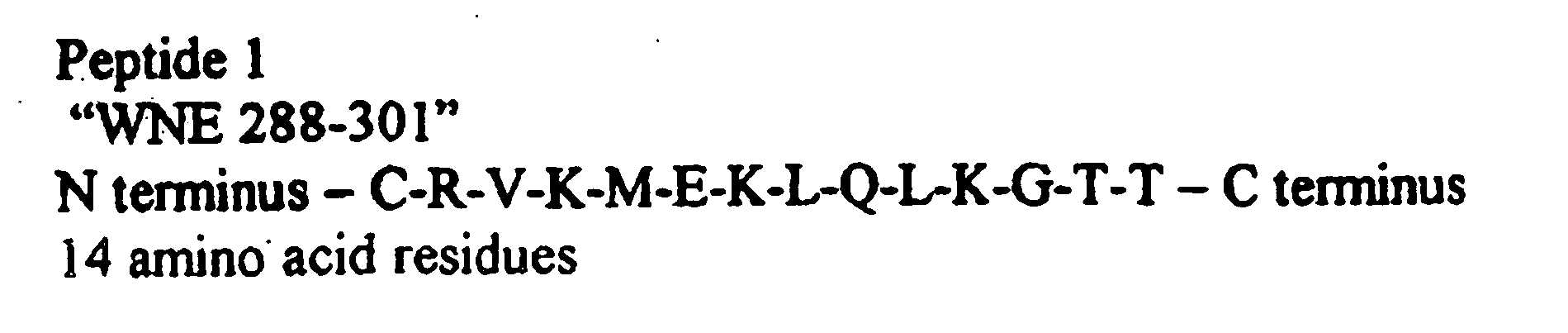Patents
Literature
321 results about "Bio-Specimen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Jump to navigation Jump to search. A biological specimen (also called a biospecimen) is a biological laboratory specimen held by a biorepository for research. Such a specimen would be taken by sampling so as to be representative of any other specimen taken from the source of the specimen.
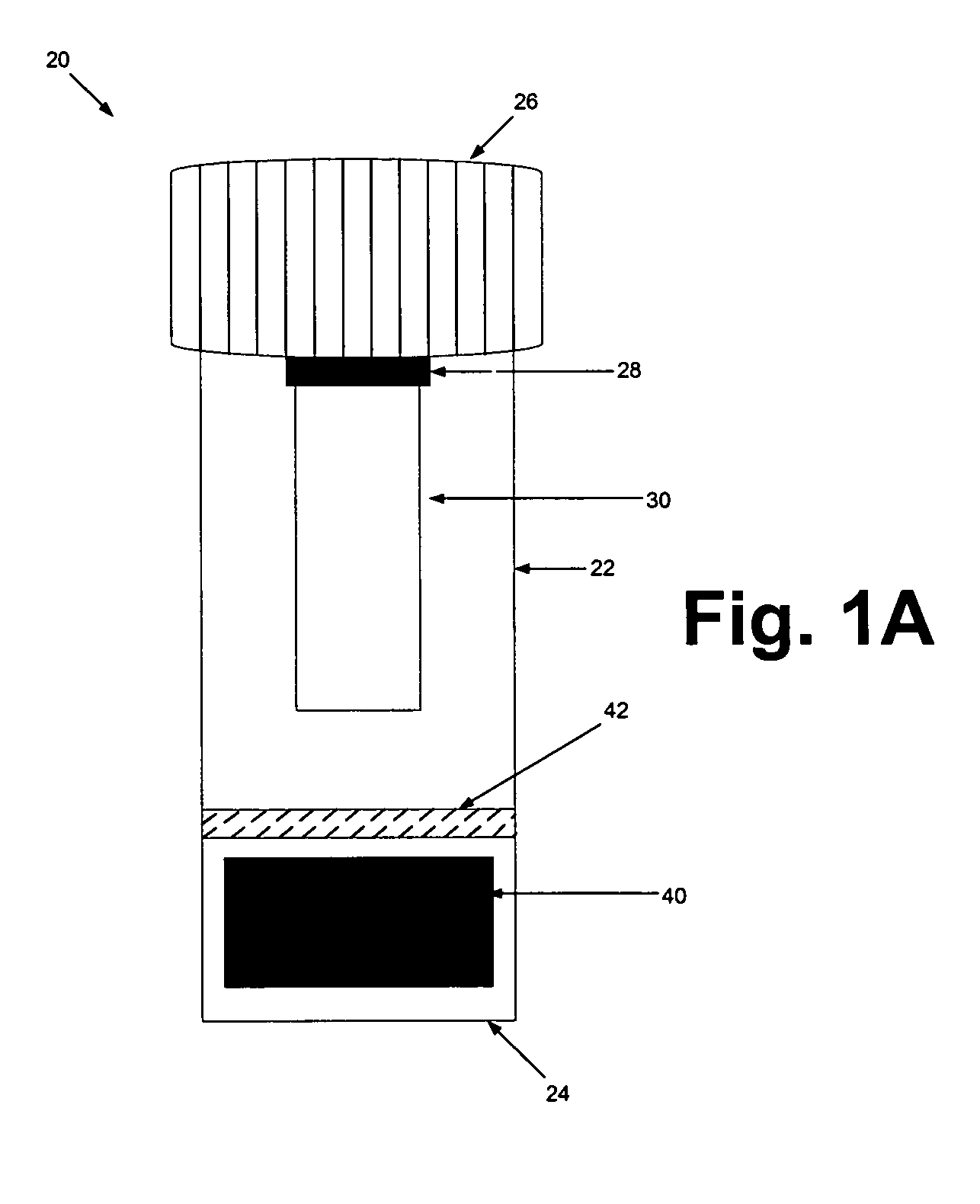
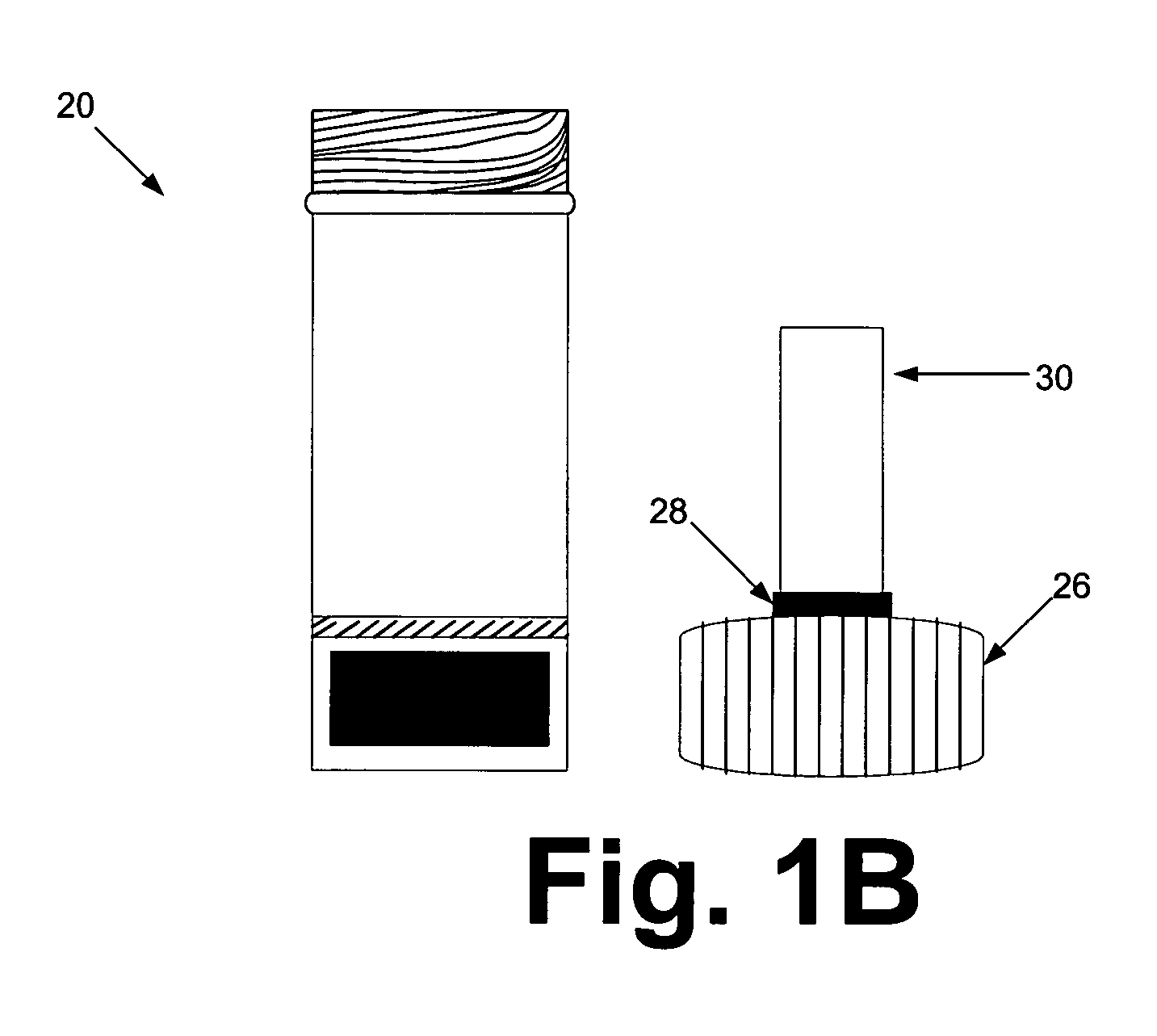
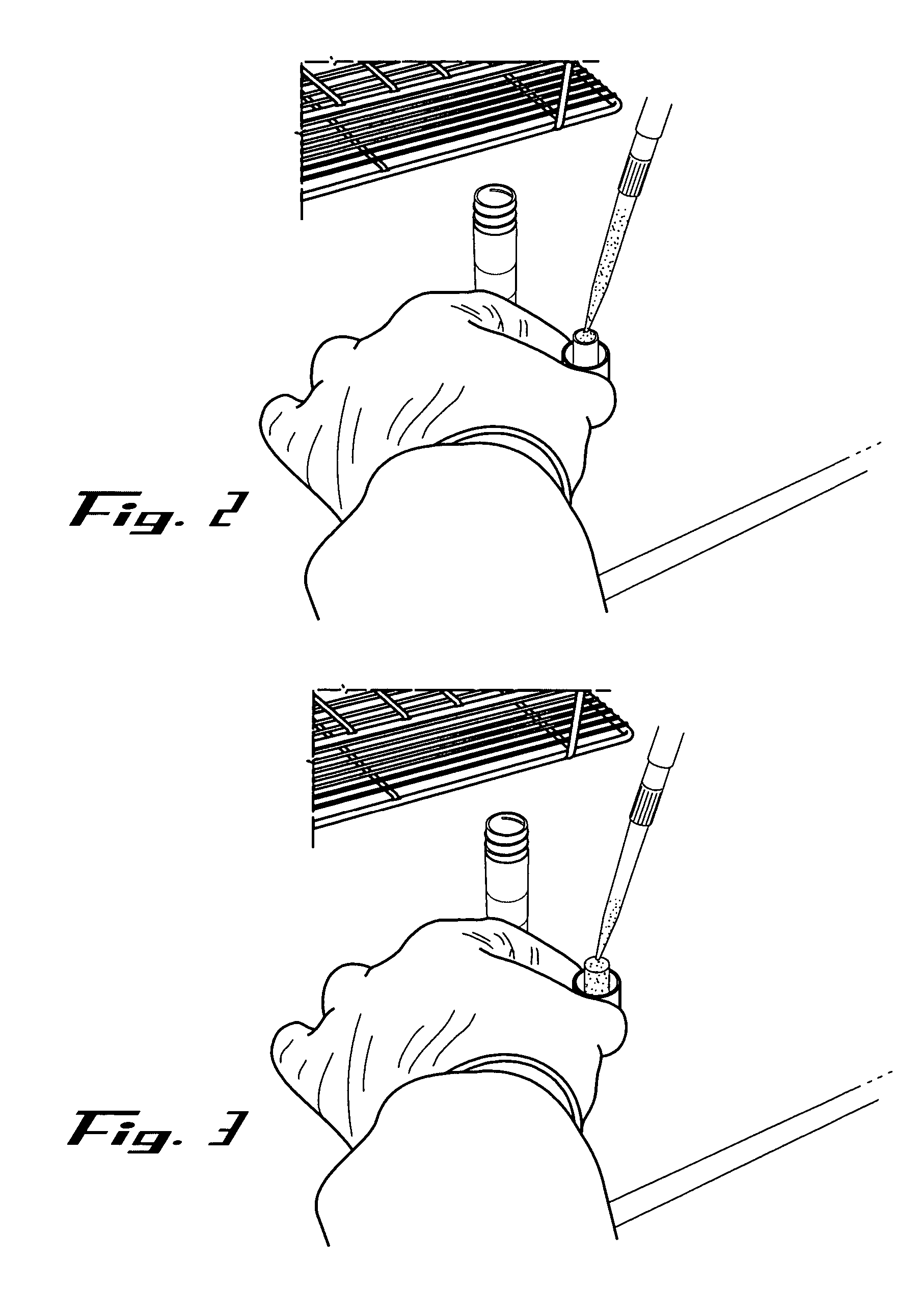
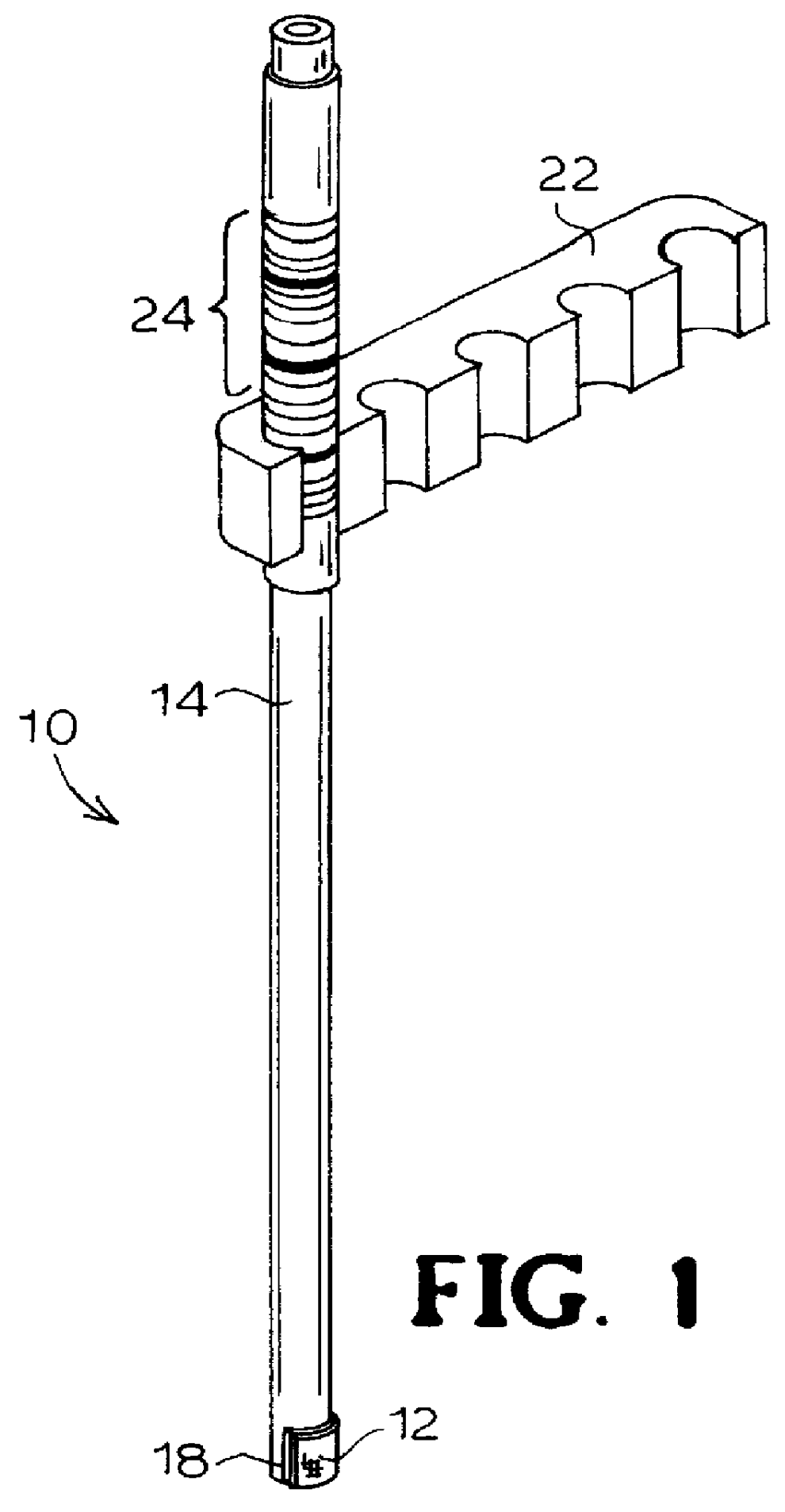
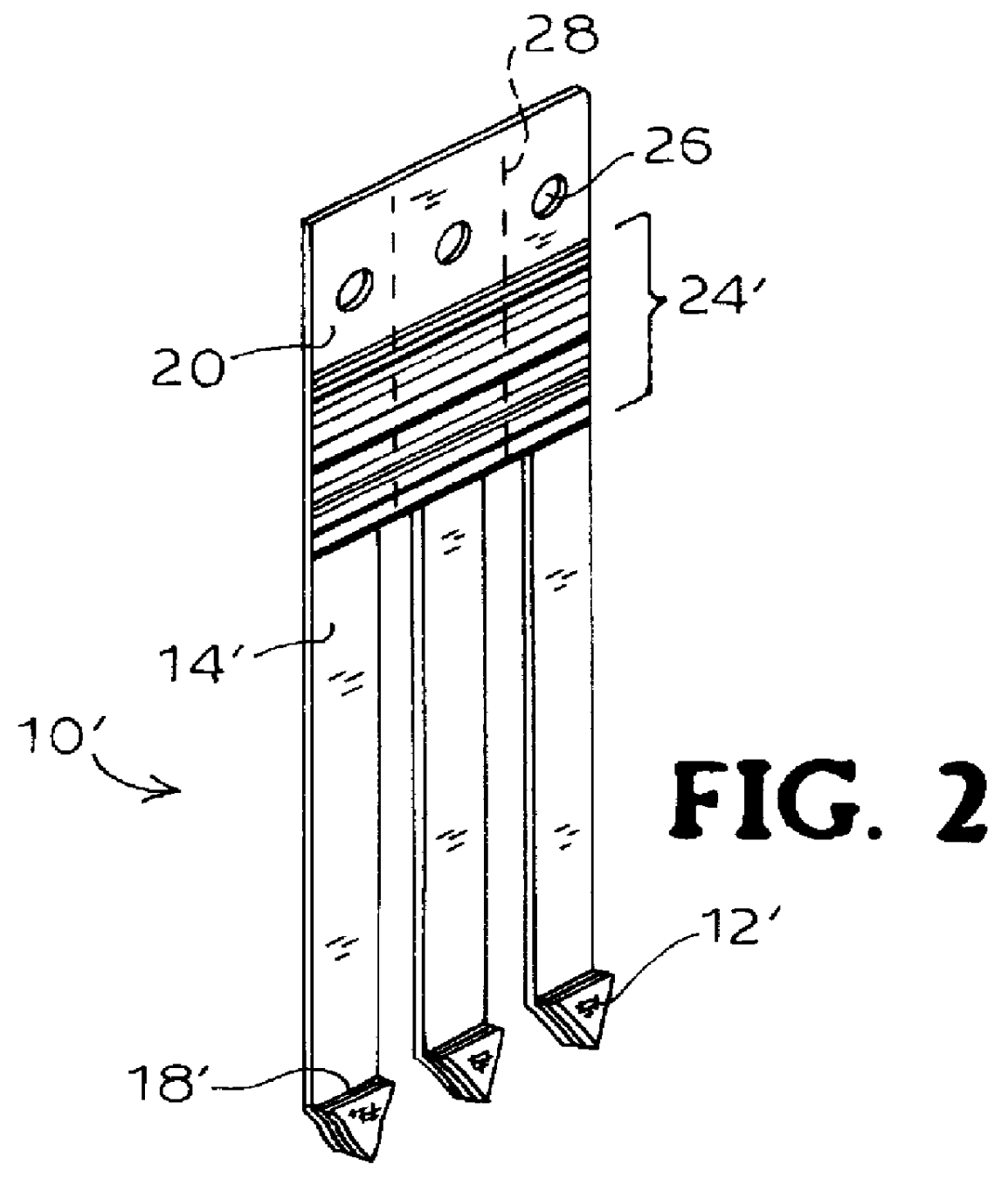
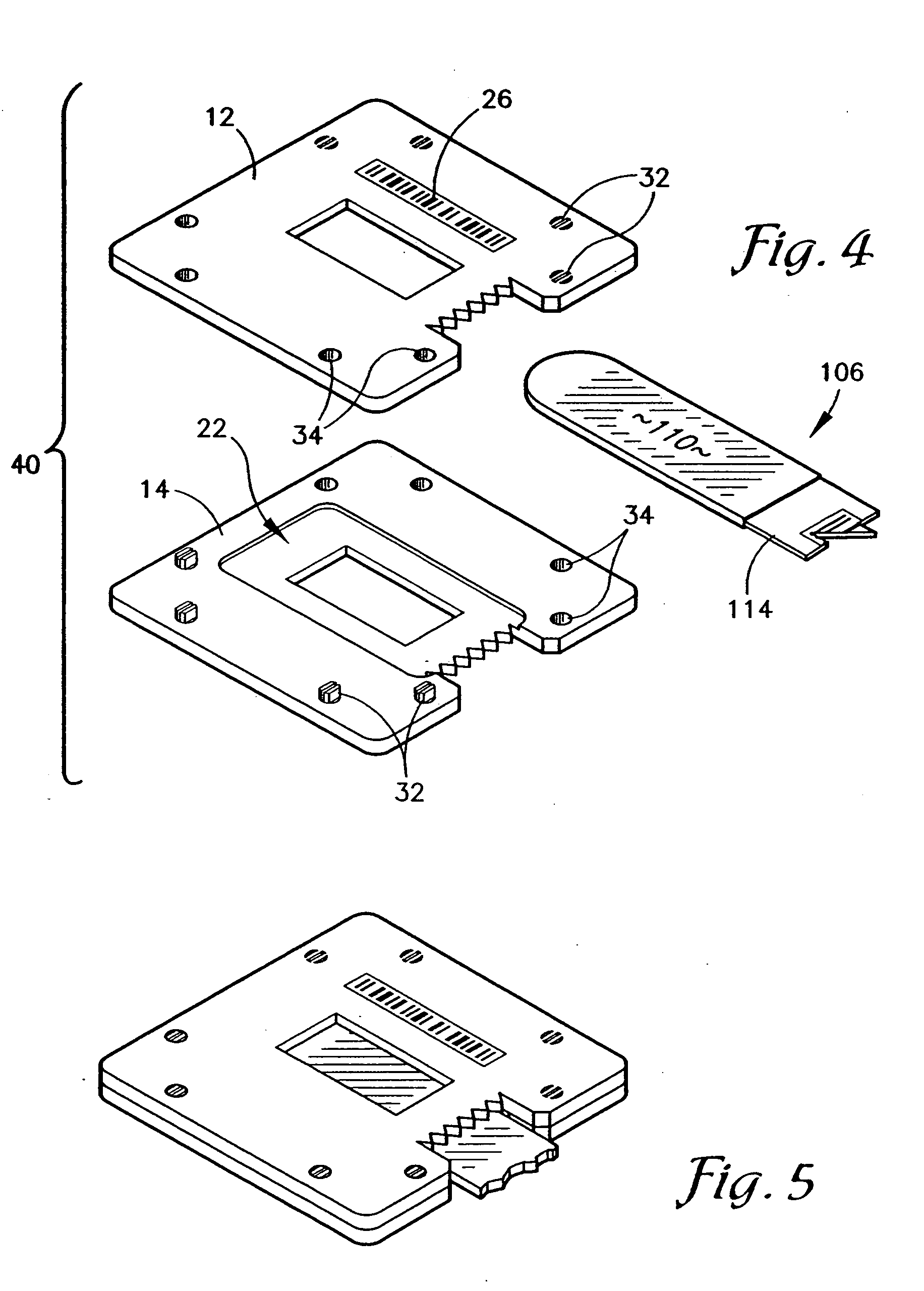
Devices and methods for collection, storage and transportation of biological specimens
InactiveUS20050227269A1Safe and convenient and simple deviceLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides devices and methods for collecting, storing or transporting liquid suspension of biological specimens containing analytes of interest in a dry state. The dried biological specimens containing analytes of interest are reconstituted and released for subsequent analysis by compressing the matrix in the device. Also provided are kits for collecting, storing, transporting and recovering biological specimens containing analytes of interest.
Owner:VIVEBIO
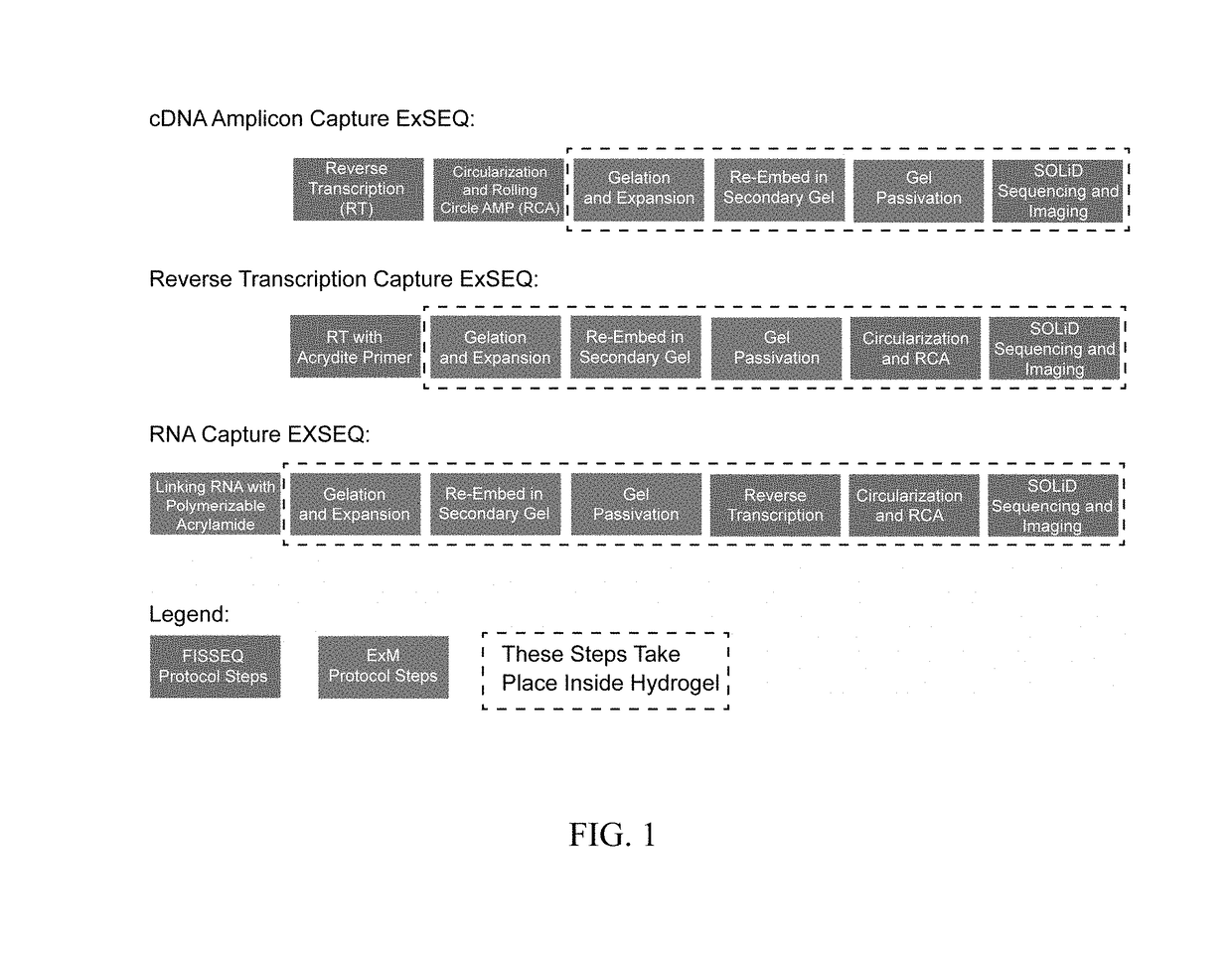
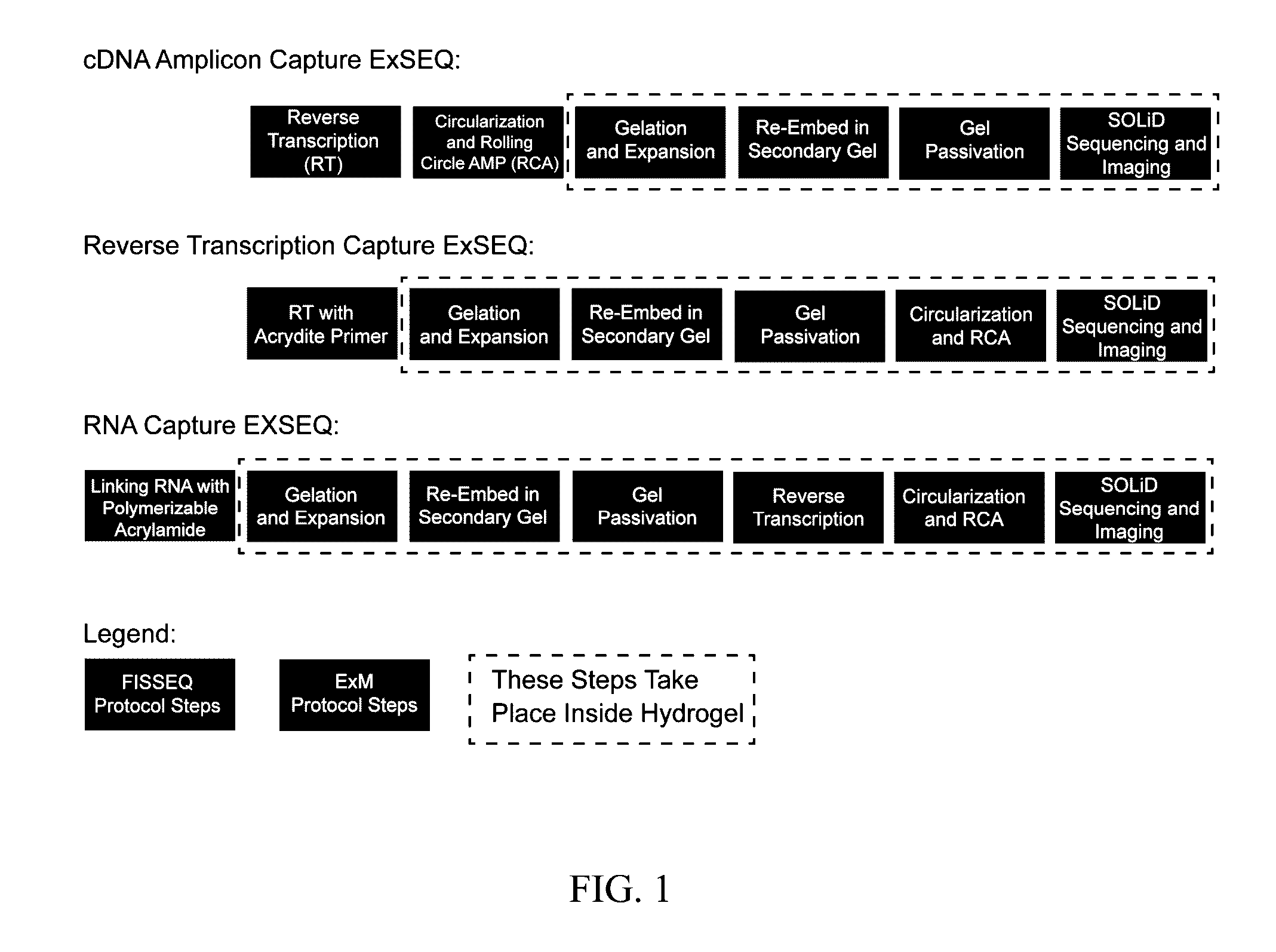
In situ nucleic acid sequencing of expanded biological samples
ActiveUS10059990B2Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory apparatusFluorescent in situ sequencingNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides in situ nucleic acid sequencing to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ sequencing of nucleic acids as well as new methods for fluorescent in situ sequencing (FISSEQ) in a new process referred to herein as “expansion sequencing” (ExSEQ).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
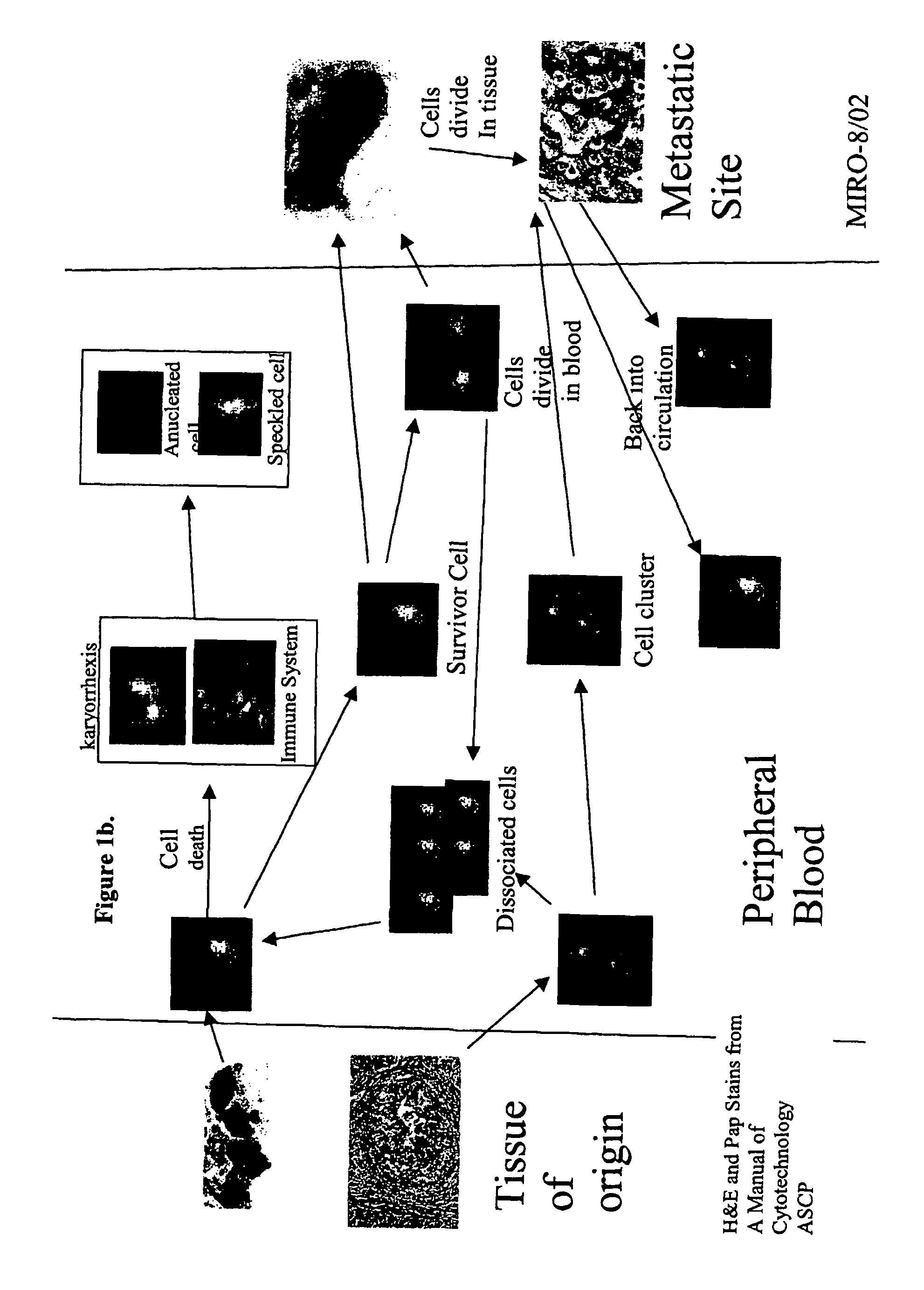
Analysis of circulating tumor cells, fragments, and debris
InactiveUS7863012B2Inhibit further damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseFluorescence
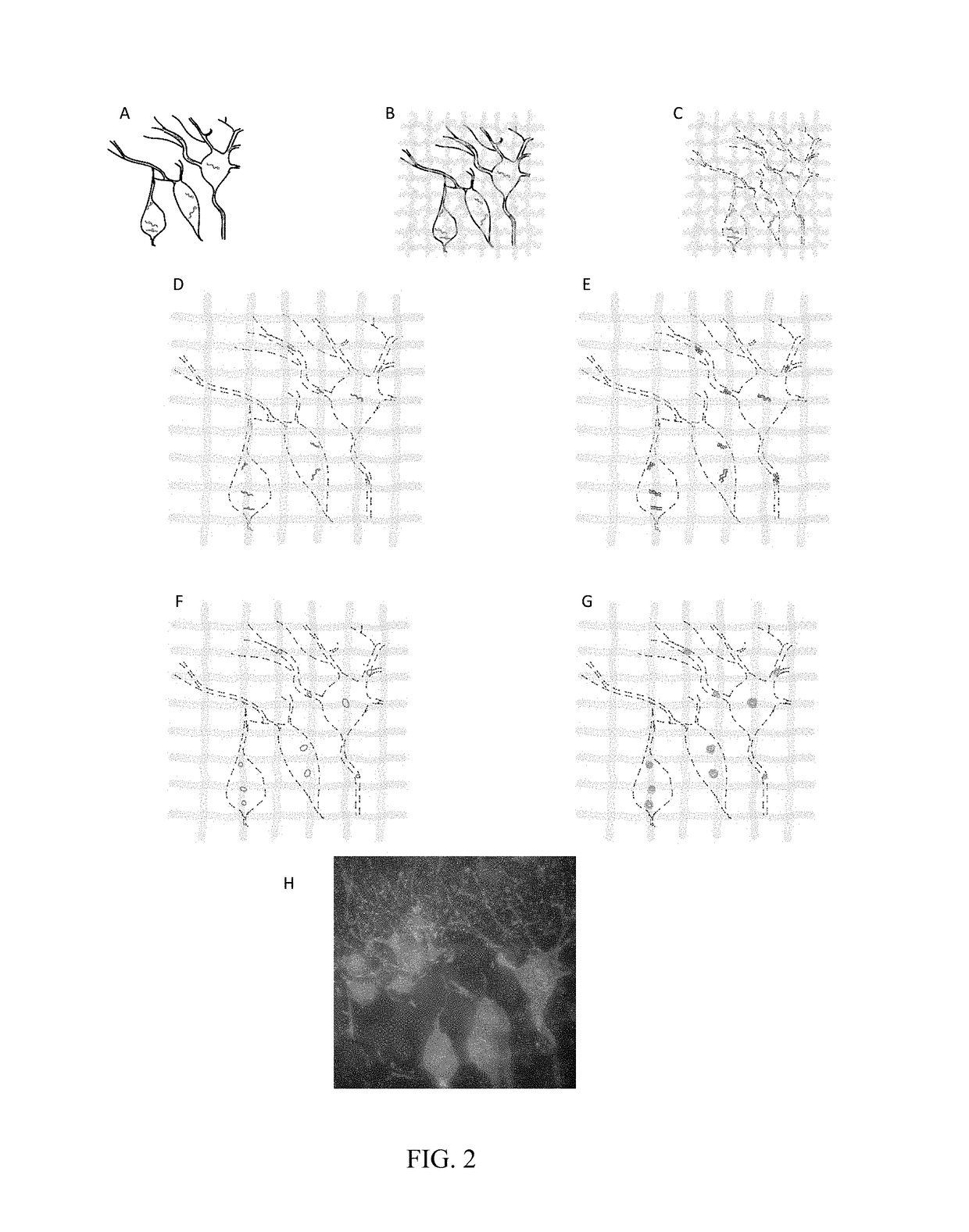
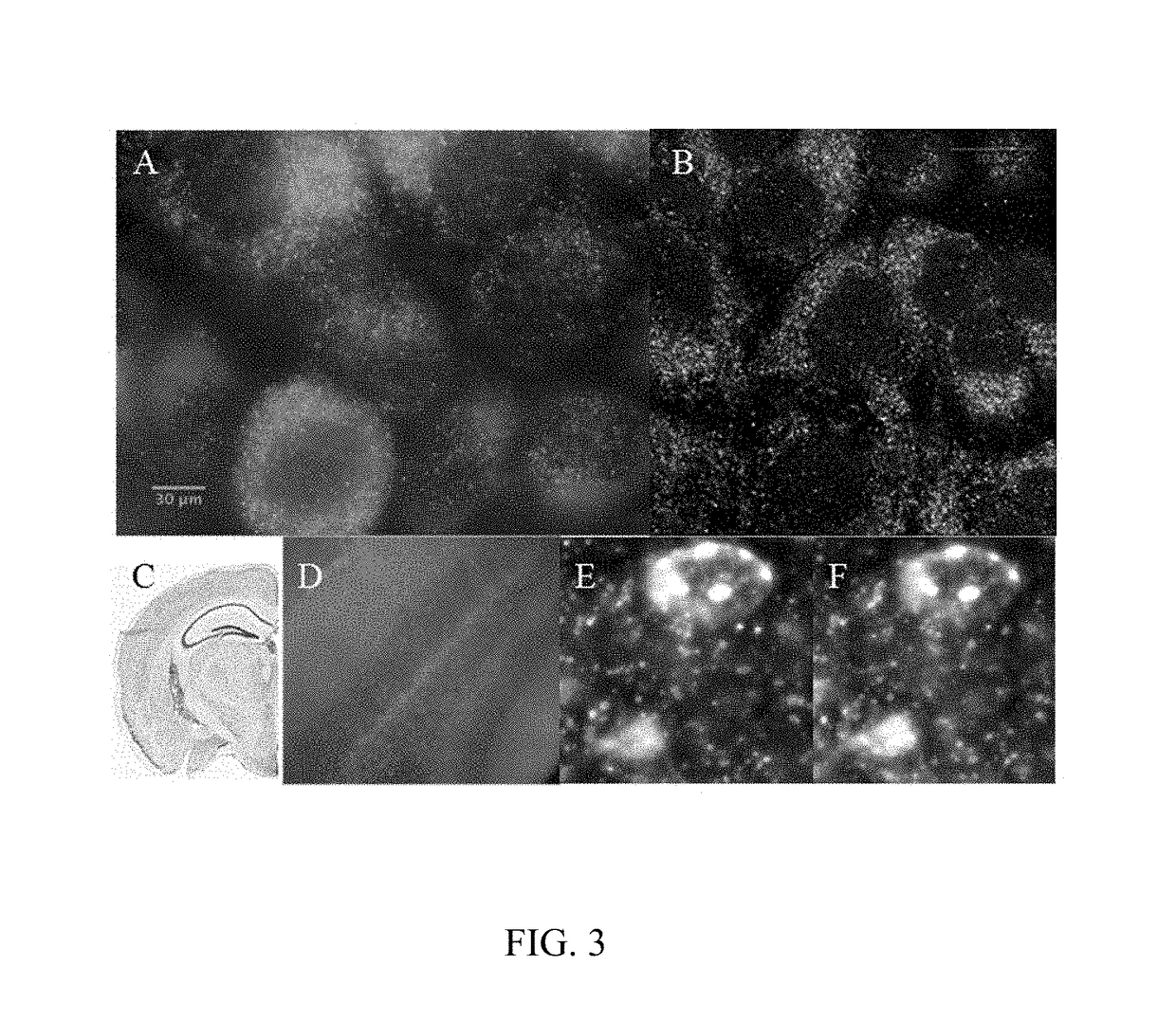
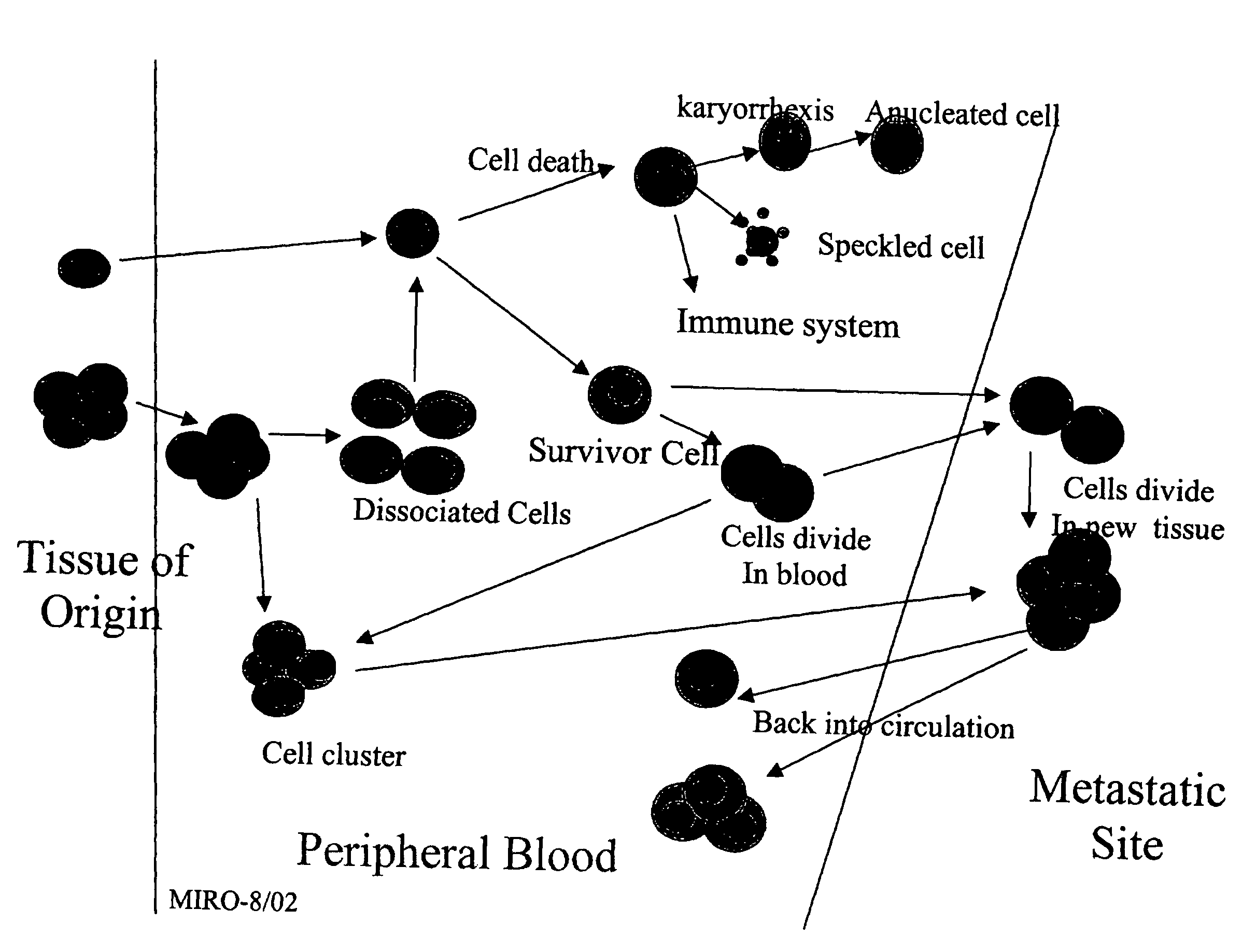
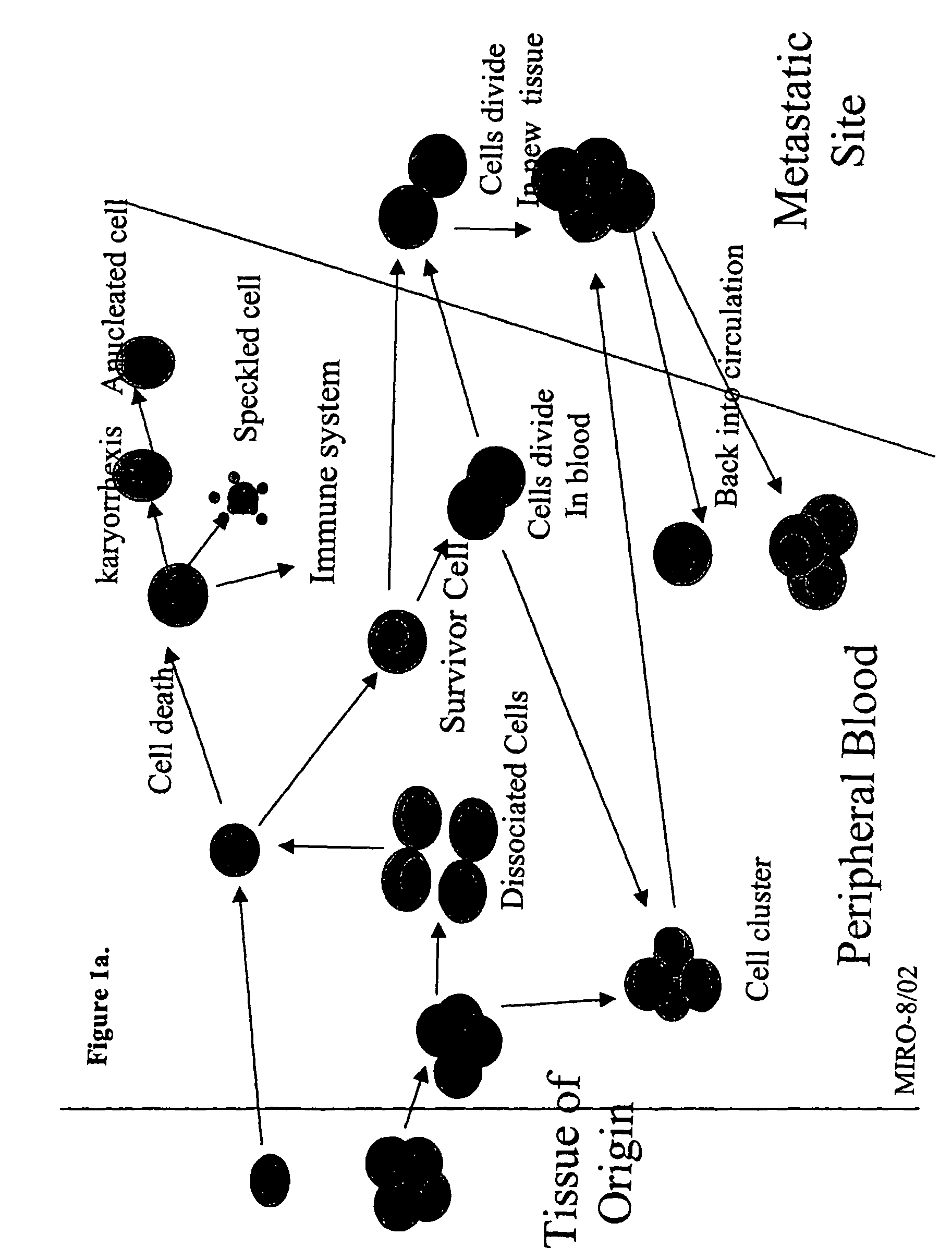
The methods and reagents described in this invention are used to analyze circulating tumor cells, clusters, fragments, and debris. Analysis is performed with a number of platforms, including flow cytometry and the CellSpotter® fluorescent microscopy imaging system. Analyzing damaged cells has shown to be important. However, there are two sources of damage: in vivo and in vitro. Damage in vivo occurs by apoptosis, necrosis, or immune response. Damage in vitro occurs during sample acquisition, handling, transport, processing, or analysis. It is therefore desirable to confine, reduce, eliminate, or at least qualify in vitro damage to prevent it from interfering in analysis. Described herein are methods to diagnose, monitor, and screen disease based on circulating rare cells, including malignancy as determined by CTC, clusters, fragments, and debris. Also provided are kits for assaying biological specimens using these methods.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
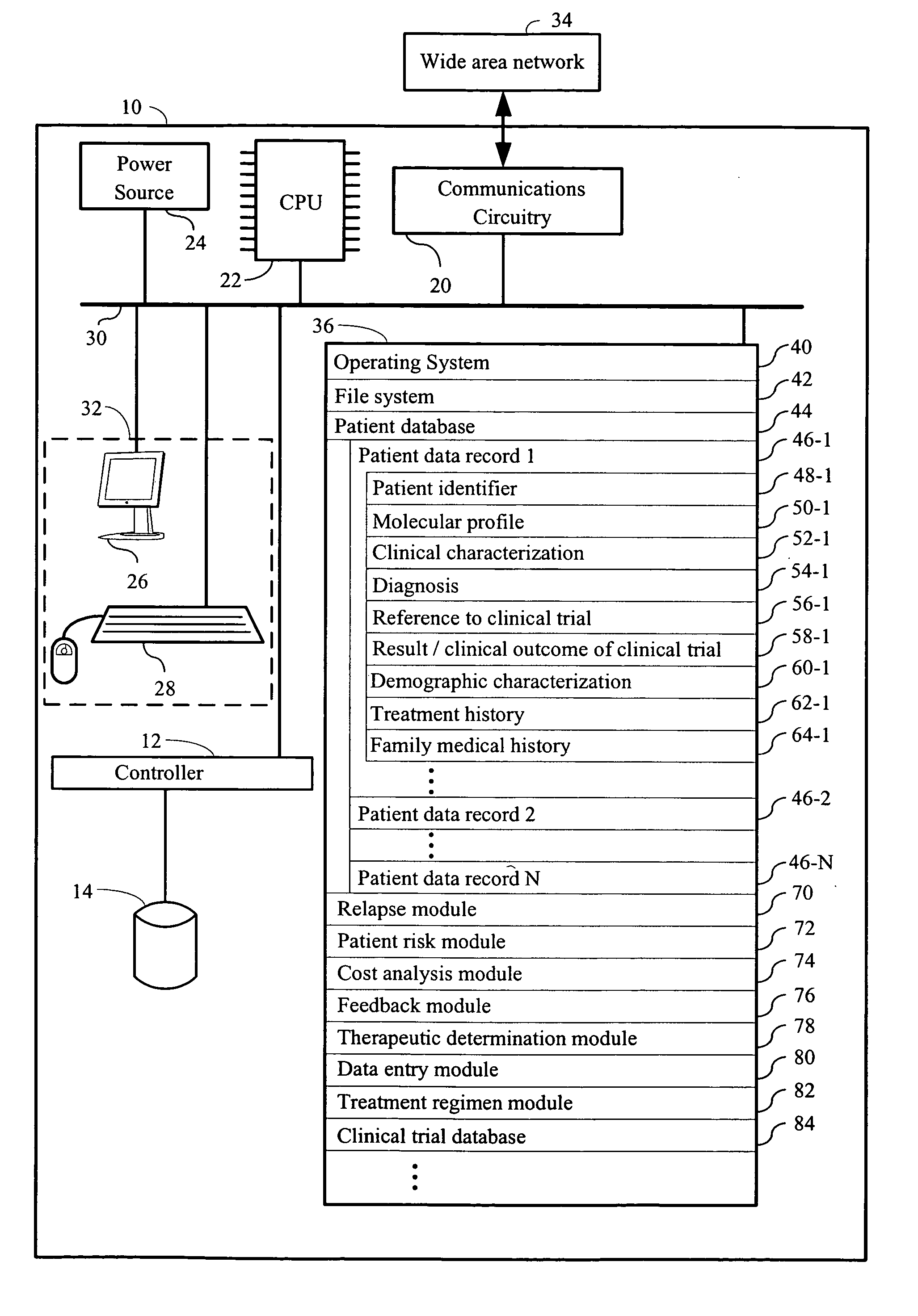
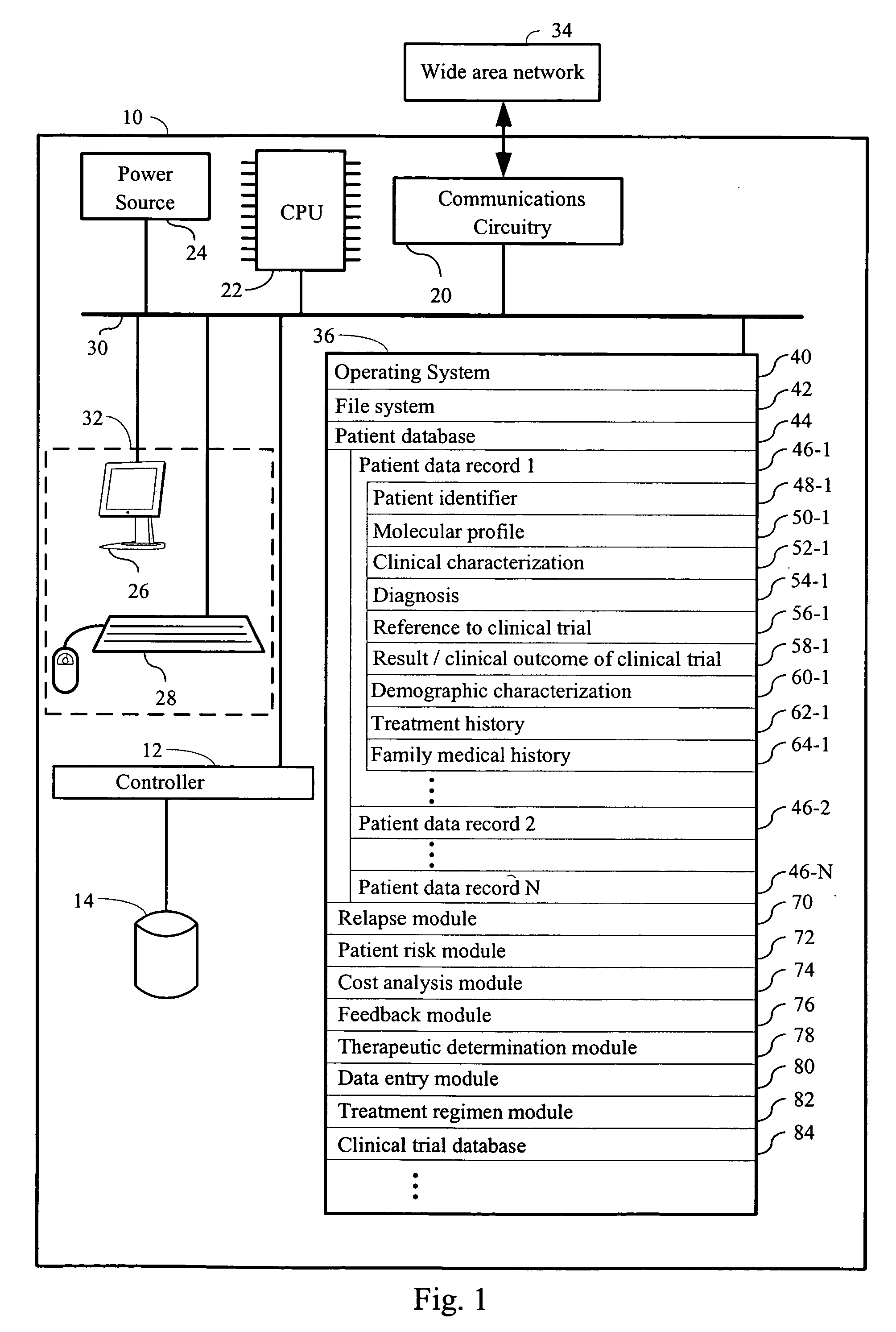
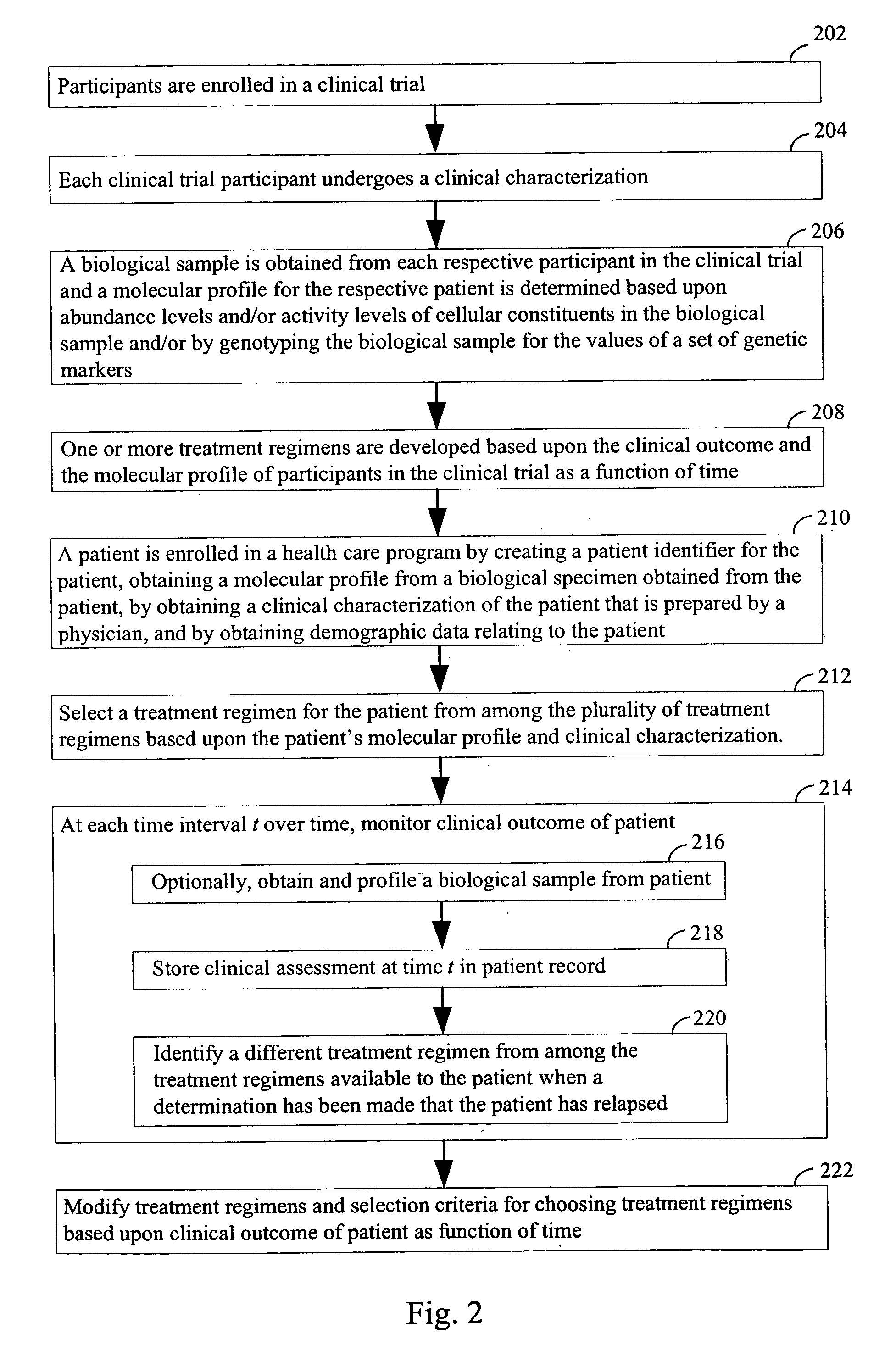
Computer systems and methods for providing health care
The invention provides a computer network comprising a first computer and one or more second computers that are in electronic communication with each other. The first computer is associated with a first health care facility and has instructions for retrieving, over a network, one or more data structures for a patient enrolled in a health care program. The one or more data structures for the patient collectively comprise (i) a patient identifier, (ii) a molecular profile from a biological specimen obtained from the patient at the first health care facility; and (iii) a clinical characterization of the patient that was made at the first health care facility. The first computer has instructions for retrieving, over the network connection, one or a plurality of treatment regimens that are deemed suitable for the patient based upon the molecular profile and the clinical characterization of the patient. The one or more second computers are at one or more locations other than the first health care facility and have one or more data structures for each patient in a plurality of patients enrolled in the health care program
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
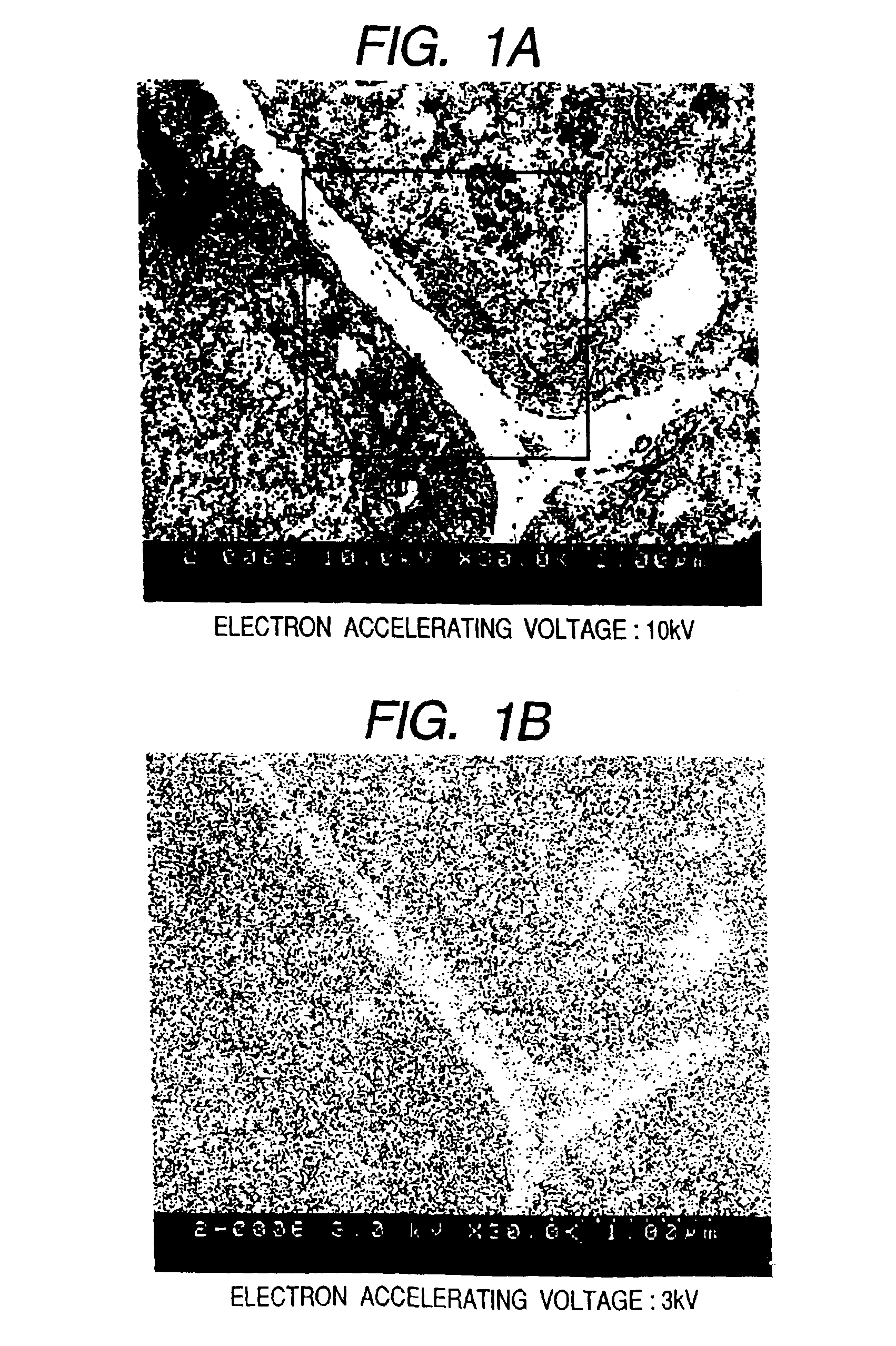
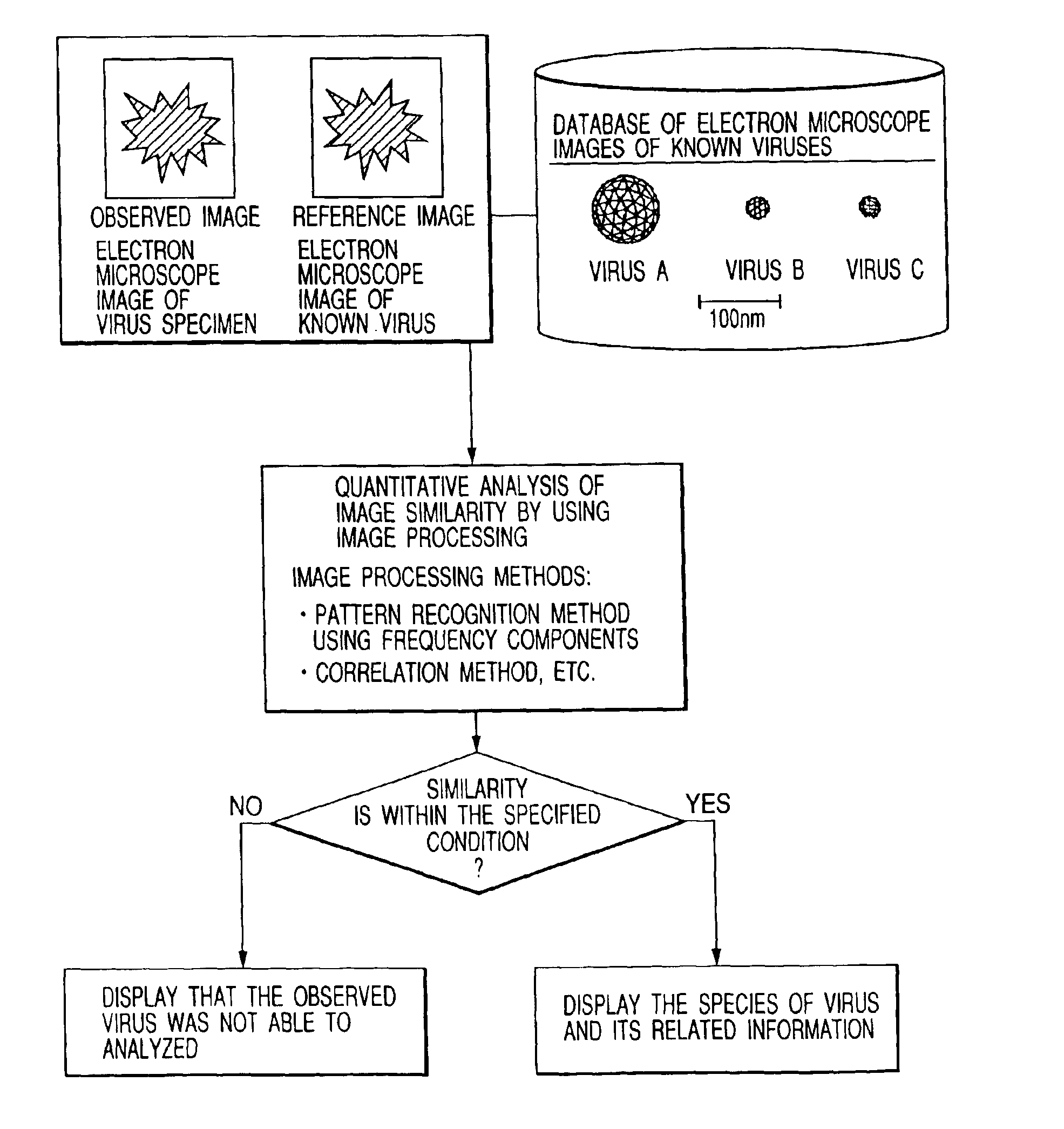
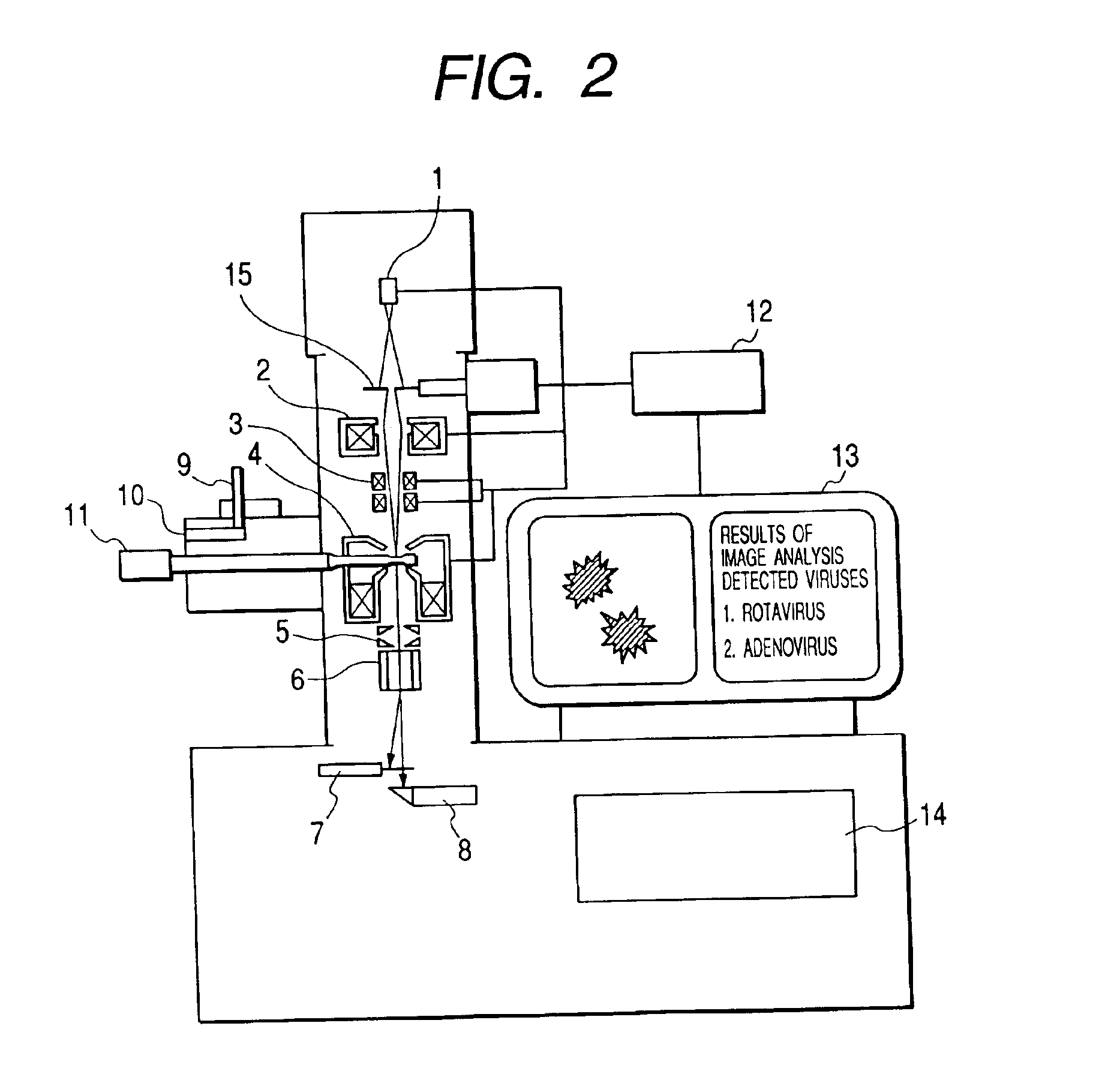
Bio electron microscope and observation method of specimen
InactiveUS6875984B2Reduce harmHigh-accuracy image analysisEnergy spectrometersPreparing sample for investigationScanning electron microscopeAcceleration voltage
A bio electron microscope and an observation method which can observe a bio specimen by low damage and high contrast to perform high-accuracy image analysis, and conduct high-throughput specimen preparation. 1) A specimen is observed at an accelerating voltage 1.2 to 4.2 times a critical electron accelerating voltage possible to transmit a specimen obtained under predetermined conditions. 2) An electron energy filter of small and simplified construction is provided between the specimen and an electron detector for imaging by the electron beam in a specified energy region of the electron beams transmitting the specimen. 3) Similarity between an observed image such as virus or protein in the specimen and a reference image such as known virus or protein is subjected to quantitative analysis by image processing. 4) A preparation protocol of the bio specimen is made into a chip using an MEMS technique, which is then mounted on a specimen stage part of an electron microscope to conduct specimen introduction, preparation and transfer onto a specimen holder.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
Nanoscale Imaging of Proteins and Nucleic Acids via Expansion Microscopy
ActiveUS20170067096A1Use diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationNew Approach to AppraisalBio-Specimen
The invention enables in situ genomic and transcriptomic assessment of nucleic acids to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ genomic and transcriptomic assessment of nucleic in a new process referred to herein as “expansion fluorescent in situ hybridization” (ExFISH).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
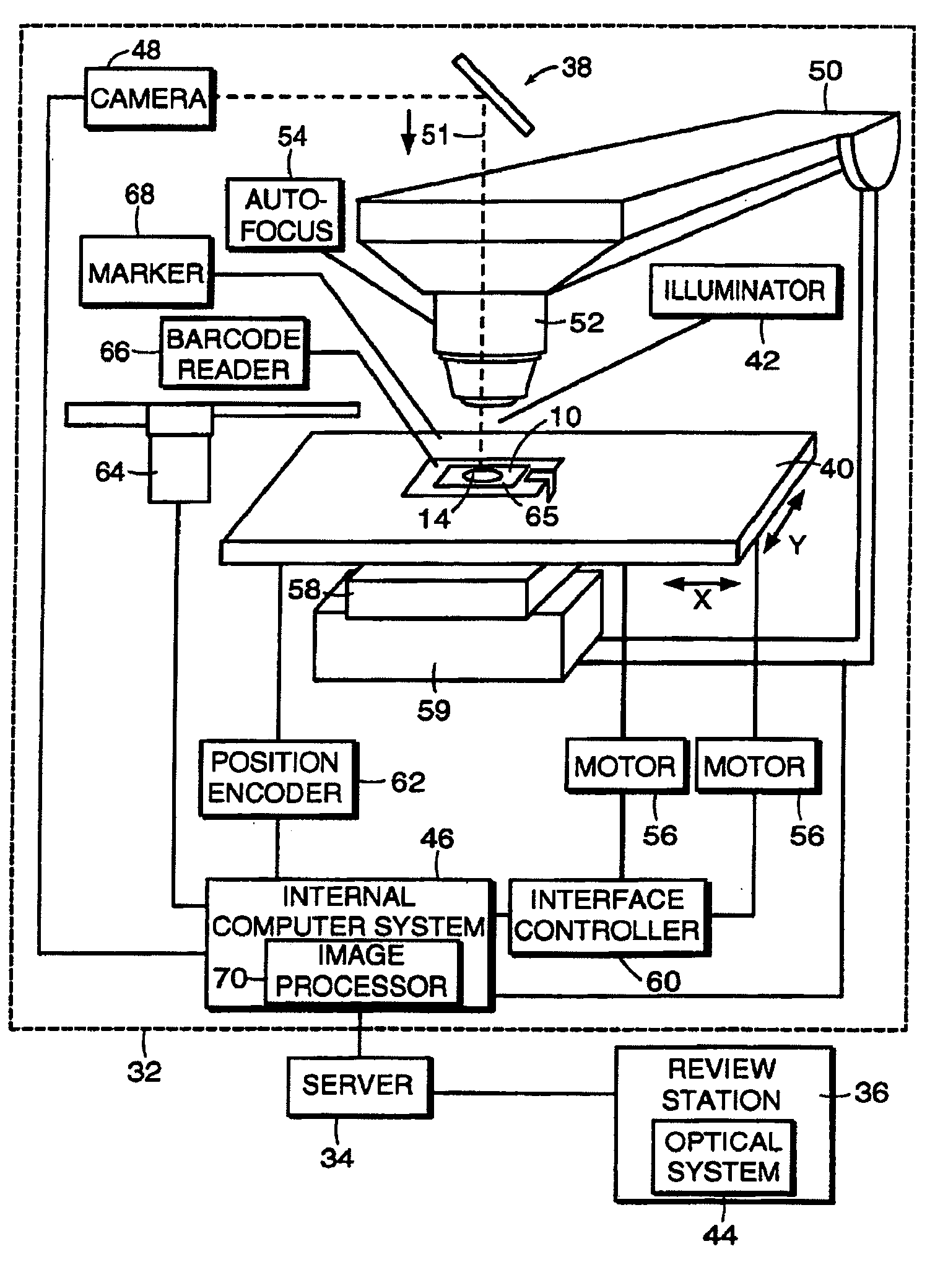
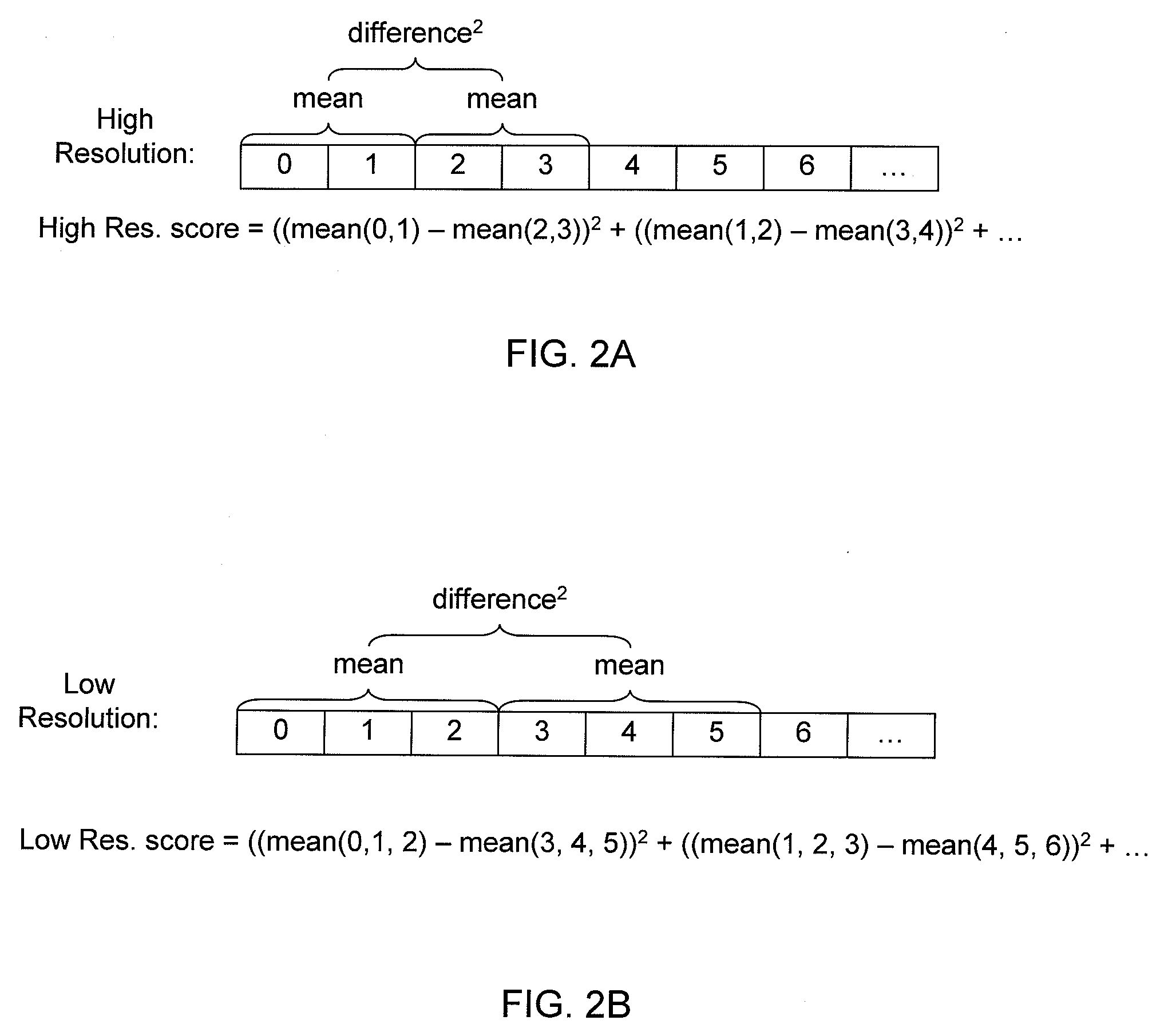
Method for assessing image focus quality
A method for determining the quality of focus of a digital image of a biological specimen includes obtaining a digital image of a specimen using a specimen imaging apparatus. A measure of image texture is calculated at two different scales, and the measurements are compared to determine how much high-resolution data the image contains compared to low-resolution data. The texture measurement may, for example, be a Brenner auto-focus score calculated from the means of adjacent pairs of pixels for the high-resolution measurement and from the means of adjacent triples of pixels for the low-resolution measurement. A score indicative of the quality of focus is then established based on a function of the low-resolution and high-resolution measurements. This score may be used by an automated imaging device to verify that image quality is acceptable. The device may adjust the focus and acquire new images to replace any that are deemed unacceptable.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Propagation of primary cells
InactiveUS20080305473A1Minimizing backgroundSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary cellBio-Specimen
The present invention provides a method of propagating cells of interest obtained from a biological specimen by enriching the cells under conditions that maintain sufficient cell viability; and propagating the cells under conditions effective to allow cell viability, proliferation and integrity.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
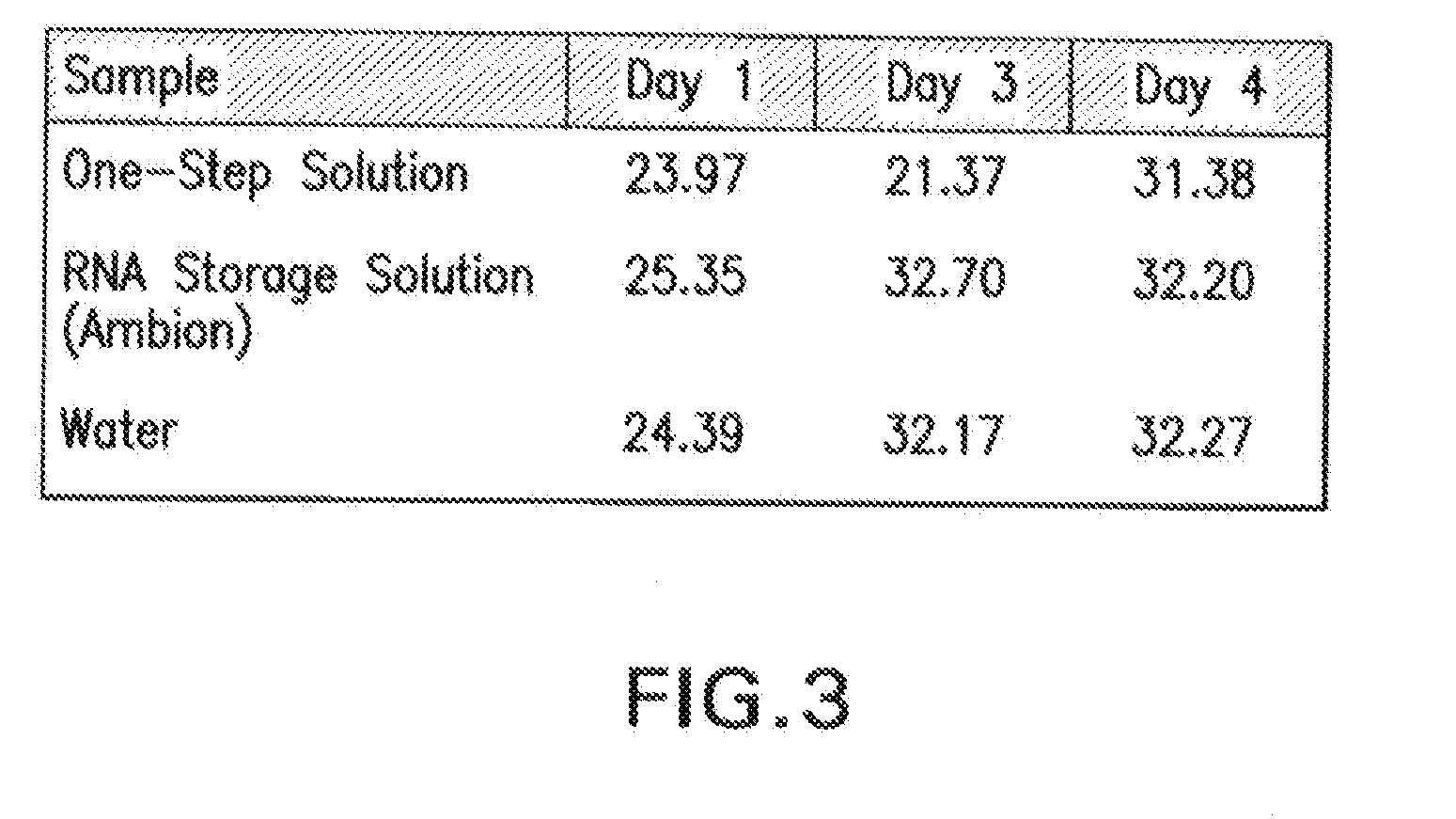
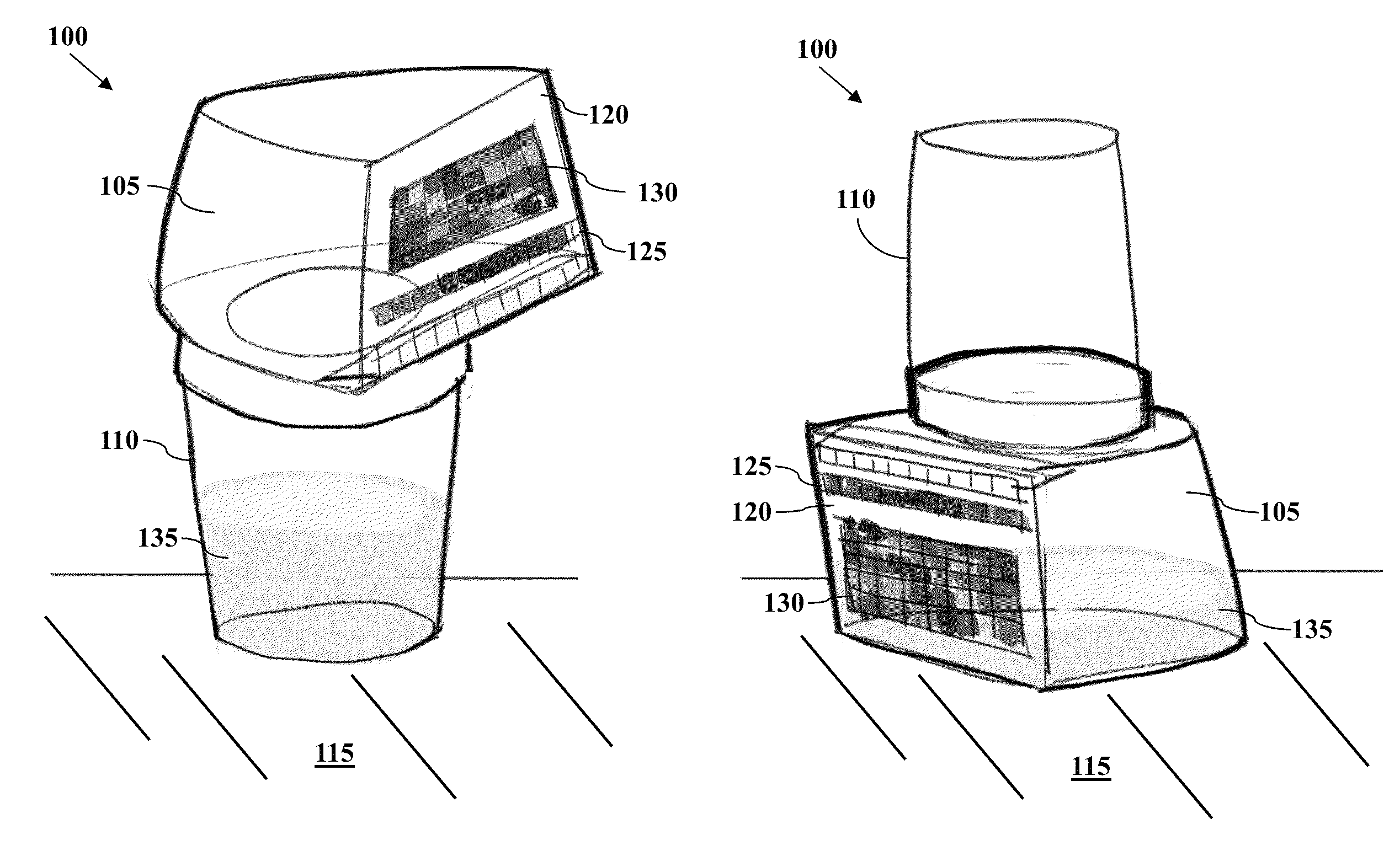
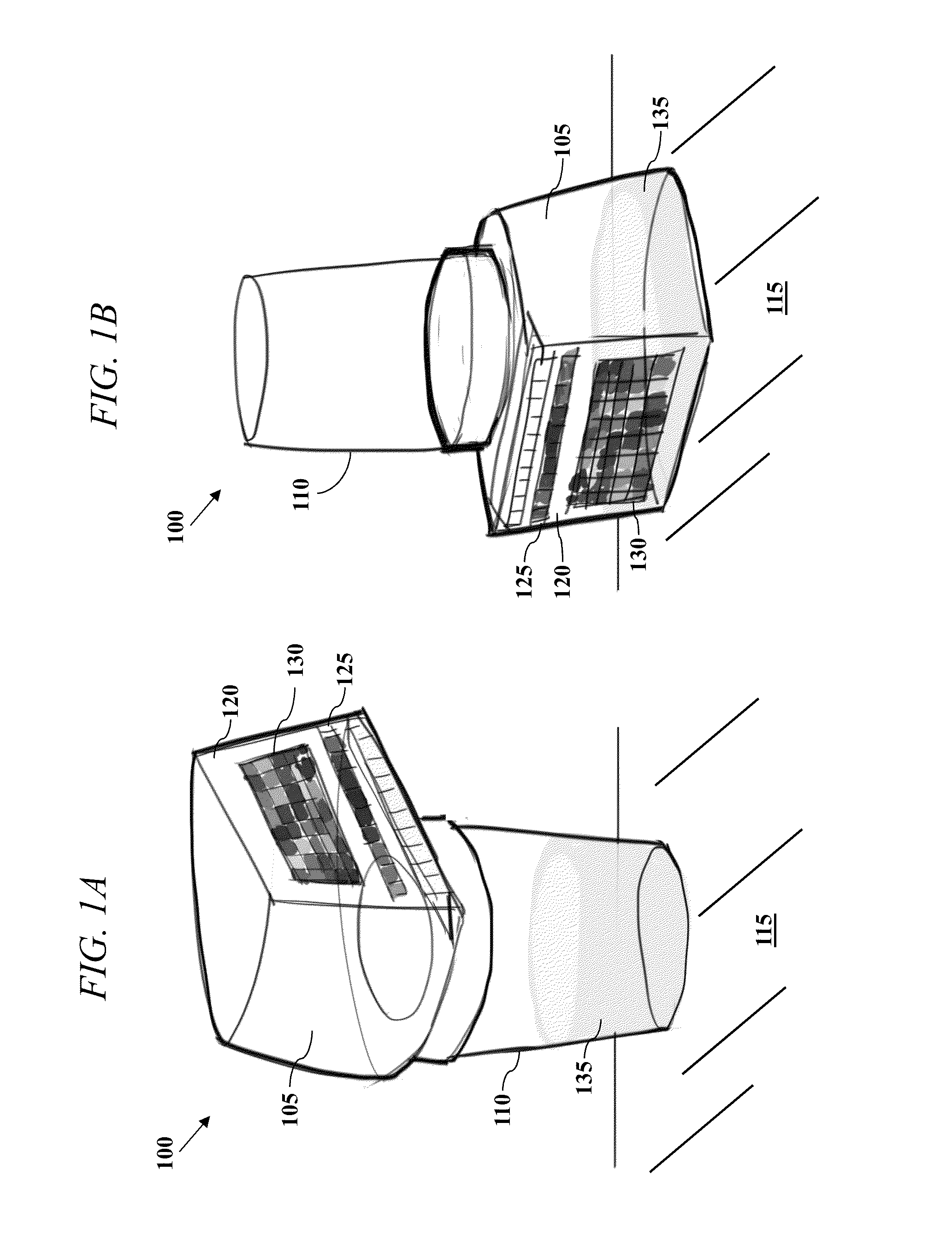
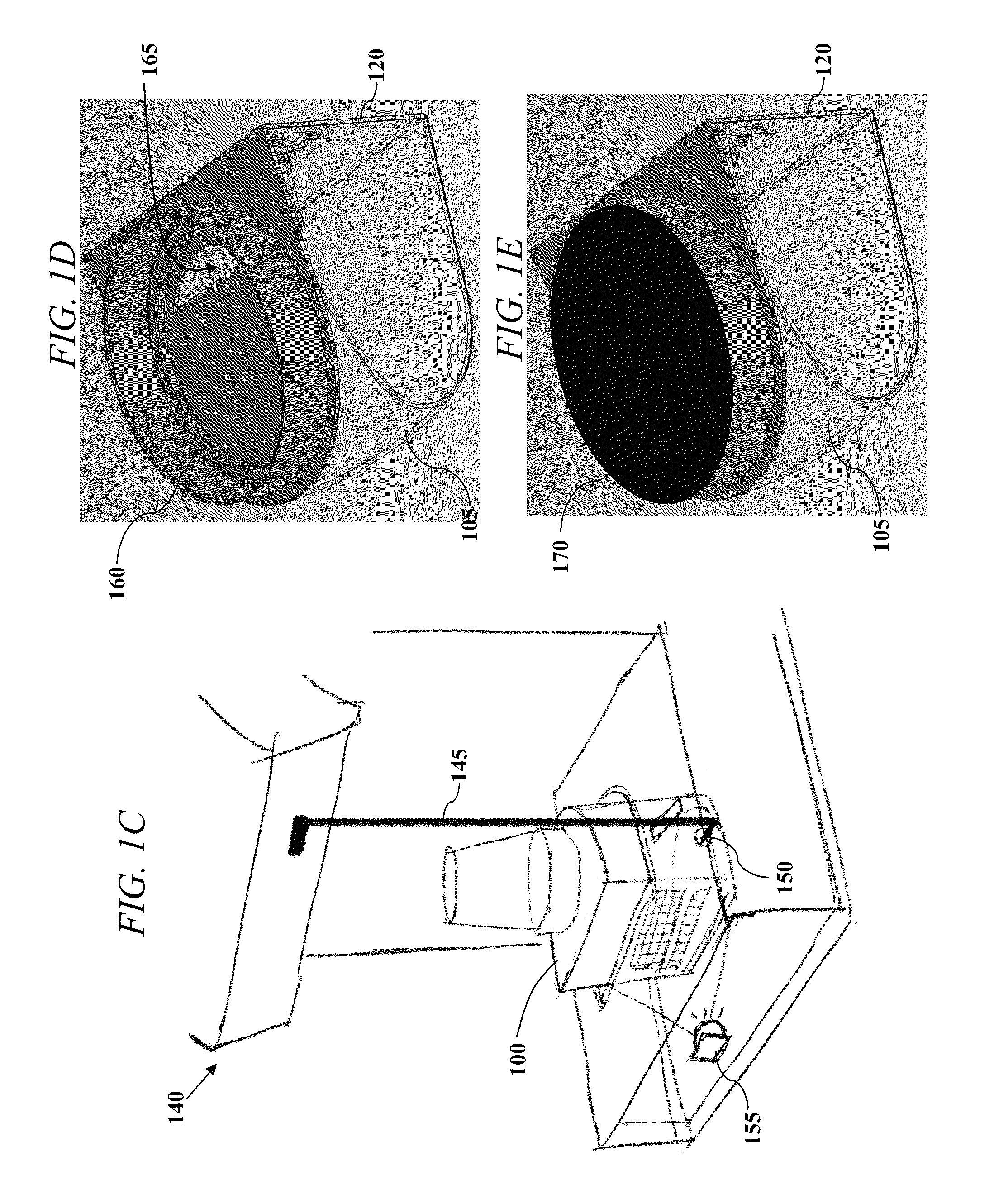
All-In-One Specimen Cup With Optically Readable Results
A biological material test strip and adjacently-located reference color chart are affixed to a lid portion of an all-in-one specimen cup to perform color-based reaction testing of collected biological specimens in an uncalibrated environment. After specimen collection, the lid portion is secured to a container portion of the specimen cup. The cup may then be rotated into an upside down position causing the specimen, under the force of gravity, to pass from the container portion and into a volume of the lid portion, such that the test strip is exposed to the specimen as it is received into the volume of the lid portion. An image of the exposed test strip and adjacently-located reference color chart may then be captured and processed to identify any color matches between the individual test pads on the test strip and the corresponding sequences of reference color blocks on the reference chart.
Owner:SCANWELL HEALTH INC
Easily retrieved biological specimen pouch
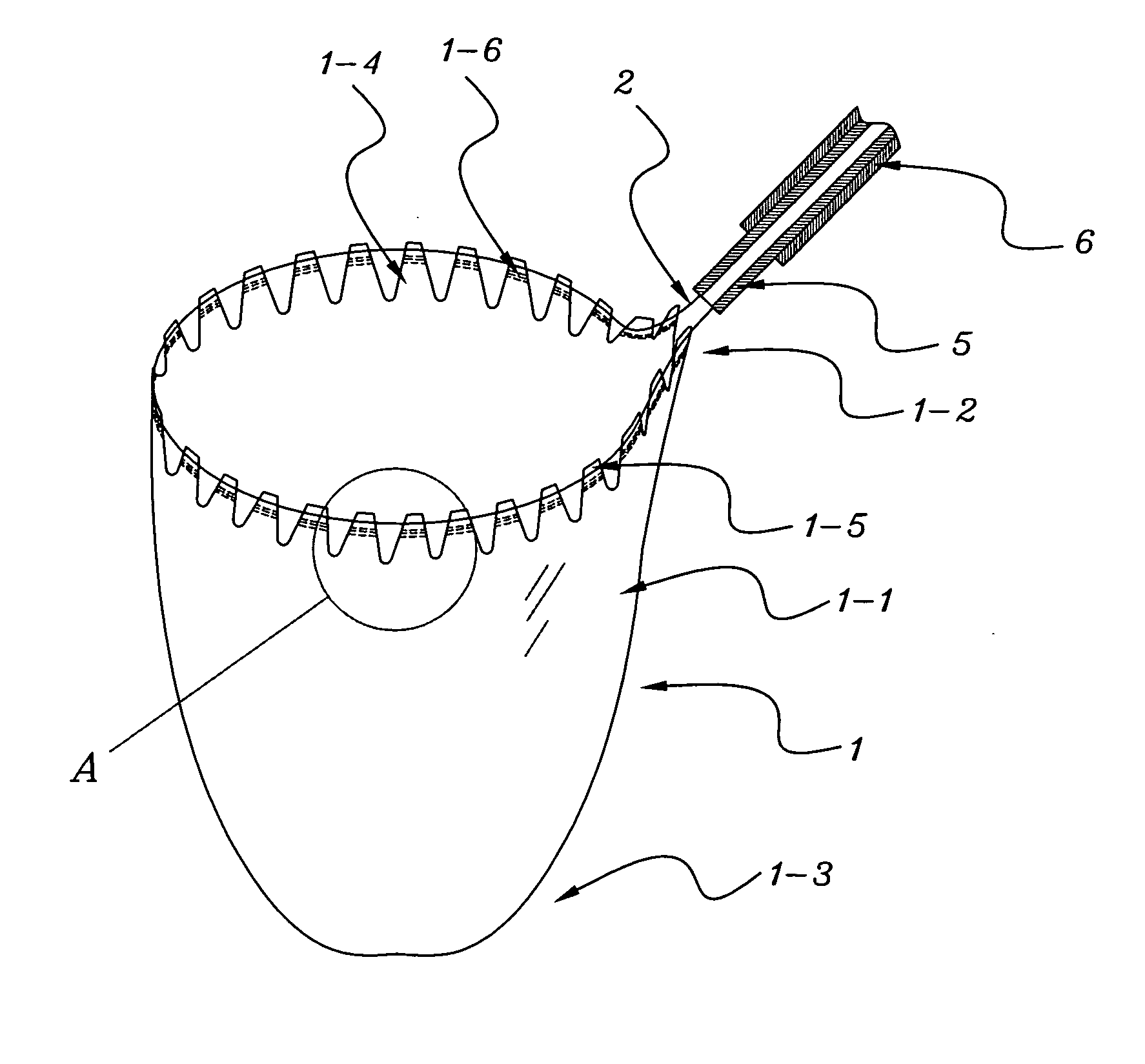
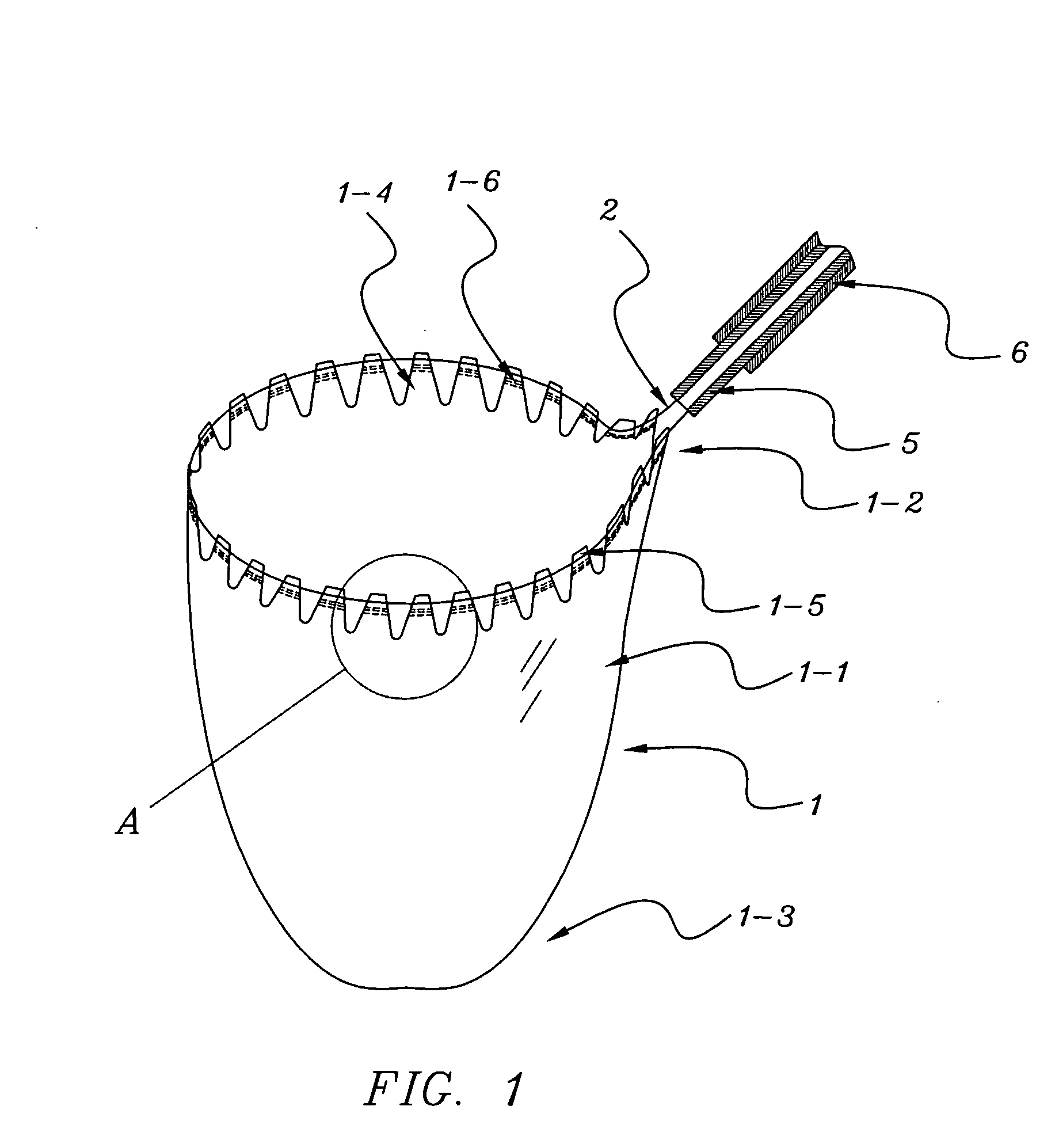
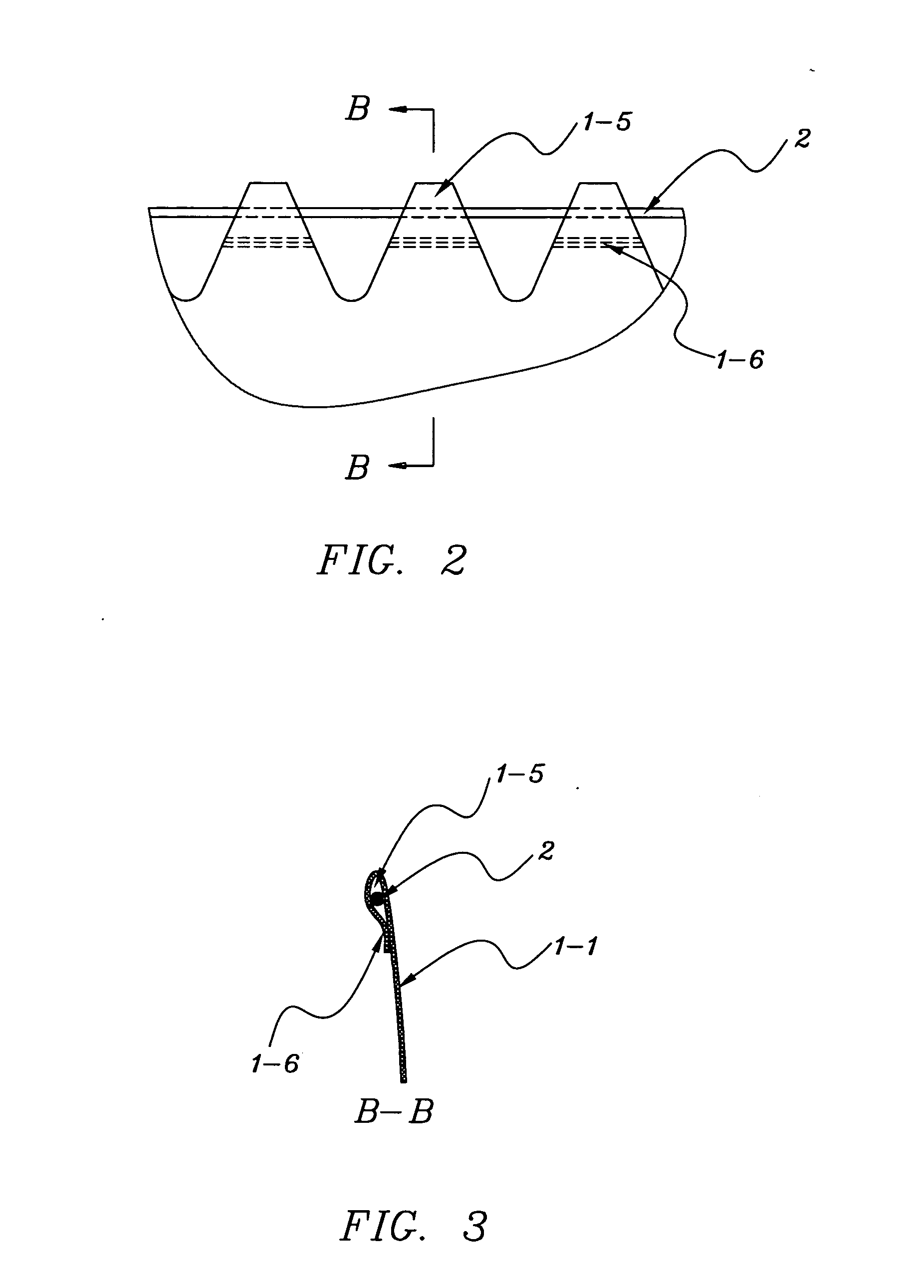
InactiveUS20070073251A1Reduce volumeEasy to closeSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBio-SpecimenSerration
The invention relates to an easily retrieved biological specimen pouch. The said easily retrieved biological specimen pouch of the invention comprises a flexible wall, an open end and a closed end, and the specimen pouch can receive a biological specimen; A) The flexible wall of the open end of the specimen pouch has discontinuous serration; B) On the said serration, there are slots through which an open and retrieval string or an open spring or a retrieval noose can pass. As the open end of the specimen pouch is provided with a flexible wall of discontinuous serration, and the open and retrieval string or the retrieval noose passes through the slots on the discontinuous serration of the flexible wall of the open end of the specimen pouch, when the open and retrieval string is pulled towards an outer sheath to retrieve the specimen pouch of the invention, the bulk of contracted open end is reduced due to the discontinuous serration of the flexible wall of the open end. It is easy to close the open end of the specimen pouch, and convenient to retrieve the specimen pouch into the outer sheath or extract it through a small incision. The specimen pouch of the invention is simple, convenient, safe and efficient.
Owner:ZHOU XING +2
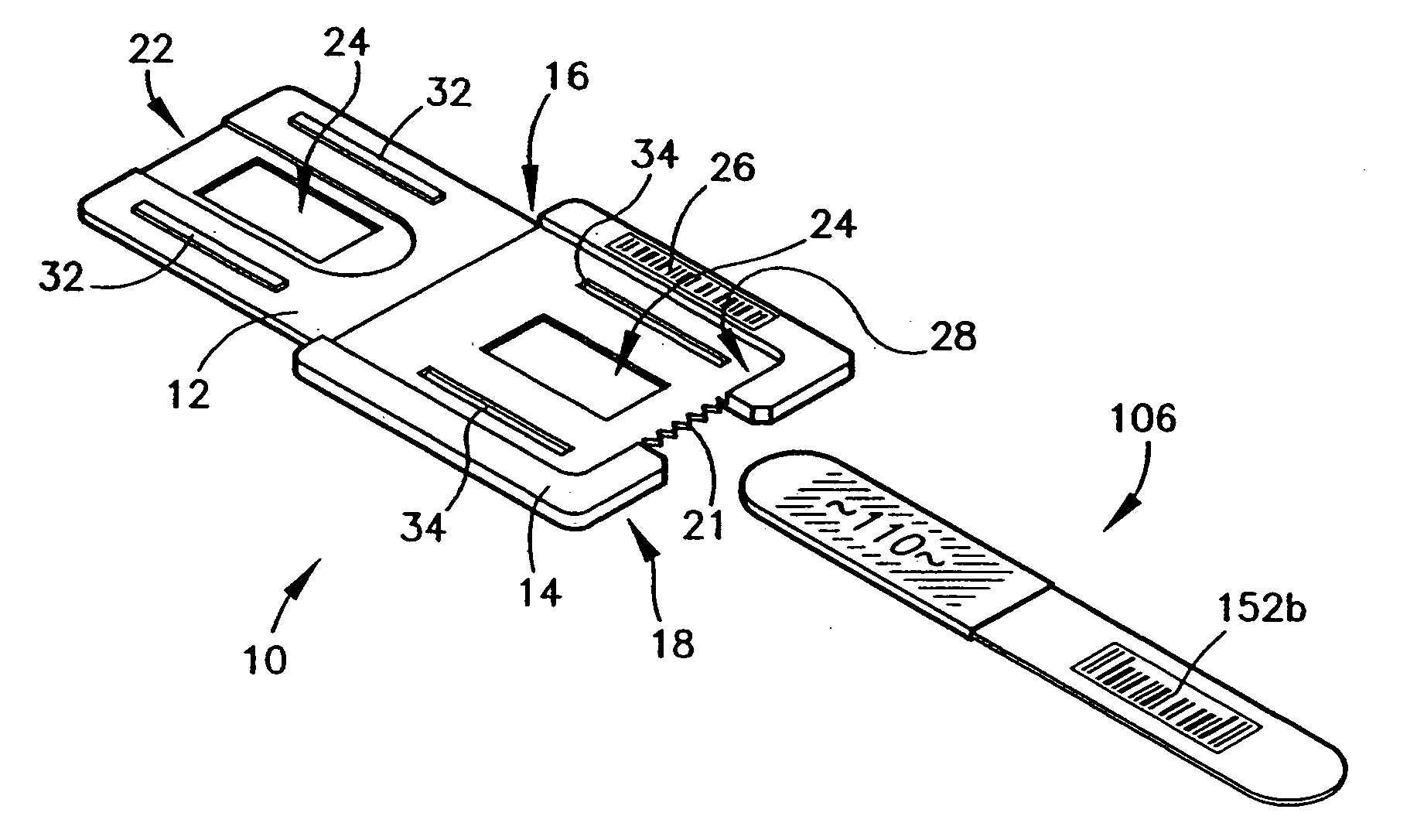
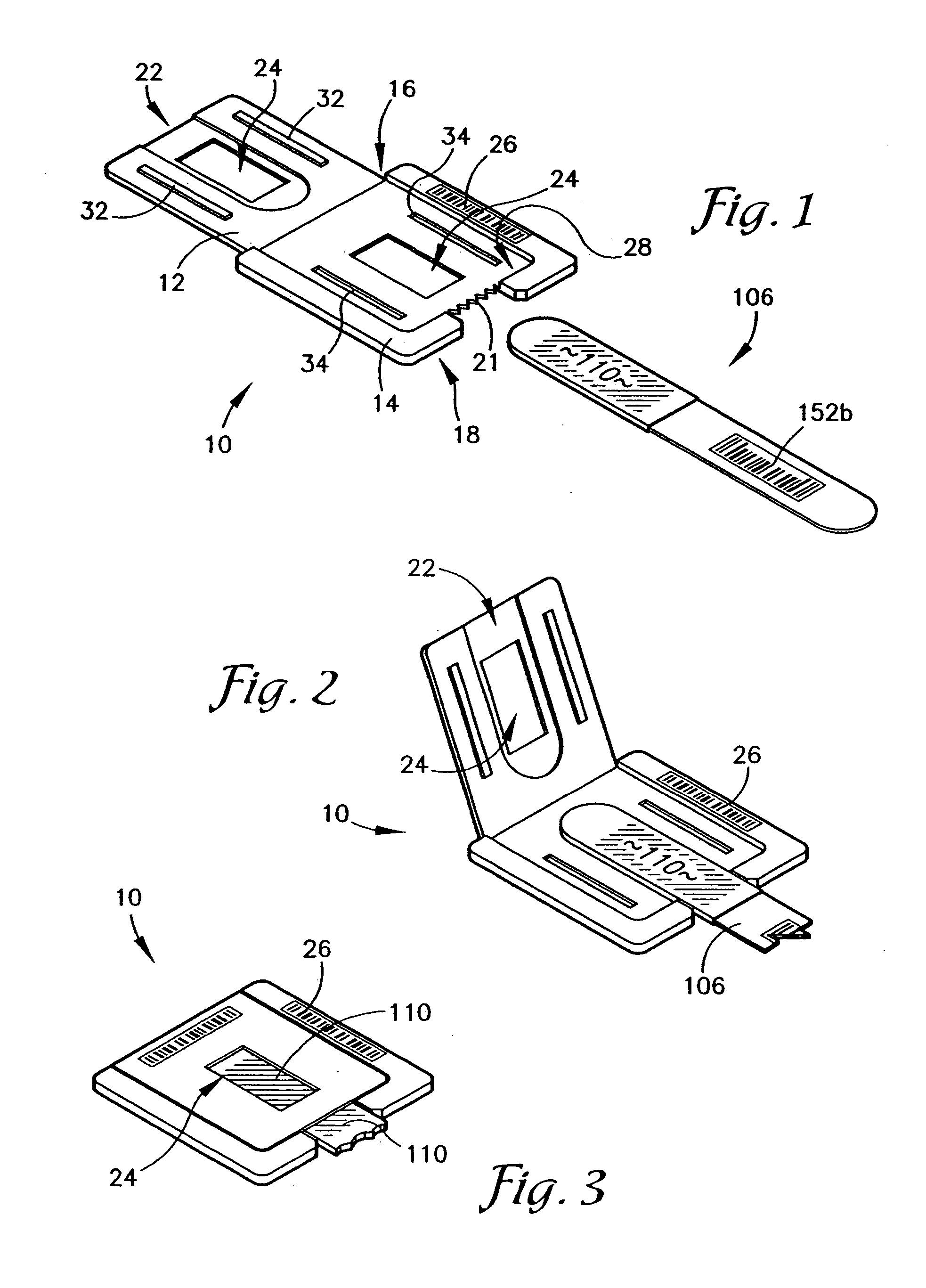
Immobilizing and processing specimens on matrix materials for the identification of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6103192AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological unitOrganism
The invention is a method and device for collecting and processing a biological specimen for the analyses of nucleic acids. A device comprises a matrix to which cells and viruses adhere and a handle to manipulate the matrix. The devices are used to collect, dry, transport, store and process small amounts of blood or other tissue. The matrix of the device is transferred to a reaction tube and amplifying reagents added to it. Nucleic acid sequences and relative quantities are detected and analyzed from the same specimen. The relative amounts of amplified nucleic acid from one or more particular RNA sequences are compared to one another and to the amount of amplified nucleic acid from DNA sequences serving as an internal control for the number of biological units per specimen. The relative amounts of amplified viral sequences from suspected viruses in the biological specimen and from recombinant viral particles serving as a viral quantitation standard enable estimation of viral burden in a given quantity of specimen.
Owner:GENETEC
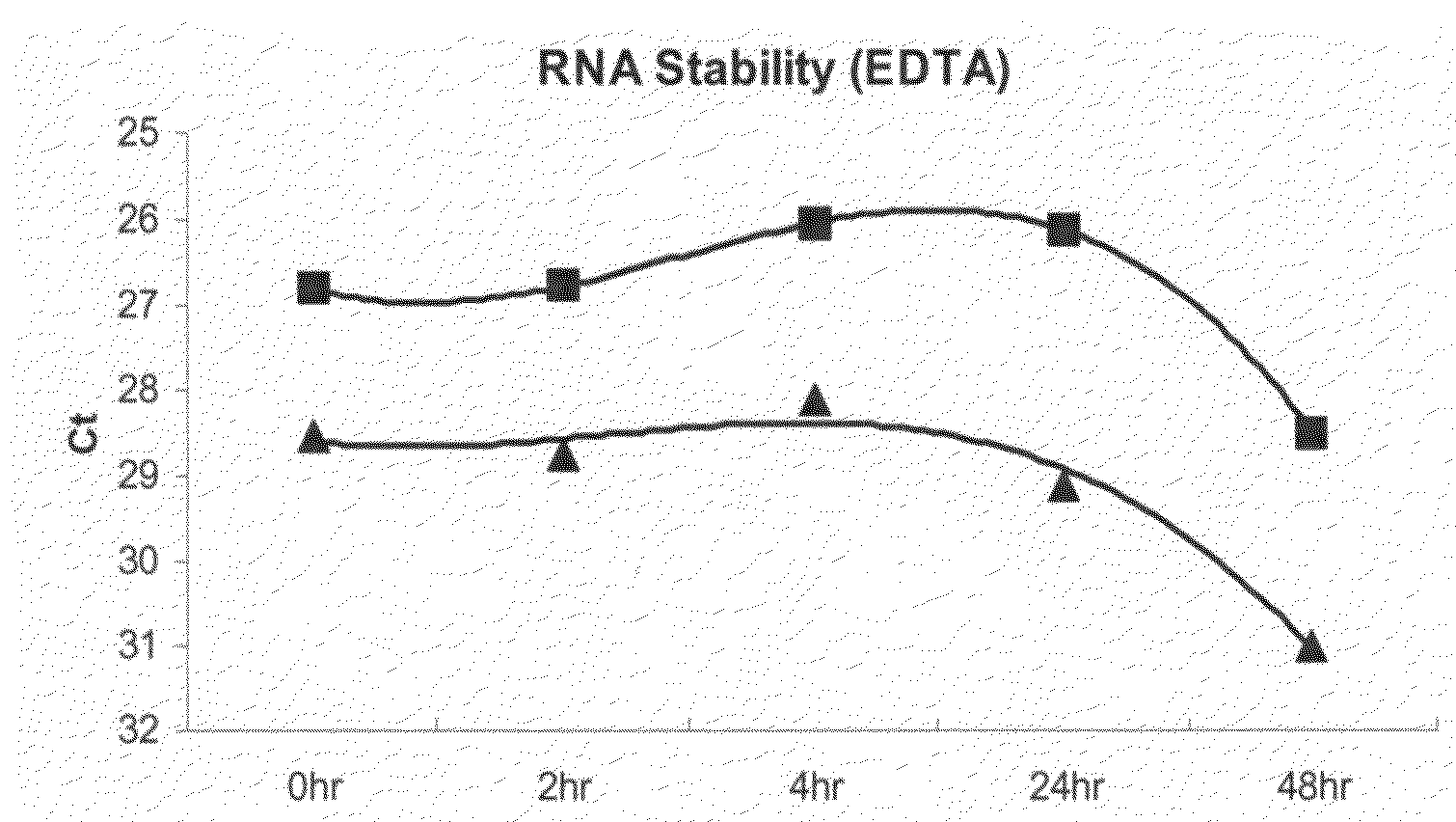
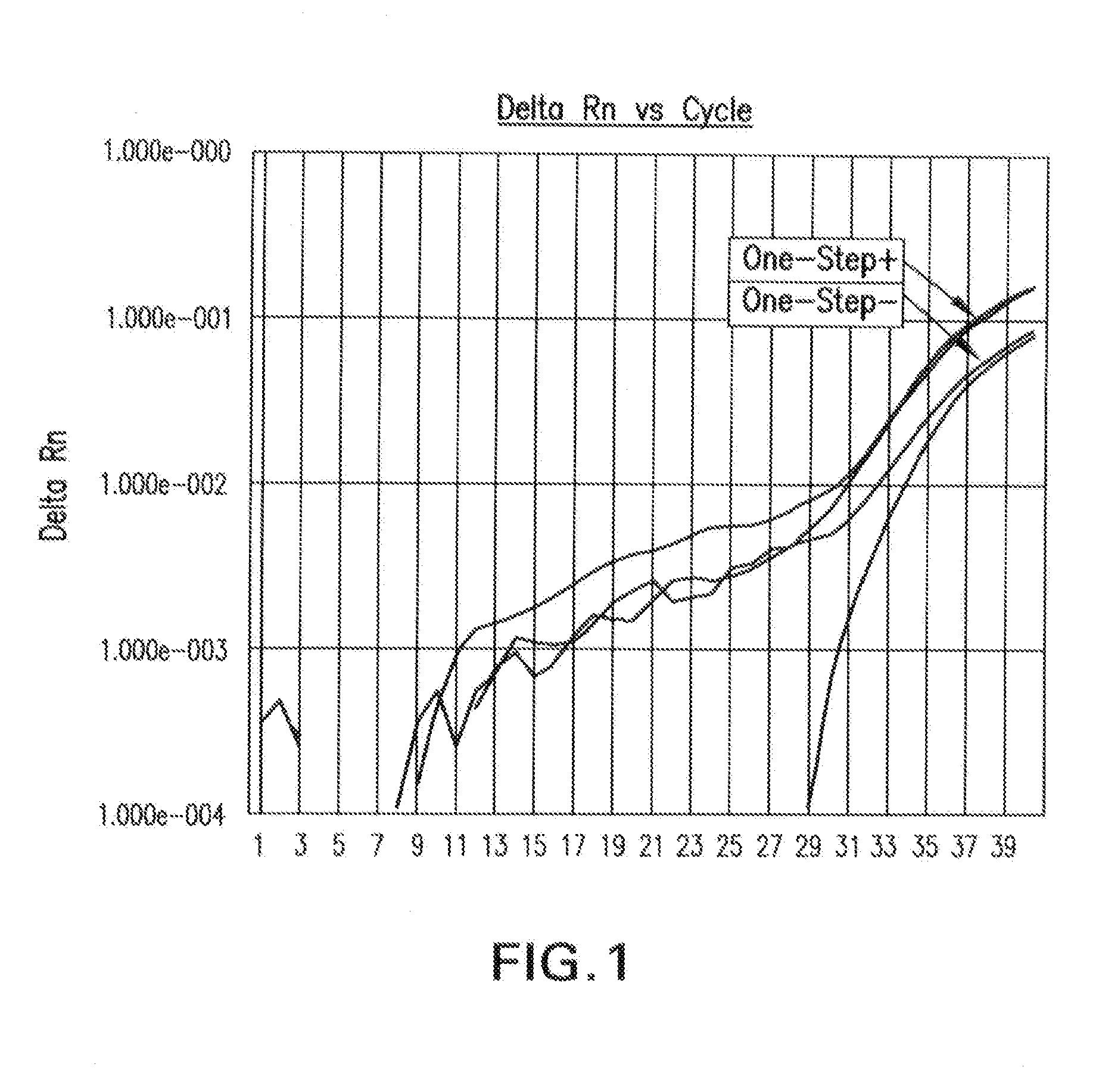
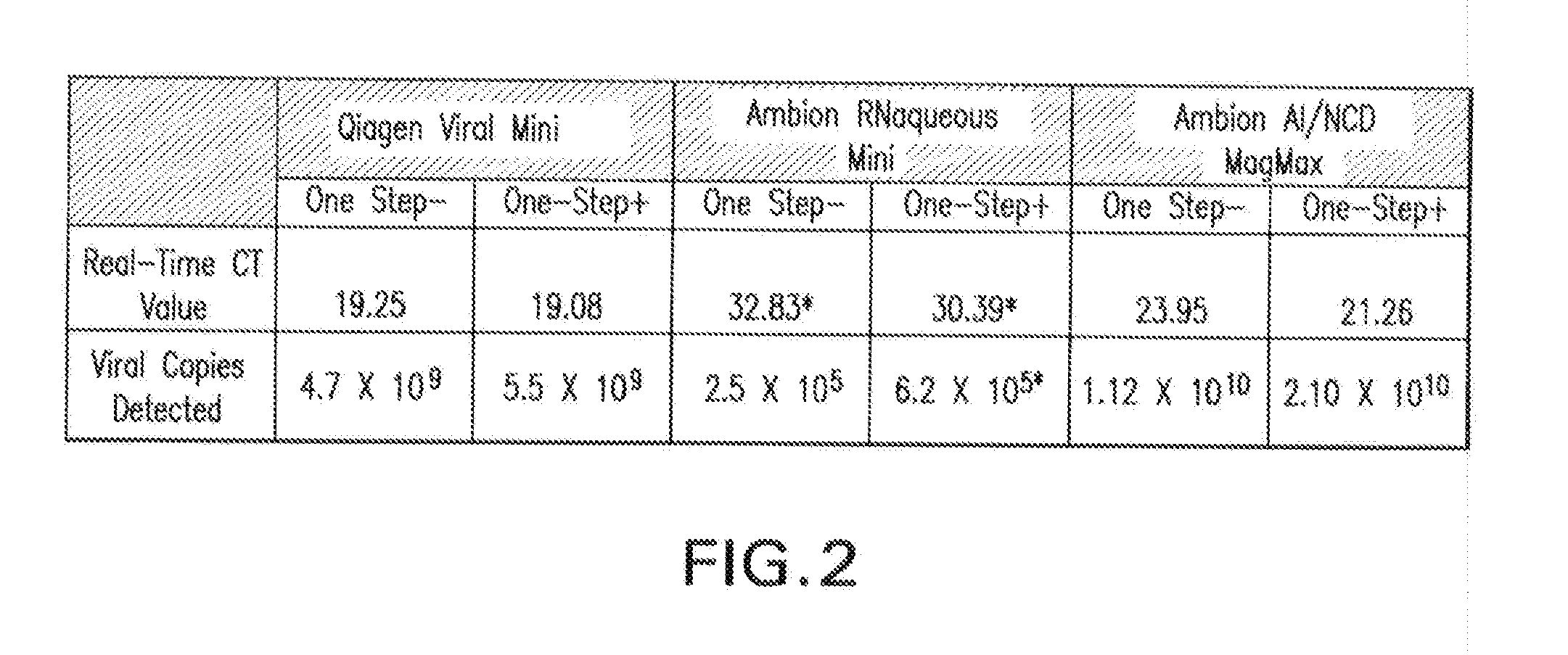
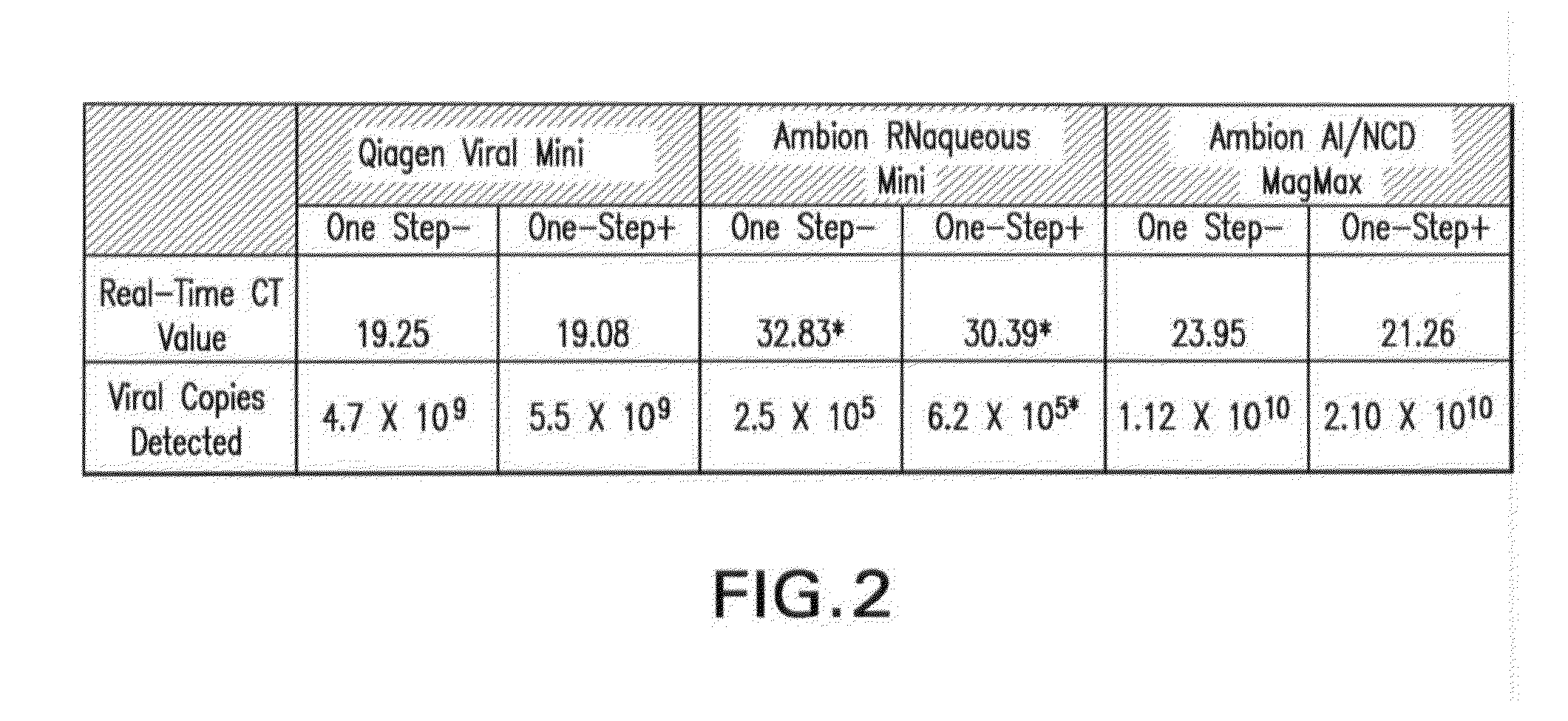
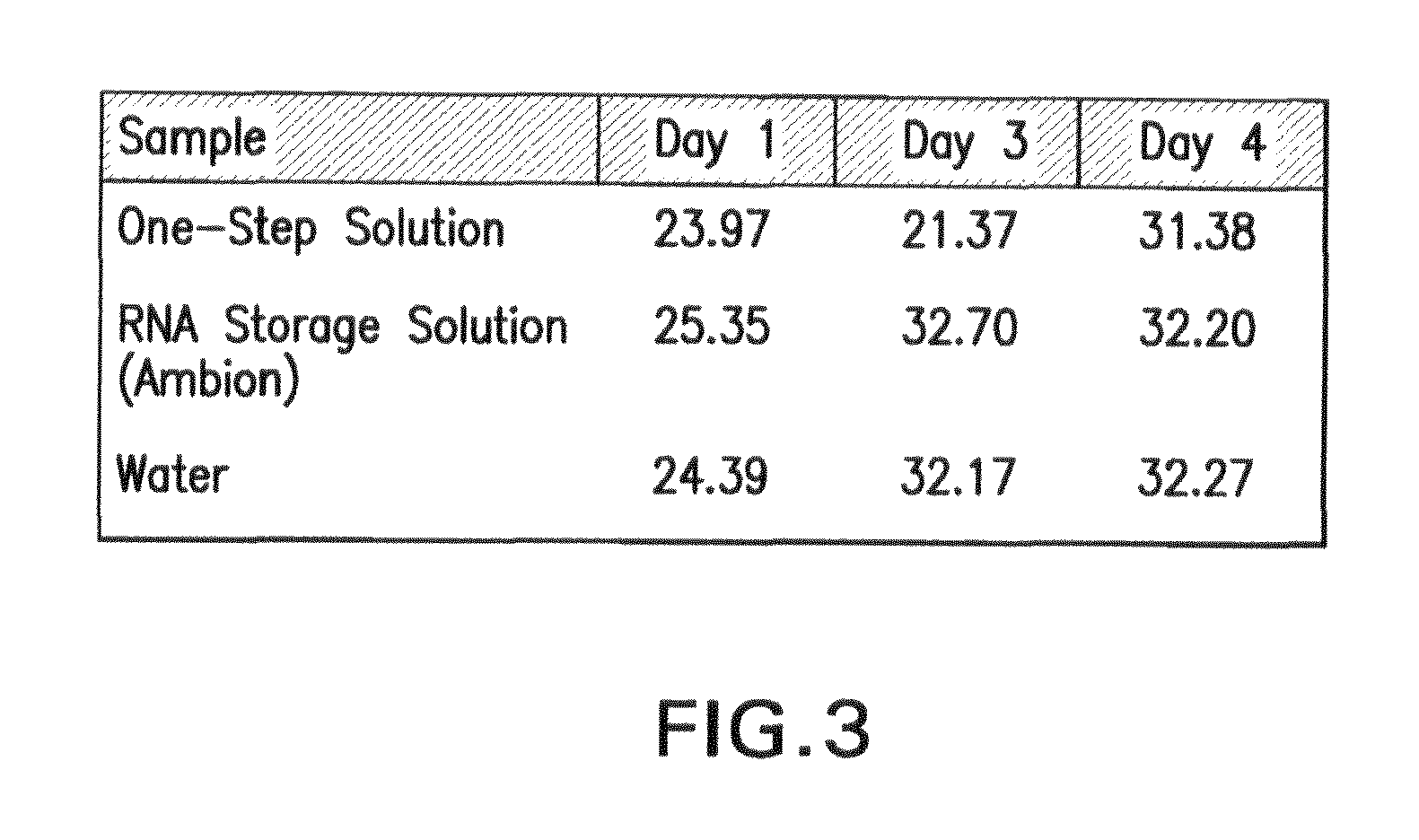
Biological specimen collection/transport compositions and methods
ActiveUS20090233309A1Preventing degradation of nucleic acidStabilizes and preserves integrityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBio-SpecimenPopulation
Disclosed are compositions for collecting, storing, and transporting populations of nucleic acids from biological specimens, and clinical, forensic, or environmental samples. Also disclosed are methods for using these compositions as one-step formulations for killing pathogens, inactivating nucleases, and releasing polynucleotides from other cellular components within the sample, and stabilizing the nucleic acids prior to further processing or assay. In particular embodiments, the invention provides a single, one-step, sample collection / transport / storage formulation containing a known quantity of a non-genomic, nucleic acid carrier molecule that serves as an internal reference control to monitor the fidelity of the collection / transportation medium, and measure the integrity of nucleic acids subsequently isolated and purified from the processed sample.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
All-in-one specimen cup with optically readable results
A biological material test strip and adjacently-located reference color chart are affixed to a lid portion of an all-in-one specimen cup to perform color-based reaction testing of collected biological specimens in an uncalibrated environment. After specimen collection, the lid portion is secured to a container portion of the specimen cup. The cup may then be rotated into an upside down position causing the specimen, under the force of gravity, to pass from the container portion and into a volume of the lid portion, such that the test strip is exposed to the specimen as it is received into the volume of the lid portion. An image of the exposed test strip and adjacently-located reference color chart may then be captured and processed to identify any color matches between the individual test pads on the test strip and the corresponding sequences of reference color blocks on the reference chart.
Owner:SCANWELL HEALTH INC
System and method for automated sample preparation
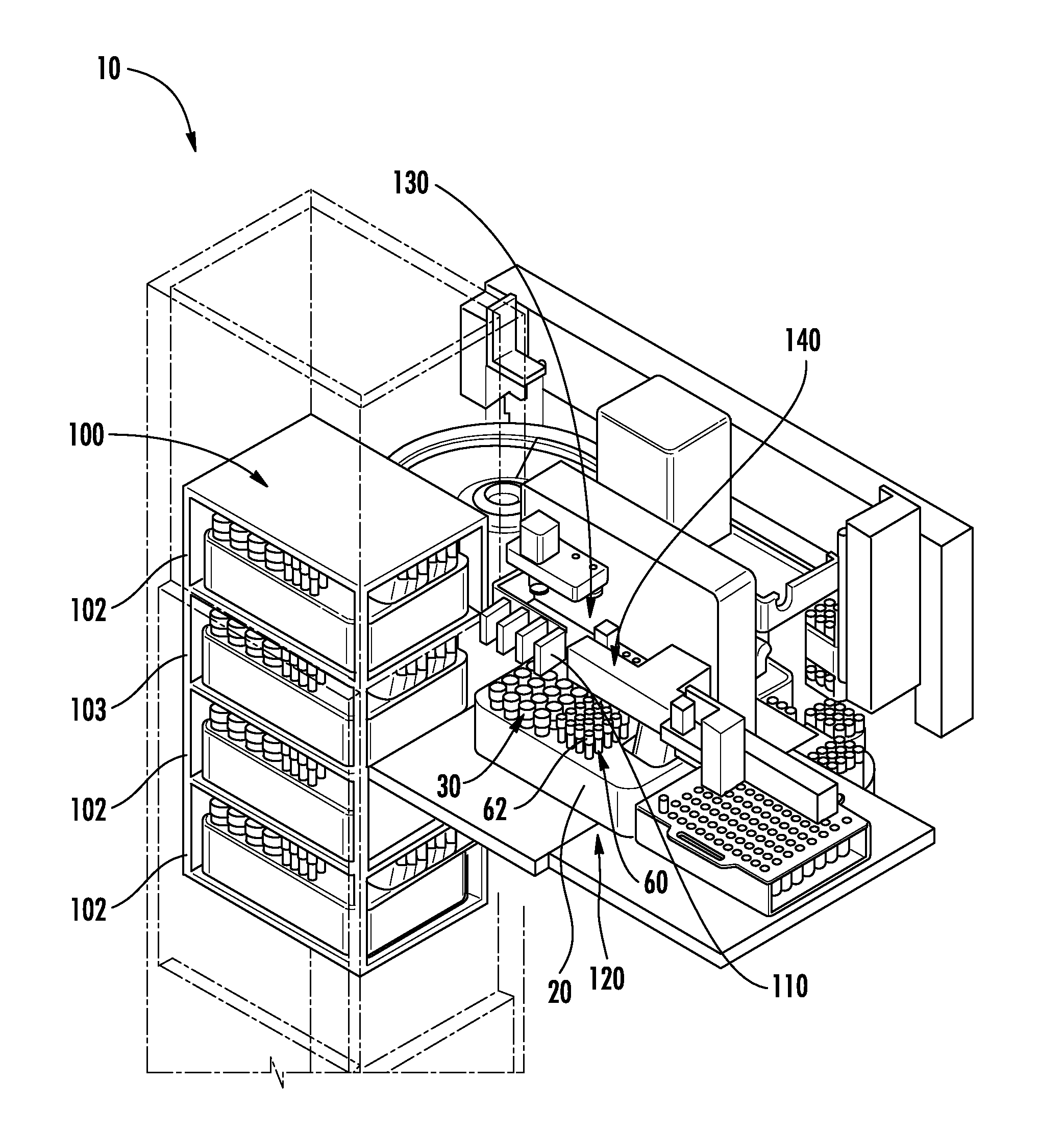
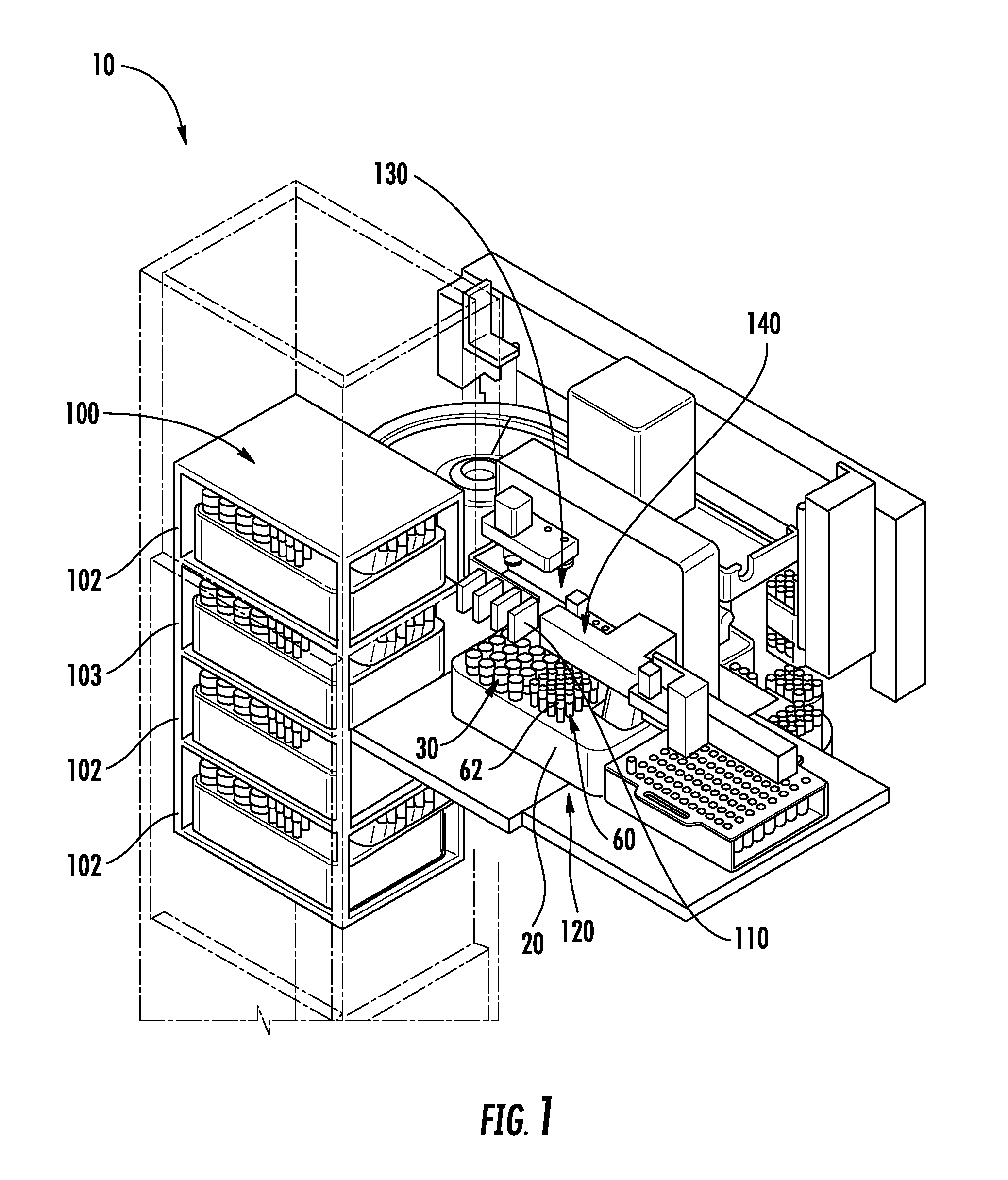
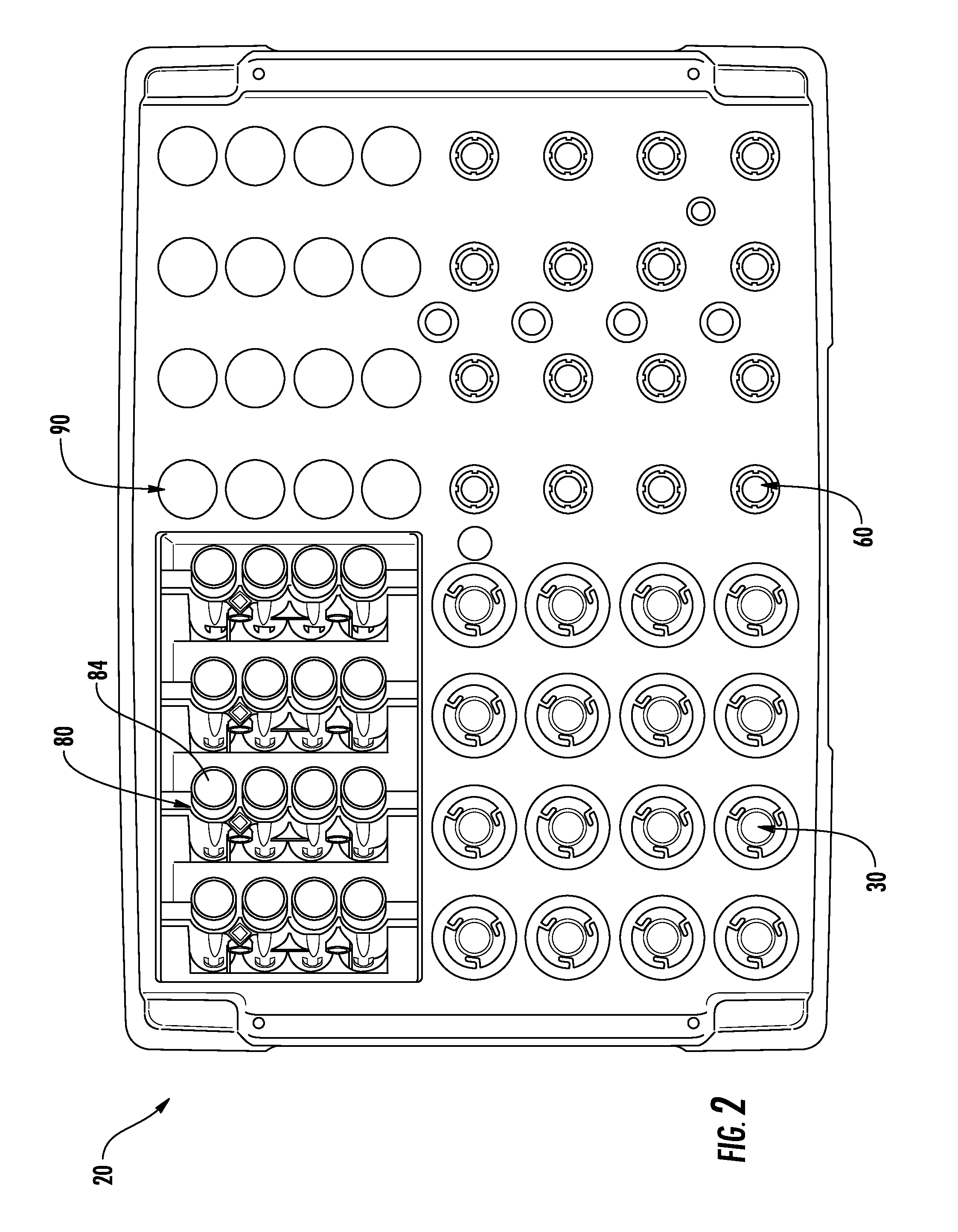
ActiveUS20130116102A1Easy accessDispersed particle separationCentrifugal force sediment separationEngineeringBio-Specimen
A system for automatically processing a biological specimen is provided that includes an elevator comprising a plurality of shelves configured to receive a plurality of sample trays. The trays may comprise a plurality of sample containers containing a sample and having a plurality of respective caps engaged therewith. The trays may further include a plurality of centrifuge tube racks each containing a plurality of centrifuge tubes. The system may include a first transport mechanism, a second transport mechanism and a third transport mechanism. The system may include a chain-of-custody device configured to read identifiers on each of the containers. The system may also include a pipetting device configured to remove a portion from the sample containers and dispense the sample into the centrifuge tubes.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
In situ nucleic acid sequencing of expanded biological samples
ActiveUS20160304952A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory apparatusFluorescent in situ sequencingNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides in situ nucleic acid sequencing to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ sequencing of nucleic acids as well as new methods for fluorescent in situ sequencing (FISSEQ) in a new process referred to herein as “expansion sequencing” (ExSEQ).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
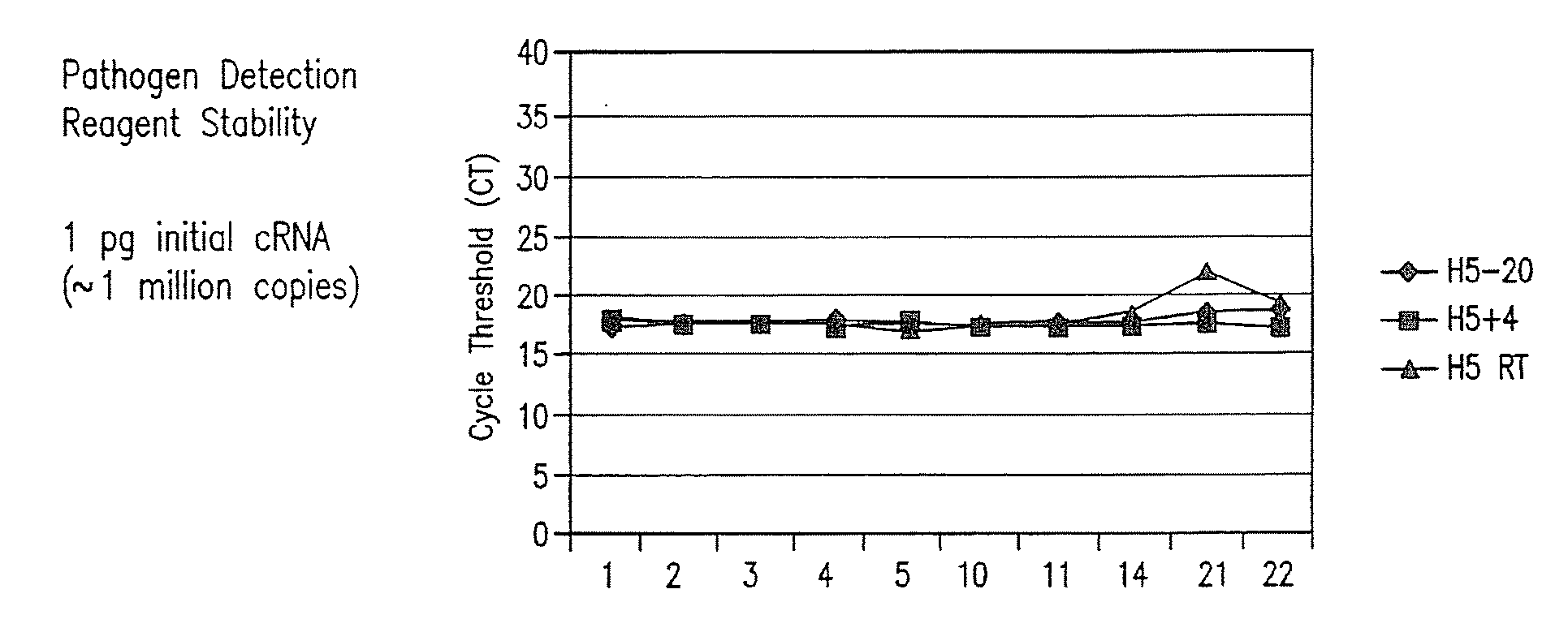
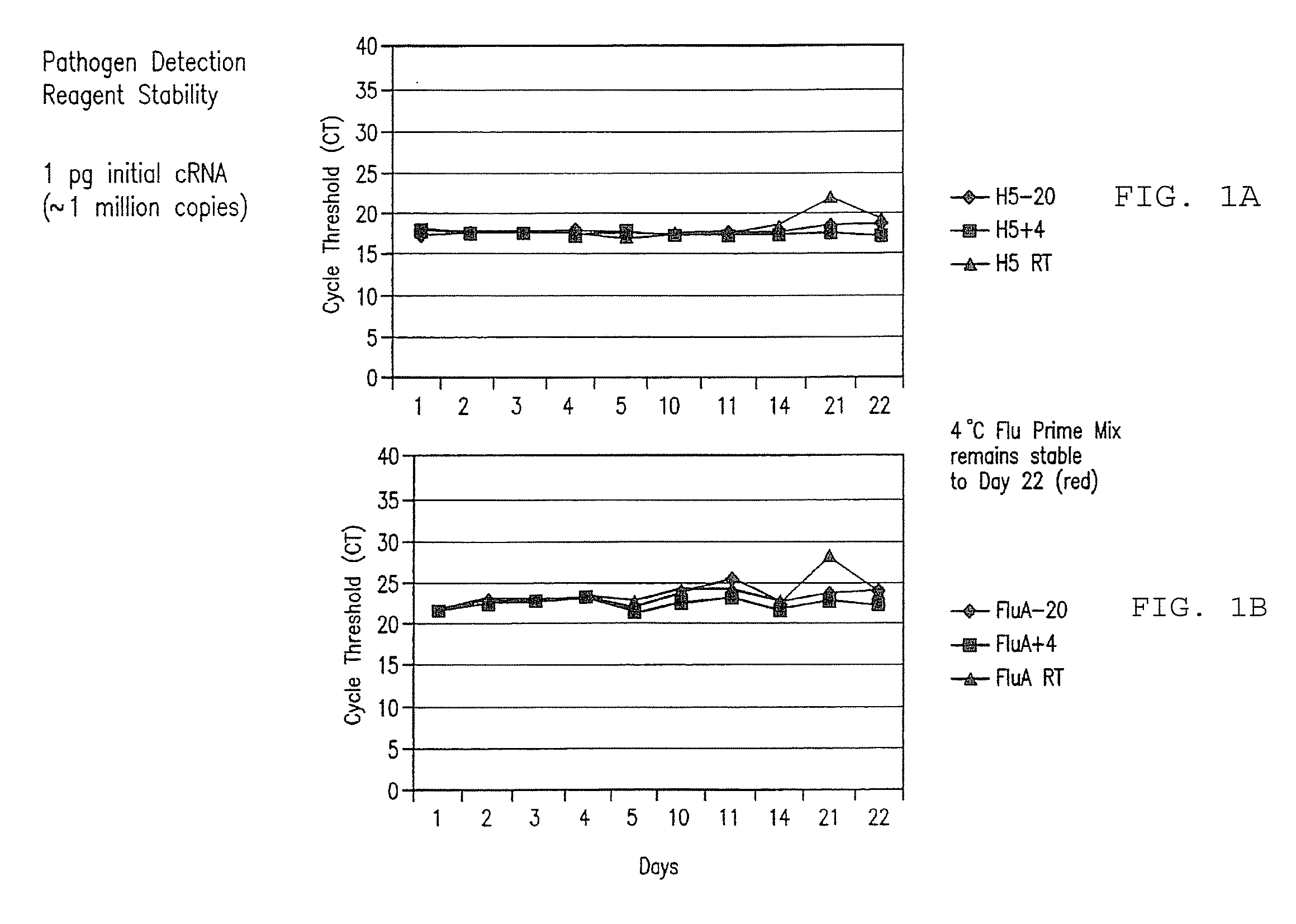
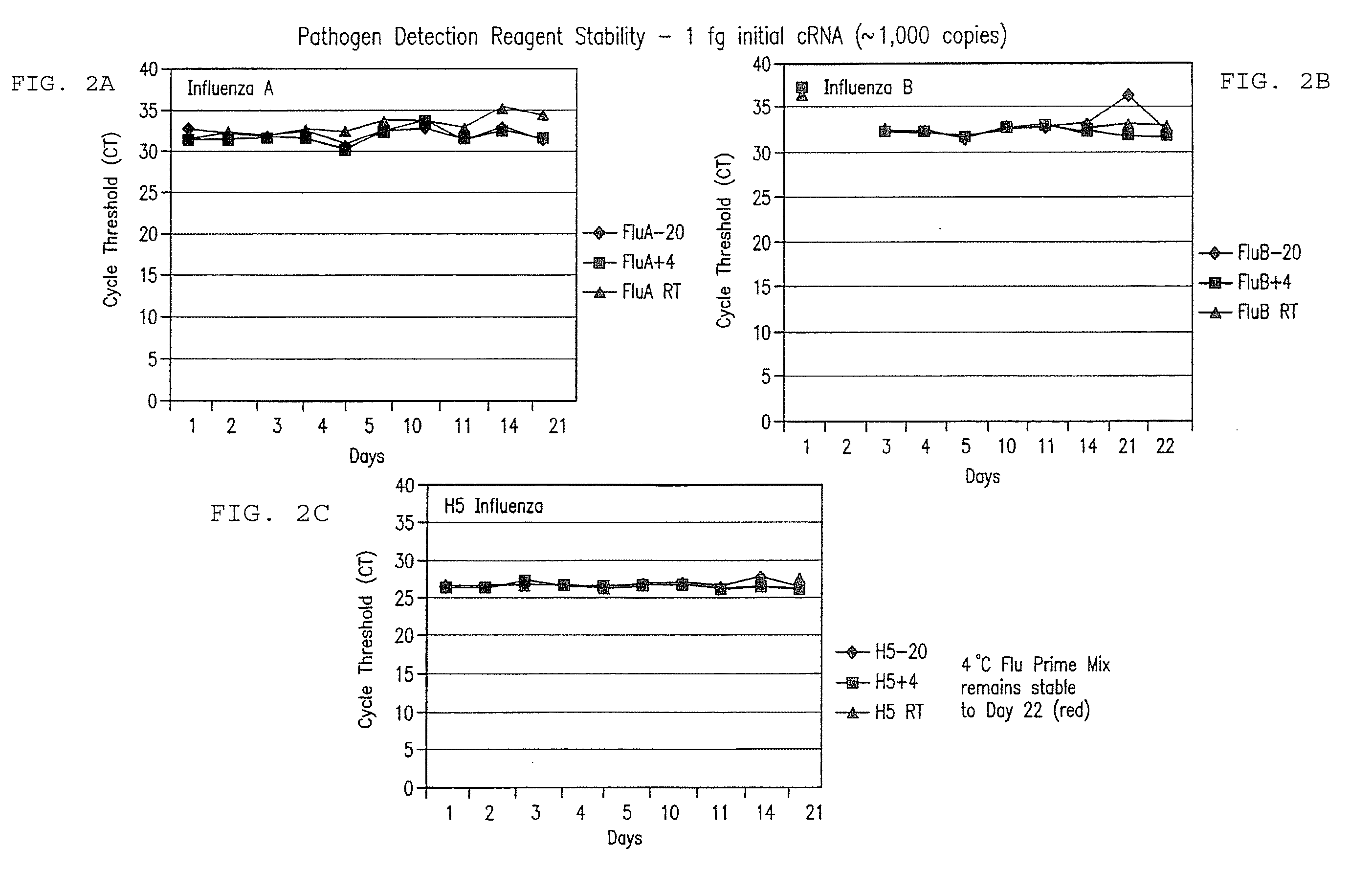
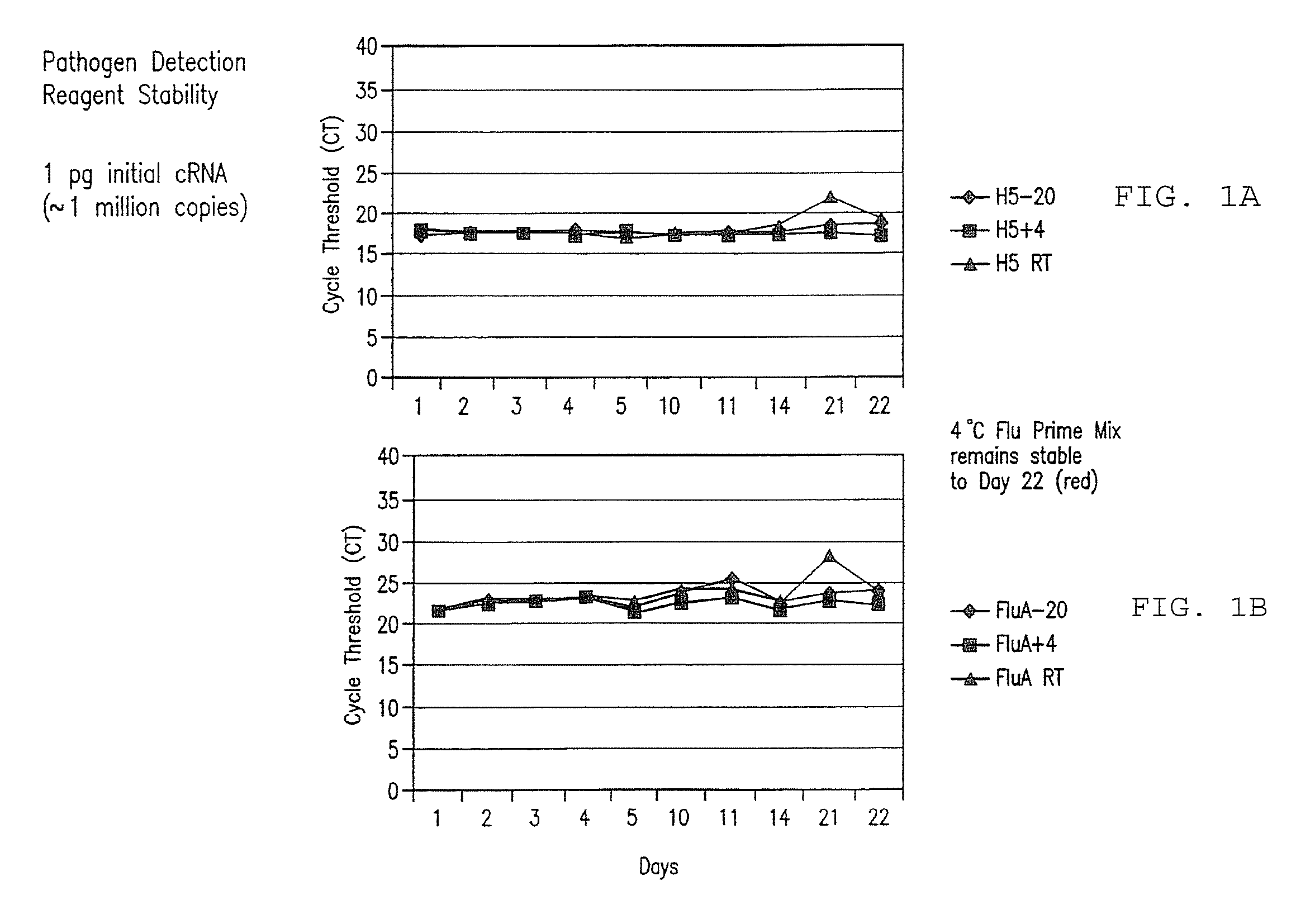
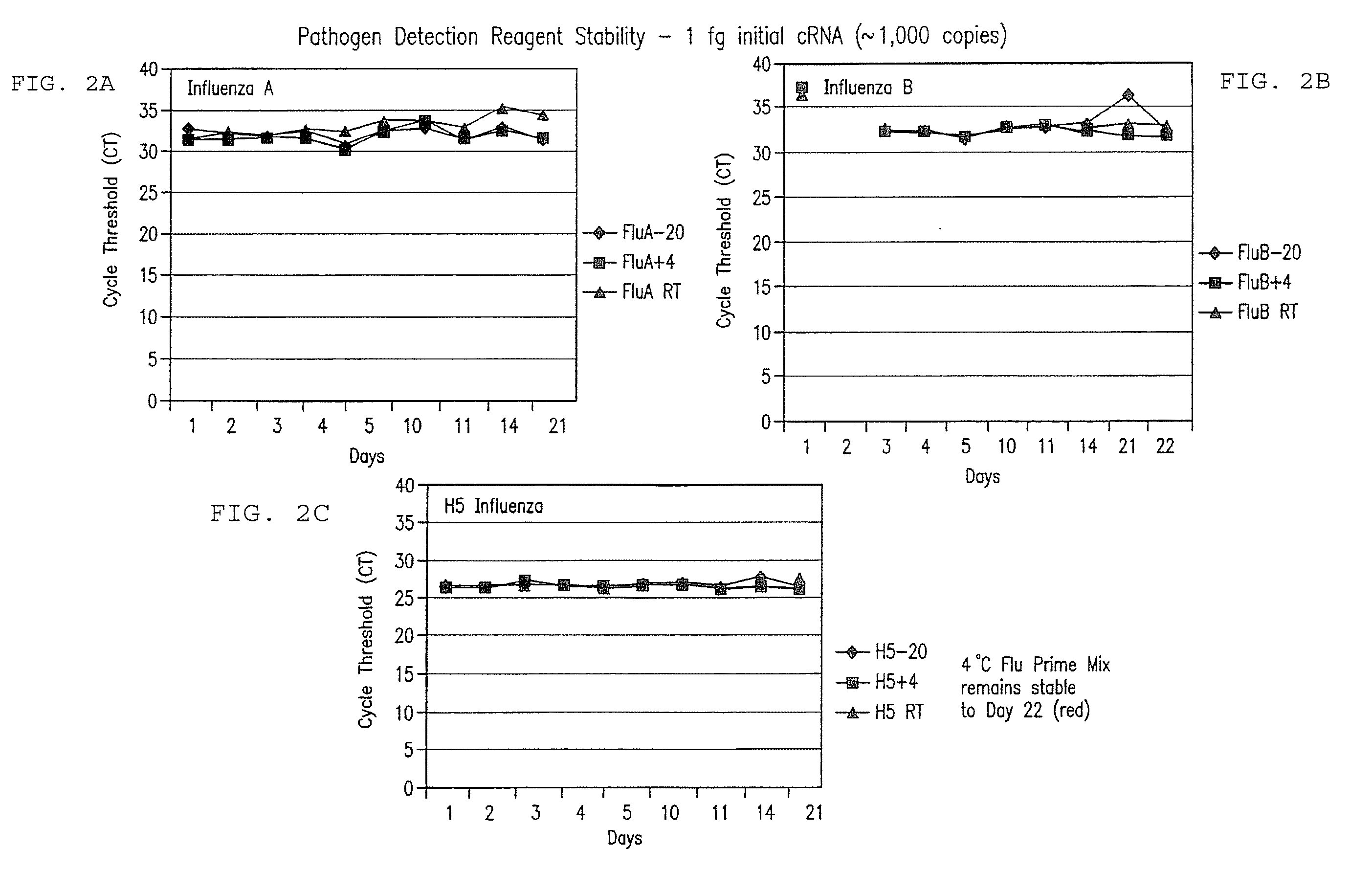
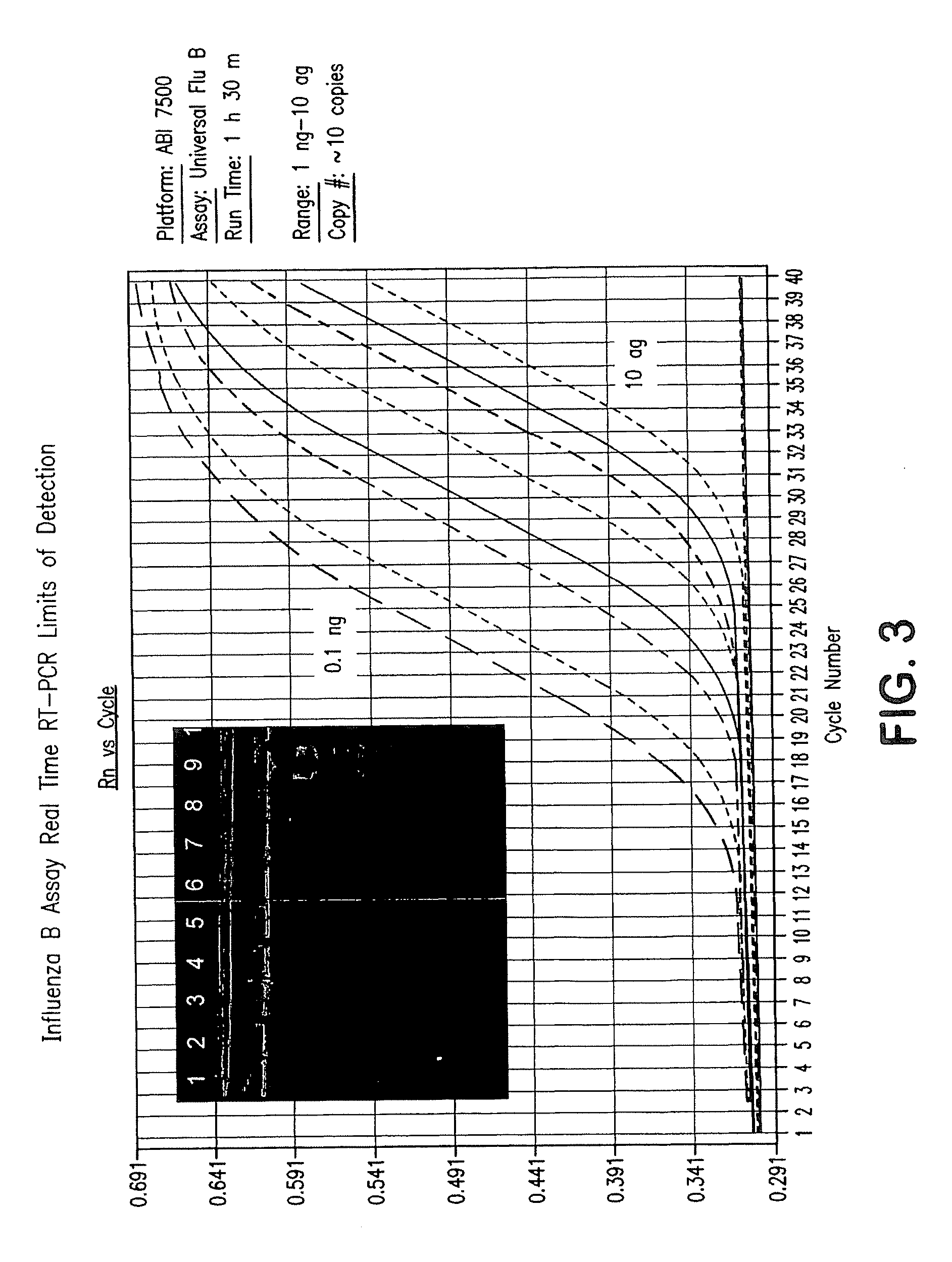
Compositions and method for rapid, real-time detection of influenza a virus (H1N1) swine 2009
ActiveUS20100009343A1Quick checkQuick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesField analysis
Disclosed are oligonucleotide amplification primers and detection probes specific for the amplification and detection of pathogenic organisms, including for example, specific Influenza A H1N1 viral isolates. Also disclosed is a biological organism identification kit including the disclosed nucleic acid probes and primers, as well as thermal cycling reagents that is both portable and durable, and may also be self-contained for remote, or in-field analysis and identification of particular influenza isolates from a variety of biological specimen types.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
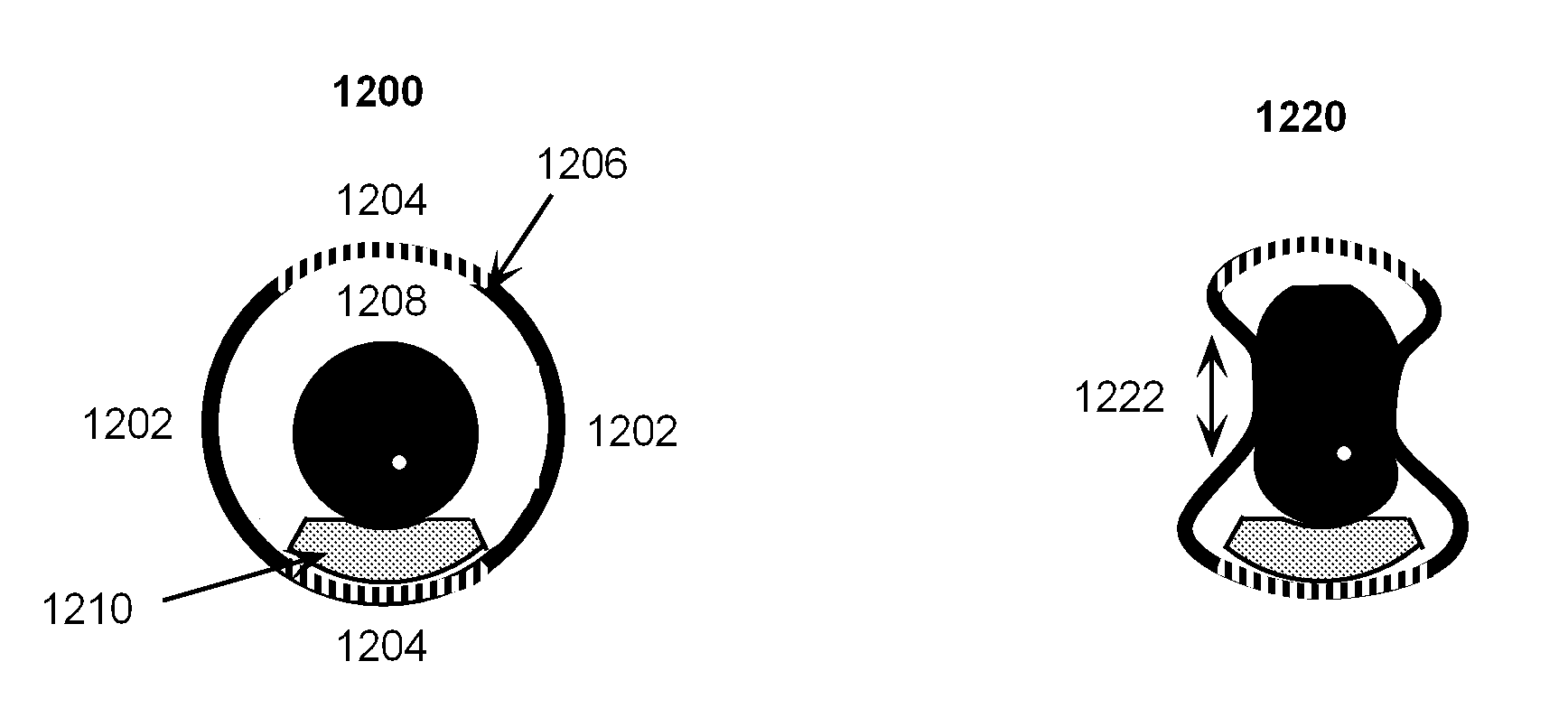
Shape-Shifting Vitrification Device
InactiveUS20090123992A1Ease of unloadingRapid coolingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVitrificationCryopreservation
This invention is a storage device (cryocontainer) for the vitrification method of cryopreservation that uses shape memory materials to create a novel shape-shifting feature in which the relevant heat transfer zone of the cryocontainer can be thermally morphed between a shape conducive to biological specimen handling and to a shape conducive to rapid heat transfer. This feature utilizes the temperature induced phase transformation of shape memory materials. The temperature inducement occurs naturally within the normal temperature changes that occur during vitrification.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
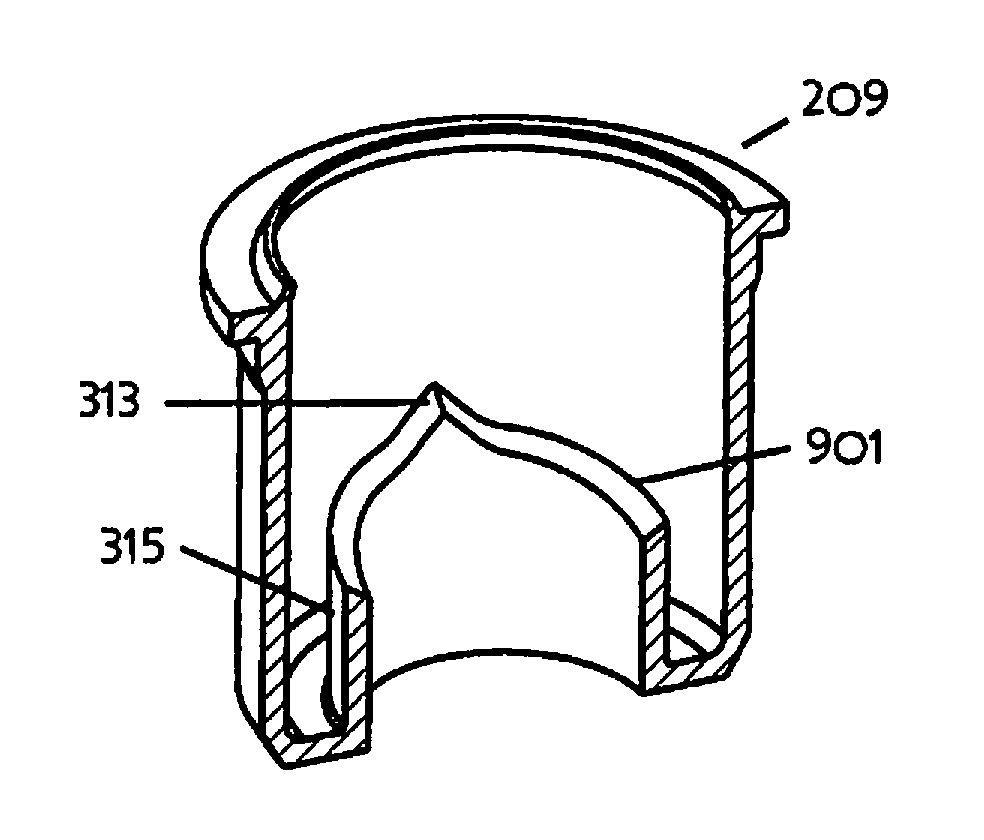
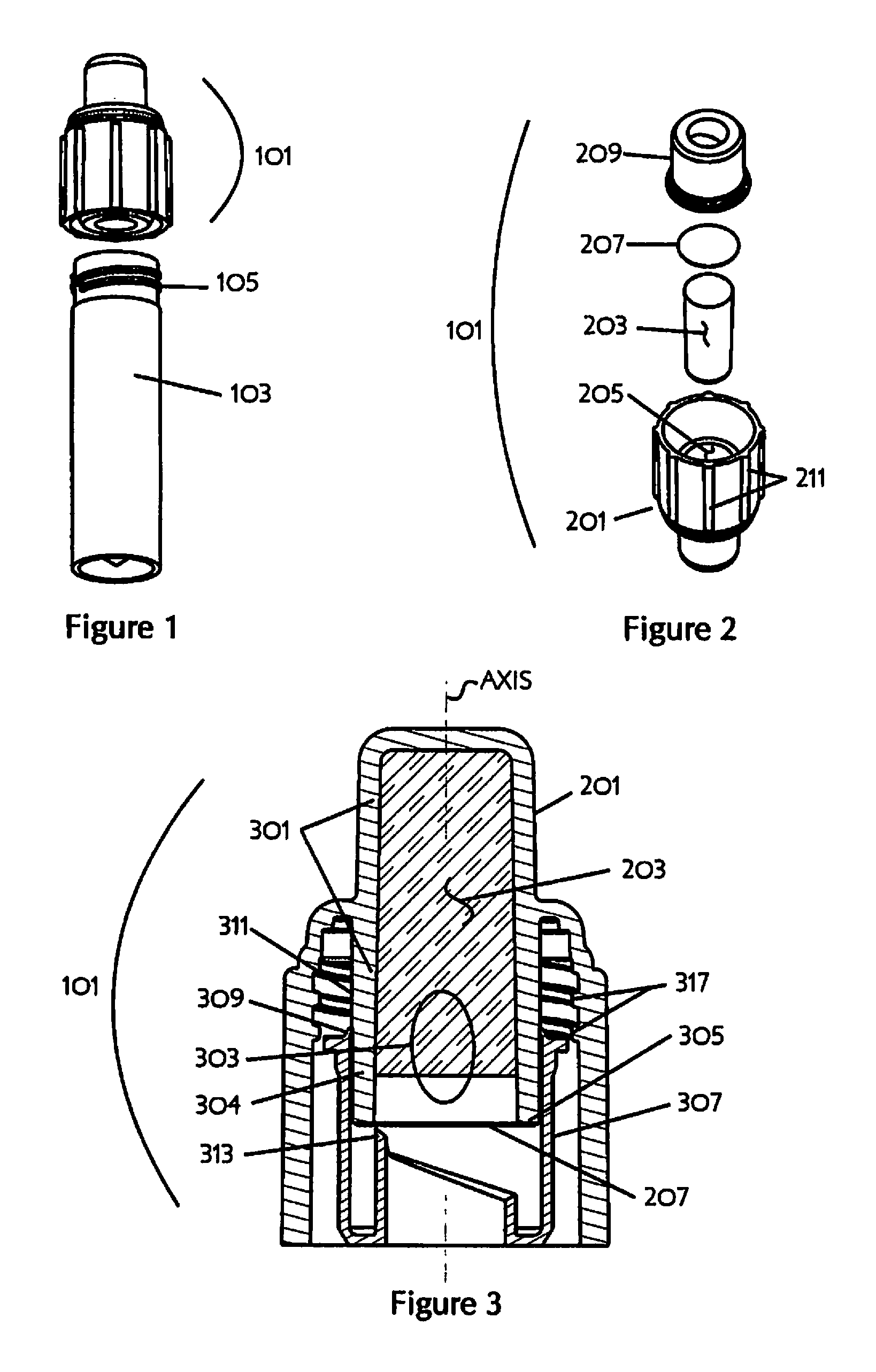
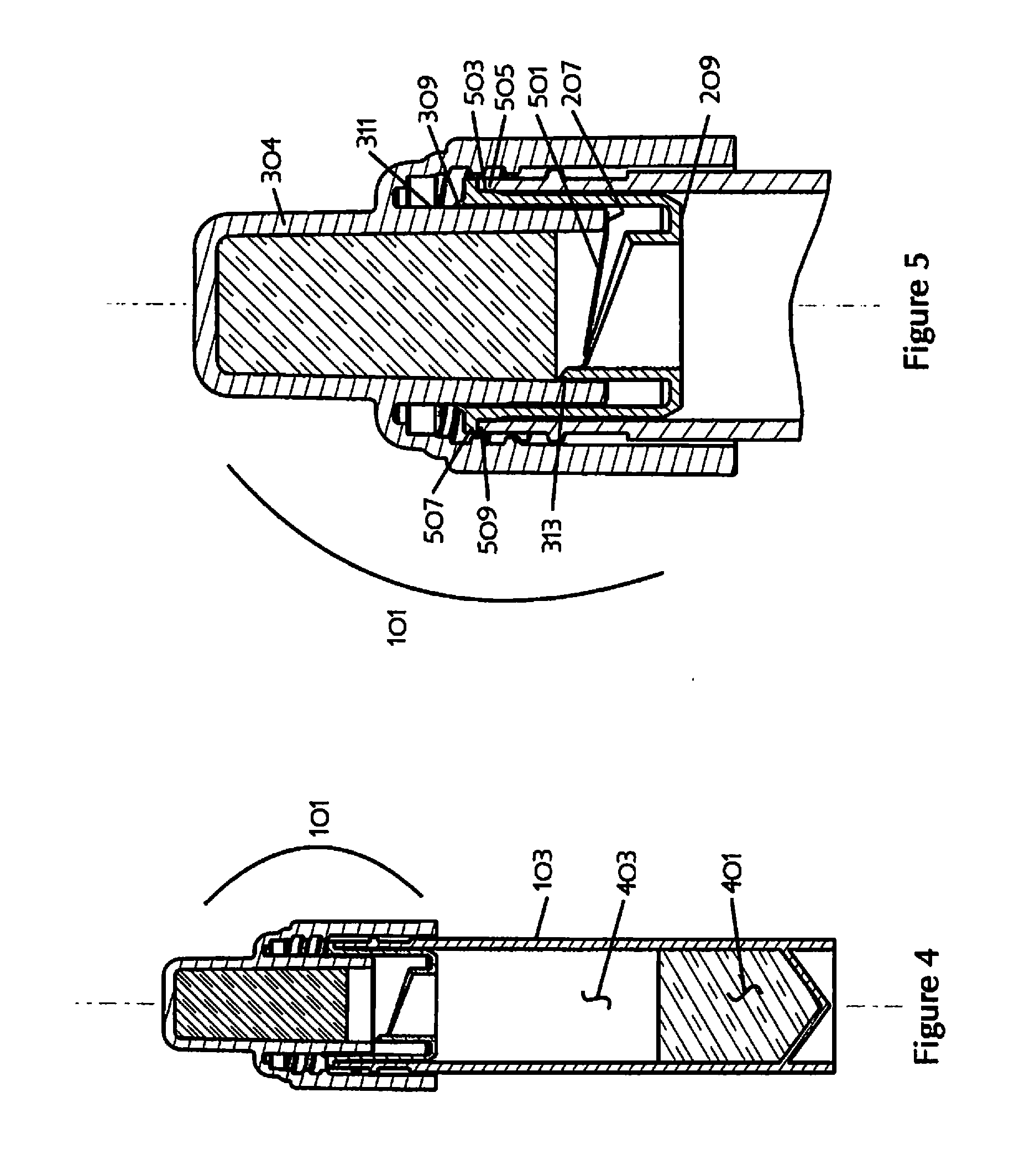
Seal cap with pre-filled agent for a specimen container
A seal cap assembly for use with a biological specimen container, the cap assembly including an integral ampoule that holds a pre-filled agent. A piercer is movably disposed in the cap assembly to pierce into the ampoule. When the cap assembly is attached to a biological specimen container, the ampoule is pierced, the pre-filled agent in the ampoule is mixed with the specimen, and the seal cap assembly seals the biological specimen container. The seal cap assembly, together with a biological specimen container, permits stabilization, storage, and transport of biological fluid samples.
Owner:REFLEX MEDICAL CORP
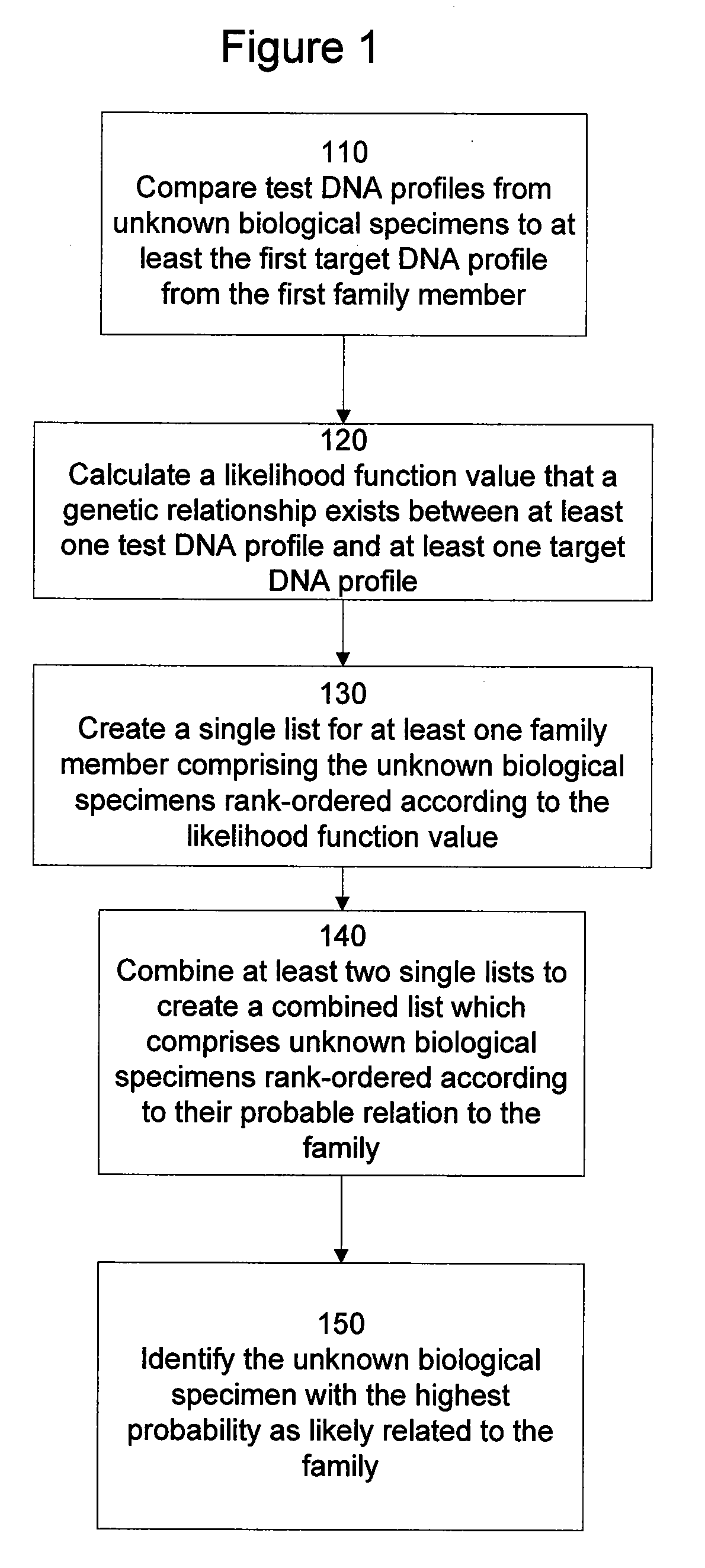
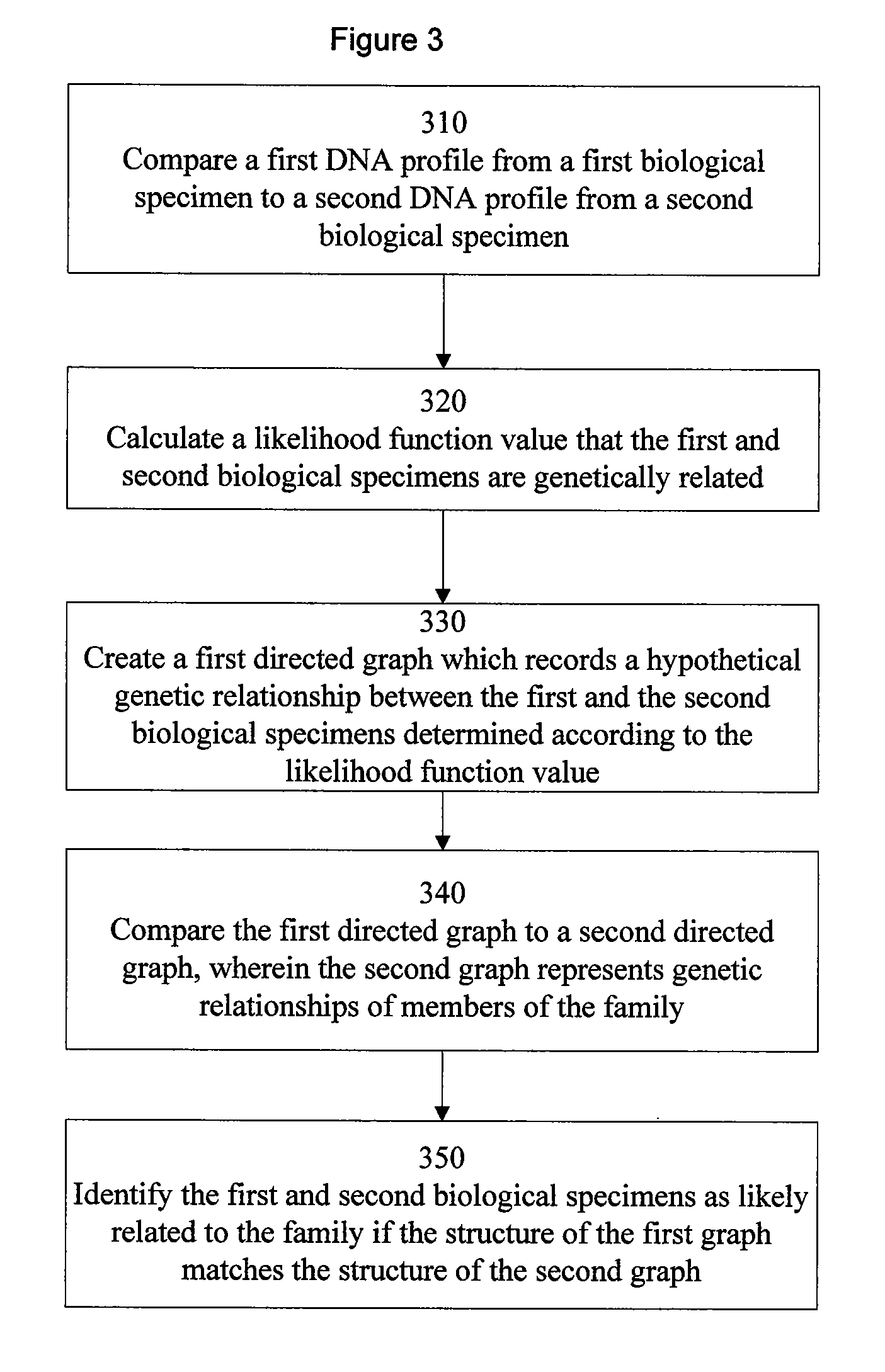
Methods of associating an unknown biological specimen with a family
The present invention provides at least three methods of predicting whether an unknown biological specimen originates from a member of a particular family. These methods compare DNA profiles from unknown biological specimens to DNA profiles of more than one family member, which significantly increases the methods' identification ability. In particular, the invention describes combining at least a ranked first family member list and a ranked second family member list to create a combined ranked list and identifying the unknown biological specimen as one contained among a list of specimens having the highest combined rankings representing the candidates that are most likely related to the family. A second method encompasses comparing test DNA profiles from unknown biological specimens to a family pedigree comprising target DNA profiles obtained from multiple biological specimens of family members. This method also embodies using a modified Elston Stewart algorithm to determine a pedigree likelihood ratio to rank and identify the test profile of the unknown biological specimen most likely to be the missing person sought after by the corresponding family represented by the family pedigree. A third method encompasses construction of a database or directed graph of discovered or known relationships between biological specimens and comparison to a graph representing a family pedigree to identify portions of the database or directed graph that correspond to portions of the family pedigree, in order to rank or identify one or more unknown biological specimens as most likely related to one or more family pedigrees.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Systems and methods for detecting biological features
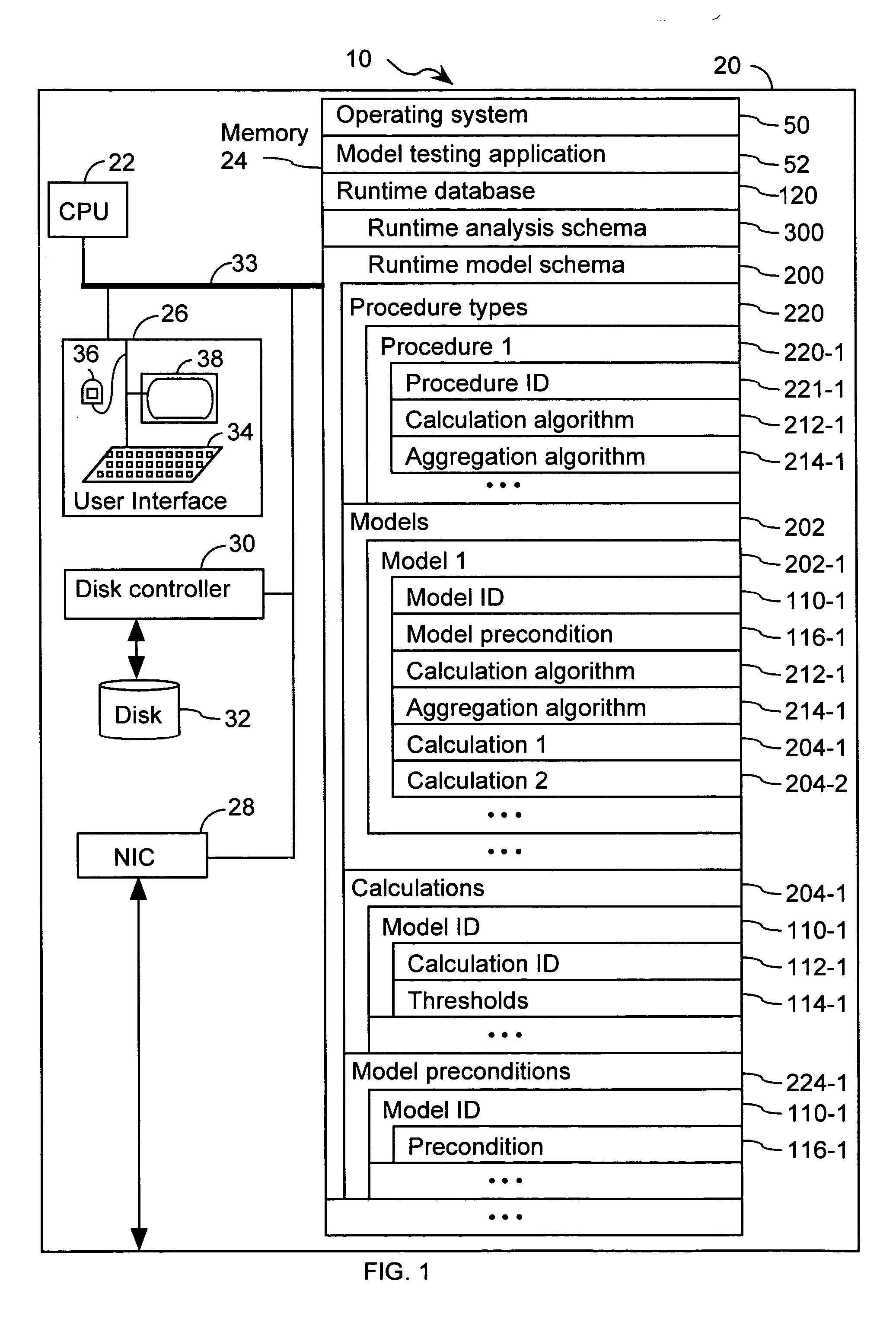
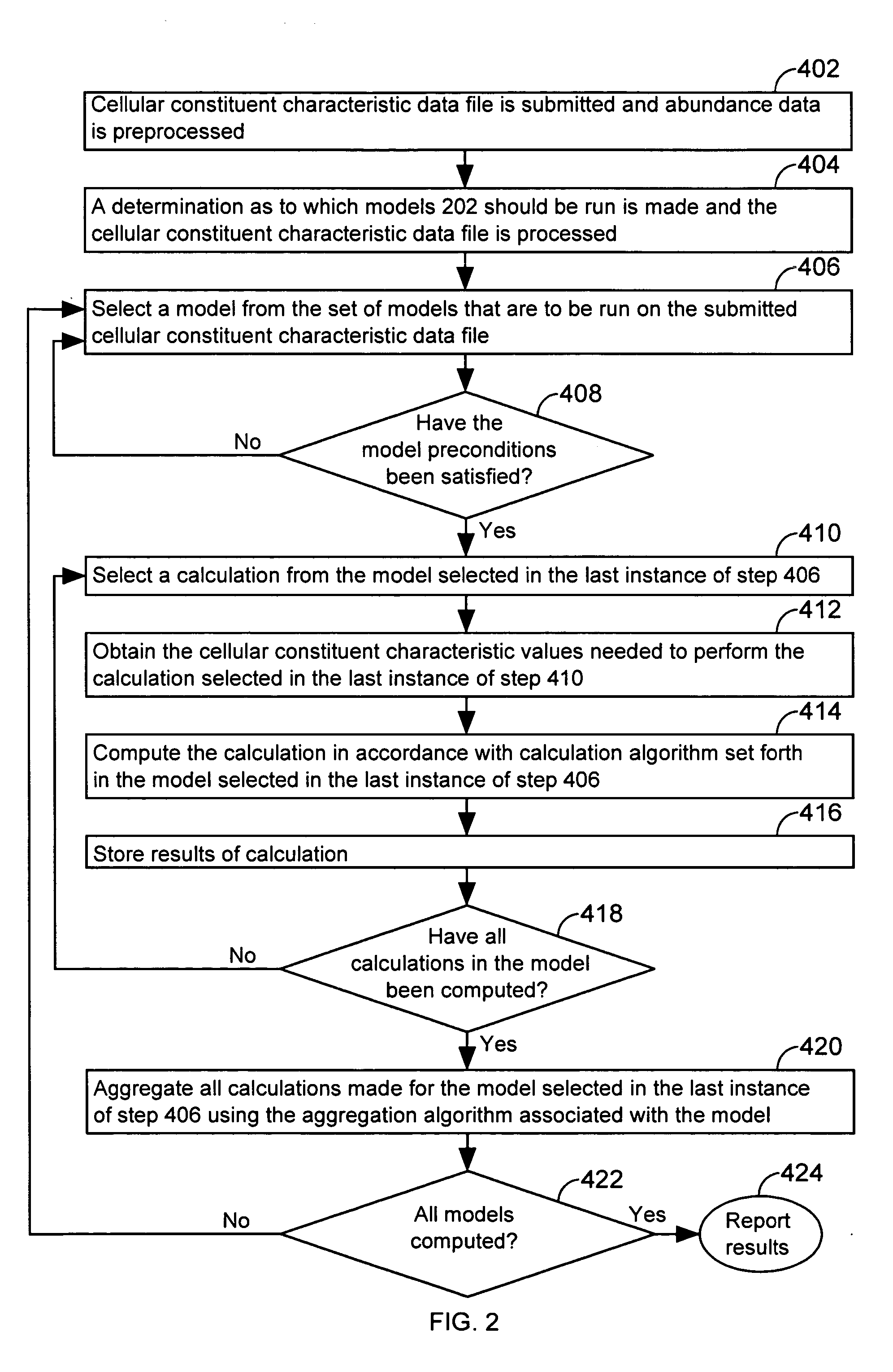
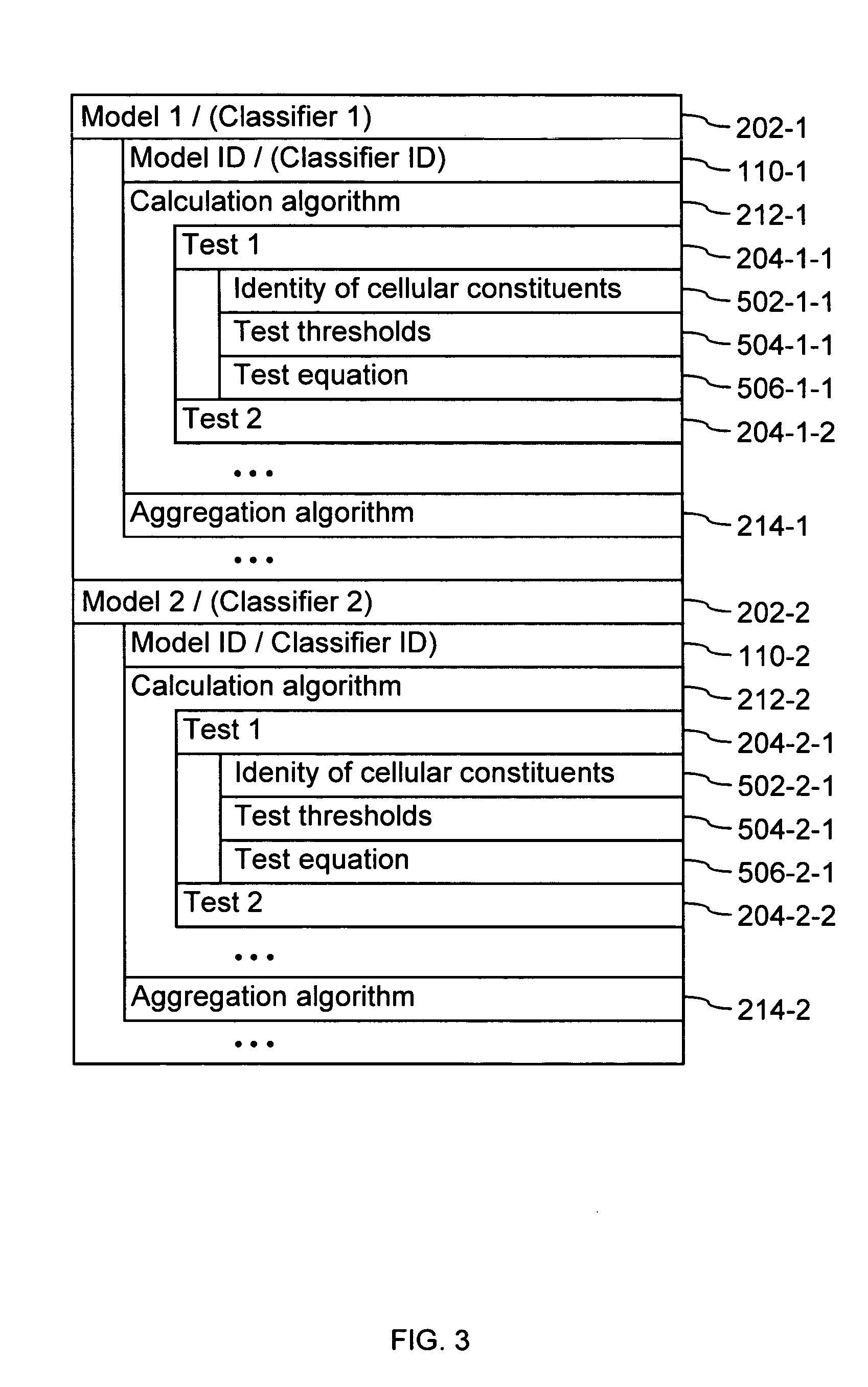
InactiveUS20050071087A1Mathematical modelsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyTest organism
A computer having a memory stores instructions for receiving data. The data comprises one or more characteristics for each cellular constituent in a plurality of cellular constituents that have been measured in a test organism of a species or a test biological specimen from an organism of the species. The memory further stores instructions for computing a model in a plurality of models, wherein the model is characterized by a model score that represents the likelihood of a biological feature in the test organism or the test biological specimen. Computation of the model comprises determining the model score using one or more characteristics for one or more cellular constituents in the plurality of cellular constituents. The memory also stores instructions for repeating the instructions for computing one or more times, thereby computing the plurality of models. The memory also stores instructions for communicating computed model scores.
Owner:CANCER GENETICS
Method for Determining the Status of an Individual
Methods of determining status of an individual based on the use of biological specimen and analysis of reference population of cells are described.
Owner:NODALITY
Apparatus for biochemical analysis
InactiveUS20050233440A1Improve thermal conductivityGood thermal responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusPre treatmentBio-Specimen
An integrated device for nucleic acid analysis having a support and a first tank for introducing a raw biological specimen includes at least one pre-treatment channel, a buried amplification chamber, and a detection chamber carried by the support and in fluid connection with one another and with the tank. The device can be used for all types of biological analyses.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
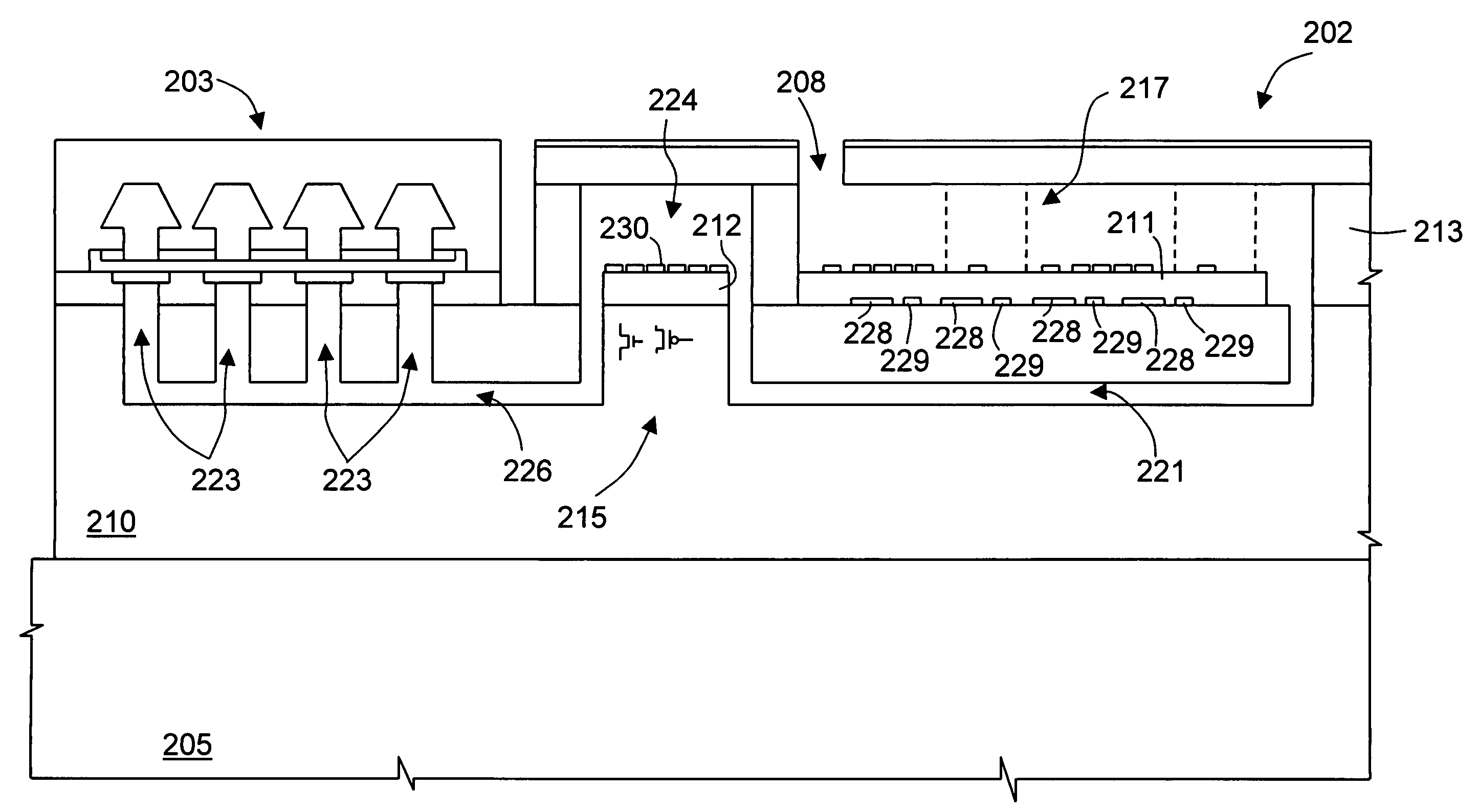
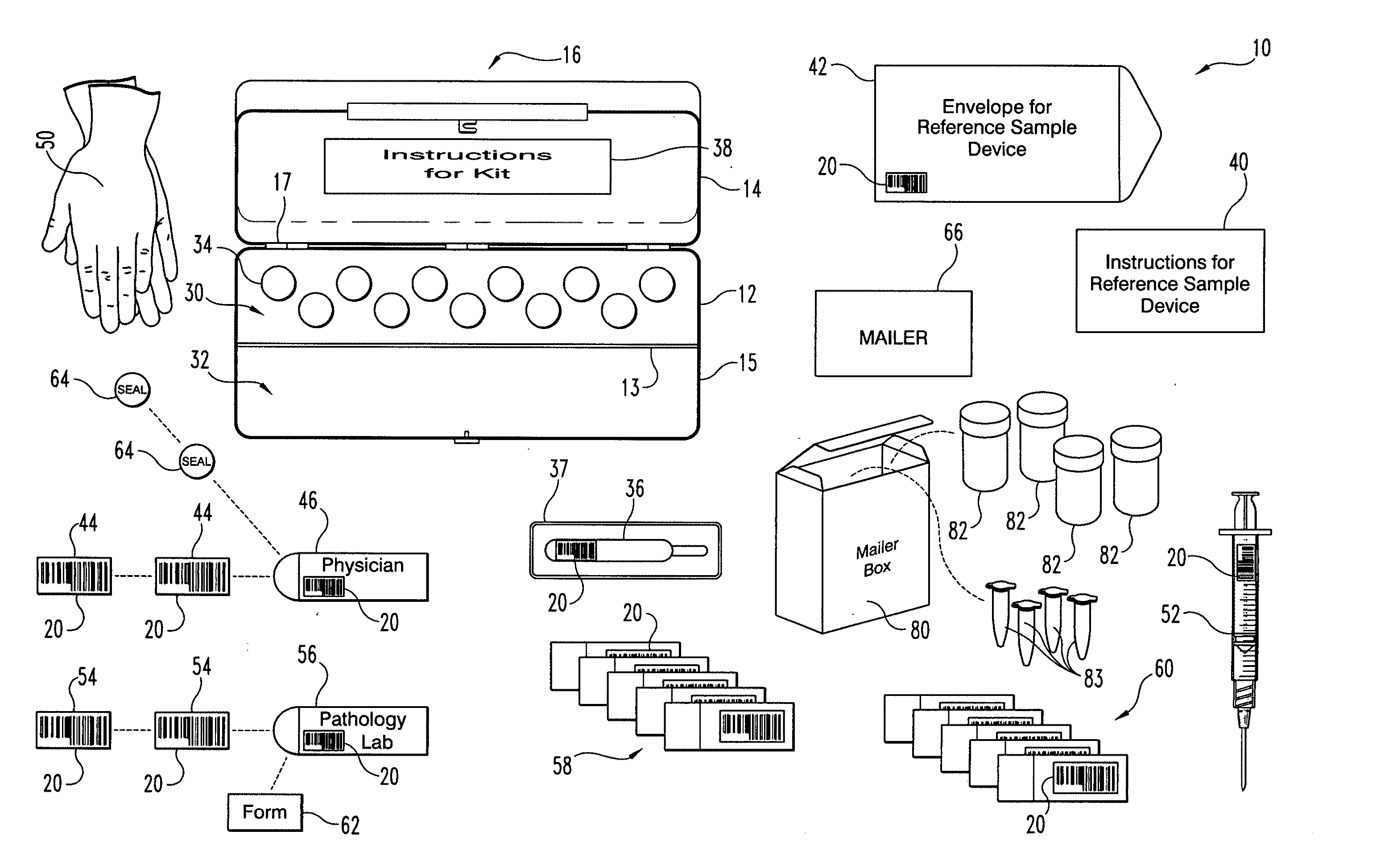
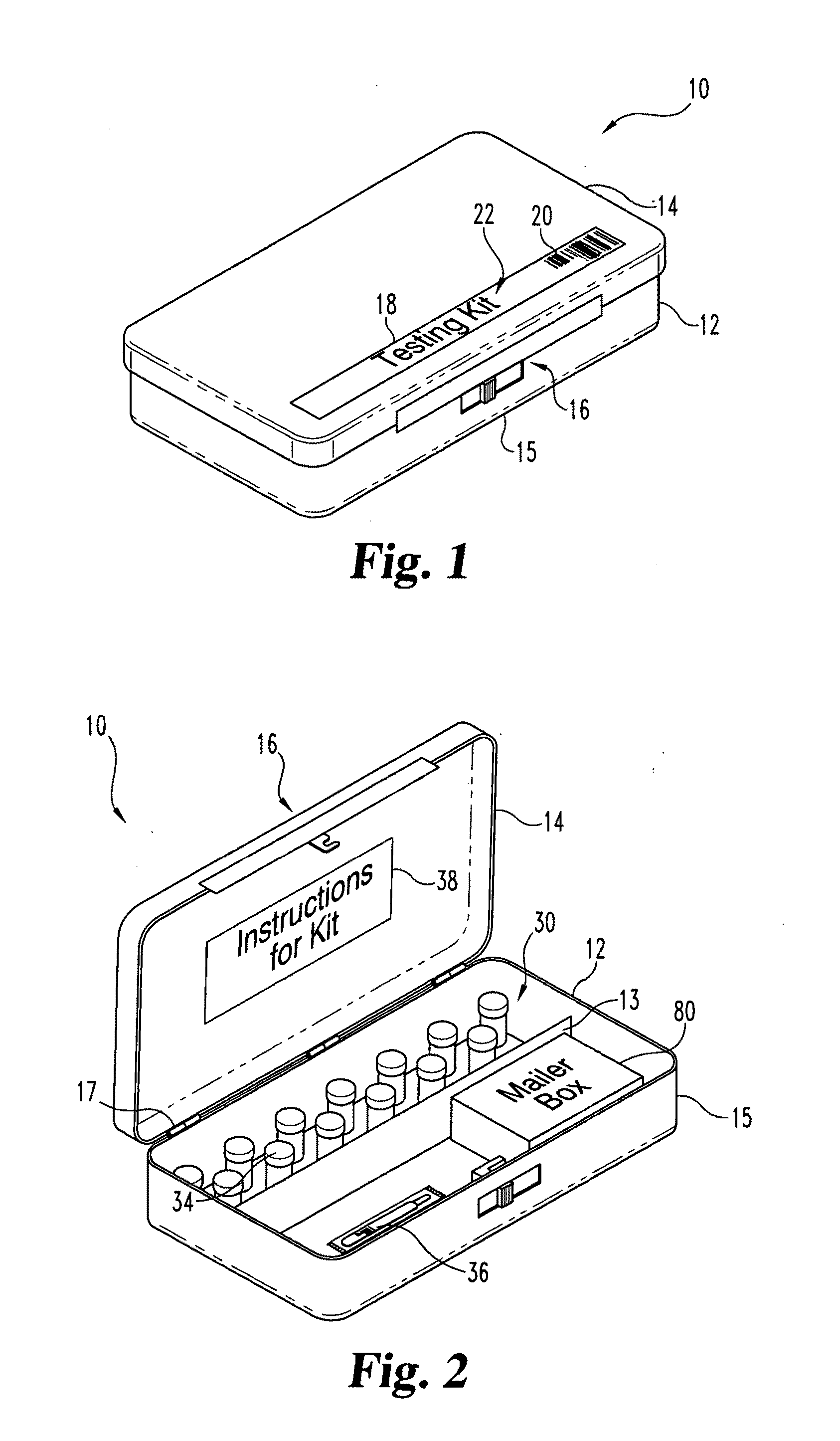
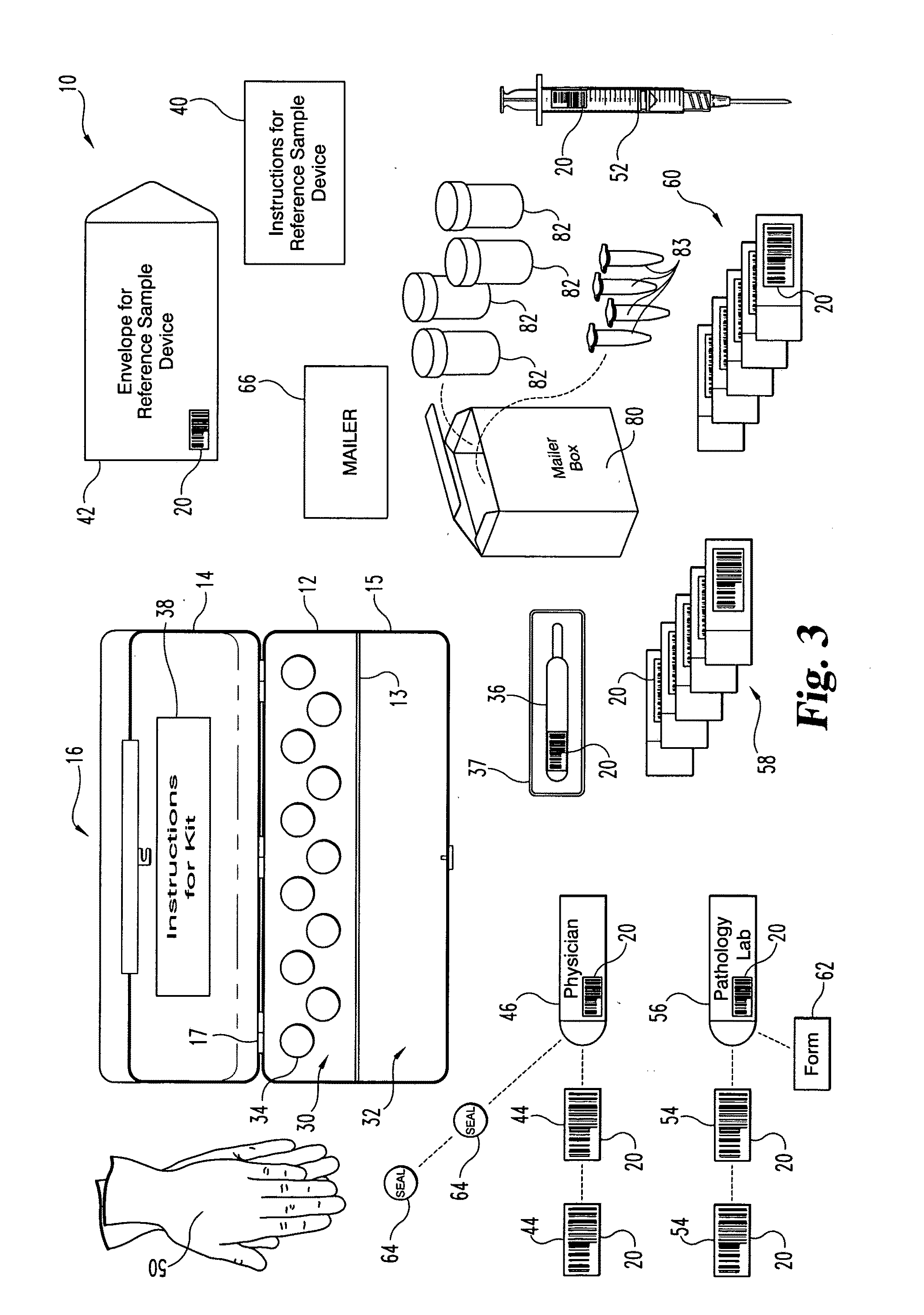
Method and apparatus to minimize diagnostic and other errors due to transposition of biological specimens among subjects
InactiveUS20120064515A2Burette/pipette supportsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyReference sample
A method and apparatus for minimizing diagnostic errors due to transposition of biological specimens among subjects provides for independent biometric confirmation that a given specimen is from a given donor. In certain embodiments, a biological specimen confirmation kit comprises a portable and openable case housing components of the kit, at least one biological specimen container adapted to receive a biological testing specimen from a donor, and at least one reference sample device adapted to receive a biological reference specimen from the same donor, such that the testing and reference specimens can later be compared for donor match verification by a reference verification entity.
Owner:STRAND DIAGNOSTICS
Evidence collection holder for sample automation
A device and method of securing the original biological specimen collection absorbent within a holder to permit use of the absorbent within automatic specimen analysis devices and to permit continuance of a chain of custody is provided.
Owner:BODE TECH GROUP
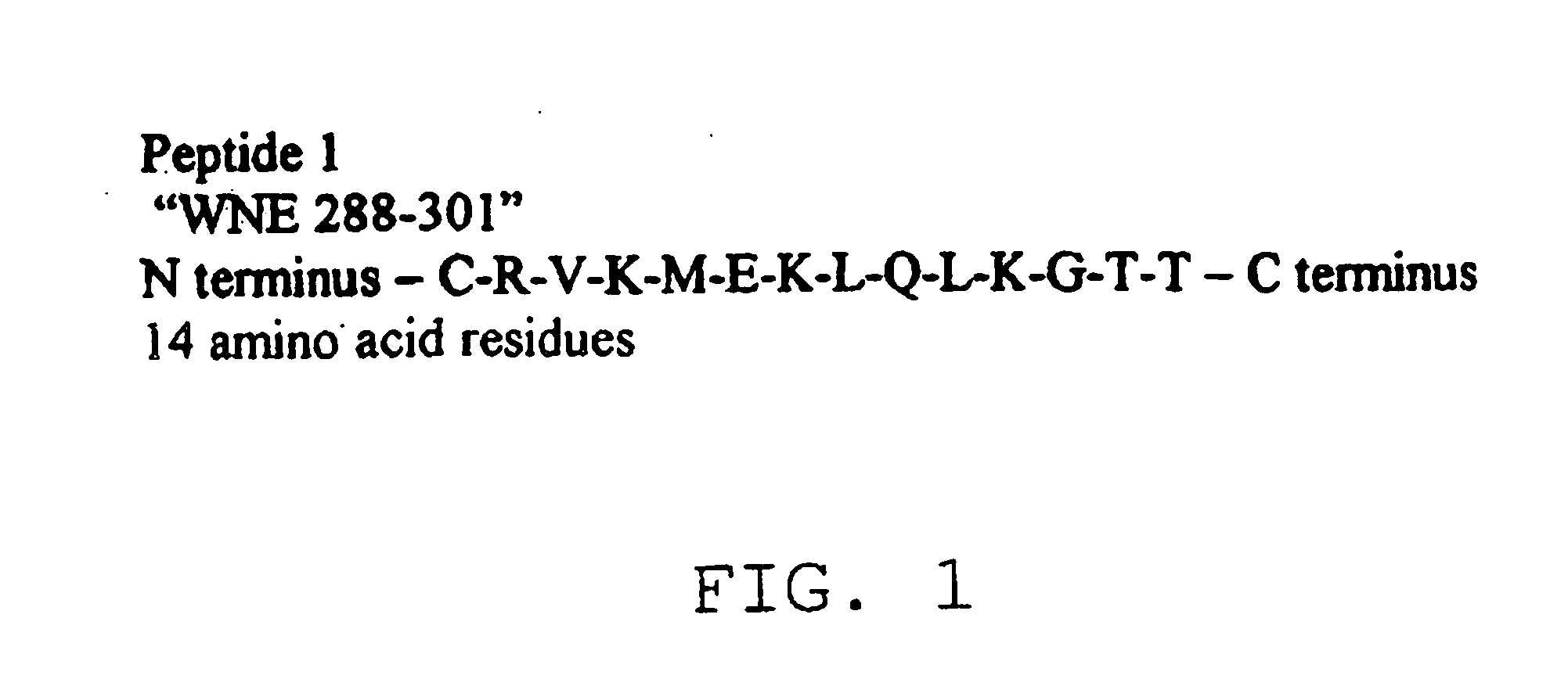
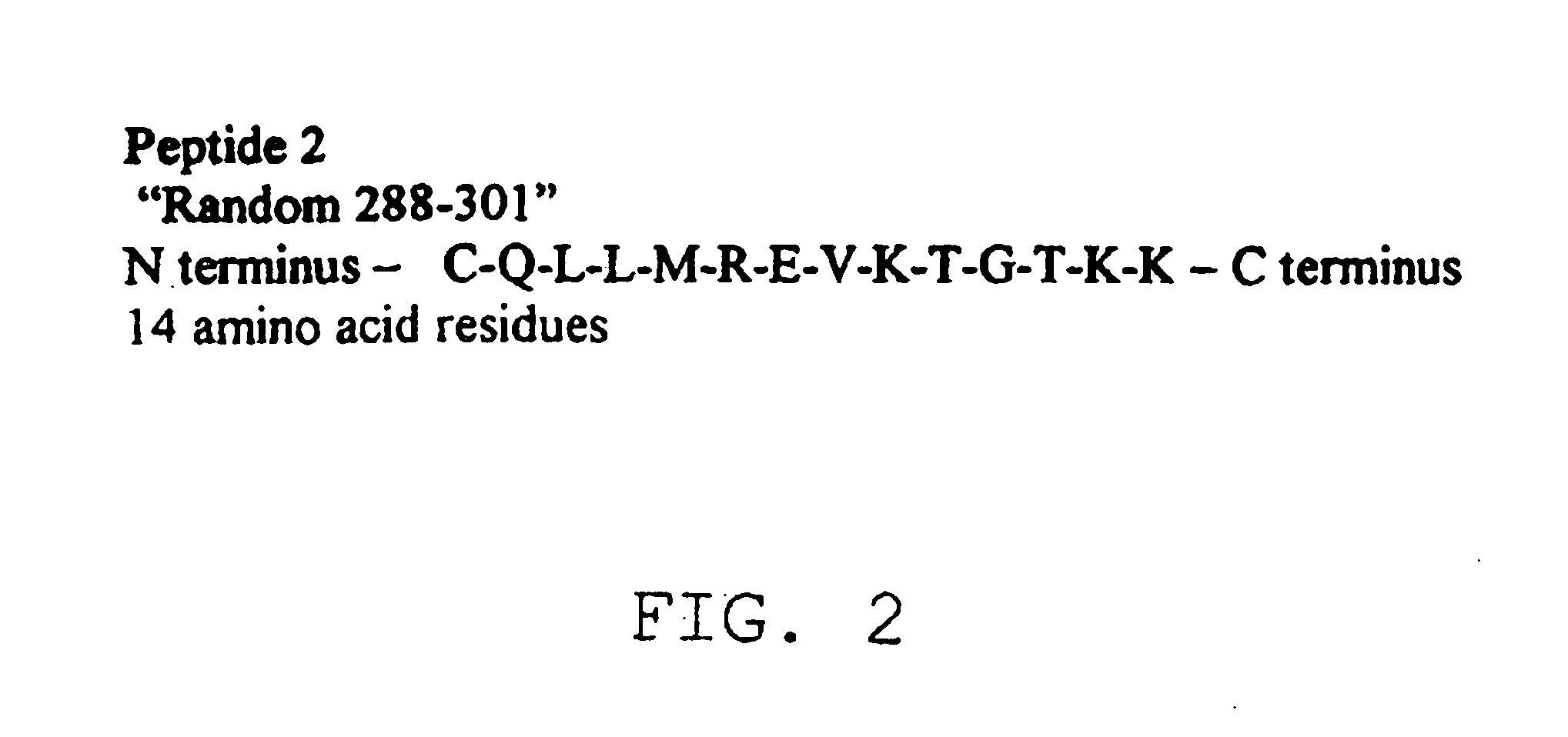
Diagnostic test for west nile virus
ActiveUS20060115896A1More sensitiveEasy to useAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic testFlavivirus
The present invention provides a rapid and sensitive method for the detection of a West Nile virus (WNV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), St. Louis encephalitis virus (SLEV) and Dengue virus (DENV) and antibodies directed against thereof involving contacting a biological specimen suspected of being infected with WNV, JE, SLE or DEN with a substantially purified and isolated WNV E glycoprotein or subfragment thereof having a native conformation wherein the E glycoprotein or subfragment thereof has a reactivity with antibodies against WNV and a cross-reactivity with antibodies against JEV, SLEV and DENV. The instant invention further provides a rapid, sensitive, and consistent method for the specific detection of WNV by employing diagnostic assays having the antigen NS5 which is specifically reactive with anti-WNV antibodies but not cross-reactive with antibodies against other flaviviruses such as JEV, SLEV, or DENV. The present invention also provides a rapid, sensitive, and consistent method for the specific detection of DENV by employing diagnostic assays having the antigen NS5 which is specifically reactive with anti-DENV antibodies but do not cross-react with antibodies against other flaviviruses such as JEV, SLEV, or WNV. Further, the DENV NS5 antigens are serospecific and do not cross react with antibodies to other DENV strains. Thus, the method of the present invention provides a manner by which to discriminate infections by each DENV strain. Further, diagnostic kits for carrying out the methods are provided. The methods and kits for carrying out the methods of the invention are rapid and require as little as 10 minutes to detect a result. The invention also provides monoclonal antibodies against WNV NS5 and DENV NS5 antigen and their use in detecting WNV and DENV infections in a biological sample.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
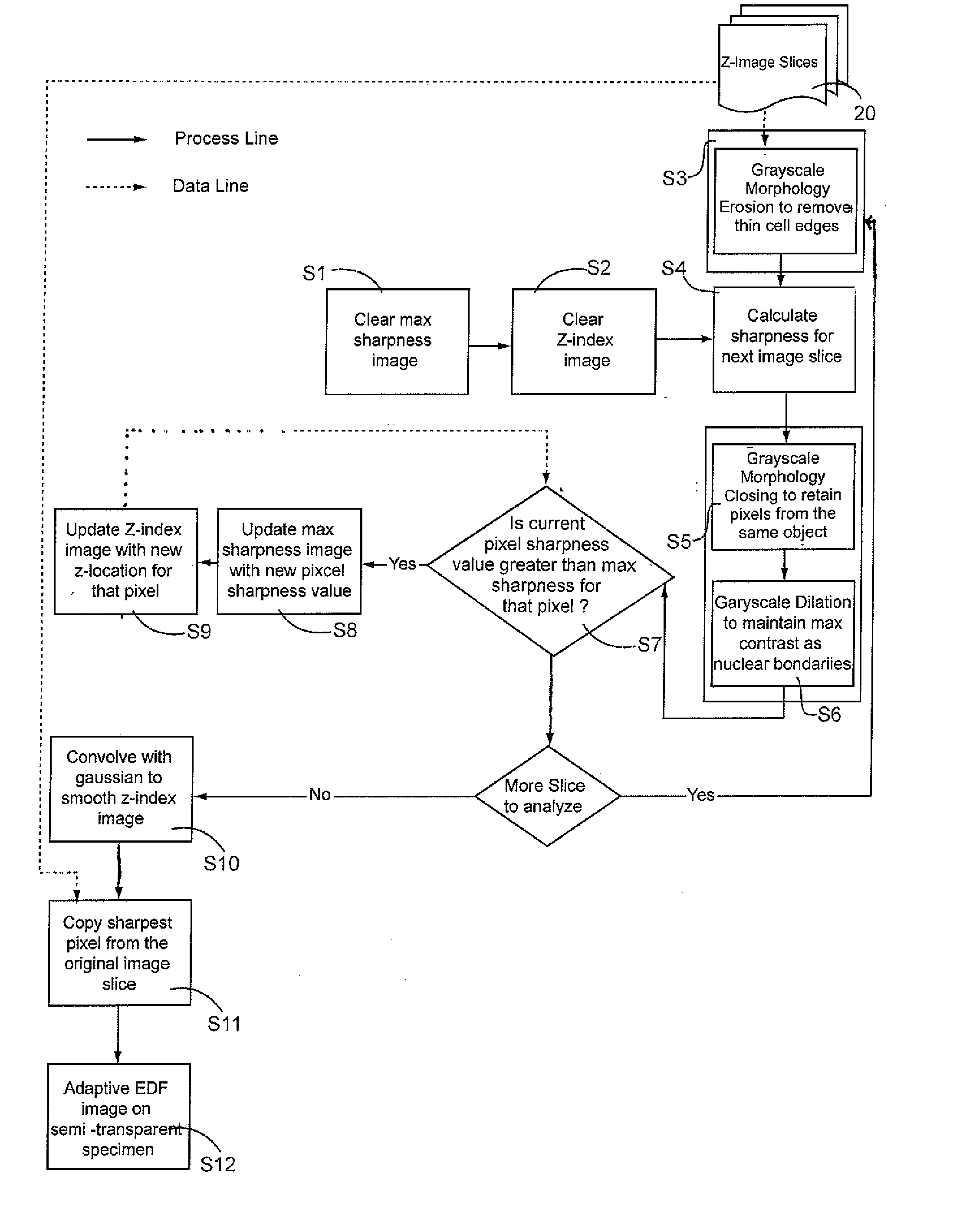
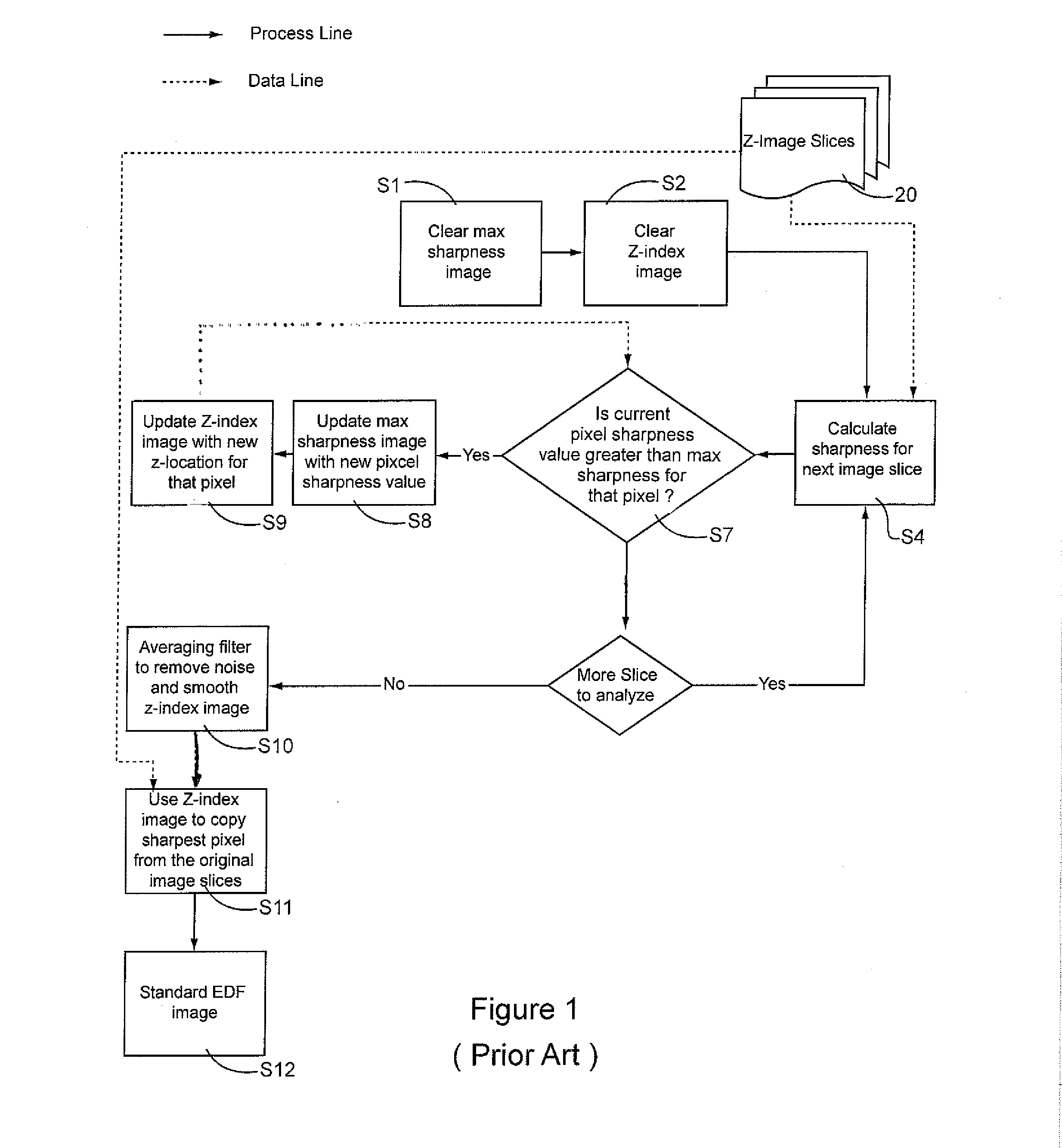
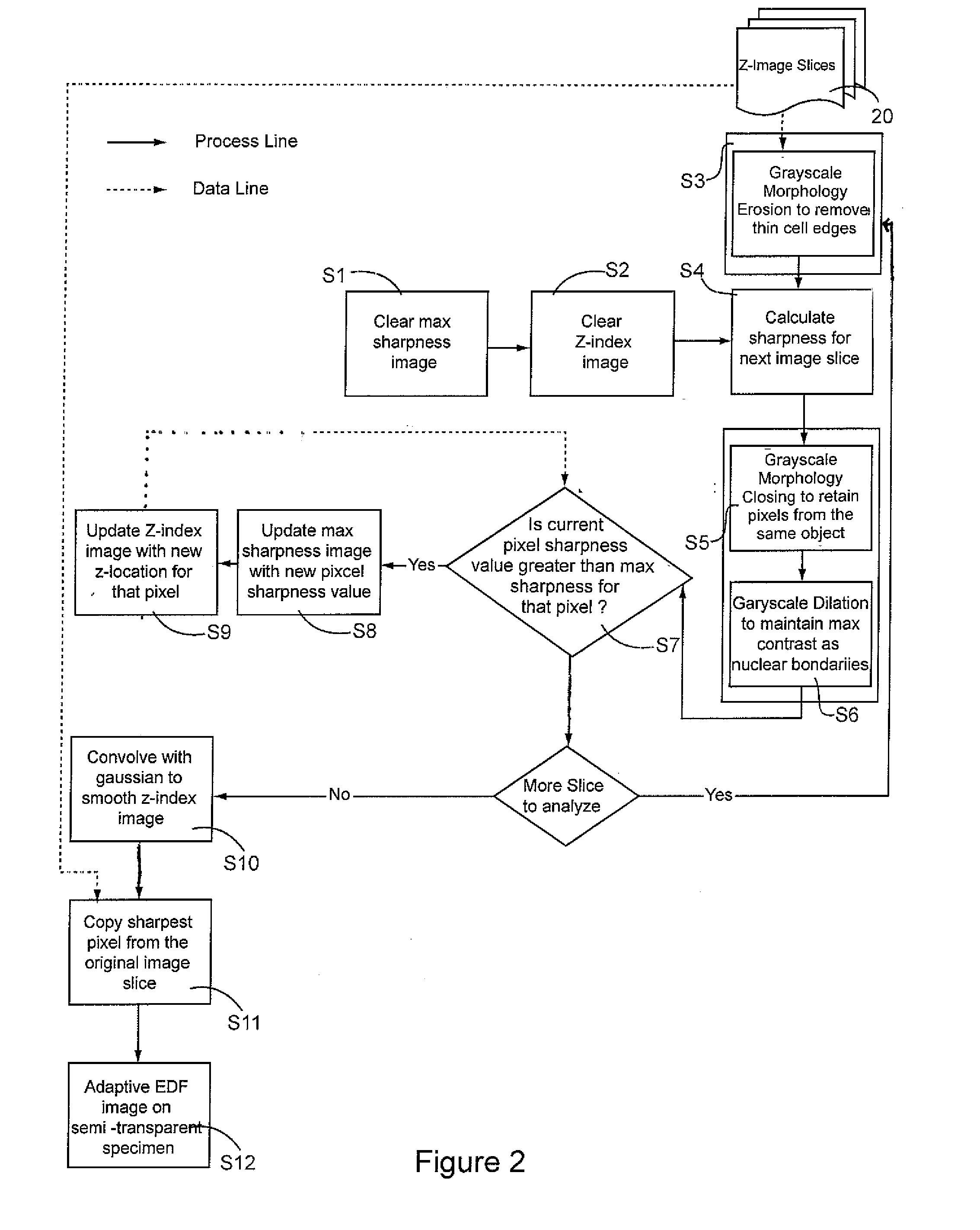
Feature Dependent Extended Depth of Focusing on Semi-Transparent Biological Specimens
A method and system for constructing a digital image of a three-dimensional biological specimen that displays diagnostically important information—substantially to the exclusion of unimportant information. The system de-enhances features in a cellular specimen which are not diagnostically important and enhances those which are The system selects the sharpest pixel for each pixel location from among a stack of image slices and copies them into a composite image
Owner:CDX MEDICAL IP INC
Assay for detection of human parvovirus B19 nucleic acid
Nucleic acid oligomers specific for human parvovirus B19 genomic DNA are disclosed. An assay for amplifying and detecting human parvovirus B19 nucleic acid in biological specimens is disclosed. Compositions for detecting the presence of parvovirus B19 genomic DNA in human biological specimens are disclosed.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Biological specimen collection/transport compositions and methods
ActiveUS8080645B2Easy to collectImprove transportAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCellular componentNuclease
Disclosed are compositions for collecting, storing, and transporting populations of nucleic acids from biological specimens, and clinical, forensic, or environmental samples. Also disclosed are methods for using these compositions as one-step formulations for killing pathogens, inactivating nucleases, and releasing polynucleotides from other cellular components within the sample, and stabilizing the nucleic acids prior to further processing or assay. In particular embodiments, the invention provides a single, one-step, sample collection / transport / storage formulation containing a known quantity of a non-genomic, nucleic acid carrier molecule that serves as an internal reference control to monitor the fidelity of the collection / transportation medium, and measure the integrity of nucleic acids subsequently isolated and purified from the processed sample.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
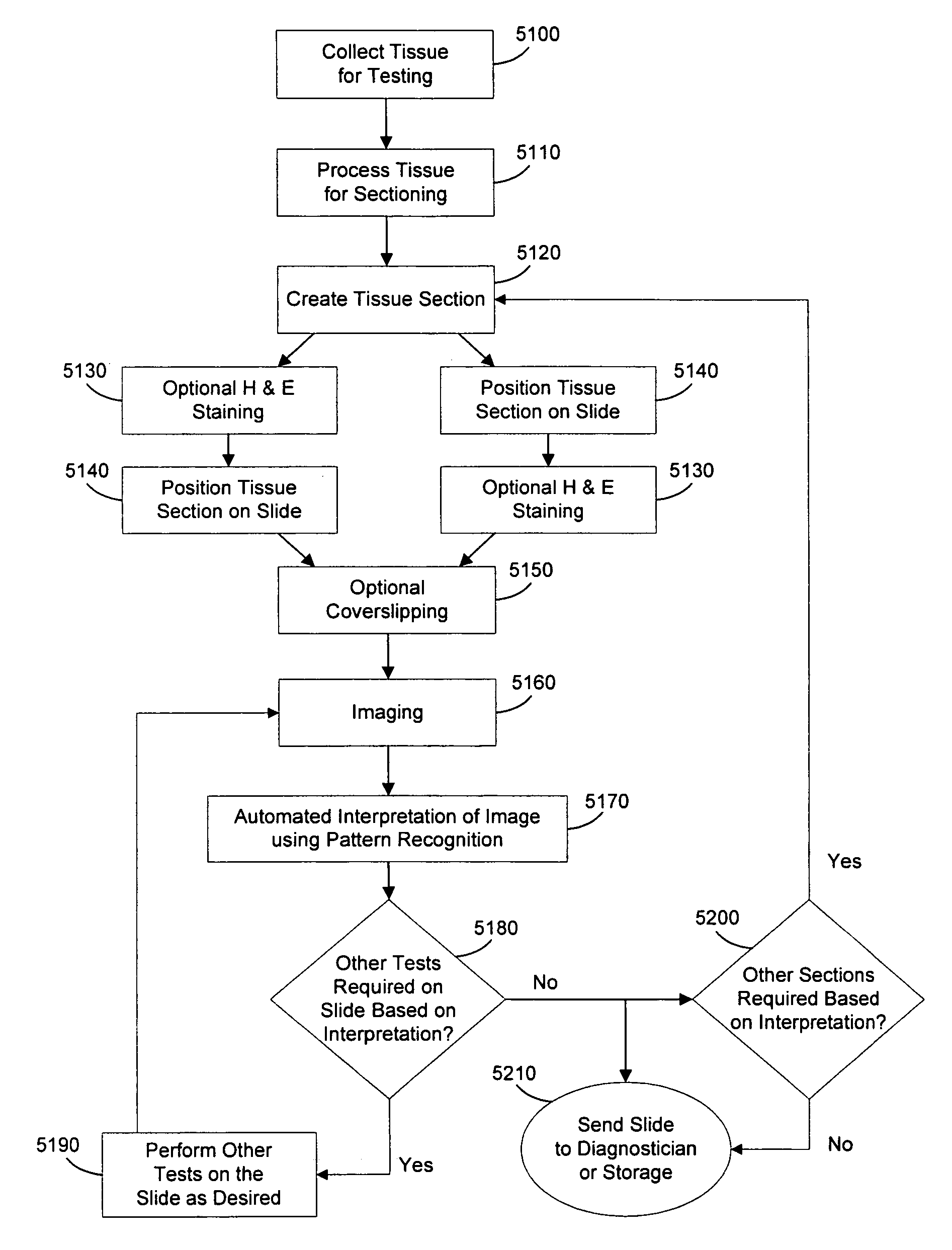
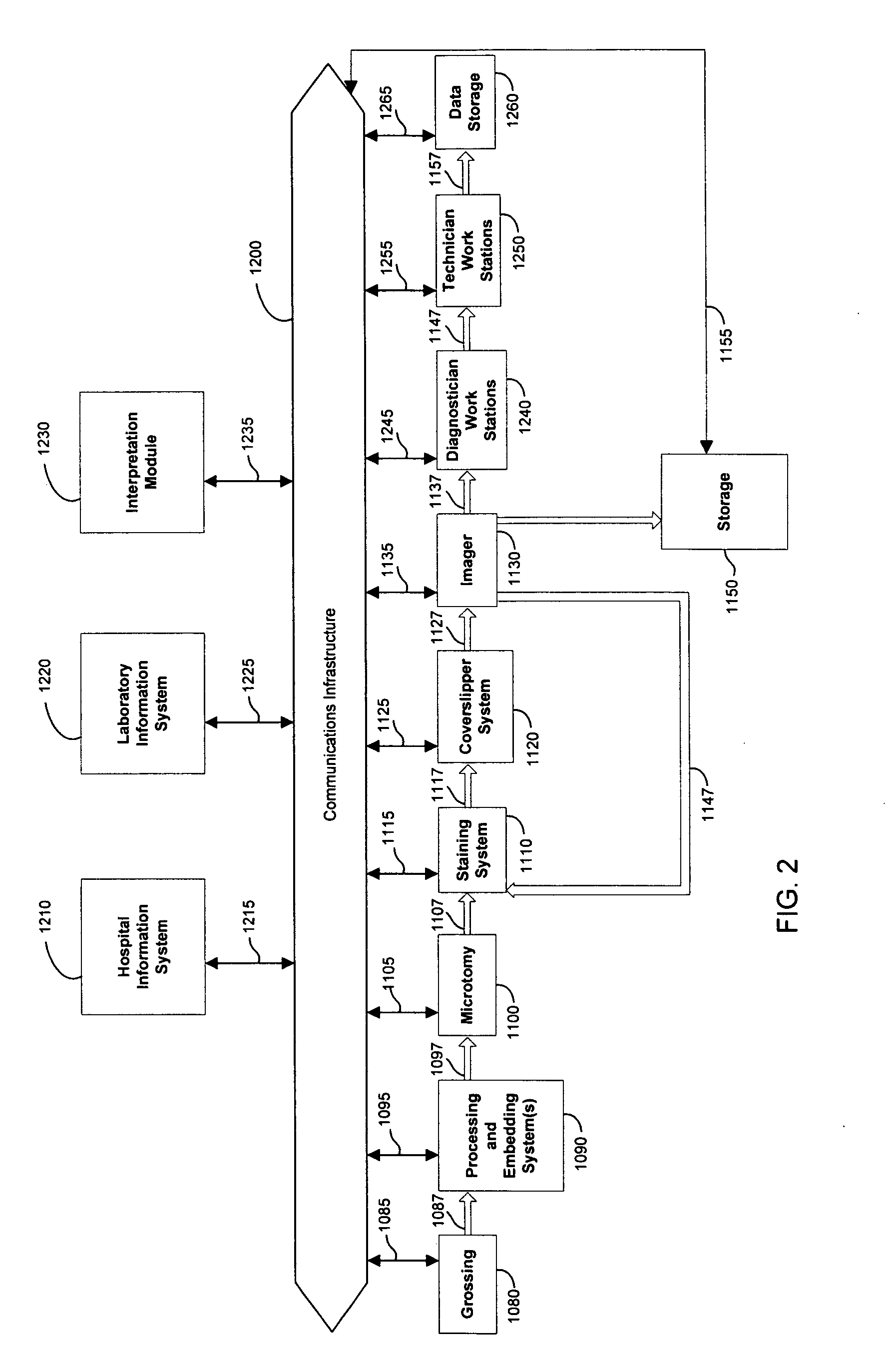
Automated system of processing biological specimens and method
ActiveUS7657070B2Reduce disadvantagesSamplingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDigital imaging
An automated laboratory slide management and interpretation system and method in which slides are stained and then digitally imaged and the images are interpreted prior to referral to a diagnostician or placement in storage. The interpretation of the images involves the application of pattern recognition principles to compare the digitized images to known sample patterns from a variety of sources. Additionally, based on the results of the interpretation, the slide may undergo additional testing or staining, and additional samples may be prepared and tested. The specimens may be delivered to the diagnostician along with a tentative diagnosis.
Owner:SAKURA FINETEK U S A
Compositions and method for rapid, real-time detection of influenza A virus (H1N1) swine 2009
ActiveUS8097419B2Rapid detection and identificationMinimize and eliminate contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsH1n1 virusNucleic Acid Probes
Disclosed are oligonucleotide amplification primers and detection probes specific for the amplification and detection of pathogenic organisms, including for example, specific Influenza A H1N1 viral isolates. Also disclosed is a biological organism identification kit including the disclosed nucleic acid probes and primers, as well as thermal cycling reagents that is both portable and durable, and may also be self-contained for remote, or in-field analysis and identification of particular influenza isolates from a variety of biological specimen types.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com