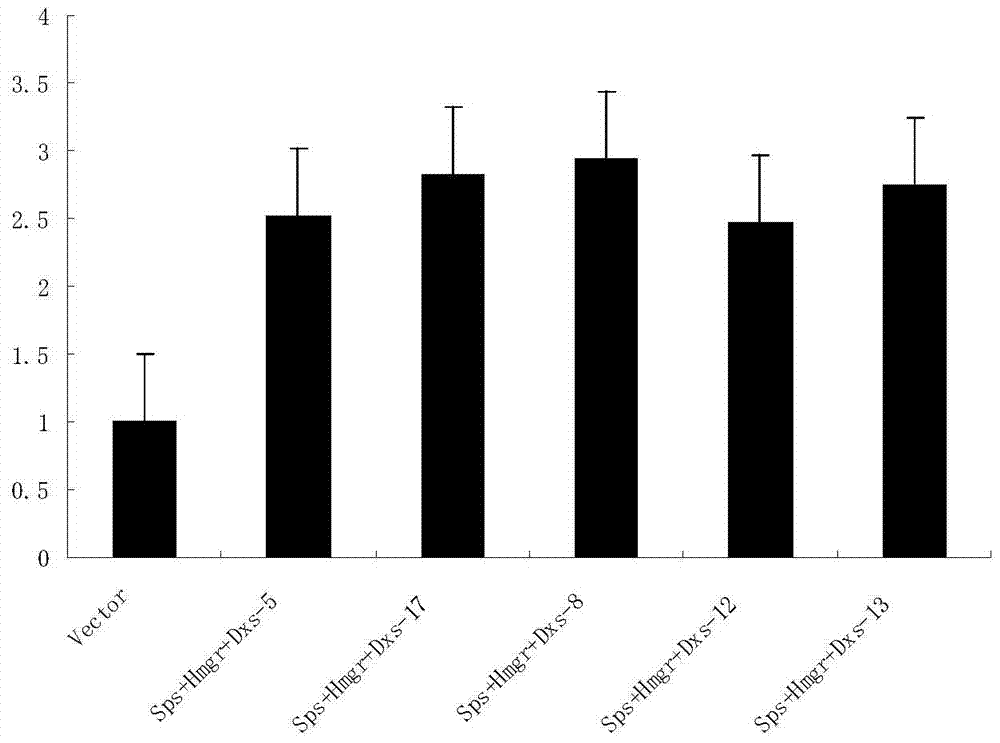
Method for co-transforming sps, hmgr and dxs genes to cultivate Artemisia annua with high artemisinin content in flower buds
A technology of co-transformation and artichoke, applied in the field of genetic engineering to cultivate plants, can solve the problems of limited drug effect and low toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1. Extraction and purification of Artemisia annua total RNA. Follow the instructions of the TRIZOL kit provided by Invitrogen. Grind the upper young leaves of Artemisia annua with liquid nitrogen, add 3mL Trizol to the EP tube, centrifuge at 15,000r / min for 15min at 5°C to discard the precipitate; add 3ml of water-saturated phenol, centrifuge at 5°C, 15,000r / min for 10min, take Add 250 μL of 5M NaCl solution to the supernatant, add 300 μL of chloroform, shake, mix well, and centrifuge at 15,000 r / min for 10 min at 4°C, and take the supernatant. Add 0.3mL isopropanol, mix well to get crude RNA extract; add 75% ethanol to wash and dry, and dissolve with DEPC-H2O. Extract according to the operating instructions of the kit RNAiso for polysaccharide-rich plant tissue RNA. Extracted total RNA was tested for integrity and purity by agarose gel electrophoresis and UV spectrophotometer. The mortar, pestle and spoon used should be baked at 160°C for more than 10 hours....
Embodiment 2
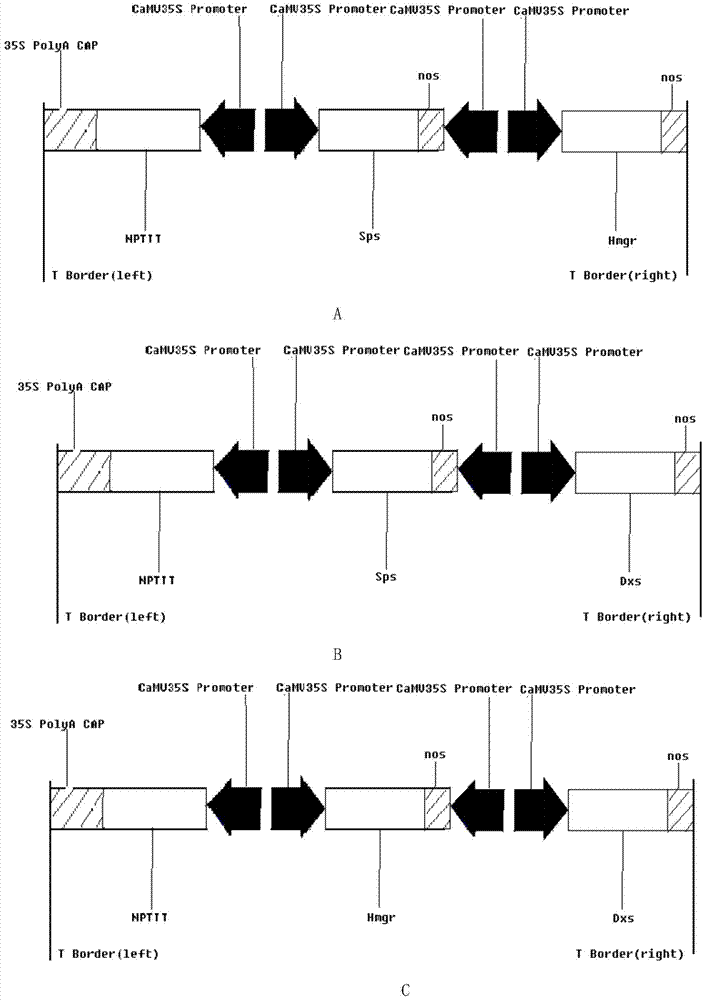
[0055] Example 2 Construction of a plant binary expression vector containing Sps, Hmgr and Dxs genes.
[0056]2.1 Construction of intermediate vector pMD19-T-p35s-gfp*gus-nos
[0057] Using pMD19-T and pCAMBIA2301 as basic construction elements, construct pMD19-T-p35s-gfp*gus-nos intermediate vector. The specific implementation steps are as follows. A pair of primers were designed based on the base sequence of p35s-gfp*gus-nos on pCAMBIA2301, and restriction endonuclease sites were introduced on the upstream and downstream primers to facilitate the construction of expression vectors. Using the pCAMBIA2301 plasmid as a template, the expression cassette of the gfp*gus fusion gene was amplified by PCR, and then connected to the pMD19-T vector. After transformation and screening, single clones were picked and sequenced for comparison and confirmation.
[0058] 2.2 Construction of intermediate vectors
[0059] Construction of pMD19-T-p35s-Dxs-nos, pMD19-T-p35s-Sps-nos and pMD19-T...
Embodiment 3
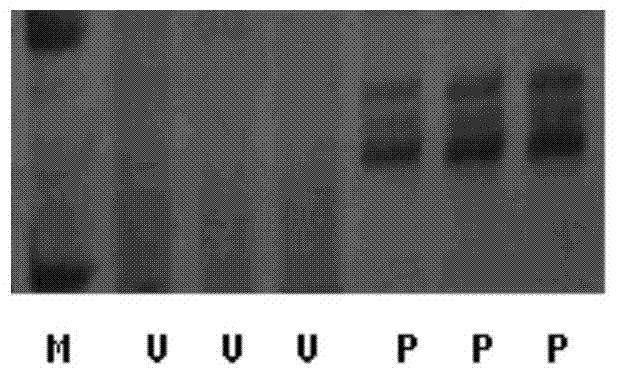
[0067] Example 3, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of young embryos of Artemisia annua and acquisition of resistant plants
[0068] Using YEB solid medium, pick a single colony of Agrobacterium carrying the recombinant plasmid the night before infection and inoculate it on YEB medium containing 45 mg / L spectinomycin, shake the bacteria at 220 rpm, and keep the temperature at 25°C overnight. Streak culture of Agrobacterium on YEB solid medium until the diameter of the circle becomes a single colony of about 1.5mm, after PCR verification, then re-streak culture on YEB solid medium, culture at 20°C for 4 days, collect the bacteria, and suspend In IM, acetosyringone (AS) was used to adjust the final concentration to 180 μmol / L, which was used to prepare bacterial solutions with different concentrations for future use. The OD of the bacterium solution used by the immature embryo 600nm They are 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 1.1 respectively, and the infection time is set to 1, 4, 7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com