Patents
Literature
46 results about "Protein Artemis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein artemis (692 aa, ~78 kDa) is encoded by the human DCLRE1C gene. This protein is involved in nuclease activity that modulates both DNA repair and V(D)J recombination.
Coding sequence of AaMYBL1 protein of artemisia apiacea and application thereof
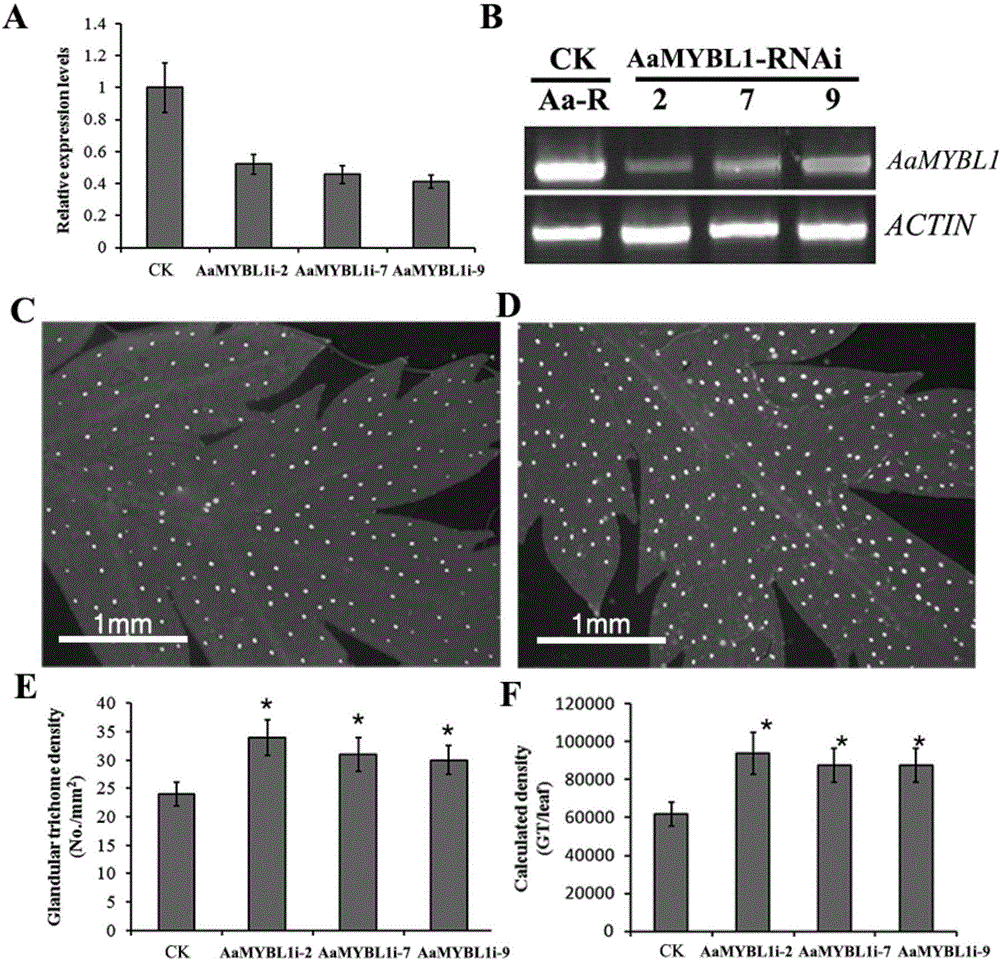
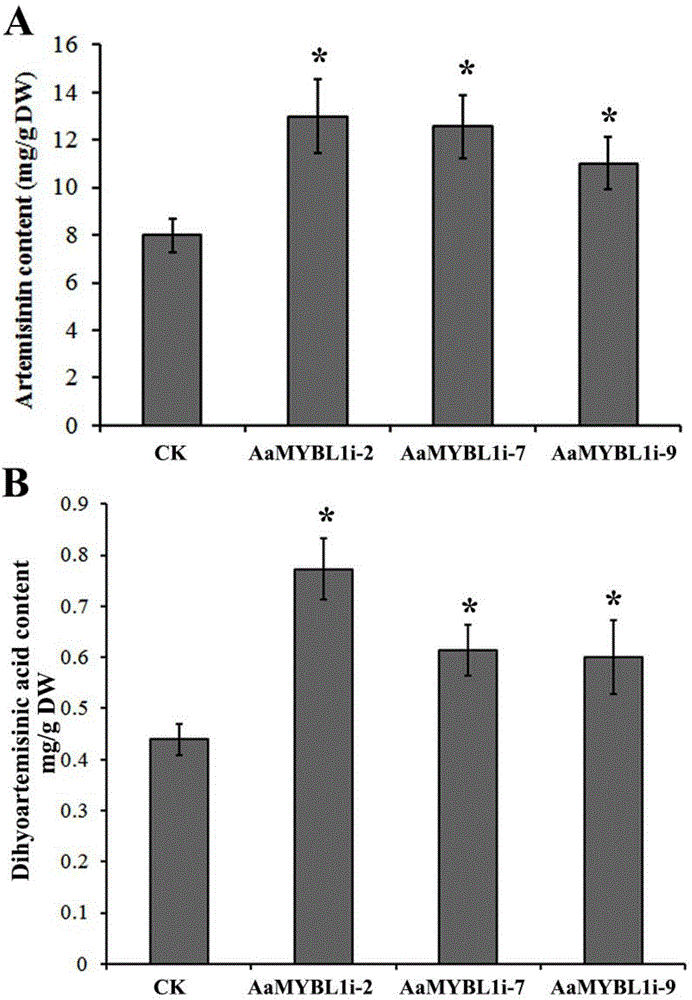
The invention relates to a coding sequence of an AaMYBL1 protein of artemisia apiacea and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence coded by the coding sequence AaMYBL1 of an MYB-like type transcription factor of artemisia apiacea is shown as SEQ ID NO:4. The AaMYBL1 which codes a R3MYB type transcription factor takes part in regulation of density of glandular hairs of artemisia apiacea. An interference vector of the AaMYBL1 transcription factor of artemisia apiacea is transformed into artemisia apiacea by means of the transgenic technology, so that the density of the glandular hairs on the surface of artemisia apiacea can be effectively regulated, thus, the content of artemisinin is improved. The density of the glandular hairs on the surface of a blade of non-transgenic common artemisia apiacea is 24 / square millimeter, and the density of the glandular hairs of a blade of transgenic artemisia apiacea inhibiting AaMYBL1 genetic expression is increased to 34 / square millimeter; the quantity of total glandular hairs of each blade is increased from 61947 to 93683; correspondingly, the content of artemisinin is improved from 8mg / g DW of non-transgenic artemisia apiacea to 12mg / g DW. The coding sequence provided by the invention is of significance for providing a high-yield stable novel medicine source for scaled production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
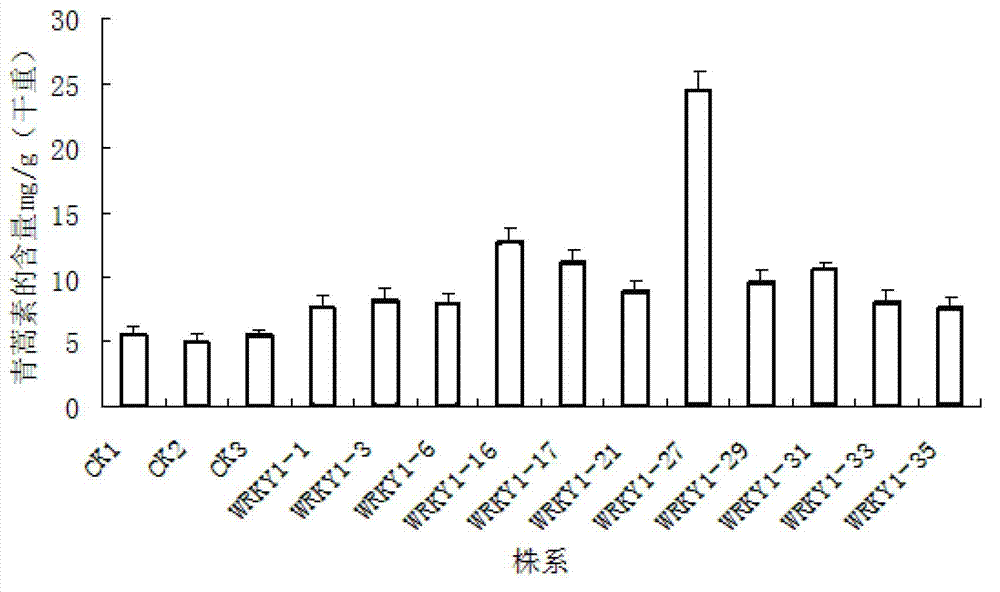
Method for increasing artemisinin content of sweet wormwood by transferring AaWRKY1 gene
InactiveCN102776225AIncrease artemisinin contentIncrease contentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein ArtemisBiology
The invention discloses a method for increasing artemisinin content of sweet wormwood by transferring AaWRKY1 gene. The method includes the steps of cloning WRKY type transcription factor AaWRKY1 gene in sweet wormwood; constructing a plant expression vector containing the AaWRKY1; introducing the AaWRKY1 gene into the sweet wormwood to regrow a plant under mediation of Agrobacterium Tumefaciens; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to detect integration status of the foreign target gene AaWRKY1; measuring the content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood by efficient liquid chromatography and an evaporative light scattering detector, and screening to obtain the plants of sweet wormwood with artemisinin content increased. The content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood with the AaWRKY1 gene is increased to 24.59mg / g DW by the method and is 4.44 times of that of the non-transgenic sweet wormwood. The method provides new high-yield and stable drug sources for large-scale production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving artemisinin content in artemisia annua L through transferring allene oxide cyclase (AOC) gene
InactiveCN102242145AIncrease contentStable new drug sourcesGenetic engineeringFermentationProtein ArtemisTransgene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for improving artemisinin content in artemisia annua L through transferring allene oxide cyclase (AOC) gene. The method is characterized by: cloning the AOC gene from the artemisia annua L; constructing a plant expression vector containing the AOC gene; transferring the AOC gene into the artemisia annua L through adopting agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation, and regenerating plants; detecting integration situations of the exogenous target gene AOC through PCR, detecting the artemisinin content in the transgenic artemisia annua L through a high performance liquid chromatography and a evaporative light scattering detector; carrying out screening to obtain the transgenic artemisia annua L plants with improved artemisinin content. The artemisinin content in the transgenic artemisia annua L provided by the present invention is substantially improved, the artemisinin content in the non-transformed normal artemisia annua L is 1.53 mg / gDW while the artemisinin content in the AOC-transferred artemisia annua L is up to 10.17 mg / gDW, such that the artemisinin content in the AOC-transferred artemisia annua L is 6.65 times as much as the artemisinin content in the non-transformed artemisia annua. Therefore, with the present invention, a method for improving the artemisinin content in the artemisia annua L t is provided, base for producing the artemisinin on a large scale through the transgene is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. by DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene transfer
InactiveCN102604987AIncrease contentStable new drug sourcesGenetic engineeringFermentationProtein ArtemisGene transfer
The invention provides a method for improving an artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. by DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene transfer. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene in the Artemisia annua L., so as to establish a plant expression carrier containing the DXR gene; transferring the DXR gene into Artemisia annua L. through agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation to grow a plant; detecting the integration condition of the exogenous target gene DXR by a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); detecting the artemisinin content in the transgenic Artemisia annua L. through high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD); and screening the transgenic Artemisia annua L. plant with improved artemisinin content. The artemisinin content of the transgenic Artemisia annua L. obtained by the invention is obviously improved and high up to 2.4 times that of the non-transferred plant. Therefore, the invention provides the method for improving the artemisinin content in the Artemisia annua L. and lays a foundation for producing artemisinin by using the transgenic Artemisia annua L. in a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
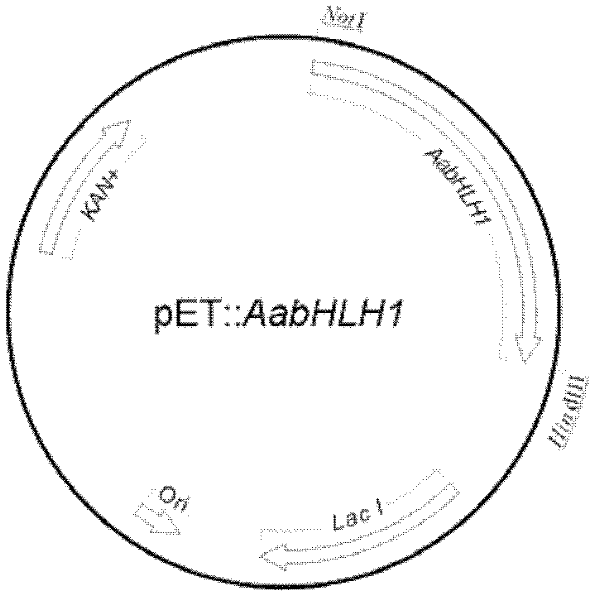
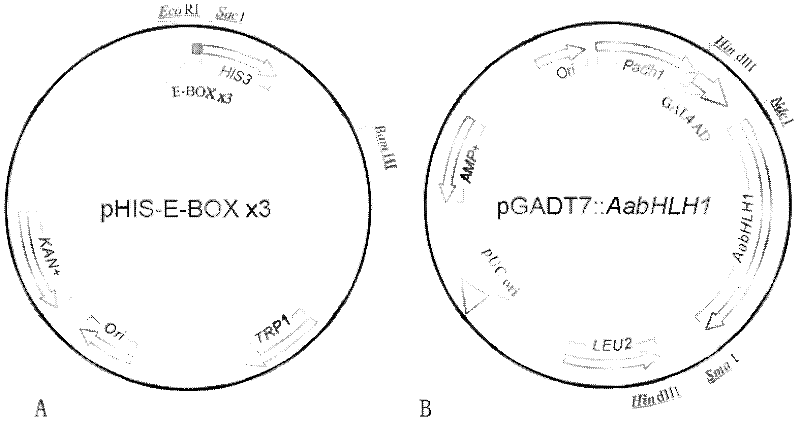
Artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102372769AConducive to large-scale industrial productionHigh expressionFungiBacteriaSynthesis methodsRaw material
The invention discloses an artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor provided by the invention is protein shown as a) or b): a) protein which consists of amino acid sequences and is shown in sequences 2 in a sequence table; and b) protein which is derived from a), is formed through substituting and / or deleting and / or adding amino acid sequences shown by the sequences 2 in the sequence table through one or a plurality of amino acid residues and is relevant to the artemisinin synthesis. The bHLH transcription factor is instantaneously translated into artemisia apiacea plants to be overexpressed, the expression quantity of the key enzyme in regulated and controlled artemisinin biosynthetic metabolism is greatly improved, and the artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor can be used for producing artemisinin. The regulated and controlled artemisinin synthesis method solves the problem of raw material limitation, has a simple production process and is favorable for the large-scale industrial production of the artemisinin.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Method of utilizing the pts gene and RNA interference of the ads gene to increase patchouli alcohol content in artemisia annua l.
InactiveUS20110300546A1Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcohol contentTerra firma
The invention relates to a method of utilizing the pts gene and RNA interference of the ads gene to increase patchouli alcohol content in Artemisia annua L. plants. Using transgenic Artemisia annua L. plants, the method of the invention consistently increases the patchouli alcohol content in those plants, thus laying down a solid foundation for large-scale production of patchouli alcohol and other secondary metabolites such as terpenes other than artemisinin.
Owner:FIRMENICH AROMATICS (CHINA0 CO LTD
Production method of high-artemisinin-content transgene sweet wormwood plants
InactiveCN102776212AIncrease contentIncrease artemisinin contentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyProtein Artemis
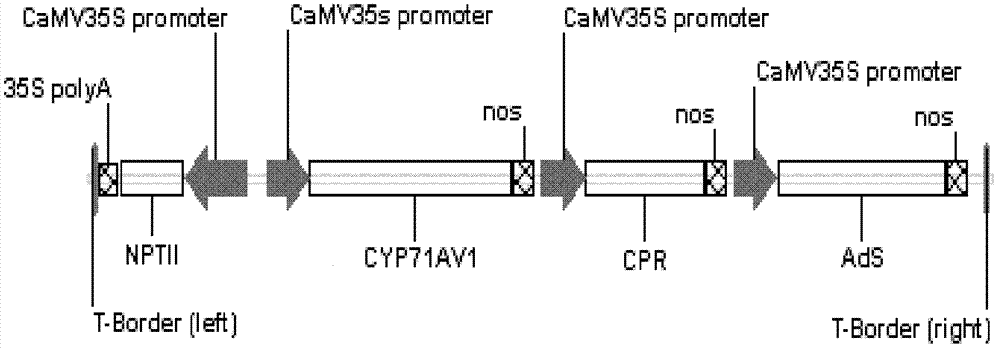
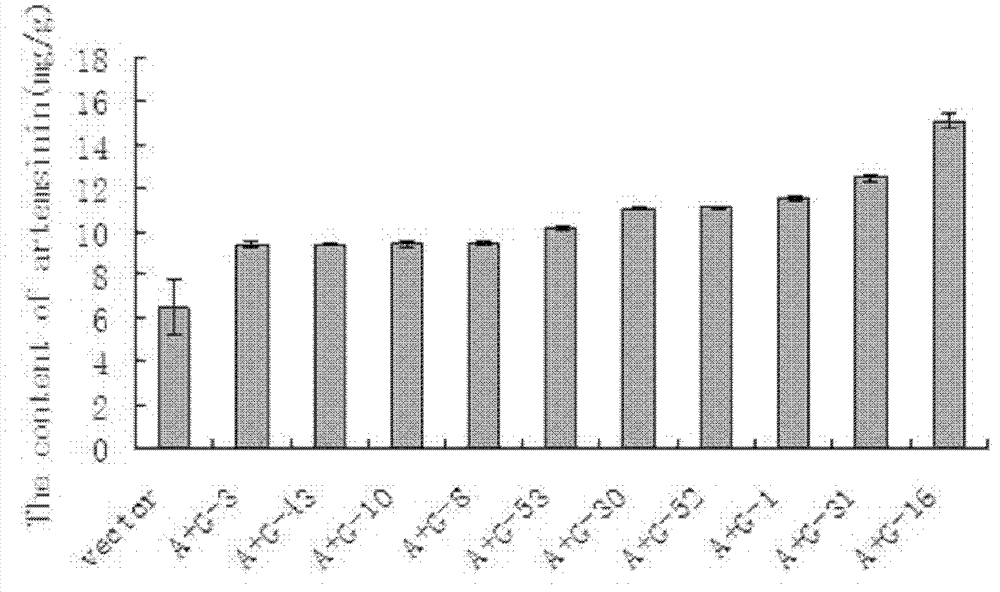
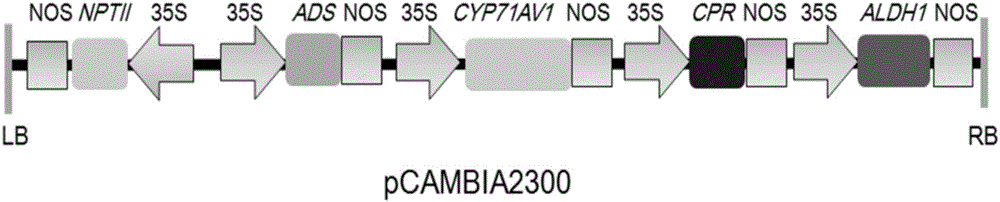
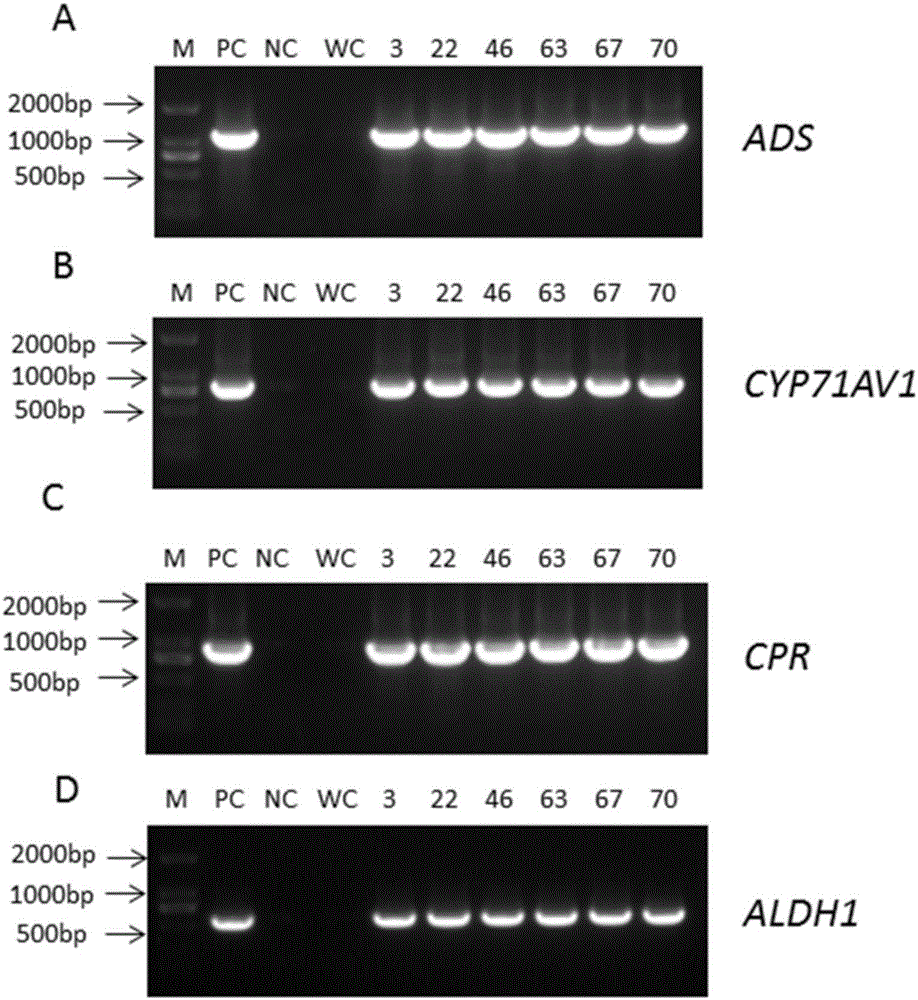
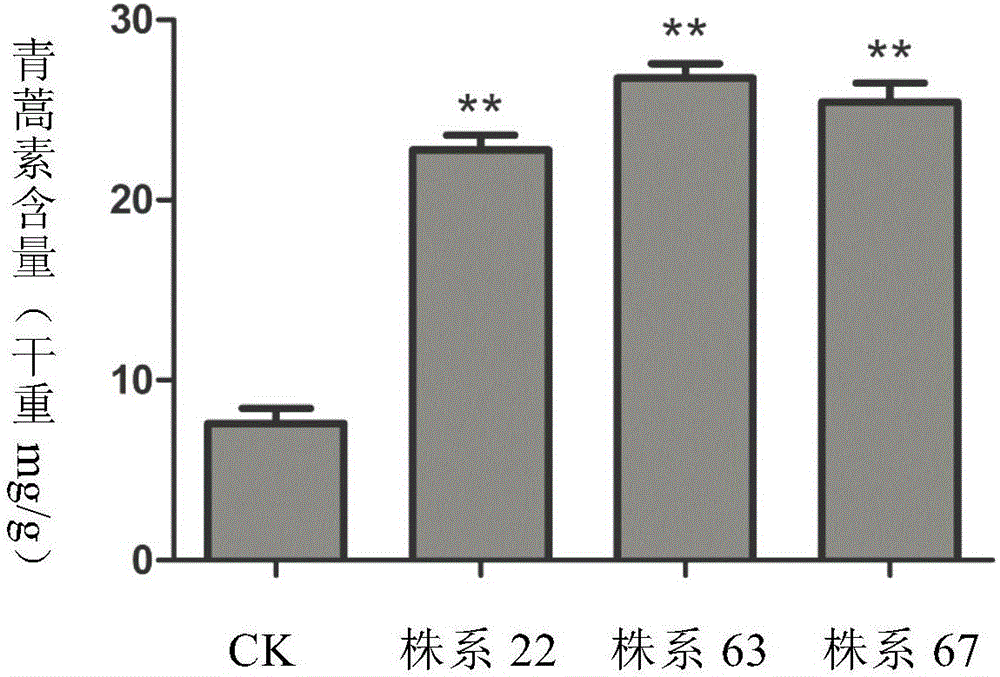
The invention relates to a production method of high-artemisinin-content transgene sweet wormwood plants in the biological technical field. The production method comprises the following steps that three genes including ADS, CYP71AV1 and CPR are cloned from sweet wormwoods, plant expression carriers containing the ADS, CYP71AV1 and CPR genes are built, agrobacterium tumefaciens are used for mediating, the ADS, CYP71AV1 and CPR genes are transferred into the sweet wormwoods, in addition, the plants are regenerated, the screening is carried out, and the transgene sweet wormwood plants with the improved artemisinin content are obtained. When the uninverted ordinary artemisinin content is 6.43mg / g DW, the artemisinin content in the obtained transgene sweet wormwood plant system is as high as 15.09 mg / g DW, and is 2.35 times of the content in the uninverted ordinary artemisinin. The method has the important significance on providing high-yield and stable new medicine sources for the large-scale production of the artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nucleotide sequences encoding enzymes in biosynthesis of dihydroartemisinic acid
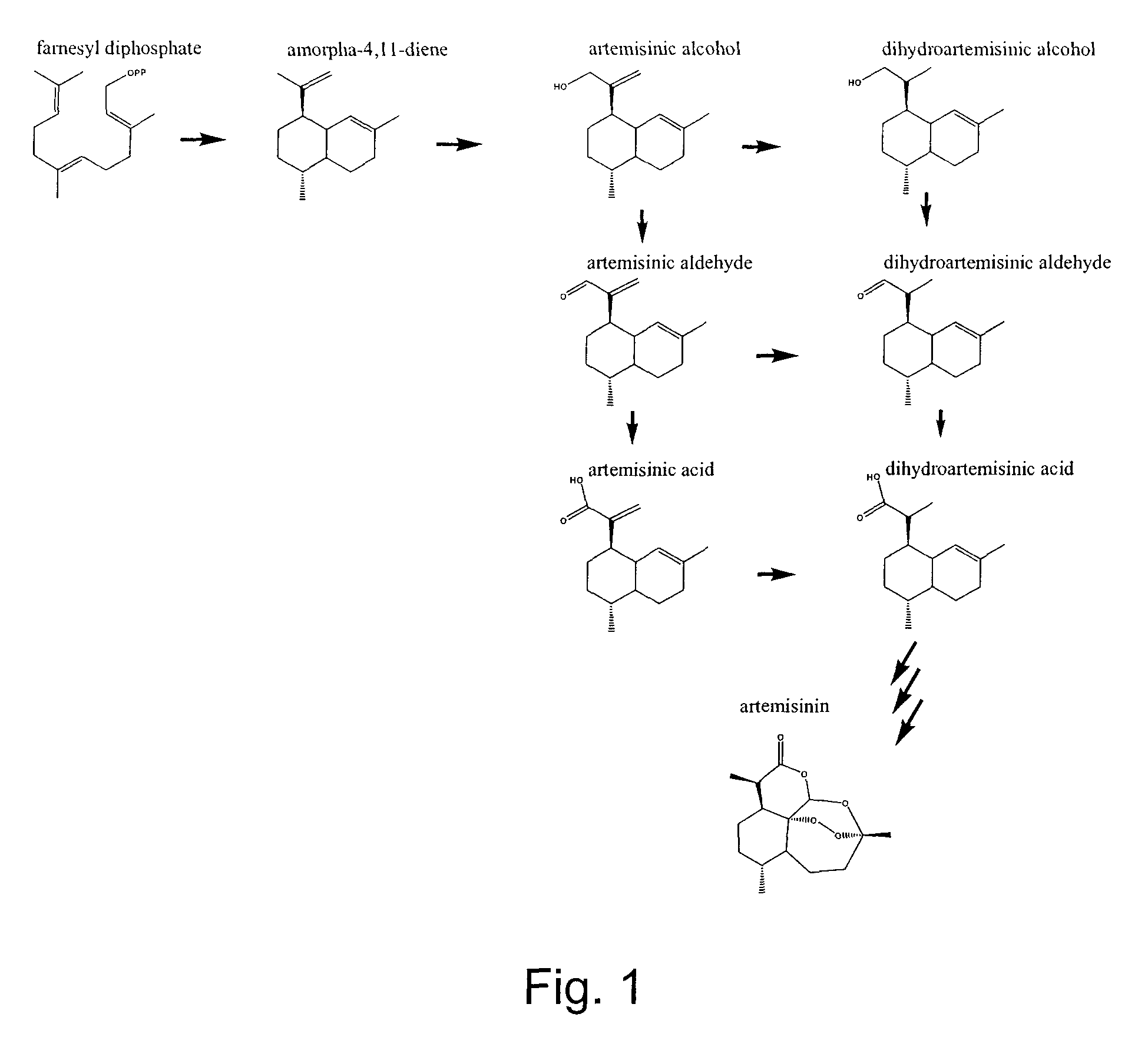
InactiveUS8207402B2Reduce in quantitySimple processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideProtein Artemis
Isolated nucleic acid molecules cloned from Artemisia annua encode artemisinic aldehyde double bond reductase and artemisinic / dihydroartemisinic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Artemisinic aldehyde double bond reductase enzymatically reduces artemisinic aldehyde to dihydroartemisinic aldehyde. Artemisinic / dihydroartemisinic aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymatically oxidizes dihydroartemisinic aldehyde to dihydroartemisinic acid and artemisinic aldehyde to artemisinic acid. The nucleic acid molecules, and the enzymes encoded thereby, may be used in processes to produce dihydroartemsinic aldehyde, dihydroartemisinic acid or artemisinic acid in a host cell. Dihydroartemisinic acid is a late precursor to the a antimalarial compound artemisinin.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Artemisia apiacea bZIP-type transcription factor encoding sequence, cloning method and application
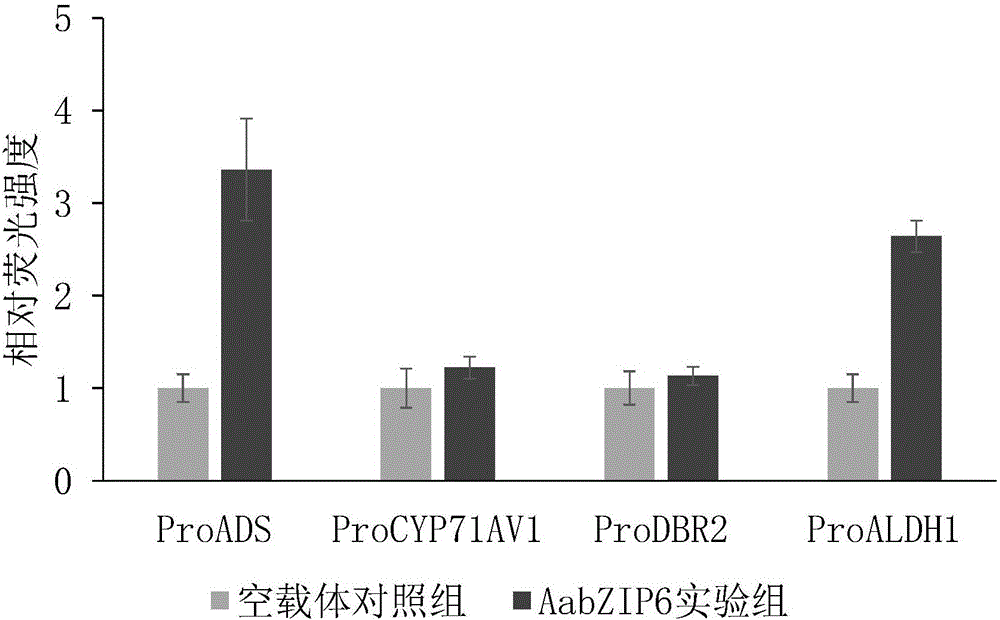
The invention discloses clone of an artemisia apiacea AabZIP6 gene encoding sequence and an application thereof, and particularly includes clone of the AabZIP6 gene, establishment of a plant expression vector containing the gene, and an activation effect of the gene on a gene promoter being specific in a bio-synthetic route of artemisinin. The nucleic acid sequence of the artemisia apiacea AabZIP6 gene is represented as the SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is represented as the SEQ ID No.2. The invention also discloses a character that the AabZIP6 gene can activate expression of the gene promoters, comprising ADS and ALDH1, which are specific in the bio-synthetic route of artemisinin. The AabZIP6 gene is applied in quality improvement of the artemisia apiacea and can increase the content of the artemisinin in the artemisia apiacea.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Transgenic sweet wormwood plant and cultivation method thereof
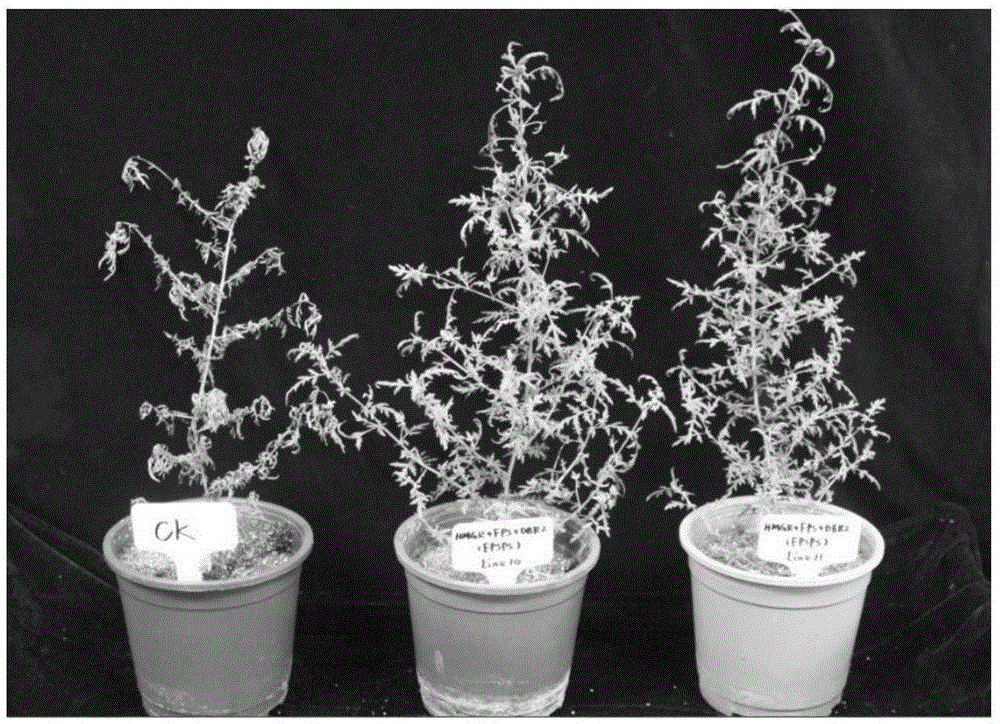
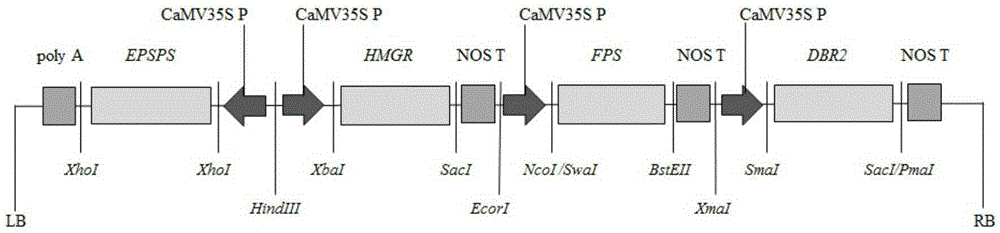
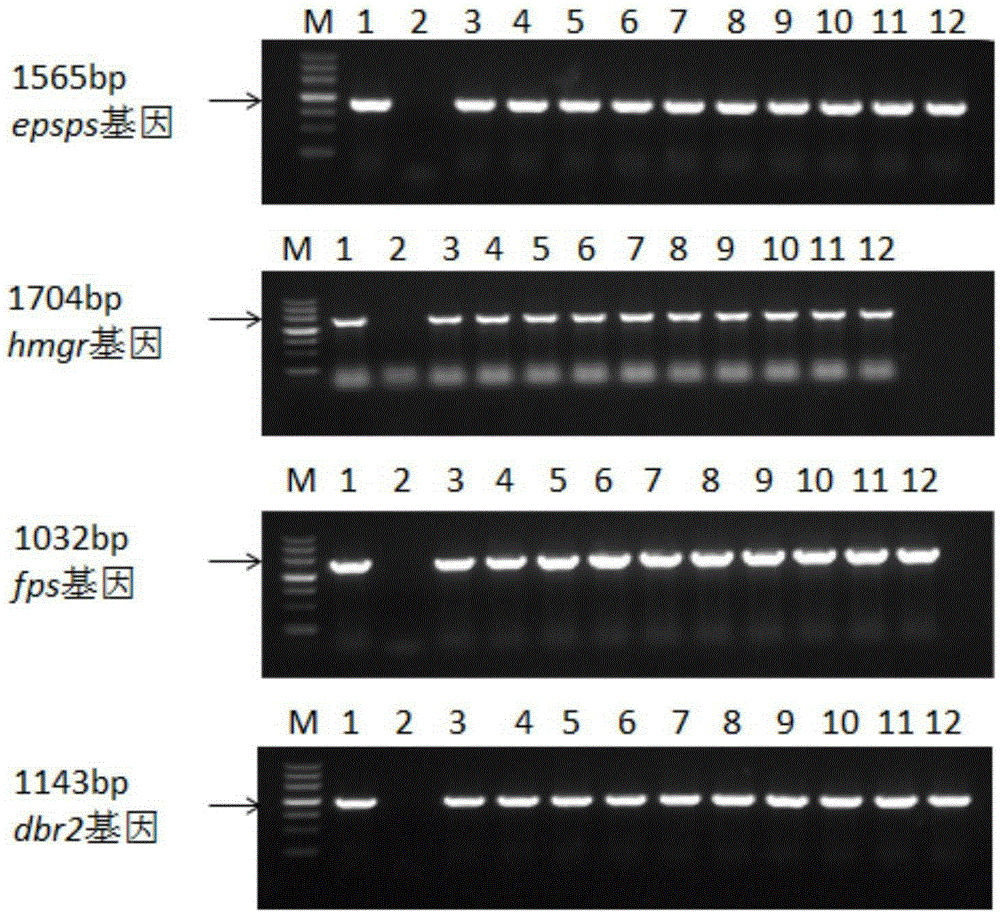
InactiveCN105296536AMaintain metabolismIncrease resistanceBacteriaComponent separationGlyphosateProtein Artemis
The invention discloses a transgenic sweet wormwood plant in which exogenous target genes consisting of hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps are introduced, and a cultivation method thereof. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a plant expression vector containing the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes; 2) transforming the obtained plant expression vector into Agrobacterium tumefaciems; 3) transforming the obtained Agrobacterium tumefaciems containing the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes into sweet wormwood and detecting obtained transgenic sweet wormwood plants; 4) measuring the content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood plants; and 5) screening transgenic sweet wormwood plants with glyphosate resistance by using glyphosate. The method capable of stably improving the artemisinin content and glyphosate resistance of sweet wormwood is established by using a metabolic engineering strategy of cotransformation of the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes; the transgenic sweet wormwood plant capable with high yield of artemisinin is obtained; and an ideal method and material are provided for large-scale production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
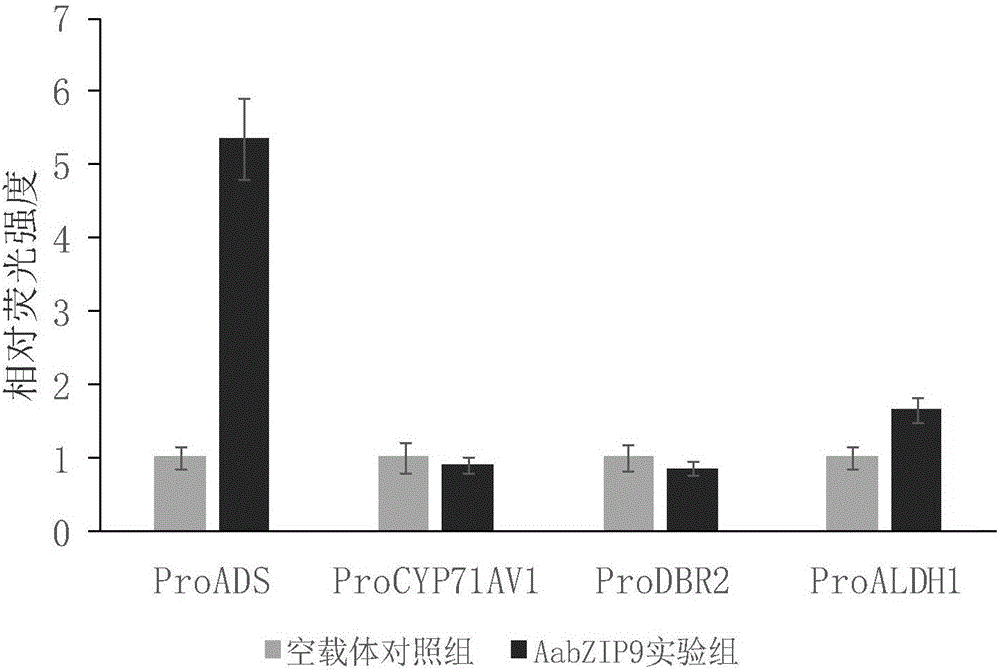
Artemisia annua L. bZIP class transcription factor coding sequence and cloning method and application
The invention discloses cloning and application of an artemisia annua L. bZIP class transcription factor coding sequence. Cloning particularly comprises cloning of a gene AabZIP9, construction of a plant expression vector containing the gene and activation of the gene on a gene promoter special for an artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. A nucleotide sequence of the artemisia annua L. AabZIP9 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and a coded nucleotide sequence of the artemisia annua L. AabZIP9 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further discloses an AabZIP9 gene which has characteristics of being capable of activating artemisinin biosynthetic pathway specific gene ADS and ALDH1 expression. The AabZIP9 gene can be used for improving the artemisia annua L. quality and can improve the content of artemisinin in artemisia annua L..
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of artemisinin AaORA protein, encoding gene and transgenic artemisinin plant
ActiveCN102558325AArtemisinin content decreasedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein ArtemisNucleic acid sequencing
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SUBEI RES INST
AaWBC1 gene promoter as well as functional verification method and application thereof
ActiveCN108441495AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMetaboliteNucleotide
The invention discloses an AaWBC1 gene promoter; the promoter can regulate and control the specific expression of an AaWBC1 gene in the secretory glandular hairs of sweet wormwood, and the nucleotidesequence of the promoter is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. Furthermore, the invention discloses the AaWBC1 gene promoter as well as a functional verification method and application thereof. The promoter provided by the invention can guide the specific expression of the reporter gene in the secretory glandular hairs of the plant, thus having a great significance for the genetic engineering breeding which uses plant glandular hair tissues to express and produce metabolites.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
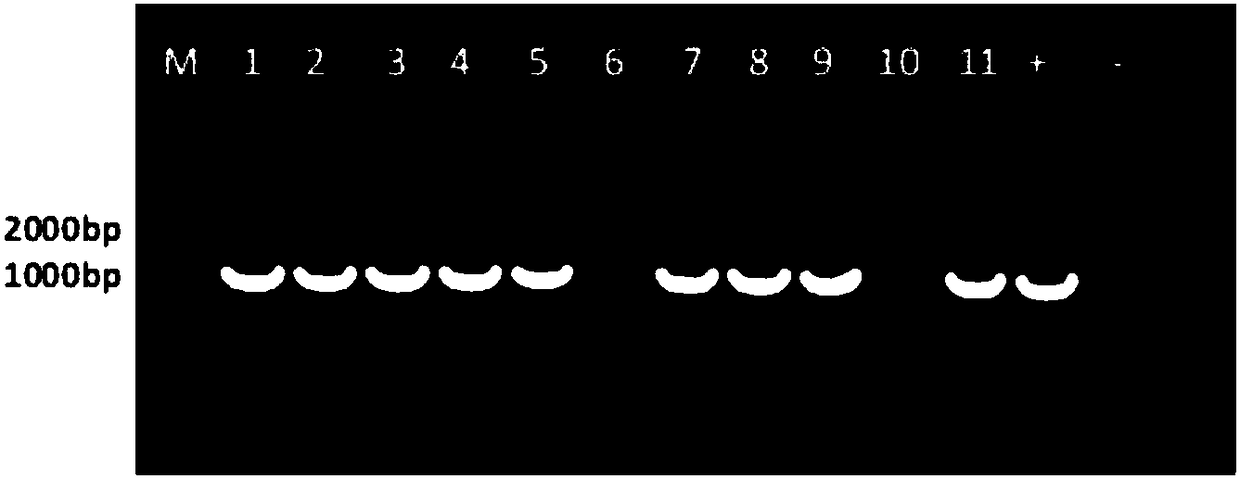
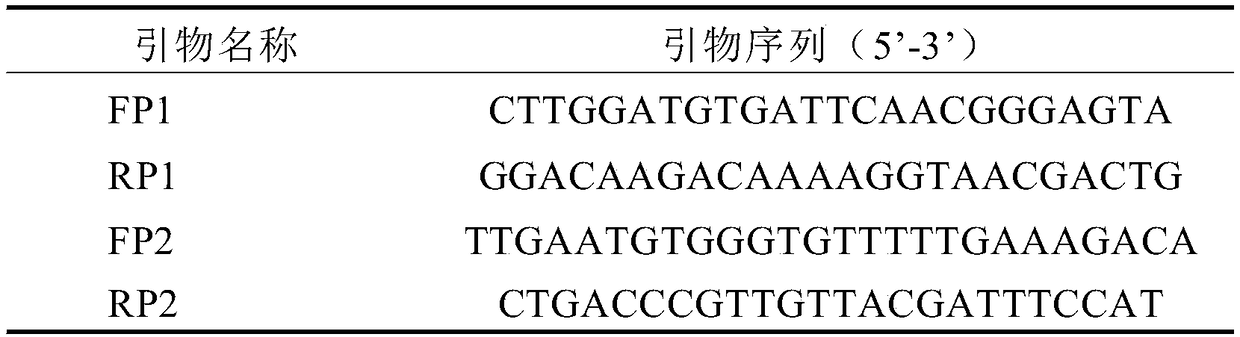
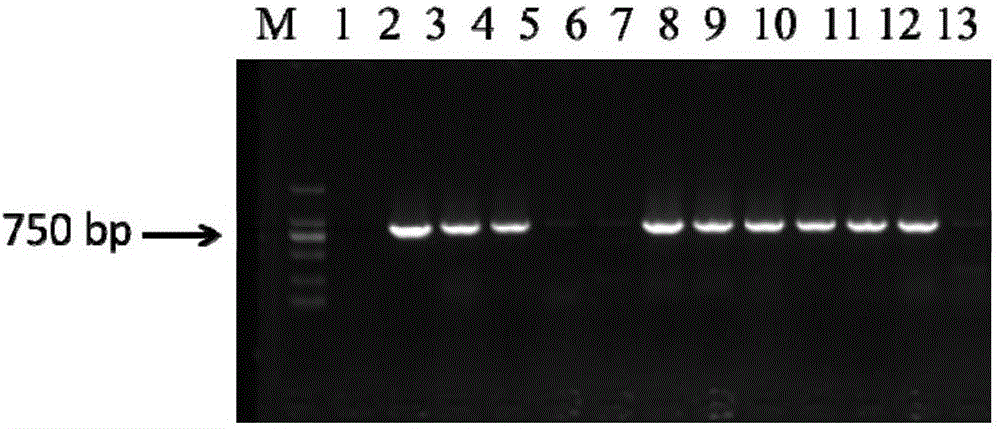
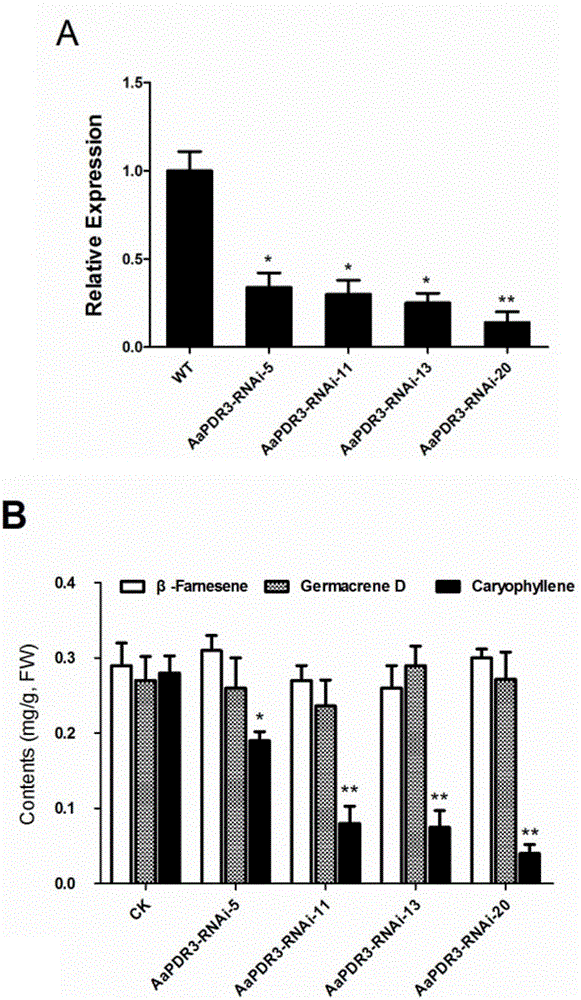
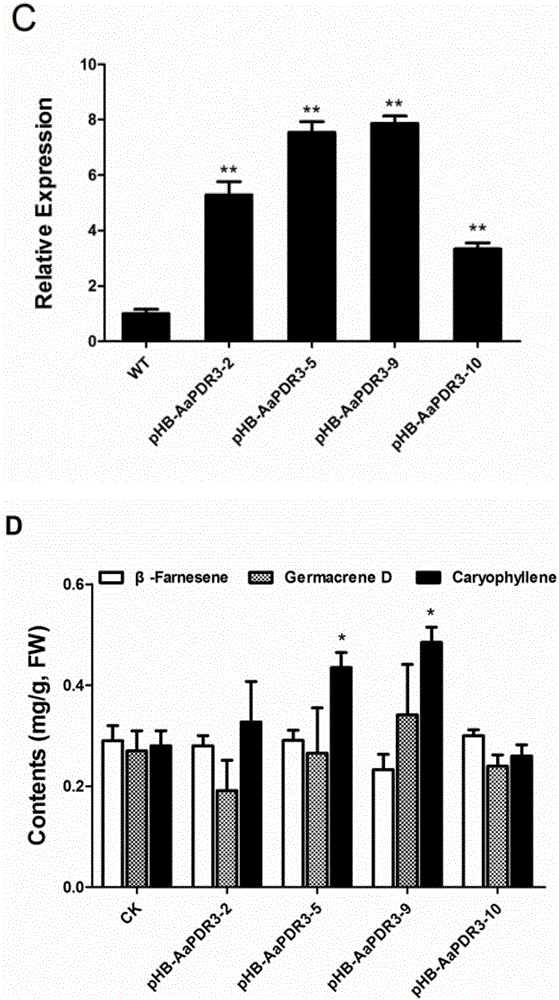
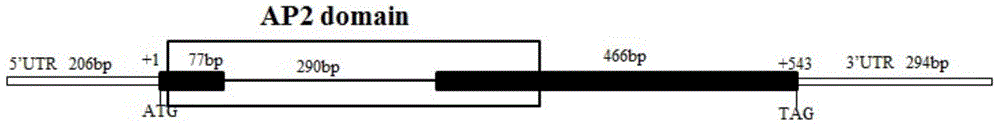
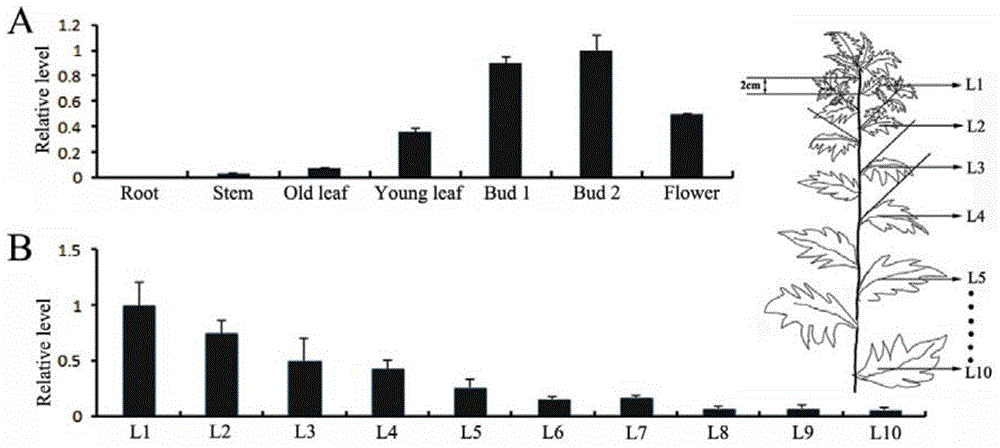
Artemisia apiacea translocator AaPDR3 and application thereof
ActiveCN106349352AInhibit synthesisIncrease contentPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringProtein ArtemisSesquiterpene
The invention relates to an artemisia apiacea translocator AaPDR3 and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.2; the artemisia apiacea translocator AaPDR3 can affect the synthesizing of sesquiterpenes in artemisia apiacea non-secreting type glandular hair; the translocator is encoded by the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention further provides a method for realizing transgenosis artemisia apiacea seedlings with the artemisia apiacea translocator AaPDR3.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Sweet wormwood AaGTD1 gene as well as coded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN104651373ASynthetic regulationIncrease artemisinin contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to the biological technical field, particularly an AaGTD1 gene for controlling artemisinin synthesis and trichome development in sweet wormwood as well as a coded protein and application thereof in preparing the artemisinin. The invention provides the sweet wormwood AaGTD1 gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; an amino acid sequence of protein AP2 / ERF transcription factors coded by the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The application disclosed by the invention refers to a method for increasing the content of artemisinin in the sweet wormwood through AaGTD1. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a plant expression vector comprising the gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 into a sweet wormwood cell; culturing the transformed sweet wormwood cell to obtain a sweet wormwood plant with increased artemisinin content. The protein coded by the AaGTD1 gene can be used for increasing the content of artemisinin, and is of great significance for providing high-yield and stable plant materials for large-scale production of the artemisinin.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Artemisia apiacea bZIP-type transcription factor encoding sequence, cloning method and application
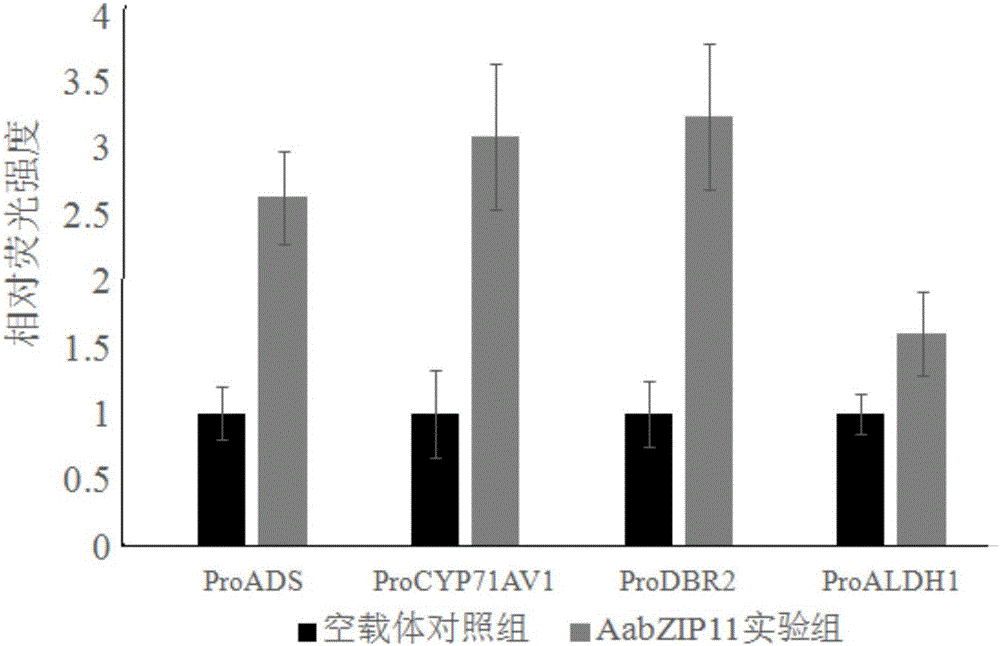
The invention discloses clone of an artemisia apiacea AabZIP11 gene encoding sequence and an application thereof, and particularly includes clone of the AabZIP11 gene, establishment of a plant expression vector containing the gene, and an activation effect of the gene on a gene promoter being specific in a bio-synthetic route of artemisinin. The nucleic acid sequence of the artemisia apiacea AabZIP11 gene is represented as the SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is represented as the SEQ ID No.2. The invention also discloses a character that the AabZIP11 gene can activate expression of four gene promoters, comprising ADS, CYP71AV1, DBR2 and ALDH1, which are specific in the bio-synthetic route of artemisinin. The AabZIP11 gene, through over-expression and the like, is applied in quality improvement of the artemisia apiacea and can increase the content of the artemisinin in the artemisia apiacea.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Artemisia-apiacea bHLH transcription factor coded sequence and clone method and application thereof
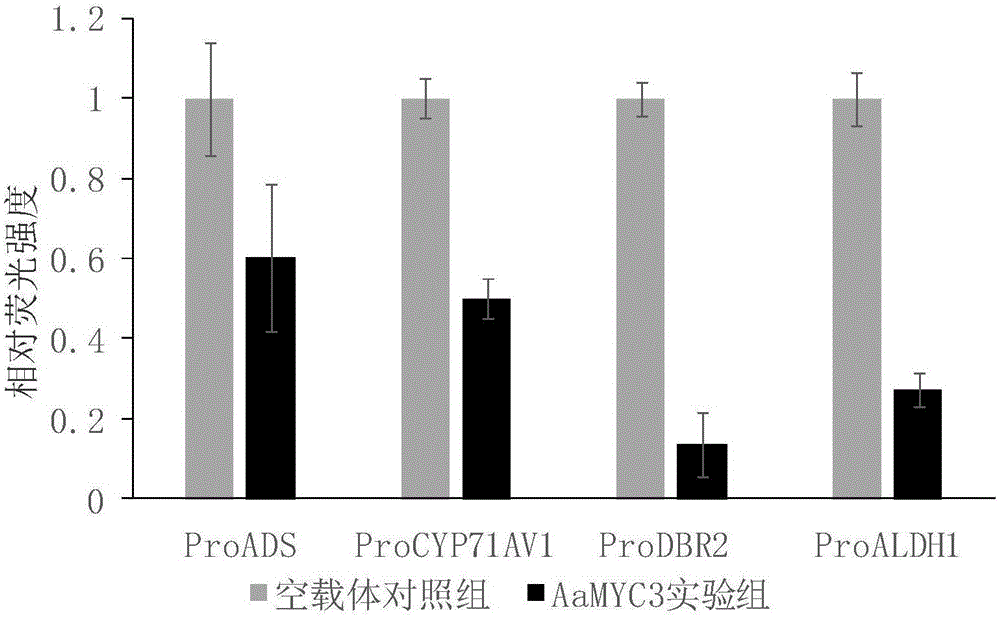
The invention discloses a cloning method and application of an artemisia-apiacea AaMYC3 gene coded sequence. The cloning method includes the specific steps of cloning of a gene AaMYC3; constructing of a plant expression vector with the gene; the activation effect of the gene on a specific gene promoter of an artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. The nucleotide sequence of the artemisia-apiacea AaMYC3 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further discloses the application of the AaMYC3 gene to activating expression of the four specific gene promoters including ADS, CYP71AV1, DBR2 and ALDH1 of the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. According to the cloning method an application, the AaMYC3 gene can be applied to artemisia apiacea with the RNAi method, the antisense inhibiting method and the like, quality is improved, and the content of artemisinin in artemisia apiacea can be increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Transgenic breeding method of sweet wormwood
InactiveCN104542295AGuaranteed uniformityImprove conversion ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsProtein ArtemisInflorescence
The invention provides a transgenic breeding method of sweet wormwood. The transgenic breeding method of sweet wormwood comprises the following steps: taking immature sweet wormwood inflorescence as an explant, infecting the explant by using an agrobacterium solution with exogenous genes, co-culturing the explant for 2-3 days, putting the explant on a selective-pressure culture medium to induce and generate a callus tissue, further inducing the callus tissue into a regeneration plant, then carrying out molecular biological detection on a reporter gene, and identifying a transgenic plant in the regeneration plant. According to the transgenic breeding method of sweet wormwood, the immature sweet wormwood inflorescence is used as the explants and is co-cultured with the agrobacterium EHA105 strains, so that a transformation rate is high; the highest transformation rate is 17.2% and is higher than that of the common leaf explant transgenic rate in the current sweet wormwood transgenosis by 8.59%. A novel transgenic system is provided for the genetic transformation of the sweet wormwood; meanwhile, the reference is provided for other plants difficult in agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
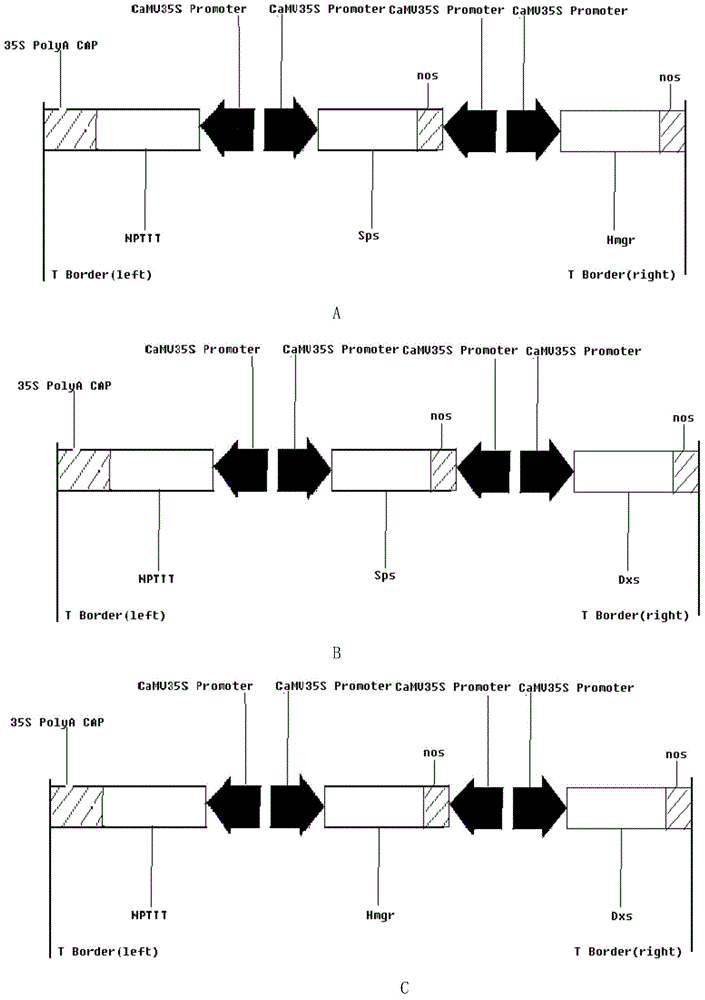
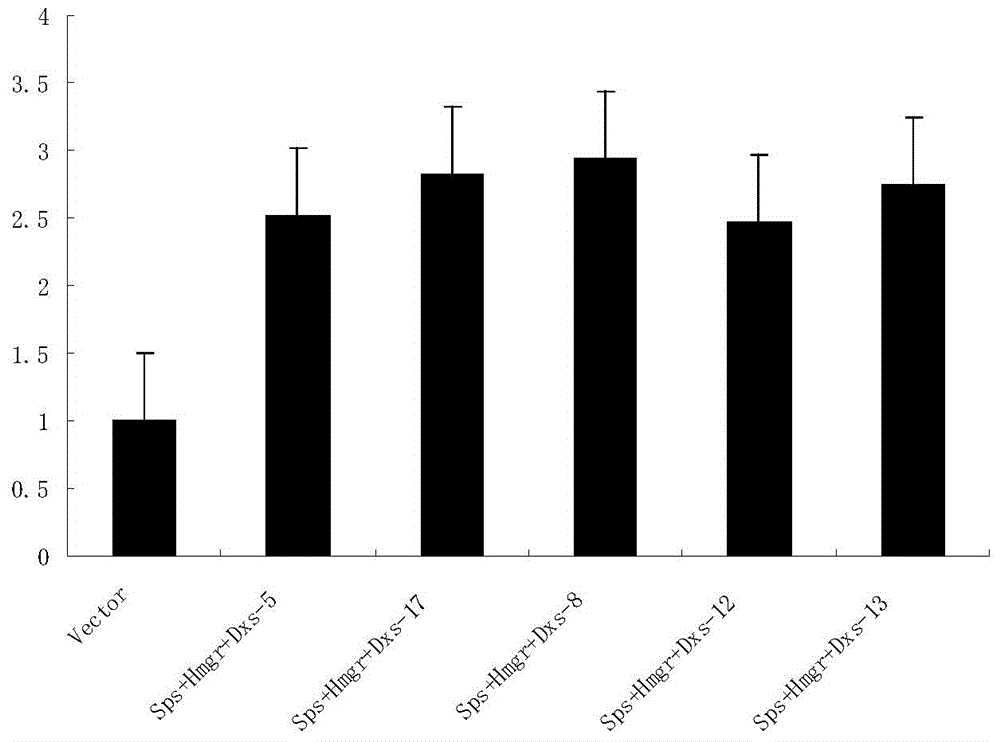
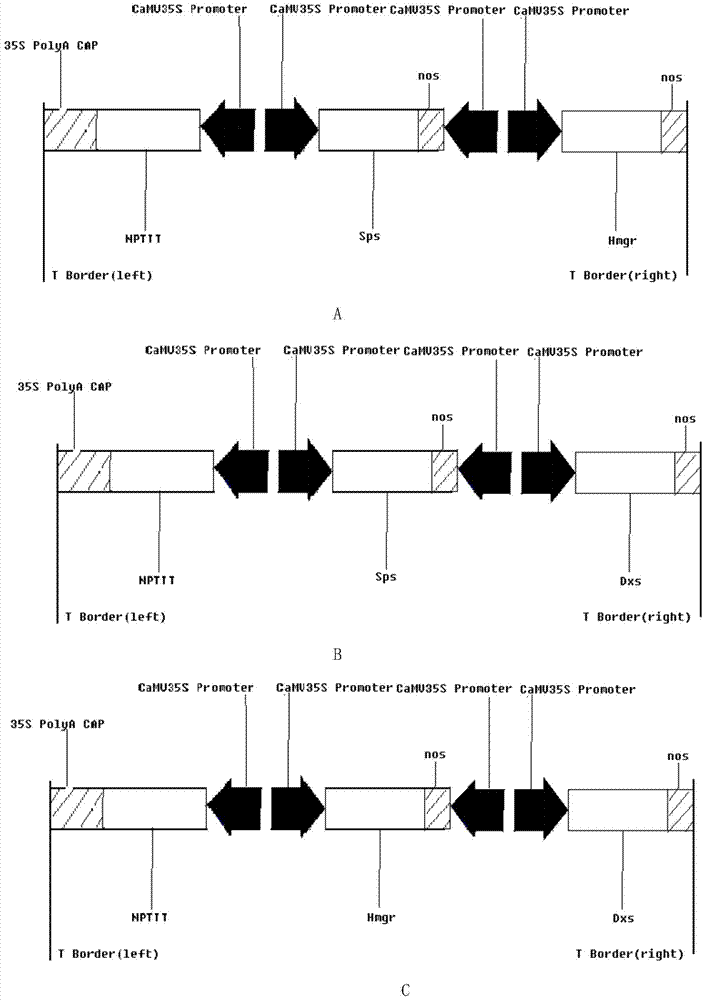
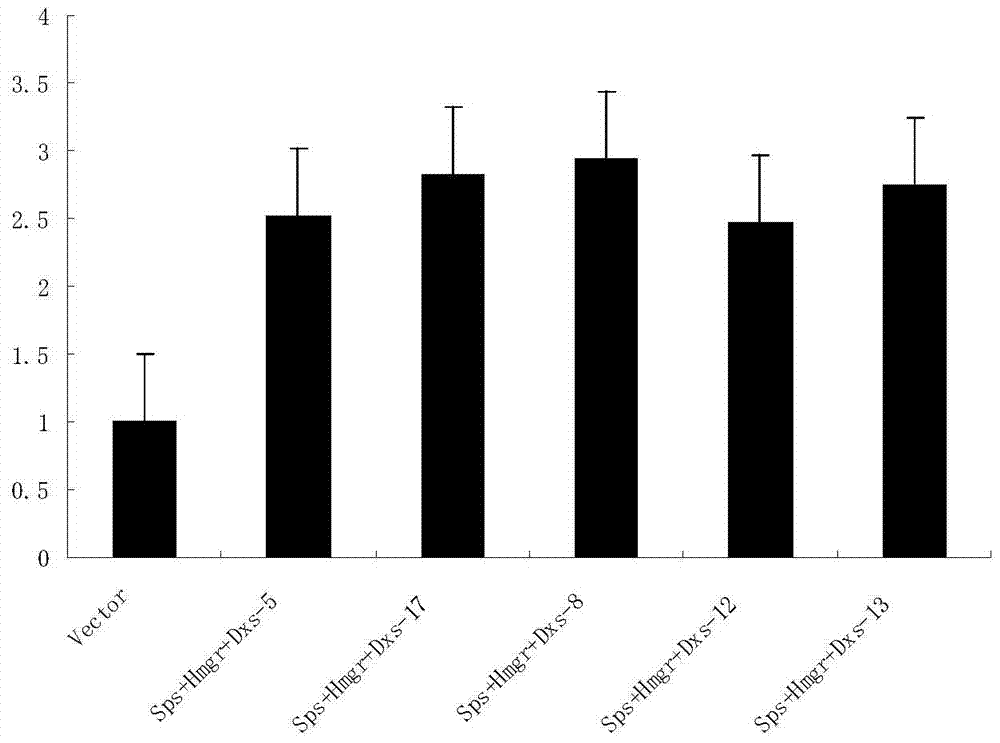
Method for cultivating sweet wormwood herb with high artemisinin content in flower buds by co-transforming Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes
InactiveCN104531753AIncreased artemisinin content in flower budsLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDry weightProtein Artemis
The invention discloses a method for cultivating sweet wormwood herb with high artemisinin content in flower buds by co-transforming Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes, relating to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: cloning three genes namely Anti-Sps, Anti-Hmgr and Anti-Dxs genes from sweet wormwood herb, constructing a plant expression vector containing three genes namely the Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes which are combined in pairs, performing mediation by using agrobacterium, transferring the three genes namely the Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes into sweet wormwood herb, and cultivating and screening regenerated plants to obtain a transgenic sweet wormwood herb plant with increased artemisinin content in the flower buds. When the content of non-transformed comparison sweet wormwood herb is 6.20mg / g of dry weight, the maximum artemisinin content in the flower buds of an obtained gene engineering sweet wormwood herb plant disclosed by the invention is 12.10mg / g of dry weight, and the artemisinin content in the flower buds is 1.95 times of the content of non-transformed comparison sweet wormwood herb. The method disclosed by the invention has great significance in saving costs for pharmaceutical factories which take sweet wormwood herb as a raw material.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL & PHARMA COLLEGE
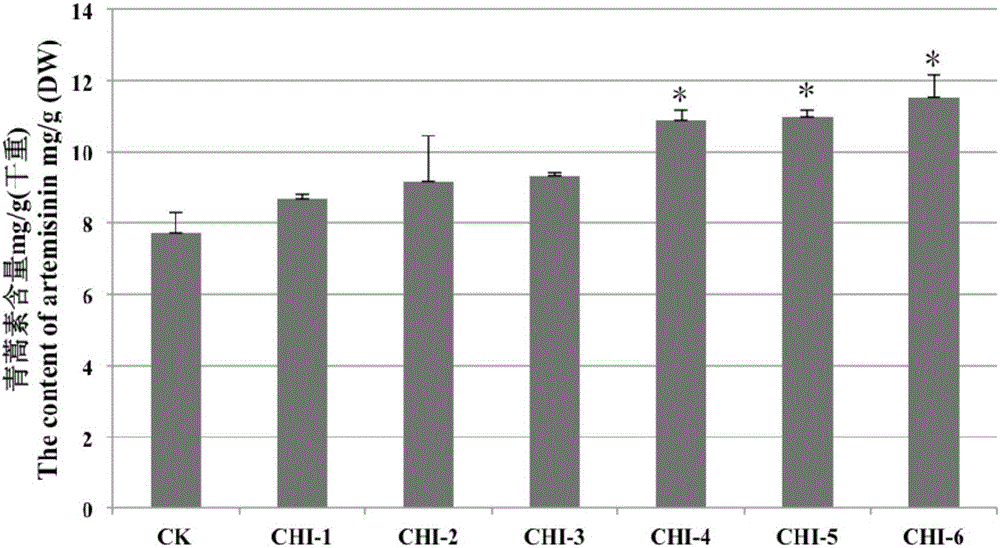
Method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by genetic modification with CHI (chalcone Isomerase) genes
The invention relates to the field of biological technologies and provides a method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by genetic modification with CHI (chalcone Isomerase) genes. According to the method, the CHI genes are cloned from Artemisia annua L., a plant expression carrier containing the CHI genes is established, the CHI genes are mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens to be transferred into Artemisia annua L. for regeneration of a plant, the integration condition of an exogenous target gene CHI is detected through the PCR (polymerase chain reaction), the content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is detected through an HPLC-ELSD (high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector), and the transgenic Artemisia annua L. plant with the content of artemisinin increased is screened out. The content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is increased and is 1.5 times that of a non-transgenic contrast plant in the highest level, and the method for increasing the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. is provided and lays a foundation for large-scale production of artemisinin from transgenic Artemisia annua L..
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua
InactiveCN106480088AEnhanced metabolic pathwaysBreak the speed-limiting bottleneck of biosynthesisOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringAmorpha fruticosaCytochrome P450 reductase
The invention discloses a method for increasing the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. The method includes jointly transforming the Artemisia annua by the aid of amorpha fruticosa diene synthetase ADS genes, amorpha fruticosa-4, 11-diene oxidase CYP71AV1 genes, cytochrome P450 reductase CPR genes and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH1 genes; measuring the content of the artemisinin in the Artemisia annua by the aid of high-performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light-scattering detectors and acquiring transgenic Artemisia annua plants with the increased artemisinin content by means of screening. The method has the advantages that the content of the artemisinin in the transgenic Artemisia annua can be obviously increased by the aid of the method, and the maximum content of the artemisinin can reach 3.4 times the content of artemisinin in non-transformation comparison plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
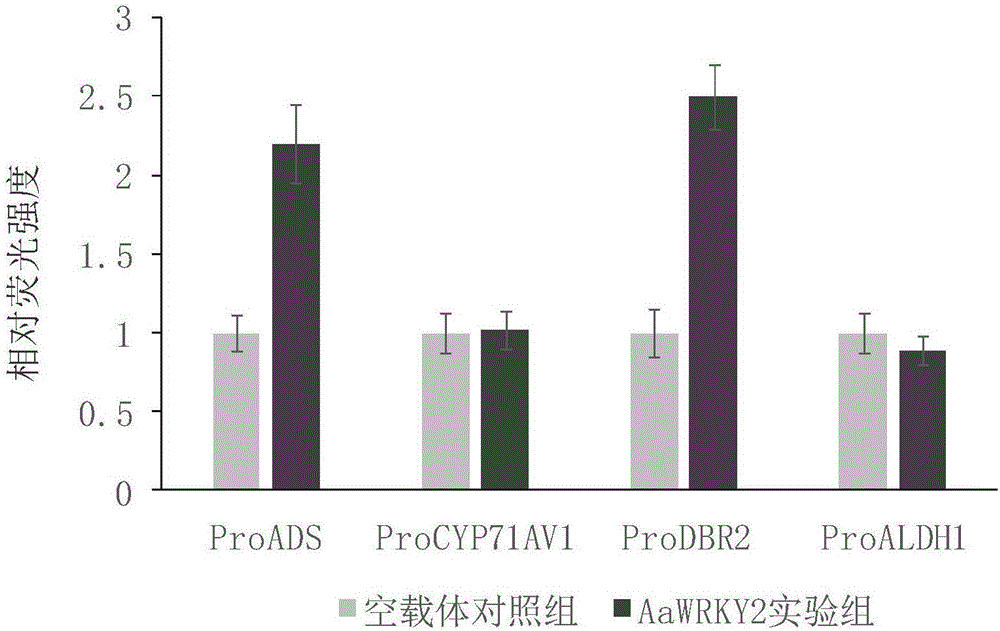
Artemisia carvifolia WRKY type transcription factor coding sequence, cloning method and application
The invention discloses cloning of an artemisia carvifolia WRKY gene coding sequence and application of cloning. Cloning of gene AaWRKY2, construction of a plant expression vector containing the gene and an activation effect of the gene on a specific gene promoter for biosynthesis of artemisinin are specifically comprised. A nucleotide sequence of the artemisia carvifolia gene AaWRKY2 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, and a coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention further discloses the characteristic of the gene AaWRKY2 that expression of two specific gene promoters ADS and DBR2 for biosynthesis of the artemisinin can be activated. The gene AaWRKY2 can be applied to quality improvement of artemisia carvifolia by excessive expression and the like, and the content of the artemisinin in the artemisia carvifolia can be increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
AaPDR2 gene promoter as well as functional verification method and application thereof
The invention relates to an AaPDR2 gene promoter as well as a functional verification method and application thereof. The AaPDR2 gene promoter comprises the following cis-acting elements: ABRE, BoxI, CAAT-box, CCAAT-box, CGTCA-motif, G-Box, G-box, GA-motif and TATA-box. Further, the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of the AaPDR2 gene promoter is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The AaPDR2 gene promoter has a function of predominantly expressing genes guided by the AaPDR2 gene promoter in glandular secretory trichome and T shape trichome of young leaves of Artemisia annua L., and the function is confirmed by a GUS reporter gene. Therefore, the AaPDR2 gene promoter disclosed by the invention has important significance for genetic engineering breeding for expressing and generating metabolites by using plant glandular trichome tissues.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
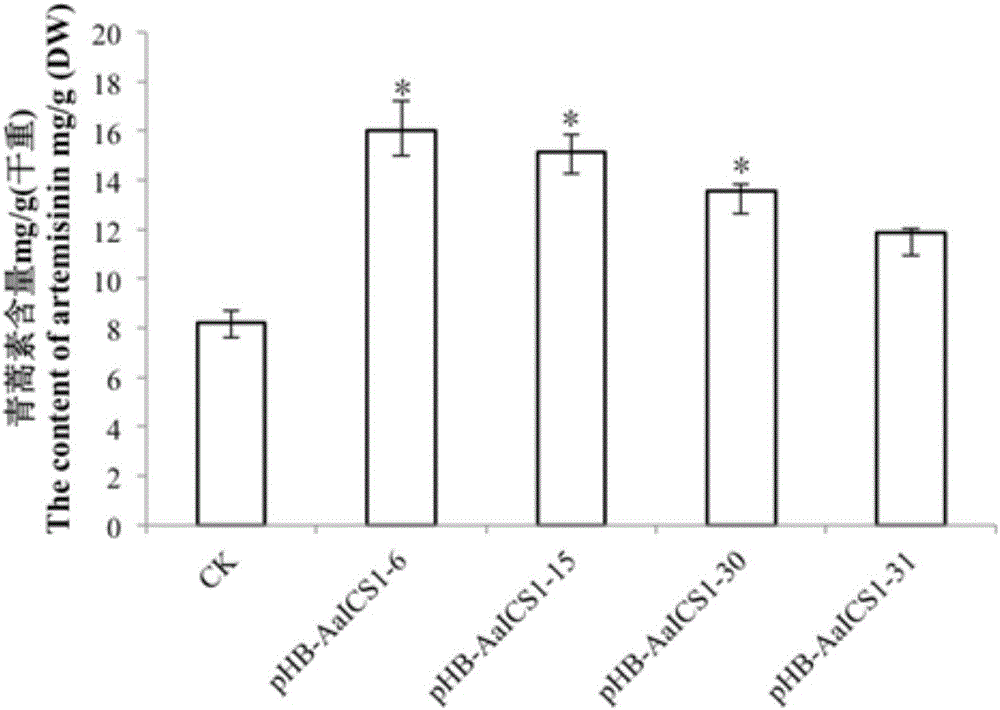
Method for increasing content of artemisinin in artemisia annua through ICS1 gene transferring
The invention relates to a method for increasing the content of artemisinin in artemisia annua through ICS1 gene transferring, and belongs to the biotechnology field.The method comprises the steps that isochorismate synthase ICS1 genes are cloned from the artemisia annua, plant expression vectors containing the ICS1 genes are constructed, the ICS1 genes are transferred into the artemisia annua through agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation to regenerate plants, the integrating condition of the exogenous target genes ICS1 is detected through PCR, the content of the artemisinin in the transgenic artemisia annua is determined through high-performance liquid chromatography and an evaporative light scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD), and the transgenic artemisia annua plants of which the artemisinin content is increased are obtained through screening.According to the method, the content of the artemisinin in the obtained transgenic artemisia annua is significantly increased, the highest content reaches 1.90 times of that of non-transgenic control plants, therefore, the method for increasing the content of the artemisinin in the artemisia annua is supplied, and a foundation is laid for massively producing the artemisinin through the transgenic artemisia annua.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
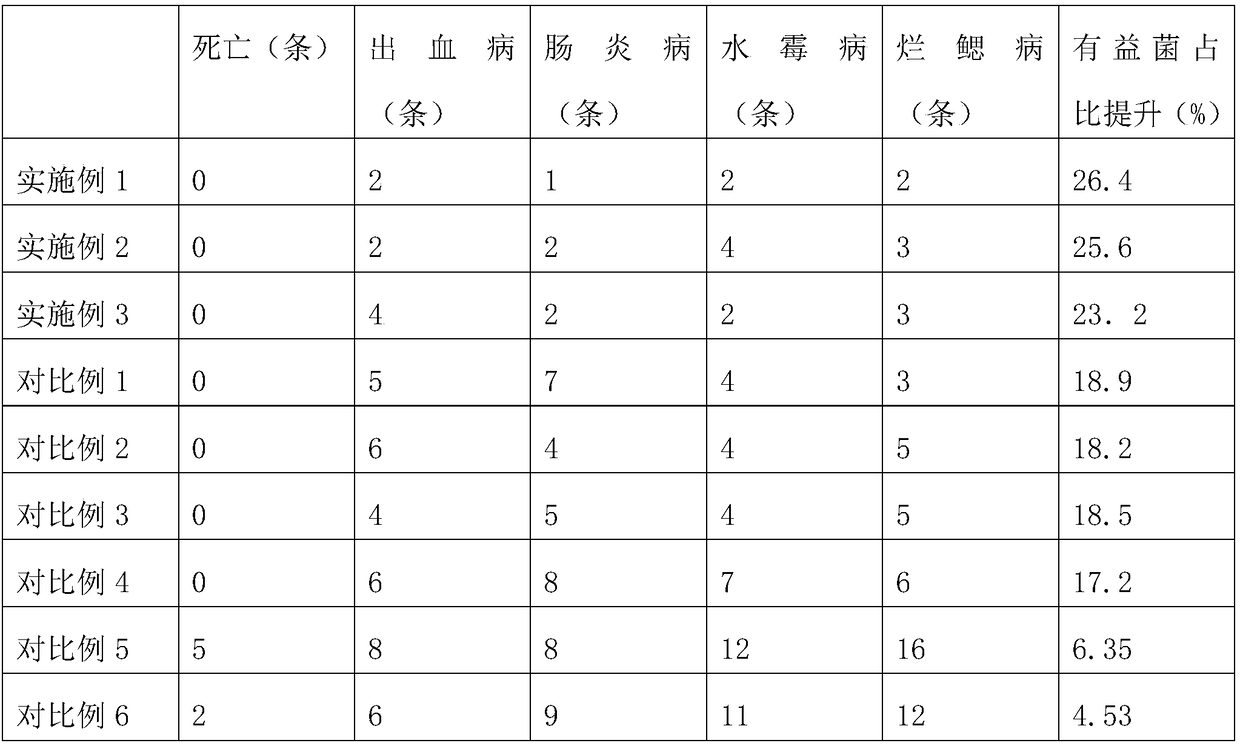
Sturgeon pathogenic bacterium inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108721594APrevent moisture deteriorationPromote absorptionAntibacterial agentsHydrolysed protein ingredientsYeastEffective microorganism
The invention discloses a sturgeon pathogenic bacterium inhibitor and belongs to the technical field of sturgeon pathogenic breeding. The sturgeon pathogenic bacterium inhibitor comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 43-52 parts of sweet wormwood, 10-16 parts of oligopeptide fish dissolution powder, 7-10 parts of choline chloride, 20-28 parts of atractylodes macrocephala, 10-20parts of rhizoma polygonati, 30-35 parts of Baijiu, 0.1-0.3 part of EM (Effective Microorganism) bacteria, 10-15 parts of beer yeast and 10-15 parts of a liver protection agent. A preparation method comprises the following steps: I, preparing the raw materials according to the parts by weight; II, baking the sweet wormwood, fumigating and baking the atractylodes macrocephala and the rhizoma polygonati on the sweet wormwood, crushing into powder, collecting sweet wormwood ash, and coating with choline chloride so as to obtain chloride granules; III, mixing the beer yeast with the EM bacteria, leaving to stand for 3-5 days so as to obtain a bacterial material, and uniformly stirring the oligopeptide fish dissolution powder, the atractylodes macrocephala powder, the rhizoma polygonati powderand the liver protection agent so as to obtain a mixture; IV, coating the chloride granules with a bacterial material, and further coating the outermost layer with the mixture, thereby obtaining the sturgeon pathogenic bacterium inhibitor. The sturgeon pathogenic bacterium inhibitor disclosed by the scheme of the invention is capable of remarkably increasing the ratio of beneficial bacterium florae in intestinal tracts of sturgeon pathogenic.
Owner:贵州龙源冷水渔业有限公司
Method for co-transforming sps, hmgr and dxs genes to cultivate Artemisia annua with high artemisinin content in flower buds
InactiveCN104531753BIncreased artemisinin content in flower budsLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDry weightProtein Artemis
The invention discloses a method for cultivating sweet wormwood herb with high artemisinin content in flower buds by co-transforming Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes, relating to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: cloning three genes namely Anti-Sps, Anti-Hmgr and Anti-Dxs genes from sweet wormwood herb, constructing a plant expression vector containing three genes namely the Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes which are combined in pairs, performing mediation by using agrobacterium, transferring the three genes namely the Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes into sweet wormwood herb, and cultivating and screening regenerated plants to obtain a transgenic sweet wormwood herb plant with increased artemisinin content in the flower buds. When the content of non-transformed comparison sweet wormwood herb is 6.20mg / g of dry weight, the maximum artemisinin content in the flower buds of an obtained gene engineering sweet wormwood herb plant disclosed by the invention is 12.10mg / g of dry weight, and the artemisinin content in the flower buds is 1.95 times of the content of non-transformed comparison sweet wormwood herb. The method disclosed by the invention has great significance in saving costs for pharmaceutical factories which take sweet wormwood herb as a raw material.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL & PHARMA COLLEGE
Farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase fusion gene carrying plastid transport peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN101033470BImprove synthesis abilityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein ArtemisPlant genetic engineering
The construction and application of fusion gene of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate synthase carrying plastid transit peptide belongs to plant genetic engineering field. This invention uses the transit peptide lstp of artesunate linalool synthase and fps gene of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate synthase to construct the fusion gene lstp-fps, and transferred the fusion gene into artesunate, to make the transgenic artesunate increase artemisinin.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
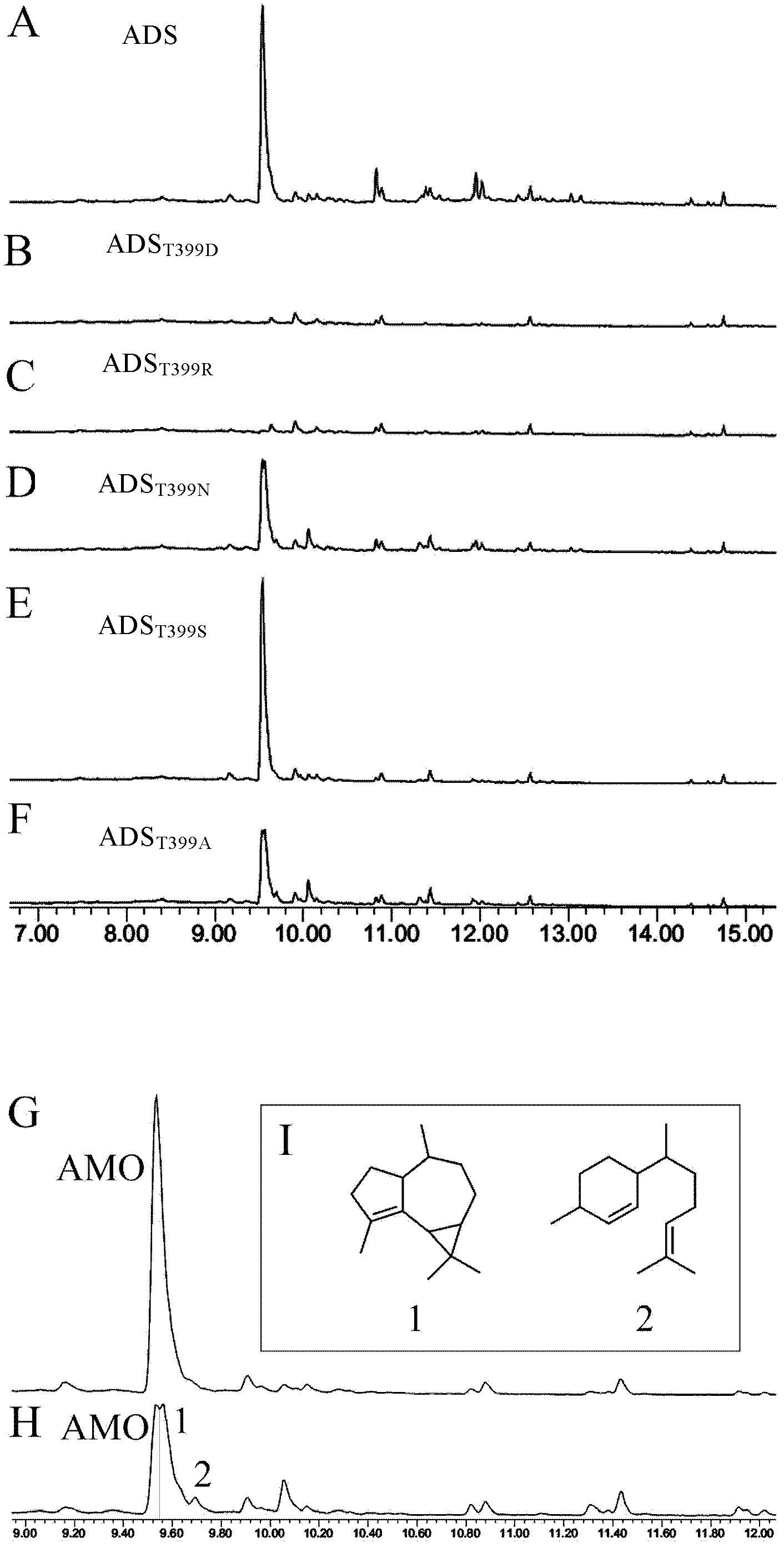
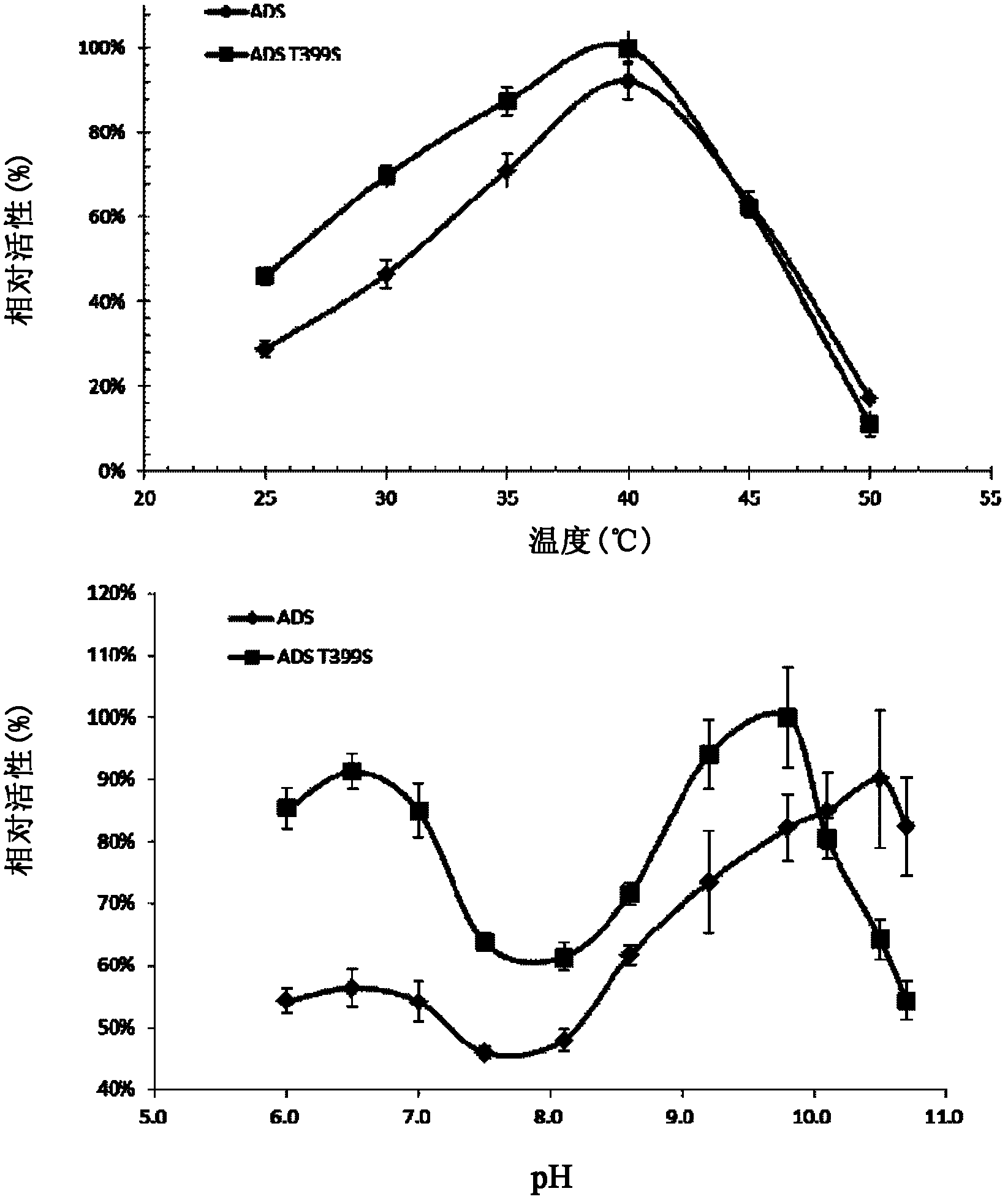
Artemisia annua amorpha-4,11-diene synthase mutant with improved enzyme activity and application thereof
The invention relates to an Artemisia annua amorpha-4,11-diene synthase mutant with improved enzyme activity and application thereof. The amorpha-4,11-diene synthase mutant has enzyme activity substantially higher than that of wild type amorpha-4,11-diene synthase under the condition that catalysate maintains unchanged. Compared to a traditional method, a method of applying the Artemisia annua amorpha-4,11-diene synthase mutant provided by the invention in enzymatic production of artemisinin has the advantages of high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for improving the content of artemisia annua patchouli calcohol by utilizing pts gene and RNA interferon ads gene
InactiveCN101597620BIncrease contentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySecondary metabolite
The invention discloses a method for improving the content of artemisia annua patchouli calcohol by utilizing pts gene and RNA interferon ads gene, including the following specific steps: obtaining the partial sequence of gene ads and all reading frame sequence of gene pts and tp segment of plasmid positioning signal titanium in arabidopsis; connecting the partial sequence of gene ads and the plasmid positioned pts gene building the hairpin structure to the expression regulating sequence respectively, forming the plant expressing carrier containing the adsi and plasmid positioned pts gene; utilizing the built plate expressing carrier to transform the agrobactrium tumefaciens; utilizing the bacterial strain of built agrobactrium tumefaciens to transform the artemisia annua explant; measuring the content of patchouli calcohol in the transgene artemisia annua by HPLS-ELSD. The invention establishes a method for improving the content of patchouli calcohol, thereby laying a strong foundation for producing the patchouli calcohol in large scale by utilizing the transgene artemisia annua and the other terpene secondary metabolites except for the artemisinin.
Owner:FIRMENICH AROMATICS (CHINA0 CO LTD
Artemisia annua aagtd1 gene and its encoded protein and application
ActiveCN104651373BIncrease artemisinin contentSynthetic regulationPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideProtein Artemis
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to an AaGTD1 gene and its encoded protein in Artemisia annua controlling the synthesis of artemisinin and the development of glandular hairs and its application in the preparation of artemisinin. The present invention provides an Artemisia annua AaGTD1 gene, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the amino acid sequence of the protein AP2 / ERF transcription factor encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The application described in the present invention refers to a method for increasing the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua through AaGTD1 involved in the present invention, comprising the following steps: transforming the plant expression vector comprising the gene shown in SEQ ID NO:1 into Artemisia annua cells: cultivating transformed Artemisia annua cells to obtain Artemisia annua plants with increased artemisinin content. The protein encoded by the AaGTD1 gene of the present invention can be used to increase the yield of artemisinin, and it is of great significance to provide high-yield and stable plant materials for the large-scale production of artemisinin.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com