Plant miticide derived from artemisia annul l and method for preparing the same
A plant-based, Artemisia annua technology, applied in the field of plant-based acaricides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
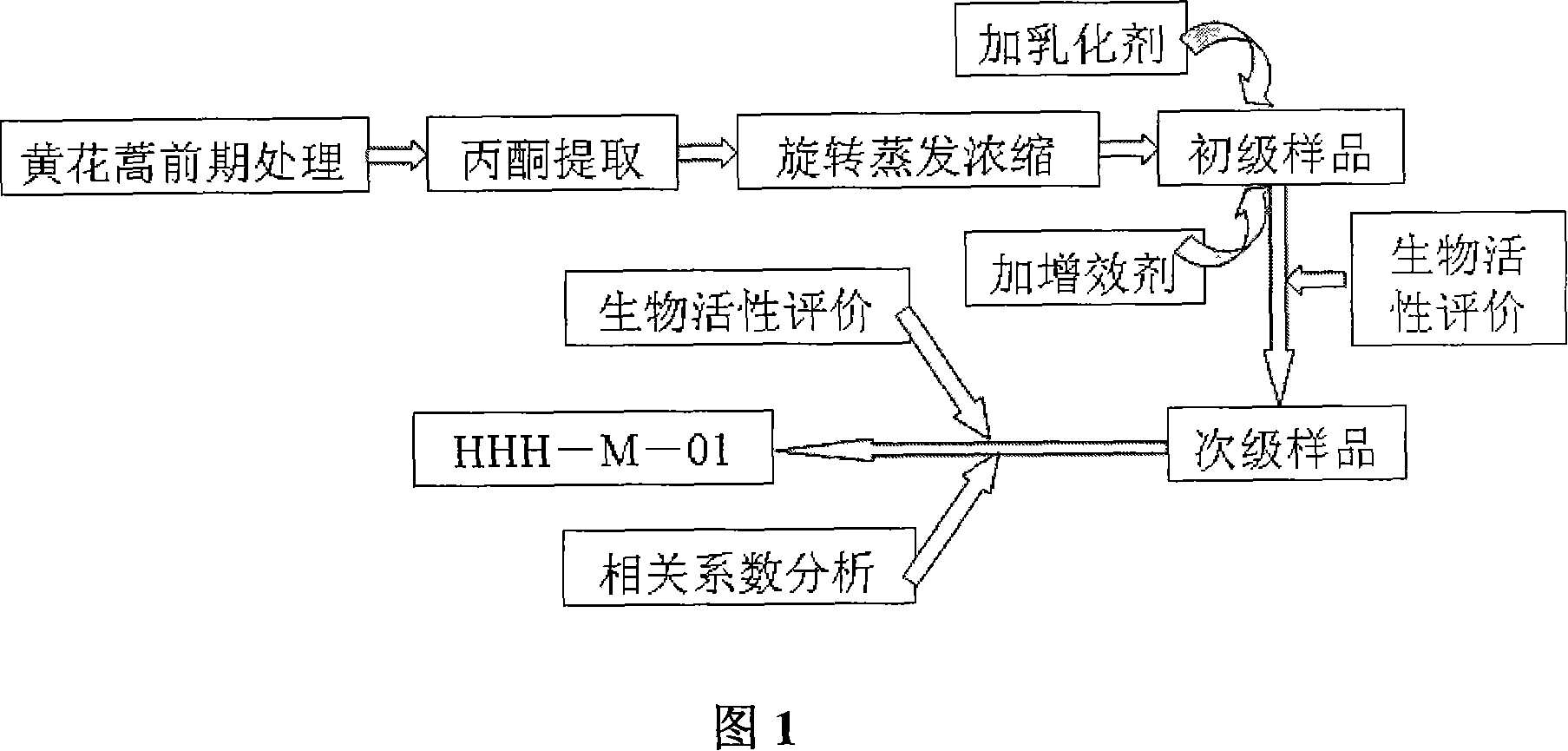
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The selection of embodiment 1 Artemisia annua plant parts
[0054] Differences in Acaricidal Activity of Different Plant Parts of Artemisia annua in June
[0055] With different solvent extracts of 5 mg / ml Artemisia annua in June, the contact toxicity of different plant parts to Tetranychus cinnabarinus was measured under laboratory conditions, and the results are shown in Table 3:
[0056] Table 3 The biological activity of different solvent extracts of Artemisia annua in June to Tetranychus cinnabarinus (5mg / ml, 48h)
[0057]
different solvent extracts
Corrected mortality % (mean ± standard error)
root
stem
leaf
water
ethanol sequence
Acetone sequence
water order
36.54±1.11cdBCD
43.64±1.82bcBC
45.10±2.26bBC
66.00±3.05aA
23.27±3.05eD
30.82±2.52dCD
46.06±1.6...
example 2
[0060] The acaricidal activity comparison of example 2 Artemisia annua leaves acetone extract
[0061] The bioassay results of more than 100 kinds of extracts of Artemisia annua in April, May, June, July and September showed that the biological activity of the parallel extracts of A. Significant differences exist. For further research on the activity difference of five kinds of extracts, the toxicity regression analysis of five kinds of extracts to Tetranychus cinnabarinus was measured, and the lethal middle time (Medianlethal time, LT 50 ). The results are listed in Table 4 and Table 5.
[0062] Table 4 The toxicity regression analysis of the acetone extract of Artemisia annua leaves to Tetranychus cinnabarinus in five months (48h)
[0063]
[0064] As can be seen from Table 4, the LC of the acetone parallel extracts of leaves of Artemisia annua in different months to Tetranychus cinnabarinus 50 Varies with the season of collection, LC in April, May, June, July...
example 3
[0068] The comparison of the acaricidal activity of the different components obtained by the column chromatography of the wormwood leaf acetone extract of example 3
[0069] The acaricidal activity of different components obtained by column chromatography of the acetone extract of Artemisia annua leaves was determined by the biological activity tracking method, and the results are shown in Table 6.
[0070] It can be seen from Table 6 that among the 13 finally separated components, component 12 had the highest acaricidal activity, and the corrected mortality rate within 48 hours reached 99.20%, and its 95% CI was 96.24-102.34. And 6 times, the average corrected mortality within 48h reached 82.52%, 89.74%, respectively, and its 95% CI were 81.79 ~ 83.24, 85.08 ~ 94.41mg / ml. It can be seen that the acaricidal active substance of Artemisia annua mainly exists in the acetone extract, and the acetone extract of the leaves has the highest content.
[0071] Table 6 Acaricidal activi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com