Method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua
A technology of artemisinin and artemisinin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of difficult maintenance, limited output, high equipment cost, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing metabolic pathways
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1, Cloning of Artemisia annua ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 Genes
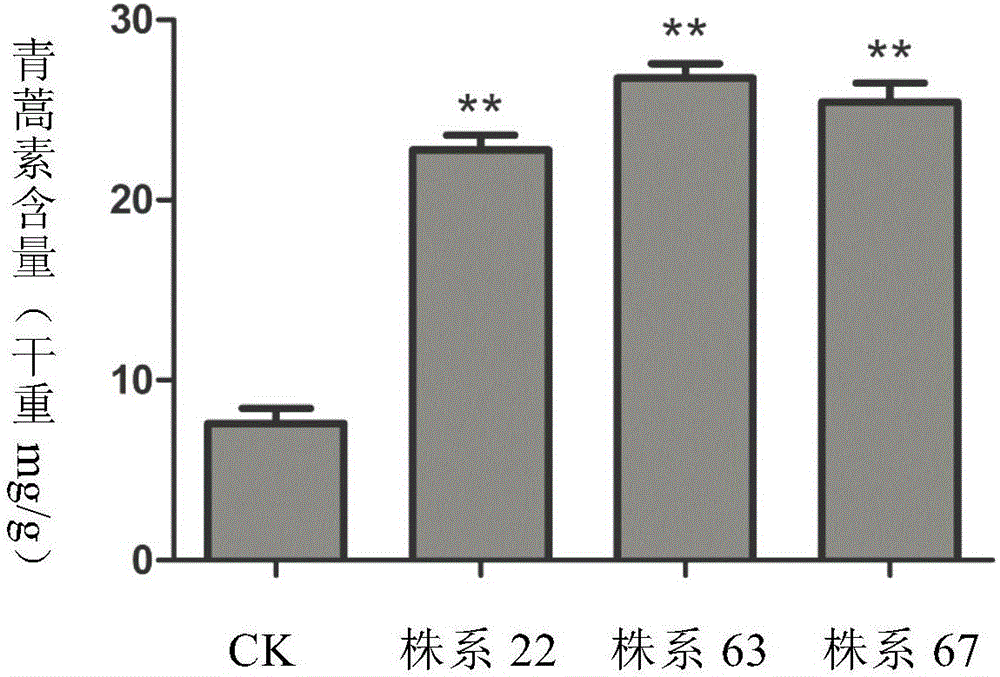
[0028] Amorphadiene synthase (ADS) is the first key enzyme in the unique pathway of artemisinin biosynthesis. It is the catalysis of ADS enzyme, which transfers the terpenoid metabolism in Artemisia annua to the direction of artemisinin synthesis. The monooxygenase CYP71AV1 (Amorpha-4,11-diene oxidase) of the P450 family is a multifunctional enzyme that can catalyze three consecutive steps in the artemisinin synthesis pathway, and finally catalyze the formation of amorphadiene Artemisinic acid. Its molecular chaperone CPR enzyme (cytochrome P450 reductase) was found in in vitro experiments to help CYP71AV1 enzyme catalyze the above reaction process. Aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH1 can convert dihydroartemisinic aldehyde into dihydroartemisinic acid.
[0029] This example adopts the method of gene cloning to obtain the key enzyme genes ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 of artemisinin biosynthesis with...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2, the construction of the plant expression vector containing ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 gene
[0038] 1. Construction of intermediate carrier
[0039] The pMD18T vector (Takara, Dalian) was selected as the cloning vector to construct intermediate vectors pMD18T-ADS, pMD18T-CYP71AV1, pMD18T-CPR and pMD18T-ALDH1. On both sides of ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 genes, primers ADS-SpeI-F and ADS-BstEII-R, CYP71AV1-SpeI-F and CYP71AV1-BstEII-R, CPR-SpeI-F and CPR-BstEII-R and ALDH1-SpeI-F and ALDH1-BstEII-R introduced SpeI and BstEII restriction sites, and the primer sequences are shown in Table 2. Those skilled in the art know that the restriction endonuclease sites can also be changed according to different subsequent applicable vectors.
[0040] The full-length gene with restriction sites was ligated to the pMD18T vector by T4 ligase, and the sequencing was completed by Shanghai Meiji Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd.
[0041] Table 2: PCR Primers
[0042]...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3, Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 gene genetic transformation Artemisia annua obtained transgene due to plant
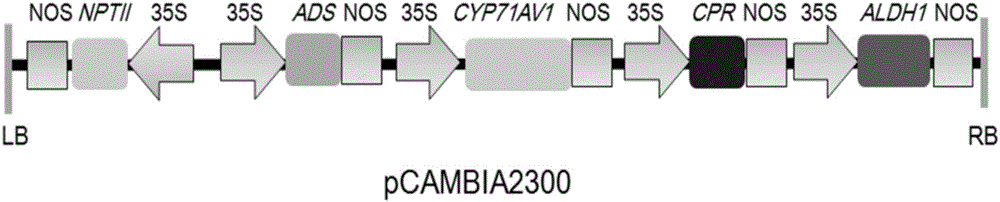
[0053] 1. Acquisition of plant expression vector Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 genes
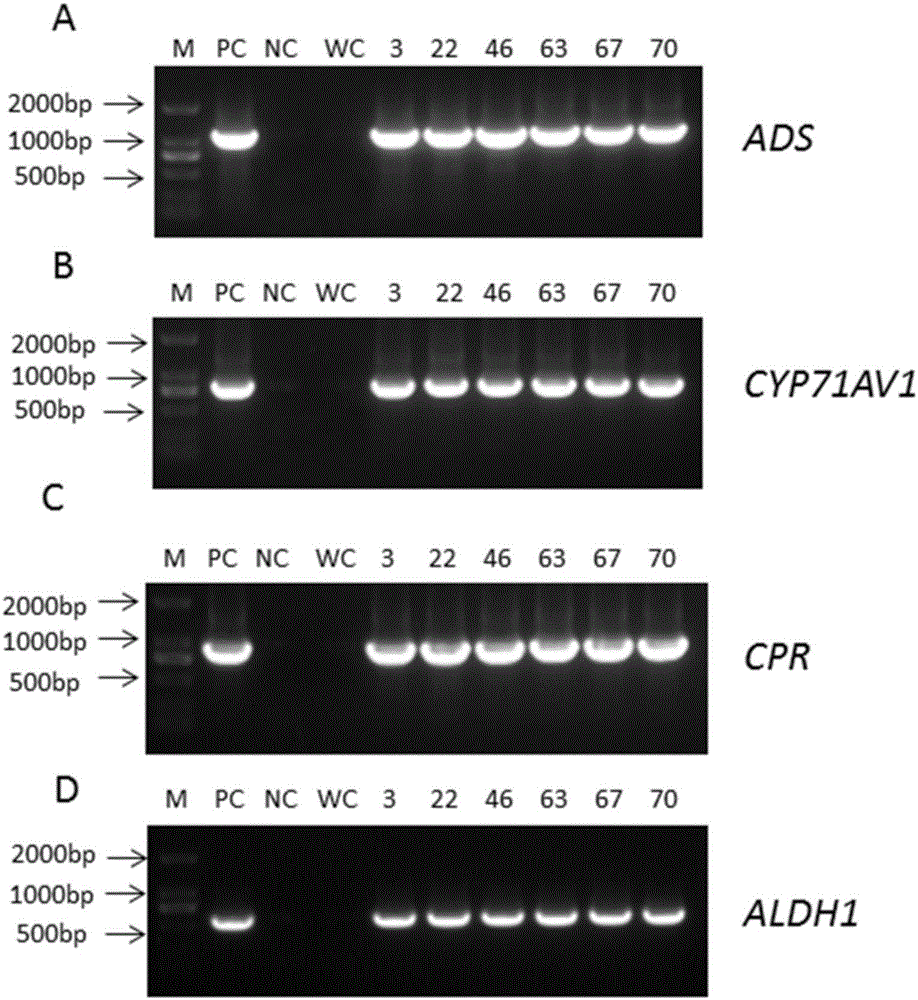
[0054] The plant expression vectors containing ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 genes obtained in Example 2 are transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens (such as EHA105, which is a publicly available biological material in the market, which can be purchased from CAMBIA, Australia. , and the strain number is Gambar 1), and was verified by PCR. The results showed that the plant expression vectors containing ADS, CYP71AV1, CPR and ALDH1 genes had been successfully transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains.
[0055] When using the freeze-thaw method to transfer the plant expression vector into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, add the plant expression vector to the competent cells of Agrobacterium ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com