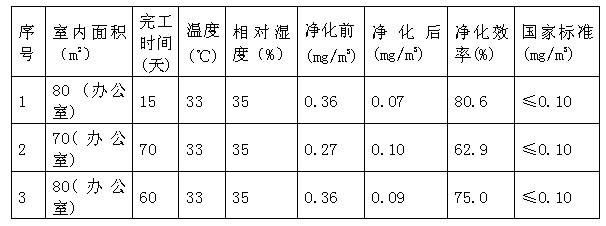
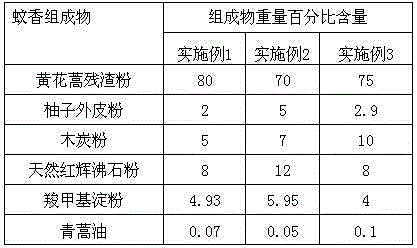
Patents
Literature
645 results about "Artemisia annua" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artemisia annua, also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood (Chinese: 黄花蒿; pinyin: huánghuāhāo), is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America.
Biological pesticidal organic fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103724139ASimple structureAddress organic matter declineFertilizer mixturesPaulownia coreanaNematode
The invention discloses a biological pesticidal organic fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The biological pesticidal organic fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of pig manure, 20-30 parts of tea seed pulp, 10-15 parts of coffee grounds, 8-12 parts of paulownia sawdust, 5-10 parts of phosphogypsum, 4-8 parts of corn cob, 5-10 parts of pepper seed cake, 10-15 parts of mushroom dreg, 8-12 parts of wheat bran, 15-20 parts of bentonite, 10-15 parts of opoka, 2-3 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1-2 parts of manganese sulfate, 3-5 parts of humic acid, 1-2 parts of chinese tallow tree root and bark, 2-3 parts of sophora alopecuroides, 1-2 parts of stemona, 1-3 parts of Artemisia annua, 1.5-2.5 parts of ailanthus leaf, 2-3 parts of derris and 1-2 parts of Radix Euphorbiae Ebractealatae. The organic fertilizer disclosed by the invention has multiple effects of providing nutrients, improving the soil structure, preventing and treating pests and diseases and the like, can promote the crops to quickly grow, enhances the stress tolerance of the crops, can have favorable preventing and treating effects on nematodes and soil insects, reduces or avoids use of chemical pesticides, enhances the soil fertility, regulates the ecological equilibrium of soil, improves the quality of agricultural products, has no chemical residues, and implements yield increase and income increase of agricultural products.
Owner:青岛米品品服装有限公司
Plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant and preparation method and application of plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant
InactiveCN103168803ASpeed up conversionGood antibacterial effectBiocideDispersed particle separationHordeum vulgareCapsaicin
The invention provides a plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant. The plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant is prepared by the following plant materials in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of tobacco stems, 12-20 parts of Ilex latifolia Thunb stems, 2-8 parts of Helianthus tuberosus Linn leaves, 5-15 parts of ginkgo biloba, 8-16 parts of capsaicin, 1-5 parts of tanshinone, 15-25 parts of orange peel, 2-8 parts of paeoniflorin, 1-5 parts of tea seed, 8-15 parts of ginger stems, 15-35 parts of wild chrysanthemum flower, 5-20 parts of garlic, 5-15 parts of ginger, 20-35 parts of sophora alopecuroides, 5-10 parts of pine needle oil, 15-30 parts of artemisia annua, 20-50 parts of green beans, 30-60 parts of barley and 20-35 parts of corn. The plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant provided by the invention has the advantages of high biological activity, strong broad-spectrum antibacterial property, fast insect and egg killing, good environment-friendly property, safety, high efficiency and the like. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the plant source bacteriostasis and detoxification deodorant.
Owner:陈士进 +2
Formulation useful as a nitrification and urease inhibitor and a method of producing the same
InactiveUS6315807B1Increase contentRestrict urea hydrolysisBiocideAnimal repellantsUrease InhibitorsArtemisia annua
The invention relates to a novel formulation useful as a nitrification and urease inhibitor, said formulation comprising an effective amount of nitrogenous fertilizer, castor oil and oil derived from Artemisia annua, in an amount sufficient to enhance the nitrification activity of the formulation, a method for producing the formulation and method for applying the same to soil.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Use of southernwood extract as plant growth regulator and adverse-resistant agent
InactiveCN101258861AMake up for the defect of single ingredientAdjustable growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSOUTHERNWOOD ExtractAmbrosia artemisiifolia extract
The invention relates to a control agent and an anti-adversity agent of plant growth, which adopts southernwood, a Chinese traditional medicine, namely Artemisia annua L, as raw material, or adopts the secondary substances (also containing small amount of the artemisinin which is not completely extracted) which are abundant in the large amount of residues and concentrated mother solution after artemisinin is extracted by organic solvent. On the one hand, the invention does not influence the extraction of the artemisinin used for pharmaceuticals, on the other hand, the invention enhances the added value of the products of the southernwood, turns wastes into benefits and is good for environment protection and green production. The product of the invention is characterized by wide physiological effect, being safe and innoxious, being no pollution, being environment-friendly, easy obtaining of raw materials and low cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Puffed snakehead compound particle feed and Chinese herbal medicine premix added therein
ActiveCN101785531AGuaranteed palatabilitySolve the non-bottleneck of developmentAnimal feeding stuffForsythia suspensaRadix bupleuri
The invention discloses a Chinese herbal medicine premix added in a puffed snakehead compound particle feed, which comprises the following components by weight proportioning: Artemisia annua to Forsythia Suspensa to radix sophorae flavescentis to radix bupleuri to folium eucalypti to radix gentianaeto common andrographis herb to folium artemisiae argyi to apocynum venetum is 3-5:1-3:1-3:2-5:3-5:2-5:2-4:1-3:1-3. The invention also discloses a puffed snakehead compound particle feed comprising the basic formula of fish meal and bean pulp, and 1-5 weight percent of the Chinese herbal medicine premix is added in the basic formula. The puffed snakehead compound particle feed of the invention can strengthen snakehead immunological capability, prevent and treat diseases and improve snakehead meat quality and flavour.
Owner:HANGZHOU FEIXUN BIO TECH
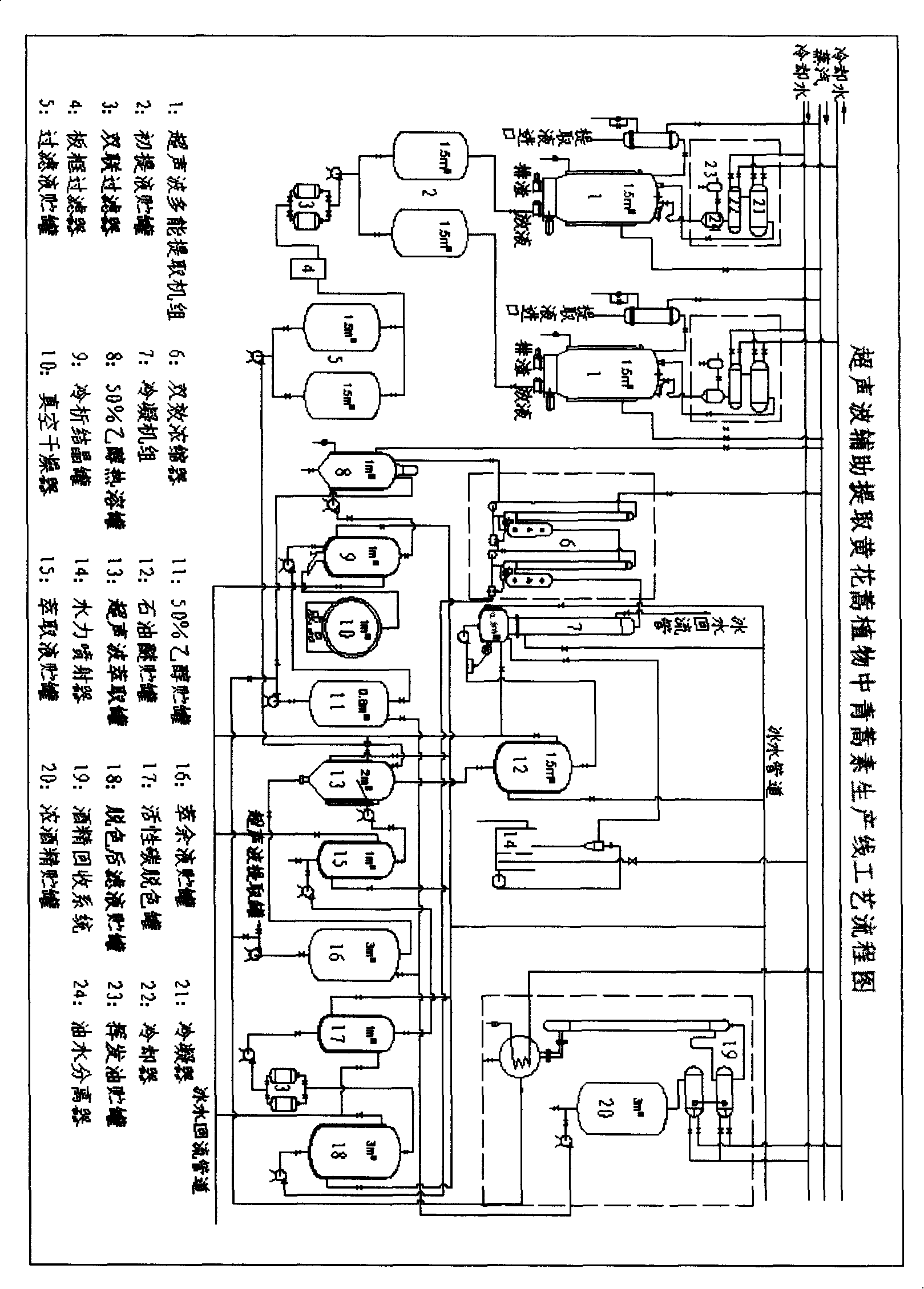
Technical new method for extracting artemisinin from sweet wormwood plants by ultrasonic assistance
InactiveCN101205232AProtectiveDoes not destroy biological activityOrganic chemistryPlant ingredientsUltrafiltrationArtemisia annua
The invention relates to a novel process method for utilizing the ultrasonic wave to extract the artemisinin from the artemisia annua Linn. By adopting the orthogonal experimental design, the method obtains the target compounds through a plurality of technical parameters in the process of screening and extraction. The stems and leaves of the artemisia annua Linn serving as the materials and 80 per cent ethanol are added in an ultrasonic extraction batch at a ratio of solid to liquid (Kg:L) ranging from 1 to 15 to 1 to 17; a separate-excited ultrasound generating device and a radial vibration columnar transducer are adopted; the ultrasonic power is 1000W, the ultrasonic frequency is 35kHz, the extraction is carried out for one time at two minutes interval with an action time of 3 minutes and the total extraction time is 30min; the temperature is 40 DEG C; the mixtures in the ultrasonic extraction batch are subject to the air-lift type stirring and the extract is put into the ultrafiltration, and the filtrates in equivalent volume are subject to the petroleum ether ultrasonic extraction at a temperature ranging from 30 DEG C to 60 DEG C on the conditions that the separate-excited ultrasound generating device and the radial vibration columnar transducer are adopted with an ultrasonic power of 1000W and a ultrasonic frequency of 30kHz and the ultrasound has a continous effect for 10 minuts with a total extraction time of 15 minutes at a temperature of 25 DEG C; the air-lift type stirring is carried out, the ether extraction liquid is decolored by the activated carbon and concentrated by reducing the pressure and then the obtained solution is cooled down to be crystalized; 50 per cent ethanol is recrystalized. The extraction rate of the artemisinin from artemisia annua Linn is 97.25 per cent.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
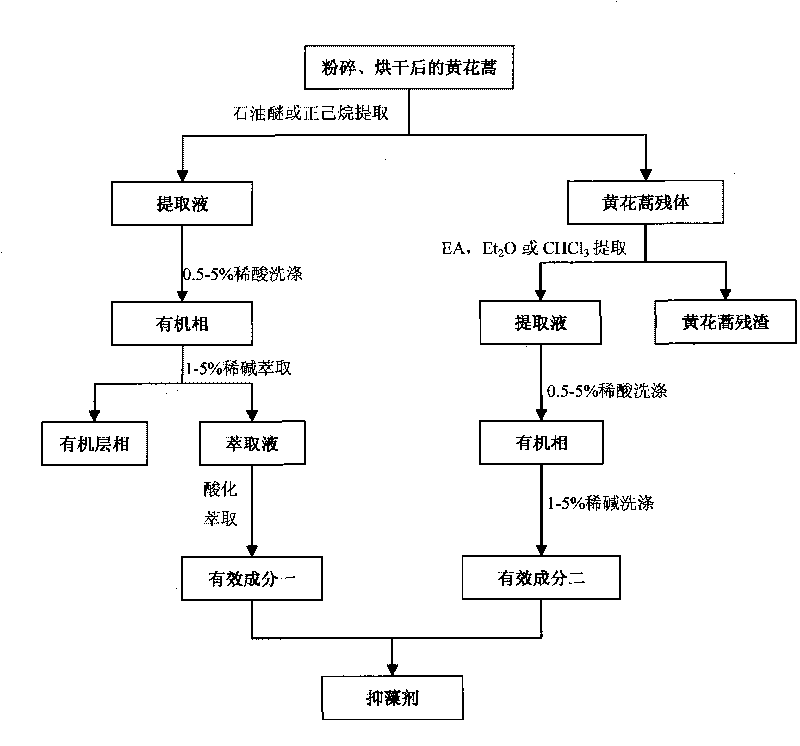
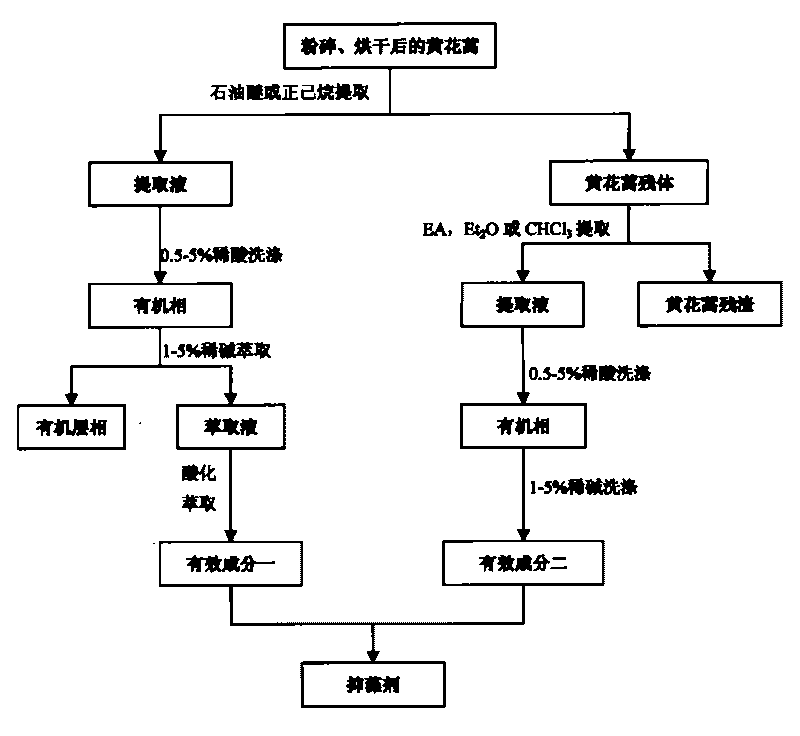
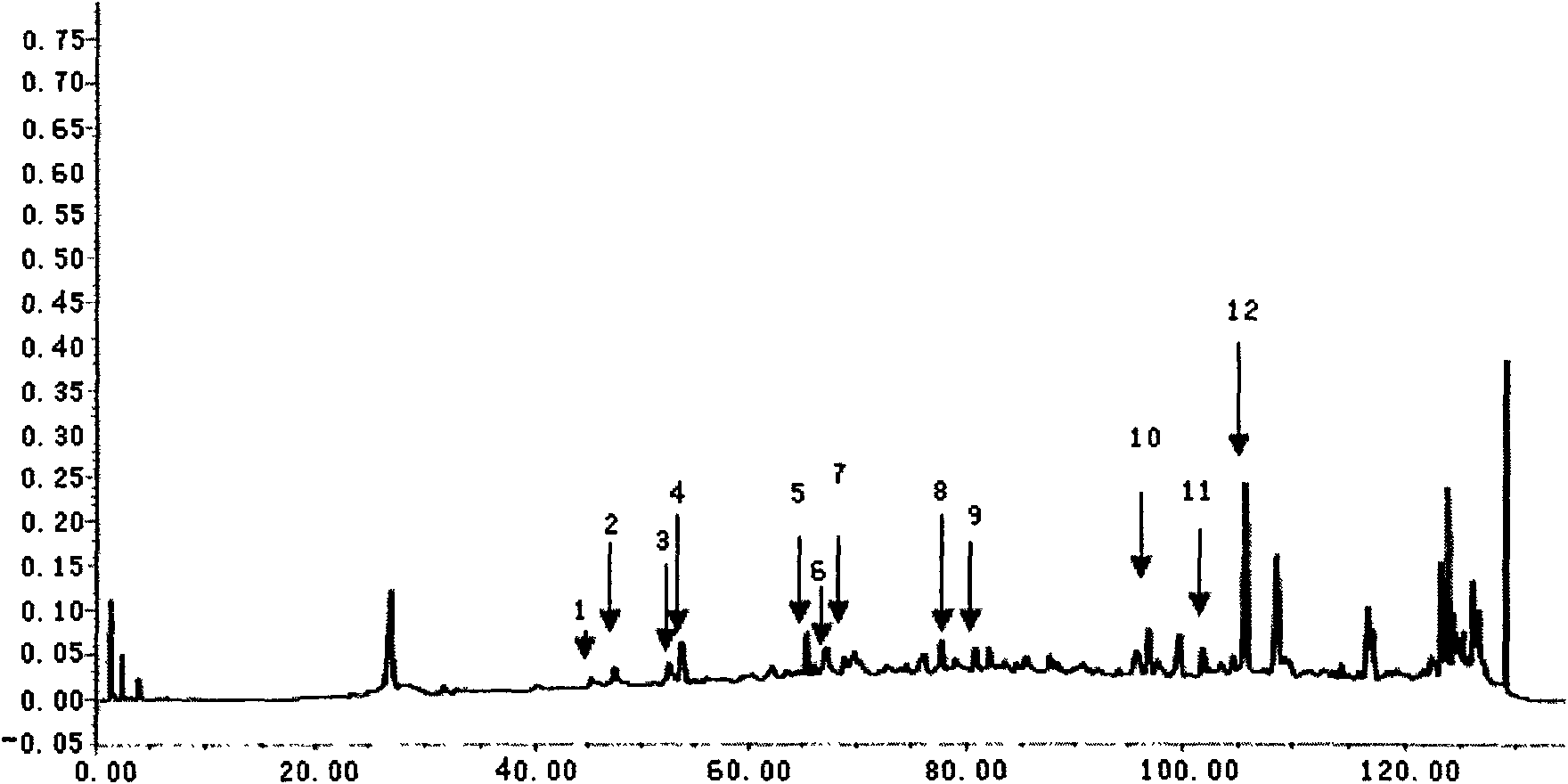
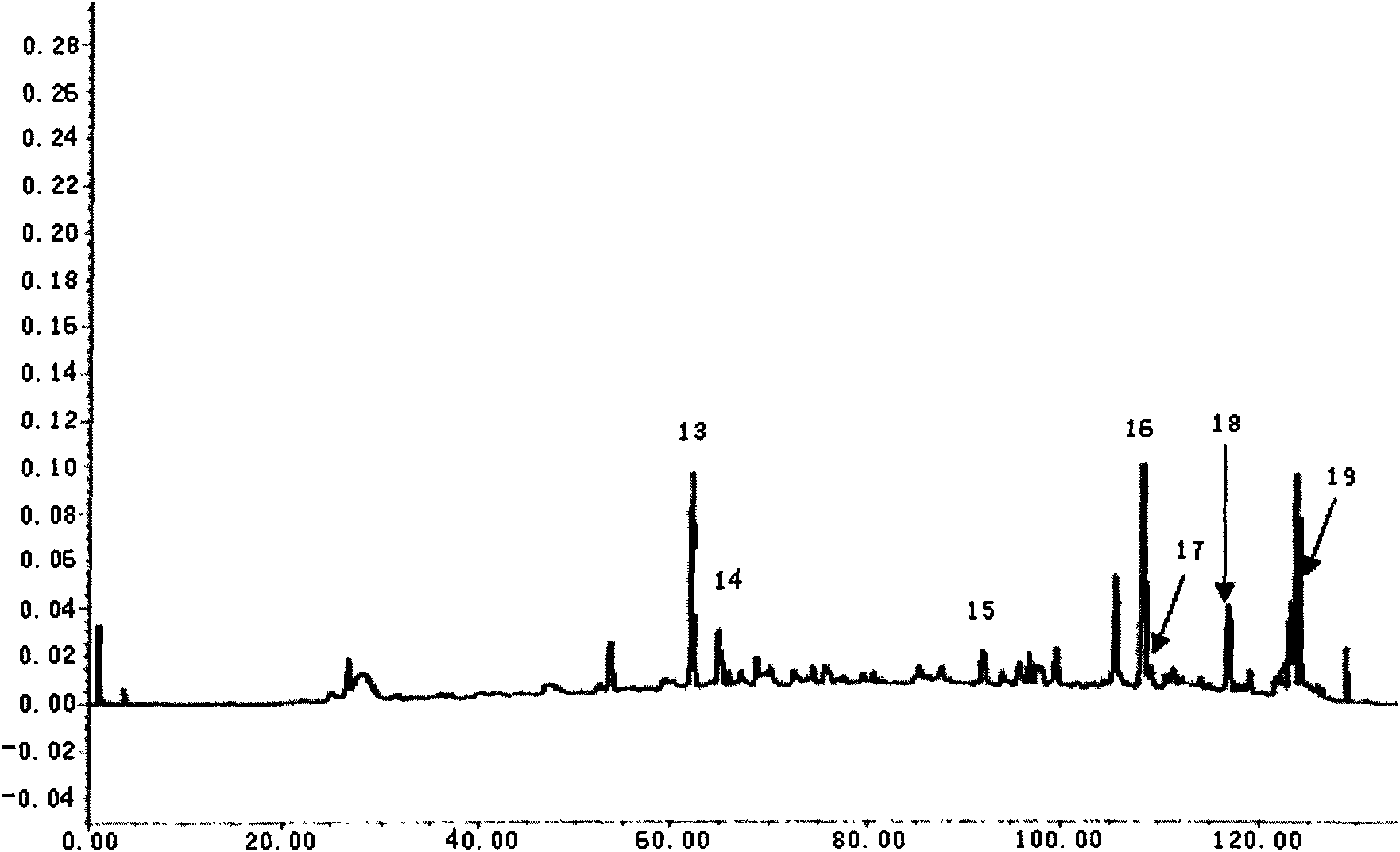
Method for extracting alga-inhibiting active ingredients from Artemisia annua L. and alga-inhibiting method
The invention discloses a method for extracting alga-inhibiting active ingredients from Artemisia annua L., and an alga-inhibiting method, and belongs to the field of water pollution control. The invention solves the problems of high cost, large ecological risk, secondary pollution and the like of the traditional alga-inhibiting technology. The device discloses a method for extracting and preparing an alga-inhibiting agent from land plant of Artemisia annua L. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the dried and crushed Artemisia annua L. by steps with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate, washing petroleum ether extracting solution with diluted acid, combining active ingredients obtained by diluted alkaline stripping and active ingredients obtained by washing ethyl acetate extracting solution with diluted acid and diluted alkaline, and then preparing the alga-inhibiting agent. The method has the advantages of simple process, easy implementation, low cost and the like, and can be widely used for waters of ponds, reservoirs, lakes and the like.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for rapidly extracting artemisinin
InactiveCN101899055ANo effect on resultAvoid thermal decompositionOrganic chemistryEthyl acetateArtemisia annua
The invention provides a method for rapidly extracting artemisinin, comprising the following steps: taking fresh and non-dry artemisia annua as an extraction raw material; extracting the artemisinin from the raw material using analytically pure ethyl acetate or chloroform or dichloromethane under the condition of normal temperature and normal pressure; filtering, collecting extracting solution, decolorizing by active carbon, concentrating and then recovering an extraction solvent to obtain a crude artemisinin product; and crystallizing and purifying the crude artemisinin product by edible ethanol or petroleum ether or n-hexane to finally obtain the artemisinin product with high purity up to over 95% and high recovery rate up to over 86%. The method has the advantages of being efficient and fast, low cost and applicability to industrial application.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicinal preparation for stopping bleeding and disinfecting
InactiveCN102552722ARelieve painReduce economyHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntisepticsSalvia miltiorrhizaSide effect
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal preparation for stopping bleeding and disinfecting, which is prepared from the following traditional Chinese medicinal materials by weight: 2-8 parts of Panax notoginseng, 2-8 parts of Flos Lonicerae, 2-6 parts of ciliate desert-grass, 2-6 parts of Artemisia argyi leaf, 1-5 parts of Corydalis yanhusuo, 1-5 parts of Imperata cylindrica root, 2-6 parts of Salvia miltiorrhiza, 1-4 parts of Ramulus Uncariae Cum Uncis, 1-4 parts of Angelica dahurica, 1-5 parts of Portulaca oleracea, 1-3 parts of Herba Taraxaci, 0.5-1.2 parts of Fuligo Plantae, 1-3 parts of Artemisia annua, and 1-3 parts of borneol. The traditional Chinese medicinal preparation for stopping bleeding and disinfecting is appropriate for cleaning and disinfecting the wound of skin, mucosa or tissue in a general surgical operation and stopping bleeding and disinfecting the traumatic wound. The traditional Chinese medicinal preparation of the invention is used to stop bleeding of the wound, resists infection, has remarkable curative effect, is fast to stop bleeding with no secondary infection of the wound, and has no toxic and side effects and no irritation. The effective rate is 100% and no scars are left after recovery. The medicines adopted by the invention are all folk herbs in China and convenient to pick up, and low in cost.
Owner:尹华山
Detection method of Chinese patent medicines containing at least two kinds of Radix Paeoniae Alba, Ginseng, Danshen, Artemisia annua, Licorice, Chuanxiong and Angelica
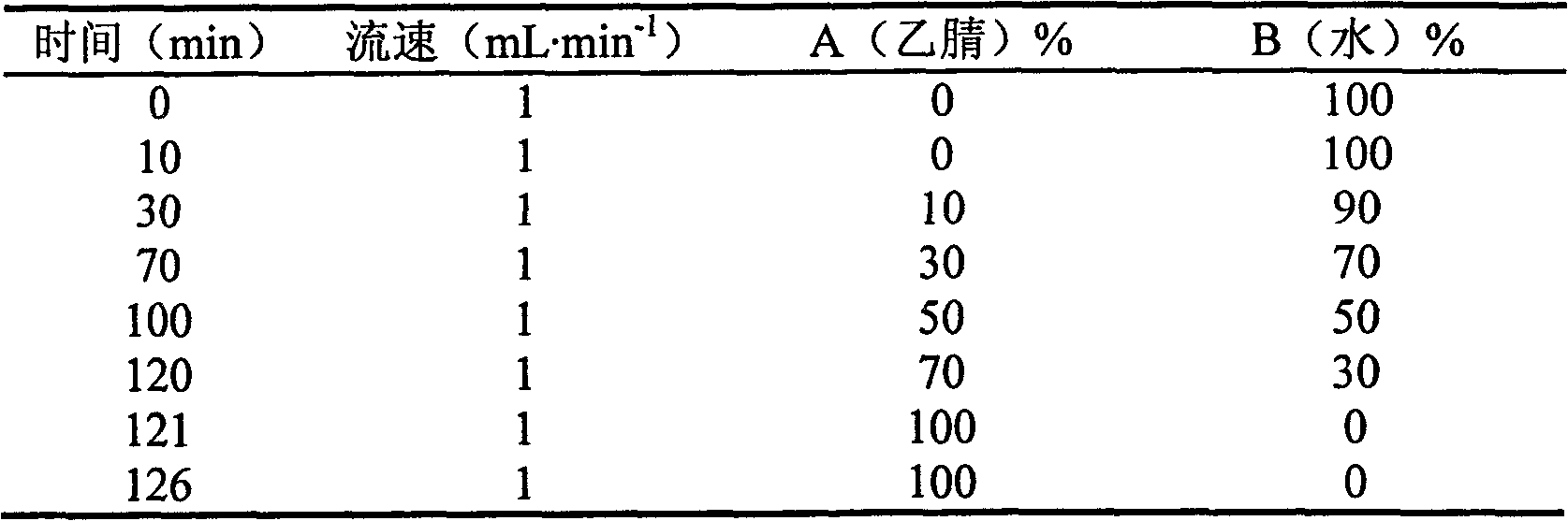
InactiveCN101991661AThe identification result is accurateChange processing methodAnthropod material medical ingredientsComponent separationSalvia miltiorrhizaDrugs solution
The invention provides a method for detecting a Chinese patent drug containing at least two of white paeony root, ginseng, salvia miltiorrhiza, sweet wormwood, liquorice and angelica sinensis, comprising the steps as follows: preparing a sample solution and a comparison product drug solution, adopting acetonitrile and water as mobile phases, and performing high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) measurement, wherein the detection wavelength is 201-290nm; and detecting whether a corresponding chromatographic peak exists at a position, which has the same reservation time with the chromatograph of a comparison drug, in the chromatography of a sample. Compared with the traditional thin-layer chromatography identification method, the detection method in the invention has the advantages that the mode of processing a sample containing various drugs in a liquid phase chromatograph is changed, the mixed peak in the liquid phase chromatography except the components to be detected in the Chinese patent drug is successfully eliminated, and results are more accurate and stable.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Multifunctional medicaments nursing shampoo and its preparation method
InactiveCN101283963AWide variety of sourcesActivate metabolismCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsGastrodia elataRaw material
The invention provides a multifunctional shampoo with medical hair caring effect and a preparation method thereof. The shampoo is prepared from the following Chinese medicinal materials of (by weight parts): dried alum 4-6, Salix babylonica twig 40-60, Morus alba leaf 20-40, Rhizoma Polygonati 20-30, Chrysanthemum morifolium flower 15-30, Mentha haplocalyx 10-20, Panax ginseng 20-40, Polygonum multiflorum 20-30, Platycladus orientalis leaf 5-7, Folium Pini 10-16, Gastrodia elata 8-12, Angelica dahurica 6-10, Ligusticum chuanxiong 5-9, Eclipta prostrata 6-8, Morus alba fruit 15-20, Spirodela polyrrhiza 20-40, Pogostemon cablin 8-12, Flos Magnoliae 6-8, Artemisia annua 8-12, Cannabis sativa seed 5-9, Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei 6-8, and Rosa rugosa flower 0-18. The shampoo has hair caring, dandruff removing, antipruritic, hair growth promoting, alopecia preventing, hair cell metabolism activating, hair quality improving, and hair blackening effects and blood circulation effect in head promoting,; and has the advantages of easily accessible raw materials, low cost, simple preparation method, and no side effects.
Owner:徐建华
Method for improving artemisinin content in artemisia annua L through transferring allene oxide cyclase (AOC) gene
InactiveCN102242145AIncrease contentStable new drug sourcesGenetic engineeringFermentationProtein ArtemisTransgene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for improving artemisinin content in artemisia annua L through transferring allene oxide cyclase (AOC) gene. The method is characterized by: cloning the AOC gene from the artemisia annua L; constructing a plant expression vector containing the AOC gene; transferring the AOC gene into the artemisia annua L through adopting agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation, and regenerating plants; detecting integration situations of the exogenous target gene AOC through PCR, detecting the artemisinin content in the transgenic artemisia annua L through a high performance liquid chromatography and a evaporative light scattering detector; carrying out screening to obtain the transgenic artemisia annua L plants with improved artemisinin content. The artemisinin content in the transgenic artemisia annua L provided by the present invention is substantially improved, the artemisinin content in the non-transformed normal artemisia annua L is 1.53 mg / gDW while the artemisinin content in the AOC-transferred artemisia annua L is up to 10.17 mg / gDW, such that the artemisinin content in the AOC-transferred artemisia annua L is 6.65 times as much as the artemisinin content in the non-transformed artemisia annua. Therefore, with the present invention, a method for improving the artemisinin content in the artemisia annua L t is provided, base for producing the artemisinin on a large scale through the transgene is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for artificially culturing artemisia annua linn in high altitude areas
InactiveCN101524029AIncrease productionImprove effectivenessFertilising methodsPlant protective coveringsActive componentPlastic film
The invention relates to a method for artificially culturing artemisia annua linn in high altitude areas and belongs to the technical field of agricultural science. The method mainly comprises the followings steps: the diameter of soil particles of a seedbed is smaller than 0.2cm, the width of furrow is 100cm, the height thereof is 15 to 20cm and the length is 5 to 10m; the seeding time is the end of February to early March and the seeding quantity is 200g / mu; transplanting is carried out when the temperature of the seedbed is 15 DEG C to 30 DEG C, the humidity is 40 to 50 percent, the height of the plant is 10 to 15cm and the length of the root is more than 5cm; the center width of a ridge and furrow is 0.8 to 1m and the depth of the ridge and furrow is 30 to 40cm; the spacing between rows is 0.40*0.80m or 0.50*1.0m and 1300 or 2000 artemisia annua linn is planted in each mu; 0.7si of plastic film are used for mulching the artemisia annua linn along furrow surface after permanent planting; seeds are compensated after ten days, watering is carried out for once to twice everyday, and after transplanting for 7 days, 10 to 15kg of fertilizers are applied for each mu or 0.3 percent of liquid fertilizers are poured and applied; the humidity of the field in seedling stage is kept between 60 and 70 percent; additional fertilizer are applied for twice; 5 to 10kg of N.P.K compound fertilizer is used in squaring stage; and pouring and applying are carried out after 1000kg of water is watered. The invention has simple and convenient operation of the method and short seedling stage, can effectively improve the yield of artemisia annua linn and the content of active components and is suitable for artificial culturing of artemisia annua linn in the areas with altitude more than 1900m.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fig/Artemisia tea and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102550766AUnique fragranceAnti-inflammatoryCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsArtemisia annuaAnimal feed
The invention relates to fig / Artemisia tea and a preparation method thereof in the field of tea substitutes, and achieves the purpose of processing a dry product from fresh fig leaves and fresh Artemisia annua, which is applied to people as a tea therapy. The dry product is further processed to fig / Artemisia powder, juice or solid products. The invention also relates to a preparation methods and application of the products. The fig / Artemisia tea and products thereof are applied in the fields of foods, pharmaceuticals, health products, cosmetics, gaseous aromas, decorations and animal feeds.
Owner:蒲增军
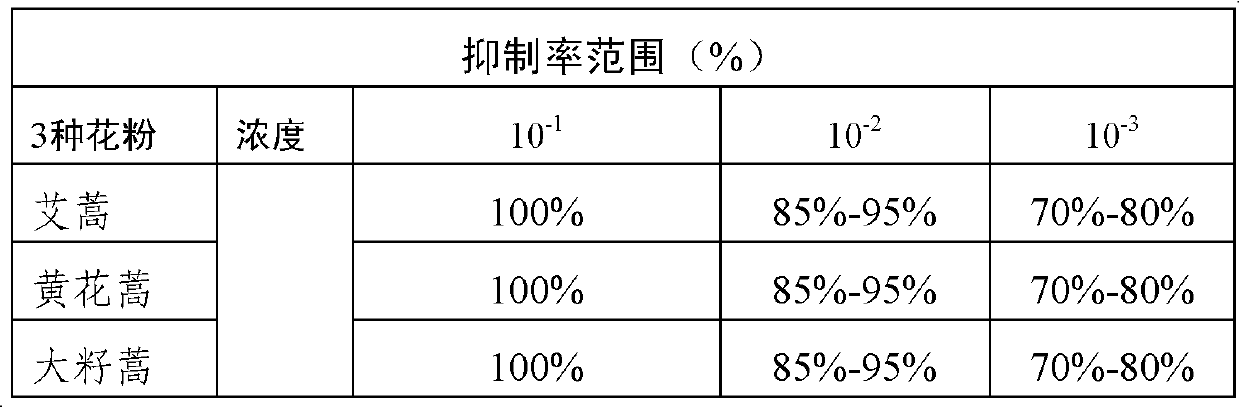
Artemisia pollen allergen vaccine, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102552900AImprove effectivenessGood curative effectAllergen ingredientsImmunological disordersAllergic dermatitisDisease
The invention provides an artemisia pollen allergen vaccine, and a preparation method and application thereof. The artemisia pollen allergen vaccine comprises an artemisia sieversiana pollen allergen, an artemisia annua pollen allergen and an artemisia argyi pollen allergen. Compared with a single artemisia pollen allergen vaccine, the combined vaccine has the advantages that the effectiveness of treatment is improved while the safety can be ensured; and the artemisia pollen allergen vaccine can be used for treating allergic dermatitis, chronic urticaria, allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma which are caused by allergy to multiple artemisia pollens.
Owner:北京新华联协和药业有限责任公司
Plant source acaricide microemulsion with 1% scopolactone and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103004767AIt has the benefit of "turning waste into treasure"Low toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsMicroemulsionArtemisia annua
The invention relates to a plant source acaricide microemulsion with 1% scopolactone and a preparation method thereof. The microemulsion comprises the following components by mass percent: 1 percent of scopolactone, 10-30 percent of solvent, 5-10 percent of emulsifier, 2-5 percent of antifreezer, 1-3 percent of foam killer and the balance of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing scopolactone active compound and the solvent, stirring at 40 DEG C to ensure complete resolution, adding the emulsifier and stirring to obtain uniform oil phase; mixing the antifreezer and water and stirring to obtain homogeneous water phase; and adding the water phase into the oil phase at the stirring rate of 5,000-10,000 turns / min, and shearing for 30-40 minutes to be emulsified into a liliquoid so as to obtain the microemulsion. The microemulsion provided by the invention is a low-toxicity, easy-to-degrade and low-residue plant source acaricide, and the scopolactone is extracted from artemisia annua residues from which artemisinin is extracted by petroleum ether and can serve contact, systemic, ovicidal, oviposition inhibition and other functions to phytophagous pest mites.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Artemisia annua wax handmade soap and production method thereof
ActiveCN105886166AImprove the bactericidal effectImprove antibacterialSoap detergents with organic compounding agentsSoap detergents with perfumesBiotechnologyArtemisinins
The invention discloses Artemisia annua wax handmade soap and a production method thereof. The Artemisia annua wax handmade soap includes Artemisia annua essential oil, Artemisia annua soap base, Artemisia annua extract and the like, wherein the Artemisia annua soap base is obtained by saponifying Artemisia annua wax, and the Artemisia annua extract mainly includes artemisinin and chlorophyll. The preparation process of the invention is simple and efficient, various effective substances in Artemisia annua are made full use, cost is greatly reduced, and this soap has significant effects such as sterilization, baceriostasis, skin care, and inflammation diminishing.
Owner:SICHUAN LAMBERT BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Chinese herbal medicine biological prevention and control method for Chinese chive maggots
InactiveCN105340999APollution controlReduce usageBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyGelsemium elegans
The invention provides a Chinese herbal medicine biological prevention and control method for Chinese chive maggots, and belongs to the technical field of biological prevention and control of insect attack. The Chinese herbal medicine biological prevention and control method for Chinese chive maggots is characterized in that biological prevention and control of the Chinese chive maggots is implemented by Chinese herbal medicines, the Chinese herbal medicines mainly comprise 19 Chinese medicines including Folium Ginkgo, Pericarpium Granati, Pericarpium Zanthoxyli, Herba Chenopodii, Cortex Acanthopancis, Semen Arecae, Flos Chrysanthemi Indici, Folium Artemisiae Argyi, Folium Ricini, Radix Strophanthi Divaricati, Gelsemium elegans Benth., leaf of Folium seu Cortex Nerii, Flos Caryophylli, Cortex Meliae, Fructus Quisqualis, Radix Sophorae Flavescentis, Artemisia annua L., Polygonum hydropiper L., Herba Houttuyniae and the like, water extracts of the 19 Chinese medicines and chitosan form chelate, the chelate and the pulverized Chinese medicine residues are applied to a Chinese chives field together, so that the Chinese chive maggots can be prevented and controlled effectively, the chelate and the pulverized Chinese medicine residues are toxic-free and do not have pesticide residues, people can eat assured and safe Chinese chives, and economic benefit, social benefit and ecological benefit are remarkable.
Owner:TAIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Extraction method of herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil, and product and application of herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil
ActiveCN104073362ALow costIncrease profitBiocideEssential-oils/perfumesArtemisia annuaExtraction methods
The invention relates to the technical field of plant insecticides and specifically discloses an extraction method of herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil, the prepared herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil and application of the herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil. The extraction method is characterized by taking the artemisia annuae oil as the raw material and extracting the artemisia annuae volatile oil by using CO2 supercritical extraction method so as to obtain the herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil with volatility, wherein the artemisia annuae oil is residue obtained after extracting artemisinin from the artemisia annuae oil. The extraction method is simple and low in cost of raw material; moreover, the utilization rate of the artemisia annua is improved; the obtained herba artemisiae annuae volatile oil is good in insecticidal activity and can be used as an effective component for killing insects in agriculture.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND
Environmentally-friendly Chinese herbal medicinal biological pesticide
InactiveCN103828855AEnvironmentally friendlyNo secondary toxicityBiocideArthropodicidesCannabisNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses an environmentally-friendly Chinese herbal medicinal biological pesticide. The pesticide comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of a synergist, 5-20 parts of Herba Taraxaci, 4-10 parts of purslane, 6-9 parts of Siberian Cocklour Fruit, 10-15 parts of pomegranate rind, 11-15 parts of Artemisia argyi, 20-30 parts of Cannabis sativa L., 10-20 parts of Chloranthus serratus, 15-20 parts of Artemisia annua L., 20-30 parts of tobacco, 10-15 parts of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb, 10-20 parts of Aconitum carmichaeli Debx., 12-18 parts of Herba Houttuyniae, 5-18 parts of Andrographis paniculata, 4-10 parts of camphor, 50-70 parts of Common Threewingnut Root and 100-150 parts of water. The environmentally-friendly Chinese herbal medicinal biological pesticide is a novel pesticide having the advantages of high effectiveness, pertinence, environmental protection, no secondary toxicity, no residual, no pollution, ecologic balance maintenance and no nuisance, is an important guarantee for realizing the ecologic agriculture, the green ecologic agriculture and green enterprises, and has a broad prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AIHUALONG BIOTECH
Plant miticide derived from artemisia annul l and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN101116451AHas acaricidal effectHas aphidicidal effectBiocideAnimal repellantsFruit treeAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a plant source acaricide made from the artemisia annua L. The invention has the artemisia annua L. extract as the main ingredient, together with additional synergist, emulsifying agent and dispersing agent, wherein the percentage by weight of the artemisia annua L. extract which consists of terpenoids, flavonoids and volatile oil compounds is 1 to 15 percent of the mixture. The acaricide is capable of being used to control phytophagous mites harming vegetables, oranges and apples and wheat mites hidden in food, in particular to control carmine spider mite, citrus red mites and copra mites; therefore, the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity and no environmental pollution, and does not harm the quality of agricultural products. In addition, the invention also relates to the method of preparation of the plant source acaricide.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Tissue culture rapid breeding method of Chinese medicine abrotanum
InactiveCN101180952AStable contentEasy to obtainHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budBud
The invention discloses a tissue culture rapid propagation method of the traditional Chinese medicine Artemisia annua. The tissue culture rapid propagation method of the traditional Chinese medicine Artemisia annua is to cultivate the terminal buds or axillary buds of the traditional Chinese medicine Artemisia annua in the primary culture medium to obtain sterile seedlings; the primary culture medium is to add 6-BA and GA to the MS medium In the obtained culture medium, the final concentration of the 6-BA is 0.1-2.0 mg / liter, and the final concentration of the GA is 0.2-2.0 mg / liter. The method of the present invention has the following advantages: easy to obtain materials, very easy to obtain aseptic materials, low variation rate, high value-added coefficient, 4-week multiplication multiple can reach 5 to 6 times, the rooting rate of tissue culture seedlings reaches more than 93%, and the transplanting survival rate Up to 95%, with a strong factory production capacity. By using the method of the invention to breed high-yielding Chinese herb Artemisia annua strains, the high artemisinin content of offspring can be stabilized, thereby increasing the artemisinin output.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plant essential oil formaldehyde remover and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103394271APromote degradationCompletely degradedDispersed particle separationBlumeaArtemisia annua
The invention provides a plant essential oil formaldehyde remover and a preparation method thereof. The plant essential oil formaldehyde remover is prepared by the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1.5-2.5 parts of blumea oil, 3-5 parts of spearmint oil, 3-5 parts of mint oil, 1.5-2.5 parts of eucalyptus oil, 1.5-2.5 parts of artemisia annua oil, 25-35 parts of ethyl alcohol, 3-7 parts of glycerinum and 45-58 parts of deionized water. The preparation method comprises the steps of proportioning the raw materials in parts by weight, placing in a reacting tank, mixing, reacting, allowing a reacting temperature to be 18-40 DEG C, uniformly stirring for 25-60min at normal pressure, and obtaining the plant essential oil formaldehyde remover. The plant essential oil formaldehyde remover is derived from a pure natural plant, is natural and non-toxic, and can purify indoor air efficiently, and the preparation method is easy to achieve and low in production cost.
Owner:阿木达草本科技(北京)有限公司
Method for rapidly breeding transgene abrotanum using micro adventive bud technique
The invention relates to a method for rapidly propagating transgenic Artemisia annua by microadventitious bud technology in the field of biotechnology. In the present invention, after the transgenic Artemisia annua explants are sterilized, they are placed on the medium for inducing adventitious buds, cultivated under light, and a large number of adventitious buds grow around the explants; the explants with a large number of adventitious buds are transferred to Micro-adventitious buds are elongated in the medium for elongation of adventitious buds; the elongated adventitious buds are cut and transferred to the rooting medium of adventitious buds to produce adventitious roots; the complete plants that grow robustly are transplanted into a medium containing transplanting A large number of normal-growing transgenic Artemisia annua plants were obtained through domestication. The present invention screens out a medium suitable for induction and rooting of transgenic Artemisia annua explants, the induction rate of adventitious buds of transgenic Artemisia annua explants exceeds 90%, the rooting rate of adventitious buds is 100%, and the survival rate of transplanted regenerated plants is 100%. , The reproduction coefficient reaches 80-100.
Owner:SUZHOU TANGJI BIOTECH CO LTD
Environment-friendly mosquito-repellent incense and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104686593AExquisite compositionGood effectBiocidePest repellentsBiotechnologyCarboxymethyl starch
The invention discloses environment-friendly mosquito-repellent incense and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of mosquito-repellent incense. The environment-friendly mosquito-repellent incense comprises the following raw material components in percentage by weight: 70-80% of artemisia annua residue powder, 2-5% of shaddock peel powder, 5-10% of wood charcoal powder, 8-12% of natural epidesmine powder, 4-5.95% of carboxymethyl starch and 0.05-0.1% of artemisia oil. Compared with current mosquito-repellent incense, the mosquito-repellent incense taking residues obtained by extracting artemisinin of artemisia annua as base materials adopts less and fine raw materials; the added artemisia annua residues, shaddock peel powder and artemisia oil have obvious effects in repelling mosquitoes; moreover, the artemisia annua residue powder is sufficiently utilized as a main raw material, so that the resources are utilized. The combustion type mosquito-repellent incense disclosed by the invention is sufficient in combustion, small in smoke, fragrant in smell and small in irritation to human body, further has functions of expelling flies and insects in addition to mosquitoes, has a special Chinese herbal medicine effect, and is a green and environment-friendly product.
Owner:柳州衍生科技有限公司
Method for improving artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. by DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene transfer
InactiveCN102604987AIncrease contentStable new drug sourcesGenetic engineeringFermentationProtein ArtemisGene transfer
The invention provides a method for improving an artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. by DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene transfer. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning DXR (1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase) gene in the Artemisia annua L., so as to establish a plant expression carrier containing the DXR gene; transferring the DXR gene into Artemisia annua L. through agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation to grow a plant; detecting the integration condition of the exogenous target gene DXR by a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); detecting the artemisinin content in the transgenic Artemisia annua L. through high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD); and screening the transgenic Artemisia annua L. plant with improved artemisinin content. The artemisinin content of the transgenic Artemisia annua L. obtained by the invention is obviously improved and high up to 2.4 times that of the non-transferred plant. Therefore, the invention provides the method for improving the artemisinin content in the Artemisia annua L. and lays a foundation for producing artemisinin by using the transgenic Artemisia annua L. in a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for efficiently separating and instantaneously converting protoplast of artemisia annua L.
ActiveCN109112093AShort experiment cycleImprove scientific research work efficiencyClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionCuticleHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for efficiently separating and instantaneously converting a protoplast of artemisia annua L., comprising the following steps: 1) selecting leaves of young and tender artemisia annua and removing lower epidermis, to obtain the leaves of the artemisia annua L. with the lower epidermis removed; 2) placing the leaves of the artemisia annua L. with the lower epidermis removed in an enzymatic hydrolysate for enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain a mixed solution of enzymatic hydrolysis; 3) filtering and centrifuging the mixed solution of enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain a protoplast precipitate, and resuspending to obtain a protoplast; and 4) instantaneously converting the protoplast. The method for separating and converting the protoplast is constructed in the artemisia annua L. for the first time, to obtain the protoplast with yield of 2.749 is multiplied by 10<5> / g FW, viability of 96%, and conversion efficiency of green fluorescent protein of 80%, and the obtained protoplast has large yield and high viability. The protoplast of the artemisia annua L. is utilized as a receptor for conversion, and green fluorescent protein GFP, luciferase LUC and sea cucumberluciferase REN can be successfully expressed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Rapid breeding method of Artemisia annua
InactiveCN102487823AEasy to get materialsA large amountHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudGenotype
A rapid breeding method of Artemisia annua. Young stems on a single plant or a plurality of plants of Artemisia annua with completely consistent genotype are cut off; the young stems are disinfected in vitro and transversely cut into stem segments, and each stem segment has a bud; and the stem segments are cultured directly in a rooting medium and transplanted for soil culture after rooting. The method of the invention has easily available material, low variation rate, high increment coefficient, short rooting period, a two-week proliferation time reaching higher than 200 times, a rooting rate reaching higher than 90%, a transplanting survival rate reaching higher than 95% and strong factory production capability. Using the method of the invention to breed high-yield Artemisia annua linescan enable progeny to get stable heredity, so as to effectively reduce production cost of artemisinin.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
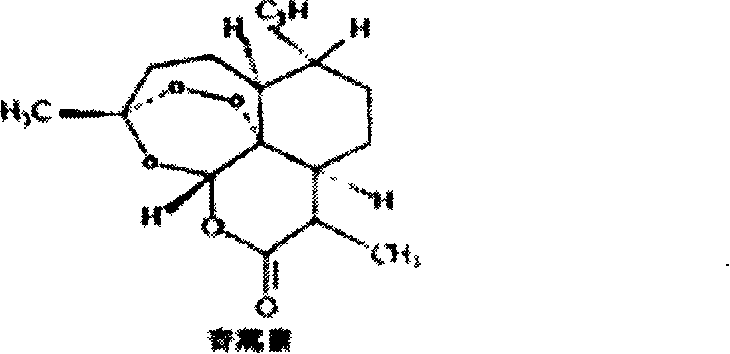
Application of artemisinin as algae inhibiting agents
InactiveCN102318617ALow toxicityImprove environmental friendlinessBiocideAnimal repellantsNatural productMicrobiology
The invention relates to an application of artemisinin as algae inhibiting agents. The algae is microcystis aeruginosa or scendesmus obliquus. The artemisinin is extracted from artemisia annua of terrestrial plant, is a degradable natural product with good environmental compatibility and lower toxicity on higher animals and has a wide application range as the algae inhibiting agents.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
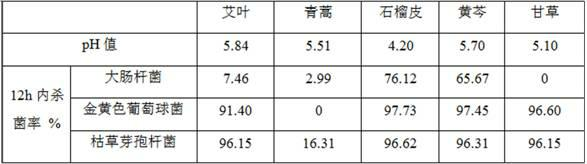
Chinese medicinal herb-inorganic antibacterial agent composite sterilization hand sanitizer and preparation thereof
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal herb-inorganic antibacterial agent composite sterilization hand sanitizer, belonging to the field of chemicals for daily use. According to the Chinese medicinal herb-inorganic antibacterial agent composite sterilization hand sanitizer provided by the invention, extractives of Artemisia argyi leaf, Artemisia annua, Scutellaria baicalensis, Punica granatumpericarp and Glycyrriza uralensis are served as a composite Chinese medicinal herb antibacterial agent, and nanometer silver oxide is served as the inorganic antibacterial agent, as a result, the potent sterilization ability of the nanometer silver oxide is combined with the long-term sterilization effect of the Chinese medicinal herbs to form a novel sterilization hand sanitizer with potent, long-term sterilization and bacteriostasis functions. According to the bacteriostatic tests of Escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, the Chinese medicinal herb-inorganic antibacterial agent composite sterilization hand sanitizer is good in performance of sterilization and bacteriostasis.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com