Paddy rice gene of synthetase of coded beta - keto acyl coenzyme A
A technology of ketoacyl coenzyme and synthetase, which can be used in genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, recombinant DNA technology, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
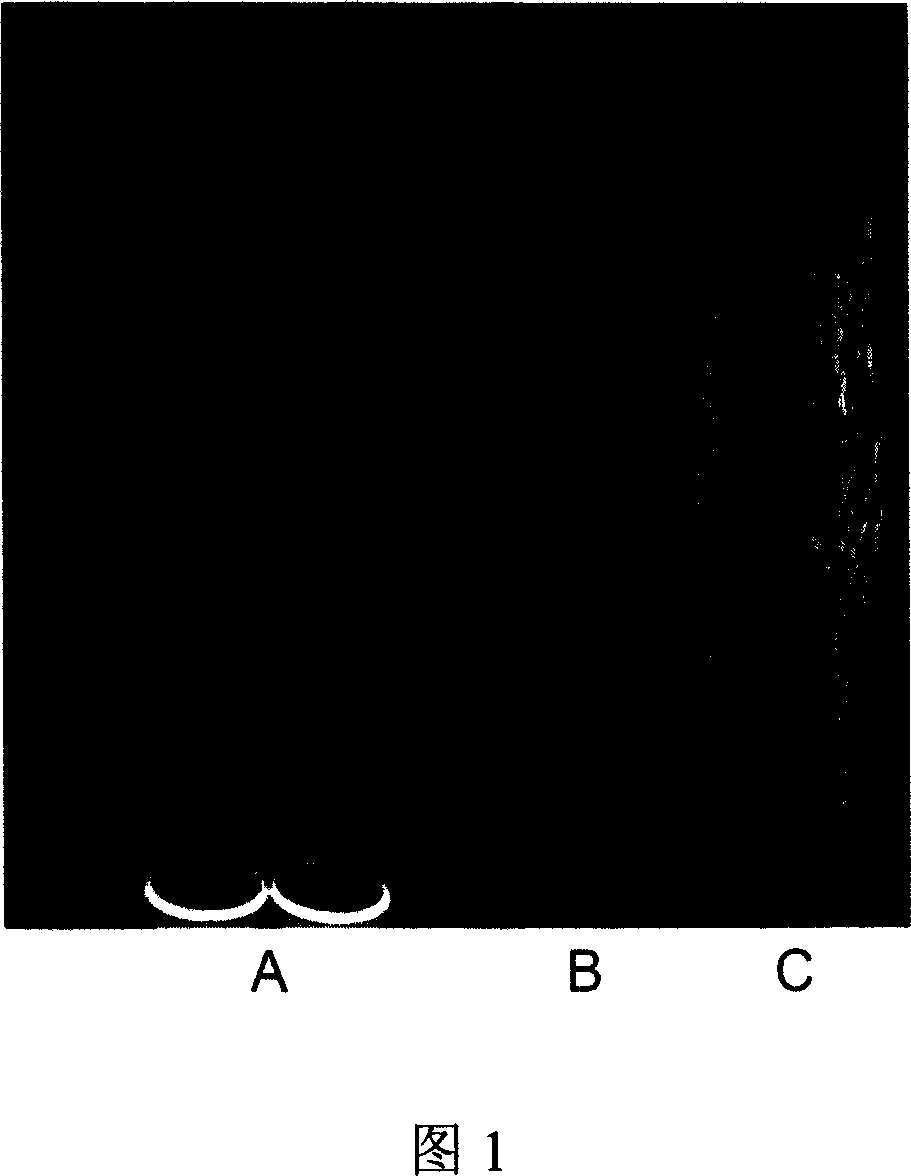
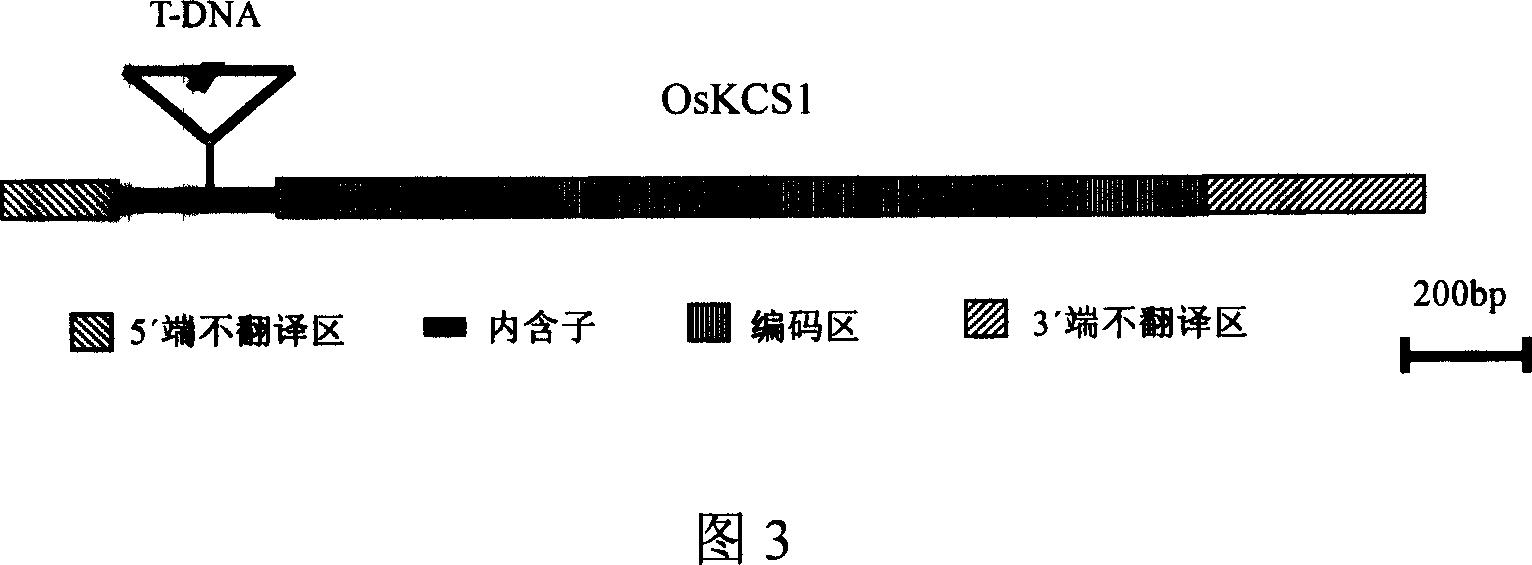
[0041] Example 1: Obtainment of Nipponbare T-DNA insertion mutant P1424
[0042] Rice mutant P1424 was obtained by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (Hiei, et al., 1994). The specific method is as follows:
[0043] 1. Induction of Rice Callus
[0044] Get mature paddy rice (Nipponbare) seeds (International Rice Research Institute, IRRI), shell, with 70% ethanol treatment 1-2min, 0.1% mercuric chloride treatment 15-20min, sterilized deionized water wash 4-6 times . After the surface moisture was blotted by sterile filter paper, inoculate into NB containing 2mg / L 2,4-D (Fluka Company) 0 On the culture medium (see attached table 1 for specific components), seal with parafilm membrane, and culture in dark in an incubator at 25°C to induce embryogenic callus. After 7-10 days, the callus induced by the scutellum was stripped and subcultured on the same medium. After dark culture in an incubator at 25° C. for about 20 days, vigorously growing embryogenic calli th...
Embodiment 2
[0054]Example 2: Genetic Analysis of Mutant P1424
[0055] The mutant phenotypes of transgenic rice plants are not all caused by T-DNA insertions (An et al., 2005), so it is necessary to confirm whether the mutant phenotypes and T-DNA insertions co-segregate through genetic analysis.
[0056] 1. Extraction and quantification of rice genomic DNA
[0057] Rice DNA extraction was performed as described by Dellaporta et al. (Malmberg et al., 1985). Specific steps are as follows:
[0058] (1) Take 3-5g of fresh rice leaves, quick-freeze in liquid nitrogen, quickly grind them into powder in a mortar, and transfer them to a 50ml centrifuge tube;
[0059] (2) Immediately add 20ml of extraction buffer preheated to 65°C (1M Tris-HCl (pH8.0) 100ml / L, 0.5M EDTA (pH8.0) 100ml / L, 5M NaCl 100ml / L, 10% SDS 125ml / L, β-mercaptoethanol 1.5ml / L), in a water bath at 65°C for 30min;
[0060] (3) Add 7.5ml of 5M potassium acetate, mix gently by inversion, place on ice for 20min, centrifuge at 40...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: T-DNA insertion site analysis
[0072] T-DNA is randomly inserted into genomic DNA. The insertion site of T-DNA in mutant P1424 was determined by thermal heterogeneous interleaved polymerase chain reaction (TAIL-PCR) method (Liu et al., 1995). The three specific primers in the TAIL-PCR reaction are:
[0073] SP1: 5'-GGTGACCAGCTCGAATTTCCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 9)
[0074] SP2: 5'-TGAATCCTGTTGCCGGTCTTG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 10)
[0075] SP3: 5'-GCGCGCGGTGTCATCTATGT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 11)
[0076] The random primer was AD4: 5'-TG(A / T)GNAG(A / T)ANCA(G / C)AGA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 12). Amplification was performed using P1424 genomic DNA as a template, and the amplification procedure was referred to the literature (Liu et al., 1995). The amplified product was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, and a specific amplification band of about 800 bp was recovered with a gel extraction kit (Shenergy Gaming Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and connected to the pGEM-T easy vector (Promega Company...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com