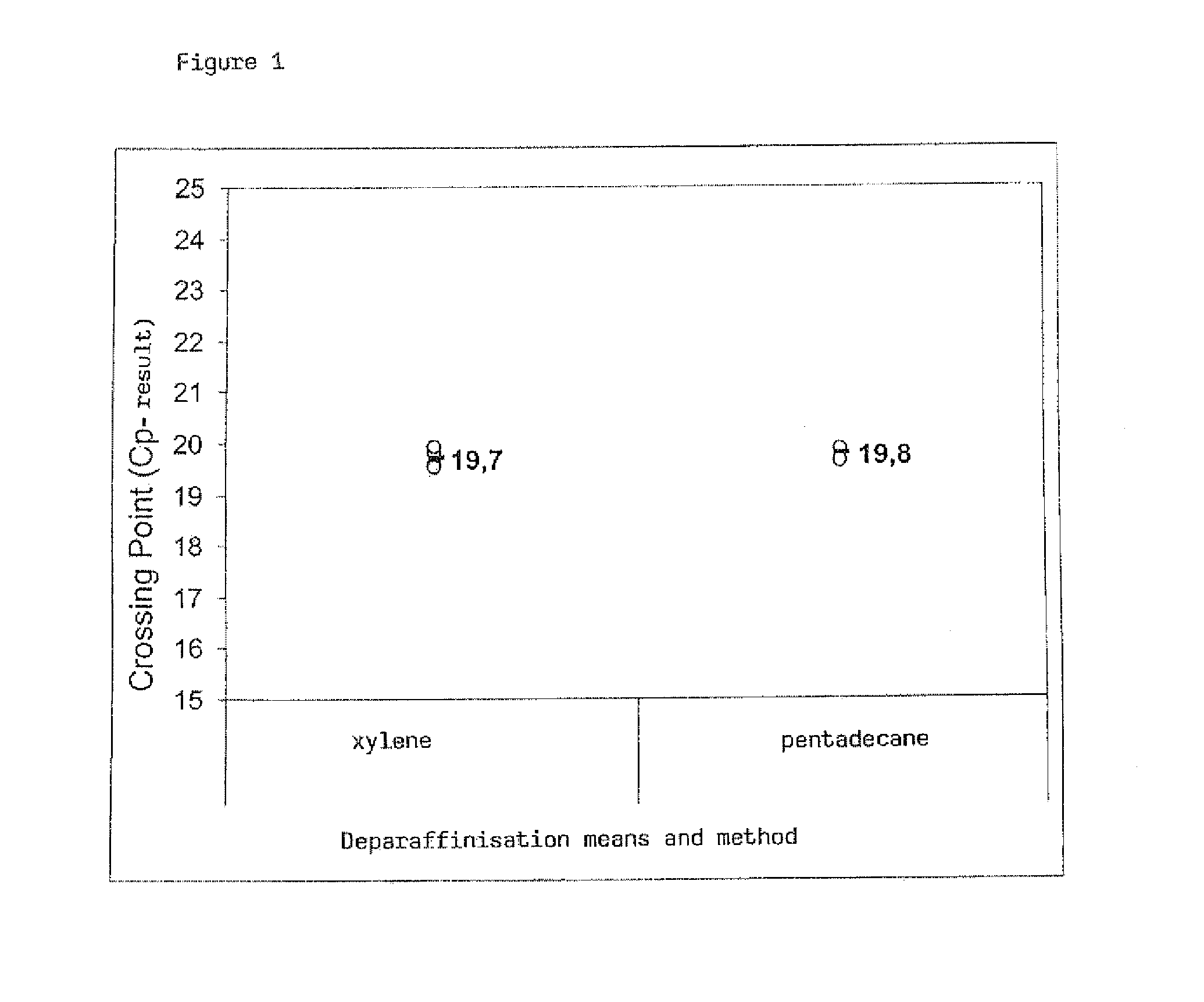
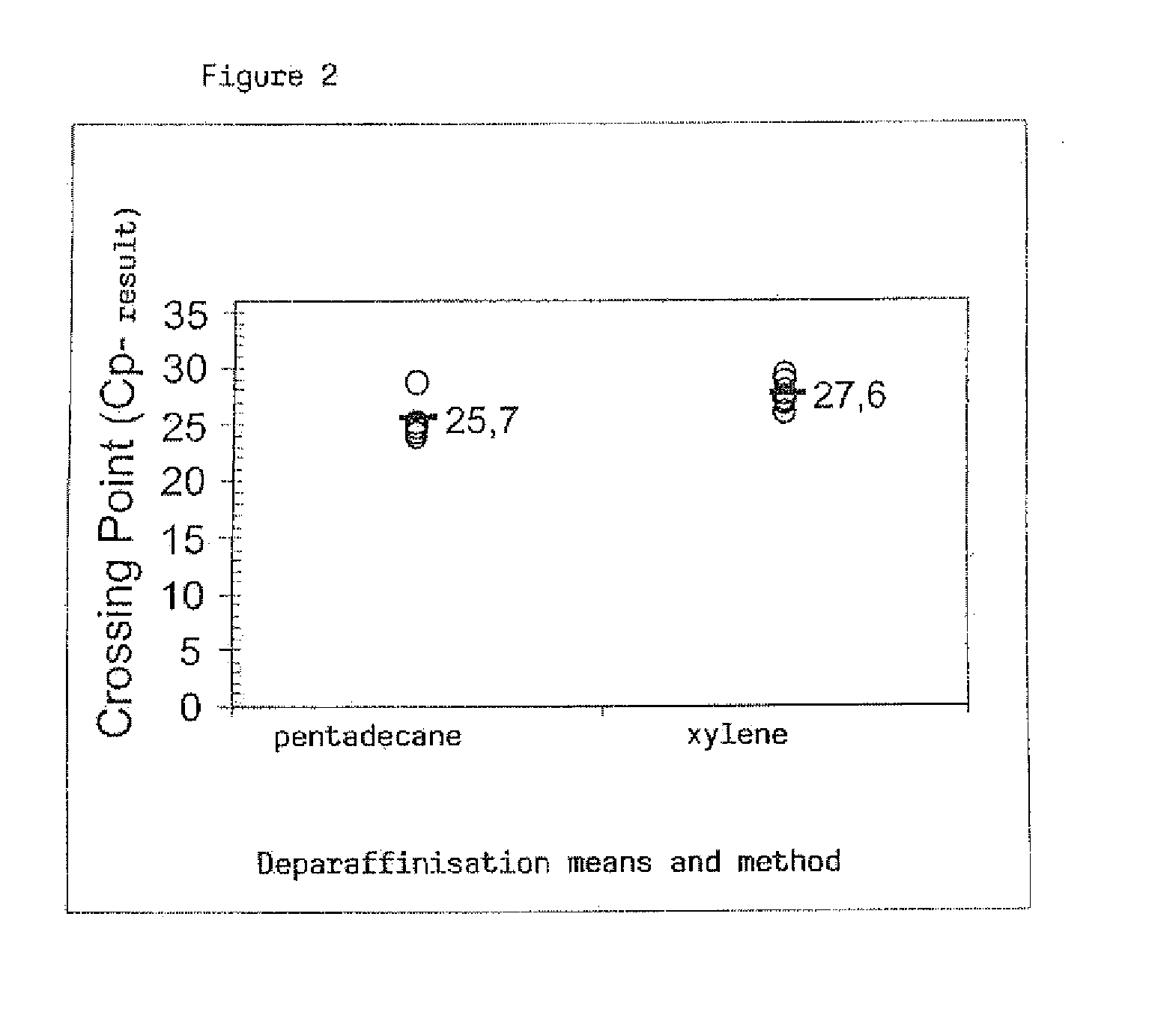
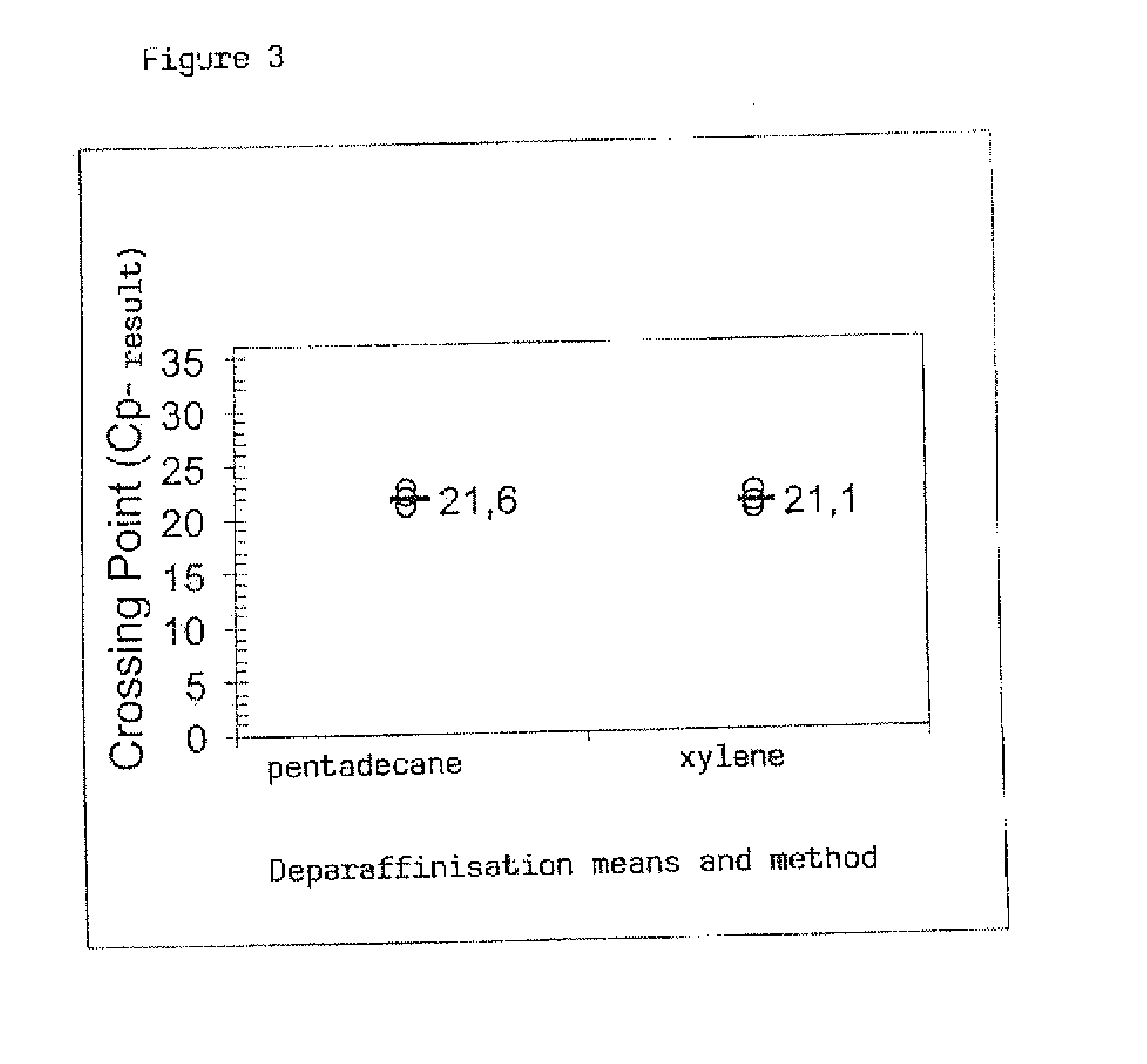
Method for the deparaffinisation of biological specimens
A method for isolating biomolecules from a fixed biological specimen embedded in paraffin, comprises the steps of bringing the specimen into contacta) with a solvent non-miscible with water and dissolving the paraffin in this solvent such as to form a liquid organic phase, andb) with an aqueous solution of at least one lysis substance and / or with water and at least one lysis substance such as to form an aqueous phase;isolation of the biomolecules from the aqueous phase. The invention further relates to a corresponding kit as well as to the use of such a kit for isolating biomolecules.
Owner:AXAGARIUS
System and method for providing a rotating magnetic field
InactiveUS20080024130A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningLive animal
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for generating a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field can be used to obtain rotating-field NMR spectra, such as magic angle spinning spectra, without having to physically rotated the sample. This result allows magic angle spinning NMR to be conducted on biological samples such as live animals, including humans.
Owner:SCHLUETER ROSS D +1
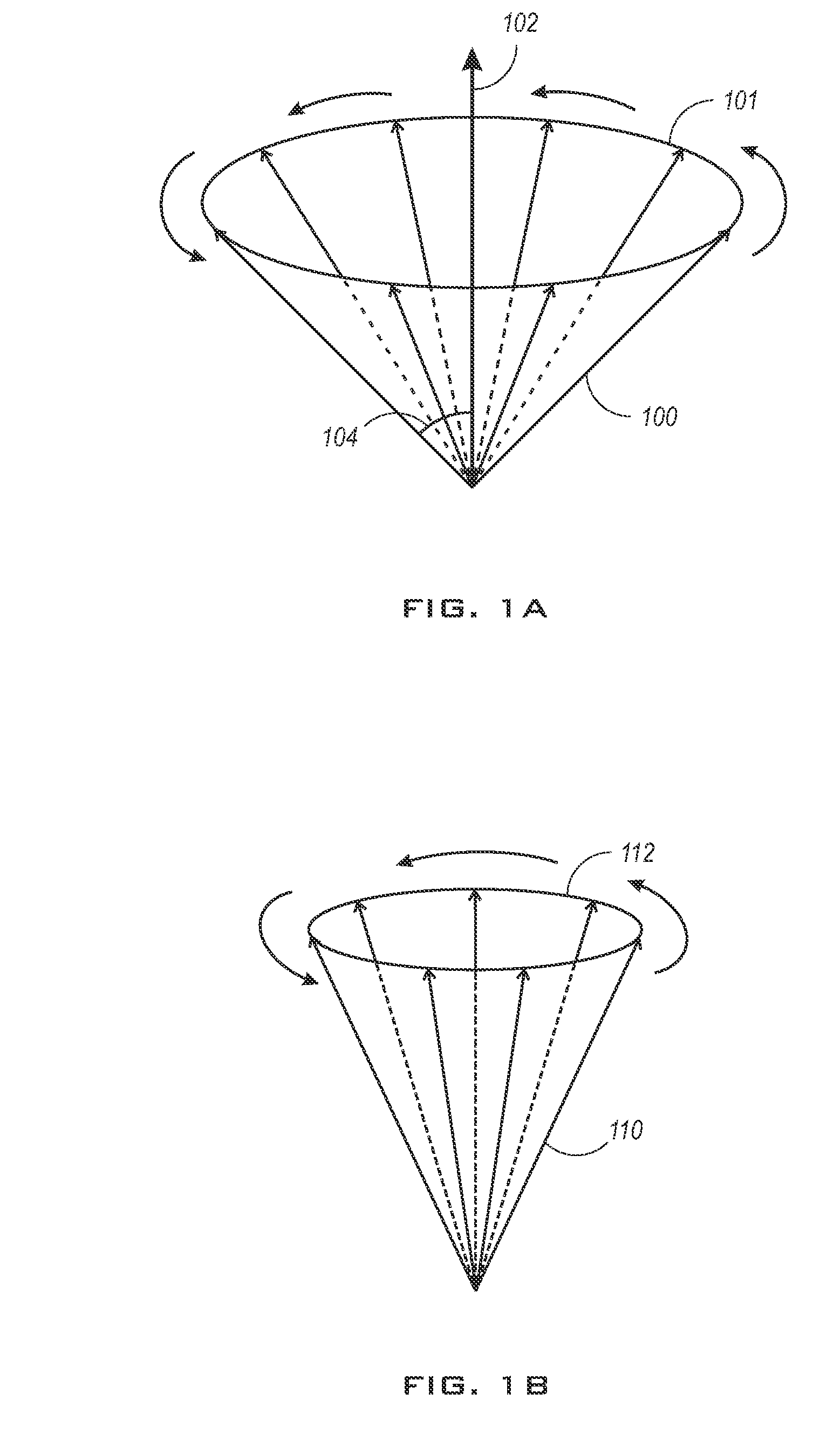
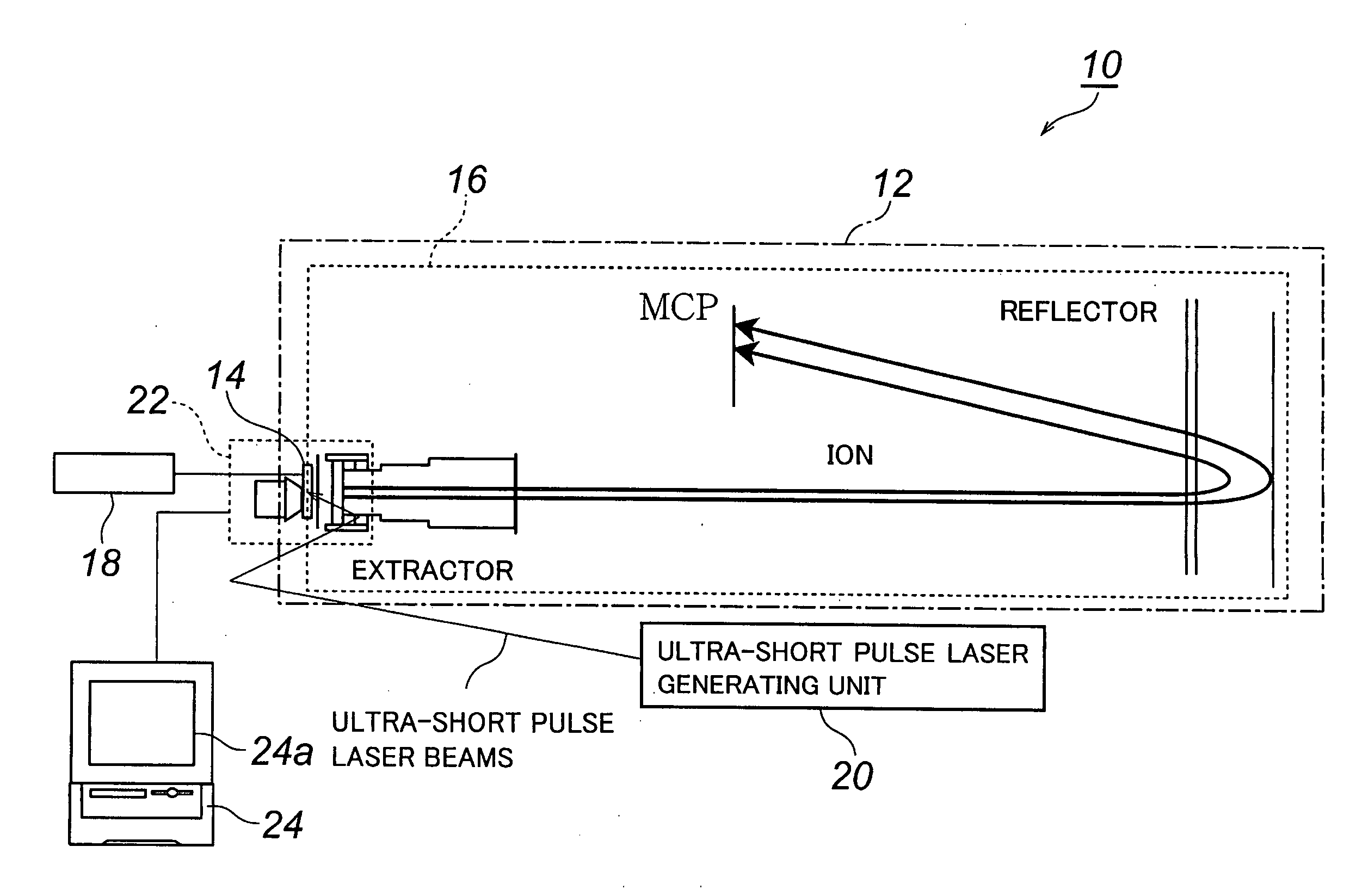
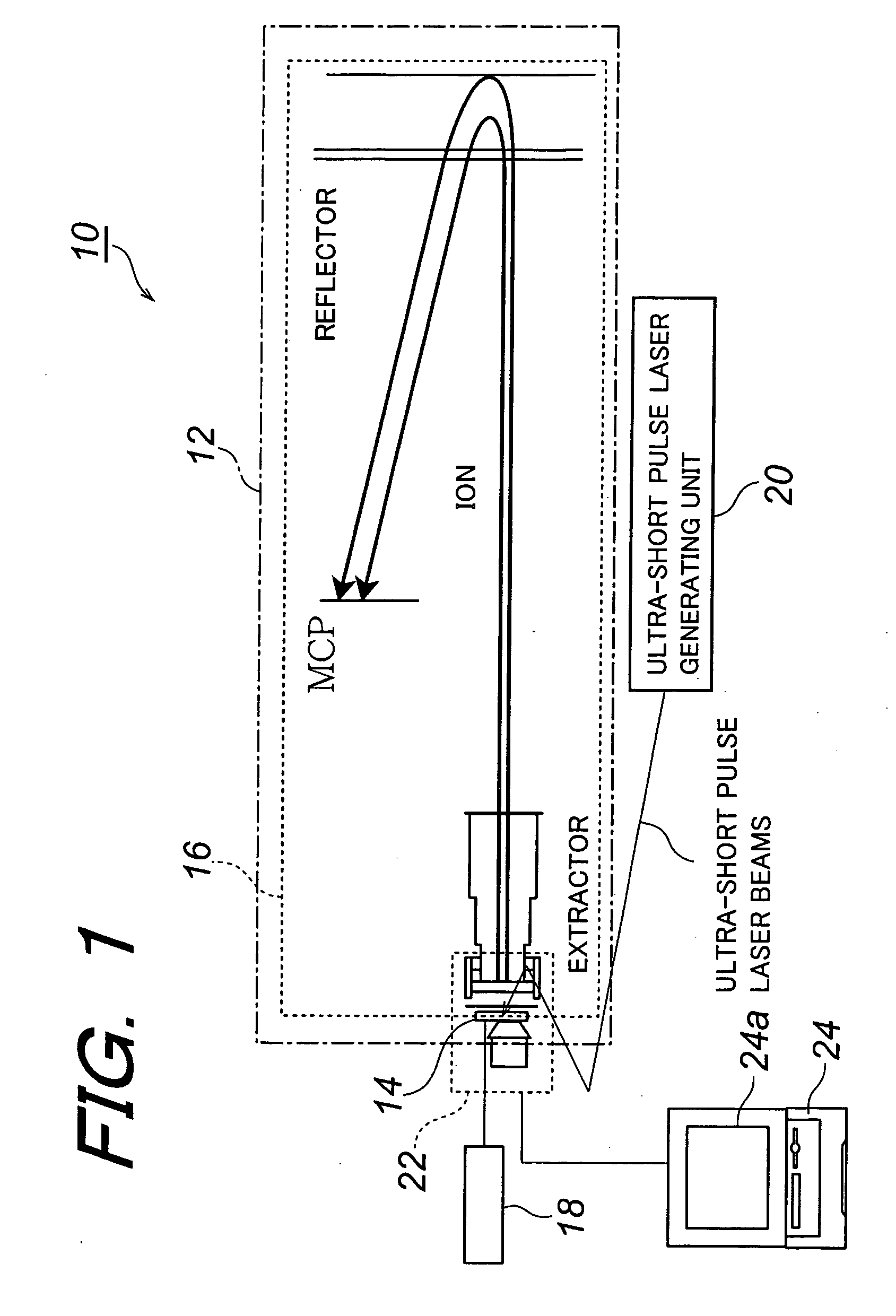
Method of Analyzing Biosample by Laser Ablation and Apparatus Therefor
InactiveUS20080020474A1Shorten the timeHigh reliability of resultsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTime-of-flight spectrometersAnalyteWorkload
A method of analyzing a biosample that enables substantial shortening of time required for analysis, further enabling obtaining highly reliable results through means for avoiding sway of analytical results depending on observers, and that enables one-time analysis of a multiplicity of genes, etc. on a single biosample to thereby enhance workload and time efficiencies, and that enables analysis of multiple genes, etc. under conditions completely free from any difference in background attributed to biosamples. There is provided a method comprising irradiating a biosample as an analyte with ultra-short pulse laser beams to thereby effect an ablation thereof so that molecules contained in the biosample are atomized into constituting elements, ionizing the constituting elements resulting from the atomization and analyzing the ionized constituting elements to thereby analyze analytical-target molecules of the biosample.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Device and method for animal tracking
ActiveUS7107936B2Eliminates and reduces disadvantageStampsCharacter and pattern recognitionIdentification deviceBiology
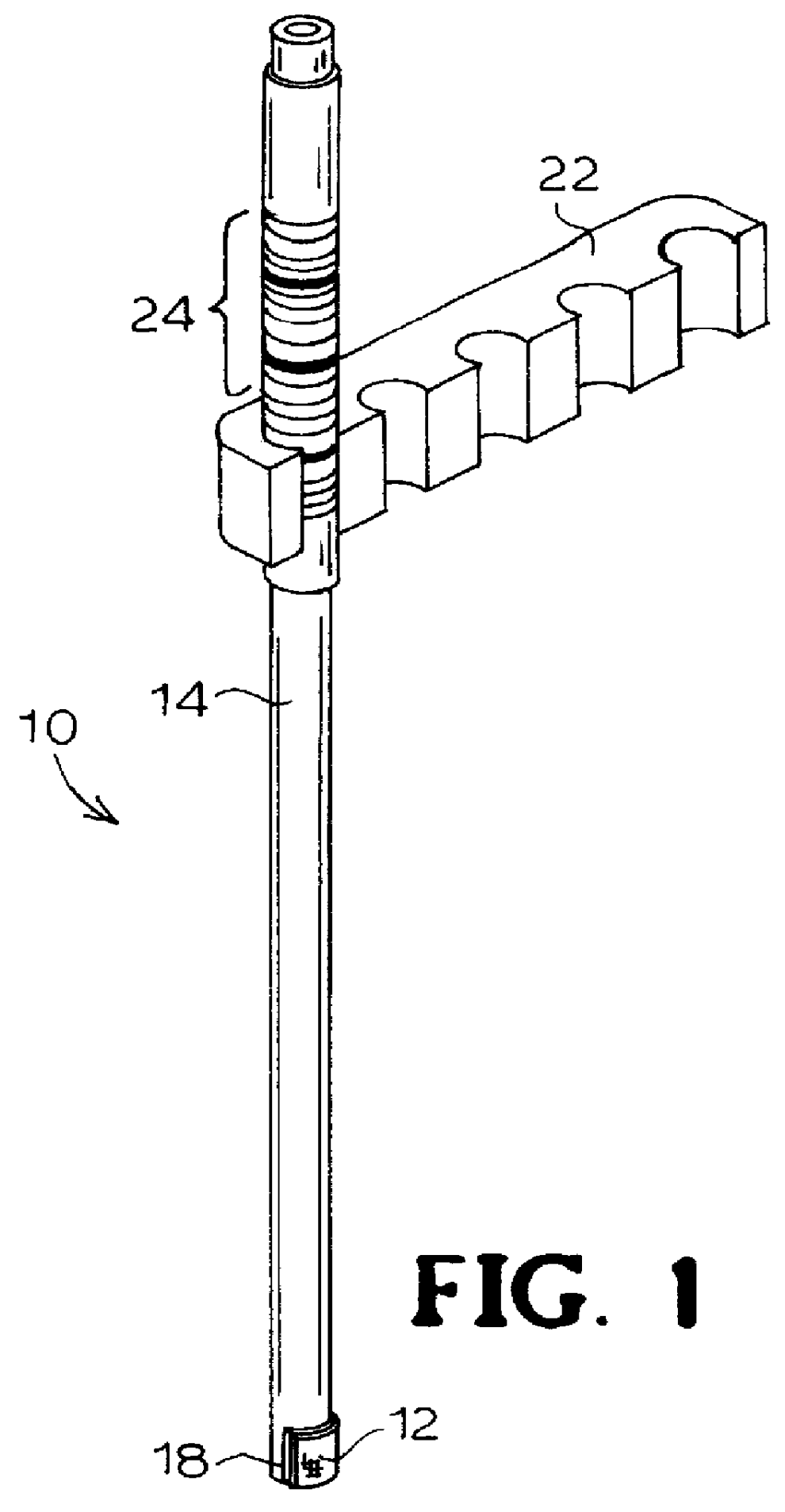
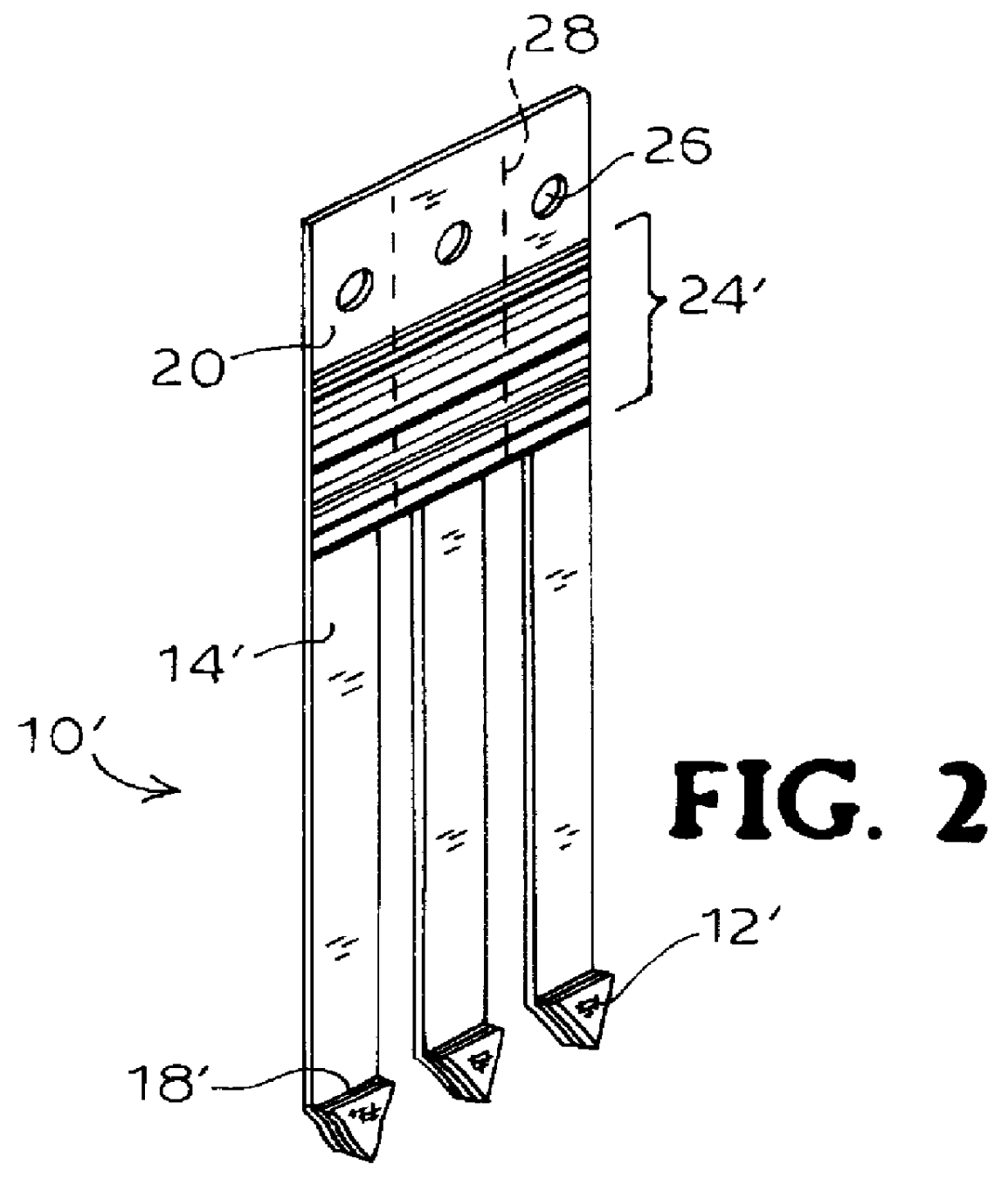
Devices and methods for tracking animals. More particularly, embodiments of the present invention provide a method of tracking an animal that includes assigning an animal identification to a first animal, collecting a biological sample from the first animal and associating the first animal with each premises at which the first animal is located. The invention further provides an identification device that includes a tag portion and a sample portion. The tag portion can be configured to be attached to animal in any method known in the art. The sample portion can be detachably coupled to the tag portion and can include a biological collector that can collect a biological sample from the animal.
Owner:BRANHAVEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com