Sweet wormwood AaGTD1 gene as well as coded protein and application thereof
A kind of gene coding, Artemisia annua technology, applied in the application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problem that there is no report on the AaGTD1 gene protein of Artemisia annua
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Cloning of Artemisia annua AaGTD1 gene
[0044] 1. Extraction of Total RNA from Artemisia annua Genome
[0045] Take an appropriate amount of fresh Artemisia annua leaves and quickly grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen, then take about 100mg of the powder and add it to a 1.5ml EP tube pre-filled with plant tissue lysate, shake and mix well, and then extract total plant RNA according to TIANGEN RNAprep Pure The kit's instructions were used to extract total RNA from Artemisia annua. The quality of RNA was identified by formaldehyde denaturing gel electrophoresis, and then the RNA concentration was determined on a spectrophotometer.
[0046] 2. Cloning of the AaGTD1 gene of Artemisia annua
[0047] Using the extracted total RNA as a template, cDNA of Artemisia annua was synthesized using the Full-Form Gold TansScript First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Supermix kit.
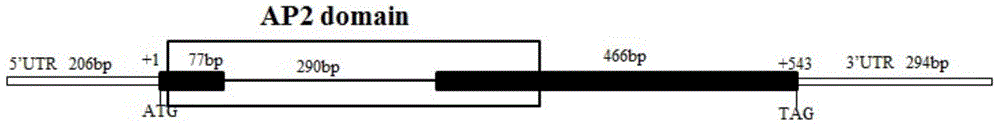
[0048] Gene-specific primers were designed according to the sequence of the AaGTD1 gene:
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Spatiotemporal expression analysis of Artemisia annua AaGTD1 gene
[0054] 1. Material preparation
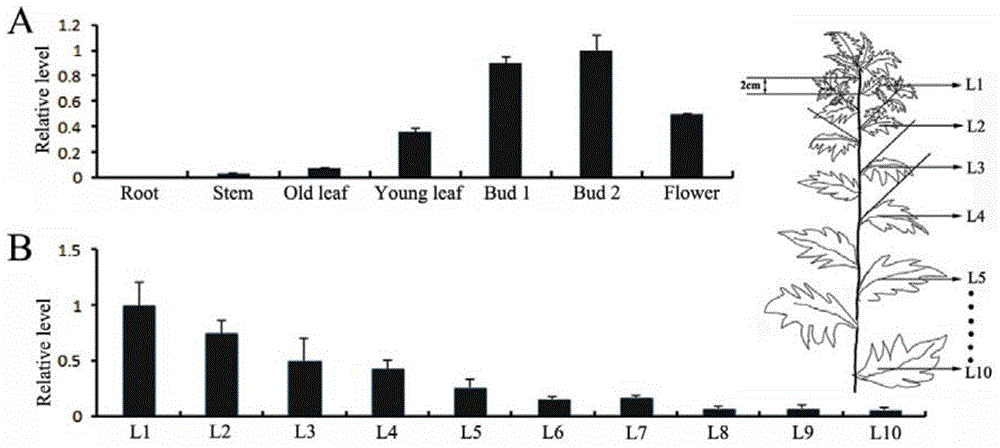
[0055] According to the extraction method of total RNA used in Example 1, different parts of Artemisia annua were extracted, including: roots, stems, old leaves, young leaves, early flower buds, flower buds before flowering, total RNA of flowers in full flowering stage, and reversed cDNA to obtain materials for spatial expression analysis; at the same time, according to the above method, obtain RNA and cDNA from leaves of different parts of Artemisia annua growing to a height of 45-55 cm, and obtain materials for AaGTD1 gene expression analysis in leaves of different developmental stages (such as figure 2 shown).
[0056] 2. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis
[0057] Quantitative PCR primers (Table 1) across introns of AaGTD1 gene and Actin internal reference gene were designed by primer 5, and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis w...
Embodiment 3
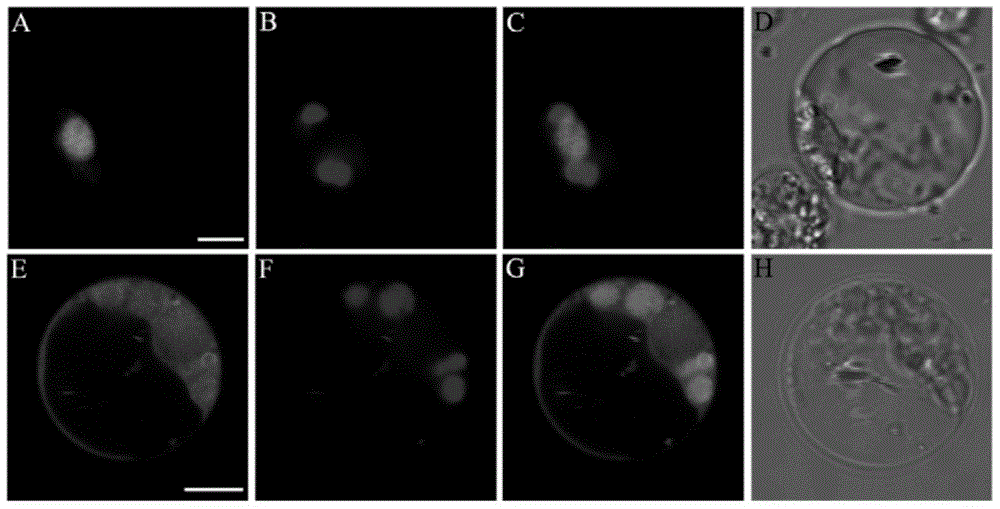
[0061] Example 3: Analysis of subcellular localization of Artemisia annua AaGTD1 gene
[0062] According to the content of the bioinformatics analysis in Example 1, the AaGTD1 gene is an AP2 / ERF type transcription factor with an AP2 domain. In order to further verify the nature of AaGTD1 gene transcription factor, we constructed the subcellular localization vector of AaGTD1 gene, and confirmed that AaGTD1 is localized in the nucleus by transforming rice protoplasts, which conforms to the characteristics of AaGTD1 gene transcription factor.
[0063] 1. Construction of subcellular localization vector
[0064] In this embodiment, the forward primer is designed as subGTD-F:aaCCATGGGA atgggtcaaaagaagtttag (SEQ ID NO:9), containing NCO I restriction site, and the reverse primer is subGTD-R:aa ACTAGTATTCGTATTAAGCAATTCTT (SEQ ID NO:10) , containing the Spe I restriction site. Perform PCR, enzyme digestion and ligation to finally obtain the AaGTD1 gene subcellular localization vector...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com